《西方文化导论》练习题 (1)
- 格式:doc
- 大小:401.00 KB
- 文档页数:6

(1) Give a brief account of the major achievements of Greek culture, such as those in religion, philosophy, literature and science.Greek religion really took shape during the Homeric Age and featured polytheism with gods taking human form and feeling. Greek religion made a great contribution to Greek literature, philosophy and art. It is an important origin of Greek mythology which was fully developed by the religious tales of the Homeric epic and thus affected the later development of all kinds of Greek culture.Greek philosophy started with Thales (640 BC–547 BC) who believed that the material world originated in water. His philosophy was materialism. He was followed by Pythagoras who assumed that the key to the understanding of the world is numbers, on the opposition of the spokesman for idealism.The core Greek philosophers are Socrates, Plato and Aristotle. Socrates had scant regard for material wealth, but was keen on probing into the definition of some ethical and behavioral issues, such as “friendship”and “courage”.Plato established the Academy -the first Greek institution of higher learning. His contributions included his theory of ideas and his arguments on “republic”which was supposed to embrace his ideals about a future state where humans could enjoy a happy life. Aristotle is also a learned man and his work covers wide-ranging areas. His reputation as a philosopher largely depends on his argument on metaphysics which he tried to achieve a compromise between matter and divinity. Literary representation centred round the two epic poems of the Iliad and the Odyssey, lyrical poetry by Sappho and Pindar and drama by Aeschylus, Euripides and Aristophanes. Their works combined Greek myths and social life and won much appreciation and enthusiasm from the public.In science the mathematician Euclid established plane geometry and Archimedes discovered the ratio of radius of a circle and the relationship between the volume and surface of a sphere.(2) What do you think of the influence Greek culture has exerted on Western civilization as a whole? Give examples.Greek culture is often termed the cradle of the Western civilization and has had an enormous impact on Western culture. The specific contributions are found in the areas of philosophy, politics, literature, art, science and architecture.Greek politics was one of the greatest influences on the Western civilization. The Greeks were the first to successfully create a government based on the consensus of the people and thus provided a foundation for Western democracy.The second significant influence was that of philosophy. The Socratic idea about ethics and knowledge helped the Westerners care more for the effect of knowledge and value of morality, both of which give sound guidance to people in the later years to improve and change the world outside themselves, i.e., human society and the natural world.Later generations of Westerners have benefited a lot from Greek culture, such as those in painting, sculpture, architecture, drama, poetry and historical works. Classicism had Greek culture as one of the crucial sources, and this has helped Westerners so much that they ascribed the origin of the Renaissance to it. This changed the intellectual conditions of the later medieval period and opened the way to the modern era in the West.Chapter 21. Tell briefly the major characteristics and contributions of Roman culture, as aredemonstrated in religion, poetry, history and architecture.In the early period, Roman culture often depended heavily on the introduction and imitation of other cultures, particularly, Greek culture. Thus Romans created their own powerful culture, laying the foundation for subsequent Western culture in many fields. According to Greek culture and others’ culture; they created their o wn gods and myth, In poetry, ancient Rome made brilliant achievements,Livy was responsible for the great History of Rome in 142 volumes. His work has always been cited by later statesmen, writers or scholars,The architecture of Ancient Rome adopted the Greek style for its own purposes, but the Romans also developed a new kind.2. In what sense do you think Roman culture owed its accomplishments to the benefits obtained from Greek culture? Give examples.Roman culture learned and inherited a lot from Greek culture.,religion, philosophy and literature. In religion, Rome had its own system of beliefs which had been simple and could hardly compare with the plurality of Greek religion. The same is true of Roman philosophy where we could find examples ,In literature, Roman men of letters also borrowed a All in all, the two cultures are closely linkedgreat deal from Greek culture.Chapter 31. How was the Jewish civilization developed after a tortuous history of split and unification? The major explanation for the development of the Jewish civilization is its strong cohesiveness and vitality,they put into effect their Judaist beliefs and what they read of Judaist scriptures.From then on Jews have begun to become aware of the necessicity to liberate themselves from the restrictive laws and acquire new knowledge and modern ideas from the Europeans, Most of Jews thus received a good education, fully armed with cultural and scientific knowledge and did well in their own position they could quickly turn it into a well developed nation in spite of its small size and small population .2.Say something about Judaism and The Old Testament.The Old Testament is the Judaist Bible. It was written in Hebrew, including the three parts:Pentateuch, Prophets and Hagiographa and Apocrypha. After The Old Testament was translated into Greek by Jewish scholars,many westerners began to understand Judaism by reading this book. It is not only of religious value but also of literatry value.Chapter 41. What are the main components of Christianity and why could it be accepted as the official religion first by the Roman Empire and then by the following kingdoms or empires in Europe?(1)The main components of Christianity are :1) The Bible as the only Christian scripture;Major Christian doctrines about Trinity and Redemption;3) Other doctrines or events of Christianity:(2 )Christianity is accepted and popular in Europe because of these factors:1).For the common people in the empire ,they needed something to fill up their spiritual vacuum. Christianity could play such a role.2). It could work together with any secular regimes to offer necessary assistance.3). The name and influence of Christiaity would be a symbol of sacredness and justification,4) Christianity is also a kind of culture, it could be tolerated because their life and property could thus be secured in the changed circumstances.2. What are the basic differences between Christianity and Judaism?In spite of the fact that the two religions derived from Jewish culture, there are some basic differences between them.First is the different image of God.Second is different view of God. Jehovah is viewed He is like fire or wind .God is kinder and more helpful, Third is the different position each religion is located in and hence would make different contribution. Fourth is Jehovah was important to Jews only in theory and affect them in spirit occasionally while Christianity moved into secular life for the Westerner as Pope and churches became very powerful .Chapter 61.Tell simply the background and development of the Renaissance.It was no accident that it first occurred in Florence and Italy where the early signs of capitalism had appeared at the same time as social chaos, political disputes and military clashes , more and more people began to suspect the justification for those who held the power,Painting and sculpture were the first area to reflect the change of subjects and tastes.(2) What are the major features and achievements of the Renaissance? Give examples.The Renaissance is characterised by seeking ideological emancipation, intellectual freedom and political awareness, based on cultural production and religious reformation. All these were undertaken or unfolded gradually but widely, extending its influences to every corner of Europe, with more and more people getting involved.The achievements were seen principally in six areas, namely, painting, sculpture, poetry, fiction, drama and religious reformation as well as the change in the cultural and intellectual climate. Instances could be located in these areas, such as the huge change of subjects and styles in painting. The medieval painting used to centre on depicting Jesus Christ and other Christian subjects, not only effecting similar and the limited subject matter, but also depicting stylistically facial expressions and manners. The great artists in the Renaissance started to focus on the images with individualistic temperament, highlighting humanity instead of divinity, thus breaking away from the medieval frozen models and linking classicalism with human nature as the centre of their representational work.。


Test 11.Two of the elements in European culture are considered to be more enduring and they are the __Greco-Roman__element and the _Judeo-Christian____ element.2.In a more remote period of Greek history,probably around__1200 B. C.____, a war was fought between Greece and Troy.3.Greek culture reached a high point of development in the__5th___ century B.C.4.The 5th century B.C.closed with civil war between__Athens___ and ___Sparta___ in Greece.5.In the second half of the _4th____ century B. C., all Greece was brought under the rule of__Alexander___, King of Macedon.6.In___146___B.C.the Romans conquered Greece.7. Athens was a democracy,where only the adult ___male___ citizens had the rights.8. The economy of Athens rested on an immense amount of___slave____ labour.9. The Greeks loved sports. Once every four years,they had a big festival on _OlympusMount_____ whichincluded contests of sports10. Revised in___1896___, the Games have become the world’S foremost ameteur sportscompetition.11. Ancient Greeks considered__Homer___ to be the author of their epics:the Iliad.12. Homer probably lived around__700 B. C.___.13.The Iliad deals with the alliance of the states of the southern mainland of Greece, led by Agamemnon in their war against the city of__Troy___.14. The heroes are Hector on the__Troy___side and and Achilles and Odysseus on the__Greek_____.15. In the final battle, Hector was killed by Achilles and Troy was sacked and burned by the ___Greeks___.16. The Odyssey deals with the __return___of Odysseus after the Trojan war to his home island Ithaca.17. The Odyssey describes many adventures Odysseus ran into on his long voyage and how he was reunited with his faithful __wife____Penelope.18.Countless writers have quoted, adapted, borrowed from and otherwise used __Homer’s____epics.19. In the early part of the 19th century, in England alone, three young Romantic poets (Byron, Shelley and Keats) expressed their _admiration____ of Greek culture in works which have themselves become classics.20 In the 20th century, there are _Homeric____parallels in the Irishman James Joyce's modernist masterpiece Ulysses.21. Early in their remote past,the Greeks started to perform plays at__religious___ Festivals.22. Out of these origins a powerful drama developed in the _____ century B.C.23. P erformances were given in__open-air___ theaters,with the audience sitting on _stone____ benches and looking down at the stage from __three__ sides.___Euripides____.25. Aeschylus is noted for his vivid__character__ portrayal and majestic __poetry____.Aeschylus wrote such plays as__Prometheus Bound____, ___ Persians___ and __Agamemnon______.Sophocles was the author of plays like __Oedipus the King_____, ___Electra_____ and ____Antigone____.28. Oedipus the King is the story of a man who unknowingly committed aterrible sin by killing his __father___ and marrying his___mother_____.29. The Austrian psychiatrist Sigmun d Freud’s term “__The Oedipus Complex_______” derived from Sophocles’s play.30. Euripides wrote mainly about___women____ in such plays as __Andromache____, ___Medea____ and ___Trojan women_____.31. Aristophanes wrote such plays as __Frogs_____, ___Clouds_______, ____ Wasps_______ and _____Birds________.32. Pythagoras was the founder of ____scientific mathematics________.33. Euclid is even now well—known for his Elements,a textbook of ___geometry_____, perhaps the most successful textbook ever written,because it was in use in English schools until the early years of the 20th century.34. We know Socrates chiefly through what Plato recorded of him in his famous ___Dialogues_____.35. The method of argument Socrates used in exposing fallacies has come to be known as the ___dialectical____method.36.Plato’s Dialogues are important not only as____philosophical___ writing but also ___imaginative_____ as literature.38. Of the Dialogues Plato wrote,27 have survived,including ___the Apology____, ___Symposium____ and ____the Republic____.39. Plato’s comprehensive system of philosophy dealt with, among other things,the problem of how,in the complex,ever-changing world,men were to attain ___knowledge____.40. Of Aristotle’s numerous works,the following are perhaps still important to scholars and general readers alike:Ethics, Politics Poetics and Rhetoric41.A ristotle’s Rhetoric dealt with the art of __persuading____an audience.42. To students of literature,Aristotle’s most influential writing is__Poetics_____.43. The most important of the temples the ancient Greeks left us is ___Parthenon______, which has always been a great tourist attraction for people all over the world.44. Greek architecture can be grouped into three styles:the __Doric____ style, ___Ionic______style and ___Corinthian____style.45. Rediscovery of Greek culture played a vital part in the __Renaissance_____ in Italy and other European countries.46. Karl Marx,once wrote about the Greeks:“Why should’t the childhood of human society...exercise an eternal charm,as _____an age will never return___________?”47. The Greeks invented mathematics and science and philosophy;they first wrote history as opposed to mere annals;they speculated freely about the _nature_____of the world and the ends of life,without being bound in the fetters of any inherited orthodoxy.48. The Greeks achieved supreme achievements in nearly all fields of ___human endeavor______.49. The Greeks set an example by the bold effort they made to understand the world by the use of______human reason_____.50. The burning of Corinth in __146 B.C._____ marked the Roman conquest of Greece,which was then reduced to a province of the Roman Empire.。


《西方文化导论》综合复习第一章西方文化的起源一、填空1 、希腊历史的第一页是 ___非洲_____ 文明的历史。
爱琴海文明指的是爱琴海地区的青铜文化,先后形成了两大中心: ________ 和 ________ ,因此又通称克里特岛—迈锡尼文化。
2 、公元前 ________ 年期间,是克里特文化最为繁盛的时代。
克里特文化的中心是 ________ ,传说中的 ________ 国王建立了海上霸权,控制了整个爱琴海地区。
克里特的文字经历了象形文字和线形文字两大发展阶段,在它的繁盛期,线形文字全岛通用,这种文字又称 ________ ,以区别迈锡尼的 ________ 。
3 、迈锡尼文化以 ________ 而得名,但它实际上是希腊本土文化青铜文化的通称,是 ________ 的继续,只不过又加上了希腊民族文化的一些要素。
4 、荷马时代的艺术主要表现为 ________ ,陶器表面多用 ________ 来装饰,所以荷马时代的考古文化通称为 ________ 风格文化。
5 、爱琴海文明经历了一个盛极而衰的过程。
随着希腊文化中心的北移,希腊文化也越来越摆脱了 ________ 和 ________ 文明的巨大影响,形成了具有特色的希腊民族文化。
奠定了日后 ________ 的根基。
二、名词解释1 、迈锡尼文化2 、荷马史诗三、问答题:1 、荷马史诗的成就是什么?第二章希腊古典时代的文化一、填空1 、在古希腊史上,通常把公元前 8 世纪—前 6 世纪称为 ________ ,这是古希腊文化发展和形成的重要时期;公元前 6 世纪以后直至马其顿征服希腊,称为 ________ ,是上古希腊文化发展的鼎盛时期;古典时代以后到奥古斯都打败安东尼这一时期,为 ________ ,是上古希腊文化广泛传播于 _______ 、________ 、 ________ 三大洲许多地区的时代,同时也是希腊文化没落的时代。

西方文化概论章节测试答案爱琴文明与希腊神话传说(一)1下列说法错误的是()。
A、希腊文明表现的是一种和谐之美B、罗马文化倾向于较功利,物质方面发展C、西方现代文明包罗万象D、西方现代文明只发展基督教文化正确答案: D2不属于欧洲伸进地中海的三个半岛的是()。
A、巴尔干半岛B、亚平宁半岛C、克里特半岛D、伊比利亚半岛正确答案: C3埃及第一法老王朝大约出现在()。
A、公元前1500年B、公元前2000年C、公元3100年D、约在公元前3100年正确答案: D4下列说法错误的是()。
A、美索不达米亚文明是已知的最古老的文明B、克里特文明晚于埃及文明C、希腊文明的第一个阶段不是克里特-迈锡尼文明D、克里特文明晚于两河流域文明正确答案: C5十九世纪下下半叶,德国的()考古发掘了克里特文明。
A、莱柯曼B、爱因斯坦C、黑格尔D、施里曼正确答案: D6哪一项不是西方文化的特点?()A、跳跃性B、动荡性C、两极的大跳跃D、平稳、以不变应万变正确答案: D7中世纪出现的基督教文化的特点是()。
A、物质主义B、为灵主义C、纵欲主义的D、关注人间、关注现世的快乐正确答案: B8西方文化发展的跳跃性和动荡性要大于中国。
()正确答案:√9西方文化的源头是基督教文化。
()正确答案:×10希腊文明的源头是克里特文明。
()正确答案:√11克里特文明不受埃及文明影响。
()正确答案:×12西方文明发展的跳跃性和动荡性远远大于东方文明。
()正确答案:√13世界上最古老的文化是中国文化。
()正确答案:×14古代希腊是大希腊,环爱琴海周边的地区的都叫希腊文化区,它不仅仅限于今天的希腊半岛的一个民族国家。
()正确答案:√爱琴文明与希腊神话传说(二)1英国考古学家()发掘了1600块刻有克里特铭文的泥板。
A、达尔文B、温特利森C、伊文思D、荷马正确答案: C2最早的希腊人是()。
A、克里特本土人B、罗马人C、多利亚人D、阿卡亚人正确答案: D3对迈锡尼文明说法错误的是()。

Chapter One Greek CultureI. Fill in the blanks:1.European culture is made up of many elements, two of theseelements are considered to be more enduring and they are the Greco-Roman(希腊罗马的)element and the Judeo-Christian (犹太教与基督教的)element.2.Greek culture reached a high point of development in the 5thcentury.3.In the second half of the 4th century B. C., all Greece wasbrought under the rule of Alexander, king of Macedon.4.In 146 B. C. the Romans conquered Greece.5.Revived in 1896, the Olympic Games have beco me the world’sforemost amateur sports competition.6.Ancient Greeks considered Homer to be the author of theirepics.7.The Homer's epics consisted of Iliad and Odyssey .8.The Iliad deals with the alliance of the states of the southernmainland of Greece, led by Agamemnon in their war against the city of Troy.9.The Odyssey deals with the return of Odysseus after the Trojanwar to his home, island of Ithaca.10.The representation form of Greek Democracy iscitizen-assembly.(公民大会)11.Of the many lyric poets of ancient Greece, two are still admiredby readers today: Sappho and Pindar.12.Sappho was considered the most important lyric poet of ancientGreece.13.Pindar is best known for his odes celebrating the victories at the athleticgames, such as the 14 Olympic odes.14.The three great tragic dramatists of ancient Greece areAeschylus, Sophocles, and Euripides.15.Aeschylus wrote such plays as Prometheus Bound, Persians andAgamemnon.16.Sophocles wrote such tragic plays as Oedipus the King(俄狄浦斯王), Electra(伊莱克特拉(谋杀其母及其情人者), and Antigone. Oedipus complex(恋母情结)and Electra complex(恋父情结) derived from Sophocles’ plays.17.Euripides(欧里庇得斯)wrote mainly about women in suchplays as Andromache, Medea, and Trojan Women.edy also flourished in the 5th century B. C.. Its best writerwas Aristophanes, who has left eleven plays, including Frogs, Clouds, Wasps and Birds.19.Euripides _ is the first writer of "problem plays".20.Herodotus(希罗多德)is often called “Father of History”. Hewrote about the wars between Greeks and Persians.21.Thucydides(修西得底斯)described the war between Athensand Sparta and between Athens and Syracuse, a Greek state on the Island of Sicily.22.Pythagoras(毕达哥拉斯)was a bold thinker who had the ideathat all things were numbers.23.Pythagoras was the founder of scientific mathematics.24.Heracleitus(赫拉克利特) believed fire to the primary element ofthe universe, out of which everything else had arisen.25.The greatest names in European philosophy are Socrates, Platoand Aristotle.26.In the 4th century B. C., four schools of philosophers oftenargued with each other, they are the Cynics(犬儒学派), the Sceptics(怀疑论学派), the Epicureans(伊壁鸠鲁学派), and the Stoics(斯多葛学派).27.Euclid(欧几里得) is well-known for his Elements《几何原本》,a textbook of geometry. 28.To illustrate the principle of the level, Archimedes is said tohave told the king: “Give me a place to stand, and I will move the world.”29.Greek architecture can be grouped into three styles: the Doric(多利安式)style which is also called the masculine style; the Ionic(爱奥尼亚式)style which is also called the feminine style;and a later style that is called the Corinthian(科林斯式)style.30.The Acropolis at Athens(雅典卫城)and the Parthenon(万神殿) are the finest monument of Greek architecture and sculpture in more than 2000 years.II. Multiple choices:1.Which culture reached a high point of development in the 5thcentury B. C.?A. Greek CultureB. Roman CultureC. Egyptian CultureD. Chinese Culture2.In _______ the Roman conquered Greece.A. 1200B.C. B. 700 B. C. C. 146 B.C.D. The 5th century3.Which of the following works described the war led byAgamemnon against the city of Troy?A. Oedipus the KingB. IliadC. OdysseyD. Antigone4.Which of the following is NOT the plays written by Aeschylus?A. AntigoneB. AgamemnonC. PersiansD. Prometheus Bound5.Which of the following is NOT the plays written by Sophocles?A. ElectraB. AntigoneC. Trojan WomanD. Oedipus the King6.Which of the following is the play written by Euripides?A. AntigoneB. PersiansC. ElectraD. Medea7.Which of the following is NOT the greatest tragic dramatist ofancient Greece?A. AristophanesB. EuripidesC. SophoclesD. Aeschylus8.Who ever said that “You can not step twice into the same river.”?A. PythagorasB. HeracleitusC. AristotleD. Plato9.Who was the founder of scientific mathematics?A. HeracleitusB. AristotleC. SocratesD. Pythagoras10.Who is chiefly noted for his doctrine that “man is the measure ofall things”?A. ProtagorasB. PythagorasC. PyrrhonD. EpicurusChapter Two Roman CultureI. Fill in the blanks:1.The burning of Corinth in 146 B. C. marked Roman conquest ofGreece, which was then reduced to a province of the Roman Empire.2.The Roman writer Horace said: “Captive Greece took her rudeconqueror captive”.大意:征服者反被被征服者所征服。

••••••••••••••当前位置:›西方文化导论课后复习题西方文化导论课后复习题1.Give a brief account of the major achievements of Greek culture, such as those in religion, philosophy, literature and science.Greek religion really took shape during the Homeric Age,and featured polytheism with gods taking human form and feeling. Greek religion made a great contribution to Greek literature, philosophy and art. It is an important origin of Greek mythology ,Greek philosophy started with Thales (640 BC-547 BC) who believed that the material world originated in water,The core Greek philosophers are Socrates, Plato and Aristotle. Socrates had scant regard for material wealth, Plato established the Academy - the first Greek institution of higher learning.Literary representation centred round the two epicpoems of the Iliad and the Odyssey。
2 What do you think of the influence Greek culture has exerted on Western Civilization as a whole? Give examples.Greek culture is often termed the cradle of the Western Civilization and has had an enormous impact on Western culture The specific contributions are found in the areas of philosophy, politics, literature, art, science and architecture.Greek politics was one of the greatest influences on Western Civilization. The second significant influence was that of philosophy,give sound guidance to later year people to improve and change the world outside themselves。

《西方文化导论》复习综合题库.doc《西方文化导论》综合复习第一章两方文化的起源一、填空1、希腊历史的第一页是__非洲 ________ 文明的历史。
爱琴海文明指的是爱琴海地区的青铜文化,先?形成了两大中心: _________ 和__________ ,因此又通称克里特岛一迈锡尼文化。
2、公元前_________ 年期间,是克里特文化最为繁盛的时代。
克里特文化的中心是________ ,传说中的_________ 国王建立了海上霸权,控制了整个爱琴海地区。
克里特的文字经历了象形文字和线形文字两大发展阶段,在它的繁盛期,线形文字全岛通用,这种文字又称____________ ,以区别迈锡尼的__________ 。
3、迈锡尼文化以_________ 而得名,但它实际上是希腊本土文化青铜文化的通称,是________ i继续,只不过乂加上了希腊民族文化的一些要素。
4、荷马时代的艺术主要表现为__________ ,陶器表面多用_________ 来装饰, 所以荷马吋代的考古文化通称为 __________ 风格文化。
5、爱琴海文明经历了一个盛极而衰的过程。
随着希腊文化屮心的北移,希腊文化也越来越摆脱了________ 和__________ 文明的巨大影响,形成了具冇特色的希腊民族文化。
奠定了日后 _________ 的根基。
二、名词解释1、迈锡尼文化2、荷马史诗三、问答题:1、荷马史诗的成就是什么?第二章希腊古典吋代的文化一、填空1、在A希腊史上,通常把公元前8世纪一前6世纪称为_______________ ,这是古希腊文化发展和形成的重耍时期;公元前6世纪以后直至马其顿征服希腊,称为________ ,是上古希腊文化发展的鼎盛时期;古典时代以后到奥古斯都打败安东尼这一吋期,为_________ ,是上古希腊文化广泛传播于________ 、、________ 三大洲许多地区的吋代,同时也是希腊文化没落的时代。
Chapter One Greek CultureI. Fill in the blanks:1. 1.European culture is made up of many elements, two of these elements are considered to be more enduring and they are the Greco-Roman(希腊罗马的)element and the Judeo-Christian (犹太教与基督教的)element.2. 2.Greek culture reached a high point of development in the 5th century.3. 3.In the second half of the 4th century B. C., all Greece was brought under the rule of Alexander, king of Macedon.4. 4.In 146 B. C. the Romans conquered Greece.5. 5.Revived in 1896, the Olympic Games have become the world’s foremost amateur sports competition.6. 6.Ancient Greeks considered Homer to be the author of their epics.7.7.The Homer's epics consisted of Iliad and Odyssey .8.8.The Iliad deals with the alliance of the states of the southern mainland of Greece, led by Agamemnon in their war against the city of Troy.9.9.The Odyssey deals with the return of Odysseus after the Trojan war to his home, island of Ithaca.10.10.The representation form of Greek Democracy is citizen-assembly.(公民大会)11.11.Of the many lyric poets of ancient Greece, two are still admired by readers today: Sappho and Pindar.12.12.Sappho was considered the most important lyric poet of ancient Greece.13.13.Pindar is best known for his odes celebrating the victories at the athletic games, such as the 14 Olympic odes.14.14.The three great tragic dramatists of ancient Greece are Aeschylus, Sophocles, and Euripides.15.15.Aeschylus wrote such plays as Prometheus Bound, Persians and Agamemnon.16.16.Sophocles wrote such tragic plays as Oedipus the King(《俄狄浦斯王》), Electra(《伊莱克特拉》(谋杀其母及其情人者), and Antigone.Oedipus complex(恋母情结)and Electra complex(恋父情结) derived from Sophocles’ plays.17.17.Euripides (欧里庇得斯) wrote mainly about women in such plays as Andromache, Medea, and Trojan Women.edy also flourished in the 5th century B. C.. Its best writer was Aristophanes, who has left eleven plays, including Frogs, Clouds, Wasps and Birds.19.19.Euripides _ is the first writer of "problem plays".20.20.Herodotus(希罗多德)is often called “Father of History”. He wro te about the wars between Greeks and Persians.21.21.Thucydides(修西得底斯)described the war between Athens and Sparta and between Athens and Syracuse, a Greek state on the Island of Sicily.22.22.Pythagoras(毕达哥拉斯)was a bold thinker who had the idea that all things were numbers.23.23.Pythagoras was the founder of scientific mathematics.24.24.Heracleitus(赫拉克利特) believed fire to the primary element of the universe, out of which everything else had arisen.25.25.The greatest names in European philosophy are Socrates, Plato and Aristotle.26.26.In the 4th century B. C., four schools of philosophers often argued with each other, they are the Cynics(犬儒学派), the Sceptics(怀疑论学派), the Epicureans (伊壁鸠鲁学派), and the Stoics(斯多葛学派).27.27.Euclid(欧几里得) is well-known for his Elements《几何原本》, a textbook of geometry.28.28.To illustrate the principle of the level, Archimedes is said to have told the king, “Give me a place to stand, and I will move the world.”29.29.Greek architecture can be grouped into three styles: the Doric (多利安式)style which is also called the masculine style; the Ionic(爱奥尼亚式)style which is also called the feminine style; and a later style that is called the Corinthian(科林斯式)style.30.30.The Acropolis at Athens(雅典卫城)and the Parthenon(万神殿) are the finest monument of Greek architecture and sculpture in more than 2000 years.II. Multiple choices:1. 1.Which culture reached a high point of development in the 5th century B. C.?A. Greek CultureB. Roman CultureC. Egyptian CultureD. Chinese Culture2. 2.In _______ the Roman conquered Greece.A. 1200B.C. B. 700 B. C. C. 146 B.C.D. The 5th century3. 3.Which of the following works described the war led by Agamemnon against the city of Troy?A. Oedipus the KingB. IliadC. OdysseyD. Antigone4. 4.Which of the following is NOT the plays written by Aeschylus?A. AntigoneB. AgamemnonC. PersiansD. Prometheus Bound5. 5.Which of the following is NOT the plays written by Sophocles?A. ElectraB. AntigoneC. Trojan WomanD. Oedipus the King6. 6.Which of the following is the play written by Euripides?A. AntigoneB. PersiansC. ElectraD. Medea7.7.Which of the following is NOT the greatest tragic dramatist of ancient Greece?A. AristophanesB. EuripidesC. SophoclesD. Aeschylus8.8.Who ever said that “You can not step twice into the same river.”?A. PythagorasB. HeracleitusC. AristotleD. Plato9.9.Who was the founder of scientific mathematics?A. HeracleitusB. AristotleC. SocratesD. Pythagoras10.10.Who is chiefly noted for his doctrine that “man is the measure of all things”?A. ProtagorasB. PythagorasC. PyrrhonD. EpicurusChapter Two Roman CultureI. Fill in the blanks:1. 1.The burning of Corinth in 146 B. C. marked Roman conquest of Greece, which was then reduced to a province of the Roman Empire.2. 2.The Roman writer Horace said: “Captive Greece took her rude conqueror captive”.(大意是:征服者反而被被征服者所征服。
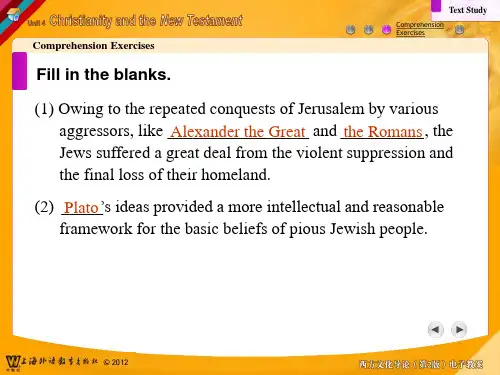
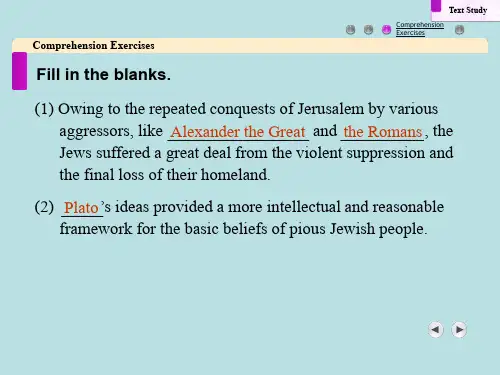
(1) Give a brief account of the major achievements of Greek culture, such as those in religion, philosophy, literature and science、Greek religion really took shape during the Homeric Age and featured polytheism with gods taking human form and feeling、Greek religion made a great contribution to Greek literature, philosophy and art、It is an important origin of Greek mythology which was fully developed by the religious tales of the Homeric epic and thus affected the later development of all kinds of Greek culture、Greek philosophy started with Thales (640 BC–547 BC) who believed that the material world originated in water、His philosophy was materialism、He was followed by Pythagoras who assumed that the key to the understanding of the world is numbers, on the opposition of the spokesman for idealism、The core Greek philosophers are Socrates, Plato and Aristotle、Socrates had scant regard for material wealth, but was keen on probing into the definition of some ethical and behavioral issues, such as “friendship”and “courage”、Plato established the Academy -the first Greek institution of higher learning、His contributions included his theory of ideas and his arguments on “republic”which was supposed to embrace his ideals about a future state where humans could enjoy a happy life、Aristotle is also a learned man and his work covers wide-ranging areas、His reputation as a philosopher largely depends on his argument on metaphysics which he tried to achieve a compromise between matter and divinity、Literary representation centred round the two epic poems of the Iliad and the Odyssey, lyrical poetry by Sappho and Pindar and drama by Aeschylus, Euripides and Aristophanes、Their works combined Greek myths and social life and won much appreciation and enthusiasm from the public、In science the mathematician Euclid established plane geometry and Archimedes discovered the ratio of radius of a circle and the relationship between the volume and surface of a sphere、(2) What do you think of the influence Greek culture has exerted on Western civilization as a whole? Give examples、Greek culture is often termed the cradle of the Western civilization and has had an enormous impact on Western culture、The specific contributions are found in the areas of philosophy, politics, literature, art, science and architecture、Greek politics was one of the greatest influences on the Western civilization、The Greeks were the first to successfully create a government based on the consensus of the people and thus provided a foundation for Western democracy、The second significant influence was that of philosophy、The Socratic idea about ethics and knowledge helped the Westerners care more for the effect of knowledge and value of morality, both of which give sound guidance to people in the later years to improve and change the world outside themselves, i、e、, human society and the natural world、Later generations of Westerners have benefited a lot from Greek culture, such as those in painting, sculpture, architecture, drama, poetry and historical works、Classicism had Greek culture as one of the crucial sources, and this has helped Westerners so much that they ascribed the origin of the Renaissance to it、This changed the intellectual conditions of the later medieval period and opened the way to the modern era in the West、Chapter 21、Tell briefly the major characteristics and contributions of Roman culture, as are demonstrated in religion, poetry, history and architecture、In the early period, Roman culture often depended heavily on the introduction and imitation of other cultures, particularly, Greek culture、Thus Romans created their own powerful culture, laying the foundation for subsequent Western culture in many fields、According to Greek culture and others’ culture; they created their own gods and myth, In poetry, ancient Rome made brilliant achievements,Livy was responsible for the great History of Rome in 142 volumes、His work has always been cited by later statesmen, writers or scholars,The architecture of Ancient Rome adopted the Greek style for its own purposes, but the Romans also developed a new kind、2、In what sense do you think Roman culture owed its accomplishments to the benefits obtained from Greek culture? Give examples、Roman culture learned and inherited a lot from Greek culture、,religion, philosophy and literature、In religion, Rome had its own system of beliefs which had been simple and could hardly compare with the plurality of Greek religion、The same is true of Roman philosophy where we could find examples ,In literature, Roman men of letters also borrowed a All in all, the two cultures are closely linkedgreat deal from Greek culture、Chapter 31、How was the Jewish civilization developed after a tortuous history of split and unification? The major explanation for the development of the Jewish civilization is its strong cohesiveness and vitality,they put into effect their Judaist beliefs and what they read of Judaist scriptures、From then on Jews have begun to become aware of the necessicity to liberate themselves from the restrictive laws and acquire new knowledge and modern ideas from the Europeans, Most of Jews thus received a good education, fully armed with cultural and scientific knowledge and did well in their own position they could quickly turn it into a well developed nation in spite of its small size and small population 、2.Say something about Judaism and The Old Testament、The Old Testament is the Judaist Bible、It was written in Hebrew, including the three parts:Pentateuch, Prophets and Hagiographa and Apocrypha、After The Old Testament was translated into Greek by Jewish scholars,many westerners began to understand Judaism by reading this book、It is not only of religious value but also of literatry value、Chapter 41、What are the main components of Christianity and why could it be accepted as the official religion first by the Roman Empire and then by the following kingdoms or empires in Europe?(1)The main components of Christianity are :1) The Bible as the only Christian scripture;Major Christian doctrines about Trinity and Redemption;3) Other doctrines or events of Christianity:(2 )Christianity is accepted and popular in Europe because of these factors:1)、For the common people in the empire ,they needed something to fill up their spiritual vacuum、Christianity could play such a role、2)、It could work together with any secular regimes to offer necessary assistance、3)、The name and influence of Christiaity would be a symbol of sacredness and justification,4) Christianity is also a kind of culture, it could be tolerated because their life and property could thus be secured in the changed circumstances、2、What are the basic differences between Christianity and Judaism?In spite of the fact that the two religions derived from Jewish culture, there are some basic differences between them、First is the different image of God、Second is different view of God、Jehovah is viewed He is like fire or wind 、God is kinder and more helpful, Third is the different position each religion is located in and hence would make different contribution、Fourth is Jehovah was important to Jews only in theory and affect them in spirit occasionally while Christianity moved into secular life for the Westerner as Pope and churches became very powerful 、Chapter 61、Tell simply the background and development of the Renaissance、It was no accident that it first occurred in Florence and Italy where the early signs of capitalism had appeared at the same time as social chaos, political disputes and military clashes , more and more people began to suspect the justification for those who held the power,Painting and sculpture were the first area to reflect the change of subjects and tastes、(2) What are the major features and achievements of the Renaissance? Give examples、The Renaissance is characterised by seeking ideological emancipation, intellectual freedom and political awareness, based on cultural production and religious reformation、All these were undertaken or unfolded gradually but widely, extending its influences to every corner of Europe, with more and more people getting involved、The achievements were seen principally in six areas, namely, painting, sculpture, poetry, fiction, drama and religious reformation as well as the change in the cultural and intellectual climate、Instances could be located in these areas, such as the huge change of subjects and styles in painting、The medieval painting used to centre on depicting Jesus Christ and other Christian subjects, not only effecting similar and the limited subject matter, but also depicting stylistically facial expressions and manners、The great artists in the Renaissance started to focus on the images with individualistic temperament, highlighting humanity instead of divinity, thus breaking away from the medieval frozen models and linking classicalism with human nature as the centre of their representational work、。
Greek CultureI. Fill in the blanks:1.European culture is made up of many elements, two of these elements are considered to be more enduring and they are the Greco-Roman(希腊罗马的)element and the Judeo-Christian (犹太教与基督教的)element.2.Greek culture reached a high point of development in the 5th century.3.In the second half of the 4th century B. C., all Greece was brought under the rule of Alexander, king of Macedon.4.In 146 B. C. the Romans conquered Greece.5.Revived in 1896, the Olympic Games have become the world’s foremost amateur sports competition.6.Ancient Greeks considered Homer to be the author of their epics.7.The Homer's epics consisted of_ Iliad and Odyssey .8.The Iliad deals with the alliance of the states of the southern mainland of Greece, led by Agamemnon in their war against the city of Troy.9.The Odyssey deals with the return of Odysseus after the Trojan war to his home, island of Ithaca.10.The representation form of Greek Democracy is __ citizen-assembly._(公民大会)11.Of the many lyric poets of ancient Greece, two are still admired by readers today: Sappho and Pindar.12.Sappho was considered the most important lyric poet of ancient Greece.13.Pindar is best known for his odes celebrating the victories at the athletic games, such as the 14 Olympic odes.14.The three great tragic dramatists of ancient Greece are Aeschylus, Sophocles, and Euripides.15.Aeschylus wrote such plays as Prometheus Bound, Persians and Agamemnon.16.Sophocles wrote such tragic plays as Oedipus the King(俄狄浦斯王), Electra(伊莱克特拉(谋杀其母及其情人者), and Antigone.Oedipus complex(恋母情结)and Electra complex(恋父情结) derived from Sophocles’ plays.17.Euripides(欧里庇得斯)wrote mainly about women in such plays as Andromache, Media, and Trojan Women.edy also flourished in the 5th century B. C.. Its best writer was Aristophanes, who has left eleven plays, including Frogs, Clouds,Wasps and Birds.19.Euripides _ is the first writer of "problem plays".20.Herodotus(希罗多德)is often called “Father of History”. He wrote about the wars between Greeks and Persians.21.Thucydides(修西得底斯)described the war between Athens and Sparta and between Athens and Syracuse, a Greek state on the Island ofSicily.22.Pythagoras(毕达哥拉斯)was a bold thinker who had the idea that all things were numbers.23.Pythagoras was the founder of scientific mathematics.24.Heracleitus(赫拉克利特) believed fire to the primary element of the universe, out of which everything else had arisen.25.The greatest names in European philosophy are Socrates, Plato and Aristotle.26.In the 4th century B. C., four schools of philosophers often argued with each other, they are the Cynics(犬儒学派), the Sceptics(怀疑论学派), the Epicureans(伊壁鸠鲁学派), and the Stoics(斯多葛学派).27.Euclid(欧几里得) is well-known for his Elements《几何原本》, a textbook of geometry.28.To illustrate the principle of the level, Archimedes is said to have told the king: “Give me a place to stand, and I will move the world.”29.Greek architecture can be grouped into three styles: the Doric(多利安式)style which is also called the masculine style; the Ionic(爱奥尼亚式)style which is also called the feminine style; and a later style that is called the Corinthian(科林斯式)style.30.The Acropolis at Athens(雅典卫城)and the Parthenon(万神殿) are the finest monument of Greek architecture and sculpture in more than2000 years.II.Choice1.Which culture reached a high point of development in the 5th century B. C.?A. Greek CultureB. Roman CultureC. Egyptian CultureD. Chinese Culture2.In ___________ the Roman conquered Greece.A.1200B.C. B.700 B. C.C.146 B. C.D. The 5th century3.Which of the following works described the war led by Agamemnon against the city of Troy?A. Oedipus the KingB. IliadC. OdysseyD. Antigone4.Which of the following is NOT the plays written by Aeschylus?A. AntigoneB. AgamemnonC. PersiansD. Prometheus Bound5.Which of the following is NOT the plays written by Sophocles?A.ElectraB.AntigoneC.Trojan WomanD.Oedipus the King6.Which of the following is the play written by Euripides?A.Antigone B PersiansC ElectraD Medea7.Which of the following is NOT the greatest tragic dramatist of ancient Greece?A AristophanesB EuripidesC SophoclesD Aeschylus8.Who ever said that “You can not step twice into the same river”?A PythagorasB HeracleitusC Aristotle9.Who was the founder of scientific mathematics?A HeracleitusB AristotleC SocratesD Pythagoras10.Who is chiefly noted for his doctrine that “man is the measure of all things”?A ProtagorasB PythagorasC PyrrhonD EpicurusIII. Interpretation:1. PlatoPlato was a very famous philosopher of ancient Greece, pupil of Socrates. Plato built up a comprehensive system of philosophy. He argued that men have knowledge because of the existence of certain general “ideas”, like beauty, truth and goodness. Only these “ideas” are completely real, while the physical world is only relatively real. For this reason, Plato’s philosophy is called Idealism, an d Plato was called idealist.2. "Democracy" in ancient Greece1)Democracy means "exercise of power by the whole people", but in Greece by "the whole people" the Greeks meant only the adult male citizens.2) Women, children, foreigners and slaves were excluded from Democracy.IV. Questions:1. How did the Greek Culture originate and develop?1) Probably around 1200 B.C., a war was fought between Greece and troy. This is the war that Homer refers to in his epics.2) Greek culture reached a high point of development in the 5th century B.C.A. The successful repulse(击退)of the Persian invasion early in the 5th century.B. The establishment of democracy.C. The flourishing of science, philosophy, literature, art and historical writing in Athens.3) The 5th century closed with civil war between Athens and Sparta.4) In the second half of the 4th century B.C., Greece was conquered by Alexander, king of Macedon. Whenever he went and conquered, whenever Greek culture was found.5) Melting between Greek culture and Roman culture in 146 B.C., the Romans conquered Greece.2. What is the great significance of Greek Culture on the later-on cultural development?There has been an enduring excitement about classical Greek culture in Europe and elsewhere rediscovery of Greek culture played a vital part in the Renaissance in Italy and other European countries.1) Spirit of innovationThe Greek people invented mathematics and science and philosophy; They first wrote history as opposed to mere annals; They speculated freely about the nature of the world and the ends of life, without being bound in the fetters(束缚) of any inherited orthodoxy(正统的实践活动、风俗或信仰).2) Supreme AchievementThe Greeks achieved supreme achievements in nearly all fields of human endeavor: Philosophy, science, epic poetry, comedy, historical writing, architecture, etc.3) Lasting effectA. Countless writers have quoted, borrowed from and otherwise used Homer's epics, the tragedies of Aeschylus and Sophocles and Euripides, Aristophanes' comedies, Plato's Dialogues, ect.B. In the early part of the 19th century, in England alone, three young Romantic poets expressed their admiration of Greek culture in works which have themselves become classics: Byron(拜伦)'s Isles of Greece(《哀希腊》), Shelley(雪莱)'s Hellas and Prometheus Unbound (《解放了的普罗米修斯》)and Keats(济慈)'s Ode on a Grecian Urn(《希腊古瓮》).C. In the 20th century, there are Homeric parallels in the Irishman James Joyce(乔伊斯)'s modernist masterpiece Ulysses.Roman Culture 1I. Fill in the blanks.1. The burning of Corinth in 146 B. C. marked Roman conquest of Greece, which was then reduced to a province of the Roman Empire.2. The Roman writer Horace said: “Captive Greece took her rude conqueror captive”.(大意是:征服者反而被被征服者所征服。
(1) Give a brief account of the major achievements of Greek culture, such as those in religion, philosophy, literature and science.Greek religion really took shape during the Homeric Age and featured polytheism with gods taking human form and feeling. Greek religion made a great contribution to Greek literature, philosophy and art. It is an important origin of Greek mythology which was fully developed by the religious tales of the Homeric epic and thus affected the later development of all kinds of Greek culture.Greek philosophy started with Thales (640 BC–547 BC) who believed that the material world originated in water. His philosophy was materialism. He was followed by Pythagoras who assumed that the key to the understanding of the world is numbers, on the opposition of the spokesman for idealism.The core Greek philosophers are Socrates, Plato and Aristotle. Socrates had scant regard for material wealth, but was keen on probing into the definition of some ethical and behavioral issues, such as “friendship”and “courage”.Plato established the Academy -the first Greek institution of higher learning. His contributions included his theory of ideas and his arguments on “republic”which was supposed to embrace his ideals about a future state where humans could enjoy a happy life. Aristotle is also a learned man and his work covers wide-ranging areas. His reputation as a philosopher largely depends on his argument on metaphysics which he tried to achieve a compromise between matter and divinity. Literary representation centred round the two epic poems of the Iliad and the Odyssey, lyrical poetry by Sappho and Pindar and drama by Aeschylus, Euripides and Aristophanes. Their works combined Greek myths and social life and won much appreciation and enthusiasm from the public.In science the mathematician Euclid established plane geometry and Archimedes discovered the ratio of radius of a circle and the relationship between the volume and surface of a sphere.(2) What do you think of the influence Greek culture has exerted on Western civilization as a whole? Give examples.Greek culture is often termed the cradle of the Western civilization and has had an enormous impact on Western culture. The specific contributions are found in the areas of philosophy, politics, literature, art, science and architecture.Greek politics was one of the greatest influences on the Western civilization. The Greeks were the first to successfully create a government based on the consensus of the people and thus provided a foundation for Western democracy.The second significant influence was that of philosophy. The Socratic idea about ethics and knowledge helped the Westerners care more for the effect of knowledge and value of morality, both of which give sound guidance to people in the later years to improve and change the world outside themselves, i.e., human society and the natural world.Later generations of Westerners have benefited a lot from Greek culture, such as those in painting, sculpture, architecture, drama, poetry and historical works. Classicism had Greek culture as one of the crucial sources, and this has helped Westerners so much that they ascribed the origin of the Renaissance to it. This changed the intellectual conditions of the later medieval period and opened the way to the modern era in the West.Chapter 21. Tell briefly the major characteristics and contributions of Roman culture, as are demonstrated in religion, poetry, history and architecture.In the early period, Roman culture often depended heavily on the introduction and imitation of other cultures, particularly, Greek culture. Thus Romans created their own powerful culture, laying the foundation for subsequent Western culture in many fields. According to Greek culture and others’ culture; they created their own gods and myth, In poetry, ancient Rome made brilliant achievements,Livy was responsible for the great History of Rome in 142 volumes. His work has always been cited by later statesmen, writers or scholars,The architecture of Ancient Rome adopted the Greek style for its own purposes, but the Romans also developed a new kind.2. In what sense do you think Roman culture owed its accomplishments to the benefits obtained from Greek culture? Give examples.Roman culture learned and inherited a lot from Greek culture.,religion, philosophy and literature. In religion, Rome had its own system of beliefs which had been simple and could hardly compare with the plurality of Greek religion. The same is true of Roman philosophy where we could find examples ,In literature, Roman men of letters also borrowed a All in all, the two cultures are closely linkedgreat deal from Greek culture.Chapter 31. How was the Jewish civilization developed after a tortuous history of split and unification? The major explanation for the development of the Jewish civilization is its strong cohesiveness and vitality,they put into effect their Judaist beliefs and what they read of Judaist scriptures.From then on Jews have begun to become aware of the necessicity to liberate themselves from the restrictive laws and acquire new knowledge and modern ideas from the Europeans, Most of Jews thus received a good education, fully armed with cultural and scientific knowledge and did well in their own position they could quickly turn it into a well developed nation in spite of its small size and small population .2.Say something about Judaism and The Old Testament.The Old Testament is the Judaist Bible. It was written in Hebrew, including the three parts:Pentateuch, Prophets and Hagiographa and Apocrypha. After The Old Testament was translated into Greek by Jewish scholars,many westerners began to understand Judaism by reading this book. It is not only of religious value but also of literatry value.Chapter 41. What are the main components of Christianity and why could it be accepted as the official religion first by the Roman Empire and then by the following kingdoms or empires in Europe?(1)The main components of Christianity are :1) The Bible as the only Christian scripture;Major Christian doctrines about Trinity and Redemption;3) Other doctrines or events of Christianity:(2 )Christianity is accepted and popular in Europe because of these factors:1).For the common people in the empire ,they needed something to fill up their spiritual vacuum. Christianity could play such a role.2). It could work together with any secular regimes to offer necessary assistance.3). The name and influence of Christiaity would be a symbol of sacredness and justification,4) Christianity is also a kind of culture, it could be tolerated because their life and propertycould thus be secured in the changed circumstances.2. What are the basic differences between Christianity and Judaism?In spite of the fact that the two religions derived from Jewish culture, there are some basic differences between them.First is the different image of God.Second is different view of God. Jehovah is viewed He is like fire or wind .God is kinder and more helpful, Third is the different position each religion is located in and hence would make different contribution. Fourth is Jehovah was important to Jews only in theory and affect them in spirit occasionally while Christianity moved into secular life for the Westerner as Pope and churches became very powerful .Chapter 61.Tell simply the background and development of the Renaissance.It was no accident that it first occurred in Florence and Italy where the early signs of capitalism had appeared at the same time as social chaos, political disputes and military clashes , more and more people began to suspect the justification for those who held the power,Painting and sculpture were the first area to reflect the change of subjects and tastes.(2) What are the major features and achievements of the Renaissance? Give examples.The Renaissance is characterised by seeking ideological emancipation, intellectual freedom and political awareness, based on cultural production and religious reformation. All these were undertaken or unfolded gradually but widely, extending its influences to every corner of Europe, with more and more people getting involved.The achievements were seen principally in six areas, namely, painting, sculpture, poetry, fiction, drama and religious reformation as well as the change in the cultural and intellectual climate. Instances could be located in these areas, such as the huge change of subjects and styles in painting. The medieval painting used to centre on depicting Jesus Christ and other Christian subjects, not only effecting similar and the limited subject matter, but also depicting stylistically facial expressions and manners. The great artists in the Renaissance started to focus on the images with individualistic temperament, highlighting humanity instead of divinity, thus breaking away from the medieval frozen models and linking classicalism with human nature as the centre of their representational work.。
Chapter One Greek CultureI. Fill in the blanks:1.European culture is made up of many elements, two of theseelements are considered to be more enduring and they are the Greco-Roman(希腊罗马的)element and the Judeo-Christian (犹太教与基督教的)element.2.Greek culture reached a high point of development in the 5thcentury.3.In the second half of the 4th century B. C., all Greece wasbrought under the rule of Alexander, king of Macedon.4.In 146 B. C. the Romans conquered Greece.5.Revived in 1896, the Olympic Games have beco me the world’sforemost amateur sports competition.6.Ancient Greeks considered Homer to be the author of theirepics.7.The Homer's epics consisted of Iliad and Odyssey .8.The Iliad deals with the alliance of the states of the southernmainland of Greece, led by Agamemnon in their war against the city of Troy.9.The Odyssey deals with the return of Odysseus after the Trojanwar to his home, island of Ithaca.10.The representation form of Greek Democracy iscitizen-assembly.(公民大会)11.Of the many lyric poets of ancient Greece, two are still admiredby readers today: Sappho and Pindar.12.Sappho was considered the most important lyric poet of ancientGreece.13.Pindar is best known for his odes celebrating the victories at the athleticgames, such as the 14 Olympic odes.14.The three great tragic dramatists of ancient Greece areAeschylus, Sophocles, and Euripides.15.Aeschylus wrote such plays as Prometheus Bound, Persians andAgamemnon.16.Sophocles wrote such tragic plays as Oedipus the King(俄狄浦斯王), Electra(伊莱克特拉(谋杀其母及其情人者), and Antigone. Oedipus complex(恋母情结)and Electra complex(恋父情结) derived from Sophocles’ plays.17.Euripides(欧里庇得斯)wrote mainly about women in suchplays as Andromache, Medea, and Trojan Women.edy also flourished in the 5th century B. C.. Its best writerwas Aristophanes, who has left eleven plays, including Frogs, Clouds, Wasps and Birds.19.Euripides _ is the first writer of "problem plays".20.Herodotus(希罗多德)is often called “Father of History”. Hewrote about the wars between Greeks and Persians.21.Thucydides(修西得底斯)described the war between Athensand Sparta and between Athens and Syracuse, a Greek state on the Island of Sicily.22.Pythagoras(毕达哥拉斯)was a bold thinker who had the ideathat all things were numbers.23.Pythagoras was the founder of scientific mathematics.24.Heracleitus(赫拉克利特) believed fire to the primary element ofthe universe, out of which everything else had arisen.25.The greatest names in European philosophy are Socrates, Platoand Aristotle.26.In the 4th century B. C., four schools of philosophers oftenargued with each other, they are the Cynics(犬儒学派), the Sceptics(怀疑论学派), the Epicureans(伊壁鸠鲁学派), and the Stoics(斯多葛学派).27.Euclid(欧几里得) is well-known for his Elements《几何原本》,a textbook of geometry. 28.To illustrate the principle of the level, Archimedes is said tohave told the king: “Give me a place to stand, and I will move the world.”29.Greek architecture can be grouped into three styles: the Doric(多利安式)style which is also called the masculine style; the Ionic(爱奥尼亚式)style which is also called the feminine style;and a later style that is called the Corinthian(科林斯式)style.30.The Acropolis at Athens(雅典卫城)and the Parthenon(万神殿) are the finest monument of Greek architecture and sculpture in more than 2000 years.II. Multiple choices:1.Which culture reached a high point of development in the 5thcentury B. C.?A. Greek CultureB. Roman CultureC. Egyptian CultureD. Chinese Culture2.In _______ the Roman conquered Greece.A. 1200B.C. B. 700 B. C. C. 146 B.C.D. The 5th century3.Which of the following works described the war led byAgamemnon against the city of Troy?A. Oedipus the KingB. IliadC. OdysseyD. Antigone4.Which of the following is NOT the plays written by Aeschylus?A. AntigoneB. AgamemnonC. PersiansD. Prometheus Bound5.Which of the following is NOT the plays written by Sophocles?A. ElectraB. AntigoneC. Trojan WomanD. Oedipus the King6.Which of the following is the play written by Euripides?A. AntigoneB. PersiansC. ElectraD. Medea7.Which of the following is NOT the greatest tragic dramatist ofancient Greece?A. AristophanesB. EuripidesC. SophoclesD. Aeschylus8.Who ever said that “You can not step twice into the same river.”?A. PythagorasB. HeracleitusC. AristotleD. Plato9.Who was the founder of scientific mathematics?A. HeracleitusB. AristotleC. SocratesD. Pythagoras10.Who is chiefly noted for his doctrine that “man is the measure ofall things”?A. ProtagorasB. PythagorasC. PyrrhonD. EpicurusChapter Two Roman CultureI. Fill in the blanks:1.The burning of Corinth in 146 B. C. marked Roman conquest ofGreece, which was then reduced to a province of the Roman Empire.2.The Roman writer Horace said: “Captive Greece took her rudeconqueror captive”.大意:征服者反被被征服者所征服。