ECE-R79 欧盟法规Steering Systems 转向系统
- 格式:pdf
- 大小:1.47 MB
- 文档页数:18


欧盟立法自1999年9月份ECE R90开始生效。
该标准规定所有市场销售的车辆用刹车片都必须符合R90标准。
欧洲市场:ECE-R90认证及TS16949,在欧洲市场上销售刹车片生产企业必须通过TS16949认证,产品必须通过ECE-R90认证。
只有这样,产品才能在欧盟市场销售。
认证测试标准:
1. 速度敏感性试验
试验条件:使用冷态效能等效试验得到的踏板力,初始制动器温度小于100℃,在以下每个速度分别进行3次制动试验:
前轴:65km/h,100km/h和135km/h(当Vmax大于150km/h),后轴:45km/h,65km/h和90km/h(当Vmax大于150km/h)
2. 热态性能试验
适用范围:M3、N2 和N3 类车辆可替代制动衬片总成及鼓式制动衬片试验过程
热态性能:一旦完成加热规程,就应使用许可制动衬片压力,在制动器初始温度≤100℃,初始速度为60km/h 条件下测定热态性能。
加热后制动器充分发出的平均减速度必须不低于冷态制动器所获得相应值的60%或4m/s。

欧盟汽车功能安全法规-概述说明以及解释1.引言1.1 概述欧盟汽车功能安全法规是指欧盟对在市场上销售的汽车必须符合的安全标准和规定。
这些法规旨在保障驾驶人员、乘客和行人的安全,并确保汽车在正常使用过程中不会造成危险。
随着汽车科技的不断发展和普及,汽车功能安全已经成为汽车行业的一个重要话题。
本文将从欧盟汽车功能安全法规的概述、重要性以及实施情况等方面进行深入探讨,希望能够为读者带来更多有关汽车安全的了解和认识。
1.2 文章结构:本文将分为三个主要部分,包括引言、正文和结论。
- 引言部分将首先介绍欧盟汽车功能安全法规的概述,然后阐述本文的结构和目的。
- 正文部分将重点讨论欧盟汽车功能安全法规的概述,探讨汽车功能安全法规的重要性,以及分析欧盟汽车功能安全法规的实施情况。
- 结论部分将总结欧盟汽车功能安全法规的影响,展望未来汽车功能安全的发展,并得出本文的结论。
1.3 目的本文的目的在于探讨欧盟汽车功能安全法规的重要性和实施情况,以及对汽车行业和消费者产生的影响。
我们将分析这些法规对汽车安全性和可靠性的提升,以及对汽车制造商和消费者的影响。
通过研究欧盟汽车功能安全法规的发展历程和实施情况,我们可以更好地了解其对汽车行业的推动作用,为未来汽车功能安全的发展提出建议和展望。
通过本文的研究,希望能够引起更多人对汽车功能安全的重视,推动汽车行业的可持续发展。
2.正文2.1 欧盟汽车功能安全法规概述欧盟汽车功能安全法规是欧盟针对汽车行业颁布的一系列法规和标准,旨在确保汽车在设计、生产和使用过程中的功能安全性。
这些法规涵盖了诸多方面,包括车辆控制系统、防撞技术、电子稳定控制系统等。
欧盟汽车功能安全法规的核心目标是保障汽车在各种情况下的安全性能,包括碰撞安全性、防护性、控制性等。
通过制定一系列技术规范和测试要求,欧盟力求提高汽车在各种极端情况下的安全表现,减少事故发生的可能性并最大限度降低事故对人身和财产造成的损害。

ece r79标准译文ECE R79标准是一项用于车辆前灯的国际性法规,旨在规定汽车前灯的技术规格和性能要求,确保驾驶人能够在夜间和恶劣天气条件下安全驾驶。
本文将介绍ECE R79标准的背景、内容以及对汽车前灯行业的影响。
ECE(联合国欧洲经济委员会)R79标准是一种欧洲法规,于1958年制定,适用于全世界范围内的车辆制造商和零部件提供商。
该标准的目的是确保车辆前灯满足安全、有效以及环保的设计要求。
ECE R79标准规定了前灯的几个关键方面,包括照明强度、光束形状、灯光颜色、光束调整、旋钮和开关、以及室外温度的影响等。
这些规定的目的是确保灯光在不同条件下提供适当的照明,并避免对其他道路使用者造成不必要的干扰。
首先,ECE R79标准规定了前灯的照明强度要求。
这包括照明强度的最小值和最大值,在不同的驾驶条件下进行调整。
照明强度的准确测量和调整对于确保车辆前灯能够在不同的道路条件下提供适当的照明非常重要。
其次,ECE R79标准规定了前灯的光束形状。
光束形状应符合特定的规定,以确保其能够提供适当的道路照明,而不会对其他道路使用者产生过多的干扰。
这包括灯光的投射角度、灯光的扩散程度等等。
此外,ECE R79标准还规定了前灯的灯光颜色。
根据标准的规定,前灯应发出白色或者黄色的灯光,以提供最佳的可见性。
这些规定对于确保前灯能够在不同的天气条件下提供适当的照明非常重要。
另外,ECE R79标准对前灯的光束调整也有明确的规定。
这些规定包括光束的垂直和水平调整,以确保灯光在不同驾驶条件下提供适当的照明,同时又不会对其他道路使用者造成干扰。
ECE R79标准还对前灯的旋钮和开关进行了规定。
标准要求这些控制器应安装在便于驾驶人操作的位置,并且能够在不同条件下轻松调整灯光的设置。
这些规定旨在确保驾驶人能够快速、安全地调整前灯照明,以适应不同的驾驶条件。
最后,ECE R79标准还指出了室外温度对前灯照明的影响。
由于温度的变化可能会导致前灯照明性能的变化,标准要求制造商要在不同温度条件下对前灯进行测试,并确保其在不同的工作条件下也能够提供适当的照明。


智能转向辅助测试标准因转向系统在车辆行驶安全中的重要性,针对转向装置也发展出了多项智能驾驶辅助系统。
新版R79对此纳入了各项针对智能驾驶辅助转向系统的技术要求及测试方法,以此提升车辆的驾驶安全性。
本文将详细介绍R79转向装置法规中关于的智能驾驶辅助转向系统的技术要求及测试规范。
考虑到技术的复杂性及篇幅原因,此次将通过上下两篇文章进行智能驾驶辅助转向系统的介绍,R79所包含的智能驾驶辅助转向系统包括ACSF-自动控制转向功能(A类含RCP/B类含B1,B2/C类/D类/E类),CSF-转向修正功能,ESF-紧急转向功能,RCM-遥控操作。
此次着重介绍A类及B1类ACSF。
法规适用范围:M,N,O类车辆的转向装置ACSF全称为 Automatically Commanded Steering Function,自动控制转向功能。
根据具体功能分为了A,B,C,D,E类。
R79考虑当前汽车智能辅助系统发展情况,着重对A类,B类,C类ACSF进行了技术规定。
本文将对A类及B类ACSF的法规要求进行详细介绍。
一、ACSF-自动控制转向功能1.1 A类ACSF1.2 B类ACSFB类ACSF分为B1类与B2类,虽然两者都同属“车道保持居中”系统,但是在智能水平上有一定差异,B1类为“hands-on”的ACSF,需要驾驶员更多的注意力及身体操控,而B2类为无需驾驶员进一步操作,可长期保持的”hands-off”的ACSF,法规关于B2类的测试要求仍处空白,因此,这里我们主要对B1类ACSF进行梳理研究。
1.2.1 B1类ACSF技术要求1.2.2 B1类ACSF的提示装置要求1.2.3 B1类ACSF的测试要求a.车道保持功能试验b.最大横向加速度试验c. 超越控制力测试。

2024年第1期97马 群毕业于武汉理工大学,机械工程及自动化专业。
现就职于国家汽车质量检验检测中心(襄阳),任海外法规研究工程师,主要从事海外法规研究工作,已发表论文多篇。
欧盟车辆标准法规制修订体系研究马群1,王聪2,王丹1(1.国家汽车质量检验检测中心(襄阳),襄阳 441004 ;2.中国合格评定国家认可中心,北京 100062)摘 要:本文研究了欧盟车辆准入相关标准法规的制修订体系、文件分类、相关组织及其运作规则等,旨在帮助车辆及其部件制造商了解这些标准法规的制修订规则,能够及时获取标准法规草案、执行时间、修订状态等相关信息,为促进国际车辆贸易,助力中国制造“走出去”提供前瞻技术支持。
关键词:标准法规制修订体系;车辆技术法规中图分类号:U461 文献标识码:A 文章编号:1005-2550(2024)01-0097-08Research on Rule-making System for EU’s Vehicle Standards andRegulationsMA Qun 1, WANG Cong 2 , WANG Dan 1( 1. National Automobile Quality Inspection and Test Center (Xiangyang), Xiangyang441004, China; 2. China National Accreditation Service for Conformity Assessment,Beijing 100062, China )Abstract: This paper studies the rule-making system of EU’s vehicle standards and regulations, classification of documents, relevant organizations and their operating rules, and aims to help manufacturers of vehicles and components to understand the rule making procedures of these standards and regulations, so as to obtain standards and regulations drafts, implementation information, revision status and other relevant information to provide forward-looking technical support for Chinese manufacturing to “go global”.Key Words: Rule-making System For Standards and Regulations; Vehicle T echnical Regulationsdoi:10.3969/j.issn.1005-2550.2024.01.016 收稿日期:2023-11-13国际上各国/地区政府管理汽车行业主要有两大制度,一个是以北美地区为典型的自我认证体系,一个是以欧盟为典型的型式认证体系。

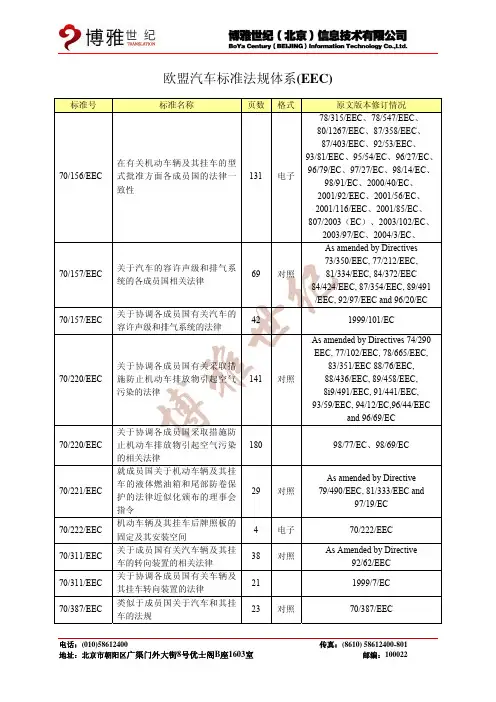
欧盟汽车标准法规体系(ECE)欧盟体系欧盟汽车标准法规体系(ECE)东方君泰序号标准号名称页数原文修订情况修订本4、修订本4-修正本1、1ECE R1关于批准发射不对称近光和/或远光并装有R2/或HS1类灯丝灯泡的机动车前照灯的统一规定电子修订本4-修正本2、修订本4-修正本3、修订本4-修正本4、修订本4-修正本52ECE R2关于批准发射不对称近光和/或远光的前照灯用白炽电灯泡的统一规定1643ECE R3关于批准机动车辆及其挂车回复反射装置的统一规定电子电子修订本2、修订本2-修正本1、修订本2-修正本2、修订本2-修正本3、修订本2-修正本1-斟误本1关于批准机动车辆(摩托车除外)及其挂车后牌照板照明装置的统一规定修订本1、修订本1-修正本1、电子修订本1-修正本2、修订本1-修正本3修订本3、修订本3-斟误本1、75电子修订本3-修正本1、修订本3-修正本2、46电子修订本3、修订本3-修正本1修订本3、修订本3-修正本1、修订本3-修正本2、4 ECE R45 ECE R5关于批准发射欧洲型不对称近光和/或远光机动车封闭式前照灯(SB) 的统一规定关于批准机动车及其挂车转向指示器的统一规定关于批准机动车(不含摩托车)及其挂车前后位置(侧边)灯、制动灯和示廓灯的统一规定关于批准发射不对称近光和/或远光并装有卤素6 ECE R67 ECE R7 电子8 ECE R8灯丝灯泡(H1、H2、H3、 HB3、HB4、H7、H8、H9、HIR1、HIR2和/或H11)的机动车前照灯的统一规定68 电子修订本4-斟误本1、修订本49 ECE R9关于就噪声方面批准L2、L4和L5类车辆的统一规定48 电子修订本2、修订本2-斟误本1、修订本2-修正本1修订本1、修订本1-斟误本1、修订本1修正本1修订本3、修订本3-斟误本1、10 关于就电磁兼容性方面批准车辆的统一规定关于就门锁和车门保持件方面批准车辆的统一规定关于就碰撞中防止转向机构伤害驾驶员方面批准车辆的统一规定98 电子11 ECE R11 25 电子12 65 电子修订本3-修正本1、修订本3-修正本2、修订本3-修正本3、致力于成为中国机械和汽车翻译的首选品牌电话:(8610)67668899 传真:(8610)67668899-801/802地址:北京市丰台区顺三条21号嘉业大厦1号楼12B09 邮编:100071修订本4、修订本4-斟误本1、修订本4-修正本1、修订本4-13关于就制动方面批准M 类、N类和O 类车辆的统一规定修正本1-斟误本1、修订本4-308电子修正本1-斟误本2、修订本4-修正本2、修订本4-修正本2-斟误本1、修订本4-修正本2-斟误本2、修订本4-修正本314 15ECE关于就制动方面批准乘用车的统一规定(欧美日94 53电子电子斟误本2、斟误本3、修正本1、修正本2修订本3、修订本3-修正本1R13--H 协调版)关于就安全带固定点方面批准车辆的统一规定关于就发动机气体污染物排放方面批准装有点16 火式发动机或压燃式发动机的车辆的统一规定--点火式发动机的功率测量方法---车辆的油耗测量方法关于:1批准机动车成年乘客用安全带和约束系统;2批准装用安全带的车辆的统一规定关于就座椅、座椅固定点和头枕方面批准车辆的统一规定电子修订本4、修订本4-修正本1、108电子修订本4-修正本2、修订本4-修正本3、修订本4-修正本458 36电子电子修订本4 修订本2修订本3、修订本3-修正本1、17 18 19ECE R17关于就防盗方面批准机动车的统一规定20 关于批准机动车前雾灯的统一规定 56 电子修订本3-修正本2、修订本3-修正本3、修订本3-修正本4、21 关于批准发射非对称近光和/或远光并装有卤素灯丝灯泡(H4)的机动车前照灯的统一规定修订本2、修订本2-修正本1、77电子修订本2-修正本2、修订本2-修正本3、修订本2-修正本4修订本2、修订本2-斟误本1、22 关于就内饰件方面批准车辆的统一规定 79 电子修订本2-修正本2、修订本2-修正本1、23 关于批准摩托车轻便摩托车驾驶员及乘客用头盔和面罩的统一规定关于批准机动车辆及其挂车的倒车灯的统一规定关于1.就可见污染物排放方面批准压燃式(C.I)发动机; 2.就已获得型式批准的C.I.发动机的110 电子24 27 电子修订本225 安装方面批准机动车; 3. 就发动机可见污染物排放方面批准装用C.I.发动机的车辆; 4 .C.I.发动机的功率测量的统一规定关于批准与车辆座椅一体或非一体的头枕的统一规定69 电子修订本2、修订本2-修正本1修订本1、修订本1-斟误本1、49电子修订本1-修正本1、修订本1-修正本242电子修正本1、修正本2、修正本3、斟误本126 27 关于就外部凸出物方面批准车辆的统一规定致力于成为中国机械和汽车翻译的首选品牌电话:(8610)67668899 传真:(8610)67668899-801/802地址:北京市丰台区顺三条21号嘉业大厦1号楼12B09 邮编:10007128 29ECE R27 关于批准提前三角警告牌的统一规定关于就声响信号方面批准声报警装置和机动车辆的统一规定关于就商用车辆驾驶室乘员防护方面批准车辆的统一规定39 35电子电子修订本1修正本1、修正本2、修正本3、30 33 电子修订本1、修订本1-修正本1修订本2、修订本2-修正本1、31 ECE R30 关于批准机动车及其挂车气压轮胎的统一规定 43 电子修订本2-修正本2、修订本2-修正本3、修订本2-修正本3-斟误本132 ECE R31关于批准发射非对称近光和/或远光的卤素封闭式(HSB)机动车前照灯的统一规定关于就追尾碰撞中被撞车辆的结构特性方面批准车辆的统一规定关于就正面冲撞中被撞的结构特性方面批准车辆的统一规定修订本1、修订本1-斟误本1、70电子修订本1-修正本1、修订本1-修正本2、 28电子修订本133 34 35 36 3730 35 28 80电子电子电子电子修订本1、修订本1-修正本1修订本1、修订本1-修正本修订本1、修订本1-斟误本修订本2、修订本2-修正本1修订本3、修订本3--斟误本1、关于就火灾预防方面批准车辆的统一规定 ECE R35关于就脚控制件的布置方面批准车辆的统一规定ECE R36 关于就一般结构方面批准大型客车的统一规定关于批准用于已经批准的机动车和挂车灯具中的白炽灯的统一规定38 180 电子修订本3-修正本1、修订本3-修正本2修订本1-修正本1、修订本1-39 ECE R38 关于批准机动车和挂车后雾灯的统一规定 8 电子修正本1、修订本1-修正本2、修订本1-修正本340 关于就车速表及其安装方面批准车辆的统一规定关于就发动机气体污染物的排放方面批准装有点火式发动机的摩托车的统一规定14 电子修订本141 42 4357 49 17电子电子电子斟误本1修订本1、修订本1-修正本1、修订本1-修正本1-斟误本1、关于就噪声方面批准摩托车的统一规定关于就车辆前、后保护装置(保险杠等)批准车辆的统一规定44 关于批准安全玻璃材料的统一规定 218 电子修订本1-修正本2、修订本1-修正本3、修订本1-修正本3-斟误本145 关于批准机动车儿童乘客约束装置(儿童约束系统)的统一规定修订本1、修订本1-修正本1、164电子修订本1-修正本2、修订本1-修正本3致力于成为中国机械和汽车翻译的首选品牌电话:(8610)67668899 传真:(8610)67668899-801/802地址:北京市丰台区顺三条21号嘉业大厦1号楼12B09 邮编:10007146关于就前照灯清洗器方面批准机动车辆和批准前照灯清洗器的统一规定关于批准后视镜和就后视镜的安装方面批准机动车辆的统一规定关于就发动机的气体污染物排放方面批准装有点火发动机的轻便摩托车的统一规定关于就灯光和光信号装置的安装方面批准车辆的统一规定关于就发动机污染物排放方面批准压燃式发动50天然气发动机和燃用液化石油气的点燃式发机、动机以及装有这些发动机的车辆的统一规定关于批准轻便摩托车、摩托车及其类似车辆前后51ECE R50 位置灯、制动灯、转向信号灯和后牌照板照明装置的统一规定关于就噪声排放方面批准四轮及四轮以上机动车的统一规定关于就一般结构方面批准小型公共运输车辆(M2、M3)的统一规定关于就灯光及光信号装置的安装方面批准L3类车辆(摩托车)的统一规定关于批准商用车辆及其挂车气压轮胎的统一规定修订本1、修订本1-修正本1-59电子斟误本1、修订本1-修正本1、修订本1-斟误本167电子修订本238电子309电子修订本1、修订本1-斟误本1、35电子修订本1-修正本1、修订本1-修正本2、修订本1-修正本3 78电子修订本1、修订本1-修正本1、修订本1-修正本2修订本2、修订本2-斟误本3、96电子修订本2-修正本1、修订本2-修正本2、修订本2-修正本3修订本3、修订本3-修正本1、修订本3-修正本247 48 50 电子49 52 53 ECE R5254 37 电子修订本1、修订本1-修正本1、55 54 电子修订本1-修正本2、修订本1-修正本3、修订本1-修正本456 57关于批准汽车列车机械联结件的统一规定关于批准轻便摩托车以及类似车辆前照灯的统一规定关于批准摩托车以及类似车辆前照灯的统一规定关于1.批准后下部防护装置; 2.就已批准的后84 39电子电子修订本1、修订本1-斟误本158 53 电子59 3.就后下ECE R58 下部防护装置的安装方面批准车辆;部防护装置方面批准车辆的统一规定128 电子修正本160 关于批准备用消声系统的统一规定关于就驾驶员操纵的控制件,包括控制件、信号30 电子修正本1、修正本2、61 装置和指示器的识别方面批准两轮摩托车的统一规定33 电子62 关于就驾驶室后挡板之前的外部凸出物方面批准商用车的统一规定关于就防盗方面批准带有操纵把的机动车的统一规定22 电子——63 16 电子修订本1-修正本1、修正本1、致力于成为中国机械和汽车翻译的首选品牌电话:(8610)67668899 传真:(8610)67668899-801/802地址:北京市丰台区顺三条21号嘉业大厦1号楼12B09 邮编:10007164关于就噪声方面批准两轮轻便摩托车的统一规定关于批准装有应急备用车轮/轮胎的车辆的统一规定47电子65 66 6717 40 34电子电子电子修正本1修正本1、修正本2、修正本3、修正本1关于批准机动车特别警告灯的统一规定 ECE R66关于就上部结构强度方面批准大型客车的统一规定关于:1批准在其驱动系统中使用液化石油气的68 机动车辆特殊装置;2 在这一装置的安装方面批准装用使其驱动系统使用液化石油气的特殊装置的车辆的统一规定修订本1、修订本1-斟误本1、180电子修订本1-斟误本2、修订本1-修正本1、修订本1-修正本269 关于就最大车速的测量方面批准包括纯电动车辆在内的机动车的统一规定关于批准低速车辆及其挂车后标志牌的统一规定23 电子修正本170 71 7250 70 17电子电子电子修正本1、修正本2、修正本3修正本1、修正本2、修正本3关于批准重,长型车辆后标志牌的统一规定关于就驾驶员视野方面批准农用拖拉机的统一规定关于批准发射非对称近光和远光并装有卤素灯(HS1灯)的摩托车前大灯统一规定关于就侧防护方面批准货车、挂车和半挂车的统一规定关于就灯光和光信号装置方面批准L1类车辆的统一规定关于批准摩托车和轻便摩托车气压轮胎的统一规定关于批准发射远光和近光的轻便摩托车前照灯的统一规定73 59 电子74 17 电子——75 ECE R74 38 电子76 56 电子77 21 电子修订本1、修订本1-修正本1、修订本1-修正本2修订本1、修订本1-修正本1、78 79关于批准机动车驻车灯的统一规定 ECE R78 关于就制动方面批准L 类车辆的统一规定31 57电子电子80 关于就转向装置方面批准车辆的统一规定 30 电子修订本1-修正本2、修订本1-修正本381 关于就座椅及其固定点方面批准大型客车座椅和车辆的统一规定关于就车把上后视镜的安装方面批准后视镜及带与不带边斗的二轮机动车的统一规定关于批准装有卤素灯丝灯泡(HS2)的轻便摩托车前照灯的统一规定75 电子修正本1、修正本2、修正本382 42 电子83 20 电子致力于成为中国机械和汽车翻译的首选品牌电话:(8610)67668899 传真:(8610)67668899-801/802地址:北京市丰台区顺三条21号嘉业大厦1号楼12B09 邮编:100071修订本1、修订本1-斟误本1、修订本1-修正本1、修订本1-84关于根据发动机燃油要求就污染物排放方面批准车辆的统一规定修正本2、修订本1-修正本3、494电子修订本1-修正本4、修订本1-修正本3-斟误本1、修订本2、修订本2-修正本1、修订本2-斟误本185关于就油耗测量方面批准装有内燃机的机动车的统一规定关于就净功率和最大30分钟电传动系功率的测86量方面批准用于驱动M 和N 类机动车辆的内燃机或电传动系的统一规定87 88 89关于就灯光和光信号装置的安装方面批准农林拖拉机的统一规定 53 29 24电子电子电子修订本156电子修正本1、修正本264电子——换向批准机动车白天行车灯的统一规定关于批准摩托车反光轮胎的统一规定关于1.就最高车速限制或其可调车速限制功能方面批准车辆; 2.就已批准型式的最高车速限90 制装置或可调车速限制装置的安装方面批准车辆; 3.批准车速限制装置或可调车速限制装置的统一规定49 电子修正本191 关于批准机动车辆及其挂车用可更替制动衬片总成和鼓式制动器衬片的统一规定41 电子修订本1、修订本1-修正本1修正本1、修正本2、修正本3、修正本4、92 关于批准机动车及其挂车侧标志灯的统一规定关于批准摩托车、轻便摩托车和三轮车辆非原装可更换排气消声系统的统一规定关于1.批准前下部防护装置; 2.就已批准型式42 电子93 27 电子94 3.就的前下部防护装置的安装方面批准车辆;前下部防护方面批准车辆的统一规定关于就前碰撞中乘员防护方面批准车辆的统一规定关于就侧碰撞中乘员防护方面批准车辆的统一规定关于就发动机污染物排放方面批准农林拖拉机30 电子——修正本1、修正本2、修正本101电子2-斟误本1、修正本3、修正本496电子修正本1、修正本2、修正本3、斟误本1、95 96 97 和非道路机动机械装用的压燃式发动机的统一规定关于批准车辆报警系统和就报警系统方面批准机动车辆的统一规定关于批准装用气体放电光源的机动车前照灯的统一规定131 电子修正本5、修正本1-斟误本1、84电子修正本1、修正本2、修正本3、修正本4-斟误本1、修正本474电子修正本1、修正本298 99致力于成为中国机械和汽车翻译的首选品牌电话:(8610)67668899 传真:(8610)67668899-801/802地址:北京市丰台区顺三条21号嘉业大厦1号楼12B09 邮编:100071100ECE R100 ECE R101 ECE R102 ECE R103 ECE R104 ECE R105 ECE R106 ECE R107 ECE R108 ECE R109关于批准用于已获得型式批准的机动车气体放电灯具的气体放电光源的统一规定关于就结构、功能安全性和氢排放的特殊要求方面批准蓄电池电动车辆的统一规定关于就CO2排放和油耗的测量方面批准装用内燃机的乘用车和就电能消耗量和范围的测量方面批准装用电传动系的M1和N1类车辆的统一规定关于1.批准紧耦合装置;2.就已批准的紧耦合装置的安装方面批准车辆的统一规定。

ece r79法规
ECE R79法规是关于转向装置的统一规定,主要对当前车辆的转向装置提出了标准化的要求。
这些要求涵盖了从产品设计、性能、安装到使用等各个方面,旨在确保车辆在正常行驶过程中的安全性和稳定性。
通过满足这些要求,车辆可以在欧盟以及其他认可ECE法规的国家内销售和使用。
对于乘用车,ECE R79法规对其转向装置的设计和性能提出了具体要求,包括转向器的设计、转向力矩、转向角度、转向噪音等方面。
此外,法规还规定了转向装置的安装和调试要求,以确保其在车辆上的正确安装和正常运行。
为了确保车辆符合ECE R79法规,制造商需要对其转向装置进行一系列的测试和验证。
这些测试包括但不限于台架试验、道路试验和耐久性试验等,以确保转向装置在各种工况下都能正常、安全地工作。
总之,ECE R79法规是确保车辆转向装置安全性和稳定性的重要法规之一。
对于制造商来说,了解并遵守该法规的要求是非常必要的,以确保其产品的质量和安全性能符合相关标准和规定。

ece r79标准译文ECE R79 标准是欧洲经济委员会(EEC)制定的关于机动车安全带和约束系统的法规。
该标准主要规定了机动车安全带、安全气囊和约束系统的设计、性能、安装和使用要求。
以下是 ECE R79 标准的部分译文:第 1 章:总则1.1 目的本法规旨在确保机动车安全带和约束系统的设计、性能、安装和使用符合安全要求,以减少机动车事故中乘员的伤害。
1.2 适用范围本法规适用于所有在成员国境内生产、销售、进口和使用的机动车。
1.3 术语和定义本法规中使用的术语和定义如下:(a)机动车:具有四个或四个以上轮子的车辆,包括乘用车、轻型商用车、中型商用车、重型商用车、公共汽车、卡车和摩托车等。
(b)安全带:用于束缚乘员身体的带子或组件。
(c)约束系统:包括安全带、安全气囊和座椅等组件,用于保护乘员在机动车事故中的安全。
1.4 豁免成员国可以对本法规的部分条款给予豁免,但需向欧洲经济委员会报告。
第 2 章:安全带和约束系统的设计、性能和安装要求2.1 设计要求安全带和约束系统的设计应符合本法规规定的技术要求,并确保在正常使用和故障情况下都能提供足够的保护。
2.2 性能要求安全带和约束系统的性能应符合本法规规定的性能指标,包括乘员约束力、碰撞减速度、撞击力等。
2.3 安装要求安全带和约束系统的安装应符合本法规规定的安装要求,包括固定方式、调整方法、使用说明等。
第 3 章:安全带和约束系统的使用要求3.1 安全带的使用乘员应在行驶过程中正确佩戴安全带,并按照使用说明调整安全带的位置和紧度。
3.2 安全气囊的使用乘员应在行驶过程中正确使用安全气囊,并按照使用说明调整安全气囊的位置和高度。
3.3 座椅的使用乘员应在行驶过程中正确使用座椅,并按照使用说明调整座椅的位置和高度。
以上是 ECE R79 标准的部分译文,具体内容请查阅原文。
如需了解更多关于 ECE R79 标准的信息,请咨询相关部门或专业人士。
欧盟r79法规和功能安全好啦,今天咱们来聊聊欧盟R79法规和功能安全。
这听起来有点高深莫测,但其实没那么复杂。
简单说,R79法规就是为了让自动驾驶的汽车更加安全,这事儿可不是小事儿,毕竟我们的命可都是宝贵的嘛。
你想想,开车的时候,路上可都是各种各样的突发情况。
有的司机心情好,乐呵呵地开车,有的却像是开战斗机,眼神儿瞄得贼准。
哎,正因为如此,汽车的安全性显得尤为重要。
说到功能安全,大家可能会想,这是什么鬼?简单点说,功能安全就是确保汽车在关键时刻不会“掉链子”。
想象一下,你正在高速公路上行驶,突然刹车失灵,那可真是让人肝儿颤的事儿。
R79法规就像是给汽车戴上了个“安全帽”,确保它在关键时刻能乖乖听话,不会让人失望。
这样一来,咱们开车的时候就能多一份心安,少一份担心,真是太美好了。
你瞧,R79法规还涵盖了许多技术方面的要求。
汽车的传感器、控制系统、通讯协议等等,都得通过严格的检测。
就像是给汽车上了一道严密的“护城河”,不让坏东西进来。
这些技术的标准不仅仅是纸上谈兵,更是经过大量测试和实践验证的,能有效降低事故发生的概率。
这种严谨态度,真是让人心里倍感踏实。
不得不提的就是那些汽车制造商们。
他们为了符合R79法规,可真是绞尽脑汁。
有些厂家甚至干脆把研发团队的工资都提高了,让他们可以吸引更多顶尖人才来解决这些难题。
想想看,能在研发团队里干活,那可真是个高薪职业,谁不想呢?在这个竞争激烈的时代,能推出符合法规的安全汽车,简直就是在给自己打广告,声誉满满。
说到声誉,很多消费者在买车的时候,往往会注意到这些法规的合规性。
这就像是吃饭之前,大家都会看菜单,点菜的时候心里总得有个谱儿。
谁都不想买到个安全隐患满满的车,对吧?R79法规的存在,就让消费者心里有了底,可以更放心地选择。
车好不好,法规来背书,心里可踏实多了。
R79法规可不止是为了保护司机自己。
它还有一个非常重要的目的,就是保护路上的行人、骑自行车的小伙伴,还有那些开摩托车的兄弟们。
EN统一文本欧洲共同体官方出版物办公室CONSLEG体系出版CONSLEG:1970L0311 —1999年2月16日页数:21页欧洲共同体官方出版社办公室本文件纯属文件编制工具,有关机构对其内容不承担任何责任。
►B1970年6月8日委员会指令关于协调各成员国有关车辆及其挂车转向装置的法律(70/311/EEC)(OJ L 133,1970年6月18日,第10页)由以下指令修订:公报编号页码日期►M1 1992年7月2日委员会指令92/62/EEC L 199 33 1992年7月18日►M21999年1月26日委员会指令1999/7/EC L 40 36 1999年2月13日由以下指令修订:►A1 丹麦、爱尔兰、英国加入欧共体L 73 14 1972年3月27日▼B1970年6月8日委员会指令关于协调各成员国有关机动车及其挂车的转向装置的法律(70/311/EEC)考虑了建立欧洲经济共同体的条约,特别是其中的第100条;考虑了委员会的提议;考虑了欧洲议会的提议;(l)考虑了经济和社会委员会的意见;(2)鉴于按照本国法律,尤其是转向装置有关法律,机动车必须满足的那些技术要求;鉴于各成员国之间对上述要求有所不同;鉴于各成员国必需在其现有法规之外另外采用同样的要求,或者用同样的要求取代其现有法规,以便达到准许实施欧洲经济共同体型式认证程序之目的。
该型式认证程序指的是1970年2月6日委员会指令(3),关于各成员国车辆及其挂车型式认证的近似法律,该法律适用于各种车型;欧洲共同体委员已采用本指令:▼M2第1条本指令中,“车辆”指的是符合《70/156/EEC指令》第二条特征的车辆。
▼B第2条如果装置满足附录中设定的有关要求,各成员国均不得以转向装置为由拒绝为车辆发放EEC型式认证或国家型式认证。
▼A1第2a条如果车辆的转向装置满足附件中的要求,各成员国不得以其转向装置为由拒绝、禁止销售、注册,进行维修或使用车辆。
Seite druckenContentsECE-R 79UNIFORM PROVISIONS CONCERNING THE APPROVAL OF VEHICLES WITH REGARD TOSTEERING EQUIPMENTECE-R 79Steering Systems060120Deutscher Text:ECE-R 79 - Lenkanlage Title of the Regulation / History0. Introduction1. Scope2. Definitions3. Application for approval4. Approval5. Construction of production6. Tests provisions7. Conformity of production8. Penalties for non-conformity of production9. Modification and extension of approval of the vehicle type10. Production definitely discontinued11. Names and adresses of technical services responsible for conduction approval tests and of administrative departments ANNEX 1 - Communication concerning the approval or refusal or extension or withdrawal of approval or production definitely discontinued of a vehicle type with regard to steering equipment pursuant to Regulation No. 79ANNEX 2 - Arrangements of approval marksANNEX 3 - Braking performance for vehicles using the same energy source to supply steering equipment and braking device ANNEX 4 - Additional provisions for vehicles equipped with ASEANNEX 5 - Provisions for trailers having hydraulic steering transmissionANNEX 6 - Special requirements to be applied to the safety aspects of complex electronic vehicle control systemsModifications:E/ECE/324-E/ECE/TRANS/505/Rev.1/Add.78/Rev.2/Corr.2 Revision 2, Erratum In force: 20.01.2006 (already included)Paragraph: 4.2. (marked red)E/ECE/324-E/ECE/TRANS/505/Rev.1/Add.78/Rev.2 Amendment 01, Supplement 3 In force: 04.04.2005 (already included)Paragraphs: 0.; 1.2. until 1.2.4.; 2.2.1.; 2.3.2. until 2.3.6.3.; 2.4.3.; 2.5.1.1.; 2.5.2.4.; 2.6.4.; 2.7.; 3.2.2.; 3.2.3.; 4.1.1.; 4.2.;5.1.1.; 5.1.3. until 5.1.6.1.; 5.1.9. until 5.5.2.1.; 6.1.2.; 6.1.4.; 6.2.2.; 6.3.2.; 6.3.4. until 6.3.5.;7. until 7.2.;8.1.Annex 1 - 6.1.; 6.2.; 6.3.Annex 3 - 1. until 1.3.Annex 4 - 1.; 2.1.1.; 2.2.1.; 2.3.1.Annex 5 - 1.; 2.1.1.Annex 6 - newE/ECE/324-E/ECE/TRANS/505/Rev.1/Add.78 Original version In force: 01.12.1988E/ECE/324-E/ECE/TRANS/505/Rev.1/Add.78/Rev.1 Original version, Supplement 1 In force: 11.02.1990E/ECE/324-E/ECE/TRANS/505/Rev.1/Add.78/Rev.1 Original version, Corr.1 In force: 09.11.1990E/ECE/324-E/ECE/TRANS/505/Rev.1/Add.78/Rev.1/Amend.1 Original version, Supplement 2 In force: 05.12.1994E/ECE/324-E/ECE/TRANS/505/Rev.1/Add.78/Rev.1/Amend.1 Amendment 01 In force: 14.08.1995E/ECE/324-E/ECE/TRANS/505/Rev.1/Add.78/Rev.1/Amend.1 Original version, Corr.2 In force: 13.11.1995 E/ECE/324-E/ECE/TRANS/505/Rev.1/Add.78/Rev.1/Amend.2 Amendment 01, Supplement 1 In force: 07.02.1999E/ECE/324-E/ECE/TRANS/505/Rev.1/Add.78/Rev.1/Amend.3 Amendment 01, Supplement 2 In force: 31.01.2003 E/ECE/324-E/ECE/TRANS/505/Rev.1/Add.78/Rev.2 Amendment 01, Supplement 3 In force: 04.04.20050. INTRODUCTION TopThe intention of the Regulation is to establish uniform provisions for the layout and performance of steeringsystems fitted to vehicles used on the road. Traditionally the major requirement has been that the main steeringsystem contains a positive mechanical link between the steering control, normally the steering wheel, and theroad wheels in order to determine the path of the vehicle. The mechanical link, if amply dimensioned, has beenregarded as not being liable to failure.Advancing technology, coupled with the wish to improve occupant safety by elimination of the mechanicalsteering column, and the production advantages associated with easier transfer of the steering control betweenleft and right hand drive vehicles, has led to a review of the traditional approach and the Regulation is nowamended to take account of the new technologies. Accordingly it will now be possible to have steering systems inwhich there is not any positive mechanical connection between the steering control and the road wheels.Systems whereby the driver remains in primary control of the vehicle but may be helped by the steering systembeing influenced by signals initiated on-board the vehicle are defined as "Advanced Driver Assistance SteeringSystems". Such Systems can incorporate an "Automatically Commanded Steering Function", for example, usingpassive infrastructure features to assist the driver in keeping the vehicle on an ideal path (Lane Guidance, LaneKeeping or Heading Control), to assist the driver in manoeuvring the vehicle at low speed in confined spaces orto assist the driver in coming to rest at a pre-defined point (Bus Stop Guidance). Advanced Driver AssistanceSteering Systems can also incorporate a "Corrective Steering Function" that, for example, warns the driver of anydeviation from the chosen lane (Lane Departure Warning), corrects the steering angle to prevent departure fromthe chosen lane (Lane Departure Avoidance) or corrects the steering angle of one or more wheels to improve thevehicle’s dynamic behaviour or stability.In the case of any Advanced Driver Assistance Steering System, the driver can, at all times, choose to overridethe assistance function by deliberate action, for example, to avoid an unforeseen object in the road.It is anticipated that future technology will also allow steering to be influenced or controlled by sensors andsignals generated either on or off-board the vehicle. This has led to several concerns regarding responsibility forthe primary control of the vehicle and the absence of any internationally agreed data transmission protocols withrespect to off-board or external control of steering. Therefore, the Regulation does not permit the generalapproval of systems that incorporate functions by which the steering can be controlled by external signals, forexample, transmitted from roadside beacons or active features embedded into the road surface. Such systems,which do not require the presence of a driver, have been defined as "Autonomous Steering Systems".This Regulation also prevents the approval of positive steering of trailers using energy supply and electricalcontrol from the towing vehicle as there are not any standards applicable to energy supply connectors or tocontrol transmission digital information interchange. It is expected that at some time in the future, theInternational Standards Organization (ISO) Standard, ISO11992, will be amended to take account oftransmission of steering control data.1. SCOPE Top 1.1.This Regulation applies to the steering equipment of vehicles of categories M, N and O. 1/1.2.This Regulation does not apply to:1.2.1.Steering equipment with a purely pneumatic transmission;1.2.2.Autonomous Steering Systems as defined in paragraph 2.3.3;1.2.3.Full power steering systems fitted to trailers where the energy necessary for operation is transmitted from thetowing vehicle;1.2.4.The electrical control of full power steering systems fitted to trailers, other than additional steering equipment asdefined in paragraph 2.5.2.4.1/ As defined in Annex 7 of the Consolidated Resolution on the Construction of Vehicles (R.E.3)(TRANS/SC.1/WP.29/78/Rev.1).2. DEFINITIONS TopFor the purposes of this Regulation:2.1."Approval of a vehicle" means the approval of a vehicle type with regard to its steering equipment.2.2."Vehicle type" means a vehicle which does not differ with respect to the manufacturer's designation of the vehicletype and in essential characteristics such as:2.2.1.type of steering equipment, steering control, steering transmission, steered wheels, and energy source.2.3."Steering equipment" means all the equipment the purpose of which is to determine the direction of movementof the vehicle.The steering equipment consists of:The steering control,The steering transmission,The steered wheels,The energy supply, if any.2.3.1."Steering control" means the part of the steering equipment which controls its operation; it may be operated withor without direct intervention of the driver. For steering equipment in which the steering forces are providedsolely or partly by the muscular effort of the driver the steering control includes all parts up to the point wherethe steering effort is transformed by mechanical, hydraulic or electrical means;2.3.2."Steering transmission" means all components which form a functional link between the steering control and theroad wheels.The transmission is divided into two independent functions:The control transmission and the energy transmission.Where the term "transmission" is used alone in this Regulation, it means both the control transmission and theenergy transmission. A distinction is drawn between mechanical, electrical and hydraulic transmission systems orcombinations thereof, according to the means by which the signals and/or energy is transmitted.2.3.2.1."Control transmission" means all components by means of which signals are transmitted for control of thesteering equipment.2.3.2.2."Energy transmission" means all components by means of which the energy required for control/Regulation ofthe steering function of the wheels is transmitted.2.3.3."Autonomous Steering System" means a system that incorporates a function within a complex electronic controlsystem that causes the vehicle to follow a defined path or to alter its path in response to signals initiated andtransmitted from off-board the vehicle. The driver will not necessarily be in primary control of the vehicle.2.3.4."Advanced Driver Assistance Steering System" means a system, additional to the main steering system, thatprovides assistance to the driver in steering the vehicle but in which the driver remains at all times in primarycontrol of the vehicle. It comprises one or both of the following functions:2.3.4.1."Automatically commanded steering function" means the function within a complex electronic control systemwhere actuation of the steering system can result from automatic evaluation of signals initiated on-board thevehicle, possibly in conjunction with passive infrastructure features, to generate continuous control action inorder to assist the driver in following a particular path, in low speed manoeuvring or parking operations.2.3.4.2."Corrective steering function" means the discontinuous control function within a complex electronic controlsystem whereby, for a limited duration, changes to the steering angle of one or more wheels may result from theautomatic evaluation of signals initiated on-board the vehicle, in order to maintain the basic desired path of thevehicle or to influence the vehicle’s dynamic behaviour.Systems that do not themselves positively actuate the steering system but that, possibly in conjunction withpassive infrastructure features, simply warn the driver of a deviation from the ideal path of the vehicle, or of anunseen hazard, by means of a tactile warning transmitted through the steering control, are also considered to becorrective steering.2.3.5."Steered wheels" means the wheels, the alignment of which may be altered directly or indirectly in relation to thelongitudinal axis of the vehicle in order to determine the direction of movement of the vehicle. (The steeredwheels include the axis around which they are rotated in order to determine the direction of movement of thevehicle);2.3.6."Energy supply" includes those parts of the steering equipment which provide it with energy, regulate thatenergy and where appropriate, process and store it. It also includes any storage reservoirs for the operatingmedium and the return lines, but not the vehicle’s engine (except for the purpose of paragraph 5.3.2.1.) or itsdrive to the energy source.2.3.6.1."Energy source" means the part of the energy supply, which provides the energy in the required form.2.3.6.2."Energy reservoir" means that part of the energy supply in which the energy provided by the energy source isstored, for example, a pressurised fluid reservoir or vehicle battery.2.3.6.3."Storage reservoir" means that part of the energy supply in which the operating medium is stored at or near tothe atmospheric pressure, for example a fluid reservoir.2.4.Steering parameters2.4.1."Steering control effort" means the force applied to the steering control in order to steer the vehicle.2.4.2."Steering time" means the period of time from the beginning of the movement of the steering control to themoment at which the steered wheels have reached a specific steering angle.2.4.3."Steering angle" means the angle between the projection of a longitudinal axis of the vehicle and the line ofintersection of the wheel plane (being the central plane of the wheel, normal to the axis around which it rotates)and the road surface.2.4.4."Steering forces" mean all the forces operating in the steering transmission.2.4.5."Mean steering ratio" means the ratio of the angular displacement of the steering control to the mean of theswept steering angle of the steered wheels for a full lock-to-lock turn;2.4.6."Turning circle" means the circle within which are located the projections on to the ground plane of all the pointsof the vehicle, excluding the external mirrors and the front direction indicators, when the vehicle is driven in acircle;2.4.7."Nominal radius of steering control" means in the case of a steering wheel the shortest dimension from its centreof rotation to the outer edge of the rim. In the case of any other form of control it means the distance betweenits centre of rotation and the point at which the steering effort is applied. If more than one such point isprovided, the one requiring the greatest effort shall be used.2.5.Types of steering equipmentDepending on the way the steering forces are produced, the following types of equipment are distinguished:2.5.1.For motor vehicles:2.5.1.1."Main steering system" means the steering equipment of a vehicle which is mainly responsible for determiningthe direction of travel. It may comprise:2.5.1.1.1."Manual steering equipment" in which the steering forces result solely from the muscular effort of the driver.2.5.1.1.2."Power assisted steering equipment" in which the steering forces result from both the muscular effort of thedriver and the energy supply (supplies).2.5.1.1.2.1.Steering equipment in which the steering forces result solely from one or more energy supplies when theequipment is intact, but in which the steering forces can be provided by the muscular effort of the driver alone ifthere is a fault in the steering (integrated power systems), is also considered to be power assisted steeringequipment;2.5.1.1.3."Full-power steering equipment" in which the steering forces are provided solely by one or more energy supplies;2.5.1.2."Self-tracking steering equipment" means a system designed to create a change of steering angle on one ormore wheels only when acted upon by forces and/or moments applied through the tyre to road contact.2.5.1.3."Auxiliary steering equipment (ASE)" means a system in which the wheels on axle(s) of vehicles of categories Mand N are steered in addition to the wheels of the main steering equipment in the same or opposite direction tothose of the main steering equipment and/or the steering angle of the front and/or the rear wheels may beadjusted relative to vehicle behaviour.2.5.2.For trailers:2.5.2.1."Self-tracking steering equipment" means a system designed to create a change of steering angle on one ormore wheels only when acted upon by forces and/or moments applied through the tyre to road contact.2.5.2.2."Articulated steering" means equipment in which the steering forces are produced by a change in direction of thetowing vehicle and in which the movement of the steered trailer wheels is firmly linked to the relative anglebetween the longitudinal axis of the towing vehicle and that of the trailer;2.5.2.3."Self-steering" means equipment in which the steering forces are produced by a change in direction of the towingvehicle and in which the movement of the steered trailer wheels is firmly linked to the relative angle between thelongitudinal axis of the trailer frame or a load replacing it and the longitudinal axis of the sub-frame to which theaxle(s) is (are) attached;2.5.2.4."Additional steering equipment" means a system, independent of the main steering system, by which thesteering angle of one or more axle(s) of the steering system can be influenced selectively for manoeuvringpurposes.2.5.3.Depending on the arrangement of the steered wheels, the following types of steering equipment aredistinguished:2.5.3.1."Front-wheel steering equipment" in which only the wheels of the front axle(s) are steered. This includes allwheels which are steered in the same direction.2.5.3.2."Rear-wheel steering equipment" in which only the wheels of the rear axle(s) are steered. This includes allwheels which are steered in the same direction.2.5.3.3. "Multi-wheel steering equipment" in which the wheels of one or more of each of the front and the rear axle(s) aresteered;2.5.3.3.1."All-wheel steering equipment" in which all the wheels are steered;2.5.3.3.2."Buckle steering equipment" in which the movement of chassis parts relative to each other is directly producedby the steering forces.2.6.Types of steering transmissionDepending on the way the steering forces are transmitted, the following types of steering transmission aredistinguished:2.6.1."Purely mechanical steering transmission" means a steering transmission in which the steering forces aretransmitted entirely by mechanical means.2.6.2."Purely hydraulic steering transmission" means a steering transmission in which the steering forces, somewherein the transmission, are transmitted only by hydraulic means.2.6.3."Purely electric steering transmission" means a steering transmission in which the steering forces, somewhere inthe transmission, are transmitted only through electric means.2.6.4."Hybrid steering transmission" means a steering transmission in which part of the steering forces is transmittedthrough one and the other part through another of the above mentioned means. However, in the case where anymechanical part of the transmission is designed only to give position feedback and is too weak to transmit thetotal sum of the steering forces, this system shall be considered to be purely hydraulic or purely electric steeringtransmission.2.7."Electric control line" means the electrical connection which provides the steering control function to the trailer. Itcomprises the electrical wiring and connector and includes the parts for data communication and the electricalenergy supply for the trailer control transmission.3. APPLICATION FOR APPROVAL Top 3.1.The application for approval of a vehicle type with regard to the steering equipment shall be submitted by thevehicle manufacturer or by his duly accredited representative.3.2.It shall be accompanied by the undermentioned documents in triplicate, and by the following particulars:3.2.1. a description of the vehicle type with regard to the items mentioned in paragraph 2.2.; the vehicle type shall bespecified;3.2.2. a brief description of the steering equipment with a diagram of the steering equipment as a whole, showing theposition on the vehicle of the various devices influencing the steering.3.2.3.in the case of full power steering systems and systems to which Annex 6 of this Regulation applies, an overviewof the system indicating the philosophy of the system and the fail-safe procedures, redundancies and warningsystems necessary to ensure safe operation in the vehicle.The necessary technical files relating to such systems shall be made available for discussion with the typeapproval authority and/or technical service. Such files will be discussed on a confidential basis.3.3. A vehicle representative of the vehicle type to be approved shall be submitted to the technical service responsiblefor conducting approval tests.4. APPROVAL Top 4.1.If the vehicle submitted for approval pursuant to this Regulation meets all relevant requirements given in thisRegulation, approval of that vehicle type with regard to the steering equipment shall be granted.4.1.1.The type approval authority shall verify the existence of satisfactory arrangements for ensuring effective controlof the conformity of production as given in paragraph 7. of this Regulation, before type approval is granted.4.2.An approval number shall be assigned to each type approved. Its first two digits (at present 01) shall indicate theseries of amendments incorporating the most recent major technical amendments made to the Regulation at thetime of issue of the approval. The same Contracting Party shall not assign this number to another vehicle type orto the same vehicle type submitted with different steering equipment from that described in the documentsrequired by paragraph 3.4.3.Notice of approval or of extension or refusal of approval of a vehicle type pursuant to this Regulation shall becommunicated to the Parties to the 1958 Agreement which apply this Regulation, by means of a form conformingto the model in Annex 1 to this Regulation.4.4.There shall be affixed, conspicuously and in a readily accessible place specified on the approval form, to everyvehicle conforming to a vehicle type approved under this Regulation, an international approval mark consistingof:4.4.1. a circle surrounding the letter "E" followed by the distinguishing number of the country which has grantedapproval; 2/4.4.2.the number of this Regulation, followed by the letter "R", a dash and the approval number to the right of thecircle prescribed in paragraph 4.4.1.4.5.If the vehicle conforms to a vehicle type approved, under one or more other Regulations annexed to theAgreement, in the country which has granted approval under this Regulation, the symbol prescribed in paragraph4.4.1. need not be repeated; in such a case the Regulation and approval numbers and the additional symbols ofall the Regulations under which approval has been granted in the country which has granted approval under thisRegulation shall be placed in vertical columns to the right of the symbol prescribed in paragraph 4.4.1.4.6.The approval mark shall be clearly legible and shall be indelible.4.7.The approval mark shall be placed close to or on the vehicle data plate affixed by the manufacturer.4.8.Annex 2 to this Regulation gives examples of arrangements of approval marks.2/ 1 for Germany, 2 for France, 3 for Italy, 4 for the Netherlands, 5 for Sweden, 6 for Belgium, 7 for Hungary, 8 for theCzech Republic, 9 for Spain, 10 for Serbia and Montenegro, 11 for the United Kingdom, 12 for Austria, 13 for Luxembourg,14 for Switzerland, 15 (vacant), 16 for Norway, 17 for Finland, 18 for Denmark, 19 for Romania, 20 for Poland, 21 forPortugal, 22 for the Russian Federation, 23 for Greece, 24 for Ireland, 25 for Croatia, 26 for Slovenia, 27 for Slovakia, 28 forBelarus, 29 for Estonia, 30 (vacant), 31 for Bosnia and Herzegovina, 32 for Latvia, 33 (vacant), 34 for Bulgaria, 35 (vacant),36 for Lithuania, 37 for Turkey, 38 (vacant), 39 for Azerbaijan, 40 for The former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia, 41(vacant), 42 for the European Community (Approvals are granted by its Member States using their respective ECE symbol),43 for Japan, 44 (vacant), 45 for Australia, 46 for Ukraine, 47 for South Africa, 48 for New Zealand, 49 for Cyprus, 50 forMalta and 51 for the Republic of Korea. Subsequent numbers shall be assigned to other countries in the chronological orderin which they ratify or accede to the Agreement Concerning the Adoption of Uniform Technical Prescriptions for WheeledVehicles, Equipment and Parts which can be Fitted and/or be Used on Wheeled Vehicles and the Conditions for ReciprocalRecognition of Approvals Granted on the Basis of these Prescriptions, and the numbers thus assigned shall be communicatedby the Secretary-General of the United Nations to the Contracting Parties to the Agreement.5. CONSTRUCTION OF PRODUCTION Top 5.1.General provisions5.1.1.The steering system shall ensure easy and safe handling of the vehicle up to its maximum design speed or incase of a trailer up to its technically permitted maximum speed. There must be a tendency to self-centre whentested in accordance with paragraph 6.2. with the intact steering equipment. The vehicle shall meet therequirements of paragraph 6.2. in the case of motor vehicles and of paragraph 6.3. in the case of trailers. If avehicle is fitted with an auxiliary steering system, it shall also meet the requirements of Annex 4. Trailersequipped with hydraulic steering transmissions shall comply also with Annex 5.5.1.2.It must be possible to travel along a straight section of road without unusual steering correction by the driverand without unusual vibration in the steering system at the maximum design speed of the vehicle.5.1.3.The direction of operation of the steering control shall correspond to the intended change of direction of thevehicle and there shall be a continuous relationship between the steering control deflection and the steeringangle. These requirements do not apply to systems that incorporate an automatically commanded or correctivesteering function, or to auxiliary steering equipment.These requirements may also not necessarily apply in the case of full power steering when the vehicle isstationary and when the system is not energised.5.1.4.The steering equipment shall be designed, constructed and fitted in such a way that it is capable of withstandingthe stresses arising during normal operation of the vehicle, or combination of vehicles. The maximum steeringangle shall not be limited by any part of the steering transmission unless specifically designed for this purpose.Unless otherwise specified, it will be assumed that for the purpose of this Regulation, not more than one failurecan occur in the steering equipment at any one time and two axles on one bogie shall be considered as one axle.5.1.5.The effectiveness of the steering equipment, including the electrical control lines, shall not be adversely affectedby magnetic or electric fields. Conformity with the technical requirements of Regulation No. 10, to theamendment in force at the time of Type Approval shall be demonstrated.5.1.6.Advanced driver assistance steering systems shall only be approved in accordance with this Regulation where thefunction does not cause any deterioration in the performance of the basic steering system. In addition they shallbe designed such that the driver may, at any time and by deliberate action, override the function.。