2013届江苏高考完形填空、任务型阅读专项训练四
- 格式:doc
- 大小:44.50 KB
- 文档页数:3

2013江苏卷第四部分:任务型阅读(共10小题;每小题1分,满分10分)请认真阅读下列短文,并根据所读内容在文章后表格中的空格里填入一.个.最恰当的单词。
注意:请将答案写在答题卡上相应题号的横线上。
每个空格只填一个单词。
Quiet Virtue: The ConscientiousThe everyday signs of conscientiousness (认真尽责)—being punctual, careful in doing work, self-disciplined, and scrupulous (一丝不苟的) in attending to responsibilities—are typical characteristics of the model organizational citizen, the people who keep things running as they should. They follow the rules, help out, and are concerned about the people they work with. It’s the conscientious worker who helps newcomers or updates people who return after an absence, who gets to work on time and never abuses sick leaves, who always gets things done on deadline.Conscientiousness is a key to success in any field. In studies of job performance, outstanding effectiveness for almost all jobs, from semi-skilled labor to sales and management, depends on conscientiousness. It is particularly important for outstanding performance in jobs at the lower levels of an organization: the secretary whose message taking is perfect, the delivery truck driver who is always on time.Among sales representatives for a large American car manufacturer, those who were most conscientious had the largest volume of sales. Conscientiousness also offers a buffer (缓冲) against the threat of job loss in today’s constantly changing market, because employees with this quality are among the most valued. For the sales representatives, their level of conscientiousness mattered almost as much as their sales in determining who stayed on.There is an air around highly conscientious people that makes them seem even better than they actually are. Their reputation for dependability influences managers’ evaluations of their work, giving them higher evaluations than objective measures of their performance would predict.But conscientiousness in the absence of social skills can lead to problems. Since conscientious people demand so much of themselves, they can hold other people to their own standards, and so be overly judgmental whe n others don’t show the same high levels of model behavior. Factory workers in Great Britain and the United States who were extremely conscientious, for example, tended to criticize co-workers even about failures that seemed unimportant to those they criticized, which damaged their relationships.When conscientiousness takes the form of living up to expectations, it can discourage creativity. In creative professions like art or advertising, openness to wild ideas and spontaneity (自发性) are scarce and in demand. Success in such occupations calls for a balance, however; without enough conscientiousness to follow through, people become mere dreamers, with nothing to show for their imaginativeness.题型自主分析:1、原词重现(信息查找):2、词性转换(信息加工):3、提炼概括(信息归纳):2012江苏卷第四部分: 任务型阅读(共10 小题;每小题1 分,满分10 分)请认真阅读下列短文,并根据所读内容在文章后表格中的空格里填入一个最恰当的单词。

2013江苏卷第四部分:任务型阅读(共10小题;每小题1分.满分10分)请认真阅读下列短文.并根据所读内容在文章后表格中的空格里填入一.个.最恰当的单词。
注意:请将答案写在答题卡上相应题号的横线上。
每个空格只填一个单词。
Quiet Virtue: The ConscientiousThe everyday signs of conscientiousness (认真尽责)—being punctual, careful in doing work, self-disciplined, and scrupulous (一丝不苟的) in attending to responsibilities—are typical characteristics of the model organizational citizen, the people who keep things running as they should. They follow the rules, help out, and are concerned about the people they work with. It’s the conscientious worker who helps newcomers or updates people who return after an absence, who gets to work on time and never abuses sick leaves, who always gets things done on deadline.Conscientiousness is a key to success in any field. In studies of job performance, outstanding effectiveness for almost all jobs, from semi-skilled labor to sales and management, depends on conscientiousness. It is particularly important for outstanding performance in jobs at the lower levels of an organization: the secretary whose message taking is perfect, the delivery truck driver who is always on time.Among sales representatives for a large American car manufacturer, those who were most conscientious had the largest volume of sales. Conscientiousness also offers a buffer (缓冲) against the threat of job loss in today’s constantly changing market, because employees with this quality are among the most valued. For the sales representatives, their level of conscientiousness mattered almost as much as their sales in determining who stayed on.There is an air around highly conscientious people that makes them seem even better than they actually are. Their reputation for dependability influences managers’ evaluations of their work, giving them higher evaluations than objective measures of their performance would predict.But conscientiousness in the absence of social skills can lead to problems. Since conscientious people demand so much of themselves, they can hold other people to their own standards, and so be overly judgmental when others don’t show the same high levels of model behavior. Factory workers in Great Britain and the United States who were extremely conscientious, for example, tended to criticize co-workers even about failures that seemed unimportant to those they criticized, which damaged their relationships.When conscientiousness takes the form of living up to expectations, it can discourage creativity. In creative professions like art or advertising, openness to wild ideas and spontaneity (自发性) are scarce and in demand. Success in such occupations calls for a balance, however; without enough conscientiousness to follow through, people become mere dreamers, with nothing to show for their imaginativeness.题型自主分析:1、原词重现(信息查找):2、词性转换(信息加工):3、提炼概括(信息归纳):2012江苏卷第四部分: 任务型阅读(共10 小题;每小题1 分,满分10 分)请认真阅读下列短文,并根据所读内容在文章后表格中的空格里填入一个最恰当的单词。

江苏省泗阳中学2013高考英语任务型阅读专项训练(四)任务型阅读1请认真阅读下列短文,并根据所读内容在文章后表格中的空格里填入一个最恰当的单词。
注意:每个空格只填1个单词。
The rate of population growth is fastest in underdeveloped countries. In these countries a high birthrate is accompanied by a lowered death rate thanks to improved standards of public health. Ideally it should be possible to counter(相反地) balance the effect of a reduced death rate by an increased use of family planning. In practice, however, population control is a complex matter. Throughout history people have determined the size of their families according to the cultural values of their societies.Population control has long been a subject of discussion among researchers. Some have argued that the supply of good land is limited. In order to feed a large population, bad land must be cultivated and the good land overworked. As a result, each person produces less in a given amount of time and this means a lower average income than could be obtained with a smaller population. Other researchers have argued that a large population gives more range for the development of facilities such as sports, roads and railways, which are not likely to be built unless there is a big demand for them. Similarly, it can be argued that the public costs of society will not be so heavy to each individual if they are shared among the members of a large population.One of the difficulties in putting birth control into practice lies in the fact that official attitudes to population growth vary from country to country. In underdeveloped countries where a large population is pressing hard upon the limits of food, space and natural resources, it will be the first concern of government to place a limit on the birthrate. In a well developed society the problem may be more complex. A declining birthrate may lead to unemployment because it results in a decreasing market. Cities with a declining population may have to face the prospect of a decreasing tax base and a fall in land values. If there are fewer children going to school, teachers may be thrown out of work. When the pressure of population on housing declines, prices also decline and the building industry is weakened. Faced with considerations such as these, the government of a developed country may well prefer to see a slowly increasing population, rather than one that is stable or in decline.Title Population controlTheme Population control causes (1)among researchers and countries.Among researchers Reasons for population control● It can (2) the effect of a reduced death rate.● Good land is limited and (3).● Each person produces less in a given amount of time.● A large population lea ds to a reduction in (4) income. Reasons against population control● A large population helps the development of facilities.● Each person (5) less of the public costs of society.Among countries For underdeveloped countries, population control can ● bring less (6) on supplies and resources.For developed countries, population control can● slow down economic (7).● lead to a (8) in tax and land values.● make many people (9).● weaken the building industry.(10) Consider countries and cultural values when introducing birthcontrol techniques.1. disagreement / argument2. balance3. overworked4. average5. shares / bears6. pressure7. growth / development8. decrease / fall9. unemployed 10. Suggestion / Advice任务型阅读2请认真阅读下列短文,并根据所读内容在文章后表格中的空格里填入一个最恰当的单词。

2013江苏卷第四部分:任务型阅读(共10小题;每小题1分,满分10分)请认真阅读下列短文,并根据所读内容在文章后表格中的空格里填入一.个.最恰当的单词。
注意:请将答案写在答题卡上相应题号的横线上。
每个空格只填一个单词。
Quiet Virtue: The ConscientiousThe everyday signs of conscientiousness (认真尽责)—being punctual, careful in doing work, self-disciplined, and scrupulous (一丝不苟的) in attending to responsibilities—are typical characteristics of the model organizational citizen, the people who keep things running as they should. They follow the rules, help out, and are concerned about the people they work with. It’s the conscientious worker who helps newcomers or updates people who return after an absence, who gets to work on time and never abuses sick leaves, who always gets things done on deadline.Conscientiousness is a key to success in any field. In studies of job performance, outstanding effectiveness for almost all jobs, from semi-skilled labor to sales and management, depends on conscientiousness. It is particularly important for outstanding performance in jobs at the lower levels of an organization: the secretary whose message taking is perfect, the delivery truck driver who is always on time.Among sales representatives for a large American car manufacturer, those who were most conscientious had the largest volume of sales. Conscientiousness also offers a buffer (缓冲) against the threat of job loss in today’s constantly changing market, because employees with this quality are among the most valued. For the sales representatives, their level of conscientiousness mattered almost as much as their sales in determining who stayed on.There is an air around highly conscientious people that makes them seem even better than they actually are. Their reputation for dependability influences managers’ evaluations of their work, giving them higher evaluations than objective measures of their performance would predict.But conscientiousness in the absence of social skills can lead to problems. Since conscientious people demand so much of themselves, they can hold other people to their own standards, and so be overly judgmental when others don’t show the same high levels of model behavior. Factory workers in Great Britain and the United States who were extremely conscientious, for example, tended to criticize co-workers even about failures that seemed unimportant to those they criticized, which damaged their relationships.When conscientiousness takes the form of living up to expectations, it can discourage creativity. In creative professions like art or advertising, openness to wild ideas and spontaneity (自发性) are scarce and in demand. Success in such occupations calls for a balance, however; without enough conscientiousness to follow through, people become mere dreamers, with nothing to show for their imaginativeness.题型自主分析:1、原词重现(信息查找):2、词性转换(信息加工):3、提炼概括(信息归纳):2012江苏卷第四部分: 任务型阅读(共10 小题;每小题1 分,满分10 分)请认真阅读下列短文,并根据所读内容在文章后表格中的空格里填入一个最恰当的单词。

2013 江苏卷第四部分:任务型阅读(共10 小题;每小题 1 分,满分10 分)请认真阅读下列短文,并根据所读内容在文章后表格中的空格里填入一.个.最恰当的单词。
注意:请将答案写在答题卡上相应题号的横线上。
每个空格只填一个单词。
Quiet Virtue: The ConscientiousThe everyday signs of conscientiousness (认真尽责 )—being punctual, careful in doing work,self-disciplined, and scrupulous ( 一丝不苟的) in attending to responsibilities —are typical characteristics of the model organizational citizen, the people who keep things running as they should. They follow the rules, help out, and are concerned about the people they work with. It the conscientious worker who helps newcomers or updates people who return after an absence, who gets to work on time and never abuses sick leaves, who always gets things done on deadline.Conscientiousness is a key to success in any field. In studies of job performance, outstanding effectiveness for almost all jobs, from semi-skilled labor to sales and management, depends on conscientiousness. It is particularly important for outstanding performance in jobs at the lower levels of an organization: the secretary whose message taking is perfect, the delivery truck driverwho is always on time.Among sales representatives for a large American car manufacturer, those who were most conscientious had the largest volume of sales. Conscientiousness also offers a buffer (缓冲) against the threat of job loss in today ’s constantly changing market, because employeeswith thisquality are among the most valued. For the sales representatives, their level of conscientiousness mattered almost as much as their sales in determining who stayed on.There is an air around highly conscientious people that makes them seem even better thanthey actually are. Their reputation for dependability influences managers ’evaluations of their work, giving them higher evaluations than objective measures of their performance would predict.But conscientiousness in the absence of social skills can lead to problems. Since conscientious people demand so much of themselves, they can hold other people to their own standards, and so be overly judgmental whe n others don’sthow the same high levels of model behavior. Factory workers in Great Britain and the United States who were extremely conscientious, for example, tended to criticize co-workers even about failures that seemed unimportant to those they criticized, which damaged their relationships.When conscientiousness takes the form of living up to expectations, it can discourage creativity. In creative professions like art or advertising, openness to wild ideas and spontaneity (自发性) are scarce and in demand. Success in such occupations calls for a balance, however;without enough conscientiousness to follow through, people become mere dreamers, with nothingto show for their imaginativeness.题型自主分析:1、原词重现(信息查找):2、词性转换(信息加工):3、提炼概括(信息归纳):2012江苏卷第四部分 : 任务型阅读(共10 小题;每小题1 分,满分10 分)请认真阅读下列短文,并根据所读内容在文章后表格中的空格里填入一个最恰当的单词。

2013年全国高考英语试题(江苏卷)及答案第一节: 单项填空(共15小题; 每小题1分,满分15分)21. Gnerally, students’inner motivation with high expectations from others _____ essential totheir development.A. isB. areC. wasD. were22. —The T-shirt I received is not the same as is shown online.—_____? But I promise you we’ll look into it right away.A. Who saysB. How comeC. What forD. Why worry23. —The town is so beautiful! I just love it.—Me too. The character of the town is well _____.A. qualitfiedB. preservedC. decoratedD. simplified24. Lionel Messi, _____ the record for the most goals in a calendar year, is considered the mosttalented football player in Europe.A. setB. settingC. to setD. having set25. —Could I use your car tomorrow morning?—Sure, I _____ a report at home.A. will be writingB. will have writtenC. have writtenD. have been writing26. I am always delighted when I recieve an e-mail from you. _____ the party on July 1st, I shallbe pleased to attend.A. On account ofB. In response toC. In view ofD. With regard to27. “Never for a second,” the boy says, “_____ that my father would come to my rescue.”A. I doubtedB. do I doubtC. I have doubtedD. did I doubt28. In the global economy, a new drug for cancer, _____ it is discovered, will create manyeconomic possibilities around the world.A. whateverB. whoeverC. whereverD. whichever29. Team leaders must ensure that all members _____ their natural desire to avoid theembarrasment associated with making mistakes.A. get overB. look overC. take overD. come over30. I should not have laughed if I _____ you were serious.A. thoughtB. would thinkC. had thoughtD. have thought31. Shortly after suffering from a massive earthquake and _____ to ruins, the city took on a newlook.A. reducingB. reducedC. being reducedD. having reduced32. The president of teh World Bank says he has a pssion for China, _____ he remembers startingas early as his childhood.A. whereB. whichC. whatD. when33. With inspiration from other food cultures, American food culture can take a _____ for thebetter.A. shareB. chanceC. turnD. when34. —What about your self-drive trip yesterday?—Tiring! The road is being widened, and we _____ a round ride.A. hadB. haveC. would haveD. have had35. —Thank you for the flowers.—_____. I thought they might cheer you up.A. That’s rightB. All rightC. I’m all rightD. It’s all right第二节: 完形填空(共20小题; 每小题1 分, 满分20 分)I used to believe in the American Dream, which meant a job, a mortgage (按揭), credit cards, success. I wanted it and worked toward it like everyone else, all of us 36 chasing the same thing.One year, through a series of unhappy events, it all fell 37 . I found myself homeless and alone. I had my truck and $56. I 38 teh countryside for some place I could rent for the 39 possible amount. I came upon a shabby house four miles up a winding mountain road 40 the Potomac River in West Virginia. It was 41 , full of broken glass and rubbish. I found the owner, rented it, and 42 a corner to camp in.The locals knew nothing about me, 43 slowly, they started teaching me the 44 of being a neighbor. They dropped off blankets, candles, and tools, and began 45 around to chat. They started to teach me a belief in a 46 American Dream—not the one of individual achievement but of 47 .What I have believed in, all those things I thought were 48 for a civilized life, were nonexistent in this place. 49 on teh mountain, my most valuable possessions were my 50 with my neighbors.Four years later, I moved back into 51 . I saw many people were having a really hard time, 52 their jobs and homes. I managed to reant a big enough house to 53 a handful of people. There are four of us now in the house, but over time I’ve had nine people come in and move on to other places. We’d all be in 54 if we had n’t banded together.The American Dream I believe in now is a shared one. It’s not so much about what I can get for mysefl; it’s about 55 we can all get by together.36. A. separately B. equally C. violently D. naturally37. A. off B. apart C. over D. out38. A. crossed B. left C. toured D. searched39. A. fullest B. largest C. fairest D. cheapest40. A. at B. through C. over D. round41. A. occupied B. abandoned C. emptied D. robbed42. A. turned B. approached C. cleared D. cut43. A. but B. although C. otherwise D. for44. A. benefit B. lesson C. nature D. art45. A. sticking B. looking C. swingting D. turning46. A. wild B. real C. different D. remote47. A. neighborliness B. happiness C. friendliness D. kindness48. A. unique B. expensive C. rare D. necessary49. A. Up B. Down C. Deep D. Along50. A. cooperation B. relationship C. satisfaction D. appointments51. A. reality B. society C. town D. life52. A. creating B. losing C. quitting D. offering53. A. put in B. turn in C. take in D. get in54. A. yards B. shelters C. camps D. cottages55. A. when B. what C. whehter D. how第三部分: 阅读理解(共15 小题; 每小题2 分, 满分30 分)AGuest ServicesFront Gate Guest Services can help you with anything from finding out what time your favourite show starts to purchasing tickets. The Guest Services location inside Front Gate also serves as a message center, lost children’s area and lost and found. Canada’s Wonderland does not offer personalized public paging (传呼).Food & Drink OptionsShops are located throughout Canada’s Wonderland. Pinic baskets and coolers are welcome at the shelter located outside Wonderland on the north side of our Front Gate. Outside food and drinks are not allowed in the Park. Bottled water may be brought into the Park.ATMsATMs are located just inside the Park beside Stroller, Locker and Wheelchair Rentals at the Front Gate, as well as KidZville (beside Guest Services), Splash Works (two locations), and outside Thunder Run.Pet CareA pet care facility is located outside our Front Gate on the south side for a daily fee. Water and air-conditioned shelters are provided. Guests are asked to provide food and exercise.First AidIf you need medical assistance, tell any park emloyee who will call First Aid and have them come to your location.Stroller, Locker and WheelchairRentalsStroller, locker and wheelchair rentals are available inside the Park at the Front Gate, beside Thrills Are Wonderland.Smoking PolicySmoking is not permitted while riding or standing in line for rides or in any of the chidren’s areas or the Water Park. Smoking is permitted in designated (指定的) areas only. Failure to observe all Park rules could result in being driven out of the Park without refund.56. The leaflet is to inform visitors of the Park’s _____.A. advanced managementB. thrill performancesC. entertainment facilitiesD. thoughtful services57. A visitor to the Park can _____.A. rent a stroller outside Front GateB. ask for first aid by Thunder RunC. smoke in the Water ParkD. leave his pet at KidZvilleBWe’ve considered several ways of paying to cut in line: hiring line standers, buying tickets fromscalpers (票贩子), or purchasing line-cutting privileges directly from, say, an airline or anamusement park. Each of these deals replaces the morals of the queue (waiting your turn) with the morals of the market (paying a price for faster service).Markets and queues—paying and waiting—are two different ways of allocating things, and each is appropriate to different activities. The morals of the queue, “First come, first served,” have an egalitarian (平等主义的) appeal. They tell us to ignore privilege, power, and deep pockets.The principle seems right on playgrounds and at bus stops. But the morals of thequeue do not govern all occasions. If I put my house up for sale, I have no duty toaccept the first offer that comes along, simply because it’s the first. Selling myhouse and waiting for a bus are different activities, properly governed by different standards.Sometimes standards change, and it is unclear which principle should apply. Think of the recorded message you hear, played over and over, as you wait on hold when calling your bank: “Your call will be answered in the order in which it was received.” This is essential for the moralsof the queue. It’s as if the company is trying to ease our impatience with fairness.But don’t take the recorded message too seriously. Today, some people’s calls are answered faster than others. Call center technology enables companies to “score” incoming calls and to give faster service to those that come from rich places. You might call this telephonic queue jumping.Of course, markets and queues are not the only ways of allocating things. Some goods we distribute by merit, others by need, still others by chance. However, the tendency of markets to replace queues, and other non-market ways of allocating goods is so common in modern life that we scarcely notice it anymore. It is striking that most of the paid queue-jumping schemes we’ve considered — at airports and amusement parks, in call centers, doctors’ offices, and national parks —are recent developments, scarcely imaginable three decades ago. The disappearance of the queues in these places may seem an unusual concern, but these are not the only places that markets have entered.58. According to the author, which of the following seems governed by the principle “Firstcome,first served”?A. Taking buses.B. Buying houses.C. Flying with an airline.D. Visiting amusement parks.59. The example of the recorded message in Paragraphs 4 and 5 illustrates _____.A. the necessity of patience in queuingB. the advantage of modern technologyC. the uncertainty of allocation principleD. the fairness of telephonic services60. The passage is meant to _____.A. justify paying for faster servicesB. discuss the morals of allocating thingsC. analyze the reason for standing in lineD. criticize the behavior of queue jumpingCIf a diver surfaces too quickly, he may suffer the bends. Nitrogen (氮) dissolved (溶解) in his blood is suddenly liberated bythe reduction of pressure. The consequence, if the bubbles (气泡) accumulate in a joint, is sharp pain and a bent body—thus the name. If the bubbles form in his lungs or his brain, the consequence can bedeath.Other air-breathing animals also suffer this decompression (减压) sickness if they surface too fast: whales, for example. And so, long ago, did ichthyosaurs. That these ancient sea animals got the bends can beseen from their bones. If bubbles of nitrogen form inside the bone they can cut offits blood supply. This kills the cells in the bone, and consequently weakens it, sometimes to the point of collapse. Fossil (化石) bones that have caved in on themselves are thus a sign that the animal once had the bends.Bruce Rothschild of the University of Kansas knew all this when he began a study of ichthyosaur bones to find out how widespread the problem was in the past. What he particularly wanted to investigate was how ichthyosaurs adapted to the problem of decompression over the 150 million years. To this end, he and his colleagues traveled the world’s natural-history museums, looking at hundreds of ichthyosaurs from the Triassic period and from the later Jurassic and Cretaceous periods.When he started, he assumed that signs of the bends would be rarer in younger fossils, reflecting their gradual evolution of measures to deal with decompression. Instead, he was astonished to discover the opposite. More than 15% of Jurassic and Cretaceous ichthyosaurs had suffered the bends before they died, but not a single Triassic specimen (标本) showed evidence of that sort of injury.If ichthyosaurs did evolve an anti-decompression means, they clearly did so quickly—and, most strangely, they lost it afterwards. But that is not what Dr Rothschild thinks happened. He suspects it was evolution in other animals that caused the change.Whales that suffer the bends often do so because they have surfaced to escape apredator (捕食动物) such as a large shark. One of the features of Jurassic oceans was an abundance of large sharks and crocodiles, both of which were fond of ichthyosaur lunches. Triassic oceans, by contrast, were mercifully shark- and crocodile-free. In the Triassic, then, ichthyosaurs were top of the food chain. In the Jurassic and Cretaceous, they were prey (猎物) as well as predator—and often had to make a speedy exit as a result.61. Which of the following is a typical symptom of the bends?A. A twisted body.B. A gradual decrease in blood supply.C. A sudden release of nitrogen in blood.D. A drop in blood pressure.62. The purpose of Rothschild’s study is to see _____.A. how often ichthyosaurs caught the bendsB. how ichthyosaurs adapted to decompressionC. why ichthyosaurs bent their bodiesD. when ichthyosaurs broke their bones63. Rothschild’s finding stated in Paragraph 4 _____.A. confirmed his assumptionB. speeded up his research processC. disagreed with his assumptionD. changed his research objectives64. Rothschild might have concluded that ichthyosaurs ______.A. failed to evolve an anti-decompression meansB. gradually developed measures against the bendsC. died out because of large sharks and crocodilesD. evolved an anti-decompression means but soon lost itDMark Twain has been called the inventor of the American novel. And he surely deserves additional praise: the man who popularized the clever literary attack on racism.I say clever because anti-slavery fiction had been the important part of theliterature in the years before the Civil War. H. B. Stowe’s Uncle Tom’s Cabin is only the most famous example. These early stories dealt directly with slavery. With minor exceptions, Twain planted his attacks on slavery and prejudice into tales that were on the surface about something else entirely. He drew his readers into the argument by drawing them into the story.Again and again, in the postwar years, Twain seemed forced to deal with the challenge of race. Consider th e most controversial, at least today, of Twain’s novels, Adventures of Huckleberry Finn. Only a few books have been kicked off the shelves as often as Huckleberry Finn, Twains most widely read tale. Once upon a time, people hated the book because it struck them as rude. Twain himself wrote that those who banned the book considered the novel “trash and suitable only for the slums (贫民窟).” More recently the book has been attacked because of the character Jim, the escaped slave, and many occurences of the word nigger. (The term Nigger Jim, for which the novel is often severely criticized, never appears in it.)But the attacks were and are silly—and miss the point. The novel is strongly anti-slavery. Jim’s search through the slave states for the family from whom he has been forcibly parted is heroic. As J. Chadwick has pointed out, the character of Jim was a first in American fiction—a recognition that the slave had two personalities, “the voice of survival within a white slave culture and the voice of the individ ual: Jim, the father and the man.”There is much more. Twain’s mystery novel Pudd’nhead Wilson stood as a challenge to the racial beliefs of even many of the liberals of his day. Written at a time when the accepted wisdom held Negroes to be inferior (低等的) to whites, especially in intelligence, Twain’s tale centered in part around two babies switched at birth. A slave gave birth to her master’s baby and, for fear that the child should be sold South, switched him for the master’s baby by his wife. The slave’s light-skinned child was taken to be white and grew up with both the attitudes and the education of the slave-holding class. The master’s wife’s baby was taken for black and grew up with the attitudes and intonations of the slave.The point was difficult to miss: nurture (养育), not nature, was the key to social status. The features of the black man that provided the stuff of prejudice—manner of speech, for example—were, to Twain, indicative of nothing other than the conditioning that slavery forced on its victims.Twain’s racial tone was not perfect. One is left uneasy, for example, by the lengthy passage in his autobiography (自传) about how much he loved what were called “nigger shows” in his youth—mostly with white men performing in black-face—and his delight in getting his mother to laugh at them. Yet there is no reason to think Twain saw the shows as representing reality. His frequent attacks on slavery and prejudice suggest his keen awareness that they did not.Was Twain a racist? Asking the question in the 21st century is as wise as asking the same of Lincoln. If we read the words and attitudes of the past through the “wisdom” of the considered moral judgments of the present, we will find nothing but error. Lincoln, who believed the black manthe inferior of the white, fought and won a war to free him. And Twain, raised in a slave state, briefly a soldier, and inventor of Jim, may have done more to anger the nation over racial injustice and awaken its collective conscience than any other novelist in the past century.65. How do Twain’s novels on slavery differ from Stowe’s?A. Twain was more willing to deal with racism.B. Twain’s attack on racism was much less open.C. Twain’s themes seemed to agree with plots.D. Twain was openly concerned with racism.66. Recent criticism of Adventures of Huckleberry Finn arose partly from its _____.A. target readers at the bottomB. anti-slavery attitudeC. rather impolite languageD. frequent use of “nigger”67. What best proves Twain’s anti-slavery stand according to the author?A. Jim’s search for his family was described in detail.B. The slave’s voice was first heard in American novels.C. Jim grew up into a man and a father in the white culture.D. Twain suspected that the slaves were less intelligent.68. The story of two babies switched mainly indicates that _____.A. slaves were forced to give up their babies to their mastersB. slaves’ babies could pick up slave-holders’ way of speakingC. blacks’ social position was shaped by how they were brought upD. blacks were born with certain features of prejudice69. What does the underlined word “they” in Paragraph 7 refer to?A. The attacks.B. Slavery and prejudice.C. White men.D. The shows.70. What does the author mainly argue for?A. Twain had done more than his contemporary writers to attack racism.B. Twain was an admirable figure comparable to Abraham Lincoln.C. Twain’s works had been banned on unreasonable grounds.D. Twain’s works should be read from a historical point of view.第四部分: 任务型阅读(共10 小题;每小题1 分,满分10 分)Quiet Virtue: The ConscientiousThe everyday signs of conscientiousness (认真尽责)—being punctual, careful in doing work, self-disciplined, and scrupulous (一丝不苟的) in attending to responsibilities—are typical characteristics of the model organizational citizen, the people who keep things running as they should. They follow the rules, help out, and are concerned about the people they work with. It’s teh conscientious worker who helps newcomers or updates people who return after an absence, who gets to work on time and never abuses sick leaves, who always gets things done on deadline.Conscientiousness is a key to success in any field.. In studies of job performance, outstanding effectivenss for almost all jobs, from semi-skilled labor to sales and management, depends on conscientiousness. It is particularly important for outstanding performance in jobs at the lower levels of an organization: the secretary whose message taking is perfect, teh delivery truck driver who is always on time.Among sales representatives for a large American car manufactures, those who were most conscientious had the largest volume of sales. Conscientiousness also offers a buffer (缓冲) against the threat of job loss in today’s constantly chaning market, because employees with thisquality are among the most valued. For the sales representatives, their level of conscientiousness mattered almost as much as their sales in determining who stayed on.But conscientiousness in the absence of social skills can lead to problems. Since conscientious people demand so much of themselves, they can hold other people to their own standards, and so be overly judgement when others don’t show the same high levels of model behavior. Factory workers in Great Britain and the United States who were extremely conscientious, for example, tended to criticize co-workers even about failures that seemed unimportant to those they citicized, which demanded their relationships.When conscientiousness takes the form of living up to expectations, it can discourage creativity. In creative professions like art or advertising, openness to wild ideas and spontaneity (自发性) are scarce and in demand. Success in such occupations calls for a balance, however; without enough conscientiousness to follow through, people become mere dreamers, with nothing to show for their imaginativeness.第五部分: 书面表达(满分25 分)81. 请根据你对以下两幅图的理解,以“Actions Speak Louder than Words”为题,用英语写一篇作文。



第二节: 完形填空(共20 小题; 每小题1 分, 满分20 分)请认真阅读下面短文, 从短文后各题所给的A、B、C、D 四个选项中, 选出最佳选项, 并在答题卡上将该项涂黑。
I used to believe in the American Dream, which meant a job, a mortgage (按揭), credit cards, success. I wanted it and worked toward it like everyone else, all of us 36 chasing the same thing.One year, through a series of unhappy events, it all fell 37 . I found myself homeless and alone. I had my truck and $56. I 38 the countryside for some place I could rent for the 39 possible amount. I came upon a shabby house four miles up a winding mountain road 40 the Potomac River in West Virginia. It was 41 , full of broken glass and rubbish. I found the owner ,rented it, and 42 a corner to camp in.The locals knew nothing about me, 43 slowly, they started teaching me the 44 of being a neighbor. They dropped off blankets, candles, and tools, and began 45 around to chat. They started to teach me a belief in a 46 American Dream—not the one of individual achievement but of 47 .What I had believed in, all those things I thought were 48 for a civilized life, were nonexistent in this place. 49 on the mountain, my most valuable possessions were my 50 with my neighbors.Four years later, I moved back into 51 . I saw many people were having a really hard time, 52 their jobs and homes. I managed to rent a big enough house to 53 a handful of people .There are four of us now in the house, but over time I’ve had nine people come in and move on to other places. We’d all be in54 if we hadn’t banded together.The American Dream I believe in now is a shared one. It’s not so much about what I can get for myself; it’s about 55 we can all get by together.36. A. separately B. equally C. violently D. naturally37. A. off B. apart C. over D. out38. A. crossed B. left C. toured D. searched39. A. fullest B. largest C. fairest D. cheapest40. A. at B. through C. over D. round41.A. occupied B. abandoned C. emptied D. robbed42. A. turned B. approached C. cleared D. cut43. A. but B. although C. otherwise D. for44. A. benefit B. lesson C. nature D. art45. A. sticking B. looking C. swinging D. turning46. A. wild B. real C. different D. remote47. A. neighborliness B. happiness C. friendliness D. kindness48. A. unique B. expensive C. rare D. necessary49. A. Up B. Down C. Deep D. Along50. A. cooperation B. relationships C. satisfaction D. appointments51. A. reality B. society C. town D. life52.A. creating B. losing C. quitting D. offering53. A. put in B. turn in C. take in D. get in54. A. yards B. shelters C. camps D. cottages55. A. when B. what C. whether D. how第三部分:阅读理解(共15小题;每小题2分,满分30分)请认真阅读下列短文,从短文后各题所给的A、B、C、D四个选项中,选出最佳选项,并在答题卡上将该项涂黑。
2013年江苏高考英语试题分析仪征市第二中学李广洲内容提要:2013年江苏高考英语试题有难度,有深度,有长度,有梯度,有效度。
它给了我们英语教学的启示:要点滴积累,不要急功近利;要了解英语国家常识,不要闭关自守。
要阅读时事,不要满足于陈题旧题。
关键词:2013江苏高考英语试题分析和前十年的江苏高考试题相比,2013年江苏高考英语试题呈现了要求高、词汇量大、语境丰富、实用性强等特点。
以下就各项作一粗略的分析。
一.听力A. 听力分析:听力题语速快,对考生平时的听力要求高。
真实交际情景的创设比较成功,10段材料的选择有典型性。
专有名词多,例如人名有:Celia, Sara, Diana, Alex, Andrea, Miranda, Jan等。
地名有:Baltimore(美国马里兰州城市), Avon(英国中部河流名,。
因与莎士比亚相关联而著名), the Plaza Leon(列昂广场,位于西班牙与墨西哥), Via del Mar Street (美国密苏里州圣路易斯城的街道名), Fernando Street(加拿大、澳大利亚和美国的佛罗里达州、加利福尼亚州城市都有这个街道名), Hernandes Street(美国加利福尼亚州街道名), Horatio Street(纽约曼哈顿街道名)等。
B. 对考生的建议:1. 学习一些专有名词,如英语国家的常见人名与地名。
2. 听不同音质的听力录音带,不要长时间听同一种录音。
3. 在班级、在操场、在宿舍、在空间适当用英语对话。
C. 对听力考查的建议:建议增加录音室的物品。
空旷的录音室影响录音的效果,造成回声大,听不清。
二.英语知识运用第一节单项填空A. 单项填空分析:单项填空题比前几年更侧重于谓语与非谓语的考查,语境考查有难度、有力度、有梯度、有效度。
第21题同时考查谓语时态与主谓一致;第27题同时考查谓语时态与倒装句;第30题考查谓语的虚拟语气时,在虚拟中有真实的谓语时态进行混淆;第31题同时考查非谓语与其中特殊情况介词after和before的用法;第34题考查过去时态时用现在时态进行干扰等等。
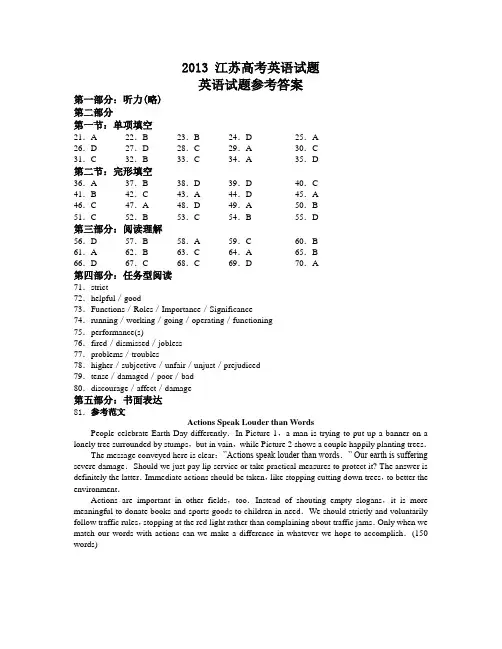
2013 江苏高考英语试题英语试题参考答案第一部分:听力(略)第二部分第一节:单项填空21.A 22.B 23.B 24.D 25.A26.D 27.D 28.C 29.A 30.C31.C 32.B 33.C 34.A 35.D第二节:完形填空36.A 37.B 38.D 39.D 40.C41.B 42.C 43.A 44.D 45.A46.C 47.A 48.D 49.A 50.B51.C 52.B 53.C 54.B 55.D第三部分:阅读理解56.D 57.B 58.A 59.C 60.B61.A 62.B 63.C 64.A 65.B66.D 67.C 68.C 69.D 70.A第四部分:任务型阅读71.strict72.helpful/good73.Functions/Roles/Importance/Significance74.running/working/going/operating/functioning75.performance(s)76.fired/dismissed/jobless77.problems/troubles78.higher/subjective/unfair/unjust/prejudiced79.tense/damaged/poor/bad80.discourage/affect/damage第五部分:书面表达81.参考范文Actions Speak Louder than WordsPeople celebrate Earth Day differently.In Picture 1,a man is trying to put up a banner on a lonely tree surrounded by stumps,but in vain,while Picture 2 shows a couple happily planting trees.The message conveyed here is clear:”Actions speak louder than words.” Our earth is suffering severe damage.Should we just pay lip service or take practical measures to protect it? The answer is definitely the latter.Immediate actions should be taken,like stopping cutting down trees,to better the environment.Actions are important in other fields,too.Instead of shouting empty slogans,it is more meaningful to donate books and sports goods to children in need.We should strictly and voluntarily follow traffic rules,stopping at the red light rather than complaining about traffic jams.Only when we match our words with actions can we make a difference in whatever we hope to accomplish.(150 words)。
2013年普通高等学校招生全国统一考试英语试题(江苏卷)第一部分: 听力(共两节,满分20分)第一节(共5小题;每小题1分,满分5分)听下面5段对话。
每段对话仅读一遍。
1. What does the man want to do ?A. Take photos .B. Buy a camera .C. Help the woman.2. What are the speakers talking about ?A. A noisy night .B. Their life in town .C. A place of living.3. Where is the man now ?A. On his way.B. In a restaurant .C. At home.4. What will Celia do ?A. Find a player .B. Watch a game.C. Play basketball .5. What day is it when the conversation takes place?A. Saturday.B. Sunday.C. Monday.第二节(共15小题;每小题1分,满分15分)听下面5段对话或独白。
每段对话或独白读两遍。
听第6段材料,回答第6、7题。
6. What is Sara going to do ?A. Buy John a gift .B. Give John a surprise .C. Invite John to France .7. What does the man think of Sara’s plan?A. Funny.B. Exciting.C. Strange.听第7段材料,回答第8、9题。
8. Why does Diana say sorry to Peter ?A. She has to give up her travel plan.B. She wants to visit another city.C. She needs to put off her test.9. What does Diana want Peter to do?A. Help her with her study.B. Take a book to her friend.C. Teach a geography lesson.听第8段材料,回答第10至12题。
专题四任务型阅读把脉近六年任务型阅读考查特点考情分析1.任务型阅读文章在体裁方面,以议论文为主,兼顾其他类型。
词数在400到500之间,选材新颖,话题贴近实际生活。
要求考生熟悉文章结构、写作特点,准确把握文章主旨大意、写作思路和作者的写作意图等等。
2.图表和阅读文章结构对应,练习中的图表——表格式和树状式都是根据阅读文章的篇章结构进行设计的。
阅读文章,通过其标题、结构和段落设置,可以预测到图表的结构设计;借助表格,我们可以更好地理解文章主题、结构和各细节的具体出处。
文章和表格互为补充,相辅相成。
在完成试题时,结合两者,可以更有效率地完成测试任务。
3.所设题型考查了考生对信息处理的多种能力,要求考生在理解文章的基础上,获得与所提供材料相关的信息,同时要按一定的要求,用特定的词汇进行信息输出。
在考查考生对直接信息的理解能力和获得能力的基础上,更注重考查考生对间接信息的获得能力以及语言概括、表达能力。
在考查中,考生对句子的主谓一致、时态与语态、非谓语动词、固定搭配等语言规则的理解和掌握的能力尤为重要。
4.文章难度大,题目设置难。
近四年的任务型阅读原文难度均比较大,同时题目设置也比较难。
即使文章大意能读懂,也很难做全对。
2014,2015,2017的该题型成为英语试卷中的“难啃的骨头”。
5.2015,2016,2018年高考任务型阅读题目使用了表格类,2013,2014,2017年的高考命题使用了树状图,无论是树状图还是表格类,都不影响学生答题。
6.任务型阅读的选文词数都在400词以上,命题词数在150词左右,需要注意的是:任务型阅读词数多,信息量大,在一定程度上提高了对考生阅读速度和理解力的要求。
7.正确答案多样性。
2013年江苏高考任务型阅读只有71题答案唯一,其他的题目的答案都不唯一,其中的74和78题各有五个答案;2014年的江苏高考任务型阅读均只有一个正确答案;2015年江苏高考任务型阅读的71和78题各有两个参考答案,其余的8个小题都是唯一答案;2016年江苏高考任务型阅读的72,74,75,78题有两个或者三个参考答案,其余的答案都是唯一的;2017年中的72,75,77题有两个参考答案,其余的都只有一个答案; 2018年72,73,74,78,79题都有两个或者三个参考答案。
2013年普通高等学校招生全国统一考试(江苏卷)英语答案解析第一部分听力第一节1.【答案】A【解析】Man: I’ve got my camera with me. Am I allowed to take photos for you?Woman: I think so. It doesn’t say you can’t.2.【答案】C【解析】A: I really like living here in this flat, because it’s so near to central town.B: That’s true. But it gets really noisy at night.3.【答案】A【解析】A: Hi, Maggie. I’m coming, but it’s snowing and the traffic is moving slowly.B: Ok, David. Take your time. We’ll wait for you, so we can have dinner together.4.【答案】C【解析】A: Celia, you see those girls over there? They need another player for a basketball game. Would you like to join them?B: Seems like it’s a game for fun. Sure, I’ll be there in minute.5.【答案】B【解析】A: I won’t have anything to wear to work on Monday unless I pick up my clothes at dry cleaner’s.B: Then you’d better hurry. It closes at noon on Sundays.A: Oh! I should have gone there on Saturday.第二节6.【答案】B7.【答案】B【解析】A: Alright, Sara, we know that you are planning something big for John’s birthday. Could you tell us just what you have in your mind?B: I want to make his birthday a very special event. John has a sister living in France. And I’ll send her a plane ticket, so that she can be here for his birthday.A: Boy! What an excellent plan! That’s something special. I can’t guess some secret plans and we are waiting forthe right time to tell him.B: Well, I didn’t want to say anything until I was sure she could come.8.【答案】A9.【答案】B【解析】A: Hey, Peter, I’m sorry!B: Hi, Diana, what’s wrong?A: We were going to Hong Kong this weekend, but I’m afraid I can’t go.B: How come?A: I have a really big geography test and I have to study for it.B: We can go next week instead.A: No, I don’t want to ruin your weekend. You go ahead and please take the book I bought to my friend Sally. Tell her I have to study all weekend, because I can’t afford to fail the test.B: Ok, then I’ll go with them. But it’s a pity you can’t come.10.【答案】A11.【答案】B12.【答案】A【解析】A: Hello, this is Andrea.B: Hello, Andrea, this is Alex. I have some very big news for you. Miranda was very satisfied with you and said she was very much looking forward to working with you. Isn’t that wonderful? Congratulations dear! How does it feel to be Miranda’s new assistant? How I imagine that you’ll just be delighted with this news. So let’s see, you can start on Monday, right?A: Umm, well, I don’t think I can start on Monday. I am visiting my father in Baltimore. And because I don’t live in New York, I’ll need a couple of days to find a flat and buy some furniture and move my things from Avon.B: Oh, well then, in that case I suppose Wednesday will be good. Ok, see you then!13.【答案】C14.【答案】A15.【答案】A16.【答案】B【解析】Woman: Hello, Mr. Jan Erick Freedman. You’re a frequent traveler. And we also know that you eat out twice a day. How can you get so far and eating out.Man: When I my first job back in 1982 and started travelling. I had no other choice but eat out I found that I feltdifferent due to what I was eating, so I tried to find places that served food that made me feel good. The secret was the quality of the food and how well the food was prepared. I made an effort to find out good restaurants as well as nice dishes.Woman: How did you manage to make a list of 218 favorite restaurants?Man: I’ve lived in cities and when I moved back to Sweden from the United States, people asked me where to go and eat and went to the cities I know. I got a lot of ideas. Then I wrote about restaurants for a Swedish club magazine and some suggested I gather information about restaurants together since I had all the facts about the restaurants I’ve been to. I started to do that.Woman: How do you find restaurants?Man: The best way is to ask the people there. I may talk to the people at the street market or take a walk and look for place for myself. I never asked hotel clerks or taxi drivers. I don’t go either restaurants or places with menus too difficult to understand.17.【答案】C18.【答案】B19.【答案】C20.【答案】C【解析】Man: At the beginning of the tour, we all started the most important place at my town which is the Plaza Leon. The Plaza Leon is more than 100 years old. It’s a gathering place for young people on Friday and Saturday nights, and for parents and children on Sunday afternoon. Four streets lead to the Plaza which have white sidewalks and tree lined. Hemandes Street which was named after writers born in the city contains all of the food stalls fish markets and vegetable stands. Femando Street which was named after a famous educator is where all of the government offices, shops and houses. Via del Mar Street which is the only street which has old stone surfaces. Finally we came to the Hewish’s Street on which there are two universities, one of which is the most famous university in my country. That’s why it’s my favorite street of all.第二部分英语知识运用第一节单项填空21.【答案】A【解析】句意:一般来说,为达到其他人的高期望而产生的内部动力对学生的自身发展是非常重要的。
2012年全国普通高等学校招生统一考试(江苏卷)英语试题第一部分:听力(共两节,满分20 分)做题时,先将答案标在试卷上。
录音内容结束后,你将有两分钟的时间将试卷上的答案转涂到答题卡上。
第一节(共5 小题;每小题1 分,满分5分)听下面5 段对话。
每段对话后有一个小题,从题中所给的A、B、C 三个选项中选出最佳选项,并标在试卷的相应位置。
听完每段对话后,你都有10秒钟的时间来回答有关小题和阅读下一小题。
每段对话仅读一遍。
例: How much is the shirt?A. £19. 15.B. £9. 15.C. £9. 18.答案是B。
1. Where does this conversation probably take place?A. In a bookstore.B. In a classroom.C. In a library.2. At what time will the film begin?A. 7:20.B. 7:15.C. 7:00.3. What are the two speakers mainly talking about?A. Their friend Jane.B. A weekend trip.C. A radio programme.4. What will the woman probably do?A. Catch a train.B. See the man off.C. Go shopping.5. Why did the woman apologize?A. She made a late delivery.B. She went to the wrong place.C. She couldn’t take the cake back.第二节 (共15 小题;每小题1 分,满分15 分)听下面5 段对话。
每段对话后有几个小题,从题中所给的A、B、C 三个选项中选出最佳选项,并标在试卷的相应位置。
2013年高考英语真题试题与答案解析——江苏2013·江苏卷第二部分英语知识运用(共两节,满分35分)第一节单项填空(共15小题;每小题1分,满分15分)请认真阅读下面各题,从题中所给的A、B、C、D四个选项中,选出最佳选项。
例:It is generally considered unwise to give a child ________ he or she wants.A.however B.whateverC.whichever D.whenever答案是B。
21.Generally,students' inner motivation with high expectations from others ________ essential to their development.A.is B.are C.was D.were21.A 考查主谓一致。
主语students' inner motivation表示单数意义,所以谓语动词用单数,并且叙述的是通常情况下的状态,所以用一般现在时,故选A项。
22.—The Tshirt I received is not the same as is shown online.—________ ?But I promise you we'll look into it right away.A.Who says B.How comeC.What for D.Why worry22.B 考查情景交际。
句意:——我收到的T恤衫跟网上展出的不一样。
——怎么会那样呢?我向你保证我们将立刻着手调查。
How come?意为“怎么会?”,符合语境。
A项意为“谁说的”;C 项意为“为何目的”;D项意为“为何担忧”,均与语境不符。
23.—The town is so beautiful! I just love it.—Me too.The character of the town is well ________.A.qualified B.preservedC.decorated D.simplified23.B 考查动词辨析。
2013江苏卷第四部分:任务型阅读(共10小题;每小题1分,满分10分)请认真阅读下列短文,并根据所读内容在文章后表格中的空格里填入一.个.最恰当的单词。
注意:请将答案写在答题卡上相应题号的横线上。
每个空格只填一个单词。
Quiet Virtue: The ConscientiousThe everyday signs of conscientiousness (认真尽责)—being punctual, careful in doing work, self-disciplined, and scrupulous (一丝不苟的) in attending to responsibilities—are typical characteristics of the model organizational citizen, the people who keep things running as they should. They follow the rules, help out, and are concerned about the people they work with. It‘s the conscientious worker who helps newcomers or updates people who return after an absence, who gets to work on time and never abuses sick leaves, who always gets things done on deadline.Conscientiousness is a key to success in any field. In studies of job performance, outstanding effectiveness for almost all jobs, from semi-skilled labor to sales and management, depends on conscientiousness. It is particularly important for outstanding performance in jobs at the lower levels of an organization: the secretary whose message taking is perfect, the delivery truck driver who is always on time.Among sales representatives for a large American car manufacturer, those who were most conscientious had the largest volume of sales. Conscientiousness also offers a buffer (缓冲) against the threat of job loss in today‘s constantly changing market, because employees with this quality are among the most valued. For the sales representatives, their level of conscientiousness mattered almost as much as their sales in determining who stayed on.There is an air around highly conscientious people that makes them seem even better than they actually are. Their reputation for dependability influences managers‘ evaluations of their work, giving them higher evaluations than objective measures of their performance would predict.But conscientiousness in the absence of social skills can lead to problems. Since conscientious people demand so much of themselves, they can hold other people to their own standards, and so be overly judgmental whe n others don‘t show the same high levels of model behavior. Factory workers in Great Britain and the United States who were extremely conscientious, for example, tended to criticize co-workers even about failures that seemed unimportant to those they criticized, which damaged their relationships.When conscientiousness takes the form of living up to expectations, it can discourage creativity. In creative professions like art or advertising, openness to wild ideas and spontaneity (自发性) are scarce and in demand. Success in such occupations calls for a balance, however; without enough conscientiousness to follow through, people become mere dreamers, with nothing to show for their imaginativeness.题型自主分析:1、原词重现(信息查找):2、词性转换(信息加工):3、提炼概括(信息归纳):2012江苏卷第四部分: 任务型阅读(共10 小题;每小题1 分,满分10 分)请认真阅读下列短文,并根据所读内容在文章后表格中的空格里填入一个最恰当的单词。
2013届江苏高考完形填空、任务型阅读专项训练四I. 完形填空The New York Times published an article recently that shows great regret for the “death of conversation”. It suggests that while technology such as cell phones, e-mails, and Internet posting makes us feel more 36 than ever, they’re also driving us 37 from people around us.Users get final connectivity 38 the price of 39 face-to-face conversation. Sherry Turkle, author of the article in The New York Times says people are 40 to a different way of being “alone together”.Actually, 41 text messages or wring micro-blogs allows us to 42 thoughts. 43 bits and pieces of online cannot 44 a “real conversation.” Lan Guo, 19, a freshman English major from Changsha University, said that she would lik e to hear people’s tone of voice and see their faces in a (n)45 . “The give and take of ideas in a conversation sharpens our minds.” she said. She also mentions that 46 ourselves in mobile technology reduces our chance of starting conversations with strangers and 47 people.Turkle mentioned the popular 48 of “I share, therefore I am” among this generation. Liu Xuan, a young writer from Taiwan and psychology graduate from Harvard University, thinks it’s a mindset adopted by most young people. They are so busy creating or polishing their online persona (网络人格)that they forget how to live a (n) 49 life. For example, They may 50 more about blogging about attending a party rather than enjoying being 51 .52 , experts remind us that i t’s un fair to blame mobile technology. Chen Chen, a sociology expert at China Youth & Children Research Center, points out that it is still owners of gadgets, such as cell phones and tablets, who’re avoiding personal 53 .We take advantage of these devices to hide ourselves 54 others. Texting messages or calling may be a (n) 55 to avoid contact with others, such as having eye contact. “Only by strengthening conversation can we understand each other. Simply throwing away the mobile gadgets is not a solution.” she said.36. A. received B. shared C. connected D. respected37. A. off B. back C. away D. down38. A. beyond B. at C. for D. above39. A. having B. risking C. sacrificing D. sharing40. A. related B. committed C. devoted D. accustomed41. A. sending B. getting C. reading D. taking42. A. change B. exchange C. deliver D. raise43. A. So B. And C. Or D. But44. A. indicate B. replace C. cover D. involve45. A. conversation B. computer C. party D. Internet46. A. abandoning B. joining C. burying D. attaching47. A. interviewing B. introducing C. knowing D. meeting48. A. feeling B. concept C. fact D. truth49. A. colorful B. interesting C. real D. meaningful50. A. worry B. care C. ask D. debate51. A. there B. out C. down D. in52. A. Therefore B. Altogether C. Instead D. However53. A. information B. space C. contact D. management54. A. from B. of C. behind D. under55. A. approach B. source C. result D. excuseII. 任务型阅读The Nature of StressWe are often faced with stressors that are outside of our control, from rare natural disasters to everyday traffic jams. There is a good deal of evidence that uncontrollable events are particularly stressful. This has been shown in studies of “executive rats,” in which two rats receive exactly the same electric shock, but one is given a lever that could be used to t urn the shock off after it occurs. Over a long series of such trials, the partner rat, helpless to do anything about its pain, is more likely to develop ulcers(溃疡)than is the “executive”.Stress is mostly caused by uncertain events. Uncertainty about an event makes it more disturbing. One study found that subjects who were told that they had a 5 percent chance of receiving an electric shock were actually more uneasy than those who were told that they had a 50 percent chance.People make various attempts to deal with their stress—removing the cause of the stress, seeking the support of friends or reinterpreting the situation to make it seem less unpleasant. Richard Lazarus and his colleagues have made a useful distinction between problem-focused and emotion-focused coping strategies. Problem-focused strategies are those aimed at doing something to change the problem causing the stress. Emotion-focused strategies tend to regulate our distressing emotional responses.Psychologists Susan Folkman and Richard Lazarus examined undergraduate students’ coping strategies at three time periods—two days before a midterm examination, a week later two days before the grades were announced, and five days after the grades were posted. Before the exam, students tended to use such problem-focused strategies as studying—a guaranteed way to reduce the potential problems. After the exam, when their fates were sealed, if they sought out others, it was usually for emotional support.Like other animals, humans have always been safer in groups. Besides physical protection, people provide emotional support that can reduce the psychological and physiological symptoms of stress. A lack of support can increase our susceptibility to illness. For instance, short-term loneliness is associated with a decrease in immune response. In contrast, people who have strong social ties are usually more resistant to disease. For instance, after being diagnosed as having a life threatening disease, married people are likely to survive longer than unmarried people.People may provide appraisal support, helping us to evaluate and clarify how serious a problem is. If a professor tells you that he had also failed his first college algebra exam, the consequences of your failure will seem less devastating. Others can also provide informational support, giving advice about how to deal with the problem. Finally, friends and relatives may give us instrumental support, providing material goods or services to overcome the stress. If your father lends you some money when your car breaks down, you can stop tearing your hair out and just fix it.(四)36. C 37. C 38. B 39. C 40. D 41. A 42. B 43. D 44. B 45. A46. C 47. D 48. B 49. C 50. B 51. A 52. D 53. C 54. A 55. D71. What 72. controlled / controled 73. uncertain 74. Turn 75. handle 76. causes 77. lonely 78. emotionally / mentally 79. helps 80. over。