医护英语大纲及原文
- 格式:doc
- 大小:338.50 KB
- 文档页数:43

mets医护英语五级考试大纲
METS医护英语五级考试大纲包括以下内容:
1. 考试目标:METS医护英语五级考试旨在测试考生在医疗场景下的英语应用能力,包括听力、阅读、写作和口语等方面。
2. 考试内容:考试内容包括医疗场景下的听力、阅读、写作和口语四个部分。
听力部分主要测试考生在医疗场景下的听力理解能力;阅读部分主要测试考生对医疗相关文章的阅读理解能力;写作部分主要测试考生在医疗场景下的英语写作能力;口语部分主要测试考生在医疗场景下的英语表达能力。
3. 考试要求:考生需要通过听力、阅读、写作和口语四个部分的测试,且总分数达到规定的合格线才算通过考试。
具体要求可以根据考试大纲进行查阅。
4. 考试形式:METS医护英语五级考试采用机考的形式进行,考试时间为120分钟。
5. 考试难度:METS医护英语五级考试的难度相对较高,要求考生具备较高的英语水平和医学知识储备。
总之,METS医护英语五级考试大纲是指导考生备考的重要文件,考生需要认真学习和掌握大纲的内容,以提高自己的英语应用能力和通过考试的几率。

医护英语ContentsUnit 1 Registration and Visiting a Doctor (3)Unit 2 Examination Process (9)Unit 3 Diagnosis (15)Unit4 Administering Medications (24)Unit 5 Hospitalization (29)Unit 6 Hospitalization (35)Registration and Visiting a Doctor 挂号与就诊Examination Process 检查过程Diagnosis 诊断Administration and Medication 门诊处置与取药Hospitalization 办入院手续与住院Rehabilitation 康复Unit 1 Registration and Visiting a DoctorReading A:Task 1 Before reading the passage, see how much you know about common diseases of the body systems by answering the following questions.1.How can you decide that a specific disease belongs to one of the body systems?2.Which hospital department might you refer a patient to if he/she has a stomachache?Common diseases of the Body SystemsHuman body diseases vary in both severity and diversity. Any body part or function can contract a disease or have s disorder. We are more capable of fighting these diseases today than ever before and medicine is advancing every day.Below are introductions to human body diseases and disorders.Skin DisordersThe skin is susceptible to physical injury and to infection by bacteria, virus, fungi, and exposure to sunlight. Almost and teenager can tell you the most common skin disorder: acne. There are other skin problems far more serious than acne, e.g. skin cancer, melanoma, psoriasis and vitiligo.Nervous System DisordersDamage to nervous system through physical injury or disease can impair both physical and mental function. Brain tumors, Parkinson’s disease and stroke are some of the nervous system conditions.Cardiovascular DisordersCardiovascular disorders are conditions of the heart and blood vessels, which consist of mainly coronary heart disease (CHD), or coronary artery disease (CAD), hypertension, arrhythmia and heart failure. What we eat and the amount of exercise we get can affect our cardiovascular system.Immune DisordersWhen the immune system does not function properly, a number of diseases can occur. There are two types of immune system disorders: allergies and autoimmune disease including juvenile diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis and anemia, etc. and immunodeficiency disease such a AIDS.Digestive DisordersMost digestive diseases are very complex. Common disorders include hepatitis, heartburn and stomach cancer. Abusing alcohol imposes the greatest risk for digestive diseases.Reproductive DisordersDisorders that may affect the proper functioning of the reproductive system include abnormal hormone secretion, sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) such as syphilis and gonorrhea, and the presence of cancerous tissue in the region. Such problems frequently affect fertility. There are also functional problems caused by infertility or sexual dysfunction.Respiratory DisordersRespiratory disorders, or lung diseases, are disorders such as pneumonia, tuberculosis, chronic bronchitis, lung cancer and others. They can affect people of all ages and both genders.Endocrine disordersEndocrine system disorders occur either due to too much or tool little or sometimes nohormone. These disorders may lead to abnormal growth pattern, diabetes, high cholesterol and triglyceride levels. Endocrine system disorders include hyperthyroidism, growth hormone deficiency and hypothyroidism.Musculoskeletal DisordersDisease of the musculoskeletal system may result in the inability to walk, sit, or even breathe. The musculoskeletal conditions having the most impact on population health will be presented: back pain, repetitive strain injury (RSI) and osteoarthritis.Task 2 Read the passage and match each common disease with one body system.1.hypertension a. respiratory system2.acne b. skin system3.bone fracture c. nervous system4.stomach cancer d. cardiovascular system5.brain tumors e. endocrine system6.AIDS f. digestive system7.lung cancer g. immune system8.hypothyroidism h. musculoskeletal systemTask 3 Read the passage again, and tick the facts mentioned in the passage about the common diseases of the body system.✧Our ability to fight human body diseases✧The case history of the patients✧Various disorders of the nine body systems✧Disorders typical of the body systems✧An introduction to the now cures for the diseases✧Two types of immune disorders✧The skin featuring its susceptibility✧Alcoholism contributing to digestive diseases✧The specialists in some ot the diseases✧Asthma as a respiratory problemListeningTask 1 Mr. Black is making a call to pre-register at a hospital. Listen to the conversation and choose the best answer to each question you hear.1.Why can’t Mr. Black register right now?A.Because of a power cut.B. Because of lack of record.C. Because of the system failure.2.Which card is NOT necessary for registration?A.ID card.B. Credit card.C. Insurance card.3.What is the registration time?A. 8 a.m. to 5 p.m.B. 9 a.m. to 4 p.m.C. 8 a.m. to 4 p. m.4. When does the nurse suggest Mr. Black come to the hospital?A. In the morning.B. In the afternoon.C. On weekdays.5. Where will Mr. Black find receptionists in the hospital?A. At the registration office.B. In the Outpatient Hall.C. Outside the consulting room. Task 2. Mr. Black is registering at the hospital in person. Listen to the conversation and fill in the blanks with what you hear.Mr. Black: Good Morning.Nurse: Good morning. Sorry to have kept you waiting. Have you ever been here before? Mr. Black: No, this is my first _______ here.Nurse: In this case, you have to fill in this registration form. Your name, age, ________ and things like that. I will make a record for you.Mr. Black:No problem.Nurse: Well, what’s troubling you?Mr. Black: I have a stomachache and feel like __________ sometimes. Besides, it’s difficult for me to swallow. Which department should I register ___________?Nurse: I think you should go to the Department of Gastroenterology (胃肠学) first. If necessary w e’ll __________ you to the Department of Chest Surgery.Mr. Black: Okay, here is my form.Nurse:Thank you. The registration ___________ is five Yuan. This is your registration card. Please don’t lose it and bring it whenever you came.Mr. Black: Thank you for your help.Nurse: That’s all rightTask 3. Mr. Liu, an overseas student in Britain, is calling at St. Paul’s Hospital to make an appointment. Listen to the conversation and help the nurse to fill in the record.Appointment RecordPatient’s name:Date of Birth:Visiting Purpose:Time:Doctor’s Name:Reading BProcedures to Visit a Doctor●How to Visit a Doctor in the West:When you get sick, you might have to make an appointment to visit a doctor for a physical checkup. Talking to the doctor and explaining your symptoms might not be too difficult. Here is how to make the most of your doctor’s visit.●Before You GoWhen you make the appointment, state the nature of your concern so that a proper length of time can be scheduled.If it’s your first visit to that clinic or with that physician, be ready to give your medical history.✧Provide information about diseases that run in your family.✧Describe current and past heath problems and treatments.✧Bring the original containers for any prescription and over-the-counter medications, herbs,supplements and vitamins you are taking.Preparing written information to bring with can help you communicate well with your doctor.✧ A short description of your health problems should include a list of symptoms and detailson when the problem started, where it is, what it fells like, and if there’s anything you do that makes it worse or better.✧ A list of medications you are taking should include the dose and frequency of prescriptionand over-the-counter drugs, as well as herbs, supplements and vitamins.●While You’re ThereWhen talking with your doctor, remember that your health is worth his or her time.✧Clearly describe you health concern (symptoms, when it started, where it is, what it fellslike). Information written in advance can help.✧Restate explanations and ask for clarification, until you’re sure that the doctorunderstands your concerns and completely answer your questions.✧Don’t forget about your emotional health; it influences your physical health. So mentionall health-related concerns, not just the visible ones.✧Make sure your provider is aware of the prescription and over-the-counter medications,herbs, supplements and vitamins you are taking.Before leaving, find out✧It and when you should return for another visit.✧Whether you are to phone in for any test results or to report on your condition.✧If there are certain warning signs you should watch for✧Whether there are materials you could take home or a website you should visit to learnmore about your diagnosis or treatmentNever leave uncertain about your diagnosis or treatment●Common Procedures to Visit a Doctor in China’s HospitalThe first thing you should know about the medical services is that you should have some basic knowledge about the procedures.In china patients simply show up at local hospitals. No preset appointment is necessary, except for surgical procedures. Treatment techniques include diagnosis, medication, injection or the necessary scans. Your doctor may give you a prescription for you to buy medicine from the in-house pharmacy, most of the time at the lobby of the outpatient section building.● A chart on how to visit a doctor in Chinese hospital:Patient pre-check register diagnosis pay feestake medicine leavecheck & test specific section observation pay fees take medicine leave Task 1 Complete the procedures to visit a doctor in Western countries according to the passage.How to Visit a Doctor in the West1.Before you goa.Make an _____________ with your ____________.b.Be ready to give your _____________ on your first visit.c.Prepare __________________________.2.While You’re Therea.When _____________ with your doctor, remember that your ____________ is worthhis or her time.b.Before leaving, make sure of __________________ things.c.Never leave _____________ about your diagnosis or treatment.Task 2 Translate the following paragraph into Chinese.In china patients simply show up at local hospitals. No preset appointment is necessary, exceptfor surgical procedures. Treatment techniques include diagnosis, medication, injection or the necessary scans. Your doctor may give you a prescription for you to buy medicine from the in-house pharmacy, most of the time at the lobby of the outpatient section building.____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ WritingPublic NoticeTask 1 A public notice is written for many reasons. By writing a public notice, you will inform people about some news. No matter which kind of public notice you write, you will find several tips useful: be brief and to the point, well-worded, coherent and smooth with a definite purpose. Now read the following sample public notice and learn about the way it is written.A Sample:Public NoticeNotice is hereby given that Liu Dan from the Department of General Surgery in our hospital won the first place in the City’s 2009 Nursing Skills Contest held on May 4th, 2009.We inform you that a commendation meeting is to be held at the hospital auditorium on Wednesday afternoon, at 1:30. Representatives from all departments are expected to attend the meeting on time.The Office of Hospital PresidentMay 5th, 2009Commendation meeting 表彰会Task 2 Suppose you are a secretary with the human resource department. Please write a public notice based on the following information.Information:Li Lan has succeeded in competing for the position of head nurse in the emergency department. She took the first place in both the theoretical examination and interview for the position. Therefore the hospital leaders and the nursing department, after due consideration, have officially decided to appoint Li Lan head nurse in the emergency department.Technical Words:Coronary artery disease (CAD) 冠状动脉疾病Coronary heart disease (CHD) 冠心病Juvenile diabetes 青少年糖尿病Parkinson’s disease 帕金森氏病;震颤性麻痹Repetitive strain injury (RSI)重复性过度劳累损伤Rheumatoid arthritis 风湿性关节炎Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) 性传播疾病Over-the-counter medication 非处方药Parkinson’s diseaseParkinson’s disease is a chronic and progressive degenerative disease of the brain marked by tremors, rigidity and slow movements.Parkinson’s disease belongs to a group of conditions called movement disorders. It is characterized by muscle rigidity, resting tremor, slowing of movement and, in extreme cases, nearly complete loss of movement. Secondary symptoms may include high level cognitive dysfunction, subtle language problems, and depression.Exercise: Fill in each blank with the appropriate form of the word given in brackets.1. At first, we didn’t realize the (severe) _______ of her wounds.2. It is reported that this disease attacks the central (nerve) _____ system.3. The (injure) ________ to their key player could be a decisive factor in the game.4. We couldn’t feel the change in the blood pressure within the (arterial) _________.5. (Diabetic) ________ is by far the most frequent disease among the over-weight people.6. These bacteria can be thought of as an additional (digest) ________ organ.7. It is (normal) ________ for a man to walk in his sleep.8. They found it stimulated the (secrete) _______ of insulin in pancreatic (胰的) cells in thelaboratory.9. Impairment of the ability to write is usually caused by brain (function) ________ or disease.10. What is severe acute (respire) _________ syndrome?Unit 2 Examination ProcessReading ATask 1 Before reading the passage, see how much you know about medical tests by answering the following questions.3.What are the most common medical tests in the hospital?4.What are the purposes of medical tests?A Directory of Medical TestsTaking a medical history and performing a physical examination usually provide the information a doctor needs to evaluate a person’s health or to understand what is causing an illness. But sometimes, doctors need to order tests to find out more.Here are some common tests and what they involve:Blood TestsComplete Blood Count (CBC). A CBC measures the levels of different types of blood cells. By determining if there are too many or not enough of each blood cell type, a CBC can help to detect a wide variety of illnesses or signs of infection.Blood Chemistry Test. Basic blood chemistry tests measure the levels of certain electrolytes, such as sodium and potassium, in the blood. Doctors typically order them to look for any sign of kidney dysfunction, diabetes, metabolic disorders, and tissue damage.Liver Function Test. Liver function tests check to see how the liver is working and look for any sort of liver damage or inflammation.Radiology TestsX-Rays. X-rays can help doctors find a variety of conditions, including broken bones and lung infections.Ultrasound. Though they’re typically associated with pregnancy, doctors order ultrasounds in lots of different cases. The images seen on most ultrasounds are difficult for the untrained eye to decipher, so a doctor will view the image and interpret it.Computed Tomography (CAT scan or CT scan). CAT scans are a kind of X-ray, and typically are ordered to look for things such as appendicitis, internal bleeding, or abnormal growths. A scan may require the use of a contrast material (a dye or other substance) to improve the visibility of certain tissues or blood vessels.Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI). MRIs use radio waves and magnetic fields to produce an image. MRIs are often used to look at bones, joints, and the brain. Contrast material is sometimes given through an IV in order to get a better picture of certain structures.Other TestsStool Test. Stool (or feces or poop) test can provide doctors with valuable information about what’s wrong when one has a problem in the stomach, intestines, or another part of the gastrointestinal system.Urine Test. Doctors order urine tests to make sure that the kidneys are functioning properly or when they suspect an infection in the kidneys or bladder.Electroencephalography (EEG). EEGs often are used to detect conditions that affect brain function, such as epilepsy, seizure disorders, and brain injury.Electrocardiography (EKG). EKGs measure the heart’s electrical activity to help evaluate its function and identify any problems. The EKG can help determine the rate and rhythm of heartbeats, the size and position of the heart’s chambers, and whether there is any damage present. EKGs can detect abnormal heart rhythms, some congenital heart defects, and heart tissue that isn’t getting enough oxygen.Task 2 After reading the passage, group the medical tests mentioned in the passage into each category.Blood Tests: Radiology Tests: Other Tests:Take 3 Read the passage again. Match each medical test with one fact as its target.9.Ultrasound a. lung infections10.X-rays b. an infection in the kidneysplete Blood Test c. metabolic disorders12.Blood Chemistry Test d. abnormal growths13.Liver Function Test e. blood cell type14.Urine Test f. heart rhythms15.EKG g. pregnancy16.Stool Test h. a problem in the intestines17.MRI a. liver inflammation18.EEG b. brain injuryputed Tomography k. joint problemsListeningTask 1 Mr. Black is having a check at the Department of Gastroenterology. A nurse will draw some blood for him. Listen to the conversation and put the following items in correct order.Sterilize the skinGet the reportTake off coat and roll up your sleeveClench your fistOpen your handSend specimen to the laboratoryTie the tourniquetPress with cotton swabTask 2 Mr. Black is going to have a gastroscopy(胃镜检查). Listen to the conversation and choose the best answer to each question you hear.1. What does an endoscope look like?A. As long as a fingerB. Thin and flexible.C. A large pipe2. What should Mr. Black do before having the gastroscopy?A. Smoke as little as possible.B. Empty the stomach.C. Drink a lot of water.3. When is Mr. Black supposed to come tomorrow?A. 6 a.m..B. 2 p.m.C. 8 a.m.4. When will Mr. Black get the result?A. In several days.B. Immediately.C. The day after tomorrow.5. What will be sent to the pathology laboratory?A. Blood Sample.B. Gastric fluid sample.C. Biology sample.Task 3. Mr. Black is in the gastroscope room. Listen to the conversation and fill in the blanks with what you hear.Nurse: Mr. Black, I’d like to know whether you ________ today.Mr. Black: Never.Nurse: Fine. The gastroscopy usually takes about ten minutes. But now we should make some ________ for it.Mr. Black:Okay. Please tell me what to do.Nurse: I will give you a ________ by an injection to help you relax.Mr. Black: When it works, shall I fall sleep?Nurse: No, it can only make you drowsy. It’s not a ___________ anesthetic.Mr. Black:Will I feel intense pain during the test?Nurse:No, the doctor will numb the back of your throat by spraying on some _________ anesthetic. You may just feel a little uncomfortable, particularly when you first swallow the _______.Mr. Black: I see. Thank you.Nurse: By the way, the doctor may take one or more _________ in the testing process. But don’t worry. That is painless.Mr. Black: Alright, I will try to cooperate.Reading BView a Sample CBCA complete blood count (CBC) is a calculation of the cellular makeup of blood. It measures the concentration of white blood cells, red blood cells, and platelets in the blood and aids in diagnosing conditions and diseases such as malignancy, anemia, or blood clotting problems. The CBC is typically reported in the format below, although different labs may use different formats.●Sample CBC TestThe sample CBC below shows that the patient’s white blood cells and red blood cells are low.Complete Blood Count (CBC) with Differential Test Results Result Units Reference Interval White Blood Count 1.5L ×103/mm3 5.0-10.0Red Blood Count 3.50L ×106/mm3 4.1-5.3 Hemoglobin 10.8L g/dl 12.0-18.0 Hematocrit 31.1L % 37.0-52.0 Platelets 302 ×103/mm3150-400 Polys(neutrophils) 23L % 45-76 Lymphs 68H % 17-44 Monocytes 7 % 3-10Eosinophil 2 % 0-4 Basophil 0.6 % 0.2Polys(absolute) 3.4L ×103/mm3 1.8-7.8 Lymphs(absolute) 1.0 ×103/mm30.7-4.5 Monocytes(absolute) 0.1 ×103/mm30.1-1.0Eos(absolute) 0.1 ×103/mm30.0-0.4 Basos(absolute) 0.0 ×103/mm30.0-0.2●Understanding the ChartResult:The “Result”column shows the counts. The “L”or “H”after the count shows whether the counts are lower (“L”) or higher (“H”) than the normal range.Reference Interval (or Reference Range): The “Reference Interval”column shows the normal range for each measurement for the lab performing the test. Note that reference intervals may vary slightly among different laboratories.White Blood Cells: The complete blood count (CBC) report shows that the patient’s total white blood cell count (WBC) is 1.5, which is lower than the normal range of 5.0-10.0. The low WBC count (leucopenia) may point toward autoimmune diseases, such as lupus erythematosus or rheumatoid arthritis, bone marrow problem, disease of the liver or spleen, or related to some medications, such as chemotherapy.Red Blood Cells: The report shows that the patient has a red blood cell count of 3.50, which is lower than the normal range of 4.1-5.3. The low red blood cell count may suggest anemia, which can have many causes. Possible causes include autoimmune diseases, bone marrow failure, leukemia, malnutrition, heavy menstrual bleeding, stomach ulcers, inflammatory bowel disease, or some tumors.Hemoglobin: The report indicates that the patient’s Hb count is 10.8, which is below the normal range of 12.0-18.0. Low hemoglobin values may indicate anemia, or blood loss.Hematocrit: Hematocrit is also low. This means that the patient has mild anemia and may be starting to notice symptoms.Platelets: The report indicates that the platelet count for this patient is normal.Differential: also known as white blood cell (WBC) differential count. This portion of the report shows the counts for the five main types of white blood cells, either as percentages (the first five counts) or as the absolute number of cells (the second five counts). Such information helps the doctor monitor patients with allergies and determine how a patient is recovering from an illness or responding to therapy.Task 1 Match the following terms with their Chinese meanings.3.reference interval a. 白血球减少症4.stomach ulcer b. 胃溃疡5.bone marrow failure c. 参考范围6.rheumatoid arthritis d. 骨髓衰竭7.leucopenia f. 风湿性关节炎Task 2 Translate the following paragraph into Chinese.The cells that circulate in the bloodstream are generally divided into three types: white blood cells (leukocytes), red blood cells (erythrocytes), and platelets (thrombocytes). Abnormally high or low counts may indicate the presence of many forms of disease, and hence blood counts areamongst the most commonly performed blood tests in medicine, as they can provide an overview of a patient’s general health status. A CBC is routinely performed during annual physical examination in some districts._____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ WritingMemorandum (Memo)Task 1 A memo is generally made up of three parts: Introduction, Body and Conclusion. It needs to be brief, to the point and clear. Now read the following sample memo and learn about how it is organized.A Sample Memo:TO: (person or group to whom the memo is addressed)FROM: (person of group sending the memo)DA TE: (current date—month /date/year)SUBJECT: (what the memo is about, this should be in bold)First Sentence:Reason for the memoe.g. I would like to remind you that…Second Sentence—Main BodyAny Instruction or InformationClosing Sentence:What is required of the readerse.g. confirmation, answers or feedbackPlease share this announcement with co-workers immediatelyTask 2 Suppose you are a clerk working in the family planning office of a hospital. Please write a memo based on the following information. Your memo should include the tips given in Task 1.Situation:A summing-up meeting on the 2008 family planning work of the hospital is to be held on April 25th, 2008. Besides, the 2009 family planning work will be assigned at the meeting. Those who are in charge of family planning work in all departments and offices are requested to attend the meeting.Technical Words:Complete Blood Count (CBC) 全血球计数Computed Tomography (CT-scan) 计算机断层摄影Contrast material 造影剂Electrocardiograph (EKG) 心电图Electroencephalograph (EEG) 脑电图Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) 核磁共振成像Basophil 嗜碱性粒细胞Eosinophil嗜酸性粒细胞Hematocrit 血细胞比容Hemoglobin 血红蛋白Leucopenia 白细胞减少Lupus erythematosus 红斑狼疮Monocyte 单核细胞Neutrophil 嗜中性粒细胞,中性白细胞Exercise: Fill in each blank with the appropriate form of the word given in brackets.1. The frontiers of (medicine) ________ knowledge are being pushed forwards as time goes on.2. The (metabolism) ________ abnormalities were corrected and renal function remained normal.3. Will you please recommend some (typical) ______ Chinese dishes to the foreign guests?4. Some women experience morning sickness during the first three months of (pregnant) ______.5. Dense fog is covering roads in the north and (visible) _______ is very poor.6. Modern machines, (range) _________ from TV to computers, can do various types of work forman.7. Dictionaries and encyclopedias are (refer) _________ books. You may (refer) _______ them while reading and writing.8. A (consult) ________ room is a place where a doctor sees his patient.9. (Immune) _________ can be acquired by having had the disease or by the use of vaccines.10. The illness was (diagnose)__________ as mumps (腮腺炎).Unit 3 DiagnosisReading A:Task 1 Before reading the passage, see how much you know about the treatment of common chronic and acute diseases by answering the following questions.1.What are the differences between acute diseases and chronic diseases?2.What are the most common chronic diseases of older adults?Treatment of Common Chronic and Acute DiseasesHealth concerns are usually classified as either acute or chronic. Acute illnesses often begin abruptly and last only a short time. Most people with an acute illness can expect to return to normal health. However, chronic diseases usually develop slowly, last a long time, and are often progressive and incurable.Chronic DiseasesChronic diseases, such as cardiovascular disease, cancer, and diabetes, are by far the leading cause of mortality in the world. Treatment includes medication and lifestyle changes such as diet and physical activity, and stress management.Cardiovascular diseases include coronary heart disease, hypertension, congenital heart disease, heart failure, etc. Once diagnosed with CVDs, patients are typically prescribed medication that will regulate cardiovascular functions and are usually taken daily for the rest of their life. Certain treatments are usually started right away if a heart attack is suspected, even before the diagnosis is confirmed. These include: oxygen, aspirin to prevent further blood clotting, nitroglycerin to reduce the workload on the heart, and treatment for chest pain.Cancer may affect people at all ages, even fetuses. The three most common types of cancer treatment are surgery, radiotherapy and chemotherapy, which aim at removing the cancer cells or destroying them in the body with medicines or other agents. Choice of treatment is influenced by several factors, including the specific characteristics of the cancer, the patient’s overall condition, and whether the goal of treatment is to cure the cancer, keep it from spreading, or relieve the symptoms.All forms of diabetes have been treatable since insulin became medically available in 1921, but there is no cure. The insulin injection is a basic treatment of type I diabetes. TypeⅡis managed with a combination of dietary treatment, exercise, medications and insulin supplementation.Acute DiseasesTreatment for acute diseases usually involves medication of antibiotics, which have direct effects on inflammation.Pneumonia is a common illness which occurs in all age groups. Most cases of pneumonia can be treated without hospitalization. Typically, oral antibiotics, rest, fluids, and home care are sufficient for complete resolution. However, if the symptoms get worse, or complications occur, the person will often have to be hospitalized.。

How are your periods? Are they heavy? 你的月经怎么样?量多吗?Have you had any pain in this area during your menstruation? 你来月经时间时这一部位疼吗?How about your menstruation cycles? 你的经期准吗?Have you had any discomfort? 有什么不舒服吗?When was your last menstruation? 你上一次月经是什么时候?How long is your period usually? 通常你的月经周期多长?Have you had any bleeding, watery discharge or pain in your lower abdomen? 你有过阴道出血、水性分泌物以及下腹部疼痛的情况吗?How long has this been bothering you? 这种不适感有多久了?Did you feel contractions regularly? 你感觉到过有规律的宫缩吗?What`s the amount of bleeding? Is it profuse? 出血量多少?很多吗?Do you mind if I examine you briefly? 我简单地给你检查一下,你介意吗?I`ll run some tests on you.我要给你做些化验。
That`s due to your heavy period.这是因为你月经过多造成的。
I think it`s carcinoma of the breasts.我认为是乳腺癌。
We`ll send her to the delivery room for further observation.我们想把她送到产房进一步观察。
Do you see dimly from distance or close by? 您看远不清还是看近不清?Do you see objects dimly? 您看东西模糊吗?What kind of pain do you have? 怎么痛法?Is there much secretion from your eyes? 眼里的分泌物多吗?Does light affect your eyes? 您的眼睛怕光吗?Do you see an object as if there were two that overlap? 您看东西有重影吗?Do you see my hand moving? 您看见我的手在动吗?T ry not to blink.不要眨眼。
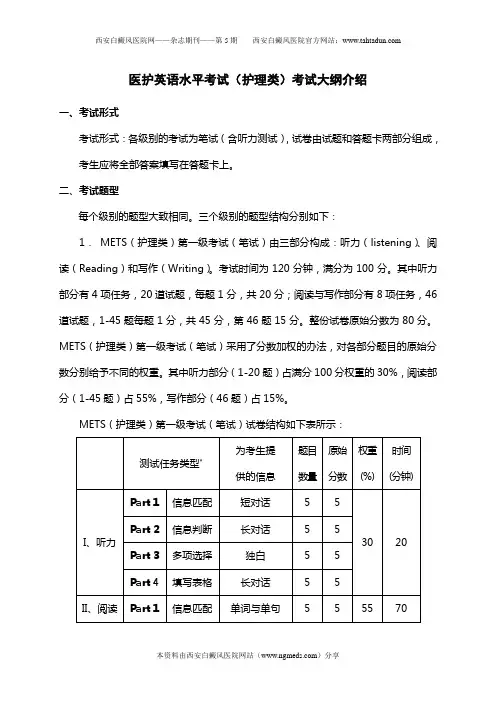
医护英语水平考试(护理类)考试大纲介绍一、考试形式考试形式:各级别的考试为笔试(含听力测试),试卷由试题和答题卡两部分组成,考生应将全部答案填写在答题卡上。
二、考试题型每个级别的题型大致相同。
三个级别的题型结构分别如下:1. METS(护理类)第一级考试(笔试)由三部分构成:听力(listening)、阅读(Reading)和写作(Writing)。
考试时间为120分钟,满分为100分。
其中听力部分有4项任务,20道试题,每题1分,共20分;阅读与写作部分有8项任务,46道试题,1-45题每题1分,共45分,第46题15分。
整份试卷原始分数为80分。
METS(护理类)第一级考试(笔试)采用了分数加权的办法,对各部分题目的原始分数分别给予不同的权重。
其中听力部分(1-20题)占满分100分权重的30%,阅读部分(1-45题)占55%,写作部分(46题)占15%。
METS(护理类)第一级考试(笔试)试卷结构如下表所示:测试任务类型*为考生提供的信息题目数量原始分数权重(%)时间(分钟)I、听力Part 1信息匹配短对话 5 530 20 Part 2信息判断长对话 5 5Part 3多项选择独白 5 5Part 4填写表格长对话 5 5II、阅读与写作Part 1信息匹配单词与单句 5 555 70 Part 2信息匹配单句与告示 5 5Part 3 信息匹配单句与图表 5 5Part 4 补全对话长对话与单句 5 5Part 5 多项选择单句7 7Part 6 信息判断短文8 8Part 7 完形填空短文10 10Part 8短文写作表格 1 15 15 30总计65+1 80 100 120 *实际考试中卷中可能会出现新任务类型2. METS(护理类)第二级考试(笔试)由三部分构成:听力(listening)、阅读(Reading)和写作(Writing)。
考试时间为120分钟,满分为100分。

《护理专业英语》课程教学大纲一.课程基本信息二。
课程内容及基本要求Unit one modern nursing课程内容:1.护理的发展历史2.护理教育的层次3。
护理理论4.美国的注册护士的种类5.对我国护理发展的憧憬基本要求:1.掌握能用英语口述现代护理的发展.护理教育的层次及不同层次人才培养的目标。
2.理解能用英语口述美国的三种注册护士。
高级实践护士的种类3。
了解护理学发展的趋势本章重点:护理教育的层次及不同层次人才培养的目标本章难点:美国注册护士的分类及其职责Unit two nursing process课程内容:1。
护理程序的步骤2.护理评估的基本类容3.护理诊断的概念及内容4。
护理计划制定的目的及过程5.护理程序的特点基本要求:1.掌握能用英语口述护理程序的五个步骤。
护理程序的特点。
护理计划内容。
护理诊断的特点2。
理解护理评估的的内容,护理资料的分类3。
了解:护理计划的目的本章重点:护理程序的五个步骤的英语表达。
护理程序的特点本章难点:护理计划的内容Unit three health assessment课程内容:1。
健康评估的内容2.评估前的准备3.身体评估的主要内容和方法4.评估方法-触诊的要点及注意事项5.评估方法-叩诊的要点及注意事项6。
护士在评估中的作用基本要求:1.掌握护理评估的概念.护理评估的内容和方法2.理解护理评估方法:触诊和叩诊的要点及注意事项3.了解身体评估前病人的准备.护士的准备本章重点:护理评估的内容。
方法.本章难点:叩诊的要点及中予以事项Unit four Community health nursing课程内容:1.社区护理的概念2.社区护理的特点3。
社区护理的基本要求4。
社区卫生保健的内容及目标5。
社区护士的工作方法6。
社区护士的主要工作内容基本要求:1.掌握社区护理的概念和特点2。
理解社区护士的要求。
工作方法.工作内容.社区护士家访的要点3.了解社区护理的发展趋势本章重点:社区护理的概念。



《医护英语》教学大纲课程类别:公共基础课开设学期:课程类型:必修开课单位:课程名称:Medical and Nursing English课程性质:Compulsory course总学时:72授课对象:Advanced Nursing Class课程基础要求:The course is designed for students who major in nursing profession. Through the course , students may realize the importance of English skills in their nursingstudy. The course will target the vocabulary, listening, speaking, reading andtranslation that are commonly required in nursing-training program.大纲内容一.前言:课程目的:Through the course,let the students understand the importance of the nursingEnglish. Let the students remember some nursing English words. Let thestudents master the skills of listening, speaking, reading and writing.教学要求:The main teaching way is class teaching. The teacher teaches and the students learn. In the class, the students should practice more, to master some skills ofEnglish learning, especially how to deal with the different situation in thehospital.二.各单元结构Five Modules:Module1: Warm-upModule2: DialogueModule3: PassageModule4: ExercisesModule5: Supplementary Reading三.教学内容及各单元教学目的四.大纲使用说明This outline is suitable to the nursing class. We maybe change the structure slightly according to the different condition. We can add more knowledge about nursing in the class.五.主要参考书目1.Wu Leida : Medical and Nursing English Shanghai: Fu Dan University Press,20152.Hu Yanping: Medical and Nursing EnglishShanghai: Shanghai Foreign Language Education Press ,20143.Wang Lei : Nursing English Beijing: People’s Medical Press, 20154.Tang Qiaoying : Medical and Nursing EnglishBeijing : Foreign Language Teaching and Research Press , 2015撰写人:审核人:审批人:。

《医护英语》教学大纲课程类别:公共基础课开设学期:课程类型:必修开课单位:课程名称:Medical and Nursing English课程性质:Compulsory course总学时:72授课对象:Advanced Nursing Class课程基础要求:The course is designed for students who major in nursing profession. Through the course , students may realize the importance of English skills in their nursingstudy. The course will target the vocabulary, listening, speaking, reading andtranslation that are commonly required in nursing-training program.大纲内容一.前言:课程目的:Through the course,let the students understand the importance of the nursingEnglish. Let the students remember some nursing English words. Let thestudents master the skills of listening, speaking, reading and writing.教学要求:The main teaching way is class teaching. The teacher teaches and the students learn. In the class, the students should practice more, to master some skills ofEnglish learning, especially how to deal with the different situation in thehospital.二.各单元结构Five Modules:Module1: Warm-upModule2: DialogueModule3: PassageModule4: ExercisesModule5: Supplementary Reading三.教学内容及各单元教学目的四.大纲使用说明This outline is suitable to the nursing class. We maybe change the structure slightly according to the different condition. We can add more knowledge about nursing in the class.五.主要参考书目1.Wu Leida : Medical and Nursing English Shanghai: Fu Dan University Press,20152.Hu Yanping: Medical and Nursing EnglishShanghai: Shanghai Foreign Language Education Press ,20143.Wang Lei : Nursing English Beijing: People’s Medical Press, 20154.Tang Qiaoying : Medical and Nursing EnglishBeijing : Foreign Language Teaching and Research Press , 2015撰写人:审核人:审批人:。

目录一、考试性质 (1)二、考试用途 (1)三、等级标准 (1)四、考试内容及要求 (3)(一)医护英语水平考试第一级考试内容及要求 (3)(二)医护英语水平考试第二级考试内容及要求 (8)(三)医护英语水平考试第三级考试内容及要求 (13)(四)医护英语水平考试第四级考试内容及要求 (18)五、考试样题及答案 (24)(一)医护英语水平考试第一级考试样题及答案 (24)(二)医护英语水平考试第二级考试样题及答案 (42)(三)医护英语水平考试第三级考试样题及答案 (64)(四)医护英语水平考试第四级考试样题及答案 (86)六、医护英语词汇表 (112)(一)医护英语水平考试第一级考试词汇表 (112)(二)医护英语水平考试第二级考试词汇表 (128)(三)医护英语水平考试第三级考试词汇表 (152)(四)医护英语水平考试第四级考试词汇表 (185)一、考试性质医护英语水平考试(Medical English Test System,以下简称METS)是为我国各类医药卫生院校学生和医药卫生行业从业人员开发设计的一项社会化英语水平考试,旨在考查应考人员在医学环境下的英语实际应用水平,属于非学历标准参照性考试。
二、考试用途作为一套针对医药卫生行业工作环境开发的英语水平考试系统,METS重点考查应考人员的英语实际应用能力,是医药卫生院校学生评价自己英语水平和求职就业的重要参考,是医药卫生部门招聘员工评估其英语能力的可靠标准,是各单位人力资源部门提升或调配员工以及制定人力资源解决方案的重要依据。
三、等级标准METS的考试级别设置为一级、二级、三级、四级;一级为初始级,四级为最高级。
级别的设定充分考虑了我国医药卫生类院校的英语教学状况和医药卫生专业技术人员的英语水平,同时也参考了国内外有影响的标准化考试,如CET-4、CET-6、PETS、TOEFL、IELTS、CEFR(Common European Framework of Reference for Languages: Learning,Teaching, Assessment“欧洲语言教学共同纲领”)等。
全国医护英语水平考试(mets)考点全文共10篇示例,供读者参考篇1Hello everyone! Today I'm going to talk about the National Medical English Test (METS) for all the medical staff. It's like a big test for the doctors, nurses, and other medical professionals to show their English skills.In the METS test, there are many different parts like listening, speaking, reading, and writing. It's really important for the medical staff to be able to understand and communicate in English because sometimes they have to talk to patients from other countries.For the listening part, you have to listen to a recording and answer questions about it. It's important to practice listening to English every day so you can understand what people are saying.Speaking is another important part of the test. You have to be able to talk to patients and other medical staff in English. It's good to practice speaking English with your friends or colleagues so you can feel more comfortable.The reading part of the test is all about understanding written English. You have to read passages and answer questions about them. Reading English books or articles can help you improve your reading skills.And finally, the writing part is where you have to write essays or reports in English. It's important to practice writing in English so you can express your ideas clearly.So, if you want to pass the METS test and show your English skills, make sure to practice listening, speaking, reading, and writing every day. Good luck, everyone!篇2Hey guys! Today I want to talk to you about the National Medical English Test (METs) exam. It's a super important test for all the doctors and nurses in China. So let's dive into it!First off, the METs exam is all about testing your English skills in the medical field. You'll be tested on things like reading medical articles, listening to medical conversations, and speaking about medical topics. It's like a big English test, but all about medicine!To do well on the METs exam, you'll need to study hard. Make sure to practice reading medical journals and listening to podcasts about health. And don't forget to practice speaking English with your friends or classmates. The more you practice, the better you'll do on the exam!During the exam, make sure to read each question carefully and answer to the best of your ability. Don't rush through it, take your time and think about each answer. And if you don't know the answer to a question, just make an educated guess.So there you have it, guys. The METs exam is super important for all the medical professionals out there. Study hard, practice your English skills, and you'll do great on the exam. Good luck!篇3Hey guys, today I want to talk to you about the National Medical English Test (METS), which is a super important test for healthcare professionals.First of all, let me tell you what METS is all about. It’s a test that measures your English language skills in a medical setting. So if you want to work as a nurse, a doctor, or any otherhealthcare professional, you need to pass this test to show that you can communicate effectively with patients and colleagues.There are different parts to the METS exam. You’ll have to do a listening test where you listen to conversations between doctors and patients and answer questions. Then there’s a reading test where you read medical articles and answer questions. You’ll also have to do a writing test where you write about medical topics. And finally, there’s a speaking test where you have to talk about a medical case study.But don’t worry, you can totally ace this test if you study hard and practice your English skills. Make sure to read medical articles, watch English movies or TV shows, and practice speaking with your friends or family.So remember, if you want to be a top-notch healthcare professional, you need to pass the METS exam with flying colors. Good luck!篇4Okey dokey, here we go!Hi everyone! Today I wanna talk about the National Medical English Test (METs) exam. It's a big deal for all the doctors and nurses out there who wanna show off their English skills.First things first, let's talk about what the METs exam is all about. It's a test that measures your ability to understand and communicate in English in a medical setting. You gotta know your medical vocab and be able to talk to patients and other healthcare professionals in English.Now, let's chat about some key points you gotta know for the exam. One big thing is being able to take a patient's history in English. You gotta know how to ask all the right questions and understand the answers. It's all about communication, baby!Another important skill for the METs exam is reading and understanding medical articles in English. You gotta be able to know what all those fancy words mean and how they relate to your own practice. So, hit those books and start practicing reading, my friends!And last but not least, you gotta be able to write in English too. Whether it's writing up patient notes or communicating with other healthcare professionals, you gotta be able to get your point across in English.So, there you have it, folks! The METs exam is all about being able to talk the talk and walk the walk in English in a medical setting. So, study hard, practice those skills, and you'll be acing that exam in no time. Good luck, my fellow medical English rockstars!篇5Hi everyone! Today I want to talk to you about the National Medical English Test (METs) exam. I know it sounds all serious and complicated, but don't worry, I'll explain it in a way that's easy to understand.So, the METs exam is a really important test for people who work in the medical field, like doctors and nurses. It tests their English skills to make sure they can communicate effectively with patients and colleagues from different countries.There are different sections in the exam, like listening, reading, writing, and speaking. In the listening section, you have to listen to conversations and answer questions. In the reading section, you have to read passages and answer questions. In the writing section, you have to write essays or reports. And in the speaking section, you have to have a conversation with an examiner.It's important to prepare for the exam so you can do your best. You can practice listening by watching English movies or listening to English songs. You can practice reading by reading English books or articles. You can practice writing by writing in a journal or sending emails in English. And you can practice speaking by talking to your friends or family in English.Remember, the METs exam is just a way to show your English skills, so don't stress too much about it. Just do your best and you'll be fine. Good luck to all the future doctors and nurses out there!篇6Hey guys! Today I want to talk to you about the National Medical English Test (METS) for medical professionals. It's a super important exam that tests your English skills in the medical field. Let's check out some of the key points you need to know for the exam!Firstly, you need to brush up on your medical vocabulary. Make sure you know all the important terms in English, like "anesthesia", "surgery", and "diagnosis". It's super important to be able to understand and communicate effectively in medical situations.Next, you need to be able to read and understand medical texts in English. This includes things like patient records, research papers, and medical guidelines. Practice reading and summarizing these texts to improve your skills.You also need to be able to write clearly and professionally in English. This includes things like writing patient reports, medical notes, and emails to colleagues. Make sure your writing is clear, concise, and free of errors.Finally, you need to be able to listen to and speak English fluently in medical settings. This includes things like taking patient histories, explaining procedures to patients, and communicating with colleagues. Practice listening to English podcasts or watching medical videos to improve your listening skills.Overall, the METS exam tests your English skills in all areas of medicine. Make sure to practice and prepare so you can ace the exam and become a top-notch medical professional! Good luck, everyone!篇7Okay, here is an article in a more casual and childlike tone for the National Medical English Proficiency Test (METS) exam:Hey everyone! Today I want to talk to you about the National Medical English Proficiency Exam, also known as METS. It's like a big test for all the doctors and nurses to show how good they are at speaking English.The METS exam has lots of different parts, like listening, reading, speaking, and writing. Doctors and nurses have to do their best in each part to pass the exam. It's super important because they need to be able to talk to patients from all over the world.In the listening part of the exam, they have to listen to conversations and answer questions about them. It's like a big game of "Simon Says" but in English! And in the reading part, they have to read passages and answer questions. It's like a puzzle that they have to solve.Then there's the speaking part, where they have to talk to the examiners about different medical topics. They have to be confident and clear in their answers. And finally, there's the writing part, where they have to write essays about medical issues. It's like being a detective and solving a case.So, the METS exam is a big challenge for doctors and nurses, but it helps them improve their English skills and become better at their jobs. If they do well on the exam, they can help morepatients and make the world a healthier place. Good luck to all the doctors and nurses taking the METS exam!篇8Hi there! Today I'm gonna tell you all about the National Medical English Proficiency Test (METS) exam! METS is a super important test for all the doctors and nurses in China. It's like a super cool challenge that helps them show off their English skills.First up, let's talk about what METS is all about. The exam is made up of four parts: listening, reading, writing, and speaking. The listening part is all about listening to conversations and answering questions. The reading part is like reading stories and answering questions. The writing part is writing about a specific topic. And the speaking part is talking to an examiner about different topics.Doctors and nurses need to do well on this test because they work with patients from all around the world. If they can't speak English well, they might not be able to communicate with their patients properly. And that's not good at all!Studying for METS can be tough, but it's super important. Doctors and nurses need to practice their English every day. Theycan watch English movies, listen to English songs, and read English books. It's all about getting better and better at English.So if you wanna be a super awesome doctor or nurse in China, make sure you study hard for METS! Good luck!篇9Hey guys! Today I want to talk about the National Medical English Test (METs) exam. Have you guys heard about it? It's a big test for doctors and nurses to show off their English skills.The METs exam has different sections, like listening, reading, speaking, and writing. It's important for medical professionals to be able to communicate with patients from all over the world, so having good English skills is super important.In the listening section, you have to listen to conversations and answer questions about them. It can be tricky because you have to understand the medical terms and also understand the English. But don't worry, just practice listening to English every day and you'll get better!The reading section is all about understanding medical texts in English. You have to read passages and answer questionsabout them. Make sure to read carefully and take your time to understand the information.The speaking section is where you have to talk about different medical topics. You might have to explain a diagnosis or talk about a treatment plan. Practice speaking English with your friends or colleagues to get more confident.Finally, the writing section is where you have to write essays or reports in English. Make sure to use proper grammar and spelling. Practice writing in English every day to improve your skills.So, if you want to be a great doctor or nurse, make sure to take the METs exam seriously and practice your English skills. Good luck!篇10Title: My Experience Taking the National Medical English Test (METS)Hi everyone! Today I want to tell you about my experience taking the National Medical English Test (METS). It was a really exciting and nerve-wracking experience, but I learned a lot from it.First of all, let me tell you what METS is all about. It's a nationwide test that measures your English proficiency in the medical field. It includes listening, reading, writing, and speaking sections, so you really have to be prepared for anything.The test day started early in the morning, and I was feeling a mix of excitement and nerves. I made sure to bring all the necessary materials: my ID, pencils, erasers, and a positive attitude. The test proctor explained the rules and the format of the test, and then we got started.The listening section was the first part of the test. We had to listen to recordings of medical conversations and answer questions about them. It was a bit challenging because the speakers talked fast, but I tried to stay focused and answer as best as I could.Next was the reading section, where we had to read passages about medical topics and answer questions. Some of the vocabulary was difficult, but I tried to use context clues to figure out the meanings of the words.The writing section was next, and we had to write an essay about a medical issue. I was a bit nervous about this part because writing isn't my strongest skill, but I tried my best to organize my thoughts and write clearly.Finally, the speaking section was last. We had to have a conversation with the test proctor about a medical topic. I tried to speak confidently and express my ideas clearly.After the test was over, I felt a mix of relief and satisfaction. I knew I had worked hard and done my best, and that was all that mattered.In the end, I learned a lot from taking the METS. It was a challenging experience, but it helped me improve my English skills and gain more confidence in my abilities. I would definitely recommend it to anyone who wants to test their English proficiency in the medical field.And that's my experience taking the National Medical English Test (METS)! I hope you enjoyed hearing about it. Thanks for listening!。
1 Introduction to Trauma Care 创伤护理导论2 Patterns of Blunt Injury 钝器损伤的类型3 Mechanisms of Injury/Penetrating Trauma 损伤发病机制/穿透性创伤4 The Physiologic Response to Injury 对损伤的生理学反应5 Shock 休克6 Measurements of Injury Severity 损伤严重程度的测定7 Prehospital Triage 送医院前伤员分类8 Prehospital Therapy 送医院前的治疗9 Field Teams:Composition,Direction, and Communication with the Trauma Center 现场救护队:组成,指导,与创伤中心的联系10 Air Medical and Interhospital Transport 空中医疗和医院间转运11 Trauma Team Activation 创伤救护队的活动12 Organization prior to Trauma Patient Arrival 创伤病人到达前的组织13 Adult Trauma Resuscitation 成人创伤复苏14 Airway Management in the Trauma Patient 创伤病人的气道处理15 Vascular Access 血管穿刺16 Imaging of Trauma Patients 创伤病人的影像17 Operating Room Practice 手术室常现18 Head Injury 头损伤19 Injuries to the Spinal Cord and Spinal Column 脊髓和脊柱损伤20 Soft Tissue Wounds of the Face 面部软组织伤21 Ophthalmic Injuries 眼损伤22 Penetrating Neck Injury 穿透性颈损伤23 Blunt Neck Injury 颈部钝器损伤24 Thoracic Injury 胸部损伤25 Thoracic Vascular Injury 胸部血管损伤26 Abdominal Injury 腹部损伤27 Abdominal Vascular Injury 腹部血管损伤28 Damage Control 损伤的控制29 Abdominal Compartment Syndrome 腹部隔室综合征30 Genitourinary Injuries 泌尿生殖系统损伤31 Orthopedic Injuries 矫形外科损伤32 Pelvic Fractures 骨盆骨折33 Hand Trauma 手创伤34 Compartment Syndrome and Rhabdomyolysis 隔室综合征和横纹肌溶解35 Peripheral Vascular Injuries 周围血管损伤36 Soft—Tissue Trauma 软组织创伤37 Priorities in the ICU Care of the Adult Trauma Patient 在ICU护理的成人创伤病人的优先项目38 Commonly Missed Injuries and Pitfalls 常遗漏的损伤和易犯的错误39 Anesthesia for the Trauma Patient 创伤病人的麻醉40 Trauma Pain Management 创伤疼痛的处理41 Hypothermia,Cold Injury,and Drowning 低温、冷损伤和淹溺42 Blood Transfusion and Complications 输血和并发症43 Nutrition/Metabolism in the Trauma Patient 创伤病人的营养/代谢44 Support of the Organ Donor 器官供体的保养45 Burns/Inhalation 烧伤/吸入46 Pediatric Trauma 儿科创伤47 Care of the Pregnant Trauma Patient 妊娠创伤病人的护理48 Geriatric Trauma 老年人创伤49 Rehabilitation 康复50 Venous Thromboembolism 静脉血栓栓塞51 Injury Prevention 损伤的预防52 House Staff Responsibilities 住院医师的责任53 Legal, Ethical and Family Issues 法律、伦理道德和家庭问题54 Miscellaneous Procedures 各种其它操作程序55 oral health education activity口腔健康教育活动56 Oral Health Education Unit [Department of Health]口腔健康教育组57 oral poliomyelitis trivalent 脊灰口服剂58 oral toilet 口腔料理59 oral-maxillofacial surgery and dental unit口腔颌面外科及牙科部60 outbreak高峰期;发作;流行61 outbreak control疫症控制;暴病控制62 outcome management project 医疗成效管理计划63 out-of—pocket expenditure by the user服务使用者自付64 out—patient appointment system门诊病人预约制度65 out—patient clinic门诊诊疗所66 out-patient clinical operations support system门诊临床运作支持系统67 out-patient consultation service门诊服务68 out-patient department门诊部69 out—patient registration system门诊病人登记制度70 outreach community care programme外展小区护理计划71 outreach health care team外展医护队72 outreach medical team外展医疗队73 outreach specialist medical team外展专科医疗队74 outside appointment book出外就医册75 ordinary diet普通膳食76 organ donation器官捐赠77 Organ Donation Card器官捐赠证78 Organ Donation Centre器官捐赠中心79 organ donation form 器官捐赠表格80 Organ Donation Register [Hong Kong Medical Association]器官捐赠册81 organ donor 器官捐赠人82 organ imaging器官造影83 organ pledge 承诺捐出的器官数目84 organ recipient器官受赠人85 organ transplant器官移植86 organic psychosis器质性精神病87 organoleptic inspection感官检查88 overall incidence总发病率89 overflow ward暂时收容病房;后备病房90 overnight room夜间当值室91 over-sensitivity过敏92 ovulation排卵93 ovulation cycle排卵周期94 ovulation method安全期避孕法95 on—call duty doctor候召当值医生96 oncology肿瘤学;肿瘤科97 one-way referral单向转介98 onset of labour分娩阵痛发作99 onset of symptom症状发作100 on-site triage treatment现场分流治疗101 occupational disease职业病102 occupational health 职业健康103 occupational health nurse职业健康护士104 Occupational Health Officer 职业健康科医生105 Occupational Hygienist职业环境生师106 occupational mortality职业性死亡率107occupational neurosis职业性神经病108 occupational therapist职业治疗师109 Occupational Therapists Board职业治疗师管理委员会110 occupational therapy assessment room职业治疗评估室111 Occupational Therapy Assistant职业治疗助理员112 ochlophobia 众恐惧113 ocular pathology眼科病理学114 ocular prosthesis假眼115 optimal health理想的健康状况116 optimum occupancy rate [hospital bed]最适度病住用率117 optometric assessment视力测验118 Operations and Training Division [Auxiliary Medical Service Headquarters] 行动及训练部〔医疗辅助队总部〕119 Operations and Training Officer [Auxiliary Medical Service行动及训练主任〔医疗辅助队〕120 Operations Section [Auxiliary Medical Service Headquarters] 行动组〔医疗辅助队总部〕121 Operations Wing [Auxiliary Medical Service volunteer structure]行动翼〔医疗辅助队志愿架构〕122 operative treatment 施手术123 oral health care口腔健康护理;口腔卫生服务124 oral health clinic口腔卫生诊疗所主任医师(讲课) Professor of Medicine主任医师(讲课) Professor of Medicine主任医师(医疗)Professor of Treatment儿科主任医师 Professor of Paediatrics主治医师 Doctor-in-charge外科主治医师 Surgeon-in-charge内科主治医师 Physician-in-charge眼科主治医师 Oculist—in—charge妇科主治医师 Gynaecologist-in-charge牙科主治医师 Dentist-in-charge医师 Doctor医士 Assistant Doctor主任药师 Professor of Pharmacy主管药师 Pharmacist—in—charge药师 Pharmacist药士Assistant Pharmacist主任护师 Professor of Nursing主管护师 Nurse—in-charge护师 Nurse Practitioner护士 Nurse主任技师 Senior Technologist主管技师 Technologist—in-charge技师Technologis技士 TechnicianHello, may (can) I help you? 您好,我可以帮您吗?What seems to be bothering you? 您觉得哪儿不舒服?Do you have a record? 您有病历吗?I`ll transfer you to the surgery department。
医护英语二级作文大纲模板Outline:I. Introduction。
A. Background information about medical English。
B. Purpose of the essay。
II. Importance of medical English。
A. Communication with patients and colleagues。
B. Understanding medical literature。
C. Enhancing career opportunities。
III. Challenges of learning medical English。
A. Technical vocabulary。
B. Grammar and syntax。
C. Pronunciation and accent。
IV. Strategies for learning medical English。
A. Immersion in English-speaking environment。
B. Use of medical dictionaries and textbooks。
C. Practice through role-playing and simulations。
V. Conclusion。
A. Recap of importance and challenges of learning medical English。
B. Encouragement to continue learning and improving language skills。
Medical English: The Importance and Challenges ofLearning。
I. Introduction。
Medical English is a specialized form of English usedin the healthcare industry. It is essential for healthcare professionals to be proficient in medical English as it enables them to communicate effectively with patients and colleagues, understand medical literature, and enhancetheir career opportunities. This essay discusses the importance of learning medical English, the challenges that come with it, and strategies for improving language skills.II. Importance of medical English。
医护英语ContentsUnit 1 Registration and Visiting a Doctor (3)Unit 2 Examination Process (9)Unit 3 Diagnosis (15)Unit4 Administering Medications (24)Unit 5 Hospitalization (29)Unit 6 Hospitalization (35)Registration and Visiting a Doctor 挂号与就诊Examination Process 检查过程Diagnosis 诊断Administration and Medication 门诊处置与取药Hospitalization 办入院手续与住院Rehabilitation 康复Unit 1 Registration and Visiting a DoctorReading A:Task 1 Before reading the passage, see how much you know about common diseases of the body systems by answering the following questions.1.How can you decide that a specific disease belongs to one of the body systems?2.Which hospital department might you refer a patient to if he/she has a stomachache?Common diseases of the Body SystemsHuman body diseases vary in both severity and diversity. Any body part or function can contract a disease or have s disorder. We are more capable of fighting these diseases today than ever before and medicine is advancing every day.Below are introductions to human body diseases and disorders.Skin DisordersThe skin is susceptible to physical injury and to infection by bacteria, virus, fungi, and exposure to sunlight. Almost and teenager can tell you the most common skin disorder: acne. There are other skin problems far more serious than acne, e.g. skin cancer, melanoma, psoriasis and vitiligo.Nervous System DisordersDamage to nervous system through physical injury or disease can impair both physical and mental function. Brain tumors, Parkinson’s disease and stroke are some of the nervous system conditions.Cardiovascular DisordersCardiovascular disorders are conditions of the heart and blood vessels, which consist of mainly coronary heart disease (CHD), or coronary artery disease (CAD), hypertension, arrhythmia and heart failure. What we eat and the amount of exercise we get can affect our cardiovascular system.Immune DisordersWhen the immune system does not function properly, a number of diseases can occur. There are two types of immune system disorders: allergies and autoimmune disease including juvenile diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis and anemia, etc. and immunodeficiency disease such a AIDS.Digestive DisordersMost digestive diseases are very complex. Common disorders include hepatitis, heartburn and stomach cancer. Abusing alcohol imposes the greatest risk for digestive diseases.Reproductive DisordersDisorders that may affect the proper functioning of the reproductive system include abnormal hormone secretion, sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) such as syphilis and gonorrhea, and the presence of cancerous tissue in the region. Such problems frequently affect fertility. There are also functional problems caused by infertility or sexual dysfunction.Respiratory DisordersRespiratory disorders, or lung diseases, are disorders such as pneumonia, tuberculosis, chronic bronchitis, lung cancer and others. They can affect people of all ages and both genders.Endocrine disordersEndocrine system disorders occur either due to too much or tool little or sometimes nohormone. These disorders may lead to abnormal growth pattern, diabetes, high cholesterol and triglyceride levels. Endocrine system disorders include hyperthyroidism, growth hormone deficiency and hypothyroidism.Musculoskeletal DisordersDisease of the musculoskeletal system may result in the inability to walk, sit, or even breathe. The musculoskeletal conditions having the most impact on population health will be presented: back pain, repetitive strain injury (RSI) and osteoarthritis.Task 2 Read the passage and match each common disease with one body system.1.hypertension a. respiratory system2.acne b. skin system3.bone fracture c. nervous system4.stomach cancer d. cardiovascular system5.brain tumors e. endocrine system6.AIDS f. digestive system7.lung cancer g. immune system8.hypothyroidism h. musculoskeletal systemTask 3 Read the passage again, and tick the facts mentioned in the passage about the common diseases of the body system.✧Our ability to fight human body diseases✧The case history of the patients✧Various disorders of the nine body systems✧Disorders typical of the body systems✧An introduction to the now cures for the diseases✧Two types of immune disorders✧The skin featuring its susceptibility✧Alcoholism contributing to digestive diseases✧The specialists in some ot the diseases✧Asthma as a respiratory problemListeningTask 1 Mr. Black is making a call to pre-register at a hospital. Listen to the conversation and choose the best answer to each question you hear.1.Why can’t Mr. Black register right now?A.Because of a power cut.B. Because of lack of record.C. Because of the system failure.2.Which card is NOT necessary for registration?A.ID card.B. Credit card.C. Insurance card.3.What is the registration time?A. 8 a.m. to 5 p.m.B. 9 a.m. to 4 p.m.C. 8 a.m. to 4 p. m.4. When does the nurse suggest Mr. Black come to the hospital?A. In the morning.B. In the afternoon.C. On weekdays.5. Where will Mr. Black find receptionists in the hospital?A. At the registration office.B. In the Outpatient Hall.C. Outside the consulting room. Task 2. Mr. Black is registering at the hospital in person. Listen to the conversation and fill in the blanks with what you hear.Mr. Black: Good Morning.Nurse: Good morning. Sorry to have kept you waiting. Have you ever been here before? Mr. Black: No, this is my first _______ here.Nurse: In this case, you have to fill in this registration form. Your name, age, ________ and things like that. I will make a record for you.Mr. Black:No problem.Nurse: Well, what’s troubling you?Mr. Black: I have a stomachache and feel like __________ sometimes. Besides, it’s difficult for me to swallow. Which department should I register ___________?Nurse: I think you should go to the Department of Gastroenterology (胃肠学) first. If necessary w e’ll __________ you to the Department of Chest Surgery.Mr. Black: Okay, here is my form.Nurse:Thank you. The registration ___________ is five Yuan. This is your registration card. Please don’t lose it and bring it whenever you came.Mr. Black: Thank you for your help.Nurse: That’s all rightTask 3. Mr. Liu, an overseas student in Britain, is calling at St. Paul’s Hospital to make an appointment. Listen to the conversation and help the nurse to fill in the record.Appointment RecordPatient’s name:Date of Birth:Visiting Purpose:Time:Doctor’s Name:Reading BProcedures to Visit a Doctor●How to Visit a Doctor in the West:When you get sick, you might have to make an appointment to visit a doctor for a physical checkup. Talking to the doctor and explaining your symptoms might not be too difficult. Here is how to make the most of your doctor’s visit.●Before You GoWhen you make the appointment, state the nature of your concern so that a proper length of time can be scheduled.If it’s your first visit to that clinic or with that physician, be ready to give your medical history.✧Provide information about diseases that run in your family.✧Describe current and past heath problems and treatments.✧Bring the original containers for any prescription and over-the-counter medications, herbs,supplements and vitamins you are taking.Preparing written information to bring with can help you communicate well with your doctor.✧ A short description of your health problems should include a list of symptoms and detailson when the problem started, where it is, what it fells like, and if there’s anything you do that makes it worse or better.✧ A list of medications you are taking should include the dose and frequency of prescriptionand over-the-counter drugs, as well as herbs, supplements and vitamins.●While You’re ThereWhen talking with your doctor, remember that your health is worth his or her time.✧Clearly describe you health concern (symptoms, when it started, where it is, what it fellslike). Information written in advance can help.✧Restate explanations and ask for clarification, until you’re sure that the doctorunderstands your concerns and completely answer your questions.✧Don’t forget about your emotional health; it influences your physical health. So mentionall health-related concerns, not just the visible ones.✧Make sure your provider is aware of the prescription and over-the-counter medications,herbs, supplements and vitamins you are taking.Before leaving, find out✧It and when you should return for another visit.✧Whether you are to phone in for any test results or to report on your condition.✧If there are certain warning signs you should watch for✧Whether there are materials you could take home or a website you should visit to learnmore about your diagnosis or treatmentNever leave uncertain about your diagnosis or treatment●Common Procedures to Visit a Doctor in China’s HospitalThe first thing you should know about the medical services is that you should have some basic knowledge about the procedures.In china patients simply show up at local hospitals. No preset appointment is necessary, except for surgical procedures. Treatment techniques include diagnosis, medication, injection or the necessary scans. Your doctor may give you a prescription for you to buy medicine from the in-house pharmacy, most of the time at the lobby of the outpatient section building.● A chart on how to visit a doctor in Chinese hospital:Patient pre-check register diagnosis pay feestake medicine leavecheck & test specific section observation pay fees take medicine leave Task 1 Complete the procedures to visit a doctor in Western countries according to the passage.How to Visit a Doctor in the West1.Before you goa.Make an _____________ with your ____________.b.Be ready to give your _____________ on your first visit.c.Prepare __________________________.2.While You’re Therea.When _____________ with your doctor, remember that your ____________ is worthhis or her time.b.Before leaving, make sure of __________________ things.c.Never leave _____________ about your diagnosis or treatment.Task 2 Translate the following paragraph into Chinese.In china patients simply show up at local hospitals. No preset appointment is necessary, exceptfor surgical procedures. Treatment techniques include diagnosis, medication, injection or the necessary scans. Your doctor may give you a prescription for you to buy medicine from the in-house pharmacy, most of the time at the lobby of the outpatient section building.____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ WritingPublic NoticeTask 1 A public notice is written for many reasons. By writing a public notice, you will inform people about some news. No matter which kind of public notice you write, you will find several tips useful: be brief and to the point, well-worded, coherent and smooth with a definite purpose. Now read the following sample public notice and learn about the way it is written.A Sample:Public NoticeNotice is hereby given that Liu Dan from the Department of General Surgery in our hospital won the first place in the City’s 2009 Nursing Skills Contest held on May 4th, 2009.We inform you that a commendation meeting is to be held at the hospital auditorium on Wednesday afternoon, at 1:30. Representatives from all departments are expected to attend the meeting on time.The Office of Hospital PresidentMay 5th, 2009Commendation meeting 表彰会Task 2 Suppose you are a secretary with the human resource department. Please write a public notice based on the following information.Information:Li Lan has succeeded in competing for the position of head nurse in the emergency department. She took the first place in both the theoretical examination and interview for the position. Therefore the hospital leaders and the nursing department, after due consideration, have officially decided to appoint Li Lan head nurse in the emergency department.Technical Words:Coronary artery disease (CAD) 冠状动脉疾病Coronary heart disease (CHD) 冠心病Juvenile diabetes 青少年糖尿病Parkinson’s disease 帕金森氏病;震颤性麻痹Repetitive strain injury (RSI)重复性过度劳累损伤Rheumatoid arthritis 风湿性关节炎Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) 性传播疾病Over-the-counter medication 非处方药Parkinson’s diseaseParkinson’s disease is a chronic and progressive degenerative disease of the brain marked by tremors, rigidity and slow movements.Parkinson’s disease belongs to a group of conditions called movement disorders. It is characterized by muscle rigidity, resting tremor, slowing of movement and, in extreme cases, nearly complete loss of movement. Secondary symptoms may include high level cognitive dysfunction, subtle language problems, and depression.Exercise: Fill in each blank with the appropriate form of the word given in brackets.1. At first, we didn’t realize the (severe) _______ of her wounds.2. It is reported that this disease attacks the central (nerve) _____ system.3. The (injure) ________ to their key player could be a decisive factor in the game.4. We couldn’t feel the change in the blood pressure within the (arterial) _________.5. (Diabetic) ________ is by far the most frequent disease among the over-weight people.6. These bacteria can be thought of as an additional (digest) ________ organ.7. It is (normal) ________ for a man to walk in his sleep.8. They found it stimulated the (secrete) _______ of insulin in pancreatic (胰的) cells in thelaboratory.9. Impairment of the ability to write is usually caused by brain (function) ________ or disease.10. What is severe acute (respire) _________ syndrome?Unit 2 Examination ProcessReading ATask 1 Before reading the passage, see how much you know about medical tests by answering the following questions.3.What are the most common medical tests in the hospital?4.What are the purposes of medical tests?A Directory of Medical TestsTaking a medical history and performing a physical examination usually provide the information a doctor needs to evaluate a person’s health or to understand what is causing an illness. But sometimes, doctors need to order tests to find out more.Here are some common tests and what they involve:Blood TestsComplete Blood Count (CBC). A CBC measures the levels of different types of blood cells. By determining if there are too many or not enough of each blood cell type, a CBC can help to detect a wide variety of illnesses or signs of infection.Blood Chemistry Test. Basic blood chemistry tests measure the levels of certain electrolytes, such as sodium and potassium, in the blood. Doctors typically order them to look for any sign of kidney dysfunction, diabetes, metabolic disorders, and tissue damage.Liver Function Test. Liver function tests check to see how the liver is working and look for any sort of liver damage or inflammation.Radiology TestsX-Rays. X-rays can help doctors find a variety of conditions, including broken bones and lung infections.Ultrasound. Though they’re typically associated with pregnancy, doctors order ultrasounds in lots of different cases. The images seen on most ultrasounds are difficult for the untrained eye to decipher, so a doctor will view the image and interpret it.Computed Tomography (CAT scan or CT scan). CAT scans are a kind of X-ray, and typically are ordered to look for things such as appendicitis, internal bleeding, or abnormal growths. A scan may require the use of a contrast material (a dye or other substance) to improve the visibility of certain tissues or blood vessels.Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI). MRIs use radio waves and magnetic fields to produce an image. MRIs are often used to look at bones, joints, and the brain. Contrast material is sometimes given through an IV in order to get a better picture of certain structures.Other TestsStool Test. Stool (or feces or poop) test can provide doctors with valuable information about what’s wrong when one has a problem in the stomach, intestines, or another part of the gastrointestinal system.Urine Test. Doctors order urine tests to make sure that the kidneys are functioning properly or when they suspect an infection in the kidneys or bladder.Electroencephalography (EEG). EEGs often are used to detect conditions that affect brain function, such as epilepsy, seizure disorders, and brain injury.Electrocardiography (EKG). EKGs measure the heart’s electrical activity to help evaluate its function and identify any problems. The EKG can help determine the rate and rhythm of heartbeats, the size and position of the heart’s chambers, and whether there is any damage present. EKGs can detect abnormal heart rhythms, some congenital heart defects, and heart tissue that isn’t getting enough oxygen.Task 2 After reading the passage, group the medical tests mentioned in the passage into each category.Blood Tests: Radiology Tests: Other Tests:Take 3 Read the passage again. Match each medical test with one fact as its target.9.Ultrasound a. lung infections10.X-rays b. an infection in the kidneysplete Blood Test c. metabolic disorders12.Blood Chemistry Test d. abnormal growths13.Liver Function Test e. blood cell type14.Urine Test f. heart rhythms15.EKG g. pregnancy16.Stool Test h. a problem in the intestines17.MRI a. liver inflammation18.EEG b. brain injuryputed Tomography k. joint problemsListeningTask 1 Mr. Black is having a check at the Department of Gastroenterology. A nurse will draw some blood for him. Listen to the conversation and put the following items in correct order.Sterilize the skinGet the reportTake off coat and roll up your sleeveClench your fistOpen your handSend specimen to the laboratoryTie the tourniquetPress with cotton swabTask 2 Mr. Black is going to have a gastroscopy(胃镜检查). Listen to the conversation and choose the best answer to each question you hear.1. What does an endoscope look like?A. As long as a fingerB. Thin and flexible.C. A large pipe2. What should Mr. Black do before having the gastroscopy?A. Smoke as little as possible.B. Empty the stomach.C. Drink a lot of water.3. When is Mr. Black supposed to come tomorrow?A. 6 a.m..B. 2 p.m.C. 8 a.m.4. When will Mr. Black get the result?A. In several days.B. Immediately.C. The day after tomorrow.5. What will be sent to the pathology laboratory?A. Blood Sample.B. Gastric fluid sample.C. Biology sample.Task 3. Mr. Black is in the gastroscope room. Listen to the conversation and fill in the blanks with what you hear.Nurse: Mr. Black, I’d like to know whether you ________ today.Mr. Black: Never.Nurse: Fine. The gastroscopy usually takes about ten minutes. But now we should make some ________ for it.Mr. Black:Okay. Please tell me what to do.Nurse: I will give you a ________ by an injection to help you relax.Mr. Black: When it works, shall I fall sleep?Nurse: No, it can only make you drowsy. It’s not a ___________ anesthetic.Mr. Black:Will I feel intense pain during the test?Nurse:No, the doctor will numb the back of your throat by spraying on some _________ anesthetic. You may just feel a little uncomfortable, particularly when you first swallow the _______.Mr. Black: I see. Thank you.Nurse: By the way, the doctor may take one or more _________ in the testing process. But don’t worry. That is painless.Mr. Black: Alright, I will try to cooperate.Reading BView a Sample CBCA complete blood count (CBC) is a calculation of the cellular makeup of blood. It measures the concentration of white blood cells, red blood cells, and platelets in the blood and aids in diagnosing conditions and diseases such as malignancy, anemia, or blood clotting problems. The CBC is typically reported in the format below, although different labs may use different formats.●Sample CBC TestThe sample CBC below shows that the patient’s white blood cells and red blood cells are low.Complete Blood Count (CBC) with Differential Test Results Result Units Reference Interval White Blood Count 1.5L ×103/mm3 5.0-10.0Red Blood Count 3.50L ×106/mm3 4.1-5.3 Hemoglobin 10.8L g/dl 12.0-18.0 Hematocrit 31.1L % 37.0-52.0 Platelets 302 ×103/mm3150-400 Polys(neutrophils) 23L % 45-76 Lymphs 68H % 17-44 Monocytes 7 % 3-10Eosinophil 2 % 0-4 Basophil 0.6 % 0.2Polys(absolute) 3.4L ×103/mm3 1.8-7.8 Lymphs(absolute) 1.0 ×103/mm30.7-4.5 Monocytes(absolute) 0.1 ×103/mm30.1-1.0Eos(absolute) 0.1 ×103/mm30.0-0.4 Basos(absolute) 0.0 ×103/mm30.0-0.2●Understanding the ChartResult:The “Result”column shows the counts. The “L”or “H”after the count shows whether the counts are lower (“L”) or higher (“H”) than the normal range.Reference Interval (or Reference Range): The “Reference Interval”column shows the normal range for each measurement for the lab performing the test. Note that reference intervals may vary slightly among different laboratories.White Blood Cells: The complete blood count (CBC) report shows that the patient’s total white blood cell count (WBC) is 1.5, which is lower than the normal range of 5.0-10.0. The low WBC count (leucopenia) may point toward autoimmune diseases, such as lupus erythematosus or rheumatoid arthritis, bone marrow problem, disease of the liver or spleen, or related to some medications, such as chemotherapy.Red Blood Cells: The report shows that the patient has a red blood cell count of 3.50, which is lower than the normal range of 4.1-5.3. The low red blood cell count may suggest anemia, which can have many causes. Possible causes include autoimmune diseases, bone marrow failure, leukemia, malnutrition, heavy menstrual bleeding, stomach ulcers, inflammatory bowel disease, or some tumors.Hemoglobin: The report indicates that the patient’s Hb count is 10.8, which is below the normal range of 12.0-18.0. Low hemoglobin values may indicate anemia, or blood loss.Hematocrit: Hematocrit is also low. This means that the patient has mild anemia and may be starting to notice symptoms.Platelets: The report indicates that the platelet count for this patient is normal.Differential: also known as white blood cell (WBC) differential count. This portion of the report shows the counts for the five main types of white blood cells, either as percentages (the first five counts) or as the absolute number of cells (the second five counts). Such information helps the doctor monitor patients with allergies and determine how a patient is recovering from an illness or responding to therapy.Task 1 Match the following terms with their Chinese meanings.3.reference interval a. 白血球减少症4.stomach ulcer b. 胃溃疡5.bone marrow failure c. 参考范围6.rheumatoid arthritis d. 骨髓衰竭7.leucopenia f. 风湿性关节炎Task 2 Translate the following paragraph into Chinese.The cells that circulate in the bloodstream are generally divided into three types: white blood cells (leukocytes), red blood cells (erythrocytes), and platelets (thrombocytes). Abnormally high or low counts may indicate the presence of many forms of disease, and hence blood counts areamongst the most commonly performed blood tests in medicine, as they can provide an overview of a patient’s general health status. A CBC is routinely performed during annual physical examination in some districts._____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ WritingMemorandum (Memo)Task 1 A memo is generally made up of three parts: Introduction, Body and Conclusion. It needs to be brief, to the point and clear. Now read the following sample memo and learn about how it is organized.A Sample Memo:TO: (person or group to whom the memo is addressed)FROM: (person of group sending the memo)DA TE: (current date—month /date/year)SUBJECT: (what the memo is about, this should be in bold)First Sentence:Reason for the memoe.g. I would like to remind you that…Second Sentence—Main BodyAny Instruction or InformationClosing Sentence:What is required of the readerse.g. confirmation, answers or feedbackPlease share this announcement with co-workers immediatelyTask 2 Suppose you are a clerk working in the family planning office of a hospital. Please write a memo based on the following information. Your memo should include the tips given in Task 1.Situation:A summing-up meeting on the 2008 family planning work of the hospital is to be held on April 25th, 2008. Besides, the 2009 family planning work will be assigned at the meeting. Those who are in charge of family planning work in all departments and offices are requested to attend the meeting.Technical Words:Complete Blood Count (CBC) 全血球计数Computed Tomography (CT-scan) 计算机断层摄影Contrast material 造影剂Electrocardiograph (EKG) 心电图Electroencephalograph (EEG) 脑电图Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) 核磁共振成像Basophil 嗜碱性粒细胞Eosinophil嗜酸性粒细胞Hematocrit 血细胞比容Hemoglobin 血红蛋白Leucopenia 白细胞减少Lupus erythematosus 红斑狼疮Monocyte 单核细胞Neutrophil 嗜中性粒细胞,中性白细胞Exercise: Fill in each blank with the appropriate form of the word given in brackets.1. The frontiers of (medicine) ________ knowledge are being pushed forwards as time goes on.2. The (metabolism) ________ abnormalities were corrected and renal function remained normal.3. Will you please recommend some (typical) ______ Chinese dishes to the foreign guests?4. Some women experience morning sickness during the first three months of (pregnant) ______.5. Dense fog is covering roads in the north and (visible) _______ is very poor.6. Modern machines, (range) _________ from TV to computers, can do various types of work forman.7. Dictionaries and encyclopedias are (refer) _________ books. You may (refer) _______ them while reading and writing.8. A (consult) ________ room is a place where a doctor sees his patient.9. (Immune) _________ can be acquired by having had the disease or by the use of vaccines.10. The illness was (diagnose)__________ as mumps (腮腺炎).Unit 3 DiagnosisReading A:Task 1 Before reading the passage, see how much you know about the treatment of common chronic and acute diseases by answering the following questions.1.What are the differences between acute diseases and chronic diseases?2.What are the most common chronic diseases of older adults?Treatment of Common Chronic and Acute DiseasesHealth concerns are usually classified as either acute or chronic. Acute illnesses often begin abruptly and last only a short time. Most people with an acute illness can expect to return to normal health. However, chronic diseases usually develop slowly, last a long time, and are often progressive and incurable.Chronic DiseasesChronic diseases, such as cardiovascular disease, cancer, and diabetes, are by far the leading cause of mortality in the world. Treatment includes medication and lifestyle changes such as diet and physical activity, and stress management.Cardiovascular diseases include coronary heart disease, hypertension, congenital heart disease, heart failure, etc. Once diagnosed with CVDs, patients are typically prescribed medication that will regulate cardiovascular functions and are usually taken daily for the rest of their life. Certain treatments are usually started right away if a heart attack is suspected, even before the diagnosis is confirmed. These include: oxygen, aspirin to prevent further blood clotting, nitroglycerin to reduce the workload on the heart, and treatment for chest pain.Cancer may affect people at all ages, even fetuses. The three most common types of cancer treatment are surgery, radiotherapy and chemotherapy, which aim at removing the cancer cells or destroying them in the body with medicines or other agents. Choice of treatment is influenced by several factors, including the specific characteristics of the cancer, the patient’s overall condition, and whether the goal of treatment is to cure the cancer, keep it from spreading, or relieve the symptoms.All forms of diabetes have been treatable since insulin became medically available in 1921, but there is no cure. The insulin injection is a basic treatment of type I diabetes. TypeⅡis managed with a combination of dietary treatment, exercise, medications and insulin supplementation.Acute DiseasesTreatment for acute diseases usually involves medication of antibiotics, which have direct effects on inflammation.Pneumonia is a common illness which occurs in all age groups. Most cases of pneumonia can be treated without hospitalization. Typically, oral antibiotics, rest, fluids, and home care are sufficient for complete resolution. However, if the symptoms get worse, or complications occur, the person will often have to be hospitalized.。