情态动词用法总结及相应练习
- 格式:doc
- 大小:87.00 KB
- 文档页数:10

情态动词一、知识梳理/提炼1. can和could的用法表示能力或客观可能性,还可以表示请求和允许。
如:Can you finish this work tonight?Man cannot live without air.— Can I go now?— Yes, you can.注意:①could也可表示请求,语气委婉,主要用于疑问句,不可用于肯定句,答语应用can (即could不能用于现在时态的简略答语中)。
如:Could I come to see you tomorrow?Yes, you can。
(否定答语可用No, I'm afraid not。
)②can表示能力时,还可用be able to代替。
如:I'll not be able to come this afternoon。
2。
may和might的用法1)表示许可.表示请求、允许时,might比may的语气更委婉一些,否定回答时要用mustn't表示“不可以"、“禁止"、“阻止”之意.如:You may drive the car.— Might I use your pen? — No,you can’t/ mustn't. Yes, you can/may. 用May I .。
. 征询对方许可在文体上比较正式,在口气上比较客气。
在日常口语中,用CanI ... 征询对方意见在现代口语中更为常见.2) 用于祈使句中表示祝愿.如:祝你成功! May you succeed!3)表示推测、可能(疑问句不能用于此意)。
他现在可能很忙. He may be very busy now。
3。
must和have to的用法1) 表示必须、必要。
如:You must come in time.回答must引出的问句时,如果是否定的回答,不能用mustn't,而要用needn't或don't have to。

情态动词用法总结及相应练习在英语中,情态动词属于助动词。
除了作简略回答外,它们一般不能单独使用,它们必须与动词原形一起使用构成句子的谓语。
不同的情态动词会有不同的意义和用法。
有时,同一个情态动词在不同的语境中也会产生不同的含义。
下面我们将讨论这些情态动词的用法。
情态动词的推测性用法和非推测性用法情态动词一般有两种用法:推测性用法(epistemic use)和非推测性用法(non-epistemic use)。
推测性用法是指做出推测,预测事物发生的可能性;非推测性用法则指情态动词本身的基本含义,如XXX表示能力,may表示许可,must和should表示必须和义务,need 表示需要等。
例如:I can swim。
(非推测性用法)This can be true。
(推测性用法)You may go now。
(非推测性用法)He may be ill now。
(推测性用法)You must finish it before lunch time。
(非猜测性用法)He must be at home for he never goes out at dinner time。
(推测性用法)我们把英语中的9大神态动词按其猜测性和非猜测性用法列表如下:情态动词非推测性用法推测性用法can/could能力/许可(ability/n)可能(possibility)may/might许可(n)可能(possibility)will/would意愿(n)预言性(predictability)XXX责任和义务(n)应该是(logical necessity)must责任和任务(n)一定,一定(logical necessity)神态动词非猜测性用法的申明1.may和might透露表现允许may能够与分歧的人称搭配,透露表现“答应、允许”。
比方:May I know your name?You may be the first to leave if you are in a hurry。

英语情态动词用法总结(完整)一、单项选择情态动词1.--- Difficulties always go with me!--- Cheer up! If God closes door in front of you, there be a window opened for you. A.must B.wouldC.could D.can【答案】A【解析】【详解】考查情态动词辨析。
句意:——困难总是伴随着我!——高兴点! 如果上帝在你面前关上了门,一定有一扇窗户为你打开。
A. must必须;B. would将要;C. could能,会;D. can能,会。
must表示对现在的状态推测时,意为“一定”,表示可能性很大的推测。
符合语境。
故选A。
【点睛】1) must用在肯定句中表示较有把握的推测,意为"一定"。
2) must表对现在的状态或现在正发生的事情的推测时, must 后面通常接系动词be 的原形或行为动词的进行式。
3) must 表示对已发生的事情的推测时,must 要接完成式。
4) must表示对过去某时正发生的事情的推测,must 后面要接完成进行式。
5) 否定推测用can't。
本句中的。
must表示对现在的状态推测时,意为一定,表示可能性很大的推测。
符合第2点用法。
2.Paul did a great job in the speech contest. He many times last week.A.need have practised B.might practiseC.must have practised D.could practise【答案】C【解析】【详解】考查情态动词。
句意:保罗在演讲比赛中表现得很好。
他上星期一定练习了很多次。
must have done是对过去发生的动作最有把握的猜测,意思是“一定”。
故C选项正确。
3.He is a bad-tempered fellow, but he ________ be quite charming when he wishes.A.shall B.shouldC.can D.must【答案】C【解析】【详解】考查情态动词辨析。
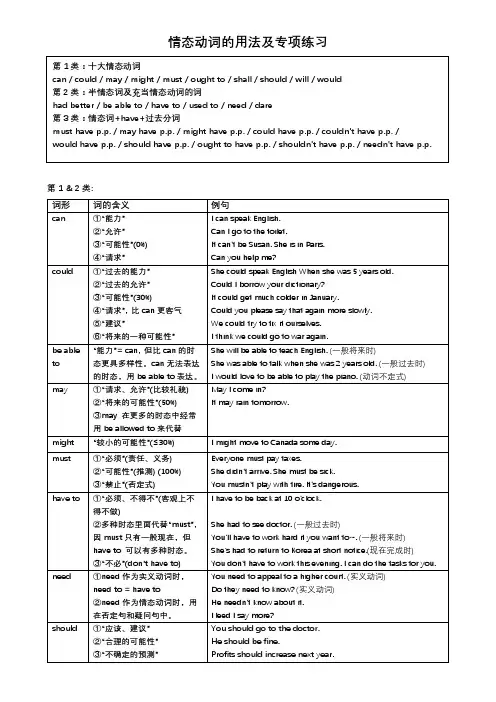
情态动词的用法及专项练习第1 & 2类:第3类1.could have p.p.①指过去某事有可能发生, 但并未.真的..发生。
They could have won the race, but they didn't try hard enough.He could have studied harder, but he was too lazy and that's why he failed the exam.②指过去有能力做某事, 但并未真的...做过。
I could have stayed up late, but I decided to go to bed early.Julie could have bought the book, but she borrowed it from the library instead.③对过去的发生事情做出一种猜测,但实际上并不知道真假。
仅仅是做一种观点上的表达。
He could have got stuck in traffic.He could have forgotten that we were meeting today.He could have overslept.2. may / might have p.p.(用法与could have p.p.第③点相同)对过去的发生事情做出一种猜测,但实际上并不知道真假。
仅仅是做一种观点上的表达。
He might have got stuck in traffic.He might have forgotten that we were meeting today.He might have overslept.3. couldn't have p.p.渴望、期望做某事, 但由于外部原因不可能做成, 即便是很想做。
是一种虚拟语气。
I couldn't have arrived any earlier. There was a terrible traffic jam (= it was impossible for me tohave arrived any earlier).He couldn't have passed the exam, even if he had studied harder. It's a really, really difficult exam.4. should / ought to have p.p.有一个好主意,该做而没有做。

情态动词的用法(附练习及参考答案)情态动词情态动词有can (could), may (might), must, have to, shall (should, will (would), dare (dared), need (needed), ought to 等。
情态动词无人称和数的变化;不能单独使用,必须与其后的动词原形构成谓语。
一、情态动词的基本句型肯定句:主语+情态动词+动词原形+......You can sleep here.否定句:主语+情态动词+not+动词原形+......You can’t sleep here.疑问句:情态动词+主语+动词原形+......Can I sleep here.二、情态动词的意义must“必须”; can/could“能,会”; may/might “可以”; should“应该”; would“愿,要”; have to“不得不”; need“需要”can 表示能力,意为―能会,表示推测,意为―可能,常用于否定句和疑问句中表示请求,允许,意为―可以could 是can 的过去式,意为―能、会,表示过去的能力在疑问句中表示委婉请求may 表示请求、许可,意为―可以表示推测,常用于肯定句中,意为―可能、也许might 是may的过去式,表推测,常用于肯定句中,意为―可能、也许must 表示主观看法,意为―必须、应该,表有把握的推测,用语肯定句Need \表示需要、必须,主要用于否定句和疑问句中dare 表示敢于,主要用于否定句和疑问句中should 意为―应该,表示要求和命令表示劝告、建议had better 意为―最好,表示建议used to意为―过去常常,表示过去的动作、行为考点一情态动词情态动词有具体的词义,但也同助动词一样,需要与其他词语一起构成句子的谓语,另外情态动词没哟人称和数的变化,情态动词后必须跟动词原形。
三、情态动词的基本用法1. can 的用法(1)表示能力、许可、可能性。
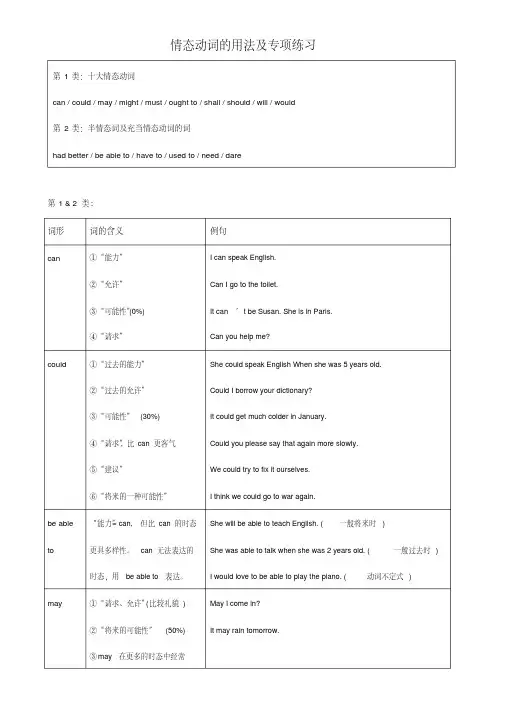
情态动词的用法及专项练习第1 & 2类:词形词的含义例句can ①“能力”②“允许”③“可能性”(0%)④“请求”I can speak English.Can I go to the toilet.It can’t be Susan. She is in Paris. Can you help me?could ①“过去的能力”②“过去的允许”③“可能性”(30%)④“请求”, 比can更客气⑤“建议”⑥“将来的一种可能性”She could speak English When she was 5 years old. Could I borrow your dictionary?It could get much colder in January.Could you please say that again more slowly.We could try to fix it ourselves.I think we could go to war again.be able to “能力”= can, 但比can的时态更具多样性。
can无法表达的时态,用be able to表达。
She will be able to teach English. (一般将来时)She was able to talk when she was 2 years old. (一般过去时)I would love to be able to play the piano. (动词不定式)may ①“请求、允许”(比较礼貌)②“将来的可能性”(50%)③may 在更多的时态中经常May I come in?It may rain tomorrow.第1类:十大情态动词can / could / may / might / must / ought to / shall / should / will / would 第2类:半情态词及充当情态动词的词had better / be able to / have to / used to / need / dare用be allowed to来代替might “较小的可能性”(≤30%)I might move to Canada some day.must ①“必须”(责任、义务)②“可能性”(推测) (100%)③“禁止”(否定式) Everyone must pay taxes.She didn’t arrive. She must be sick.You mustn’t p l ay with fire. It’s dangerous.have to ①“必须、不得不”(客观上不得不做)②多种时态里面代替“must”,因must只有一般现在,但have to 可以有多种时态。

情态动词详解、典型例题及模拟试题(含答案)1 . must、can、could、may、might、will / would 、shall / should 、need、dare △must的肯定式表示必须”否定式must n't表示禁止,严禁"的意思。
如:You must come here .You mustn' t take the book away from the library .同义词为have to do ,表示不得不”一般表示客观原因造成的不得不、被迫”女口:My car was broken , so I had to walk home .△can的肯定式表示能、会”可以”否定式ca n't表示不能,不会,不可以”。
女口:He can swim . I can ' t swim . You can go now同义词为be able to do ,也表示能,会”一般表示经过努力才具有的能力与can 的区别,主要是它可有时态。
如:He was able to cou nt to 10 , 000 whe n he was 3 .He will be able to walk n ext month△may表示可以”否定式may not 表示不可以"表示经某人允许。
女口:You may go home now . You may not go home now△will表示将要,打算"用于将来时,否定式will not / won '表示将不”不打算”。
女口:He will come here next week . He won' t come home .△shall用于第一人称后表示将要”打算”否定式shall not表示将不,不打算”。
女口:We shall go home together . I shall go there first .用于其他人称后表示必须,得”与must相近,但表示别人认为主语应该,得”女口:He shall go and see his aunt . Shall he open the door ?△need表示需要”否定式need n't表示不需要,不用”女口:He need do some washing . You needn' t stay here any more .△dare表示敢于.... "否定式dare not 表示不敢....... ”女口:He dare say no to wrong things . He dare not go home alone at night .注:need与dare除情态动词用法外还有实意动词用法,且意义不变。

情态动词情态动词有can (could), may (might), must, have to, shall (should, will (would), dare (dared), need (needed), ought to等。
情态动词无人称和数的变化;不能单独使用,必须与其后的动词原形构成谓语。
一、can, could1) 表示能力(体力、知识、技能)。
如:Can you lift this heavy box? (体力)Mary can speak three languages.(知识)Can you skate?(技能)此时可用be able to代替。
Can只有一般现在式和一般过去式;而be able to则有更多的时态。
如:I’ll not be able to come this afternoon.当表示“经过努力才得以做成功某事”时应用be able to,不能用Can。
如:He was able to go to the party yesterday evening in spite of the heavy rain.2) 表示请求和允许。
-----Can I go now?----- Yes, you can. / No, you can’t.此时可与may互换。
在疑问句中还可用could, might代替,不是过去式,只是语气更委婉,不能用于肯定句和答语中。
---- Could I come to see you tomorrow?---- Yes, you can. ( No, I’m afraid not. )3) 表示客观可能性(客观原因形成的能力)。
They’ve changed the ti metable, so we can go by bus instead.This hall can hold 500 people at least.4) 表示推测(惊讶、怀疑、不相信的态度),用于疑问句、否定句和感叹句中。

情态动词的用法总结及例句解析情态动词是英语中常用的一类动词,用来表示说话人的态度、情绪、推测、能力等。
它在句子中通常与动词原形搭配使用,起到强调、修饰或者推测的作用。
本文将对情态动词的用法进行总结,并通过例句解析来帮助读者更好地理解。
一、情态动词的基本用法情态动词通常没有人称和数的变化,也没有时态的变化,后面接动词原形。
有以下几种情态动词:can,could,may,might,shall,should,will,would,must,ought to等。
1. 表示能力或可能性- I can swim.(我会游泳。
)- He may come to the party.(他可能会来参加派对。
)2. 表示允许或禁止- You may go now.(你现在可以走了。
)- You must not smoke here.(你不能在这里抽烟。
)3. 表示建议或命令- You should take a break.(你应该休息一下。
)- You ought to apologize to him.(你应该向他道歉。
)4. 表示推测或猜测- He could be there.(他可能在那里。
)- It might rain tomorrow.(明天可能会下雨。
)5. 表示义务或必须- We must finish the project on time.(我们必须按时完成这个项目。
)- You ought to help him.(你应该帮助他。
)二、情态动词的细分用法除了以上的基本用法外,情态动词还有一些特殊的用法,需要注意其具体含义和用法。
1. can 和 could- 表示能力和技能:I can play the piano.(我会弹钢琴。
)- 表示请求或许可:Can I use your computer?(我可以用你的电脑吗?)- could 还可以用来表示过去的能力或许可:When I was young, I could run very fast.(小时候,我跑得很快。

情态动词表推测用法总结(一)情态动词表推测的三种句式能用于表推测的情态动词:must, can, could, will, would, may, might, should, ought to1.在肯定句中一般用must (一定),may(可能),might / could(也许,或许)。
(1)He must/may/might know the answer to this question? 他一定/可能/也许知道这个问题的答案。
(2)It is cold in the room. They must have turned off the heating. 屋里很冷,他们肯定把暖气关了。
2.否定句中用can’t /couldn’t(不可能), may not/might not(可能不)。
(1)It can’t/couldn’t be the headmaster. He has gone to America. 这不可能是校长,他去美国了。
(2)He may not/might not know the scientist. 他也许不认识那位科学家。
3.疑问句中用can/could (能……?)。
(1)Could he have finished the task? 他可能把任务完成了吗?(2)Can he be at home now? 他现在能在家吗?注:以上三种句式中情态动词的语气按程度都是依次递减的。
might, could 并非may, can 的过去式,而表示语气较为委婉或可能性较小。
Couldn’t 比can’t 语气弱一些。
(二)情态动词表推测的三种时态1.对将来情况的推测,用“情态动词+ 动词原形”。
(1)She must / may / might / could arrive before 5. 5:00 前她一定/可能/也许到。
(2)She must/may/might/could walk miles and miles among the hills without meeting anyone.她一定/可能/也许会在ft里一连走好几英里而遇不到一个人。

一、情态动词的基本用法1.can(1)(表示能力)能……;会…… She can drive,but she can’t ride a bicycle.【注】could表示“原来具备某种能力,现在没有这种能力了”,但was/were able to则表示过去成功地做成了某事。
I could swim all the way across the lake,but I can’t now. 我原来能游过这个湖,但现在不能了。
The fire spread through the hotel very quickly but everyone was able to get out.大火很快蔓延了整个旅馆,但全体人员都脱离了危险。
(2)(表示可能、许可)能够……;可以……“Can I use your telephone?”“Yes,of course you can.”You can’t park your car in this street.【注】can可作“有时候会……”解,意思是平时或大部分时间不是这样子,只是偶尔发生的事情。
如:Jogging can be harmful to the health. 慢跑有时候会对身体健康有害。
(3)(表温和的命令)请做……,得……I’ll do the cooking,and you can do the washing. 我来做饭,请你去洗衣服。
(4)(用于疑问句中,表请求、提议)能不能……;要不要……Can you give me a lift to the station?Can’t you lend me ten dollars?请你借给我10美元吧?(5)(用于疑问句中,表惊讶、怀疑等)“(到底)可能有这样的事吗?”Can it be that it was I,not he,who was mistaken?难道错的会是我,而不是他吗?(6)构成下列特殊句式:①can not/can never...too...或cannot...enough “无论怎么……也不过分;越……越好;非常……”。
初中情态动词的用法猜测及练习(经典)情态动词是英语中的一类特殊动词,它具有一些特殊的用法和含义。
初中阶段是研究情态动词的关键时期,通过了解情态动词的用法,学生能够更好地运用它们来表达意愿、建议、能力、推测等。
本文档旨在介绍初中情态动词的用法,并提供一些经典的练题,帮助学生巩固所学的知识。
一、情态动词的基本用法- 情态动词的用法1:情态动词可以用于表示能力和技能,例如:情态动词的用法1:情态动词可以用于表示能力和技能,例如:- can: 能够、会- could: 可以、会- may: 可能、可以- might: 可能、可以- 情态动词的用法2:情态动词可以用于表示推测和猜测,例如:情态动词的用法2:情态动词可以用于表示推测和猜测,例如:- must: 必须、一定- should: 应该、应当- ought to: 应该、应当- might: 可能、也许- 情态动词的用法3:情态动词可以用于表示意愿和建议,例如:情态动词的用法3:情态动词可以用于表示意愿和建议,例如:- would: 愿意、将要- should: 应该、应当- ought to: 应该、应当二、练题以下是一些经典的情态动词练题,供学生参考和练:1. 选择合适的情态动词填空:- I __________ go to the party with you, but I have to study for the test tomorrow.- He __________ be a doctor when he grows up.2. 根据语境选择合适的情态动词填空:- A: Can you help me with this math problem?B: Of course! I __________ help you.- A: It's late. We should go home now.B: You're right. We __________ leave.3. 根据句意写出合适的情态动词:- You __________ call your parents and tell them you'll be home late.- I'm not sure, but he __________ be at the library.以上是一些情态动词的用法及练题,学生可以通过不断的练来加深对情态动词的理解和运用。
大学英语情态动词完整详细版附练习题情态动词概述情态动词是英语中一类特殊的动词,用于表达说话人的意愿、能力、推测、建议、许可等。
常见的情态动词有 "can"、"could"、"may"、"might"、"shall"、"should"、"will"、"would"、"must" 等。
以下是对每个情态动词的详细解释和用法:1. Can 表示能力、许可或请求。
例如:Can表示能力、许可或请求。
例如:- I can swim.(我会游泳。
)- Can I use your pen?(我可以用你的钢笔吗?)2. Could 过去式形式的 "can",表示能力、请求或礼貌的请求。
例如:Could过去式形式的"can",表示能力、请求或礼貌的请求。
例如:- I could ride a bike when I was five.(我五岁时就会骑自行车了。
)- Could you please open the window?(可以请你打开窗户吗?)3. May 表示许可或推测。
例如:May表示许可或推测。
例如:- May I go to the bathroom?(我可以去洗手间吗?)- It may rain tomorrow.(明天可能会下雨。
)4. Might 过去式形式的"may",表示推测或可能性较小。
例如:Might过去式形式的 "may",表示推测或可能性较小。
例如:- I thought it might be too late.(我想可能太晚了。
)5. Shall 表示将来时态的意愿、建议或命令。
例如:Shall表示将来时态的意愿、建议或命令。
初中英语情态动词详细用法归纳(含练习及答案)情态动词有具体的词义, 但也同助动词一样, 需要与其他词语一起构成句子的谓语, 另外情态动词没有人称和数的变化, 情态动词后必须跟动词原形。
1.ca.的用法:(1).表示能力、许可、可能性.表示能力时一般译为“能、会”.即有种能力, 尤其是生来具备的能力.如:Sh.ca.swi.fast.bu..can’.. 她能游得很快, 但我不能。
.ca.se.wit.m.eyes.我用眼睛看。
could是can的过去式。
表示过去的能力.b.abl.t.d.sth.常常指经过努力,花费了时间和劳力之后才能做到某事。
is/am/ar.abl.t.d.sthwas/were able to do sth.(2).表示许可, 常在口语中。
如: .m.dictionary..你可以用我的字典。
(3).表示推测, 可能性, 意为“可能”.常用于否定句和疑问句中.此时can’.译为.不可能”.如:Ca.th.new.b.true.这个消息会是真的吗?—Ca.i.b.ou.teacher?那个人有可能是我们老师吗?—No.i.can’.b.ou.teacher.H.i.o..visi.t.th.Grea.Wall.不可能。
咱们老师正在游览长城呢。
【例题】—.thin.Mis.Ga.mus.b.i.th.library.Sh.sai.sh.woul.g.there.—No.Sh.__b.there..hav.jus.bee.there..A.can’.B.mustn’.C.needn’.D.wouldn’t【解析】根据下文“我刚去过那儿”可知, 应为“不可能”, can’t 表示推测[答案] Acould的用法:(1).can的过去式, 意为.能.会”, 表示过去的能力。
如: H.coul.writ.poem.whe.h.wa.10. 他十岁时就会写诗。
(2).could在疑问句中, 表示委婉的语气, 此.coul.没有过去式的意思。
情态动词常见的情态动词有:can 能may 可以will,would (表意愿)need 需要dare 敢must 必须have to 不得不shall,should 应该(表义务)ought to 应该1.can,could 的用法1.1表能力,有“能”、“会”、“能够”的意思例如:Can you drive a car? 你会开车吗?-----Yes, I can. 我会。
-----No, I can't. 我不会。
1.2表允许,在口语中代替may,有“可以”的意思例如:Can I use your bike?我可以用你的自行车吗?1.3表示可能性,常用于否定句和疑问句例如:Can it be true?那会是真的吗?Today is Sunday. He can't be at school.今天是星期天。
他不可能在学校里。
1.4过去式could表示的语气更加委婉、客气例如:Could I come to see you tomorrow?明天我可以来见你吗?1.5 can 和be able to 的比较1) can 只有一般现在时和一般过去时两种时态(could),其他时态要用be able to的形式例如:I haven't been able to get in touch with her.我一直没能和她联系上。
2) 通常can 和be able to 可以互换例如:He will come if he can.如果可能的话,他一定会来。
2.may,might的用法2.1表示许可或征求对方的许可,有“可以”的意思。
例如:You may go now.你可以走了。
May I use your computer?我用一下你的电脑可以吗?2.2回答以may开头的疑问句有如下表达法:例如:May I smoke here? 我可以在这儿抽烟吗?-----Yes, you may.-----Yes, please.------No, you can't.------No, you mustn't.------No, you'd better not.2.3表示猜测,通常只用于陈述句例如:You may be right.你可能是对的。
1 / 11情态动词的用法一.分类:1.只做情态动词:can(could)、may(might)、must....后接动词原形。
2.可做情态动词又可做实义动词。
如:need,dare3.具有情态动词特征:have(has,had)to,used to(过去常常)。
二.情态动词的用法:情态动词后接动词原形1.must的用法1)must意为“必须;应该;一定”。
表示说话人的主观意志,表示必须要做的。
如:We must finish reading the book in two weeks.我们必须在两周内看完这本书。
2)表示说话人对事物的推测,语气比may肯定,只用于肯定句中。
Must be译为“一定是”如:Mr. Liu must be in the office.刘老师一定在办公室。
3)用must提问时,如果是否定回答,多用needn't或don't have to,表示“不必,没必要”,而mustn't表示“绝对不行,不可以,禁止”的意思。
如:---Must I finish my homework now?---Yes,you must.---No,you needn't/don't have to2 / 114)have to意为“必须;不得不”,有人称、时态和数的变化,后跟动词原形,表示客观需要。
如:When I was your age,I already had to work. 2.can的用法:1)can意为“能;会;可以”。
表示能力,其否定式是cannot=can't。
如:She can sing.她会唱歌。
2)表示请求许可。
Can I ... ?意思是“我可以……吗?”,较口语化。
3)can的过去式是could,如:Lucy could swim at the age of five.露西五岁时就会游泳了。
could也可表示较can更为委婉的语气。
表推测的情态动词用法小结英语中有不少情态动词都可以表示推测,其语气有强有弱,表示的可能性有大有小,现将它们的用法归纳如下:1. 接近100%的可能这当然只有must才具有这么高的可能性,它的意思是“一定”“肯定”,所作出的推测几乎接近事实。
如:That hat must be Tom’s.那帽子一定是汤姆的。
He must be coming by bus. 他一定是乘公共汽车来。
2. 很有可能表示可能性较大的情态动词主要有may, should, ought to,它们大致相当于汉语的“可能”“应该”“按理会”。
如:She should [ought to] be here soon. 她应该很快就到。
We may be buying a new house. 我们可能要买一座新房子。
3. 一般性的可能在所有表示推测的情态动词中,might和could所表示的可能性最小,由于它们的语气较委婉,较不确定,所以往往相当于汉语的“可能”“也许”“说不定”等。
如:He might be waiting for you. 他可能在等你。
We could all be millionaires one day. 我们有一天可能都成为百万富翁。
4. 理论上的可能性表示理论上的可能通常是用can,且可以用于肯定句中。
如:Food poisoning can cause death. 食物中毒可导致死亡。
This kind of thing can happen every now and then. 这种事情是随时可能发生的。
所谓理论上的可能性,就是指仅从理论上去考虑其可能性,至于实际情况如何,则不作考虑,比如说“食物中毒可导致死亡”,这只是理论上的一种推断,至于某人某次食物中毒了,他是否会死亡,则不在考虑之列,所以说,这种推测是非常“宏观”的!5. 表示对过去情况作推测如果表示对已经发生的情况作推测,不能用“情态动词+动词原形”,也不能用“情态动词的过去式+动词原形”,而是要使用“情态动词+动词完成式”。
Modal Verbs在英语中,情态动词属于助动词。
除了作简略回答外,它们一般不能单独使用,它们必须与动词原形一起使用构成句子的谓语。
不同的情态动词会有不同的意义和用法。
有时,同一个情态动词在不同的语境中也会产生不同的含义。
下面我们将讨论这些情态动词的用法。
情态动词的推测性用法和非推测性用法情态动词一般有两种用法:推测性用法(epistemic use) 和非推测性用法(non-epistemic use) 。
推测性用法是指做出推测,预测事物发生的可能性; 非推测性用法则指情态动词本身的基本含义,如can表示能力,may 表示许可,must和should表示必须和义务,need表示需要等。
例如:I can swim. (非推测性用法)This can be true. (推测性用法)You may go now. (非推测性用法)He may be ill now. (推测性用法)You must finish it before lunch time. (非推测性用法)He must be at home for he never goes out at dinner time. (推测性用法)我们把英语中的9大情态动词按其推测性和非推测性用法列表如下:情态动词非推测性用法的说明1. may和might表示允许may可以与不同的人称搭配,表示“许可、允许”。
例如:May I know your name?You may be the first to leave if you are in a hurry. (我允许你第一个离开。
)You may keep the book for two months. (我允许你借。
)In certain circumstances a police officer may ask a driver to take a breath test.may用在疑问句中,经常表示“允许、许可”的意思。
例如:May I know your name?May I come in?might可以用来表示过去时态,也可以表示委婉语气。
例如:She said that he might take her dictionary. (may的过去式)Might I have a word with you? (委婉用法)I wonder if I might have more salad. (委婉用法)但在回答中,我们一般用may加强肯定的语气,而不用might.例如:Yes, of course you may.may not可用来表示“禁止”或“不许”,因语气较强,所以不用might not.例如:Students may not stay out of the dormitory after midnight without written permission.must not也可以表示“禁止”,而且语气比may not更强,强调上级对下级的不允许。
另外,may/might as well也是一个常用的词组,后接动词原形,意思是“不妨,最好”相当于had better.例如:It's very late. We might as well go home.2. can和could1) 表示能力can,could和be able to都可以表示能力。
但若要表示在过去某个具体场合下能够做某事的能力,我们用was/were able to.例如:— Thank you for your help.—I‘m glad I was able to help you. (在这种情况下能够帮你,而且已经帮了。
)所以was/were able to不仅表示过去的某个具体场合下的能力,还强调动作已经成功完成,相当于manage to do或succeed in doing.例如:We were able to save him. (把他救活了。
)He was able to explain what had happened. (他能解释,而且也解释了。
)He could explain what had happened. (他能做出解释,但可能没有说。
)但这种区别只局限在陈述句,在否定句中,be able to和could可以互换。
有时,could表示的并不是can的过去式,而是一种委婉的语气。
例如:Could you run the business yourself?I could give you a chance.Could you please give me your reply as soon as possible?could have done有虚拟的含义,即“本来能够做,但事实上却没有做”。
例如:You could have told me earlier.I could have helped her.I could have passed the exam if I had worked harder.2) 表示许可can也可以用来表示“允许”,例如:Can I smoke here?You can use my dictionary now.The policeman says we can't park our car here.could可以使句子更显礼貌,但在肯定回答中,我们一般用can代替could,加强肯定的语气。
即:Yes, of course you can.3) 其他用法can not与help, bear, stand等动词连用,表示“禁不住,受不了”。
例如:If one had talent, one can't help showing it.I can't stand waiting any longer.但是can’t help but 后面接动词原形,表示“只能”。
I can not help but ask you: “do you have loved me?”I can’t help but wait.3. must表示必须must的这种用法,体现了说话者的权威性,所以must通常用于上级对下级、长辈对小辈。
例如:You must be back by ten o'clock.Teacher: You must use a dictionary. I’m tired of your spelling mistakes.[注意]must和have to的区别:must表示出于说话者本人的主观愿望,必须去做某事;而have to表示受外部条件的影响,不得不做某事。
例如:I must leave now. (我自己想离开,主观愿望。
)I have to leave now. (也许我还想坐一会儿,但我有要事,不得不走了。
)He must say it in English. (除了英语,他可能还懂其他语言,但我的主观愿望是他必须说英语。
)He has to say it in English. (客观条件是他只懂英语,所以不得不用英语说。
)另外,由于must没有将来时态,所以我们通常用will/shall have to来表示;由于must没有过去时态,所以我们通常用had to来表示。
例如:We will have to do it again.I had to leave at 6:30 yesterday.但有时,我们也可以在表示过去的上下文中使用must.例如:I told him that he must mind his own business.must有两种否定形式:mustn't和needn't/don't have to.mustn't表示"不可以“,needn't/don't have to表示“不必”,例如:You mustn't talk like that. (不可以= You are not allowed to talk like that.)— Must you leave so soon?— No, I needn't.4. should和ought tos hould和ought to通常可以交互使用,意义没有多大的区别,表示“应该”。
should和ought to的这种用法通常表示“建议、敦促或怂恿”。
[比较]must, have to和should/ought to所表示的不同语气:钢琴老师对某学生说:You must practice at least an hour a day. (must 显示了老师的权威。
)这个学生然后对他的朋友说:I have to practice an hour a day! (have to表示我本身不想练,但迫于老师的压力,不得不练。
)他的朋友会说:You ought to/should practice for more than an hour. (表示不是来自外界的权威或压力,而是来自平辈同学或朋友的建议:如要做个好学生,弹好钢琴。
)另外,should have done/ought to have done表示“本该发生的事没有发生;例如:You should have told me earlier.You ought to have been more careful.5. will和wouldwill和would作情态动词使用,主要有以下的用法:1) 表示意愿will和would表示的意愿可强可弱,意愿弱时表示“愿意做某事”(willingness) ;意愿强时表示“坚持要做某事”(insistence) .例如:Will you go with us?(愿意)Will you pass me the salt? (愿意)Let us have a talk, will you? (愿意)I will marry her although my parents are strongly against our marriage.(表示坚持)would可以表示“过去的愿意”,一般用于间接引语中,例如:He said he would come.在其他情况下,would不表示过去,而表示"委婉的语气“,例如:Would you please make a copy for me?但在回答中,为了加强肯定的语气,我们用will.例如:— Would you let me hear from you soon?— Yes, I will.2) 表示能力、趋势或必然性will和would的这种用法一般以东西作为主语,表示“其内在的性能或特征性倾向”。