罗宾斯《管理学》第九版题库 16
- 格式:doc
- 大小:122.50 KB
- 文档页数:21

管理学第9版练习题附答案Chapter 6 Decision Making: The Essence of the Manager’s JobTRUE/FALSE QUESTIONSTHE DECISION-MAKING PROCESS1.Problem identification is purely objective.2.The second step in the decision-making process is identifying a problem.3. A decision criterion defines what is relevant in a decision.4.The fourth step of the decision-making process requires the decision maker tolist viable alternatives that could resolve the problem.5.Once the alternatives have been identified, a decision maker must analyze eachone.6.The step in the decision-making process that involves choosing a best alternativeis termed implementation.THE MANAGER AS DECISION MAKER7.Making decisions is with the essence of management.8.Managerial decision making is assumed to be rational.9.One assumption of rationality is that we cannot know all of the alternatives.10.Managers tend to operate under assumptions of bounded rationality.11.Studies of the events leading up to the Challenger space shuttle disaster pointto an escalation of commitment by decision makers.12. Managers regularly use their intuition in decision making.13.Rational analysis and intuitive decision making are complementary.14.Programmed decisions tend to be repetitive and routine.15.Rules and policies are basically the same.16.A policy is an explicit statement that tells a manager what he or she ought orought not to do.17.The solution to nonprogrammed decision making relies on procedures, rules, andpolicies.18.Most managerial decisions in the real world are fully nonprogrammed.19.The ideal situation for making decisions is low risk.20.Risk is the condition in which the decision maker is able to estimate thelikelihood of certain outcomes.21.Risk is a situation in which a decision maker has neither certainty norreasonable probability estimates.22.People who have a low tolerance for ambiguity and are rational in their way ofthinking are said to have a directive style.23.Decision makers with an analytic style have a much lower tolerance for ambiguitythan do directive types.24.Individuals with a conceptual style tend to be very broad in their outlook andwill look at many alternatives.25. Behavioral-style decision makers work well with others.26.Most managers have characteristics of analytic decisionmakers.27.According to the boxed feature, “Managing Workforce Diversity,” diverseemployees tend to make decisions faster than a homogeneous group of employees.28.The anchoring effect describes when decision makers fixate on initial informationas a starting point and then, once set, they fail to adequately adjust for subsequent information.29.The availability bias describes when decision makers try to create meaning out ofrandom events.30. The sunk cost error is when decision makers forget that current choices cannotcorrect the past.DECISION MAKING FOR T ODAY’S WORLD31.Today’s business world revolves around making decisions, usually with completeor adequate information, and under minimal time pressure.32.Managers need to understand cultural differences to make effective decisions intoday’s fast-moving world.33.According to the boxed feature, “Focus on Leadership,” when identifyingproblems, managers might be from a culture that is focused on problem solving, or their culture might be one of situation acceptance.34.According to the boxed feature, “Focus on Leadership,” findings from studies byGeert Hofstede and from GLOBE researchers show that inhigh uncertainty avoidance countries, decision making tends to be based more on intuition than on formal analysis.35.Highly reliable organizations (HROs) are easily tricked by their success.MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONSFor each of the following choose the answer that most completely answers the question.THE DECISION-MAKING PROCESS36.Decision making is typically described as ________________, which is a view thatis too simplistic.a.deciding what is correctb.putting preferences on paperc.choosing among alternativesd.processing information to completion37.A series of eight steps that begins with identifying a problem and concludes withevaluating the decision’s effectiveness i s the ________________.a.decision-making processb.managerial processc.maximin styled.bounded rationality approach38.________________ is the existence of a discrepancy between an existing and adesired state of affairs.a.An opportunityb. A solutionc. A weaknessd. A problem39.In identifying the problem, a manager _________________./doc/d417811801.html,pares the current state of affairs with where they would like to beb.expects problems to be defined by neon lightsc.looks for discrepancies that can be postponedd.will not act when there is pressure to make a decision40.Which of the following statements is true concerning problem identification?a.Problems are generally obvious.b. A symptom and a problem are basically the same.c.Well-trained managers generally agree on what is considered a problem.d.The problem must be such that it exerts some type of pressure on the managerto act.41. What is the second step in the decision-making process?a.identifying decision criteriab.allocating weights to the criteriac.analyzing alternativesd.identifying a problem42.To determine the _____________, a manager must determine what is relevant orimportant to resolving the problem.a.geocentric behavior neededb.number of allowable alternativesc.weighting of decision criteriad.decision criteria43.What is the third step in the decision-making process?a.allocating weights to the criteriab.analyzing the alternativesd.implementing the alternative44.If all criteria in the decision making are equal, weighting the criteria______________.a.improves decision making when large numbers of criteria are involvedb.is not neededc.produces excellent decisionsd.improves the criteria45.In allocating weights to the decision criteria, which of the following is helpfulto remember?a.All weights must be the same.b.The total of the weights should sum to .c.Every factor criterion considered, regardless of its importance, must receivesome weighting.d.Assign the most important criterion a score, and then assign weights againstthat standard.46.What is the step where a decision maker wants to be creative in coming up withpossible alternative?a.allocating weights to the criteriab.analyzing alternativesc.developing alternativesd.identifying decision criteria47. When analyzing alternatives, what becomes evident?a.the strengths and weaknesses of each alternativec.the list of alternativesd.the problem48.When developing alternatives in the decision-making process, what must a managerdo?a.list alternativesb.evaluate alternativesc.weight alternativesd.implement alternatives49.Selecting an alternative in the decision-making process is accomplished by__________________.a.choosing the alternative with the highest scoreb.choosing the one you like bestc.selecting the alternative that has the lowest priced.selecting the alternative that is the most reliable50.In Step 6 of the decision-making process, each alternative is evaluated byappraising it against the _____________.a.subjective goals of the decision makerb.criteriac.assessed valuesd.implementation strategy51.______________ includes conveying a decision to those affected and getting theircommitment to it.a.Selecting an alternativeb.Evaluating the decision effectivenessc.Implementing the alternativesd.Analyzing alternatives52.Which of the following is important in effectively implementing the chosenalternative in the decision-making process?a.getting upper-management supportb.double-checking your analysis for potential errorsc.allowing those impacted by the outcome to participate in the processd.ignoring criticism concerning your chosen alternative53. The final step in the decision-making process is to _______________.a.pick the criteria for the next decisionb.reevaluate the weightings of the criteria until they indicate the correctoutcomec.evaluate the outcome of the decisiond.reassign the ratings on the criteria to find different outcomes54.Which of the following is important to remember in evaluating the effectivenessof the decision-making process?a.You should ignore criticism concerning the decision-making process.b.You may have to start the whole decision process over.c.You will have to restart the decision-making process if the decision is lessthan 50 percent effective.d.Ninety percent of problems with decision making occur in the implementationstep.THE MANAGER AS DECISION MAKER55.Managers are assumed to be ______________; they make consistent, value-maximizingchoices within specified constraints.a.rationalb.leaders/doc/d417811801.html,anizedd.satisficers56.It is assumed that a perfectly rational decision maker ______________.a.does not follow rational assumptionsb.does not consider value maximizing as an objectivec.offers inconsistent decisionsd.would be objective and logical57.Managers can make rational decisions if _________________.a.the problem is ambiguousb.the goals are unclearc.the alternatives are limitedd.time constraints exist58. Which of the following is not a valid assumption about rationality?a.The problem is clear and unambiguous.b. A single, well-defined goal is to be achieved.c.Preferences are clear.d.Preferences are constantly changing.59.When managers circumvent the rational decision-making model and find ways tosatisfice, they are following the concept of _________________.a.jurisprudenceb.bounded rationalityc.least-squared exemptionsd.self-motivated decisions60.B ecause managers can’t possibly analyze all information on all alternatives,managers ______________, rather than ______________.a.maximize; satisficeb.maximize; minimizec.satisfice; minimized.satisfice; maximize61.The type of decision making in which the solution is considered “good enough”is known as _________________.a.intuitionb.satisfyingc.maximizingd.satisficing62.When a decision maker chooses an alternative under perfect rationality, she______________ her decision, whereas under bounded rationality she chooses a ______________ decision.a.minimizes; satisficingb.satisfices; maximizingc.maximizes; satisficingd.maximizes; minimizing63. An increased commitment to a previous decision despite evidence that it may havebeen wrong is referred to as _______________.a.economies of commitmentb.escalation of commitmentc.dimensional commitmentd.expansion of commitment64.Intuitive decision making is _______________.a.not utilized in organizationsb. a conscious process based on accumulated judgmentc.making decisions based on experience, feelings, and accumulated judgmentd.important in supporting escalation of commitment65.In studying intuitive decision making, researchers have found that__________________.a.managers do not make decisions based on feelings or emotionsb.managers use data from their subconscious mind to help make their decisionsc.rational thinking always works better than intuitived.accumulated experience does not support intuitive decisions66.All of the following are aspects of intuition except __________________.a.experienced-based decisionsb.affect-initiated decisionsc.cognitive-based decisionsd.programmed decisions67._____________ are straightforward, familiar, and easily defined.a.Unstructured problemsb.Structured problemsc.Unique problemsd.Nonprogrammed problems68.Structured problems align well with which type ofdecision making?a.programmedb.satisficingc.intuitiond.gut feeling69. ______________ decision making is relatively simple and tends to rely heavily onprevious solutions.a.Nonprogrammedb.Linearc.Satisficingd.Programmed70.A procedure _______________.a.is an explicit statement detailing exactly how to deal with a decisionb.is a series of interrelated sequential steps to respond to a structuredproblemc.is a set of guidelines that channel a manager’s thinking in dealing with aproblemd.allows a manager to use broad decision-making authority71.A ______________ is an explicit statement that tells a manager what he or she canor cannot do.a.procedureb.policyc.ruled.solution72.A policy ____________.a.typically contains an ambiguous termb.is used frequently when a manager faces a structured problemc.allows little discretion on the part of the managerd.offers strict rules as to how a problem should be solved73.What is a difference between a policy and a rule?a. A policy establishes parameters.b. A rule establishes parameters.c. A policy is more explicit.d. A rule is more ambiguous.74.A ______________ typically contains an ambiguous term that leaves interpretationup to the decision maker.a.systemb.rulec.solutiond.policy75.A business school’s statement that it “strives for productive relationshipswith local org anizations” is an example of a ________________.a.ruleb.policyc.procedure/doc/d417811801.html,mitment76.Unstructured problems _____________.a.are easily solvedb.present familiar circumstancesc.force managers to deal with incomplete or ambiguous informationd.are routine77.Nonprogrammed decisions are best described as ________________.a.recurring, but difficult to makeb.very similar to problems in other areas of the organizationc.requiring more aggressive action on the decision maker’s thought processesd.unique and nonrecurring78.When problems are ______________, managers must rely on ______________ in orderto develop unique solutions.a.structured; nonprogrammed decision makingb.structured; pure intuitionc.unstructured; nonprogrammed decision makingd.unstructured; programmed decision making79.Lower-level managers typically confront what type of decision making?a.uniqueb.nonroutinec.programmedd.nonprogrammed80.Which of the following is likely to make the most programmed decisions?a.the CEO of PepsiCo.b.the vice president of General Motors Cadillac Division.c.the head of the Minute Maid Division at Coca-Cola.d.the manager of the local McDonald’s.81.______________ is a situation in which a manager can make accurate decisionsbecause the outcome of every alternative is known.a.Certaintyb.Riskc.Uncertaintyd.Maximaxe.Maximin82.If an individual knows the price of three similar cars at different dealerships,he or she is operating under what type of decision-making condition?a.riskb.uncertaintyc.certaintyd.factual83.A retail clothing store manager who estimates how much to order for the currentspring season b ased on last spring’s outcomes is operating under what kind of decision-making condition?a.seasonalb.riskc.uncertaintyd.certainty84.______________ is a situation in which a decision maker has neither certainty norreasonable probability estimates available.a.Certaintyb.Riskc.Uncertaintyd.Maximax85.Nonprogrammed decisions are typically made under a condition of ________________.a.certaintyb.low levels of riskc.uncertaintyd.reliability86. A person at a horse racetrack who bets all of his or her money on the odds-basedlong shot to “win” (rather than “place” or “show”) is making what kind of choice?a.maximaxb.maximinc.minimaxd.minimin87.What best describes the psychological orientation of an individual making a“maximax” choice?a.optimistb.realistc.pessimistd.satisficer88.Optimistic managers could be expected to utilize their maximax orientation whenthey _______________.a.maximize the maximum payoffb.maximize the minimum payoffc.minimize the maximum regretd.minimize the minimum regret89.What is the psychological orientation of a decision maker who makes a “maximin”choice?a.optimistb.realistc.pessimistd.satisficer90.Which of the following best describes “maximizing the minimum possible payoff”?a.maximaxb.maximinc.minimaxd.minimin91.A manager who desires t o minimize his or her maximim “regret” will opt for a______________ choice.a.maximaxb.maximinc.minimaxd.minimin92. Decision makers using what decision-making style make fast decisions and focuson the short run?a.directiveb.behavioralc.analyticd.conceptual93.What types are characterized as careful decision makers with the ability to adaptor cope with unique situations?a.directive decision makersb.behavioral decision makersc.analytic decision makersd.conceptual decision makers94.Who are concerned about the achievements of thosearound them and are receptiveto suggestions from others?a.directive decision makersb.behavioral decision makersc.analytic decision makersd.conceptual decision makers95.Many managers use __________ or rules of thumb to simplify their decision making.a.heuristicsb.biasesc.errorsd.habits96.When decision makers tend to think they know more than they do or holdunrealistically positive views of themselves and their performance, they are exhibiting _______________.a.self-serving biasb.the anchoring effectc.immediate gratification biasd.overconfidence bias97.When decision makers seek out information that reaffirms their past choices anddiscount information that contradicts past judgments, they are exhibiting _______________.a.availability biasb.the anchoring effectc.self-serving biasd.confirmation bias98.When decision makers assess the likelihood of an event based on how closely itresembles other events or sets of events, they are using _______________.a.availability biasb.framing biasc.selective perception biasd.representation bias99.What is the tendency for decision makers to falsely believe that they would haveaccurately predicted the outcome of an event once that outcome is actually known?a.the hindsight biasb.the sunk costs errorc.the randomness biasd.the selective perception biasDECISION MAKING FOR TODAY’S WORLD100.According to the boxed feature, “Focus on Leadership,” when _______________, managers might come from a culture that gathers facts or from a culture that is more intuitive in gathering ideas and possibilities.a.developing alternativesb.implementing alternativesc.searching for informationd.identifying problems101.To make effective d ecisions in today’s fast-moving world, managers need to -_______________./doc/d417811801.html,e the five-stage decision-making processb.know when it is time to call it quitsc.ignore cultural differencesd.identify their style of decision making102.What is a characteristic that the experts say an effective decision-making process has?a.It is inconsistent.b.It acknowledges only objective thinking.c.It focuses on all factors—even those that do not seem important.d.It requires only as much information and analysis as is necessary.103. What term is used by Navy aviators to describe a gut feeling that something isn’t right?a.leemersb.the creepsc.uneasinessd.regret104.Managers of highly reliable organizations (HROs) get the input of _______________ and let them make decisions.a.CEOsb.frontline workersc.customersd.suppliers105.When highly reliable organizations (HROs) face complexity, they -_______________.a.try to simplify datab.aim for deeper understanding of the situationc.defer to the expertsd.act, then thinkSCENARIOS AND QUESTIONSFor each of the following choose the answer that most completely answers the question.THE DECISION-MAKING PROCESSDecisions, Decisions (Scenario)Sond ra needed help. Her insurance company’s rapid growth was necessitating making some changes, but what changes? Should they add to the existing information system or should they buy a new system? She was given the responsibility of analyzing the company’s pr esent information system and deciding what the company should do that would give them plenty of room. She was confused and needed help in making the correct decision.106.According to the decision-making process, the first step Sondra should take is to _____________.a.analyze alternative solutionsb.identify decision criteriac.evaluate her decision’s effectivenessd.identify the problem107. According to the decision-making process, the second step Sondra should take is to ____________.a.analyze alternative solutionsb.identify decision criteriac.evaluate her decision’s effectivenessd.allocate weights to the criteria108.Allocating weights to the criteria is the step in the decision-making process that occurs between identifying the decision criteria and ______________.a.developing the alternativesb.selecting alternativesc.implementing the alternatived.identifying the problem109.When Sondra is conveying her decision to those affected and getting their commitment to it, she is performing which stepin the decision-making process?a.analyzing alternative solutionsb.selecting alternativesc.implementing the alternatived.identifying the problem110.The very last step Sondra should take, according to the decision-making process, is to __________.a.analyze alternative solutionsb.select alternativesc.implement the alternatived.evaluate the decision’s effectivenessThe Car (Scenario)Colleen is a student, and her older brother has loaned her an old car. The car is in need of several repairs before she will feel comfortable driving it.111.Colleen needs a vehicle, but she has to decide if the vehicle is worth repairing. She is facing a(n) _____________, a discrepancy between an existing and a desired state of affairs.a.alternativeb.weighted problem setc.problemd.certainty avoidance situation112.In talking with an automotive repair person, Colleen needs to prioritize the repairs. Her first concern is safety of the vehicle. This step in the decision-making process is called __________________.a.weighting the decision criteriab.analyzing of alternativesc.identifying decision criteriad.selecting an alternativeTHE MANAGER AS DECISION MAKERThe Car (Scenario)Colleen is a student, and her older brother has loaned her an old car. The car is in need of several repairs before she will feel comfortable driving it.113.Colleen decides to have all of the problems fixed on the car. She assumes that the repair person has found all the problems and that there will be no problem correcting the imperfections within a specified budget. This is an example of a __________ decision.a.parochialb.irrationalc.ethicald.rational114.Colleen’s brother has a different view of the repairs. He assumes that the repair person is using the best information available, but there may be other unexpected repairs that might surface and that a higher budget might be more reasonable. He is using ______________.a.rational decision makingb.risk avoidancec.bounded rationalityd.Stage 4 decision making115.Colleen’s brother feels the car is worth repairing because he has owned several cars made by the same manufacturer as this car, and he has driven this car for several years. He is using _________ to determine that the car has value despite its need of repair.a.intuitive decision makingb.selective coordination of thought processesc.sunk costsd.return on investmentThe First Job (Scenario)Upon graduation, you search for a job with the university’s job placement center. Although you have studied and prepared to work in an advertising agency, the first job that you are offered is a supervisor in a manufacturing company working the afternoon shift from 3:00 . until 11:00 .116.If you had made a larger search using the Internet and other employment search processes, you might have been able to find more employment opportunities. This would have been a more _________ decision-making process.a.nonprogrammableb.uncertaind.perfectly rational117.Under bounded rationality, you would be expected to search for a job by ________________.a.looking at all the opportunities that can be analyzed in the time availableb.looking at all the opportunities availablec.looking “outside the box” in your searchd.analyzing all the opportunities until you find the perfect job118.If you use a shortened process of searching for a job, it is likely that you ___________ rather than maximized in your decision process.a.minimizedb.rationalizedc.satisficedd.agreed119.During your job search, you depend on __________ decision making by making your decision based on accumulated judgment and experience.a.experientialb.legalc.intuitived.formidableIs the Picture Clear? (Scenario)Sharon was the regional manager of a large cable television company. She faced many problems and decisions daily, such as how to price each market, who to hire, what kind of technology she should purchase, and how she should handle the increasing customer complaints. She needed some help sorting these issues out.120.When a customer calls and requests a refund for a partial month’s usage of cable, the fact that such situations are routine and most likely have a standard response would make the response a ______________ decision.a.standardb.routinec.policyd.programmed121.Sometimes Sharon follows a ______________, a series of interrelated sequential steps for responding to a structured problem.a.rulec.procedured.suggestion122.Sometimes Sharon instructs her local managers to follow ______________ when confronted with problem situations. Theseestablish parameters for the manager making the decision rather than specifically stating what should or should not be done.a.rulesb.proceduresc.policiesd.orders123.Unfortunately, Sharon also faces issues containing information that is ambiguous or incomplete, such as what kind of technology to purchase. These are known as ______________ problems.a.unstructuredb.variablec.randomd.hit-and-missManaging Your Career (Scenario)Michelle has a new job and is learning to perform the tasks assigned to her. Different situations demand different decision-making processes.124.Michelle finds a situation that instructs her in specific, interrelated, sequential steps to respond to a problem. This is referred to as a _____________.a.ruleb.policyc.broad guidelined.procedure125.Michelle finds a company directive that specifically restricts her from taking certain actions. This is a _____________.a.ruleb.policyc.broad guidelined.procedure。

管理学第9版练习题附答案3Chapter 3 Organizational Culture and Environment: The Constraints TRUE/FALSE QUESTIONSTHE MANAGER: OMNIPOTENT OR SYMBOLIC?1.In the symbolic view of management, managers are seen as directly responsible for anorganization’s success or failure.2.The current dominant assumption in management theory suggests that managers areomnipotent.3.The view of managers as omnipotent is consistent with the stereotypical picture of thetake-charge business executive who can overcome any obstacle in carrying out the organization’s objectives.4.The symbolic view of management impact is useful in explaining the high turnoveramong college and professional sports coaches, who can be considered the “managers” of their teams.5.In the omnipotent view of management, much of an organization’s success or failureis due to forces outside management’s control.6.In the symbolic view of management, it is unreasonable to expect managers to have asignificant effect on the organization’s performance.7.In the omnipotent view of management, a manager’s role is to create meaning out ofrandomness, confusion, and ambiguity.THE ORGANIZATION’S CULTURE8.An organizational culture refers to a system of shared meaning./doc/588564acd6d8d15abe23482fb4daa58da0111ce5.html anizational cultures influence how employees behave in an organization./doc/588564acd6d8d15abe23482fb4daa58da0111ce5.html anizational culture is a perception, not reality.11.Presently, there is no method for analyzing or assessing organizational culture.12.Strong cultures have more influence on employees than do weak cultures.13.An increasing body of evidence suggests that strong cultures are associated with highorganizational performance./doc/588564acd6d8d15abe23482fb4daa58da0111ce5.html pensation structures are considered to be a primary dimension of organizationalculture.15.Most organizations have very weak cultures.16.An organization’s founder has little influence on its culture.17.Rituals are repetitive sequences of activities that express and reinforce the key valuesof an organization./doc/588564acd6d8d15abe23482fb4daa58da0111ce5.html anizational stories typically contain a narrative regarding significant events orpeople.19.Employee stock options are one example of a material symbol that might representorganizational culture.20.The link between values and managerial behavior is fairly straightforward. CURRENT ORGANIZATIONAL CULTURE ISSUES FACING MANAGERS21.A strong ethical culture is likely to have a powerful positive influence on employeebehavior.22.Low risk tolerance generally leads to high ethical standards within an organization./doc/588564acd6d8d15abe23482fb4daa58da0111ce5.html panies that allow their employees freedom tend to encourage innovative cultures.24.To encourage a customer-responsive culture, organizations should formalize andenforce strict customer service policies.25.Customer service employees tend to provide better customer service when they arevery clear about their employee roles.26.To increase customer responsiveness, organizations should hire employees who areoutgoing and friendly.THE ENVIRONMENT27.The part of the environment directly related to achievement of an organization’s goalsis the specific environment.28.The general environment refers to environmental factors operating inside anorganization.29.Environmental uncertainty can be divided into two dimensions: degree of trust anddegree of integration.30.Because certainty is a threat to an organization’s effectiveness, managers try tominimize it.31.The term suppliers includes providers of financial and labor inputs.32.Industry conditions are an example of an organization’s general environment.33.Economic conditions are part of the organization’s specific environment. MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONSFor each of the following choose the answer that most completely answers the question. THE MANAGER: OMNIPOTENT OR SYMBOLIC?34.Which of the following represent the two views of managerial impact on the successor failure of the organization?a.omnipotent and symbolicb.omnipotent and reflectivec.symbolic and interactived.reflective and interactive35.The omnipotent view of management states that ________________.a.the top manager is the only person in chargeb.managers are directly responsible for an organization’s success or failurec.that there is only one boss in the organization, and she or he is responsible for delegating ordersd.managers have little or no responsibility for an organization’s success or failure36.The __________ view of management is consistent with the stereotypicalpicture of the take-charge business executive who can overcome any obstaclein carrying out the organization’s objectives.a.omnipotentb.symbolicc.functionald.systems37.Which of the following most accurately reflects the symbolic view of management?a.M anagers are directly responsible for an organization’s success or failure.b.Managers have little or no responsibility for an organization’s success or failure.c.E xternal forces are directly responsible for an organization’s success or failure.d.E mployees are directly responsible for an organization’s success or failure.38.Internal constraints that restrict a manager’s decision options _______________.a.exist within every organizationb.do not exist, as all managers have decision-making discretionc.exist only to the extent that upper management imposes themd.exist only to the extent that followers won’t do as they are told39.The current dominant assumption in management theory suggests _______________.a. a balanced view of managers as symbolic and omnipotentb.an emphasis on the view that managers are symbolicc.an emphasis on the view that managers are omnipotentd.that both the symbolic and omnipotent views are obsolete40.According to the symbolic view, managers have a(n) _____________ effect on substantive organizational outcomes.a.neutralb.controllingc.limitedd.unlimited41.Managers may be able to expand their areas of discretion by_______________.a.telling their employees what to dob.changing and influencing their organization’s culture and environmentc.electing new government officials at the federal and state leveld.changing employers and working for a different boss42.The symbolic view of management is based upon the belief that managerssymbolize _________.a.control and influenceb.ambiguity and confusionc.stakeholders’ interestsd.decisions of top management43.In reality, managers are most accurately viewed as _________.a.dominant over an organization’s environmentb.neither helpless nor all powerfulc.powerless to influence an organization’s performanced.ultimately responsible for organizational outcomesTHE ORGANIZATION’S CULTURE44.The culture of an organization is analogous to the _____________ of an individual.a.skillsb.personalityc.motivationd.ability45.All organizational cultures consist of each of the following except _________.a.shared valuesb.principlesc.innovationd.traditions/doc/588564acd6d8d15abe23482fb4daa58da0111ce5.html anizational culture is concerned with how members perceive theorganization, not whether they __________.a.like the organizationb.like their peersc.like their bossesd.like their customers47.Strong cultures _____________.a.are found in organizations with high employee turnoverb.have a minimal influence on employee decision makingc.can be found in all organizations that existd.have a greater influence on employees than do weak cultures48.Employees in organizations with strong cultures _______________.a.are more committed to their organizationsb.are more likely to leave their organizationsc.are more willing to perform illegal activitiesd.are more likely to follow directives from peers49.Which of the following phrases is associated with the definition of organizational culture?a.individual responseb.shared meaningc.diversity of thoughtd.explicit directions50.Which of the following is not considered to be a dimension of organizational culture?a.attention to detailb.people orientation。
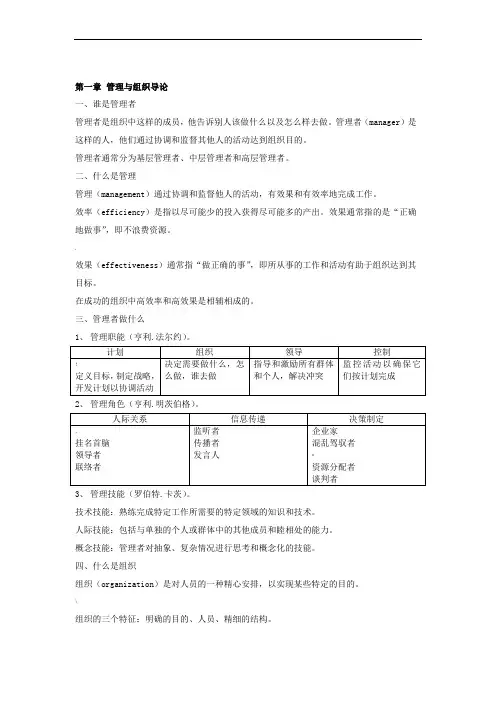
第一章管理与组织导论一、谁是管理者管理者是组织中这样的成员,他告诉别人该做什么以及怎么样去做。
管理者(manager)是这样的人,他们通过协调和监督其他人的活动达到组织目的。
管理者通常分为基层管理者、中层管理者和高层管理者。
二、什么是管理管理(management)通过协调和监督他人的活动,有效果和有效率地完成工作。
效率(efficiency)是指以尽可能少的投入获得尽可能多的产出。
效果通常指的是“正确地做事”,即不浪费资源。
,效果(effectiveness)通常指“做正确的事”,即所从事的工作和活动有助于组织达到其目标。
在成功的组织中高效率和高效果是相辅相成的。
三、管理者做什么1、管理职能(亨利.法尔约)。
2、管理角色(亨利.明茨伯格)。
3、管理技能(罗伯特.卡茨)。
技术技能:熟练完成特定工作所需要的特定领域的知识和技术。
人际技能:包括与单独的个人或群体中的其他成员和睦相处的能力。
概念技能:管理者对抽象、复杂情况进行思考和概念化的技能。
四、什么是组织组织(organization)是对人员的一种精心安排,以实现某些特定的目的。
\组织的三个特征:明确的目的、人员、精细的结构。
现在的组织更倾向于依靠灵活的工作安排、雇员工作团队、开放的沟通系统和供应商联盟。
第二章管理的昨天和今天一、!二、管理的历史背景两个重大事件:1776年,亚当.斯密发表《国富论》主张组织和社会将从劳动分工或工作专业化中获得经济利益。
工业革命,机械力代替了人力。
三、科学管理(1911年泰罗发表《科学管理原理》)四、一般行政管理理论(亨利.法尔约)五、;六、权变理论权变理论强调这样一个事实,因为组织不同,面对的情境不同,所以可能要求不同的管理方式。
七、当前的趋势和问题全球化、道德、劳动力多元化、创业精神(对机会的追求、创新、增长)、在电子领域中进行管理、知识管理和学习型组织、质量管理(TQM)质量管理受到不断改进和响应顾客需求与期望的驱动。

罗宾斯《管理学》第九版题库-6Chapter 6 –Decision-Making: The Essence of the Manager’s JobTrue/False Questions4. The first step in the decision-making process is identifyinga problem.True (easy)6. It is possible at the end of the decision-making process that you may be required to start the decisionprocess over again.True (easy)10. Decision-making is synonymous with managing.True (easy)12. One assumption of rationality is that we cannot know all of the alternatives.False (difficult)13. Accepting solutions that are "good enough" is termed satisfying.False (easy)15. Managers regularly use their intuition in decision-making.True (easy)16. Rational analysis and intuitive decision-making are complementary.True (moderate)18. Programmed decisions tend to be repetitive and routine.True (easy)21. Most managerial decisions in the real world are fully nonprogrammed.False (easy)24. Risk is a situation in which a decision maker has neither certainty nor reasonable probability estimates.False (difficult)25. An optimistic manager will follow a maximin approach.False (moderate)Multiple ChoiceTHE DECISION-MAKING PROCESS34. A series of eight steps that begins with identifying a problem and decision criteria and allocating weights to those criteria; moves to developing, analyzing, and selecting an alternative that can resolve the problem;implements the alternative; and concludes with evaluating the decision's effectiveness is the ______________.a. decision-making process. (easy)b. managerial process.c. maximin style.d. bounded rationality approach.e. legalistic opportunism process.36. "A discrepancy between an existing and a desired state of affairs" describes which of the steps in thedecision-making process?a. criteria weight allocationb. analysis of alternativesc. problem identification (difficult)d. decision effectiveness evaluatione. decision criteria identification38. Which of the following must be present in order to initiate the decision-making process?a. plenty of timeb. pressure to act (moderate)c. a lack of authorityd. a lack of resourcese. environmental certainty39. Managers aren't likely to characterize something as a problem if they perceive ______________.a. they don't have authority to act. (difficult)b. pressure to act.c. a discrepancy.d. they have sufficient resources.e. they have budgetary authority.44. Selecting an alternative in the decision-making process is accomplished by ______________.a. choosing the alternative with the highest score. (easy)b. choosing the one you like best.c. selecting the alternative that has the lowest price.d. selecting the alternative that is the most reliable.e. choosing the alternative you think your boss would prefer.47. Which of the following is the final step in the decision-making process?a. identifying the problemb. evaluating the decision's effectiveness (easy)c. identifying decision criteriad. selecting an alternative that can resolve the probleme. allocating weights to alternatives.48.Which of the following is important to remember in evaluating the effectiveness of the decision-makingprocess?a. Ignore criticism concerning the decision-making.b. You may have to start the whole decision process over.(difficult)c. Restart the decision-making process if the decision is less than 50% effective.d. 90% of problems with decision-making occur in the implementation step.e. Keep track of problems with the chosen alternative, but only change those issues that uppermanagement demand.49. Decision-making is synonymous with ______________.a. managing. (easy)b. leading.c. controlling.d. planning.e. organizing.51. Which of the following is not an "organizing" decision?a. What are the organization's long-term objectives? (moderate)b. How many employees should I have report directly to me?c. How should jobs be designed?d. How much centralization should there be in the organization?e. When should the organization implement a different structure?52. Which of the following is not a "leading" decision?a. How do I handle employees who appear to be low in motivation?b. What is the most effective leadership style in a given situation?c. How will a specific change affect worker productivity?d. When is the right time to stimulate conflict?e. How should jobs be designed? (moderate)53. Which of the following is not a "controlling" decision?a. What activities in the organization need to be controlled?b. How should those activities be controlled?c. When is a performance deviation significant?d. When is the right time to stimulate conflict? (moderate)e. What type of management information system should the organization have?54. Managers are assumed to be ______________; they make consistent, value-maximizing choices withinspecified constraints.a. rational (easy)b. leadersc. organizedd. satisficerse. programmed57. Which of the following is not a valid assumption about rationality?a. The problem is clear and unambiguous.b. A single well-defined goal is to be achieved.c. Preferences are clear.d. Preferences are constantly changing. (difficult)e. No time or cost constraints exist.58. In "bounded rationality," managers construct ______________ models that extract the essential features from problems.a. multipleb. bindingc. interactived. simplified (difficult)e. past59. According to the text, because managers can’t possibly analyze all information on all alternatives, managers______________, rather than ______________.a.maximize; satisficeb.maximize; minimizec.satisfice; minimized.satisfice; maximize (moderate)62. An increased commitment to a previous decision despite evidence that it may have been wrong is referredto as _____________.a.economies of commitmentb.escalation of commitment (moderate)c.dimensional commitmentd.expansion of commitment64. According to the text, all of the following are aspects of intuition EXCEPT:a.experienced-based decisionsb.affect-initiated decisionsc.cognitive-based decisionsd.values or ethics-based decisionse.programmed decisions (easy)65.According to the text, _____________ are straightforward, familiar, and easily defined problems.a.poorly-structured problemsb.well-structured problems (moderate)c.unique problemsd.non-programmed problemse.programmed problems68. ______________ decision-making is relatively simple andtends to rely heavily on previous solutions.a. Nonprogrammedb. Linearc. Satisficingd. Integrativee. Programmed (moderate)70. A ______________ is a series of interrelated sequential steps that a manager can use for responding to astructured problem.a. procedure (easy)b. rulec. policyd. systeme. solution71. A ______________ is an explicit statement that tells a manager what he or she ought or ought not to do.a. procedureb. policyc. rule (moderate)d. solutione. system72. A ______________ provides guidelines to channel a manager's thinking in a specific direction.a. systemb. rulec. solutiond. policy (moderate)e. procedure75. A business school's statement that it "strives for productive relationships with local organizations," is anexample of a ______________.a. rule.b. policy. (moderate)c. procedure.d. commitment.e. contract.78. Which of the following terms is associated with nonprogrammed decisions?a. unique (moderate)b. recurringc. routined. repetitivee. well-defined79. Lower-level managers typically confront what type of decision-making?a. uniqueb. nonroutinec. programmed (moderate)d. nonprogrammede. nonrepetitive83. If an individual knows the price of three similar cars at different dealerships, he/she is operating under what type of decision-making condition?a. riskb. uncertaintyc. certainty (easy)d. factuale. unprogrammed84. ______________ is those conditions in which the decision maker is able to estimate the likelihood ofcertain outcomes.a. Certaintyb. Risk (easy)c. Uncertaintyd. Maximaxe. Maximin85. A retail clothing store manager who estimates how much to order for the current spring season based on lastspring's outcomes is operating under what kind of decision-making condition?a. seasonalb. risk (difficult)c. uncertaintyd. certaintye. cyclical86. ______________ is a situation in which a decision maker has neither certainty nor reasonable probabilityestimates available.a. Certaintyb. Riskc. Uncertainty (easy)d. Maximaxe. Maximin87. A person at a horse racetrack who bets all of his/her money on the odds-based longshot to "win" (ratherthan "place" or "show") is making what kind of choice?a. maximax (moderate)b. maximinc. minimaxd. minimin89. An individual making a "maximin" type of choice has what type of psychological orientation concerninguncertain decision-making?a. optimistb. realistc. pessimist (moderate)d. satisficere. extremist91. According to the text, a manager who desires to minimize his or her maximim “regret” will opt for a______________ choice.a. maximaxb. maximinc. minimax (moderate)d. minimin93. Which of the following decision-making styles have low tolerance for ambiguity and are rational in theirway of thinking?a.directive (moderate)b.egotisticalc.analyticd.conceptuale.behavioral95. The decision-making style that makes fast decisions and focuses on the short terms is referred to as the______________ style.a.directive (moderate)b.egotisticalc.analyticd.conceptuale.behavioral98. According to the text, ______________ are best characterized as careful decision makers with the ability to adapt or cope with unique situations.a. conceptualb. behavioralc. empiricald. analytic (moderate)e. spatial99. Which of the following is the decision-making style that would most likely look at as many alternatives aspossible and focus on the long run?a. analyticalb. directivec. conceptual (moderate)d. behaviorale. spatial101. A manager who would decide what computer system to purchase for the department by holding a meeting and receiving feedback from his/her subordinates matches with which type of decision-making style?a. analyticalb. behavioral (difficult)c. conceptuald. directivee. empiricalScenariosDecision-Making Conditions (Scenario)Sandy Jo is the manager for TrucksRUs, a medium-sized hauling service located in the Southeast. She is responsible forscheduling trucks, initiating new routes, and staffing both existing and new routes. She is currently struggling with existing information about the profitability of existing and future truck routes.116. Bubba, Sandy Jo's best driver tells her that he believes that he can estimate that there is a 75% probability that they can get the business of Pork Brothers Inc. if they initiate a truck route through rural North Carolina. Bubba is operating under a condition of ______________.a. certainty.b. risk. (difficult)c. uncertainty.d. maximax.e. maximin.117. Sandy Jo can make accurate decisions if she is willing to pay $5,000 for research about the profitability of various truck routes. If she pays for the research, she believes that she is operating under a condition of ______________.a. certainty. (difficult)b. risk.c. uncertainty.d. maximax.e. maximin.118. Sandy Jo knows that she is operating in an uncertain environment. She is basically an optimist, and we would, therefore, expect her to follow a ______________ strategy.a. certaintyb. riskc. uncertaintyd. maximax (moderate)e. maximin119. Sandy Jo knows that she is operating in an uncertain environment. She is basically a pessimist, and we would, therefore, expect her to follow a ______________ strategy.a. certaintyb. riskc. minimaxd. maximaxe. maximin (moderate)120. Sandy Jo wishes to minimize her regret and will probably opt for a ______________ strategy.a. certainty.b. risk.c. minimax (moderate)d. maximax.e. maximin.Essay QuestionsTHE DECISION-MAKING PROCESS121. In a short essay, list and discuss the eight steps in the decision-making process.Answera.Step 1: Identifying a problem– the decision-making process begins with t he existence of a problem ora discrepancy between an existing and a desired state of affairs.However, a discrepancy withoutpressure to take action becomes a problem that can be postponed.b.Step 2: Identify decision criteria–once the manager has identified a problem that needs attention, thedecision criteria important to resolving the problem must beidentified. That is, managers must determine what’s relevant in making a decision.c.Step 3: Allocating weights to the criteria: at this step, the decision maker must weigh the items inorder to give them the correct priority in the decision. A simple approach is to give the most important criterion a weight of 10 and then assign weights to the rest against that standard.d.Step 4: Developing alternative s –the fourth step requires the decision maker to list the viablealternatives that could resolve the problem. No attempt is made in this step to evaluate the alternative, only to list them.e.Step 5: Analyzing alternative s – once the alternatives have been identified, the decision maker mustcritically analyze each one. From this comparison, the strengths and weaknesses of each alternative become evident.f.Step 6: Selecting an alternative–the sixth step is the important act of choosing the best alternative fromamong those considered. All the pertinent criteria in the decision have now been determined, weighted, and the alternatives have been identified and analyzed.g.Step 7: Implementing the alternativ e –implementation involves conveying the decision to thoseaffected by it and getting their commitment to it. If the people who must carry out a decision participate in the process, they’re more likely to enthusiastically support the outcome than if they are just told what to do.h.Step 8: Evaluating decision effectiveness –the last step in the decision-making process involvesappraising the outcome of the decision to see if the problem has been resolved. Did the alternative chose and implementedaccomplish the desired result? If not, the manager may consider returning to a previous step or may even consider starting the whole decision process over.(difficult)123. In a short essay, discuss the assumptions of rationality and the validity of those assumptions.AnswerA decision maker who was perfectly rational would be fully objective and logical. He or she wouldcarefully define a problem and would have a clear and specific goal. Moreover, making decisions using rationality would consistently lead toward selecting the alternative that maximizes the likelihood of achieving that goal. The assumptions of rationality apply to any decision. Rational managerial decision making assumes that decisions are made in the best economic interests of the organization. That is, the decision maker is assumed to be maximizing the organization’s interests, not his or her own interests.Managerial decision making can follow rational assumptions if the following conditions are met: The manager is faced with a simple problem in which the goals are clear and the alternatives limited, in which the time pressures are minimal and the cost of seeking out and evaluating alternatives is low, for which the organizational culture supports innovation and risk taking, and in which o utcomes are relatively concrete and measurable. However, most decisions that managers face in the real world d on’t meet all those tests.(moderate)126. In a short essay, discuss the difference between well-structured and poorly structured problems. Include specificexamples of each type of problem to support your answer. Next discuss the type of decisions that would be used to address each of these problems.Answera.Well-structured problems - the goal of the decision marker is clear, the problem is familiar, andinformation about the problem is easily defined and complete. Examples of these types of problems might include a customer’s wanting to return a purchase to a retail store, a supplier’s being late with an important delivery, a news team’s responding to an unexpected and fast-breaking event, or a college’s handling of a student wanting to drop a class. Such situations are called well-structured problems since they are straightforward, familiar, and easily defined problems. In handling these problem situations, the manager uses a programmed decision. Decisions are programmed to the extent that they are repetitive and routine a nd to the extent that a definite approach has been worked out for handling them.Because the problem is well structured, the manager doesn’t have to go to the trouble and expense of going through an involved decision progress. Programmed decision making is relatively simple and tends to rely heavily on previous solutions.b.Poorly-structured problems –these problems are new or unusual and for which information isambiguous or incomplete.For example, the selection of an architect to design a new corporate manufacturing facility in Bangkok is an example of a poorly-structured problem. When problems are poorly-structured, managers must rely on nonproprammed decision making in order to develop unique solutions.Nonprogrammed decisions are unique andnonrecurring. When a manager confronts a poorly-structured problem, or one that is unique, there is no cut-and-dried solution. It requires a custom-made response through nonprogrammed decision making.(difficult)130. In a short essay, list and discuss the four decision-making styles as described in the text.Answera.Directive style – people using the directive style have low tolerance for ambiguity and are rational intheir way of thinking. They’re efficient and logical. Directive types make fast decisions and focus on the short run. Their efficiency and speed in making decisions often result in their making decisions with minimal information and assessing few alternatives.b.Analytic style – decision-makers with an analytic style have much greater tolerance for ambiguity thando directive types. They want more information before making a decision and consider more alternatives than a directive style decision-maker does. Analytic decision-makers are best characterized as careful decision-makers with the ability to adapt or cope with unique situations.c.Conceptual style – individuals with a conceptual style tend to be very broad in their outlook and willlook at many alternatives. They focus on the long run and are very good at finding creative solutions to problems.d.Behavioral style –these decision markers work well with others. They’re concerned about theachievements of subordinates and are receptive to suggestions from others. They often use meetings tocommunicate, although they try to avoid conflict. Acceptance by others is important to this decision-making style.(moderate)。

Chapter 1 – Introduction to Management and OrganizationsTrue/False QuestionsThe four contemporary functions of management are planning, organizing, leading, and controlling.True (easy)Effectiveness refers to the relationship between inputs and outputs.False (moderate)Efficiency is often referred to as "doing things right."True (moderate)When managers meet organizational goals, they are efficient and effective.False (difficult)According to Mintzberg’s management roles, the information al role involves receiving, collecting, and disseminating information.True (moderate)Technical skills become less important as a manager moves into higher levels of management.True (moderate)The systems perspective underscores and emphasizes the fact that organizations are different, face different circumstances, and thus may require different ways of managing.False (moderate)Multiple Choice_____________ are organizational members who integrate and coordinate the work of others.a. Managers (easy)b. Team leadersc. Subordinatesd. Operativese. AgentsTypically, in organizations it is the _____________ who are responsible for making organizational decisions and setting policies and strategies that affect all aspects of the organization.a. team leadersb. middle managersc. first-line managersd. top managers (easy)e. subordinates_____________ distinguishes a managerial position from a nonmanagerial one.a. Manipulating othersb. Concern for the lawc. Increasing efficiencyd. Coordinating and integrating others' work (moderate)e. Defining market sharea.spokesperson (moderate)b.entrepreneurc.disturbance handlerd.resource allocatore.negotiatora.human skillsb.technical skills (easy)c.conceptual skillsd.empirical skillsUnderstanding building codes would be considered a _____________ skill for a building contractor.a. humanb. technical (easy)c. conceptuald. empiricale. functionala. decision-making (easy)b. communicating with customersc. motivating subordinatesd. product knowledgee. technical skillsAccording to the text, _____________ are not influenced by and do not interact with their environment.a.open systemsb.closed systems (easy)c.d.reverse systemse.forward systemsThe _____________ view of a manager's job implies that decisions and actions taken in one organizational area will impact other areas.a. systems (moderate)b. contingencyc. conceptuald. functionale. environmentala.the partiality of managementb.the segmentation of managementc.the universality of management (moderate)d.the cultures of managementScenarios and QuestionsThe Busy Day (Scenario)Don Eskew, plant manager at Control Systems, Inc., sighed as he sipped his first cup of coffee at 5 a.m. and read his agenda for the day. He is giving two company tours in the morning; the first to a newspaper reporter who is writing a story on the new plant expansion and has several questions, and the second to a group of ControlSystems, Inc., managers from the east coast. He then has a meeting with unit manager, Phil Johnson, to discuss Phil's recent drop in performance (a task he always hates). Next, he is spending a couple of hours reviewing the trade journals he receives from his high-tech association and writing up a brief synopsis for his presentation next week to the Division President. Finally, in late afternoon, he will be reviewing the new equipment malfunction and deciding whether to bring in extra people to get the equipment running as soon as possible. Whew! Just another day in the glamorous life of a manager.a. Herzbergb. Skinnerc. Mintzberg (easy)d. Fayole. Maslowa. leader (difficult)b. figureheadc. monitord. disturbance handlere. spokespersona. monitorb. figureheadc. disseminatord. spokesperson (difficult)e. resource allocatora. monitorb. disseminatorc. resource allocator (moderate)d. disturbance handlere. figureheadEssay QuestionsIn a short essay, discuss the difference between efficiency and effectiveness and include a specific example to support each concept.Answera.b.Effectiveness is often described as “doing the right things”—that is, those work activities that will helpthe organization reach its goals.For instance, at the Biersdorf factory, goals included open communication between managers and employees, and cutting costs. Through various work programs, these goals were pursued and achieved. Whereas efficiency is concerned with the means of getting things done, effectiveness is concerned with the ends, or attainment of organizational goals.(moderate)In a short essay, list and explain the four basic functions of management.Answera.Planning – involves the process of defining goals, establishing strategies for achieving those goals, anddeveloping plans to integrate and coordinate activities.anizing – involves the process of determining what tasks are to be done, who is to do them, how thetasks are to be grouped, who reports to whom, and where decisions are to be made.c.Leading – when managers motivate subordinates, influence individuals or teams as they work, select themost effective communication channel, or deal in any way with employee behavior issues, they are leading.d.Controlling –to ensure that work is going as it should, managers must monitor and evaluateperformance. The process of monitoring, comparing, and correcting is what is meant by the controlling function.(moderate)In a short essay, list and discuss the three essential skills according to Katz that managers need to perform the duties and activities associated with being a manager.Answera.Technical skills – include knowledge of an proficiency in a certain specialized field, such as engineering,computers, accounting, or manufacturing. These skills are more important at lower levels of management since these managers are dealing directly with employees doing the organization’s work.b.Human skills –involve the ability to work well with other people both individually and in a group.Managers with good human skills are able to get the best out of their people. They know how to communicate, motivate, lead, and inspire enthusiasm and trust. These skills are equally important at all levels of management.c.Conceptual skills –these are the skill that managers must have to think and to conceptualize aboutabstract and complex situations. Using these skills, managers must be able to see the organization as a whole, understand the relationships among various subunits, and visualize how the organization fits into its broader environment. These skills are most important at the top management levels.(moderate)。


Chapter 3 Organizational Culture and Environment: The Constraints TRUE/FALSE QUESTIONSTHE MANAGER: OMNIPOTENT OR SYMBOLIC1.In the symbolic view of management, managers are seen as directlyresponsible for an organization’s success or failure.2.The current dominant assumption in management theory suggests thatmanagers are omnipotent.3.The view of managers as omnipotent is consistent with thestereotypical picture of the take-charge business executive who can overcome any obstacle in carrying out the orga nization’s objectives.4.The symbolic view of management impact is useful in explaining thehigh turnover among college and professional sports coaches, who can be considered the “managers” of their teams.5.In the omnipotent view of management, much of an o rganization’ssuccess or failure is due to forces outside management’s control.6.In the symbolic view of management, it is unreasonable to expectmanagers to have a significant effect on the organization’s performance.7.In the omnipotent view of management, a manager’s role is to createmeaning out of randomness, confusion, and ambiguity.THE ORGANIZATION’S CULTURE8.An organizational culture refers to a system of shared meaning.anizational cultures influence how employees behave in anorganization.anizational culture is a perception, not reality.11.Presently, there is no method for analyzing or assessingorganizational culture.12.Strong cultures have more influence on employees than do weakcultures.13.An increasing body of evidence suggests that strong cultures areassociated with high organizational performance.pensation structures are considered to be a primary dimension oforganizational culture.15.Most organizations have very weak cultures.16.An organization’s founder has little influence on i ts culture.17.Rituals are repetitive sequences of activities that express andreinforce the key values of an organization.anizational stories typically contain a narrative regardingsignificant events or people.19.Employee stock options are one example of a material symbol thatmight represent organizational culture.20.The link between values and managerial behavior is fairlystraightforward.CURRENT ORGANIZATIONAL CULTURE ISSUES FACING MANAGERS21.A strong ethical culture is likely to have a powerful positiveinfluence on employee behavior.22.Low risk tolerance generally leads to high ethical standards withinan organization.panies that allow their employees freedom tend to encourageinnovative cultures.24.To encourage a customer-responsive culture, organizations shouldformalize and enforce strict customer service policies.25.Customer service employees tend to provide better customer servicewhen they are very clear about their employee roles.26.To increase customer responsiveness, organizations should hireemployees who are outgoing and friendly.THE ENVIRONMENT27.The part of the environment directly related to achievement of anorganization’s goals is the specific environment.28.The general environment refers to environmental factors operatinginside an organization.29.Environmental uncertainty can be divided into two dimensions: degreeof trust and degree of integration.30.Because certainty is a threat to an organization’s effectiveness,managers try to minimize it.31.The term suppliers includes providers of financial and labor inputs.32.Industry conditions are an example of an organization’s generalenvironment.33.Economic conditions are part of the organization’s specificenvironment.MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONSFor each of the following choose the answer that most completely answers the question.THE MANAGER: OMNIPOTENT OR SYMBOLIC34.Which of the following represent the two views of managerial impacton the success or failure of the organizationa.omnipotent and symbolicb.omnipotent and reflectivec.symbolic and interactived.reflective and interactive35.The omnipotent view of management states that ________________.a.the top manager is the only person in chargeb.managers are directly responsible for an organization’s successor failurec.that there is only one boss in the organization, and she or he isresponsible for delegating ordersd.managers have little or no responsibility for an organization’ssuccess or failure36.The __________ view of management is consistent with thestereotypical picture of the take-charge business executive whocan overcome any obstacle in carrying out the organization’sobjectives.a.omnipotentb.symbolicc.functionald.systems37.Which of the following most accurately reflects the symbolicview of managementa.Managers are directly responsible for an or ganization’s successor failure.b.M anagers have little or no responsibility for an organization’ssuccess or failure.c.E xternal forces are directly responsible for an organization’ssuccess or failure.d.E mployees are directly responsible for an organization’s successor failure.38.Internal constraints that restrict a manager’s decision options_______________.a.exist within every organizationb.do not exist, as all managers have decision-making discretionc.exist only to the extent that upper management imposes themd.exist only to the extent that followers won’t do as they are told39.The current dominant assumption in management theory suggests_______________.a. a balanced view of managers as symbolic and omnipotentb.an emphasis on the view that managers are symbolicc.an emphasis on the view that managers are omnipotentd.that both the symbolic and omnipotent views are obsolete40.According to the symbolic view, managers have a(n) _____________effect on substantive organizational outcomes.a.neutralb.controllingc.limitedd.unlimited41.Managers may be able to expand their areas of discretion by_______________.a.telling their employees what to dob.changing and influencing their organization’s culture andenvironmentc.electing new government officials at the federal and state leveld.changing employers and working for a different boss42.The symbolic view of management is based upon the belief thatmanagers symbolize _________.a.control and influenceb.ambiguity and confusionc.stakeholders’ interestsd.decisions of top management43.In reality, managers are most accurately viewed as _________.a.dominant over an organization’s environmentb.neither helpless nor all powerfulc.powerless to influence an organization’s performanced.ultimately responsible for organizational outcomesTHE ORGANIZATION’S C ULTURE44.The culture of an organization is analogous to the _____________ ofan individual.a.skillsb.personalityc.motivationd.ability45.All organizational cultures consist of each of the following except_________.a.shared valuesb.principlesc.innovationd.traditionsanizational culture is concerned with how members perceivethe organization, not whether they __________.a.like the organizationb.like their peersc.like their bossesd.like their customers47.Strong cultures _____________.a.are found in organizations with high employee turnoverb.have a minimal influence on employee decision makingc.can be found in all organizations that existd.have a greater influence on employees than do weak cultures48.Employees in organizations with strong cultures _______________.a.are more committed to their organizationsb.are more likely to leave their organizationsc.are more willing to perform illegal activitiesd.are more likely to follow directives from peers49.Which of the following phrases is associated with the definition oforganizational culturea.individual responseb.shared meaningc.diversity of thoughtd.explicit directions50.Which of the following is not considered to be a dimension oforganizational culturea.attention to detailb.people orientationc.purchasing policiesd.aggressiveness51.Which of the following dimensions of organizational culture isdefined as the degree to which an organization’s actions and decisions emphasize maintaining the status quoa.stabilityb.outcome orientationc.team orientationd.innovation and risk taking52.A company whose managers focus on results, rather than how resultsare achieved, most likely possesses a high degree of which of the followinga.outcome orientationb.people orientationc.team orientationd.aggressiveness53.Sony Corporation’s focus on product innovation is an example ofwhich of the following dimensions of organizational culturea.attention to detailb.people orientationc.outcome orientationd.aggressiveness54.Which of the following most accurately reflects the differencebetween strong cultures and weak culturesa.Strong cultures tend to encourage employee innovation, while weakcultures do not.b.Weak cultures are found in most organizations, whereas strongcultures are relatively rare.c.Strong cultures have less of an influence on employee behaviorthan do weak cultures.pany values are more deeply held and widely shared in strongcultures than in weak cultures.55.Corporate ___________ are repetitive sequences of activitiesthat express and reinforce the values of an organization.nguagesb.ritualsc.symbolsd.ceremonies56. Which of the following represents the most significant waysthrough which corporate cultures are transmitted to employeesa.rituals, myths, competitions, and languageb.symbols, rituals, language, and business systemsc.stories, rituals, symbols, and languagenguage, stories, rituals, and rewards57.When employees at Microsoft use terms such as work judo, eatingyour own dog food, and flat food, they are using organizational__________.nguagesb.ritualsc.symbolsd.ceremonies58.Most organizations have ____________ cultures.a.very weakb.weak to moderatec.moderated.moderate to strong59.The original source of an organization’s culture usually________________.a.is shared among the first workers hired into the organizationb.is formulated by the board of directors when the organization isformedc.identifies what the organization is successful doingd.reflects the vision or mission of the organization’s founderanizational _____________ typically contain narratives aboutsignificant events or people in the organization.a.storiesb.ritualsc.chartsd.material symbols61.All of the following are mentioned in the textbook as examples ofmaterial symbols except ____________.a.employee dress attireb.size of employee officesc.availability of stock optionsd.reserved parking spaces for certain employees62.The link between organizational values and managerial behavior is_____________.ually uncertainb.fairly straightforwardc.often highly complexd.relatively dynamic63.In learning an organization’s specific language, members aredisplaying their _________________.a.willingness to communicate with the organization’s stockholdersb.confidence that they will soon be promoted to greaterresponsibilityc.willingness to help preserve the culture of the organizationd.consent to share material symbols with the other members of theorganization64.An organization’s culture affects managers by ______________.a.providing them with additional decision-making powerb.restricting them from disciplining certain employeesc.encouraging them to bend or even break company rulesd.establishing what is appropriate and expected behaviorCURRENT ORGANIZATIONAL CULTURE ISSUES FACING MANAGERS65.Which of the following is most likely to have a highly ethicalorganizational culturea. a highly aggressive, competitive businessb. a company with high risk tolerancec. a business that focuses strictly on outcomesd. a business with outgoing and friendly employees66.To encourage ethical cultures, managers should_________________.a.enforce strict discipline policiesb.encourage employees to competec.act in their own self-interestd.serve as visible role models67.A company that primarily values a strong sense of purposethrough meaningful work has a(n) _________________ organizational culture.a.spiritualb.customer-responsivec.ethicald.innovative68.Conscientious employees with good listening skills are highlyvaluable for building a(n) _________________ organizational culture.a.ethicalb.innovativec.customer-responsived.spiritual69.An innovative organizational culture is characterized by all ofthe following characteristics except _________________.a.freedomb.conformityc.debatesd.risk taking70.Workplace spirituality has become important in the contemporaryworkplace because it helps to _________________.a.reduce unemployment ratesb.boost company profitsc.restore a sense of communityd.bring religion into business71.Which of the following is most characteristic of anorganization with a strong spiritual culturea.Employees are encouraged to express themselves.b.Such companies experience high employee turnover.c.Employees are rewarded for innovation and risk taking.d.Employees are required to join organized religions.72.Which of the following best characterizes the relationshipbetween spirituality and business profitabilitya.Evidence shows that spirituality and business profitability areincompatible.b.Limited evidence suggests that spirituality may be compatible withprofitability.c.Research shows that workplace spirituality constrains employeeperformance.d.High productivity has been extensively documented in spiritualworkplaces.THE ENVIRONMENT73.External environment refers to _________________.a.forces outside the organization that limit the organization’sperformanceb.factors and forces outside the organization that affect theorganization’s performancec.forces and institutions inside the organization that affect theorganization’s performanced.forces inside the organization that increase the organization’sperformance74.According to the textbook, the _______________ environment includesthose constituencies that have a direct and immediate impact on mana gers’ decisions and actions and are directly relevant to the achievement of the organization’s goals.a.generalb.specificc.secondaryd.forward75.An organization’s specific environment ________________.a.is unique and changes with conditionsb.is the same regardless of the organization’s agec.is determined by the top level of managementd.must be quantified to establish its existence76.The main forces that make up an organization’s specificenvironment are __________.a.suppliers, legislators, customers, and employeesb.customers, suppliers, competitors, and pressure groupsc.employees, competitors, pressure groups, and regulatorsd.suppliers, employees, competitors, and legislatorsanizations exist to meet the needs of which of the followingconstituenciesa.customersb.legislatorsc.supplierspetitors78.When you think of an organization’s suppliers, you________________.a.know that they are the main customers of the organizationb.typically think of governments that pass the laws the organizationmust followc.know that they are located close to the organization itselfd.typically think in terms of organizations that provide materialsand equipment79.Managers seek to ensure a steady __________________.a.cash flow from stockholders into the organizationb.flow of needed inputs at the lowest price availablec.flow of customers at the company’s outlet stored.flow of suppliers to keep the competition among suppliers at apeak80.Each of the following is considered an organizational supplierexcept providers of __________________.a.financial inputsbor inputsc.materialsd.political pressure81.The Internet is having an impact on determining whom anorganization’s competitors are because it has _____________.a.defined the common markets for organizationsb.made certain products invaluable to customerc.virtually eliminated the need for shopping mallsd.virtually eliminated geographic boundaries82.For a company such as Walt Disney World in Florida, a bank would bean example of what kind of factor in their specific environmentpetitorb.supplierc.special-interest groupernment agency83.Which of the following is not an example of a specific environmentalfactora.population demographicsb.political conditionsc.federal lawsd.all of the above84.For organizations such as hospitals, which hire nurses, the laborunion and the local labor market are examples of which of the following specific environmental factorspetitor and supplierb.customer and pressure groupc.both are examples of suppliersd.both are examples of pressure groups85.Typically, the specific organizational environment includes which ofthe followinga.economic factorsb.political conditionsc.technological factorspetitors86.United Parcel Service represents which of the following to the .Postal Servicepetitorb.supplierc.customerernment agency87.The general environment factor of economic conditions consists of allof the following except _______________.a.legislation recently passed by Congressb.interest ratesc.changes in disposable incomed.stock market fluctuations88.Sociocultural conditions consist of _______________.a.demographic profiles of an organization’s suppliersb.legal issues as determined by court decisionsc.the level of unemployment and real economic incomes of workersd.changing expectations and values within society89.To a national broadcast network such as NBC, your home DVD player isconsidered a _____________.a.customerb.supplierc.special-interest grouppetitor90.Groups such as Mothers Against Drunk Driving (MADD) are examples ofwhat factor in the specific external environmentpetitorsb.pressure groupsc.customersernment agencies91.Typically, the general organizational environment includes which ofthe followinga.political conditionsb.business plansc.stakeholdersd.supplierspared to the specific environment, which of the following is anaccurate statement about the general environment of an organizationa.It has less impact on the organization’s operations.b.It has more impact on the organization’s operations.c.It has about the same impact on an organization’s operations.d.It is predominantly the concern of upper management.93.Which of the following is not a component of an organization’sgeneral environmenta.economic conditionsb.political conditionsc.social conditionsd.industry conditions94.Interest rates, inflation rates, and stock market fluctuations areall e xamples of what factor in an organization’s general environmenta.economicb.politicalc.sociald.technological95.The Americans with Disabilities Act of 1990 is an example of a__________.a.sociolegal conditionb.political/legal conditionc.political/sociological conditiond.sociocultural condition96.A decrease in contributions from the public to the United Way charityis most likely the result of which of the following general environmental factorsa.politicalb.socialc.technologicald.economic97.Which of the following groups includes individuals who were bornbetween the years 1946–1964a.the Depression groupb.the World War II groupc.the baby boomersd.Generation X98.The members of which of the following groups are behaving infundamentally different ways that are likely to greatly impact organizations and managersa.the Depression groupb.the World War II groupc.the baby boomersd.Generation Y99.Automation represents an example of a(n) __________ generalenvironmental factor.a.technologicalb.demographicc.political/legald.economic100.Which of the following has been the most rapidly changing component in an organization’s general environmenta.globalb.economicc.sociald.technological101.Which of the following best represents a global general environmental factora.increased surveillancecation levelsc.electronic meetingsd.international markets102.Which of the following are the two dimensions of environmental uncertaintya.degree of change and degree of complexityb.degree of change and degree of volumec.degree of complexity and degree of impactd.degree of impact and degree of timing103.If the components of an organization’s environment changefrequently, the organization is operating in a __________environment.a.disruptiveb.diversec.dynamicd.difficult104.Managers try to minimize __________ because it threatensorganizational effectiveness.a.product developmentb.uncertaintyc.price chargesd.the number of suppliers105.__________ are any constituencies in an organization’s external environment that are affected by the organization’sdecisions and actions.a.Stockholdersb.Pressure groupsc.Suppliersd.Stakeholders106.Degree of _______________ refers to the number of components in an organization’s environment and the extent of the knowledge that the organization has about those components.a.stabilityb.opennessplexityd.transition107.The first step of managing external stakeholder relationships is to identify whom the stakeholders are. The second step is to _________________.a.determine what specific approach should be used to manage thestakeholder relationshipb.determine what the courts might do when stakeholder files a claimagainst the organizationc.determine what particular interests or concerns these stakeholdersmight haved.determine how many stakeholders there are in each stakeholdergroupSCENARIOS AND QUESTIONSFor each of the following, choose the answer that most completely answers the question.THE MANAGER: OMNIPOTENT OR SYMBOLICApex Construction has hired Wendell Phillips to provide management consulting for the organization. Wendell’s first assignment involves helping the company to improve productivity by recommending ways to strengthen managers’ supervisory skills.108.Wendell notices that the company’s top executives share a belief that managers are directly responsible for the organization’s success or failure. This belief reflects a(n) ______________ view of management.a.traditionalb.omnipotentc.standardd.symbolic109.Wendell interviews many middle-level managers and discovers that they share a different view of management. These individuals believe that external factors constrain managers’ inf luence over outcomes.The mid-level managers have a _____________ view of management.a.traditionalb.omnipotentc.standardd.symbolicTHE ORGANIZATION’S CULTURECorporate Takeover (Scenario)Todd works for SeaLan Tech, an environmental consulting firm that has just been purchased by Zerex, Inc., a biomedical research organization. Based on his early encounters with the new upper management from Zerex, Todd feels that SeaLan is a “lower-key, friendlier” organization. He is concerned that the new company will eliminate SeaLan’s old culture, and he does not like the prospects.110.If you were talking with Todd and asked him what the term culture meant, he would reply that, basically, it is _________________.a.the formal rules of an organizationb.the nationality of the workers in the companyc. a system of shared meaningd. a system that reflects diversity and respect for differences111.Todd is concerned with the degree to which managers focus on results or outcomes rather than techniques and the processes used to achieve those outcomes. He is concerned with _____________.a.stabilityb.aggressivenessc.team orientationd.outcome orientation112.Todd notices that management is very concerned with the effects of outcomes on people within the organization. This is referred to as _____________.a.stabilityb.aggressivenessc.team orientationd.people orientation113.Todd is assessing the organization’s _____________, the degree to which organizational activities emphasize maintaining the status quo in contrast to growth.a.stabilityb.aggressivenessc.team orientationd.outcome orientation114.Todd has been learning the seven dimensions of organizational culture. Which of the following is not one of those seven dimensionsa.stabilityb.aggressivenessc.member orientationd.outcome orientationChanging Organizational Culture (Scenario)Mary has been asked by the company president to change the organizational culture to reflect the company’s new organizational goals. As executive vice president, she certainly understands the goals, but is really not sure that she understands what to do about the culture.115.Mary asked employees if they knew what constituted “good employee behavior.” She found that very few understood, and most had a variety of ideas. This is one indication that her company _______________.a.has a strong cultureb.has a weak culturec.has no cultured.must have high turnover116.Mary also found out that in order to build a strong new culture, she should do all but which of the followinga.hire employees who fit in with the company’s cultureb.develop socialization practices to build culturec.encourage a high turnover rate among employeesd.have management make organizational values clear117.Mary was surprised to find that most organizational cultures are ____________.a.weakb.weak to moderatec.moderate to strongd.strongTHE ENVIRONMENTEnvironmental Constraints (Scenario)It is safe to say that managers do not have complete control over organizational outcomes; the environment has a significant impact. However, there are different environmental factors that shape a manager’s wor k life.118.As a manager, if you were working in an industry that was dependent on rapidly changing software technologies, with many new companies competing for the same customers, you would be working in what kind of environmenta.generalb.staticc.stabled.dynamic119.Political conditions, which include attitudes that officials hold toward specific industries, fall within an organization’s _____________ environment.a.globalb.internalpetitived.generalThe Election (Scenario)At the present time, your organization is faced with many changes. One of these is the election of a new president and Congress. Another concerns new requests from customers for changes to the look of your product design. A third involves changes in the ages and education levels of your customer base. Your customers have also recently expressed a desire to have your product manufactured using a newly discovered type of plastic.120.The changes in the presidency and Congress represent which of thefollowing environmental factors for your organizationa.general environmentb.specific environmentc.pressure groupd.customers121.The change in how customers want your product to look indesign is an example of which of the following types of factorsa.political/legalb.specific environmentc.globald.demographic122.The changes in the ages and education levels of yourcustomers are an example of which of the following conditionsa.economicb.political/legalc.demographic。

管理学复习资料1.管理:通过协调和监督他人的活动,有效率和有效果地完成工作。
2.计划:包括定义组织的目标,制定全局战略以实现目标,以及开发一组广泛的相关计划以整合和协调组织的工作。
3.组织:组织是对人员的一种精心的安排,以实现某些特定的目的。
4.领导:是领导者所做的事情,更具体地说,它是一个影响群体实现目标的过程。
5.控制:控制就是对工作情况进行监督、对比并纠正的过程。
6.目标管理:一个组织成员共同确定组织目标并依据这些目标的达成与否来评估员工绩效的过程。
7.激励员工:激励也是人力资源的重要内容,是指激发人的行为的心理过程。
激励这个概念用于管理,是指激发员工的工作动机,也就是说用各种有效的方法去调动员工的积极性和创造性,使员工努力去完成组织的任务,实现组织的目标。
附区嘉颖对激励员工那一章的理解和总结:管理者在设计具有激励作用的工作时可以遵循什么方法?1、工作扩大化2、工作丰富化3、工作特征模型根据工作特征模型,任何工作都可以用以下五种核心纬度进行描述:1)技能多样性2)任务完整性3)任务重要性4)工作自主性5)工作反馈具体的指导原则:1)合并任务2)形成自然的工作单元3)建立客户关系4)纵向拓展工作5)开通反馈渠道管理者如何有效地激励当前劳动力的特殊群体?管理者必须做的是,了解包括多元化员工、专业人员、应急工以及低能、工资最低的员工在内的这些群体的动机要求。
管理者如何设计恰当的奖励制度?1、账目公开管理2、运用员工认可方案3、运用绩效工资方案4、运用股票期权方案P458当代动机观点包括哪些?(备用参考)三种需要理论、目标设置理论、强化理论、具有激励作用的工作设计、公平理论、期望理论。
8.职务设计:是将职务任务组合起来构成一项完整职务的过程,是对现有职务的认定、修改或产生新的职务。
9.组织文化:组织文化是组织成员共有的价值观、行为准则、传统习惯个做事的方式,它影响了组织成员的行为方式并影响他们如何看待、定义、分析、解决问题。

第一章管理与组织导论......1 一、管理及其具体含义......1 二、管理的职能 (1)管理角色(简述)三、管理角色(09 简述)……1 管理技能与管理层次之间的关系(名词解释)四、管理技能与管理层次之间的关系(06 名词解释)……1 五、管理者工作的变化……2 组织的特征(简述)六、组织的特征(06 简述)……2 七、职责和职权……2 八、管理和领导的联系与区别……2 第二章管理理论……3 一、管理理论……3 二、科学管理理论……3 三、一般行政管理理论……3 四、定量方法理论……3 五、组织行为理论……3 六、系统论……3 七、权变理论……4 八、管理理论当前的问题……4 第三章组织文化环境……4 管理万能论,一、管理万能论,管理象征论……4 组织文化及如何评价一个组织的文化(简述)二、组织文化及如何评价一个组织的文化(08 简述)……4 三、组织文化对管理实践的影响……5 环境对管理者的影响(判断分析)四、环境对管理者的影响(05 判断分析)……5 五、管理与组织环境的关系……5 利益相关者及其如何管理利益相关者关系(名词解释,论述)六、利益相关者及其如何管理利益相关者关系(05 名词解释,06 论述)……5 第五章社会责任与管理道德……6 社会义务和社会响应(名词解释)一、社会义务和社会响应(05 名词解释)……6 社会责任的两种观点,为什么出现关于社会责任的争论(论述)二、社会责任的两种观点,为什么出现关于社会责任的争论(08 论述)……6 管理的绿色化及组织走向绿色化的主要方式的绿色化及组织走向绿色化的主要方式(简答)三、管理的绿色化及组织走向绿色化的主要方式(07 简答)……7 共享价值观的作用及其建立共享价值观的建议(,简述)四、共享价值观的作用及其建立共享价值观的建议(05,09 简述)……7 五、影响管理道德的因素……7 第六章制定决策……7 决策假设的前提,结合实际论述理性和有限理性的决策观点(简述)一、决策假设的前提,结合实际论述理性和有限理性的决策观点(08 简述)……7 决策制定的过程(简述、判断分析)二、决策制定的过程(05 简述、判断分析) (8)决策风格(简述)三、决策风格(06 简述)……8 如何制定合理的决策(论述,简述)四、如何制定合理的决策(05 论述,09 简述)……9 第七章计划的基础……9 计划(分析判断,名词解释,案例分析)一、计划(05 分析判断,名词解释,08 案例分析)……9 区别传统的目标设立与目标管理(简答)二、区别传统的目标设立与目标管理(07 简答)......10 第八章战略管理......11 一、战略管理......11 管理者如何选择企业战略(论述,,案例)二、管理者如何选择企业战略(05 论述,07,08 案例)......11 三、公司业务组合分析中的BCG 矩阵法......12 业务层战略的特点、实现途径和适用条件(案例分析)四、业务层战略的特点、实现途径和适用条件(05,07 案例分析) (12)五、波特五力(05 案例分析)……13 波特五力(案例分析)核心竞争力(案例分析)六、核心竞争力(05,07 案例分析)……13 公司战略、七、公司战略、业务层战略和职能层战略的关系……14 第十章组织结构与设计……14 一、组织结构……14 影响组织集权和分权的因素(简答,论述)二、影响组织集权和分权的因素(07 简答,09 论述)……14 机械式组织和有机式组织的异同……15 三、机械式组织和有机式组织的异同指挥链(名词解释)四、指挥链(06 名词解释)……15 传统的组织设计(简述)五、传统的组织设计(05 简述)……15 现代的组织设计(简答)六、现代的组织设计(07 简答)……15 项目型结构和矩阵型结构的异同……16 七、项目型结构和矩阵型结构的异同第十一章第十一章管理沟通与信息技术……16 沟通(名词解释)一、沟通(05 名词解释)……16 二、沟通障碍……17 跨部门沟通的方法(案例分析)三、跨部门沟通的方法(05 案例分析)……17 小道消息,对付小道消息的方法……18 四、小道消息,对付小道消息的方法第十二章人力资源管理……18 一、人力资源管理……18 人力资源规划过程(简述)二、人力资源规划过程(06 简述)……18 三、人力资源管理过程……18 四、绩效评估方法……19 人力资源管理中面临的新问题(简述)五、人力资源管理中面临的新问题(09 简述)……19 第十三章变革与创新管理……20 一、变革的两种力量……20 二、变革过程的两种观点……20 管理变革的方法(,简答)三、管理变革的方法(07,08 简答)……20 四、创造与创新……21 管理者如何减缓员工压力(论述)五、管理者如何减缓员工压力(06 论述)……21 第十五章群体和团队……21 群体的发展阶段(名词解释)一、群体的发展阶段(05 名词解释)……21 二、群体决策的优缺点……22 关于冲突的不同观点(简述)三、关于冲突的不同观点(05 简述)……22 四、团队……22 工作团队的类型(简述)五、工作团队的类型(06 简述)……23 如何管理高效率团队(论述)六、如何管理高效率团队(05 论述)……23 第十六章激励……23 动机(名词解释)一、动机(05 名词解释)……23 早期动机理论(案例分析)二、早期动机理论(06 案例分析)……24 当代动机理论(简述,论述,案例分析)三、当代动机理论(05 简述,07 论述,09 案例分析)……25 联系实际,如何激励员工(年论述)四、联系实际,如何激励员工(09 年论述)……27 职务设计选择(简述)五、职务设计选择(08 简述)……28 工作特征模型(论述)六、工作特征模型(05 论述)……28 第十七章领导……29 领导者权力体系的来源与构成……29 一、领导者权力体系的来源与构成二、早期领导理论(06、08 论述,09 论述、案例分析)......29 早期领导理论(、论述,论述、案例分析)领导的权变理论(论述,案例分析)三、领导的权变理论(07,08 论述,09 案例分析)......30 领导的最新观点(案例分析)四、领导的最新观点(09 案例分析)......32 第十八章控制......33 一、控制......33 控制的焦点的内容(简述)二、控制的焦点的内容(08 简述)......33 三、控制的类型及其优缺点 (34)第一章管理与组织导论一、管理及其具体含义管理及其具体含义管理是在特定的组织内外环境下,通过协调和监督他人的活动,能够有效率和有效果地管理与别人一起或者通过别人实现组织目标的过程。


罗宾斯.管理学第九版案例分析题管理学案例分析题案例分析题1某建筑公司,经过⼏⼗年的发展,已经成为当地知名的建筑龙头企业。
总结企业成功的经验,许多管理⼈员归结为天时、地利、⼈和,如国家经济的持续发展、与当地政府、银⾏的良好关系,⼏⼗年形成的固定客户和良好的信誉,良好的员⼯素质等等。
在2008年北京奥运景⽓⿎舞下,公司确⽴了打破地区界限,成为全国乃⾄世界知名建筑企业的远景和使命。
当企业树⽴这样的远景和使命并为之努⼒时,发现曾经作为优势的“天时、地利、⼈和”似乎不在。
例如,就在前不久,⽇本⼀家建筑企业在与公司谈判时,让公司在两天内给出⼀个项⽬的报价。
由于公司没有既懂建筑专业⼜精通⽇语的⼈员,没有能够及时报价,很遗憾地没有抓住公司项⽬。
请分析该公司的内外部环境,以及应采取的措施。
(1)天、地、⼈是对公司内外部环境的概括描述。
从案例中可以看出公司过去的成功来⾃天时、地利、⼈和,构成了公司的竞争优势。
当公司重新确⽴了“成为全国乃⾄世界的建筑企业”时,从案例中可以看出在政府、银⾏关系⽅⾯、在地理⽅⾯、在⼈员素质要求等⽅⾯,都发⽣了变化,所谓的天、地、⼈已经不再成为优势。
(2)因此公司要真正认清所处的内外部环境,确定公司的使命和愿景,并围绕天、地、⼈等制定相应措施。
具体措施应围绕培育公司的核⼼竞争⼒⽅⾯:具有建⽴电⼦商务⽹络和系统的技能;迅速把新产品投⼊市场的能⼒;更好的售后服务能⼒;⽣产制造⾼质量产品的技能;开发产品特性⽅⾯的创新能⼒;对市场变化作出快速反应;准确迅速满⾜顾客定单的系统;整和各种技术创造新产品的技能等⽅⾯。
案例分析题2某地⽅⽣产传统⼯艺品的企业,伴随着我国对外开放政策,逐渐发展壮⼤起来。
销售额和出⼝额近⼗年来平均增长15%以上。
员⼯也有原来的不⾜200⼈增加到了2000多⼈。
企业还是采⽤过去的类似直线型的组织结构,企业⼀把⼿王⼚长既管销售,⼜管⽣产,是⼀个多⾯全能型的管理者。
最近企业发⽣了⼀些事情,让王⼚长应接不暇。
Chapter 4 Managing in a Global EnvironmentWHAT’S YOUR GLOBAL PERSPECTIVE?1.In a global marketplace ____________.a.the entire world is a marketplaceb.national borders are irrelevantc.the potential for organizations to grow expands dramaticallyd.all of the above(d; moderate; p. 90; AACSB: Globalizations)2.To succeed in a global marketplace, managers must _____________.a.constantly develop new strategies to maintain their parochial viewsb.expect competitors to suddenly appear at any time from any placec.implement only the best practices of their home countriesd.downplay the effect of the values and customs of other cultures(b; difficult; p. 90; AACSB: Globalizations)3.One reason for parochialism in the United States is that Americans tend to study_____________ in school.a.only Englishb.only two languagesc.English and Frenchd.English and Spanish(a; easy; p. 91; AACSB: Globalizations)4.Which of the following describes the current state of the world use of languages?a.Germans and Italians, unlike other Europeans, only speak their native language.b.Americans tend to study many other languages in school.c.More than 75 percent of all primary school children in China now learn English.d.Americans tend to think of English as the only international business language.(d; moderate; p. 91; AACSB: Globalizations)5.Ethnocentric views concentrate on their _____________.a.home countryb.host countryc.world orientationd.racial orientation(a; easy; p. 92; AACSB: Globalizations)6.Parochialism is ____________.a.acceptance of diverse points of viewb. a desire to leave one’s own culture for a foreign culturec. a tendency to view the world through a single perspectived.recognition of diverse religious beliefs(c; moderate; p. 91; AACSB: Globalizations)7.For U.S. businesses to have successful global management, which of the following statementsprovides the best advice?a.Americans should continue to push for the use of English only.b.Stick to your own customs to avoid embarrassing incidents.c.Make sure foreign businesspeople know you are American so they will speak to you inEnglish.d.Develop an understanding of multicultural differences.(d; moderate; p. 93; AACSB: Globalizations)8.Which of the following is the least favorable attitude for an American manager who wishes tobe successful in international business?a.multiculturalb.multicentricc.ethnocentricd.polycentric(c; easy; p. 92; AACSB: Globalizations)9.Managers with a(n) ___________ attitude view every foreign operation as different and hardto understand.a.geocentricb.polycentricc.ethnocentricd.transnational(b; moderate; p. 92; AACSB: Globalizations)10.Successful global management requires an attitude that is best described as _____________ .a.ethnocentricb.parochialc.polycentricd.geocentric(d; easy; p. 92; AACSB: Globalizations)11.A(n) __________ attitude is characterized by parochialism.a.geocentricb.acculturatedc.polylinguisticd.ethnocentric(d; moderate; p. 92; AACSB: Globalizations)12.A(n) _____________ attitude is the view that host-country managers know the best practicesfor running their operations.a.ethnocentricb.polycentricc.geocentricd.international(b; easy; p. 92; AACSB: Globalizations)13.The geocentric attitude is a _____________ view.a.nationalisticb.world-orientedc.culture-boundd.franchise-based(b; moderate; p. 92; AACSB: Globalizations)14.Successful _____________ management requires enhanced sensitivity to differences innational customs and practices.a.ethnocentricb.polycentricc.globald.parochial(c; moderate; p. 93; AACSB: Globalizations)UNDERSTANDING THE GLOBAL ENVIRONMENT15.The _____________ was created by the unification of 12 countries in Europe.a.European Common Marketb.European Unionc.Western European Allianced.Trans-European Market (TEM)(b; moderate; p. 94; AACSB: Globalizations)16.The principle reason for the formation of a regional trading alliance in Europe was to reassertmembers’ economic positions against the strength of the United States and _________.a.Canadab.Mexicoc.Japand.Russia(c; moderate; p. 94; AACSB: Globalizations)17.The European Union covers ______________.a.border controls, taxes, and subsidiesb.nationalistic policies and travelc.employment, investment, and traded.all of the above(d; moderate; p. 94; AACSB: Globalizations)18.The _____________ is a collection of countries that use a common currency.a.European Common Marketb.European Unionc.Western European Allianced.Economic and Monetary Union (EMU)(d; difficult; p. 94; AACSB: Globalizations)19.The single EU currency is called the ____________.a.francb.franc-markc.poundd.euro(d; moderate; p. 94; AACSB: Globalizations)20.The European Union currently consists of ___________.a.12 countriesb.15 countriesc.10 countriesd.25 countries(d; difficult; p. 94; AACSB: Globalizations)21.Which of the following countries is not a member of the European Union?a.Icelandb.Irelandc.Cyprusd.Slovenia(a; moderate; p. 94; AACSB: Globalizations)22._______ is expected to join the European Union in 2007.a.Hungaryb.Estoniac.Romaniad.Turkey(c; moderate; p. 95; AACSB: Globalizations)23.The executive body of the EU, based in Brussels, is known as the ________.a.Maastricht Officeb.FTAAc.Euro Protectorated.European Commission(a; moderate; p. 95; AACSB: Globalizations)24.Among the member countries of the North American Free Trade Agreement, trade has___________ since the treaty was signed.a.decreased initially, but increased steadilyb.increasedc.decreasedd.increased in commodities, but decreased in manufactured goods(b; moderate; p. 95; AACSB: Globalizations)25.The North American Free Trade Agreement includes _________________.a.Mexico, Canada, and the United Statesb.Canada, Mexico, and Brazilc.the United States, Canada, and Hondurasd.Columbia, Mexico, and the United Sates(a; easy; p. 95; AACSB: Globalizations)26.The North American Free Trade Agreement has resulted in which of the following?a.It increased imports from Mexico by 106 percent.b.It eliminated duties on imports from Venezuela.c.It increased exports to Canada by 62 percent.d.It increased trade with the European Union.(a; easy; p. 95; AACSB: Globalizations)27.Which of the following is currently under negotiation by thirty-four countries inthe Western Hemisphere?a.NAFTAb.FTAAc.Mercosurd.ASEAN(b; difficult; p. 95; AACSB: Globalizations)28.The North American Free Trade Agreement eliminated all of the following except________________.a.the need for import licensingb.tariffs on traded commoditiesc.customs user feesd.China’s role as a U.S. trading partner(a; moderate; p. 95; AACSB: Globalizations)29.The Association of Southeast Asian Nations includes ________________.a.the members of the European Union and Indiab.the members of NAFTA and CAFTAc. a membership of 10 Southeast Asian nationsd.none of the above(c; moderate; p. 95; AACSB: Globalizations)30.Each of the following is a member of ASEAN except ________________.a.Bruneib.Singaporeosd.Japan(d; moderate; p. 96; AACSB: Globalizations)31.How many member nations belong to the African Union (AU)?a.46b.53c.62d.67(b; moderate; p. 96; AACSB: Globalizations)32.Nepal belongs to which of the following regional trade alliances?a.EUb.SAARCc.AUd.ASEAN(b; moderate; p. 96; AACSB: Globalizations)33.The World Trade Organization evolved from which of the following?a.GATTb.Mercosurc.UNIDIRd.Marshall Plan(a; moderate; p. 96; AACSB: Globalizations)34.The World Trade Organization is centered around which of the following?a.public protestsb.economic sanctionsc.trade agreementsd.peace treaties(c; moderate; p. 96; AACSB: Globalizations)35.The goal of the World Trade Organization is to ___C_____.a.help develop environmental policyb.help regulate international marketsc.help businesses conduct their businessd.help reduce conflicts between nationsc moderate; p. 96; AACSB: Globalizations)DOING BUSINESS GLOBALLY36.International businesses have been around since about what date?a.the fifteenth centuryb.the seventeenth centuryc.the nineteenth centuryd.the twentieth century(c; difficult; p. 97; AACSB: Globalizations)37.Multinational corporations (MNCs) have only become commonplace since approximatelywhat date?a.mid-1960sb.mid-1970sc.1945d.mid-1980s(a; moderate; p. 97; AACSB: Globalizations)38.Multidomestic corporations are known for _______________.a.ethnocentric attitudesb.polycentric attitudesc.multicentric attitudesd.having their holdings in one country(b; moderate; p. 97; AACSB: Globalizations)39.Which of the following is an MNC that tailors marketing strategies to the host country’sunique characteristics?a.borderless organizationb.global companyc.multidomestic corporationd.transnational organization(c; moderate; pp. 97-98; AACSB: Globalizations)40.Multidomestic corporations _________________.a.maintain operations in multiple counties, but do not allow managers in eachcountry to make their own decisionsb.utilize ethnocentric attitudes in financial decisions, but favor polycentricviews in human resources issuesc.utilize decentralization to make decisions in management in local countriesd.follow the tastes, preferences, and values of the home country(c; moderate; p. 97; AACSB: Globalizations)41.When an organization drops its structure based on countries and reorganizes according toindustries, it is pursuing a global organizational operation known as ___________.a.ethnocentrismb.polycentrismc.borderless organizationd.multinational organization(c; moderate; p. 98; AACSB: Globalizations)42.Transnational organizations are also known as ________.a.ethnocentric organizationsb.polycentric organizationsc.borderless organizationsd.multidomestic organization(c; moderate; p. 98; AACSB: Globalizations)43.Transnational organizations are focused on _________________.a.increasing efficiencyb.developing INVsc.reinforcing structural divisionsd.all of the above(a; moderate; p. 98; AACSB: Globalizations)44.Which of the following types of business is global from its inception?a.international new ventureb.global companyc.born globald.joint economic market(c; difficult; p. 98; AACSB: Globalizations)45.Which of the following is a basic definition of a multinational corporation?a. a company that maintains operations in multiple countriesb. a company that maintains franchises in multiple countriesc. a company that has multiple home bases and manufacturing plantsd. a company that pays corporate taxes in at least two countries(a; difficult; p. 98; AACSB: Globalizations)46.Which of the following is the basic difference between multidomestic corporations and globalcompanies?a.Multidomestic corporations typically do business with more countries than globalcompanies do.b.Multidomestic corporations are run by global companies but must be owned by a local,national company.c.Multidomestic corporations decentralize management to the local country,while global companies centralize management in the home country.d.Multidomestic corporations pay more in taxes than global companies do.(c; difficult; pp. 97-98; AACSB: Globalizations)47.Which of the following is not a feature of a multidomestic corporation?a.Decision making takes place at the local level.b.Nationals are typically hired to run operations in each country.c.Marketing strategies are tailored to each country’s culture.d.Products are manufactured only in the local country.(d; easy; pp. 97-98; AACSB: Globalizations)48.Which of the following types of global organizations reflects the geocentric attitude?a.multidomestic corporationb.transnational organizationc.global companyd.regional organization(b; difficult; p. 98; AACSB: Globalizations)HOW ORGANIZATIONS GO GLOBAL49.Importing and exporting represent a more significant global investment than which of thefollowing?a.licensingb.franchisingc.global sourcingd.strategic alliance(c; easy; p. 98; AACSB: Globalizations)50.In an attempt to be more aggressive, a company might export and import more. These stepsusually require ____________.a.minimal investment and minimal riskb.conducting business in a polycentric mannerc.the establishment of strategic alliancesd.abnormal operations for a geocentric organization(a; easy; p. 99; AACSB: Globalizations)51.Franchising is primarily used by ________________.a.political organizationsb.manufacturing organizationsc.service organizationsd.legal organizations(c; moderate; p. 99; AACSB: Globalizations)52.In the later stages of doing business globally, if an organization is ready to make a more directinvestment, it might utilize ______________.a.foreign subsidiariesb.strategic alliancesc.joint venturesd.all of the above(d; moderate; pp. 99-100; AACSB: Globalizations)53.An international company is most likely to develop foreign subsidiaries _______________.a.before it develops licensing agreementsb.before it develops franchising agreementsc.before it begins importing and exportingd.after it establishes strategic alliances(d; moderate; p. 100; AACSB: Globalizations)54.The process of making products domestically and selling them abroad is known as ________.a.exportingb.importingc.franchisingd.joint ventures(a; moderate; p. 99; AACSB: Globalizations)55.Which of the following is usually found in the final stage of an organization’s globalevolution?a.exporting its products to other countriesb.cross-culturally training its managersc.establishing strategic alliances with partnersd.licensing another firm to use its brand name(c; moderate; p. 99; AACSB: Globalizations)56.Joint ventures are a type of ____________.a.licenseb.franchisec.foreign subsidiaryd.strategic alliance(d; moderate; p. 99; AACSB: Globalizations)57.Foreign subsidiaries are usually managed ______________.a.through local control onlyb.through centralized control onlyc.through local or centralized controld.none of the above(c; easy; p. 100; AACSB: Globalizations)58.A domestic firm and a foreign firm sharing the cost of developing new products orbuilding production facilities in a foreign country is called a ____________.a.franchising agreementb.joint venturec.foreign subsidiaryd.brokering agreement(b; moderate; p. 99; AACSB: Globalizations)59.Which of the following would most likely occur last in an organization’s global evolution?a.cross-cultural training of the company’s managersb.sending domestic employees on regular foreign business tripsc.hiring foreign brokers to represen t the organization’s product lined.creating a joint venture with suppliers around the globe(d; moderate; p. 99; AACSB: Globalizations)60._____________ present(s) the greatest risk to an organization going international.a.Joint venturesb.Strategic alliancesc.Licensingd.Foreign subsidiaries(d; difficult; p. 99; AACSB: Globalizations)MANAGING IN A GLOBAL ENVIRONMENT61.Which of the following is not considered to be one of the three major areas of significantchallenge for an American manager working in a foreign country?a.legal environmentb.economic environmentc.cultural environmentd.religious environment(d; difficult; pp. 101-103; AACSB: Globalizations)62.From an economic standpoint, a threat to the global manager is _________________.a.widely fluctuating inflation rates in foreign countriesb.marginal revenues exceeding marginal costsc. a stable exchange rate between currencies in various countriesd.all of the above(a; moderate; p. 102; AACSB: Globalizations)pared to many other countries, the U.S. legal–political environment is considered____________.a.radicalb.stablec.unstabled.fixed(b; moderate; p. 101; AACSB: Globalizations)pared to many other countries, changes to the U.S. legal–political environment areconsidered ___________.a.very fast and effectiveb.fast, but not efficientc.radicald.slow(d; moderate; p. 101; AACSB: Globalizations)65.The reason that a nation’s cultural differences are the most difficult to gain information aboutis because __________________.a.people tend to be sensitive about their own cultureb.providing this information to foreign organizations reduces a competitive businessadvantagec.there is little written on the issued.“natives” are least capable of explaining the unique characteristics of theirown culture(d; difficult; p. 104; AACSB: Globalizations)66.Which of the following developed a valuable framework to help managers better understanddifferences between national cultures?ton Friedmanb.Michael Porterc.Geert Hofsteded.Abraham Maslow(c; moderate; p. 104; AACSB: Globalizations)67._____________ is a cultural dimension in which people expect others in their group to lookafter them and protect them when they are in trouble.a.Power distanceb.Collectivismc.Achievementd.Uncertainty avoidance(b; easy; p. 105; AACSB: Globalizations)68.Which of the following would you find in a country with a high power distance?a.Society accepts narrow differences in organizations.b.Title carries little power, but status power is high.c.There is little respect for those in authority.d.Titles, rank, and status carry a lot of weight.(d; moderate; p. 105; AACSB: Globalizations)69.The GLOBE framework assesses how many cultural dimensions?a.fiveb.sixc.nined.twelve(c; moderate; p. 106; AACSB: Globalizations)70._____________ is a cultural measure of the degree to which people will tolerate risk andunconventional behavior.a.Power distanceb.Uncertainty avoidancec.Achievementd.Nurturing(b; easy; p. 105; AACSB: Globalizations)anizations in which of the following cultures are likely to have formal rules and littletolerance for unusual ideas and behaviors?a.high power distanceb.low power distancec.high uncertainty avoidanced.low uncertainty avoidance(c; easy; p. 105; AACSB: Globalizations)72.In a society with a highly ______________ culture, strong value is placed on relationshipsand concern for others.a.collectivistb.achievement-orientedc.nurturingd.uncertainty avoidant(c; moderate; p. 105; AACSB: Globalizations)73._____________ is a national culture attribute describing the extent to which societal valuesare characterized by assertiveness and materialism.a.Power distanceb.Uncertainty avoidancec.Achievement orientationd.Long-term orientation(c; moderate; p. 105; AACSB: Globalizations)74._____________ is a national culture attribute that places a high value on future occurrences.a.Power distanceb.Uncertainty avoidancec.Long-term orientationd.Leisure orientation(c; moderate; p. 105; AACSB: Globalizations)75.Which of the following are most alike in terms of individualism, power distance, anduncertainty avoidance?a.Singapore and Swedenb.Australia and Englandc.France and Greeced.United States and V enezuela(b; easy; p. 106; AACSB: Globalizations)76.Which of the following scores the highest in terms of power distance?a.Greeceb.Swedenc.Canadad.England(a; easy; p. 106; AACSB: Globalizations)77.Which of the following dimension from the GLOBE framework has no equivalent inHofstede’s framework?a.future orientationb.humane orientationc.gender differentiationd.uncertainty avoidance(c easy; p. 106; AACSB: Globalizations)SCENARIOS AND QUESTIONSFor each of the following choose the answer that most completely answers the question.WHAT’S YOUR GLOBAL PERSPECTIVE?First Visit Abroad (Scenario)Bill Sanderson is halfway over the Atlantic and is excited about his first European business trip. Bill is confident about this trip but is somewhat concerned about the strange habits and foreign languages he will encounter. “If only they would just speak English like everyone else!” Bill thinks.78.Bill’s tendency to view the world only through his U.S.-based perspective is an internationalbusiness problem known as which of the following?a.nondiversityb.discriminationc.parochialismd.monolingualism(c; moderate; p. 92; AACSB: Globalizations)79.If Bill is to become successful as a global manager, he must _______________.a.attempt to change other cultures to American waysb.learn and accept other culturespete internationally but remain in the United Statesd.learn to manipulate other business cultures(b; moderate; p. 93; AACSB: Globalizations)Cultural Training (Scenario)Jane wants to expand her career opportunities in international operations of a company. She is 19 years old and currently attends a university. She has only lived in her current country and has never traveled to foreign countries.80.Jane decides to enroll in a foreign language class to help her overcome her ______________.a.parochialismb.ethnocentric attitudec.monolingualismd.polycentric attitudes(c; moderate; p. 91; AACSB: Globalizations)81.In talking with her advisor at the university, Jane decides she probably has a(n)__________ attitude, as she has never traveled abroad and only relates well to people from her home country.a.culturally focusedb.polycentricc.ethnocentricd.geocentric(c; moderate; p. 92; AACSB: Globalizations)82.Jane becomes involved with an international student association to give her experiences thatwill allow her to understand the views of students from other countries. She is trying to become more _________ in her attitude.a.parochialisticb.polycentricc.ethnocentricd.geocentric(d; difficult; p. 92; AACSB: Globalizations)UNDERSTANDING THE GLOBAL ENVIRONMENTA Foreign Alliance Talk (Scenario)As manager of the international department for your company, you have been asked by the local Chamber of Commerce to deliver a speech on foreign trade. The Chamber president even goes so far as to say “and be sure to include the EU, NAFTA, and all that stuff because we’re afraid that Ross Perot is right—all the good jobs will leave the United States.” As you pour over your notes, you try to choose the best information to present in the allotted half hour.83.You plan to explain during your talk that the acronyms EU, NAFTA, FTAA, and ASEANrefer to ________________.a.regional trade alliancesb.foreign airlinesc.soccer teams in Europed.new multinational corporations(a; difficult; p. 94; AACSB: Globalizations)84.One of the hottest topics of your talk will be NAFTA. One of the points that you emphasize isthat ______________.a.the United States has definitely come out the worst of the three nationsb.Canada is profiting the most in this arrangementc.the expansion of NAFTA has benefited North America’s competitiveness andeconomic powerd.U.S. high-tech companies, such as computer manufacturers, have been hit hard by theNAFTA provisions(c; difficult; p. 95; AACSB: Globalizations)85.You will also give participants a likely view of the future of the EU, which suggests that_______________.a.it will likely disband by the year 2010b.it is expected to merge with NAFTA by 2020c.Bulgaria will probably join in 2007d.Cuba has applied to join the EU(c; moderate; p. 94; AACSB: Globalizations)DOING BUSINESS GLOBALLYBusiness Expansion Plan (Scenario)As a business expansion director, Shana’s goal is to scout out potential locations and basically provide input on how her company should proceed with its planned expansion to Europe. There are many options, including maintaining the business’s head office in the United States and sending over company representatives when necessary or establishing separate operations facilities abroad and hiring locals as managers.86.If Shana’s company decides to open another company in France but maintain its managementin the United States, it would be considered _________________.a. a transnational corporationb. a global companyc. a regional trade allianced. a multidomestic corporation(b; moderate; p. 98; AACSB: Globalizations)87.If Shana’s company decides to open a completely new operation in Germany, tailoring thecompany to local customs and marketing strategies and hiring local managers, they would beconsidered _______________.a. a transnational corporationb. a global companyc. a regional trade allianced. a multidomestic corporation(d; moderate; p. 97; AACSB: Globalizations)88.If Shana’s company eliminates country-designated locations and reorganizes based onindustry groups, it would best be considered a __________________.a.borderless organizationb.strategic partnershipc.global business allianced.multidomestic corporation(a; moderate; p. 98; AACSB: Globalizations)89.One section of Shana’s company’s business plan involves strategic alliance s and jointventures. This section is most likely focused on the _________ phase of the company’s global business expansion.a.legalb.middlec.finald.preliminary(c; moderate; p. 99; AACSB: Globalizations)The European Expansion (Scenario)You have been hired by a company to look at the ways to best move the company into the European market, but you have to first determine what kind of company you are dealing with.90.If the company that has hired you is primarily used by manufacturingorganizations, it is a ___________.a.licensing companyb.franchising companyc.strategic allianced.joint venture(a; moderate; p. 99; AACSB: Globalizations)123.If the company that has hired you is really a partnership between an organization and a foreign company, in which both share resources and knowledge in developing new products, then it is a _______________.a.licensing companyb.franchising companyc.strategic allianced.joint venture(c; moderate; p. 99; AACSB: Globalizations)Software Entrepreneurial Venture (Scenario)Theodore and James have formed an entrepreneurial venture to develop software for banks and other financial institutions. Their company is growing, but in looking for opportunities in the future, they decide to explore international operations.124.The international operations in their firm continue to grow. Theodore and James have come to see that decentralized management using foreign nationals to run operations in the host countries works well. Their firm has developed into a(n) ____________ organization.a.transnationalb.multidomesticc.borderlessd.franchise(b; moderate; p. 97; AACSB: Globalizations)125.A new and exciting opportunity has appeared that enables Theodore and James to form a joint venture with an insurance company in Japan. This will move their firm into the global role of an organization with a(n) ______________.a.minimized level of business riskb.indirect international investmentc.direct international investmentd.independent foreign subsidiary(c; moderate; p. 99; AACSB: Globalizations)126.Theodore and James decide to allow a firm in Europe to use the rights to their software, its brand name, and software specifications in return for a lump-sum payment. The firm is a service organization that plans to use the software to assist its customers. This agreement is known as a ________________.a.strategic allianceb.licensing agreementc.franchised.foreign subsidiary(c; difficult; p. 99; AACSB: Globalizations)MANAGING IN A GLOBAL ENVIRONMENTA Different View (Scenario)John has done well in his company. In only 5 years, he has risen to the position of divisional manager. However, he knows that in order to rise to the level of senior management, he needs to spend some time managing abroad in his company’s foreign subsidiaries. Although he has。
Chapter 7 –Foundations of PlanningTrue/False Questions4.Research indicates that managers who plan always outperform managers who do not plan.False (moderate)9.Plans that specify the details of achievement of the overall objectives arecalled operational plans.True (difficult)10.Directional plans have clearly defined objectives.False (moderate)12.Standing plans are created in response to programmed decisions that managers make andinclude policies, rules, and procedures.True (moderate)13.The greater the environmental certainty, the more plans need to be directional andemphasis placed on the short term.False (moderate)22.An organization's real goals are what they actually plan on accomplishing, ratherthan what they hope to accomplish.False (moderate)24.Real goals are official statements of what an organization says its goals are.False (easy)Multiple Choice36.One purpose of planning is that it minimizes ______________ and ______________.a.cost; timeb.time; personnel needsc.waste; redundancy (difficult)d.time; wastee.mistakes; cost38.What does the evidence suggest about organizations that plan compared toorganizations that do not plan?a.Planning organizations always outperform nonplanning organizations.b.Nonplanning organizations always outperform planning organizations.c. Planning organizations generally outperform nonplanning organizations (easy)d.Nonplanning organizations generally outperform planning organizations.e.They generally perform at about the same level.45.Which of the following is the foundation of planning?a.employeesb.goals (easy)c.outcomesputerse. the planning department46.According to the text, _____________ are documents that outline how goals are going toand other be met and which typically describe resource allocations, schedules, necessary actions toaccomplish the goals.a.strategiesb.goalsc.plans (moderate)d.policiese.procedures50.Which of the following is true concerning an organization's stated objectives?a.They issue identical objectives to all constituents.anizations typically have internal and external sets of objectives.c.They may issue different objectives to stockholders, customers, employees, andthe public.(moderate)d.It is illegal to issue conflicting stated objectives.e.Stated objectives are usually in line with short-term actions.54.What should a person do to understand what are the real objectives of the organization?a.observe organizational member actions (moderate)b.attend a stockholders annual meetingc.read their statement of purposed.read their annual reporte.watch television news reports59.When we categorize plans as being single-use versus standing, we categorize them by______________.a.breadth.b.specificity.c.frequency of use. (easy)d.depth.e.time frame.61.Based on the information presented in the text,______________ are short term,specific, and standing.a.operational (moderate)b.long-termc.strategicd.specifice.directional67.An organizational plan that has a 6-year time frame would be considered what type ofplan?a.operationalb.short-termc.strategicd.intermediatee.long-term (moderate)68.Strategic plans tend to include a time period of usually ______________.a. 1 year.b.1-3 years.c. 3 years or more. (moderate)d. 5 years or more.e.at least 10 years.pared to directional plans, what type of plan has clearly defined objectives?a.strategicb.single-usec.short-termd.specific (moderate)e.standing76.Planning accuracy with a high degree of environmental change tends to produce whichof the following results?a.Planning accuracy is likely.b.Planning accuracy becomes much more important.c.Planning accuracy becomes less important.d.Planning accuracy is less likely. (moderate)e.Planning accuracy occurs in the long-run.78. A ______________ plan is a one-time plan designed to meet the needs of a unique situation and createdin response to nonprogrammed decisions that managers make.a.single-use (easy)b.short-termc.directionald.standinge.strategic79. A small town's preparation for a visit by the President of the United States wouldbe considered what type of plan?a.strategicb.directionalc.standingd.long-terme.single-use (moderate)81. A city's policy concerning skateboarding on downtown sidewalks providing guidance forpolice action would be considered what type of plan?a.standing (difficult)b.contingencyc.directionald.single-usee.strategic84.Where in the organizational hierarchy are traditional goals determined?a.front-line employeesb.team leadersc.lower-level managersd.middle managerse.top managers (moderate)89. A management system in which specific performance goals are jointly determined byemployees and their managers is known as ______________.a.management by objectives. (moderate)b.means-ends chain.c.traditional goal setting.d.management by opinions.91.Which of the following is not one of the four common elements of Management ByObjectives (MBO)?a.goal specificityb.participative decision-makingc.an explicit time periodd. a systems loop (difficult)e.performance feedback93.Management By Objectives (MBO) can be described by which of the following statements?a.an autocratic systemb. a "bottom up" systemc. a "top down" systemd.both a "top down" and a "bottom up" system (difficult)e. a static system105. According to the boxed feature,“Managing in an E- Business World, ”probably the biggest change for planning in e-business is that ______________.a.the environment is more stable.b.customers are calling the shots. (moderate)c.employees are making the demands.d.only a few competitors exist.Essay Questions122.In a short essay, list and discuss the four reasons for planning.Answera.Planning establishes coordinated effort .It gives direction to managers andnonmanagers alike.When employees know where the organization or work unit are going and what they must contribute to reach goals,they can coordinate theiractivities,cooperate with each other,and do what it takes to accomplish those goals.Without planning,departments and individuals might be working at cross-purposes, preventing the organization from moving efficiently toward its goals.b.Planning reduces uncertainty by forcing managers to look ahead, anticipate change,consider the impact of change,and develop appropriate responses.It also clarifies the consequences of actions managers might take in response to change.Even though planning can ’t eliminate change, managers plan in order to anticipatechanges and develop the most effective response to them.c.Planning reduces overlapping and wasteful activities.When work activities arecoordinated around established plans, wasted time and resources and redundancy canbe minimized.Furthermore,when means and ends are made clear through planning,inefficiencies become obvious and can be corrected or eliminated.d.Planning establishes goals or standards that are used in controlling. If managersare unsure of what they are trying to accomplish, they will be unable to determinewhether or not the goal has actually been achieved. In planning, goals and plansare developed. Then, through controlling, actual performance is compared againstthe goals, significant deviations are identified, and necessary correctiveaction is taken. Without planning, there would be no way to control.(moderate)127.In a short essay, list and discuss five characteristics of well-defined goals.Answer(1) A well-designed goal should be written in terms of outcomes rather than actions.The desired end result is the most important element of any goal and, therefore, thegoal should be written to reflect this.(2)Next,a goal should be measurable and quantifiable.It’s much easier to determine if a goal has been met if it’s measurable. In line with specifying a quantifiable measure of accomplishment, (3) awell-designed goal should also be clear as to a time frame.Although open-ended goalsmay seem preferable because of their supposed flexibility,in fact,goals without a time frame make an organization less flexible because a manager is never sure when thegoal has been met or when he or she should call it quits because the goal will neverbe met regardless of how long he or she works at it. (4) Next a well-designed goalshould be challenging but attainable.Goals that are too easy to accomplish are notmotivating and neither are goals that are not attainable even with exceptional effort.(5) Next, well-designed goals should be written down. Although actually writing downgoals may seem too time consuming, the process of writing the goals forces people tothink them through.In addition,the written goals become visible and tangible evidence of the importance of working toward something.(6)Finally,well-designed goals are communicated to all organizational members who need to know the goals.Making people aware of the goals ensures that they ’re“on the same page” and working in ways to ensure the accomplishment of the organizational goals.(moderate)128.In a short essay, list and discuss the five steps in the goal-setting process.Answera.Step1:Review the organization’s mission,the purpose of the organization.These broad statements of what the organization’s purpose is and what it hopes toaccomplish provide an overall guide to what organizational members think isimportant. It’s important to review these statements before writing goals because the goals should reflect what the mission statement says.b.Step 2:Evaluate available resources. A manager doesn ’t want to set goals thatare impossible to achieve given the available resources. Even though goals shouldbe challenging, they should be realistic. If the resources a manager has to workwith doesn ’t allow for the achievement of that goal no matter how had the managertries of how much effort is exerted, that goal shouldn’t be set.c.Step 3:Determine individually, or with input from others, the goals.These goalsreflect desired outcomes and should be congruent with the organizational mission and goals in other organizational areas.These goals should be measurable, specific, and include a time frame for accomplishment.d.Step4:Write down the goals and communicate them to all who need to know.Writing goals down forces people to think them through and also makes those goalsvisible and tangible evidence of the importance of working toward something.e.Step 5:Review results and whether goals are being met.Make changes, as needed.Once the goals have been established, written down, and communicated, a manager isready to develop plans for pursuing the goals.(difficult)129. In a short essay, list and discuss the three contingency factors that affect planning.Answera.Level in the organization–for the most part,operational planning dominatesmanagers’ planning efforts at lower levels. At higher organizational levels, theplanning becomes more strategy oriented.b.Degree of environmental uncertainty–when environmental uncertainty is high,plans should be specific, but flexible. Managers must be prepared to reword andamend plans as they’re implemented. At times, managers may even have to abandon their plans.c. Length of future commitments–the more that current plans affectcommitments, the longer the time frame for which managers should plan.commitment concept means that plans should extend far enough to meet commitments made when the plans were developed.Planning for too long or for too short a time period is inefficient and ineffective.(moderate)future This those。
管理学罗宾斯第九版课后答案(超强版)1.是的。
他也要进行计划,组织,领导,操纵。
他是一个领导者与监听者。
他拥有沟通技能与人际技能。
2.由于每一个组织都有自己的目标,目标的表达就表现在员工的绩效,因此说管理者的最基本的职责是关注员工的工作绩效。
还应注重效率。
3.职位候选人的技能分为技术技能,人际技能与概念技能。
作为雇主他不可能同时所有能力,因此雇主需要聘请其他人来帮忙。
这给我的启示是要提升自己各方面的能力。
4.没有的。
管理是一门艺术,每个人都有自己的特色,没有最佳的。
假如有最佳的,人们不就都往这方面进展了,那有什么意思。
5.新型组织的动态,灵活性,根据任务定义工作,团队导向等特征有兴趣。
由于这些特征能够促使企业更灵活,能够根据市场情况更快的作出反应。
有利于提高雇员的劳动积极性,促进雇员间的团队意识,合理高效地完成任务。
但我对雇员参与决策制定,在任何地点、任何时间工作,工作日长没有限制等特征不感兴趣。
由于假如过多的给予员工太多的自由,不仅不可能使他们的工作效率上升,反而还会让他们感到没有压力,继而变得懒散,工作效率反而会下降。
同时过于宽松的环境也不利于管理者的管理。
而雇员参与决策的制定在一定程度上能够团结员工,但却会带来很大的弊端,由于雇员的思考方向是有利于自己的,而不可能考虑整个企业的进展,同时雇员无法熟悉企业的整体情况,不能作出最好的决策。
只是总体上来说,新型组织在原有的基础上取得了很大的进步。
6.在今天的环境中,单从效率与效果而言,效果对组织更重要。
由于效果通常是指“做正确的事”,即所从事的工作与活动有助于组织达到其目标。
而效率是指以尽可能少的投入获尽可能多的产出。
在如今的社会中,具有高效率与高效果则企业将立于不败之地,正如UPS。
但要在二者择其一时,效果显然更重要,假如所做的工作不能达到组织的目标,那么所做的事就等于白做,即使是再高的效率也没用。
就像往常中国的很多企业尽管资源利用率低,但只要能达到顾客的要求,它们仍然能够在市场上生存。
第一章口选择题1·治理者是()。
a.不需要补偿的雇员b·为实现组织目标协调工作活动的人c.组织的首脑d.一线工人2·地区经理、工程主管和事业部经理都能够被称为()。
a.基层治理者b.非治理雇员c.中层治理者d.高层治理者3·玛丽向营销副总裁上报工作内容,同时她又是监督者,一些小时工雇员直截了当向她汇报,那么玛丽是()。
a.基层治理者b.中层治理者c.高层治理者d.执行者4·那些负责作出组织层面的决策,并为整个组织制定方案和目标的治理者被定义为()。
a·高层治理者b.中层治理者c.基层治理者d.非治理雇员5·以下能区不治理职位和非治理职位的是()。
a·工资金额的多少b.是否协调他人的工作c·是否组织新的工程d.是否拥有技术技能6·假如比安卡的工作专注在减少白费上,那么她更应该是()治理者。
a·有效率的b.有效果的c.目标导向的d.拥有技术技能的7.效果通常被描述为()。
a.工作活动有助于关心组织实现其目标b.委任尽可能多的责任c.通过自己来治理过程d.通过资金情况来定义一个工程的结果8·()可被理解为正确地做事,()可被理解为一种结果,或者到达组织目标。
a.效果;经济b.效果;效率c.效率;效果d.经济;效率9.方案包括()。
a.指导和鼓舞他人b.适时监控以确保完成任务c.决定某事需要由谁来做d.确定目标、制定策略10.当一个治理者决定需要做什么以及怎么样完成时,他是在()。
a.方案b.组织c.领导d.操纵11.将实际业绩和预先设定的目标进行比照可视为()。
a.方案b.组织c.领导d.操纵12·珍妮弗的上司要求她解释其所属部门的实际开支与公司预算数额不符之处。
在那个地点,上司执行的是()治理职能。
a.方案b.组织c.领导c1.操纵13·在组织成员之间选择最有效的沟通渠道应属于()治理职能。
第七章一、选择题1·( )是正式计划而非非正式计划的特征。
a.组织内部很少或没有共同目标 b.计划工作是普遍的c.为实现目标存在具体的行动计划 d.关注结果2·( )属于计划工作的四个原因之一。
a.计划自动地增加灵活性 b.计划减少不确定性c.计划即使不确定也具有价值d·计划不是件容易的工作,需要经过高强度训练才能制定好的计划3·( )是个体、群体和整个组织期望的产出。
a.计划 b.目 c.战略 d.政策4·( )是组织向外界宣称的试图使各种利益相关群体相信的正式的陈述。
a.真实目标 b.陈述目标c·目标管理 d.方向性计划5.不是融资目标例子的是( )。
a.较大的现金流 b.较高的分红、c·较高的红利和较好的信用等 d.较大的市场份额6·( )构成了组织的整体目标,( )具体表明整体目标怎样达到。
a.战略计划;运营计划 b.长期计划;短期计划c.具体计划;方向性计划 d.持续性计划;一次性计划7.长期计划的时间框架是( )。
a·小于一年 b.大于一年c·超过两年 d.超过三年8·短期计划的时间框架是( )。
a.一年左右 b.两年左右 c.三年左右 d.四年左右9·制定一般指导原则的灵活性计划是( )。
a·运营计划 b.战略计划 c.具体计划 d.方向性计划l0·当环境的不确定性很高时,( )更好。
a·战略计划 b.方向性计划c·运营计划 d.持续性计划11为满足特定情况需要,对非程序性决策作出反应而制定的计划是L )。
a·短期计划 b.具体计划 c.方向性计划 d.一次性计划12·( )计划提供了对重复进行的活动的持续指导。
a·方向性 b.持续性c·运营 d.一次性13‘窑三…:中j首先设立组织的最高目标,然后将其分解为每一个组织层次的子目标。
Chapter 16 – Motivating EmployeesTrue/FalseA MANAGER’S DILEMMA1. According to the company profile in ―A Manager’s Dilemma,‖ the majority of employees at Grupo Mconsist of highly educated professionals who work from their homes?False (easy)2. Ba sed on the company profile in ―A Manager’s Dilemma,‖ Grupo M has been profiled as a sweatshopwhere employees work long hours in dirty, dimly lit factories.False (easy)WHAT IS MOTIVATION?3. Motivation is an internal state that makes certain outcomes appear attractive.True (easy)4. The three key elements in the definition of motivation are effort, organizational goals, and needs.True (difficult)EARLY THEORIES OF MOTIVATION5. Based on McClelland's three-needs theory, high achievers perform best when the odds are against them.False (moderate)CONTEMPORARY THEORIES OF MOTIVATION6. The best managers are high in the need for power and high in the need for affiliation.False (difficult)7. People with a high need for affiliation prefer cooperative situations over competitive ones.True (moderate)8. People will do better when they get feedback on how well they're progressing toward their goals.True (easy)9. Reinforcement theory is related to an individual's belief that she is capable of performing a task.False (moderate)10. The key to reinforcement theory is that it ignores factors such as goals, expectations, and needs, andfocuses solely on what happens to a person when he takes some action.True (difficult)11. The lower a person's self-efficacy, the more confidence he has in his ability to succeed in a task.False (moderate)12. Reinforcement theorists believe that behavior is a function of its consequences.True (easy)MANAGING YOUR CAREER13. According to a recent survey, the primary reason employees stay with their jobs is because of flexible workhours.False (moderate)14. Adding vertical depth to a job is called job enlargement.False (moderate)15. Job design refers to the way tasks are combined to form complete jobs.True (easy)16. When a mail sorter's job is expanded to include mail delivery, the mail sorter has experienced jobenlargement.True (easy)17. Job enlargement increases job depth.False (easy)18. In the job characteristics model, task significance refers to the degree to which a job requires completion ofa whole and identifiable piece of work.False (moderate)19. According to the job characteristics model, task autonomy is not important.False (moderate)20. Guidance from the job characteristics model suggests that job enlargement should take place rather thantask specialization.True (moderate)21. According to equity theory, a person who earns $50,000 will be less satisfied with their pay than a personwho earns $100,000.False (moderate)22. Equity theory has three referent categories: other, system, and self.True (moderate)23. The three variables in Vroom's expectancy theory are valence, instrumentality, and expectancy.True (moderate)24. Vroom would say that if a person values an outcome, their effort to obtain that outcome will always begreat.False (moderate)CURRENT ISSUES IN MOTIVATION25. Flextime is a scheduling system in which employees work four 10-hour days.False (easy)26. Performance-based compensation is probably most compatible with expectancy theory.True (difficult)27. Open-book management is a motivational approach in which an organization's financial statements areopened to and shared with all employees.True (moderate)28. The loyalty of professionals is to their organization.False (easy)MANAGING IN AN E-BUSINES WORLD29. The challenge to motivating employees in an e-business is much less compared to motivating employees ina traditional organization.False (easy)30. Many employers are installing Web-monitoring software since there is no evidence that such efforts cannegatively affect employee morale.False (moderate)Multiple ChoiceA MANAGER’S DILEMMA31. According to the company profile in ―A Manager’s Dilemma,‖ Grupo M is the largest employer in______________.a.the United States.b.Mexico.c.Brazil.d.Dominican Republic. (moderate)e.SwitzerlandWHAT IS MOTIVATION?32. ______________ is the willingness to exert high levels of effort to reach organizational goals, conditions bythe effort’s ability to satisfy some individual need.a.Attributionb.Motivation (easy)c.Leadershipd.Goal settinge.Tenure33. The three key elements in the definition of organizational motivation are ______________, organizationalgoals, and needs.a. personalityb. abilityc. effort (easy)d. tenuree. strategy34. ______________ is an internal state that makes certain outcomes appear attractive.a. A need (easy)b. Motivationc. Leadershipd. Goal settinge. AttributionEARLY THEORIES OF MOTIVATION35. Who developed the Hierarchy of Needs motivational theory?a. Herzbergb. Vroomc. McGregord. Lawlere. Maslow (easy)36. An individual who wants to buy a home in an expensive neighborhood with a low crime rate is satisfyingwhich psychological needs state?a. esteemb. safety (moderate)c. physiologicald. self-actualizatione. social37. The drive to find food, drink, and sexual satisfaction is based on what level of need?a. physiological (easy)b. safetyc. self-actualizationd. sociale. esteem38. The need for such factors as status, recognition, attention, self-respect, autonomy, and achievement areexamples of which of the following needs according to Maslow’s hierarchy of needs?a. physiologicalb. esteem (moderate)c. sociald. self-actualizatione. safety39. Joining a civic club because the members are considered to be very powerful and popular would besatisfying which needs state?a. safetyb. socialc. esteem (moderate)d. self-actualizatione. physiological40. Enjoying friendship with coworkers satisfies what need?a. physiologicalb. esteemc. social (moderate)d. self-actualizatione. safety41. Growth, achieving one’s potential, and self-fulfillment, and the drive to become what one is capable ofbecoming are characteristics of which need according to Maslow’s hierarchy?a. physiologicalb. esteemc. sociald. self-actualization (moderate)e. safety42. A manager who believes that employees need constant control would be described as ______________according to McGregor.a. a Theory X manager (easy)b. a Theory Y managerc. a Theory Z managerd. a human relations managere. needs hierarchy43. Which of the following would describe the beliefs of a Theory Y manager?a. People have little ambition.b. Work is acceptable because of financial needs, but play is more natural.c. Employees readily accept responsibility. (easy)d. People dislike work.e. Managerial direction of employees is essential.44. According to Herzberg, in order to provide employees with job satisfaction, managers should concentrateona. hygiene factors.b. issues such as pay.c. motivator factors. (moderate)d. extrinsic factors.e. non-motivators.CONTEMPORARY THEORIES OF MOTIVATION45. An individual who would enjoy taking on the challenge of personally redesigning the workflow of amanufacturing line to improve employee productivity would probably be rated high on which of the following?a. need for affiliationb. need for impactc. need for achievement (difficult)d. need for powere. need for control46. According to McClelland, the need to make others behave in a way they wouldn't have behaved otherwiseis which of the following work motives?a. need for achievementb. need for power (easy)c. need for affiliationd. need for motivatione. need for self-fulfillment47. Which of the following suggests that there is a need to have good relationships at work?a. need for achievementb. need for powerc. need for fulfillmentd. need for affective connectione. need for affiliation (moderate)48. Which of the following is not true concerning high achievers?a. They perform best when the success probability is fifty-fifty.b. They dislike gambling when the odds are high.c. They like a high probability of success. (moderate)d. They like goals that cause themselves to stretch a bit.e. They dislike achievement from accidents.49. Which of the following is true concerning individuals who have a high need for achievement?a. They desire to do many things with medium impact on quality.b. They seek achievement but not personal responsibility.c. They want slow but sure feedback on their performance.d. They dislike succeeding by chance. (difficult)e. They enjoy very difficult tasks.50. Employees can be trained to stimulate their ______________ needs.a. affiliationb. self-esteemc. achievement (difficult)d. powere. self actualization51. The best managers are high in the need for ______________ and low in the need for ______________.a. achievement; powerb. power; affiliation (difficult)c. affiliation; powerd. achievement; affiliatione. power; achievement52. Which of the following is an accurate statement concerning McClelland's three-needs theory?a. High achievers are best motivated in jobs with low personal responsibility but high task difficulty.b. High achievers tend to be good managers.c. The best managers are high in need for power and low in need for affiliation. (difficult)d. Employee need for achievement is innate and cannot be changed.e. High achievers are poor salespersons.53. The proposition that specific goals increase performance and that difficult goals, when accepted, result inhigher performance than easy goals is termed ______________.a. self-efficacy.b. reinforcement theory.c. path-goal theory.d. goal-setting theory. (moderate)e. equity theory.54. Which of the following best summarizes the relationship between goal setting and need for achievementfindings?a. Goal setting is superior because it recommends setting difficult goals.b. They are incompatible theories but there is no empirical research to support either claim.c. Difficult goals are still recommended for most people because only 10-20 percent of people arehigh achievers. (difficult)d. Goal setting is not needed with high achievers.e. They are very similar theories.55. People will do better when they get ______________ because it helps identify discrepancies between whatthey have done and what they want to do.a. inputb. goalsc. equityd. powere. feedback (easy)56. The higher your ______________ , the more confidence you have in your ability to succeed in a task.a. self-efficacy (easy)b. self-esteemc. reinforcersd. job scopee. motivation57. Reinforcement theorists believe that behavior results from which of the following?a. external consequences (moderate)b. internal personality traits, such as need for achievementc. setting high goalsd. intrinsic satisfierse. hygiene factors58. A ______________ is any consequence immediately following a response that increases the probabilitythat the behavior will be repeated.a. goalb. reinforcer (moderate)c. conclusiond. job characteristics modele. valence59. ______________ is the way tasks are combined to form complete jobs.a. Job scopeb. Job enlargementc. Job enrichmentd. Job design (moderate)e. Job criteriaMANAGING YOUR CAREER60. According to a recent survey, which of the following is the main reason employees stay with their jobs?a.pleasant work environmentb.easy commutec.challenging workd.like co-workers (moderate)e.flexible work hours61. According to reinforcement theory, an individual would behave in a desired manner if which of thefollowing occurred?a. Nothing happened when they acted appropriately.b. They are punished for doing the wrong behavior.c. They set specific, difficult goals to achieve.d. They are immediately rewarded, such as a monthly bonus. (moderate)e. Their inner drives create the necessary tension level.62. According to reinforcement theory, if a manager catches an employee exhibiting unproductive behavior,the recommended action for eliminating the behavior would be to ______________.a. punish the behavior.b. reward their good behavior.c. reward other employees' good behavior.d. punish other employees exhibiting similar unproductive behavior.e. ignore the behavior. (difficult)63. The number of different tasks required in a job and the frequency with which those tasks are repeated is______________.a. job scope. (moderate)b. job enlargement.c. job enrichment.d. job design.e. job criteria.64. Horizontally expanding the tasks of a job is known by which of the following terms?a. job enrichmentb. job enlargement (moderate)c. task improvementd. job expansione. right sizing tasks65. ______________ is vertical expansion of a job by adding planning and evaluating responsibilities.a. Job scopeb. Job enlargementc. Job enrichment (moderate)d. Job designe. Job criteria66. Job enrichment increases job ______________, which is the degree of control employees have over theirwork.a. breadthb. scopec. varietyd. depth (moderate)e. feedback67. Which of the following is not associated with job enrichment?a. vertical expansionb. adding planning tasksc. increasing job scope (moderate)d. adding evaluating responsibilitye. increased employee control68. The research evidence on the use of job enrichment programs could be classified as ______________.a. encouraging.b. strongly supportive.c. moderately supportive.d. inconclusive. (moderate)e. unsupportive.69. What theory provides a conceptual framework for analyzing jobs by analyzing five core dimensions?a. reinforcement theoryb. job characteristics model (moderate)c. job designd. equity theorye. expectancy theory70. Which of the following, according to the job characteristics model, is the degree to which a job requires avariety of activities so that an employee can use a number of different skills and talents?a. task identityb. autonomyc. feedbackd. task significancee. skill variety (easy)71. Which of the following, according to the job characteristics model, is the degree to which a job requirescompletion of a whole and identifiable piece of work?a. skill varietyb. autonomyc. task significanced. task identity (easy)e. feedback72. The job characteristics model identifies ______________ as the degree to which a job has substantialimpact on the lives or work of other people.a. task significance (moderate)b. task identityc. skill varietyd. autonomye. feedback73. ______________ is the degree to which a job provides substantial freedom, independence and discretion tothe individual in scheduling the work and determining the procedures to be used in carrying it out.a. Task significanceb. Task identityc. Skill varietyd. Autonomy (easy)e. Feedback74. ______________ is the degree to which carrying out the work activities required by a job results in anindividual's obtaining direct and clear information about the effectiveness of her performance.a. Task significanceb. Task identityc. Skill varietyd. Autonomye. Feedback (moderate)75. In the job characteristics model, which combination of core job dimensions combine to produceexperienced meaningfulness of work by the employee?a. skill variety, feedback, and autonomyb. autonomy, task significance, and task identityc. task identity, skill variety, and task significance (moderate)d. task significance, task identity, and feedbacke. task identity, feedback, and autonomy76. Which of the following personality variables moderates the relationship between job dimensions andoutcomes according to the job characteristics model?a. need for achievementb. growth need (difficult)c. locus of controld. risk takinge. need for power77. The job characteristics model provides guidance to managers concerning ______________.a. job redesign. (easy)b. employee selection.c. pay satisfaction.d. collective bargaining.e. strategic planning.78. According to the job characteristics model, ______________ suggests that managers should design tasksthat form an identifiable and meaningful whole.a. combining tasksb. creating natural work units (moderate)c. opening feedback channelsd. expanding jobs verticallye. establishing client relationships79. Which of the following is an accurate statement about equity theory?a. It explains why a factory worker resents how much professional baseball players make.b. It suggests that people will feel fairly treated if they receive pay increases.c. It is based on perceptions of our own situation to others who are like us. (moderate)d. It is a theory based on needs.e. It is a motivational theory based on our job characteristics.80. In ______________ an employee compares his job's inputs-outcomes ratio with that of relevant others andthen corrects any inequity.a. reinforcement theoryb. the job characteristics modelc. job designd. equity theory (moderate)e. expectancy theory81. Which of the following is not an input according to equity theory?a. effortb. experiencec. pay level (easy)d. educatione. job tenure82. If a manager seeks equity by rethinking his situation and deciding that "on second thought my office isnicer because it has better carpet," this manager is seeking equity through which of the following methods?a. increasing his outcomesb. decreasing comparison other outcomesc. distorting others' outcomes (difficult)d. leaving the situatione. choosing a new comparison other83. Based on equity theory, asking the boss to give a "comparison other" at work more responsibility is to seekequity through which of the following methods?a. decreasing your inputsb. increasing comparison other outcomesc. decreasing your outcomesd. cognitively distorting the situatione. increasing comparison other inputs (moderate)84. Organizational pay policies are what type of referent according to equity theory?a. otherb. system (difficult)c. internald. externale. self85. In general, the research support for equity theory could be described as ______________.a. strong. (moderate)b. moderate.c. weak.d. inconclusive.e. there has been very little research on equity theory.86. In expectancy theory, the probability perceived by the individual that exerting a given amount of effort willlead to a certain level of performance is ______________.a. valence.b. expectancy. (moderate)c. consistency.d. flexibility.e. instrumentality.87. Which expectancy theory linkage explains the belief by a student that studying hard results in obtaininghigh test grades?a. valence of rewardb. expectancy (difficult)c. input to outcomed. goal setting to achievemente. instrumentality to reward88. In expectancy theory, the degree to which the individual believes that performing at a particular level isinstrumental in leading to the attainment of a desired outcome is ______________.a. valence.b. expectancy.c. consistency.d. flexibility.e. instrumentality. (moderate)89. Which expectancy theory linkage explains the belief that having a high grade point average is critical inobtaining a good job?a. instrumentality (difficult)b. expectancyc. goal setting to achievementd. valencee. input to outcome90. Which expectancy theory linkage explains the degree to which a student desires a good job?a. expectancyb. effort to performancec. input to outcomed. instrumentalitye. valence (moderate)91. Which of the following is not an important issue surrounding equity theory?a. It emphasizes payoffs.b. It is important to understand why outcomes are important or unimportant.c. Expected behaviors are important.d. Reality is key. (difficult)e. Individuals are expected to maximize needs and/or wants.CURRENT ISSUES IN MOTIVATION92. To maximize motivation among today's diverse work force, managers need to think in terms of______________.a. flexibility. (easy)b. consistency.c. needs.d. wants.e. organizational strategy.93. A ______________ workweek is a workweek where employees work longer hours per day but fewer daysper week.a.flexiblepressed (easy)c.congruentd.parallel94. ______________ is a scheduling system in which employees are free to vary work hours within certainlimits.a. Compressed work weekb. Job sharingc. Flextime (moderate)d. Telecommutinge. Job enlargement95. What type of job scheduling option would allow two different employees to share one forty-hour-a-weeksystem's analyst position?a. compressed work weekb. job sharing (easy)c. flextimed. telecommutinge. job enlargementMANAGING WORK FORCE DIVERSITY96. At which of the following companies do new employees become a part of a mentoring group called―Horizons?‖a.Microsoftb.Hewlett-Packardc.IBMd.Silicon Graphics (moderate)e.Lucent Technologies97. The linking by computer and modem of workers at home with co-workers and management at an office istermed ______________.a. job sharing.b. compressed work week.c. flextime.d. telecommuting. (easy)e. job enlargement.98. Piece-rate pay plans, wage incentive plans, profit-sharing and lump-sum bonuses are examples of______________ programs.a. open-book managementb. expectancy theoryc. pay-for-performance (easy)d. equity theorye. job characteristics model99. Performance-based compensation is probably most compatible with which motivational theory?a. equity theoryb. goal setting theoryc. job characteristics modeld. expectancy theory (difficult)e. reinforcement theory100. ______________ is a motivational approach in which an organization's financial statements are opened to and shared with all employees.a. Open-book management (easy)b. Expectancy theoryc. Pay-for-performanced. Equity theorye. Job characteristics model101. Successful motivation of professions requires that managers recognize that the loyalty of professionals is usually toward their ______________.a. employer.b. short-term financial well being.c. long-term financial well being.d. family.e. profession. (moderate)102. All of the following are mentioned in the text as suggestions to motivating professionals EXCEPT:a.providing them with ongoing challenging projects.ing money and promotions. (moderate)c.allowing them to structure their work in ways they find productive.d.rewarding them with recognition.103. Which of the following is not a suggestion for motivating employees?a. recognize individual differencesb. make goals very difficult to achieve (easy)c. match people to jobsd. individualize rewardse. don't ignore money104. A review of eighty studies found which of the following methods produced the highest increases in productivity?a. goal settingb. job redesignc. employee participationd. monetary increases (moderate)e. job/person match105. Which of the following is NOT mentioned in the text as a suggestion to motivating employees in general?a.recognize individual differences.e goals.e collective rewards. (moderate)d.don’t ignore money.e.link rewards to performance.Scenarios and QuestionsCONTEMPORARY THEORIES OF MOTIVATIONChanging Jobs (Scenario)Marty sat in his favorite chair at home and pondered his work situation. The funding in his division had been cut by twenty-five percent but the numerical goals did not budge. Something had to change and he knew it was his job to figure out how to make the goals reachable. He had decided to try to make it work by changing the way tasks are combined in each job. First, he needed to know how many tasks there were to each job and how frequently each task is repeated. He also knew that because of the funding cut, people were going to be asked to increase their job tasks horizontally. But, he also felt that to balance this he should add planning and evaluating responsibilities. Together, even though the employees were clearly being asked to contribute more, he felt they would have a greater degree of control over their work. No one looked forward to this coming year ÄÄ managers or staff ÄÄ but it was do or die.106. Which of the following is the term that describes "the way tasks are combined in each job"?a. job enlargementb. job scopec. job enrichmentd. job design (difficult)e. job depth107. ______________ describes the degree of control employees have over their work.a. job enlargementb. job scopec. job enrichmentd. job designe. job depth (difficult)108. Marty was also going to ask people to horizontally increase their jobs, also known as ______________.a. job enlargement. (moderate)b. job scope.c. job enrichment.d. job design.e. job depth.109. The vertical expansion of employees, or ______________, was also suggested by Marty.a. job enlargementb. job scopec. job enrichment (moderate)d. job designe. job depthA Management Tool (Scenario)The managers wanted and needed something they could actually use as a tool for redesigning the jobs in their departments. They had now sat through four days of management training but so far, with all of the fancy theories, they had not received any specific guidance in this area. Finally, on the last day of the training, they learned about the job characteristics model. Sure, it still had all of the theory and other academic jargon, but it also provided some specific steps to help improve the core job dimensions.110. One suggestion, ______________, encourages putting existing fragmented tasks back together to increase skill variety and task identity.a. combining tasks (easy)b. creating natural work unitsc. establishing client relationshipsd. expanding jobs verticallye. opening feedback channels111. Another suggestion, ______________, allows employees to judge the level of their performance.a. combining tasksb. creating natural work unitsc. establishing client relationshipsd. expanding jobs verticallye. opening feedback channels (moderate)112. ______________ can help partially close the gap between the "doing" and the "controlling" aspects of the job and increases employee autonomy.a. combining tasksb. creating natural work unitsc. establishing client relationshipsd. expanding jobs vertically (difficult)e. opening feedback channels113. The model also suggests that ______________ will increase employee "ownership" of the work and help them view their work as meaningful.a. combining tasksb. creating natural work units (difficult)c. establishing client relationshipsd. expanding jobs verticallye. opening feedback channelsWhat Do You Expect? (Scenario)The employees at Acme Toilets Inc. are not working as hard as Jill, their supervisor, would like. The salesmen aren't meeting their sales quotas, and Jill can't seem to motivate them to try harder. Jill has been studying expectancy theory and has decided to try to put it into practice.114. Employees are never able to meet their sales quotas and believe that no matter how hard they work, they'll never meet them. They perceive the ______________ of their success to be low.a. instrumentalityb. expectancy (difficult)c. valenced. performance-reward linkagee. attractiveness of reward。