2_Cell Membrane
- 格式:pps
- 大小:4.01 MB
- 文档页数:36

高中必修二生物的名词解释生物学作为一门自然科学,研究生物的结构、功能、发展和演化规律。
在高中生物课程中,学生们需要理解并掌握许多关键性的名词和概念。
本文将解释一些高中必修二生物的名词,以帮助读者更好地理解这些概念。
1. 细胞膜(Cell membrane)细胞膜是位于细胞外层的一层薄膜,由磷脂、蛋白质和其他生物分子组成。
它控制物质的进出,保护细胞免受外界环境的侵害,并维持细胞内外环境的稳定。
细胞膜是细胞结构的重要组成部分,也参与细胞间的信号传递和相互作用。
2. 染色体(Chromosome)染色体是细胞中的一种结构,由DNA和蛋白质组成。
染色体携带着生物个体的遗传信息,并在细胞的分裂过程中传递给下一代。
人类的染色体呈现出一对一对的特点,其中包含有关遗传特征和性别决定的基因。
3. 基因(Gene)基因是生物体内控制遗传信息的单位,由DNA序列编码。
它们决定了生物的特征和表型,包括外貌、性状、身体功能等。
基因可以通过遗传传递给后代,而且能在不同环境条件下发生突变,导致基因型和表型的变化。
4. 光合作用(Photosynthesis)光合作用是绿色植物和一些细菌利用光能转化为化学能的过程。
光合作用中,植物通过叶绿素吸收光能,并将其转化为ATP和NADPH,然后使用这些能量去固定二氧化碳,合成有机物质(如葡萄糖)。
光合作用是地球上生物能量和物质循环的重要过程,同时也释放出氧气。
5. 基因工程(Genetic engineering)基因工程是通过改变生物体的基因组来改变其性状和功能的技术。
它可以通过插入、删除或修饰基因,来改变生物的遗传性状,以实现人类的需求。
基因工程在医学、农业、环境等领域具有广泛的应用,如生物药物的生产、农作物的转基因改良等。
6. 进化(Evolution)进化是指生物种群在长时间内的遗传变化和适应性逐渐改变的过程。
通过自然选择和遗传突变等因素,有利的性状将得到保存和传递,从而使物种适应环境的变化。

初中生物英语词汇一、细胞(Cell)1. 细胞膜 (Cell membrane)- 定义:包围和保护细胞的薄膜,控制物质的进出。
- 示例:The cell membrane allows nutrients to enter the cell.2. 细胞核 (Cell nucleus)- 定义:细胞的控制中心,包含遗传物质 DNA。
- 示例:The cell nucleus controls all the activities of the cell.3. 基因 (Gene)- 定义:生物体传递给后代的遗传信息单位。
- 示例:Genes determine the traits and characteristics of an organism.二、遗传(Genetics)1. 遗传学 (Genetics)- 定义:研究遗传现象和规律的学科。
- 示例:Genetics helps us understand how traits are passed from one generation to another.2. 遗传物质 (Genetic material)- 定义:决定物种遗传特性的DNA和RNA。
- 示例:The genetic material carries the instructions for the development and functioning of organisms.3. 遗传变异 (Genetic variation)- 定义:个体之间遗传特征的差异。
- 示例:Genetic variation is important for the survival and adaptation of a species.三、进化(Evolution)1. 进化论 (Theory of evolution)- 定义:生物种类在长时间内发生的变化和适应环境的过程。
2. 适应性 (Adaptation)- 定义:生物体对环境变化做出的结构或行为上的调整。

10+细胞生物学A一、名词解释(15小题,每小题2分,共30分)1.Cell2.古核细胞3.细胞培养4.Cell membrane5.受体介导的胞吞作用6.半自主性细胞器7.Endomembrane system8.细胞信号转导9.Cytoskeleton10.核仁组织区11.多聚核糖体12.Cell cycle13.程序性细胞死亡14.单能干细胞15.胞间连丝二、填空题(40个空,每空1分,共40分)1.2009年有两项与细胞生物学有关的研究获得诺贝尔奖:;。
2.细胞组分的分离方法有、和。
3.构成动物细胞胞外基质的主要成分是、、和。
4.膜脂主要包括、和,其中以为主。
5.在细胞世代中确保染色体复制和稳定遗传,染色体起码具备三种功能元件:、和。
6.分子马达(molecular motor)主要是指依赖于微管的、和依赖于微丝的这三类蛋白质超家族的成员。
7.核仁超微结构普遍存在三种基本组分:、和。
8.负责物质跨膜转运的蛋白可分为两类:和,前者既可介导运输,又可介导运输;后者只能介导运输。
9.细胞通讯可概括为3种方式:(28)。
(29)。
(30)。
10.体外培养的细胞,不论是原代细胞还是传代细胞,一般不保持体内原有的细胞形态,而呈现出两种基本形态:和。
11.单细胞向多细胞有机体进化的过程中,主要的特点是出现了。
12.迄今发现能独立生活的最小的原核细胞是,它的结构简单,是其细胞内唯一的细胞器。
13.高尔基体是一种有极性的细胞器,由相互联系的几个部分组成,即:、、、、。
三、问答题(8小题,每题10分,共80分)1.什么是细胞生物学?细胞生物学研究最终要解决的问题是什么?2.细胞生物学研究的主要内容是什么,你对哪方面了解的较为深入,请阐述。
3.细胞生物学研究有哪些方法?4.举例说明细胞分化是基因选择性表达的结果。
5.简述细胞间连接的类型、结构特点、存在部位和功能。
6.简述物质跨膜运输的主要方式及其特点。
7.简述核被膜在细胞周期中的崩解与重建。
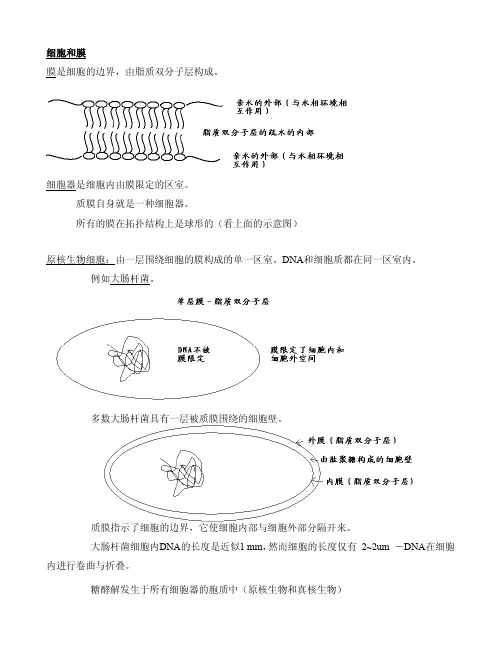
膜是细胞的边界,由脂质双分子层构成。
细胞器是细胞内由膜限定的区室。
质膜自身就是一种细胞器。
所有的膜在拓扑结构上是球形的(看上面的示意图)原核生物细胞:由一层围绕细胞的膜构成的单一区室。
DNA和细胞质都在同一区室内。
例如大肠杆菌。
多数大肠杆菌具有一层被质膜围绕的细胞壁。
质膜指示了细胞的边界,它使细胞内部与细胞外部分隔开来。
大肠杆菌细胞内DNA的长度是近似1 mm,然而细胞的长度仅有 2~2um -DNA在细胞内进行卷曲与折叠。
糖酵解发生于所有细胞器的胞质中(原核生物和真核生物)细胞被质膜围绕。
内部的区室(也称为细胞器)也被膜围绕。
细胞空间被外层质膜限定。
质膜也限定细胞内区室空间。
一个真核生物细胞:注:Mitochondrion,线粒体;Centrioles,中心粒;Lysosome,溶酶体;Golgi Apparatus,高尔基器;Smooth ER,滑面内质网;Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum,粗面内质网;Nucleolus,核仁;Nucleus,细胞核;Cell Membrane,细胞膜(引自:8001/esgbio/cb/org/animal.gif)质膜-由一个脂质双分子层构成细胞核与线粒体分别都被两层膜围住(内膜与外膜)细胞质-细胞核外部的水性区域,细胞质不包括细胞器细胞有许多区室,每一个区室的空间都被一层膜限定例子:溶酶体:一个小泡或区室,蛋白质和其它分子在溶酶体内被降解;包含了有消化作用的酶溶酶体内的环境具有很强的酸性。
溶酶体含有蛋白水解酶(降解蛋白质)和核酸酶(降解核酸-DNA, RNA)细胞核:包含DNA的细胞区室RNA在细胞核内制造出来,然后被送入细胞质用于翻译。
线粒体:真核生物细胞内的细胞器,是产生ATP(能量之源)的主要部位。
线粒体由一层外膜和一层高度折叠的内膜构成。
包括质膜在内的每一种细胞器都有其自身的蛋白质成分。
注:Cristae,嵴;Martix,基质;Granule,颗粒;Outer Membrane,外膜;Inner Membrane,内膜;Ribosome,核糖体(引自:8001/esgbio/cb/org/mito.gif)膜结构-磷脂双分子层-包含蛋白质(一些是细胞内蛋白质,其它的是穿膜蛋白质,这些穿膜蛋白质用于运输分子进出细胞,或者作为细胞表面的受体)膜蛋白的例子:所有的膜由一个脂质双分子层构成,该双分子层包含了由饱和或不饱和脂肪酸构成的磷脂。





生物学英语中英对照1. 遗传学 Genetics基因 Gene染色体 Chromosome遗传变异 Genetic variation2. 细胞生物学 Cell Biology细胞 Cell细胞核 Nucleus细胞膜 Cell membrane3. 生态学 Ecology生态系统 Ecosystem生物多样性 Biodiversity生物群落 Biome4. 分子生物学 Molecular Biology蛋白质 Protein核酸 Nucleic acid酶 Enzyme5. 发育生物学 Developmental Biology胚胎发育 Embryonic development细胞分化 Cell differentiation形态发生 Morphogenesis6. 植物学 Botany叶绿体 Chloroplast光合作用 Photosynthesis根系 Root system7. 动物学 Zoology器官 Organ组织 Tissue神经系统 Nervous system8. 微生物学 Microbiology细菌 Bacteria病毒 Virus真菌 Fungus9. 生物化学 Biochemistry代谢 MetabolismATP(三磷酸腺苷) ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate)酶促反应 Enzymatic reaction10. 生理学 Physiology心脏 Heart肺 Lung肝脏 Liver生物学英语中英对照(续)11. 进化生物学 Evolutionary Biology自然选择 Natural selection物种形成 Speciation进化树 Evolutionary tree12. 行为生物学 Behavioral Biology繁殖行为 Reproductive behavior领域行为 Territorial behavior社会行为 Social behavior13. 神经生物学 Neurobiology神经元 Neuron突触 Synapse神经递质 Neurotransmitter14. 免疫学 Immunology抗体 Antibody免疫系统 Immune system炎症 Inflammation15. 营养学 Nutrition蛋白质 Protein碳水化合物 Carbohydrate脂肪 Fat16. 遗传工程 Genetic Engineering基因克隆 Gene cloning基因编辑 Gene editing转基因技术 Genetic modification 17. 生态遗传学 Ecological Genetics种群 Population环境适应性 Environmental adaptation遗传漂变 Genetic drift18. 生物信息学 Bioinformatics基因组学 Genomics蛋白质组学 Proteomics生物数据挖掘 Bioinformatics data mining19. 生物统计学 Biostatistics实验设计 Experimental design数据分析 Data analysis显著性检验 Significance test20. 环境生物学 Environmental Biology环境污染 Environmental pollution生态修复 Ecological restoration生物降解 Biodegradation这份生物学英语中英对照文档旨在帮助您更全面地了解生物学领域的专业术语。

Botany植物学Cell theory细胞学说cell membrane细胞膜nucleus 细胞核Organelle 细胞器cell wall细胞壁cytoplasm细胞质protoplast原生质体cell cycle细胞周期mitochondrion 线粒体photosynthesis光合作用unit membrane 单位膜chloroplast 叶绿体chlorophyll叶绿素xanthophyll叶黄素carotene胡萝卜素golgiosome高尔基体ribosome 核糖体lysosome溶酶体microfilament微丝nuclear fission核分裂reproduction繁殖primary wall初生壁secondary wall次生壁plasmodesma胞间连丝mitosis有丝分裂amitosis无丝分裂meiosis减数分裂cytokinesis胞质分裂interphase间期prophase前期metaphase中期anaphase后期telophase末期tissue组织pistil 雌蕊stamen雄蕊ovary子房pollination传粉pollen tube花粉管porogamy珠孔受精chalazogamy合点受精mesogamy中部受精apomixis无融合生殖apogamy无配子生殖patrogenesis孤雄生殖parthenogensis 孤雌生殖apospory无孢子生殖pericarp果皮life history生活史root system根系main root主根lateral root侧根taproot system直根系fibrous root system须根系cortex皮层vascular cylinder 维管柱pericycle中柱鞘xylem ray 木射线vascular ray 维管射线phloem ray韧皮射线root cap根冠Casparian strip凯氏带primary xylem初生木质部primary phloem初生韧皮部vascular ray 维管射线xylem ray 木射线phelloderm栓内层phloem ray韧皮射线embryo胚homologous organ同源器官analogous organ同功器官endosperm胚乳seed coat种皮radicle胚根plumule胚芽hypocotyl下胚轴cotyledon子叶dormancy休眠seed germination种子萌发eukaryote真核生物prokaryote原核生物algae藻类blue-green algae蓝藻trichogyne受精丝mucopolysaccharide黏多糖gelatinous sheath 胶质鞘exospore外生孢子heterosexual cell异性细胞green algae绿藻isogamy同配生殖anisogamy 异配生殖anisogamy 卵式生殖zygogamy 接合生殖haploid单倍体diploid二倍体polyploid多倍体carposporophyte孢子体brown algae褐藻sea-tangle海带agar琼脂fungi菌类parasitism寄生saprophytic腐生的lichen地衣archegonium颈卵器antheridium精子器antiphyte孢子体gametophyte配子体protonema原丝体bryophyta 苔藓植物cruciferae十字花科vascular plants微管植物aquatic plant水生植物salicaceae杨柳科angiosperm被子植物endoplasmic reticulum内质网vegetative reproduction营养繁殖intercellular layer胞间层phellogen& cork cambium木栓形成层asexual reproduction无性繁殖sexual propagation有性繁殖tetradynamous stamen四强雄蕊didynamous stamen二强雄蕊monodelphous stamen单体雄蕊diadelphous stamen二体雄蕊triadelphous stamen三体雄蕊polyadelphous stamens多体雄蕊synantherous stamen聚药雄蕊primary wall cells初生壁细胞vegetative cell营养细胞male sterility雄性不育filiform apparatus丝状器meristem zone 分生区elongation zone伸长区maturation zone成熟区embryophyte有胚植物specific parasitism专性寄生specific saprophyte专性腐生facultative parasitism兼性寄生facultative saprophyte兼性腐生sexual generation有性世代asexual generation无性世代Zoology动物学cell细胞prokaryotic cell原核细胞eukaryotic cell真核细胞protein蛋白质nucleic acid核酸carbohydrate糖lipid脂质protoplasm原生质inclusion内含物cell cycle细胞周期pulmonary alveolus肺泡flagellum鞭毛food vacuole食物泡pinocytosis胞饮作用fission裂体生殖microgamete小配子zygote合子microtubule微管contraction silk 收缩丝merogenesis 卵裂blastocoele 囊胚腔complete cleavage完全卵裂layering分层cynapse突触myoneme肌丝myocyte肌细胞mesoglea中胶层monoecism雌雄同体dioecism雌雄异体velum缘膜radial symmetry辐射对称nerve net神经网planula 浮浪幼虫bilateral symmetry两侧对称mesoderm中胚层tubule cell 管细胞osmoregulation渗透调节acetabulum 腹吸盘oral sucker口吸盘metacercaria囊蚴pseudocoel假体腔cuticle角质膜cloacal pore泄殖孔renette腺肾细emunctory排泄管resting egg休眠卵metamere体节metamerism分节现象sense organ 感觉器periostracum壳皮层prismatic layer壳层nacreous layer珍珠层veliger 面盘幼虫glochidium 钩介幼虫adductor闭壳肌segmentation异律分节linear animal线形动物pericardial cavity围心腔cervical vertebra颈椎sacral vertebra荐椎pulmonary vein肺静脉precaval vein 前腔静脉bladder气囊middle ear中耳tympanum cavity中耳腔amnion羊膜neopallium新皮层lagena 瓶状囊wishbone叉骨postcaval vein后腔静脉glandular stomach腺胃air sac气囊salt gland盐腺sclerotic ring 巩膜骨viviparity胎生placenta胎盘allantois尿囊rumen瘤胃bursa of fabricius 腔上囊masticatory stomach肌胃reticulum网胃omasum瓣胃abomasum皱胃cochlea耳蜗earthworm蚯蚓internal naris内鼻孔amniota羊膜动物arthropod节肢动物coelenterate腔肠动物annelid环节动物cell membrane&plasma membrane细胞膜epithelial tissue上皮组织connective tissue结缔组织cartilage tissue软骨组织osseous tissue骨组织muscular tissue肌肉组织cardiac muscle心肌intercalated disc闰盘Nissl's body尼氏小体colony &group群体meroblastic cleavage不完全卵裂colonial theory 群体说gastrovascular cavity消化循环腔muscle system肌肉体系excretory system排泄系统reproductive system生殖系统digestive system消化系统archinephric duct原肾管basal lamina & basal membrane基膜cross-fertilization异体受精self-fertilization自体受精final host终寄主first intermidate host第一中间寄主semicircular canal半规管second intermediate host第二中间寄主Genetics遗传学heredity 遗传variation 变异gene 基因pisum sativum 豌豆segregation 分离gamete 生殖细胞zygote 合子allele 等位基因genotype 基因型phenotype 表现型test cross 测交oryza sativa 水稻diploid 二倍体haploid 单倍体centromere 着丝粒satellite 随体linker 连丝mitosis 有丝分裂mesoblast中胚层spindle 纺锤体interphase 间期spindle fiber 纺锤丝vicia faba蚕豆nucleoplasm 核质spermatogenous 精原细胞oogonium 卵原细胞spermatid 精细胞Phenocopy 拟表型epistasis上位效应mutant突变型gametic lethal配子致死zygotic lethal合子致死autosome 常染色体dominant lethal显性致死carrier 携带者homozygote 纯合体heterozygote 杂合体genotype 基因型phenotype 表现型linkage group 连锁群interference 干涉coincidence 并发率genetic map 遗传学图wild type野生型mutation 突变heterokaryon 异核体auxotroph 营养缺陷型strain 菌株recipient 受体donor 供体fragment 片段induction 诱导prophage 原噬菌体transduction 转导Mendel’s laws 孟德尔定律law of segregation 分离定律first filial generation 子一代parental generation 亲代dominant character 显性性状recessive character 隐性性状hereditary determinant 遗传因子parental combination 亲组合recombination 重组合punnett square 棋盘法Mendelian character 孟德尔性状primary constriction 初级缢痕secondary constriction 次级缢痕nucleolar organizer 核仁形成区first polar body 第一极体second polar body 第二极体sister chromatids 姐妹染色单体female gametic nucleus 卵核multiple alleles 复等位基因sex-chromosome性染色体sex-linked inheritance 伴性遗传primary constriction 初级缢痕secondary constriction 次级缢痕complementary gene互补基因homologous chromosome 同源染色体sister chromatids 姐妹染色单体secondary oocyte 次级卵母细胞three-point testcross 三点测交primary spermatocyte 初级精母细胞secondary spermatocyte 次级精母细胞first division segregation 第一次分裂分离second division segregation 第二次分裂分离law of independent assortment 自由组合定律Biochemistry 生物化学essential element必需元素trace elements微量元素proteoglycan蛋白聚糖amino acid氨基酸primary structure 一级结构random coil无规卷曲structural domain 结构域subunit亚基degeneration变性adenine腺嘌呤guanine鸟嘌呤cytosine胞嘧啶thymine胸腺嘧啶uracil尿嘧啶nucleoside 核苷nucleotide核苷酸base pairing碱基配对base pair碱基对数base碱基数gyrase旋转酶nucleosome核小体complementary DNA互补DNA plasmid质粒transposons转座子repetitive sequence重复序列exon外显子intron内含子variable loop可变环ribonuclease核糖核酸酶renaturation复性hyperchromic effect增色效应base stacking force碱基堆积力annealing退火melting-out temperature熔解温度hypochromic effect减色效应maltose麦芽糖sucrose蔗糖lactose乳糖starch淀粉glycogen糖原cellulose纤维素cellulase纤维素酶selectivity选择性substrate底物holoenzyme全酶cofactor辅因子coenzyme辅酶oxidase氧化酶metabolism新陈代谢assimilation同化作用catabolism异化作用metabolite代谢产物biological oxidation 生物氧化cytochrome细胞色素rotenone鱼藤酮amytal阿密妥antimycin A抗霉素A cyanide氰化物glycolysis糖酵解ethanol乙醇citrate柠檬酸cis-aconitate 顺乌头酸succinic acid琥珀酸oxaloacetic acid草酰乙酸acetyl-coenzyme乙酰辅酶fumarate延胡索酸glyoxylate cycle 乙醛酸循环malate苹果酸fatty acid 脂肪酸carbon unit一碳单位replicon复制子core enzyme 核心酶primosome引发体Okazaki fragment冈崎片段leading chain 前导链lagging strand后随链terminator终止子telomere端粒telomerase端粒酶replication fork复制叉vector载体promoter启动子terminator终止子operon操纵子codon密码子degeneracy简并性hormone激素citric acid cycle 柠檬酸循环deamination脱氨基作用urea cycle尿素循环euchromatin常染色质messenger RNA信使RNAtransfer RNA转移RNA ribosome RNA核糖体RNA metabolic regulation代谢调节feedback regulation反馈调节structural gene结构基因promoter gene启动基因operator gene操纵基因regulator gene调节基因termination factor终止因子triplet code三联体密码initiator codon起始密码termination codon终止密码semiconservative replication半保留复制ornithine cycle鸟氨酸循环ketogenic amino acid生酮氨基酸glucogenic amino acid生糖氨基酸oxidative deamination氧化脱氨作用transamination转氨基作用reverse transcription逆转录decarboxylation脱羧作用semidiscontinuous replication半不连续复制reverse transcriptase 逆转录酶missense mutation错义突变synonymous mutation同义突变neutral mutation中性突变nonsense mutation无义突变phosphatidic acid 磷脂酸essential amino acids 必需氨基酸dihydrouracil loop二氢尿嘧啶环anticodon loop反密码子环double-strand circular DNA 双链环形DNA superhelical DNA 超螺旋DNA open circular DNA 开环DNA linear DNA 线形DNAbase stacking force 碱基堆积力secondary structure二级结构super-secondary structure超二级结构tertiary structure三级结构quaternary structure四级结构negative supercoil DNA负超螺旋DNA positive supercoil DNA正超螺旋DNAGlyceraldehyde-3-phosphate甘油醛-3-二磷酸glucogenic and ketogenic amino acid生糖兼生酮氨基酸restriction endonuclease限制性内切酶polymerase chain reaction聚合酶链反应Microbiology微生物学living creatures 生物culture medium 培养基lawn菌苔culture plate 培养平板bacteria 细菌archaea 古生菌eukaryote真核生物prokaryote 原核生物protozoan 原生动物hypha 菌丝mycoplasma 支原体yeast 酵母菌plasmolysis 质壁分离Escherichia Coli大肠杆菌murein胞壁质peptidoglycan 肽聚糖mucopeptide黏肽outer membrane外膜chromosome染色体nucleolus 核仁nucleoid 拟核chromatin 染色质centromere 着丝粒telomere 端粒protoplast 原生质体mycoplasma 支原体glycoprotein 糖蛋白mesosome 间体cytoplasm细胞质megnetosome磁小体nucleoid拟核glycocalyx 糖被capsule 荚膜flagellum 鞭毛lysosome 溶酶体chloroplast 叶绿体thylakoid类囊体inorganic salt 无机盐peptone 蛋白胨sulfur bacteria 硫细菌beef extract牛肉膏vitamin 维生素inclusion body 内含物lithotroph 无机营养型medium 培养基agar 琼脂organotroph 有机营养型antiport 逆向运输active transport 主动运输pinocytosis 胞饮作用catabolism 分解代谢passive transport 被动运输uniport 单向运输anabolism 合成代谢fermentation发酵batch culture 分批培养log phase 对数生长期stationary phase 稳定生长期lag phase 迟缓期decline phase衰亡期aerobe 好氧菌antibiotic 抗生素antigenome 反基因组transformation 转化genome 基因组plasmid 质粒transforming factor 转化因子diploid 二倍体haploid 单倍体transposable element 转座因子conjugation接合作用transposon转座子phenotype 表型genotype基因型auxotroph营养缺陷型wild-type野生型transition 转换transversion 颠换spontaneous mutation 自发突变reverse mutation 回复突变sexduction 性导transduction 转导promoter 启动子operon 操纵子recombination repair 重组修复repressor 阻遏蛋白corepressor辅阻遏物clone 克隆denaturation 变性annealing 退火extension 延伸cloning vector 克隆载体replicon 复制子telomere 端粒cohesive end 黏性末端promoter 启动子terminator 终止子gene therapy 基因治疗phylogeny 系统发育ammonification 氨化作用nitrification 硝化作用denitrification 反硝化作用expression vector 表达载体aerobic respiration有氧呼吸anaerobic respiration无氧呼吸origin of replication 复制起始点incompatibility 不亲和性gene mutation 基因突变synonymous mutation 同义突变chromosomal aberration 染色体畸变missense mutation 错义突变frame-shift mutation 移码突变lactose operon 乳糖操纵子negative transcription control 负转录调控tryptophan operon 色氨酸操纵子cytoplasmic inheritance 细胞质遗传genetic engineering 基因工程recombinant DNA technology 重组DNA技术palindromic structure 回文结构spread plate method 涂布平板法pour plate method 倾注培养法streak plate method 平板划线法shake tube method 稀释摇管法continuous culture 连续培养。
CELL MEMBRANE(细胞膜)1.The cell membrane is also called plasma membrane. It's a layer separating the inside of the cell from the outside of the cell.2.The cell membrane is composed of a bi-layer of phospholipids(磷脂双分子层)with proteins embedded in it.3. One molecule of phospholipid is composed of a polar(极性)head which contains phosphate(磷酸盐)and a nonpolar(非极性) tail which contains fatty acid(脂肪酸). The polar head loves water, so it's hydrophilic(亲水的). The nonpolar tail hates water, so it's hydrophobic(疏水的).4.The cell membrane is selectively permeable(选择透过性). It controls what comes in and out of the cell. It does not let large, charged(带电的)or polar things through.5.Glycoproteins(糖蛋白)、Glycolipids(糖脂):Basically, they are carbohydrates(糖类/碳水化合物). If the carbohydrates are attached to protein, it's called glycoprotein. If they are attached to lipid, it's called glycolipids.Glycoproteins and glycolipids have the same function. They both act as receptors: receive information from outside the cell.6.Integral proteins(贯穿载体蛋白)assist specific larger molecules(glucose,葡萄糖)and charged molecules(ion,离子)to move in and out of the cell.7.Peripheral proteins(镶嵌、嵌入载体蛋白)assist integral proteins and glycoproteins.8.Cholesterol(胆固醇)reduces membrane fluidity by reducing phospholipid movement.9. The model used to explain the cell membrane is called the Fluid Mosaic Model(流动镶嵌模型).KEY WORDScell membrane 细胞膜bi-layer of phospholipids 磷脂双分子层glucose 葡萄糖polar 极性的ion 离子nonpolar 非极性的cholesterol 胆固醇phosphate 磷酸盐fatty acid 脂肪酸hydrophilic 亲水的hydrophobic 疏水的selectively permeable 选择透过性charged 带电的glycoprotein 糖蛋白glycolipid 糖脂carbohydrates 碳水化合物/糖类。
细胞生物学考研名词解释汇总以下是细胞生物学考研常见的名词解释:1. 细胞膜(cell membrane):细胞外界环境与细胞质之间的物质透过口。
它是由脂质双层以及被嵌入其中的蛋白质所组成的。
2. 细胞质(cytoplasm):细胞膜与细胞核之间的区域,含有细胞器和细胞基质。
3. 细胞核(cell nucleus):细胞的控制中心,含有遗传物质DNA和RNA。
4. 粒线体(mitochondria):细胞内的能量中心,通过产生三磷酸腺苷(ATP)参与能量代谢。
5. 液泡(vacuole):在植物细胞中,贮存水分、养分和废物的泡状结构。
6. 淋巴液(lymph):细胞之间的液体介质,含有细胞中的营养物质和废物。
7. 核糖体(ribosome):负责转录mRNA并合成蛋白质的细胞质小颗粒。
8. 高尔基体(Golgi apparatus):负责蛋白质的修饰、分拣和包装。
9. 酶(enzyme):催化化学反应的蛋白质分子,通过降低活化能来加速反应速率。
10. 膜蛋白(membrane protein):嵌入细胞膜内的蛋白质,负责物质的转运、信号传导和细胞识别。
11. 染色体(chromosome):DNA和蛋白质的结合体,包含基因信息。
12. 胞吐(exocytosis):通过细胞膜的融合,将细胞内物质排出细胞体外。
13. 胞吞(endocytosis):通过细胞膜的包裹,将细胞外物质引入细胞内。
14. 细胞周期(cell cycle):细胞从一个完整的分裂到下一个分裂的过程。
15. 细胞分裂(cell division):细胞繁殖过程,包括有丝分裂和减数分裂两种方式。
细胞生物学名词解释(完整)翟中和2006-3-29 19:17:00细胞生物学名词解释全集(1)1. 细胞(cell)细胞是由膜包围着含有细胞核(或拟核)的原生质所组成, 是生物体的结构和功能的基本单位, 也是生命活动的基本单位。
细胞能够通过分裂而增殖,是生物体个体发育和系统发育的基础。
细胞或是独立的作为生命单位, 或是多个细胞组成细胞群体或组织、或器官和机体;细胞还能够进行分裂和繁殖;细胞是遗传的基本单位,并具有遗传的全能性。
2. 细胞质(cell plasma)是细胞内除核以外的原生质, 即细胞中细胞核以外和细胞膜以内的原生质部分, 包括透明的粘液状的胞质溶胶及悬浮于其中的细胞器。
3. 原生质(protoplasm)生活细胞中所有的生活物质, 包括细胞核和细胞质。
4. 原生质体(potoplast)脱去细胞壁的细胞叫原生质体, 是一生物工程学的概念。
如植物细胞和细菌(或其它有细胞壁的细胞)通过酶解使细胞壁溶解而得到的具有质膜的原生质球状体。
动物细胞就相当于原生质体。
5. 细胞生物学(cell biology)细胞生物学是以细胞为研究对象, 从细胞的整体水平、亚显微水平、分子水平等三个层次,以动态的观点, 研究细胞和细胞器的结构和功能、细胞的生活史和各种生命活动规律的学科。
细胞生物学是现代生命科学的前沿分支学科之一,主要是从细胞的不同结构层次来研究细胞的生命活动的基本规律。
从生命结构层次看,细胞生物学位于分子生物学与发育生物学之间,同它们相互衔接,互相渗透。
6. 细胞学说(cell theory)细胞学说是1838~1839年间由德国的植物学家施莱登和动物学家施旺所提出,直到1858年才较完善。
它是关于生物有机体组成的学说,主要内容有:①细胞是有机体,一切动植物都是由单细胞发育而来,即生物是由细胞和细胞的产物所组成;②所有细胞在结构和组成上基本相似;③新细胞是由已存在的细胞分裂而来;④生物的疾病是因为其细胞机能失常。
Cell Membrane
Variation of biomembranes in different cells
The faces of cellular membranes
•Cytosolic face
•Exoplasmic
face
Phospholipid bilayers •The phospholipid bilayer, the basic structural unit of all biomembranes, is a two-dimensional lipid sheet with hydrophilic faces and a hydrophobic core, which is impermeable to water-soluble molecules and ions.
Properties:
•Semi-permeable barrier
•Stable structure maintained by van der Vaals and hydrophobic interaction.
•Lipid •Protein •Carbohydrate
•The primary lipid components of biomembranes are phosphoglycerides, sphingolipids, and steroids.
磷酸甘油脂
glycerol
sphingosine 鞘磷脂
•A phospholipid is a lipid that has a positively charged head that is linked by a phosphate group to the fatty acid tails.
•A glycolipid has a head consisting of an oligosaccharide, linked to a fatty acid tail. •A sterol is a compound containing a planar steroid ring.
General features of lipids
•Amphipathic structures have two surfaces, one hydrophilic and one hydrophobic. •Lipids are amphipathic.
•Some protein regions may form amphipathic helices, with one charged face and one neutral face.
•Different cellular membranes vary in lipid composition .
•Phospholipids and sphingolipids are asymmetrically distributed in the two leaflets of the bilayer, whereas cholesterol is fairly evenly distributed in both leaflets.
Asymmetry of lipids
Phosphatidylserine(PS) only locates on the cytosolic face and glycolipids (oligosaccharide) on the exoplasmic face.
Fluidity of Biomembrane •Most lipids and many proteins are laterally mobile in biomembranes.
Fluorescence recovery after photobleaching (FRAP) experiments.
•Natural biomembranes generally have a fluidlike consistency. In general, membrane fluidity is decreased by sphingolipids and cholesterol and increased by phosphoglycerides.
Lipid rafts
PM
PC
Placental alkaline phosphatase (yellow peaks)
•Lipid rafts are microdomains containing cholesterol, sphingolipids, and certain membrane proteins that form in the plane of the bilayer. These aggregates are sites for signaling across the plasma membrane.
Protein Composition •On the basis of the nature of the membrane–protein interactions.–Integral protein
–Lipid-anchored protein
–Peripheral protein
Carbohydrates
•O-link, Ser
•N-link, Asp
Common features of biomembrane
•Selectively permeable, fluidity and asymmetry.。