2.2 Compile the Java class............................... 5
- 格式:pdf
- 大小:282.60 KB
- 文档页数:41
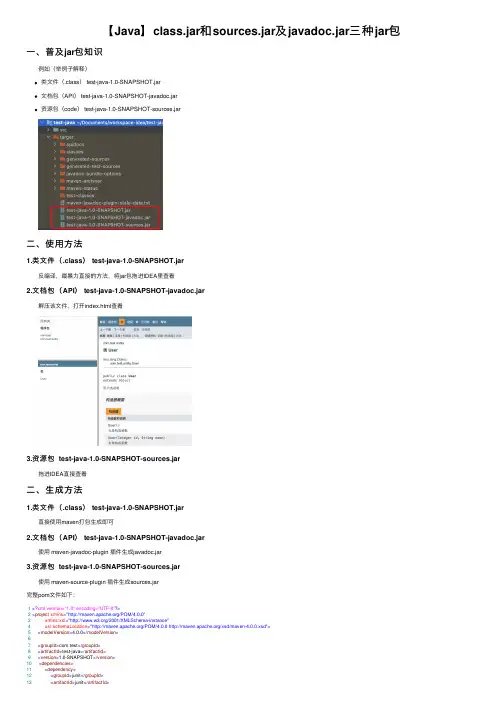
【Java】class.jar和sources.jar及javadoc.jar三种jar包⼀、普及jar包知识 例如(举例⼦解释)类⽂件(.class) test-java-1.0-SNAPSHOT.jar⽂档包(API) test-java-1.0-SNAPSHOT-javadoc.jar资源包(code) test-java-1.0-SNAPSHOT-sources.jar⼆、使⽤⽅法1.类⽂件(.class) test-java-1.0-SNAPSHOT.jar 反编译,最暴⼒直接的⽅法,将jar包拖进IDEA⾥查看2.⽂档包(API) test-java-1.0-SNAPSHOT-javadoc.jar 解压该⽂件,打开index.html查看3.资源包 test-java-1.0-SNAPSHOT-sources.jar 拖进IDEA直接查看⼆、⽣成⽅法1.类⽂件(.class) test-java-1.0-SNAPSHOT.jar 直接使⽤maven打包⽣成即可2.⽂档包(API) test-java-1.0-SNAPSHOT-javadoc.jar 使⽤ maven-javadoc-plugin 插件⽣成javadoc.jar3.资源包 test-java-1.0-SNAPSHOT-sources.jar 使⽤ maven-source-plugin 插件⽣成sources.jar完整pom⽂件如下:1<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>2<project xmlns="/POM/4.0.0"3 xmlns:xsi="/2001/XMLSchema-instance"4 xsi:schemaLocation="/POM/4.0.0 /xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">5<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>67<groupId>com.test</groupId>8<artifactId>test-java</artifactId>9<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>10<dependencies>11<dependency>12<groupId>junit</groupId>13<artifactId>junit</artifactId>14<version>4.12</version>15<scope>compile</scope>16</dependency>17</dependencies>1819<build>2021<plugins>22<plugin>23<!-- Maven 编译插件24指定maven编译的jdk版本,如果不指定,25 maven3默认⽤jdk 1.5 maven2默认⽤jdk1.3 -->26<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>27<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>28<version>3.8.1</version>29<configuration>30<!-- ⼀般⽽⾔,target与source是保持⼀致的,但是,有时候为了让程序能在其他版本的jdk中运⾏(对于低版本⽬标jdk,源代码中不能使⽤低版本jdk中不⽀持的语法),会存在target不同于source的情况 --> 31<source>1.8</source><!-- 源代码使⽤的JDK版本 -->32<target>1.8</target><!-- 需要⽣成的⽬标class⽂件的编译版本 -->33<encoding>UTF-8</encoding><!-- 字符集编码 -->34<verbose>true</verbose>35<showWarnings>true</showWarnings>36<fork>true</fork><!-- 要使compilerVersion标签⽣效,还需要将fork设为true,⽤于明确表⽰编译版本配置的可⽤ -->37<executable><!-- path-to-javac --></executable><!-- 使⽤指定的javac命令,例如:<executable>${JAVA_1_4_HOME}/bin/javac</executable> -->38<compilerVersion>1.3</compilerVersion><!-- 指定插件将使⽤的编译器的版本 -->39<meminitial>128m</meminitial><!-- 编译器使⽤的初始内存 -->40<maxmem>512m</maxmem><!-- 编译器使⽤的最⼤内存 -->41<!-- <compilerArgument>-verbose -bootclasspath ${java.home}\lib\rt.jar</compilerArgument><!– 这个选项⽤来传递编译器⾃⾝不包含但是却⽀持的参数选项 –>-->42</configuration>43</plugin>4445<!-- ⽣成javadoc⽂档包的插件 -->46<plugin>47<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>48<artifactId>maven-javadoc-plugin</artifactId>49<version>3.2.0</version>50<executions>51<execution>52<id>attach-javadocs</id>53<goals>54<goal>jar</goal>55</goals>56</execution>57</executions>58</plugin>5960<!-- ⽣成sources源码包的插件 -->61<plugin>62<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>63<artifactId>maven-source-plugin</artifactId>64<version>3.2.1</version>65<configuration>66<attach>true</attach>67</configuration>68<executions>69<execution>70<!-- 在package阶段之后会执⾏源代码打包 -->71<phase>package</phase>72<goals>73<goal>jar-no-fork</goal>74</goals>75</execution>76</executions>77</plugin>78</plugins>79</build>8081</project>配置好插件后,使⽤maven package命令既能在target⽬录中查看到三个jar包 命令:mvn package如果要把三种jar包安装到本地仓库 命令:mvn install如果要把三种jar包发布到远程仓库 命令:mvn deploy。

maven增量编译最近由于不清楚maven(2.2.x)增量编译的机制,导致应⽤出现了⼀个当时觉得⾮常诡异的⼀个问题。
先描述⼀下问题。
背景是应⽤A有⼀个公⽤的base包,版本为1.6.6-SNAPSHOT,应⽤B依赖于这个公⽤的base包。
我在base包中修改了⼀个字符串变量的值,该变量是⼀个缓存的key(如下⾯代码的Constants类,中的CACHE_KEY)。
然后使⽤mvn deploy 命令把base包上传到中⼼库中。
出现的问题是应⽤B打包部署,应⽤上线后,使⽤后台功能删除"cache.key.new"对应的缓存值,提⽰删除成功。
但是前台展⽰的还是⽼的值(前台展⽰取的数据是从缓存取出的,简化代码后,参考下⾯的CategoryManager的showCategory()⽅法,根据key在缓存中取出值,然后前台展⽰)。
public Interface Constants{public interface Cache{String CACHE_KEY = “cache.key.new”;//旧值为"cache.key"}}public Class CategoryManager{private static Map<int, String> keyMaps = new HashMap<String, String>();static {keyMaps.put(1, Constants. Cache. CACHE_KEY);//把缓存的key存到map中.........}public Object showCategory(){return cacheManager.get(keyMaps.get(1));//在缓存中获取数据}}⼀开始怀疑是包没有成功deploy到中⼼库中,然后在中⼼库中把1.6.6-SNAPSHOT的源码包拉了下来,发现⾥⾯的代码是新的。

idea class 编译
IDEA是一款流行的Java集成开发环境,提供了丰富的功能用于编写和调试Java 程序。
在IDEA中进行class编译是开发过程中的重要步骤,通过编译可以将Java源代码转换为字节码文件,以便在Java虚拟机上运行。
本文将介绍在IDEA中进行class编译的方法和注意事项。
编译Java Class文件:
在IDEA中编译Java Class文件非常简单,只需在项目中找到需要编译的Java文件,右键点击选择“Compile Java Class”即可开始编译。
IDEA会自动检查代码并生成相应的字节码文件,如果存在语法错误会在编译过程中提示。
编译过程中的注意事项:
1. 确保项目配置正确:在进行class编译前,要确保项目的依赖和配置正确,包括Java SDK版本、编译输出路径等。
2. 检查代码质量:编译前应该检查代码的质量,避免语法错误和逻辑问题导致编译失败。
3. 处理依赖关系:如果项目有依赖其他库或模块,要确保这些依赖正确引入并配置。
总结:
IDEA提供了便捷的class编译功能,开发者可以通过简单的操作完成编译过程,同时要注意项目配置和代码质量,以确保编译成功并生成可运行的字节码文件。
在开发过程中,熟练掌握IDEA的编译功能可以提高开发效率和代码质量。

java二级考试历年真题及答案1. 以下哪个选项是Java中关键字?A. classB. publicC. intD. all of the above答案:D2. 在Java中,哪个关键字用于定义一个类?A. classB. structC. interfaceD. enum答案:A3. Java程序的执行入口是?A. main方法B. run方法C. start方法D. init方法答案:A4. 以下哪个数据类型是Java中的原始数据类型?A. StringB. intC. ArrayListD. HashMap答案:B5. 在Java中,哪个关键字用于声明一个方法?A. methodB. functionC. defD. void答案:D6. Java中用于定义一个接口的关键字是?A. interfaceB. classC. structD. abstract class答案:A7. 在Java中,哪个关键字用于声明一个抽象方法?A. abstractB. virtualC. overrideD. final答案:A8. Java中用于抛出异常的关键字是?A. throwC. exceptionD. error答案:B9. 在Java中,哪个关键字用于声明一个私有方法?A. privateB. publicC. protectedD. default答案:A10. Java中用于声明一个静态方法的关键字是?A. staticB. finalC. constD. synchronized答案:A11. 在Java中,哪个关键字用于声明一个常量?A. finalB. constC. staticD. volatile答案:A12. Java中用于创建一个对象实例的关键字是?B. createC. instanceD. clone答案:A13. 在Java中,哪个关键字用于声明一个同步方法?A. synchronizedB. threadC. mutexD. lock答案:A14. Java中用于声明一个线程安全的类,应该使用哪个关键字?A. synchronizedB. thread-safeC. volatileD. immutable答案:D15. 在Java中,哪个关键字用于声明一个单例类?A. singletonB. uniqueC. finalD. none of the above答案:D请注意,以上题目及答案仅供示例,实际的Java二级考试内容可能会有所不同。

Java基础常见英语词汇(共70个) ['ɔbdʒekt]['ɔ:rientid]导向的['prəʊɡræmɪŋ]编程OO: object-oriented ,面向对象OOP: object-oriented programming,面向对象编程[dɪ'veləpmənt][kɪt]工具箱['vɜːtjʊəl]虚拟的JDK:Java development kit, java开发工具包JVM:java virtual machine ,java虚拟机['dʒɑːvə][mə'ʃiːn]机器[kəm'paɪl]Compile:编绎Run:运行['veərɪəb(ə)l] [ɒpə'reɪʃ(ə)n] [pə'ræmɪtə]variable:变量operation:操作,运算parameter:参数['fʌŋ(k)ʃ(ə)n]function:函数member-variable:成员变量member-function:成员函数[dɪ'fɔːlt] ['ækses] ['pækɪdʒ] [ɪm'pɔːt] ['stætɪk]default:默认access:访问package:包import:导入static:静态的[vɔid] ['peər(ə)nt] [beɪs] ['sjuːpə]void:无(返回类型) parent class:父类base class:基类super class:超类[tʃaɪld] [di'raivd] [əʊvə'raɪd] [əʊvə'ləʊd] child class:子类derived class:派生类override:重写,覆盖overload:重载['faɪn(ə)l] ['ɪmplɪm(ə)nts]final:最终的,不能改变的implements:实现[rʌn'taim] [æriθ'metik][ik'sepʃən]Runtime:运行时ArithmeticException:算术异常[ə'rei]['indeks] [baundz][ik'sepʃən] [nʌl] ['pɔintə]指针ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException:数组下标越界异常Null Pointer Exception:空引用异常ClassNotFoundException:类没有发现异常['nʌmbə]['fɔ:mæt]NumberFormatException:数字格式异常(字符串不能转化为数字)[θrəuz]Throws: (投掷)表示强制异常处理Throwable:(可抛出的)表示所有异常类的祖先类[læŋ]['læŋɡwidʒ][ju'til] [,dis'plei] [ə'rei] [list]Lang:language,语言Util:工具Display:显示ArrayList:(数组列表)表示动态数组[hæʃ][mæp]HashMap: 散列表,哈希表[swiŋ] ['æbstrækt] ['windəu] ['tu:lkit]Swing:轻巧的Awt:abstract window toolkit:抽象窗口工具包[freim] ['pænl] ['leiaut] [skrəul] ['və:tikəl] Frame:窗体Panel:面板Layout:布局Scroll:滚动Vertical:垂直['hɔri'zɔntəl] ['leibl] [tekst] ['fi:ld]Horizontal:水平Label:标签TextField:文本框['εəriə] ['bʌtən] [tʃek] [bɔks]TextArea:文本域Button:按钮Checkbox:复选框['reidiəu] ['kɔmbəu] ['lisənə]Radiobutton:单选按钮Combobox:复选框Listener:监听['bɔ:də] [fləu] [ɡrid] ['menju:] [bɑ:]Border:边界Flow:流Grid:网格MenuBar:菜单栏['menju:] ['aitəm] ['pɔpʌp]Menu:菜单MenuItem:菜单项PopupMenu:弹出菜单['daiəlɔɡ] ['mesidʒ] ['aikɔn] [nəud]Dialog:对话框Message:消息Icon:图标Node:节点['dʒa:və]['deitəbeis] [,kɔnek'tivəti]Jdbc:java database connectivity :java数据库连接[draivə] ['mænidʒə] [kə'nekʃən] ['steitmənt]DriverManager:驱动管理器Connection:连接Statement:表示执行对象[pri'peəd] [ri'zʌlt]Preparedstatement:表示预执行对象Resultset:结果集['eksikju:t] ['kwiəri]executeQuery:执行查询Jbuilder中常用英文(共33个)[kləuz] [ik'sept] [peinz]Close all except…:除了..全部关闭Panes:面板组[bi:n] ['prɔpətiz] [meik] [bild] [,ri:'bild]Bean:豆子Properties:属性Make:编绎Build:编绎Rebuild:重编绎[ri'freʃ] ['prɔdʒekt] [di'fɔ:lt]Refresh:刷新Project properties:项目属性Default project properties:默认的项目属性[di:'bʌɡ] ['prefərənsiz] [kən'fiɡə] ['laibrəriz] Debug:调试Preferences:参数配置Configure:配置Libraries:库JSP中常用英文[,ju:ni'və:səl] [ri'sɔ:s] [ləu'keiʃən]URL: Universal Resource Location:统一资源定位符['intənet] [ik'splɔ:rə] ['dʒa:və] ['sə:və] [peidʒ]IE: Internet Explorer 因特网浏览器JSP: java server page:java服务器页面['mɔdəl] [kən'trəulə] ['tɔmkæt]Model:模型C:controller:控制器Tomcat:一种jsp的web服务器['mɔdju:l] ['sə:vlet][i'niʃəlaiz] ['sta:tʌp] WebModule:web模块Servlet:小服务程序Init: initialize,初始化Startup:启动['mæpiŋ][pə'ræmitə] ['seʃən] [,æpli'keiʃən] Mapping:映射Getparameter:获取参数Session:会话Application:应用程序['kɔntekst] [,ri:di'rekt] [dis'pætʃ] ['fɔ:wəd]Context:上下文redirect:重定向dispatch:分发forward:转交['ætribju:t] ['kɔntent] [taip]setattribute:设置属性getattribute:获取属性contentType:内容类型[tʃɑ:] [in'klu:d] [tæɡ][lib]charset:字符集include:包含tag:标签taglib:标签库[ik'spreʃən] ['læŋɡwidʒ][skəup] ['empti] EL:expression language,表达式语言Scope:作用域Empty:空['stændəd][tæɡ] ['laibrəri]JSTL:java standard tag library :java标准标签库[di'skripʃən] [kɔ:]TLD:taglib description,标签库描述符Core:核心Foreach:表示循环[va:(r)] ['vεəriəbl] ['steitəs] ['aitəm]Var:variable,变量Status:状态Items:项目集合['fɔ:mæt] [filtə]Fmt:format,格式化Filter:过滤器(报错英文['strʌktʃəz]Data Structures 基本数据结构['dikʃənəriz]Dictionaries 字典[prai'ɔrəti] [kju:z]Priority Queues 堆[ɡrɑ:f] ['deɪtə] ['strʌktʃəz]Graph Data Structures 图[set] ['deɪtə]['strʌktʃəz]Set Data Structures 集合[tri:s]Kd-Trees 线段树[nju:'merikəl] ['prɔ:bləms]Numerical Problems 数值问题[sɔlviŋ] ['liniə] [i'kweiʃənz]Solving Linear Equations 线性方程组['bændwidθ] [ri'dʌkʃən]Bandwidth Reduction 带宽压缩['meitriks] [,mʌltipli'keiʃən]Matrix Multiplication 矩阵乘法[di'tə:minənt] ['pə:mənənt]Determinants and Permanents 行列式[kən'streind] [ʌnkən'streɪnd] [,ɔptimai'zeiʃən]Constrained and Unconstrained Optimization 最值问题['liniə] ['prəuɡræmiŋ]Linear Programming 线性规划['rændəm] ['nʌmbə] [,dʒenə'reiʃən]Random Number Generation 随机数生成['fæktərɪŋ] [prai'mæləti] ['testɪŋ]Factoring and Primality Testing 因子分解/质数判定['ɑːbɪtrərɪ][prɪ'sɪʒən][ə'rɪθmətɪk]Arbitrary Precision Arithmetic 高精度计算['næpsæk] ['prɒbləm]Knapsack Problem 背包问题[dɪ'skriːt] ['fʊriər][træns'fɔːm]Discrete Fourier Transform 离散Fourier变换Combinatorial Problems 组合问题Median and Selection 中位数Generating Permutations 排列生成Generating Subsets 子集生成Generating Partitions 划分生成Generating Graphs 图的生成Calendrical Calculations 日期Job Scheduling 工程安排Satisfiability 可满足性Graph Problems -- polynomial 图论-多项式算法Connected Components 连通分支Topological Sorting 拓扑排序Minimum Spanning Tree 最小生成树Shortest Path 最短路径Transitive Closure and Reduction 传递闭包Matching 匹配Eulerian Cycle / Chinese Postman Euler回路/中国邮路Edge and Vertex Connectivity 割边/割点Network Flow 网络流Drawing Graphs Nicely 图的描绘Drawing Trees 树的描绘Planarity Detection and Embedding 平面性检测和嵌入Graph Problems -- hard 图论-NP问题Clique 最大团Independent Set 独立集Vertex Cover 点覆盖Traveling Salesman Problem 旅行商问题Hamiltonian Cycle Hamilton回路Graph Partition 图的划分Vertex Coloring 点染色Edge Coloring 边染色Graph Isomorphism 同构Steiner Tree Steiner树Feedback Edge/Vertex Set 最大无环子图Computational Geometry 计算几何Convex Hull 凸包Triangulation 三角剖分V oronoi Diagrams V oronoi图Nearest Neighbor Search 最近点对查询Range Search 范围查询Point Location 位置查询Intersection Detection 碰撞测试Bin Packing 装箱问题Medial-Axis Transformation 中轴变换Polygon Partitioning 多边形分割Simplifying Polygons 多边形化简Shape Similarity 相似多边形Motion Planning 运动规划Maintaining Line Arrangements 平面分割Minkowski Sum Minkowski和Set and String Problems 集合与串的问题Set Cover 集合覆盖Set Packing 集合配置String Matching 模式匹配Approximate String Matching 模糊匹配Text Compression 压缩Cryptography 密码Finite State Machine Minimization 有穷自动机简化Longest Common Substring 最长公共子串Shortest Common Superstring 最短公共父串DP——Dynamic Programming——动态规划recursion ——递归)报错英文第一章:JDK(Java Development Kit) java开发工具包JVM(Java Virtual Machine) java虚拟机Javac 编译命令java 解释命令Javadoc 生成java文档命令classpath 类路径Version 版本static 静态的String 字符串类JIT(just-in-time) 及时处理第二章:第三章:OOP object oriented programming 面向对象编程Object 对象Class 类Class member 类成员Class method 类方法Class variable 类变量Constructor 构造方法Package 包Import package 导入包第四章:Base class 基类Super class 超类Overloaded method 重载方法Overridden method 重写方法Public 公有Private 私有Protected 保护Static 静态Abstract 抽象Interface 接口Implements interface 实现接口第五章:RuntimeExcepiton 运行时异常ArithmeticException 算术异常IllegalArgumentException 非法数据异常ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException 数组索引越界异常NullPointerException 空指针异常ClassNotFoundException 类无法加载异常(类不能找到)NumberFormatException 字符串到float类型转换异常(数字格式异常)IOException 输入输出异常FileNotFoundException 找不到文件异常EOFException 文件结束异常InterruptedException (线程)中断异常throws 投、掷、抛print Stack Trace() 打印堆栈信息get Message()获得错误消息get Cause()获得异常原因method 方法able 能够instance 实例Byte (字节类)Character (字符类)Integer(整型类)Long (长整型类)Float(浮点型类)Double (双精度类)Boolean(布尔类)Short (短整型类)Digit (数字)Letter (字母)Lower (小写)Upper (大写)Space (空格)Identifier (标识符)Start (开始)String (字符串)length (值)equals (等于)Ignore (忽略)compare (比较)sub (提取)concat (连接)trim (整理)Buffer (缓冲器)reverse (颠倒)delete (删除)append (添加)Interrupted (中断的)第七章:toString 转换为字符串GetInstance 获得实例Util 工具,龙套Components 成分,组成Next Int 下一个整数Gaussian 高斯ArrayList 对列LinkedList 链表Hash 无用信息,杂乱信号Map 地图Vector 向量,矢量Collection 收集Shuffle 混乱,洗牌RemoveFirst 移动至开头RemoveLast 移动至最后lastElement 最后的元素Capacity 容量,生产量Contains 包含,容纳InsertElementAt 插入元素在某一位置第八章:io->in out 输入/输出File 文件isFile 是文件isDirectory 是目录getPath 获取路径getAbsolutePath 获取绝对路径lastModified 最后修改日期Unicode 统一的字符编码标准, 采用双字节对字符进行编码FileInputStream 文件输入流FileOutputStream文件输出流IOException 输入输出异常fileobject 文件对象available 可获取的BufferedReader 缓冲区读取FileReader 文本文件读取BufferedWriter 缓冲区输出FileWriter 文本文件写出flush 清空close 关闭DataInputStream 二进制文件读取DataOutputStream二进制文件写出EOF 最后encoding 编码Remote 远程release 释放第九章:JBuider Java 集成开发环境(IDE)Enterprise 企业版Developer 开发版Foundation 基础版Messages 消息格Structure 结构窗格Project 工程Files 文件Source 源代码Design 设计History 历史Doc 文档File 文件Edit 编辑Search 查找Refactor 要素View 视图Run 运行Tools 工具Window 窗口Help 帮助Vector 矢量addElement 添加内容Project Winzard 工程向导Step 步骤Title 标题Description 描述Copyright 版权Company 公司Aptech Limited Aptech有限公司author 作者Back 后退Finish 完成version 版本Debug 调试New 新建ErrorInsight 调试第十章:JFrame 窗口框架JPanel 面板JScrollPane 滚动面板title 标题Dimension 尺寸Component 组件Swing JA V A轻量级组件getContentPane 得到内容面板LayoutManager 布局管理器setVerticalScrollBarPolicy 设置垂直滚动条策略AWT(Abstract Window Toolkit)抽象窗口工具包GUI (Graphical User Interface)图形用户界面VERTICAL_SCROLLEARAS_NEEDED 当内容大大面板出现滚动条VERTICAL_SOROLLEARAS_ALWAYS 显示滚动条VERTICAL_SOROLLEARAS_NEVER 不显示滚动条JLabel 标签Icon 图标image 图象LEFT 左对齐RIGHT 右对齐JTextField 单行文本getColumns 得到列数setLayout 设置布局BorderLayout 边框布局CENTER 居中对齐JTextArea 多行文本setFont 设置字体setHorizontalAlignment 设置文本水平对齐方式setDefaultCloseOperation 设置默认的关闭操作add 增加JButton 按钮JCheckBox 复选框JRadioButton单选按钮addItem 增加列表项getItemAt 得到位置的列表项getItemCount 得到列表项个数setRolloverIcon 当鼠标经过的图标setSelectedIcon 当选择按钮的图标getSelectedItem 得到选择的列表项getSelectedIndex 得到选择的索引ActionListener 按钮监听ActionEvent 按钮事件actionPerformed 按钮单击方法(编程词汇A2A integration A2A整合abstract 抽象的abstract base class (ABC)抽象基类abstract class 抽象类abstraction 抽象、抽象物、抽象性access 存取、访问access level访问级别access function 访问函数account 账户action 动作activate 激活active 活动的actual parameter 实参adapter 适配器add-in 插件address 地址address space 地址空间address-of operator 取地址操作符ADL (argument-dependent lookup)ADO(ActiveX Data Object)ActiveX数据对象advanced 高级的aggregation 聚合、聚集algorithm 算法alias 别名align 排列、对齐allocate 分配、配置allocator分配器、配置器angle bracket 尖括号annotation 注解、评注API (Application Programming Interface) 应用(程序)编程接口app domain (application domain)应用域application 应用、应用程序application framework 应用程序框架appearance 外观append 附加architecture 架构、体系结构archive file 归档文件、存档文件argument引数(传给函式的值)。

使用Java混淆工具yguard在某些情况下,java开发者可能希望保护自己的劳动成果,防止自己编写的源代码被竞争对手或者其他组织和个人轻易获取而危害自己的利益,最简单有效的办法就是对编译后的java类文件进行混淆处理。
本文介绍一款这样的工具yguard。
yGruard是一个功能比较强大的java类文件的混淆工具,特别适合与ant工具集成使用。
本文对yguard的基本元素做一些简单的介绍,并列举了一些简单的ant任务例子,在实际工程项目中可以参考这些样例。
1. 安装2. 创建初始ant任务我们从经典的helloworld示例入手,逐步学习使用yguard混淆器工具。
2.1.编写helloword程序2.2.创建ant任务2.3.执行ant任务3. 第一个混淆任务3.1.执行混淆任务4.Obfuscate元素Obfuscate是整个混淆任务定义的元素,下面我们对它及其子元素进行详细的介绍。
4.1.Obfuscate元素在当前版本中,Obfuscate元素有如下一些属性,●mainclass:简写你的应用的主程序类名,主类的类名和它的主方法名都会被修改。
你可能想仅仅暴露主方法(main),如果你的jar文件描述文件中MANIFEST.MF包含了Main-Class属性,yguard将会自动调整成混淆后的主类名。
●logfile:混淆过程产生的日志文件名称,这个日志文件包含了混淆过程的任何警告信息和映射信息。
●conservemanifest:(取值为boolean类型-true/false),表示混淆器是否应改保持jar包的manifest清单文件不变。
缺省值为false,表示这个清单文件将会被混淆器修改用来反映新的信息摘要。
replaceClassNameStrings:(也是一个boolean属性值),设定yguard 是否需要取代某些硬编码的字符串。
(本文英文水平有限,这个属性没有理解清楚)。

JAVA集成开发环境----IntellijIDEA操作总结IDEA 全称 IntelliJ IDEA,是款优秀的 java语⾔开发的集成环境。
本⽂是对 IDEA 中常⽤配置的整理。
开始前需先准备环境,并激活。
本⽂基于:IntelliJ IDEA 2020.3.1(Ultimate Edition)注意IDEA 中没有⼯作空间 workspace 这个概念,IDEA 的设置分两类:默认配置 VS 当前项⽬配置默认配置:顶部导航栏 -> File -> New Projects Settings -> Settings for new projects / Structure for new projects当前项⽬配置:顶部导航栏 -> File -> Settings / Project Structure⼀. 项⽬结构配置File -> Project Structure)是 IDEA 中最重要的设置项,关乎到项⽬的运⾏1.1 Project Settings -> ProjectProject name:定义项⽬的名称;Project SDK:设置该项⽬使⽤的JDK,也可以在此处新添加其他版本的JDK;Project language level:这个和JDK的类似,区别在于,假如你设置了JDK1.8,却只⽤到1.6的特性,那么这⾥可以设置语⾔等级为1.6,这个是限定项⽬编译检查时最低要求的JDK特性;Project compiler output:项⽬中的默认编译输出总⽬录,实际上每个模块可以⾃⼰设置特殊的输出⽬录(Modules - (project) - Paths -Use module compile output path),所以这个设置有点鸡肋。
1.2 Project Settings -> ModulesIDEA 每个项⽬默认开⼀个窗⼝,即单⼦项⽬的形式。

Java2实用教程第六版知识点汇总1.引言本文档旨在对Ja va2实用教程第六版涉及的主要知识点进行全面的汇总和总结。
通过学习该教程,读者将能够全面掌握Ja va2编程的核心概念和技巧,为日后的J av a开发工作打下坚实的基础。
2.数据类型J a va2实用教程第六版详细介绍了Ja va中的各种数据类型及其使用方法。
以下是一些关键的知识点:2.1基本数据类型J a va的基本数据类型包括整型、浮点型、字符型和布尔型。
本教程提供了详细的介绍和示例代码,帮助读者理解这些数据类型的特点和用法。
2.2引用数据类型除了基本数据类型外,J av a还提供了多种引用数据类型,如数组、类、接口等。
教程中的例子演示了如何声明和使用这些引用数据类型,帮助读者熟悉它们的基本概念和操作。
3.控制流程控制流程是编程中的重要概念,决定了程序的执行顺序和逻辑。
J a va2实用教程第六版涵盖了常见的控制流程语句,包括条件语句和循环语句。
3.1条件语句条件语句用于根据条件的真假来选择性地执行不同的代码块。
本教程提供了i f语句、swi t ch语句等条件语句的详细说明和示例,让读者明白如何正确运用它们。
3.2循环语句循环语句用于重复执行某段代码,直到满足退出条件为止。
Ja v a2实用教程第六版介绍了三种循环语句:f or循环、w hi le循环和d o-wh il e循环。
读者将学会如何正确选择和使用不同类型的循环语句,以解决各种实际问题。
4.类与对象面向对象编程是J ava的核心思想之一。
J a va2实用教程第六版详细讲解了类与对象的概念、属性和方法的定义与使用等内容。
4.1类的定义与使用教程中提供了清晰的例子,介绍了如何定义类、声明对象、调用类的方法等操作。
读者将了解到如何通过类和对象来构建复杂的应用程序。
4.2构造方法与析构方法构造方法用于在创建对象时进行初始化操作,而析构方法则在对象销毁时执行清理工作。
本教程详细说明了构造方法和析构方法的特点和使用方法,帮助读者正确地管理对象的生命周期。

上海德邦物流股份有限公司招聘java面试真题一、选择题(20) [含多选]。
(请在正确的答案上打”√”)Question 1)Which of the following statements are true?1) An interface can only contain method and not variables2) Interfaces cannot have constructors3) A class may extend only one other class and implement only one interface4) Interfaces are the Java approach to addressing its lack of multiple inheritance, but require implementing classes to create the functionality of the Inter faces.Question 2)Which of the following statements are true?1) The garbage collection algorithm in Java is vendor implemented2) The size of primitives is platform dependent3) The default type for a numerical literal with decimal component is a float.4) You can modify the value in an Instance of the Integer class with the setValue methodQuestion 3)Which of the following are true statements?1) I/O in Java can only be performed using the Listener classes2) The RandomAccessFile class allows you to move directly to any point a file.3) The creation of a named instance of the File class creates a matching file in the underlying operating system only when the close method is called.4) The characteristics of an instance of the File class such as the directoryseparator, depend on the current underlying operating systemQuestion 4)What will happen when you attempt to compile and run the following codeclass Base{public void Base(){System.out.println(“Base”);}}public class In extends Base{public static void main(String argv[]){In i=new In();}}1) Compile time error Base is a keyword2) Compilation and no output at runtime3) Output of Base4) Runtime error Base has no valid constructorQuestion 5)You have a public class called myclass with the main method defined as follows public static void main(String parm[]){System.out.println(parm[0]);}If you attempt to compile the class and run the program as followsjava myclass helloWhat will happen?1) Compile time error, main is not correctly defined2) Run time error, main is not correctly defined3) Compilation and output of java4) Compilation and output of helloQuestion 6)Which of the following statements are NOT true?1) If a class has any abstract methods it must be declared abstract itself.2) When applied to a class, the final modifier means it cannot be sub-classed3) All methods in an abstract class must be declared as abstract4) transient and volatile are Java modifiersQuestion 7)What will happen when you attempt to compile and run the following class?class Base{Base(int i){System.out.println(“Base”);}}class Severn extends Base{public static void main(String argv[]){Severn s = new Severn();}void Severn(){System.out.println(“Severn”);}}1) Compilation and output of the string ”Severn”at runtime2) Compilation and no output at runtime3) Compile time error4) Compilation and output of the string ”Base”Question 8)Which of the following statements are true?1) Static methods cannot be overriden to be non static2) Static methods cannot be declared as private3) Private methods cannot be overloaded4) An overloaded method cannot throw exceptions not checked in the base class Question 9)Which of the following statements are true?1) The automatic garbage collection of the JVM prevents programs from ever running outof memory2) A program can suggest that garbage collection be performed but not force it3) Garbage collection is platform independent4) An object becomes eligible for garbage collection when all references denoting it are set to null.Question 10)Given the following codepublic class Sytch{int x=2000;public static void main(String argv[]){System.out.println(“Ms”+argv[1]+”Please pay $”+x);}}What will happen if you attempt to compile and run this code with the command linejava Sytch Jones Diggle1) Compilation and output of Ms Diggle Please pay $20002) Compile time error3) Compilation and output of Ms Jones Please pay $20004) Compilation but runtime errorQuestion 11)You need to read in the lines of a large text file containing tens of megabyt es of data. Which of the following would be most suitable for reading in sucha file1) new FileInputStream(“”)2) new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(“”))3) new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(“”)));4) new RandomAccessFile raf=new RandomAccessFile(“myfile.txt”,”+rw”);Question 12)Which of the following statements are true?1) Constructors cannot have a visibility modifier2) Constructors are not inherited3) Constructors can only have a primitive return type4) Constructors can be marked public and protected, but not privateQuestion 13)Which statement is true?1)An anonymous inner class may be declared as final.2)An anonymous inner class can be declared as private.3)An anonymous inner class can implement multiple interfaces .4)An anonymous inner class can access final variables in any enclosing scope.5)Construction of an instance of a static inner class requires an instance of t he enclosing outer class.Question 14)public class Foo{public static void main(String sgf[]){StringBuffer a = new StringBuffer(“A”);StringBuffer b = new StringBuffer(“B”);operate(a,b);System.out.println(a+”,”+b);}static void operate(StringBuffer x,StringBuffer y){x.append(y);y=x; }}What is the result?1)The code compiles and prints “A.B”.2)The code compiles and prints “A.A”.3)The code compiles and prints “B.B”.4)The code compiles and prints “AB.B”.5)The code compiles and prints “AB.AB”.Question 15)Which of the following thread state transitions are valid?1) From ready to running.2) From running to ready.3) From running to waiting.4) From waiting to running.5) From waiting to ready.6) From ready to waiting.Question 16)What is the result of attempting to compile and run the following program?public class Test {private int i = j;private int j = 10;public static void main(String args[]) {System.out.println((new Test()).i);}}1) Compiler error complaining about access restriction of private variables of Te st.2) Compiler error complaining about forward referencing.3) No error - The output is 0;4) No error - The output is 10;Question 17)Which two cannot directly cause a thread to stop executing?1)exiting from a synchronized block2)calling the wait method on an object3)calling the notify method on an object4)calling a read method on an InputStream object5)calling the setPriority method on a thread objectQuestion 18)Which of the following are correct, if you compile the following code?public class CloseWindow extends Frame implements WindowListener {public CloseWindow() {addWindowListener(this); // This is listener registrationsetSize(300, 300);setVisible(true); }public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e) {System.exit(0); }public static void main(String args[]) {CloseWindow CW = new CloseWindow(); } }1) Compile time error2) Run time error3) Code compiles but Frames does not listen to WindowEvents4) Compile and runs successfullyQuestion 19)Which statements describe guaranteed behavior of the garbage collection and finali zation mechanisms?1) Objects are deleted when they can no longer be accessed through any reference.2) The finalize() method will eventually be called on every object.3) The finalize() method will never be called more than once on an object.4) An object will not be garbage collected as long as it is possible for an active part of the program to access it through a reference.5) The garbage collector will use a mark and sweep algorithm.Question 20)A class design requires that a member variable should be accessible only by sam e package,which modifer word should be used?1) protected2) public3) no modifer4) private二.简答题。

Java (programming language)From Wikipedia,the free encyclopediaJava is a programming language originally developed by James Gosling at Sun Microsystems (which has since merged into Oracle Corporation)and released in 1995 as a core component of Sun Microsystems' Java platform. The language derives much of its syntax from C and C++ but has a simpler object model and fewer low—level facilities. Java applications are typically compiled to bytecode (class file) that can run on any Java Virtual Machine (JVM)regardless of computer architecture. Java is a general-purpose,concurrent,class-based,object-oriented language that is specifically designed to have as few implementation dependencies as possible. It is intended to let application developers "write once, run anywhere," meaning that code that runs on one platform does not need to be edited to run on another. Java is currently one of the most popular programming languages in use, particularly for client—server web applications,with a reported 10 million users.[10][11] The original and reference implementation Java compilers,virtual machines, and class libraries were developed by Sun from 1995。

Java2实用教程(第三版)课后习题参考答案第1章 Java入门1. 开发与运行Java程序需要经过哪些主要步骤和过程?答:(1)编写Java源文件:使用文本编辑器(Edit或记事本),拓展名为.java(2)编译Java源文件:使用Java编译器(javac.exe)。
得到字节码文件*.class(3)运行Java程序:Java应用程序使用Java解释器(java.exe)执行字节码文件;Java小应用程序使用支持Java标准的浏览器来执行。
2. 怎样区分应用程序和小应用程序?应用程序的主类或小应用程序的主类必须用public修饰吗?答:①应用程序必须有main方法,这个方法是程序执行的入口。
小应用程序没有main方法。
②应用程序的主类不一定用public修饰;小应用程序的主类必须用public修饰。
3. Java程序是由什么组成的?一个程序中必须要有public类吗?Java源文件的命名规则是怎样的?答:①Java程序由类组成。
②应用程序可以没有public类;小应用程序一定有一个类是public类(主类)。
③应用程序:如果只有一个类,源文件名与该类的类名相同,拓展名为.java;有多个类时,如果有public类(最多一个),源文件名与public类的类名相同,拓展名是.java;没有public类,源文件名与任何一个类的类名相同即可,拓展名为.java。
小应用程序:源文件名与主类的类名相同,拓展名是.java。
4. 在运行小程序的HTML文件中可以使用codebase属性指定小程序的字节码所驻留的目录。
如果不使用codebase属性,小程序的字节码文件必须和运行它的HTML文件在同一目录中。
编写一个小程序并将小程序的字节码存放在某个目录中,比如C:\5000;把运行该小程序的HTML文件(注意其中的codebase属性): <applet code=你的小程序的字节码 width=200 height=300 codebase=C:\5000></applet>存放在另一个目录中。
java语言程序设计单词Java语言程序设计是一种强大而受欢迎的编程语言,用于开发各种应用程序和软件。
在本文中,将逐步介绍与Java语言程序设计相关的关键词。
1. Java(Java)Java是一种跨平台的面向对象编程语言,最初由Sun Microsystems(现在是Oracle Corporation的一部分)于1995年发布。
Java以其简单易学、可移植性和强大的功能而广受欢迎,并在世界范围内得到广泛应用。
2. 编程语言(Programming Language)编程语言是用于定义计算机程序的形式化语言。
它们被设计用来与计算机进行交互,以实现特定的任务和操作。
Java是一种高级编程语言,它提供了丰富的功能和库,使开发人员能够轻松地创建各种应用程序。
3. 面向对象编程(Object-oriented programming,简称OOP)面向对象编程是一种编程范式,其中程序由对象的组合构成。
每个对象都有其自己的状态和行为,并且能够与其他对象进行交互。
Java是一种面向对象的编程语言,它通过类和对象的概念来实现面向对象编程的特性。
4. 开发者(Developer)开发者是指编写和创建计算机程序的人员。
Java开发者使用Java语言来编写和开发各种应用程序和软件。
他们使用Java开发工具包(JavaDevelopment Kit,简称JDK)来编译、运行和调试Java程序。
5. JDK(Java Development Kit)JDK是一套用于开发Java应用程序的软件开发工具包。
它包含了Java编译器、调试器和其他必要的工具,以及Java运行时环境(Java Runtime Environment,简称JRE)。
JDK是每个Java开发者必备的工具之一。
6. 编译(Compile)编译是将源代码转化为可执行代码的过程。
在Java中,开发者使用Java 编译器将Java源代码(以.java扩展名结尾的文件)编译为字节码(以.class 扩展名结尾的文件),然后可以在Java虚拟机(Java Virtual Machine,简称JVM)上运行。
J A V A编程常用英文单词汇总The saying "the more diligent, the more luckier you are" really should be my charm in2006.Java基础常见英语词汇共70个OO: object-oriented ,面向对象OOP: object-oriented programming,面向对象编程JDK:Java development kit, java开发工具包JVM:java virtual machine ,java虚拟机Compile:编绎Run:运行Class:类Object:对象System:系统out:输出print:打印line:行variable:变量type:类型operation:操作,运算array:数组parameter:参数method:方法function:函数member-variable:成员变量member-function:成员函数get:得到set:设置public:公有的private:私有的protected:受保护的default:默认access:访问package:包import:导入static:静态的void:无返回类型extends:继承parent class:父类base class:基类super class:超类child class:子类derived class:派生类override:重写,覆盖overload:重载final:最终的,不能改变的abstract:抽象interface:接口implements:实现exception:异常Runtime:运行时ArithmeticException:算术异常ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException:数组下标越界异常NullPointerException:空引用异常ClassNotFoundException:类没有发现异常NumberFormatException:数字格式异常字符串不能转化为数字Catch:捕捉Finally:最后Throw:抛出Throws: 投掷表示强制异常处理Throwable:可抛出的表示所有异常类的祖先类Lang:language,语言Util:工具Display:显示Random:随机Collection:集合ArrayList:数组列表表示动态数组HashMap: 散列表,哈希表Swing:轻巧的Awt:abstract window toolkit:抽象窗口工具包Frame:窗体Size:尺寸Title:标题Add:添加Panel:面板Layout:布局Scroll:滚动Vertical:垂直Horizonatal:水平Label:标签TextField:文本框TextArea:文本域Button:按钮Checkbox:复选框Radiobutton:单选按钮Combobox:复选框Event:事件Mouse:鼠标Key:键Focus:焦点Listener:监听Border:边界Flow:流Grid:网格MenuBar:菜单栏Menu:菜单MenuItem:菜单项PopupMenu:弹出菜单Dialog:对话框Message:消息 Icon:图标Tree:树Node:节点Jdbc:java database connectivity, java数据库连接DriverManager:驱动管理器Connection:连接Statement:表示执行对象Preparedstatement:表示预执行对象Resultset:结果集Next:下一个Close:关闭executeQuery:执行查询Jbuilder中常用英文共33个File:文件New:新建New Project:新建项目New Class: 新建类New File:新建文件Open project:打开项目Open file:打开文件Reopen:重新打开Close projects:关闭项目Close all except…:除了..全部关闭Rename:重命名Exit:退出View:视图Panes:面板组Project:项目Content:内容Structure:结构Message:消息Source:源文件Bean:豆子Properties:属性Make:编绎Build:编绎Rebuild:重编绎Refresh:刷新Project properties:项目属性Default project properties:默认的项目属性Run:运行Debug:调试Tools:工具Preferences:参数配置Configure:配置Libraries:库JSP中常用英文URL: Universal Resource Location:统一资源定位符IE: Internet Explorer 因特网浏览器JSP:java server 服务器页面Model:模型View:视图C:controller:控制器Tomcat:一种jsp的web服务器WebModule:web模块Servlet:小服务程序Request:请求Response:响应Init: initialize,初始化Service:服务Destroy:销毁Startup:启动Mapping:映射pattern:模式Getparameter:获取参数Session:会话Application:应用程序Context:上下文redirect:重定向dispatch:分发forward:转交setAttribute:设置属性getAttribute:获取属性page:页面contentType:内容类型charset:字符集include:包含tag:标签taglib:标签库EL:expression language,表达式语言Scope:作用域Empty:空JSTL:java standard tag library,java标准标签库TLD:taglib description,标签库描述符Core:核心Test:测试Foreach:表示循环Var:variable,变量Status:状态Items:项目集合Fmt:format,格式化Filter:过滤器报错英文第一章:JDKJava Development Kit java开发工具包JVMJava Virtual Machine java虚拟机Javac编译命令java解释命令Javadoc生成java文档命令classpath 类路径Version版本author作者public公共的class类static静态的void没有返回值String字符串类System系统类out输出print同行打印println换行打印JITjust-in-time及时处理第二章:byte 字节char 字符boolean 布尔short 短整型int 整形long 长整形float 浮点类型double 双精度if 如果else 否则switch 多路分支case 与常值匹配break 终止default 默认while 当到循环do 直到循环for 已知次数循环continue结束本次循环进行下次跌代length 获取数组元素个数第三章:OOPobject oriented programming 面向对象编程Object 对象Class 类Class member 类成员Class method类方法Class variable 类变量Constructor 构造方法Package 包Import package 导入包第四章:Extends 继承Base class 基类Super class 超类Overloaded method 重载方法Overridden method 重写方法Public 公有Private 私有Protected 保护Static 静态Abstract抽象Interface 接口Implements interface 实现接口第五章:Exception 意外,异常RuntimeExcepiton 运行时异常ArithmeticException 算术异常IllegalArgumentException 非法数据异常ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException 数组索引越界异常NullPointerException 空指针异常ClassNotFoundException 类无法加载异常类不能找到NumberFormatException 字符串到float类型转换异常数字格式异常IOException 输入输出异常FileNotFoundException 找不到文件异常EOFException 文件结束异常InterruptedException 线程中断异常try 尝试catch 捕捉finally 最后throw 投、掷、抛throws 投、掷、抛print Stack Trace 打印堆栈信息get Message 获得错误消息get Cause 获得异常原因method 方法able 能够instance 实例check 检查第六章:byte字节char字符int整型long长整型float浮点型double双精度boolean布尔short短整型Byte 字节类Character 字符类Integer整型类Long 长整型类Float浮点型类Double 双精度类Boolean布尔类Short 短整型类Digit 数字Letter 字母Lower 小写Upper 大写Space 空格Identifier 标识符Start 开始String 字符串length 值equals 等于Ignore 忽略compare 比较sub 提取concat 连接replace 替换trim 整理Buffer 缓冲器reverse 颠倒delete 删除append 添加Interrupted 中断的第七章:Date 日期,日子After 后来,后面Before 在前,以前Equals 相等,均等toString 转换为字符串SetTime 设置时间Display 显示,展示Calendar 日历Add 添加,增加GetInstance获得实例getTime 获得时间Clear 扫除,清除Clone 克隆,复制Util 工具,龙套Components成分,组成Random 随意,任意Next Int 下一个整数Gaussian 高斯ArrayList 对列LinkedList链表Hash 无用信息,杂乱信号Map 地图Vector 向量,矢量Size 大小Collection收集Shuffle 混乱,洗牌RemoveFirst移动至开头RemoveLast 移动至最后lastElement最后的元素Capacity 容量,生产量Contains 包含,容纳Search 搜索,查询InsertElementAt 插入元素在某一位置第八章:io->in out 输入/输出File文件import导入exists存在isFile是文件isDirectory 是目录getName获取名字getPath获取路径getAbsolutePath 获取绝对路径lastModified 最后修改日期length长度InputStream 输入流OutputStream 输出流Unicode统一的字符编码标准, 采用双字节对字符进行编码Information 信息FileInputStream 文件输入流FileOutputStream文件输出流IOException 输入输出异常fileobject 文件对象available 可获取的read读取write写BufferedReader 缓冲区读取FileReader 文本文件读取BufferedWriter 缓冲区输出FileWriter 文本文件写出flush清空close关闭DataInputStream 二进制文件读取DataOutputStream二进制文件写出EOF最后encoding编码Remote远程release释放第九章:JBuiderJava 集成开发环境IDEEnterprise 企业版Developer 开发版Foundation 基础版Messages 消息格Structure 结构窗格Project工程Files文件Source源代码Design设计History历史Doc文档File文件Edit编辑Search查找Refactor 要素View视图Run运行Tools工具Window窗口Help帮助Vector矢量addElement 添加内容Project Winzard 工程向导Step步骤Title标题Description 描述Copyright 版权Company公司Aptech Limited Aptech有限公司author 作者Back后退Finish完成version版本Debug调试New新建ErrorInsight 调试第十章:JFrame窗口框架JPanel 面板JScrollPane 滚动面板title 标题Dimension 尺寸Component组件SwingJAVA轻量级组件getContentPane 得到内容面板LayoutManager布局管理器setVerticalScrollBarPolicy设置垂直滚动条策略AWTAbstract Window Toolkit 抽象窗口工具包GUI Graphical User Interface 图形用户界面VERTICAL_SCROLLEARAS_NEEDED当内容大大面板出现滚动条VERTICAL_SOROLLEARAS_ALWAYS显示滚动条VERTICAL_SOROLLEARAS_NEVER不显示滚动条JLabel标签Icon 图标image图象LEFT 左对齐RIGHT右对齐JTextField单行文本getColumns得到列数setLayout设置布局BorderLayout 边框布局CENTER居中对齐JTextArea多行文本setFont设置字体setHorizontalAlignment设置文本水平对齐方式setDefaultCloseOperation设置默认的关闭操作add增加JButton 按钮JCheckBox 复选框JRadioButton单选按钮addItem 增加列表项getItemAt 得到位置的列表项getItemCount 得到列表项个数setRolloverIcon 当鼠标经过的图标setSelectedIcon 当选择按钮的图标getSelectedItem 得到选择的列表项getSelectedIndex 得到选择的索引ActionListener按钮监听ActionEvent 按钮事件actionPerformed按钮单击方法附加.............可能有重复编程英语:手摘abstract 关键字抽象 'bstrktaccessvt.访问,存取 'kses'n.入口,使用权algorithmn.算法 'lgriemAnnotationjava 代码注释 nu'teinanonymousadj.匿名的'nnims'反义:directly adv.直接地,立即di'rektli, dai'rektli apply v.应用,适用 'plaiapplication n.应用,应用程序 ,pli'kein' application crash 程序崩溃arbitrarya.任意的 'ɑ:bitrriargument n.参数;争论,论据 'ɑ:gjumnt'缩写 argsassert 关键字断言 's:t ' java 之后成为关键字associaten.关联同伴,伙伴 'suieitattributen.属性品质,特征 'tribju:tboolean关键字逻辑的, 布尔型call .调用; 呼叫; k:lcircumstancen.事件环境,状况 's:kmstnscrash n.崩溃,破碎 krcohesion 内聚,黏聚,结合 ku'hi:na class is designed with a single, well-focoused purpose. 应该不止这点command n. 命令,指令 k'mɑ:nd指挥, 控制 command-line 命令行Comments java 文本注释 'kmentscompilejava v.编译 km'pail' Compilation n.编辑,kmpi'leinconst 保留字constant n. 常量, 常数, 恒量 'knstntcontinue 关键字coupling 耦合,联结 'kplimaking sure that classes know about other classes only through their APIs. declarejava 声明 di'kldefault关键字默认值; 缺省值 di'f:ltdelimiter定义符; 定界符Encapsulationjava 封装 hiding implementation detailsException java 例外; 异常 ik'sepnentry n.登录项, 输入项, 条目'entrienum关键字execute vt.执行 'eksikju:texhibit v.显示, 陈列 ig'zibitexist 存在, 发生 ig'zist 'SQL关键字 existsextends关键字继承、扩展 ik'stendfalse 关键字final 关键字 finally 关键字fragments段落; 代码块 'frgmntFrameWork java 结构,框架 'freimw:kGenericjava 泛型 di'nerikgoto保留字跳转heap n.堆 hi:pimplements关键字实现 'implimntimport 关键字引入进口,输入Info n.信息 information ,inf'meinInheritance java 继承 in'heritns 遗传,遗产initialize 预置初始化 i'nilaizinstanceof关键字运算符,用于引用变量,以检查这个对象是否是某种类型;返回 boolean 值; interface 关键字接口 'intfeisinvokevt.调用 in'vuk' invocation ,invu'keinIterator java 迭代器, 迭代程序legal 合法的 'li:gllogn.日志,记录 lgnative 关键字 'neitivnested java 嵌套的 'nestid '如:内部类nested classesObject java 对象 'bdektOverload java 方法的重载不同参数列表的同名方法 ,uv'ludOverride java 方法的覆盖覆盖父类的方法 ,uv'raidpolymiorphismjava 多态 polymorphism 多形性,pli'm:fizmallowing a single object to be seen as having many types.principlen.原则,原理,主义 'prinsiplpriority n. 优先级 prai'ritiprocess n. 程序, 进程 'prsesprotected 关键字受保护的,私有的 pr'tektidprovide v.规定供应,准备,预防pr'vaidrefer to v.引用 ri'f:tu:referencen. 参考引用,涉及'refrns' -->reference variable 参量, 参考变量,引用变量Reflectionjava 反射 ri'fleknscriptn.手写体,小型程序 skriptserialized vt.序列化,串行化 'sirilaiz'serializable adj.deserialize反序列化,反串行化Socket java 网络套接字'skitstack n.堆栈 stk 对应 heap 堆statement程序语句; 语句 'steitmnt' n. 陈述,指令subclass n.子类 'sbklɑ:s' supertype 父类switch 关键字选择语句; n.开关,道岔 switsynchronized 关键字同步锁 'sikrnaizThread java 线程θredthrow 关键字 throws 关键字θru 抛出异常transient 关键字瞬变;临时的'trnzint'可序列化valid 正确的,有效的 'vlidvariable n.变量 a.可变的'vriblvolatile 关键字不稳定的'vltailwhile 关键字循环语句; 当...的时候 hwailabstract 关键字抽象 'bstrktaccessvt.访问,存取 'kses'n.入口,使用权algorithmn.算法 'lgriemAnnotationjava 代码注释 nu'teinanonymousadj.匿名的'nnims'反义:directly adv.直接地,立即di'rektli, dai'rektli apply v.应用,适用 'plaiapplication n.应用,应用程序 ,pli'kein' application crash 程序崩溃arbitrarya.任意的 'ɑ:bitrriargument n.参数;争论,论据 'ɑ:gjumnt'缩写 argsassert 关键字断言 's:t ' java 之后成为关键字associaten.关联同伴,伙伴 'suieitattributen.属性品质,特征 'tribju:tboolean关键字逻辑的, 布尔型call .调用; 呼叫; k:lcircumstancen.事件环境,状况 's:kmstnscrash n.崩溃,破碎 krcohesion 内聚,黏聚,结合 ku'hi:na class is designed with a single, well-focoused purpose. 应该不止这点command n. 命令,指令 k'mɑ:nd指挥, 控制 command-line 命令行Comments java 文本注释 'kmentscompilejava v.编译 km'pail' Compilation n.编辑,kmpi'leinconst 保留字constant n. 常量, 常数, 恒量 'knstntcontinue 关键字coupling 耦合,联结 'kplimaking sure that classes know about other classes only through their APIs. declarejava 声明 di'kldefault关键字默认值; 缺省值 di'f:ltdelimiter定义符; 定界符Encapsulationjava 封装 hiding implementation detailsException java 例外; 异常 ik'sepnentry n.登录项, 输入项, 条目'entrienum关键字execute vt.执行 'eksikju:texhibit v.显示, 陈列 ig'zibitexist 存在, 发生 ig'zist 'SQL关键字 existsextends关键字继承、扩展 ik'stendfalse 关键字final 关键字 finally 关键字fragments段落; 代码块 'frgmntFrameWork java 结构,框架 'freimw:kGenericjava 泛型 di'nerikgoto保留字跳转heap n.堆 hi:pimplements关键字实现 'implimntimport 关键字引入进口,输入Info n.信息 information ,inf'meinInheritance java 继承 in'heritns 遗传,遗产initialize 预置初始化 i'nilaizinstanceof关键字运算符,用于引用变量,以检查这个对象是否是某种类型;返回 boolean 值; interface 关键字接口 'intfeisinvokevt.调用 in'vuk' invocation ,invu'keinIterator java 迭代器, 迭代程序legal 合法的 'li:gllogn.日志,记录 lgnative 关键字 'neitivnested java 嵌套的 'nestid '如:内部类nested classesObject java 对象 'bdektOverload java 方法的重载不同参数列表的同名方法 ,uv'ludOverride java 方法的覆盖覆盖父类的方法 ,uv'raidpolymiorphismjava 多态 polymorphism 多形性,pli'm:fizmallowing a single object to be seen as having many types.principlen.原则,原理,主义 'prinsiplpriority n. 优先级 prai'ritiprocess n. 程序, 进程 'prsesprotected 关键字受保护的,私有的 pr'tektidprovide v.规定供应,准备,预防pr'vaidrefer to v.引用 ri'f:tu:referencen. 参考引用,涉及'refrns' -->reference variable 参量, 参考变量,引用变量Reflectionjava 反射 ri'fleknscriptn.手写体,小型程序 skriptserialized vt.序列化,串行化 'sirilaiz'serializable adj.deserialize反序列化,反串行化Socket java 网络套接字'skitstack n.堆栈 stk 对应 heap 堆statement程序语句; 语句 'steitmnt' n. 陈述,指令subclass n.子类 'sbklɑ:s' supertype 父类switch 关键字选择语句; n.开关,道岔 switsynchronized 关键字同步锁 'sikrnaizThread java 线程θredthrow 关键字 throws 关键字θru 抛出异常transient 关键字瞬变;临时的'trnzint'可序列化valid 正确的,有效的 'vlidvariable n.变量 a.可变的'vriblvolatile 关键字不稳定的'vltailwhile 关键字循环语句; 当...的时候 hwailargument 参量 abstract 抽象ascent 提升 already 已经 AWTAbstract Window Toolkit抽象窗口工具 APIApplication Programming Interface应用程序接口B. byte 字节 Boolean 布尔 banana香蕉base 基础 buffer缓冲器 button 按钮 break 中断body 身体C. color颜色 class类 count计数 client客户 code代码calculation计算 cell单元 circle圆capital首都 catch捕获 check检查 container容器 component 组件 command 命令 cube立方,三次方 char=character字符 cancel取消 case 情况 choice选择 click单击 center 中心compile编译 clone克隆,复制 continue 继续 create建立D. draw 绘图 data数据 demo示例 DLLDynamic Link Library动态链接库 document 文档descent 继承 division 分裂,除法 define定义,说明 display显示E. error 错误 extends 扩展 executed 执行 event 事件 enter 输入,回车键 exception 异常except 除外 employee 雇员environment 环境 east 东方 equal 相等 Echo 重复F. false 假的 float 单精度型 fruit 水果 file 文件 find 发现found 发现 field 域 final 终结的 friend 朋友 fill 填充 focus 焦点font 字体 factorial 阶乘G. graphic 图像 grid 方格 GUI图形化用户接口 get 得到H. host 主机 height 高度I. init=initialize初始化 input 输入 implement 实现 instance 实例 io=input/output输出输入 interrupted 中断 int=integer整型 item元素 interface 接口 inner 内部的 import 导入index 索引image 图像J. Java 爪哇 JDKJava Development Kit Java开发工具 JSPJava Server Page Java服务页JVMJava Virtual Machine Java虚拟机K. Kit 工具L. language 语言 loop 循环 long 长整型 label 标签 layout 布局 list 列表 listener 收听者M. move 移动 menu 菜单 mode 模式 method 方法 metric 米的,公尺 motion 运动 manager 经理 main 主要的 msg=message 消息N. new 新的 number 数字 north 北方 null 空的 native 本地的O. override 过载 orange 橘子 output 输出 object 对象 out 外部的 oval 椭圆P. public 公共的 protected 保护的 private 私有的 property 属性 point 点 price 价格 problem 问题 package 打包,包裹 print 打印 path 路径 po;ygon 多边形 program 程序 prompt 提示parse 分析 press 按,压 panel 面板 paint 画Q. q无R. return 返回 runnable 可捕获的 radius 半径 round 环绕 release 释放 rect=rectangle长方形radio 无线电 resolve 解析S. short 短整型 south 南方的 string 字符串 static 静态的 system 系统 seed 种子 seasonal 季节的 set 设置 super 超级 square 平方,二次方 sub 替代的 screen 屏幕 sound声音 state 状态salary 薪水 sleep 睡觉 size 大小,尺寸 start 开始 sort 排序 status 状态 synchronize 同步发生switch 开关 stream 流 symbol 符号T. true 真的 title 标题 type 类型 temp=temporary暂时的 throw 扔 thread 线程 temperate 温度 tool 工具 try 试图U. undefined 未定义 UIUser Interface 用户接口 update 更新 URLUniform Resource Locator 统一资源定位器V. volatile 挥发性 visible 不可见的 virtual 虚拟的 variable 变量 value 数值 void 无返回值的 volume 列 viewer 观察者 vector 矢量●我喜欢「式」:constructor 建构式declaration 宣告式definition 定义式destructor 解构式expression 算式运算式function 函式pattern 范式、模式、样式program 程式signature 标记式签名式/署名式●我喜欢「件」:这是个弹性非常大的可组合字assembly 装配件component 组件construct 构件control 控件event 事件hardware 硬件object 物件part 零件、部件singleton 单件software 软件work 工件、机件●我喜欢「器」:adapter 配接器allocator 配置器compiler 编译器container 容器iterator 迭代器linker 连结器listener 监听器interpreter 直译器translator 转译器/翻译器●我喜欢「别」:class 类别type 型别●我喜欢「化」:generalized 泛化specialized 特化overloaded 多载化重载●我喜欢「型」:polymorphism 多型genericity 泛型●我喜欢「程」:process 行程/进程大陆用语thread 绪程/线程大陆用语programming 编程●英中繁简编程术语对照英文繁体译词有些是侯捷个人喜好,普及与否难说大陆惯用术语--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- define 定义预定义abstract 抽象的抽象的abstraction 抽象体、抽象物、抽象性抽象体、抽象物、抽象性access 存取、取用存取、访问access level 存取级别访问级别access function 存取函式访问函数activate 活化激活active 作用中的adapter 配接器适配器address 位址地址address space 位址空间,定址空间address-of operator 取址运算子取地址操作符aggregation 聚合algorithm 演算法算法allocate 配置分配allocator 空间配置器分配器application 应用程式应用、应用程序application framework 应用程式框架、应用框架应用程序框架architecture 架构、系统架构体系结构argument 引数传给函式的值;叁见 parameter 叁数、实质叁数、实叁、自变量array 阵列数组arrow operator arrow箭头运算子箭头操作符assembly 装配件assembly language 组合语言汇编语言assertion 断言assign 指派、指定、设值、赋值赋值assignment 指派、指定赋值、分配assignment operator 指派赋值运算子 = 赋值操作符associated 相应的、相关的相关的、关联、相应的associative container 关联式容器对应 sequential container 关联式容器atomic 不可分割的原子的attribute 属性属性、特性audio 音讯音频. 人工智慧人工智能background 背景背景用於图形着色後台用於行程backward compatible 回溯相容向下兼容bandwidth 频宽带宽base class 基础类别基类base type 基础型别等同於 base classbatch 批次意思是整批作业批处理benefit 利益收益best viable function 最佳可行函式最佳可行函式从 viable functions 中挑出的最佳吻合者binary search 二分搜寻法二分查找binary tree 二元树二叉树binary function 二元函式双叁函数binary operator 二元运算子二元操作符binding 系结绑定bit 位元位bit field 位元栏位域bitmap 位元图位图bitwise 以 bit 为单元逐一┅bitwise copy 以 bit 为单元进行复制;位元逐一复制位拷贝block 区块,区段块、区块、语句块boolean 布林值真假值,true 或 false 布尔值border 边框、框线边框bracecurly brace 大括弧、大括号花括弧、花括号bracketsquare brakcet 中括弧、中括号方括弧、方括号breakpoint 中断点断点build 建造、构筑、建置MS 用语build-in 内建内置bus 汇流排总线business 商务,业务业务buttons 按钮按钮byte 位元组由 8 bits 组成字节cache 快取高速缓存call 呼叫、叫用调用callback 回呼回调call operator call函式呼叫运算子调用操作符同 function call operatorcandidate function 候选函式候选函数在函式多载决议程序中出现的候选函式chain 串链例 chain of function calls 链character 字元字符check box 核取方块 . check button 复选框checked exception 可控式异常Javacheck button 方钮 . check box 复选按钮child class 子类别或称为derived class, subtype 子类class 类别类class body 类别本体类体class declaration 类别宣告、类别宣告式类声明class definition 类别定义、类别定义式类定义class derivation list 类别衍化列类继承列表class head 类别表头类头class hierarchy 类别继承体系, 类别阶层类层次体系class library 类别程式库、类别库类库class template 类别模板、类别范本类模板class template partial specializations类别模板偏特化类模板部分特化class template specializations类别模板特化类模板特化cleanup 清理、善後清理、清除client 客端、客户端、客户客户client-server 主从架构客户/服务器clipboard 剪贴簿剪贴板。
运⾏java的class⽂件⽅法详解⼀、运⾏class⽂件执⾏带main⽅法的class⽂件,命令⾏为:java <CLASS⽂件名>注意:CLASS⽂件名不要带⽂件后缀.class例如:复制代码代码如下:java Test如果执⾏的class⽂件是带包的,即在类⽂件中使⽤了:package <包名>那应该在包的基路径下执⾏,命令⾏为:java <包名>.CLASS⽂件名例如:PackageTest.java中,其包名为:com.ee2ee.test,对应的语句为:package com.ee2ee.test;PackageTest.java及编译后的class⽂件PackageTest.class的存放⽬录如下:classes|__com|__ee2ee|__test|__PackageTest.java|__PackageTest.class要运⾏PackageTest.class,应在classes⽬录下执⾏:复制代码代码如下:java com.ee2ee.test.PackageTest⼆、运⾏jar⽂件中的class原理和运⾏class⽂件⼀样,只需加上参数-cp <jar⽂件名>即可。
例如:执⾏test.jar中的类com.ee2ee.test.PackageTest,命令⾏如下:复制代码代码如下:java -cp test.jar com.ee2ee.test.PackageTest三、显⽰jdk版本信息当⼀台机器上有多个jdk版本时,需要知道当前使⽤的是那个版本的jdk,使⽤参数-version即可知道其版本,命令⾏为:复制代码代码如下:java -version四、增加虚拟机可以使⽤的最⼤内存java虚拟机可使⽤的最⼤内存是有限制的,缺省值通常为64MB或128MB。
如果⼀个应⽤程序为了提⾼性能⽽把数据加载内存中⽽占⽤较⼤的内存,⽐如超过了默认的最⼤值128MB,需要加⼤java虚拟机可使⽤的最⼤内存,否则会出现Out of Memory(系统内存不⾜)的异常。
前言翻译初衷,记录JNI编程经验以备后查,并奢望以JNI为蓝本,写一本更深入的关于虚拟机的书。
真做起来,才发现以现有水平只能仰望这个目标,要达到它,还需要几年积累。
本书没有采用逐字逐句的翻译,更多采用意译,请大家在阅读时多参考原著;对于书中夹杂的评论,如有伤观感,请大家见谅。
现在有无数优秀的开源项目,以前高深莫测的技术(虚拟机、编译器、操作系统、协议栈和IDE...), 我们终于有机会一探究竟了,真令人兴奋。
我们学习,我们参与,希望有一天我们中国人也能创一门牛技术。
感谢Die...ken的审稿,他严谨和认真的态度,深感敬佩;哥们儿祝你:天天开心,早结连理。
感谢老婆。
老婆读书时,看见别人写的书总会感谢太太云云,煞是羡慕,总追问:你什么时候写书感谢我?难!翻译都这么费劲,写书就不知猴年马月了,在这儿感谢一下,糊弄糊弄得了。
do.chuan@Preface 本书涵盖了Java Native Interface(JNI)的内容,将探讨以下问题:•在一个Java项目中集成一个C/C++库•在一个用C/C++开发的项目中,嵌入JavaVM•实现Java VM•语言互操作性问题,特别是互操作过程中的垃圾回收(GC, garbage collection)和并发编程(multithreading)首先,通过本书,你会很容易的掌握JNI开发,并能了解到方方面面的关于JNI的知识。
本书详尽的叙述,会带给你你很多如何高效使用JNI的启示。
JNI自1997年初发布以来,Sun的工程师们和Java社区使用JNI的经验造就了本书。
第二,本书介绍了JNI的设计原理。
这些原理,不仅会使学术界感兴趣,也是高效使用JNI的前提。
第三,本书的某些部分是Java 2平台规范的最终版本。
JNI程序员可以此书作为规范的参考手册,Java虚拟机实现者必须遵循规范,以保证各平台实现的一致性。
(...几段不重要,未翻译...)C HA P T E R1IntroductionJNI是Java平台中的一个强大特性。
恩士迅java面试英文题Enson Java Interview English Questions1. What is Java?Java is a high-level, object-oriented programming language developed by Sun Microsystems (now owned by Oracle) in 1995. It is known for its platform independence, which means that Java programs can run on any device or operating system that has a Java Virtual Machine (JVM). Java is widely used for creating web applications, mobile applications, desktop software, and enterprise solutions.2. What are the main features of Java?Java has several key features that make it popular among developers:- Object-oriented: Java follows the principles ofobject-oriented programming (OOP), allowing developers to create reusable and modular code.- Platform independence: Java's 'write once, run anywhere' approach allows programs to be run on any device with a JVM, making it highly portable.- Memory management: Java uses automatic garbage collection, freeing developers from managing memory manually. - Multi-threading: Java supports concurrent programmingwith its built-in support for threads, allowing multiple tasks to run simultaneously.- Security: Java provides a secure environment with its built-in security features, such as sandboxing and permission-based access control.3. What is the difference between JDK and JVM?JDK (Java Development Kit) and JVM (Java Virtual Machine) are both essential components of the Java platform, but they serve different purposes.- JDK: JDK is a software development kit that provides tools and libraries necessary for Java development. It includes the Java compiler, debugger, and other utilities required to write, compile, and run Java programs.- JVM: JVM is a runtime environment that executes Java bytecode. It interprets the compiled Java code and converts it into machine code that can be understood by the underlying operating system. JVM also handles memory management and provides various runtime services.4. What is the difference between an abstract class and an interface?- Abstract class: An abstract class is a class that cannot be instantiated and is typically used as a base class for otherclasses. It can contain both abstract and non-abstract methods. Subclasses of an abstract class must implement its abstract methods. An abstract class can also have fields and constructors.- Interface: An interface is a collection of abstract methods and constants. It cannot be instantiated and is used to define a contract for implementing classes. A class can implement multiple interfaces, but it can only extend a single class. Interfaces are used to achieve multiple inheritance in Java.5. What are the different types of exceptions in Java? Java has two types of exceptions: checked exceptions and unchecked exceptions.- Checked exceptions: These are exceptions that are checked at compile-time. The developer must either handle these exceptions using try-catch blocks or declare them in the method signature using the 'throws' keyword. Examples of checked exceptions include IOException and SQLException.- Unchecked exceptions: These are exceptions that are not checked at compile-time. They are subclasses of RuntimeException and Error classes. Unchecked exceptions do not need to be declared or caught explicitly. Examples ofunchecked exceptions include NullPointerException and ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException.These are just a few sample questions that can be asked during a Java interview. It is important to remember that the depth and complexity of questions may vary depending on the level of the position being applied for. It is advisable to thoroughly prepare and revise various topics related to Java programming to increase the chances of success in a Java interview.。
java程序调用javac编译.java文件生成.class文件public class Test{public void compile(String path) throws IOException {Runtime rt = Runtime.getRuntime();String command = "javac ";rt.exec(command + path);rt.gc();}}初学Java时教科书告诉我们,若要运行Java程序,必需为其设置环境变量。
有时候为了实现某种功能(例如动态加载Class)我们需要在程序中来实现这个功能。
我们经常使用的Eclipse就是很好的例子,它的所有插件的.jar文件都是放在plugin目录下的,如何加载这些包并使用其中的类成了一个棘手的问题。
(关于Eclipse的类加载机制,大家可以参考《Contributing to Eclipse》p54)下面我们就来看看,在程序中如何实现这个功能。
1、建立一个工程,并为其增加一个Interface,命名为ActionInterface.java。
该接口为使用者公开了一个方法,如下:程序代码package org.junesky.classPathTest;public interface ActionInterface {public String action();}编译后,将该工程打包为.jar文件。
打包方法:在包的顶级目录(也就是例子中的org所在的目录)建立一个名为MANIFEST.MF的文件,键入:Manifest-Version: 1.0保存。
在ms-doc窗口中键如命令:jar cvfm classLoader.jar MANIFEST.MF org/其中classLoader.jar是打包后的文件名,org/是path。
2、建立一个新工程,将classLoader.jar导入,新建class文件MyAction并实现ActionInterface。
Speeding up Java Programs by calling native methodsStudienarbeitInstitut für elektrische NachrichtentechnikRWTH-AachenFelix EngelMatrikelnummer:222750Betreuer:Holger CrysandtJuly21,2004Contents1Introduction42The Java Native Interface52.1Declare a Java method as native (5)2.2Compile the Java class (5)2.3Create a C-headerfile from the compiled Java Class (6)2.4Implement the functions declared in the headerfile (6)2.5Create a shared library (7)2.6Load the library into the Java class (7)3Test Procedure83.1Tests involved (8)4Analysing Test Results104.1Description of the plots (10)4.2Represantative cases (11)4.2.1Worst case order n:copy (11)4.2.2Best case order n:dot (12)4.2.3Order n2:gemv (12)4.2.4Order n3:gemm (13)5Conclusions20 References20A Test routines22B Hardware configurations242CONTENTS3Chapter1IntroductionThe popularity and widespread use of the Java Programming Language are constantly increasing. The main reasons for this development are:•Cross platform availability•Pure object Orientation•A garbage collector which autmatically frees memory that is not being referenced anymore •A wide set of tested“off the shelf“libraries for a vast number of tasks are provided by the Java Runtime Environment(JRE)and third party vendors.However,Java bytecode cannot be as performant as highly optimized C or FORTRAN code. Especially for numerical computations,hardware vendors like SUN Microsystems[1],Intel[2] and Silicon Graphics provide libraries which generally include the“Basic Linear Algebra Sub-programs“(BLAS)[3].The BLAS standardize FORTRAN subroutines and functions for basic vector and matrix operations.Java specifies an interface to call native methods written in any language from within Java classes,using the“Java Native Interface“(JNI)[4].In order to benefit from the availability of vendor supplied libraries and thereby speed up numerical computations in Java,the use of the JNI is a promising approach.In this paper,an analysis of the potential speed gain which can be achieved by calling opti-mized BLAS routines via the Java Native Interface will be done.A similar analysis has been done by Bik and Gannon[5]in1997.This paper will show, that due to the rapid developement the Java platform has experienced since then,their results are outdated by now.4Chapter2The Java Native InterfaceThe Java specification by SUN Microsystems includes the“Java Native Interface“,a C/C++API1 to•Call native methods from within Java classes•Load a Java virtual machine into a running C-Program and thereby call Java software from C-CodeIn this paper,thefirst option is used:Calling native methods from java.In this chapter the steps necessary to call native code from a Java class are described.2.1Declare a Java method as nativeBy using the keyword native a method is declared as native and its body is not implemented. public static final native void scal(int n,float alpha, float[]x,int off_x,int inc_x);2.2Compile the Java classTo compile the class,a command like the following can be used:javac de/smurflord/BlasJNI/BlasL1.javaThis command has to be called from the toplevel directory,otherwise the linker cannot properly resolve the name of the native methods.6T HE J AVA N ATIVE I NTERFACE 2SDK:S oftware D evelopement K it2.5C REATE A SHARED LIBRARY7Chapter3Test Procedure3.1Tests involvedIn order to evaluate the factors which contribute to the total execution time of JNI wrapped functions,benchmarks were run on seven BLAS routines.The tested routines were nrm2,copy, scal,axpy and dot from the Level1BLAS,gemv from the Level2BLAS and gemm from the Level3BLAS.Time measurements were done by saving the system time before and after the calls to an operation and then taking the difference.Since most architectures do not contain a high precision clock,the Level1BLAS timings were taken for800iterations,while the Level2and Level3 timings were taken for1iteration.The corresponding code samples are listed infigure A.1and A.2.For all tested functions the following execution times were taken:•A native function call to a vendor supplied library.No Java code is used here.•The operation written in pure Java•The native function from a vendor supplied library called via the JNI•A function which only copies the routines from the JVM’s heap to C memory and back (seefigure A.3).For the Level2and3BLAS(GEMV and GEMM)the following additional timings were measured:•A pure C implementation(Fig.A.4and A.5)83.1T ESTS INVOLVED9Chapter4Analysing Test Results4.1Description of the plotsFor each test the results are plotted in a diagram combining four test series for the scalar functions and six for the Level2and3BLAS(tables4.1and4.2).Since the results were the same for different members of the same architecture(for example AMD and Intel Processors)and for different operating systems on the same machine,only a few representative cases are discussed here.The complete set of results is given in the appendix.Note that the scalar functions are plotted using a logarithmic scale on both axes,whereas gemm and gemv are plotted using a linear scale on the vector size axis and a logarithmic scale on the time axis.TitleJavaAn optimized library called from CJNIThe time it takes to copy the data from4.2R EPRESANTATIVE CASES11DescriptionA naive Java implementationNative CThe native C algorithm wrapped via the JNILibraryAn optimized library called from JA V AJNI to C copythe JVM to C memory and back(if necessary)Table4.2:Test series plotted for Level2and3BLASFunction Complexityn2n2n2n3nn+n24n212A NALYSING T EST R ESULTS 1SIMD:S ingle I nstruction M ultiple D ata4.2R EPRESANTATIVE CASES1314A NALYSING T EST R ESULTSI NSTITUT FÜR N ACHRICHTENTECHNIK4.2R EPRESANTATIVE CASES1516A NALYSING T EST R ESULTSI NSTITUT FÜR N ACHRICHTENTECHNIK4.2R EPRESANTATIVE CASES1718A NALYSING T EST R ESULTSI NSTITUT FÜR N ACHRICHTENTECHNIK4.2R EPRESANTATIVE CASES19Chapter5ConclusionsThe tests have shown,that invoking native functions always imposes a overhead because the native code works on copies of the original data.These copies have to be synchronised with the original data,which is an expensive operation.Furthermore,for the straightforward operations tested,Java code has proven to be slower than native code by only a factor1.5−2.As long as the complexity of the calculation is the same as the order of copy operations that have to be done, this speed advantage is consumed by the copy operations and the best choice is to use a Java method.In the case where the complexity of the operation itself is higher than the complexity of the copy operation,a speed gain in the magnitude of approximately1.5−3can be obtained by replacing Java methods with calls to native methods.A notable speed gain in order of a magnitude could,however,only be achieved for the matrix-matrix multiplication,a calculation where the main speedup can be attributed to algorithms which provide reduced complexity.These results demonstrate the rapid improvement the Java platform has undergone since Bik and Gannon[5]did their tests in1997.The speed of the Java platform has greatly improved.The advantages provided by the Java environment,most notably the excellent portability,will be lost, if the Java Native Interface is used.Due to the comparably small speedup for most calculations, the Java Native Interface should be used with care.In most cases the better solution will be to provide efficient algorithms in Java.20Bibliography[1]Sun Performance Library,/prodtech/cc/reference/docs/index.html(06/2003)[2]Intel Math Kernel Library,/software/products/mkl,June2003[3]Blas Quick Reference GuideUniversity of Tennesse,Oak Ridge National Laboratory,Numerical Algorithms Group Ltd.,May11, 1997[4]SUN Microsystems:Java Native Interface Specification/j2se/1.3/docs/guide/jni/spec/jniTOC.doc.html,May16,1997[5]Aart J.C.Bik,Dennis B.Gannon:A Note on Native Level1BLAS in JAVA,Inidana University,Computer Science Department,1997[6]Jack J.Dongarra,Jeremy Du Croz,Sven Hammarling,Richard J.Hanson:An Extended Set of Fortran Basic Linear Algebra Subprograms,Argonne National Laboratory,Math-ematics and Computer Science Division,September1986[7]V olker Strassen:Gaussian Elimination is not Optimal,Numerische Mathematik,13(1969)354-35621Appendix ATest routineslong start=System.currentTimeMillis();for(int i=0;i<m_Schleifen;i++){scal((int)m_Vektorgroesse,alpha,vector,0,1);}long end=System.currentTimeMillis();long dauer=end-start;Figure A.1:Java source code to measure CPU time start=clock();int inc=1;for(i=0;i<Schleifen;i++){dscal_(&VektorGroesse,&alpha,Vector,&inc);}free(Vector);stop=clock();dauer=((stop-start)*1000)/CLOCKS_PER_SEC;Figure A.2:C source code to measure CPU time2223Appendix BHardware configurationsThe following hardware/software configurations were tested:•Sun Ultra10,300MHz Ultra Sparc II Processor,192MB RAM,16Kb L1Instruction Cache,16Kb L1Data Cache,512Kb L2Cache.SunOS5.7,gcc2.95.2•Intel Pentium III,450MHz Processor,386MB SDRAM,16Kb L1Instruction Cache, 16Kb L1Data Cache,512Kb L2Cache.Linux2.4.18,gcc2.95.3•AMD Duron,1.3GHz Processor,512MB DDR RAM,64Kb L1Instruction Cache64Kb L1Data Cache.Linux2.4.18,gcc2.95.4.•AMD Duron,1.3GHz Processor,512MB DDR RAM,64Kb L1Instruction Cache64Kb L1Data Cache.Windows XP Professional,gcc2.95.3,cygwin(creating a native dll).24Appendix CResults2526R ESULTSI NSTITUT FÜR N ACHRICHTENTECHNIKC.1R ESULTS FOR THE U LTRA102728R ESULTSI NSTITUT FÜR N ACHRICHTENTECHNIKC.1R ESULTS FOR THE U LTRA102930R ESULTSI NSTITUT FÜR N ACHRICHTENTECHNIKC.2R ESULTS FOR THE P ENTIUM III3132R ESULTSI NSTITUT FÜR N ACHRICHTENTECHNIKC.2R ESULTS FOR THE P ENTIUM III3334R ESULTSI NSTITUT FÜR N ACHRICHTENTECHNIKC.3R ESULTS FOR THE AMD RUNNING LINUX3536R ESULTSI NSTITUT FÜR N ACHRICHTENTECHNIKC.3R ESULTS FOR THE AMD RUNNING LINUX3738R ESULTSI NSTITUT FÜR N ACHRICHTENTECHNIKC.4R ESULTS FOR THE AMD RUNNING W INDOWS3940R ESULTSI NSTITUT FÜR N ACHRICHTENTECHNIKC.4R ESULTS FOR THE AMD RUNNING W INDOWS41。