2001年国际燃油污染损害民事责任公约(中英文对照)
- 格式:doc
- 大小:94.00 KB
- 文档页数:18

《2001年国际燃油污染损害民事责任公约》第一条定义就本公约而言:(一)“船舶”系指无论何种类型的任何海船和海上航行器。
(二)“人”系指任何个人或合伙或任何公共或私人机构,无论是否系法人,包括国家或其任何构成部分。
(三)“船舶所有人”系指船舶的所有人,包括船舶的登记所有人、光船承租人、管理人和经营人在内。
(四)“登记所有人”系指登记为船舶的所有人的一个或多个人,或在没有登记时,拥有船舶的一个或多个人。
然而,当船舶为国家所有并由在该国登记为该船经营人的公司营运时,“登记所有人”应系指此种公司。
(五)“燃油”系指用于或拟用于船舶运行或推进的包括润滑油在内的任何烃类矿物油,以及此类油的任何残余物。
(六)“《民事责任公约》”系指经修正的《1992年国际油污损害民事责任公约》。
(七)“预防措施”系指事故发生后任何人采取的防止或尽量减少污染损害的任何合理措施。
(八)“事故”系指具有同一起源的、造成污染损害或造成引起此种损害的严重和紧迫威胁的一起事件或一系列事件。
(九)“污染损害”系指:由任何地点发生的船舶燃油逸出或排放引起的污染在该船之外造成的损失或损害,但是对环境损害的赔偿(不包括此种损害的利润损失在内),应限于实际采取或将要采取的合理恢复措施的费用;和预防措施的费用和由预防措施造成的进一步损失或损害。
(十)“船舶登记国”对登记船舶,系指该船的登记国家;对未登记船舶,系指该船有权悬挂其国旗的国家。
(十一)“总吨位”系指按照《1969年国际船舶吨位丈量公约》附件1中所载吨位丈量规则计算的总吨位。
(十二)“本组织”系指国际海事组织。
(十三)“秘书长”系指本组织秘书长。
第二条适用范围本公约应仅适用于:(一)下列区域内造成的污染损害:1. 当事国的领土,包括领海,和2. 当事国按照国际法确定的专属经济区,或者,如当事国未确定此种区域,由该国按照国际法确立的在该国领海外并与之毗邻的、从其领海宽度基线测量向外延伸不超过200海里的区域;(二) 无论何处采取的防止或尽量减少此种损害的预防措施。


我国船舶油污损害责任限制的公约适用及完善作者:蒋琳来源:《哈尔滨师范大学·社会科学学报》2013年第06期[摘要] 我国作为CLC1992和BUNKER2001的缔约国,因“船舶”以及“油类”的定义的区分将适用不同的国际公约,船舶油污损害赔偿责任限制的公约适用具有一定复杂性。
与国际公约相比,我国在船舶油污损害责任限额方面的差距巨大,这种差距直接影响到油污事故的索赔,提高船舶油污责任限额将成为完善我国船舶油污损害责任制度的步骤之一。
[关键词] 船舶;油污损害;责任限制[中图分类号]D99619 [文献标识码]A [文章编号]2095-0292(2013)06-0037-04随着海洋船舶运输量的剧增,船舶所造成的油污问题日益严重,海运业属于资金密集型行业,具有较大的风险性,一旦发生船舶污染事故,其损失会非常惨重,很多情况下甚至远远超过船舶本身的价值。
船舶污染损害赔偿责任限制制度也应运而生。
无论国际还是国内船舶油污损害法律制度在平衡责任方和受害方利益的同时,为了保障受害方进一步实现充分赔偿,需不断地提高船舶油污事故法定赔偿限额。
一、国际公约下对“船舶”及“油类”的界定有鉴于国际公约对“船舶”“油污”定义的各不相同。
确定一起船舶油污损害事故所适用的法律,首先需厘清国际公约以及国内法项下的“船舶”及“油污”的定义。
相似的船舶污染事故,由于不同的性质将导致截然不同的船舶油污损害责任限制。
(一)船舶的定义目前,无论国际公约均未对“船舶”的内涵有过一致的定义。
根据1969年《国际油污损害民事责任公约》(以下简称“CLC1969”)第一条第一款,“引起油污损害赔偿的船舶”指的是“装运散装油类货物的任何类型的远洋船舶和海上船艇”。
但对于那些能够运输散装油类货物的非油船是否包括在内,CLC1969并未做出明确说明。
为完善公约船舶定义不周全这一问题,CLC1969的1992年议定书(以下简称“CLC1992”)第二条第一款第一项对此进行了补充:“为运输散装油类货物而建造或改建的任何类型的海船和海上航行器;但是,能够运输油类和其他货物的船舶,仅在其实际运输散装油类货物时,以及在此种运输之后的任何航行(已证明船上没有此种散装油类运输的残余物者除外)期间,才应视作船舶。


2001年国际燃油污染损害民事责任公约(中英文对照)简介:由于1967年Torry Canyon轮近十万桶原油货油的污染事故,导致了国际间制定了1969年的油污民事责任公约,然其仅适用于来自油轮货油的污染。
燃油污染问题于八十年代初逐渐受到重视,CLC公约于1992年修订时(1992年CLC议定书),进一步将“油轮”的燃油污染损害纳入规范。
在1992年CLC议定书的研拟期间,部分国家主张应将“所有船舶”的燃油污染纳入规范的提议或讨论。
然而由于CLC所规范的“油轮的货油或燃油”与“一般船舶的燃油”有相当差异,为避免复杂及困扰从而影响议定书的通过,1992年CLC议定书最后仅将“油轮的燃油污染”纳入,而不包括“一般船舶的燃油污染”。
在1994年IMO海洋环境保护委员会(MEPC)第三十八届会议上,澳洲提议MEPC发展国际燃油污染损害赔偿机制。
MEPC随后请IMO法律委员会考虑,法律委员会于稍后的1995年第七十三届会议组成工作小组讨论此课题。
实际上在1996年HNS公约起草阶段,IMO 法律委员会曾建议将燃油污染纳入该公约,但因许多国家主张燃油污染应独立立法,而使燃油污染未被纳入1996年HNS公约架构之下。
燃油污染损害赔偿稍后成为1996年的IMO法律委员会第七十五届大会的主要议题。
在该大会上,英国代表提出一份由U.K. P&I Club于1993年制作的重大赔偿案件分析报告,该报告指出,有近半数的污染索赔是来自“非货油”。
同年,IMO法律委员会提出燃油公约草案,在经过前后六年的讨论后,公约于2001年3月23日完成签署。
在整个燃油公约的起草过程中,有几个重要的争议主题,分别为:燃油污染是否应为严格责任 strict liability;燃油污染责任限额 limitation of liability;及强制保险及证明 compulsory insurance and certificate。

3月9日,《2001年国际燃油污染损害民事责任公约》(简称《燃油公约》)对我国生效。
这意味着,航行于我国沿海水域的1000总吨以上的船舶,全部需要办理强制性油污保险。
而在过去,只有载运2000吨以上持久性油类的国际航行油船才有此规定。
加入《燃油公约》,对我国而言有何意义?它适用于哪些船舶?我国船东会承担哪些责任?如何办理“燃油污染损害民事责任保险或其他财务保证证书”(以下简称“证书”)?日前,部海事局船舶处副调研员徐石明对这些问题进行了详细解答。
确保燃油污染及时得到治理海上航行的船舶一旦发生燃油泄漏污染,不但企业赔偿风险大,清污难、费用高,而且相关的污染受害方得不到合理的赔偿,这一直是船舶污染民事赔偿的一大难题。
据介绍,上世纪90年代以来,船舶燃油污染问题越来越受到重视。
1992年,油轮的燃油污染损害被纳入《1992年国际油污损害民事责任公约》(简称CLC公约)。
它虽然解决载运2000吨以上持久性油类船舶的油污染问题(包括货油和燃油),但其他船舶的燃油污染问题由于没有强制保险的规定,一直悬而未决。
1996年,燃油污染损害赔偿成为国际海事组织(IMO)法律委员会第75届大会的主要议题。
在这次大会上,一份重大赔偿案件分析报告指出,有近半数的污染索赔是针对“非货油”的。
另据《石油泄露信息导报》(Oil Spill Intelligence Report)指出,非油轮溢油的风险,无论在个案数量还是溢油总量上,均大于油轮溢油污染。
据《石油泄露信息导报》统计,全球约有1.3亿吨的货油通过油轮运输,而全球船舶的燃油总量却高达1.4亿吨。
有数据显示,自1975年至1996年间,澳洲邻近水域油污事件的83%由非油轮所致;在油污清除费用方面,用于清除燃油油污的费用占全部清除费用的78%。
基于此,IMO法律委员会于1996年拟定了《燃油公约》草案,并于2001年3月23日获得通过,已于2008年11月21日开始生效。

2001年国际燃油污染损害民事责任公约(中英文对照)简介:由于1967年Torry Canyon轮近十万桶原油货油的污染事故,导致了国际间制定了1969年的油污民事责任公约,然其仅适用于来自油轮货油的污染。
燃油污染问题于八十年代初逐渐受到重视,CLC公约于1992年修订时(1992年CLC议定书),进一步将“油轮”的燃油污染损害纳入规范。
在1992年CLC 议定书的研拟期间,部分国家主张应将“所有船舶”的燃油污染纳入规范的提议或讨论。
然而由于CLC 所规范的“油轮的货油或燃油”与“一般船舶的燃油”有相当差异,为避免复杂及困扰从而影响议定书的通过,1992年CLC议定书最后仅将“油轮的燃油污染”纳入,而不包括“一般船舶的燃油污染”。
在1994年IMO海洋环境保护委员会(MEPC)第三十八届会议上,澳洲提议MEPC发展国际燃油污染损害赔偿机制。
MEPC随后请IMO法律委员会考虑,法律委员会于稍后的1995年第七十三届会议组成工作小组讨论此课题。
实际上在1996年HNS公约起草阶段,IMO法律委员会曾建议将燃油污染纳入该公约,但因许多国家主张燃油污染应独立立法,而使燃油污染未被纳入1996年HNS公约架构之下。
燃油污染损害赔偿稍后成为1996年的IMO法律委员会第七十五届大会的主要议题。
在该大会上,英国代表提出一份由U.K. P&I Club于1993年制作的重大赔偿案件分析报告,该报告指出,有近半数的污染索赔是来自“非货油”。
同年,IMO法律委员会提出燃油公约草案,在经过前后六年的讨论后,公约于2001年3月23日完成签署。
在整个燃油公约的起草过程中,有几个重要的争议主题,分别为:燃油污染是否应为严格责任 strict liability;燃油污染责任限额 limitation of liability;及强制保险及证明 compulsory insurance and certificate。
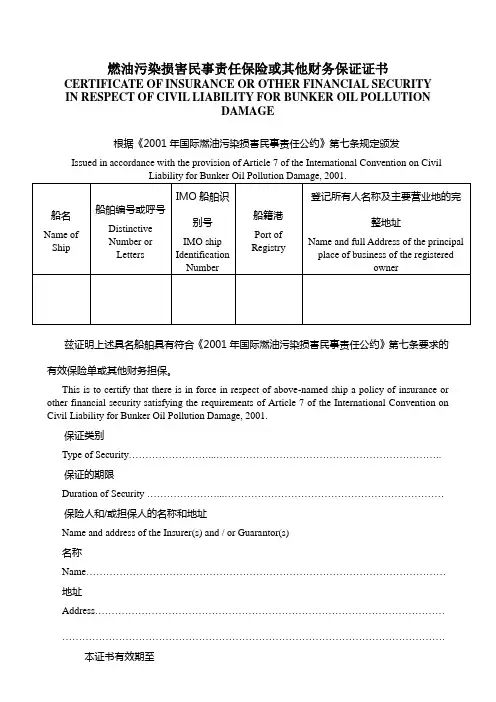
燃油污染损害民事责任保险或其他财务保证证书CERTIFICATE OF INSURANCE OR OTHER FINANCIAL SECURITY IN RESPECT OF CIVIL LIABILITY FOR BUNKER OIL POLLUTIONDAMAGE根据《2001年国际燃油污染损害民事责任公约》第七条规定颁发Issued in accordance with the provision of Article 7 of the International Convention on Civil兹证明上述具名船舶具有符合《2001年国际燃油污染损害民事责任公约》第七条要求的有效保险单或其他财务担保。
This is to certify that there is in force in respect of above-named ship a policy of insurance or other financial security satisfying the requirements of Article 7 of the International Convention on Civil Liability for Bunker Oil Pollution Damage, 2001.保证类别Type of Security……………………...…………………………………………………………..保证的期限Duration of Security …………………...…………………………………………………………保险人和/或担保人的名称和地址Name and address of the Insurer(s) and / or Guarantor(s)名称Name………………………………………………………………………………………………地址Address………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….本证书有效期至This certificate is valid until…………………………………………………………………颁发证书或签证的政府Issued or certified by the Government of …………...………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………地点日期At ……………………………………. On………………………………………………………………………………………………….发证或认证官员的签字和职务Signature and Title of issuing or certifying official说明Explanatory Notes:1. 如需要,颁发国名称中可包括颁发证书的国家主管当局的名称。

![上海海事局关于《2001年国际燃油污染损害民事责任公约》实施要求的通知-沪海危防[2009]73号](https://uimg.taocdn.com/2ef50732cec789eb172ded630b1c59eef9c79a5f.webp)
上海海事局关于《2001年国际燃油污染损害民事责任公约》实施要求的通知正文:----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------上海海事局关于《2001年国际燃油污染损害民事责任公约》实施要求的通知(沪海危防〔2009〕73号)各有关船公司:根据中华人民共和国海事局《关于实施〈2001年国际燃油污染损害民事责任公约〉的通知》(海船舶〔2008〕623号)(以下简称《通知》,见附件1),《2001年国际燃油污染损害民事责任公约》(以下简称《燃油公约》)将于2009年3月9日正式对我国生效。
为做好《燃油公约》实施工作,现将《通知》予以转发,并就相关实施要求通知如下:一、凡在上海港登记的1000总吨及以上的海船,且船上载有用于或拟用于操作或推进船舶的任何碳氢矿物油及其任何残余物(包括润滑油)的,均应持有我局签发的《燃油污染损害民事责任保险或其他财务保证证书》(以下简称《证书》),其中国际航行船舶应在2009年3月9日前持有《证书》,沿海运输船舶应在2009年7月1日前持有《证书》。
对于载运2000吨以上的散装持久性油类的船舶,如已持有《1992年国际油污损害民事责任公约》规定的《油污损害民事责任保险或其他财务保证证书》的,不需要持有上述《证书》。
二、需办理《证书》的各有关船公司应持船舶燃油污染保险或其他财务保证单据的原件、船舶防污文书申请书、船舶国籍证书复印件、船舶防止油污证书复印件、委托书及其身份证明(委托代理人办理时),向我局政务受理中心(四平路190号)提交申请,我局将在收到申请后7个工作日内办结。
三、船舶燃油污染保险单或财务保证应由中华人民共和国海事局公布的中国籍船舶油污损害民事责任保险人出具(保险人名单见附件2)。

“2001燃油公约”评述与建议(一)摘要:对《2001年燃油污染损害民事责任国际公约》的订立背景和内容进行了简要介绍,同时对公约在履行过程中可能会遇到的问题进行了分析,并探讨了我国加入该公约的必要性。
关键词:燃油污染责任公约一、序言自1967年TorryCanyon事故之后,船舶污染问题就逐渐引起了各界的关注,并导致了一系列国际公约的诞生。
其中,1969年制定的《油污损害民事责任公约》(CLC69、CLC92),1973年制定的MARPOL公约和1996年制定的《国际海上运输有毒害物质损害责任及赔偿公约》(HNS公约)奠定了船舶污染防护和赔偿框架。
但是,从船舶污染赔偿的角度而言,由于CLC公约原则上只适用于油轮,HNS公约仅适用于载运有毒有害物质的船舶,绝大多数的船舶燃油污染被排除在此框架之外。
与货油污染相比,燃油污染有诸多特殊性。
首先,燃油污染事故数量大。
据英国船东互保协会统计,燃油污染索赔事故占全部污染事故的1/2以上1]。
鉴于以上原因,燃油污染是国际海运界不可回避的挑战。
2001年3月23日,IMO通过了《2001年燃油污染损害民事责任国际公约》(以下简称“燃油公约”),终于填补了这一法律空白。
根据规定,该公约必须得到18个国家,其中包括5个各拥有不少于100万总吨船队的国家加入和批准才能生效2]。
业界最初普遍认为其门槛过高,生效期尚远,但这一情况目前已发生了变化。
截至本文撰稿时止,已有7个国家批准了该公约。
加之在近年一系列重大溢油事故重压下,欧盟于2002年以决定形式3]敦促各成员国尽可能于2006年6月底以前批准该公约。
在此影响下,公约很可能在2007年6月前生效。
因此,我们对该公约应给予必要的重视。
本文先就公约的订立背景和内容作简要介绍,然后探讨公约履行中可能遇到的问题,并对我国在燃油污染方面的立法提出建议。
希望本文能起到一个抛砖引玉的作用。
二、公约订立背景有关燃油污染的问题早在1969年制定CLC公约时就已提上了议事日程4]。
上海海事局关于《2001年国际燃油污染损害民事责任公约》
实施要求的通知
【法规类别】法制工作综合规定
【发文字号】沪海危防[2009]73号
【发布部门】上海海事局
【发布日期】2009.02.09
【实施日期】2009.02.09
【时效性】现行有效
【效力级别】XP10
上海海事局关于《2001年国际燃油污染损害民事责任公约》实施要求的通知
(沪海危防〔2009〕73号)
各有关船公司:
根据中华人民共和国海事局《关于实施〈2001年国际燃油污染损害民事责任公约〉的通知》(海船舶〔2008〕623号)(以下简称《通知》,见附件1),《2001年国际燃油污染损害民事责任公约》(以下简称《燃油公约》)将于2009年3月9日正式对我国生效。
为做好
1 / 1。
2001年国际燃油污染损害民事责任公约文章属性•【缔约国】国际海事组织•【条约领域】海事•【公布日期】2001.03.23•【条约类别】公约•【签订地点】伦敦正文2001年国际燃油污染损害民事责任公约(2001年3月23日,订于伦敦,我国于2008年12月9日递交加入书,根据交通运输部国际合作司公告2009年第1号本公约于2009年3月9日对我生效)本公约各当事国,忆及《1982年联合国海洋法公约》第194条规定,各国应采取所有必要措施、防止、减少和控制海洋环境污染,还忆及该公约第235条规定,为确保对海洋环境污染引起的所有损害做出迅速和适当的赔偿,各国应进行合作,进一步制定有关国际法律规则,注意到《1992年国际油污损害民事责任公约》和《1992年设立国际油污损害赔偿基金国际公约》,在确保因船舶海上散装运输的油类的逸出或排放而蒙受污染损害的人员获得赔偿方面的成功,还注意到通过了《1996年国际海上运输有害有毒物质损害的责任和赔偿公约》,以便对海上运输有害有毒物质事故造成的损害提供适当、迅速和有效赔偿,认识到确立与该责任程度的适当限制相关的对各种形式油污的严格责任的重要性,考虑到补充措施对于确保对因船舶燃油的逸出或排放而造成的污染损害做出适当和有效的赔偿支付是必要的,期望通过在此类事件中确定责任问题和提供适当赔偿的统一国际规则和程序,兹协议如下:第1条定义就本公约而言:1 “船舶”系指无论何种类型的任何海船和海上航行器。
2 “人员”系指任何个人或合伙人或任何公共或私人机构,无论是否系法人,包括国家或其任何构成部分。
3 “船舶所有人”系指船舶的所有人,包括船舶的登记所有人、光船承租人、管理人和经营人在内。
4 “登记所有人”系指登记为船舶的所有人的一个或多个人员,或在没有登记时,拥有船舶的一个或多个人员。
然而,当船舶为国家所有并由在该国登记为该船经营人的公司营运时,“登记所有人”应指此种公司。
5 “燃油”系指用于或拟用于船舶运行或推进的包括润滑油在内的任何烃类矿物油,以及此类油的任何残余物。
燃油污染损害民事责任国际公约
佚名
【期刊名称】《中国海商法研究》
【年(卷),期】2001(012)001
【摘要】本公约各当事国:忆及《1982年联合国海洋公约》第194条之规定.即.各国应采取一切必要的措施,防止、减少和控制对海洋环境的污染;【总页数】8页(P445-452)
【正文语种】中文
【中图分类】D996.9
【相关文献】
1.我国船舶燃油污染损害民事责任限制法律制度反思--从北方海航道船舶燃油污染损害民事责任限制法律适用谈起 [J], 白佳玉;杨占波
2.IMO通过《燃油污染损害民事责任国际公约》 [J], 刘昭青
3.国际海事组织制定和通过《船舶燃料油污染损害民事责任国际公约》概要 [J], 傅国民;徐庆岳
4.船用燃油污染损害民事责任国际公约即将生效 [J],
5.船舶燃油污染损害责任国际公约缔结 [J], 陈正才
因版权原因,仅展示原文概要,查看原文内容请购买。
交通运输部国际合作司关于国际海事组织《2001年国际燃油污染损害民事责任公约》生效的公告
文章属性
•【制定机关】交通运输部
•【公布日期】2009.01.19
•【文号】交通运输部国际合作司公告2009年第1号
•【施行日期】2009.03.09
•【效力等级】部门规范性文件
•【时效性】现行有效
•【主题分类】环境保护综合规定
正文
交通运输部国际合作司关于国际海事组织《2001年国际燃油污染损害民事责任公约》生效的公告
(交通运输部国际合作司公告2009年第1号)经国务院批准,我国于2008年12月9日向国际海事组织递交了有关加入《2001年国际燃油污染损害民事责任公约》(以下简称公约)的加入书,同时声明如下:
一、本公约第七条不适用于中华人民共和国内河航行船舶
;
二、根据《中华人民共和国香港特别行政区基本法》和《中华人民共和国澳门特别行政区基本法》,中华人民共和国政府决定,本公约适用于中华人民共和国澳门特别行政区;在另行通知前,本公约不适用于中华人民共和国香港特别行政区。
公约将于2009年3月9日对我生效,同时适用于澳门特区,暂不适用于香港
特区。
现将公约中文本予以公告,请遵照执行。
中华人民共和国交通运输部(章)
二〇〇九年一月十九日。
2001年国际燃油污染损害民事责任公约(中英文对照)简介:由于1967年Torry Canyon轮近十万桶原油货油的污染事故,导致了国际间制定了1969年的油污民事责任公约,然其仅适用于来自油轮货油的污染。
燃油污染问题于八十年代初逐渐受到重视,CLC公约于1992年修订时(1992年CLC议定书),进一步将“油轮”的燃油污染损害纳入规范。
在1992年CLC议定书的研拟期间,部分国家主张应将“所有船舶”的燃油污染纳入规范的提议或讨论。
然而由于CLC所规范的“油轮的货油或燃油”与“一般船舶的燃油”有相当差异,为避免复杂及困扰从而影响议定书的通过,1992年CLC议定书最后仅将“油轮的燃油污染”纳入,而不包括“一般船舶的燃油污染”。
在1994年IMO海洋环境保护委员会(MEPC)第三十八届会议上,澳洲提议MEPC发展国际燃油污染损害赔偿机制。
MEPC随后请IMO法律委员会考虑,法律委员会于稍后的1995年第七十三届会议组成工作小组讨论此课题。
实际上在1996年HNS公约起草阶段,IMO 法律委员会曾建议将燃油污染纳入该公约,但因许多国家主张燃油污染应独立立法,而使燃油污染未被纳入1996年HNS公约架构之下。
燃油污染损害赔偿稍后成为1996年的IMO法律委员会第七十五届大会的主要议题。
在该大会上,英国代表提出一份由U.K. P&I Club于1993年制作的重大赔偿案件分析报告,该报告指出,有近半数的污染索赔是来自“非货油”。
同年,IMO法律委员会提出燃油公约草案,在经过前后六年的讨论后,公约于2001年3月23日完成签署。
在整个燃油公约的起草过程中,有几个重要的争议主题,分别为:燃油污染是否应为严格责任 strict liability;燃油污染责任限额 limitation of liability;及强制保险及证明 compulsory insurance and certificate。
公约草案最早是由英国于1996年提出,整部草案基本上是在1992年CLC公约议定书及1996年HNS公约的架构及责任基础上拟定。
草案拟定当时,本拟有二套草案,一为独立的燃油公约草案;另一是以修订CLC公约的议定书方式,将燃油污染纳入CLC体系中,以较具弹性为由,公约后来决定以单独立法(free-standing convention)方式处理。
国际间经过将近十年来的发展及五年来的密集讨论,燃油污染损害民事责任国际公约于2001年3月23日在国际海事组织IMO伦敦总部由各国代表完成签署。
燃油公约规定该公约在十八个缔约国(其中应包括五个船舶吨位超过一百万总吨的国家)批准、认可或加入的一年后生效。
虽然具同性质的1992年油污民事责任公约CLC及1992年基金公约FUND 议定书已广为各国接受,并均于签署四年后的1996年即已生效实施,然而由于燃油公约所规定的保险证明及财务担保制度尚未取得全面共识,特别是来自P&I保险方面的明确全面支持,加上要求的生效国门槛过高,因此燃油公约何时生效还有待观察。
在整体规范及责任架构上,燃油公约与1992油污民事责任公约CLC或1996年国际海上运送有毒有害物质损害责任和赔偿公约(HNS公约)甚为相似。
事实上,燃油公约多数条文,甚至用语,亦多援用前述两公约内容。
值得注意的是,由于燃油公约是适用于所有船舶(一千总吨以上的船舶须具备财务担保证明),而非像CLC公约原则上仅适用于油轮(及载有货油的油矿船),或HNS公约原则上仅适用于运载有毒有害物质的船舶,其结果是,几乎所有的海船船舶所有人均有适用的余地。
而其中影响最大的是财务担保的适用,亦即,在公约生效后,一千总吨以上的所有船舶,其船上均应备有不低于1976年海事索赔责任限制公约(或该公约的任何修订议定书)最高责任限额的保险证明或财务担保。
正文:本公约各缔约国,根据1982年联合国海洋法公约第194条,缔约国应该采取所有必要的措施防止、减少和控制海洋环境污染,同时根据上述公约第235条,为了确保能对由海洋环境污染所导致的所有损害进行及时和充足的赔偿,各缔约国应该在相关国际法规则的进一步发展中进行合作,注意到《1992年国际油污损害民事责任公约》和《1992年设立国际油污损害赔偿基金国际公约》在确保向由于海船承载的油类泄露或卸载所导致的损害的受害人进行赔偿过程中所取得的成功,也注意到为向海上运输有毒有害物质所导致的损害提供适当、及时和有效的赔偿,《1996关于海上运输有害有毒物质损害责任和赔偿的国际公约》的适用,认识到对与责任限制有关的任何形式的油类污染建立严格责任的重要性,考虑到为保证对船舶燃料油泄露或卸载造成的污染损害进行及时和适当的赔偿而采取补充方法是必要的,本着通过统一的国际规则和程序,以便确定在这类事件下的责任问题,并提供适当赔偿的愿望,兹协议如下:第一条定义就本公约而言:1.“船舶”是指任何类型的海船和海上航行器。
2.“人员”是指任何个人或合伙人或任何公共或私人机构,不论是否为法人,包括国家或其任何组成部分。
3.“船舶所有人”是指船舶所有人包括船舶登记所有人、光船承租人、船舶经营人和管理人。
4.“船舶登记所有人”是指登记为船舶所有人的一个或多个人员,或者没有登记时,则是指拥有船舶的人。
然而,当船舶为国家所有并由在该国登记为船舶经营人的公司所经营时,“船舶登记所有人”即指这种公司。
5.“燃油”是指任何用来或者拟用来操纵和推进船舶的烃类矿物油,包括润滑油,以及此类油的任何残余物。
6.“民事责任公约”是指修改后的《1992年国际油污损害民事责任公约》。
7.“预防措施”是指事件发生后由任何人采取的为防止或减轻污染损害的任何合理措施。
8.“事件”是指造成污染损害或导致这种损害的严重而紧迫的危险的由同一原因所引起的事件或一系列事件。
9.“油污损害”是指:(a) 由于船舶泄漏或排放油类,而在船舶之外因污染而造成的损失和损害,不论这种泄漏或排放发生于何处,但是,对环境损害的赔偿,除这种损害所造成的利润损失外,应限于已实际采取或行将采取的合理复原措施的费用;(b) 预防措施的费用和因预防措施而造成的进一步损失或损害。
10.“船舶登记国”,就登记的船舶而言,是指对船舶进行登记的国家,就未登记的船舶而言,是指此船舶有权悬挂该国国旗的国家。
11.“总吨位”是指根据《1969年国际船舶吨位丈量公约》附件1中规定的丈量规则计算出来的总吨位。
12. “本组织”是指国际海事组织。
13. “秘书长”是指本组织的秘书长。
第二条适用范围本公约仅适用于:(a) 在下列区域内造成的污染损害:(i)缔约国的领土,包括领海,以及,(ii)缔约国根据国际法设立的专属经济区,或者,如果缔约国尚未设立这种区域,则为该国根据国际法所确定的超出并毗连其领海的区域,且自该国测量其领海宽度的基线算起,外延不超过200海里;(b)为防止或减轻这种损害而在无论何地所采取的预防措施。
第三条船舶所有人责任1.除本条第3款和第4款的规定外,在事故发生时,船舶所有人应对事故引起的任何由于船上装载的或者来源于船舶的燃料油所造成的污染损害负责,如果该事件包括一系列事故,则船舶所有人的赔偿责任自第一次事故发生时起算。
2.如果根据第1款有一个以上的人应对事件负责,那么这些人负连带责任。
3.船舶所有人如能证实损害系属于以下情况,即对之不负责任:(a)由于战争行为、敌对行为、内战或武装暴动或特殊的、不可避免的和不可抗拒性质的自然现象所引起的损害;(b) 完全是由于第三者有意造成损害的行为或不作为所引起的损害;(c)完全是由于负责灯塔或其他助航设备的维修、保养的政府或其他主管当局在履行其职责时的疏忽或其它过失行为所造成的损害。
4.如船舶所有人证明,污染损害完全或部分地是由于受害人有意造成损害的行为或不为,或是其疏忽而引起的,则该船舶所有人即可全部或部分地免除对该人所负的责任。
5.不得对船舶所有人作出本公约规定以外的污染损害赔偿。
6.本公约的任何条款不得有损于船舶所有人拥有的独立于本公约之外的追偿权利。
第四条除外责任1.本公约不适用于民事责任公约所规定的污染损害,而不论这种污染在该公约下能否得到赔偿。
2.除本条第3款规定外,本公约各项规定不适用于军舰、海军辅助船舶或其他为国家所有或经营的、在当时仅用于政府的非商业性服务的船舶。
3.缔约国可以决定对其军舰或本条第2款所规定的其它船舶适用本公约,在此种情况下,缔约国应通知秘书长适用本公约的条款和条件。
4.对于为一缔约国所有并用于商业目的的船舶,每一国家都应接受第9条所规定的管辖权范围内的诉讼,并放弃一切以主权国地位为根据的抗辩。
第五条涉及两艘或多艘船舶的事故当发生涉及两艘或两艘以上船舶的事故并造成污染损害时,所有有关船的所有人,除按第3条获得豁免者外,应对所有无法合理分开的这类损害负连带责任。
第六条责任限制本公约的任何条款不得影响船舶所有人与提供保险和经济担保的人在任何可以适用的内国或国际法律制度中,诸如经修订的《1976年海事赔偿责任限制公约》,的情况下,享受责任限制的权利。
第七条强制保险和财务担保1.已登记的船舶所有人在一缔约国内登记拥有1000总吨以上船舶的,必须进行保险或取得其他财务担保,诸如银行或类似金融机构的担保,以便按其适用的内国或国际责任限制法律中的规定承担其对油污损害所应负的责任,但是在任何情况下不得超过修改后的《1976年海事赔偿责任限制公约》中所规定的数额。
2.缔约国的主管当局在确信第1款的要求已经得到满足之后,应向每艘船舶颁发一份证明保险或其它财务担保根据本公约的规定乃属有效的证书。
对于在缔约国登记的船舶,这种证书应由船舶登记国的主管当局颁发或认证;对于非在缔约国登记的船舶,证书可由任何一个缔约国的主管当局颁发或认证。
证书应以所附样本的格式为准,并应包括下列各项:(a) 船名、识别号或字母和登记港;(b) 船舶登记所有人的名称和主要营业地;(c) IMO船舶辨认号码;(d) 担保的类别和期限;(e) 保险人或提供保证的其他人的名称及主要营业地点,如可能,则包括设立的保险或担保的营业地点;(f) 证书的有效期,该有效期不得超过保险或其他担保的有效期限。
3.(a)缔约国可以授权其认可的机构或组织签发第2款所规定的证书。
该机构或组织应向该国报告每张证书的签发。
在任何情况下,该缔约国应完全保证其签发证书的完整性和准确性,还应该承诺保证为履行其义务作出必要的安排。
(b)缔约国应通知秘书长:(i)向其认可的机构或组织授权的具体责任和条件;(ii)对该授权的撤销;(iii)授权或撤销授权的生效日期。
该授权应自向秘书长递交有关通知的日期起三个月后方能生效。
(c)依据本款可以签发证书的授权机构或组织至少应该被授予,在签发这些证书的条件无法得到维持时可撤销这些证书的权力.在任何情况下,该机构或组织应向其代表的缔约国报告证书的撤销。