人教版英语必修三unit4知识点以及相应练习(超级好).doc
- 格式:doc
- 大小:599.02 KB
- 文档页数:9

人教版高中英语必修三Unit4SpaceExploration全部重要知识点单选题1、The difficult exercise was ________ the abilities of most of the class, making us upset. A.beyondB.besidesC.behindD.below答案:A考查介词词义辨析。
句意:这个困难的练习超出了班上大多数人的能力,这使我们很沮丧。
A. beyond超过,在……较远的一边;B. besides除……之外(还);C. behind在……后面,落后;D. below在……下面,低于。
据句意和所给部分可知这里使用介词beyond意为“超出”,beyond the abilities of 意为“超出……能力”符合题意。
故选A。
2、If you do that again, you will be severely punished. Do I make myself ________? A.sharpB.positiveC.shallowD.plain答案:D考查形容词词义辨析。
句意:如果再那么干,你会受到严厉惩罚的。
我说清楚了吗?A. sharp锋利的;B. positive积极的;C. shallow浅的;D. plain清楚的;明白的。
分析句子可知,本处表达的是提问者在警告另一个人,然后问对方自己有没有说清楚,强调对方到底有没有听清。
故选D项。
3、Many enterprising young people present their ideas________ getting investment and advice to start their own b usiness.A.at the cost ofB.by means ofC.as a result ofD.in the hope of答案:D考查介词短语辨析。
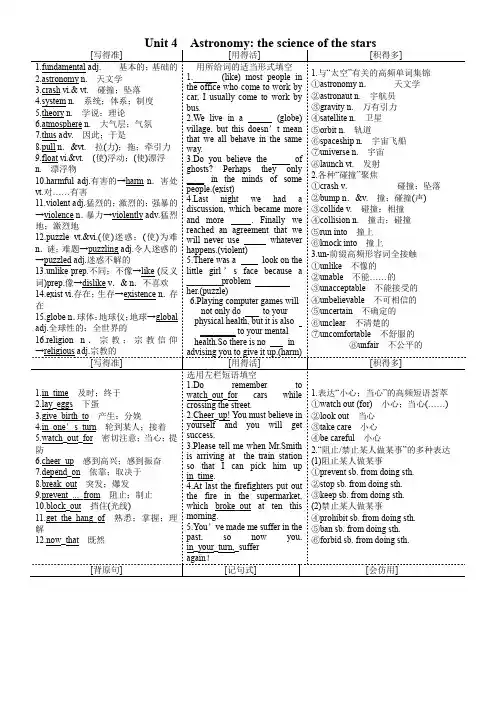
1.fundamental2.astronomy n . 天文学3.crash vi .& vt . 碰撞;坠落4.system n . 系统;体系;制度5.theory n . 学说;理论6.atmosphere n . 大气层;气氛7.thus adv . 因此;于是8.pull n .&vt . 拉(力);拖;牵引力9.float vi .&vt . (使)浮动;(使)漂浮n . 漂浮物10.harmful adj .有害的→harm n .害处vt .对……有害11.violent adj .猛烈的;激烈的;强暴的→violence n .暴力→violently adv .猛烈地;激烈地12.puzzle vt .&vi .(使)迷惑;(使)为难n .谜;难题→puzzling adj .令人迷惑的→puzzled adj .迷惑不解的13.unlike prep .不同;不像→like (反义词)prep .像→dislike v .& n .不喜欢14.exist vi .存在;生存→existence n .存在15.globe n .球体;地球仪;地球→globaladj .全球性的;全世界的16.religion n .宗教;宗教信仰1. (like) most people in the office who come to work by car, I usually come to work by bus.2.We live in a (globe) village, but this doesn ’t mean that we all behave in the same way.3.Do you believe the of ghosts? Perhaps they only ____ in the minds of some people.(exist)st night we had a discussion, which became more and more . Finally we reached an agreement that we will never use whatever happens.(violent)5.There was a look on the little girl ’s face because a ________problem her.(puzzle)6.Playing computer games will not only do to your physical health, but it is also ________ to your mental health.So there is no in 1.与“太空”有关的高频单词集锦 ①astronomy n . 天文学 ②astronaut n . 宇航员 ③gravity n . 万有引力 ④satellite n . 卫星 ⑤orbit n . 轨道 ⑥spaceship n . 宇宙飞船 ⑦universe n . 宇宙 ⑧launch vt . 发射 2.各种“碰撞”聚焦 ①crash v . 碰撞;坠落 ②bump n .&v . 撞;碰撞(声) ③collide v . 碰撞;相撞 ④collision n . 撞击;碰撞 ⑤run into 撞上⑥knock into 撞上 3.un-前缀高频形容词全接触 ①unlike 不像的 ②unable 不能……的 ③unacceptable 不能接受的 ④unbelievable 不可相信的 ⑤uncertain 不确定的 ⑥unclear 不清楚的 ⑦uncomfortable 不舒服的 ⑧unfair 不公平的 1.in_time 及时;终于y_eggs 下蛋3.give_birth_to 产生;分娩4.in_one ’s_turn 轮到某人;接着5.watch_out_for 密切注意;当心;提防6.cheer_up 感到高兴;感到振奋7.depend_on 依靠;取决于8.break_out 突发;爆发9.prevent_..._from 阻止;制止10.block_out 挡住(光线)11.get_the_hang_of 熟悉;掌握;理解12.now_that 既然1.Do remember to watch_out_for cars while crossing the street.2.Cheer_up! You must believe in yourself and you will get success.3.Please tell me when Mr.Smith is arriving at the train station so that I can pick him up in_time.4.At last the firefighters put out the fire in the supermarket, which broke_out at ten this morning.5.You ’ve made me suffer in the past, so now you, in_your_turn,_suffer 1.表达“小心;当心”的高频短语荟萃 ①watch out (for) 小心;当心(……) ②look out 当心 ③take care 小心 ④be careful 小心 2.“阻止/禁止某人做某事”的多种表达 (1)阻止某人做某事 ①prevent sb. from doing sth. ②stop sb. from doing sth. ③keep sb. from doing sth. (2)禁止某人做某事 ④prohibit sb. from doing sth. ⑤ban sb. from doing sth. ⑥forbid sb. from doing sth.1.This produced a chain reaction, which made it possible for life to develop.这就产生了一系列的反应,使得生命就有可能开始发展了。

必修四Unit4 知识点笔记和练习一、复习such 和so 的语序句型:such + ______________ so + ________________________________ _____________________________ __________________答案:such + a+ (adj)+ n.so + a dj. / adv.(adj.)+ ns adj. + a + n.(adj.) + <u>n. many/ much/ few/ little + ns/ <u>n.小练习:1. He was________excited that he couldn't get sleep.2. This teacher is_________ kind that we all like him.3.There is ________ much food in the refrigerator that we don’t need to buy anything.4. He ran____________quickly that I couldn't catch up with him.5. This is____________interesting a book that we all enjoy reading it.6.This is____________ interesting book that we all enjoy reading it.7. They are__________interesting books that we all enjoy reading them.8. He has_________many books that I can't count them.9. This is_________ a funny story that we all enjoy listening to it.10. There was ________ much food that we couldn't eat it all.11. I have________ little money that I cannot afford a car.12. He is ________ a good student that we all like him.13. He is ________ good a student that we all like him.14. It was ________bad weather that he had to stay at home.答案:1. so 2. so 3 so 4 so 5 so 6 so 7 such 8 so 9 such 10 so 11 so 12 such 13 so 14 such二、复习名词性从句:1.做题步骤:()划出:_____________________; 划出_____________;查看,如果缺少主,宾,表,或者谁的,在引导_______词里面选:who: whoever:whom: whomever:what: whatever:which: whichever:whose:查看,如果不缺少主,宾,表,或者谁的,在引导_______词或者引导________词里面选:where whereverwhen wheneverwhyhowas if/thoughweather/ if(少用)becausethat答案:1.做题步骤:()划出:_从句_; 划出_从句中的谓语动词;查看,如果缺少主,宾,表,或者谁的,在引导代_词里面选:who: 指人(作主语)whoever: 无论任何人whom: 指人(作宾语)whomever: 无论任何人what: 东西whatever:无论任何东西which: 东西(有范围)whichever: 无论任何东西(有范围)whose: ……的查看,如果不缺少主,宾,表,或者谁的,在引导__副__词或者引导__连_词里面选:where 的地方wherever:无论...的地方when 的时间whenever:无论…的时间why 的原因how 的方式as if/though 好像whether/ if(少用) 是否because 因为that 无语意,只连接2.有用的小公式:1)和doubt 相关的从句,肯定句中,用_________引导;否定句中,用________引导。

考点分布备考指南1.重点单词的识记、理解、固定搭配。
词汇的理解和记忆不是孤立的,需要结合具体的句子和语境进行准确理解,掌握其基本用法和固定搭配。
同时要对所学单词进行多方面的应用,及时复习巩固。
2.词性转化、固定搭配在语法填空、短文改错中的考查。
3.写作经典句式的应用。
在理解的基础上背诵写作经典句式,并多加练习,以达到熟练掌握和灵活运用的目的。
astronomy [əˈstrɔnəmi]n.天文学△astronomer n.天文学家△solar [ˈsəulə]adj.太阳的;日光的system [ˈsistəm] n.系统;体系;制度solar system 太阳系religion [riˈlidʒən]n.宗教;宗教信仰theory [ˈθiəri]n.学说;理论△Big Bang 宇宙大爆炸;创世大爆炸atom [ˈætəm]n.原子billion [ˈbiljən] pron. & n. & adj.<英>万亿;<美>十亿globe [gləub] n.球体;地球仪;地球△global [ˈgləubəl]adj.全球性的;全世界的violent [ˈvaiələnt]adj.猛烈的;激烈的;强暴的in time 及时;终于carbon [ˈkɑ:bən]n.碳△nitrogen [ˈnaitrədʒən]n.氮△vapour [ˈveipə]n.蒸气;水蒸气atmosphere [ˈætməsfiə]n.大气层;气氛unlike [ˌʌnˈlaik]prep.不同;不像fundamental [ˌfʌndəˈmentl]adj.基本的;基础的△presence [ˈprezəns] n.出席;到场;存在△dissolve [diˈzɔlv]vt. & vi.溶解;解散harmful [ˈhɑ:mful]adj.有害的专题解读知识清单词汇学习与应用必修三Unit4单词表acid [ˈæsid] n.酸chain [ˈtʃein] n.链子;连锁;锁链△reaction [riˈækʃən]n.反应;回应multiply [ˈmʌltiplai]vi. & vt.乘;增加oxygen [ˈɔksidʒən]n.氧△shellfish ['ʃelfiʃ]n.水生有壳动物△amphibian [æmˈfibiən]n.两栖动物△reptile [ˈreptail]n.爬行动物;爬虫lay eggs 下蛋△dinosaur [ˈdainəsɔ:]n.恐龙exist [igˈzist]vi.存在;生存△mammal [ˈmæməl]n.哺乳动物give birth to产生;分娩thus [ðʌs] adv.因此;于是in one’s turn轮到某人;接着dioxide [daiˈɔksaid]n.二氧化物carbon dioxide 二氧化碳prevent ... from阻止;制止puzzle [ˈpʌzl]n.谜;难题vt. & vi.(使)迷惑;(使)为难biology [baiˈɔlədʒi]n.生物学biologist [ˌbaiəˈlɔdʒikəl]n.生物学家gravity [ˈgræviti]n.万有引力;重力satellite [ˈsætəlait]n.卫星;人造卫星gentle [ˈdʒentl]adj.温和的;文雅的△geologist [dʒi'ɔlədʒist]n.地质学家physicist [ˈfizisist]n.物理学家block out 挡住(光线)△extinct [ikˈstiŋkt]adj.灭绝的;绝种的climate [ˈklaimit]n.气候△comet [ˈkɔmit]n.慧星crash [kræʃ]vi. & vt.碰撞;坠落△Isaac Newton 艾萨克·牛顿(英国科学家)△Albert Einstein 艾伯特·爱因斯坦(德裔美国科学家)△Stephen Hawking 斯蒂芬·霍金(英国科学家)spaceship [ˈspeisˌʃip]n.宇宙飞船pull [pul]n. & vt.拉(力);拖;牵引力△lessen [ˈlesən]vi. & vt.减少;减轻cheer up感到高兴;感到振奋float [fləut]vi. & vt.(使)浮动;(使)漂浮n. 漂浮物△weightlessly ['weitlis]adv.失重地△cabin [ˈkæbin]n.小屋;船舱mass [mæs]n.质量;团;块;大量;<复>群众now that既然△get the hang of 熟悉;掌握;理解break out突发;爆发△exhaust [igˈzɔ:st]vt.用尽;耗尽;使精疲力尽watch out密切注视;当心;提防项目单词及其词性变化(语法填空必备)重点单词1.astronomy n.天文学→astronomer n.天文学家2.system n.系统;体系;制度3.theory n.学说;理论→theoretical adj.理论上的4.globe n.球体;地球仪;地球→global adj.全球性的;全世界的5.violent adj.猛烈的;激烈的;强暴的→violence n.暴力→violently adv.猛烈地6.atmosphere n.大气层;气氛7.unlike prep.不同;不像→dislike vt.不喜欢8.presence n.出席;到场;存在→present adj. n. v.在场的;目前,现在;出席;颁发,授予9.harmful adj.有害的;伤害的→harm n.危害,害处→harmless adj.无害的10.exist vi.存在,生存→existence n.存在,生存11.puzzle n.谜;难题vt. vi.(使)迷惑;(使)为难→puzzled adj.迷惑的→puzzling adj.令人迷惑的12.gravity n.万有引力;重力13.satellite n.卫星;人造卫星14.climate n.气候15.spaceship n.宇宙飞船16.pull n. vt.拉(力);拖;牵引力17.float vi. vt.(使)浮动;(使)漂浮n.漂浮物18.mass n.质量;团;块;大量;(复)群众重点短语1.in time及时;终于y eggs 下蛋3.give birth to 产生;分娩4.in on e’s turn 轮到某人;接着5.prevent...from 阻止;制止6.block out 挡住(光线)7.cheer up 感到高兴;感到振奋8.now that 既然单元知识预览9.break out 突发;爆发10.watch out 密切注视;当心;提防11.cool down 冷却12.as well as 也;还有……13.depend on 依靠;依赖,取决于14.get close to 靠近1.This produced a chain reaction, which made it possible for life to develop.这就形成一个连锁反应,使生命发展成为可能。

人教版高中英语必修三Unit4SpaceExploration重点知识归纳单选题1、【2018·北京】During the Mid-Autumn Festival, family members often gather together _________ a meal, admire the moon and enjoy moon cakes. A.shareB.to shareC.having sharedD.shared答案:B考查非谓语动词。
句意:在中秋节期间,家人们通常会聚在一起吃饭,赏月,品尝月饼。
gather是谓语动词,“_________ a meal, admire the moon and enjoy moon cakes”是状语,家人聚在一起的目的是吃饭,赏月,品尝月饼,表目的用动词不定式,故B选项正确。
点睛:动词不定式可以做主语,状语,定语,宾语,表语等。
动词不定式做目的状语时,可以置于主句之前也可以置于主句之后,通常译为“为了”。
2、Walk along this road for 100 meters ________ you’ll see the hospital.A.orB.otherwiseC.andD.or else答案:C考查连词词义辨析。
句意:沿着这条街走100米,然后你就会看到医院。
A. or或者;B. otherwise否则;C. and然后、和;D. or else否则。
“祈使句+and/or+简单句”为固定句型,此处应填and表示“然后”。
故选C项。
3、Come to Dolly wood ________learning all about America’s historical southeastern culture !A.have funB.to have funC.having funD.had fun答案:B考查非谓语动词。

人教版高中英语必修三Unit4SpaceExploration重点知识点大全单选题1、Each one of us are highly recommended to ________ oil and gas by taking advantage of the renewable energy s ources.A.dismissB.concentrateC.possessD.conserve答案:D考查动词词义辨析。
句意:我们每个人都被强烈建议通过使用可再生能源来节约石油和天然气。
A. dismiss解雇;B. concentrate集中注意力;C. possess拥有;D. conserve节约,保护。
根据句意及常识可知,人们通过使用可再生资源,以到达节约石油和天然气的目的。
conserve意为“节约”符合题意。
故选D项。
2、China is fully capable to supply the raw materials needed to produce COVID-19 vaccines; in other words, China has a/an ________ raw material supply. A.optionalB.vitalC.instantD.sufficient答案:D考查形容词词义辨析。
句意:中国完全有能力提供生产COVID-19疫苗所需的原材料;换句话说,中国有充足的原料供应。
A. optional可选择的;选修的;B. vital至关重要的;必不可少的;C. instant立刻的;马上的;D. sufficient足够的;充足的。
根据前文“China is fully capable to supply the raw materials needed to produce COVID-19 vaccines(中国完全有能力提供生产新冠肺炎疫苗所需的原材料)”语境可知,中国在新冠疫苗原材料方面原料充足。

人教版高中英语必修三Unit4SpaceExploration知识点归纳总结(精华版) 单选题1、— I have heard that Cao Wenxuan had won the Hans Christian Anderson prize.— Great! His books always bring me to places I might not _______ have been either in thoughts or reality. A.regardlessB.otherwiseC.thereforeD.anyhow答案:B考查副词词义辨析。
句意:——我听说曹文轩获得了汉斯·克里斯蒂安·安德森奖。
——太好了!他的书总是把我带到一些地方,否则我可能无论是在思想上还是在现实中都不会到达的地方。
A. regardless不管; B. otherwise否则;C. therefore因此;D. anyhow不管怎样。
结合句中“either in thoughts or reality”可知,此处指在思想和现实中我都不会去到的地方,但他的书可以把我带着去这些地方。
故选B。
2、The difficult exercise was ________ the abilities of most of the class, making us upset. A.beyondB.besidesC.behindD.below答案:A考查介词词义辨析。
句意:这个困难的练习超出了班上大多数人的能力,这使我们很沮丧。
A. beyond超过,在……较远的一边;B. besides除……之外(还);C. behind在……后面,落后;D. below在……下面,低于。
据句意和所给部分可知这里使用介词beyond意为“超出”,beyond the abilities of 意为“超出……能力”符合题意。

人教版高中英语必修三Unit4全解(含练习和答案)常考单词、高频短语和写作句式Ⅰ. 常考单词必背1.harmful adj. 有害的It's harmful to your eyes to read books in the bus.在公共汽车上看书对你的眼睛有害。
[快速闪记](1)be harmful to... 对……有害(2)harmless adj. 无害的harm n. 损害;伤害v. 对……有害;伤害;损害2.exist vi. 存在;生存Nothing exists on the moon as there is no water and no air.月球上没有东西生存,因为那里没有水和空气。
[快速闪记](1)exist in 存在于exist on 靠……生存There exist(s)/existed... 某地有/存在……(2)existence n. 存在;生存3.puzzle n. 谜;难题vt.&vi. (使)迷惑;(使)为难The puzzled look on her face suggested she was puzzling over the puzzling math problem.她困惑的表情暗示了她正在思考那个令人困惑的数学问题。
[快速闪记](1)be in a puzzle 感到困惑;不知如何是好puzzle about/over 冥思苦想;苦苦思索(2)puzzling adj. 令人迷惑的puzzled adj. 感到迷惑的4.pull n. &vt. 拉(力);拖;牵引力She pulled his sleeve to get his attention.她拉拉他的袖子以引起他的注意。
[快速闪记]pull down 摧毁、推翻、拆除pull in 进站停靠;驶向路边(或某处)停靠pull out 离站;(使)摆脱困境pull through 恢复健康;渡过危机5.mass n. 质量;团;块;大量;(复)群众I have masses of work to do.我有大量工作要做。

人教版高中英语必修三Unit4SpaceExploration知识点归纳超级精简版单选题1、She was greatly surprised when her brother ________ at the door, whom she hadn’t seen for years. A.popped upB.carried onC.set outD.turned over答案:A考查动词短语词义辨析。
句意:当她哥哥突然出现在门口时,她感到非常惊讶,她已经多年没见到他了。
A. popped up突然出现;B. carried on 继续;C. set out出发;D. turned over反复考虑。
根据空后的“whom she hadn’t seen for years”可知她已经好多年没见到她的哥哥了,说明她惊讶的原因就是又见到她哥哥了。
故选A。
2、The branch of olive is the ________ of peace.A.symbolB.signC.signalD.mark答案:A考查名词词义辨析。
句意:橄榄枝是和平的象征。
A. symbol象征;B. sign招牌,迹象;C. signal信号;D. mark符号,记号。
结合常识可知,橄榄枝是和平的象征,symbol符合题意。
故选A。
3、He never complains about the difficulties he has in life. ________, he always has ways to overcome them. A.HoweverB.OtherwiseC.InsteadD.Therefore答案:C考查副词词义辨析。
句意:他从不抱怨生活中的困难。
相反,他总是有办法克服它们。
A. However然而;B. Otherwise否则;C. Instead相反;D. Therefore因此。
根据句中complains和overcome可知,此处表达的是“相反”关系。
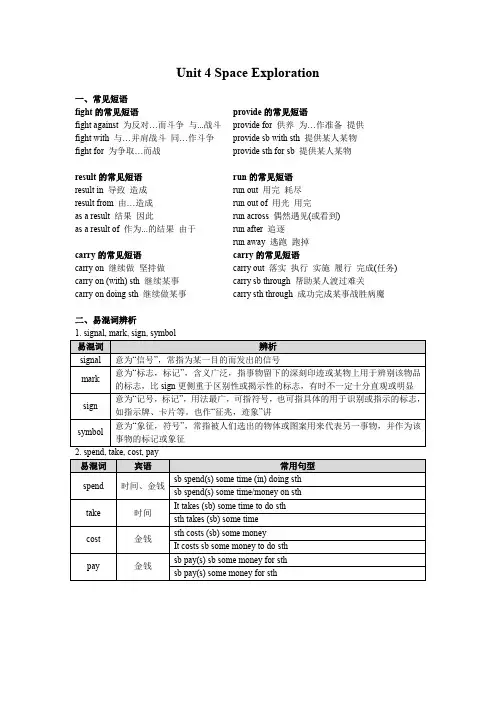
Unit 4 Space Exploration 一、常见短语fight的常见短语fight against 为反对…而斗争与...战斗fight with 与…并肩战斗同…作斗争fight for 为争取…而战provide的常见短语provide for 供养为…作准备提供provide sb with sth 提供某人某物provide sth for sb 提供某人某物result的常见短语result in 导致造成result from 由…造成as a result 结果因此as a result of 作为...的结果由于run的常见短语run out 用完耗尽run out of 用光用完run across 偶然遇见(或看到) run after 追逐run away 逃跑跑掉carry的常见短语carry on 继续做坚持做carry on (with) sth 继续某事carry on doing sth 继续做某事carry的常见短语carry out 落实执行实施履行完成(任务) carry sb through 帮助某人渡过难关carry sth through 成功完成某事战胜病魔二、易混词辨析三、常见句型与表达1. “not only…but also…”结构的用法①语法功能:连接平行结构——名词、代词、动词、非谓语动词、介词短语、句子等。
He not only read the book, but also remembered what he had read.他不仅读了这本书,而且记得所读的内容。
②主谓一致:其连接的并列成分做主语时,谓语动词的人称和数遵循“就近原则”。
Not only the students but also the teacher was against the plan.不但同学们反对这个计划,老师也反对。
③倒装: not only...but also...连接并列分句,且not only位于句首时,not only所在的分句要部分倒装。

3.crash vi.& vt. 碰撞;坠落②astronaut n . 宇航员4.system n . 系统;体系;制度 ③gravity n . 万有引力5.theory n . 学说;理论 ④satellite n . 卫星that we all behave in the same ⑤orbit n . 轨道 7.thus adv . 因此;于是 ⑥spaceship n . 宇宙飞船vt.对……有害坠落11.violent adj.猛烈的;激烈的;强暴 ②bump n .&v . 撞;碰撞(声)reached an agreement that we ③collide v . 碰撞;相撞 will never use whatever ④collision n . 撞击;碰撞n .存在 ④unbelievable 不可相信的15.globe n .球体;地球仪;地球 ⑤uncertain 不确定的health.So there is no in ⑥unclear 不清楚的the little girl ’s face because a 1.in_time 及时;终于 1.表达“小心;当心 ”的高频短 y_eggs 下蛋1.Do remember to 3.give_birth_to 产生;分娩①watch out (for) 小心;当心4.in_one ’s_turn 轮到某人; crossing the street.②look out 当心 2.Cheer_up! Y ou must believe inyourself and you will get 5.watch_out_for 密切注意; ③tak e care 小心 ①prevent sb. from doing sth.8.break_out 突发;爆发②stop sb. from doing sth.9.prevent_..._from 阻止;制③k eep sb. from doing sth. morning.握;理解 ⑤ban sb. from doing sth. 学习-----好资料Unit 4 Astronomy: the science of the starsⅠ.单词—在语境中默写,在联想中积累[写得准] [用得活] [积得多]1.fundamental adj. 基本的;基础 用所给词的适当形式填空 1.与“太空”有关的高频单词集的 1. (like) most people in 锦2.astronomy n . 天文学 the office who come to work by ①astronomy n . 天文学 car , I usually come to work by bus.2.We live in a (globe)village, but this doesn ’t mean6.atmosphere n . 大气层;气氛way .8.pull n .&vt. 拉(力);拖;牵引力 3.Do you believe the of ⑦universe n . 宇宙 9.float vi.&vt. (使)浮动;(使)漂浮 ghosts? P erhaps they only ⑧launch vt. 发射n . 漂浮物____ in the minds of some 2.各种“碰撞”聚焦 10.harmful adj.有害的→harm n .害处 people.(exist)①crash v . 碰撞; st night we had a discussion, which became moreand more . Finally we的→violence n .暴力→violently adv . 猛烈地;激烈地12.puzzle vt.&vi.(使)迷惑; (使)为难 happens.(violent)⑤run into 撞上 n .谜;难题→puzzling adj.令人迷惑 5.There was a look on ⑥knock into 撞上 的→puzzled adj.迷惑不解的 3.un-前缀高频形容词全接触13.unlike prep.不同;不像→like (反义 ________problem①unlike 不像的 词)prep.像→dislike v .& n .不喜欢 her .(puzzle) ②unable 不能……的14.exist vi. 存 在 ; 生 存 →existence 6.Playing compute r games will ③unacceptable 不能接受的not only do to yourphysical health, but it is also________ to your mental→global adj.全球性的;全世界的 16.religion n . 宗 教 ; 宗 教 信 仰 advising you to give it⑦uncomfortable 不舒服的 →religious adj.宗教的 up.(harm)⑧unfair 不公平的Ⅱ.短语—在应用中记牢,在归纳中记多[写得准] [用得活] [积得多]选用左栏短语填空 语荟萃 watch_out_for cars while(……) 接着success.当心;提防 3.Please tell me when Mr .Smith ④be careful 小心6.cheer_up 感到高兴;感到 is arriving at the train station 2.“阻止/禁止某人做某事”的多振奋so that I can pick him up 种表达 7.depend_on 依靠;取决于in_time. (1)阻止某人做某事 4.At last the firefighters put out the fire in the supermarket, which broke_out at ten this止10.block_out 挡住(光线)5.Y ou ’ve made me suffer in the (2)禁止某人做某事11.get_the_hang_of 熟悉;掌 past, so now you, ④prohibit sb. from doing sth.in_your_turn,_suffer12.now_that 既然 again !⑥forbid sb. from doing sth.”“学习-----好资料[背原句]1.This p r od u ce d a chain reaction,whichmade it possible for life to develop.这就产生了一系列的反应,使得生命就有可能开始发展了。
2019-2020学年高中英语人教版必修三UNIT 4 Astronomy: the science of the stars Wordssolar system planet circle astronomy origin religionwidely theory universe atoms billion dust solidglobe violent explode carbon vapor nitrogenproduce atmosphere appear surface unlike obviousfundamental presence dissolve harmful acids chainreaction extremely multiplied oxygen encourage development shellfish insect amphibians reptiles huge dinosaursexist rise mammal spread thus dioxide removepuzzle presence chemistry planet gravity evidencesatellite violent shocked gentle rude biology provediscovery physicist supply decrease species extinctclimate concern disappear spaceship force escapepull lessen float weight painful frighteningamazed increase exhausting structure theory situationcrashPhrases: in all directions combine to settle into in time cool downfill....with as well as lay eggs remain a mystery give birth toin one’s turn prevent...from as a result of depend on no longerdie out block out crash into dozens of fall back tocheer up twice as far as fall over now that get the hang ofstep forward break out pay attention to watch out be make up ofbe fundamental to begin with in all directions according towatch out for 密切注意;当心;提防Grammar:1.What it was to become was uncertain until between 4.5 and 3.8 billion years ago when the dust settled into a solid. (随后)它变成什么没人知道,知道38~45亿年前,这团尘埃才慢慢地形成一个固体的球状物。
Unit 4 Astronomy :the science of the star Lecture 1 words and phrases1.天文学大气层;氛围2.重力;万有引力系统3.链子;连锁碰撞4.(使)漂浮;浮动温和的5.阻止;制止对...迷惑不解6.熟悉;掌握突发;爆发7.分娩;产生轮到某人8.既然为...奠定基础9.产生;存在保护...免受...伤害10.苦苦思索 ...对某人来说仍是个谜11.摧毁康复;痊愈12.结果是为某人加油13.密切注视照看;看守14.警告某人当心某事15.警告某人做/不要做某事16.失去耐性/用尽力气17.exhaust one’s patience/strengthLecture 2 Key structures1.倍数的表达方式①倍数+ as + adj/adv + as②倍数+ adj/adv 比较级+ than③倍数+ the size/height/weight/depth...+ of④倍数+ as many/much + n +as2.it作为形式宾语的用法Obviously , it is the internet that makes it easy to communicate with each other. 句中it作形式宾语,真正的宾语是life to develop,possible作宾语补足语。
常用于此结构的词还有think,feel,find,consider等。
构成:He feels it his pleasure to help me .我发现那让他们感到很高兴。
老师提高了嗓音以便于被别人听到。
3.“be to+动词原形”的用法(1)表示按计划或安排要做的事。
When are you to leave for home?你什么时候回家?(2)表示命中注定要发生的事。
He was to become a pianist after so many years of hard work .这么多年的艰苦训练之后他注定会成为一个钢琴家。
U n i t4A s t r o n o m y:t h e s c i e n c e o f t h e s t a r s 单元要点预览语言要点Ⅰ.词语辨析Ⅱ.词性变化Ⅲ.重点词汇1.system n.[c] 系统;体系;制度;方法systematic adj 有系统的; 有条理的[典例]1).The solar system includes the sun and its eight planets. 太阳系包括太阳和它的八颗行星。
2).Alcohol is bad for your system. 喝酒对身体有害。
[练习] 根据句子的意思完成句子。
1). The (教育系统) operates very differently in the US and China.2). He introduced us a well-designed (铁路系统).y vt. (laid, laid, laying) 把放下;摆设;铺(地毯) ;产(蛋)[典例]1).He laid his hand on my shoulder. 他把手放在我的肩上。
2).Who should we lay the blame on? 我们该责备谁?[重点用法] lay 短语:lay eggs 下蛋lay sth. aside 把某物放在一边;积蓄(钱)lay sth. down 把某物放下lay the blame on sb.责备某人lay the table 摆桌子lay emphasis / stress on sth. 把重点放在某事上[练习] 根据句子的意思在括号里填入适当的词或翻译。
1).The bird its eggs in other birds’ nests.2).He is a political leader that (非常强调) individual responsibility.3).He some money for rainy days.3.harmful adj. 有害的;伤害的harm n.&vt. 伤害(某人)[典例]Many people are aware of the harmful effects of smoking.很多人都意识到吸烟的危害。
Unit 4 Astronomy: the science of the starsⅠ .单词—在语境中默写,在联想中积累[写得准 ][用得活 ] [积得多 ]1.fundamental adj .基本的;基础的2.astronomy n.天文学3.crash vi.& vt.碰撞;坠落4.system n.系统;体系;制度5.theory n.学说;理论6.atmosphere n.大气层;气氛7.thus adv.因此;于是8.pull n. & vt.拉(力);拖;牵引力9.float vi .& vt.(使 )浮动; (使 )漂浮n.漂浮物10.harmful adj .有害的→harm n.害处vt.对有害11.violent adj .猛烈的;激烈的;强暴的→ violence n.暴力→ violently adv. 猛烈地;激烈地12.puzzle vt.& vi .(使 )迷惑; (使 ) 为难n.谜;难题→ puzzling adj.令人迷惑的→ puzzled adj .迷惑不解的13.unlike prep.不同;不像→like ( 反义词) prep.像→dislike v. & n.不喜欢14.exist vi. 存在;生存→ existence n.存在15.globe n .球体;地球仪;地球→g lobal adj .全球性的;全世界的16.religion n .宗教;宗教信仰→religious adj.宗教的用所给词的适当形式填空1.(like) most people inthe office who come to work bycar, I usually come to work bybus.2.We live in a (globe) village, butthis doesn ’ t mean that we allbehave in the same way.3.Do you believe the ofghosts? Perhaps they only____ in the minds of somepeople.(exist)st night we had a discussion,which became moreand more . Finally we reachedan agreement that wewill never use whateverhappens.(violent)5.There was a look onthe little girl ’s face because a________problemher.(puzzle)6.Playing computer games willnot only do to yourphysical health, but it is also________ to your mentalhealth.So there is no inadvising you to give itup.(harm)1.与“太空”有关的高频单词集锦① astronomy n.天文学②astronaut n. 宇航员③ gravity n. 万有引力④ satellite n. 卫星⑤ orbit n. 轨道⑥ spaceship n. 宇宙飞船⑦ universe n. 宇宙⑧ launch vt. 发射2.各种“碰撞”聚焦① crash v.碰撞;坠落②bump n.& v. 撞;碰撞 (声 )③ collide v. 碰撞;相撞④ collision n. 撞击;碰撞⑤ run into撞上⑥ knock into撞上3.un-前缀高频形容词全接触①unlike 不像的②unable 不能的③unacceptable 不能接受的④ unbelievable 不可相信的⑤ uncertain 不确定的⑥ unclear 不清楚的⑦uncomfortable 不舒服的⑧u nfair 不公平的[写得准 ] Ⅱ .短语—在应用中记牢,在归纳中记多[用得活 ][积得多 ]1.in_time及时;终于y_eggs下蛋3.give_birth_to产生;分娩4.in_one’ s_turn轮到某人;接着5.watch_out_for 密切注意;当心;提防6.cheer_up 感到高兴;感到振奋7.depend_on依靠;取决于8.break_out突发;爆发9.prevent_..._from 阻止;制止10.block_out挡住(光线)11.get_the_hang_of熟悉;掌握;理解12.now_that既然选用左栏短语填空1.Do remember towatch_out_for cars whilecrossing the street.2.Cheer_up! You must believe inyourself and you will get success.3.Please tell me when Mr.Smithis arriving at the train station sothat I can pick him up in_time.4.At last the firefighters put outthe fire in the supermarket, whichbroke_out at ten this morning.5.You’ve made me suffer in thepast, so now you,in_your_turn,_sufferagain!1.表达“小心;当心”的高频短语荟萃① watch out (for)小心;当心( )② look out当心③take care 小心④ be careful 小心2.“阻止 /禁止某人做某事”的多种表达(1)阻止某人做某事①prevent sb. from doing sth.② stop sb. from doing sth.③keep sb. from doing sth.(2)禁止某人做某事④prohibit sb. from doing sth.⑤ban sb. from doing sth.⑥forbid sb. from doing sth.Ⅲ .句式—在解读中学懂,在仿写中学通[背原句 ][记句式 ][ 会仿用 ]1.This produced a chain reaction, which made it possible for life to develop .这就产生了一系列的反应,使得生命就有可能开始发展了。
.Unit 4Astronomy: the science of the starsⅠ .单词—在语境中默写,在联想中积累[写得准 ][用得活 ]用所给词的适当形式填空1.fundamentaladj .1.(like) most people基本的; 基office who cometo础的in thework by car, I usually come2.astronomyn .天文学3.crash vi .& vt . to work by bus.碰撞;坠落 livein a4.system n . 2.We系统;体系;制度 village,butthis5.theory n . (globe)学说;理论 ’t mean that we all6.atmospheredoesnn . 大气层;气氛7.thus adv .behave in the same way.因此;于是you believethe 8.pull n .& vt . 3.Do 拉 (力 ) ;拖;牵引力Perhapsthey9.float vi .& vt . of ghosts? (使 )浮动; (使 )漂浮____ in the minds ofn . 漂浮物onlysome people.(exist)10.harmfuladj . 有 害 的 →harmnightwehad an .害处 vt .对 有害stdiscussion, whichbecame 11.violentadj .猛烈的;激烈的;强. Finally暴的→ violencemore and moren .暴力→ violentlyan agreementadv .猛烈地;激烈地we reached thatwe willneveruse12.puzzlevt .& vi .(使 )迷惑;(使 )为难n .谜;难题→ puzzlingwhatever happens.(violent)adj .令人迷was alook5.There惑的→ puzzled adj .迷惑不解的little girl ’ s face13.unlikeon theprep .不同;不像→ like ( 反a义词 ) prep .像→ dislike becausev . & n .不喜欢________problemher.(puzzle)14.existvi .存在;生存→ existencen .存在6.Playing computer gameswill not only doto15.globen .球体;地球仪;地球→globalyour physical health, but itadj .全球性的;全世界的________ to your16.religionis alson . 宗 教 ; 宗 教 信 仰→religious adj .宗教的mental health.So there is noin advising you togive it up.(harm)[积得多 ]1. 与“太空”有关的高频单词集锦① astronomy n .天文学② astronaut n . 宇航员③ gravity n . 万有引力④ satellite n . 卫星⑤ orbit n . 轨道⑥ spaceship n . 宇宙飞船⑦ universe n . 宇宙⑧ launch vt . 发射2.各种“碰撞”聚焦 ① crash v . 碰撞;坠落② bump n . & v . 撞;碰撞 (声 )③ collide v . 碰撞;相撞④ collision n . 撞击;碰撞⑤ run into撞上 ⑥ knock into 撞上3.un-前缀高频形容词全接触① unlike 不像的② unable不能 的③ unacceptable 不能接受的④ unbelievable 不可相信的⑤ uncertain 不确定的 ⑥ unclear不清楚的⑦ uncomfortable 不舒服的⑧ unfair 不公平的Ⅱ .短语—在应用中记牢,在归纳中记多[写得准 ][用得活 ][积得多 ].y_eggs 下蛋 1.Do remember to 短语荟萃3.give_birth_to 产生;分娩 watch_out_forcars while① watch out (for) 小心;当4.in_one ’s_turn 轮到某人; crossing the street.心( )接着2.Cheer_up!Youmust ② look out 当心 5.watch_out_for 密 切 注 believe in yourself and you③ take care 小心意;当心;提防will get success.④ be careful小心6.cheer_up 感到高兴; 感到 3.Pleasetell mewhen2. “阻止/ 禁止某人做某事” 振奋Mr.Smith is arriving atthe的多种表达7.depend_on 依靠;取决于 train station so that I can(1) 阻止某人做某事8.break_out突发;爆发pick him up in_time.① prevent sb. from doing 9.prevent_..._from 阻止;制 4.At last the firefighters putsth.止outthefirein the ② stop sb. from doing sth. 10.block_out挡住 (光线 ) supermarket,which③ keep sb. from doing sth. 11.get_the_hang_of 熟悉; broke_out attenthis(2) 禁止某人做某事掌握;理解morning.④ prohibit sb. from doing 12.now_that既然5.You ’ve made me suffer in sth.thepast,sonowyou, ⑤ ban sb. from doing sth. in_your_turn,_suffer ⑥ forbid sb. fromdoingagain !sth.Ⅲ .句式—在解读中学懂,在仿写中学通[背原句 ][记句式 ][会仿用 ]1.This produced a chain reaction,这个女孩懂三门外语,这使她更容易找到一份好工作。
which made it possible for life to句中的 it 是形式宾语,真正girlknowsthreeforeign develop .The的 宾 语 是 不 定 式 短 语 towhich这就产生了一系列的反应,使得生命 develop 。
languages,makes_it_easier_for_her_to_find a就有可能开始发展了。
good job.2.But when I tried to step forward,杰西卡付出的是以前三倍的时间和精力,I found I was carried twice as far “ ...倍数as ++形容词 / 副词所 以 我 相 信 她 这 次 能 成 功 。
Jessicaas on the earth and fell over. 原级+ as ...”是倍数表达法devoted 而当我试着向前迈步时,我发觉我被 之一,意为“ 是 的多 three_times_as_much_time_and_ener 送出去很远,步子的跨度竟是在地球 少倍”。
gy_as she did before, so I believe she 上的两倍,因而我摔倒了。
will succeed this time.3. “ Oh, dear ,” I cried,“ walkingdoes need a bit of practice now “既然;由于”, 既然它对我们的好处如此多,为什么不试that g ravity has changed.now that”一 试 呢 ? Now_that_it_benefits_usso “天哪,”我大声说,“既然重力改 引导原因状语从句,有时 that 可以省略。
much, why not have a try?变了,看来走路也的确需要练一练 了。
”第一板块 | 核心单词归纳集释1 . harmful adj .有害的[经典例句 ] Experts point outthat fruit juices can be harmful to children’steeth.专家指出果汁可能损害儿童的牙齿。
① Some boys are too crazy about playing games on the computer, which is very(harm) to their health. 有些男生对玩电脑游戏简直到了痴迷的程度,这对他们的健康非常有害。
2 . exist vi . 存在;生存[教材原句 ]They laid eggs too and existed on the earth for more than 140million years.它们也生蛋,在地球上生存了一亿四千多万年。
(1)There exists ... 某地有 ;存在(2)existence n . 存在;生存come into existence产生;成立;开始存在① There_exists a generation gap between the young and the old.青年人和老年人之间存在着代沟。
② You can ’t imagine whatdifficulty they have existing on the money he ’searning.你无法想象他们靠他挣的那点钱维持生活是多么的困难。
③ Scientistshave many theories about how the universe first came into(exist) .关于一开始宇宙是如何产生的,科学家们有多种观点。
[ 名师指津 ] exist 是不及物动词,没有被动语态,也不用于进行时态。
3 . puzzle vt .使迷惑;使为难n .谜;难题; ( 游戏的 ) 猜谜scientists found hard to solve.地球生命如何起源是科学家们觉得很难解决的最大的难题之一。