2002年MBA英语真题及答案
- 格式:doc
- 大小:104.50 KB
- 文档页数:20

2002年全国攻读硕士学位研究生入学考试英语试题Section I Use of EnglishDirections:Read the following text. Choose the best word(s) for each numbered blank and mark A, B, C OR D on ANSWER SHEET 1. (10 points)Comparisons were drawn between the development of television in the 20th century and the diffusion of printing in the 15th and 16th centuries. Yet much had happened 1 . As was discussed before, it was not 2 the 19th century that the newspaper became the dominant pre-electronic_ 3 _ ,following in the wake of the pamphlet and the book and in the 4 of the periodical. It was during the same time that the communications revolution 5 up, beginning with transport, the railway, and leading 6 through the telegraph, the telephone, radio, and motion pictures 7 the 20th century world of the motor car and the air plane. Not everyone sees that Process in 8 . It is important to do so.It is generally recognized, 9 , that the introduction of the computer in the early 20th century, 10 by the invention of the integrated circuit during the 1960s, radically changed the process, 11 its impact on the media was not immediately 12 . As time went by, computers became smaller and more powerful, and they became “personal” too, as well as 13 , with display becoming sharper and storage 14 increasing. They were thought of, like people, 15 generations, with the distance between generations much 16 .It was within the computer age that the term “information society” began to be widely used to describe the 17 within which we now live. The communications revolution has 18 both work and leisure and how we think and feel both about place and time, but there have been 19 view about its economic, political, social and cultural implication s. “Benefits” have been weighed 20 “harmful” outcomes. And generalizations have proved difficult.1. [A]between [B]before [C]since [D]later2. [A]after [B]by [C]during [D]until3. [A]means [B]method [C]medium [D]measure4. [A]process [B]company [C]light [D]form5. [A]gathered [B]speeded [C]worked [D]picked6. [A]on [B]out [C]over [D]off7. [A]of [B]for [C]beyond [D]into8. [A]concept [B]dimension [C]effect [D]perspective9. [A]indeed [B]hence [C]however [D]therefore10. [A]brought [B]followed [C]stimulated [D]characterized11. [A]unless [B]since [C]lest [D]although12. [A]apparent [B]desirable [C]negative [D]plausible13. [A]institutional [B]universal [C]fundamental [D]instrumental14. [A]ability [B]capability [C]capacity [D]faculty15. [A]by means of [B]in terms of [C]with regard to[D]in line with16. [A]deeper [B]fewer [C]nearer [D]smaller17. [A]context [B]range [C]scope [D]territory18. [A]regarded [B]impressed [C]influenced [D]effected19. [A]competitive [B]controversial [C]distracting [D]irrational20. [A]above [B]upon [C]against [D]withSection II Reading ComprehensionPart ADirections:Read the following four texts. Answer the questions below each text by choosing [A], [B], [C] or [D]. Mark your answers on ANSWER SHEET 1. (40 points)Text 1If you intend using humor in your talk to make people smile, you must know how to identify shared experiences and problems. Your humor must be relevant to the audience and should help to show them that you are one of them or that you understand their situation and are in sympathy with their point of view. Depending on whom you are addressing, the problems will be different. If you are talking to a group of managers, you may refer to the disorganized methods of their secretaries; alternatively if you are addressing secretaries, you may want to comment on their disorganized bosses.Here is an example, which I heard at a nurses’ convention, of a story which works well because the audience all shared the same view of doctors. A man arrives in heaven and is being shown around by St. Peter. He sees wonderful accommodations, beautiful gardens, sunny weather, and so on. Everyone is very peaceful, polite and friendly until, waiting in a line for lunch, the new arrival is suddenly pushed aside by a man in a white coat, who rushes to the head of the line, grabs his food and stomps over to a table by himself. “Who is that?”the new arrival asked St. Peter. “Oh, that’s God,” came the reply, “but sometimes he thinks he’s a doctor.”If you are part of the group which you are addressing, you will be in a position to know the experiences and problems which are common to all of you and it’ll be appropriate for you to make a passing remark about the inedible canteen food or the chairman’s notorious bad taste in ties. With other audiences you mustn’t attempt to cut in with humor as they will resent an outsider making disparaging remarks about their canteen or their chairman. You will be on safer ground if you stick to scapegoats like the Post Office or the telephone system.If you feel awkward being humorous, you must practice so that it becomes more natural. Include a few casual and apparently off-the-cuff remarks which you can deliver in a relaxed and unforced manner. Often it’s the delivery which causes theaudience to smile, so speak slowly and remember that a raised eyebrow or an unbelieving look may help to show that you are making a light-hearted remark.Look for the humor. It often comes from the unexpected. A twist on a familiar quote “If at first you don’t succeed, give up”or a play on words or on a situation. Search for exaggeration and understatement. Look at your talk and pick out a few words or sentences which you can turn about and inject with humor.21. To make your humor work, you should .[A] take advantage of different kinds of audience[B] make fun of the disorganized people[C] address different problems to different people[D] show sympathy for your listeners22. The joke about doctors implies that, in the eyes of nurses, they are .[A] impolite to new arrivals[B] very conscious of their godlike role[C] entitled to some privileges[D] very busy even during lunch hours23. It can be inferred from the text that public services .[A] have benefited many people[B] are the focus of public attention[C] are an inappropriate subject for humor[D] have often been the laughing stock24. To achieve the desired result, humorous stories should be delivered .[A] in well-worded language[B] as awkwardly as possible[C] in exaggerated statements[D] as casually as possible25. The best title for the text may be .[A] Use Humor Effectively[B] Various Kinds of Humor[C] Add Humor to Speech[D] Different Humor StrategiesText 2Since the dawn of human ingenuity, people have devised ever more cunning tools to cope with work that is dangerous, boring, burdensome, or just plain nasty. That compulsion has resulted in robotics—the science of conferring various human capabilities on machines. And if scientists have yet to create the mechanical version of science fiction, they have begun to come close.As a result, the modern world is increasingly populated by intelligent gizmos whose presence we barely notice but whose universal existence has removed much human labor. Our factories hum to the rhythm of robot assembly arms. Our banking is done at automated teller terminals that thank us with mechanical politeness for thetransaction. Our subway trains are controlled by tireless robot-drivers. And thanks to the continual miniaturization of electronics and micro-mechanics, there are already robot systems that can perform some kinds of brain and bone surgery with submillimeter accuracy—far greater precision than highly skilled physicians can achieve with their hands alone.But if robots are to reach the next stage of laborsaving utility, they will have to operate with less human supervision and be able to make at least a few decisions for themselves—goals that pose a real challenge. “While we know how to tell a robot to handle a specific error," says Dave Lavery, manager of a robotics program at NASA, “we can't yet give a robot enough ‘common sense’ to reliably interact with a dynamic world.”Indeed the quest for true artificial intelligence has produced very mixed results. Despite a spell of initial optimism in the 1960s and 1970s when it appeared that transistor circuits and microprocessors might be able to copy the action of the human brain by the year 2010, researchers lately have begun to extend that forecast by decades if not centuries.What they found, in attempting to model thought, is that the human brain's roughly one hundred billion nerve cells are much more talented—and human perception far more complicated—than previously imagined. They have built robots that can recognize the error of a machine panel by a fraction of a millimeter in a controlled factory environment. But the human mind can glimpse a rapidly changing scene and immediately disregard the 98 percent that is irrelevant, instantaneously focusing on the monkey at the side of a winding forest road or the single suspicious face in a big crowd. The most advanced computer systems on Earth can't approach that kind of ability, and neuroscientists still don’t know quite how we do it.26. Human ingenuity was initially demonstrated in .[A] the use of machines to produce science fiction.[B] the wide use of machines in manufacturing industry.[C] the invention of tools for difficult and dangerous work.[D] the elite’s cunning tackling of dangerous and boring work.27. The word “gizmos” (line 1, paragraph 2) most probably means .[A] programs[B] experts[C] devices [D] creatures28. According to the text, what is beyond man's ability now is to design a robotthat can .[A] fulfill delicate tasks like performing brain surgery.[B] interact with human beings verbally.[C] have a little common sense.[D] respond independently to a changing world.29. Besides reducing human labor, robots can also .[A] make a few decisions for themselves.[B] deal with some errors with human intervention.[C] improve factory environments.[D] cultivate human creativity.30. The author uses the example of a monkey to argue that robots are .[A] expected to copy human brain in internal structure.[B] able to perceive abnormalities immediately.[C] far less able than human brain in focusing on relevant information.[D] best used in a controlled environment.Text 3Could the bad old days of economic decline be about to return? Since OPEC agreed to supply-cuts in March, the price of crude oil has jumped to almost $26 a barrel, up from less than $10 last December. This near-tripling of oil prices calls up scary memories of the 1973 oil shock, when prices quadrupled, and 1979-1980, when they also almost tripled. Both previous shocks resulted in double-digit inflation and global economic decline. So where are the headlines warning of gloom and doom this time?The oil price was given another push up this week when Iraq suspended oil exports. Strengthening economic growth, at the same time as winter grips the northern hemisphere, could push the price higher still in the short term.Yet there are good reasons to expect the economic consequences now to be less severe than in the 1970s. In most countries the cost of crude oil now accounts for a smaller share of the price of petrol than it did in the 1970s. In Europe, taxes account for up to four-fifths of the retail price, so even quite big changes in the price of crude have a more muted effect on pump prices than in the past.Rich economies are also less dependent on oil than they were, and so less sensitive to swings in the oil price. Energy conservation, a shift to other fuels and a decline in the importance of heavy, energy-intensive industries have reduced oil consumption. Software, consultancy and mobile telephones use far less oil than steel or car production. For each dollar of GDP (in constant prices) rich economies now use nearly 50% less oil than in 1973. The OECD estimates in its latest Economic Outlook that, if oil prices averaged $22 a barrel for a full year, compared with $13 in 1998, this would increase the oil import bill in rich economies by only 0.25-0.5% of GDP. That is less than one-quarter of the income loss in 1974 or 1980. On the other hand, oil-importing emerging economies—to which heavy industry has shifted—have become more energy-intensive, and so could be more seriously squeezed.One more reason not to lose sleep over the rise in oil prices is that, unlike the rises in the 1970s, it has not occurred against the background of general commodity-price inflation and global excess demand. A sizable portion of the world is only just emerging from economic decline. The Economist’s commodity price index is broadly unchanging from a year ago. In 1973 commodity prices jumped by 70%, and in 1979 by almost 30%.31. The main reason for the latest rise of oil price is_______[A] global inflation. [B] reduction in supply.[C]fast growth in economy. [D] Iraq’s suspension of exports.32. It can be inferred from the text that the retail price of petrol will go updramatically if______.[A] price of crude rises. [B] commodity prices rise.[C] consumption rises. [D] oil taxes rise.33. The estimates in Economic Outlook show that in rich countries_______.[A]heavy industry becomes more energy-intensive.[B]income loss mainly results from fluctuating crude oil prices.[C]manufacturing industry has been seriously squeezed.[D]oil price changes have no significant impact on GDP.34. We can draw a conclusion from the text that_______.[A]oil-price shocks are less shocking now.[B]inflation seems irrelevant to oil-price shocks.[C]energy conservation can keep down the oil prices.[D]the price rise of crude leads to the shrinking of heavy industry.35. From the text we can see that the writer seems__________.[A]optimistic. [B]sensitive. [C]gloomy. [D]scared.Text 4The Supreme Court’s decisions on physician-assisted suicide carry important implications for how medicine seeks to relieve dying patients of pain and suffering.Although it ruled that there is no constitutional right to physician-assisted suicide, the Court in effect supported the medical principle of “double effect”, a centuries-old moral principle holding that an action having two effects—a good one that is intended and a harmful one that is foreseen—is permissible if the actor intends only the good effect.Doctors have used that principle in recent years to justify using high doses of morphine to control terminally ill patients’pain, even though increasing dosages will eventually kill the patient.Nancy Dubler, director of Montefiore Medical Center, contends that the principle will shield doctors who “until now have very, very strongly insisted that they could not give patients sufficient medication to control their pain if that might hasten death”.George Annas, chair of the health law department at Boston University, maintains that, as long as a doctor prescribes a drug for a legitimate medical purpose, the doctor has done nothing illegal even if the patient uses the drug to hasten death. “It’s like surgery,” he says. “We don’t call those deaths homicides because the doctors didn’t intend to kill their patients, although they risked their death. If you’re a physician, you can risk your patient’s suicide as long as you don’t intend their suicide.”On another level, many in the medical community acknowledge that the assisted-suicide debate has been fueled in part by the despair of patients for whom modern medicine has prolonged the physical agony of dying.Just three weeks before the Court’s ruling on physician-assisted suicide, theNational Academy of Science (NAS) released a two-volume report, Approaching Death: Improving Care at the End of Life. It identifies the undertreatment of pain and the aggressive use of “ineffectual and forced medical procedures that may prolong and even dishonor the period of dying” as the twin problems of end-of-life care.The profession is taking steps to require young doctors to train in hospices, to test knowledge of aggressive pain management therapies, to develop a Medicare billing code for hospital-based care, and to develop new standards for assessing and treating pain at the end of life.Annas says lawyers can play a key role in insisting that these well-meaning medical initiatives translate into better care. “Large numbers of physicians seem unconcerned with the pain their patients are needlessly and predictably suffering”, to the extent that it constitutes “systematic patient abuse”. He says medical licensing boards “must make it clear...that painful deaths are presumptiv ely ones that are incompetently managed and should result in license suspension”.36. From the first three paragraphs, we learn that .[A] doctors used to increase drug dosages to control their patients’pain[B] it is still illegal for doctors to help the dying end their lives[C] the Supreme Court strongly opposes physician-assisted suicide[D] patients have no constitutional right to commit suicide37. Which of the following statements its true according to the text?[A] Doctors will be held guilty if they risk their patients’death.[B] Modern medicine has assisted terminally ill patients in painless recovery.[C] The Court ruled that high-dosage pain-relieving medication can beprescribed.[D] A doctor’s medication is no longer justified by his intentions.38. According to the NAS’s report, one of the problems in end-of-life care is .[A] prolonged medical procedures [B] inadequate treatment of pain[C] systematic drug abuse [D] insufficient hospital care39. Which of the following best defines the word “aggressive”(line 4, paragraph7)?[A] Bold. [B] Harmful. [C] Careless. [D] Desperate40. George Annas would probably agree that doctors should be punished if they .[A] manage their patients incompetently[B] give patients more medicine than needed[C] reduce drug dosages for their patients[D] prolong the needless suffering of the patientsPart BDirections:Read the following text carefully and then translate the underlined segments into Chinese. Your translation should be written clearly on ANSWER SHEET 2. (10 points)Almost all our major problems involve human behavior, and they cannot be solved by physical and biological technology alone. What is needed is a technology of behavior, but we have been slow to develop the science from which such a technology might be drawn.(41)One difficulty is that almost all of what is called behavioral science continues to trace behavior to states of mind, feelings, traits of character, human nature, and so on. Physics and biology once followed similar practices and advanced only when they discarded them. (42)The behavioral sciences have been slow to change partly because the explanatory items often seem to be directly observed and partly because other kinds of explanations have been hard to find. The environment is obviously important, but its role has remained obscure. It does not push or pull, it selects, and this function is difficult to discover and analyze.(43)The role of natural selection in evolution was formulated only a little more than a hundred years ago, and the selective role of the environment in shaping and maintaining the behavior of the individual is only beginning to be recognized and studied. As the interaction between organism and environment has come to be understood, however, effects once assigned to states of mind, feelings, and traits are beginning to be traced to accessible conditions, and a technology of behavior may therefore become available. It will not solve our problems, however, until it replaces traditional prescientific views, and these are strongly entrenched. Freedom and dignity illustrate the difficulty. (44)They are the possessions of the autonomous(self-governing)man of traditional theory, and they are essential to practices in which a person is held responsible for his conduct and given credit for his achievements. A scientific analysis shifts both the responsibility and the achievement to the environment. It also raises questions concerning “values”. Who will use a technology and to what ends? (45)Until these issues are resolved, a technology of behavior will continue to be rejected, and with it possibly the only way to solve our problems.Section III Writing46. Directions:Study the following picture carefully and write an es say entitled “Cultures National and International”.In the essay you should1. describe the picture and interpret its meaning, and2. give your comment on the phenomenon.You should write about 200 words neatly on ANSWER SHEET 2. (20 points)An American girl in traditional Chinese costume(服装)第一部分英语知识应用试题解析一、文章总体分析本文主要介绍了计算机的发展对通信革命及人们的生存方式产生的影响。
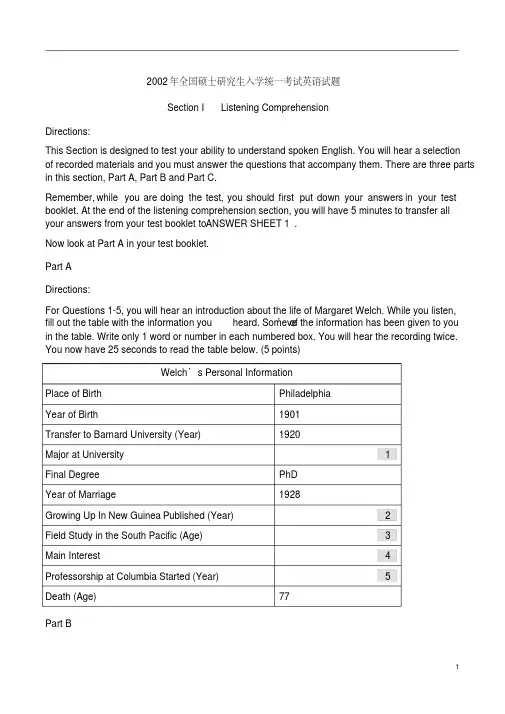
2002年全国硕士研究生入学统一考试英语试题Section I Listening ComprehensionDirections:This Section is designed to test your ability to understand spoken English. You will hear a selectionof recorded materials and you must answer the questions that accompany them. There are three parts in this section, Part A, Part B and Part C.Remember, while you are doing the test, you should first put down your answers in your test booklet. At the end of the listening comprehension section, you will have 5 minutes to transfer allyour answers from your test booklet to A NSWER SHEET 1.Now look at Part A in your test booklet.Part ADirections:For Questions 1-5, you will hear an introduction about the life of Margaret Welch. While you listen,heard. Some of the information has been given to youfill out the table with the information you’vein the table. Write only 1 word or number in each numbered box. You will hear the recording twice. You now have 25 seconds to read the table below. (5 points)Welch’s Personal InformationPlace of Birth PhiladelphiaYear of Birth 1901Transfer to Barnard University (Year) 1920Major at University 1Final Degree PhDYear of Marriage 1928Growing Up In New Guinea Published (Year) 2Field Study in the South Pacific (Age) 3Main Interest 4Professorship at Columbia Started (Year) 5Death (Age) 77Part BDirections:For questions 6-10, you will hear a talk by a well-known U.S. journalist. While you listen, completethe sentences or answer the questions. Use not more than 3 words for each answer. You will hear the recording twice. You now have 25 seconds to read the sentences and questions below. (5 points)Besides reporters, who else were camped out 6for days outside the speaker’s home?apartmentOne reporter got to the speaker’s 7pretending to pay.The speaker believed the reporter wanted a 8picture of her lookingWhere is a correction to a false story usually 9placed?According to the speaker, the press will lose10readers unless the editors and the newsdirectorsPart CDirections:You will hear three pieces of recorded material. Before listening to each one, you will have time to read the questions related to it. While listening, answer each question by choosing [A], [B], [C] or[D]. After listening, you will have time to check your answers. You will hear each piece once only.(10 points)Questions 11-13 are based on a report about children’s healthy development. You now have 15 seconds to read Questions 11-13.11. What unusual question may doctors ask when giving kids a checkup next time? [A] How muchexercise they get every day.[B] What they are most worried about.[C] How long their parents accompany them daily.[D] What entertainment they are interested in.12. The academy suggests that children under age two ________.[A] get enough entertainment[B] have more activities[C] receive early education[D] have regular checkups13. According to the report, children’s bedrooms should ________.[A] be no place for play[B] be near a common area[C] have no TV sets[D] have a computer for studyQuestions 14-16 are based on the following talk about how to save money. You now have 15 seconds to read Questions 14-16.14. According to the speaker, what should one pay special attention to if he wants to save up?[A] Family debts.[B] Bank savings.[C] Monthly bills.[D] Spending habits.15. How much can a person save by retirement if he gives up his pack-a-day habit?[A] $190,000.[B] $330,000.[C] $500,000.[D] $1,000,000.16. What should one do before paying monthly bills, if he wants to accumulate wealth?[A] Invest into a mutual fund.[B] Use the discount tickets.[C] Quit his eating-out habit.[D] Use only paper bills and save coins.Questions 17-20 are based on an interview with Herbert A. Glieberman, a domestic-relations lawyer. You now have 20 seconds to read Questions 17-20.17. Which word best describes the lawyer’s prediction of the change in divorce rate?[A] Fall[B] Rise[C] V-shape[D] Zigzag18. What do people nowadays desire to do concerning their marriage?[A] To embrace changes of thought.[B] To adapt to the disintegrated family life.[C] To return to the practice in the ‘60s and ‘70s.[D] To create stability in their lives.19. Why did some people choose not to divorce 20 years ago?[A] They feared the complicated procedures.[B] They wanted to go against the trend.[C] They were afraid of losing face.[D] they were willing to stay together.20. Years ago a divorced man in a company would have ________.[A] been shifted around the country.[B] had difficulty being promoted.[C] enjoyed a happier life.[D] tasted little bitterness of disgrace.You now have 5 minutes to transfer all your answers from your test booklet to ANSWER SHEET 1.THIS IS THE END OF SECTION IDO NOT READ OR WORK ON THE NEXT SECTIONUNTIL YOU ARE TOLD TO CONTINUE全国硕士研究生入学考试英语试题(二)National Entrance Test of English for MA/MS Candidates (2002)考生注意事项1. 考生必须严格遵守各项考场规则,得到监考人员指令后方可开始答题。

2002年全国硕士研究生招生考试英语试题Section I Listening Comprehension(略)Section II Use of EnglishDirections:Read the following text. Choose the best word(s) for each numbered blank and mark A, B, C or D on ANSWER SHEET 1. (10 points)①Comparisons were drawn between the development of television in the 20th century and the diffusion of printing in the 15th and 16th centuries. ②Yet much had happened 21 . ③As was discussed before, it was not 22 the 19th century that the newspaper became the dominant pre-electronic 23 , following in the wake of the pamphlet and the book and in the 24 of the periodical. ④It was during the same time that the communications revolution 25 up, beginning with transport, the railway, and leading 26 through the telegraph, the telephone, radio, and motion pictures 27 the 20th-century world of the motor car and the airplane. ⑤Not everyone sees that process in 28 . ⑥It is important to do so.①It is generally recognized, 29 , that the introduction of the computer in the early 20th century, 30 by the invention of the integrated circuit during the 1960s, radically changed the process, 31 its impact on the media was not immediately 32 . ②As time went by, computers became smaller and more powerful, and they became “personal” too, as well as 33 , with display becoming sharper and storage 34 increasing. ③They were thought of, like people, 35 generations, with the distance between generations much 36 .①It was within the computer age that the term “information society” began to be widely used to describe the 37 within which we now live. ②The communications revolution has 38 both work and leisure and how we think and feel both about place and time, but there have been39 views about its economic, political, social and cultural implications. ③“Benefits” have been weighed 40 “harmful” outcomes. ④And generalizations have proved difficult.21. [ A ] between [ B ] before [ C ] since [ D ] later22. [ A ] after [ B ] by [ C ] during [ D ] until23. [ A ] means [ B ] method [ C ] medium [ D ] measure24. [ A ] process [ B ] company [ C ] light [ D ] form25. [ A ] gathered [ B ] speeded [ C ] worked [ D ] picked26. [ A ] on [ B ] out [ C ] over [ D ] off27. [ A ] of [ B ] for [ C ] beyond [ D ] into28. [ A ] concept [ B ] dimension [ C ] effect [ D ] perspective29. [ A ] indeed [ B ] hence [ C ] however [ D ] therefore30. [ A ] brought [ B ] followed [ C ] stimulated [ D ] characterized31. [ A ] unless [ B ] since [ C ] lest [ D ] although32. [ A ] apparent [ B ] desirable [ C ] negative [ D ] plausible33. [ A ] institutional [ B ] universal [ C ] fundamental [ D ] instrumental34. [ A ] ability [ B ] capability [ C ] capacity [ D ] faculty35. [ A ] by means of [ B ] in terms of [ C ] with regard to [ D ] in line with36. [ A ] deeper [ B ] fewer [ C ] nearer [ D ] smaller37. [ A ] context [ B ] range [ C ] scope [ D ] territory38. [ A ] regarded [ B ] impressed [ C ] influenced [ D ] effected39. [ A ] competitive [ B ] controversial [ C ] distracting [ D ] irrational40. [ A ] above [ B ] upon [ C ] against [ D ] withSection III Reading ComprehensionPart ADirections:Read the following four texts. Answer the questions below each text by choosing A, B, C or D. Mark your answers on ANSWER SHEET 1. (40 points)Text 1①If you intend using humor in your talk to make people smile, you must know how to identify shared experiences and problems. ②Your humor must be relevant to the audience and should help to show them that you are one of them or that you understand their situation and are in sympathy with their point of view. ③Depending on whom you are addressing, the problems will be different. ④If you are talking to a group of managers, you may refer to the disorganized methods of their secretaries; alternatively if you are addressing secretaries, you may want to comment on their disorganized bosses.①Here is an example, which I heard at a nurses’ convention, of a story which works well because the audience all shared the same view of doctors. ②A man arrives in heaven and is being shown around by St. Peter. ③He sees wonderful accommodations, beautiful gardens, sunny weather, and so on. ④Everyone is very peaceful, polite and friendly until, waiting in a line for lunch, the new arrival is suddenly pushed aside by a man in a white coat, who rushes to the head of the line, grabs his food and stomps over to a table by himself. ⑤“Who is that?” the new arrival asked St. Peter. ⑥“Oh, that’s God,” came the reply, “but sometimes he thinks he’s a doctor.”①If you are part of the group which you are addressing, you will be in a position to know the experiences and problems which are common to all of you and it’ll be appropriate for you to make a passing remark about the inedible canteen food or the chairman’s notorious bad taste in ties. ②With other audiences you mustn’t attempt to cut in with humor as they will resent an outsider making disparaging remarks about their canteen or their chairman. ③You will be on safer ground if you stick to scapegoats like the Post Office or the telephone system.①If you feel awkward being humorous, you must practice so that it becomes more natural.②Include a few casual and apparently off-the-cuff remarks which you can deliver in a relaxed and unforced manner. ③Often it’s the delivery which causes the audience to smile, so speak slowly and remember that a raised eyebrow or an unbelieving look may help to show that you are makinga light-hearted remark.①Look for the humor. ②It often comes from the unexpected. ③A twist on a familiar quote “If at first you don’t succeed, give up” or a play on words or on a situation. ④Searchfor exaggeration and understatement. ⑤Look at your talk and pick out a few words or sentences which you can turn about and inject with humor.41.To make your humor work, you should_______.[A] take advantage of different kinds of audience[B] make fun of the disorganized people[C] address different problems to different people[D] show sympathy for your listeners42. The joke about doctors implies that, in the eyes of nurses, they are_______.[A] impolite to new arrivals [B] very conscious of their godlike role[C] entitled to some privileges [D] very busy even during lunch hours43.It can be inferred from the text that public services_______.[A] have benefited many people [B] are the focus of public attention[C] are an inappropriate subject for humor [D] have often been the laughing stock44.To achieve the desired result, humorous stories should be delivered_______.[A] in well-worded language [B] as awkwardly as possible[C] in exaggerated statements [D] as casually as possible45.The best title for the text may be_______.[A] Use Humor Effectively [B] Various Kinds of Humor[C] Add Humor to Speech [D] Different Humor StrategiesText 2①Since the dawn of human ingenuity, people have devised ever more cunning tools to cope with work that is dangerous, boring, burdensome, or just plain nasty. ②That compulsion has resulted in robotics—the science of conferring various human capabilities on machines. ③And if scientists have yet to create the mechanical version of science fiction, they have begun to come close.①As a result, the modern world is increasingly populated by intelligent gizmos whose presence we barely notice but whose universal existence has removed much human labor. ②Our factories hum to the rhythm of robot assembly arms. ③Our banking is done at automated tellerterminals that thank us with mechanical politeness for the transaction. ④Our subway trains are controlled by tireless robot-drivers. ⑤And thanks to the continual miniaturization of electronics and micro-mechanics, there are already robot systems that can perform some kinds of brain and bone surgery with submillimeter accuracy—far greater precision than highly skilled physicians can achieve with their hands alone.①But if robots are to reach the next stage of laborsaving utility, they will have to operate with less human supervision and be able to make at least a few decisions for themselves—goals that pose a real challenge. ②“While we know how to tell a robot to handle a specific error,”says Dave Lavery, manager of a robotics program at NASA, “we can’t yet give a robot enough ‘common sense’ to reliably interact with a dynamic world.”①Indeed the quest for true artificial intelligence has produced very mixed results. ②Despitea spell of initial optimism in the 1960s and 1970s when it appeared that transistor circuits and microprocessors might be able to copy the action of the human brain by the year 2010, researchers lately have begun to extend that forecast by decades if not centuries.①What they found, in attempting to model thought, is that the human brain’s roughly one hundred billion nerve cells are much more talented—and human perception far more complicated —than previously imagined. ②They have built robots that can recognize the error of a machine panel by a fraction of a millimeter in a controlled factory environment. ③But the human mind can glimpse a rapidly changing scene and immediately disregard the 98 percent that is irrelevant, instantaneously focusing on the monkey at the side of a winding forest road or the single suspicious face in a big crowd. ④The most advanced computer systems on Earth can’t approach that kind of ability, and neuroscientists still don’t know quite how we do it.46. Human ingenuity was initially demonstrated in_______.[A] the use of machines to produce science fiction[B] the wide use of machines in manufacturing industry[C] the invention of tools for difficult and dangerous work[D] the elite’s cunning tackling of dangerous and boring work47. The word “gizmos” (line1, paragraph2) most probably means_______.[A] programs [B] experts [C] devices [D] creatures48. According to the text, what is beyond man’s ability now is to design a robot thatcan_______.[A] fulfill delicate tasks like performing brain surgery[B] interact with human beings verbally[C] have a little common sense[D] respond independently to a changing world49. Besides reducing human labor, robots can also_______.[A] make a few decisions for themselves[B] deal with some errors with human intervention[C] improve factory environments[D] cultivate human creativity50. The author uses the example of a monkey to argue that robots are_______.[A] expected to copy human brain in internal structure[B] able to perceive abnormalities immediately[C] far less able than human brain in focusing on relevant information[D] best used in a controlled environmentText 3①Could the bad old days of economic decline be about to return? ②Since OPEC agreed to supply-cuts in March, the price of crude oil has jumped to almost $26 a barrel, up from less than $10 last December. ③This near-tripling of oil prices calls up scary memories of the 1973 oil shock, when prices quadrupled, and 1979-1980, when they also almost tripled. ④Both previous shocks resulted in double-digit inflation and global economic decline. ⑤So where are the headlines warning of gloom and doom this time?①The oil price was given another push up this week when Iraq suspended oil exports.②Strengthening economic growth, at the same time as winter grips the northern hemisphere, could push the price higher still in the short term.①Yet there are good reasons to expect the economic consequences now to be less severe than in the 1970s. ②In most countries the cost of crude oil now accounts for a smaller share of the price of petrol than it did in the 1970s. ③In Europe, taxes account for up to four-fifths of the retail price, so even quite big changes in the price of crude have a more muted effect on pump pricesthan in the past.①Rich economies are also less dependent on oil than they were, and so less sensitive to swings in the oil price. ②Energy conservation, a shift to other fuels and a decline in the importance of heavy, energy-intensive industries have reduced oil consumption. ③Software, consultancy and mobile telephones use far less oil than steel or car production. ④For each dollar of GDP (in constant prices) rich economies now use nearly 50% less oil than in 1973. ⑤The OECD estimates in its latest Economic Outlook that, if oil prices averaged $22 a barrel for a full year, compared with $13 in 1998, this would increase the oil import bill in rich economies by only 0.25-0.5% of GDP. ⑥That is less than one-quarter of the income loss in 1974 or 1980. ⑦On the other hand, oil-importing emerging economies—to which heavy industry has shifted—have become more energy-intensive, and so could be more seriously squeezed.①One more reason not to lose sleep over the rise in oil prices is that, unlike the rises in the 1970s, it has not occurred against the background of general commodity-price inflation and global excess demand. ②A sizable portion of the world is only just emerging from economic decline.③The Economist’s commodity price index is broadly unchanging from a year ago. ④In 1973 commodity prices jumped by 70%, and in 1979 by almost 30%.51. The main reason for the latest rise of oil price is________.[A] global inflation [B] reduction in supply[C] fast growth in economy [D] Iraq’s suspension of exports52. It can be inferred from the text that the retail price of petrol will go up dramatically if________.[A] price of crude rises [B] commodity prices rise[C] consumption rises [D] oil taxes rise53. The estimates in Economic Outlook show that in rich countries________.[A] heavy industry becomes more energy intensive[B] income loss mainly results from fluctuating crude oil prices[C] manufacturing industry has been seriously squeezed[D] oil price changes have no significant impact on GDP54. We can draw a conclusion from the text that________.[A] oil price shocks are less shocking now[B] inflation seems irrelevant to oil-price shocks[C] energy conservation can keep down the oil prices[D] the price rise of crude leads to the shrinking of heavy industry55. From the text we can see that the writer seems________.[A] optimistic [B] sensitive [C] gloomy [D] scaredText 4①The Supreme Court’s decisions on physician-assisted suicide carry important implications for how medicine seeks to relieve dying patients of pain and suffering.①Although it ruled that there is no constitutional right to physician-assisted suicide, the Court in effect supported the medical principle of “double effect”, a centuries-old moral principle holding that an action having two effects—a good one that is intended and a harmful one that is foreseen—is permissible if the actor intends only the good effect.①Doctors have used that principle in recent years to justify using high doses of morphine to control terminally ill patients’ pain, even though increasing dosages will eventually kill the patient.①Nancy Dubler, director of Montefiore Medical Center, contends that the principle will shield doctors who “until now have very, very strongly insisted that they could not give patients sufficient medication to control their pain if that might hasten death.”①George Annas, chair of the health law department at Boston University, maintains that, as long as a doctor prescribes a drug for a legitimate medical purpose, the doctor has done nothing illegal even if the patient uses the drug to hasten death. ②“It’s like surgery,” he says. ③“We don’t call those deaths homicides because the doctors didn’t intend to kill their patients, although they risked their death. ④If you’re a physician, you can risk your patient’s suicide as long as you don’t intend their suicide.”①On another level, many in the medical community acknowledge that the assisted-suicide debate has been fueled in part by the despair of patients for whom modern medicine has prolonged the physical agony of dying.①Just three weeks before the Court’s ruling on physician-assisted suicide, the National Academy of Science (NAS) released a two-volume report, Approaching Death: Improving Care atthe End of Life. ②It identifies the undertreatment of pain and the aggressive use of “ineffectual and forced medical procedures that may prolong and even dishonor the period of dying” as the twin problems of end-of-life care.①The profession is taking steps to require young doctors to train in hospices, to test knowledge of aggressive pain management therapies, to develop a Medicare billing code for hospital-based care, and to develop new standards for assessing and treating pain at the end of life.①Annas says lawyers can play a key role in insisting that these well-meaning medical initiatives translate into better care. ②“Large numbers of physicians seem unconcerned with the pain their patients are needlessly and predictably suffering,” to the extent that it constitutes “systematic patient abuse.”③He says medical licensing boards “must make it clear... that painful deaths are presumptively ones that are incompetently managed and should result in license suspension.”56. From the first three paragraphs, we learn that________.[A] doctors used to increase drug dosages to control their patients’ pain[B] it is still illegal for doctors to help the dying end their lives[C] the Supreme Court strongly opposes physician-assisted suicide[D] patients have no constitutional right to commit suicide57. Which of the following statements is true according to the text?[A] Doctors will be held guilty if they risk their patients’ death.[B] Modern medicine has assisted terminally ill patients in painless recovery.[C] The Court ruled that high-dosage pain-relieving medication can be prescribed.[D] A doctor’s medication is no longer justified by his intentions.58. According to the NAS’s report, one of the problems in end-of-life care is________.[A] prolonged medical procedures [B] inadequate treatment of pain[C] systematic drug abuse [D] insufficient hospital care59. Which of the following best defines the word “aggressive” ( line 3, paragraph 7 )?[A] Bold. [B] Harmful. [C] Careless. [D] Desperate.60. George Annas would probably agree that doctors should be punished if they________.[A] manage their patients incompetently[B] give patients more medicine than needed[C] reduce drug dosages for their patients[D] prolong the needless suffering of the patientsPart BDirections:Read the following text carefully and then translate the underlined segments into Chinese. Your translation should be written carefully on ANSWER SHEET 2. (10 points) Almost all our major problems involve human behavior, and they cannot be solved by physical and biological technology alone. What is needed is a technology of behavior, but we have been slow to develop the science from which such a technology might be drawn. (61) One difficulty is that almost all of what is called behavioral science continues to trace behavior to states of mind, feelings, traits of character, human nature, and so on. Physics and biology once followed similar practices and advanced only when they discarded them. (62) The behavioral sciences have been slow to change partly because the explanatory items often seem to be directly observed and partly because other kinds of explanations have been hard to find. The environment is obviously important, but its role has remained obscure. It does not push or pull, it selects, and this function is difficult to discover and analyze. (63) The role of natural selection in evolution was formulated only a little more than a hundred years ago, and the selective role of the environment in shaping and maintaining the behavior of the individual is only beginning to be recognized and studied. As the interaction between organism and environment has come to be understood, however, effects once assigned to states of mind, feelings, and traits are beginning to be traced to accessible conditions, and a technology of behavior may therefore become available. It will not solve our problems, however, until it replaces traditional prescientific views, and these are strongly entrenched. Freedom and dignity illustrate the difficulty. (64) They are the possessions of the autonomous (self-governing) man of traditional theory, and they are essential to practices in which a person is held responsible for his conduct and given credit for his achievements. A scientific analysis shifts both the responsibility and the achievement to the environment. It also raises questions concerning “values”. Who will use a technology and to what ends? (65) Until these issues are resolved, a technology of behavior will continue to be rejected, and with it possibly the only way to solve our problems.Section IV Writing66. Directions:Study the following picture carefully and write an essay entitled “Cultures—National and International”. In the essay you should1) describe the picture and interpret its meaning, and2) give your comment on the phenomenon.You should write about 200 words neatly on ANSWER SHEET 2. (20 points)An American girl in traditional Chinese costume(服装)Section III Reading ComprehensionPart AText141. C. address different problems to different people42. B. very conscious of their godlike role43. D. have often been the laughing stock44. D. as casually as possible45. A. Use Humor EffectivelyText246. C. the invention of tools for difficult and dangerous work47. C. devices48. D. respond independently to a changing world49. B. deal with some errors with human intervention50. C. far less able than human brain in focusing on relevant informationText351. B. reduction in supply52. D. oil taxes rise53. D. oil price changes have no significant impact on GDP54. A. oil price shocks are less shocking now55. A. optimisticText456. B. it is still illegal for doctors to help the dying end their lives57. C. The Court ruled that high-dosage pain-relieving medication can be prescribed.58. B. inadequate treatment of pain59. A. Bold60. D. prolong the needless suffering of the patientsPart B61.难题之一在于几乎所有所谓的行为科学都继续从心态、情感、性格特征、人性等方面去寻找行为的根源。

2002年全国硕士研究生入学统一考试英语试题参考答案参考答案Section Ⅰ Listening ComprehensionPart A1 sociology2 19303 234 religions5 1954Part B6 cameramen / camera men7 a personal visit8 depressed9 among advertisements 10 take firm actionPart C11.D 12.B 13.C 14.D 15.B 16.A 17.A 18.D 19.C 20.BSection Ⅱ Use of English21.A 22.D 23.C 24.B 25.B 26.A 27.D 28.D 29.C 30.B 31.D 32.A 33.A 34.C 35.B 36.D 37.A 38.C 39.B 40.CSection Ⅲ Reading Comprehension41.C 42.B 43.D 44.D 45.A 46.C 47.C 48.D 49.B 50.C 51.B 52.D 53.D 54.A 55.A 56.B 57.C 58.B 59.A 60.D答案解析Section ⅠListening Comprehension听力部分原文Part AM:Margaret Welch was born in Philadelphia in 1901.She began her studies at DePauw University in 1919,but after a year she transferred to study at Barnard University,Majoring in sociology.She received her undergraduate degree from Barnard in 1923.She ultimately acquired a PhDfrom Columbia University in 1929.She married Dr.Reo Fortune in 1928. Together they wrote Growing Up In New Guinea,published in 1930.Welch worked with her husband on another book called Balanese Character that was published in 1942.At the age of 23,Dr.Welch undertook a field study in the South Pacific.The experience resulted in her writing of her highly popular bookComing of Age In Samoa,published in 1928.Dr.Welch s interests andwritings centered on religions.She worked in the Department of Anthropology at the American Museum of Natural History from 1926 through to the end of her life.She was a professor of anthropology at Columbia starting in the year 1954,working with her old associate Ruth Benedict. She wrote a book entitled An Anthropologist At Work about Benedict.It was published in 1959.Margaret Welch died in 1978.W:You now have 30 seconds to check you answers to Questions 1-5.Part BW:When I was getting divorced in 1975,reporters and cameramen were camped out for days in the lobby and on the sidewalk outside.They came from all over the country.Foreign reporters too.It was terrible.My neighbors could barely get in and out of the building. One reporter,who had been a friend of mine,got up to my apartment after persuading the doorman into believing that he was there on a personal visit.I wouldnt let him in .He just wanted to talk,he said.I was certain that he had a camera and wanted a picture of me looking depressed.I just couldn t believe this attempt to invade my is the reporters present themselves as having the perfect right to be anywhere,to ask any question.It doesn t matter how personal the matter may be.People don t trust the press the way they used to. In most cases,stories are sensationalized in order to attract more public attention. Some papers print things that simply are not true.In many papers,if acorrection has to be made,it s usually buried among advertisements.I ve received hundreds of letters from people asking me how do you know what s true in the press these days.I find it difficult to respondsometimes.I tell them that there are good newspapers and serious,responsible and honest reporters.Don t judge all of us by the standardsof the bad ones.Unless the guys at the top—the editors and the news directors-take firm action,pretty soon no one is going to believe anything they read in the papers of see on television news.M:You now have 50 seconds to check your answers to Questions 6-10.Part C(一)M:Next time you bring your kids in for a checkup,don t be surprisedif the doctor asks about their tastes in entertainment.The American Academy of Medicine suggested last week that doctors work with parents to evaluate how much TV kids watch and what they see, what video and computer games they play,which websites they visit on the Internet,whether they view R-rated videos without the company of their parents,what music they like and what books they read.Doctors are worried thatkids who spend too much time in front of the tube don t get enoughexercise and can become overweight.The academy is also concerned that the messages kids get from entertainment media can make them more violent and sexually active.The academy recommends that children under age two not watch any TV.“Children need activities to stimulate the brain during the first twoyears of life,”says Dr.Miriam Baron,who chairs the academy s committeeon public education.“They need feedback and socialization.”Older children,she says,should watch TV in a common area.Their bedrooms should be “electronic media-free”zones where they can have a quiet place to read,study,play or just relax.W:You now have 30 seconds to check your answers to Questions 11-13.(二)W:If you re in your 20s,you own your first car,your career is more or less launched,and you re starting to look forward to owning a home.But you re worried,too.Perhaps you ve got some debt.You probably don t have much in the way of savings.And with all your expenses,it doesn t look like you ll be able to improve that situationsoon.If you wonder how to cut corners,there s an obvious place to look-at your spending habits.Do you buy a soda each weekend?Waste $ 1 a day for 40 years and,when you re set to retire,you ll find your account is short by $ 190,000.Grab a calculator and you ll discover that,over 40 years going outto dinner twice a month at $ 40 each time amounts to half a million.Even a pack-a day cigarette habit will lighten your retirement account by $ 330,000.And the same with cable TV and those cool earrings.They will probably amount to as much as one million.So,the first clue to accumulating wealth is this:focus on your spending habits.Here are a couple of tricks to help you save even if youswear you can t afford to. Stop buying things that fall rather than risein value.Pay yourself first:Before you pay the monthly bills,send $ 25 to a mutual fund. Stop spending coins.From nwo on,spend only paper currency,and keep the change every day.Get your family involved,and youll double your e discount tickets at the supermarket—butuse them correctly.How? If you really want to make these tickets worthwhile,you actually must invest into your mutual fund the amount yousave by using the tickets.Otherwise,you re wasting your time—and yourmoney.M:You now have 30 seconds to check your answers to Questions 14-16.(三)W:Mr. Glieberman,do you see any change in the high rate of broken marriages?M:The divorce rate is beginning to level off and probably will begin to drop in the next year or two,though not significantly.The tight economy has made it more difficult for troubled couples to handle all the costs associated with setting up separate house-holds.Also,I believe theres a comeback of thought—after the turbulent60s and70s—that thefamily does have value.In the midst of change and family disintegration,people seem to have a greater desire now to create stability in their lives.W:What is the divorce rate now?M:About 1 in 3 marriages ends in divorce,a ratio far higher than it was 20 years ago when the philosophy was “We ll tough it out no matter what.Society demands that,for appearances sake,we stay together.”Divorce no longer carries much disgrace.There s no way,for example,that Ronald Reagan,a divorced man,could have been elected President in 1960.And there are countless other divorced politicians who years ago would have been voted out of office if they had even considered a divorce,let alone gotten one.The same was true in the corporate structure,where divorced people rarely moved up the executive ladder.Now corporations welcome a divorced man,because they can shift him around the country without worrying about relocating his family or making certain that they are happy.W:You now have 40 seconds to check your answers to Questions 17-20.Section Ⅱ Use of English21[答案]A[注释]本题固然涉及副词的使用知识,然而,更重要的是考查考生句与句之间语义逻辑的理解能力。

2002年全国攻读硕士学位研究生入学考试英语试题第一部分英语知识应用试题解析一、文章总体分析本文主要介绍了计算机的发展对通信革命及人们的生存方式产生的影响。
文章第一段从早期的通信革命入手,指出在15、16世纪和20世纪之间发生了很多事情,特别是通信革命加快了步伐。
第二段接着提到20世纪计算机的出现极大地改变了这一进程。
第三段指出随着计算机的发展,我们步入了一个信息社会。
在计算机影响下,通信革命改变了我们的工作和休闲方式,也影响了我们的思考和感知方式。
在结尾部分,文章提到,当然,关于这种通信革命在经济、政治、社会和文化各方面的影响是利大于弊还是弊大于利,还存在争议。
二、试题具体解析1. [A] between在…当中,在空间、位置或时间的中间[B] before在此之前早些时候,在…前面[C] since自从…以后,以前[D] later 后来,稍后,随后[答案] A[解析] 本题考核的知识点是:时间副词的用法辨析。
解此题关键看两个方面,一是理解文章第一句话的含义:人们曾对20世纪电视的发展以及15世纪和16世纪印刷术的传播进行了比较。
二是注意转折连词yet的用法,yet一般标志着接下来的内容与前面的内容出现了较大的不同,如:She said she would be late, yet she arrived on time.(她说她会迟到,但她却准时到达了)。
文中第二句话结构非常简单,主语和谓语都无法体现与第一句话的强烈对照,这时只能通过空格里填入的时间状语来体现了,因此这个时间副词应与第一句话中的时间状语in the 20th century和 in the 15th and 16th centuries相呼应并对照。
接下来关键看这个时间副词表示的是哪个时间段,15、16世纪之前,20世纪之后还是两者之间。
其实我们从下文中的the 19th century也可以推断出正确答案是between,即“然而,在这两个时段之间却发生了很多事情”。

2002年1月研究生英语学位课统考真题PAPER ONEPart I LISTENING COMPREHENSION (15 minutes, 15 points)Section A ( 1 point each )Directions:In this part, you will hear nine short conversations between two speakers. At the end of each conversation a question will be asked about what was said. The questions will be spoken only once. Choose the best answer from the four choices given by marking the corresponding letter with a single bar across the square bracket on your Answer Sheet.1. A. In about 10 minutes.B. In about 20minutes.C. In about 30 minutes.D. In about 40 minutes.2. A. They don't like their next-door neighbor.B. They feel lonely here.C. They find the life here tough.D. They don t feel safe in this neighborhood.3. A. The manager was impatient with John.B. John was afraid of talking with the manager.C. John was not interested in the business.D. The room where they had the talk was a mess.4. A. It was interesting.B. It was boring.C. It was moving.D. It was an empty talk.5. A. She often goes outing with her neighbors.B. She thinks that her neighbors are trustworthy.C. She thinks that her neighbors are very friendly.D. She has much in common with her neighbors.6. A. Jane has changed a lot.B. Jane is artistic.C. Jane is conscientious.D. Jane's idea is not good enough.7. A. She didn't like them from the very beginning.B. She doesn't like their color.C. Their color is too close to that of the walls.D. Their color doesn't match that of the walls.8. A. They are amusing and instructive.B. They are popular and interesting.C. They are ridiculous and boring.D. They are uninteresting and outdated.9. A. Because John is as clumsy as a pig.B. Because John has never played a game like this.C. Because John is not as competitive as other players.D. Because John has no confidence in himself.Section B (1 point each)Directions: In this part you will hear two short passages. At the end of each passage, there will be some questions. Both the passages and the questions will be read to you only once.After each question, there will be a pause. During the pause, you must choose the best answer from the four choices given by marking the corresponding letter with a single bar across the square brackets on your Answer Sheet.10. A. Being compulsory in most countries.B. Covering differently according to different situations.C. Helping the needy to survive.D. Sharing risks of possible losses.11. A. To prove that it is wise to spend money on insurance.B. To prove that buying insurance is a wasted investment.C. To tell us that the sense of security is very important in driving.D. To tell us that accidents may take place at any time.12. A. Business, poverty and health insurance.B. Car, liability and life insurance.C. Possessions, disability and health insurance.D. Liability, home and life insurance.13. A. They live on their parents' income.B. They live on food given by others.C. They live on begged food.D. They live on potatoes only.14. A. Their teachers died of AIDS.B. Their parents died of AIDS.C. They had no money to pay for the tuition.D. They were infected with HIV.15. A. About 4.2%.B. About 10%.C. About 20%.D. Less than 30%.Part II VOCABULARY (10 minutes, 10 points )Section A (0. 5 point each )Directions: There are ten questions in this section. Each question is a sentence with one word or phrase underlined. Below the sentence are four words or phrases marked A, B, C and D. Choose the word or phrase that is closest in meaning to the underlined one. Mark the corresponding letter with a single bar across the square brackets on your Answer Sheet.16. Terrorist activities, in whatever forms, are to be denounced by peace-loving peopleworldwide.A. announcedB. forgivenC. condemnedD. despised17. Problems with respiration are often associated with smoking and air pollution as has beenproved.A. aspirationB. inspirationC. creativityD. breathing18. The military operations commenced yesterday were targeted at the Taliban's militaryinstallations.A. set aboutB. set outC. set apartD. set aside19. No merchandise is currently in short supply thanks to the market economy.A. businessmanB. commodityC. substanceD. talent20. It is becoming increasingly difficult for an only child to live up to the expectations of theirparents.A. encourageB. surviveC. arouseD. fulfill21. This summit talk is thought to be instrumental in bringing about peace in this region.A. helpfulB. uselessC. harmlessD. inappropriate22. Faced with this grim situation, top executives of this company are trying to find quicksolutions.A. unexpectedB. undesirableC. comfortingD. grave23. The bill was passed unanimously as a result of the intensive lobbying of some senators.A. without any objectionsB. in the endC. in the darkD. against heavy odds24. Nobel Prize winners have been mostly scientists of international renown in some field.A. institutionsB. standardC. prestigeD. application25. These natural resources will be depleted sooner or later if the present rate of exploitationcontinues.A. exhaustedB. evaluatedC. deployedD. popularized Section B (0. 5 point each)Directions: There are ten questions in this section. Each question is a sentence with something missing. Below each sentence are four words or phrases marked A, B, C and D. Choose one word or phrase that best completes the sentence. Mark the corresponding Letter with a single bar across the square brackets on your Answer Sheet.26. Harry Potter was originally __B___ for children or teenagers, yet many adults have cometo be crazy about the book.A. extendedB. intendedC. inclinedD. directed27. This experienced author was able to _B____ the lifetime's work of Jefferson into onevolume.A. suppressB. compressC. expressD. depress28. A Frenchman who has an unusually sensitive nose can __D___ hundreds of different smells.A. nominateB. dominateC. eliminateD. discriminate29. The Chinese share the ___A____ that their life will become better and the country moreprosperous.A. convictionB. speculationC. elaborationD. perspiration30. After weeks of __B____, the owners and the union leaders have finally agreed on thequestion of sick benefits.A. administrationB. arbitrationC. authorizationD. alternation31. It took this disabled boy a long time to ___D__ the fact that he was not qualified foradmission to college.A. come up withB. come down withC. come up toD. come to terms with32. The authorities claim that the rate of crime is declining, but statistics show___B___.A. clockwiseB. otherwiseC. elsewhereD. likewise33. Air attacks in Afghanistan are focused on airports and training camps to avoid civilian __C___.A. involvementB. rebellionC. casualtiesD. anguish34. After all, people across the Taiwan Straits are of the same race, so this island and the mainland are ___D__.A. inexplicableB. irreplaceableC. indispensableD. inseparable35. President Bush said that the most urgent mission was to bring the wrongdoers to _A_____.A. justiceB. justificationC. adjustmentD. justifiabilityPart III CLOZE TEST (10 minutes. 15 points, 1 point each)Directions: There are 15 questions in this part of the test. Read the passage through. Then, go back and choose one suitable word or phrase marked A, B, C, or D for each blank in the passage. Mark the corresponding Letter of the word or phrase you have chosen with a single bar across the square brackets on your Answer Sheet.It has been said that in a high-divorce society, not only are more unhappy marriages likely to end in divorce, but in addition, more marriages are likely to become unhappy. Much of life's happiness and much of its misery36 come from the same source — one's marriage. Indeed, few things in life have the potential to provide as much delight37 or as much anguish. As the accompanying box indicates, many couples are having more than their share of the latter38 .But divorce statistics reveal only part of the problem. For each marriage that sinks, countless others remain afloat 39 but are stuck in stagnant waters. ―We used to be a happy family, but the last 12 years have been horrible,‖condided40 a woman married for more than 30 years. ―My husband is not interested in my feelings. He is truly my worst emotional41 enemy.‖ Similarly, a husband of nearly 25 years said, ―My wife has told me that she doesn't love me anymore. She says that if we can just exist as roommates and each go our 42separate ways when it comes to leisure time, the situation can be tolerated43 .‖Of course, some in such terrible straits terminate44 their marriage. For many, however, divorce is out of the question45 . Why? According to Dr. Karen Kavser, factors such as children, community disgrace, finances, friends, relatives, and religious beliefs might keep a couple together, even in a loveless46 state.“Unlikely to divorce legally,‖she says, ―these spouses choose to remain with47 a partner from whom they are emotionally divorced.‖Must a couple whose relationship has cooled resign48 themselves to a life of dissatisfaction? Is a loveless marriage the only alternative49 to divorce? Experience proves that many troubled marriages can be saved — not only from the agony50 of breakup but also from the misery of lovelessness.36. A. mighty B. misery C. mystery D. myth37. A. delight B. dismay C. dignity D. destiny38. A. late B. later C. latter D. last39. A. ashore B. afloat C. arrogant D. ascended40. A. conferred B. compromised C. confessed D. confided41. A. passional B. feeling C. emotional D. sensational42. A. separate B. parting C. different D. divided43. A. excused B. forgiven C. comprehended D. tolerated44. A. intensify B. terminate C. reinforce D. betray45. A. in the end C. in the wayB. out of the count D. out of the question46. A. loving B. lovely C. loved D. loveless47. A. insist on B. persist in C. remain with D. keep in with48. A. resign B. deposit C. expel D. return49. A. pattern B. destination C. alternative D. route50. A. addiction B. agony C. abuse D. abolitionPart IV READING COMPREHENSION (45 minutes, 30 points, 1 point each) Directions: In this part of the test, there are five short passages. Read each passage carefully, and then do the questions that follow. Choose the best answer A, B, C, or D and mark the corresponding letter with a single bar across the square brackets on your Answer Sheet.Passage OneMoviegoers may think history is repeating itself this weekend. The summer's most anticipated film, Pearl Harbor, which has opened recently, painstakingly re-creates the Japanese attack that drew the United States into World War II. But that isn't the film's only reminder of the past. Harbor invites comparison to Titanic, the biggest hit of all time. Like Titanic, Harbor heaps romance and action around a major historical event. Like Titanic,Harbor attempts to create popular global entertainment from a deadly real-life tragedy. Like Titanic, Harbor costs a pretty penny and hopes to get in even more at the box office.Both Titanic and Pearl Harbor unseal their tales of love and tragedy over more than three hours. Both stories center on young passion, triangles of tension with one woman and two men; In Titanic, Leonardo DiCaprio and Billy Zane compete for the love of the same woman, a high-society type played by a British actress named Kate (Winslet). In Harbor, two pilots (Ben Affleck, Josh Hartnett) fall for the same woman, a nurse played by a British actress named Kate (Beckinsale).The scenes of peril also have similarities. Harbor has a shot in which soldiers cling for dear life as the battleship USS Oklahoma capsizes. The moment is recalled of the Titanic's climactic sinking scene in which DiCaprio and Winslet hang from the ocean liner as half of the ship vertically plunges into the water. In Harbor, one of its stars floats atop a piece of debris in the middle of the night, much like Winslet's character does in Titanic.And the jaw-dropping action of Titanic is matched by Harbor's, 40-minute re-creation of the Dec. 7, 1941 attack on the United States' Pacific Fleet. Both films spent heavily on special effects. Harbor director, Michael Bay, for example, says he kept salaries down so more could be spent on the visuals. Both movies even shot their ship-sinking scenes at the same location; Fox Studios Baja in Mexico.Harbor's makers have even taken a Titantic-like approach to the soundtrack. The film includes one song. There You'll be, performed by country music superstar Faith Hill. Titanic, which is one of the best selling soundtracks of all time, also has only one pop song: Celine Dion's MY Heart Will Go On.―If Harbor becomes a major moneymaker, filmmakers may comb history books searching for even more historical romance-action material.‖ says a critic.51. What are the two things that the author of this article tries to compare?A. The attack on Pearl Harbor and the sinking of the Titanic.B. Historical fiction movies and successful box office hits.C. The movie Titanic and the on-show movie Pearl Harbor.D. Sinking boats and famous actors.52. Pearl Harbor and Titanic are similar in all of the following aspects EXCEPT_____.A. both spent large amount of money on special effectsB. both have soundtracks starring a major pop starC. both added made-up stories to historical eventsD. both are documentary movies of historical events53. Who plays the leading female role in Pearl Harbor?A. Kate Beckinsale.B. Ben Affleck.C. Kate Winslet.D. Faith Hill.54. What does the phrase ―cost a pretty penny‖ in the first paragraph mean?A. To be very attractive.B. To cost a lot.C. To have big box office returns.D. To require a lot of effort to accomplish.55. If Pearl Harbor is as successful as Titanic, which of the following movies might we see next?A. The Battle of Waterloo.B. The Advents of Mr. Bean.C. Space Invaders.D. The Haunted House.56. It is said in the passage that ____.A. major historical events can never repeat themselvesB. both Titanic and Pearl Harbor are the historical reappearanceC. Pearl Harbor may have a better box office return than TitanicD. Titanic is the most successful film in historyPassage TwoA few weeks ago my mother called to say there was a warrant out for my arrest. I was mystified. I’d like to think myself dangerous but I’m a mild-mannered journalist. I don't have a criminal record, though the address on my driver’s license is my mother’s - thus the ―rai d.‖ I hadn’t robbed any convenience stores lately, nor fled the scene after backing a Jeep into a crowd of people.But this is Mayor Giuliani s New York, where it doesn’t take much to draw the attention of cops. New Yorkers know all about Hizzonor’s banning homeless cleaning men fromapproaching drivers and offering to clean their windshields. H’s also cracked down on street vendors. Yuppie that 1 am. I’ve never given much thought to what it felt like to be on the other side of the law.So when the cops came knocking, I thought there must be some mistake. Imagine my embarrassment upon discovering my crime. One Saturday night in March, I strolled out of apartment after dinner, a Coors Light beer in hand. Suddenly a police officer came up and wrote me a ticket. The charge: violating New York City’s open-container laws. Yeah. I probably should have paid it then and there. But instead I stuck the pink slip in my back pocket and forgot about it.When I called to inquire about my case. I was told to ―speak with Officer Kosenza.‖ But I didn’t get a chance. Kosenza called me that night while I was having dinner with my girlfriend. He wanted me to come to court, right then. But I was cautious. It seems New York’s police are in a bind. With crime falling to record lows, it's getting harder and harder for cops to ―make the numbers‖that show they’re doing a better and better job. What to do? The answer is to rifle through out-of-date tickets that haven’t been paid –anything they could turn into a ―crime.‖ I finally decided to turn myself in. which is how 1 found myself, one August evening, handcuffed at the downtown Manhattan police station with an older officer telling us tales of his days in the 1980s. ―Times sure have changed.‖ he said, shaking his head at us statistically useful nuisances.Eventually I was led into a courtroom. Very quickly, it was done. Handcuffs off, out the door. I wanted to complain but went quietly home, promising not to do whatever I was guilty of for another six months. I got off easy. But I also learned a lesson: Giuliani s clean streets come with a price. If only the mayor would neglect to pay a ticket.57. According to the passage, the author is probably _____.A. an urban young professionalB. a narrow-minded journalistC. a criminal wanted by the policeD. a traffic offender58. The author was arrested primarily because _____.A. he once stuck a piece of pink paper in his back pocketB. he used his mother's address on the driver's licenseC. he had robbed convenience shops beforeD. he drank some beer one night on the street59. The word "nuisances" in the fourth paragraph may mean _____.A. mild-mannered prisonersB. trouble makersC. new arrivalsD. hardened criminals60. Through the passage, the author wants to convey the idea that _____.A. New York policemen are doing a good job cracking down on crimesB. not everyone agrees with the mayor's management of the cityC. the crime rate has been reduced at the expense of citizens' convenienceD. everyone including the mayor should be punished if he is guilty of crime61. According to the passage, which of the following statements is NOT true?A. The author pleaded guilty and was set free.B. Policemen were trying hard to please their superiors.C. Many so-called crimes were only trifle things.D. It's no use complaining to cops when you are caught.62. The tone of the passage is ______.A. satiricalB. objectiveC. praisefulD. complainingPassage ThreeEwen Cameron is long dead but his ghost appears to haunt Canada, where extraordinarily strict rules are being considered to protect the subjects of psychological research.Cameron was a scientist straight from a horror movie. On the surface, he was a respectable academic. But after the end of the Second World War, he visited the Nuremberg trials, superficially to examine Rudolf Hess's psychological state. Many people believe that healso studied Nazi methods of mind control. Certainly, he never internalized the Nuremberg declaration that prohibits human experiments where risk outweighs ―humanitarian importance.‖Throughout the 1950s, Cameron ran a CIA-funded laboratory at McGill University where patients were used as guinea pigs in brainwashing experiments. Some patients were given ECT ―therapy‖twice daily, others were drugged and kept unconscious for weeks or months, injected with huge amounts of drugs, and subjected to long-term sensory deprivation.Compensation has been paid to most surviving patients. But suspicion of the psychological sciences has not entirely gone away. Nor has the need for patients’ rights to be guaranteed. Cameron, after all, ensured that every patient signed a consent form, even though many were not in position to understand what it meant.The strict new rules for psychological research now under discussion can partly be understood in the light of special Canadian sensitivities. They are designed to ensure that no one can be involved in an experiment that might damage their own interests.All well and good, except that psychological sciences aren’t going to advance if anyone can leave an experiment if they don’t like the results. Obviously, many psychological experiments would not be possible if the experimenters had to reveal exactly what they were testing.There is much to debate about the rights of patients and experimental subjects. The committee drawing up the code has apparently received 2,000 pages of comment on its draft.No one should do anything until this committee has had all the time it needs to read, digest and study these submissions. And then reach a truly balanced position.63. According to the author, we may conclude that _____.A. Cameron was a dedicated and responsible scientistB. Cameron was interested in unveiling the myths about Rudolf Hess’s psychological stateC. Cameron tried to ensure that his subjects clearly understood the purpose of the experimentsD. Cameron unmistakably violated the subjects’ rights64. Which of the following statements is NOT true based on the second paragraph?A. Cameron’s appearance might misrepresent his true personality.B. Probing into the psychological state of the Nazi was outside Cameron’s profession.C. Cameron did not observe the stipulation relating to human experiments.D. People believed that he had undisclosed motives for attending the Nuremberg trials.65. We can infer from this passage that _____.A. making compensation for the subjects’ loss was illegalB. some subjects in Cameron’s experiments diedC. people have been quite indifferent to the subjects’ rightsD. as a rule, people are fully supportive of psychological sciences66. The committee responsible for working out the rules governing psychological research _____.A. has to give top priority to psychological advancesB. is bombarded with criticisms from the publicC. is expected to take into account all the reactions to the draftingD. should rely on those willing to sacrifice their own interests67. One of the problems with the new rules for psychological research is that _____.A. the rules can do little to protect the patients’ rightsB. people may withdraw from the experiments in fear of damage to their own interestsC. it would be impossible to sort out anything valuable from the comments on the rulesD. people’s response to psychological sciences is overwhelmingly negativePassage FourSome accept their fate. Others try to reason with the police officer who has pulled them over for some real or imagined traffic offense. But when law enforcement is represented by a computer-driven camera that has immortalized your violation on film —as is the case at hundreds of intersections in more than 60 cities around the U. S. — it's hard to talk your way out of a heavy fine. Yet that is precisely what some 300 motorists in San Diego succeeded in doing last week when a superior court judge rules that pictures taken by the so-called red-light cameras were unreliable and therefore unacceptable.The first U. S. Court decision to reject all the traffic violations caught on camera, the ruling by judge Ronald Styn has fueled debate over the growing use of the devices. Police departments swear, and studies indicate, that the robocams (robot cameras) deter people from speeding and running red lights. A Lou Harris poll set for release this week finds that 69% of Americans support their use. Yet at least seven states have blocked proposals to implement them, and opponents —ranging from House majority leader Dick Armey to the American Civil Liberties Union — argue that the cameras violate privacy and place profit above public safety.Part of the problem is that virtually all the devices in place are operated by private firms that handle everything from installing the machinery to identifying violations —often with minimal police oversight — and have an incentive to pull in as many drivers as they can. The companies get paid as much as $ 70 a ticket, and the total revenue is hardly chump change. San Diego has got in $15. 9 million since October 1998, and Washington $12. 8 million since August 1999. ―It's all about money,‖says Congressman Bob Barr, a leading critic. Not so, insists Terrance Gainer, Washington's executive assistant chief of police. ―We have reduced fatalities. If some company is making money off that, that is American way.‖Critics counter that there must be other, less intrusive ways to make intersections safer, such as lengthening the yellow light and adding turn lanes. ―I object to this fixation we have with cameras and electronically gathered information,‖says Barr. ―It places too much confidence in technology.‖That confidence, as Washington residents have learned, can be misplaced. The city removed one camera last May that had generated more than 19,000 tickets at a particularly confusing intersection. In San Diego, faulty sensors made drivers appear to be going faster than they really were. The city suspended the system in July.Another concern is privacy. While systems in Washington, Maryland and North Carolina photograph nothing but the rear of the car, others in Arizona, California and Colorado take a picture of the driver s seat as well — a bit of electronic monitoring that could land straying spouses in trouble a lot more serious than a traffic violation.In Europe, where speedcams are deployed by the thousands and are even less popular than they are here, resentful drivers have started to take matters into their own hands, seeking out hidden cameras and knocking them over with their cars.68. It is mainly indicated in the first paragraph that _____.A. people respond differently when caught in traffic offenseB. motorists can be wrongly accused by police officersC. speeders cannot defend themselves before red-light camerasD. computer-driven cameras sometimes do tell lies69. The court decision last week _____.A. triggered a dispute over the use of robocamsB. immuned few camera-caught violators from punishmentC. found fewer red-light camera supporters in AmericaD. deterred some states from implementing camera devices70. Opponents’ arguments against cameras include all the following EXCEPT _____.A. they intrude into people’s privacyB. they give priority to the pursuit of profitC. they are operated by private firmsD. they are under the supervision of police71. Police department believes that _____.A. robocams should not be operated by private firmsB. robocams arc effective in maintaining traffic orderC. speeding is the major cause of traffic fatalitiesD. companies operating cameras should riot pursue money only72. The phrase ―chump change‖ in the third paragraph is closest in meaning to _____.A. trivialB. moderateC. enormousD. indefinite73. According to the passage. Bob Barr _____.A. is the majority leader in the House of RepresentativesB. is strongly against the American way of making moneyC. lacks confidence in modern technologyD. doubts the authenticity of electronically gathered information74. The writer s attitude towards speedcams can be best expressed as _____.A. positiveB. negativeC. indifferentD. uncertain75. Drivers in European countries _____.A. get angry at the red-light camerasB. destroy thousands of the speedcamsC. take the initiative in the use of speedcamsD. take drastic measures with speedcamsPassage FiveNow and then, researchers retreat from the trackless jungle at the edge of knowledge and set up camp in more familiar territory. Such expeditions don’t often yield surprises, but it’s always reassuring to know that the back yard looks much as we thought it did.Among those scientists were psychologists from the State University of New York at Stony Brook. To prove their theory — that people are more likely to yell at a family member or a peer than a superior — they asked 100 college students to wear blood-pressure cuffs and to keep notes about when they got angry and what they did about it.The momentous conclusion: people tend to bottle up anger felt toward an authority figure, and are more likely to vent it instead at family members or friends.While these findings are far from earth-shattering, one researcher pointed out that nobody had ever looked at anger this way before.Big words can make a self-evident result seem weightier. Psychologists at the National Institute for Healthcare Research in Maryland used this technique when they announced that when one person hurts another, forgiveness ―is associated with restored relational closeness following an interpersonal transgression.‖Couples who have adopted the kiss-and-make-up strategy will no doubt be pleased to learn that there is now a sound scientific basis for their actions.Psychologists, however, aren’t the only ones taking pains to prove the obvious.Some boldl y going where few have gone don’t always lead to radical conclusions. Over the years, researchers have set up weather-monitoring stations in remote areas of Antarctica. According to data from stations on the Ross Ice Shelf — where almost all those taking part in Robert Scott's ill-fated South Pole expedition perished sometime between late February and mid-March of 1912 —temperatures as low as those recorded in Scott’s journal have been documented only once in the past 15 years.This evidence led to one inexorable conclusion about what killed Scott and most of his party: it was the cold.76. According to the author, the scientists who do researches in more familiar territory _____.A. have confirmed what we have already knownB. have looked at things in new waysC. have had important discoveries by studying the obviousD. have done some useless work77. Which of the following is NOT true according to the psychologists at Stony Brook?A. When people get angry, their blood pressure changes.B. People are less likely to show their anger to their family members.C. People tend to let off their grievance at home.D. They have looked at anger in a unique way.78. The psychologists in Maryland have proved that when one person hurts another, ______.A. it is easier for them to make up if they have very close relationsB. it is easier for them to make up if they show their intimacyC. they should kiss each other to make it upD. they should find a sound scientific basis to make up79. According to the research on the Ross Ice Shelf, Robert Scott’s expedition failed because _____.A. most of the expeditioners couldn't stand hardshipsB. Robert Scott should not have chosen to go there in winterC. it was exceptionally cold on Antarctica that yearD. Robert Scott did not pay much attention to the temperature record of Antarctica80. It is implied in the passage that _____.A. people should not bottle up their anger at their family members or friendsB. bold researches would lead to radical conclusions。

2002年全国硕士研究生入学统一考试英语试题答案与解析第一部分英语知识应用试题解析一、文章总体分析本文主要介绍了计算机的发展对通信革命及人们的生存方式产生的影响。
文章第一段从早期的通信革命入手,指出在15、16世纪和20世纪之间发生了很多事情,特别是通信革命加快了步伐。
第二段接着提到20世纪计算机的出现极大地改变了这一进程。
第三段指出随着计算机的发展,我们步入了一个信息社会。
在计算机影响下,通信革命改变了我们的工作和休闲方式,也影响了我们的思考和感知方式。
在结尾部分,文章提到,当然,关于这种通信革命在经济、政治、社会和文化各方面的影响是利大于弊还是弊大于利,还存在争议。
二、试题具体解析1.[A]between在…当中,在空间、位置或时间的中间[B]before在此之前早些时候,在…前面[C]since自从…以后,以前[D]later后来,稍后,随后[答案]A[解析]本题考核的知识点是:时间副词的用法辨析。
解此题关键看两个方面,一是理解文章第一句话的含义:人们曾对20世纪电视的发展以及15世纪和16世纪印刷术的传播进行了比较。
二是注意转折连词yet的用法,yet一般标志着接下来的内容与前面的内容出现了较大的不同,如:She said she would be late,yet she arrived on time.(她说她会迟到,但她却准时到达了)。
文中第二句话结构非常简单,主语和谓语都无法体现与第一句话的强烈对照,这时只能通过空格里填入的时间状语来体现了,因此这个时间副词应与第一句话中的时间状语in the20th century和in the15th and16th centuries相呼应并对照。
接下来关键看这个时间副词表示的是哪个时间段,15、16世纪之前,20世纪之后还是两者之间。
其实我们从下文中的the19th century也可以推断出正确答案是between,即“然而,在这两个时段之间却发生了很多事情”。

2002年7月商务英语试题课程代码:0796(阅读与写作部分)注意:写在答题纸上的答案为有效答案《商务英语》试题词汇注释(阅读部分)PART ONEQuestions 1-51.quotation 报价2.decoration 装修、装饰3.adjust 调整Questions 6-104.job vacancies 空缺5.Advertising Executive 主管6.retailing 零售7.chief accountant 主管会计Questions 11-158.constant 不变的,常数的9.dramatically 戏剧性地,急剧地10.fluctuation 波动PART TWOQuestions 16-2011.air cargo 空运货物12.in the hold of plane 货舱13.consigament 运送14.automated 自动化的15.process 处理Questions 21-2516.features 特点,特征17.specialists 专家18.a range of 一系列Questions 26-3519.check-in lounge 休息室20.discounted 打折的,折扣过的Questions 36-4521.qualifications 资格,资历PART THREEQuestions 53-6022.essential 必要的23.administrative 行政管理的PART FOURQuestions 61-651.VENUE 地点Questions 662.refreshments 点心,小食品Questions 673.presentation 演示,展示4.Line manager 部门经理Questions 685.initial 首批,首次6.assume 估计7.enclosing 随函附寄READI NG PART ONEQuestions 1-5•Look at questions1-5•In each question,which phrase or sentence is correct?A We will diver the goods as soon as we can.B Thank you for delivering the goods so quickly.C Please deliver the goods as quickly as you can.2.A The courses are taught by people working in banking finance.B The courses are designed by people working in banking finance.C The courses are aimed at people working in banking finance.3.Contact Neil Smith if you want toA obtain information about the compan y’s prices.B arrange a visit to the showroom.C speak to a representative about special offers.4A The company is going to close its staff restaurant.B The company is improving its staff restaurant.C The company has opened a new staff restaurant.5A We may have to change our prices without informing you firs.B We will not change our prices even if our costs rise.C We will warn you if we have to put up our prices.Questions 6-10•Look at the list below. It shows eight job vacancies advertised in a newspaper.•For questions 6-10, decide which job (A-H) is the most suitable for each person.•For each question, mark the correct letter (A-H) on your Answer Sheet.•6 Ms Pina has just left college and needs some experience of retailing.7 Mrs Lang has worked for many years as a chief accountant in the head office of a supermarketchain.8 Mr Tan specialises in company law in his present post as a lawyer.9 Mr Soares has been working as a purchaser for an electronics factory for six years.10 Ms Stanley wants to move from her present post as a clerical assistant to a position with moreresponsibility.Questions 11-15•Look at the charts below. They show the number of visitors to eight different tourist attractions over a three month period.•Which chart does each sentence (11-15) describe?•For each sentence, mark one letter (A-H) on your Answer Sheet.•Do not use any letter more than once.11 After rising to a peak at the end of the first month, the number of visitors remained constant for therest of the period.12 The number of visitors in the first two months was low, but rose dramatically near the end of theperiod.13 Although the number of visitors dipped slightly during the second month, the figures were highthroughout the period.14 The number of visitors fell during the first month,but recovered slightly by the end of the period.15 The number of visitors fell significantly over the period, though there were fluctuations in the rate ofdecline.PART TWOQuestions 16-20•Read the passage below about air cargo.•Choose the correct word to fill each gap, from A, B, C or D.•For each question, mark one letter (A, B, C or D) on your Answer Sheet.16 A dividing B sharing C dealing D adjusting17 A saved B supplied C reserved D stored18 A carries B pulls C fetches D passes19 A series B link C chain D cycle20 A full B whole C total D completeQuestions 21-25•Read the passage below about air brands.•Choose the correct word to fill each gap, from A, B, C or D.•For each question, mark one letter (A, B, C or D) on your Answer Sheet.21 A made B stood C meant D intended22 A opened B spread C stretched D reached23 A add B grow C build D develop24 A asks B wants C claims D demands25 A decline B fail C lack D miss•Read the advice below about travelling on business. •Choose the correct word to fill each gap, from A, B, C or D. •26 A allow B allowed C allowing27 A them B this C these28 A on B of C with29 A what B where C which30 A figure B number C amount31 A or B either C unless32 A to B for C by33 A Any B Some C Every34 A like B such C so35 A although B despite C even•Read the text below about consultants.•Choose the correct word from A, B, C or D to fill each gap.•36 A range B travel C reach37 A exact B specialist C detailed38 A largely B widely C heavily39 A standard B usual C typical40 A orders B habits C rules41 A advise B suggest C warm42 A thinking B considering C understanding43 A every B total C all44 A charge B amount C price45 A select B prefer C decidePART THREEQuestions 46-52•Read the newspaper article below about a partnership between industry and schools. •Are sentences 46-52 on the opposite page 'Right' or 'wrong'?If there is not enough information to answer 'Right' or 'wrong', choose 'Doesn’t say'. •For each question 46 to 52, mark one letter (A, B or C) on your Answer Sheet.46One aim of the programme is to increase manufacturing employees' knowledge of schools.A RightB WrongC Doesn't say47 Manufacturing employees think the programme will not benefit them.A RightB WrongC Doesn't say48 Peter Davies believes that sending employees into schools will help develop their professional abilities.A RightB WrongC Doesn't say49 Manufacturing companies already send many employees into schools.A RightB WrongC Doesn't say50 Davies thinks that many teachers do not want to visit factories.A RightB WrongC Doesn't say51 Andrew Morris used to be an engineer.A RightB WrongC Doesn't say52 The Director of KTM wasn't sure about the benefits of this programme.A RightB WrongC Doesn't sayQuestions 53-60•Read the advertisement below, and answer questions 53-60 on the opposite page.•For questions 53-56 ,choose the correct answer.•For each question mark one letter (A,B or C) on your Answer Sheet.53 What do J.K. Masters market?A rail travelB office spaceC Books54 The Marketing Manager is required toA recruit a team.B write reports on a team.C Lead a team.55 How many specialist staff are there to carry out the company ’s promotional plans?A oneB TwoC Five56 Applicants for the Publicity Co-ordinator's post are asked to send inA examples of recent work.B copies of university certificates.C a completed test of professional skills.• Using the information in the text complete each sentence 57-60 with the title of a job from the list (A-G). • For each question 57-60, mark one letter (A-G) on your Answer Sheet.• Do not use any letter more than once.57 The ……….. is in charge of a team of six.58A ………… needs the ability to organise his /her own scredule. 59Applicants for the position of ………… have to fill in a form. 60 The position of ………. Would suit acandidate with experience as a buyer.WRITING PART FOURQuestions 61-65•Read the mamo and the notice below.•Complete the booking form on the opposite page.••You have agreed to take two clients on a tour of your company next Wednesday. •Write a note to your personal assistant cailed Chris:·informing him or her of the visit·telling him or her what time the tour will start·asking him or her to order refreshments for your visitors.•Write 30 to 40 words.•Write on your Answer Sheet. Do not write in capital letters.Questions 67•Your department has developed a new product and is arranging a presentation of this product for staff in other departments. Your line manager has asked you to write a memo to the staff.•Write the memo to the staff:•describing the new product•inviting them to a presentation•telling them what will happen in the presentation•saying where and when the presentation will be.•Write 50 words on your Answer sheet.Read this letter from the owner of a clothes shop.•Write a fetter in reply to Mr Lim:·thanking him for his letter·saying that you are enclosing a price list·informing him what discount you can give him·telling him the colours in which the shirts are availabie.•Write 60-80 words.•Write on your Answer Sheet. Do not write in capital letters. Do not include any postal addresses.。

2002年全国硕士研究生入学统一考试英语试题答案与解析第一部分英语知识应用试题解析一、文章总体分析本文主要介绍了计算机的发展对通信革命及人们的生存方式产生的影响。
文章第一段从早期的通信革命入手,指出在15、16世纪和20世纪之间发生了很多事情,特别是通信革命加快了步伐。
第二段接着提到20世纪计算机的出现极大地改变了这一进程。
第三段指出随着计算机的发展,我们步入了一个信息社会。
在计算机影响下,通信革命改变了我们的工作和休闲方式,也影响了我们的思考和感知方式。
在结尾部分,文章提到,当然,关于这种通信革命在经济、政治、社会和文化各方面的影响是利大于弊还是弊大于利,还存在争议。
二、试题具体解析1.[A]between在…当中,在空间、位置或时间的中间[B]before在此之前早些时候,在…前面[C]since自从…以后,以前[D]later后来,稍后,随后[答案]A[解析]本题考核的知识点是:时间副词的用法辨析。
解此题关键看两个方面,一是理解文章第一句话的含义:人们曾对20世纪电视的发展以及15世纪和16世纪印刷术的传播进行了比较。
二是注意转折连词yet的用法,yet一般标志着接下来的内容与前面的内容出现了较大的不同,如:She said she would be late,yet she arrived on time.(她说她会迟到,但她却准时到达了)。
文中第二句话结构非常简单,主语和谓语都无法体现与第一句话的强烈对照,这时只能通过空格里填入的时间状语来体现了,因此这个时间副词应与第一句话中的时间状语in the20th century和in the15th and16th centuries相呼应并对照。
接下来关键看这个时间副词表示的是哪个时间段,15、16世纪之前,20世纪之后还是两者之间。
其实我们从下文中的the19th century也可以推断出正确答案是between,即“然而,在这两个时段之间却发生了很多事情”。

2002年研究生入学考试英语试题及解析(2) National Entrance Test of English for MA/MS Candidates(2002)考生注意事项1.考生必须严格遵守各项考场规则,得到监考人员指令后方可开始答题。
2. 全国硕士研究生入学考试英语分为试题(一)、试题(二)。
3.本试题为试题(二),共11页(5~15页),含有英语知识运用、阅读理解、写作三个部分。
英语知识运用、阅读理解A节的答案必须用2B铅笔按要求直接填涂在答题卡1上,如要改动,必须用橡皮擦干净。
阅读理解B节和写作部分必须用蓝(黑)圆珠笔在答题卡2上答题,注意字迹清楚。
4.考试结束后,考生应将答题卡1、答题卡2一并装入原试卷袋中,将试题(一)、试题(二)交给监考人员。
Section II Use of EnglishDirections:Read the following text. Choose the best word(s) for each numbered blank and mark A, B, C or D on ANSWER SHEET 1. (10 points)Comparisons were drawn between the development of television in the 20th century and the diffusion of printing in the 15th and 16th centuries. Yet much had happened 21.As was discussed before, it was not 22 the 19th century that the newspaper became the dominant pre-electronic 23, following in the wake of the pamphlet and the book and in the 24 of the periodical. It was during the same time that the communications revolution 25up,beginning with transport, the railway, and leading 26 through the telegraph, the telephone, radio, and motion pictures 27 th e 20th-century world of the motor car and the airplane. Not everyone sees that process in 28 . It is important to do so.It is generally recognized, 29 , that the introduction of the computer in the early 20th century, 30 by the invention of the integrated circuit during the 1960s, radically changed the process, 31 its impact on the media was not immediately 32 . As time went by, computers became smaller and more powerful,and they became “personal” too, as well as 33 , with display becoming sharper and storage 34 in creasing. They were thought of, like people, 35 generations, with the distance between generations much 36 .It was within the computer age that the term“information society” began to be widely used to describe the 37 within which we now live. The communications revolution has 38 both work and leisure and how we think and feel both about place and time, but therehave been 39 views about its economic ,political, social and cultural implications. “Benefits” have been weighed40 “harmful” outcomes. And generalizatio ns have proved difficult.21. [A] between [B] before [C] since [D] later22. [A] after [B] by [C] during [D] until23. [A] means [B] method [C] medium [D] measure24. [A] process [B] company [C] light [D] form25. [A] gathered [B] speeded [C] worked [D] picked26. [A] on [B] out [C] over [D] off27. [A] of [B] for [C] beyond [D] into28. [A] concept [B] dimension [C] effect [D]perspective29. [A] indeed [B] hence [C] however [D] therefore30. [A] brought [B] followed [C] stimulated [D]characterized31. [A] unless [B] since [C] lest [D] although32. [A] apparent [B] desirable [C] negative [D]plausible33. [A] institution [B] universal [C] fundamental [D]instrumental34. [A] ability [B] capability [C] capacity [D] faculty35. [A] by means of [B] in terms of [C] with regard to[D] in line with36. [A] deeper [B] fewer [C] nearer [D] smaller37. [A] context [B] range [C] scope [D] territory38. [A] regarded [B] impressed [C] influenced [D]effected39. [A] competitive [B] controversial [C] distracting [D] irrational40. [A] above [B] upon [C] against [D] withSection III Reading ComprehensionPart ADirections:Read the following four texts. Answer the questions below each text by choosing A, B, C or D. Mark your answers on ANSWER SHEET 1. (40 points)Text 1If you intend using humor in your talk to make people smile, you must know how to identify shared experiences and problems. Your humor must be relevant to the audience and should help to show them that you are one of them or that you understand their situation and are in sympathy with their point of view. Depending on whom you are addressing, the problems will bedifferent. If you are talking to a group of managers, you may refer to the disorganized methods of their secretaries; alternatively if you are addressing secretaries, you may want to comment on their disorganized bosses.Here is an example, which I heard at a nurses' convention, of a story which works well because the audience all shared the same view of doctors. A man arrives in heaven and is being shown around by St. Peter. He sees wonderful accommodations, beautiful gardens, sunny weather, and so on. Everyone is very peaceful, polite and friendly until, waiting in a line for lunch, the new arrival is suddenly pushed aside by a man in a white coat, who rushes to the head of the line, grabs his food and stomps over to a table by himself. “Who is that?” the new arrival asked St. Peter. “Oh, that's God,” came the reply, “but sometimes he thinks he's a doctor.”If you are part of the group which you are addressing, you will be in a position to know the experiences and problems which are common to all of you and it'll be appropriate for you to make a passing remark about the inedible canteen food or the chairman's notorious bad taste in ties. With other audiences you mustn't attempt to cut in with humor as they will resent an outsider making disparaging remarks about their canteen ortheir chaiman. You will be on safer ground if you stick to scapegoats like the Post Office or the telephone system.If you feel awkward being humorous, you must practice so that is becomes more natural. Include a few casual and apparently off-the-cuff remarks which you can deliver in a relaxed and unforced manner. Often it's the delivery which causes the audience to smile, so speak slowly and remember that a raised eyebrow or an unbelieving look may help to show that you are making a light-hearted remark. Look for the humor. It often comes from the unexpected. A twist on a familiar quote “If at first you don't succeed, give up” or a play on words or on a situation. Search for exaggeration and understatements. Look at your talk and pick out a few words or sentences which you can turn about and inject with humor.41. To make your humor work, you should .[A] take advantage of different kinds of audience.[B] make fun of the disorganized people.[C] address different problems to different people.[D] show syMPAthy for your listeners.42. The joke about doctors implies that, in the eyes of nurses, they are .[A] impolite to new arrivals.[B] very conscious of their godlike role.[C] entitled to some privileges.[D] very busy even during lunch hours.43. It can be inferred from the text that public services .[A] have benefited many people.[B] are the focus of public attention.[C] are an inappropriate subject for humor.[D] have often been the laughing stock.44. To achieve the desired result, humorous stories should be delivered .[A] in well-worded language.[B] as awkwardly as possible.[C] in exaggerated statements.[D] as casually as possible.45. The best title for the text may be .[A] Use Humor Effectively.[B] Various Kinds of Humor.[C] Add Humor to Speech.[D] Different Humor Strategies.Text 2Since the dawn of human ingenuity, people have devised ever more cunning tools to cope with work that is dangerous, boring, burdensome, or just plain nasty. That compulsion has resulted in robotics-the science of conferring various human capabilities on machines. And if scientists have yet to create the mechanical version of science fiction, they have begun to come close.As a result, the modern world is increasingly populated by intelligent gizmos whose presence we barely notice but whose universal existence has removed much hum an labor. Our factories hum to the rhythm of robot assembly arms. Our banking is done at automated teller terminals that thank us with mechanical politeness for the transaction. Our subway trains are controlled by tireless robo-drivers. And thanks to the continual miniaturization of electronics and micro-mechanics, there are already robot systems that can perform some kinds of brain and bone surgery with submillimeter accuracy-far greater precision than highly skilled physicians can achieve with their hands alone. But if robots are to reach the next stage of laborsaving utility, they will have to operate with less human supervision and be able to make at least a few decisions forthemselves-goals that pose a real challenge. “While we know how to tell a robot to handle a specific error,” says Dave Lavery, manager of a robotics program at NASA, “we can't yet give a robot enough ‘commonsense’ to reliably interact with a dynamic world.”Indeed the quest for true artificial intelligence has produced very mixed results. Despite a spell of initial optimism in the 1960s and 1970s when it appeared that transistor circuits and microprocessors might be able to copy the action of the human brain by the year 2010, researchers lately have begun to extend that forecast by decades if not centuries. What they found, in attempting to model thought, is that the human brain's roughly one hundred billion nerve cells are much more talented-and human perception far more complicated-than previously imagined. They have built robots that can recognize the error of a machine panel by a fraction of a millimeter in a controlled factory environment. But the human mind can glimpse a rapidly changing scene and immediately disregard the 98 percent that is irrelevant, instantaneously focusing on the monkey at the side of a winding forest road or the single suspicious face in a big crowd. The most advanced computer systems on Earth can't approach that kind of ability, and neuroscientists still don't know quite how we do it.46. Human ingenuity was initially demonstrated in .[A] the use of machines to produce science fiction.[B] the wide use of machines in manufacturing industry. [C] the invention of tools for difficult and dangerous work.[D] the elite's cunning tackling of dangerous and boring work.47. The word “gizmos" (line 1, paragraph 2) most probab ly means .[A] programs.[B] experts.[C] devices. [D]creatures.48. According to the text, what is beyond man's ability now is to design a robot that can .[A]fulfill delicate tasks like performing brain surgery.[B] interact with human beings verbally.[C] have a little common sense.[D] respond independently to a changing world.49. Besides reducing human labor, robots can also .[A] make a few decisions for themselves.[B] deal with some errors with human intervention.[C] improve factory environments.[D] cultivate human creativity.50. The author uses the example of a monkey to argue that robots are .[A] expected to copy human brain in internal structure.[B] able to perceive abnormalities immediately.[C] far less able than human brain in focusing on relevant information.[D] best used in a controlled environment.。

2002年在职攻读硕士学位全国联考英语试题Paper OnePart I Vocabulary and Structure(25 minutes,10 points)Directions:There are 20 incomplete sentences in this section.For each sentence there are 4 choices marked A,B,C and D.Choose the one that best completes the sentence.Mark your answer on the ANSWER SHEET with a single line through the center.1.Experiments in the photography of moving objects in both the United States and Europe well before 1990.A.have been conducting B.were conductingC.had been conducted D.are conducted2.After long negotiations,the firm to build a double-purpose bridge across the river.A.contracted B.contacted C.consulted D.Convinced3.Diderot was also a philosophical materialist,that thought developed from the movements and changes of matter.A.believing B.have been located C.believes D.be locating4.We felt to death because we could make nothing of the lecturer’s speech.A.exposed B.tired C.exhausted D.bored5.The population of many Alaskan cities has doubled in the past three years.A.larger than B.more than C.as great as D.as many as6.It was very difficult to build a power station in the deep valley,but it as we had hoped.A.came off B.went off C.brought out D.made out7.A baby might show fear of an unfamiliar adult,he is likely to smile and reach out to another infant.A.if B.whenever C.so that D.whereas8.Christmas is a holiday usually celebrated on December 25th the birth of Jesus Christ.A.in accordance with B.in terms ofC.in favor of D.in honor of9.Weather ,there will be an open air party with live music here this weekend.A.permits B.should permitC.will permit D.permitting10.When workers are organized in trade unions,employers find it hard to lay them ..A.off B.asideC.out D.down11.The symbols of mathematics we are most familiar are the signs of addition,subtraction,multiplication,division and equality.A.to which B.whichC.with which D.in which12.The machines in this workshop are not regulated but are jointly controlled by a central computer system.A.inevitably B.individuallyC.irrespectively D.irregularly13.We are sure that to do this face to face,he would find it difficult to express himself without losing his temper.A.were he to try B.would he tryC.was he trying D.if he triesl4.The local people were joyfully surprised to find the prices of vegetables no longer according to the weather.A.evaluated B.convertedC.fluctuated D.modifiedl5.he realized it was already too late for us to return home.A.No sooner it grew dark when B.Hardly it grew dark thanC.It was not until dark that D.Scarcely it grew dark than16.Without computer network,it would be impossible to carry on any business operation in the advanced countries.A.practically B.preferablyC.precisely D.possibly17.will Mr.Forbes be able to regain control of the company.A.With hard work B.As regards his hard workC.Only if he works hard D.Despite his hard Work18.From the incident they have learned a lesson:decisions often lead to bitter regrets.A.urgent B.hastyC.instant D.prompt19.What the teacher of the science class does and says of great importance to the students at college.A.was B.areC.is D.were20.The Chinese community there,consisting of 67 000 ,is the largest concentration of Chinese outside Asia.A.visitors B.workersC.adults D.inhabitantsPart II Reading Comprehension(70 minutes,40 points)Directions:There are 5 passages in this part.Each of the passages is followed by 4 questions or unfinished statements.For each of them there are 4 choices marked A,B,C and D.Choose the best one and mark your answer on the ANSWER SHEET with a single line through the center.Passage OneIn the United States the way people spend their leisure time is an important part of their identity.Perhaps everybody does nearly the same thing all day in the office or the factory,but leisure time is what makes people distinct and reveals who they are.Some people like rock music,for example,and others may like jazz or classical music.Some people are runners or swimmers,and others are“couch(睡椅)potatoes”who“surf”the television channels with a remote control.Some go to museums while others spend long hours at a shopping centre.These kinds of choices are ways that people define themselves.It hasn’t always been this way.“Leisure time”was almost unknown in the United States in the eighteenth and nineteenth centuries.When most people worked on farms,the workday was from sunrise to sunset every day except Sunday,which was devoted to church.Later,with the rise of factories and city populations,people worked equally long hours and had only Sunday for rest.Some people did many of the things then that they do now—attend concerts,have parties,go to restaurants.read novels,or play sports—but to a much lesser extent.Slowly,throughout the twentieth century,leisure time grew.Technology made farm work less burdensome.and changes in laws shortened the factory work day and week.New inventions such as the phonograph(留声机)and the radio gave people access to music and mass entertainment on a scale unknownbefore.People gradually became consumers of entertainment,and businesses competed fiercely for their dollars.For many people leisure time means going somewhere—to a museum , to a concert , to a restaurant, or to a baseball game , for example. Or it means doing something such as playing volleyball,backpacking,swimming,biking,or playing in a park with their children.For other people free time means staying home with wonderful sources of entertainment,such as a VCR,stereo(立体声系统),or cable TV with dozens of channels.Others pursue creative activities such as cooking,gardening,and home improvement.The latest stay-at-home activity is“surfing the net”—that is.looking for information and entertainment on the Internet.People in the United States are basically not much different from others in what they do in their leisure time.The real difference may lie in the energy,time,money,and sheer enthusiasm that they devote to it.21.“Couch potatoes”in paragraph 1 refers to those who .A.control their viewing of TV programs B.are happy watching situation comediesC.watch TV while eating potato chips D.are crazy about watching TV programs 22.According to the passage,in the eighteenth and nineteenth centuries,some Americans .A.worked from sunrise to sunset seven days a weekB.preferred working in factories to working on farmsC.had many of the leisure time activities that people now haveD.fought for shorter working hours and more leisure time23.Apart from technology,the growing leisure time throughout the twentieth century is also due to.A.changes in laws B.mass entertainmentC.new types of consumption D.competitive businesses24.In terms of leisure time activities,people in the United States.A.enjoy a larger variety than people in other countriesB.are not much different from people in other countriesC.enjoy more stay—at—home activities such as“surfing the net’’D.are less energetic and enthusiastic than othersPassage TwoWhether you are logging on to your personal computer,using a credit card,or disarming a door security system,passwords or PINs (personal identification numbers)jealously guard access to numerous regular operations.It is estimated that within ten years,consumers could be faced with handling more than 100 passwords! Given the popularity of passwords,how Can you choose ones that are sufficiently complicated to be secure yet are simple enough to remember?There are basic guidelines to bear in mind.First,the don’ts.Don’t use as a password your name or that of a member of your family,even in modified form.Also avoid use of your telephone number,your Social Security number,or your address.Such information Can easily be obtained by a determined hacker(黑客).In addition,if possible,don’t use passwords made up entirely of letters or digits.A relatively simple computer program can crack such a code quickly.Finally,do not use a word that can be found in any dictionary,even a foreign-language one.Huge lists are available that contain words,place names,and proper names from all languages.Programs can test for variations of these words,such as if they are spelled backward,capitalized,or combined.So,what kinds of passwords should be used? Usually ones that have a minimum of six to eight characters and that have a mixture of upper—and lower-case letters,digits,and punctuation(标点)symbols.How difficult is it to crack such a combination of characters? One source says that“a machine that could try one million passwords per second would require,on the average,over one hundred years.”How can you choose a combination that is easy to remember?Some suggest that you take the title ofa favorite book or film or a line from a song or poem and use the first letter from each word as your password,adding capital letters,punctuation,or other characters.For example,“to be or not to be”could become“2B /not2B”.Other suggestions include taking two short words and link them with a punctuation character.such as “High。
[真题] 2002年在职攻读硕士联考英语Part II Vocabulary and Structure (20 minutes, 10 points)第1题:Experiments in the photography of moving objects ______ in both the United States and Europe well before 1990.A.have been conductingB.were conductingC.had been conductedD.are conducted参考答案:C 您的答案:答案解析:该题测试考生的基本时态和语态概念。
首先,这道题必须是被动语态。
其次,试验是在1990年之前做的,所以必须用过去完成时态。
第2题:After long negotiations, the firm ______ to build a double-purpose bridge across the river.A.contractedB.contactedC.consultedD.convinced参考答案:A 您的答案:答案解析:该题测试contract作为动词的用法,意思是“签约,订约”,属经贸用语,列在大纲contract词条动词定义的第三项。
大多数考生对contract的名词用法比较熟悉,对其动词用法可能比较陌生,尤其是作为不及物动词的用法,因此,虽然选A的考生所占比例略高,但四个选项百分比接近,尤其是B、C和D。
consult和convince一般接宾语。
第3题:Diderot was also a philosophical materialist,______ that thought developed from the movements and changes of matter.A.believingB.have been locatedC.believesD.be locating参考答案:A 您的答案:答案解析:这道题测试句子结构知识。
精品资料2002年考研英语(yīnɡyǔ)真题及解析........................................2002二、试题(shìtí)具体解析21. 要使自己的幽默(yōumò)让人发笑,你应当_ 。
[A] 利用不同(bù tónɡ)类型的听众[B] 取笑(qǔxiào)杂乱无章的人[C] 对不同(bù tónɡ)的人谈不同的问题[D] 对你的听众表示同情[答案] C[解析]本题考核的知识点是:段落主旨题。
本题考查的是局部信息,考生关键要理解第一段。
该段首句指出,如果你想在谈话中用幽默使人发笑,你就必须知道如何辨别共同的经历和共同的问题。
接着作者又对此进行了解释,即:你的幽默必须与听众相关,显示你是他们中的一员,或你理解他们的处境并赞成他们的观点。
作者在第三句得出结论,即“Depending on whom you are addressing, the problems will be different(针对不同的听众,谈及不同的问题)”。
由此可知,C选项恰好是对该段中心的概括,为正确答案。
A选项虽然在某种程度上谈到了“不同的听众”的重要性,但没有接着阐述听众不同应该怎样做,而且它出现了文中没有的内容:利用听众。
B选项是该段最后举例说明的内容,if you are talking to a group of managers, you may refer to the disorganized methods of their secretaries; alternatively if you are addressing secretaries, you may want to comment on their disorganized bosses。
但这只是用来论证“听众不同问题不同”这个论点的一个具体个案,缺乏普遍性,无法由此而得出取笑他们就总会使幽默起作用的结论,因此不能选。
2 002 年全国攻读硕士学位研究生入学考试英语试题Section I Use of EnglishDirections :Read the following text. Choose the best word(s) for each numbered blank and mark A, B, C OR D on ANSWER SHEET 1. (10 points)Comparisons were drawn between the development of television in the 20th century and the diffusion of printing in the 15th and 16th centuries. Yet much had happened 1 . As was discussed before, it was not became the dominant pre-electronic_ 3 _ ,following in the wake of the pamphlet and the book and in the of the periodical. It was during the same time that the communications revolution up, beginning with transport, the railway, and leading through the telegraph, the telephone, radio, and motion pictures the 20th century world of the motor car and the air plane. Not everyone sees that Process in . It is important to do so.It is generally recognized, , that the introduction of the computer in the early 20th century, 10 by the invention of the integrated circuit during the 960s, radically changed the process, 11 its impact on the media was not . As time went by, computers became smaller and more powerful, 13 , with display becoming sharper increasing. They were thought of, like people, 15 generations, with the distance between generations much 16 It was within the computer age that the term “information society” began to be widely used to describe the 17 within which we now live. The communications revolution has 18 both work and leisure and how we think and feel both about place and time, but there have been 19 view about its economic, political, social 2 the 19th century that the newspaper 4 5 6 7 8 9 1immediately 12 and they became “personal” too, as well as and storage 14 .and cultural implications. “Benefits” have been weighed outcomes. And generalizations have proved difficult.20 “harmful” 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 1 1 . [A ]between. [A ]after. [A ]means. [A ]process. [A ]gathered. [A ]on[B ]before [B ]by [C ]since [C ]during [C ]medium [C ]light [D ]later [D ]until [D ]measure [D ]form [B ]method [B ]company [B ]speeded [B ]out [C ]worked [C ]over [D ]picked [D ]off . [A ]of[B ]for [C ]beyond [C ]effect [C ]however [C ]stimulated [C ]lest [D ]into . [A ]concept. [A ]indeed0. [A ]brought1. [A ]unless2. [A ]apparent [B ]dimension [B ]hence [B ]followed [B ]since [B ]desirable [D ]perspective [D ]therefore [D ]characterized [D ]although [C ]negative [D ]plausible1 1 1 1 1 1 1 23.[A]institutional4.[A]ability5.[A]by means of6.[A]deeper[B]universal[B]capability[B]in terms of[B]fewer[C]fundamental[D]instrumental[C]capacity[D]faculty[C]with regard to[D]in line with[C]nearer[C]scope[D]smaller[D]territory[D]effected7.[A]context8.[A]regarded9.[A]competitive0.[A]above[B]range[B]impressed[C]influenced[B]controversial[C]distracting[D]irrational[B]upon[C]against[D]withSection II Reading ComprehensionPart ADirections:Read the following four texts.Answer the questions below each text by choosing[A], [B],[C]or[D].Mark your answers on ANSWER SHEET1.(40points)Text1If you intend using humor in your talk to make people smile,you must know how to identify shared experiences and problems.Your humor must be relevant to the audience and should help to show them that you are one of them or that you understand their situation and are in sympathy with their point of view.Depending on whom you are addressing,the problems will be different.If you are talking to a group of managers,you may refer to the disorganized methods of their secretaries; alternatively if you are addressing secretaries,you may want to comment on their disorganized bosses.Here is an example,which I heard at a nurses’convention,of a story which works well because the audience all shared the same view of doctors.A man arrives in heaven and is being shown around by St.Peter.He sees wonderful accommodations, beautiful gardens,sunny weather,and so on.Everyone is very peaceful,polite and friendly until,waiting in a line for lunch,the new arrival is suddenly pushed aside by a man in a white coat,who rushes to the head of the line,grabs his food and stomps over to a table by himself.“Who is that?”the new arrival asked St.Peter.“Oh,that’s God,”came the reply,“but sometimes he thinks he’s a doctor.”If you are part of the group which you are addressing,you will be in a position to know the experiences and problems which are common to all of you and it’ll be appropriate for you to make a passing remark about the inedible canteen food or the chairman’s notorious bad taste in ties.With other audiences you mustn’t attempt to cut in with humor as they will resent an outsider making disparaging remarks about their canteen or their chairman.You will be on safer ground if you stick to scapegoats like the Post Office or the telephone system.If you feel awkward being humorous,you must practice so that it becomes more natural.Include a few casual and apparently off-the-cuff remarks which you can deliver in a relaxed and unforced manner.Often it’s the delivery which causes theaudience to smile,so speak slowly and remember that a raised eyebrow or an unbelieving look may help to show that you are making a light-hearted remark.Look for the humor.It often comes from the unexpected.A twist on a familiar quote“If at first you don’t succeed,give up”or a play on words or on a situation. Search for exaggeration and understatement.Look at your talk and pick out a few words or sentences which you can turn about and inject with humor.2 2 2 2 21.To make your humor work,you should.[[[[A]take advantage of different kinds of audienceB]make fun of the disorganized peopleC]address different problems to different peopleD]show sympathy for your listeners2.The joke about doctors implies that,in the eyes of nurses,they are.[[[[A]impolite to new arrivalsB]very conscious of their godlike roleC]entitled to some privilegesD]very busy even during lunch hours3.It can be inferred from the text that public services.[[[[A]have benefited many peopleB]are the focus of public attentionC]are an inappropriate subject for humorD]have often been the laughing stock4.To achieve the desired result,humorous stories should be delivered.[[[[A]in well-worded languageB]as awkwardly as possibleC]in exaggerated statementsD]as casually as possible5.The best title for the text may be.[[[[A]Use Humor EffectivelyB]Various Kinds of HumorC]Add Humor to SpeechD]Different Humor StrategiesText2Since the dawn of human ingenuity,people have devised ever more cunning toolsto cope with work that is dangerous,boring,burdensome,or just plain nasty.That compulsion has resulted in robotics—the science of conferring various human capabilities on machines.And if scientists have yet to create the mechanical version of science fiction,they have begun to come close.As a result,the modern world is increasingly populated by intelligent gizmos whose presence we barely notice but whose universal existence has removed much human labor.Our factories hum to the rhythm of robot assembly arms.Our banking is done at automated teller terminals that thank us with mechanical politeness for thetransaction.Our subway trains are controlled by tireless robot-drivers.And thanks to the continual miniaturization of electronics and micro-mechanics,there are already robot systems that can perform some kinds of brain and bone surgery with submillimeter accuracy—far greater precision than highly skilled physicians can achieve with their hands alone.But if robots are to reach the next stage of laborsaving utility,they will have to operate with less human supervision and be able to make at least a few decisions for themselves—goals that pose a real challenge.“While we know how to tell a robot to handle a specific error,"says Dave Lavery,manager of a robotics program at NASA,“w e can't yet give a robot enough‘common sense’to reliably interact with a dynamic world.”Indeed the quest for true artificial intelligence has produced very mixed results.Despite a spell of initial optimism in the1960s and1970s when it appeared that transistor circuits and microprocessors might be able to copy the action of the human brain by the year2010,researchers lately have begun to extend that forecast by decades if not centuries.What they found,in attempting to model thought,is that the human brain's roughly one hundred billion nerve cells are much more talented—and human perception far more complicated—than previously imagined.They have built robots that can recognize the error of a machine panel by a fraction of a millimeter in a controlled factory environment.But the human mind can glimpse a rapidly changing scene and immediately disregard the98percent that is irrelevant,instantaneously focusing on the monkey at the side of a winding forest road or the single suspicious face in a big crowd.The most advanced computer systems on Earth can't approach that kind of ability,and neuroscientists still don’t know quite how we do it.26.Human ingenuity was initially demonstrated in.[ [ [ [A]the use of machines to produce science fiction.B]the wide use of machines in manufacturing industry.C]the invention of tools for difficult and dangerous work.D]the elite’s cunning tackling of dangerous and boring work.2 27.The word“gizmos”(line1,paragraph2)most probably meansA]programs[B]experts[C]devices[D]creatures8.According to the text,what is beyond man's ability now is to design a robotthat can.[.[[[[A]fulfill delicate tasks like performing brain surgery.B]interact with human beings verbally.C]have a little common sense.D]respond independently to a changing world.29.Besides reducing human labor,robots can also.[ [ [ [A]make a few decisions for themselves.B]deal with some errors with human intervention.C]improve factory environments.D]cultivate human creativity.30.The author uses the example of a monkey to argue that robots are.[ [ [ [A]expected to copy human brain in internal structure.B]able to perceive abnormalities immediately.C]far less able than human brain in focusing on relevant information.D]best used in a controlled environment.Text3Could the bad old days of economic decline be about to return?Since OPEC agreed to supply-cuts in March,the price of crude oil has jumped to almost$26a barrel, up from less than$10last December.This near-tripling of oil prices calls up scary memories of the1973oil shock,when prices quadrupled,and1979-1980,when they also almost tripled.Both previous shocks resulted in double-digit inflation and global economic decline.So where are the headlines warning of gloom and doom this time?The oil price was given another push up this week when Iraq suspended oil exports. Strengthening economic growth,at the same time as winter grips the northern hemisphere,could push the price higher still in the short term.Yet there are good reasons to expect the economic consequences now to be less severe than in the1970s.In most countries the cost of crude oil now accounts for a smaller share of the price of petrol than it did in the1970s.In Europe,taxes account for up to four-fifths of the retail price,so even quite big changes in the price of crude have a more muted effect on pump prices than in the past.Rich economies are also less dependent on oil than they were,and so less sensitive to swings in the oil price.Energy conservation,a shift to other fuels and a decline in the importance of heavy,energy-intensive industries have reduced oil consumption.Software,consultancy and mobile telephones use far less oil than steel or car production.For each dollar of GDP(in constant prices)rich economies now use nearly50%less oil than in1973.The OECD estimates in its latest Economic Outlook that,if oil prices averaged$22a barrel for a full year,compared with$ 013in1998,this would increase the oil import bill in rich economies by only .25-0.5%of GDP.That is less than one-quarter of the income loss in1974or1980.On the other hand,oil-importing emerging economies—to which heavy industry has shifted—have become more energy-intensive,and so could be more seriously squeezed.One more reason not to lose sleep over the rise in oil prices is that,unlike the rises in the1970s,it has not occurred against the background of general commodity-price inflation and global excess demand.A sizable portion of the world is only just emerging from economic decline.The Economist’s commodity price index is broadly unchanging from a year ago.In1973commodity prices jumped by70%,and in1979by almost30%.3 31.The main reason for the latest rise of oil price is_______[[A]global inflation.[B]reduction in supply.C]fast growth in economy.[D]Iraq’s suspension of exports.2.It can be inferred from the text that the retail price of petrol will go updramatically if______.[ [A]price of crude rises.C]consumption rises.[B]commodity prices rise.[D]oil taxes rise.3 3 33.The estimates in Economic Outlook show that in rich countries_______.[[[[A]heavy industry becomes more energy-intensive.B]income loss mainly results from fluctuating crude oil prices.C]manufacturing industry has been seriously squeezed.D]oil price changes have no significant impact on GDP.4.We can draw a conclusion from the text that_______.[[[[A]oil-price shocks are less shocking now.B]inflation seems irrelevant to oil-price shocks.C]energy conservation can keep down the oil prices.D]the price rise of crude leads to the shrinking of heavy industry.5.From the text we can see that the writer seems__________.A]optimistic.[B]sensitive.[C]gloomy.[D]scared.Text4The Supreme Court’s decisions on physician-assisted suicide carry important [implications for how medicine seeks to relieve dying patients of pain and suffering.Although it ruled that there is no constitutional right to physician-assisted suicide,the Court in effect supported the medical principle of“double effect”, a centuries-old moral principle holding that an action having two effects—a good one that is intended and a harmful one that is foreseen—is permissible if the actor intends only the good effect.Doctors have used that principle in recent years to justify using high doses of morphine to control terminally ill patients’pain,even though increasing dosages will eventually kill the patient.Nancy Dubler,director of Montefiore Medical Center,contends that the principle will shield doctors who“until now have very,very strongly insisted that they could not give patients sufficient medication to control their pain if that might hasten death”.George Annas,chair of the health law department at Boston University,maintains that,as long as a doctor prescribes a drug for a legitimate medical purpose,the doctor has done nothing illegal even if the patient uses the drug to hasten death.“It’s like surgery,”he says.“We don’t call those deaths homicides because the doctors didn’t intend to kill their patients,although they risked their death. If you’re a physician,you can risk your patient’s suicide as long as you don’t intend their suicide.”On another level,many in the medical community acknowledge that the assisted-suicide debate has been fueled in part by the despair of patients for whom modern medicine has prolonged the physical agony of dying.Just three weeks before the Court’s ruling on physician-assisted suicide,the National Academy of Science(NAS)released a two-volume report,Approaching Death: Improving Care at the End of Life.It identifies the undertreatment of pain and the aggressive use of“ineffectual and forced medical procedures that may prolong andeven dishonor the period of dying”as the twin problems of end-of-life care.The profession is taking steps to require young doctors to train in hospices, to test knowledge of aggressive pain management therapies,to develop a Medicare billing code for hospital-based care,and to develop new standards for assessing and treating pain at the end of life.Annas says lawyers can play a key role in insisting that these well-meaning medical initiatives translate into better care.“Large numbers of physicians seem unconcerned with the pain their patients are needlessly and predictably suffering”, to the extent that it constitutes“systematic patient abuse”.He says medical licensing boards“must make it clear...that painful deaths are presumptively ones that are incompetently managed and should result in license suspension”.36.From the first three paragraphs,we learn that.[ [ [ [A]doctors used to increase drug dosages to control their patients’painB]it is still illegal for doctors to help the dying end their livesC]the Supreme Court strongly opposes physician-assisted suicideD]patients have no constitutional right to commit suicide37.Which of the following statements its true according to the text?[ [ [A]Doctors will be held guilty if they risk their patients’death.B]Modern medicine has assisted terminally ill patients in painless recovery.C]The Court ruled that high-dosage pain-relieving medication can be prescribed.[D]A doctor’s medication is no longer justified by his intentions.3 3 48.According to the NAS’s report,one of the problems in end-of-life care is.[[A]prolonged medical proceduresC]systematic drug abuse[B]inadequate treatment of pain[D]insufficient hospital care9.Which of the following best defines the word“aggressive”(line4,paragraph7[)?A]Bold.[B]Harmful.[C]Careless.[D]Desperate0.George Annas would probably agree that doctors should be punished if they.[[[[A]manage their patients incompetentlyB]give patients more medicine than neededC]reduce drug dosages for their patientsD]prolong the needless suffering of the patientsPart BDirections:Read the following text carefully and then translate the underlined segments into Chinese.Your translation should be written clearly on ANSWER SHEET 2.(10 points)Almost all our major problems involve human behavior,and they cannot be solved by physical and biological technology alone.What is needed is a technology of behavior,but we have been slow to develop the science from which such a technologymight be drawn.(41)One difficulty is that almost all of what is called b ehavioral science continues to trace behavior to states of mind,feelings,traits of character, human nature,and so on.Physics and biology once followed similar practices and advanced only when they discarded them.(42)The behavioral sciences have been slow to change partly because the explanatory items often seem to be directly observed and partly because other kinds of explanations have been hard to find.The environment is obviously important,but its role has remained obscure.It does not push or pull,it selects,and this function is difficult to discover and analyze.(43)The role of natural selection in evolution was formulated only a little more than a hundred years ago,and the selective role of the environment in shaping and maintaining the behavior of the individual is only beginning to be recognized and studied.As the interaction between organism and environment has come to be understood,however,effects once assigned to states of mind,feelings,and traits are beginning to be traced to accessible conditions,and a technology of behavior may therefore become available.It will not solve our problems,however,until it replaces traditional prescientific views,and these are strongly entrenched. Freedom and dignity illustrate the difficulty.(44)They are the possessions of the autonomous(self-governing)man of traditional theory,and they are essential to practices in which a person is held responsible for his conduct and given credit for his achievements.A scientific analysis shifts both the responsibility and the achievement to the environment.It also raises questions concerning“values”.Who will use a technology and to what ends?(45)Until these issues are resolved,a technology of behavior will continue to be rejected,and with it possibly the only way to solve our problems.Section III Writing46.Directions:Study the following picture carefully and write an essay entitled“Cultures National and International”.In the essay you should1.describe the picture and interpret its meaning,and2.give your comment on the phenomenon.You should write about200words neatly on ANSWER SHEET 2.(20points)An American girl in traditional Chinese costume(服装)第一部分英语知识应用试题解析一、文章总体分析本文主要介绍了计算机的发展对通信革命及人们的生存方式产生的影响。
2002年全国攻读硕士学位研究生入学考试英语试题Section I Use of EnglishDirections:Read the following text. Choose the best word(s) for each numbered blank and mark A, B, C OR D on ANSWER SHEET 1. (10 points)Comparisons were drawn between the development of television in the 20th century and the diffusion of printing in the 15th and 16th centuries. Yet much had happened1. As was discussed before, it was not2the 19th century that the newspaper became the dominant pre-electronic_ 3 _ ,following in the wake of the pamphlet and the book and in the 4 of the periodical. It was during the same time that the communications revolution 5 up, beginning with transport, the railway, and leading 6 through the telegraph, the telephone, radio, and motion pictures 7 the 20th century world of the motor car and the air plane. Not everyone sees that Process in8. It is important to do so.It is generally recognized,9, that the introduction of the computer in the early 20th century, 10 by the invention of the integrated circuit during the 1960s, radically changed the process, 11 its impact on the media was not immediately 12 . As time went by, computers became smaller and more powerful, and they became “personal” too, as well as 13, with display becoming sharper and storage 14 increasing. They were thought of, like people, 15 generations, with the distance between generations much 16.It was within the computer age that the term “information society” bega n to be widely used to describe the 17 within which we now live. The communications revolution has 18 both work and leisure and how we think and feel both about place and time, but there have been 19 view about its economic, political, social and cultural implications. “Benefits” have been weighed 20“harmful” outcomes. And generalizations have proved difficult.1. [A]between [B]before [C]since [D]later2. [A]after [B]by [C]during [D]until3. [A]means [B]method [C]medium [D]measure4. [A]process [B]company [C]light [D]form5. [A]gathered [B]speeded [C]worked [D]picked6. [A]on [B]out [C]over [D]off7. [A]of [B]for [C]beyond [D]into8. [A]concept [B]dimension [C]effect [D]perspective9. [A]indeed [B]hence [C]however [D]therefore10. [A]brought [B]followed [C]stimulated [D]characterized11. [A]unless [B]since [C]lest [D]although12. [A]apparent [B]desirable [C]negative [D]plausible13. [A]institutional [B]universal [C]fundamental [D]instrumental14. [A]ability [B]capability [C]capacity [D]faculty15. [A]by means of [B]in terms of [C]with regard to[D]in line with16. [A]deeper [B]fewer [C]nearer [D]smaller17. [A]context [B]range [C]scope [D]territory18. [A]regarded [B]impressed [C]influenced [D]effected19. [A]competitive [B]controversial [C]distracting [D]irrational20. [A]above [B]upon [C]against [D]withSection II Reading ComprehensionPart ADirections:Read the following four texts. Answer the questions below each text by choosing [A], [B], [C] or [D]. Mark your answers on ANSWER SHEET 1. (40 points)Text 1If you intend using humor in your talk to make people smile, you must know how to identify shared experiences and problems. Your humor must be relevant to the audience and should help to show them that you are one of them or that you understand their situation and are in sympathy with their point of view. Depending on whom you are addressing, the problems will be different. If you are talking to a group of managers, you may refer to the disorganized methods of their secretaries; alternatively if you are addressing secretaries, you may want to comment on their disorganized bosses.Here is an example, which I heard at a nurses’convention, of a story which works well because the audience all shared the same view of doctors. A man arrives in heaven and is being shown around by St. Peter. He sees wonderful accommodations, beautiful gardens, sunny weather, and so on. Everyone is very peaceful, polite and friendly until, waiting in a line for lunch, the new arrival is suddenly pushed aside by a man in a white coat, who rushes to the head of the line, grabs his food and stomps over to a table by himself. “Who is that?” the new arrival asked St. Peter. “Oh, that’s God,” came the reply, “but sometimes he thinks he’s a doctor.”If you are part of the group which you are addressing, you will be in a position to know the experiences and problems which are common to all of you and it’ll be appropriate for you to make a passing remark about the inedible canteen food or the chairman’s notorious bad taste in ties. With other audiences you mustn’t attempt to cut in with humor as they will resent an outsider making disparaging remarks about their canteen or their chairman. You will be on safer ground if you stick to scapegoats like the Post Office or the telephone system.If you feel awkward being humorous, you must practice so that it becomes more natural. Include a few casual and apparently off-the-cuff remarks which you can deliver in a relaxed and unforced manner. Often it’s the delivery which causes the audience to smile, so speak slowly and remember that a raised eyebrow or an unbelieving look may help to show that you are making a light-hearted remark.Look for the humor. It often comes from the unexpected. A twist on a familiar quote “If at first you don’t succeed, give up” or a play on words or on a situation. Search for exaggeration and understatement. Look at your talk and pick out a few words or sentences which you can turn about and inject with humor.21. To make your humor work, you should.[A] take advantage of different kinds of audience[B] make fun of the disorganized people[C] address different problems to different people[D] show sympathy for your listeners22. The joke about doctors implies that, in the eyes of nurses, they are.[A] impolite to new arrivals[B] very conscious of their godlike role[C] entitled to some privileges[D] very busy even during lunch hours23. It can be inferred from the text that public services.[A] have benefited many people[B] are the focus of public attention[C] are an inappropriate subject for humor[D] have often been the laughing stock24. To achieve the desired result, humorous stories should be delivered.[A] in well-worded language[B] as awkwardly as possible[C] in exaggerated statements[D] as casually as possible25. The best title for the text may be.[A] Use Humor Effectively[B] Various Kinds of Humor[C] Add Humor to Speech[D] Different Humor StrategiesText 2Since the dawn of human ingenuity, people have devised ever more cunning tools to cope with work that is dangerous, boring, burdensome, or just plain nasty. That compulsion has resulted in robotics—the science of conferring various human capabilities on machines. And if scientists have yet to create the mechanical version of science fiction, they have begun to come close.As a result, the modern world is increasingly populated by intelligent gizmos whose presence we barely notice but whose universal existence has removed much human labor. Our factories hum to the rhythm of robot assembly arms. Our banking is done at automated teller terminals that thank us with mechanical politeness for the transaction. Our subway trains are controlled by tireless robot-drivers. And thanks to the continual miniaturization of electronics and micro-mechanics, there are already robot systems that can perform some kinds of brain and bone surgery with submillimeter accuracy—far greater precision than highly skilled physicians can achieve with their hands alone.But if robots are to reach the next stage of laborsaving utility, they will have to operate with less human supervision and be able to make at least a few decisions for themselves—goals that pose a real challenge. “While we know how to tell a robot to handle a specific error," says Dave Lavery, manager of a robotics program atNASA, “we can't yet give a robot enough ‘common sense’ to reliably interact with a dynamic world.”Indeed the quest for true artificial intelligence has produced very mixed results. Despite a spell of initial optimism in the 1960s and 1970s when it appeared that transistor circuits and microprocessors might be able to copy the action of the human brain by the year 2010, researchers lately have begun to extend that forecast by decades if not centuries.What they found, in attempting to model thought, is that the human brain's roughly one hundred billion nerve cells are much more talented—and human perception far more complicated —than previously imagined. They have built robots that can recognize the error of a machine panel by a fraction of a millimeter in a controlled factory environment. But the human mind canglimpse a rapidly changing scene and immediately disregard the 98 percent that is irrelevant, instantaneously focusing on the monkey at the side of a winding forest road or the single suspicious face in a big crowd. The most advanced computer systems on Earth can't approach that kind of ability, and neuroscientists still don’t know quite how we do it.26. Human ingenuity was initially demonstrated in.[A] the use of machines to produce science fiction.[B] the wide use of machines in manufacturing industry.[C] the invention of tools for difficult and dangerous work.[D] the elite’s cunning tackling of dangerous and boring work.27. The word “gizmos” (line 1, paragraph 2) most probably means.[A] programs[B]experts[C]devices [D]creatures28. According to the text, what is beyond man's ability now is to design a robot that can.[A] fulfill delicate tasks like performing brain surgery.[B] interact with human beings verbally.[C] have a little common sense.[D] respond independently to a changing world.29. Besides reducing human labor, robots can also.[A] make a few decisions for themselves.[B] deal with some errors with human intervention.[C] improve factory environments.[D] cultivate human creativity.30. The author uses the example of a monkey to argue that robots are.[A] expected to copy human brain in internal structure.[B] able to perceive abnormalities immediately.[C] far less able than human brain in focusing on relevant information.[D] best used in a controlled environment.Text 3Could the bad old days of economic decline be about to return? Since OPEC agreed to supply-cuts in March, the price of crude oil has jumped to almost $26 a barrel, up from less than $10 last December. This near-tripling of oil prices calls up scary memories of the 1973 oil shock, when prices quadrupled, and 1979-1980, when they also almost tripled. Both previous shocks resulted in double-digit inflation and global economic decline. So where are the headlines warning of gloom and doom this time?The oil price was given another push up this week when Iraq suspended oil exports. Strengthening economic growth, at the same time as winter grips the northern hemisphere, could push the price higher still in the short term.Yet there are good reasons to expect the economic consequences now to be less severe than in the 1970s. In most countries the cost of crude oil now accounts for a smaller share of the price of petrol than it did in the 1970s. In Europe, taxes account for up to four-fifths of the retail price, so even quite big changes in the price of crude have a more muted effect on pump prices than in the past.Rich economies are also less dependent on oil than they were, and so less sensitive to swingsin the oil price. Energy conservation, a shift to other fuels and a decline in the importance of heavy, energy-intensive industries have reduced oil consumption. Software, consultancy and mobile telephones use far less oil than steel or car production. For each dollar of GDP (in constant prices) rich economies now use nearly 50% less oil than in 1973. The OECD estimates in its latest Economic Outlook that, if oil prices averaged $22 a barrel for a full year, compared with $13 in 1998, this would increase the oil import bill in rich economies by only 0.25-0.5% of GDP. That is less than one-quarter of the income loss in 1974 or 1980. On the other hand, oil-importing emerging economies—to which heavy industry has shifted—have become more energy-intensive, and so could be more seriously squeezed.One more reason not to lose sleep over the rise in oil prices is that, unlike the rises in the 1970s, it has not occurred against the background of general commodity-price inflation and global excess demand. A sizable portion of the world is only just emerging from economic decline. The Economist’s commodity price index is broadly unchanging from a year ago. In 1973 commodity prices jumped by 70%, and in 1979 by almost 30%.31. The main reason for the latest rise of oil price is_______[A] global inflation.[B] reduction in supply.[C]fast growth in economy.[D] Iraq’s suspension of exports.32. It can be inferred from the text that the retail price of petrol will go up dramatically if______.[A] price of crude rises. [B] commodity prices rise.[C] consumption rises. [D] oil taxes rise.33. The estimates in Economic Outlook show that in rich countries_______.[A]heavy industry becomes more energy-intensive.[B]income loss mainly results from fluctuating crude oil prices.[C]manufacturing industry has been seriously squeezed.[D]oil price changes have no significant impact on GDP.34. We can draw a conclusion from the text that_______.[A]oil-price shocks are less shocking now.[B]inflation seems irrelevant to oil-price shocks.[C]energy conservation can keep down the oil prices.[D]the price rise of crude leads to the shrinking of heavy industry.35. From the text we can see that the writer seems__________.[A]optimistic. [B]sensitive. [C]gloomy. [D]scared.Text 4The Supreme Court’s decisions on physician-assisted suicide carry important implications for how medicine seeks to relieve dying patients of pain and suffering.Although it ruled that there is no constitutional right to physician-assisted suicide, the Court in effect supported the medical principle of “double effect”, a centuries-old moral principle holding that an action having two effects—a good one that is intended and a harmful one that is foreseen—is permissible if the actor intends only the good effect.Doctors have used that principle in recent years to justify using high doses of morphine to control terminally ill patients’pain, even though increasing dosages will eventually kill the patient.Nancy Dubler, director of Montefiore Medical Center, contends that the principle will shield doctors who “until now have very, very strongly insisted that they could not give patients sufficient medication to control the ir pain if that might hasten death”.George Annas, chair of the health law department at Boston University, maintains that, as long as a doctor prescribes a drug for a legitimate medical purpose, the doctor has done nothing illegal even if the patient uses the drug to hasten death. “It’s like surgery,” he says. “We don’t call those deaths homicides because the doctors didn’t intend to kill their patients, although they risked their death. If you’re a physician, you can risk your patient’s suicide as long as you don’t intend their suicide.”On another level, many in the medical community acknowledge that the assisted-suicide debate has been fueled in part by the despair of patients for whom modern medicine has prolonged the physical agony of dying.Just three weeks before the Court’s ruling on physician-assisted suicide, the National Academy of Science (NAS) released a two-volume report, Approaching Death: Improving Care at the End of Life. It identifies the undertreatment of pain and the aggressive use of “ineffectual and forced medical procedures that may prolong and even dishonor the period of dying” as the twin problems of end-of-life care.The profession is taking steps to require young doctors to train in hospices, to test knowledge of aggressive pain management therapies, to develop a Medicare billing code for hospital-based care, and to develop new standards for assessing and treating pain at the end of life.Annas says lawyers can play a key role in insisting that these well-meaning medical initiatives translate into better care. “Large numbers of physicians seem unconcerned with the pain their patients are needlessly and predictably suffering”, to the extent that it constitutes “systematic patient abuse”. He says medical licensing boards “must make i t clear...that painful deaths are presumptively ones that are incompetently managed and should result in license suspension”.36. From the first three paragraphs, we learn that.[A] doctors used to increase drug dosages to control their patients’pain[B] it is still illegal for doctors to help the dying end their lives[C] the Supreme Court strongly opposes physician-assisted suicide[D] patients have no constitutional right to commit suicide37. Which of the following statements its true according to the text?[A]Doctors will be held guilty if they risk their patients’death.[B]Modern medicine has assisted terminally ill patients in painless recovery.[C]The Court ruled that high-dosage pain-relieving medication can be prescribed.[D]A doctor’s medication is no longer justified by his intentions.38. According to the NAS’s report, one of the problems in end-of-life care is.[A] prolonged medical procedures [B] inadequate treatment of pain[C] systematic drug abuse [D] insufficient hospital care39. Which of the following best defines the word “aggressive” (line 4, paragraph 7)?[A] Bold. [B] Harmful. [C] Careless. [D] Desperate40. George Annas would probably agree that doctors should be punished if they.[A]manage their patients incompetently[B]give patients more medicine than needed[C]reduce drug dosages for their patients[D]prolong the needless suffering of the patientsPart BDirections:Read the following text carefully and then translate the underlined segments into Chinese. Your translation should be written clearly on ANSWER SHEET 2. (10 points)Almost all our major problems involve human behavior, and they cannot be solved by physical and biological technology alone. What is needed is a technology of behavior, but we have been slow to develop the science from which such a technology might be drawn.(41)One difficulty is that almost all of what is called behavioral science continues to trace behavior to states of mind, feelings, traits of character, human nature, and so on. Physics and biology once followed similar practices and advanced only when they discarded them. (42)The behavioral sciences have been slow to change partly because the explanatory items often seem to be directly observed and partly because other kinds of explanations have been hard to find. The environment is obviously important, but its role has remained obscure. It does not push or pull, it selects, and this function is difficult to discover and analyze.(43)The role of natural selection in evolution was formulated only a little more than a hundred years ago, and the selective role of the environment in shaping and maintaining the behavior of the individual is only beginning to be recognized and studied. As the interaction between organism and environment has come to be understood, however, effects once assigned to states of mind, feelings, and traits are beginning to be traced to accessible conditions, and a technology of behavior may therefore become available. It will not solve our problems, however, until it replaces traditional prescientific views, and these are strongly entrenched. Freedom and dignity illustrate the difficulty. (44)They are the possessions of the autonomous(self-governing)man of traditional theory, and they are essential to practices in which a person is held responsible for his conduct and given credit for his achievements. A scientific analysis shifts both the responsibility and the achievement to the environment. It also raises questions concerning “values”. Who will use a technology and to what ends?(45)Until these issues are resolved, a technology of behavior will continue to be rejected, and with it possibly the only way to solve our problems.Section III Writing46. Directions:Study the following picture carefully and write an essay entitled “CulturesNational andInternational”.In the essay you should1. describe the picture and interpret its meaning, and2. give your comment on the phenomenon.You should write about 200 words neatly on ANSWER SHEET 2. (20 points)An American girl in traditional Chinese costume(服装)第一部分英语知识应用试题解析一、文章总体分析本文主要介绍了计算机的发展对通信革命及人们的生存方式产生的影响。
2002年全国硕士研究生入学统一考试英语试题全国硕士研究生入学考试英语试题(一)Section I Listening ComprehensionDirections:This Section is designed to test your ability to understand spoken English.You will hear a selection of recorded materials and you must answer the questions that accompany them.There are three parts in this section,Part A,Part B and Part C.Remember,while you are doing the test,you should first put down your answers in your test booklet.At the end of the listening comprehension section,you will have5minutes to transfer all your answers from your test booklet to ANSWER SHEET1.Now look at Part A in your test booklet.Part ADirections:For Questions1-5,you will hear an introduction about the life of Margaret Welch.While you listen,fill out the table with the information you’ve heard.Some of the information has been given to you in the table.Write only1word or number in each numbered box.You will hear the recording twice.You now have25seconds to read the table below.(5points)Death(Age)77Part BDirections:For questions6-10,you will hear a talk by a well-known U.S.journalist.While you listen, complete the sentences or answer the e not more than3words for each answer.You will hear the recording twice.You now have25seconds to read the sentences and questions below.(5points)Besides reporters,who else were camped out for days6outside the speaker’s home?One reporter got to the speaker’s apartment7 pretending to pay.The speaker believed the reporter wanted a picture of8her lookingWhere is a correction to a false story usually placed?9According to the speaker,the press will lose readers10unless the editors and the news directorsPart CDirections:You will hear three pieces of recorded material.Before listening to each one,you will have time to read the questions related to it.While listening,answer each question by choosing[A],[B],[C] or[D].After listening,you will have time to check your answers.You will hear each piece once only.(10points)Questions11-13are based on a report about children’s healthy development.You now have15 seconds to read Questions11-13.11.What unusual question may doctors ask when giving kids a checkup next time?[A]Howmuch exercise they get every day.[B]What they are most worried about.[C]How long their parents accompany them daily.[D]What entertainment they are interested in.12.The academy suggests that children under age two________.[A]get enough entertainment[B]have more activities[C]receive early education[D]have regular checkups13.According to the report,children’s bedrooms should________.[A]be no place for play[B]be near a common area[C]have no TV sets[D]have a computer for studyQuestions14-16are based on the following talk about how to save money.You now have15 seconds to read Questions14-16.14.According to the speaker,what should one pay special attention to if he wants to save up?[A]Family debts.[B]Bank savings.[C]Monthly bills.[D]Spending habits.15.How much can a person save by retirement if he gives up his pack-a-day habit?[A]$190,000.[B]$330,000.[C]$500,000.[D]$1,000,000.16.What should one do before paying monthly bills,if he wants to accumulate wealth?[A]Invest into a mutual fund.[B]Use the discount tickets.[C]Quit his eating-out habit.[D]Use only paper bills and save coins.Questions17-20are based on an interview with Herbert A.Glieberman,a domestic-relations lawyer.You now have20seconds to read Questions17-20.17.Which word best describes the lawyer’s prediction of the change in divorce rate?[A]Fall[B]Rise[C]V-shape[D]Zigzag18.What do people nowadays desire to do concerning their marriage?[A]To embrace changes of thought.[B]To adapt to the disintegrated family life.[C]To return to the practice in the‘60s and‘70s.[D]To create stability in their lives.19.Why did some people choose not to divorce20years ago?[A]They feared the complicated procedures.[B]They wanted to go against the trend.[C]They were afraid of losing face.[D]they were willing to stay together.20.Years ago a divorced man in a company would have________.[A]been shifted around the country.[B]had difficulty being promoted.[C]enjoyed a happier life.[D]tasted little bitterness of disgrace.You now have5minutes to transfer all your answers from your test booklet to ANSWER SHEET1.THIS IS THE END OF SECTION IDO NOT READ OR WORK ON THE NEXT SECTIONUNTIL YOU ARE TOLD TO CONTINUE全国硕士研究生入学考试英语试题(二)National Entrance Test of English for MA/MS Candidates(2002)考生注意事项1.考生必须严格遵守各项考场规则,得到监考人员指令后方可开始答题。
全国硕士研究生入学考试英语试题(一)National Entrance Test of English for MA/MS Candidates (2002)考生注意事项1. 考生必须严格遵守各项考场规则, 得到监考人员指令后方可开始答题。
3. 全国硕士研究生入学考试英语分为试题(一) 、试题(二) 。
4. 本试题为试题(一), 共4页(1~4页) 。
考生必须在规定的时间内作答。
5. 试题(一) 为听力部分。
该部分共有A、B、C三节, 所有答案都应填写或填涂在答题卡1上。
A、B两节必须用蓝(黑) 圆珠笔答题, 注意字迹清楚。
C节必须用2B铅笔按照答题卡上的要求填涂, 如要改动, 必须用橡皮擦干净。
6. 听力考试进行时, 考生应先将答案写或标记在试题上, 然后在听力部分结束前专门留出的5分钟内, 将答案整洁地誊写或转涂到答题卡1上。
仅写或标记在试题上不给分。
Directions:Now look at Part A in your test booklet.Part ADirections:For Questions 1-5, you will hear an introduction about the life of Margaret Welch. While you listen, fill out the table with the information you’ve heard. Some of the information has been given to you in the table. Write only 1 word or number in each numbered box. You will hear the recording twice. You now have 25 seconds to read the table below. (5 points)Welch’s Personal InformationPlace of Birth PhiladelphiaYear of Birth 1901Transfer to Barnard University (Year) 1920Major at University1Final Degree PhDYear of Marriage 1928Growing Up In New Guinea Published (Year)2Field Study in the South Pacific (Age)3Main Interest4Professorship at Columbia Started (Year)Death (Age) 77Part BDirections:Besides reporters, who else were camped out for days outside the speaker’s home?6. ________One reporter got to the speaker’s apartment pretending to pay7. ________The speaker believed the reporter wanted a picture of her looking8. ________Where is a correction to a false story usually placed?9. ________According to the speaker, the press will lost readers unless the editors and the news directors10. ________Part CDirections:Questions 11-13 are based on a report about children’s healthy development. You now have 15 seconds to read Questions 11-13.[B] What they are most worried about.[D] What entertainment they are interested in.12. The academy suggests that children under age two ________.[A] get enough entertainment[B] have more activities[C] receive early education[D] have regular checkups13. According to the report, children’s bedrooms should ________.[A] be no place for play[C] have no TV setsQuestions 14-16 are based on the following talk about how to save money. You now have 15 seconds to read Questions 14-16.14. According to the speaker, what should one pay special attention to if he wants to save up?[A] Family debts.[B] Bank savings.[C] Monthly bills.[D] Spending habits.15. How much can a person save by retirement if he gives up his pack-a-day habit?[A] $190,000.[B] $330,000.[C] $500,000.[D] $1,000,000.16. What should one do before paying monthly bills, if he wants to accumulate wealth?[A] Invest into a mutual fund.[B] Use the discount tickets.[C] Quit his eating-out habit.[D] Use only paper bills and save coins.Questions 17-20 are based on an interview with Herbert A. Glieberman, a domestic-relations lawyer. You now have 20 seconds to read Questions 17-20.17. Which word best describes the lawyer’s prediction of the change in divorce rate?[A] Fall[B] Rise[C] V-shape[D] Zigzag18. What do people nowadays desire to do concerning their marriage?[A] To embrace changes of thought.[B] To adapt to the disintegrated family life.[C] To return to the practice in the ‘60s and ‘70s.[D] To create stability in their lives.19. Why did some people choose not to divorce 20 years ago?[B] They wanted to go against the trend.[C] They were afraid of losing face.[D] they were willing to stay together.[A] been shifted around the country.[B] had difficulty being promoted.[C] enjoyed a happier life.[D] tasted little bitterness of disgrace.You now have 5 minutes to transfer all your answers from your test booklet to ANSWER SHEET 1.THIS IS THE END OF SECTION IDO NOT READ OR WORK ON THE NEXT SECTIONUNTIL YOU ARE TOLD TO CONTINUE全国硕士研究生入学考试英语试题(二)National Entrance Test of English for MA/MS Candidates (2002)考生注意事项1. 考生必须严格遵守各项考场规则,得到监考人员指令后方可开始答题。
2002年MBA英语真题及答案 考生须知 选择题的答案须用2B铅笔填涂在答题卡上,其它笔填涂的或做在试卷或其它类型答题卡上的答案无效。 其他题一律用蓝色或黑色钢笔或圆珠笔在答题纸上按规定要求作答,凡做在试卷上或未做在指定位置的答案无效。
交卷时,请配合监考人员验收,并请监考人员在准考证相应位置签字(作为考生交卷的凭据)。否则,所产生的一切后果由考生自负。
2002年全国攻读工商管理硕士研究生入学考试 英语试题 Section I Vocabulary (10 points) Directions: There are 20 incomplete sentences in this section. For each sentence there are four choices marked A, B, C and D. Choose the one that best completes the sentence and mark your answers on ANSWER SHEET 1.
21.The precious manuscripts were hopelessly by long exposure in the cold, damp cellar. A.ruined B. damaged C. destroyed D. harmed 22. the board of the company has decided to its operation to include all aspects of the clothing business. A. extend B. enlarge C. expand D. amplify 23.That sound doesn’t in his language, so it’s difficult for him to pronounce it . A. happen B. occur C. have D. take place 24. the accommodation was cheap, but the food was very . A. high B. costly C. dear D. overpaid/ 25.My boss insists on seeing everything in before he makes a decision. A. black and blue B. red and blue C. black and white D. green and yellow 26. The work is not very profitable cash, but I am getting valuable experience from it.
A. in the light of B. according to C. on the basis of D. in terms of 27. At the meeting ,Smith argued in favor of the proposal. A. severely B. warmly C. forcefully D. heavily 28. His attention often at lectures, No wonder he failed the exam. A. branched B. wondered C. wandered D. went out 29.It’s often a mistake to appearance: that poor-looking individual is anything but poor. In fact, he is a millionaire.
A. go over B. go by C. go against D. go for 30. He doesn‘t seem to be able to any interest in his studies. A. make up B. work up C. turn up D. use up 31.Man has used metals for centuries in gradually increasing quantities but it was the Industrial Revolution that they came to be employed in really vast quantities.
A. till B. until C. not until D. not till 32. His brother had become a financier, he wanted to be. A. who B. what C. which D. that 33. These goods are sold at reduced prices, . A. the defects are pointed out to the customers B. the defects pointed out to the customers C. the defects have been pointed out to the customers D. the defects being pointed out to the customers 34. Basic research provides the capital fund of scientific knowledge, which the applied researchers drew to give society a rich rate of interest.
A. on B. up C. out D. to 35. I’ve kept up a friendship with a girl who I was at school twenty years ago. A. about B. since C. with D. till 36. is generally accepted, economical growth is determined by the smooth development of production./
A. What B. That C. it D. As 37. The Social Security Retirement Program is made up of two trust funds, could go penniless by next year.
A. the larger one B. the larger of which C. the largest one D. the largest of which 38. For my own part, in seems that the main requirement of an international language is that it .
A. would be easily learned B. is easily learned C. will be easily learned D. be easily learned 39. There ought to be less anxiety over the perceived risk of getting cancer than in the public mind today.
A. exist B. exists C. existing D. existed 40. the government is believed to be considering a law making it a crime to import any kind of weapon.
A. to pass B. to have passed C. passing D. having passed Section II Cloze (10 points) Directions: Read the following text. Choose the best word(s) for each numbered blank and mark A, B, C or D on ANSWER SHEET 1.
In order to work here the foreigner needs a work permit, which must be applied for by his prospective employer. The problem here is that the Department of Employment has the right to 41 or refuse these permits, and there is little that can be 42 about it, it would be extremely unwise 43 a foreign visitor to work without a permit, since anyone doing so is 44 to immediate deportation. There are some 45 to this rule, most notably people from the Common Market countries, who are 46