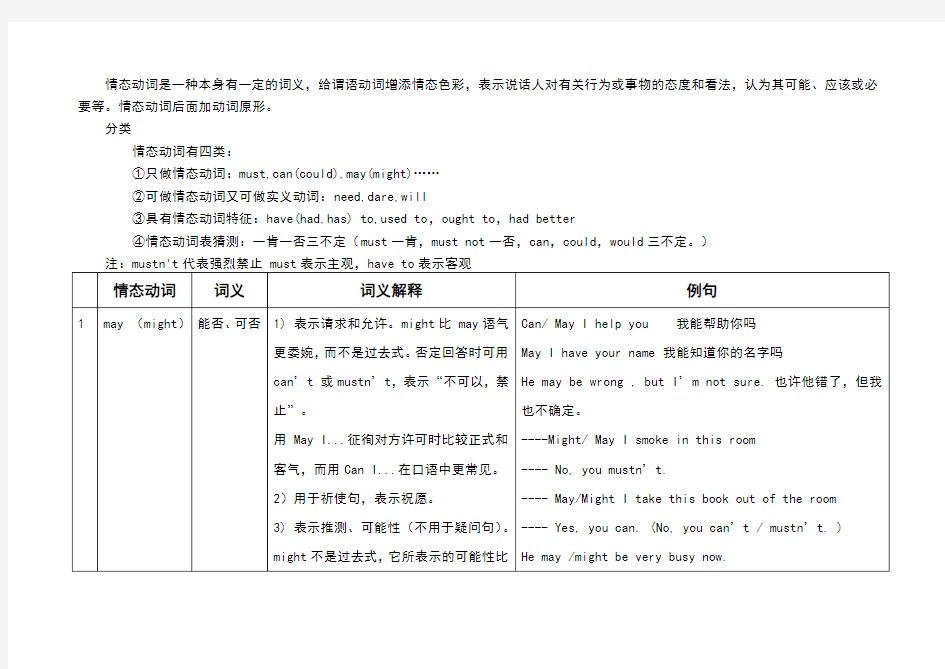
情态动词是一种本身有一定的词义,给谓语动词增添情态色彩,表示说话人对有关行为或事物的态度和看法,认为其可能、应该或必要等。情态动词后面加动词原形。
分类
情态动词有四类:
①只做情态动词:must,can(could),may(might)……
②可做情态动词又可做实义动词:need,dare,will
③具有情态动词特征:have(had,has) to,used to,ought to,had better
④情态动词表猜测:一肯一否三不定(must一肯,must not一否,can,could,would三不定。)
【模拟试题】(答题时间:30分钟)单项选择:
1. John___ come to see us tonight, but he isn’t very sure yet.
A. may
B. can
C. has to
D. must
2. They ___ do well in the exam.
A. can be able to
B. be able to
C. can able to
D. are able to
3. —May I take this book out—No, you___.
A. can’t
B. may not
C. needn’t
D. aren’t
4. You___ go and see a doctor at once because you’re got a fever.
A. can
B. must
C. dare
D. would
5. —Can you speak Japanese—No, I____.
A. mustn’t
B. can’t
C. needn’t
D. may not
6. —He___ be in the classroom, I think.
—No, he ___ be in the classroom. I saw him go home a minute ago.
A. can; may not
B. must; may not
C. may; can’t
D. may; mustn’t
7. —Shall I get one more cake for you, Dad—Thanks, but you___, I’ve had enough.
A. may not
B. must not
C. can’t
D. needn’t
8. Even the top students in our class can’t work out this problem, so it ___be very difficult.
A. may
B. must
C. can
D. need
9. He isn’t at school. I think he ___ be ill.
A. can
B. shall
C. must
D. has to
10. ___ I take this one
A. May
B. Will
C. Are
D. Do
11. The children___ play football on the road.
A. can’t
B. can
C. mustn’t
D. must
12. You ___ be late for school again next time.
A. mustn’t
B. needn’t
C. don’t have to
D. don’t need to
13. —Must I do my homework at once—No, you___.
A. needn’t
B. mustn’t
C. can’t
D. may not
14. His arm is all right. He___ go and see the doctor.
A. has not to
B. don’t have to
C. haven’t to
D. doesn’t have to
15. He had to give up the plan, ___ he
A. did
B. didn’t
C. does
D. doesn’t
16. They had to walk here, ___ they
A. mustn’t
B. did
C. didn’t
D. hadn’t
17. He had better stay here, ___ he
A. didn’t
B. don’t
C. hadn’t
D. isn’t
18. You’d better___ late next time.
A. not to be
B. not be
C. won’t be
D. don’t be
19. You’d better ___ your hair ___ once a month.
A. had; cut
B. had; cutted
C. have; cut
D. have; cutted
20. You___ ask that man over there. Maybe he knows the way.
A. had better not to
B. had not better
C. had better
D. had better not
21. —Shall we go and visit the History Museum next Sunday —______
A. Here you are
B. Sorry, I can’t
C. Yes, please
D. Let me try
22. —Why don’t you ask Mike to go with us
—Thanks, ___.
A. I will
B. I won’t
C. I can
D. I may
23. —___ I take the newspaper away
—No, you mustn’t. You____ read it only here.
A. Must; can
B. May; can
C. Need; must
D. Must; must
24. Excuse me. ___ you please pass me that cup
A. Do
B. Should
C. Would
D. Must
25. ___ you like to have another try
A. Could
B. Will
C. Would
D. Do
26. —Would you like to go boating with us
—Yes, ___.
A. I’d like
B. I want
C. I’d like to
D. I do
27. You___ worry about your son. He will get well soon.
A. needn’t
B. can’t
C. mustn’t
D. have to
28. The poor man needs our help, ___ he
A. need
B. needn’t
C. does
D. doesn’t
29. —Must we do our homework first
—No, you___. You may have a rest first.
A. mustn’t
B. needn’t
C. may not
D. can’t
【试题答案】
1—5 A D A B B 6—10 C D B C A 11—13 C A A 14—16 D B C 17—20 C B C C 21—23 B A B 24—26 C C C 27—29 A D B
英语情态动词用法总结(完整) 一、单项选择情态动词 1.--- Difficulties always go with me! --- Cheer up! If God closes door in front of you, there be a window opened for you. A.must B.would C.could D.can 【答案】A 【解析】 【详解】 考查情态动词辨析。句意:——困难总是伴随着我!——高兴点! 如果上帝在你面前关上了门,一定有一扇窗户为你打开。A. must必须;B. would将要;C. could能,会;D. can能,会。must表示对现在的状态推测时,意为“一定”,表示可能性很大的推测。符合语境。故选A。 【点睛】 1) must用在肯定句中表示较有把握的推测,意为"一定"。 2) must表对现在的状态或现在正发生的事情的推测时, must 后面通常接系动词be 的原形或行为动词的进行式。 3) must 表示对已发生的事情的推测时,must 要接完成式。 4) must表示对过去某时正发生的事情的推测,must 后面要接完成进行式。 5) 否定推测用can't。 本句中的。must表示对现在的状态推测时,意为一定,表示可能性很大的推测。符合第2点用法。 2.Paul did a great job in the speech contest. He many times last week. A.need have practised B.might practise C.must have practised D.could practise 【答案】C 【解析】 【详解】 考查情态动词。句意:保罗在演讲比赛中表现得很好。他上星期一定练习了很多次。must have done是对过去发生的动作最有把握的猜测,意思是“一定”。故C选项正确。 3.He is a bad-tempered fellow, but he ________ be quite charming when he wishes. A.shall B.should C.can D.must 【答案】C 【解析】 【详解】 考查情态动词辨析。句意:他是个脾气不好的家伙,但当他希望自己有魅力的时候,他可
情态动词表推测用法总结 (一)情态动词表推测 能用于表推测的情态动词: 英语情态动词表推测的时态构成 (1)语气部分:(以下情态动词语气由强至弱) 肯定句:must、may、might(=could) 否定句:can’t(=couldn’t)、mayn’t、mightn’t 疑问句:can、could(语气更加委婉不确定) (2)时态部分: 一般现在或一般将来时间的推测:情态动词+be;情态动词+v. 对过去时间的推测:情态动词+have done 对正在进行的时态的推测:情态动词+be doing (二)表许可、请求 1、 can, could 2、may, might 3、must 4、shall 5、will, would 1. can, could 1) 用在疑问句中,表示一般的请求。两者不同在于:用could 要比用can更加委婉,特别是没有把握得到允许时。 Can I go with you? 我能和你一起去吗?Could I ask you something? 我能问你一个问题吗? 2) 用在陈述句中,表示许可:You can leave when you finish your work. 做完事情后你才可以走。 2. may, might 1) may用在疑问句中,也表示一般的请求。同can相比,may比较正式,常常表示尊敬之意。并且,may在疑问句中常用于第一人称,很少有May you…/they…这样的句型。Might比较少用在疑问句中,它表示请求的时候常用陈述句。 May I make a suggestion? 我可以提个建议? 2) 用在陈述句中,表示许可,此时与can, could相近。 You may have a rest before we set out again. 我们再次出发之前你可以先休息一下。 3. must 1) 表示说话人“不许”和“禁止”某人做某事,有很强的劝告语气。 Cars must not be parked here.此地不准停车。 2) Must的一般疑问句的回答有两种,表示肯定,用Yes, you must. 表示否定,用No, you needn’t. Must I post this letter tomorrow? 我明天必须得寄掉这封信吗? Yes, you must. 是的,你必须明天寄掉。
情态动词的基本用法及其区别 最近几年高考试题中常常借助语境来考查情态动词的基本用法及其区别,因此在平时学习时准确理解和掌握情态动词的基本用法十分重要。情态动词的用法复杂多变,在高考试题中,命题者常常利用语境和句子之间意义上的细微差别来考查学生对情态动词的理解和掌握。对于情态动词,除了要求考生能够准确掌握它们的基本用法外,还要充分利用高考试题所设置的语境来分析句子之间所体现的特殊关系。下面就近几年来高考试题中出现的情态动词的考点进行归纳分析,以便同学们复习掌握。 一、用“情态动词+have +done”结构表示对过去动作的推测,高考试题中常用过去时态或过去的时间状语给以暗示。情态动词的这一用法可以用“对立统一”来概括。 1.当试题的前句和后句在动作和意义上相互补充说明,且整个句意在动作和时间上是一个整体时,我们可用“统一”关系来解决这样的试题。常见的结构有: must have done: 表示对过去动作的肯定推测,常译作“一定做了……”,只能用于肯定句中。其否定形式为can’t/couldn’t have done 疑问式为Can/Could...have done﹖。 could /might have done:表示对过去发生的动作的可能性推测,常译作“可能做了……”。如: 1) My sister met him at the Grand Theater yesterday afternoon, so he _____your lecture. A.couldn’t have attended B.needn’t have attended C.mustn’t have attended D.shouldn’t have attended 本题选A。 2) Jack ____yet, otherwise he would have telephoned me. A.mustn’t have arrived B.shouldn’t have arrived C.can’t have arrived D.need not have arrived (C) 2.当试题的前后句在动作和意义上构成转折关系时,常借助“but, however, instead”等词来表示过去的动作与客观事实不符,这时我们就可以用“对立”关系来解决这样的试题。这种结构常见的有: should have done /ought to have done:表示过去本应该做某事而实际上没有做。 should not have done /ought not to have done:表示过去本不应该做某事但事实上却做了。 need have done:表示过去本来有必要去做某事,但事实上没有做。 need not have done:表示过去本来没有必要做某事,但事实上却做了。如: 3) I was really anxious about you.You _____home without a word.(NMET2001) A.mustn’t leave B.shouldn’t have left C.couldn’t have left D.needn’t leave “本不应该离家出走却走了”,故本题选B。 4) I told Sally how to get here, but perhaps I _____for her.
情态动词表猜测的用法 情态动词must,can,could,should,may,might 等可以用在句中表示猜测。 1.“情态动词+动词原形”表示对现在或将来情况的猜测 I don’t know where she is. She may be in Wuhan. 2.“情态动词+进行式”表示对现在或将来正在进行的情况的猜测 At this moment, our teacher must be correcting our exam papers. 3.“情态动词+完成式”表示对过去情况的猜测 You must have been caught in the rain on your way home yesterday. 4.“情态动词+完成进行式”表示对过去正在进行的情况的猜测 Your mother must have been looking for you. 5.推测的否定形式用can’t/couldn’t,may not/might not表示
Mike can’t have found his car, for he came to work by bus this morning. 6.句子中含有表示猜测的情态动词时,其反 意疑问句的构成不能再用原句中的情态动词,而应根据原句在去掉情态动词的情况下的主谓关系来确定其反问形式。 ①The man in the white clothes must be a doctor, isn’t he? ②She must have seen the film before, hasn’t she? ③He must have an uncle abroad, doesn’t he? ④You must have met Uncle Wang in the shop yesterday, didn’t you? 7.在表示“猜测”方面的区别 情态动词must,can,could,should,may,might 都可以用于表示“猜测”(注意:could, might 表示推测时不表示时态, 其推测的程度不如can, may)。实际上,“猜测”与“可能性”在逻辑上是有必然联系的。如果认为没有某种可能性,人们就不会作出某些猜测。因此,请注意六个情态动词之间的区别与它们各
情态动词must, can, could, may, might表推测的用法 情态动词中的must, can, could, may, might都表推测。其中must的可能性最大,can / could 次之,may / might最小。具体用法如下: 1.must的用法 (1)表示推测“可能性”时,意思是“一定、准是”,语气较肯定,较有把握。 He must be American. = It is certain that he is American. 他准是个美国人。 (2)must表推测只能用于肯定句。如果要表示“一定不、肯定不”的意思时,应用can’t,如询问某种可能时,应用can。 He must know my address. 他肯定知道我的地址。(一定) He can’t know my address. 他肯定不知道我的地址。(一定不) Can he know my address? 他知道我的地址吗?(询问可能性) (3)must表示推测时,可以推测现在/正在发生的动作/过去发生的动作。 He must have a car now. (现在)他一定有辆小汽车。 He must be doing his exercises in the classroom.(正在进行)他一定在教室里做练习。 He must have finished the work.(过去发生)他一定已完成了工作。 注:must表示推测时很少用于将来的情况。一般不用He must come tomorrow.可用It`s certain / I’m sure that he will come tomorrow. (4)在反意疑问句中,当附属部分含有表示推测意义的must时,疑问部分的助动词应与must后面的动词在非推测情况下的用法保持一致。 He must be a worker, isn’t he? (现在)他准时个工人,是吗? It must have rained last night, didn’t it? (过去)昨晚一定下雨了,是不是? You must have learned English for many years, haven’t you? (完成时)你一定学了好多年英语,是吗? 2.?can / could的用法 (1)can表示推测“可能性”时,往往用于否定句或疑问句。Can’t“一定不”,语气很肯定。can在疑问句中意思是“会、可能”。 He can’t be at home. = It is impossible that he is at home. 他一定不在家。 (2)can /can’t后可接进行时/完成时,表示对现在发生的动作或过去发生的动作进行推测。They can’t be reading in the library. 他们一定不在图书馆读书。 He can’t have gone to Shanghai for I saw him a minute ago. 他不可能去了上海,我刚才还看见他。 It’s so late. Where can she have gone? 天晚了,她可能去哪儿了呢? (3)在反意疑问句中,当陈述部分含有表示推测意义的can’t时,疑问部分的助动词应与can’t后面的动词在非推测情况下的用法保持一致. He can’t be a teacher, is he? 他不是教师,是吗? She can’t have finished her homework, has she? 她一定没有完成家庭作业,是不是? (4)could可用于表示某事有可能发生或可能是事实。 Don’t eat it. It could be poisonous. 不要吃它,可能有毒。 The plane could be delayed by fog. 飞机可能会因为雾晚点。 (5)could还可以用于表示客气、委婉、礼貌的请求语气。 Excuse me, could you tell me the way to the bus station?
一、考点回顾 1、情态动词的基本用法 (1)can、be able to 和could ①can和be able to都表示能力,意思上没多大区别。 can只有现在和过去时,而be able to则有更多的形式。 但当成功地完成某一具体动作时,通常不用could而用was/were able to来表示。 这时was/were able to 相当于managed to,表示经过一番努力,终于能够完成某事。 ②can和could can和could都可以表示能力、技能、许可、建议或请求和可能性。但比较委婉客气地提出问题或陈述看法,一般用could,回答时则用can。 (2)may/might ①may/might表示可能,但may比might可能性大。 ②may/might表示“允许”,may用于现在时或将来时,might常用在间接引语中表过去时,但might也可用于现在时间,表示比较委婉的语气,回答用may。如: ③may / might 表示建议或请求,但might比may 更客气,意思更肯定而无过去时态的含义 用may表示推测一般不用于疑问句,在疑问句中通常用can来代替。 May I ... 问句常见的肯定回答和否定回答。 肯定回答 Yes, please.Certainly.Yes, of course.Sure.Go ahead, please. 否定回答 No, you can't. (最常见)No, you mustn't. (具有强烈禁止的意思) Please don't. You'd better not.I don't think you can.I'm sorry it's not allowed. (3)must ①must表示必须,应该,没有时态变化。 ②must表示肯定的推测。如: ③mustn’t 表示禁止做某事。如: (4)have to have to 表示“必须、不得不”,是由于某种外界(客观)原因而“必须”,“不得不”做某事,也可表示经常的或习惯性的事“必须”做。have to的否定形式表示不必。have to可用于多种时态中。如: (5)should / ought to ①should和ought to表示应当、应该,前者比后者语气轻。 ②should / ought to 表推测。 ③should / ought to的否定形式表示禁止之意。如: ④should可表示陈述意见,推出建议或请求;而ought to可以表示劝告之意。如: (6)will / would ①will 用于各种人称表示“意志”、“意愿”或“决心”等,否定式won’t + 动词。如: ②will用于疑问句中,常用在第二称时表示说话人向对方提出“请求”或“询问”如: ③will 表示习惯性的动作,有“总是”、“惯于”的含义。如: ④would 表示客气的请求、建议或意愿。如: ⑤would 表示过去反复发生的动作,总是会。 (7)need need 作“必要”讲,既可作情态动词,也可作实义动词。作实义动词时后面的动词不定式要
补充强调:推测的句型特点(对某一次的推测句型有两部分:语气和时态) (1)语气部分:(以下情态动词语气由强至弱) 肯定句:must、may might ( =could) 否定句:can,t ( =couldn 't )、mayn t> mightn 't 疑问句:can> could (语气更加委婉不确定 (2)时态部分: have done 表示对过去的推测 be doing 表示对正在进行的推测 be表示对现在的推测 语气部分写在前时态部分写在后,组合在一起就是推测 (-)情态动词表推测的三种句_ 能用于表推测的情态动词:must, can, could, will, would, may, might, should, ought to 1. 在肯定句中一般用must (一定),may (可能),might / could (也许,或许)。 (1)He must/may/might know the answer to this question? 他一定/可能/也许知道这个问题的答案。 (2)It is cold in the room? They must have turned off the heating? 屋里很冷,他们肯定把暖气关了。 2. 否定句中用can't / couldn 't (不可能),may not/might not (可能不)。 (1)It can J t/couldn 't be the headmaster? He has gone to America.这不可能是校长,他去美国了。 (2)He may not/might not know the scientist. 他也许不认识那位科学家。 3. 疑问句中用can /could (能..?)。 (1) Could he have finished the task? 他可能把任务完成了吗? (2) Can he be at home now? 他现在能在家吗? 注:以上三种句式中情态动词的语气按程度都是依次递减的。Might, could并非的过may, can 去式,而表示语气较为委婉或可能性较小。 (二)情态动词表推测的三种时丄
专项:情态动词 一考点:情态动词的用法和辨析,情态动词表示推测和可能,由情态动词引导的一般疑问句的回答。 二类型:1 只是情态动词:can, could, may, might, must 2 可做情态动词,可做实义动词:need, dare 3 可做情态动词,可做助动词:will, would, shall, should 4 特殊:have to, ought to, used to 三特征:1 有一定的词义,但不能单独作谓语,必须与行为动词和系动词连用构成谓语。 2 无人称和数的变化。(have to 除外) Eg: He has to stay here. 3 后接动词原形。 4 具有助动词作用,可构成否定,疑问或简短回答。 四用法: 1. can ①表示能力,“能,会”。Eg : Can you play basketball? ②表示怀疑,猜测,常用于否定句或疑问句。 Eg :Li hua can’t be in the classroom. ③表示请求,允许,多用于口语,译“可以”= may. Eg: you can go now. ④can 开头的疑问句,肯定句,否定句用can或can’t. 2.could①can 的过去式,表示过去的能力。 Eg :I could swim when I was seven years old. ②could 开头的疑问句,肯定和否定回答用could, couldn’t如果could 表示现在的委婉,用can 回答。 Eg: Could I have a drink? Yes, you can. 3.may①表示推测,“可能,也许”,用于肯定句。 Eg: He may come tomorrow. ②表示请求,“许可,可以”。Eg: May I borrow your book? 注:表示请求,许可时,主语为第一人称的一般疑问句,否定回
九年级英语表推测语气的讲解与练习 表推测时,英语中只使用must,may,might,may not和can't。这五个表达的语气依次递减: must:一定(语气肯定) may:也许(不很肯定) might:或许(比may语气更弱) may not:也许不(表否定) can't:一定不(must的反义) 推测现在的事情用must,may,might,may not和can't+do或be e.g.She must be at home now. The boy may play now. 推测过去的事情用must,may,might,may not和can't+have done e.g.She might have been ill yesterday. He must have hold the party. 情态动词must, can, could, may, might表推测的用法 情态动词中的must, can, could, may, might都表推测。其中must的可能性最大,can / could次之,may / might最小。具体用法如下: 1.must的用法 (1)表示推测“可能性”时,意思是“一定、准是”,语气较肯定,较有把握。He must be American. = It is certain that he is American. 他准是个美国人。 (2)must表推测只能用于肯定句。如果要表示“一定不、肯定不”的意思时,应用can’t,如询问某种可能时,应用can。 He must know my address. 他肯定知道我的地址。(一定) He can’t know my address. 他肯定不知道我的地址。(一定不) Can he know my address? 他知道我的地址吗?(询问可能性) (3)must表示推测时,可以推测现在/正在发生的动作/过去发生的动作。 He must have a car now. (现在)他一定有辆小汽车。 He must be doing his exercises in the classroom.(正在进行)他一定在教室里做练习。 He must have finished the work.(过去发生)他一定已完成了工作。 注:must表示推测时很少用于将来的情况。一般不用He must come tomorrow.可用It`s certain / I’m sure that he will come tomorrow. (4)在反意疑问句中,当附属部分含有表示推测意义的must时,疑问部分的助动词应与must后面的动词在非推测情况下的用法保持一致。 He must be a worker, isn’t he? (现在)他准是个工人,是吗? It must have rained last night, didn’t it? (过去)昨晚一定下雨了,是不是?
情态动词表推测用法总结及专项练习 1.can / could用于表推测的用法 (1) 从使用句型上看,can 通常只用于否定句或疑问句,一般不用于肯定句,而could 可用于肯定句、否定句和疑问句。两者没有时间上的差别,只是could 比 can 更委婉,更不确定。如: It can’t [couldn’t] be true. 那不可能是真的。 What can [could] they be doing? 他们会在干什么呢? We could go there this summer. 今年夏天我们可能要去那儿。 注:can 有时也用于肯定句中表示推测,主要用于表示理论上的可能性(即 从理论上看是可能的,但实际未必会发生),或表示“有时”之意。如: Even experienced teachers can make mistakes. 即使是有经验的教师也可 能出错。 She can be very unpleasant. 她有时很令人讨厌。 (2) 从时间关系看,对现在或将来情况作推测,后接动词原形;对正在进行 的情况作推测,后接 be doing 结构;对过去情况作推测,后接动词完成式。如: He could have gone home. 他可能已经回家了。 He can’t [couldn’t] have understood. 他不可能理解了。 Why does he know this? Can [Could] someone have told him about it? 他 怎么知道? 会是哪个人告诉他了吗? (3) “could+完成式”除表示对过去的推测外,还有以下重要用法: ①表示过去没有实现的可能性,常译为“本来可以”。如: I could have lent you the money.Why didn’t you ask me? 我本来可以借 这笔钱给你的。你为什么不向我提出? ②用来委婉地责备某人过去应该做某事而没有去做,常译为“本来应该”。如: You could have helped him. 你本来应该帮助他的。 ③表示“差点儿就要”。如: I could have died laughing. 我差点儿笑死了。
情态动词 定义: 情态动词是一种本身有一定的词义,但要与动词原形一起使用,给谓语动词增添情态色彩,表示说话人对有关行为或事物的态度和看法,认为其可能、应该或必要等。 情态动词后面加动词原形。 分类: 情态动词有四类: ①只做情态动词:must,can(could),may(might),ought to ②可做情态动词又可做实义动词:need,dare ③可做情态动词又可做助动词:shall(should),will(would) ④具有情态动词特征:have(had) to,used to 位置: 情态动词在句中放在谓语动词之前, 谓语动词前若有助动词,则在助动词之前,疑问句中, 情态动词 则在主语之前。 I can see you. Come here. 我能看见你,过来吧。 He must have been away. 他一定走了。 What can I do for you? 我能帮你吗? How dare you treat us like that! 你怎能那样对待我们! 特点: 情态动词无人称和数的变化, 情态动词后面跟的动词需用原形,否定式构成是在情态动词后面加"not"。个别情态动词有现在式和过去式两种形式, 过去式用来表达更加客气, 委婉的语气, 时态性不强, 可用于过去,现在或将来。情态动词属非及物动词,故没有被动语态。情态动词没有非谓语形式,即没有不定式,分词,等形式。 He could be here soon. 他很快就来。 We can't carry the heavy box. 我们搬不动那箱子。 I'm sorry I can't help you. 对不起,我帮不上你。 基本助动词与情态助动词最主要的区别之一是,基本助动词本身没有词义,而情态助动词则有自己的词义,能表示说话人对有关动作或状态的看法,或表示主观设想: What have you been doing since? (构成完成进行体,本身无词义) I am afraid I must be going. (一定要) You may have read some account of the matter. (或许已经) 除此之外,情态助动词还有如下词法和句法特征:
初中英语情态动词用法归纳 情态动词有具体的词义,但也同助动词一样,需要与其他词语一起构成句子的谓语,另外情态动词没有人称和数的变化,情态动词后必须跟动词原形。 考点一:can,may,must 等情态动词在陈述句中的用法: 1. can 的用法: (1).表示能力、许可、可能性。表示能力时一般译为“能、会”,即有种能力,尤其是生来具备的能力,此时may和must均不可代替它。如:She can swim fast, but lean 她能游.得很快,但我不能。I can see with my eyes我用眼睛看。 (2).表示许可,常在口语中。如:You can use my dictionary. 你可以用我的字典。 (3).表示推测,意为可能”常用于否定句和疑问句中,此时can'译为不可能”女口:Can the news be true?这个消息会是真的吗?一Can it be our teacher那个人有可能是我们老师吗?一No, it can' t be our teacher. He is on a visit to the GreatlW不可能。咱们老师正在游览长城呢。 【例题】一I think Miss Gao must be in the library. She said she would go ther—No. She __be there, I have just been there. A.can ' t B.mustn ' t C.needn ' t D.wouldn 't 【解析】根据下文我刚去过那儿”可知,应为不可能” can'表示推测[答案]A 2. could 的用法: (1).can的过去式,意为能、会”表示过去的能力。女口:He could write poems when he was 10. 他十岁时就会写诗。 (2). could在疑问句中,表示委婉的语气,此时could没有过去式的意思。如:Could you do me a favour?你能帮我个忙吗?一Could I use your pen?我能用一下你的钢笔吗?一Yes, you can可以。(注意回答) 3. may 的用法: (1) .表示请求、许可,比can正式,如:May I borrow your bike?我可以借你的自行车吗?You may go home now现在你可以回家了。 【例题】一______ I borrow your MP3?- Sure . Here you are. A. May B.Should C.Must D. Would 【解析】在此处表示请求,意为做……可以吗”答案:A (2) .表示推测,谈论可能性,意为“可能,或许”,一般用于肯定句中。如:It may rain tomorrow .
情态动词表推测的用法 一、must表示推测的用法 must表示推测时,只用于肯定句,表示很大的可能性,意为“一定,准是,必然会”。其否定形式是can’t/couldn’t (不可能)。例如: 1. You haven’t eaten anything since this morning; you must be hungry. 2. That can’t be Mary —she’s in hospital. 二、can/could表示推测的用法 1. can表示推测时,多用于肯定句和疑问句。当用于肯定句时,指“有时可能会”,是理论上的可能,其时间意义宽泛不具体。例如: Even experienced teachers can make mistakes. 2. could表示推测时,既可以用于肯定句,又可以用于疑问句。例如: My book has disappeared. Who could have taken it? 3. can’t/couldn’t表示推测时,用于否定句,是语气最强的否定推测,意为“不可能,一定不(是)”。例如: He can’t/couldn’t have see n her there. 【即学即练】 一、用表示推测的情态动词must, could, , can的适当形式填空。 1. — Hi, Tom. Any idea where Jane is? — She be in the classroom. I saw her there just now. 2. — I hear they went skiing in the mountains last winter. — It be true because there was little snow there. 3. Accidents happen on such rainy days. 二、翻译下列句子,注意情态动词的推测用法和情态动词后动词的形式。 —那个人一定是布朗先生。—不可能是他,他去纽约了。 【反义疑问句】又叫附加疑问句。它表示提问人的看法,没有把握,需要对方证实。反义疑问句由两部分组成:前一部分是一个陈述句,后一部分是一个简短的疑问句,两部分的人称时态应保持一致。如:She was ill yesterday, wasn’t she? They don’t work hard, do they?
第五单元:情态动词表示推测的用法 一,对不同时态的推测 情态动词+do sth表示对现在事情的推测。 情态动词+be doing sth表示对正在发生的事情的推测。 情态动词+have done sth表示对过去或已完成的事情的推测。如: 1、They must be in the classroom now. 他们现在一定在教室里。 2、The light in the teachers’ office is still on. Miss Gao must be working. 老师办公室的灯还亮着,高老师肯定正在工作着。 3、Mike may (might) hurt in the traffic accident. 迈克可能在这次交通事故中受了伤。 4、He must have finished his homework yesterday. 他昨天肯定完成了作业。 二、情态动词表示推测,在不同句型中的用法: 1、在肯定句中,可使用的情态动词有:must, could, may, might,等;其肯定程度逐渐减弱,must表示一种很有把握的推测,意为“一定,肯定”,could/may/might表示一种不太有把握的推测,may意为“可能”,might意为“或许”could意为“可能”,could/may/might在表示推测时,无时态区别,只表示语气差异。如: (1)You have worked all this week .You must be tired. 你辛苦工作了一周,一定累坏了。 (2)Will you please answer the phone? It could /may/might be your mother. 请接一下电话好吗?可能是你的母亲打来的。 (3)According to the radio ,it may/might/could rain this evening. 根据广播,今晚可能下雨。 2、在否定句中使用can’t和may not/might not. can’t表示很有把握的否定推测,意为“不可能”;may not/ might not 表示不太有把握的否定推测,意为“可能不”如:(1)She can’t be at school .It’s Sunday today. 她不可能在学校,今天是星期天。 (2)She may not be there today. 今天她可能不在那儿。 (3)I think he might not come. 我认为他可能不来了。 3、在疑问中,一般只用can或could,意为“可能”如: (1)Who can it be at the door ?Can it be Tom? 门口会是谁呢?会不会是汤姆呢? (2)Where could it be? 它可能在哪儿呢? 三、在表示推测时,反意疑问句的两种情况; 1、对现在进行推测时,反意疑问句中的动词用一般现在时。如: (1)He must be good at English, isn’t he? (2)You might be watching TV at home ,aren’t you? 2、对过去进行推测时,若有明确的、表示过去的时间状语,反意疑问句中的动词用过去式;若没有明确的、表示过去的时间状语,反意疑问句中的动词用现在完成时。如:(1)It must have rained last night , didn’t it? (2)You might have been to the Great Wall, haven’t you? 附:belong to的用法 belong to 是动词+介词构成的短语,它表示所属关系,注意其用法:
情态动词can的基本用法: 情态动词can有一定的词义,但不能独立存在,它必须与动词原形一起构成谓语。情态动词can没有人称和数的变化。其具体用法如下: 1. 表示"能、会",指脑力或体力方面的"能力"。例如: I can speak En glish. 我会讲英语。 Jim can swim but I can't. 吉姆会游泳,但我不会。 2. 表示"可能",常用于否定句或疑问句中,指某种可能性,此时can 't译为“不可能”。例如: Han Mei ca n't be in the classroom. 韩梅不可能在教室里。 Can he come here today, please? 请问他今天能到这里来吗? 3. 表示"可以",常用于口语中,指许可或请求做某事,可以代替 may。例如: Can I have a cup of tea, please? 请问我可以喝一杯茶吗? You can go out. 你可以出去了。 补充:can的过去式could,意为“能、会”,表示过去的能力 女口: He could write poems when he was 10. 他十岁时就会写诗。 could在疑问句中,表示委婉的语气,此时could没有过去式的意思。 如:Could you do me a favour? 你能帮我个忙吗?一 Could I use your pen?我能用一下你的钢笔吗?一Yes, you can.可以。(注意回答) 情态动词can的基本句型:
1. 肯定句型为:主语+can+动词原形+其它。例如: They can play basketball. 他们能打篮球。 She can dance.她会跳舞。 You can go to watch TV. 你可以去看电视了。 2. ........................... 否定句型为:主语+can not(can't/cannot)+ 动词原形+其它。表示"某人不能(不会。不可能)做其中can't是can not的缩略式,英国多写成cannot。例如: You cann ot pass the ball like this. 你不能像这样传球。 I ca n't ride a motorbike. 我不会骑摩托车。 3. 疑问句句型分为:一般疑问句句型和特殊疑问句句型两种类型。 ⑴一般疑问句句型为:Can+主语+动词原形+其它。表示"某人会(能。可以)做吗?",用于口语时,常表示请求或许可。其肯定答语用""Yes,主语+can."作答; 否定答语用"No,主语+can't."作答。注意答语中做主语的人称代词,应根据问句中的主语作相应的变化。其变化规则为:第一人称问,则第二人称答;第二人称问,则第一人称答;第三人称问,第三人称答。例如: ①-Can you sing an En glish song for us? 你可以为我们大家唱一首英语歌吗?
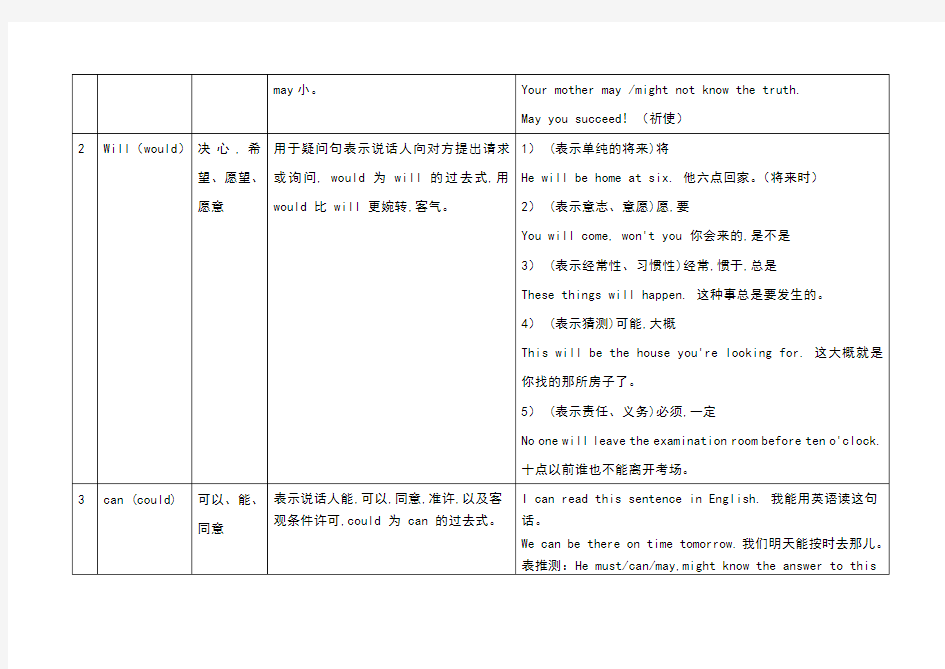
情态动词的基本用法归纳 情态动词有can (could), may (might), must, have to, shall (should, will (would), dare (dared), need (needed), ought to等。情态动词无人称和数的变化;不能单独使用,必须与其后的动词原形构成谓语。 一、can, could 1) 表示能力(体力、知识、技能)。 Can you lift this heavy box?(体力) Mary can speak three languages.(知识) Can you skate?(技能) 此时可用be able to代替。Can只有一般现在时和一般过去式;而be able to则有更多的时态。 I’ll not be able to come this afternoon. 当表示“经过努力才得以做成功某事”时应用be able to,不能用Can。如: He was able to go to the party yesterday evening in spite of the heavy rain. 2) 表示请求和允许。 -----Can I go now? ----- Yes, you can. / No, you can’t. 此时可与may互换。在疑问句中还可用could,might代替,不是过去式,只是语气更委婉,不能用于肯定句和答语中。 ---- Could I come to see you tomorrow? ---- Yes, you can. ( No, I’m afraid not. ) 3) 表示客观可能性(客观原因形成的能力)。 T hey’ve changed the timetable, so we can go by bus instead. This hall can hold 500 people at least. 4) 表示推测(惊讶、怀疑、不相信的态度),用于疑问句、否定句和感叹句中。 Can this be true? This can’t be done by him. How can this be true? 二、may, might 1) 表示请求和允许。might比may语气更委婉,而不是过去式。否定回答时可用can’t 或mustn’t,表示“不可以,禁止”。 ----Might/ May I smoke in this room? ---- No, you mustn’t. ---- May/Might I take this book out of the room? ---- Yes, you can. (No, you can’t / mustn’t. ) 用May I...?征徇对方许可时比较正式和客气,而用Can I...?在口语中更常见。 2)用于祈使句,表示祝愿。 May you succeed! 3) 表示推测、可能性(不用于疑问句)。 might不是过去式,它所表示的可能性比may小。 1.He may /might be very busy now. 2.Your mother may /might not know the truth.