
初中动词时态总结
一、概述
1.动词:表示动作、状态或性质的词称为动词。例如:write、read、speak、listen、leave、walk等等。
2.时态:作谓语的动词用来表示动作或状况发生时间的各种形式称为时态(Tense)。
3.动词的基本形式(通常有5种):
原形、现在时第三人称单数形式、过去式、过去分词、现在分词4.归纳:英语中不同时间和方式发生的动作或状态要用谓语动词的不同形式来表示,这种表示动作或状态发生时间和方式的动词形式称作动词时态。
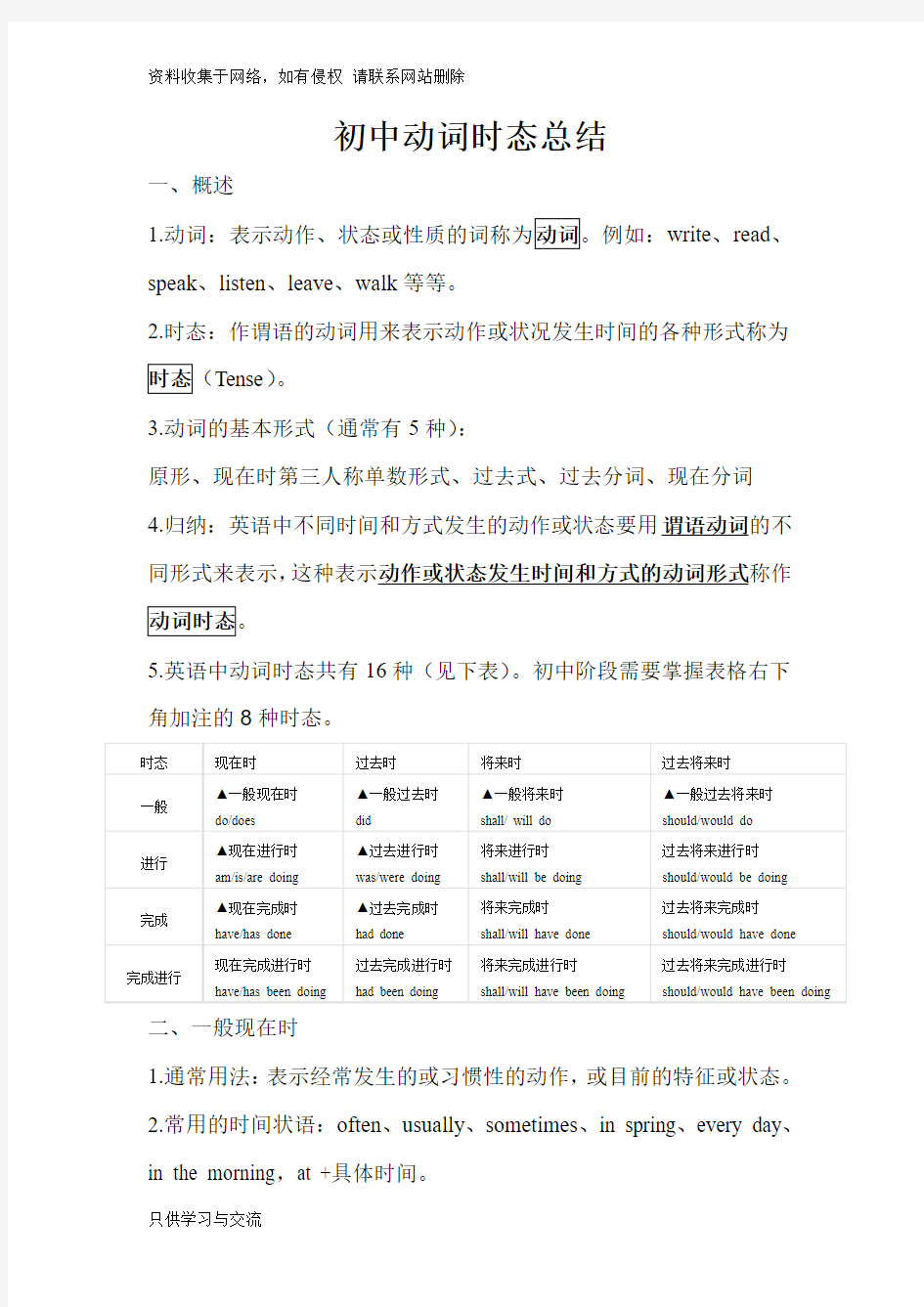
5.英语中动词时态共有16种(见下表)。初中阶段需要掌握表格右下角加注的8种时态。
时态现在时过去时将来时过去将来时
一般▲一般现在时
do/does
▲一般过去时
did
▲一般将来时
shall/ will do
▲一般过去将来时
should/would do
进行▲现在进行时
am/is/are doing
▲过去进行时
was/were doing
将来进行时
shall/will be doing
过去将来进行时
should/would be doing
完成▲现在完成时
have/has done
▲过去完成时
had done
将来完成时
shall/will have done
过去将来完成时
should/would have done
完成进行现在完成进行时
have/has been doing
过去完成进行时
had been doing
将来完成进行时
shall/will have been doing
过去将来完成进行时
should/would have been doing
二、一般现在时
1.通常用法:表示经常发生的或习惯性的动作,或目前的特征或状态。
2.常用的时间状语:often、usually、sometimes、in spring、every day、in the morning,at +具体时间。
3.构成:
1)动词原形(主要),如:work;
2)第三人称单数形式,如:works;
3)be & have,特殊的人称形式,随主语变化,如:am/is/are,have/has. 4)一般疑问句构成及简答:
Do+主语+动原+其它?Yes , I do./No, I don’t.
Does+主语+动原+其它?Yes ,he does./No,he doesn’t.
Be+主语+其它?Yes , I am./No,I’m not.
5)特殊疑问句举例:
What do you often do on sundays?
Where does he live?
4.具体用法:
1)目前经常性或习惯性的动作,常与表示频度的时间状语连用。
I go to work on foot every day.
She often speaks English,so her English is very nice.
2)客观真理,客观存在,科学事实。
The earth goes round the sun.
Quzhou lies in the southwest of Hangzhou.
3)一个按规定、计划、安排要发生的动作,仅限于少数动词,如:begin,come,leave,go,start等。
The train leaves at 8:15.
4)表示格言或者警句中。
Pride goes before a fall.(骄者必败)
注意:此用法如果出现在宾语从句中,即使主句是过去时,从句谓语也要用一般现在时。
例:Columbus proved that the earth is round.
5)现在的特征、状况或能力。
Guomingyi is always ready to help others.
Lilei writes good English but does not speak well.
6)主将从现﹝主句用将来时从句用现在时﹞
I will tell you,When Li Ming comes.
I'll e-mail you as soon as I get to Beijing.
注:一般从句为时间状语从句「由When /As soon as...引导的从句」条件状语从句「由If...引导的从句」
7)在“时间、条件、方式、让步”等状语从句中表示“将来”的动作或状况。
If it doesn’t rain tomorrow, our company will start business.
8)在某些以here 、there开头句子中用一般现在时表示现在正在或已经发生的动作。
Here we are at last!(我们终于到了)
9)用于电影、电视、戏剧、图文、标题等的解说或介绍。
Jeanne is sitting in the park. Mathilde walks towards her.(剧本说明)
5.练习题:
1). _________Alice often play the piano. No, she __________.
A. Do; do
B. Does; does
C. Does; doesn’t
2). ________ your penfriend _______ in Beijing?
A. Do; live
B. Do; lives
C. Does; live
3. Tom and Mike _______ very excited, they will take a trip.
A. is
B. are
C. am
4. I like ________ very much. What about you?
A. dance
B. danced
C. dancing
5. I can’t find my pen. Let me _______.
A. go and ask her
B. go and ask hers
C. go and ask she
答案:CCBCA
三、一般过去时
1.通常用法:过去的习惯动作或过去某时发生的动作或状态。
2.常用的时间状语:yesterday、an hour ago、last night、two days ago、in 2012、at that time、before liberation(解放)、when等引导的含过去时的句子。
3.构成:
1)动词过去式(did),如:worked/used to work;
2)否定构成:
didn’t+动原,如:didn’t work/used not(didn’t use)to work;
3)一般疑问构成及简答:
Did+主语+动原+其它?Yes,I did./No,I didn’t.
Was/Were+主语+其它?Yes , she was./No,she wasn’t.
4)特殊疑问句举例:
What did you do yesterday?
When did he get up this morning?
4.具体用法:
1)在确定的过去时间里所发生的动作或存在的状态。
Where did you go just now?
2)表示在过去一段时间内,经常性或习惯性的动作。
When I was a child,I often played football in the street.
She often came to help me with my English.
3)在“时间、条件、方式、让步”等状语从句中表示“过去将来”。They planned to go outing if it was fine the next day.
4)在虚拟语气中,可表示“现在、将来”的动作或状态。
Were I you(=If I were you),I would go abroad.
5)在谈到已逝的人的情况(包括后人对他们的评价)多用一般过去时。Newton was a great scientist.
6)用“used to +动原”或用“would +动原”,可表示过去经常或反复发生的动作。
Whenever we were in trouble,he would help us.
That is where I used to live when I was a child.
5.练习题:
1).I _____ a cartoon on Saturday.
A.watch
B. watched
C. watching
2). We ______ to zoo yesterday, and we also _____ to the park. (go)
A. go; go
B. went; go
C. went; went
3). _____ you _____ your relatives last Spring Festival?
A. Did; visit
B. Does; visit
C. Do; visit
4).The twins in Dalian last year.They here now.
A.was;are
B. were; are
C. are;are
5).——Who was on duty last Friday?
—— .
A.I am
B. I was
C. Yes,I was.
答案:BCABB
四、现在进行时
1.通常用法:现在或现阶段正在进行的动作。
2.常用时间状语:now、these days。
3.构成:
1)is(am,are)+现在分词,如:am/is/are working.
2)否定构成:
is(am,are) +not+现在分词,如:am/is/are not working.
3)一般疑问构成及简答:
Am/Is/Are +主语+现在分词+其它?Yes,I am./No,I’m not.
4)特殊疑问句举例:
What are you doing now?
Who is flying a kite there?
注意:go、come、leave、arrive、return、die等的进行时可表示即将要发生的动作。
4.具体用法:
1)说话时正在发生或者进行着的动作。
What are you doing now?
--I’m doing my maths homework.
2)表示现阶段在进行的动作(说话时不一定在进行)。
Are you working hard this term?
Mr. Green is writing another novel.(说话时并未在写,只处于写作的状态。)
3)表示即将发生的动作,尤其是表示按“计划”或“安排”要进行的动作。
When are you going off to Shenzhen?
4)表示反复性或习惯性的动作,常与副词always、constantly、continually 连用,常带有说话的某种感情色彩,如:赞扬、厌恶、不满、遗憾等。
She is always thinking of her son.
Language is always changing.
5)表示情况的暂时性。
Charlie isn’t feeling too well this morning.(平时不这样)
6)be 动词有时可用于进行时态,表示“一时的表现”。
You are not being friendly.(你这样说不够友好)。
7)表示渐变的动词有:get、grow、become、turn、run、go、begin 等。
The leaves are turning red.
It's getting warmer and warmer.
注意:不用进行时的动词
1) 事实状态的动词
have,belong,possess,cost,owe,exist,include,contain,matter,weigh,measure ,continue
例如:
I have two brothers.
This house belongs to my sister.
2) 心理状态的动词
know,realize,think,believe,see,suppose,imagine,agree,recognize,forget, remember,want,need,prefer,mean,understand,love,hate
例如:
I need your help.
He loves her very much.
3 ) 瞬间动词
accept,receive,complete,finish,give,allow,decide,refuse.
例如:
I accept your advice.
4) 系动词
seem,remain,lie,see,hear,smell,feel,taste,get,become,turn
例如:
You seem a little tired.
5.练习题:
1). Who _____ over there now?
A. singing
B. are sing
C. is singing
D. sing
2). It’s eight o’clock. The students _____ an English class.
A. have
B. having
C. is having
D. are having
3). Listen! The baby _____ in the next room.
A. crying
B. cried
C. is crying
D. cries
4). Look! The twins _____ new sweaters.
A. are wearing
B. wearing
C. are wear
D. is wearing
5. Don’t talk here. Grandparents _____.
A. is sleeping
B. are sleeping
C. sleeping
D. sleep
答案:CDCAB
五、过去进行时
1.通常用法:表示在过去某一时刻或某一时间正在进行的动作,强调在这一过程中所进行的动作或展开的情景。
2.常用时间状语:at this time yesterday、at that time、from nine to ten last evening、when/while引导的从句。
3.构成:
1)was/were +现在分词,如:was/were working.
2)否定构成:
was/were not+现在分词,如:wasn’t/were not working.
3)一般疑问构成及简答:
Were/Was +主语+现在分词+其它?Yes,I was./No,I wasn’t.
4)特殊疑问句举例:
What were you doing this time yesterday?
Where was he standing when the teacher came in?
4.具体用法:
1)表示过去某一时刻正在进行着的动作。
Most of the people were still sleeping when the earthquake happened. 2)表示过去某一阶段在进行的动作。
Last month they were building a bridge over a river in their hometown.
3)表示过去即将发生的动作。
She asked him whether he was coming back for lunch.
4)表示过去的反复性或习惯性的动作,常与副词always、constantly、continually、frequently等连用,常带有说话人的某种感情色彩。
Her father was always working like that.
5)可用来描写故事发生时的背景。
It was dark and a strong wind was blowing.
5.练习题:
1).My brother ___ while he ___ his bicycle and hurt himself.
A. fell, was riding
B. fell, were riding
C. had fallen, rode
D. had fallen, was riding
2). Tom ___ into the house when no one ___.
A. slipped, was looking
B. had slipped, looked
C. slipped, had looked
D. was slipping, looked
3).The last time I __ Jane she ___ cotton in the fields.
A. had seen, was picking
B. saw, picked
C. had seen, picked
D. saw, was picking
4).I don ' t think Jim saw me; he ___ into space.
A. just stared
B. was just staring
C. has just stared
D. had just stared
5).I first met Lisa three years ago. She ___ at a radio shop(无线电商店)at the
time.
A. has worked
B. was working
C. had been working
D. had worked
答案:AADBB
六、一般将来时
1.通常用法:将来发生的动作或状况。
2.常用时间状语:tomorrow、next year/month、in a few of minutes、tonight等。
3.构成:
1)shall/will+动原,如:shall/will work;
2)am/is/are going to+动原,如:am/is/are going to work;
3)am/is/are(about )to+动原,如:am/is/are (about) to work;
4)否定构成:
shall/will not+动原,如:shall/will work.
am/is/are not...
5)特殊疑问句举例:
What will you do tomorrow?
When are we going to have a class meeting?
4.具体用法:
1)表示将要发生的动作或状态。
Xiaoming shall be eleven years old next year.
She won’t be free tonight.
2)表示一种倾向性或习惯性的动作。
People will die without air.
3)其他表示将要发生的动作或情况的结构和时态。
①am/is/are going to+动原.——该结构表示“即将发生”或“打算要做”某事。
I think it is going to rain.
He is going to find a part-time job for a year or two and save some money.
②am/is/are to+动原.——该结构表示(按计划、安排)“要求”、“约定”、
“必须”做某事。
They are to be back by 6 o’clock.
You are to hand your homework tomorrow.
③am/is/are about to+动原.——该结构表示“即将”、“就要”做某事。We are about to go home.
We are about to send leaflets(宣传页).
5.练习题:
1). There __________ a meeting tomorrow afternoon.
A. will be going to
B. will going to be
C. is going to be
D. will go to be
2). Charlie ________ here next month.
A. isn’t working
B. doesn’t working
C. isn’t going to working
D. won’t work
3). He ________ very busy this week, he ________ free next week.
A. will be; is
B. is; is
C. will be; will be
D. is; will be
4). Mother ________ me a nice present on my next birthday.
A. will gives
B. will give
C. gives
D. give
5). –________ you ________ free tomorrow?
– No. I ________ free the day after tomorrow.
A. Are; going to; will
B. Are; going to be; will
C. Are; going to; will be
D. Are; going to be; will be
答案:CDDBD
七、过去将来时
1.通常用法:表示从过去某时看来将要发生的动作或状态。
2.常用时间状语:the next day、the next week.
3.构成:
1)should/would+动原,如:should/would work;
2)was/were going to+动原,如:was/were going to work;
3)was/were(about )to+动原,如:was/were(about) to work;
4)否定构成:
should/would not+动原,如:should/would not work;
was/were not...
5)一般疑问构成:
常用If或Whether引导宾语从句。
6)特殊疑问句举例:
He asked what they would the next week.
4.具体用法与一般将来时相似,但时间基点是“过去”,不再具体论述。
He said he would join us in playing basketball if he had time.
She was about to leave when the telephone rang.
He said he was going to have a try.
I told her that they were to hold a meeting the next day.
5.练习题:
1). Li Ming said he _____happy if Brian_____to China next month.
A. as; come
B. was; would come
C. would be; came
D. will be; come
2). Jenny said she _____her holiday in China.
A. spent
B. would spent
C. was going to spent
D. would spend
3). —What did your son say in the letter?
—He told me that he ______ the Disney World the next day.
A. will visit
B. has visited
C. is going to visit
D. would visit
4). I hoped Tina ______ to my birthday party on time the next Wednesday.
A. to come
B. is coming
C. will come
D. was coming
5). Father said that he ______ me to Beijing the next year.
A. took
B. would take
C. takes
D. will take
答案:CCDDB
八、现在完成时
1.通常用法:①表示在说话之前已经完成的动作,而且这个动作的结果对现在仍有影响;②表示过去已经开始而持续到现在的动作或状态;③说话之前发生的动作,这种动作多次发生,成为一种经验。
2.常用时间状语:already、just、never、before、recently、in the past few years、ever、so far、since+过去的点时间、for+段时间。
3.构成:
1)have/has + 过去分词,如:have/has worked;
2)否定构成:have/has not+ 过去分词,如:have/has not worked;3)一般疑问构成:
Have/Has +主语+过去分词....?
4)特殊疑问句举例:
What have you done recently?
How long has he lived in Shanghai?
4. 具体用法:
1)
2)表示动作发生在过去,但对现在有影响或联系。
He has gone to Hangzhou.(现在不在这里)
3)表示从过去某时起一直持续到现在的动作或状态。
We have studied English for ten years.
4)
5)表示迄今为止的某动作或状态的结局或总和。
This is the first time I’ve been here.
5.使用现在完成时需注意的几个问题:
1)
2)终止性动词不能和表示一段时间的状语连用。
不能连用的时间状语,如:yesterday,last week,five years ago,in 1980等。但可以和不确定的时间状语连用,如:ever、already、often、not...yet、once、twice等。
3)
4)have/has been to a place:去过某地(已回来);
5)
6)have/has gone to a place:已去某地(已动身走了,人不在说话现场)。
He has been to Beijing.(现在已回来,人不在北京)
He has gone to Beijing.(已动身走了,人不在此处,可能已到北京,也可能在去北京的路上)
6.练习题:
1)、Both his parents look sad . Maybe they ______what's happened to him .
A. knew
B. have known
C. must know
D.will know
2)、—______ you ___ your homework yet ?
—Yes . I _____ it a moment ago .
A.Did ; do ; finished
B.Have ; done ; finished
C.Have ; done ; have finished
D.will ; do ; finish
3)、Have you met Mr Li ______?
A. just
B. ago
C.before
D. a moment ago
4)、The famous writer _____ one new book in the past two year .
A. is writing
B.was writing
C.wrote
D.has written
5)、—Our country ______ a lot so far .
—Yes . I hope it will be even ______ .
A.has changed ; well
B.changed ; good
C.has changed ; better
D.changed ; better 答案:BBCDC
九、过去完成时
1.通常用法:表示在过去某一时间之前,或在过去某一动作发生,已经发生了或完成的动作(过去的过去)。
2.常用时间状语:by that time、by the end of...、when/before+从句、said/knew/asked+宾语从句。
3.构成:
1)had +过去分词,如:had worked;
2)否定构成:had not+过去分词,如:had not worked;
3)一般疑问构成:
Had+主语+过去分词+其它?Yes,I had./No,I hadn’t.
4)特殊疑问句举例:
How many English words had you learned by the end of last term?
4.具体用法:
1)表示在过去某时间之前发生的动作或状态(过去的过去)。
He suddenly remembered that he had left his key in the lab.
Tom had learned some Chinese before he came to China.
2)表示从过去某时间前起一直延续到过去这一时间的动作或状态。’By six o’clock we had worked for seven hours.
3)表示到过去某时间为止,某动作或状态的总结或总和。
That was the second time he had visited our school.
5.练习题:
1).He asked me __ _ during the summer holidays.
A. where I had been
B. where I had gone
C. where had I been
D. where had I gone
2). He ___ to play ____ before he was 11 years old.
A had learned, piano B. had learned, the piano
C. has learned, the piano
D. learns ,piano.
3). I _____ 900 English words by the time I was ten。
A. learned
B. was learning
C. had learned
D. learnt
4). The students ________ their classroom when the visitors arrived.
A . have cleaned B. had cleaned C. was cleaned D. have been cleaned
5. By the time my parents reached home yesterday, I _ _ the dinner already.
A had cooked B. cooked C. have cooked D. was cooked
答案:ABCBA
初中英语语法八大时态 1.结构 肯定句式: 主语+动词原形/动词的第三人称单数+其他 否定句式: 主语+(助动词)don't/doesn't +动词原形+其他 一般疑问句式: Do/Does+主语+动词原形+其他 简略回答: (肯)Yes,主语+do/does (否)No,主语+do/does not 缩写形式: don't = do not doesn't = does not 例句:He often goes swimming in summer. I usually leave home for school at 7 every morning. 2.用法 1)表示经常的、习惯性的动作或存在的状态,常与表示频度的副词连用。 常用的频度副词有:always、often、usually、seldom、never、sometimes, every week (day, year, month…), once a week, on Sundays.频度副词在句中通常放在行为动词之前,系动词、助动词之后。 例如: He often goes swimming in summer. I usually leave home for school at 7 every morning. 2)表示主语具备的性格、特征和能力等。 例如:All my family love football . My sister is always ready to help others . Ann writes good English but does not speak well. 3)表示客观真理、客观存在、自然现象。 例如:The earth moves around the sun. Shanghai lies in the east of China. 4)表示按计划或安排好的,或将要发生的动作,可用一般现在时表将来。 但只限于start,begin,leave,go,come,arrive,return,take place等。 例如:The train leaves at six tomorrow morning. He comes back tonight. 5)在复合句中,当主句是一般将来时,时间或条件状语从句的谓语动词只能用一般现在时来表示将来要发生的动作。 例如:I'll tell him the news when he comes back. If you take the job , they will talk with you in greater details. 1.结构 肯定句式: 主语+动词过去式+其他 否定句式: 主语+(助动词)didn’t +动词原形+其他 一般疑问句式: Did+主语+动词原形+其他
初中英语动词时态归纳总结对照表
初中英语时态专项练习 1、一般现在时。 通常用“usually, often, every day, sometimes”。 一般现在时基本用法介绍 一、一般现在时的功能 1.表示事物或人物的特征、状态。如:The sky is blue.天空是蓝色的。 2.表示经常性或习惯性的动作。如:I get up at six every day.我每天六点起床。
3.表示客观现实。如:The earth goes around the sun.地球绕着太阳转。 二、一般现在时的构成: 肯定句: 1).主语+系动词 be(is, am, are )+名词(形容词,介词短语) 2) .其他主语+动词原形+其它 第三人称单数+动词-s+其它 如:I am a boy.我是一个男孩。 We study English.我们学习英语。Mary likes Chinese.玛丽喜欢汉语。 三、一般现在时的变化 否定句:1)主语+ be (is,am,are)+ not +其它。如:He is not a worker.他不是工人。 2)其他主语+do not(don’t)动词原形+其它I don't like bread 第三人称单数+does not(doesn’t)动词原形+其它He doesn't often play. 一般疑问句:1)Be(Is,Are) +主语+其它?如:-Are you a student? -Yes. I am. / No, I'm not. 2)Do其他主语+动词原形+其它? Does+第三人称单数+动词原形+其它+? 注意:遇I/we—you, my—your, some—any.
英语语法大全 初中英语语法 学习提纲 一、词类、句子成分和构词法: 1、词类:英语词类分十种: 名词、形容词、代词、数词、冠词、动词、副词、介词、连词、感叹词。 1、名词(n.):表示人、事物、地点或抽象概念的名称。如:boy, morning, bag, ball, class, orange. :who, she, you, it . 主要用来代替名词。如): 2、代词(pron.3、形容词(adj..):表示人或事物的性质或特征。如:good, right, white, orange . 4、数词(num.):表示数目或事物的顺序。如:one, two, three, first, second, third, fourth. 5、动词(v.):表示动作或状态。如:am, is,are,have,see . 6、副词(adv.):修饰动词、形容词或其他副词,说明时间、地点、程度等。如:now, very, here, often, quietly, slowly. 7、冠词(art..):用在名词前,帮助说明名词。如:a, an, the. 8、介词(prep.):表示它后面的名词或代词与其他句子成分的关系。如in, on, from, above, behind. 9、连词(conj.):用来连接词、短语或句子。如and, but, before . 10、感叹词(interj..)表示喜、怒、哀、乐等感情。如:oh, well, hi, hello. 2、句子成分:英语句子成分分为七种:主语、谓语、宾语、定语、状语、表语、宾语补足语。 1、主语是句子所要说的人或事物,回答是“谁”或者“什么”。通常用名词或代词担任。如:I'm Miss Green.(我是格林小姐) 2、谓语动词说明主语的动作或状态,回答“做(什么)”。主要由动词担任。如:Jack cleans the room every day. (杰克每天打扫房间) 3、表语在系动词之后,说明主语的身份或特征,回答是“什么”或者“怎么样”。通常由名词、 代词或形容词担任。如:My name is Ping ping .(我的名字叫萍萍) 4、宾语表示及物动词的对象或结果,回答做的是“什么”。通常由名词或代词担任。如:He can spell the word.(他能拼这个词) 有些及物动词带有两个宾语,一个指物,一个指人。指物的叫直接宾语,指人的叫间接宾语。间接 宾语一般放在直接宾语的前面。如:He wrote me a letter . (他给我写了 一封信) 有时可把介词to或for加在间接宾语前构成短语,放在直接宾语后面,来强调间接宾语。如:He wrote a letter to me . (他给我写了一封信)
中考初中英语语法八大时态总结(附答案) 初中英语语法八大时态 1.结构 肯定句式: 主语+动词原形/动词的第三人称单数+其他 否定句式: 主语+(助动词) don't/doesn't +动词原形+其他 一般疑问句式: Do/Does+主语+动词原形+其他 简略回答: (肯)Yes,主语+do/does (否)No,主语+do/does not 缩写形式: don't = do not doesn't = does not 例句:He often goes swimming in summer. I usually leave home for school at 7 every morning. 2.用法 1)表示经常的、习惯性的动作或存在的状态,常与表示频度的副词连用。 常用的频度副词有: always、often、 usually、seldom、never、sometimes, every week (day, year, month…), once a week, on Sundays.频度副词在句中通常放在行为动词之前,系动词、助动词之后。 例如: He often goes swimming in summer. I usually leave home for school at 7 every morning. 2)表示主语具备的性格、特征和能力等。 例如:All my family love football . My sister is always ready to help others . Ann writes good English but does not speak well. 3)表示客观真理、客观存在、自然现象。 例如:The earth moves around the sun. Shanghai lies in the east of China. 4)表示按计划或安排好的,或将要发生的动作,可用一般现在时表将来。 但只限于start,begin,leave,go,come,arrive,return,take place等。 例如:The train leaves at six tomorrow morning. He comes back tonight. 5)在复合句中,当主句是一般将来时,时间或条件状语从句的谓语动词只能用一般现在时来表示将来要发生的动作。 例如: I'll tell him the news when he comes back. If you take the job , they will talk with you in greater details. 1.结构 肯定句式: 主语+动词过去式+其他 否定句式: 主语+(助动词)didn’t +动词原形+其他
英语语法大全 初中英语语法学习提纲 一、词类、句子成分和构词法: 1、词类:英语词类分十种: 名词、形容词、代词、数词、冠词、动词、副词、介词、连词、感叹词。 1、名词(n.):表示人、事物、地点或抽象概念的名称。如:boy, morning, bag, ball, class, orange. 2、代词(pron.):主要用来代替名词。如:who, she, you, it . 3、形容词(adj..):表示人或事物的性质或特征。如:good, right, white, orange . 4、数词(num.):表示数目或事物的顺序。如:one, two, three, first, second, third, fourth. 5、动词(v.):表示动作或状态。如:am, is,are,have,see . 6、副词(adv.):修饰动词、形容词或其他副词,说明时间、地点、程度等如:now, very, here, often, quietly, slowly. 7、冠词(art..):用在名词前,帮助说明名词。如:a, an, the. 8、介词(prep.):表示它后面的名词或代词与其他句子成分的关系。如in, on, from, above, behind. 9、连词(conj.):用来连接词、短语或句子。如and, but, before .
10、感叹词(interj..)表示喜、怒、哀、乐等感情。如:oh, well, hi, hello. 2、句子成分:英语句子成分分为七种:主语、谓语、宾语、定语、状语、表语、宾语补足语。 1、主语是句子所要说的人或事物,回答是“谁”或者“什么”。通常用名词或代词担任。如:I’m Miss Green.(我是格林小姐) 2、谓语动词说明主语的动作或状态,回答“做(什么)”。主要由动词担任。如:Jack cleans the room every day. (杰克每天打扫房间) 3、表语在系动词之后,说明主语的身份或特征,回答是“什么”或者“怎么样”。通常由名词、代词或形容词担任。如:My name is Ping ping .(我的名字叫萍萍) 4、宾语表示及物动词的对象或结果,回答做的是“什么”。通常由名词或代词担任。 如:He can spell the word.(他能拼这个词) 有些及物动词带有两个宾语,一个指物,一个指人。指物的叫直接宾语,指人的叫间接宾语。间接宾语一般放在直接宾语的前面。如:He wrote me a letter . (他给我写了一封信) 有时可把介词to或for加在间接宾语前构成短语,放在直接宾语后面,来强调间接宾语。如:He wrote a letter to me . (他给我写了一封信) 5、定语修饰名词或代词,通常由形容词、代词、数词等担任。如: Shanghai is a big city .(上海是个大城市)
一、一般现在时: 1. .概念:经常、反复发生的动作或行为及现在的某种状况。 2.用法 1).表示经常的或习惯性的动作,常与表示频率的时间状语连用。 2).表示主语具备的性格、能力、特征和状态 3).表示客观事实和普遍真理。 4).在时间状语从句和条件状语从句中,常用一般现在时代替将来时。 5)表示预先计划或安排好的行为。 6)表示格言或警句中。Pride goes before a fall. 骄者必败。 一般现在时常与下列时间状语连用:always, usually, often, s ometimes, every week (day, year, month…), once a week, on Sundays, He is always ready to help others. Action speaks louder than words. 3.基本结构:动词原形(如主语为第三人称单数,动词上要加- (e)s ) It seldom snows here. 4.否定形式:am/is/are+not;此时态的谓语动词若为行为动词,则在其前加don't,如主语为第三人称单数,则用doesn't,同时还原行为动词。 5.一般疑问句:把be动词放于句首;用助动词do提问,如主语为第三人称单数,则用does,同时,还原行为动词。 二、一般过去时: 1.概念:过去某个时间里发生的动作或状态;过去习惯性、经常性的动作、行为。 .基本结构: be动词(was/ were);行为动词的过去式;情态动词的过去式+动词原形 否定形式:was/were+not;在行为动词前加didn't,同时还原行为动词。
初中英语语法的八种时态的具体用法: 一般现在时表示现阶段经常或习惯发生的动作或存在的状态,或说明主语的特征。 ①一般现在时句子中常有的时间状语:often,usually,sometimes,always,every (day等), once/twice,a (week等), on (Sunday等),never,in the (morning等)。如:They go to the Palace Museum once a year.(他们每年去一次故宫)/ They often discuss business in the evening.(他们经常在晚上商谈生意) ②表示客观真理、事实、人的技能或现在的状态时句子里一般不用时间状语。如:The earth turns round the sun.(地球绕着太阳转)/ Light travels faster than sound.(光传播比声音快) ③表示十分确定会发生(如安排好的事情)或按照时间表进行的事情,用一般现在可以表达将来,句子中可以有将来时间。如:The train for Haikou leaves at 8:00 in the morning.(开往汉口的列车上午8点开车) ④在时间状语从句中(以when, after, before, while, until, as soon as等引导)和条件状语从句中(以if,unless引导),用一般现在时代替一般将来时,句子可以有将来时间。如:Please ring me up as soon as you arrive in Germany.(你一到德国就给我打电话) / If it rains tomorrow,we will have to stay at home.(如果明天下雨我们就只好呆在家) ⑤一般现在时用于倒装句中可以表示正在发生的动作,动词以come, go为主。如:Here comes the bus. (车来了) / There goes the bell.(铃响了)。 ⑥一般现在时常用于体育比赛的解说或寓言故事中。Now the midfield player catches the ball and he keeps it.
(1)一般现在时 基本形式(以do为例): 第三人称单数:does(主语为非第三人称单数); 肯定句:主语+动词原形+其他; He works for us. 否定句:主语+don‘t/doesn't+动词原形+其他; He doesn't work for us. 一般疑问句:Do/Does+主语+动词原形+其他。 肯定回答:Yes,(+主语+do/does). 否定回答:No,(+主语+don't/doesn't.) 特殊疑问句:疑问词+一般疑问句语 Does he work for us? Yes, he does. No, he doesn't What does he do for us? He works for us. (2)一般过去时 be动词+行为动词的过去式 否定句式:在行为动词前加didn‘t,同时还原行为动词,或was/were+not; was或were放于句首;用助动词do的过去式did提问,同时还原行为动词例如:Did he work for us? He didn't work for us. He worked for us. (3)一般将来时 am/are/is+going to+do 或 will/shall+do am/is/are/about to + do am/is/are to + do; 一般将来时的表达方法 be going to +动词原形 be +不定式,be to+动词原形,be about to +动词原形 be able to +不定式 be about to+动词原形 will + 动词原形; 例如:He is going to work for us.
初中英语语法大全汇总 (一) 一.词类(Parts of Speech) 名词英文名称The Noun(缩写为n.) 表示人或事物的名称例词boy,clock,book等 冠词英文名称The Article(缩写为art.) 用在名词前帮助说明名词所指的人和或事物。例词a(an),the 代词英文名称The Pronoun(缩写为pron) 用来代替名词、形容词或是数词例词we,that,his,what 形容词英文名称The Adjective(缩写为adj.) 用以修饰名词,表示人或事物的特征 例词old,red,fine,good. 数词英文名称The Numeral(缩写为num.) 表示数量或是顺序。例词one,thirteen first 动词英文名称The Verb(缩写为v.) 表示动作或状态。例词sit,go,be(am,is,are) 副词英文名称The Adverb(缩写为adv.) 修饰动词、形容词或其他副词。例词not too,here,very 介词英文单词The Preposition(缩写为prep.) 表示名词、代词等和句中其他词的关系。例词in,on,of,to,under. 连词英文单词The Conjunction(缩写为conj.) 用来连接词与词、短语与短语或句与句。例词and,or,but. 感叹词英文单词The Interjection(缩写为interj.) 表示说话时的喜悦、惊讶等情感。例词oh,hello,hi,er. 二.名词(Nouns) 1.总的说来,名词分专有名词和普通名词两类。 专有名词: 表示具体的人,事物,地点或机构的专有名称。 Lucy China 中国Asia 亚洲Beijing 北京。 专有名词的第一个字母要大写。 普通名词: 表示某些人,某类事物,某种物质或抽象概念的名称。例如: teacher 老师tea 茶reform 改革 普通名词又可进一步分为四类 1) 个体名称: 表示单个的人和事物。 house 马car 汽车room 房间apple 苹果fun 风扇picture 照片 2) 集体名称: 表示一群人或一些事物的名称。 people 人们family 家庭army 军队government 政府group 集团 3) 物质名词:表示物质或不具备确定形状和大小的个体的物质。 fire 火steel 钢air 空气water 水milk 牛奶 4)抽象名词:表示动作,状态,品质或其他抽象概念。 labour 劳动health 健康life 生活friendship友情patience耐力 2.名词按其所表现的事物的性质分为可数名词和不可数名词。 可数名词(Countable Nouns)有复数形式,如: an apple two apples a car some cars 不可数名词(Uncountable Nouns)一般没有复数形式. 抽象名词, 物质名词和专有名词一般是不可数名词。 sand 沙sugar 糖 有少数名词即可作可数名词,也可作不可数名词,但含义不同。 glass 玻璃glass 玻璃杯paper 纸paper 报纸,文件 名词的功能 名词在句中作主语, 宾语,介词宾语,宾语补助语,表语以及名词短语作状语。 The bag is in the desk. bag 作主语。 书包在桌子里边。 I washed my clothes yesterday. clothes 作宾语。 昨天我洗了我的衣服。
一、选择题 1.--Look! Someone the classroom. --Well,it wasn't me. I didn't do it. A.is cleaning B.was cleaning C.has cleaned D.will clean 2.—Mom, can you teach me how to pronounce the words? —Wait a minute. I ________. A.am cooking B.cook C.cooked D.will cook 3.— Look at my new watch. —Well, it’s so cool! When and where________you buy it? A.Do B.will C.did D.Are 4.Boys and girls, there ________an English speech competition in two weeks. A.will have B.has C.is going to be D.are going to be 5.Wang Wei often ________ TV on Sunday evenings, but now he is _______ stories. A.watches; reading B.watching; reads C.looks; reading D.watches; looking 6.It’s 4:00 p.m. The students _____ in the pool. A.swim B.swam C.swims D.are swimming 7.I like this dress very much. It soft and smooth. A.feels B.touches C.is felt D.is touched 8.My mother will be very angry with me when she out where I have been. A.finds B.found C.will find D.has found 9.—________ a remake (翻拍) of the famous Disney movie Lion King in July, 2019. — Really? I can't wait to see it. A.There will have B.There is going to have C.There will be 10.Sorry, Jenny isn’t here. She________ up some lights in the garden. A.put B.puts C.is putting D.has put 11.—I called you at three yesterday afterno on, but you weren’t in. —I ________ a meeting at that time. A.had B.was having C.have had D.would have 12.—How long can I _____ the English workbook? —For two weeks. A.borrow B.to borrow C.keep D.to keep 13.— Could you please tell me yesterday? — In the bookshop nearby. A.Where you bought the book B.Where you buy the book C.Where did you buy the book D.Where do you buy the book 14.— Have you ever been anywhere for a trip? — A trip? I ________ away from my hometown even once. A.went B.have gone C.have been D.have never been
资料收集于网络,如有侵权请联系网站删除 1 (see 、hear 、notice 、find 、feel 、listen to 、look at (感官动词)+do eg:I like watching monkeys jump 2 (比较级and 比较级)表示越来越怎么样 3 a piece of cake =easy 小菜一碟(容易) 4 agree with sb 赞成某人 5 all kinds of 各种各样a kind of 一样 6 all over the world = the whole world 整个世界 7 along with同……一道,伴随…… eg : I will go along with you我将和你一起去 the students planted trees along with their teachers 学生同老师们一起种树 8 As soon as 一怎么样就怎么样 9 as you can see 你是知道的 10 ask for ……求助向…要…(直接接想要的东西)eg : ask you for my book 11 ask sb for sth 向某人什么 12 ask sb to do sth 询问某人某事ask sb not to do 叫某人不要做某事 13 at the age of 在……岁时eg:I am sixteen I am at the age of sixteen 14 at the beginning of …… ……的起初;……的开始 15 at the end of +地点/+时间最后;尽头;末尾eg : At the end of the day 16 at this time of year 在每年的这个时候 17 be /feel confident of sth /that clause +从句感觉/对什么有信心,自信 eg : I am / feel confident of my spoken English I feel that I can pass the test 18 be + doing 表:1 现在进行时2 将来时 19 be able to (+ v 原) = can (+ v 原)能够…… eg : She is able to sing She can sing 20 be able to do sth 能够干什么eg :she is able to sing 21 be afraid to do (of sth 恐惧,害怕…… eg : I'm afraed to go out at night I'm afraid of dog 22 be allowed to do 被允许做什么 eg: I'm allowed to watch TV 我被允许看电视I should be allowed to watch TV 我应该被允许看电视 23 be angry with sb 生某人的气eg : Don't be angry with me 24 be angry with(at) sb for doing sth 为什么而生某人的气 25 be as…原级…as 和什么一样eg : She is as tall as me 她和我一样高 26 be ashamed to 27 be away from 远离 28 be away from 从……离开 29 be bad for 对什么有害eg : Reading books in the sun is bad for your eyes 在太阳下看书对你的眼睛不好 30 be born 出生于 31 be busy doing sth 忙于做什么事be busy with sth 忙于…… 32 be careful 当心;小心 33 be different from…… 和什么不一样 34 be famous for 以……著名
初中英语语法总结 ( 动词的时态) 11.1 一般现在时的用法 1)经常性或习惯性的动作,常与表示频度的时间状语连用。时间状语:every…, sometimes, at…, on Sunday。例如: I leave home for school at 7 every morning. 每天早上我七点离开家。 2)客观真理,客观存在,科学事实。例如: The earth moves around the sun. 地球绕太阳转动。 Shanghai lies in the east of China. 上海位于中国东部。 3)表示格言或警句。例如: Pride goes before a fall. 骄者必败。 注意:此用法如果出现在宾语从句中,即使主句是过去时,从句谓语也要用一般现在时。例:Columbus proved that the earth is round. 哥伦布证实了地球是圆的。 4)现在时刻的状态、能力、性格、个性。例如: I don't want so much. 我不要那么多。 Ann writes good English but does not speak well. 安英语写得不错,讲的可不行。 比较:Now I put the sugar in the cup. 把糖放入杯子。 I am doing my homework now. 我正在做功课。 第一句用一般现在时,用于操作演示或指导说明的示范性动作,表示言行的瞬间动作。第二句中的now是进行时的标志,表示正在进行的动作的客观状况,所以后句用一般现在时。11.2 一般过去时的用法 1)在确定的过去时间里所发生的动作或存在的状态。例如:时间状语有:yesterday, last week, an hour ago, the other day, in 1982等。例如: Where did you go just now? 刚才你上哪儿去了? 2)表示在过去一段时间内,经常性或习惯性的动作。例如: When I was a child, I often played football in the street. 我是个孩子的时候,常在马路上踢足球。 Whenever the Browns went during their visit, they were given a warm welcome.
初中英语八种时态归纳总结 时态是英语学习中一个至关重要的内容,初中学生在实际运用时,往往对时态总是倍感棘手,下面我们就归纳一下这几种时态。 一、一般现在时: 概念:经常、反复发生的动作或行为及现在的某种状况。 时间状语: always, usually, often, sometimes, every week (day, year, month…), once a week, on Sundays, etc. 基本结构:①主语+ be动词+ 其他;②主语+ 行为动词+ 其他 否定形式:①主语+ am/is/are + not + 其他;②此时态的谓语动词若为行为动词,则在其前加don't,主语为第三人称单数,则用doesn't,同时还原行为动词。 一般疑问句:①把be动词放于句首;②用助动词do提问,如主语为第三人称单数,则用does,同时还原行为动词。 二、一般过去时: 概念:过去某个时间里发生的动作或状态;过去习惯性、经常性的动作、行为。 时间状语:ago, yesterday, the day before yesterday, last week(year, night, month…), in 1989, just now, at the age of 5, one day, long long ago, once upon a time, etc. 基本结构:①主语+ be动词+ 其他;②主语+ 行为动词+ 其他 否定形式:①主语+ was/were + not + 其他;②在行为动词前加didn't,同时还原行为动词。 一般疑问句:①was或were放于句首;②用助动词do的过去式did 提问,同时还原行为动词。 三、现在进行时: 概念:表示现阶段或说话时正在进行的动作及行为。 时间状语:now, at this time, these days, etc. 基本结构:主语+ am/is/are + doing + 其他. 否定形式:主语+ am/is/are + not + doing + 其他. 一般疑问句:把be动词放于句首。 四、过去进行时: 概念:表示过去某段时间或某一时刻正在发生或进行的行为或动作。 时间状语:at this time yesterday, at that time或以when引导的谓语动词是一般过去时的时间状
初中英语语法八大时态 一.一般现在时 1.结构 肯定句式: 主语+动词原形/动词的第三人称单数+其他 否定句式: 主语+(助动词)don't/doesn't +动词原形+其他 一般疑问句式: Do/Does+主语+动词原形+其他 简略回答: (肯)Yes,主语+do/does (否)No,主语+do/does not 缩写形式: don't = do not doesn't = does not 例句:He often goes swimming in summer. I usually leave home for school at 7 every morning. 2.用法 1)表示经常的、习惯性的动作或存在的状态,常与表示频度的副词连用。 常用的频度副词有:always、often、usually、seldom、never、sometimes, every week (day, year, month…), once a week, on Sundays.频度副词在句中通常放在行为动词之前,系动词、助动词之后。 例如: He often goes swimming in summer. I usually leave home for school at 7 every morning. 2)表示主语具备的性格、特征和能力等。 例如:All my family love football . My sister is always ready to help others . Ann writes good English but does not speak well. 3)表示客观真理、客观存在、自然现象。 例如:The earth moves around the sun. Shanghai lies in the east of China. 4)表示按计划或安排好的,或将要发生的动作,可用一般现在时表将来。 但只限于start,begin,leave,go,come,arrive,return,take place等。 例如:The train leaves at six tomorrow morning. He comes back tonight. 5)在复合句中,当主句是一般将来时,时间或条件状语从句的谓语动词只能用一般现在时来表示将 来要发生的动作。 例如:I'll tell him the news when he comes back. If you take the job , they will talk with you in greater details. 二.一般过去时态 1.结构 肯定句式: 主语+动词过去式+其他 否定句式: 主语+(助动词)didn’t +动词原形+其他 一般疑问句式: Did+主语+动词原形+其他 简略回答: (肯)Yes,主语+did (否)No,主语+did not 基本结构否定句一般疑问句
初中英语语法---时态归纳 动词时态的句子结构及关键词 动词时态的句子结构及关键词: 一般现在时: 句子结构: 肯定句主语+be (am, is, are ) + 其他 否定句主语+be not +其他 疑问句Be+主语+其他 或: 肯定句主语+动词原型+其他( 第三人称单数作主语动词要加"s" ) 否定句主语+don't+动词原型+其他(第三人称单数作主语don't改为doesn't) 疑问句DO+主语+动词原型+其他(第三人称单数作主语do改为doess) 关键词: sometimes, often, usually, always, every day, on Sunday afternoon, at 10 o'clockin the morning, five days a week, three times a month等. 注:在时间壮语从句,条件壮语从句中,常用一般现在时表示将来时,这时一般从句用一般现在时,主句用将来时
现在进行时: 句子结构:肯定句主语+be +动词的现在分词+其他 否定句主语+be not+动词的现在分词+其他 疑问句Be +主语+动词的现在分词+其他 关键词:now, right now, at the moment, It's+几点钟等的句子.或look, listen, keep quiet等提示语. 一般将来时: 句子结构: 肯定句主语+will+动词原型+其他 否定句主语+will not +动词原型+其他 疑问句Will +主语+动词原型+其他 (will 可改为be going to ,当主语是第一人称时will可用shall) 关键词:tomorrow, tomorrow morning, at seven o'clock tomorrow evening, next year, at ten o'clock next Sunday, this year, at the end of this term, from now on, in the year 2008, soon, in a few days' time, in the future 等.
初中英语八种时态总结归纳 一、大凡现在时: 概念:经常、反复发生的动作或行为及现在的某种状况。 时间状语:often,usually,always,sometimes,everyweek(day,year,month...),once a week,on sundays,etc. 基本结构:①be动词;②行为动词 否定形式:①am/is/are+not;②此时态的谓语动词若为行为动词,则在其前加don“t,如主语为第三人称单数,则用doesn“t,同时还原行为动词。 大凡疑问句:①把be动词放于句首;②用助动词do提问,如主语为第三人称单数,则用does,同时,还原行为动词。 二、大凡过去时: 概念:过去某个时间里发生的动作或状态;过去习惯性、经常性的动作、行为。 时间状语:ago,yesterday,the day before yesterday,last week(year,night,month...),in 1989,just now,at the age of 5,one day,long long ago,once upon a time,etc.基本结构:①be动词;②行为动词 否定形式:①was/were+not;②在行为动词前加didn“t,同时还原行为动词。 大凡疑问句:①was或were放在句首;②用助动词do的过去式did提问,同时还原行为动词。 三、现在进行时: 概念:表示现阶段或说话时正在进行的动作及行为。 时间状语:now,at this time,these days,etc. 基本结构:am/is/are+doing
否定形式:am/is/are+not+doing 大凡疑问句:把be动词放在句首 四、过去进行时: 概念:表示过去某段时间或某一时刻正在发生或进行的行为或动作。 时间状语:at this time yesterday,at that time或以when引导的谓语动词是大凡过去时的时间状语等。 基本结构:was/were+doing 否定形式:was/were+not+doing 大凡疑问句:把was或were放在句首 五、现在完成时: 概念:过去发生或已经完成的动作对现在造成的影响或结果,或从过去已经开始,持续到现在的动作或状态。 时间状语:recently,lately,since...,for...,in the past few years,etc. 基本结构:have/has+done 否定形式:have/has+not+done 大凡疑问句:have/has放于句首 六、过去完成时: 概念:以过去某一时间为标准,在此以前发生的动作或行为,或在过去某动作之前完成的行为,即“过去的过去”。 时间状语:before,by the end of last year(term,month...),etc. 基本结构:had+done