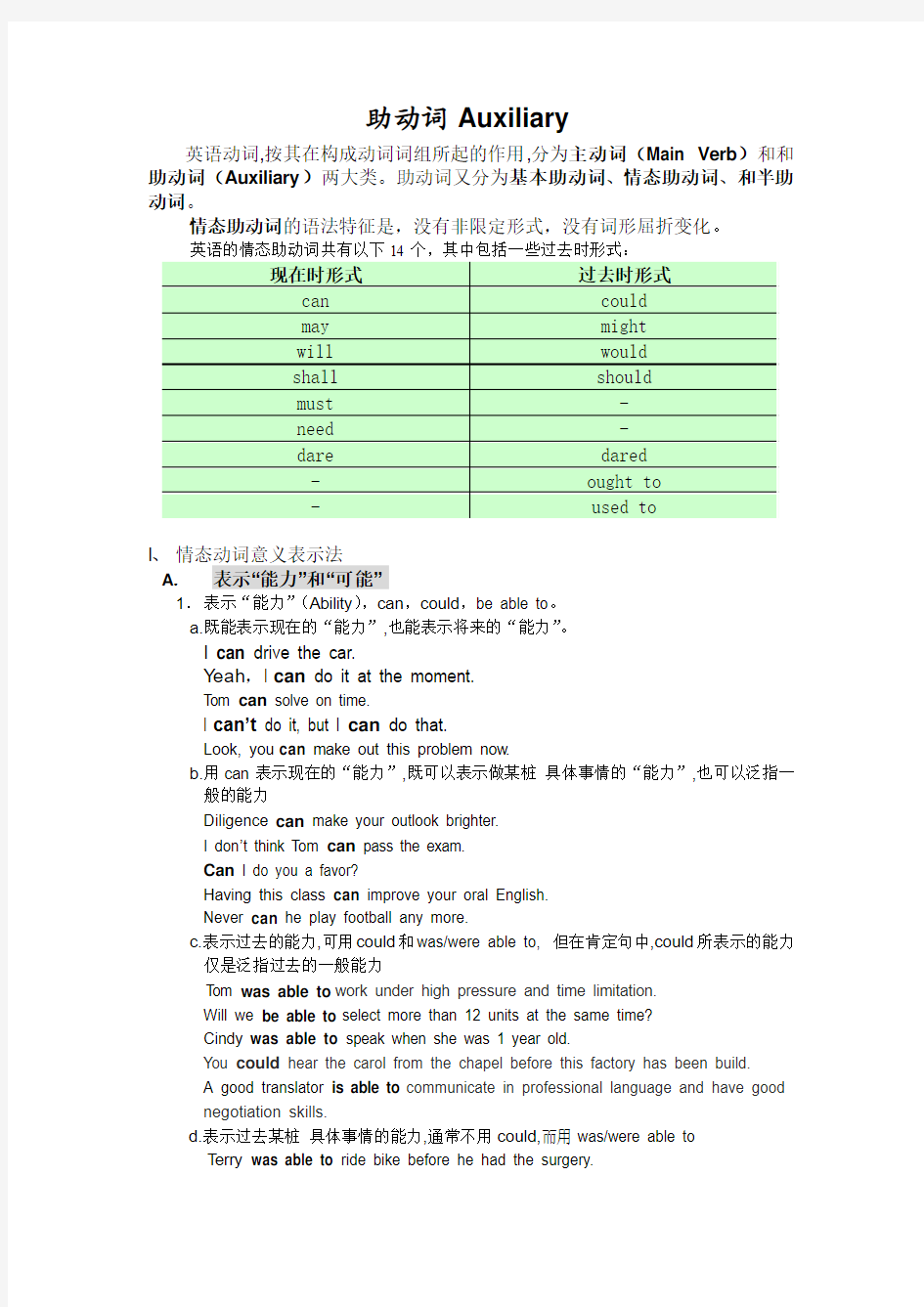

助动词Auxiliary
091021049 范穗宁Class8
英语动词,按其在构成动词词组所起的作用,分为主动词(Main Verb)和和助动词(Auxiliary)两大类。助动词又分为基本助动词、情态助动词、和半助动词。
情态助动词的语法特征是,没有非限定形式,没有词形屈折变化。
I、情态动词意义表示法
A.表示“能力”和“可能”
1.表示“能力”(Ability),can,could,be able to。
a.既能表示现在的“能力”,也能表示将来的“能力”。
I can drive the car.
Yeah,I can do it at the moment.
Tom can solve on time.
I can’t do it, but I can do that.
Look, you can make out this problem now.
b.用can表示现在的“能力”,既可以表示做某桩具体事情的“能力”,也可以泛指一
般的能力
Diligence can make your outlook brighter.
I don’t think Tom can pass the exam.
Can I do you a favor?
Having this class can improve your oral English.
Never can he play football any more.
c.表示过去的能力,可用could和was/were able to, 但在肯定句中,could所表示的能力
仅是泛指过去的一般能力
Tom was able to work under high pressure and time limitation.
Will we be able to select more than 12 units at the same time?
Cindy was able to speak when she was 1 year old.
You could hear the carol from the chapel before this factory has been build.
A good translator is able to communicate in professional language and have good
negotiation skills.
d.表示过去某桩具体事情的能力,通常不用could,而用was/were able to
Terry was able to ride bike before he had the surgery.
Zoe’s factory was able to pay for the service before the economic crisis.
Sam was able to pass the exam without any training.
Richard was able to finish the project with his wife’s help.
We were able to cross the river without a bridge there.
2. 表示“可能”,可用may, might, can, could. may/might表示”可能”,往往可以交替使用,
并无时间上的差异,只是用might在口气上比用may更加不肯定,从而比较委婉.
a. may/might既可以表示现在的可能,也可以表示将来的可能
That may/might be the reason why you don’t achieve your objective.
He may/might get the present at the performance now.
That may/might be the result of this case.
Crime may/might be a threatened of the society nowadays.
This boss may/might give you more than that one.
b.在疑问句中表示可能,须用can而不用may
What can I do for you?
Can you help me?
Can I help you?
Can you tell me how to get there?
Where can she live when she got there?
c.用can表示可能,较多的用于否定句和疑问句,而could则不受此限
You could call me if you need my help.
Can the monkey climb on the tree in 3 seconds?
It could be a suitable way for you to grapple with this matter.
The man could be a crime of this case.
Can you have missed the train?
d.在肯定句中,用can表示可能与用may表示可能往往产生含义上的微妙差别:用can
表示可能往往指逻辑上的可能性;而用may表示可能则指事实上的可能性
The train may be delayed. (It is possible that the train was delayed.)
The train can be delayed. (It is possible for the train to be delayed.)
You can miss the bus today. (It is possible for you to miss the bus.)
You may miss the bus today. (It is possible that you miss the bus.)
3.表示过去的可能,可用may/might+不定式完成体或不定式完成进行体,在这里用
may/might,也只有口气上婉转程度的差异,而没有时间上的差别.
You may/might have got a prefect life.
She may/might have a wonderful job at that moment.
I may/might have been student of senior high school already.
He may/might have got a good mark in the final exam last semester.
He may/might have brought that car already.
B、表示“许可”和“不许”
1、请求对方许可用can, could, may, might.
a. may/might与can/could相比,前者比较正式;may/can与might/could相比,后者较为婉
转,更有礼貌.在口语中特别常用can表示许可
Can/Could; May/Might I smoke in here.
Yes, you can.
Can I take the seat?
Can I have the bill?
Could you please come here?
b. 表示给予许可通常用can/may,而不用could/might.
Could I use your phone? Yes, you can.
Might I take you one minute? Yes, you may.
Could I take the seat? Yes, you can
Could I borrow your pen? Yes, you can.
c. 用may/can与might/could都不存在时间的差异,但在上下文中,便存在这种差异.
Anyone may/can enroll for this course.
All students may/can go now.
In those days anyone might/could enroll for this course.
Last week, all students might/could go now.
2、表示不许可用may not或者cannot
a. may not也可表示一般的不许可,即表示根据一般规定,而不是说话人不许可.
He may not keep more than two books more than a week from library.
He may not bring the food to the shop.
He may not bring his pet to the bus.
He may not get some food from the library.
C、表示“义务”和“必然”
1. 所谓表示义务,即表示必须,应该做某事.表示这些意义,可用should, ought to, must.用
这三个情态助动词表示义务,其语气强弱略有差异.
a) 用should/ought to表示应该,带有表示劝说或敦促的含义
We should learn from the model workers
You should do what your teachers tell you
He should do something to help her
We should clean up the classroom after class
We should hand on our homework in this week
b) Should与ought to同义,都能表示应该,往往可以交替使用.用should口气比较肯
定一些,说话人的主观信心要强烈一些,而用ought to则在语气上不是那么坚定.
You should/ought to drink less
You should/ought to tell the police
He shouldn’t/oughtn’t to stay up so late
I should go now
I should go to bed
c) 用must表示敦促或命令,在口气上比should更加强烈,这意味着说话人是权威的
一方,对人对己都适用.
We must do it again
You must hand on your homework
You must be back by 10 o’clock
I really must stop smoking
d) 表示必须,must与have to意义接近,但在用法上略有区别:用must表示必须,侧重
于说话人的主观一直,用have to表示必须则侧重于客观的需要.
He must say it in English. He has to say it in English
He must move the furniture himself. He has to move the furniture himself.
He must go to school on foot. He has to go to school on foot.
e) 在特定语境中,用will也可以表示义务.常用于第二人称主语,这实际上是一种强化
的祈使句,比带有第二人称主语的祈使句口气更为强化
You will wait outside the gate
You will report to me afternoon
You will tell me the truth
You will do it yourself
2. 所谓表示必然就是根据说话人的判断和推测认为必然会有某种情况.表示这种意义,
可用should, ought to和must,其中以用must口气最为肯定.
a) 用should表示必然,指说话人根据一定情况做出推测或者推断
She should be here in a minute
The book should appeal to all lovers of poetry
That should not be difficult problem of Mary
He should leave now
b) 用ought to表示必然也是根据一定情况做出推测或推断.用ought to表示推断或
推测与must同义,但语气较弱,从而也比较委婉.
These young trees ought to provide shade in ten years
He ought to be able to help you
He ought to give you a hand
These ought to be kept safe
c) 用must表示必然,也是推断或推断,其口气最为肯定,一般用于可定陈述句.
All men must die
Careless reading must give poor results
It must be very late because the streets are quite deserted
Your father must be expecting you home
He must be excited if you tell him these
D、表示“预见”和“推测”
1. 表示预见,即表示单纯将来,可用will/shall+不定式
a) will可用于一切人称表示将来
I will be a different person when I live in England
We will have a great time if we go to the party
You will be hearing from me
What will you do when the war is over?
She’ll probably last longer than you will
b) 非正式用语中,will更是常用于第一人称主语表示将来,尤其常用will/shall的缩略
形式’ll, 从而进一步模糊了will/shall的界限
I’ll book a table at the shop
I’ll come in after church and give you a hand
We’ll be going on later for bridge
We’ll go to the party if we are invited
2. 表示推测,除用should, ought to和must外,还可用will/would
用will/would表示推测可有三种情况
a) 对特定事态的推测
That won’t be him
She will be all right now
By now he will be eating dinner
They will have arrived by now
b) 对某些习惯性事态的推测,用will指现在习惯,用would指过去习惯
A lion will attack a man only when hungry
He will work all day without a rest
He will stay at home all day
Every day she will sit there for hour doing nothing
c) 对某些不受时限的客观过程的推测,只用will,表示现在时间,可与一般现在时的
类似用法交替使用
Oil will float on water
Pigs will eat anything
Leaves will turn yellow in autumn
E、表示“意愿”、“意图”和“决心”
1. 表示意愿,即愿意做某事,可用will, would, shall.
a) 用will表示意愿,可用于一切人称的主语
I will lend you the money if you need it
Who will go with me
My sister will help you
You can help me if you will
b) 表示过去的意愿或过去不愿意做某事,可用would和would not
I asked him if he would help me
I wouldn’t read any book
He would never do anything like that
c) 用shall表示意愿一般适用第二三人称主语,在疑问句中是征询听话人的意愿
You shall stay with us as long as you like
He shall be praised if he works for the people
Shall you take a holiday this summer?
Shall my daughter do the shopping for you?
2. 表示意图,即打算做某事,也可用will, would, shall
a) 用will表示意图,可用于一切人称主语
I will write to you
Why will you go there?
I will get some drink
What will you want?
b) 表示过去的意图或用在间接引语中可用would
He would see her the next day
He wouldn’t have any cold drinks
He wouldn’t write to her
He would talk to her
c) 用shall表示意图用于疑问句中式征询听话人的意见或意图
Shall I walk with you?
Shall I borrow your pen?
Shall I take the seat?
Shall I ask you a question?
3. 表示决心,即坚持要做某事, 也可用will, would, shall
a.用will表示决心或坚持决心或坚持,可用于一切人称的主语
I will take the job
I won’t go back on my words
He will go out without money
b.表示过去的决心,即过去坚持做某事,便可用would
She would married him
He would climb the mountain regardless of danger
The annoying thing was that she would make a muddle of almost anything
c. Shall表示决心主要用于第二三人称主语, 表示说话人的强烈意志和决心
You shall obey my orders
He shall leave the country at once
They shall do what I told them do
F、其他情态意义
1、should
a、should可以在某些语境中表示惋惜、忧虑、欢欣、惊讶等感情色彩
It’s a pity that he should leave so soon
They were sorely distressed that their motherland should be in such great danger
They were amazed that she should have done so much in so short a time
It’s unbelievable that he should be working so hard
It’s marvelous that somebody should have imaginations like that
b、可用在某些语境中并不表示具体的情态意义
I insisted that he should go with me
It is imperative that we should have a strong air force
The order that all civilians should be evacuated was soon carried out
2、would
a、would可用于委婉的陈述
I don’t think he would be so careless
It would be a shame to stop our work halfway
It would be done by me
b、可用于客气的请求
Would you like to stay here for the night?
What would you advise me to do?
Would you please come here?
Would you come with me?
c、用于委婉的建议
Wouldn’t it be better for us to start off a little earlier?
It wouldn’t be a bad idea for us to hold two separate meetings for the two problem
It would be done in this way
3、dare
a、作为情态助动词表示胆敢,dare通常只用于否定陈述句和疑问句
I dare not go there
He dare not jump from the top of the wall
How dare he say such rude things about me?
b、dare还可用作助动词。作为助动词,dare也通常用于否定句和疑问句,随后的不定式可带to,也可不带to
She didn’t dare say anything about me
He does not dare answer
Does she dare go there alone?
4、need
a、need既可作情态助动词,也可作助动词,作必须,需要解。作情态助动词,need也
只用于否定句和疑问句
He needn’t work about it
Need I collect the parcel myself?
I need work more hard
b、询问对方是否需要、必须做某事,既可用need,也可用must
Must I see a doctor at once?
You need see a doctor at once
Must I go now?
No, you needn’t.
5、used to
used to表示过去习惯动作或状态,这种情况现已不存在
There used to be an old temple.
He used to smoke a lot
He used to swim in the morning
He used to have lunch at 12
目录 1助动词和情态动词的定义 (2) 2 can,may,must (3) 3 Will you~?和Shall I(we)~? (10) 4 would和should (14) 5 have to (16) 练习题 (17) 答案 (18)
1助动词和情态动词的定义 在英语中,助动词一般没有词义,主要帮助构成谓语,表示时态、语态或构成疑问及否定形式。对于助动词,同学们一般了解即可。 情态动词与助动词不同,它有词义,但它也和助动词一样,不能单独作谓语,它必须和其他动词一起构成谓语,另外重要的一点是情态动词没有人称和数的变化;情态动词后必须跟动词原形。 (×)She cans swim well. (×)She can swims well. (○)She can swim well. (○)She swims well. 即使主语是第三人称单数(例如she)can也不能加“s”。 句子中有情态动词can时,即使主语是第三人称单数,也不能在一般动词(例如swim)上加“s”。 1 助动词的种类 1.be(am,are,is,was,were,been,being) 它与现在分词结合,可以构成进行时态(参见第九章),与过去分词结合可以构成被动语态(参见第十三章)。 I am reading the book.我正在读这本书。 The book was written by me. 这本书是我写的。 2. have(has,had,having) 它与过去分词结合,构成完成时态(参见第十一章)。 I have finished my homework. 我已经写完作业了。 3.shall(should),will(would)
be动词,情态动词,助动词do/does的用法区别及练习 助动词,顾名思义就是帮助动词完成疑问及否定的,本身没有什么含义。主要的助动词有be,do,will,have等,其用法详述如下: 一、⑴由连系动词am,is,are构成的句子:变一般疑问句时把am,is,are提到句子的前面,句尾用问号即可。变否定句时直接在am,is,are后面加not即可。例如: 肯定句:He is a student. 一般疑问句: Is he a student? 否定句: He is not a student. 画线提问: 对he提问: Who is a student? 对a student 提问: What is he? (2)was 是am,is的过去式,were是are的过去式,若句子中有以上两词时,变疑问句及否定句方法与(1)相同。 二、(1) 由情态动词can, may,will ,shall等构成的句子: 变一般疑问句时把can, may,will ,shall提到句子的前面,句尾用问号即可.变否定句时直接在can,may,后面加not即可. 例如: 肯定句: She can swim. 一般疑问句: Can she swim? 否定句: She can not swim. 画线提问: 对she提问: Who can swim? 对swim提问: What can she do? (2)could,might,would,should是can,may,will,shall的过去式,若句子中有以上两词时,变疑问句及否定句方法与(1)相同。 三、(1)由行为动词构成的句子: 需要加助词do或does. 变一般疑问句时把do/does放在句子前面. 变否定句时把don’t/doesn’t放在动词的前面。要注意观察动词的形式并对号入座。一般疑问句和否定句的动词三单式都要变回原型。 play-----do plays-----does 例如: 肯定句: They play football after school. He plays football after school. 一般疑问句: Do they play football after school? Does he play football after school? 否定句: They don't (do not) play football after school. He doesn’t’ play football after school. 画线提问: 对they/he提问: Who plays football after school? 对play football提问: What do they do after school? What does he do after school? 对after school提问: When do they play football? When does he play football? (2)did是do和did的过去式,变一般疑问句时把did放在句子前面. 变否定句时把didn’t 放在动词的前面, 要注意观察动词的形式并对号入座。一般疑问句和否定句的动词都要变回原型。
be 动词、助动词、情态动词讲解(基础篇) 1、 用单数,反之用复数。 ◆ 句中含有be动词时: 肯定句:主语+be +其他 否定句:主语+be +not +其他 一般疑问句:Be +主语+其他+? 特殊疑问句:疑问词(what / who / when / where)+be +主语+其 他+? I am a teacher. You are right. She is 16 years old. My father is at home. The students are playing games. My teacher was ill yesterday. There is a picture on the wall. There are two books on the table. ★ be 动词用法歌: 我用am,你用are,is 连接他她它。单数名词用is,复数名词全用are。 变疑问,往前提,句末问号莫丢弃;变否定,更容易,be 后not 莫忘记; 疑问否定任你变,句首大写莫迟疑。 ★ be 动词作谓语,它后面一般跟名词、形容词或介词短语。她个子很高。 她在教室里。她是一个高个子的女孩。 2、助动词的用法。 英语句子按正常语序是“什么人或事物” + “做什么”,即,我们常说的“主语+ 谓语+ 其他” 。 ①主语为I 或复数名词、代词时:肯定句:I / We / They / The students
+动词原形+其他+。 We watch TV every night. 变否定:主语+don't +动词原形+其他+。 We don't watch TV every night. 一般疑问句Do + 主语+ 动词原形+ 其他+ ? Do you watch TV every night? Yes, we do. / No, we don 't. 特殊疑问句:疑问词+ do + 主语+ 动词原形+ 其他+ ? How often do you watch TV? ②主语为单数名词或代词时:肯定句:主语+ 动词第三人称单数形式 + 其他+ 。 He watches TV every night. 否定句:主语+ doesn't+动词原形+其他+。 He doesn't watch TV every night. 一般疑问句:Does + 主语+ 动词原形+ 其他+ ? Does he watch TV every night? Yes, he does. / No, he doesn 't. 特殊疑问句:疑问词+ does + 主语+ 动词原形+ 其他+ ? How often does he watch TV? ★主语为单数或不可数名词,谓语要用单数第三人称,反过来,看见动词用了单数第三人称,可以推知主语是单数或不可数名词。 ( )1. How __ ______ your dad help at home? A. do B. does C. is ( )2. ______ goes bad easily in summer. A. Milk B Apples C. Cakes ③过去时的句式(当句子时态为过去时时,动词用过去式,不受主语单复数的影响) 肯定句:主语+ 过去式+ 其他+ 。 He / We got up early every morning last year. 否定句:主语+ didn't + 动词原形+ 其他+ 。 He / We didn't get up early every morning last year. 一般疑问句:Did + 主语+ 动词原形+ 其他+ ? Did he / you get up early every morning last year? Yes, he
助动词在英语学习当中作了解,不需要重点把握,但是助动词也是很好理解的,希望回答能够帮到你。 1.助动词:Be 助动词不能作述语动词,要与本动词一起构成动词片语,表示时态、语态等。 1. BE作为本动词表示状态或客观存在等意思。 Your house is bigger and nicer than mine. 你的房子比我的又大又好。 2. BE+不定词连用,表示约定、义务、命令等未来的动作或状态。 I am to go abroad on business tomorrow. 明天我要去外国出公差。 表示未来的安排。 The meeting is to be held as scheduled. 会议将按原计划召开。 表示计划好的安排。 You are not to bark at my friend. 你不许对我的朋友叫。 表示命令或要求。 3. BE+现在分词构成各种进行时态。 Who are you talking to? 你在和谁说话? I am talking to my dog. 我在和我的狗说话。 4. BE+过去分词构成被动语态。 That means I will be promoted as scheduled. 这就意味着我将要按原计划得到提升。 2. dare和used to 作为情态助动词的dare一般只能用于疑问句或否定句中,dare+原形动词表示敢。
I dare not say it is ugly. 我不敢说它丑。 How dare you say so? 你怎么敢这么说? dare也可以作本动词,用于肯定句,后面要接带to的不定词;主词若是第三人称单数,简单现在式时,dare要变为dares。 You, you dare to talk to me like this! 你、你竟敢这样和我讲话! used to+原形动词表示过去的习惯或状态,而现在已经不存在了。 You're not what you used to be. 你不是以前的你了。 used to构成疑问句时有两种形式。即used + 主词+ to + 其他成份?;Did + 主词+ use to+ 其他成份。 How used I to be? 我以前什么样? How did you use to be? 你以前什么样? used to构成否定句时有两种形式,即used not to和didn't use to。 You didn't use to say things like this. You used not to say things like this. 你以前不会说这样的话的。 be used to表示习惯于,其中used是形容词,to是介系词,后接名词、代名词或动名词等,可用于不同的时态。 You're used to hearing words of praise. 你是听好话听惯了。 3. 助动词:Do 1. DO作为助动词时的时态、人称和数的变化与它作为本动词相同,有do, does, did三种形式。 Yes, it seems he doesn't really want to have a haircut.
英语助动词和情态动词及练习 一、概述 不同的时态(一般式、进形式、完成式、将来式),不同的语态(主动、被动),不同的语气(祈使、陈述、虚拟),不同的结构(肯定、否定、疑问),以及说话者本身的态度或命令、请求、愿望、可能等,所有这些都要借助于助动词和情态动词表达出来。助动词一般没有词意,不能单独作谓语动词,除非省略句中。他们只参加时态、语态、语气或否定、疑问结构。情态动词有词义,可以用来表示说话者的语气和态度。主要的助动词和情态动词如下表: 二、助动词 助动词一般没有词意,不能单独作谓语动词。其作用在于帮助构成各种时态、语态、否定、疑问等。 1、助动词be(am, is, are, was, were, being, been)的用法 (1) be后跟现在分词构成进行时态。 Who is playing the violin?谁在拉小提琴? She was reading a book then.那时她正在读书。 (2)be后跟过去分词构成被动语态。 He was asked to do the work.有人要他干这件工作。 You are invited to attend the meetintg.有人邀请你参加会议。 (3)be 后跟不定式作谓语,有如下几种情况: ①表示计划、安排将要发生的事。 Who are we to meet?我们要见谁呀? I'm to have supper with John this afternoon.今天下午我要与约翰一起吃晚饭。 ②表示指示、命令,否定式表禁止。 You are to see the headmaster today.今天你必须去见校长。 You are not to enter the room without permission.未经允许你不能进入房间。 ③表示义务、责任等,同should。 You are to be back before 5.你得在5点钟以前回来。 What is to be done?该干什么。 ④表示可能性,与情态动词may, can同义。 Such books are to be found in any library.这种书任何图书馆都有。 Not a sound was to be heard.一点声响也没有。 ⑤表示后来发生的事,可以用来表示命运或注定 They say good-bye, little knowing that they were never to meet again.他们告别了,没想到再也不能相见了。 He was to regret the decision.他有一天会后悔做出这一决定的。 ⑥用于习语 Where am I to go? 我该向何处去? What am I to do? 我该怎么办? 2、助动词have(has, had, having)的用法 (1)助动词have可以构成完成时或完成进行时
be动词与助动词的用法 1.陈述句:be动词第一人称用am,第二人称用are,第三人称单数用is复数用are. 助动词do一般省略,直接用动词,注意动词时态和人称变化.有时在动词前加do,表示强调,加强语气.如:Do be quiet! 2.疑问句:be动词直接提前,其他部分不变(由陈述句转变).助动词do同样,由省略直接提前放置,后面动词不变,注意do的时态和人称变化. 3.否定句:be动词和助动词do后面加not. be作助动词用的形式如下: ①am, is, are, was, were ②助动词+be:shall be, will be, can be, etc. ③have/has/had + been(完成时) ④am, is, …being(进行时) (1)表达进行时态 句型be + V-ing…(进行时态) 例:What are you reading? (你正在阅读什么?) I am reading a magazine. (我正在阅读杂志。) 例:He will be taking a walk in the park at this time tomorrow morning. (明天早晨此时他将会正在公园散步。) 例:She has been teaching English in our school for years. (她已在我们学校教英语许多年了。) 解说第一例句是表达现在进行时,第二例句是将来进行时,第三例句是现在完成进行时。(2)表达被动语态 句型be +p.p. …(被动语态) 例:English is spoken in both Canada and the United States. (加拿大和美国都讲英语。)
助动词 协助主要动词构成谓语动词词组的词叫助动词(Auxiliary Verb)。被协助的动词称作主要动词(Main Verb)。构成时态和语态。助动词是语法功能词,自身没有词义,不可单独使用,它没有对应的汉译,例如:He doesn't like English. 他不喜欢英语。(does是助动词,无词义;like是主要动词,有词义) 最常用的助动词有:be, have, do, shall, will, should, would 他们表示时态,语态,构成疑问句与否定副词not合用,加强语气助动词半助动词 2 半助动词 功能介绍 在功能上介乎主动词和助动词之间的一类结构,称为半助动词。常见的半助动词有be about to, be due to, be going to, be likely to, be meant to, be obliged to, be supposed to, be willing to, have to, seem to, be unable to, be unwilling to等。......情态助动词 情态助动词1.情态助动词包括will(would), shall(should), can(could), may(might), must, need, dare, ought to, used to, had better后接原形不定词。2.情态助动词不受主语的人称和数的限制。3.两个情态助动词不能连用。中文:他将能够及时完成此事。(误)He will can finish it i...... 3 基本助动词 基本助动词基本助动词只有三个:be, do, have, 他们没有词汇意义,只有语法作用,如协助构成进行体,完成体,被动态,否定句,疑问句等。例如He is giving a lecture. 他在作报告He has made a plan. 他已经订了计划The small animals are kept in the cages. 小动物都关在笼子里。 助动词协助主要动词完成以下功用 a. 表示时态,例如: He is singing. 他在唱歌。 He has got married. 他已结婚。 b. 表示语态,例如: He was sent to England. 他被派往英国。 c. 构成疑问句,例如: Do you like college life? 你喜欢大学生活吗? Did you study English before you came here? 你来这儿之前学过英语吗? d. 与否定副词not合用,构成否定句,例如: I don't like him. 我不喜欢他。 e. 加强语气,例如: Do come to the party tomorrow evening. 明天晚上一定来参加晚会。 He did know that. 他的确知道那件事。 3)最常用的助动词有:be, have, do, shall, will, should, would 4 具体用法 have的用法 一、have作助动词 形式 主要变化形式:have,has,had 动名词/现在分词:having 1)have +过去分词,构成完成时态,例: He has left for London.他已去了伦敦。
七年级英语双休日作业 班级:姓名:等级 英语句型变化总结练习 1、含有be动词am,is,are构成的句子: 变一般疑问句时把am,is,are提到句子的前面,句尾用问号即可。 变否定句时直接在am,is,are后面加not即可。例如: 肯定句:He is a student. 一般疑问句: a student? 否定句: He a student. 肯定句:We are from China. 一般疑问句: from China? 否定句:We from China 2. 由情态动词can, may, should等构成的句子: 变一般疑问句时把can, may,提到句子的前面,句尾用问号即可. 变否定句时直接在can, may,后面加not即可. 例如: 肯定句: She can swim. 一般疑问句:she swim? 否定句: She swim. 3. 由行为动词构成的句子: 需要加助词do或does. 变一般疑问句时把do/does放在句子前面. 变否定句时在主语后面加don’t / doesn’t , 谓语用动词原形。例如: 肯定句: They play football after school. 一般疑问句: play football after school? 否定句: They football after school. 肯定句:Tom watches TV every day. 一般疑问句: Tom TV every day? 否定句: Tom TV every day.
注意:变否定句时相关词的改变 肯定句变否定句时,除将谓语变为否定式外,句中其他词语也可能随之改变: 如将some改为any,too和also改为either,and改为or等:There are some birds in the tree. 树上有些鸟。 →There aren’t ______ birds in the tree. 树上没有鸟。 He likes the book, too. 他也喜欢这本书。 →He doesn’t like the book, ______. 他也不喜欢这本书。He likes singing and dancing. 他喜欢唱歌和跳舞。 →He doe sn’t like singing ______dancing. 他不喜欢唱歌也 不喜欢跳舞。补充练习: 根据句后括号内的要求,填入句中所缺的词: 1. I know the answer. (一般疑问句) ______ ______ know the answer? 2. We can see some birds. (一般疑问句) ______ ______ see ______ birds? 3. There is a computer in the house. (一般疑问句) ______ ______ a computer in the house? 4. There are some flowers on the teachers’ desk. (一般疑问句) ______ ______ any flowers on the teachers’ desk? 5. There are some apples on the tree. (否定式) There ______ ______ ______ apples on the tree. 6. I think he is old. (否定句) I ______ think he ______ old.
助动词(Auxiliary Verb):协助主要动词构成谓语动词词组的词。自身没有词义,不可单独使用。 主要动词(Main Verb):是被协助的动词,构成时态和语态。 He doesn't like English. 他不喜欢英语。(doesn't是助动词,无词义;like是主要动词,有词义) 最常用的助动词有:be, have, do, shall, will, should, would 等。 基本助动词只有三个:be, do, have 他们没有词汇意义,只有语法作用,如协助构成进行时,完成时,被动态,否定句,疑问句等。 一、be 动词的用法 既可作系动词,又可作助动词,做助动词有人称和数的变化,第一人称用am,第二人称及复数用are,第三人称及单数用is,am,is 过去式
为was, are的过去式为were,它与现在分词构成进行时态和过去分词一起构成被动语态。 a. 表示时态be+doing(现在分词)表示现在进行的动作 He is singing. 他正在唱歌。 b. 表示语态be+done(过去分词)表被动语态 He was sent to England. 他被派往英国。 c. be+to do(动词不定式)表示计划安排命令。 We are to plant trees next week. 下周我们将要去植树。 You are to explain this 。对此你要做出解释。 二、do的用法 Do主要帮助实意动词构成否定和疑问句,后跟动词原形,有时放在实意动词前起强调作用,还可代替前文出现的动词,避免重复。Do 有人称和数的变化,第一、二人称及复数用do,第三人称及单数用does,过去式为did。 1)构成一般疑问句。DO +主语+动词原形+其他 I like singing 变为疑问句为Do you like singing ? 2)do + not 构成否定句。主语+do +not +动词原形。 I do not want to be criticized.我不想挨批评。 He doesn't like to study.他不想学习。 Many students didn’t know the importance of English before.过去好多学生不知道英语的重要性. 3)构成否定祈使句。
助动词与情态动词 一、助动词 助动词有be, have, do, will, shall。它们本身没有词义,只和实义动词的一定形式构成复合谓语,用来表示时态和语态,构成否定、疑问及加强语气等。 1、be (am, is, are, were, been) (l)“be + -ing”构成进行时态; (2)“be + 过去分词”构成被动语态; (3)“be + 动词不定式”构成复合谓语: ①表按计划安排要发生的事。The prime minister is to visit Japan next year.总理将于明年访问日本。 ? “do + 动 只有 (1)表示能力,如:He can speak English better than you. (2)在疑问句和否定句中表示“怀疑”、“猜测”或“可能性”,如:Can this green bike be Liu Dong's? (3)表示“许可”时can可以和may换用,如:You can (may) go home now. (4)如果要表示语气婉转,可用could代替can,这时could不再是can的过去式,如:Could you come again tomorrow? (5)can和be able to都可表示能力,两者在意思上没有什么区别。但是can只能有现在式和过去式,而be able to 则有更多的形式,如:He will be able to do the work better. 2、may和might (might为may的过去式)的基本用法 (1)表示允许或征询对方许可,有“可以”之意, 如:You may use my dictionary. 在回答对方说“可以做某事”或“不可以做某事”时,一般多不用may或may not,以避免语气生硬或不容气。而用比较婉转的说法进行回答。如:---- May I use this dictionary? ---- Yes, please. 或---- Certainly. 在请求对方许可时,如果Might I…? 就比用May I…? 语气更婉转些,如:May I have a look at your new
助动词的用法大全 助动词的形式与作用 1)英语常用的助动词(auxiliary verb)有shall,will,should,would,be,have,do等。助动词一般无词义,不能单独作谓语动词。助动词在句中的作用,在于帮助构成各种时态、语态、语气、否定和疑问结构等。如:China has entered a great new era. 中国已进入了一个伟大的新时期。(帮助构成完成时态) Some boys are playing on the grass. 一些男孩正在草地上玩。 (帮助构成进行时态) Mother is written by Gorky. 《母亲》是高尔基写的。 (帮助构成被动语态) We Shall have the football match if it does not rain.如果不下雨,我们就赛足球。(帮助构成将来时态和否定结构) Do you see my point? 你明白我的意思吗?(帮助构成疑问结构) [注]在否定结构中,not须放在助动词后面。 2)助动词加not一般都有简略式,用于口语中。如: is not-isn't would not--wouldn't are not--aren't [B:nt] have not--haven't was not -- wasn't has not--hasn't were not-- weren't [wE:nt] had not--hadn't shall not--shan't [FB:nt] do not--don't [dEunt] will not--won't [wEunt] does not--doesn't
专四语法练习2 助动词、情态动词 1. It’s wonderful that you ___C___ have achieved so much in these years. a. may b. can c. should d. would 2. He ___D___ hardly say anything more, since you know about it. a. don’t need to b. needn’t c. needs d. need 3. You __B____ the look on his face when he won the prize. a. would have seen b. should have seen c. must see d. can be seeing 4. Some people think the stock market will crash, but ___B___. a. I wonder if it happens b. I doubt if it will happen c. I am afraid it wouldn’t happen d. I doubt if it does happen 5. “Whatever has happened to George?” “I don’t know. He _B_____ lost.” a. can have got b. may have got c. might get d. could get 6. He has no idea what the book is about. He ___B___read the book.
中考英语情态动词、助动词、系动词专项讲解 中考英语情态动词、助动词、系动词专项讲解 语法精讲 1.can 和could 2.may 和might 3.need, must和have to 情态动词 4. should和ought to 5. shall, will和would 6. had better 1.can和coul d ① can表示能力,意为“能够,可以”,could用于过去时, 例如He can finish his homework al one. 他可以单独完成作业的。 He couldn’t cook when he was 18 years old. 他18岁时还不会做饭。 ② can表示推测,意为“可能”,在否定句中表示否定的猜测,意为“不可能”,could用于对过去的猜测,can’t be 不可能 例如:He could be cooking at this time yesterday. 他昨天这个时候有可能正在做饭。 He can’t be here be cause he has gone to American.他不可能会在这里,因为他已经去美国了。 ③ can表示请求语气,coul d的语气更委婉, 例如:Can I help you? / Coul d I help you? 有什么我可以为您效吗? 拓展:be abl e to=can也为“能够”,用来表示能力(有人称和时态的变化) 例如:He is able to d eal with this problem. 他能解决这个问题的。 2.may和 might
① may表示请求,might语气更委婉, 例如:May I help you? Might I sit here? ② may表示肯定的推测,语气比can更弱,might对过去的推测 例如:Mary may be doing her homework now. May can be doing her homework now. can表达的推测语气比may更强,更有把握。 3. must和have to ①must表示命令、责任,意为“一定,必须”,must not/ mustn’t表禁止,“一定不要”, 例如:Children must stay away from strangers.孩子一定要远离陌生人。 You mustn’t play fire because it’s dangerous. 千万不要玩火,因为太危险了。 拓展:在表示禁止时,会用“No Doing”来表示,如No Smoking. / No Walking.等。 ② must表示推测,语气比can更强. 例如:Mr. Liu must be on holiday now because he is wearing pants. 刘老师现在肯定在度假因为他正穿着平底裤呢!(上课是要穿正装的) ③ Must作一般疑问句开头提问时:肯定用must回答,否定用needn’t或d on’t have to回答。 例如:Must I finish my homework now? Yes, you must. / No, you ne edn’t. ④ must 和have to 的区别: a) must没有人称、时态的变化,而have to根据人称、时态的变化,有不同的形式。 b) Must表示主观上必须做,而have to 表示客观需要。
助动词用法归纳小学 -CAL-FENGHAI-(2020YEAR-YICAI)_JINGBIAN
助动词(Auxiliary Verb):协助主要动词构成谓语动词词组的词。自身没有词义,不可单独使用。 主要动词(Main Verb):是被协助的动词,构成时态和语态。 He doesn't like English. 他不喜欢英语。(doesn't是助动词,无词义;like是主要动词,有词义) 最常用的助动词有:be, have, do, shall, will, should, would 等。 基本助动词只有三个:be, do, have 他们没有词汇意义,只有语法作用,如协助构成进行时,完成时,被动态,否定句,疑问句等。 一、be 动词的用法 既可作系动词,又可作助动词,做助动词有人称和数的变化,第一人称用am,第二人称及复数用are,第三人称及单数用is, am,is 过去
式为was, are的过去式为were,它与现在分词构成进行时态和过去分词一起构成被动语态。 a. 表示时态 be+doing(现在分词)表示现在进行的动作 He is singing. 他正在唱歌。 b. 表示语态 be+done(过去分词)表被动语态 He was sent to England. 他被派往英国。 c. be+to do(动词不定式)表示计划安排命令。 We are to plant trees next week. 下周我们将要去植树。 You are to explain this 。对此你要做出解释。 二、do的用法 Do主要帮助实意动词构成否定和疑问句,后跟动词原形,有时放在实意动词前起强调作用,还可代替前文出现的动词,避免重复。Do 有人称和数的变化,第一、二人称及复数用do,第三人称及单数用does,过去式为did。 1)构成一般疑问句。 DO +主语+动词原形 +其他 I like singing 变为疑问句为 Do you like singing 2)do + not 构成否定句。主语+do +not +动词原形。 I do not want to be criticized.我不想挨批评。 He doesn't like to study.他不想学习。 Many students didn’t know the importance of English before. 过去好多学生不知道英语的重要性.
Period Ten 情态动词和助动词 重点掌握情态动词can, may, must, need等词在语境中的运用,情态动词在句子中常用来表示“能力,允许,禁止,意愿,可能”等情感或态度。掌握助动词do, will, shall, have, be在句中的作用。 一、情态动词 1. 情态动词的定义 情态动词表示说话人对所述动作或状态的态度或看法。情态动词本身有词义,但不能独立作谓语,必须和动词一起构成谓语,在各种人称后都用同样的形式。 2. 情态动词的用法 (1)can的用法 ①表示人或物本身所具有的能力,意为“能,能够,会”。eg: Can you skate? 你会滑冰吗? She can speak a little Chinese. 她能讲一点儿汉语。 ②表示可能性,意为“可能会”,常用于否定句或疑问句。eg: Can it be true? 那会是真的吗? That can’t be Mary; she’s in hospital. 那不可能是玛丽;她住院了。 (2) could的用法 ①could可以表示过去的能力,若表示现在的能力时,语气比can委婉。eg: She couldn’t swim half a year ago. 她半年前不会游泳。 What a good idea! Maybe I could talk about English names. 你的想法太好!也许我能谈谈英国人的名字问题。 ②表示礼貌,常用在疑问句中,意为“能,可以”,答语一般用can。 —Could I borrow your bicycle? 我可以借一下你的自行车吗? —Yes, you can./ No, you can’t. 是的,可以。/不,不行。 ③表示猜测、怀疑等态度,一般用于否定句、疑问句或感叹句中。对现在情况表示猜测时,could 比can更 不确定,其结构为“can/could+动词原形”;对过去表示猜测时,结构为“can/could+ have+过去分词”。eg: You could be right, I suppose.我想可能是你对。 Don’t worry. They could have just forgotten to phone. 别担心。他们很可能只是忘了打电话。 (3) may和might的用法 ①表示允许,用于肯定句。eg: You may come if you wish. 你要来就来吧。 Passenges may cross by the footbridge. 乘客可使用步行桥。 ②表示许可,用于疑问句。might是may 的过去式,比may语气委婉。eg: May I come in? 我可以进来吗? Might I make a suggestion ? 我可以提个建议吗? ③表示客观不可能性。eg: Take an umbrella with you. It may rain. 带上雨伞,可能会下雨。 (4) must的用法 ①must表示“必须”时多用于肯定句或疑问句,其否定回答用needn’t;,用于否定句时,表示“不应该,不 许可,不准,禁止”。eg: I must go to the bank to get some money. 我得到银行去取些钱。 Cars mustn’t park in front of the entrance. 入口处不得停放汽车。 ②它在肯定句中,还可表示“推测”,意为“一定”。“must be”表示对现在某事的推测;“must have done” 表示对过去的推测;反意疑问时,要根据must后的be或have来做。eg:
1、be动词的用法。 be am / is are 现在时 was were 过去时 单数复数 英语中,be动词选用单数还是复数,要由主语来定,主语是单数,就用单数,反之用复数。 ◆句中含有be动词时: 肯定句:主语+be +其他 否定句:主语+ be + not +其他 一般疑问句: Be +主语+其他+? 特殊疑问句:疑问词(what / who / when / where)+ be +主语+其他+? I am a teacher. You are right. She is 16 years old. My father is at home. The students are playing games. My teacher was ill yesterday. There is a picture on the wall. There are two books on the table. ★ be动词用法歌: 我用am,你用are,is 连接他她它。单数名词用is,复数名词全用are。 变疑问,往前提,句末问号莫丢弃;变否定,更容易,be后not莫忘记; 疑问否定任你变,句首大写莫迟疑。 ★ be动词作谓语,它后面一般跟名词、形容词或介词短语。 2、助动词的用法。 英语句子按正常语序是“什么人或事物” + “做什么”,即,我们常说的“主语 + 谓语 + 其他”。 ①主语为I 或复数名词、代词时: 肯定句: I / We / They / The students +动词原形+其他+。 We watch TV every night. 变否定:主语+don’t +动词原形+其他+。 We don’t watch TV every night. 一般疑问句 Do + 主语 + 动词原形 + 其他 + ? Do you watch TV every night? Yes, we do. / No, we don’t. 特殊疑问句:疑问词 + do + 主语 + 动词原形 + 其他 + ? How often do you watch TV? ②主语为单数名词或代词时: 肯定句:主语 + 动词第三人称单数形式 + 其他 + 。 He watches TV every night. 否定句:主语+ doesn’t+动词原形+其他+。