
参考答案( Communication English )
第一章电子通信导论
1.将表1-1译成中文。
表1-1 通信大事纪
年代事件
公元前3000年埃及人发明象形文字
公元800年借鉴印度, 阿拉伯人使用我们的现行数制
1440年约翰.戈登贝尔发明可移动的金属记录带
1752年贝莱明.富兰克林的风筝证明了雷闪是电
1827年欧姆发表欧姆定律( I = E / R)
1834年 C.F.高斯和E.H.韦伯发明电磁电报
1838年W.F.库克和C.维特斯通发明电报
1844年S.F.B.莫尔斯演示巴尔的摩和华盛顿的电报线路
1850年G.R.基尔赫夫发表基尔赫夫电路定律
1858年铺设第一条越洋电缆, 并于26天后举办博览会
1864年J.C.麦克斯威尔预言电磁辐射
1871年电报工程师协会在伦敦成立
1876年 A.G.贝尔发明电话并获专利
1883年 A.爱迪生发现真空管中的电子流
1884年美国电气工程师协会(AIEE)成立
1887年H.赫兹证明麦克斯威的理论
1900年G.马可尼传送第一个越洋无线电信号
1905年R.芬森登利用无线电传送语音和音乐
1906年L.弗雷斯特真空三极管放大器
1915年贝尔系统完成美国大陆电话线路
1918年 E.H.阿尔莫斯通发明超外差接收机电路
1920年第一个定时无线广播
J.R.卡尔松将取样用于广播
1926年美国演示电视
1927年H.布兰克在贝尔实验室发明负反馈放大器
1931年电传打字机投入运营
1933年 E.H.阿尔莫斯通发明调频
1935年R.A.沃特森-瓦特发明第一个实用雷达
1936年英国广播公司(BBC)开办第一个电视广播
1937年 A.雷弗斯提出脉冲编码调制(PCM)
1941年J.V.阿当拉索夫在依俄华州立大学发明计算机
1945年ENIAC电子数字计算机研发于宾夕伐尼亚大学
1947年布雷登、巴登和肖克利在贝尔实验室研制晶体管
S.O.莱斯在贝尔实验室研究噪声的统计表征1948年 C.E.香农发表他的信息理论
1950年时分多路用于电话
1953年美国提出NTSC彩色电视
1957年苏联发射第一个地球卫星Sputnik I
1958年 A.L.肖洛和C.H.托莱斯发表激光原理
仙童公司的R.诺依斯生第一硅集成电路
1961年美国开始立体声调频广播
1962年第一个有源卫星, Telstar I , 实现美国与欧洲的电视中继
1963年贝尔系统推出按键式电话
电气与电子工程师协会(IEEE)成立
1963~66年研究纠错码和自适应均衡
1964年电子电话交换系统(No.1ESS)投入运营
1965年笫一个商用通信卫星,Early Bird,发射
1968年开发电缆电视系统
1971年Intel公司研制第一个单片微处理器—4004
1972年摩托罗拉向美国联邦通信委员会(FCC)演示蜂窝式电话
1976年推出个人计算机
1979年64-kb随机存取存储器标志着进入VLSI时代
1980年贝尔系统研发FT3光纤通信, Philips和Sony研发光碟(CD) 1984年苹果公司研发Macintosh计算机
1985年传真机普及
1989年摩托罗拉推出袖珍移动电话
1990~现在用微处理器进行数字信号处理的时代, 数字示波器, 数字调谐接收机, 扩频系统, ISDN, HDTV, 数字卫星系统
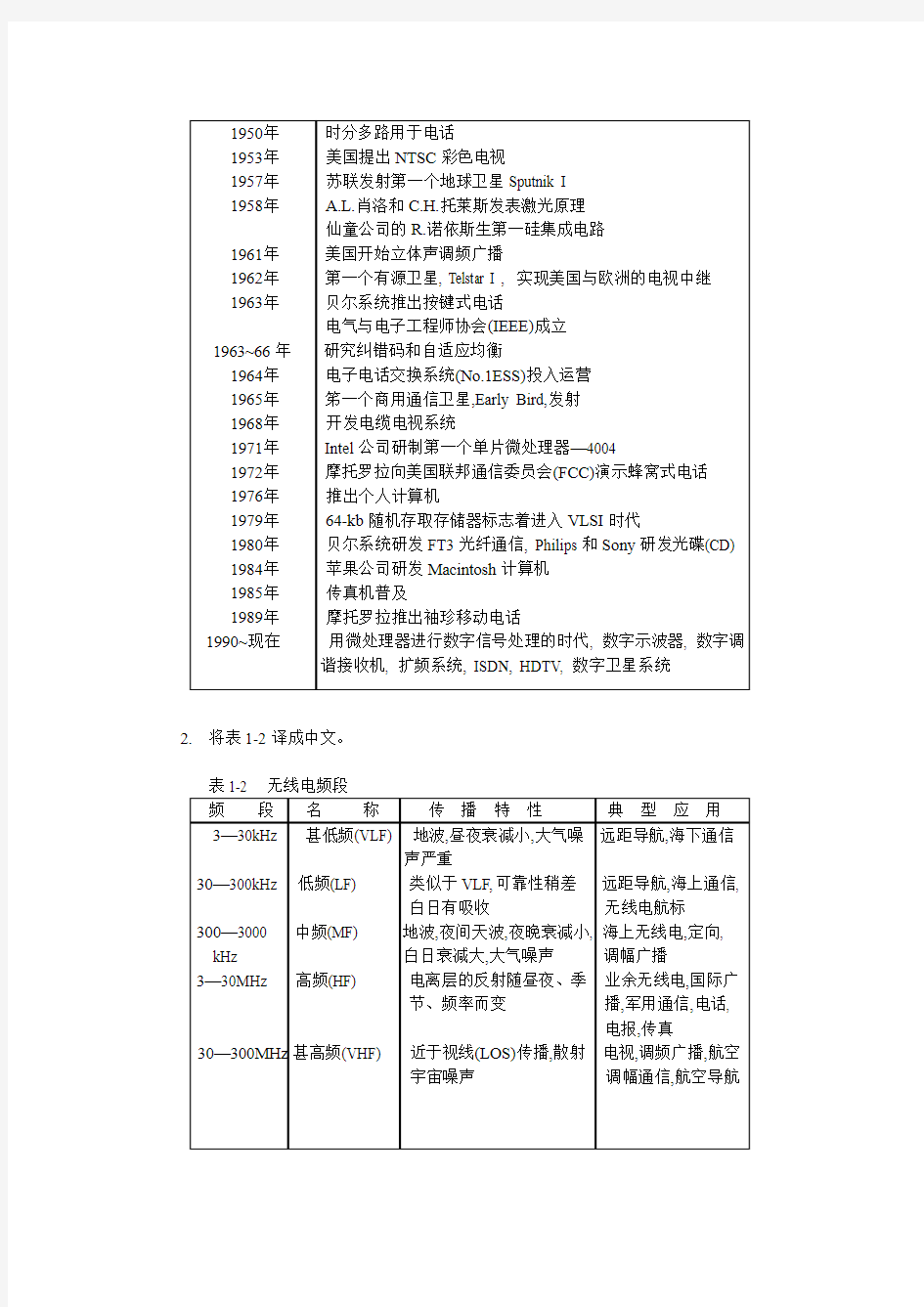
2.将表1-2译成中文。
表1-2 无线电频段
频段名称传播特性典型应用3—30kHz 甚低频(VLF) 地波,昼夜衰减小,大气噪远距导航,海下通信
声严重
30—300kHz 低频(LF) 类似于VLF,可靠性稍差远距导航,海上通信,
白日有吸收无线电航标300—3000 中频(MF) 地波,夜间天波,夜晚衰减小, 海上无线电,定向, kHz 白日衰减大,大气噪声调幅广播
3—30MHz 高频(HF) 电离层的反射随昼夜、季业余无线电,国际广
节、频率而变播,军用通信,电话,
电报,传真30—300MHz甚高频(VHF) 近于视线(LOS)传播,散射电视,调频广播,航空
宇宙噪声调幅通信,航空导航
0.3—3GHz 超高频(UHF) 视线传播,宇宙噪声电视,移动电动,导航
雷达,微波链路,个人通
信系统
3—30GHz 特高频(SHF) 视线传播,降雨衰减,大气衰卫星通信,
减,大的水汽衰减雷达微波链
30—300GHz 极高频(EHF) 视线传播,大的水汽衰减, 雷达,卫星,科学实验
氧吸收
>1000GHz 红外线,可见光视线传播光通信
紫外线
3.将1.4节的课文译成中文。
1.4带宽和信息容量
限制通信系统性能的两个最重要的因素是噪声和带宽。噪声将在以后讨论。信息信号的带宽就是信息中包含的最高与最低频率之间的频差;通信信道的带宽(也就是它的通带)是可通过该信道的最高与最低频率之差。信道的带宽必须足够大(宽),以便所有重要的信息频率都能通过。换句话说,信道的带宽必须等于或大于信息的带宽。例如,话音频率包含300Hz 到3000Hz的信号。因此,话音频率的信道必须具有等于或大于2700Hz的带宽。假如一个电缆电视传输系统具有从500kHz到5000kHz的通带,则其带宽为4500kHz。一般说来,信道不能通过含有变化速率大于其通带的信号。
信息论是一种深邃的理论研究,以便通过电子通信系统传送信息时,能有效地利用带宽。可用信息论来确定通信系统的信息容量。信息容量是在给定时间内,能通过通信系统传送多少信息的量度。通信系统能传送的信息量是系统带宽和传输时间的函数。1920年,贝尔电话实验室的R.哈特莱(Hartley)提出了带宽、传输时间和信息容量之间的关系。哈特莱定律表明,带宽越宽,传输时间越长,通过系统传送的信息就越多。在数学上,哈特莱定律表示为I∝B×t。式中,I=信息容量,B=系统带宽(Hz),t=传输时间(秒)。这个公式表明,信息容量是正比于系统带宽和传输时间的线性函数。如果信道带宽增加一倍,可传送的信息量也增加一倍。如果传输时间增长或缩短,那么通过系统传送的信息量也成比例的变化。
一般说来,信息信号越复杂,在给定时间内传送它所需要的带宽也越大。传送话音质量的电话信号大约需要3kHz的带宽。相比之下,传送高保真音乐的商用调频信号需配置200kHz的带宽;而传送广播级的电视信号则需要差不多6MHz的带宽。
1948年,C.E.香农(也是贝尔电话实验室的)在贝尔系统技术杂志上发表论文,论述了以每秒比特数(bps)表示的通信信道的信息容量与带宽及信噪比的关系。在数学上,香农极限信息容量表示为I=Blog2(1+S/N)。式中,I=信息容量(bps),B=带宽(Hz),S/N=功率信噪比(无量纲)。对标准的话音级通信信道,功率信噪比为1000(30dB),带宽为2.7kHz,相应的香农极限信息容量为I=26.9kbps。
香农公式常被误解。上述例子的结果表示,通过2.7kHz的信道可传送26.9kbps的信息。这是可能的,但不是用二进制系统。为了通过2.7kHz的信道,达到26.9kpbs的传输速率,所传送的每一个符号必须包含多于一个比特的信息。因此,为了达到香农极限信息容量,须采用多于两种输出状态(符号)的数字传输系统。
4.将下述句子译成英文。
(1) An analog information source produces messages that are defined on a continuum, while
a digital information source produces a finite set of possible messages.
(2) The beacon-fire tower in ancient China was a communications system.
(3) Show that the entropy is a maximum when the probability of sending a binary 1 is equal
to the probability of sending a binary 0 .
(4) Information capacity is a measure of how much information can be transferred through a
communications system in a given period of time .
(5) The wider the bandwidth and the longer the time of transmission, the more information
can be conveyed through the system .
5.Answer the following questions :
(1) Samuel Morse developed the first electronic communications system in 1837 .
(2) Yes.
(3) The vacuum-tube triode .
(4) Hartley’s law simply states that the wider the bandwidth and the longer the transmission
time, the more information that can be conveyed through the system . The Shannon’s formula is I=B log2(1+S/N) , where I=information capacity(bps), B=bandwidth(Hz), S/N=signal-to-noise power ratio(unitless) .
(5) (a) VLF, (b) MF, (c) SHF
第二章信息源
1.根据课文回答下列问题。
(1) There are four important information sources: speech, music, pictures, and computer data.
(2) Three successive stages: production, propagation, and perception.
(3) The bandwidth of 300 to 3100Hz.
(4) A musical signal differs from a speech signal in that its spectrum occupies a much wider
band of frequencies that may extend up to about 15kHz.
(5) The dynamic pictures, as in television, are in motion; while the static pictures, as in
facsimile, are still.
(6) In black-white TV, only a luminance signal is needed. However, in color TV, there are
three signals: a luminance signal and a pair of chrominance signals.
(7) Yes.
(8) Suppose the seven data bits are 0110101. For the odd parity, an extra parity bit of 1
should be ended, so that the total number of 1s is 5, which is odd.
(9) Lossless compression operates by removing the redundant information contained in the
data of interest. Lossy compression involves the loss of information in a controlled manner.
Lossy compression may achieve a compression ratio higher than that attainable with lossless methods.
(10) There are four distinct operations: time-frequency mapping, psychoacoustic modeling,
quantization and coding, and frame-packing.
2.将2.3节译成中文。
2.3 计算机数据
个人计算机(PC)已成为我们日常生活不可或缺的一部分。我们用计算机收发电子邮件,交换软件,共享资源。由PC传送的文本通常用美国标准信息交换码(ASCII)进行编码。ASCII是最早开发的专用于计算机通信的编码, 它的每一个字符都表示为
7位数据,即用0和1组成的唯一的二进制形式。这里所谓的位(比特bit)是二进制数(binary digit)的缩写。因此,ASCII总共可表示27=128个不同的字符。这些字符是各种小写和大写字母、数字、专用控制符号和常用标点符号, 例如@、$、%等。有些专用控制符, 例如BS(退格)和CR(回车), 用来控制字符在页面上的打印。另一些字符, 例如ENQ(询问)和ETB(传输块终止), 则用于通信。这7位数据位由最高位b1开始, 依序降至最低位b7, 如图2-2所示。在数据位的后面, 添加一位b8用作误码检测。这个检错位称为奇偶校验位。顺序的8个比特称为一个拜特(byte或octet)。
奇偶校验位应这样设置, 使得在奇校验时, 一个拜特中的1的数目是奇数; 若为偶校验, 则为偶数。例如, 假设通信采用偶校验, 那么当数据位中的1的个数为偶数时, 奇偶校验位应置为0; 若为奇数, 则置为1。因此, 如果在收到的一个拜特中错了一个比特位, 那么偶的奇偶规则就被破坏, 也就是查出了差错, 从而可通过重发来纠正。个人计算机常通过RS-232(RS是”推荐标准”的英文缩写)口互相连接。当ASCII 数据(实际上, 所有的字符数据)通过RS-232口传送时, 须添加一个置0的起始位和一个或多个置1的终止位以构成字符帧, 如图2-2所示。当传送空闲时, 须发送一长串的1, 以保持电路的连接。在图2-2中, 符号0和1分别表示”低”和”高”。有时它们也分别称为”空号”和”占号”。这后一种说法源自电报。在PC上准备好的文本通常先存储, 然后一次一个字符地通过通信信道(例如,电话信道)传送。这种形式的数据传输称为异步传输。相反, 在同步传输时, 整个编码的字符串由一次长的传输沿信道发送。由异步和同步的混合终端所产生的编码字符借助于多路技术进行组合。
这样形成的多路数据流, 加到调制解调器(modem)以便沿信道传输。
概言之, 计算机产生的数据和电视信号, 两者都是宽带信号, 即它们的功率占有宽的频率范围。个人计算机之间的通信数据还有另外一个重要的特点, 那就是突发性。这就意味着信息通常是突然地从一个终端发到另一个终端, 而突发之间有静止期。的确, 涉及计算机的数据交换具有某种形式的突发性或突发倾向。相比之下, 涉及语音或交互式视频的数字传输网络中的通信, 就可以说成是连续的。
另外, 我们用计算机从远地的服务供应者, 下载压缩的文本、音频和视频数据。
数据压缩提供了一种实用的方法, 以便有效地存储和传输这些数据。数据压缩系统包括编码器和解码器, 分别执行压缩和解压。基本上, 有两种形式的数据压缩: ①无损压缩, 它去除有用数据中的冗余信息。之所以称为无损, 是因为它是完全可逆的, 原始数据可以准确地恢复。无损压缩又称为数据紧缩。②有损压缩, 按某种可控的方式允许信息损失。因此, 这种压缩不是完全可逆的。然而, 有损压缩可以达到比无损压缩更高的压缩比
3.翻译下列词汇。
声道滤波器韵律结构谐波结构交替的场水平(行)回程基色
交互式视频美国标准信息交换码离散余弦变换联合图像专家组
活动图像专家组传真
synchronous transmission asynchronous transmission mutiplexer
frame frame-packing modeling
4.选择最佳答案。
(1) c (2) c (3) b (4) d (5) a
5.用英文描述摄像机的扫描过程。
The type of scanning used in TV camera is a form of spatial sampling called raster scanning, which converts a two-dimensional image intensity into a one-dimensional waveform; it is somewhat analogous to the manner in which we read a printed paper in that the scanning is
performed from left to right on a line-by-line basis.
第三章 信号与噪声
1. 请将下列词组译成英文。
mathematic model rms value orthogonal series power density spectrum
instantaneous power common logarithm(the base 10 logarithm)
block diagram signal-to-noise ratio DC power supply AC ripple
AM receiver thermal noise
2. 请写出下列缩写词的原文。
root-mean-square alternating current direct current decibel
radio frequency cable(common antenna) television Fourier series
amplitude modulation frequency modulation phase modulation
bipolar junction transistor field-effect transistor
3. 根据课文判定下列句子的真伪。
(1) T (2) F (3) T (4) F (5) T
(6) F (7) F (8) T (9) T
4. 请将”Frequency noise effect ”和”Signal-to-noise ratio and noise figure ”两小节译成中
文。
频率噪声效应 在很低和很高的频率会出现两种鲜为人知的器件噪声。低频效应称为过量噪声, 产生在1kHz 以下的频率。它反比于频率, 正比于温度和直流电平。它被认为是由半导体晶体表面的缺陷所引起, 其变化率反比于频率。过量噪声常称为闪烁噪声、粉红噪声或1/f 噪声。在双极型晶体管和场效应晶体管中都会出现。在高频, 邻近器件的高频截止频率时, 器件的噪声开始迅速增加。当载流子穿越结的渡越时间可与信号周期相比拟时, 有些载流子可能会扩散回源极或发射极。这种高频噪声称为渡越时间噪声。
信噪比和噪声系数 信噪比(S/N)是最常用的噪声性能, 它是有用信号功率与噪声功率的相对量度。S/N 能很好地判定某特定点上的噪声含量。 但是, 当关系到某特定晶体管注入从输入到输出的信号中的附加噪声时, S/N 就没什么用。噪声系数(NF)这个术语常用来描述一个器件的噪声性能, 它定义为10/10 log /i i o o
S N NF S N 。式中, S i /N i 是器件输入端的信噪比, S o /N o 是输出端的信噪比。
第四章 信号的产生
1. 将下列词汇译成英文。
inductive coil capacitor impedance reactance susceptance
radio frequency oscillator flywheel effect rating power
piezoelectric crystal quality factor
2. 将下列词汇译成中文。
能耗 安装电容 反馈放大器 陷波式滤波器 槽路 正弦信号
晶体振荡器 单片 甚高频 带宽 射频扼流圈
3. 根据课文回答下列问题。
(1) The Q factor of a component is the ratio of the energy stored to that which is
lost in the component .
(2)The component dissipation is the reciprocal of its Q factor .
(3)Resonance can be defined as a circuit condition whereby the inductive and
capacitive reactance have been balanced .
(4)The bandwidth of a filter is the frequency range from its low-cutoff to
high-cutoff frequency .
(5) A bandpass filter can be built by using the circuit shown in Fig.4-3(a) . If the
output voltage e out is across the series of capacitor C and resistor R2 , then it is
a lowpass filter .
4.用英文描述RLC电路中的飞轮效应。
Suppose a charged capacitor is connected to an inductor and a resistor in series. Once the circuit is closed, a current starts as the capacitor begins to discharge through the inductor. The inductor, which resists a change in current flow, cause a gradual sinusoidal current buildup that reaches maximum when the capacitor is fully discharged. At this point the potential energy is zero, but since current is maximum, the magnetic field energy around the inductor is maximum. The magnetic field no longer maintained by capacitor voltage then starts to collapse, and its counter EMF will keep current flowing in same direction, thus charging the capacitor to the opposite polarity of its original charge. This repetitive exchange of energy is known as the flywheel effect.
5.将4.3节译成中文。
用集成电路产生波形
在最简单的情况下, 波形发生器就是一个振荡器。它产生预定的稳定波形, 然后可再进行调制, 或在给定的频率范围内扫描。一个典型的波形发生器由四个基本部分组成:
①振荡器, 用来产生基本的周期波形。②波形成形器。③幅度调制器(选用)。④输
出缓冲放大器, 它把振荡器与负载隔离开来, 并提供必要的驱动电流。
图4-9画出了一个集成电路波形发生器的简化方框图, 表明了上述四部分之间的关系。多年来, 每个部分分别作成单片形式。然而, 把所有四个部分制作到一个单片上, 是已有技术的自然延伸。振荡器部分产生基本的振荡频率。波形成形器把振荡器的输出转变为正弦波、或方波、或三角波、或锯齿波。如果选用调制器, 那么这个电路就可产生调幅信号。输出缓冲放大器把振荡器和负载隔离开来, 同时也为向输出波形添加直流电平提供了一个方便的地方。同步输出既可用作方波信号源, 也可作为外部定时电路的同步脉冲。
第五章随机过程
1.翻译下列词汇。
随机信号随机过程数学模型确定信号被积函数
各态遍历(埃尔哥德)过程联合概率分布统计参数
数学期望高斯白噪声
ensemble average (mean) time average correlation function
autocovariance the first-order moment power spectral density
sample space random variable wide-sense stationary process
unbiased estimation normalized linear functional
2.将下列句子译成中文。
(1)在这里, 我们将描述两类数学模型。
(2) 如果它随时间的变化规律没有不确定性, 那么这种模型称为确定的。
(3) 现在假设此随机过程是严格平稳的。
(4) 相关函数的物理意义在于, 它提供了一种方法来描述两随机变量之间的相互依赖
关系。
(5) 两随机变量的互相关函数由下式定义。
3.将下列句子译成英文。
(1) The time average of a stationary process may be used to estimate its ensemble
average.
(2) The noise at the front of a receiver is greatly significant to a communications system.
(3) The autocorrelation function of a random process has some important properties.
(4) Many phenomena can be described as a Gaussian process, therefore, the Gaussian
process is termed as the normal process.
(5) The mathematic expectation of a random process is its first-order moment related to
the original point.
4.用英文回答下列问题。
(1) If a process is divided into a number of time intervals, the various sections of a
stationary process exhibit essentially the same statistic properties.
(2) If the statistic properties of a process can be estimate by its time behavior, it is
ergodic.
(3) Each outcome of a random experiment is associated with a sample point. The totality
of sample points corresponding to the aggregate of all possible outcomes of the
experiment is called the sample space.
(4) If the first- and second-order distribution function of a random process are
independent of time, it is weakly stationary; while if its arbitrary order distribution
is independent of time, it is strictly stationary.
(5) Because a random process is not just a time function, it is a random variable also.
笫六章调幅发射
1. 区分下列词汇。
modulation: 调制过程modulator: 实现调制的电路
modulating signal: 调制信号, 即调制过程中加载的信息信号
modulated wave: 已调波, 即完成调制后的输出信号
demodulation: 在接收端从已调波中恢复调制信号的过程
2. 翻译下列词汇。
双边带单边带调幅调频城市公用频带场效应晶体管
射频扼流圈射频
调幅包络载波信号话音级调制系数下边带
上边频相量矢量非线性混频频域
耦合电容(器) 末级(电路)
modulating signal modulated wave emitter modulator DSB AM
transistorized transmission unitless lo-level modulator DC power suply
3. 0.15 V。
4. LSF=1MHz-1kHz, USF=1MHz+1kHz 。999kHz ~ 1001kHz 。
Unchanged .
5. 根据课文回答下列问题。
(1) Modulation is defined as the process of impressing low-frequency information signals
onto a high-frequency carrier signal. May be more than ten types of modulation have
been heard, such as AM, FM, PM, QAM, FSK, PSK, and so on.
(2) Two inputs and one output.
(3) No.
(4) The location in a transmitter where modulation occurs determines whether the circuit is a
low- or high-level transmitter.
(5) This is accomplished by placing several final power amplifiers in parallel such that their
output signals combine in phase. In addition, to achieve high power efficiency, medium-
and high-power AM modulator generally operate class C.
第七章单边带调制
2.Fill in the blanks with proper words, phrases and clauses.
AM vestigial sideband(VSB) is a form of _amplitude modulation__(幅度调制) in which the _carrier__(载波) and one complete sideband are transmitted, but only part of the second sideband is transmitted. In VSB, the lower modulating-signal frequencies are transmitted double band__(双边带) and the higher modulating-signal frequencies are transmitted_ single band___(单边带)。Consequently ,the low-frequency modulating signals are _emphasized____(加重) and produce larger-amplitude signals in the__demodulator_(解调器) than the high frequencies.
3.Translate the following sentences into English.
(1) The amount of frequency shift is equal to the absolute value of the difference between the
frequencies of the quadrature oscillators
(2)This type of distortion caused by frequency error in the demodulation process is
unique to SSB modulation system.
(3)Any error in the frequency or the phase of the local oscillator signal in the receiver,
with respect to the carrier wave, gives rise to distortion in the demodulated
signal.
(4)In order to reduce the effect of frequency error distortion in telephone systems, we
have to limit the frequency error to 2-5 Hz
(5)A phase-lock-loop (PLL) circuit can be implemented that will give a higher
frequency quadrature oscillator
第八章角度调制
1.Fill in the blanks with proper words, phrases and clauses.
(1)When thermal noise with a constant spectral density, FM, deviation, carrier
frequency, relative amplitude of the noise, demodulated, frequency
component, The spectral shape of the demodulated noise depend on, whereas
the noise voltage at the output of an FM demodulator increases linearly with
frequency, commonly called.
(2)In essence, frequency and phase modulators, modulating signal, the carrier
oscillator, indirect, When the phase of the carrier signal is modulated by the
information signal, direct PM (indirect FM) result.
2.Translate the following passages into Chinese or English.
(1)直接调频法主要的缺点是载波频率必须使用稳定性相对较差的LC振荡
器来产生,而不能用晶体震荡器。因此,直接FM法需要自动频率控制
电路来将载波频率保持在FCC要求的频率范围内。直接FM最显著的优
点是由于震荡器的频率不稳定,所以很容易获得相对较高的频率偏移和
调制指数。
(2)直接PM法主要的优点是载波振荡器与实际的调制电路是分开的,因此
可以采用稳定性好的晶体震荡器。直接PM的主要缺点是由于晶体震荡
器产生的频率很稳定,所以很难获得较大的相移和调制指数。
(3)使用FM和PM调制器的时候,调制器的输出载频通常比传输所希望的
频率要低。
(4)与幅度调制传输相比,角度调制传输(FM和PM)最主要的优点是抗噪
声性能好。
(5)With the use of limiters, FM and PM demodulators can actually reduce the
noise level and improve the signal-to-noise ratio during the demodulation
process.
(6)High-quality angle modulation produces many side frequencies, thus
necessitating a much wider bandwidth than is necessary for AM
transmission.。
(7)Whenever the period (T) of a sinusoidal carrier changes, its frequency and
phase also change, and if the changes are continuous, the wave is no longer a
single frequency.
第九章传输线
1.Fill in the blanks with proper words, phrases and clauses.
(1)radiation losses and interference, a conductive metal braid, connected to
ground and acts as a shield, electromagnetic interference, A shielded-parallel
wire pair consists of two parallel wire conductors separated by a solid
dielectric material, enclosed, a protective plastic coating
(2)balanced mode, potential, coaxial cable, prevent static interference from
penetrating the center conductors.
2.Translate the following passages into Chinese or English.
(1)这种类型传输线唯一的优点是结构简单。但是由于这种传输线没有屏蔽
层,所以辐射损耗很高,也容易受到噪声影响。这些都是明线主要的缺
点。因此,明线通常用于平衡式传输中。
(2)刚性空气填充型同轴电缆的制造成本相对较高,同时为了将损耗降到最
低,空气绝缘体应该不受湿度影响。柔性同轴电缆比刚性同轴电缆的损
耗低,而且制造更简单。两种类型的同轴电缆都不容易受到外界辐射的
影响,而且它们自己的辐射也很低,因此和结构相似的平行传输线相比,同轴电缆可以应用于更高的频率。同轴电缆传输线的主要缺点是成本高,而且必须在非平衡式传输中使用。
(3)The characteristics of a transmission line are determined by its electrical
properties, such as wire conductivity and insulator dielectric constant, and its
physical properties, such as wire diameter and conductor spacing.
(4)Because current flows through a transmission line and the transmission line
has a finite resistance, there is an inherent and avoidable power loss.
第十章电磁波传播
2.Fill in the blanks with proper words, phrases and clauses.
Long-range communication in the (高频段)high-frequency band is possible because of (折射)_ refraction __in a region of the upper(大气层) atmosphere called the (电离层) ionosphere,where some of the air(分子)_ molecules_are(电离)_ ionized by(太阳辐射) sun radiant .
In Earth's atmosphere, ray-wavefront propagation may be altered from ( 自由空间)free-space behavior by optical effects such as(折射) refraction ,(反射)_reflection_,(衍射)diffraction , and(干涉) interference .
3. Translate the following sentence into English
(1)The velocity at which an electromagnetic wave propagates is inversely proportional to the density of the medium in which it is propagating.
(2) Refraction occurs whenever a radio wave passes from one medium into another medium of different density.
(3)When the reflecting surface is not plane (i.e., it is curved), the curvature of the reflected wave is different from that of the incident wave.
(4)As an electromagnetic wave propagates through Earth's atmosphere, energy is transferred from the wave to the atoms and molecules of the atmosphere.
(5)Absorption of radio frequencies in a normal atmosphere depends on frequency and is relatively insignificant below approximately 10 GHz.
第十一章天线和波导
2. Fill in the blanks with proper words, phrases and clauses.
If the maximum radiation of antenna is along its main axis, the antenna is an(端射阵) end-fire array ,if the maximum radiation is at(直角) right angle to this axis, the array has a (侧射) broadside configuration
Antenna arrays can also be classified according to how the elements are
connected. In a (相控阵)phased array, there may be (移相器)phase shifters ,(功率分配器) power splitters ,and (阻抗匹配器) impedence matchers arrangements for individual elements, but all receive power from the feedline. In some arrays, only one element is connected to the feedline, while the others work by absorbing and(再辐射) reradiating power radiated from the driven element. The elements are called(寄生阵元).parasitic element
3.Translate the following sentences into English.
(1) If the radiation pattern is plotted in terms of electric field strength or power density, it is called an absolute radiation pattern.
(2) A narrow beamwidth minimizes the effects of interference from outside sources and adjacent antennas.
(3)The primary application of phased arrays is in radar when radiation patterns must be capable of being rapidly changed to follow a moving object.
(4)Radiation directivity can be increased in the either horizontal or vertical plane, depending on the placement of the elements and whether they are driven.
(5)Parasitic elements are not connected to the transmission line; they receive energy only trough mutual induction with a driven element or another parasitic element.
第十二章光纤通信
2. Fill in the blanks with proper words, phrases and clauses.
Both (发射机) transmitters and(接收机) receivers have finite(上升时间) rising time that limit their (带宽) bandwidth , and their effects must be included when calculating the maximum(数据率)data rate.
All the (波长)wavelengths in a (密集波分复用) dense-WDM _system can be (放大) amplified using one (掺铒光纤放大器) erbium-doped fiber amplifiers . 3.Translate the following sentences into English.
(1)A WDM transmitter is more complex because it contains many light sources
operating at different wavelengths, each with its own associated electronics. (2)The light source or external modulator limits the raw speed and power of
transmitter.
(3) Because laser wavelength is temperature-sensitive, the control circuits also
monitor temperature and control coolers when they are included.
(4) Demultiplexers must reliably separate the optical channels, with low leakage of
light from one optical channel into an adjacent channel.
(5) Although lasers can be directly modulated at data rates of 2.5Gbit/s, this induces
a chirp in wavelength which can cause excessive dispersion in long-distance
systems.
第十三章数字调制
1.Fill in the blanks with proper words, phrases and clauses.
At the receiver, an FM detector, a resettable integrator, the derivative of the phase, the phase shift that, The result is one of the four possible phase shifts, the corresponding detected data are 10, differential detection, Computer simulations, In an AWGN channel, the three differential (noncoherent) detectors. For the case of nonrectangular data pulses, the maximum phase shift, cellular telephone systems. 2.Translate the following passages into Chinese or English.
(1)OOK波形的解调既可以采用相干检波,也可以采用非相干检波,只是两
种方法在性能上有很小的区别。使用模拟载波的幅度调制技术来传输数
字信息是一种质量和成本相对较低的数字广播技术,因此,OOK几乎不
用于容量大、性能要求高的通信系统中。
(2)然而,必须解决180o相位模糊的问题。这可以通过在发射机输入端进行
差分编码,同时在接收机输出端进行差分解码来实现。
(3)最简单的数字调制技术是数字调幅,这种技术是简单的双边带、全载波
幅度调制,只是输入的调制信号是二进制波形。
(4)To conserve bandwidth, the number of levels M cannot be increased too
much, since, for a given peak envelope power (PEP), the spacing between the signal points in the signal constellation will decrease and noise on the
received signal will cause errors.
第十四章数据通信,差错控制
1.Fill in the blanks with proper words, phrases and clauses.
Trade-off, parallel and serial transmission, data transmission, between the source and destination, short-distance communications, and serial transmission is used for long-distance communications.
2.Translate the following passages into Chinese or English.
(1)回送是一个简单的概念,需要相对简单的电路。当传送的字符已经正确
地接收,但是在回送的时候却发生了传输错误,这时就会造成一次不必
要的重传,这就是回送的一个缺点。回送的另一个缺点是需要人工的检
错和纠错。另外,如果有用信息只在一个方向上传输的时候,回送仍然
需要全双工电路。
(2)尽管RS-232接口只是一根电缆和两个连接器,但是该标准还规定了DTE
和DCE输出到电缆或者从电缆接收的电平极值。在DTE和DCE两端都
有将内部逻辑电平转换成RS-232值的电路。例如,使用TTL逻辑电平
的DTE端与使用ECL逻辑的DCE端连接时,二者是不兼容的。通过电
压-电平电路将DTE和DCE的内部电压值转换成RS-232值。如果DCE
和DTE的输出和输入都是RS-232电平,则它们是电气兼容的,而不用
关心它们内部使用的是哪一种逻辑。如果电平转换电路是将信号电平输
出到电缆上,就称作驱动器;假如是从电缆上接收信号电平就称为终端
连接器。注意,数据线使用负逻辑,而控制线使用的是正逻辑。
(3)To ensure an orderly flow of data between the line control unit and the
modem, a serial interface is placed between them.
(4)In data communications, there are four types of synchronization that must be
achieved: bit or clock synchronization, modem or carrier synchronization,
character synchronization, and message synchronization.
第十五章通信网
1.Fill in the blanks with proper words, phrases and clauses.
the serial port of computer devices, This standard is for low bit rate transmissions (up to 38kbps) over short distances (less than 30m), one character at a time, they can add a parity bit for error detection, successive characters, time interval, When the receiver detects the beginning of a new character, untwisted wires, as the rate and the distance increase
1.Translate the following passages into Chinese or English.
(1)电话技术中关键的革新有电路交换、数字化、话音传输与呼叫控制的独
立、光链接以及综合业务。
(2)1876年,亚历山大?格雷厄姆?贝尔发明了一对电话。到了1890年,出现
了由人工操作进行交换的简单电话网络。在这种网络中,信号是模拟的。
假如用户要呼叫另一个电话,他首先要呼叫接线员并把被叫号码告诉接
线员,然后由接线员来决定是直接连接被叫电话呢,还是通过另一个接
线员经由其它线路来连接。在后面这种情况下,接线员之间通过互相交
谈来决定如何处理当前的呼叫,以继续建立到被叫电话的路径,在这个
过程中可能还会需要其他接线员的参与。最后,由其中的某位接线员连
通远端的电话,这时,如果被叫方的电话摘机,两端的电话就接通了。
在整个会话过程中,通话双方始终保持连接状态,当会话结束后,接线
员将取消该连接。
(3)Studies have indicated that most (80%) of the communications among data
terminals and other data equipment occurs within a relatively small local
environment. A local area network (LAN) provides the most economical and
effective means of handling local data communication needs.
(4)Ethernet is a baseband data communication system designed by Xerox
Corporation in the middle 1970s. A man named Robert Metcalfe, who later
became the founder of 3COM Corporation, generally is considered to be the
original inventor of Ethernet.
(5)FDDI was originally designed to be used with an optical fiber transmission
line rather than copper wires. Optical fiber cables can support higher data
transmission rates, are much more immune to noise interference, and do not
radiate electromagnetic energy as do their metallic counterparts.
第十六章语音编码
1.Fill in the blanks with proper words, phrases and clauses.
(1) Linear predictive coders, time domain, extract the significant features of speech from the time waveform, low bit rate vocoders, it is possible to transmit good quality voice at 4.8 kbps and poorer quality voice at even lower rates, an all pole filter, a gain, a unit delay operation, excitation, a pulse at the pitch frequency, random white noise, coefficients, linear prediction techniques, The prediction principles used are similar to those in ADPCM coders, instead of transmitting quantized values of the error signal representing the difference between the predicted and actual waveform, the gain factor, determine the appropriate excitation for synthesis filter, the decoder, the received predictor coefficients, represent the error signal and can be directly synthesized by the receiver
2.Translate the following passages into Chinese.
(1)人耳对600Hz到6000Hz之间的语音信号最敏感。Fletscher和Munson的
研究表明人耳对频率较低或很高频率的语音信号的敏感度要比对频率在
1kHz 左右的语音信号的敏感度低。
(2)语音信号子带分解的另一种方法是将语音划分成相同宽度的子带,在对
各子带进行编码时,所分配的比特位数与人的感知重要性成正比。八子
带分解是常用的一种划分方法,它不是直接将语音划分成均等宽度的子
带,这种划分方法更符合人的感知特性,因为人耳对频率的敏感度是按
指数衰减的。
(3)The formant vocoder is similar in concept to the channel vocoder.
Theoretically, the format vocoder can operate at lower bit rates than the
channel vocoder because it uses fewer control signals. Instead of sending
samples of the power spectrum envelope, the formant vocoder attempts to
transmit the positions of the peaks (formants) of the spectral envelope.
Typically, a formant vocoder must be able to identify at least three formants
for representing the speech sounds, and it must also control the intensities of
the formants.
第十七章微波通信
2. Fill in the blanks with proper words, phrases and clauses.
The (载噪比)__ carrier -to-noise ratio (C/N)____is simply the (信噪比)_ signal-to-noise ratio (S/N) _ measured before the signal is (调制)modulated .
At the output of the FM detector, a (去加重网络) deemphasis network __restores the (基带信号)baseband signal to its original(幅频特性) amplitude-versus-frequency characteristics .
2.Translate the following sentences into English.
(1) In digital microwave communications systems, phase shift keying (PSK) is usually used to modulate the HF carrier by baseband signal.
(2) The receive module down-converts the RF carrier to IF. The IF AMP/AGC and equalizer circuits amplify and reshape the IF
(3) The received RF signal enters the receiver through the channel separation network and bandpass filter.
(4) The term "digital radio" is used to refer to any microwave radio that transmits PCM carrier signals, regardless of how or at what point the signals are inserted into the radio equipment.
(5) The equalizer compensates for gain-versus-frequency nonlinearities and envelope delay distortion introduced in the system.
第十八章卫星通信
2. Fill in the blanks with proper words, phrases and clauses.
The signal path from the (地球站) Earth station transmitter to the satellite receiver is called the (上行线路) uplink , and the path from the satellite to earth is known as the (下行线路) downlink .
(同步卫星) Geostationary Satellite should remain stationary above a closen
location over the (赤道) Equator in an (近赤道轨道)equatorial orbit_.
3. Translate the following sentences into English
(1) The satellite link is probably the most basic in microwave communications since a line-of-sight path typically exists between the Earth and space
(2) The ground segment consists of three main network elements: gateways, sometimes called fixed Earth stations (FES), the network control centre (NCC) and the satellite control center (SCC).
(3) In order to provide continuous global coverage, the satellite constellation has to be designed very carefully, taking into account technical and commercial requirements of the network.
(4) The path of each channel in a multi-channel repeater is called a transponder, which is responsible for signal amplification, interference suppression and frequency
translation.
(5) The space segment can be designed in a number of ways, depending on the orbital type of the satellites and the payload technology available on board
第十九章多址及复用
2. Fill in the blanks with proper words, phrases and clauses.
When using(频分多址)___FDMA__or(时分多址)_TDMA_in a (多点波束)__ multi-spot-beam satellite configuration, adjacent(波束)__ spot beam
_____cannot be configured with the same carrier frequency.
The other form of(频分多址)___FDMA implementation is(每载波单路)__ single channel per carrier _ (SCPC).
3. Translate the following sentences into English .
(1) There are three main methods in multiple-access systems: FDMA, TDMA,
and CDMA.
(2) TDMA is a truly digital technology, requiring that all information be converted
into bit streams or data packets before transmission to the satellite.
(3) CDMA was originally developed for use in military satellite communication
where its inherent antijam and security features are highly desirable.
(4)An optimally and fully loaded TDMA network can achieve 90% throughput
(5)The most widely used contention access scheme is ALOHA and its associated
derivatives
第二十章移动电话服务
1.Fill in the blanks with proper words, phrases and clauses.
The system architecture, specified network interfaces, Base Station Subsystem, Network, Switching Subsystem, Operational Support Subsystem, it is generally considered to be part of the base station subsystem.
2.Translate the following passages into Chinese or English.
(1)PCSS的多数缺点都是和成本紧密相连的,其最主要的缺点是高成本设
计、建造和发射卫星带来的高风险。另外一个高成本是地面站网络和接
口建设,一旦运行,就需要对网络进行维护、调整和管理。另外,复杂、低功率的双模式收发器比传统移动电话系统中的电话机更笨重、更昂贵
(2)基站到移动电话之间的传输称为前向链路,而从移动电话到基站之间的
传输则称为反向链路。接收频率比发射频率高45MHz。因此,信道1的
接收频率是870.03 MHz,信道666的接收频率是889.98 MHz。因此,每
个双工无线信道都包含了一对相隔45MHz的单工信道。
(3)Analog cellular channels carry both voice using FM and digital signaling
information using binary FSK. When transmission digital signaling
information, voice transmissions are inhibited.
(4)Frequency reuse is the process in which the same set of frequencies (channels)
can be allocated to more than one cell, provided the cells are a certain
distance apart. Reduci ng each cell’s coverage area invites frequency reuse.
Cells using the same set of radio channels can avoid mutual interference
providing they are a sufficient distance apart. Each cell base station is
allocated a group of channel frequencies that are different from those of
neighboring cells, and base station antennas are chosen to achieve a desired coverage pattern (footprint) within its cell.
信息与通信工程专业英语习题2018
一:专业词汇 1、SIFT:尺度不变特征转换; 2、ANMS:自适应非极大值抑制法; 3、BM3D:三维块匹配; 4、binary thresholding segmentation:最优二值阈值分割 5、rough entropy:粗糙熵 6、rough fuzzy set:粗糙模糊集/粗模糊集 7、Plasma resonance sensing:等离子体共振传感 8、Long period grating:长周期光栅 9、Optical sensor:光学传感器 10、optical fiber sensors:光纤传感器 11、Evanescent field::倏逝场 12、biochemical sensing:生物医学传感 13、Simultaneous Localization and Mapping(SLAM):同时定位与地图构建 14、Loop Closure Detection:回环检测 15、General Graph Optimization(g2o):开源的图优化库 16、Massive multiple-input multiple output (MIMO):大容量多输入多输出 17、time-division duplex system(TDD:时分双工系统
18、frequency-division duplex system(FDD):分频双工系统 19、spectral efficiency:频谱效率 20、joint transmission coordinated multipoint:联合传动协调多点 21、GSM:全球移动通信系统(Global System for Mobile communications) 22、MSC:移动业务交换中心(mobile switching center) 23、WAP:无线应用通讯协议(Wireless Application Protocol) 24、redundancy :冗余度 25、sampling :抽样 26、quantitative:量化 27、demodulate:解调 28、multiplexable:多路复用的 29、resolution:分辨率 30、Simultaneous Localization and Mapping:即时定位与建图 31、Visual Odometry:视觉里程计 32、Laser Scanner:激光雷达 33、Time-domain:时域 34、Finite-element:有限元
通信一班序号:28 姓名:粟清明学号:14102301239 JXTA is a crystallization by Sun company's chief scientist Bill Joy's more than twenty years of brewing."JXTA technology is a platform for Network programming and calculation.To solve the modern distribution calculation especially peer-to-peer (Peer to Peer, P2P) in the calculation of the problem". [1] JXTA research project,which will provide a new framework that make the user more convenient to access to connect on the Internet's personal computer resources, thus further expand Internet 's space. At the same time JXTA is also the Sun's "ONE Internet" strategic continuance, and will take a more positive attitude to compete with the .net strategy of Microsoft and Hailstorm plan . JXTA agreement defines a set of six agreement based on XML, the organization of node into node group, release and found some resources, communication and mutual monitoring provides standardized method. (Endpoint Routing Protocol,ERP) is used for node found routing.To send a message to other nodes, and through the potential firewall and connection. (Rendezvous Protocol,RVP) s used for the nodes in the group to spread information.(Peer Resolver Protocol,PRP) is Used to one or more points to send general inquiries, and receive the response of inquiries. (Peer Discovery Protocol, PDP) is used to release and found advertising resources. (Peer Information Protocol, PIP) used to get other nodes state Information. (Peer Binding Protocol, PBP), can let a node with another node or between more nodes to set up virtual communication channel or pipeline. Compared to the nowadays general communication mode .P2P has many advantages, but it also has a lot of problems waiting to be solved.Firstly, each Peer in P2P is an active participant,in order to make the network performance increase, they need more Peer's participation, so that will result in the network's huge, manage this network will is a complex project; Secondly, P2P agreement compares with traditional
果粒橙 图解:译文“蓝色” Unit 6 The Principle of PCM PCM原理 Pcm is dependent on three separate operations, sampling, quantizing, and coding. Many different schemes for performing these three functions have evolved during recent years, and we shall describe the main ones. In these descriptions we shall see how a speech channel of telephone quality may be conveyed as a series of amplitude values, each value being represented, that is, coded as a sequence of 8 binary digits. Furthermore, we shall prove that a minimum theoretical sampling frequency of order 6.8 kilohertz(khz) is required to convey a voice channel occupying the range 300 HZ to 3.4 Khz. Practical equipments, however, normally use3 a sampling rate of 8 khz, and if 8-digits per sample value are used, the voice channel becomes represented by a stream of pulses with a repetition rate of 64khz. Fig .1-1 illustrates the sampling, quantizing, and coding processes. PCM的构成依赖于三个环节,即采样、量化和编码。近年来,人们对这三个环节的实现提出了许多不同的方案,我们将对其中的一些主要的方案进行讨论。在这些讨 论中,我们会看到话路中的语声信号是如何转换成幅值序列的,而每个幅值又被编码,即以8位二进制数的序列表示。而且,我们将证明,为了转换频率范围为300HZ— 3.4KHZ的话路信号,理论上最小采样频率须为6.8khz。但是,实际设备通常用8khz 的采样速率,而如果每个样值用8位码的话,则话路是由一个重复速率为64khz的脉 冲流来表示的。图1-1表示了采样、量化、编码的过程。 Reexamination of our simple example shows us that the speech signal of maximum frequency 3.4khz has been represented by a signal of frequency 64khz. However, if only 4-digits per sample value had been used, the quality of transmission would drop, and the repetition rate of the pulses would be reduced to 32khz. Thus the quality of transmission is dependent on the pulse repetition rate, and for digital communication systems these two variables may be interchanged most efficiently. 让我们再研究一下上面提到的简单例子。可以看出,最高频率为3.4khz的话音信号适用64khz的(脉冲流)信号来表示的。但是,如果每个样值中用4位(码)表示,则传输质量会下降,而脉冲的重复速率也将减小到32khz。因而传输质量是取决于脉 冲重复速率的。对于数字通信系统,这两个量之间极明显的互相影响着。 Digital transmission provides a powerful method for overcoming noisy environments. Noise can be introduced into transmission patch in many different ways : perhaps via a nearby lightning strike, the sparking of a car ignition system, or the thermal low-level noise within the communication equipment itself. It is the relationship of the true signal to the noise signal, known as the signal-to-noise ratio, which is of the most interest to the communication engineer.Basically, if the signal is very large compared to the noise level, then a perfect message can take place; however, this is not always the case. For example, the signal received from a
参考答案( Communication English ) 第一章电子通信导论 1.将表1-1译成中文。 表1-1 通信大事纪 年代事件 公元前3000年埃及人发明象形文字 公元800年借鉴印度, 阿拉伯人使用我们的现行数制 1440年约翰.戈登贝尔发明可移动的金属记录带 1752年贝莱明.富兰克林的风筝证明了雷闪是电 1827年欧姆发表欧姆定律( I = E / R) 1834年 C.F.高斯和E.H.韦伯发明电磁电报 1838年W.F.库克和C.维特斯通发明电报 1844年S.F.B.莫尔斯演示巴尔的摩和华盛顿的电报线路 1850年G.R.基尔赫夫发表基尔赫夫电路定律 1858年铺设第一条越洋电缆, 并于26天后举办博览会 1864年J.C.麦克斯威尔预言电磁辐射 1871年电报工程师协会在伦敦成立 1876年 A.G.贝尔发明电话并获专利 1883年 A.爱迪生发现真空管中的电子流 1884年美国电气工程师协会(AIEE)成立 1887年H.赫兹证明麦克斯威的理论 1900年G.马可尼传送第一个越洋无线电信号 1905年R.芬森登利用无线电传送语音和音乐 1906年L.弗雷斯特真空三极管放大器 1915年贝尔系统完成美国大陆电话线路 1918年 E.H.阿尔莫斯通发明超外差接收机电路 1920年第一个定时无线广播 J.R.卡尔松将取样用于广播 1926年美国演示电视 1927年H.布兰克在贝尔实验室发明负反馈放大器 1931年电传打字机投入运营 1933年 E.H.阿尔莫斯通发明调频 1935年R.A.沃特森-瓦特发明第一个实用雷达 1936年英国广播公司(BBC)开办第一个电视广播 1937年 A.雷弗斯提出脉冲编码调制(PCM) 1941年J.V.阿当拉索夫在依俄华州立大学发明计算机 1945年ENIAC电子数字计算机研发于宾夕伐尼亚大学 1947年布雷登、巴登和肖克利在贝尔实验室研制晶体管 S.O.莱斯在贝尔实验室研究噪声的统计表征1948年 C.E.香农发表他的信息理论
一、二、 十一、汉译英时分多址:TDMA (Time Division Multiple Address/ Time Division Multiple Access)2、通用无线分组业务:GPRS General Packet Radio Service 3、国际电报电话咨询委员会:CCITT 4、同步数字体系:SDH Synchronous Digital Hierarchy (同步数字序列) 5、跳频扩频:FHSS frequency hopping spread spectrum 6、同步转移模块:STM synchronous transfer module 7、综合业务数字网:ISDN Integrated Services Digital Network 8、城域网:MAN Metropolitan Area Network 9、传输控制协议/互联网协议:TCP/IP Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol 10、服务质量:QOS Quality of Service 11、中继线:trunk line 12、传输速率:transmission rate 13、网络管理:network management 14、帧结构:frame structure 15、移动手机:Mobile Phone 手机 Handset 16、蜂窝交换机:(Cellular switches)(电池开关cell switch)(cell 蜂房) 17、天线:Antenna 18、微处理器:microprocessor 19、国际漫游:International roaming 20、短消息:short message 21、信噪比:SNR(Signal to Noise Ratio) 22、数字通信:Digital communication 23、系统容量:system capacity 24、蜂窝网:cell network(cellular network)(Honeycomb nets) 25、越区切换:Handover 26、互联网:internet 27、调制解调器:modem 28、频谱:spectrum 29、鼠标:Mouse 30、电子邮件:electronic mail E-mail 31、子网:subnet 32、软件无线电:software defined radios 33、网络资源:network resources 十二、英译汉 1、mobile communication:移动通信 2、Computer user:计算机用户 3、Frame format:帧格式 4、WLAN:wireless local area network 无线局域网络 5、Communication protocol:通信协议 6、Transmission quality:传输质量 7、Remote terminal:远程终端 8、International standard:国际标准 9、GSM:全球移动通信系统 Global System for Mobile Communications 10、CDMA:码分多址Code Division Multiple Access 11、ITU:国际电信联盟 International Telecommunication Union 12、PCM:pulse code modulation 脉冲编码调制 13、WDM:波分复用Wavelength Division Multiplex 14、FCC:联邦通信委员会 Federal communications commission 15、PSTN:公用电话交换网 Public Switched Telephone Network 16、NNI:网络节点借口Network Node Interface 17、WWW:万维网World Wide Web 18、VOD:视频点播Video-On-Demand 19、VLR:访问位置寄存器 Visitor Location Register 20、MSC:移动交换中心Mobile Switching Centre 21、HLR:原籍位置寄存器Home Location Register 22、VLSI:超大规模集成电路 Very Large Scale Integrated Circuits 23、Bluetooth technology:蓝牙技术 24、Matched filter:匹配滤波器 25、ADSL:非对称数字用户环路Asymmetrical Digital Subscriber Loop非对称数字用户线路(Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line) 26、GPS:全球定位系统Global Position System 27、ATM:异步传输模式Asynchronous Transfer Mode
Lesson eight 第八课 Ⅱ.翻译句子,并注意remain和above的词类和词义 2. In this case the voltage applied must remain unchanged. 在这种情况下,那个应用电压必须保持不变 4. If you take 3 from 8, 5 remain. 如果从8中拿走3,剩5. 6. The above property was discovered by Faraday. 法拉第发现以上性质。 8. Lenz states that the self-induced emf impedes any change of current and tends to support the former current value. The above is known as Lenz’s law. 楞茨陈述自感电动势阻止电流的变化而保持先前电流的值。上面就是我们所知的楞 次定律。 Ⅲ.翻译句子,注意some的词义 2. That radio receiver weighs some five kilograms. 那个无线接收器重五公斤。 4. Some element in the substance is not known. 物质中的一些元素是人们不知道的。 Ⅳ.翻译句子,注意句中one 的不同用法和词义。 2. This concept was discussed in Chapter One. 这个概念在第一张讨论过。 4. No one can lift this equipment. 没人能举起这件设备。 6. This chapter will deal with one of the three functions of a turning circuit. 这章我们将介绍螺旋电路三个功能中的一个。 8. Before one studies a system, it is necessary to define and discuss some important terms. 在研究一个系统之前,确定且讨论一些重要的术语是有必要的。 Ⅴ.画出句中的名词从句,说明其种类,并将句子译成汉语。 2. These experiments do not show which particles. 这些实验不能显示他们的粒子结构。 4. The operating point is determined by how much bias is used. 操作要点是被用多少偏压决定的。 6. It is not important how this voltage is produced. 这个电压是怎么产生的并不重要。 8. It may be questioned whether this approach is the best for the physicist. 这种方式最适合于医生可能会被质疑。 10. This ball may be used to determine whether that body is charged. 这个球可能用于检测是否身体是带电的。 12. It is known that charged particles emit electromagnetic waves whenever they are accelerated. 众所周知的当电子被加速他们就会发射电磁波。 14. The value of this factor determines how fast the amplitude of the current
琼州学院 09通信工程专业《专业英语》试卷 2011 ——2012学年度第 1 学期期末考试( C )卷答案 注意事项: 1、考前请将密封线内填写清楚 2、所有答案请直接答在试卷上(或答题纸上) 3、考试形式:(闭)卷 4、本试卷共 大题,满分100分。考试时间120分钟 5 一、科技常用词组翻译(本题共20 小题,每小题 1.5 分,共 30 分) 1、英翻中 (1)client 客户机 (2)router 路由器 (3)hub 集线器 (4)destination address 目的地址 (5)datagram 数据报 (6)amplify 放大 (7)medium 媒介 (8)information 信息 (9)transmission 传输 (10)multimedia 多媒体 2、中翻英 (1)超链接 hyperlink (2)交易 transation (3)电子商务 E-commerce (4)适配器 adapter (5)调制解调器 modem (6)中国电信 China Telecom (7)数字业务 digital service (8)虚拟现实 virtual reality (9)分组交换网 packet-switching network (10)子网 subnetwork 二、英、中词组正确搭配(每组 1 分,共 10 分) 班 级 姓名 学 号 密 封 装 订 线
1.Bearer channel 数据信道5. 2.Terminal Adapter 处理信号4. 3.analog system 用户设备6. 4.handle signaling 载波信道1. 5.data channel 模拟系统3. 6.customer equipment 终端适配器2. 7.service type 端到端数字连接10. 8.Integrated Services Digital Network 数字交换系统 9. 9.digital switching system 综合业务数字网8. 10.end-to-end digital connectivity 业务类型7. 三、把下面句子翻译成中文(本题共 5 小 题,每题 4 分,共 20 分) 1、Data is a collection of un_organized facts. 数据是无组织的事实的集合. https://www.doczj.com/doc/359773370.html,rmation is data that is organized ,has meaning,and is useful. 信息是有组织的,有意义的和有用的数据. 3.The system unit is a box-like case made of metal or plastic. 系统单元是金属或塑料制成的象盒般的箱子. 4.Storage hold data,instruction,and information for future use. 存储器保存数据,指令和信息以便将来使用. 5.Modems are available as both external and internal devices. 调制解调器可作为内部或外部的设备.
通信工程专业英语翻译 JXTA is a crystallization by Sun company's chief scientist Bill Joy's more than twenty years of brewing."JXTA technology is a platform for Network programming and calculation.To solve the modern distribution calculation especially peer-to-peer (Peer to Peer, P2P) in the calculation of the problem".[1] JXTA research project,which will provide a new framework that make the user more convenient to access to connect on the Internet's personal computer resources, thus further expand Internet 's space. At the same time JXTA is also the Sun's "ONE Internet" strategic continuance, and will take a more positive attitude to compete with the .net strategy of Microsoft and Hailstorm plan . JXTA agreement defines a set of six agreement based on XML, the organization of node into node group, release and found some resources, communication and mutual monitoring provides standardized method.(Endpoint Routing Protocol,ERP) is used for node found routing.To send a message to other nodes, and through the potential firewall and connection.(Rendezvous Protocol,RVP) s used for the nodes in the group to spread information.(Peer Resolver Protocol,PRP) is Used to one or more points to send general inquiries, and receive the response of inquiries.
transistor n 晶体管 diode n 二极管semiconductor n 半导体 resistor n 电阻器 capacitor n 电容器 alternating adj 交互的 amplifier n 扩音器,放大器integrated circuit 集成电路 linear time invariant systems 线性时不变系统voltage n 电压,伏特数 tolerance n 公差;宽容;容忍condenser n 电容器;冷凝器dielectric n 绝缘体;电解质electromagnetic adj 电磁的 adj 非传导性的 deflection n偏斜;偏转;偏差 linear device 线性器件 the insulation resistance 绝缘电阻 anode n 阳极,正极 cathode n 阴极 breakdown n 故障;崩溃 terminal n 终点站;终端,接线端emitter n 发射器 collect v 收集,集聚,集中insulator n 绝缘体,绝热器oscilloscope n 示波镜;示波器 gain n 增益,放大倍数 forward biased 正向偏置 reverse biased 反向偏置 P-N junction PN结 MOS(metal-oxide semiconductor)金属氧化物半导体 enhancement and exhausted 增强型和耗尽型 integrated circuits 集成电路 analog n 模拟 digital adj 数字的,数位的horizontal adj, 水平的,地平线的vertical adj 垂直的,顶点的amplitude n 振幅,广阔,丰富attenuation n衰减;变薄;稀薄化multimeter n 万用表 frequency n 频率,周率 the cathode-ray tube 阴极射线管 dual-trace oscilloscope 双踪示波器 signal generating device 信号发生器 peak-to-peak output voltage 输出电压峰峰值sine wave 正弦波 triangle wave 三角波 square wave 方波 amplifier 放大器,扩音器 oscillator n 振荡器 feedback n 反馈,回应 phase n 相,阶段,状态 filter n 滤波器,过滤器 rectifier n整流器;纠正者 band-stop filter 带阻滤波器 band-pass filter 带通滤波器 decimal adj 十进制的,小数的hexadecimal adj/n十六进制的 binary adj 二进制的;二元的octal adj 八进制的 domain n 域;领域 code n代码,密码,编码v编码 the Fourier transform 傅里叶变换 Fast Fourier Transform 快速傅里叶变换microcontroller n 微处理器;微控制器assembly language instrucions n 汇编语言指令 chip n 芯片,碎片 modular adj 模块化的;模数的 sensor n 传感器 plug vt堵,塞,插上n塞子,插头,插销coaxial adj 同轴的,共轴的 fiber n 光纤relay contact 继电接触器 single instruction programmer 单指令编程器 dedicated manufactures programming unit 专 供制造厂用的编程单元 beam n (光线的)束,柱,梁 polarize v(使)偏振,(使)极化 Cathode Ray Tube(CRT)阴极射线管 neuron n神经元;神经细胞 fuzzy adj 模糊的 Artificial Intelligence Shell 人工智能外壳程序 Expert Systems 专家系统 Artificial Intelligence 人工智能 Perceptive Systems 感知系统 neural network 神经网络 fuzzy logic 模糊逻辑 intelligent agent 智能代理 electromagnetic adj 电磁的 coaxial adj 同轴的,共轴的 microwave n 微波 charge v充电,使充电 insulator n 绝缘体,绝缘物 nonconductive adj非导体的,绝缘的 antenna n天线;触角 modeling n建模,造型 simulation n 仿真;模拟 prototype n 原型 array n 排队,编队 vector n 向量,矢量 wavelet n 微波,小浪 sine 正弦cosine 余弦 inverse adj倒转的,反转的n反面;相反v 倒转 high-performance 高精确性,高性能 two-dimensional 二维的;缺乏深度的 three-dimensional 三维的;立体的;真实的 object-oriented programming面向对象的程序 设计 spectral adj 光谱的 attenuation n衰减;变薄;稀释 distortion n 失真,扭曲,变形 wavelength n 波长 refractive adj 折射的 ATM 异步传输模式Asynchronous Transfer Mode ADSL非对称用户数字线Asymmetric digital subscriber line VDSL甚高速数字用户线very high data rate digital subscriber line HDSL高速数据用户线high rate digital subscriber line FDMA频分多址(Frequency Division Multiple Access) TDMA时分多址(Time Division Multiple Access) CDMA同步码分多址方式(Code Division Multiple Access) WCDMA宽带码分多址移动通信系统(Wideband Code Division Multiple Access) TD-SCDMA(Time Division Synchronous Code Division Multiple Access)时分同步码分多址 SDLC(synchronous data link control)同步数据 链路控制 HDLC(high-level data link control)高级数据链路 控制 IP/TCP(internet protocol /transfer Control Protocol)网络传输控制协议 ITU (International Telecommunication Union) 国际电信联盟 ISO国际标准化组织(International Standardization Organization); OSI开放式系统互联参考模型(Open System Interconnect) GSM全球移动通信系统(Global System for Mobile Communications) GPRS通用分组无线业务(General Packet Radio Service) FDD(frequency division duplex)频分双工 TDD(time division duplex)时分双工 VPI虚路径标识符(Virtual Path Identifier); ISDN(Integrated Services Digital Network)综 合业务数字网 IDN综合数字网(integrated digital network) HDTV (high definition television)高清晰度电视 DCT(Discrete Cosine Transform)离散余弦变换 VCI(virtual circuit address)虚通路标识 MAN城域网Metropolitan area networks LAN局域网local area network WAN广域网wide area network 同步时分复用STDM Synchronous Time Division Multiplexing 统计时分复用STDM Statistical Time Division Multiplexing 单工传输simplex transmission 半双工传输half-duplex transmission 全双工传输full-duplex transmission 交换矩阵Switching Matrix 电路交换circuit switching 分组交换packet switching 报文交换message switching 奇偶校验parity checking 循环冗余校验CRC Cyclic Redundancy Check 虚过滤Virtual filter 数字滤波digital filtering 伪随机比特Quasi Random Bit 带宽分配Bandwidth allocation 信源information source 信宿destination 数字化digitalize 数字传输技术Digital transmission technology 灰度图像Grey scale images 灰度级Grey scale level 幅度谱Magnitude spectrum 相位谱Phase spectrum 频谱frequency spectrum 智能设备Smart Device 软切换Soft handover 硬切换Hard Handover 相干检测Coherent detection 边缘检测Edge detection 冲突检测collision detection 业务集合service integration 业务分离/综合service separation/ integration 网络集合network integration 环形网Ring networks 令牌环网Token Ring network 网络终端Network Terminal 用户终端user terminal 用户电路line circuit 电路利用率channel utilization(通道利用率) 相关性coherence 相干解调coherent demodulation 数字图像压缩digital image compression 图像编码image encoding 有损/无损压缩lossy/lossless compression 解压decompression 呼叫控制Call Control 误差控制error control 存储程序控制stored program control 存储转发方式store-and-forward manner 语音\视频传输voice\video transmission 视频点播video-on-demand(VOD) 会议电视Video Conference 有线电视cable television 量化quantization 吞吐量throughput 话务量traffic 多径分集Multipath diversity 多媒体通信MDM Multimedia Communication 多址干扰Multiple Access Interference 人机交互man machine interface 交互式会话Conversational interaction
通信专业英语复习题Part B 一、基础词汇 1.Inductor电感 2.Alternative Curren t交流电流 3.DC直流 4.Plastic 塑料 5.LED发光二极管 6.fuse保险丝 7.Electric Potential 电势能 8.V oltage电压 9.Ohm’s Law欧姆定律10.Solid 固体12Rectifier 整流器13.Bias 偏置14.FET 场效应晶体管15.Frequency Drift 频率漂移16.Temperature Drift温度漂移 2.OA 18.Gain 增益19.Couple耦合20.Feedback 反馈21.Crystal Oscillator晶体振荡器 22.Conversion 转换23.Phase Detector鉴相器24.Local Oscillator 本机振荡器25.ANT SWITCH天线开关26V oltage Controlled Oscillator 压控振荡器27.Ethernet 以太网28.Configure 配置29.Digital Interface数字接口 30.Frame Relay 帧中继31.TCP 传输控制协议32.PCS 个人通信系统33.DNS 域名服务器34.decode 解码35.Description概述 3.36.Base Station基站37.Mobile 移动39.Transmitter 发送器40.Receiver接收器 二、词汇缩写与翻译 1.High Fidelity,缩写HI-FI,中文翻译高保真; 2.Field Effect Transistor,缩写FET,中文翻译场效应晶体管; 3.Central Processing Unit,缩写CPU ,中文翻译中央处理机; 4.Carrier Sense Multiple Access,缩写CSMA,中文翻译载波监听多址访问; 5.Digital to Analog Converter,缩写DAC ,中文翻译数模转换器; 6.Arithmetic Logic Unit,缩写ALU,中文翻译算术逻辑单元; 7.American National Standards Institute,缩写ANSI,中文翻译美国国家标准协会; 8.Asynchronous Transfer Mode,缩写ATM,中文翻译异步传输模式; 9.Bit Error Ratio,缩写BER ,中文翻译误码率; https://www.doczj.com/doc/359773370.html,mon Traffic Channel,缩写CTCH,中文翻译公共业务信道; 11.Enhanced Data rates for GSM Evolution,缩写EDGE,中文翻译增强型的GSM环境; 12.Frequency Division Duplex,缩写FDD ,中文翻译频分双工; 13.Global Positioning System,缩写GPS ,中文翻译全球定位系统; 14.Media Access Control,缩写MAC ,中文翻译媒体访问控制; 15.Mobile Broadcast Wireless Access,缩写MBWA ,中文翻译移动广播无线接入; 16.Operation And Maintenance center,缩写OMC ,中文翻译操作维护中心; 17.Orthogonal Variable Spreading Function,缩写OVSF ,中文翻译正交可变扩频函数; 18.Primary Synchronization Code,缩写PSC ,中文翻译主同步码; 19.Real Time Protocol,缩写RTP ,中文翻译实时协议; 20.Total Access Communications System,缩写TACS ,中文翻译全接入通信系统; 21.Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter,缩写UART : 中文翻译通用异步收发器; 22.Wireless Fidelity,缩写WIFI ,中文翻译无线网; 23.Wideband Code Division Multiple Access,缩写WCDMA,中文翻译宽带码分多址;Watch Dog Timer,缩写WDT,中文翻译监视计时器;