Chapt3
- 格式:ppt
- 大小:1.13 MB
- 文档页数:113
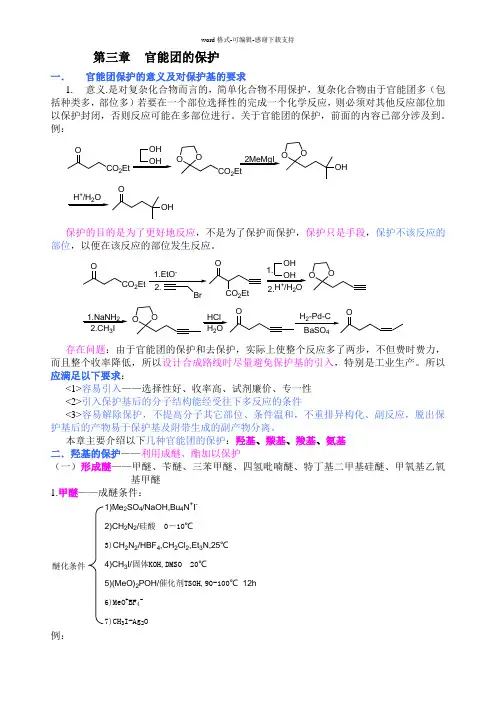
第三章 官能团的保护一. 官能团保护的意义及对保护基的要求1. 意义.是对复杂化合物而言的,简单化合物不用保护,复杂化合物由于官能团多(包括种类多,部位多)若要在一个部位选择性的完成一个化学反应,则必须对其他反应部位加以保护封闭,否则反应可能在多部位进行。
关于官能团的保护,前面的内容已部分涉及到。
例:CO 2EtOOH OHOOCO 2Et2MeMgI OOOH+2OOH保护的目的是为了更好地反应,不是为了保护而保护,保护只是手段,保护不该反应的部位,以便在该反应的部位发生反应。
CO 2EtOOH OH O O+2O-CO 2Et 1.2.1.NaNH 23OOHCl H 2O存在问题:由于官能团的保护和去保护,实际上使整个反应多了两步,不但费时费力,而且整个收率降低,所以设计合成路线时尽量避免保护基的引入,特别是工业生产。
所以应满足以下要求:<1>容易引入——选择性好、收率高、试剂廉价、专一性 <2>引入保护基后的分子结构能经受往下多反应的条件<3>容易解除保护,不提高分子其它部位、条件温和,不重排异构化、副反应,脱出保护基后的产物易于保护基及附带生成的副产物分离。
本章主要介绍以下几种官能团的保护:羟基、羰基、羧基、氨基 二.羟基的保护——利用成醚、酯加以保护(一)形成醚——甲醚、苄醚、三苯甲醚、四氢吡喃醚、特丁基二甲基硅醚、甲氧基乙氧基甲醚1.甲醚——成醚条件:1)Me 2SO 4/NaOH,Bu 4N +I -2)CH 2N 2/硅酸 0-10℃3)CH 2N 2/HBF 4,CH 2Cl 2,Et 3N,25℃4)CH 3I/固体KOH,DMSO 20℃5)(MeO)2POH/催化剂TSOH,90-100℃ 12h 6)MeO +BF 4-7)CH 3I-Ag 2O醚化条件例:OH+Me 2SO 4NaOHMeOSO 3Na+OCH3CH 2N 2+RCH 2OH RO -RCH 2OCH 3R 2CN 2ArOHR 2CHOAr CH2N 2ROHHBF 4ROCH 3+++N 2特别是酚羟基一般用MeO -醚保护,反应容易,解脱也容易,醇羟基形成甲醚较稳定,不易脱掉,故少用,在糖类化合物中羟基的保护勿用形成醚。


第3章 保险合同 (上)[思考与练习]1. 保险合同与一般的合同相比有什么共性与特性?为什么保险合同会具有射幸性和个人性的特征?2. 试从主体、客体和内容三个方面分析保险合同的要件。
3. 继承人与保单受益人的区别是什么?4. 在人身保险中,“被保险人”与“保单所有人”各自角色的规定是什么?为什么需要有“保单所有人”这个角色?5. 以下哪些情况中,投保人对保险标的具有保险利益?(1)王先生因病去世,其家人要承受每年3万元的收入损失。
王先生的家人以王先生为被保险人投保终身寿险。
(2)与妻子离婚之后,在双方对子女监护权协商未果之时,王先生欲为其子女购买人身保险。
(3)A公司已为一批进口货物缴纳了预付款,货物在对方国家港口即将启运,提单尚未转手。
A公司就该批货物向保险公司投保货物运输保险。
6.在保险实践中,如果不遵循保险利益原则可能会出现什么样的后果?第4章 保险合同(下)[思考与练习]1. 保险合同从订立到生效需经过哪些阶段?2.投保人有哪些义务?规定投保人负有“危险增加”的通知义务对保险公司而言有什么好处?3.保险人有哪些义务?试说明规定除外风险的必要性。
对于被普通保险合同排除在外的风险,投保人可以采取什么措施来进行防范和补偿?4.周先生在为其房屋投保财产保险时,将门牌号“9”误写为“6”,并且向保险公司隐瞒了其房屋毗邻一家烟花爆竹厂的事实。
投保三个月以后,周先生的房屋失火,损毁了一些物件。
上述哪项事实会影响保险合同的效力?该事实又会对合同产生什么样的影响?5.王先生为一批货物投保了运输险。
载货车辆在运输途中发生车祸,因此导致货物损毁。
保险公司在实地勘察时发现此批货物属于走私物品。
保险公司是否可以据此宣告保险合同无效?6.保险合同在满足一定条件的情况下可以复效。
这一规定对保险公司和投保人而言各有什么好处?7.保险合同的解释原则是什么?为什么在当事人对合同条款有争议时,法院通常会做出对投保人有利的解释?2。








Chapter 3 Transport Layer1.One of the main duties of the transport layer is to provide ____________ communication.A) node-to-nodeB) host-to-hostC) process-to-processD) None of the choices are correct2.A client program normally uses ____________ port number. A server program normally uses __________ port number.A) a well-known; an ephemeralB) an ephemeral; a well-knownC) a private; a well-knownD) None of the choices are correct3.A socket address is a combination of __________.A) A MAC address and a logical addressB) A MAC address and a port numberC) a user-specific address and a logical addressD) None of the choices are correct4.______________ means accepting items from more than one source. ______________ means delivering items to more than one source.A) Demultiplexing; MultiplexingB) Multiplexing; DemultiplexingC) Encapsulation; DecapsulationD) Pulling; Pushing5.________ means the producer delivers the items when they are produced. _______ means the consumer takes the items when it is ready to do so.A) Pushing; pullingB) Pulling; pushingC) Forwarding; acceptingD) None of the choices are correct6.In the stop-and-wait protocol, the maximum send window size is ______ and the maximum receive window size is _______ where m is the number of bits in the sequence.A) 1; 1B) 2m; – 1C) 1; 2mD) 2m; 2m7.In the Go-Back-N protocol, the maximum send window size is ______ and the maximum receivewindow size is _______, where m is related to the number of bits in the sequence. number.A) 1; 1B) 1; 2mC) 2m – 1; 1D) 2m – 1; 2m – 18.In the selective-repeat protocol, the maximum send window size is ______ and the maximum receive window size is _______, where m is the number of bits in the sequence.A) 1; 1B) 1; 2m – 1C) 2m – 1; 1D) 2m – 1; 2m – 19.UDP is a ________________ transport protocol.A) connectionless, reliableB) connection-oriented, unreliableC) connectionless, unreliableD) None of the choices are correct10.UDP is an acronym for _______.A) User Delivery ProtocolB) User Datagram ProcedureC) User Datagram ProtocolD) None of the choices are correct11.At the transport layer, to define the processes, we need two identifiers called ____________.A) logical addressesB) physical addressesC) port addressesD) None of the choices are correct12.The ports ranging from 0 to 1,023 are called the ___________ ports. The ports ranging from 1,024 to 49,151 are called ___________ ports. The ports ranging from 49,152 to 65,535 are called the ___________ ports.A) well-known; registered; dynamic or privateB) registered; dynamic or private; well-knownC) private or dynamic; well-known; registeredD) private or dynamic; registered; well-known13.UDP and TCP are two protocols at the ___________ layer.A) data linkB) networkC) transportD) application14.Which of the following functions are performed by UDP?A) process-to-process communicationB) host-to-host communicationC) node-to-node communicationD) None of the choices are correct15.A port number is _______ bits long.A) 8B) 16C) 32D) 6416.Which of the following does UDP provide?A) flow controlB) connection-oriented deliveryC) error controlD) None of the choices are correct17.The source port number on the UDP user datagram header defines _______.A) the sending computerB) the receiving computerC) the process running on the sending computerD) None of the choices are correct18.To use the services of UDP, we need ________ socket addresses.A) fourB) twoC) threeD) None of the choices are correct19.UDP packets are called __________ .A) user datagramsB) segmentsC) framesD) None of the choices are correct20.UDP packets have a fixed-size header of _______ bytes.A) 16B) 8C) 40D) 3221.TCP is a __________ protocol.A) byte-orientedB) message-orientedC) block-orientedD) None of the choices are correct22.TCP groups a number of bytes together into a packet called a ___________.A) user datagramB) segmentC) datagramD) None of the choices are correct23.TCP is a(n) ___________ protocol.A) connection-orientedB) connectionlessC) both connection-oriented and connectionlessD) None of the choices are correct24.TCP is a(n) _______ transport protocol.A) unreliableB) best-effort deliveryC) reliableD) None of the choices are correct25.TCP uses _________________ to check the safe and sound arrival of data.A) an acknowledgment mechanismB) out-of-band signalingC) the services of another protocolD) None of the choices are correct26.The bytes of data being transferred in each connection are numbered by TCP. The numbering starts with a __________________.A) 0B) 1C) randomly generated numberD) None of the choices are correct27.In TCP, the sequence number for each segment is the number of the _______ byte (virtual byte) carried in that segment.A) firstB) lastC) middleD) None of the choices are correct28.Communication in TCP is ___________.A) simplexB) half-duplexC) full-duplexD) None of the choices are correct29.In TCP, the value of the acknowledgment field in a sent segment defines the sequence number related to the ______ byte a party expects to receive next.A) firstB) lastC) nextD) None of the choices are correct30.The inclusion of the checksum in the TCP segment is ________.A) optionalB) mandatoryC) depends on the type of dataD) None of the choices are correct31.In TCP, a SYN segment consumes _____ sequence number(s).A) noB) oneC) twoD) None of the choices are correct32.In TCP, a SYN + ACK segment consumes _____ sequence numbers.A) noB) threeC) twoD) one33.In TCP, an ACK segment, if carrying no data, consumes ______ sequence number(s).A) noB) oneC) twoD) None of the choices are correct34.The connection establishment procedure in TCP is susceptible to a serious security problem called the _________ attack.A) ACK floodingB) FIN floodingC) SYN floodingD) None of the choices are correct35.The SYN flooding attack belongs to a group of security attacks known as a _____ attack.A) denial of serviceB) replayC) man-in-the middleD) None of the choices are correct36.In TCP, a FIN segment consumes ____ sequence numbers if it does not carry data.A) twoB) threeC) noD) one37.In TCP, a FIN + ACK segment consumes _____ sequence number(s) if it does not carry data.A) twoB) threeC) oneD) no38.In TCP, one end can stop sending data while still receiving data. This is called a ______ termination.A) half-closeB) half-openC) full-closeD) None of the choices are correct39.TCP sliding windows are __________ oriented.A) packetB) segmentC) byteD) None of the choices are correct40.In TCP, the size of the send window is the ________ of rwnd and cwnd.A) maximumB) sum ofC) minimumD) None of the choices are correct41.In TCP, the window should not be _________.A) openedB) closedC) shrunkD) slide42.In TCP, the receiver can temporarily shut down the window; the sender, however, can always send a segment of _____ byte(s) after the window is shut down.A) tenB) zeroC) oneD) None of the choices are correct43.A serious problem can arise in the sliding window operation when either the sending application program creates data slowly or the receiving application program consumes data slowly, or both. This problem is called the ______.A) silly window syndromeB) unexpected syndromeC) window bugD) None of the choices are correct44.Nagle's algorithm can solve the silly window syndrome created by the _________.A) senderB) receiverC) both sender and receiverD) None of the choices are correct45.Clark's solution can solve the silly window syndrome created by the _________.A) senderB) receiverC) both sender and receiverD) None of the choices are correct46.Delayed acknowledgment can solve the silly window syndrome created by the _________.A) senderB) receiverC) both sender and receiverD) None of the choices are correct47.In TCP, an ACK segments that carry no data consumes _______ sequence number(s).A) noB) oneC) twoD) None of the choices are correct48.In modern implementations of TCP, a retransmission occurs if the retransmission timer expires or ________ duplicate ACK segments have arrived.A) oneB) twoC) threeD) None of the choices are correct49.In TCP, ________ retransmission timer is set for an ACK segment.A) oneB) a previousC) noD) None of the choices are correct50.In TCP, there can be ______ RTT measurement(s) in progress at any time.A) twoB) only oneC) severalD) None of the choices are correct51.We need to multiply the header length field by _______ to find the total number of bytes in the TCP header.A) 2B) 4C) 6D) None of the choices are correct52.In TCP, urgent data requires the urgent pointer field as well as the URG bit (to be set) in the _______ field.A) controlB) offsetC) sequence numberD) None of the choices are correct53.In TCP, if the ACK value is 200, then byte _______ has been received successfully.A) 199B) 200C) 201D) None of the choices are correct54.In TCP, the _______ timer prevents a long idle connection between two TCPs.A) retransmissionB) persistenceC) keepaliveD) None of the choices are correct55.In TCP, the _______ timer is needed to handle the zero window-size advertisement.A) retransmissionB) persistenceC) keepaliveD) None of the choices are correct56.In TCP, Karn's algorithm is used in calculations by the _______ timer.A) retransmissionB) persistenceC) keepaliveD) None of the choices are correct57.In TCP, a special segment called a probe is sent by a sending TCP when the _______ timer goes off.A) transmissionB) persistenceC) keepaliveD) None of the choices are correct58.__________ control refers to the mechanisms and techniques to keep the load below the capacity.A) flowB) errorC) congestionD) None of the choices are correct59.In TCP's ________ algorithm the size of the congestion window increases exponentially until it reaches a threshold.A) congestion avoidanceB) congestion detectionC) slow startD) None of the choices are correct60.In TCP's __________ algorithm the size of the congestion window increases additively until congestion is detected.A) congestion avoidanceB) congestion detectionC) slow startD) None of the choices are correct61.________ treats the two signs of congestion detections, timeout and three duplicate ACKs, in the same way.A) Taho TCPB) Reno TCPC) new Reno TCPD) None of the choices are correct62.In ______ TCP, when the connection is established, TCP starts the slow start algorithms and sets the ssthresh variable to a pre-agreed value (normally 64 or 128 kilobytes) and the cwnd variable to 1 MSS.A) Taho TCPB) Reno TCPC) new Reno TCPD) None of the choices are correct63.The ___________ added a new state to the congestion control FSM, called the fast recovery state.A) Taho TCPB) Reno TCPC) new Reno TCPD) None of the choices are correct64.The ___________ treated the two signals of congestion, timeout and arrival of three duplicate ACKs, differently.A) Taho TCPB) Reno TCPC) new Reno TCPD) None of the choices are correct65.The __________ state in Reno TCP is a state somehow between the slow start and the congestion avoidance states.A) congestion avoidanceB) congestion detectionC) slow recoveryD) None of the choices are correct66.In the Reno TCP, when TCP enters the fast recovery, if duplicate ACKs continue to come, TCP ____________________________________.A) stays in this state, but the cwnd grows additivelyB) stays in this state, but the cwnd grows exponentiallyC) moves to slow start stateD) moves to the congestion avoidance state but deflate the size of the cwnd to ssthresh value67.In the Reno TCP, when TCP enters the fast recovery, if a timeout occurs, TCP ____________________________________.A) stays in this state, but the cwnd grows additivelyB) stays in this state, but the cwnd grows exponentiallyC) moves to slow start stateD) moves to the congestion avoidance state but deflate the size of the cwnd to ssthresh value68.In the Reno TCP, when TCP enters the fast recovery, if a new (non duplicate) ACK arrives TCP.____________________________________.A) stays in this state, but the cwnd grows additivelyB) stays in this state, but the cwnd grows exponentiallyC) moves to slow start stateD) moves to the congestion avoidance state but deflate the size of the cwnd to ssthresh value69.A later version of TCP, called ______ TCP, made an extra optimization on the _______ TCP.A) New Reno; RenoB) New Taho; TahoC) New Reno; TahoD) New Taho; Reno70.In the slow start algorithm, the size of the congestion window grows ______________ until ___________________.A) exponentially; it reaches a thresholdB) exponentially; congestion is detectedC) additively; it reaches a thresholdD) additively; congestion is detected71.In the congestion avoidance algorithm, the size of the congestion window grows ______________ congestion is detected.A) exponentially; it reaches a thresholdB) exponentially; congestion is detectedC) additively; it reaches a thresholdD) additively; congestion is detected72.The congestion window size, after it passes the initial slow start state, follows a saw tooth pattern called _________________________________.A) exponential increase, additive decreaseB) additive increase, exponential decreaseC) multiplicative increase, additive decreaseD) additive increase, multiplicative decreaseCBDBA ACDCC CACAB DCBAB ABACA CACCB BDACA DCACC CCAAB BACCB BAACB ABCCA AABBD BCDAA DD.。
Chapt3 锁存器与触发器一、选择题1.N个触发器可以构成能寄存位二进制数码的寄存器。
A.N-1B.NC.N+1D.2N2.一个触发器可记录一位二进制代码,它有个稳态。
A.0B.1C.2D.33.对于D触发器,欲使Q n+1=Q n,应使输入D= 。
A.0B.1C.QD.Q4.存储8位二进制信息要个触发器。
A.2B.3C.4D.85.对于T触发器,若原态Q n=0,欲使新态Q n+1=1,应使输入T= 。
A.0B.1C.QD.Q6.对于T触发器,若原态Q n=1,欲使新态Q n+1=1,应使输入T= 。
A.0B.1C.QD.Q7.在下列触发器中,有约束条件的是。
A.主从JK F/FB.主从D F/FC.同步RS F/FD.边沿D F/F8.对于JK触发器,若J=K,则可完成触发器的逻辑功能。
A.RSB.DC.TD.Tˊ9.欲使JK触发器按Q n+1=Q n工作,可使JK触发器的输入端。
A.J=K=0B.J=Q,K=QC.J=Q,K=QD.J=Q,K=0E.J=0,K=Q10.欲使JK触发器按Q n+1=Q n工作,可使JK触发器的输入端。
A.J=K=1B.J=Q,K=QC.J=Q,K=QD.J=Q,K=1E.J=1,K=Q11.欲使JK触发器按Q n+1=0工作,可使JK触发器的输入端。
A.J=K=1B.J=Q,K=QC.J=Q,K=1D.J=0,K=1E.J=K=112.欲使JK触发器按Q n+1=1工作,可使JK触发器的输入端。
A.J=K=1B.J=1,K=0C.J=K=QD.J=K=0E.J=Q,K=0 13.欲使D触发器按Q n+1=Q n工作,应使输入D= 。
A.0B.1C.QD.Q14.下列触发器中,克服了空翻现象的有。
A.边沿D触发器B.主从RS触发器C.同步RS触发器D.主从JK触发器15.下列触发器中,没有约束条件的是。
A.基本RS触发器B.主从RS触发器C.同步RS触发器D.边沿D触发器16.为实现将JK触发器转换为D触发器,应使。