高中英语语法之特殊句式的结构
- 格式:doc
- 大小:43.00 KB
- 文档页数:5


高中英语语法讲义第二讲——特殊句式倒装句通常句式为自然语序“主语+谓语”,有时为了强调句子的某一部分,或者出于词汇用法、语法结构或修辞上的需要,将这种比较固定的语序加以颠倒,就形成了倒装。
分为完全倒装,部分倒装和形式倒装。
一.完全倒装:谓语动词完全置于主语之前,主语为名词不为代词,谓语不用进行时。
1.一些表示地点、时间或方位等的副词或介词短语。
如:here, there, now, then, up, down ,in, out,away, off, in the room, on the wall等置于句首。
Down came the rain and up went the umbrella.Then followed three days of heavy rain.Out rushed the children laughing loudly.Away flew the plane.2.such 位于句首。
Such was Albert Einstein, a simple man and the 20th century’s greatest sc ientist.注:此句型中的such多被认为是表语,所以such后的be动词应与其后真正的主语保持一致。
Such are the facts; no one can deny them.二.部分倒装:只把谓语的一部分(助动词,情态动词或be动词)置于主语之前1.so+ be 动词/ 助动词/ 情态动词+主语,意为“...也是如此”。
They love making lots of friends; so do I.2.neither/nor+ be动词/助动词/情态动词+主语,意为“...也不这样”。
Lily can’t ride a bicycle; neither/nor can Lucy.3.否定词never, seldom, nor, not, little, hardly, scarcely等或表示否定意义的介词短语at no time,under/in no circumstances, in no case, by no means, on no condition 等置于句首时。
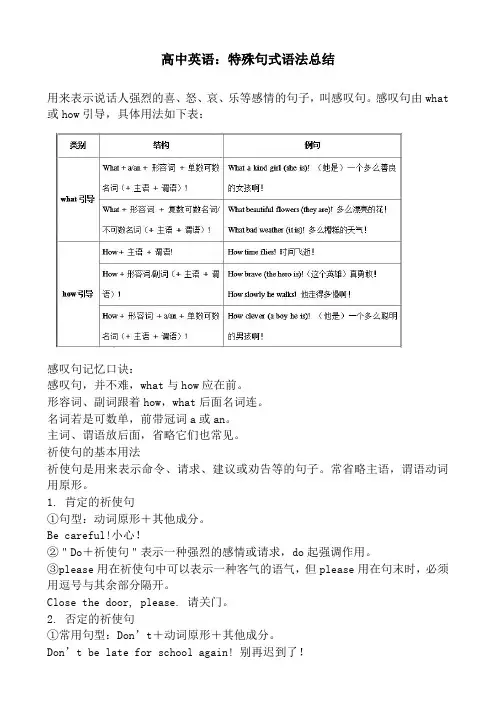
高中英语:特殊句式语法总结用来表示说话人强烈的喜、怒、哀、乐等感情的句子,叫感叹句。
感叹句由what 或how引导,具体用法如下表:感叹句记忆口诀:感叹句,并不难,what与how应在前。
形容词、副词跟着how,what后面名词连。
名词若是可数单,前带冠词a或an。
主词、谓语放后面,省略它们也常见。
祈使句的基本用法祈使句是用来表示命令、请求、建议或劝告等的句子。
常省略主语,谓语动词用原形。
1. 肯定的祈使句①句型:动词原形+其他成分。
Be careful!小心!②"Do+祈使句"表示一种强烈的感情或请求,do起强调作用。
③please用在祈使句中可以表示一种客气的语气,但please用在句末时,必须用逗号与其余部分隔开。
Close the door, please. 请关门。
2. 否定的祈使句①常用句型:Don’t+动词原形+其他成分。
Don’t be late for school again! 别再迟到了!②用Never开头:Never+动词原形+其他成分。
Never leave today’s work for tomorrow! 不要把今天的工作留到明天!3. Let引导的祈使句以Let开头的句子也是祈使句,表示陈述和建议。
其否定形式有两种:Let...not 或Don’t...Let us not be late. 让我们不要迟到。
Don’t let the boy play football in the street. 不要让这个男孩在街上踢足球。
祈使句与简单句、复合句之间的转换1. "Let’s + 动词原形 + 其他"可转换为"Shall we + 动词原形 + 其他? "。
Let’s go fishing thi s afternoon. =Shall we go fishing this afternoon?2. "祈使句 + and/or + 简单句"可转换为含if引导的条件状语从句的复合句。

高中英语语法:特殊句式之强调句一、It is ...that/who 强调句1、基本结构:“It is/was +被强调部分+that/who+其他成分”强调句结构可用来强调句子的主语、宾语和状语等。
◇It was a European chemistwho produced the medicine.(强调主语)是一位欧洲药剂师发明了这种药。
◇It was him that we met at the school gate.(强调宾语)我们在学校门口见到的是他。
◇It was at three o'clock that we finished the work(强调状语)我们是在三点钟完成工作的。
★ 2、who/that的选用强调句中,引导词一般用that,that只起连接作用,没有实际意义,而且不能够省略掉。
指人时,that可以用who替代,其他情况下均用that。
◇It is our parents who/that we depend on when we are in trouble.当我们遇到困难时是我们的父母值得依靠。
(所强调的是人,所以who和that都可以用)◇It is a wallet that he picked up.他捡起来的是一个钱包。
(所强调的wallet是物,只能用that)3、is/was的选用原句谓语动词是过去的某种时态时,被强调部分用“It was...”;原句为现在的某种时态时,被强调部分用“It is...”。
4、主谓一致强调句中被强调部分如果是句子的主语,that/who之后的谓语动词在人称和数词上应与被强调的主语保持一致。
◇It is you whoare in charge of it.是你应该为此负责。
◇It is I who am to blame for the fault.是我应该因这个过失而受责备。
辨析:强调句和其他从句的区别一般来说,如果把句子中的It is/was ...that/who...去掉后稍加调整语序,能还原成完整的句子,并且句子意思依然完整,则为强调句。

四大特殊结构1、强调结构:It is+被强调部分+that\who +(照抄)剩余部分。
通常翻译为“正是”“就是”。
It is you who I love. 强调宾语It is I who love you。
强调主语It is when I was a child that I fell in love with you. 强调状语注意:强调结构与it 做形式主语的区别:如果把“It is … that…”这一部分去掉时,剩下的部分仍然能组成一个完整的句子,那么这个句子就是强调句型。
如果去掉以后,不能再组成一个完整的句子,就是it做形式主语的结构。
比如:It is you who I love. 去掉“It is … that…”后,句子还是可以写成:I love you.这个句子绝对是强调句。
It is necessary that we should study hard。
去掉“It is … that…”后,剩下的成分就不能再重新组合成一个新句子,因此这个句子是It做形式主语。
It is under the correct\wise leadership of Communist Party of China that we live a happy life.在句子强调谓语动词时,通常是在动词前加助动词do。
I do love you。
He does study hard.2、倒装句型1)so、介词短语、方位副词放在句首时,全部倒装。
Tom likes to play football, so do I。
In the room are 150 students.注意:表示方位的副词:here\there\up\down这类词后面的主语是名词时,句子用倒装。
但是如果是主语是代词,句子就不用倒装。
比如:Here you are. Here it is。
2)only +状语+句子Only by (taking) a training class can we pass TDXL examination。

特殊结构的用法总结与归纳倒装句省略句被动语态等特殊句型解析特殊结构是指在英语语法中,具有一定特殊用法或形式的句子结构。
这些特殊结构包括倒装句、省略句和被动语态等。
本文将对这些特殊句型进行总结与归纳,并解析其具体用法。
1. 倒装句(Inversion Sentences)倒装句是指将主语和谓语的语序颠倒的句型。
主要分为完全倒装和部分倒装两种情况。
1.1 完全倒装(Full Inversion)完全倒装句的结构是将助动词、情态动词或者be动词放在句首,其后紧跟主语,再接上谓语动词。
例:Never have I seen such a beautiful sunset.Not only does she play the violin, but she also sings beautifully.1.2 部分倒装(Partial Inversion)部分倒装句通常在以下情况下使用:1)当表示否定意义的副词或短语放在句首时;2)当表示“只有”之类的副词或短语放在句首时;3)当表示“地方状语+副词”或“副词+副词”时。
例:Under no circumstances can you leave the classroom.Only in this way can we solve the problem.Upstairs in his room sat the boy.2. 省略句(Elliptical Sentences)省略句是指在句子中省略了某些成分,但读者或听者通过上下文仍能理解被省略的内容。
省略句可以简化表达,增强语言流畅性。
2.1 主语的省略当前后两个句子的主语一致时,可以省略第二个句子中的主语。
例:Mary is playing basketball. John is playing basketball too.→ Mary is playing basketball. So is John.2.2 谓语的省略在某些情况下,如果主语都一样,谓语动词可以省略。

高考英语特殊句式分类汇总在高考英语中,掌握各种特殊句式是提高语言表达能力和得分的关键。
下面是对高考英语特殊句式进行详细介绍。
1. 强调句型强调句型是通过强调句子中的某个成分来突出其重要性或特殊性。
在高考英语中,常见的强调句型有两种形式:It is/was…that和What…。
(1) It is/was…that该形式中,强调句子的主语、宾语、状语等成分,一般将被强调的成分放在it后面,用that引导的从句作为原句的主句。
例如:- It was Mary who won the first prize in the English contest.- It is the teacher who inspired me to study hard.(2) What…该形式中,强调句子的谓语动词,用what引导的名词从句位于句首。
例如:- What makes him different from others is his positive attitude towards life. - What we need to do now is to find a solution to the problem.2. 倒装句型倒装句型是指把句子的主语和谓语动词的位置颠倒过来的结构。
在高考英语中,常见的倒装句型有两种形式:完全倒装和部分倒装。
(1) 完全倒装在完全倒装句中,谓语动词位于主语之前,主语位于动词之后。
例如:- Not only did he pass the exam, but he also got a high score.- Never have I seen such a beautiful sunset.(2) 部分倒装在部分倒装句中,只有助动词、情态动词或系动词的前移。
例如:- Should you have any questions, feel free to ask.- Can you imagine how excited I was when I received the good news?3. 条件句型条件句型是指表示条件关系的句子结构。

高中英语语法:特殊句式最常见到的四种特殊句式:全部倒装、部分倒装、省略句和反意疑问句。
1 全部倒装1. There be句型:可以用在这类句型中的动词除be外,还可用live,exist,remain,stand等作谓语。
例如:(1) There are many students in the classroom.(2) Long long ago, there lived a king who loved horses very much.2. 用于“here(there,now,then)+不及物动词+主语”的句型中,或以out,in,up,down,away等副词开头的句子里,以表示强调。
例如:Here comes the bus.Out went the children.3. 由then引起,谓语为come,follow的句子。
例如:(1) Then came a new difficulty.(2) Then followed eight years of the Anti-Japanese War.4. 当句首状语为表示地点的介词短语时,也常常引起全部倒装。
例如:In the middle of our school stands a high building.5. 表语放在句首时,倒装结构为“表语+系动词+主语”。
表语常为形容词、过去分词和介词短语。
例如:(1) Gone are the days when they would do what they liked.(2) Present at the meeting were Professor White, Professor Smith and many other guests.2 部分倒装1. only+副词/介词短语/状语从句置于句首。
例如:Only then did I realize the importance of English.注意:①在only+状语从句+主句结构中,主句用倒装结构但从句用正常语序。

特殊句式的类型特殊句式是指在语法结构或表达方式上有一定巧妙之处,增加信息或引起读者的注意。
以下是几种常见的特殊句式类型及相关参考内容。
1. 倒装句式倒装句式是指将谓语动词或助动词提前,与主语的位置对调。
常见的倒装有完全倒装和部分倒装两种形式。
例句:Not only does she speak fluent English, but also she is a talented musician.参考内容:- "Inversion: Definition and Examples in English Grammar" - ThoughtCo- "Inversion in English Grammar" - Learn English2. 强调句式强调句式是通过对句子成分进行特殊处理,使得某个成分在句子中得到特别强调。
例句:It was John who ate all the cookies.参考内容:- "Emphatic Structures" - English Practice- "The Passive and Indirect Questions for Focus and Emphasis" - English Grammar3. 平行结构平行结构是指在一个句子中使用相同的语法结构或句式,以增强表达的逻辑关系或节奏感。
例句:She likes swimming, running, and cycling.参考内容:- "Parallel Structure" - Grammar Monster- "Parallelism: How to Write and Identify Parallel Sentences" - ThoughtCo4. 带有省略的句式带有省略的句式是指在句中可以省略某些成分或词语,但仍然能保持句子的完整性和可理解性。


高考英语语法填空之特殊句式一:知识讲解1:考查祈使句、感叹句和省略句1.祈使句的4种句式①动词原形(+宾语+其他成分)②Be+表语,如Be honest.③Let’s/Let us do/not do sth.④祈使句+and/or+简单句(简单句谓语用一般将来时)2.感叹句的3种句式①What(+a/an)+形容词+名词+主语+谓语!②How+形容词+a/an+单数可数名词+主语+谓语!③How+形容词/副词+主语+谓语!3.记准省略规则在when,while,Whenever,till,as soon as,if,unless,as if,though,as等引导的状语从句中,若谓语有be动词,而主语又与主句主语一致或主语是it时,从句的主语和be动词常被省略。
2:考查强调句、倒装句和there be句型1.牢记强调句的2个句式及1个方法①强调句型的基本构成:It is/was+被强调的部分+that/who+其他部分。
被强调部分可以是主语、宾语和状语等。
②not...until的强调句型:It is/was not until...+that+其他部分。
2.部分倒装的3个句式①利用否定词定位法确定倒装句。
否定词(短语)置于句首,句子要用倒装语序。
特别要注意某些表否定意义的短语或否定词如:at no time, by no means, in no case, on no condition/account, not until, not only等。
②熟悉only置于句首倒装的条件。
只有当“only+状语”置于句首时,句子才倒装,“only+主语”置于句首,句子不倒装。
③当so...that,such...that中的so...和such...置于句首时,主句主谓部分倒装。
3.there be句式的2个关键点①there be结构中的谓语动词be可与there seem to be(似乎有);there happen to be(碰巧有)等替换。
英语特殊句式语法英语语法中存在一些特殊的句式结构,它们具有独特的语法规则和用法。
在本文中,我们将介绍一些常见的英语特殊句式,并通过示例来解释它们的用法。
一、倒装句倒装句是英语中常见的特殊句式之一,它采取了主语和谓语动词的位置颠倒。
倒装句的用法多种多样,下面是一些常见的情况:1. 完全倒装:当句子以表示地点状态的副词(如here, there, now, then等)开头时,需要完全倒装。
例如:Here comes the bus.There goes my hat.2. 部分倒装:在某些特定的条件下,主语和谓语动词的位置需要部分颠倒。
a. 在用于表示否定的副词或短语(如never, seldom, hardly, not until 等)开头的句子中,需要将助动词或情态动词与主语颠倒。
例如:Never have I seen such a beautiful sunset.Not until she left did I realize how much I loved her.b. 在以表示条件的状语从句(如if, unless, whether等)开头的句子中,需将助动词和主语颠倒。
例如:If only I had more time, I would travel around the world.Whether it rains or not, we will go camping.二、虚拟语气虚拟语气是英语中常见的特殊句式之一,用于表示与事实相反、假设或愿望等情况。
以下是虚拟语气的几种常见形式:1. 虚拟条件句:用于表示与事实相反的假设情况,包括类型1、类型2和类型3三种类型。
a. 类型1:表示真实可能发生的假设例如:If she studies hard, she will pass the exam.b. 类型2:表示与事实相反,但在理论上有可能实现的假设例如:If I were you, I would quit that job.c. 类型3:表示与过去事实相反的假设例如:If I had studied harder, I would have passed the exam.2. 虚拟表达愿望例如:I wish I could play the piano like a professional.3. 虚拟表达建议、命令等例如:The teacher suggested that they should review the material again.三、强调句强调句是一种特殊的句式,它通过强调句子中的某个成分来表达特殊的意义。
高考英语特殊句式汇总一、强调句型句型结构形式:It is/was…that/who…be的时态:that/who前面be的时态一般是一般现在时,当它后面的句子为过去时时,才用过去时。
判断方法:将(It is/was)...(that/who)…括号中的词同时去掉,看剩下的部分是否仍然成立。
若成立,则是强调句型;若不成立,则为状语从句、定语从句或主语从句。
They met the manager in the coffee shop the other day.*It was they that / who met the manager in the coffee shop the other day.*Was it they that / who met the manager in the coffee shop the other day?*Who was it that met the manager in the coffee shop the other day?*I wonder who it was that met the manager in the coffee shop the other day.*Can it be in the coffee shop where they once had a cup that they met the manager.* --- Who is making such noise downstairs?--- It is the children.二、祈使句祈使句的主语是you,但一般被省略;当前面有呼语时,一般得补出主语;否定式一般是在前面加Don’t,或是Never。
**在“祈使句,+ and/or/and then+句子”句型中,当祈使句中含有比较级时,可将祈使句中的谓语部分省略,只留下“比较级或比较级与名词,+and/or/and then+句子”。
特殊句式的结构1.It结构一、强调句强调句的基本句型是“It is/was+被强调的部分+that/who+其他部分”。
被强调的部分可以是主语、宾语和状语等。
强调句型的使用特点主要有以下几个方面:(1)被强调的是状语或状语从句时,要用that引导从句,而不能用which,而且通常不能省略。
(2)被强调的是人时,引导词可用who,也可用that。
Was it you that/who let out the secret to her?是你把这个秘密泄露给她的吗?(3)被强调的不管是单数还是复数名词,主句的be动词都用单数is或was。
It was Marie Curie and her husband who discovered radium.是居里夫人和她的丈夫发现了镭。
It is the PLA men who/that are safeguarding our country day and night.是解放军战士日夜保卫着我们的祖国。
(4)对not...until时间状语从句进行强调时,其句型是:It is/was not until...that从句,即not和until在强调句中总是紧挨着的。
注意习惯上不用not till,而且从句不能用when引导。
It was not until the last operation was finished that Bethune left the battle hospital.(5)强调句的疑问形式:When was it that he made up his mind to take this course?他是什么时候决定选修这一门课程的?Why is it that he doesn’t like th e book?他为什么不喜欢这本书?Was it in 1939 that the Second World War broke out?(6)强调句型与It is/was+时间+when从句:在上述句型中it指时间,when引导的是时间状语从句。
十五特殊句式及结构
以下是一些特殊句式和结构:
1. 条件句:如果/假如...,就...(If...,then...),表达其中一种条件或假设。
例句:如果你学习努力,就会取得好成绩。
2.排比句:使用类似的结构或语法对不同的事物或观点进行排列,以增加修辞效果。
例句:今天我们要学习的不仅仅是知识,还有勇气、智慧和毅力。
3.比喻句:利用比喻手法将两种不同的事物进行比较,以便更好地表达其中一种含义或形象。
例句:他是教育事业的火炬,把知识的火焰传递给每个学生。
4.并列句:使用连词将两个或多个并列的句子连接起来,表达相同的重要性或关联。
例句:她喜欢唱歌,跳舞,画画,对艺术充满了热情。
5.疑问句:一种用来提问的句子形式,以引起注意或寻求回答。
例句:你愿意和我一起去旅行吗?
6.倒装句:将主语和谓语的语序颠倒,以强调其中一种句子成分或使语言更具艺术感。
例句:Not only does she speak English fluently, but she also speaks French and Spanish.
7.强调句:通过使用强调的句式或结构来强调句子中的一些部分,使之在句子中更加突出。
8.反问句:通过提出一个反问来表达其中一种观点或态度,通常不需要得到肯定或否定的回答。
例句:You didn't forget my birthday, did you?
这些特殊句式和结构可以帮助我们更加灵活地表达和交流,增强语言表达的魅力和效果。
英语语法之特殊句式特殊句型特殊句型包括祈使句、感叹句、强调句型、反意疑问句和There be句型。
祈使句祈使句用于表示请求、命令、建议或劝告等。
一般使用降调,为使语气婉转,可使用低升调。
句末使用句号或感叹号。
肯定的祈使句:关上门。
请安静!有时为了加强语气,可以在动词之前加上do,表示“务必,一定”。
一定要按时来。
一定要小心!否定的祈使句:祈使句的否定形式一般是在句首加don’t或never构成。
不要迟到。
做事不可马虎。
其他形式的祈使句:以let开头的祈使句:咱们休息一会。
我们不要大声说话。
以no开始的禁止性祈使句:禁止停车。
禁止吸烟。
祈使句+陈述句句型:在“祈使句+陈述句”这种结构中,祈使句和陈述句之间要用连接词。
连接词分为两类:第一类:and。
then。
and then。
意思是“就”、“那么(就)”、“(刚)才“。
第二类:or。
or else。
otherwise。
意思是“否则”、“要不”、“不然的话”。
使用and和or的方法:选择连接词,只看陈述句。
and叫人心欢畅,or的后果不好尝。
使用第一类连接词和第二类连接词的方法:比较下面三组例句:1)Come early。
and you’ll catch the first bus.早点来,你就能赶上第一班汽车。
Come early。
or you’ll miss the first bus.来早点,不然的话,你就赶不上第一班汽车。
2)Use your head。
then you’ll find a way.开动脑筋,那么你就会找到办法。
Use your head。
or else you won’t find a way.开动脑筋,否则,你就找不到办法。
Work hard。
otherwise you will fail。
This shows that when stating the desired e。
one should use "and"。
特殊句式I There beA 定义表达“某处/某时存在某人/某物”。
B 结构一般结构:There + be + 名词+ 地点将来结构:There will be + 名词+ 地点完成结构:There has been + 名词+ 地点含情态动词结构:There + 情态动词+ be + 名词+地点C 用法a. 就近原则例:There is some juice and some cakes on the table.b. 衍生结构①There be + 名词+ doing(与名词形成主动关系)例:There must be something blocking the pipe.②There be + 名词+ done(与名词形成被动关系)例:T here’s only four days left.③There be + 名词+ to do(未发生,表将要做…)例:There is still a lot of work for me to do.拓展:there be句型中,其结构中谓语动词和非谓语结构的变化·there be中的be有时可用seem to be,happen to be,is likely to be或go,remain,stand,lie,exist,follow,live,come,occur等替换例:There existed different opinions on this problem.·there be结构的非谓语形式:there to be 和there being。
there to be结构可用作动词的宾语,也可用作介词for的宾语;there being可用作除for外的介词宾语或状语例:I expect there to be no argument about this.(作宾语)I have never dreamed of there being a chance to go abroad.(作宾语)There being no enough time left, we have to hurry.(独立主格结构作状语)注:·跟动名词的动词后用there being,常见的有:deny,mind,admit,imagine等·跟不定式的动词后用there to be,常见的动词有:expect,want,hope,wish,like,hate,would like,prefer,mean,intend等c. 固定句型①There is no point/sense (in) doing sth “做某事没意义”例:There is no point/sense arguing further.②There is no doubt that…“毫无疑问…”例:There is no doubt that the new technology is changing the way we work.③There is no need to do sth “没必要做某事“例;There is no need to get up early tomorrow.④There is no possibility/ chance that…“……是不可能的”例:There is no chance that he will change his mind.⑤There is no denying (the fact) that…“不可否认……”例:There is no denying (the fact) that our life has gone from bad to worse.⑥There is no difficulty/ trouble in doing sth“作某事没困难”例:There is no trouble in solving the problem.d. 区分:there be 和have①there be与have都可表示“有”,但在意义上,have表示所有关系,即“拥有”,there be则表示“客观存在”。
特殊句式的结构1.It结构一、强调句强调句的基本句型是“It is/was+被强调的部分+that/who+其他部分”。
被强调的部分可以是主语、宾语和状语等。
强调句型的使用特点主要有以下几个方面:(1)被强调的是状语或状语从句时,要用that引导从句,而不能用which,而且通常不能省略。
(2)被强调的是人时,引导词可用who,也可用that。
Was it you that/who let out the secret to her?是你把这个秘密泄露给她的吗?(3)被强调的不管是单数还是复数名词,主句的be动词都用单数is或was。
It was Marie Curie and her husband who discovered radium.是居里夫人和她的丈夫发现了镭。
It is the PLA men who/that are safeguarding our country day and night.是解放军战士日夜保卫着我们的祖国。
(4)对not...until时间状语从句进行强调时,其句型是:It is/was not until...that从句,即not和until在强调句中总是紧挨着的。
注意习惯上不用not till,而且从句不能用when引导。
It was not until the last operation was finished that Bethune left the battle hospital.(5)强调句的疑问形式:When was it that he made up his mind to take this course?他是什么时候决定选修这一门课程的?Why is it that he doesn’t like th e book?他为什么不喜欢这本书?Was it in 1939 that the Second World War broke out?(6)强调句型与It is/was+时间+when从句:在上述句型中it指时间,when引导的是时间状语从句。
注意两种句型“时间”表达方式的不同。
It was at midnight that I got back home yesterday.昨天晚上我半夜才回到家。
It was midnight when I got here yesterday.昨天当我到达这儿时,已是半夜了2.but 的用法a.anything but…一点儿也不She was anything but mad.b.nothing but…仅仅,只She heard nothing but the wind.c. but for….除非,要不是But for your help, I wouldn’t have succeed.d. can’t help but do (can’t help doing…) 禁不住…We cannot help but admit that the Chinese people are a great people.e. have no choice but to do 不得不She had no choice but to wait.f. not…but…不是…而是…I meant not he but you should pay attention to pronunciation.He failed not because he isn’t clever but he didn’t work hard.3.倒装句型全部倒装是只将句子中的谓语动词全部置于主语之前。
此结构通常只用与一般现在时和一般过去时。
常见的结构有:1) here, there, now, then, thus等副词置于句首, 谓语动词常用be, come, go, lie, run。
There goes the bell.Then came the chairman.Here is your letter.2) 表示运动方向的副词或地点状语置于句首,谓语表示运动的动词。
Out rushed a missile from under the bomber.Ahead sat an old woman.注意:上述全部倒装的句型结构的主语必须是名词,如果主语是人称代词则不能完全倒装。
Here he comes部分倒装是指将谓语的一部分如助动词或情态倒装至主语之前。
如果句中的谓语没有助动词或情态动词,则需添加助动词do, does或did,并将其置于主语之前。
1)句首为否定或半否定的词语,如no, not, never, seldom, little, hardly, at no time, in no way, not until… 等。
Never have I seen such a performance.Not until the child fell asleep did the mother leave the room.当Not until引出主从复合句,主句倒装,从句不倒装。
注意:如否定词不在句首不倒装。
I have never seen such a performance.如Not only…but also,Hardly/Scarcely…when, No sooner… thanNot only did he refuse the gift, he also severely criticized the sender.注意:只有当Not only… but also连接两个分句时,才在第一个分句用倒装结构。
如果置于句首的Not only… but also仅连接两个并列词语,不可用倒装结构。
Not only you but also I am fond of musicSo neither nor 表示"也"、"也不" 的句子要部分倒装。
Tom can speak French. So can Jack.If you won't go, neither will IOnly in this way, can you learn English well.Only after being asked three times did he come to the meeting.如果句子为主从复合句,则主句倒装,从句不倒装Only when he is seriously ill, does he ever stay in bedas / though引导的让步从句必须将表语或状语提前(形容词, 副词, 分词, 实义动词提前)。
注意:1) 句首名词不能带任何冠词。
2) 句首是实义动词, 其他助动词放在主语后。
如果实义动词有宾语和状语,随实义动词一起放在主语之前。
Try hard as he will, he never seems able to do the work satisfactorily.注意:让步状语从句中,有though,although时,后面的主句不能有but,但是though 和yet可连用1)so… that 句型中的so 位于句首时,需倒装。
So frightened was he that he did not dare to move an inch.2)在某些表示祝愿的句型中:May you all be happy.3)在虚拟语气条件句中从句谓语动词有were, had, should等词,可将if 省略,把were, had, should 移到主语之前,采取部分倒装。
Were I you, I would try it again反意疑问句1)陈述部分的主语是I,疑问部分要用aren't I.I'm as tall as your sister,aren't I?2)陈述部分的谓语是wish,疑问部分要用may +主语。
I wish to have a word with you, may I?3)陈述部分用no, nothing, nobody, never, few, seldom, hardly, rarely, little等否定含义的词时,疑问部分用肯定含义。
The Swede made no answer, did he / she?Some plants never blown (开花), do they ?4)含有ought to 的反意疑问句,陈述部分是肯定的,疑问部分用shouldn't / oughtn't +主语。
He ought to know what to do, oughtn't he? / shouldn't he?5)陈述部分有have to +v. (had to + v.),疑问部分常用don't +主语(didn't +主语)。
We have to get there at eight tomorrow, don't we?6)陈述部分的谓语是used to 时,疑问部分用didn't +主语或usedn't +主语。
He used to take pictures there, didn't he? / usedn't he?7)陈述部分有had better + v. 疑问句部分用hadn't you?You'd better read it by yourself, hadn't you?8)陈述部分有would rather +v.,疑问部分多用wouldn't +主语。
He would rather read it ten times than recite it, wouldn't he?9)陈述部分有You'd like to +v. 疑问部分用wouldn't +主语。
You'd like to go with me, wouldn't you?10) 陈述部分有must 的疑问句,疑问部分根据实际情况而定。
He must be a doctor, isn't he?You must have studied English for three years, haven't you? / didn't you?He must have finished it yesterday, didn't he?11) 感叹句中,疑问部分用be +主语。