信用卡常用术语
- 格式:doc
- 大小:40.50 KB
- 文档页数:9

工行信用卡名词解释“信用额度”:指银行根据申请人的资信状况等为其核定、在卡片有效期内可循环使用的最高授信限额。
“可用额度”:指持卡人当前实际可使用的额度,包括可取现额度和可消费额度。
“透支”:指持卡人使用银行为其核定的信用额度进行支付的方式,包括消费透支、取现透支、转账透支和透支扣收等。
“银行记账日”:指银行根据持卡人发生的交易将交易款项记入其信用卡账户,或根据规定将费用(包括但不限于超限费、滞纳金、年费、手续费、追索费,下同)、利息等记入其信用卡账户的日期。
“账单日”:指银行每月定期对持卡人的信用卡账户当期发生的各项交易款项、费用等进行汇总结算,并结计利息,计算出持卡人当期应还款的日期。
“到期还款日”:指银行规定的贷记卡持卡人应该偿还其全部应付款项或最低还款额的最后日期。
即本期账单还款的最后日期,如果持卡人在此日之前全额归还欠款,则透支消费部分可免收贷款利息。
“免息还款期”:指对于贷记卡持卡人,除取现及转账透支交易外,其他透支交易从银行记账日起至到期还款日(含)之间可享受免息待遇的时间段。
“全部应付款项”:指截至当前账单日,贷记卡持卡人累计已经银行记账但未偿还的交易款项,以及利息、费用等的总和。
“最低还款额”:指银行规定的贷记卡持卡人在到期还款日(含)前应该偿还的最低金额,是上一期账单中最低还款额未还部分和当前账单日账户透支余额10%的总和。
“超限费”:指贷记卡持卡人超额使用银行为其核定的账户信用额度,且在账户超限当日(即发卡机构对该笔交易金额的记账日)未偿还超额部分,按规定应向银行支付的款项。
牡丹双币贷记卡超限费按超信用额度部分的5%收取,最低1元人民币,最高500元人民币。
暂不收取。
“滞纳金”:指贷记卡持卡人未能在到期还款日(含)前偿还最低还款额,按规定应向银行支付的款项。
牡丹双币贷记卡滞纳金按最低还款额未还部分的5%收取,最低1元人民币,最高500元人民币。
“自动还款”:持卡人可通过工行或网上银行办理自动还款注册,每月到期还款日前工行将自动从转出账户扣款为您还款。


信用卡各名词解释说明信用卡各名词解释说明银行卡:银行卡包括借记卡和贷记卡。
中国人民银行1999年1月5日颁布的《银行卡业务管理办法》将银行卡定义为由商业银行(含邮政金融机构)向社会发行的具有消费信用、转账结算、存取现金等全部或部分功能的信用支付工具。
银行卡按币种不同分为人民币卡、外币卡;按发行对象不同分为单卡(商务卡)、个人卡;按信息载体不同分为磁条卡、芯片(IC)卡。
此外,大家选贷记卡一些银行根据银行授予的信用等级、品牌、是否联名(认同)等具体分类。
如按信用等级不同分为白金卡、金卡、普通卡;按国际发卡组织的品牌不同分为威士卡(VISA)、万事达卡(MasterCard)、运通卡(Express)、大来卡(Din-nerCardExpress)、JCB卡等;按是否联名(认同)分为联名(认同)卡和非联名(认同)卡;按是否带有持卡人彩色照片分为彩照卡和非彩照卡。
贷记卡:银行卡包括贷记卡和借记卡。
信用卡贷记卡也就是通常所说的信用卡,分为人民币信用卡(准贷记卡)、国际标准信用卡(贷记卡),但习惯上人们把能够透支的卡都叫信用卡,其实它们还是有一定区别的。
准贷记卡是指持卡人须先按发卡银行要求交存一定金额的备用金,当备用金账户金额不足支付时,可在发卡银行规定的信用额度内透支的信用卡。
国际标准贷记卡是指发卡银行给予持卡人一定的信用额度,持卡人可在信用额度内先消费、后还款的信用卡,对于信用额度内的消费透支,持卡人在对账单规定的还款日期前全部还款,即可享受最短25天、最长56天的免息还款期,若选择最低还款额方式还款,信用额度按还款金额恢复。
国际标准双币信用卡(贷记卡)指在国内特约单位和指定营业网点、国内和国外信用卡组织或国际信用卡公司受理点使用,以人民币和某一指定外币两种货币结算,具有信用消费、转账结算、存取现金等功能。
使用国际信用卡在境外消费或支取外币现金所产生的外币欠款,可以使用人民币购汇还款。
借记卡:借记卡与信用卡最大的不同是不具备透支功能。

AA(Approval Code)核准密码(AA为电报简码),消费款项(超过商户最低免授权交易金额者经授权后给予的核准密码)。
每笔需授权的消费都有授权密码,包含人工、CED、POS。
Account use (手工授权,包括MO/TO/网上授权)ACD(Automatic Call Distribution),程控交换机自动分配拨入(Call-in)的电话并提交管理层统计资料的电脑系统。
ACD in + Available,计算客服人员 productivity的统计量, 即接听客户电话和等候客户电话的时间比例.Acquiring Bank 收单银行,办理签定特约商户以接受信用卡客户消费的银行.AFF(Air Frequent Flyer),飞行里程奖励办法. 持卡人使用信用卡购买机票, 可按里程折合点数, 到达一定点数时, 可以换乘头等舱或享受免费机票优惠. Affinity Card(认同卡),其他商业机构借助银行的发卡系统或资源, 发行类似信用卡的认同卡, 以达到宣传或服务自身会员目的。
一般而言,认同卡为发卡行与非营利机构发行的信用卡。
Annual Fee 年费,信用卡每年所缴的年费, 在会计处理上按12个月分摊记帐. ANR(Average Net Receivables) 平均余额,发卡单位平均应收客户款. Application 申请书,客户申请信用卡时填写的表格, 包含个人资料, 财务状况等。
A/R(Accounts Recievables)应收帐款, 三个月未收回者,应转入PDO(Post Due Obligation)。
Arbitration 仲裁,对于争议帐款,当收单行与发卡行在扣款流程进行完毕后仍争执不下时,交VISA或MCI的仲裁法庭裁决。
Attrition 剪卡,取消卡片。
Authorization 授权,持卡人在商户消费时,需经授权系统或授权人员取得交易核准码,这一过程称为授权。


信用卡名词解释信用卡是一种金融产品,它的消费受到一定限制,但可以为消费者提供灵活的资金支持。
下面将对一些常见的信用卡术语进行解释,以便消费者了解信用卡及其使用规则。
信用卡发卡机构:信用卡发卡机构是为消费者提供信用卡服务的机构,这些机构包括各大银行、信用合作社以及特约商户等。
消费者可以根据自身情况,选择合适的发卡机构,申请相应的信用卡。
信用卡额度:每种信用卡都有不同的信用额度,当用户需要使用信用卡购买物品或服务时,要根据信用卡的额度来决定是否可以完成支付。
一般来说,信用卡的额度越高,表明对发卡机构越有信心。
信用卡账户:每张信用卡都要关联一个账户,当消费者使用信用卡消费时,账户内的金额会发生变化,同时发卡机构也会向消费者收取一定的手续费。
账户的余额为零,消费者必须及时充值账户,以便通过信用卡继续进行消费支付。
信用卡利率:当消费者使用信用卡消费时,发卡机构会根据用户的消费金额和消费期限,向消费者收取一定的利息。
一般来说,信用卡利率和消费者的信用状况有关,信用越好,利率越低。
信用卡分期:信用卡分期是指信用卡发卡机构为消费者提供的一种分期付款方式,消费者可以将消费金额分拆成多次,以期限的形式进行付款。
这种方式可以为消费者提供灵活的资金支持,但也会增加消费者的finance cost,因此需要消费者谨慎斟酌。
信用卡信用记录:信用卡信用记录是消费者使用信用卡的详细记录,包括消费金额、消费时间、支付方式等,用于反映消费者每一笔消费的行为。
信用卡发卡机构会定期检视消费者的信用记录,根据消费者的行为表现来评估消费者的信用状况。
信用卡安全验证:信用卡安全验证指的是信用卡发卡机构为消费者提供的一种防止信用卡诈骗的服务,通常会要求消费者提供身份信息或信用卡信息,以确保消费者的身份安全。
在安全验证过程中,消费者也可以自身采取一些措施,以避免信用卡诈骗的发生。
从上面可以看出,信用卡是消费者在消费时的一种金融产品,也是一项金融服务。

信用卡常用术语Credit card term信用卡常用术语Credit card term信用卡常用术语Credit card term国外留学与银行打交道的常用术语:cash card(现金卡):可以从银行或atm机提取现金cheque guarantee card (支票保证卡)debit card(借记卡)credit card(信用卡)current account(现金帐户):用于存(deposit),取(withdraw),日常开支,通常利息较低或没有利息。
saving account(存款帐户)overdraft(透支)account number 帐目编号depositor 存户pay-in slip 存款单a deposit form 存款单a banding machine 自动存取机to deposit 存款deposit receipt 存款收据private deposits 私人存款certificate of deposit 存单deposit book, passbook 存折credit card 信用卡principal 本金overdraft, overdraw 透支to counter sign 双签to endorse 背书endorser 背书人to cash 兑现to honor a cheque 兑付to dishonor a cheque 拒付to suspend payment 止付cheque,check 支票cheque book 支票本order cheque 记名支票bearer cheque 不记名支票crossed cheque 横线支票blank cheque 空白支票rubber cheque 空头支票cheque stub, counterfoil 票根cash cheque 现金支票traveler s cheque 旅行支票cheque for transfer 转帐支票outstanding cheque 未付支票canceled cheque 已付支票forged cheque 伪支票bandar s note 庄票,银票balance sheet 资产负债表cash flow 现金流转glossary 术语表money order 汇款单,汇票letter of credit n.[商](银行发行的)信用证charge for 想...收费overdraw v.透支overdraft n.透支, 透支之款项endorse [in5dc:s] v.在(票据)背面签名, 签注(文件), 认可, 签署liability n.责任, 义务, 倾向, 债务, [负债], 与assets相对asset n.[资产], 有用的东西solvent adj. 有偿付能力的n.溶媒, 溶剂, 解决方法securities n.有价证券time hull insurance 船舶定期保险marine insurance 海损保险maritime transportation insurance 海洋运输保险fire insurance 火险cargo insurance 货物保险account number - a unique number assigned by a financial institution to a customer. on a credit card, this number is embossed and encoded on the plastic card.additional cardholder - when you have a credit card, it is often possible to add an additional card to the account for use by someone else. the main cardholder holds responsibility for ensuring payments on the additional card are made. purchases are shown on the credit card statement, which is sent monthly.american express - also known as amex, this company is one of the main international credit card issuing schemes. it issues its own credit cards unlike visa and mastercard and is responsible for its own relationships with retailers.annual fee- an annual (yearly) fee associated with having a credit card. this is a separate fee from interest rate on purchases.annual percentage rate (apr)- the yearly percentage rate charged when a balance is held on a credit card. this rate is applied each month that an outstanding balance is present.approval response - an authorization response that is received when a transaction is approved.atm - automated teller machines or cash points allow youto access cash with a credit card or other card associated with your bank account. you need to enter your personal identification number (pin) into the machine to access cash.authentication - the process of assuring that data has come from its claimed source, or a process of corroborating the claimed identity of a communicating party.authorization - every retailer has a purchase limit above which they must seek authorization from the card issuer before they can complete the sale. such authorization can be done by telephone or electronically at the cash till. authorization is used to control credit card fraud. the cardholder s available credit limit is reduced by the authorized amount.authorization amount - currency amount approved.authorization code - a code that an issuer or its authorizing processor provides to indicate approval or denial for an authorization request.authorization date - date and time when the transaction was authorized.authorization only - a transaction that is created to reserve an amount against a credit card s available limit for intended purchases; the actual settlement may occur withinthree to five days, depending on the card type.authorized amount - currency amount approved.authorized transaction - transaction that has been approved.balance transfer - when the outstanding balance of one credit card (or several credit cards) is moved to another credit card account.balance transfer fee - a fee charged by a credit card company to transfer a balance from one account to another. this fee can be anywhere from 1%-5% of the balance amount. however, many credit card companies do not charge this fee. contact the credit card issuer for their specific fees.bad credit - a term used to describe a poor credit rating. common practices that can damage a credit rating include making late payments, skipping payments, exceeding card limits or declaring bankruptcy. bad credit can result in being denied future credit.bank account - bank account number for the merchant to which funds will be deposited.bank identification number (bin) - the first six digits of a visa or mastercard account number. this number is used to identify the card-issuing institution.bankcard - a payment card issued by a bank.billing cycle - the time between billing statements, usually 28-31 days.business card (business credit card) - usually issued to corporate executives or business owners in order to more easily keep business expenses separate from personal charges.card issuer - any association member financial institution, bank, credit union, or company that issues, or causes to be issued, plastic cards to cardholders.card reader - a device that is capable of reading the encoding on plastic cards.cardholder - an individual to whom a card is issued, or who is authorized to use an issued card.cash advance - a cash loan from a credit card using an atm or bank withdrawal.cash back - cash back returns to you a percentage of the total amount spent on your credit card over a specific period of time, usually monthly or quarterly. this feature is particularly useful if you normally pay your credit card bills in full each month, as it means you get an effective discount on the products bought with your credit card.chargeback - a transaction returned through interchangeby an issuer to an acquirer. a transaction may be returned because of it was non-compliant with the association rules and regulations or because it was disputed by a cardholder.chargeback period - the number of days from the transaction s processing date or endorsement date, during which the issuer may initiate a chargeback.co-branded card - a co-branded credit card is sponsored by both the issuing bank and a retail organization, such as a department store or an airline. cardholders may get benefits, such as discounts or free merchandise, from the sponsoring merchant, based on account usage and terms.commercial cards - a general name for cards typically issued for business use and which may include corporate cards, purchase cards, business cards, travel and entertainment cards.credit card number - unique number assigned to a credit card.credit limit - how much total money can be charged to a credit card account, for example $5,000.credit history - a partial profile of your financial life, given within a particular timeframe (usually measured in years). your credit history shows the extent to which you pay your bills ontime and how much you may owe particular parties. credit card issuers use this information to decide whether to provide customers with credit cards.debit - a charge to a customer s bankcard account. a transaction, such as a check, automated teller machine (atm) withdrawal or point-of-sale (pos) debit purchase that debits a demand deposit account.expired card - a card on which the embossed, encoded or printed expiration date has passed.finance charge - fees and other costs billed to you on your statement for using the credit cards (i.e., balance transfer fees, cash advance fees, late fees, overlimit fees, etc.).fixed rate (or fixed apr) -an annual percentage rate that does not change throughout the year, unlike an introductory apr that changes after a specific period of time.floor limit - an amount that visa and mastercard have established for single transactions at specific types of merchant outlets and branches, above which authorization is required.fraudulent transaction - a transaction unauthorized by the cardholder of a bankcard. such transactions are categorized as lost, stolen, not received, issued on a fraudulent application,counterfeit, fraudulent processing of transactions, account takeover or other fraudulent conditions as defined by the card company or the member company.fraudulent user - an individual who is not the cardholder or designee and who uses a card (or, in a mail/phone order or recurring transaction, an account number) to obtain goods or services without the cardholder s consent.grace period - a period of time during which you are allowed to pay your credit card bill without being charged a finance and/or late fee. this period is usually 10-28 days.introductory rate (or intro apr) - a temporary, lower annual percentage rate, after which the apr is raised.issuer - any association member financial institution, bank, credit union or company that issues, or causes to be issued, plastic cards to cardholders.magnetic stripe - a stripe of magnetic information that is affixed to the back of a plastic credit or debit card. this stripe contains customer and account information that is required to complete electronic financial transactions. the physical and magnetic characteristics of this stripe are specified in the international organization for standardization standards 7810, 7811 and 7813.mail/phone order merchant - a merchant that transacts business by mail or phone.mail/phone order transaction - a transaction where a cardholder orders goods or services from a merchant by telephone, mail or other means of telecommunication, and where neither the card nor the cardholder is present at the merchant outlet.mastercard - mastercard international inc. and all of its subsidiaries and affiliates.mastercard acquirer - a member that signs a mastercard merchant agreement or disburses currency to a mastercard cardholder in a cash disbursement, and directly or indirectly enters the resulting transaction receipt into interchange.mastercard card - a card that bears the mastercard symbol, enabling a mastercard cardholder to obtain goods, services or cash from a mastercard merchant or acquirer.mastercard issuer - a member that issues mastercard cards.merchant - an entity that contracts with merchant banks or iso s to originate transactions.merchant agreement - a written agreement between a merchant and a bank that contains their respective rights,duties and warranties, with respect to acceptance of the bankcard and matters related to the bankcard activity.merchant bank - bank that has a merchant agreement with a merchant to accept (acquire) deposits generated by bankcard transactions.minimum payment - the lowest amount of money that you are required to pay on your credit card statement each month.online financial transaction - a transaction that is authorized, cleared and settled in a single online message.overlimit - this refers to a cardholder account that has surpassed its credit limit with a transaction (i.e., the cardholder s outstanding balance is beyond his/her credit limit).overlimit fee - a fee charged when your balance goes over your credit limit.password - a sequence of characters that allows users access to a system. although they are supposed to be unique, experience has shown that most people s password choices are highly insecure. humans tend to choose short words, such as names, which are easy to guess.per transaction fees - fees paid by the merchant to the merchant bank or other contracted party on a per-transactionbasis.pin (personal identification number) - a sequence of digits used to verify the identity of the holder of a token. the pin is a kind of password.plastic (card) - this is a generic term that is used to identify any of the various cards issued to cardholders.point of sale (pos) - location in a merchant establishment at which the sale is consummated by payment for goods or services received.policy - an informal, generally natural language description of desired system behavior. policies may be defined for particular requirements, such as confidentiality, integrity, availability, safety, etc.posting - the process of updating individual cardholder account balances to reflect merchandise sales, instant cash, cash advances, adjustments, payments and any other charges or credits.primary account number (pan) - the number that is embossed and/or encoded on a plastic card that identifies the issuer and the particular cardholder account.prime rate (or prime interest rate) - the interest rate at which banks lend to their most creditworthy (prime)customers. the prime rate is known to change but not on a regular basis.processing date - the date on which the transaction is processed by the acquiring bank.receipt - a hard copy document that records when a transaction took place at the point of sale. the receipt contains a description of the transaction, which usually includes the date, the merchant name/location, the primary account number, the amount and the reference number.recurring billing - transactions for which a cardholder grants permission to the merchant to periodically charge his account number for recurring goods or services.reference number - number assigned to each monetary transaction in a descriptive billing system. each reference number is printed on the monthly statement to aid in retrieval of the document, should it be questioned by the cardholder.refund the creation of a credit to a cardholder account, usually as a result of a product return or to correct an error.retail merchant - a merchant that provides goods and/or services in the retail industry, but that is not a mail/phone merchant, a recurring services merchant or a t e merchant.sales draft - a paper record that evidences the purchase of goods or services by a cardholder.secured credit cards - credit cards that require collateral (property, such as a house, car or deposit of money) for approval. generally, secured credit cards are for people with no credit or poor credit who are trying to build or rebuild their credit history.service charge - a component of some finance charges, such as the fee for triggering an overdraft checking account into use.settlement - the reporting of settlement amounts owed by one member to another, or to a card issuing concern, as a result of clearing. settlement is the actual buying and selling of transactions between the merchants, processors and acquirers; along with the card-issuing entities.settlement bank - a bank, including a correspondent or intermediary bank, that is both located in the country where a member s settlement currency is the local currency, and is authorized to execute settlement of interchange on behalf of the member or the member s bank.smart card - a plastic card containing a computer chip with memory and cpu capabilities. such a card may be used foridentification or to store information, financial amounts or other forms of data. also called an integrated circuit card or a chip card.standard floor limit - a floor limit that varies by merchant type. this refers to a currency limit on transactions, above which authorization requests are required.statement - a written record prepared by a financial institution, usually once a month, listing all transactions for an account, including deposits, withdrawals, checks, electronic transfers, fees and other charges, and interest credited or earned. the statement is usually mailed to the customer.stored-value card - a stored-value card is a credit-card-sized device that is implanted with a computer chip with stored money value. a reloadable stored-value card can be reused by transferring a dollar value to it from an automated teller machine or other device. a disposable card cannot be reloaded.transaction - (1) any agreement between two or more parties that establishes a legal obligation. (2) the act of carrying out such an obligation. (3) all activities affecting a deposit account that are performed at the request of the account holder. (4) all events that cause some change in theassets, liabilities or net worth of a business. (5) an action between a cardholder and a merchant or a cardholder and a member that results in activity on the cardholder account.transaction identifier - a unique 15-character value that visa assigns to each transaction and returns to the acquirer in the authorization response. visa uses this value to maintain an audit trail throughout the lifecycle of the transaction and all related transactions, such as reversals, adjustments, confirmations and chargebacks.unsecured credit cards - credit cards that are not secured by collateral. customers qualify for such cards based on their credit history, their financial strength and their earnings potential.user authentication - process of validating that a user is who s/he represents her/himself to be.validation code - a unique 4-character value that visa includes as part of the cps/atm program in each authorization response. this code ensures that key authorization fields are preserved in the clearing or settlement record.variable interest rate - with variable-rate cards, the apr changes when interest rates or other economic indicators change. also known as a floating rate.visa - visa international service association and all of its subsidiaries and affiliates.visa card - a card that bears the visa symbol and which enables a visa cardholder to obtain goods, services or cash from a visa merchant or acquirer.visa issuer - a member that issues visa cards.visa merchant - a merchant that displays the visa symbol and accepts all visa cards.voice authorization - an approval response that is obtained through interactive communication between an issuer and an acquirer, their authorizing processors or stand-in processing or through telephone, facsimile or telex communications.void transaction - a deletion of the transaction information.void(ed) - nullifies a transaction that has been recorded for settlement, but has not yet been settled. this removes the transaction from the batch of transactions to be settled.信用卡常用术语Credit card term 相关内容:。

信用卡专用名词解释信用卡专用名词解释信用卡信用卡是银行或其它财务机构签发给那些资信状况良好的人士用于在指定的商家购物和消费、或在指定银行机构存取现金的特制卡片是一种特殊的信用凭证。
银行卡银行卡是指由商业银行含邮政金融机构向社会发行的具有消费信用、转帐结算、存取现金等全部或部分功能的信用支付工具。
贷记卡贷记卡是指发卡银行给予持卡人一定的信用额度持卡人可在信用额度内先消费后还款的信用卡。
准贷记卡准贷记卡是指持卡人须先按发卡银行要求交存一定金额的备用金当备用金帐户余额不足支付时可在发卡银行规定的信用额度内透支的信用卡。
借记卡借记卡是指先存款后、消费或取现没有透支功能的信用卡。
其按功能不同又可分为转帐卡含储蓄卡、专用卡及储值卡。
转帐卡转帐卡是实时扣帐的借记卡。
其具有转帐结算、存取现金和消费功能。
专用卡专用卡是具有专门用途、在特定区域使用的借记卡。
其具有转帐结算、存取现金和消费功能。
注专门用途是指在百货、餐饮、饭店及娱乐行业以外的用途。
储值卡储值卡是发卡银行根据持卡人要求将其资金转至卡内储存交易时直接从卡内扣款的预付钱包式借记卡。
联名认同卡联名认同卡是商业银行与盈利性机构非盈利机构合作发行的银行卡附属产品。
银行卡分类银行卡分类1银行卡分为信用卡和借记卡信用卡又分为贷记卡和准贷记卡。
贷记卡是指发卡银行给予持卡人一定的信用额度持卡人可在信用额度内先消费、后还款的信用卡。
准贷记卡是指持卡人先按银行要求交存一定金额的备用金当备用金不足支付时可在发卡银行规定的信用额度内透支的信用卡。
借记卡按功能不同分为转账卡、专用卡、储值卡。
借记卡不能透支。
转账卡具有转账、存取现金和消费功能。
专用卡是在特定区域、专用用途是指百货、餐饮、娱乐行业以外的用途使用的借记卡具有转账、存取现金的功能。
储值卡是银行根据持卡人要求将资金转至卡内储存交易时直接从卡内扣款的预付钱包式借记卡。
2银行卡的其他分类银行卡按发行对象不同分为单位卡和个人卡按币种不同分为人民币卡和外币卡按信息载体不同分为磁条卡和芯片卡。

银行术语大全100个银行术语是银行业务的专业术语,它包括银行业务中的各种操作、流程、制度等,是金融学中的重要内容之一。
以下是100个银行术语,按照不同的业务范畴划分。
一、账户类1. 储蓄账户:提供存款、取款、转账等常规操作服务的账户。
2. 支票账户:银行代理客户发行支票,供客户支付、转账使用的账户。
3. 对公账户:面向企事业单位和政府机关等法人或其他组织开立的账户。
4. 微信支付宝账户:用于移动支付的账户,可与银行账户实现绑定。
5. 电子账户:基于互联网、手机等电子渠道进行操作的账户,不需要纸质存折或银行卡。
6. 固定存款账户:客户将资金存入银行,一定期限内不能取出,从而获得更高的利息收益。
7. 通知存款账户:客户在提前通知银行的情况下,才能取出存款的特殊账户。
8. 定期存款账户:客户在银行存款一定期限,到期时取出本息,获得固定的利息收益。
二、贷款类9. 个人贷款:向个人客户提供的各类贷款,如个人消费贷款、个人房屋贷款、个人汽车贷款等。
10. 对公贷款:向企业、事业单位及政府机关等组织提供的贷款。
11. 授信额度:银行为客户授予的贷款额度。
12. 贷款利率:按照一定的计算方式计算出的借款方应支付的费用。
13. 贷款期限:通常指借款方从银行贷到款到还款日之间的时间。
14. 抵押贷款:借款方根据借款合同的约定,将其所有财产或部分财产抵押给银行,作为还款担保的一种方法。
15. 担保贷款:借款方找到担保人,担保借款方还款的一种方式。
16. 垫款:在借款人未按照贷款合同约定的时间和方式归还贷款的情况下,银行为保障自身权益向借款人垫付还款,以维护银行的良好信誉度。
17. 逾期罚息:借款人未按照合同约定的还款时间和方式进行还款,在规定的逾期时间范围内向银行缴纳的罚金。
三、理财类18. 理财产品:由银行或基金公司发行的,具有一定收益性、流动性的投资产品。
19. 开放式基金:能够不断发行新份额并回购已有份额的基金。

信用卡名词解释信用卡是一种允许持卡人在一定时期内借款并购物的金融工具。
以下是一些常见的信用卡名词解释:1. 信用额度:信用卡发卡银行或金融机构允许持卡人借款的最大金额。
信用额度通常根据持卡人的信用记录、收入情况和其他因素来确定。
2. 最低还款额:持卡人需要每个账单周期还款的最低金额。
如果持卡人只还最低还款额,则余额将被视为“滚动”至下个期间,并附加利息。
3. 透支:持卡人在信用额度之外使用信用卡进行消费的行为。
透支将产生高额利息和其他费用。
4. 利息:持卡人透支或未能全额还款时需支付的费用。
利息根据欠款余额和信用卡的年利率来计算。
5. 年费:信用卡发行银行收取的一次性费用,以提供信用卡的服务。
6. 优惠:持卡人使用信用卡时可以获得的折扣、回馈或其他福利。
7. 信用记录:一个人的信用历史记录,包括他们在过去的借贷和还款中的表现。
信用记录对信用卡申请和贷款申请的批准和条件有重要影响。
8. 还款期限:持卡人需要在账单周期结束前还清信用卡欠款的日期。
9. 逾期金:持卡人在还款期限后未能还清欠款时产生的罚款。
10. 外币交易费:在使用信用卡进行外币交易时,持卡人需要支付的费用。
外币交易费通常是交易金额的一定比例。
11. 国际交换费:当持卡人在国外使用信用卡时,发卡银行收取的一种费用。
国际交换费通常是交易金额的一定比例。
12. 分期付款:将较大的消费分为几个固定期限的付款。
持卡人需要支付每月分期付款金额和相应的利息。
13. 提额:持卡人向信用卡发行银行申请增加信用额度的行为。
14. 额外费用:信用卡持有人除了利息之外需要支付的其他费用,如提款费、转账费等。
15. 锁定期:信用卡发行银行规定的持卡人开卡一段时间内,不能调整信用额度、申请提额等操作的时期。
以上是一些常见的信用卡名词解释。
熟悉这些名词可以帮助持卡人更好地了解信用卡的相关费用和服务,并更好地管理自己的信用卡账户。
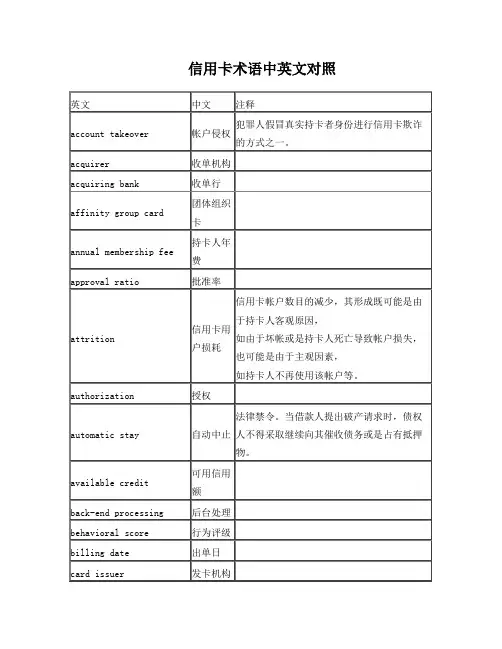
信用卡术语中英文对照英文中文注释account takeover帐户侵权犯罪人假冒真实持卡者身份进行信用卡欺诈的方式之一。
acquirer收单机构acquiring bank收单行affinity group card团体组织卡annual membership fee持卡人年费approval ratio批准率attrition信用卡用户损耗信用卡帐户数目的减少,其形成既可能是由于持卡人客观原因,如由于坏帐或是持卡人死亡导致帐户损失,也可能是由于主观因素,如持卡人不再使用该帐户等。
authorization授权automatic stay自动中止法律禁令。
当借款人提出破产请求时,债权人不得采取继续向其催收债务或是占有抵押物。
available credit可用信用额back-end processing后台处理behavioral score行为评级billing date出单日card issuer发卡机构card mailer信用卡送达邮件card reissue信用卡更换cardholder agreement持卡人协议cardholder bank持卡人银行cardholder masterfile持卡人主档案cash advance预支现金chargeback退单charge off核销chip card芯片卡corporate card公司卡credit analyst信用分析员credit balance信用余额credit card信用卡credit limit信用限额credit loss信用损失credit scoring信用评分cross-sell交叉销售current account正常帐户cutoff score信用评分底线cycle帐户分类将持卡人帐户进行分组,以此进行工作量分配并简化帐户识别。
cycle period循环周期在出单前对交易的借贷事项进行记录并累加的固定时间段。
信用卡常用术语1Cash Card(现金卡):可以从银行或ATM机提取现金Cheque Guarantee Card (支票保证卡)Debit Card(借记卡)Credit card(信用卡)Current Account(现金帐户):用于存(Deposit),取(Withdraw),日常开支,通常利息较低或没有利息。
Saving Account(存款帐户)Overdraft(透支)account number 帐目编号depositor 存户pay-in slip 存款单a deposit form 存款单a banding machine 自动存取机to deposit 存款deposit receipt 存款收据private deposits 私人存款certificate of deposit 存单deposit book, passbook 存折credit card 信用卡principal 本金overdraft, overdraw 透支to counter sign 双签to endorse 背书endorser 背书人to cash 兑现to honor a cheque 兑付to dishonor a cheque 拒付to suspend payment 止付cheque,check 支票cheque book 支票本order cheque 记名支票bearer cheque 不记名支票crossed cheque 横线支票blank cheque 空白支票rubber cheque 空头支票cheque stub, counterfoil 票根cash cheque 现金支票traveler s cheque 旅行支票cheque for transfer 转帐支票outstanding cheque 未付支票canceled cheque 已付支票forged cheque 伪支票Bandar s note 庄票,银票balance sheet 资产负债表cash flow 现金流转glossary 术语表money order 汇款单,汇票letter of credit n.[商](银行发行的)信用证charge for 想...收费overdraw v.透支overdraft n.透支, 透支之款项endorse [In5dC:s] v.在(票据)背面签名, 签注(文件), 认可, 签署liability n.责任, 义务, 倾向, 债务, [负债], 与assets相对asset n.[资产], 有用的东西solvent adj. 有偿付能力的 n.溶媒, 溶剂, 解决方法securities n.有价证券time hull insurance 船舶定期保险marine insurance 海损保险maritime transportation insurance 海洋运输保险fire insurance 火险cargo insurance 货物保险Account Number - A unique number assigned by a financial institution to a customer.On a credit card, this number is embossed and encoded on the plastic card.Additional Cardholder - When you have a credit card, it is often possible to add an additional card to the account for use by someone else. The main cardholder holds responsibility for ensuring payments on the additional card are made. Purchases are shown on the credit card statement, which is sent monthly.American Express - Also known as AMEX, this company is one of the main international credit card issuing schemes. It issues its own credit cards—unlike Visa and MasterCard—and is responsible for its own relationships with retailers.Annual Fee- An annual (yearly) fee associated with having a credit card. This isa separate fee from interest rate on purchases.Annual Percentage Rate (APR)- The yearly percentage rate charged when a balance is held on a credit card. This rate is applied each month that an outstanding balanceis present.Approval Response - An authorization response that is received when a transactionis approved.ATM - Automated Teller Machines or cash points allow you to access cash with a credit card or other card associated with your bank account. You need to enter your personal identification number (PIN) into the machine to access cash.Authentication - The process of assuring that data has come from its claimed source, or a process of corroborating the claimed identity of a communicating party.Authorization - Every retailer has a purchase limit above which they must seek authorization from the card issuer before they can complete the sale. Such authorization can be done by telephone or electronically at the cash till. Authorization is used to control credit card fraud. The cardholder’s available credit limit is reduced by the authorized amount.Authorization Amount - Currency amount approved.Authorization Code - A code that an issuer or its authorizing processor provides to indicate approval or denial for an authorization request.Authorization Date - Date and time when the transaction was authorized.Authorization Only - A transaction that is created to reserve an amount against a credit card’s available limit for intended purchases; the actual settlement mayoccur within three to five days, depending on the card type.Authorized Amount - Currency amount approved.Authorized Transaction - Transaction that has been approved.Balance Transfer - When the outstanding balance of one credit card (or several credit cards) is moved to another credit card account.Balance Transfer Fee - A fee charged by a credit card company to transfer a balance from one account to another. This fee can be anywhere from 1%-5% of the balance amount. However, many credit card companies do not charge this fee. Contact the credit card issuer for their specific fees.Bad Credit - A term used to describe a poor credit rating. Common practices that can damage a credit rating include making late payments, skipping payments, exceeding card limits or declaring bankruptcy. “Bad Credit” can result in beingdenied future credit.Bank Account - Bank account number for the merchant to which funds will be deposited.Bank Identification Number (BIN) - The first six digits of a Visa or MasterCard account number. This number is used to identify the card-issuing institution.Bankcard - A payment card issued by a bank.Billing Cycle - The time between billing statements, usually 28-31 days.Business Card (Business Credit Card) - Usually issued to corporate executives orbusiness owners in order to more easily keep business expenses separate frompersonal charges.Card Issuer - Any association member financial institution, bank, credit union, or company that issues, or causes to be issued, plastic cards to cardholders.Card Reader - A device that is capable of reading the encoding on plastic cards.Cardholder - An individual to whom a card is issued, or who is authorized to usean issued card.Cash Advance - A cash loan from a credit card using an ATM or bank withdrawal.Cash Back - Cash back returns to you a percentage of the total amount spent on your credit card over a specific period of time, usually monthly or quarterly. This feature is particularly useful if you normally pay your credit card bills in full each month, as it means you get an effective discount on the products bought withyour credit card.Chargeback - A transaction returned through interchange by an issuer to an acquirer.A transaction may be returned because of it was non-compliant with the associationrules and regulations or because it was disputed by a cardholder.Chargeback Period - The number o f days from the transaction’s processing date or endorsement date, during which the issuer may initiate a chargeback.Co-Branded Card - A co-branded credit card is sponsored by both the issuing bank and a retail organization, such as a department store or an airline. Cardholders may get benefits, such as discounts or free merchandise, from the sponsoring merchant, based on account usage and terms.Commercial Cards - A general name for cards typically issued for business use and which may include Corporate Cards, Purchase Cards, Business Cards, Travel andEntertainment Cards.Credit Card Number - Unique number assigned to a credit card.Credit Limit - How much total money can be charged to a credit card account, forexample $5,000.Credit History - A partial profile of your financial life, given within a particular timeframe (usually measured in years). Your credit history shows the extent to which you pay your bills on time and how much you may owe particular parties. Credit card issuers use this information to decide whether to provide customers with creditcards.Debit - A charge to a customer’s bankcard account. A transaction, such as a check, automated teller machine (ATM) withdrawal or point-of-sale (POS) debit purchasethat debits a demand deposit account.Expired Card - A card on which the embossed, encoded or printed expiration datehas passed.Finance Charge - Fees and other costs billed to you on your statement for using the credit cards (i.e., balance transfer fees, cash advance fees, late fees,overlimit fees, etc.).Fixed Rate (or Fixed APR) -An annual percentage rate that does not change throughout the year, unlike an introductory APR that changes after a specific period of time.Floor Limit - An amount that Visa and MasterCard have established for single transactions at specific types of merchant outlets and branches, above whichauthorization is required.Fraudulent Transaction - A transaction unauthorized by the cardholder of a bankcard. Such transactions are categorized as lost, stolen, not received, issued on a fraudulent application, counterfeit, fraudulent processing of transactions, account takeover or other fraudulent conditions as defined by the card company orthe member company.。
信用卡的八大名词解释在如今的消费社会中,信用卡已经成为人们日常生活不可或缺的支付工具。
然而,对于信用卡的一些专业术语,很多人可能并不熟悉。
在这篇文章中,我将就信用卡的八大名词进行解释,帮助读者更好地理解和使用信用卡。
1. 信用额度(Credit Limit)信用额度是指信用卡发卡银行为持卡人设定的最高可用于消费和借款的金额。
每个持卡人的信用额度会根据其个人信用记录、收入水平和还款能力等因素而定。
持卡人可以通过还清信用卡欠款、提高收入状况等方式来逐渐提高信用额度。
但需要注意的是,超出信用额度的消费或借款可能会导致额外费用或信用记录的损害。
2. 最低还款额(Minimum Payment)最低还款额是持卡人每个周期最少需要偿还的金额,通常为总欠款的一小部分。
持卡人只需支付最低还款额,便可避免逾期还款产生的费用和信用记录的负面影响。
然而,只支付最低还款额可能会导致高利息的累积和长期债务,建议尽量偿还更多的欠款以减少利息支出。
3. 年费(Annual Fee)年费是信用卡发卡银行为提供信用卡服务而收取的一项固定费用,通常在持卡人账单中显示。
年费的金额根据信用卡类型和发卡银行的政策而有所不同,有些信用卡可能会免除首年或前几年的年费。
持卡人可以根据自己的使用情况和需求选择是否申请年费信用卡。
4. 利息(Interest)利息是指持卡人因为借款或透支信用卡而需要支付给发卡银行的费用。
信用卡的利息通常以年利率的形式计算,并根据持卡人的实际欠款金额和账期来计算利息费用。
持卡人可以通过按时还款或提前还款来减少利息支出。
5. 信用记录(Credit History)信用记录是信用卡持卡人在使用信用卡过程中形成的个人信用历史。
信用记录会记录持卡人的还款情况、逾期情况、信用额度使用情况等信息,对持卡人的信用评级和信用额度审批起着重要作用。
良好的信用记录可以帮助持卡人提高信用额度、获得更低的利率和更多的信用福利。
6. 外币交易费(Foreign Transaction Fee)外币交易费是持卡人在境外或使用外币进行交易时需要支付给发卡银行的费用。
信用卡对账单术语
信用卡对账单术语,你多少要了解它的含义。
本期应缴金额:这是你这个月所欠银行的钱,如果全额还款,你就不用交给银行利息(提现除外)
最低还款金额:如果你本月手头紧,可以只交最低还款金额,但没还的部分银行就要收利息信用额度:指每月你可以从银行借出多少钱,你可在额度内循环使用。
交易日:指实际刷卡消费、取现或转账的日期。
银行记账日:指银行把你的交易记在账上的日期。
账单中的交易日是指刷卡当天,记账日则有所不同,店家刷卡信息传输到银行需要时间,境外消费一般都会一到两天的时差。
账单日:指银行对你每个月用信用卡交易“算总账”的日期。
到期还款日:一定要在这个日期前还款,若超过此期限,你对本期所欠银行的款项就要缴纳利息及其他相关费用了。
本期已还款:在本期,你已经还给了银行多少钱。
交易金额:指你用信用卡进行交易的币种及金额。
要注意,交易金额一列中标注的数额,采用的是消费当地国的货币单位,比如你在欧洲消费,这一列中所列的数额就是以欧元为单位的。
结算金额:指银行实际结算的货币币种及金额。
我爱卡提醒大家:要合理使用信用卡消费,切不可恶意拖欠信用卡还款,逾期不好可导致犯罪。
国外留学与银行打交道的常用术语:Cash Card(现金卡):可以从银行或A TM机提取现金Cheque Guarantee Card (支票保证卡)Debit Card(借记卡)Credit card(信用卡)Current Account(现金帐户):用于存(Deposit),取(Withdraw),日常开支,通常利息较低或没有利息。
Saving Account(存款帐户)Overdraft(透支)account number 帐目编号depositor 存户pay-in slip 存款单a deposit form 存款单a banding machine 自动存取机to deposit 存款deposit receipt 存款收据private deposits 私人存款certificate of deposit 存单deposit book, passbook 存折credit card 信用卡principal 本金overdraft, overdraw 透支to counter sign 双签to endorse 背书endorser 背书人to cash 兑现to honor a cheque 兑付to dishonor a cheque 拒付to suspend payment 止付cheque,check 支票cheque book 支票本order cheque 记名支票bearer cheque 不记名支票crossed cheque 横线支票blank cheque 空白支票rubber cheque 空头支票cheque stub, counterfoil 票根cash cheque 现金支票traveler s cheque 旅行支票cheque for transfer 转帐支票outstanding cheque 未付支票canceled cheque 已付支票forged cheque 伪支票Bandar s note 庄票,银票balance sheet 资产负债表cash flow 现金流转glossary 术语表money order 汇款单,汇票letter of credit n.[商](银行发行的)信用证charge for 想...收费overdraw v.透支overdraft n.透支, 透支之款项endorse [In5dC:s] v.在(票据)背面签名, 签注(文件), 认可, 签署liability n.责任, 义务, 倾向, 债务, [负债], 与assets相对asset n.[资产], 有用的东西solvent adj. 有偿付能力的n.溶媒, 溶剂, 解决方法securities n.有价证券time hull insurance 船舶定期保险marine insurance 海损保险maritime transportation insurance 海洋运输保险fire insurance 火险cargo insurance 货物保险Account Number - A unique number assigned by a financial institution to a customer. On a credit card, this number is embossed and encoded on the plastic card.Additional Cardholder - When you have a credit card, it is often possible to add an additional card to the account for use by someone else. The main cardholder holds responsibility for ensuring payments on the additional card are made. Purchases are shown on the credit card statement, which is sent monthly.American Express - Also known as AMEX, this company is one of the main international credit card issuing schemes. It issues its own credit cards—unlike Visa and MasterCard—and is responsible for its own relationships with retailers.Annual Fee- An annual (yearly) fee associated with having a credit card. This is a separate fee from interest rate on purchases.Annual Percentage Rate (APR)- The yearly percentage rate charged when a balance is held on a credit card. This rate is applied each month that an outstanding balance is present.Approval Response - An authorization response that is received when a transaction is approved.A TM - Automated Teller Machines or cash points allow you to access cash with a credit card or other card associated with your bank account. Y ou need to enter your personal identification number (PIN) into the machine to access cash.Authentication - The process of assuring that data has come from its claimed source, or a processof corroborating the claimed identity of a communicating party.Authorization - Every retailer has a purchase limit above which they must seek authorization from the card issuer before they can complete the sale. Such authorization can be done by telephone or electronically at the cash till. Authorization is used to control credit card fraud. The cardholder’s available credit limit is reduced by the authorized amount.Authorization Amount - Currency amount approved.Authorization Code - A code that an issuer or its authorizing processor provides to indicate approval or denial for an authorization request.Authorization Date - Date and time when the transaction was authorized.Authorization Only - A transaction that is created to reserve an amount against a credit card’s available limit for intended purchases; the actual settlement may occur within three to five days, depending on the card type.Authorized Amount - Currency amount approved.Authorized Transaction - Transaction that has been approved.Balance Transfer - When the outstanding balance of one credit card (or several credit cards) is moved to another credit card account.Balance Transfer Fee - A fee charged by a credit card company to transfer a balance from one account to another. This fee can be anywhere from 1%-5% of the balance amount. However, many credit card companies do not charge this fee. Contact the credit card issuer for their specific fees.Bad Credit - A term used to describe a poor credit rating. Common practices that can damage a credit rating include making late payments, skipping payments, exceeding card limits or declaring bankruptcy. ―Bad Credit‖ can result in being denied future credit.Bank Account - Bank account number for the merchant to which funds will be deposited.Bank Identification Number (BIN) - The first six digits of a Visa or MasterCard account number. This number is used to identify the card-issuing institution.Bankcard - A payment card issued by a bank.Billing Cycle - The time between billing statements, usually 28-31 days.Business Card (Business Credit Card) - Usually issued to corporate executives or business owners in order to more easily keep business expenses separate from personal charges.Card Issuer - Any association member financial institution, bank, credit union, or company that issues, or causes to be issued, plastic cards to cardholders.Card Reader - A device that is capable of reading the encoding on plastic cards.Cardholder - An individual to whom a card is issued, or who is authorized to use an issued card.Cash Advance - A cash loan from a credit card using an A TM or bank withdrawal.Cash Back - Cash back returns to you a percentage of the total amount spent on your credit card over a specific period of time, usually monthly or quarterly. This feature is particularly useful if you normally pay your credit card bills in full each month, as it means you get an effective discount on the products bought with your credit card.Chargeback - A transaction returned through interchange by an issuer to an acquirer. A transaction may be returned because of it was non-compliant with the association rules and regulations or because it was disputed by a cardholder.Chargeback Period - The numbe r of days from the transaction’s processing date or endorsement date, during which the issuer may initiate a chargeback.Co-Branded Card - A co-branded credit card is sponsored by both the issuing bank and a retail organization, such as a department store or an airline. Cardholders may get benefits, such as discounts or free merchandise, from the sponsoring merchant, based on account usage and terms.Commercial Cards - A general name for cards typically issued for business use and which may include Corporate Cards, Purchase Cards, Business Cards, Travel and Entertainment Cards.Credit Card Number - Unique number assigned to a credit card.Credit Limit - How much total money can be charged to a credit card account, for example $5,000.Credit History - A partial profile of your financial life, given within a particular timeframe (usually measured in years). Y our credit history shows the extent to which you pay your bills on time and how much you may owe particular parties. Credit card issuers use this information to decide whether to provide customers with credit cards.Debit - A charge to a customer’s bankcard account. A transaction, such as a check, automated teller machine (A TM) withdrawal or point-of-sale (POS) debit purchase that debits a demand deposit account.Expired Card - A card on which the embossed, encoded or printed expiration date has passed.Finance Charge - Fees and other costs billed to you on your statement for using the credit cards(i.e., balance transfer fees, cash advance fees, late fees, overlimit fees, etc.).Fixed Rate (or Fixed APR) -An annual percentage rate that does not change throughout the year, unlike an introductory APR that changes after a specific period of time.Floor Limit - An amount that Visa and MasterCard have established for single transactions at specific types of merchant outlets and branches, above which authorization is required.Fraudulent Transaction - A transaction unauthorized by the cardholder of a bankcard. Such transactions are categorized as lost, stolen, not received, issued on a fraudulent application, counterfeit, fraudulent processing of transactions, account takeover or other fraudulent conditions as defined by the card company or the member company.Fraudulent User - An individual who is not the cardholder or designee and who uses a card (or, in a mail/phone order or recurring transaction, an account number) to obtain goods or services without the cardholder’s consent.Grace Period - A period of time during which you are allowed to pay your credit card bill without being charged a finance and/or late fee. This period is usually 10-28 days.Introductory Rate (or Intro APR) - A temporary, lower annual percentage rate, after which the APR is raised.Issuer - Any association member financial institution, bank, credit union or company that issues, or causes to be issued, plastic cards to cardholders.Magnetic Stripe - A stripe of magnetic information that is affixed to the back of a plastic credit or debit card. This stripe contains customer and account information that is required to complete electronic financial transactions. The physical and magnetic characteristics of this stripe are specified in the International Organization for Standardization standards 7810, 7811 and 7813.Mail/Phone Order Merchant - A merchant that transacts business by mail or phone.Mail/Phone Order Transaction - A transaction where a cardholder orders goods or services from a merchant by telephone, mail or other means of telecommunication, and where neither the card nor the cardholder is present at the merchant outlet.MasterCard - MasterCard International Inc. and all of its subsidiaries and affiliates.MasterCard Acquirer - A member that signs a MasterCard merchant agreement or disburses currency to a MasterCard cardholder in a cash disbursement, and directly or indirectly enters the resulting transaction receipt into interchange.MasterCard Card - A card that bears the MasterCard symbol, enabling a MasterCard cardholder toobtain goods, services or cash from a MasterCard merchant or acquirer.MasterCard Issuer - A member that issues MasterCard cards.Merchant - An entity that contracts with merchant banks or ISO’s to originate transactions.Merchant Agreement - A written agreement between a merchant and a bank that contains their respective rights, duties and warranties, with respect to acceptance of the bankcard and matters related to the bankcard activity.Merchant Bank - Bank that has a merchant agreement with a merchant to accept (acquire) deposits generated by bankcard transactions.Minimum Payment - The lowest amount of money that you are required to pay on your credit card statement each month.Online Financial Transaction - A transaction that is authorized, cleared and settled in a single online message.Overlimit - This refers to a cardholder account that has surpassed its credit limit with a transaction (i.e., the cardholder’s outstanding balance is beyond his/her credit limit).Overlimit Fee - A fee charged when your balance goes over your credit limit.Password - A sequence of characters that allows users access to a system. Although they are supposed to be unique, experience has shown that most people’s password choices are highly insecure. Humans tend to choose short words, such as names, which are easy to guess.Per Transaction Fees - Fees paid by the merchant to the merchant bank or other contracted party on a per-transaction basis.PIN (Personal Identification Number) - A sequence of digits used to verify the identity of the holder of a token. The PIN is a kind of password.Plastic (Card) - This is a generic term that is used to identify any of the various cards issued to cardholders.Point Of Sale (POS) - Location in a merchant establishment at which the sale is consummated by payment for goods or services received.Policy - An informal, generally natural language description of desired system behavior. Policies may be defined for particular requirements, such as confidentiality, integrity, availability, safety, etc.Posting - The process of updating individual cardholder account balances to reflect merchandise sales, instant cash, cash advances, adjustments, payments and any other charges or credits.Primary Account Number (PAN) - The number that is embossed and/or encoded on a plastic card that identifies the issuer and the particular cardholder account.Prime Rate (or Prime Interest Rate) - The interest rate at which banks lend to their most creditworthy (prime) customers. The prime rate is known to change but not on a regular basis.Processing Date - The date on which the transaction is processed by the acquiring bank.Receipt - A hard copy document that records when a transaction took place at the point of sale. The receipt contains a description of the transaction, which usually includes the date, the merchant name/location, the primary account number, the amount and the reference number.Recurring Billing - Transactions for which a cardholder grants permission to the merchant to periodically charge his account number for recurring goods or services.Reference Number - Number assigned to each monetary transaction in a descriptive billing system. Each reference number is printed on the monthly statement to aid in retrieval of the document, should it be questioned by the cardholder.Refund – The creation of a credit to a cardholder account, usually as a result of a product return or to correct an error.Retail Merchant - A merchant that provides goods and/or services in the retail industry, but that is not a mail/phone merchant, a recurring services merchant or a T&E merchant.Sales Draft - A paper record that evidences the purchase of goods or services by a cardholder.Secured Credit Cards - Credit cards that require collateral (property, such as a house, car or deposit of money) for approval. Generally, secured credit cards are for people with no credit or poor credit who are trying to build or rebuild their credit history.Service Charge - A component of some finance charges, such as the fee for triggering an overdraft checking account into use.Settlement - The reporting of settlement amounts owed by one member to another, or to a card issuing concern, as a result of clearing. Settlement is the actual buying and selling of transactions between the merchants, processors and acquirers; along with the card-issuing entities.Settlement Bank - A bank, including a correspondent or intermediary bank, that is both located in the country where a member’s settlement currency is the local curr ency, and is authorized to execute settlement of interchange on behalf of the member or the member’s bank.Smart Card - A plastic card containing a computer chip with memory and CPU capabilities. Such a card may be used for identification or to store information, financial amounts or other forms of data. Also called an integrated circuit card or a chip card.Standard Floor Limit - A floor limit that varies by merchant type. This refers to a currency limit on transactions, above which authorization requests are required.Statement - A written record prepared by a financial institution, usually once a month, listing all transactions for an account, including deposits, withdrawals, checks, electronic transfers, fees and other charges, and interest credited or earned. The statement is usually mailed to the customer.Stored-value Card - A stored-value card is a credit-card-sized device that is implanted with a computer chip with stored money value. A reloadable stored-value card can be reused by transferring a dollar value to it from an automated teller machine or other device. A disposable card cannot be reloaded.Transaction - (1) Any agreement between two or more parties that establishes a legal obligation. (2) The act of carrying out such an obligation. (3) All activities affecting a deposit account that are performed at the request of the account holder. (4) All events that cause some change in the assets, liabilities or net worth of a business. (5) An action between a cardholder and a merchant or a cardholder and a member that results in activity on the cardholder account.Transaction Identifier - A unique 15-character value that VISA assigns to each transaction and returns to the acquirer in the authorization response. VISA uses this value to maintain an audit trail throughout the lifecycle of the transaction and all related transactions, such as reversals, adjustments, confirmations and chargebacks.Unsecured Credit Cards - Credit cards that are not secured by collateral. Customers qualify for such cards based on their credit history, their financial strength and their earnings potential.User Authentication - Process of validating that a user is who s/he represents her/himself to be.V alidation Code - A unique 4-character value that VISA includes as part of the CPS/A TM program in each authorization response. This code ensures that key authorization fields are preserved in the clearing or settlement record.V ariable Interest Rate - With variable-rate cards, the APR changes when interest rates or other economic indicators change. Also known as a floating rate.Visa - V isa International Service Association and all of its subsidiaries and affiliates.Visa Card - A card that bears the V isa symbol and which enables a V isa cardholder to obtain goods, services or cash from a Visa merchant or acquirer.Visa Issuer - A member that issues V isa Cards.Visa Merchant - A merchant that displays the V isa symbol and accepts all Visa cards.V oice Authorization - An approval response that is obtained through interactive communication between an issuer and an acquirer, their authorizing processors or stand-in processing or through telephone, facsimile or telex communications.V oid Transaction - A deletion of the transaction information.V oid(ed) - Nullifies a transaction that has been recorded for settlement, but has not yet been settled. This removes the transaction from the batch of transactions to be settled.。