
Review Exercises
1.True/False Questions.(10×1.5=15 points)
2.Multiple Choice Questions (10×1.5=15 points)
3.Essay Questions (3×10=30 points)
4.Case Analysis (2×20=20 points)
Essay Questions:
1. Describe the roles played by line managers and human resource professionals with respect to HRM. P7-8
(1) HR professionals typically assume the four areas of responsibility:
Establish HRM procedures
Develop/choose HRM methods
Monitor/evaluate HR practices
Advise/assist managers on HRM-related matters
(2) Line managers dir ect employees’day-to-day tasks.From an HRM perspective, line managers are the main people responsible for:
Implementing HRM practices
Providing HR professionals with needed input
2. What are the 16 HRM practices that enhance a firm’s competitive advantage suggested by Professor Jeffrey Pfeffer ? P12
Employment security Selectivity in recruiting
High wage Incentive pay
Employee ownership Information sharing
Participation and empowerment Teams and job redesign
Training and development Cross-utilization and cross-training
Symbolic egalitarianism Wage compression
Promotion from within Long-term perspective
Measurement of practices Overarching philosophy
3. Discuss how job analysis lays the foundation for HRM practices that lead to competitive advantage.P45-46
(1)Laying the foundation for recruitment and selection practice
(2)Laying the foundation for Training and development programs
(3)Laying the foundation for performance appraisal forms
(4)Laying the foundation for compensation decisions
……..
4. Understand how a firm’s human resource management practices can help it gain a competitive advantage. P11 P12-17
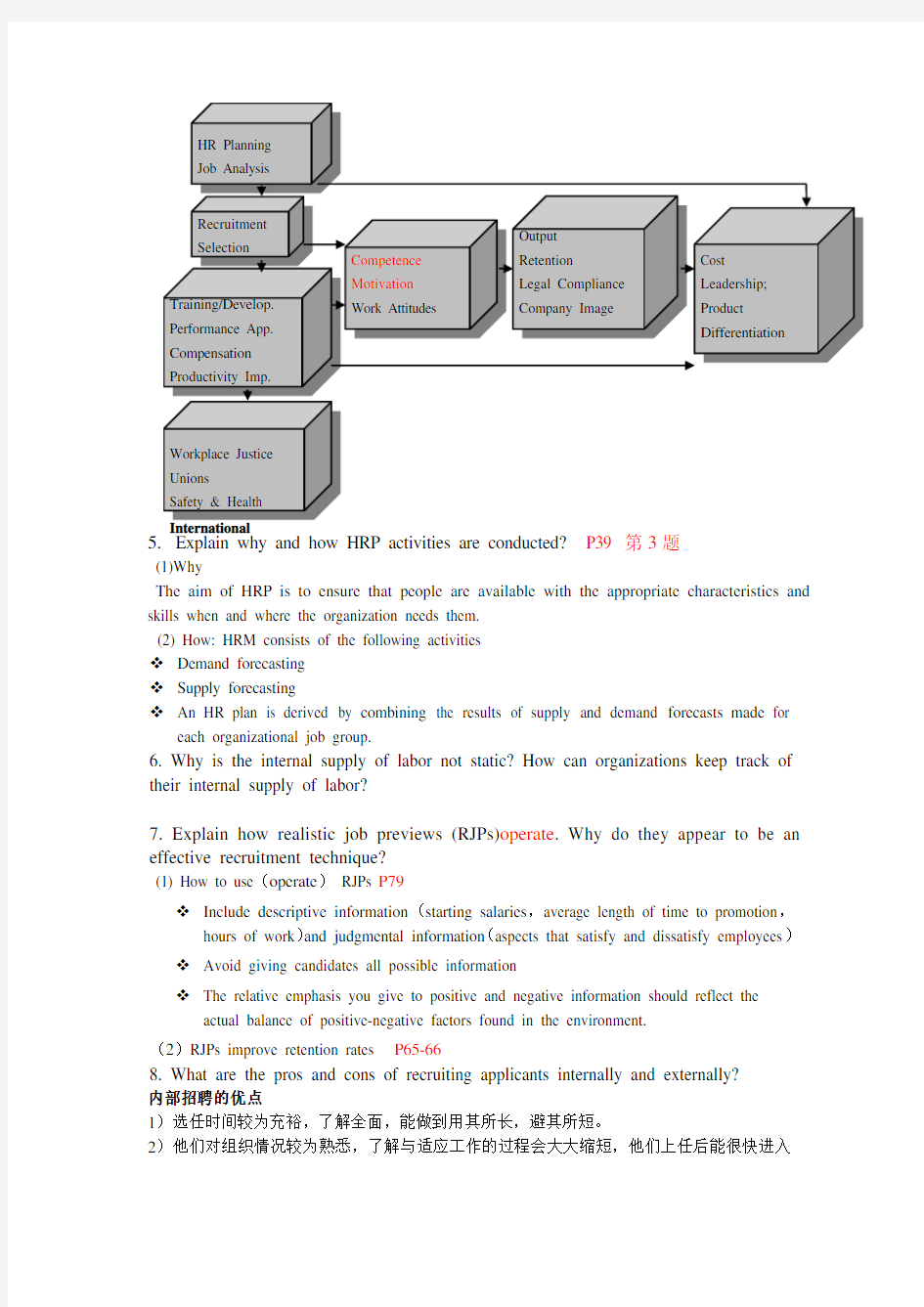
5.Explain why and how HRP activities are conducted?P39 第3题
(1)Why
The aim of HRP is to ensure that people are available with the appropriate characteristics and skills when and where the organization needs them.
(2) How: HRM consists of the following activities
Demand forecasting
Supply forecasting
An HR plan is derived by combining the results of supply and demand forecasts made for each organizational job group.
6. Why is the internal supply of labor not static? How can organizations keep track of their internal supply of labor?
7. Explain how realistic job previews (RJPs) operate. Why do they appear to be an effective recruitment technique?
(1) How to use(operate)RJPs P79
Include descriptive information(starting salaries,average length of time to promotion,hours of work)and judgmental information(aspects that satisfy and dissatisfy employees) Avoid giving candidates all possible information
The relative emphasis you give to positive and negative information should reflect the actual balance of positive-negative factors found in the environment.
(2)RJPs improve retention rates P65-66
8. What are the pros and cons of recruiting applicants internally and externally?
内部招聘的优点
1)选任时间较为充裕,了解全面,能做到用其所长,避其所短。
2)他们对组织情况较为熟悉,了解与适应工作的过程会大大缩短,他们上任后能很快进入
角色。
3)内部提升给每个人带来希望,有利于鼓舞士气,提高工作热情,调动员工的积极性,激发他们的上进心。
内部招聘的缺点
1)容易造成“近亲繁殖”。老员工有老的思维定势,不利于创新,而创新是组织发展的动力。2)容易在组织内部形成错综复杂的关系网,任人唯亲,拉帮结派,给公平、合理、科学的管理带来困难。
3)内部备选对象范围狭窄。
外部招聘的优点
1)来源广泛,选择空间大。特别是在组织初创和快速发展时期,更需要从外部大量招聘各类员工。
2)可以避免“近亲繁殖”,能给组织带来新鲜空气和活力,有利于组织创新和管理革新。此外,由于他们新近加入组织,与其他人没有历史上的个人恩怨关系,从而在工作中可以很少顾忌复杂的人情网络。
3)可以要求应聘者有一定的学历和工作经验,因而可节省在培训方面所耗费的时间和费用。外部招聘的缺点
1)难以准确判断他们的实际工作能力。
2)容易造成对内部员工的打击。
3)费用高。
9. What is meant by “transfer of training?” What can be done to help ensure transfer?
(1) Transfer of training: material learned in training is applied to the job P126
(2)A manager can help ensure transfer by these means:
Discuss with employees what the program covered and how it can be applied to the job.
Assign employees tasks that require them to apply the knowledge learned in training
Give employees coaching and feedback regarding their performance of assigned tasks. 10. Describe how training evaluations should be conducted.
Level I: Reaction—How did the student feel and what did they think about the training? Distribute an evaluation or feedback form. This is often called a “smilesheet”
and can be administered in either paper format or online format. This type of evaluation is usually inexpensive and used by most organizations. Be sure to distribute evaluations immediately after training ends. You can include questions to evaluate the instructor, material covered, training materials and audio visual equipment.
Level II: Learning—How much did the student learn?To assess the amount of learning, consider using pre-tests and post-tests. The tests attempt to determine how students have advanced with regards to skills, knowledge and attitude.
Level III: Behavior—What is the extent of behavior and capability improvement and implementation/application? To determine the extent of behavior and capability improvement, consider observing learners for an extended period of time after training is completed. This can be measured via post training interviews, monitoring progress and meeting with headmasters of the learners to determine if the training has allowed the learner to excel in his/her study.
Level IV: Results—What impact on the organization did the training have as a result of the learner’s performance? T o determine the impact of the training program,
key performance indicators include student satisfaction, achievements, social status and other types of quantifiable aspects of the performance of the organization.
11. Discuss the pros and cons of using different potential raters to appraise a person’s performance.
Supervisory ratings
Peer ratings
Self-ratings
Using multiple raters: 360-degree feedback systems
各类考评者的具体优劣势分析详见课本P145-146
12. Explain how a firm should develop its performance appraisal system. P143-147 Gainning support for the system
Gain the support of upper-level managers
Gain the support of employees
Choosing the appropriate rating instrument
Choosing the raters
Supervity ratings
Peer ratings
Self-ratings
Using multiple raters: 360-degree feedback systems
Determing the appropriate timing of appraisals
Ensuring appraisal fairness
Upper-level management review
Appeals system
13. How organizations can build an equitable pay system? P160-167 &P177第2题(1)Internal consistency
job evaluation: A systematic process for determining the worth of a job
Pay grades: Job groupings in which all jobs assigned to the same group are subject to the same range of pay
(2) External competitiveness
salary survey
pay policies
pay rates
(3) Employee contributions
pay range
skill-based pay
14. Explain why an organization may choose to develop a cafeteria benefits plan for its employees? P 172
. Why should we conduct cafeteria (flexible)benefit plan?
Such plans enable employees to choose options that best fit their own needs. New workers, for example, may prefer cash; parents may prefer to invest their benefit dollars in
employer-sponsored child-care programs; and older workers may decide to increase their pension and health care coverage.
Deciding among the various options makes employees more aware of the cost of the benefits, giving them a real sense of the value of the benefits their employers provide.
Flexible benefit plans can lower compensation costs because employers no longer have to pay for unwanted benefits.
Employers and empolyees can save on taxes. Many of the premiums may be paid with pretax dollars, thus lowering the amount of taxes to be paid by both the empolyee and the employer. True/False Questions:
1. Human resources management practices and issues are primarily a concern for the human resources department. F
2. The HR department conducts performance appraisals, develops the appraisal tools, and monitors the appraisal system. F
3. Most human resources practices have little relevance for line managers. F
4. The division of human resource responsibilities for line managers and staff managers varies from organization to organization. T
5.Because HR managers function in a support role, their job knowledge needs to focus primarily on HR issues rather than the operating goals of the company. F
6. Conducting the job analysis is the sole responsibility of the HR specialist. F
7. A job specification is a statement of the tasks, duties, and responsibilities of a job.F
8. Job specifications describe the duties, tasks, and responsibilities performed on the job and therefore play a key role in performance appraisal. F
9. Observation as a data collection method in a job analysis is most appropriate for jobs entailing a lot of mental activity. F
10. Effective recruiting results in a large number of applicants. F
11. Selection tests should be used as supplements to other tools like interviews and background checks. T
12. When it refers to filling jobs like that of a maintenance clerk, personnel planning is called succession planning. F
13. Apprenticeship training combines the practical and theoretical aspects of the work both on and off the job. T
14. Sensitivity training seeks to increase participants’ insight into their own behavior and the behavior of others by encouraging an open expression of feelings in a trainer guided t-group. T
15. Orientation refers to the methods used to give new or present employees the skills they need to perform their jobs. F
16. The real issue in evaluating training is whether training efforts translate to changes in job performance. T
17. Interviewers tend to be more influenced by unfavorable than favorable information about a candidate.T
18. 360-degree feedback is generally used for development purposes, rather than for pay increases. T
19. A job specification is a statement of the tasks, duties, and responsibilities of a job.F
20. Appraisal discussions should focus on the employee rather than on his or her behaviors. F
21. Managers who receive feedback from subordinates who identify themselves view the upward appraisal process more negatively than do managers who receive anonymous feedback. F
22.Succession planning is the process of identifying, developing, and tracking key individuals so that they may eventually assume top-level positions. T
23. Like any other component of the human resources program, an employee benefits program should be based on specific objectives. T
24. Broadbanding refers to collapsing many traditional salary grades into a few wide salary bands. T
25. External equity refers to how fair the job’s pay rate is, when compared to other jobs within the same company. F
26. The four categories of training outcomes are reactions, learning, behavior, and results. T
27. The forced distribution method is similar to grading on a curve meaning that predetermined percentages of those being rated are placed into performance categories. T
28. Self-appraisals should be used primarily for administrative purposes. F P145
29. Competency-based pay plans tie pay to seniority as well as to competence. F
30. There is no standard format for writing a job description. T
Multiple Choice Questions:
B. dependent on government employment statistics to be completed accurately
C. combined to identify a firm’s specific staffing needs
D. more difficult to complete in times of business stability
2. Suppose a salesperson traditionally generates $500,000 in sales and the company wishes to increase sales by $4 million dollars per year. Using ratio analysis, how many new salespeople are required? D
A. 4
B. 5
C. 6
D. 8
3. In general, HR managers do not: A
A. conduct performance evaluations of production employees
B. investigate accident reports
C. develop training programs
D. negotiate collective bargaining agreements
4. When Amanda interviewed for a job with the employment commission, the interviewer warned her that the job could be very stressful with long hours and a lot of bureaucracy. The interviewer was trying to provide __B___.
A. reality shock
B. a realistic job preview
C. a disincentive
D. a challenge
4.Sources of performance deficiencies in an employee may develop from a lack of
__E___.
A. training
B. supplies
C. support systems
D. rewards
E. all of the above
5. HR planning is defined as. C
A. reactive method of dealing with human resource problems
B. a self-contained process that seeks to identify the strengths and weaknesses of human resource systems apart from general strategic planning
C. a process and a set of activities that attempts to respond to an organization’s need for human resources under changing conditions
D. the process by which resources (e.g., equipment, raw materials) are allocated to specific individuals (i.e., humans) in the work organization
6. The best way of reducing the problem of central tendency in performance appraisals is to __A___.
A. rank employees
B. be aware of the problem
C. train supervisors to avoid it
D. impose a distribution for performance
E. consider the purpose of the appraisal
7. Which statement best describes the relationship between line management and HR Professionals? A
A. HR professionals focus more on developing human resource programs; line managers are more involved in implementing those programs
B. HR professionals are solely responsible for evaluating programs designed to manage human resources
C. Line management requires the services of the HR professional only infrequently
D. Line management focuses more on developing human resource programs; the HR professional is more involved in implementing programs
8. __B__ means that the order in which an interviewer sees applicants affects how the candidates are rated.
A. Context error
B. Contrast error
C. Order effect
D. Recency error
E. Primacy effect
9. An advantage of conventional lecturing over the use of audiovisual-based training is that ___B__.
A. audiovisuals are more boring
B. audiovisuals are more expensive
C. audiovisuals allow for instant replay and stop-action
D. audiovisuals can show events that are not easily demonstrated in live lectures
E. audiovisuals can be easily sent to all locations
10. When conducting an appraisal interview, supervisors should do all of the following except D
A. talk in terms of objective work data
B. compare the person’s performance to a standard
C. give specific examples of poor performance
D. compare the person’s performance to that of other employees
11. Graphic rating scales are subject to all of the following problems except __C___.
A. unclear standards
B. halo effects
C. complexity
D. central tendency
E. leniency
12.For which of the following jobs is direct observation not recommended to collect data used in a job analysis? C
A. assembly-line worker
B. accounting clerk
C. engineer
D. receptionist
E. salesperson
13. What type of information is contained in the job identification section of a job description? A
A. job title
B. job summary
C. relationships statement
D. major functions or activities
E. all of the above
14.When a company decides on how to fill top executive positions, the process is called __B___.
A. employment planning
B. succession planning
C. selection
D. interviewing
15.When designing an actual appraisal method, the two basic considerations are
__D______.
A. who should measure and when to measure
B. when to measure and what to measure
C. what to measure and who should measure
D. what to measure and how to measure
16.When __D___ are measured to assess the effectiveness of a training program, variables such as liking of the program, satisfaction with the program, and attitude toward the program are assessed.
A. learning outcomes
B. behavioral outcomes
C. results
D. reactions
16. The use of HRM practices can promote a sustained competitive advantage because D
A. being the first to institute an innovative HR practice discourages a firm’s competition
B. HR practices cannot be imitated
C. people are a firm’s most valuab le resource
D. the organizational environment in which innovative HR practices are implemented can rarely be duplicated
17. For which of the following jobs is direct observation not recommended to collect data used in a job analysis? C
A. assembly-line worker
B. accounting clerk
C. engineer
D. receptionist
18.The use of HRM practices can promote a sustained competitive advantage because
A. being the first to institute an innovative HR practice discourages a firm’s competition D
B. HR practices cannot be imitated
C. people are a firm’s most valuable resource
D. the organizational environment in which innovative HR practices are implemented can rarely be duplicated
19.Which type of job analysis information would be most useful for communicating job tasks to a new worker? A
A. Job content
B. Job context
C. Worker requirements
D. Performance standards
20. On-the-job training can be accomplished through the use of all of the following techniques except ___B_____.
A. coaching
B. programmed learning
C. understudy
D. job rotation
21. All of the following occupations except __D___ use apprenticeship training to prepare trainees.
A. cook
B. electrician
C. operating engineer
D. teacher
22. Organizational citizenship concerns. A
A. an employee’s willingness to engage in work behaviors that are not usually specified in a job description
B. the relative strength of an employee’s identification with and involvement in a particular organization
C. the favorableness of an employee’s attit ude toward his or her job
D. the tendency of an organization to be involved in the civic affairs of the community in which it reside
23. When a supervisor must criticize a subordinate in an appraisal interview, it is best to ___B__.
A. hold the meeting with other people who can diffuse the negative situation
B. provide examples of critical incidents
C. acknowledge the supervisor’s personal biases in the situation
D. provide feedback once per year
E. surprise the employee so they cannot develop excuses for poor performance
24. Which of the following methods is not used to recruit outside candidates? B
A. advertising
B. job postings
C. employment agencies
D. executive recruiters
25. Rebekah was hired soon after graduation and assigned to complete a management trainee program. She will move to various jobs each month for a nine-month period of time. Her employer is utilizing the __A___ form of training.
A. job rotation
B. understudy
C. coaching
D. special assignments
26.___B____ means that the order in which an interviewer sees applicants affects how the candidates are rated.
A. Context error
B. Contrast error
C. Order effect
D. Recency error
27. ____B____ is established by setting the organization’s pay level in comparison with what the competition pays for similar work.
A. Internal consistency B .External competitiveness C. Employee contributions
D. Administration
28. A company using competency-based pay compensates for all of the following except an employee’s ____B____.
A. range of skills
B. job title
C. depth of knowledge
D. type of skills
29. Which of the following pieces of information deals with job content? A
A. Greets visitors as they enter the store
B. Works in cramped quarters with poor ventilation
C. Able to type at least 40 words per minute
D. Must possess a CPA (accounting)
30. __C___ is the procedures through which one determines the duties associated with positions and the characteristics of people to hire for those positions.
A. Job description
B. Job specification
C. Job analysis
D. Job context
《人力资源管理》复习资料 一、选择题(含多项选择) 1、下列不包括在现实的人力资源数量内的是(B ) A未成年就业人口B暂不能参加社会劳动的人口 C适龄就业人口D老年就业人口 A失业人口B暂不能参加社会劳动的人口 C老年就业人口D其他人口 2、下列选项中现实的人力资源数量是(A. C ) A人口资源〉人才资源〉人力资源B人力资源〉人口资源〉3、人口资源、人力资源和人才资源的关系正确的是(D ) C人才资源〉人口资源〉人力资源D人口资源〉人力资源〉人才资源 人才资源 4、人力资源的特征有(A、B、C、D、E) A能运性B时效性C生物性 D社会性E双重性 5、人力资源管理的主要任务有(A、B、C、E ) A识才B用才C人才开发 D激励人才E留住人才 6、人力资源管理的工作内容有(A、C、D、E、F ) A制订人才资源计划B招聘人员C培训与教育员工D绩效考核E薪酬管理F劳动关系管理
7.工作设计的主要内容包括(A、B、
8、企业进行工作分析是因为出现了(A、B、C、E ) A新建企业或新组的部门为满足组织设计与人员招聘的需要 B企业的工作内容、工作性质发生变化 C企业劳动生产率的提高 D企业想看新制定薪酬激励制度 E企业完善员工培训机制 A工作内容B工作职责C工作环境 9、工作说明书包括(A、B、C、D ) D工作任务E任职者所需的资格要求 10.工作规范一般包括(A、B. C、E ) A—般要求:包括年龄、性别、学历.工作经验等 B生理要求:包括健康状况、力量与体力、运动的灵活性、感觉器官的灵敏度等 C心理要求:包括观察能力、集中能力、记忆能力、理解能力等D工作任务要求 E考核项目和标准 A统一规范B清晰具体 11、工作说明书编写的原则有(A、B. C、D ) C范围明确D共同参与 12、业务规划是指在总体规划指导下的各种专项业务规划,具体包括(A、B、C. D、E )等内容。 A人员补充计划B人员配备计划
人力资源管理试题及答案
人力资源管理复习题 、单项选择题 现代人力资源管理中,“以人为本”的理念是指( B ) 把人当成“上帝”,一切都服从、服务于“上帝” 把人当成组织中最具活力、能动性和创造性的要素 坚持群众路线,尊重群众意见 关心员工生活,提高员工物质文化生活水平 “深入工作现场,能比较全面地了解工作情况”是以下哪种工作分析法的优点( B ) 写实法 B.观察法 C.问卷法 D.参与法 由于人力资源管理正在向着战略性的方向发展,在人力资源管理领域中发展最为 速的是( A ) 人力资源规划 B.人力资源成本管理 .人力资源开发 D.人力资源绩效管理 对组织内部人力资源供给的预测,常用的方法有:马尔可夫分析法、档案资料分 法和( B ) 趋势分析法 B.管理者继任模型 C.德尔菲法 D.回归预测法 某公司今年离职人员数为30,而今年在职人员的平均数为150,那么,该公司的人员变动率是 A ) 20% B.10% C.15% D.25% 我国组织目前面临的一个重大问题是( A ) 人力资源过剩 B.人力资源浪费 .人力资源不足 D.人力资源管理不当 当职位空缺有许多种,而且在某一特定地区内又有足够的求职者的情况下,应该使用以下哪种招募形式 B ) 报纸 B.广播电视 C.杂志 D.招募现场的宣传资料 在人员甄选活动中,对一个人所学知识和技能的基本检测称之为( C ) 能力测试 B.人格测试 C.成就测试 D.兴趣测试 在人力资源规划中,为了保持组织在中、长期内可能产生的职位空缺而制定的人 资源规划称为( D ) 人力分配规划 B.调配规划 C.晋升规划 D.招聘规划 .世界上第一个兴趣测验量表是( A ) 斯特朗男性职业兴趣量表 比奈-西蒙量表 库德职业兴趣测验 爱德华个性偏好量表 .用轻的秤砣冒充重的秤砣会造成( B ) 随机误差 B.系统误差 信度变化 D.效度升高 .下图反映的是( C ) 信度高效度高 B.信度高效度低 信度低效度低 D.信度低效度高
人力资源管理练习题参考答案 一、单项选择题: 1.人力资源管理的最终目标是( D ) A.有效管理员工 B.达到组织体系和文化体系的协同发展 C.提高组织的生产力 D.组织目标的达成与组织战略的实现 2.在企业培训中( A )是最基本的培训方法。 A.讲授法 B.专题讲座法 C.角色扮演法 D.拓展法 3.在现代人力资源管理理念中,人力资源管理部门被视为 ( D ) A.事务性机构 B.服务性机构 C.非生产非效益部门 D.生产与效益部门 4.在招聘录用过程中,如果人力资源部与用人部门在人选上意见冲突时,应尊重( B ) A.人力资源部的意见 B.用人部门的意见 C.企业主管领导的意见 D.相关部门的意见 5.企业招聘测试中,完全不准备问题和答案的面试被称之为( B ) A.结构化面试 B.非结构化面试 C.半结构化面试 D.系列化面试 6.人力资源开发的主要途径之一是(A )。 A.培训 B.激励 C.招聘 D.选拔 7.我国职工的社会保险是(C ) A.自愿性保险 B.商业性保险 C.强制性保险 D.任意性保险 8. 企业发展与薪酬管理的关系是(D ) A.互相对立 B.互相矛盾 C.互相联系 D.相辅相成 9.人力资源质量指标主要体现为(D ) A.劳动力人数的多少 B.劳动者体质的好坏 C.劳动者智力的高低 D.劳动者体质和智力的和谐统一 10.绩效考核涉及的人员不包括( B ) A.高层领导 B.外部客户 C.全体员工 D. 人力资源部门人员 二、多项选择题: 1.企业进行薪酬管理的目的是(ABCE ) A.合理控制人工成本 B.吸引人才 C.激励员工 D.获取更大效益 E.留住人才 2.影响员工职业生涯选择的个人因素主要有( ABCD )。 A.个人心理特质 B.个人生理特征 C.学历经历 D.家庭背景 E.组织特色 三、名词解释: 1.招聘是寻找空缺职位的合格候选人的可能来源,并采用适当的方式吸引他们到企业来的应聘过程。 2.报酬指员工作为个人劳动的回报而从企业得到的各种类型的酬劳。包括经济报酬和非经济报酬。 3.人力资源管理简称HRM,是指有效的运用人力资源,以实现组织目标的过程。 四、简答题 1. 人力资源部门的职责建立人力资源管理的程序;开发与选择人力资源管理的方法;监控与评价人力资源管理活动;向直线管理者 提供建议咨询和服务。 2. 内部招聘的缺点申请岗位而未录用的员工积极性受到打击;在空缺岗位内定的情况下,还要与所有申请人面试,浪费时间;可 能引起妒忌、攀比的心理,或引发拉帮结派等派生问题;被提升的人面临艰难的角色转换;近亲繁殖,被提拔的人缺乏创造性。 3. 内部招聘的优点。 答: 能够鼓舞员工的士气,防止人才外流;企业对员工有很好的了解;员工对企业的情况较熟悉,容易进入工作状态,需要培训较少;员工对企业的目标有认同感并且不易辞职;节省招聘费用。 4. 培训的作用。 答: 消除员工因能力不足差劲的工作表现,降低员工的缺勤率和流动率;使员工掌握新技术,提高企业的生产力和竞争力;改善员
现代人力资源管理考试试题 一、辨析题。 1、人力资源和人力资本是同一个意思的两种说法,人力资本就是人力资源。(错)答:人力资源是指人所具有的对价值创造起贡献作用,并且能够被组织所利用的体力和脑力的总和。 对人力资本的解释 (1)人们以某种代价获得并能在劳动力市场上具有一种价格的能力或技能。(2)对人力资源进行开发性投资所形成的可以带来财富增殖的资本形式。 (3)人力资本指凝聚在劳动者身上的知识、技能及其表现出来的能力。 人力资源与人力资本比较: 人力资源和人力资本都是以人为基础而 产生的概念,研究的对象都是人所具有的脑力和体力,这一点是一致的。 不同点: (1)、社会财富和社会价值关系上,人力资本是由投资形成的,人力资源是劳动者本身所拥有的。 (2)、角度和关注重点不同。人力资本是从成本收益角度研究的,人力资源将人本身作为财富,从投入产出角度研究人对经济发展的作用。 (3)、计量形式不同,人力资源是存量概念,人力资本是流量和存量的结合。 (4)、人力资源包括现实的和潜在的劳动能力,人力资本则是能够直接创造价值的劳动能力。 2、人才属于人力资源,人力资源属于人口资源。(错) 答:人力资源是指人所具有的对价值创造起贡献作用,并且能够被组织所利用的体力和脑力的总和。 人口资源:一个国家或地区所拥有的人口的总量,它是一个最基本的底数,一切人力资源、人才资源皆产生于这个最基本的资源中。 人才资源:一个国家或地区中具有较多科学知识、较强劳动技能,在价值创造过程中起关键或重要作用的那部分人。人才资源是人力资源的一部分,即优质的人力资源。 在本质上,人口资源和人才资源是人,人力资源是能力,完全不同。 从数量上,人口资源>人力资源>人才资源3、职位分析是人力资源其他几个职能的基础。(对) 答:人力资源管理的基本职能:人力资源规划、职位分析、招聘录用、绩效管理、薪酬管理、培训与开发、员工关系管理。
人力资源管理专业词汇(中英文对照) 人力资源管理:(Human Resource Management ,HRM) 人力资源经理:( human resource manager) 高级管理人员:(executive) 职业:(profession) 道德标准:(ethics) 操作工:(operative employees) 专家:(specialist) 人力资源认证协会:(the Human Resource Certification Institute,HRCI) 外部环境:(external environment) 内部环境:(internal environment) 政策:(policy) 企业文化:(corporate culture) 目标/使命:(mission) 股东:(shareholders/stakeholder) 非正式组织:(informal organization) 跨国公司:(multinational corporation,MNC) 管理多样性:(managing diversity) 二、工作:(job) 职位:(posting) 工作分析:(job analysis) 工作说明:(job description) 工作规范:(job specification) 工作分析计划表:(job analysis schedule,JAS) 职位分析问卷调查法:(Management Position Description Questionnaire,MPDQ)行政秘书:(executive secretary) 地区服务经理助理:(assistant district service manager) 三、人力资源计划:(Human Resource Planning,HRP) 战略规划:(strategic planning) 长期趋势:(long term trend) 要求预测:(requirement forecast) 供给预测:(availability forecast) 管理人力储备:(management inventory) 裁减:(downsizing) 人力资源信息系统:(Human Resource Information System,HRIS) 四、招聘:(recruitment) 员工申请表:(employee requisition) 招聘方法:(recruitment methods) 内部提升:(Promotion From Within ,PFW) 工作公告:(job posting) 广告:(advertising) 职业介绍所:(employment agency) 特殊事件:(special events) 实习:(internship)
人力资源管理复习题 1.从微观的角度看,人力资源就是组织中的全体员工。 2.人力资源的构成包括:体质、智质、心理素质、品德、能力素养和情商。 3.人力资源的双重性是指人力资源具有生产性和消费性。 4.人力资源管理和人力资本理论的研究对象都是人,但人力资本主要研究投资 和收益问题,而人力资源则主要研究如何对企业内的员工进行管理。 5.人力资源对于企业的作用可以这样描述:通过提供人力资源产品和服务,员 工的需要得到满足,员工的生产率得以提高,员工为顾客提供满意的产品,顾客的需求得到满足,从而企业可以持续发展。 6.人力资源管理是指各种社会组织对员工的招募、录取、培训、使用、升迁、 调动直至退休的一系列管理活动。 7.人力资源开发:指国家或地区、企业、家庭、个人的正规国民教育、在职学 历教育、职业技能培训以及人的使用和启智等一系列活动,从而达到培养各类人才、开发人的潜能、提升人的质量的目的。 8.人力资源开发活动贯穿人的一生,人力资源管理只局限在人的从业阶段。 9.廖建桥认为人力资源管理是P1、P2、P3、P4、P5的函数,P1是指组织结构 设计和岗位分析,P2是指招聘和培训,P3是指绩效考核,P4是指薪酬福利,P5是指员工关系、员工激励和企业文化。 10.一般地认为,人力资源的职能主要包括:职位分析,人力资源规划、招聘与 甄选、培训管理、职业管理、绩效考核、薪酬管理和劳动关系管理,其中职位分析是其他所有管理职能的前提和基础。 11.企业高层管理者在人力资源管理中的责任是:组织结构设计、重大人事变更、 公司的薪酬方案和公司重人事政策的提议和批准。 12.在人力资源管理理论与职能的演进过程中,从人际关系阶段开始,人的社会 需要开始受到企业管理当局的重视。 13.从组织职责阶段,即上个世纪80年代开始,人事管理一词正式让位地人力资 源管理。 14.科学管理阶段、人际关系阶段,劳动运动阶段对人的管理可以称作是人事管
西安邮电学院高等函授 《人力资源管理》练习册 一、单项选择题 1.下面的(B)选项对“人力资源总量”的表述是正确的。 A、即人力资源的数量 B、即人力资源数量×质量 C、即总人口-非就业人口 D、即国内人力资源+驻外人员+海外留学生2.“现实人力资源”=(A)。 A、在业人口与求业人口总和 B、在业人口与军队服役人口 C、求业人口与老年就业人口 D、家务劳动人口与在业人口 3.中国规定的最低就业年龄是(A ) A、16岁 B、18岁 C、15岁 D、14岁 4.人力资源存在于两种不同条件之下, 即为(B ) A、现实人力资源和经济活动人口 B、现实人力资源和潜在人力资源 C、在业人口和求业人口 D、潜在人力资源和在业人口 5.人力资源与人力资本在(C)这一点上有相似之处。 A、价值 B、内涵 C、形式 D、人员素质 6.人力资源管理与人事管理的主要区别体现在(B)。 A、内容上 B、观念上 C、工作程序上 7.下列属于人力资源管理内部环境的项目是:C A、经济体制 B、法律制度 C、发展战略 D、政治体制 8.关于人力资源管理环境的辨识,变化小且数量大的是:B A、低度不确定性的环境 B、中低不确定性的环境 C、中高不确定性的环境 D、高度不确定性的环境 9.企业生命周期包括四个阶段,下列正确的是: A A、创业、集体化、正规化和合作 B、创业、发展、正规化和合作 C、集体化、发展、创业和正规化 D、创业、集体化、正规化和发展10.工作丰富化是指从(B )上赋予员工更复杂、更系列化的工作。A、横向 B、纵向 C、交叉 D、其他
11.工种轮换是让员工在(A )相似的工作之间不断调换,以减少枯燥单调感。 A、能力要求 B、技术要求 C、经验要求 D、个性要求 12.企业对新录用的员工进行集中的培训,这种方式叫做(A )。 A、岗前培训 B、在岗培训 C、离岗培训 D、业余自学 13.在培训中,先由教师综合介绍一些基本概念与原理,然后围绕某一专题进行讨论的培训方式是(B )。 A、讲授法 B、讨论法 C、角色扮演法 D、案例分析法 14.在培训中,利用受训者在工作过程中实际使用的设备或者模拟设备以及实际面临的环境来对他们进行培训的方式是(C )。 A、网络培训法 B、角色扮演法 C、工作模拟法 D、案例分析法 15.下面培训方法中不属于在职培训的方法是(D )。 A、学徒培训 B、辅导培训 C、工作轮换 D、案例分析法 16.对受训人员在接受培训后工作行为的变化的考察,反映了培训评估中对(C )的评估。 A、反应层 B、结果层 C、行为层 D、学习层 17.在培训需求分析中,针对员工进行的分析叫做(A )。 A、人员分析 B、任务分析 C、组织分析 D、工作分析 18.在培训需求分析中,针对企业内各个职位所进行的分析是(B) A、人员分析 B、任务分析 C、组织分析 D、工作分析 19.培训开发的主体是(C) A、员工 B、社会组织 C、企业 D、政府 20.对受训人员或企业绩效变化的考察,反映了培训评估中对(B)的评估。 A、反应层 B、结果层 C、行为层 D、学习层 21.目标管理法能使员工个人的(A)保持一致。 A、个人目标与组织目标 B、努力目标与组织目标 C、努力目标与集体目标 D、个人目标与集体目标 22.将人的资质作为确定等级结构主要依据的薪酬模式为(C) A、计件工资制 B、绩效工资制 C、技能工资制 D、职位工资制 23.目前在激励员工方面应用最普遍的员工所有权形式是(A) A、员工持股计划 B、股票期权计划 C、收益分享计划 D、利润分享计划
人力资源管理期末复习题及答案 一、单选题(每小题2分,共8分) 1、“社会人”人性理论假设的基础是什么?(D) A、泰勒的科学管理原理 B、梅奥的人际关系理论 C、马斯洛的需要层次理论 D、霍桑试验 2、根据劳动的复杂程度、繁重与精确程度和责任大小来划分等级,根据等级规定工资标准。这是种什么工资制度?(A) A.技术等级工资制 B.职务等级工资制 C.结构工资制 D.多元化工资制度 3、学术界经常提到的评价中心法是人力资源选拔的哪种方法?(D)
A、心理测验 B、面试 C、知识考试 D、情景模拟与系统仿真 4、教员请学员在可以全面观察操作的位置上观察,教员可以把工作的操作步骤向学员解释清楚,把这一步与下一步的联系是什么交待清楚。这是培训工作的哪一阶段?(B) A、准备阶段 B、演示阶段 C、试行操作阶段 D、随访阶段 5、一个国家或地区有较强的管理能力、研究能力、创造能力和
专门技术能力的人口总称为(C) A、人力资源 B、人口资源 C、人才资源 D、劳动力资源 6、制定利益相关者(包括股东、管理层、员工、监管机构、客户等)、财务增长标准、市场增长标准、品牌增长标准等指标体系、方法和工具。这是制定人力资源战略中的哪个步骤?(C) A、战略分析 B、战略选择 C、战略衡量 D、战略实施
7、通过检查人力资源目标的实现程度,提供关于人力资源计划系统的反馈信息。这是人力资源规划工作的哪项活力?(D) A、人员档案资料 B、人力资源预测 C、行动计划 D、控制与评估 8、员工离开组织之前由于工作效率低下而造成的损失费用应从人力资源成本的哪个项目中列支?(D) A、保障成本 B、开发成本 C、使用成本 D、离职成本 9、人力资源管理工作科学化的基础是(B)。 A、工作评价 B、工作分析
《人力资源管理》模拟题2 一、名词解释 1.人员甄选 俗称选拔,指采取科学的人员测评方法选择具有资格的人来填补职务空缺的过程。 2.晕轮效应 所谓晕轮效应是指在他人的某种特殊表现突出时,印象深刻,由此引起对其他特征的忽视, 从而产生以点概面的现象。 3.企业文化 企业文化是指在一定的社会大环境影响下,经过企业领导者的倡导和全体员工的认同与实践所形成的整体价值观念、信仰追求、道德规范、行为准则、经营特色、管理风格以及传统和 习惯的总和。 二、简答题 4.简述人力资源管理的目标。 5.简述问卷法的优缺点。 6.简述绩效工资制存在的问题。 7.简述加强人力资源成本管理的意义。 参考答案: 4.答:(1)建立科学的人力资源管理系统,达到有效管理员工的目的。(2)通过人与人、事与事、人与事关系的管理,在实现人员管理的同时,达到组织体系、文化体系协同发展的目的。(3)通过人力资源的管理,提高组织的生产率、实现组织目标。 5.优点:可以面面俱到,在短时间内收集尽可能多的工作信息;比较规范化、数量化,适合于用计算机对结果进行统计分析;可以收集到准确规范、含义清晰的工作信息;成本低,工作人员比较容易接受,可以随时安排调查。 缺点:问题事先已经设定,调查难以深入;设计质量难以保证,工作信息的采集受问卷设计水平的影响较大;对任职人员的知识水平要求较高;不能面对面地交流信息,从而了解不到被调查对象的态度和动机等较深层次的信息;不易唤起被调查对象的兴趣;除非问卷很 长,否则就不能获得足够详细的信息。 6.答:(1)对于员工而言,绩效工资制存在着风险,带来收入的不稳定。 (2)绩效与能力和态度并不完全相等。短期的业绩有时并不符合组织战略的需要。绩效工资制的关键是设置合理的业绩衡量指标,这些指标必须符合组织战略,将团队绩效与个体 绩效结合起来。 (3)绩效产生的原因是多方面的,有时与个人关系并不那么直接,市场、环境、组织系 统、工具设备、同事合作等都是影响绩效的重要因素。 (4)很多常规工作、基础工作并不直接与绩效相联系,因此很难用绩效来衡量。 (5)导致机会主义和实用主义,追求短期的绩效,不利于组织的长远发展。 7.答:(1)合理利用人力资源,提高企业效益 (2)加强人力资源成本管理有利于提高员工的劳动生产率 (3)有利于正确核算企业当期利益,合理分配利润 (4)有利于国家对全体社会人力资源进行宏观调控 三、论述题 8.为使组织的人力资源规划能充分体现弹性,应重点做好哪些工作 9.试述针对不同职位的员工培训内容的针对性。 参考答案: 8.答:为使组织的人力资源规划能充分体现弹性,适应未来高速变化的环境,应重点做好
页眉内容 Managing human resource Introduction Nowadays, as the stress of the competition become heavier and heavier, people who go to an interview or work in a firm pay more and more attention to the EEO. The EEO is the law of the Civil Rights Act of 1964 was the first federal law designed to protect most U.S. employees from employment discrimination based upon that employee's (or applicant's) race, color, religion, sex, or national origin. The Title also established the U.S. Equal Employment Opportunity Commission to assist in the protection of U.S. employees from discrimination.EEO legislation requires fair treatment for all members of the community and the elimination of discrimination. It means selecting the best person for the job in terms of their job-related skills. EEO includes following aspects: RACE, COLOR, RELIGION, SEX, NATIONAL ORIGIN Title VII of the Civil Rights Act of 1964, as amended, protects applicants and employees from discrimination in hiring, promotion, discharge, pay, fringe benefits, job training, classification, referral, and other aspects of employment, on the basis of race, color, religion, sex (including pregnancy), or national origin. Religious discrimination includes failing to reasonably accommodate an employee’s reli gious practices where the accommodation does not impose undue hardship. DISABILITY Title I and Title V of the Americans with Disabilities Act of 1990, as amended, protect qualified individuals from discrimination on the basis of disability in hiring, promotion, discharge, pay, fringe benefits, job training, classification, referral, and other aspects of employment. Disability discrimination includes not making reasonable accommodation to the known physical or mental limitations of an otherwise qualified individual with a disability who is an applicant or employee, barring undue hardship. AGE The Age Discrimination in Employment Act of 1967, as amended, protects
人力资源管理期末复习题 一.名词解释: 1.人力资源管理中的招聘:为了实现企业目标和完成任务,由人力资源管理部门和其他部门按照科学的方法,运用先进的手段,选拔岗位所需要的人力资源的一个过程。 2.培训:各组织为适应业务及培育人才的需要,采用补习、进修、考察等方式进行有计划地培养和训练,使员工适应新的要求,不断更新知识,更能胜任现职工作及将来能担任更重要的职务。 3.绩效:某一组织或员工在一定时间与条件下完成某一工作所表现出的工作行为和取得的工作结果。 4.绩效管理:为了更有效地实现组织目标,由专门的绩效管理人员运用人力资源管理的知识、技术和方法与员工一起进行绩效计划、绩效沟通、绩效考评、绩效反馈与改进、绩效结果应用的五个基本过程。 5.薪酬:企业向员工提供的报酬,用以吸引、保留和激励员工,具体包括:工资、奖金、福利、股票期权等。 6.经验推断法:企业的各级管理者,根据自己工作中的经验对企业未来业务量增减情况的直接考虑,自上而下地确定未来所需人员的方法。 7.劳动争议:又称劳动纠纷,许多国家和地区则称劳资争议和劳资纠纷,是指劳动法律关系当事人关于劳动权利、义务的争执。 8.职务分析:又称工作分析、岗位分析或职务分析,是人力资源管理的一项核心基础职能,它是一种应用系统的方法,收集、分析、确定组织中职位的定位、目标、工作内容、职责权限、工作关系、业绩标准、人员要求等基本因素的过程。 9.职业生涯管理:通过分析、评价员工的能力、兴趣、价值观等,确定双方能够接受的职业生涯目标,并通过培训、工作轮换、丰富经验等一系列措施,逐步实现员工职业生涯目标的过程。 10.直接观察法:职务分析人员观察所需要分析的工作过程,以标准格式记录各个环节的内容、原因和方法,这可以系统地收集一种工作的任务、责任和工作环境等方面的信息。 二.简答题: 1.人力资源规划的意义 (1)人力资源规划有助于企业发展战略的制定 (2)人力资源规划有助于企业保持人员状况相对的稳定 (3)人力资源规划有助于企业降低人力成本 (4)人力资源规划为人力资源管理的其他活动提供依据 2.人力资源管理有哪些重要意义
人力资源管理试题含答案 现代人力资源管理考试试题 一、辨析题。 1、人力资源和人力资本是同一个意思的两种说法,人力资本就是人力资源。(错) 答:人力资源是指人所具有的对价值创造起贡献作用,并且能够被组织所利用的体力和脑力的总和。 对人力资本的解释 (1)人们以某种代价获得并能在劳动力市场上具有一种价格的能力或技能。 (2)对人力资源进行开发性投资所形成的可以带来财富增殖的资本形式。 (3)人力资本指凝聚在劳动者身上的知识、技能及其表现出来的能力。人力资源与人力资本比较: 人力资源和人力资本都是以人为基础而产生的概念,研究的对象都是人所具有的脑力和体力,这一点是一致的。 不同点: (1)、社会财富和社会价值关系上,人力资本是由投资形成的,人力资源是劳 动者本身所拥有的。 (2)、角度和关注重点不同。人力资本是从成本收益角度研究的,人力资源将 人本身作为财富,从投入产出角度研究人对经济发展的作用。 (3)、计量形式不同,人力资源是存量概念,人力资本是流量和存量的结合。 (4)、人力资源包括现实的和潜在的劳动能力,人力资本则是能够直接创造价 值的劳动能力。 2、人才属于人力资源,人力资源属于人口资源。(错)
答:人力资源是指人所具有的对价值创造起贡献作用,并且能够被组织所利用的体力和脑力的总和。 人口资源:一个国家或地区所拥有的人口的总量,它是一个最基本的底数,一切人力资源、人才资源皆产生于这个最基本的资源中。 第 1 页共 13 页 人才资源:一个国家或地区中具有较多科学知识、较强劳动技能,在价值创造过程中起关键或重要作用的那部分人。人才资源是人力资源的一部分,即优质的人力资源。在本质上,人口资源和人才资源是人,人力资源是能力,完全不同。从数量上,人口资源>人力资源>人才资源 3、职位分析是人力资源其他几个职能的基础。(对) 答:人力资源管理的基本职能:人力资源规划、职位分析、招聘录用、绩效管理、薪酬管理、培训与开发、员工关系管理。 职位分析是现代人力资源管理所有职能工作的基础和前提。只有做好了职位分析与设计工作,才能据此完成以下具体的现代人力资源管理工作:(1)制定企业人力资源 2)核定人力资源成本,并提出相关的管理决策(3)让企业及所有员工明确各规划( 自的工作职责和工作范围(4)组织招聘、选拔、使用所需要的人员(5)制定合理的员工培训、发展规划(6)制定考核标准及方案,科学开展绩效考核工作(7)设计出公平合理的薪酬福利及奖励制度方案(8)为员工提供科学的职业生涯发展咨询(9)设计、制定高效运行的企业组织结构(10)提供开展人力资源管理自我诊断的科学依据。 4、绩效管理是人力资源管理各个职能的核心。(对)
人力资源管理英文专业词汇[第二部分]- - Cafeteria benefit programs:Cafeteria benefit programs allow employees toselect the fringe benefits and services that answer their individual needs. career:A career is all the jobs that are held during one's working life. career counseling:Career counseling assists employees in finding appropriate career goals and paths.career development Career development consists of those experiences and improvements that one undertakes to achieve a career plan. career goals: Career goals are the future positions that one strives to reach. These goals serve as benchmarks along one's career path. career path:A career path is the sequential pattern of jobs that form one'scareer. career planning:Career planning is the process by which one selects career goals and paths to those goals. career plateau: A career plateau occurs when an employee is in a position he or she does well enough not to be demoted or fired but not wellenough to be promoted. change agents: Change agents are people who have the role of stimulatingchange within a group. checkoff :A checkoff provision in a union-management labor agreement requires the employer to deduct union dues from employee paychecks and to remit those moneys to the union. Civil Rights: Act of 1964 This act was passed to make various forms of discrimination illegal. closed shop: A closed shop is a workplace where all employees are required to be members of the union before they are hired. These arrangementsare illegal under the National Labor Relations Act. codetermination :Codetermination is a form of industrial democracy
一、单项选择题 1、失业保险所属得员工福利类型就是( B ) A、企业福利 B、法定福利 C、生活福利 D、有偿假期 2、下面哪一项不属于工作说明书得基本内容( D )。 A.工作职责 B.工作环境 C.工作权限 D.工作中晋升 3、企业对新员工上岗前进行得培训称为( B )。 A.培训 B.岗前培训 C.脱产培训 D.在职培训 4.一名工人得绩效,除了产量指标完成情况外,质量、原材料消耗率、能耗、出勤,甚至 服从纪律等硬、软方面得表现,都需要综合考虑,逐一评估,这体现了绩效得( B ) A.多因性 B.多维性 C.动态性 D.不确定性 5、最早产生得最简单得集权式组织架构形式就是(B ) A、职能制架构 B、直线制架构 C、直线职能制架构 D、矩阵制组织架构 5、通过对人力资源得开发与配置,消除劳动力耗费并获得劳动生产力得能力。这就是指人力资源得什么特性?(C) A、能动性 B、双重性 C、再生持续性 D、社会性 6、“深入工作现场,能比较全面地了解工作情况”就是以下哪种工作分析法得优点( B ) A、写实法 B、观察法 C、问卷法 D、参与法 7、下列不属于人力资源性质得就是( D ) A.能动性 B.时效性 C.社会性 D.不变性 8、下列说法错误得就是( A ) A.人力资源就是指一个国家或地区所拥有得人口得总量 B.人口资源就是指一个国家或地区所拥有得人口得总量 C.人才资源就是指一个国家或地区中具有较多科学知识、较强劳动技能,在价值创造过程 中起关键或重要作用得那部分人 D.人才资源就是人力资源得一部分,即优质得人力资源 9、.下面不属于潜在人力资源得就是( B ) A.病残人口 B.老年人口 C.失业人口 D.未成年就业人口 10、在辞退解雇方面, 我国劳动法规定, “劳动者有下列情形之一得, 用人单位可以解除劳动合同。”其中不包括( B ) A.在试用期间被证明不符合录用条件 B.女职工在孕期、产期、哺乳期内得 C.被依法追究刑事责任得 D.严重失职,营私舞弊,对用人单位利益构成重大损害 11、、双因素理论中得双因素指得就是( D) A 人与物得因素 B 信息与环境 C自然因素与社会因素D 保健因素与激励因素 12、俗话说“饥寒起盗心”,但古人云“廉者不受嗟来之食,志士不饮盗泉之水”,根据激励机制得有关原理,以下哪一项对这一俗语、格言所做得解释比较恰当( B) A 此俗语体现了马斯洛得需求层次理论,而格言与马斯洛得需求层次理论相侼 B 此俗语、格言均符合马斯洛得需求层次理论,只不过需求层次不同 C 此俗语符合马斯洛得需求层次理论,而格言符合赫兹伯格得双因素理论 D 此俗语符合期望理论,格言符合需求层次理论 13、根据双因素理论,下列可激励员工得因素就是( D) A 工资、成就、公司得政策、责任 B 晋升、工作条件、良好得工作关系
人力资源管理期末考试试题及答案 、简答题 (本题共 3题,第 1小题10分,第 2小题12分,第 3小题16分,共 38分) 1、简述制定企业各类人员规划的基本程序。 (10 分) ① 调查、收集和整理涉及企业战略决策和经营环境的各种信 息。 ② 根据企业或部门实际情况确定其人员规划期限, 准备精确而翔实的资料。 (2 分) ③ 在分析人力资源需求和供给的影响因素的基础上, 各种 科学预测方法,对企业未来人力资源供求进行预测。 ④ 制定人力资源供求协调平衡的总计划和各项业务计划, 求或求大于供的政策措施。 (2 分 ) ⑤ 人员规划的评价与修正。 人员规划并非是一成不变的, 实施过程及结果进行监督、评估,并重视信息的反馈,不断调整规划,使其更切合实际,更 好地促进企业目标的实现。 (2 分) 2、简述绩效考评指标体系设计的程序以及绩效考评标准的设计原则。 (12 分) (1) 绩效考评指标体系设计和程序: ① 进行工作岗位分析 ;(2 分 ) ②进行理论验证 ;(2 分 ) ③ 进行指标调查,确定指标体系 ;(2分) ④对指标体系进行必要的修改和调整。 (2分) (2) 绩效考评标准的设计原则 ① 定量准确的原则 ;(2分) ②先进合理的原则 ;(2分) ③突出特点的原则 ;(2分) ④简洁扼要的原则。 (2分) 3、简述工作岗位分类以及采用点数法对生产性岗位进行纵向分级的主要步骤。 (16 分) (1)岗位分类的主要步骤: ① 岗位的横向分类, 即根据岗位的工作性质及特征,将它们划分为若干类别。 (2分) ② 岗位的纵向分级, 即根据每一岗位的繁简难易程度、责任轻重以及所需学识、技能、 经验 水平等因素,将它们归入一定的档次级别。 (2 分) ③ 根据岗位分类的结果, 制定各类岗位的岗位规范即岗位说明书, 并以此作为各项人力资源 管理工作的依据。 (2 分) ④ 建立企业岗位分类图表, 说明企业各类岗位的分布及其配置状况, 为企业员工的分类管理 提供依据。 (2 分) (2 分 ) 了解企业现有人力资源状况, 为预测工作 采用定性和定量相结合, 以定量为主的 (2分) 并分别提出各种具体的调整供大于 它是一个动态的开放系统, 应对其
人力资源管理练习题库 一、判断题 1.在所有的资源中,人力资源是第一资源,也是一种能动资源。√ 2.人力资源与其他资源一样具有不可再生性。× 3.人力资源开发的对象是人的智力与才能。√ 4.人力资本的核心是教育投资。√ 5.物质资本需要投资才能形成,而人力资本不需要。× 6.根据组织专业化分工的原则,人力资源职能是由人力资源部门来承担的,绝大多数运营经理(或直线经理)各司其职,并不履行人力资源职能。× 7. 人力资源管理就是对人力这一资源进行有效开发、合理利用和科学管理,以实现组织的目标。√ 8.现代人力资源管理中,人力资源部门要从“策略的筹划及执行者”转变为“行政支持”。× 9.人力资源管理可以分为人事管理阶段和人力资源管理阶段。其中人力资源管理阶段已经有比较长的历史。× 10.人力资源规划,是各项具体人力资源管理活动的起点和依据,它直接影响着组织整体人力资源管理的效率。√ 11.人力资源供求预测是人力资源规划过程中的最关键性环节。√ 12.组织人力资源需求量主要取决于组织的业务量和产量,由此推算出人力资源需求量。√ 13.宏观经济形势越好,失业率越低,劳动力供给越紧张,招聘就越困难。√ 14.人口总量越大,人力资源率越高,人力资源供给越充分。√ 15.一个组织有可能人力资源总量是平衡的,但是结构不平衡。√ 16.工作分析是在工作岗位没有确定前进行的。× 17.工作分析的目的是为了使现有的工作内容和工作要求更加明确合理,以便制定切合实际的管理制度和管理机制,调动员工的积极性。√ 18.工作说明书是一份提供有关工作任务、职责与责任信息的文件。√ 19.工作分析中的观察法是通过工作分析人员与员工和管理者面对面的谈话来收集信息资料的方法。× 20.动作研究用来分析一项工作或任务,以确定完成这项工作或任务所需要的工作要素,以及这些要素发生的先后顺序及有效地完成它们所需要的时间。× 21.工作评价是确定职位等级的手段。√ 22.员工招聘是从组织外部吸收人力资源的过程。× 23.如果招聘成本低,录用人员质量低,就意味着招聘效率低;反之,则意味着招聘效率高。× 24.甄选是员工招聘的关键环节。√ 25.一般认为,“猎头”公司是一种专门为雇主“猎取”普通员工的职业中介机构。× 26.员工推荐的优点是招聘成本小,可靠性高。√ 27.美国微软公司近一半的员工都是通过人才猎取方式获得的。× 28.学生实习也是组织解决人力资源缺乏的一个方法,而且这种方法企业不必承担永久雇佣学生的义务。√
人力资源管理复习题 一、单项选择题 )现代人力资源管理中, “以人为本”的理念是指 ( B 1. A. 把人当成“上帝” ,一切都服从、服务 于“上帝” 把人当成组织中最具活力、能动性和创造性的要素 B. 坚持群众路线,尊重群众意见 C. 关 心员工生活,提高员工物质文化生活水平 D. ) 2. “深入工作现场,能比较全面地了解工作情 况”是以下哪种工作分析法 的优点 ( B D. 参与法观察法 C. 问卷法 A. 写实法 B. 3. 由于人力资源管理正在向着战略性的方 向发展,在人力资源管理领域中发展最为 ) ( A 迅速的是 B. 人力资源成本管理 A. 人力资源规划 人力资源绩 效管理 D. C. 人力资源开发 对组织内部人力资源供给的预测,常用的方法 有:马尔可夫分析法、档案资料分 4. ) ( B 析法和 回归预测法 C. 德尔菲法 D. 管理者继任模型 A. 趋势分析法 B. ,那么,该公司的人员变动率是 30,而今年在职人员的平均数为 1505. 某公司 今年离职人员数为 )( A A. 20% B.10% C.15% D.25% ( A )6. 我国组织目前面临的一个重大问题是 A. 人力 资源过剩 B. 人力资源浪费 C. 人力资源管理不当人力资源不足 D. 当职位空缺有许多种, 而且在某一特定地区内又有足够的求职者的情况下, 应该使用以下哪种 7. )( B 招募形式 D. 招募现场的宣传资料 C.A. 报纸 B. 广播电视杂志 C )8. 在人员甄选活动中, 对一个人所学知识和技能的基本检测称之为 ( 兴趣测试 C.A. 能力测试 B. 个不断成长以及挖掘个人最大潜力和建立成功职业的机会。 A )( D. 积极性 A. 能力 B. 知识 C. 工作时间 )( 17. 将人的资质作为确定等级结构主要依 人格测试成就测试 位空缺而制定的人 ( D 招聘规划 B. 验量表是 奈-西 蒙量表 B. 在人力资源规划中,为了保持组织在中、长期内可能产生的职 9. )力资源规划称为 D. 调配规划 C. 晋升规划 库德职业兴趣测验 C. () 11. 用轻的秤砣冒充重的秤砣会造成 度变化 D.C. C 下图反映的是(信度高效 度高 C. 信度低效度低 D. B. 信度低效度高 13. 考核绩效中最简单也最常用的工具是 A.图表评定法 强制分布法 )( A D. 型是 D. 人力分配规划 A. )世界上第一个兴趣测 ( A 10. 斯特朗男性职业兴趣量表 A. 比 爱德华个性偏好量表 D. 随机误差 信度高效度低 A. B. 12. 系统误差 A. 效度升高信 交替排序法 配对比较法 C. 度考核所面临的最大难题是 B. C. 可接受度 B. D. 14.360 完备性效度 A. 信度 )( B 15. 失业保险所属的员工福利类 有偿假期 C. 生活福利,并要为每 一位员工人力资源管理的一个基本假设就是,企业有义务最大限度地利用员工的 16. 都提供一 B. 企业福利法定福利 A. D.