电力系统外文翻译
- 格式:docx
- 大小:27.59 KB
- 文档页数:7


power output 功率输出,输出功率power output 功率输出,输出功率short circuita great deal 大量ac交流(电)admittance 导纳amp安培amp安培amplitude振幅arc电弧,弧光arise from 起于,由...出身armature电木区armature winding 电枢绕组arrangement布置,排列;设备,装置;安装,装配;置配;安排arrangement布置,排列;安装,装配;assemblage 与会者(集合称),集合,集会,装配assume假定,设想,采取,呈现automatic voltage regulator自动电压调节器,自动稳压器,自动调压器autotransformer 自耦变压器backup protection后备保护,后备保护装置block 组[件],单元,部件;机组,单元机组;滑轮;字组,块,程序块,数据块break down 毁掉,制服,压倒,停顿,倒塌,中止,垮掉,分解bus bar汇流条,母线bus impedance matrix 母线阻抗矩阵,节点阻抗矩阵bus impedance matrix 母线阻抗矩阵,节点阻抗矩阵busbar母线,汇流条,结点,节点,汇流排bushing [电工]套管capacitor bank 电容器组carrier protection载波保护,高频保护carrier relaying 载波继电保护,高频保护,载波中继[制]carry 携带,搬运,传送,传播;支持,执行,进位,进列changing 转换charging currents 充电电流circuit breaker [电工]断路开关,断路器Circuit breaker 电路断路器circuit layout电路布线,线路布置circuit-breaker〈电〉断路器,断路开关circuit-breaker〈电〉断路器,断路开关clearing time通信连络断开时间,电话的话终时间clearing time通信连络断开时间,电话的话终时间combine with 与…结合come into 得到communication circuit 通讯电路conductance [电工]电导,导率,电导系数contact 接触contact (电流的)接触;接通;接触器core loss current 铁耗电流core type 铁心式(变压器)critical point 临界点cross-sectional 横截[断]面current density 电流密度current flow 电流current transformator变流器,电流互感器 cut-and-try method 渐近法,试探法Cycle 循环、周期、周波cylindrical rotor [电]鼓形转子,隐极转子damage 损害,伤害,损伤,破坏,损坏;事故,故障damp 阻尼,减幅,衰减damper winding阻尼绕组de-剥夺,分离 断开,去能,去激励;断电 断开,断电 不赋能的,除去电源的,去激励的demagnetizing effect :消磁效果;去磁效应;消磁作用401丽皿0导数401丽皿0导数desired 期待的desired value 期待值,给定值,预定值,所需值,预期值detection 察觉,发觉,侦查,探测,发现determine 确定:在考虑,调查或计算之后,决定性地确认参见控制,限制development stage 发展阶段dielectric 电介质,绝缘体dielectric loss 介电损失differential protection 差动保护[装置]differential relay 差动继电器differentiate 求…的微分:计算导数或(函数的)微分difficulty 困难:困难的环境或程序:The condition or quality of being difficult:developed power 发出功率deenergizede-energizede-energized digital computer )direct proportiondirectional relaydirect-wire circuitdisconnect switch数字计算机正比例,正比方向继电器,定向继电器单线线路隔离刀闸隔离开关 调度,迅速处理,输送,发运,发货 调度,迅速处理,输送,发运,发货distance relay 距离继电器distribution substation 配电站distribution transformer 配电变压器 disturbance 扰动 double-breaker 双断开关double-bus双母线dynamic performance 动态特性 dynamic system performance 系统动态运行特性economic dispatch 经济调度economic dispatch 经济调度economic dispatch 经济调度economic planning 经济计划 eddy curren 涡流,涡电流 eddy current 涡流,涡电流 electrical contact 电连接,电接点,电触点,电触头electromagnetic 电磁的 emf 电动势 energize 给与...电压 energize 使带电流;使通电 energy 热能源,电能:可用的热量或能量: energy 热能源,电能:可用的热量或能量 engine 发动机,机械,机器,引擎,工具 engine-driven generator [发动]机[驱]动的发电机 equivalent circuit 等效电路 excess load 过载,过负荷,超载,过荷载 fault detection 故障检验 feature 要素 feed water 锅炉给水field winding 激励绕组,励磁绕组,场绕组 flux 磁通focal point 焦点force outage 事故停用,强迫停机,强制停机 force outage 事故停用,强迫停机,强制停机 fraction 【数学】分数:表明两个量的商的表达式 ft (foot, feet )英尺 fuel cost 燃料费 fuel cost 燃料费 fuel input 燃料加入(量) fuel input 燃料加入(量) full load 满载,满负荷 fundamental 【物理学】基波的: Gauss-Seidel method 高斯-塞德尔法(潮流计算的) Gauss-Seidel procedure 高斯-塞德尔法generating plant 发电厂,电厂,电站,发电设备 generating system 发电系统 generation 产生;代;发电,发生,振荡,改进阶段generation schedule 发电计划 gradient approachgradient approach 梯度方法ground current 大地电流ground relay 接地继电器 ground relaying接地继电保护 guard against 提防,预防harmonic 谐波head (水站等的)蓄水高度,水头,落差,压力;势头high-speed reclosure 快速重合闸horizontal axis 水平轴线disconnected switchdispatch 发送,horizontal axis 水平轴线hydroelectric水力发电的hysteresis 磁滞hysteresis滞后作用,[物]磁滞现象identical【数】恒等的impedance [电]阻抗,全电阻,[物]阻抗in any case 无论如何in phase adv.同相地in terms of 根据,按照,用…的话,在…方面in the case of 在…的情况incremental cost 边际成本incremental cost 边际成本incremental cost curveincremental cost curveincremental generating cost 发电成本增量incremental generating cost 发电成本增量inductive 电感性的,电感的,感应的;吸入的inductive circuit 有感电路,电感电路,感性电路inflammable 易燃的inflammable liquid 易燃液(体)injection current 注入电流instantaneous relay 瞬动继电器(电流速断保护)instantaneous value 瞬时值instrument transformator 仪表用互感器instrument transformator 仪表变压器insulation breakdown 绝缘击穿insulation deterioration 绝缘老化insulation failure 绝缘事故,绝缘损坏insure against 给...保险interconnected electric power system 互联电力系统internal voltage 内电压,电动势internal voltage 电动势,内电压internal voltage 内电压,电动势(发电机的),反电动势(电动机的) inverse time 反时,逆时inverse time current protection 反时限[过]电流保护[装置]inverse time relay 反时限继电器inverse-time definite-time limit relay 逆时定时限继电器,定时限反时继电器ionize 电离ionize 电离it follows that由此得出结论…,因而断定…key diagram 原理草图,工作图know-how >实际知识,技术秘诀,诀窍lagging current 滞后电流layout 设计,布置,规划;草图,布置图,线路图;排列;layout diagram 布置图layout drawing 布置图,配线图,定位图leakage flux 漏通量leakage inductance 漏电感lightning 闪电lightning arrester 避雷器limit界限,限度,限制line conductor 导线line flashover 线路闪络line terminal线路线端,线路终端line trap线路陷波器,阻波器line-to-line 两线间的,相间的,线间短路live 有电的,带电的,活动的,正极接地的load characteristic 负荷特性,负载特性load factor 负载系数long-range 远大的,长期的loop system 环形线路制,闭环系统;回路系统m.m.f 磁动势magnetize vt 使磁化magnetizing current 磁化电流,起磁电流maximum power transfer 最大传输功率mechanical stress 机械应力memory capacity 存储容量motor starter 电动机起动器multi-winding transformer 多绕组变压器mutual coupling 互耦mutual flux 互(感)磁通mutual impedance 互阻抗navigation 航海,航空,导航,领航,航行navigation 航运negative damping 负阻尼network system 网络系统,供电网系统neutral conductor 中性导线Newton-Raphson牛顿-拉夫逊nodal admittance matrix 节点导纳矩阵normal load 额定负荷,正常负载normal-voltage 正常电压Norton's theorem诺敦定理,等值电流源定理offset wave 偏移波open 开的,敞开的,打开,断路,断开,公开的,断路的open-circuit 开路的open-circuit voltage 开路电压,空载电压operating coil动作线圈,工作线圈operating frequency 工作频率,操作频率,运行频率operating range 运转范围,工作范围,作用距离,作用半径,(堆功率)运行区段out of 与…不相宜,不相称,在…范围,缺乏,放弃outage 断电output power 输出功率over-current 过电流overflash闪络,飞弧Overhead line 架空线over-load超过负荷over-voltage 过电压parallel resonance 并联谐振parallel resonance 并联谐振permeable 可渗透的,能透过的phase displacement 相(位)移phase displacement 相(位)移phase displacement 相位移phase shift 周相移动phase shifters 移相器phase-angle 相角;相位角,相移角;相(位)角phase-angle 相角;相位角,相移角;相(位)角phase-comparison 相位比较phase-displacementphase-to-ground 相对地pick-up current 接触电流,起动电流,拾音器电流planner 规划人员plunger relay插棒式继电器,螺管式继电器polarity 极性pondage power plant 抽水蓄能电站positive sequence network 正序网路potential transformator电压互感器,测量用变压器power circuit 电源电路,电力电路;动力线路,电力网,电力线路,电源线路power flow 电力潮流、功率潮流、功率通量,能流power level 功率级,[功率]电平;功率水平power line 动力线,动力网,电力线,电源线,输电线power swing功率波动,功率摆动,功率摇摆power transfer功率传输,电和输送power transfer 功率传输,电力传送power transfer 功率传输,电力传送power transformator 电源[电力,功率]变压器prefault 故障前的primary grid substation 主网变电站prime mover 原动力,发动者prime mover 原动力,发动者problem问题:应该考虑、解决或回答的问题:protective relay 保护继电器protruding-pole 凸极public hazard 公害pumped storage station 提水蓄能站pumped storage station 抽水蓄能电站quadratic formula 二次公式radial system 辐射状配电制,径向配电制radian 弧度rate current 反应[额定]电流reactance 电抗reactance drop 电抗电压下降reactive power 无功功率real number [数]实数rectification 整流regulate管制,控制,调节,校准relative movement 相对运动relative position 相对位置relative position 相对位置relay继电器relay element继电器元件relay inverse time继电器反时限特性relay system 继电保护系统reluctance 【物理学】磁阻:reservoir水库,蓄水池resistance 电阻resistance drop 电阻(性电)压降resistivity电阻系数resistor [电]电阻器ring bus 环形母线rpm每分钟转数run-off-river station 径流式水电厂,河流式水电厂run-of-the -riversalient pole rotor 凸极转子saturation饱和度scheme方案,线路图,电路,图表,图解,计划,线路,路,设计图,规划secondary substation 二次变电所sensor 传感器sequence component 序分量sequential tripping顺序脱扣,顺序跳闸series capacitor 串联电容器,附加电容器(仪表)series capacity串联电容series inductance 串联电感setting 装配,调整,炉墙,支座,调节,置位,装定,整定值,起动,装置,设置short-cut 短路,捷路,简化side effect 副作用single-busbar system 单母线系统single-pole switch单极开关,单刀开关sinusoidal 正弦曲线slope 【数学】斜率:slope 【数学】斜率:solid insulation 固体绝缘solid insulation 固体绝缘sparse matrix 稀疏矩阵specific loading 单位负载,比负载,比负荷specification详述,规格,说明书,规范specified load 额定负荷,设计负荷,规定负荷,标准荷载specify把…列为条件,规定,指定,确定;详细说明,具体说明squirrel cage 鼠笼stability limit 稳定极限,稳定限度,稳定度极限steady-state 稳定工况,稳定状态,稳恒状态,静态,稳态steady-state stability 稳态steam trap 凝汽阀steam turbine蒸汽轮机steam turbine 汽轮机steam valve 蒸汽阀step down 降低,降压step-type voltage regulator 分级式电压调整器step-up 升压,升高,加速step-up substation 升压变电站stir up 激起,鼓动,煽动stray flux杂散磁通Stray loss杂散损耗substation transformator 配电变压器subtransient 次暂态suffer from 忍受,遭受susceptance 电纳(导纳的虚数分量swing 摆动,动荡,摆度,振幅,摆幅switchboard 配电盘,配电屏;配电板,switching 开关switching 开关,开闭,转接,切换,换向,整流switching surge 操作过电压synchronous condenser 同步调相机synchroscope同步指示器,同步示波器system design 系统设计system layout 系统布置system reliability 系统可靠性system reliability 系统可靠性tapped抽头的;分接的;带向分接头的,带分接头的term [数学]项:terminal voltage 端电压Thevenin theory 戴维宁理论throttle setting节流阀调整time delay relay 延时继电器,缓动继电器time setting 时间整定timer 计时器,定时器,时间发送器,时间继电器,延时调节器;程序装置torque 扭矩,转矩transfer bus 切换母线transfer传递,传送,输送;转换,转移;调动,变换;传输,传导,迁移;进位transformer bank 变压器组transformer bushing 变压器套管transformer bushing 变压器套管transformer tap 变压器分接头transient stability 瞬态[暂]态稳定性transmission capacity 输电能力,输电量transmission capacity 输电能力,输电量transmission capacity 输电能力,输电量transmission line 输电线transmission line 输电线,输电线路;谐振线transmission system 传动系统,输电系统,传输系统,发射系统transmitting capacity 输电能力;传输能力,发送能力traveling wave 行波trial and error method 试凑法,尝试法,逐次逼近法,试探,试配,试错trial-and-error 尝试法[的],逐步逼近[法]tune谐调turbine 涡轮turbo 涡轮(发动机)unit transformer 单元[机组]变压器unity power factor [电]整功率因数valve 阀,valving设置阀门;[阀门]关闭voltage drop 电压降落voltage rate 电压比voltage rating额定电压 电压调整器,电压调节器,稳压器,调压器 电压调整、电压调整率、电压变动率 电压调整器,电压调节器,稳压器,调压器 电压传感器 voltage transformation 变压water storage reservoir 水库water turbine 水轮机 wave shape 波形 wave shape 波形 wrap around 卷绕的,环绕的 zero sequence 零[相]序,零序 voltage regualator voltage regulation voltage regulator voltage sensor。

电力系统powersystem发电机generator励磁excitation励磁器excitor电压voltage电流current升压变压器step-uptransformer母线bus变压器transformer空载损耗no-loadloss铁损ironloss铜损copperloss空载电流no-loadcurrent有功损耗activeloss无功损耗reactiveloss输电系统powertransmissionsystem 高压侧highside输电线transmissionline高压highvoltage低压lowvoltage中压middlevoltage功角稳定anglestability稳定stability电压稳定voltagestability暂态稳定transientstability 电厂powerplant能量输送powertransfer交流AC直流DC电网powersystem落点droppoint开关站switchstation调节regulation高抗highvoltageshuntreactor 并列的apposable裕度margin故障fault三相故障threephasefault 分接头tap切机generatortriping高顶值highlimitedvalue 静态staticstate动态dynamicstate机端电压控制AVR电抗reactance电阻resistance功角powerangle有功功率activepower电容器Capacitor电抗器Reactor断路器Breaker电动机motor功率因数power-factor定子stator阻抗impedance功角power-angle电压等级voltagegrade有功负载:activeloadPLoad无功负载reactiveload档位tapposition电阻resistor电抗reactance电导conductance电纳susceptance上限upperlimit下限lowerlimit正序阻抗positivesequenceimpedance 负序阻抗negativesequenceimpedance 零序阻抗zerosequenceimpedance无功功率reactivepower功率因数powerfactor无功电流reactivecurrent斜率slope额定rating变比ratio参考值referencevalue电压互感器PT分接头tap仿真分析simulationanalysis 下降率drooprate传递函数transferfunction框图blockdiagram受端receive-side同步synchronization保护断路器circuitbreaker摇摆swing阻尼damping无刷直流电机BruslessDCmotor 刀闸隔离开关Isolator机端generatorterminal变电站transformersubstation永磁同步电机Permanent-magnetSynchronismMotor异步电机AsynchronousMotor三绕组变压器three-columntransformerThrClnTrans 双绕组变压器double-columntransformerDblClmnTrans 固定串联电容补偿fixedseriescapacitorcompensation 双回同杆并架double-circuitlinesonthesametower单机无穷大系统onemachine-infinitybussystem励磁电流Magnetizingcurrent补偿度degreeofcompensation电磁场:Electromagneticfields失去同步lossofsynchronization装机容量installedcapacity无功补偿reactivepowercompensation故障切除时间faultclearingtime极限切除时间criticalclearingtime强行励磁reinforcedexcitation并联电容器shuntcapacitor<下降特性droopcharacteristics线路补偿器LDClinedropcompensation电机学ElectricalMachinery自动控制理论AutomaticControlTheory电磁场ElectromagneticField微机原理PrincipleofMicrocomputer电工学Electrotechnics电路原理Principleofcircuits电机学ElectricalMachinery电力系统稳态分析Steady-StateAnalysisofPowerSystem电力系统暂态分析Transient-StateAnalysisofPowerSystem电力系统继电保护原理PrincipleofElectricalSystem'sRelayProtection电力系统元件保护原理ProtectionPrincipleofPowerSystem'sElement 电力系统内部过电压PastVoltagewithinPowersystem模拟电子技术基础BasisofAnalogueElectronicTechnique数字电子技术DigitalElectricalTechnique电路原理实验电气工程讲座Lecturesonelectricalpowerproduction电力电子基础Basicfundamentalsofpowerelectronics高电压工程Highvoltageengineering电子专题实践Topicsonexperimentalprojectofelectronics 电气工程概论Introductiontoelectricalengineering电子电机集成系统Electronicmachinesystem电力传动与控制ElectricalDriveandControl电力系统继电保护PowerSystemRelayingProtection主变压器maintransformer升压变压器step-uptransformer降压变压器step-downtransformer工作变压器operatingtransformer备用变压器公用变压器commontransformer三相变压器three-phasetransformer单相变压器single-phasetransformer带负荷调压变压器on-loadregulatingtransformer 变压器铁芯transformercore变压器线圈transformercoil变压器绕组transformerwinding变压器油箱transformeroiltank变压器外壳变压器风扇transformerfan变压器油枕transformeroilconservator∽drum 变压器额定电压transformerretedvoltage变压器额定电流transformerretedcurrent变压器调压范围transformervoltageregulationrage 配电设备powerdistributionequipmentSF6断路器SF6circuitbreaker开关switch按钮button隔离开关isolator,disconnector 真空开关vacuumswitch刀闸开关knife-switch接地刀闸earthingknife-switch 电气设备electricalequipment 变流器currentconverter电流互感器currenttransformer电压互感器voltagetransformer电源powersource交流电源ACpowersource 直流电源DCpowersource 工作电源operatingsource 备用电源Standbysource 强电strongcurrent 弱电weakcurrent继电器relay信号继电器signalrelay电流继电器currentrelay电压继电器voltagerelay跳闸继电器trippingrelay合闸继电器closingrelay中间继电器intermediaterelay时间继电器timerelay零序电压继电器zero-sequencevoltagerelay 差动继电器differentialrelay闭锁装置lockingdevice遥控telecontrol遥信telesignalisation遥测telemetering遥调teleregulation断路器breaker,circuitbreaker少油断路器mini-oilbreaker,oil-mini-mumbreaker 高频滤波器high-frequencyfilter组合滤波器combinedfilter常开触点normallyopenedcontaact常闭触点normallyclosedcontaact 并联电容parallelcapacitance保护接地protectiveearthing熔断器cutout,fusiblecutout 电缆cable跳闸脉冲trippingpulse合闸脉冲closingpulse一次电压primaryvoltage二次电压secondaryvoltage并联电容器parallelcapacitor无功补偿器reactivepowercompensationdevice 消弧线圈arc-suppressingcoil母线Bus,busbar三角接法deltaconnection星形接法Wyeconnection原理图schematicdiagram一次系统图primarysystemdiagram二次系统图secondarysystemdiagram两相短路two-phaseshortcircuit三相短路three-phaseshortcircuit单相接地短路single-phasegroundshortcircuit短路电流计算calculationofshortcircuitcurrent 自动重合闸automaticreclosing高频保护high-freqencyprotection距离保护distanceprotection横差保护transversedifferentialprotection 纵差保护longitudinaldifferentialprotection 线路保护lineprotection过电压保护over-voltageprotection母差保护busdifferentialprotection 瓦斯保护Buchholtzprotection变压器保护transformerprotection电动机保护motorprotection远方控制remotecontrol用电量powerconsumption载波carrier故障fault选择性selectivity速动性speed灵敏性sensitivity可靠性reliability电磁型继电器electromagnetic无时限电流速断保护instantaneouslyover-currentprotection 跳闸线圈tripcoil工作线圈operatingcoil制动线圈retraintcoil主保护mainprotection后备保护back-upprotection定时限过电流保护definitetimeover-currentprotection 三段式电流保护thecurrentprotectionwiththreestages 反时限过电流保护inversetimeover-currentprotection 方向性电流保护thedirectionalcurrentprotection零序电流保护zero-sequencecurrentprotection阻抗impedance微机保护MicroprocessorProtection。

1FACTS : 柔性交流输电系统Flexible AC TransmissionAC: alternating current Power system:电力系统telecontrol:远动GIS :Gas lnsulated Switchgear全封闭组合电器DC: direct currentWAMS: Wide Area Measurement System广域监测系统OPF: optimal flow 最优潮流潮流计算:load flow calculationUHV: ultra high voltage 特高r Standards 国际标准化组织EMS: Electric Managerment System 电能管理系统PSS: power system stabilizer 电力系统稳定器HVDC: high-voltage direct current高压直流(电)AGC: Automatic Generation Control自动发电量控制SVC: Static Var Compensator静止无功补偿器TCSC: Thyristor Controlled Series Capacitor晶闸管控制的串联电容器二极管:diode 晶闸管:Thyristor 电流互感器,CT即:current transformer PT:电压互感器电力系统分析综合程序(Power System Analysis Software Package)简称PSASP有功:active power 无功:reactive powerRTU:Remote Terminal Units远程终端单元SCADA:Supervisory Control And Data Acquisition数据采集与监视控制系统断路器:Breaker 电容器:Capacitor电抗器:Reactor继电器:relay 母线:Busbar 稳定stability电压稳定voltage stability 功角稳定angle stability 暂态稳定transient stabilityOSI: Open System Interconnect 开放式系统互联。
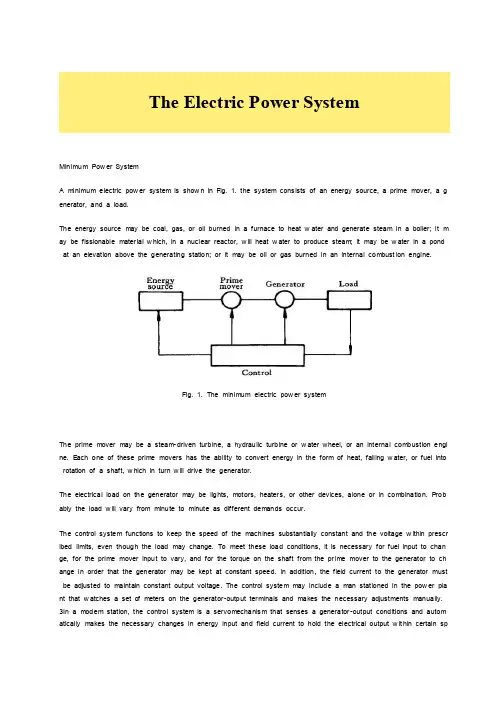
Minimum Pow er SystemA minimum electric pow er system is show n in Fig. 1. the system cons ists of an energy source, a prime mover, a g enerator, and a load.The energy source may be coal, gas, or oil burned in a furnace to heat w ater and generate steam in a boiler; it m ay be fissionable mater ial w hich, in a nuclear reactor, w ill heat w ater to produce steam; it may be w ater in a pond at an elevation above the generating station; or it may be oil or gas burned in an internal combust ion engine.Fig. 1. The minimum electric pow er systemThe prime mover may be a steam-driven turbine, a hydraulic turbine or w ater wheel, or an internal combustion engi ne. E ach one of these prime movers has the ability to convert energy in the form of heat, falling w ater, or fuel into rotation of a shaft, w hich in turn w ill drive the generator.The electrical load on the generator may be lights, motors, heaters, or other devices, alone or in combination. P rob ably the load w ill vary from minute to minute as different demands occur.The control system functions to keep the speed of the machines substantially constant and the voltage w ithin prescr ibed limits, even though the load may change. To meet these load conditions, it is necessary for fuel input to chan ge, for the prime mover input to vary, and for the torque on the shaft from the pr ime mover to the generator to ch ange in order that the generator may be kept at constant speed. In addition, the field current to the generator must be adjusted to maintain constant output voltage. The control system may include a man stationed in the pow er pla nt that w atches a set of meters on the generator-output ter minals and makes the necessary adjustments manually. 3In a modem station, the control system is a servomechanis m that senses a generator-output conditions and autom atically makes the necessary changes in energy input and field current to hold the electrical output w it hin certain specifications.More Complicated SystemsIn most situations the load is not directly connected to the generator ter minals. More commonly the load is some di stance from the generator, requir ing a pow er line connecting them. It is desirable to keep the electric pow er supply at the load w ithin specifications. How ever, the controls are near the generator, w hich may be in another building, p erhaps several miles aw ay.If the distance from the generator to the load is considerable, it may be desir able to install transformers at the gen erator and at the load end, and to trans mit the pow er over a high-voltage line (Fig. 2). For the same pow er, the hi gher-voltage line carries less current, has low er losses for the same w ire size, and provides more stable v oltage.In some cases an overhead line may be unacceptable. Instead it may be advantageous to use an under ground ca ble. With the pow er systems talked above, the pow er supply to the load must be interrupted if, for any reason, any component of the system must be removed from service for maintenance or repair..Fig 2A generators connected through transfor mers and a high-voltage line to a distant loadAdditional system load may requir e more pow er than the generator can supply. Another generator w ith its associate d transformers and high-voltage line might be added.It can be show n that there are some advantages in making ties betw een the generators (1) and at the ends of the high-voltage lines (2and 3), as show n in Fig. 3. This system w ill operate satisfactorily as long as no trouble develo ps or no equipment needs to be taken out of service.The above system may be vastly improved by the introduction of circuit br eakers, w hich may be opened and closed as needed. Circuit breakers added to the system, Fig. 4, per mit selected piece of equipment to sw itch out of servi ce w ithout disturbing the remainder of system. With this arrangement any element of the system may be r eenergize d for maintenance or repair by oper ation of circuit breakers. Of course, if any piece of equipment is taken out of s ervice, the total load must then carried by the remaining equipment. Attention must be given to avoid over loads dur i ng such circumstances. If possible, outages of equipment are scheduled at times w hen load requirements are below nor mal.Fig. 1-3 A system w ith parallel oper ation of the generators, of the transformers and of the trans mission linesFig. 4A system w ith necessary circuit breakersFig. 5Three generators supplying three loads over high-voltage trans mission linesFig. 5 show s a system in w hich three generators and three loads are tied together by three trans mission lines. No circuit breakers are show n in this diagram, although many w ould be required in such a system.Typical System LayoutThe gener ators, lines, and other equipment w hich form an electric system are arranged depending on the manner in w hich load grow s in the area and may be rearranged from time to time.Fig. 6 A radial pow er system supply ing several loadsHow ever, there are certain plans in to w hich a particular system des ign may be classified. Three types are illustrate d: the radial system, the loop system, and the netw ork system. All of these are show n w ithout the necessary circuit breakers. In each of these systems, a single generator serves four loads.The radial system is show n in Fig. 6. Here the lines form a “tree” spreading out from the generator. Opening any li ne results in interruption of pow er to one or more of the loads.The loop system is illustrated in Fig. 7. With this arrangement all loads may be served even though one line sectio n is removed from service. In some instances dur ing nor mal operation, the loop may be open at some point, such as A. In case a line section is to be taken out, the loop is first closed at A and then the line section removed. In this manner no service interruptions occur.Fig. 1-7A loop arrangement of lines for supplying several loadsFig. 8 show s the same loads being served by a netw ork. With this arrangement each load has tw o or more circuits over w hich it is fed.Distribution circuits are commonly des igned so that they may be classified as radial or loop circuits. The high-voltag e trans mission lines of most pow er systems are arranged as netw orks. The interconnection of major pow er systems results in netw orks made up many line sections.Fig. 8A netw ork of lines for supplying several loadsAuxiliary E quipmentCircuit breakers are necessary to deenergize equipment either for normal operation or on the occurrence of short ci rcuits. Circuit breakers must be designed to carry nor mal-load currents continuously, to w ithstand the extremely high currents that occur during faults, and to separate contacts and clear a circuit in the presence of fault. Circuit break ers are rated in ter ms of these duties.When a circuit breaker opens to deenergize a piece of equipment, one side of the circuit breaker usually rem ains e nergized, as it is connected to operating equipment. Since it is sometimes necessary to w ork on the circuit breaker itself, it is also necessary to have means by w hich the circuit breaker may be completely disconnected from other energized equipment. For this purpose disconnect sw itches are placed in series w ith the circuit breakers. By openin g these disconnests, the circuit breaker may be completely deenergized, per mitting w ork to be carried on in safety.Various instruments are necessary to monitor the operation of the electr ic pow er system. Usually each generator, ea ch transformer bank, and each line has its ow n set of instruments, frequently consisting of voltmeters, ammeters, w attmeters, and var meters.When a fault occurs on a system, conditions on the system undergo a sudden change. Voltages usually drop and currents increase. These changes are most noticeable in the immediate vicinity of fault. On-line analog computers, c ommonly called relays monitor these changes of conditions, make a deter minat ion of w hich breaker should be open ed to clear the fault, and energize the trip circuits of those appropriate breakers. 'With modern equipment, the relay action and breaker opening causes removal of fault w ithin three or four cycles after its initiation.The instruments that show circuit conditions and the relays that protect the circuits are not mounted directly on the pow er lines but are placed on sw itchboards in a control house. Instrument transformers are installed on the high-vol tage equipment, by means of which it is possible to pass on to the meters and relays representative samples of th e conditions on the operating equipment. The primary of a potential transformer is connected directly to the high-vol tage equipment. The secondary provides for the instruments and relays a voltage w hich is a constant fraction of vol tage on the operating equipment and is in phase w ith it. Similarly, a current transformer is connected w ith its primar y in the high-voltage circuit. The secondary w inding provides a current w hich is a know n fraction of the pow er-equip ment current and is in phase w ith it.Bushing potential devices and capac itor potential devices serve the same purpose as potential transformers but usually w ith less accuracy in regard to ratio and phase angle.Faults on Pow er SystemsFaults and its DamageEach year new designs of pow er equipment bring about increased reliability of operation. Nevertheless, equipment f ailures and interference by outside sources occasionally result in faults on electric pow er syst ems. On the occurrenc e of a fault, current and voltage conditions become abnor mal, the delivery of pow er from the generating stations to the loads may be unsatisfactory over a considerable area, and if the faulted equipment is not promptly disconnected from the remainder of the system, damage may result to other pieces of operating equipment.A fault is the unintentional or intentional connecting together of tw o or more conductors w hich ordinarily operate w it h a difference of potential betw een them. The connection betw een the conductors may be by physical metallic cont act or it may be through an arc. At the fault, the voltage betw een the tw o parts is reduced to zero in the case of metal-to-metal contacts, or to a very low value in case the connection is through an arc. Currents of abnor mally hig h magnitude flow through the netw ork to the point of fault. These short-circuit currents w ill usually be much greater than the designed ther mal ability of the conductors in the lines or machines feeding the fault. The resultant rise in t emperature may cause damage by the annealing of conductors and by the charring of insulation. In the period duri ng w hich the fault is per mitted to exist, the voltage on the system in the near vicinity of the fault w ill be so low th at utilization equipment w ill be inoperative. It is apparent that the pow er system designer must anticipate points at which faults may occur, be able to calculate conditions that exist during a fault, and provide equipment properly adj usted to open the sw itches necessary to disconnect the faulted equipment from the remainder of the system1. Ordi narily it is desirable that no other sw itches on the system are opened, as such behavior w ould result in unnecessar y modification of the system circuits.OverloadA distinction must be made betw een a fault and an overload. An overload implies only that loads greater than the designed values have been imposed on system. Under such a circumstance the voltage at the overload point may be low, but not zero. This under voltage condition may extend for some distance beyond the overload point into the remainder of the system. The currents in the overloaded equipment are high and may exceed the ther mal des ign l imits. Nevertheless, such currents are substantially low er than in the case of a fault. Service frequently may be mai ntained, but at below-standard voltage.Overloads are rather common occurrences in homes. For example, a housew ife might plug five w affle irons into the kitchen circuit during a neighborhood party. Such an overlo ad, if per mitted to continue, w ould cause heating of the w ires from the pow er center and might eventually start a fire. To prevent such trouble, residential circuits are prote cted by fuses or circuit breakers w hich open quickly w hen currents above specified values persist. Distribution transf or mers are sometimes overloaded as customers install more and more appliances. The continuous monitoring of dist ribution circuits is necessary to be certain that transfor mer sizes are increased as load grow s.Various FaultsFaults of many types and causes may appear on electric pow er systems. Many of us in our homes have seen fray ed lamp cords w hich permitted the tw o conductors of the cord to come in contact w ith each other. When this occur s, there is a resulting flash, and if breaker or fuse equipment functions properly, the circuit is opened.Overhead lines, for the most part, are constructed of bare conductors. These are sometimes accidentally brought to gether by action of w ind, sleet, trees, cranes, airplanes, or dama ge to supporting structures. Over voltages due to li ghtning or sw itching may cause flashover of supporting or from conductor to conductor. Contamination on insulators sometimes results in flashover even dur ing nor mal voltage conditions.The conductors of underground cables are separated from each other and from ground by solid insulation, w hich m ay be oil-impregnated paper or a plastic such as polyethylene. These materials undergo some deter ioration w ith ag e, particularly if overloads on the cables have resulted in their operation at elevated temperature. Any small void pr esent in the body of the insulating material w ill result in ionization of the gas contained therein, the products of w hi ch react unfavorably w ith the insulation, deterior ation of the insulation may result in failur e of the material to retain i ts insulating properties, and short circuits w ill develop betw een the cable conductors. The possibility of cable failure is increased if lightning or sw itching produces transient voltage of abnor mally high values betw een the conductors.Transfor mer failures may be the result of insulation deterioration combined w ith over-voltages due to lightning or sw i tching trans ients. Short circuits due to insulation failure betw een adjacent turns of the same w inding may result from suddenly applied over voltages. Major insulation may fail, per mitting arcs to be established betw een primary and se condary w indings or betw een a w inding and grounded metal part such as the core or tank.Generators may fail due to breakdow n of the insulation betw een adjacent turns in the same slot, resulting in a shor t circuit in a single turn of the generator. Insulation breakdow n may also occur betw een one of the w indings and th e grounded steel structure in w hich the coils are embedded. Breakdow n betw een different w indings lying in the sam e slot results in short-circuiting extensive sections of machine.Balanced three- phase faults, like balanced three-phase loads, may be handled on a line to-neutr al bas is or on an equivalent single-phase basis. P roblems may be solved either in ter ms of volts, amperes, and ohms. The handling of faults on single-phase lines is of course identical to the method of handling three-phase faults on an equivalent s ingle-phase basis.Per manent Faults and Temporary FaultsFaults may be classified as per manent or temporary. P er manent faults are those in w hich insulation failure or struct ure failure produces damage that makes operation of the equipment impossible and requires repairs to be made. T emporary faults are those w hich may be removed by deenergiz ing the equipment for a short period of time, short ci rcuits on overhead lines frequently are of this nature. High w inds may cause tw o or more conductors to sw ing toget her momentar ily. During the short period of contact, an arc is formed w hich may continue as long as the line remai ns energized. How ever i f automatic equipment can be brought into operation to deenergize the line quickly, little ph ysical damage may result and the line may be restored to service as soon as the are is extinguished. Arcs across insulators due to over voltages from lightning or sw itching trans ients usually can be cleared by automatic circuit-brea ker operation before significant structure damage occurs.Because of this characteristic of faults on lines, many companies operate follow ing a procedure know n as high-spee d reclosing. On the occurrence of a fault, the line is promptly deenergized by opening the circuit breakers at each end of the line. The breakers remain open long enough for the arc to clear, and then reclose automatically. In man y instances service is restored in a fraction of a second. Of course, if structure damage has occurred and the fault persists,it is necessary for the breakers to reopen and lock open.电力系统最低限度的电力系统最低电力系统显示图.1 .该系统包括能源,主要动力,一台发电机和负荷。

Electric Power SystemElectrical power system refers to remove power and electric parts of the part,It includes substation, power station and distribution. The role of the power grid is connected power plants and users and with the minimum transmission and distribution network disturbance through transport power, with the highest efficiency and possibility will voltage and frequency of the power transmission to the user fixed .Grid can be divided into several levels based on the operating voltage transmission system, substructure, transmission system and distribution system, the highest level of voltage transmission system is ZhuWangJia or considered the high power grids. From the two aspects of function and operation, power can be roughly divided into two parts, the transmission system and substation. The farthest from the maximum output power and the power of the highest voltage grade usually through line to load. Secondary transmission usually refers to the transmission and distribution system is that part of the middle. If a plant is located in or near the load, it might have no power. It will be direct access to secondary transmission and distribution system. Secondary transmission system voltage grade transmission and distribution system between voltage level. Some systems only single second transmission voltage, but usually more than one. Distribution system is part of the power system and its retail service to users, commercial users and residents of some small industrial users. It is to maintain and in the correct voltage power to users responsible. In most of the system, Distribution system accounts for 35% of the total investment system President to 45%, and total loss of system of the half .More than 220kv voltage are usually referred to as Ultra high pressure, over 800kv called high pressure, ultra high voltage and high pressure have important advantages, For example, each route high capacity, reduce the power needed for the number of transmission. In as high voltage to transmission in order to save a conductor material seem desirable, however, must be aware that high voltage transmission can lead to transformer, switch equipment and other instruments of spending increases, so, for the voltage transmission to have certain restriction, allows it to specific circumstances in economic use. Although at present, power transmission most is through the exchange of HVDC transmission, and the growing interest in, mercury arc rectifier and brake flow pipe into the ac power generation and distribution that change for the high voltage dc transmission possible.Compared with the high-voltage dc high-voltage ac transmission has the following some advantages: (1) the communication with high energy; (2) substation of simple maintenance and communication cost is low; (3) ac voltage can easily and effectively raise or lower, it makes the power transmission and high pressure With safety voltage distributionHVDC transmission and high-voltage ac transmission has the following advantages: (1) it only need two phase conductors and ac transmission to three-phase conductors; (2) in the dc transmission impedance, no RongKang, phase shift and impact overvoltage; (3) due to the same load impedance, no dc voltage, and transfer of the transmission line voltage drop less communication lines, and for this reason dc transmission line voltage regulator has better properties; (4) in dc system without skin effect. Therefore, the entire section of route conductors are using; (5) for the same work, dc voltage potential stress than insulation. Therefore dc Wire need less insulation; (6) dc transmission line loss, corona to little interference lines of communication; (7) HVDC transmission without loss of dielectric, especially in cable transmission; (8) in dc system without stability and synchronization of trouble.A transmission and the second transmission lines terminated in substation or distribution substations, the substation and distribution substations, the equipment including power and instrument transformer and lightning arrester, with circuit breaker, isolating switch, capacitor set, bus and a substation control equipment, with relays for the control room of the equipment. Some of the equipment may include more transformer substations and some less, depending on their role in the operation. Some of the substation is manual and other is automatic. Power distribution system through the distribution substations. Some of them by many large capacity transformer feeders, large area to other minor power transformer capacity, only a near load control, sometimes only a doubly-fed wire feeders (single single variable substation)Now for economic concerns, three-phase three-wire type communication network is widely used, however, the power distribution, four lines using three-phase ac networks.Coal-fired power means of main power generating drive generators, if coal energy is used to produce is pushing the impeller, then generate steam force is called the fire. Use coal produces steam to promote the rotating impeller machine plant called coal-fired power plants. In the combustion process, the energy stored in the coal to heat released,then the energy can be transformed into the form within vapor. Steam into the impeller machine work transformed into electrical energy.Coal-fired power plants could fuel coal, oil and natural gas is. In coal-fired power plant, coal and coal into small pieces first through the break fast, and then put out. The coal conveyer from coal unloader point to crush, then break from coal, coal room to pile and thence to power. In most installations, according to the needs of coal is, Smash the coal storage place, no coal is through the adjustable coal to supply coal, the broken pieces of coal is according to the load changes to control needs. Through the broken into the chamber, the coal dust was in the second wind need enough air to ensure coal burning.In function, impeller machine is used to high temperature and high pressure steam energy into kinetic energy through the rotation, spin and convert electricity generator. Steam through and through a series of impeller machine parts, each of which consists of a set of stable blade, called the pipe mouth parts, even in the rotor blades of mobile Li called. In the mouth parts (channel by tube nozzle, the steam is accelerating formation) to high speed, and the fight in Li kinetic energy is transformed into the shaft. In fact, most of the steam generator is used for air is, there is spread into depression, steam turbine of low-pressure steam from the coagulation turbine, steam into the condenses into water, and finally the condensate water is to implement and circulation.In order to continuous cycle, these must be uninterrupted supply: (1) fuel; (2) the air (oxygen) to the fuel gas burning in the configuration is a must; (3) and condenser, condensed from the condensed water supply, sea and river to lake. Common cooling tower; (4) since water vapour in some places in circulation, will damage process of plenty Clean the supply.The steam power plant auxiliary system is running. For a thermal power plant, the main auxiliary system including water system, burning gas and exhaust systems, condensation system and fuel system. The main auxiliary system running in the water pump, condensation and booster pump, coal-fired power plants in the mill equipment. Other power plant auxiliary equipment including air compressors, water and cooling water system, lighting and heating systems, coal processing system. Auxiliary equipment operation is driven by motor, use some big output by mechanical drive pump and some of the impeller blades, machine drive out from the main use of water vaporimpeller machine. In coal-fired power plant auxiliary equipment, water supply pump and induced draft fan is the biggest need horsepower.Most of the auxiliary power generating unit volume increased significantly in recent years, the reason is required to reduce environment pollution equipment. Air quality control equipment, such as electrostatic precipitator, dust collection of flue gas desulfurization, often used in dust in the new coal-fired power plants, and in many already built in power plant, the natural drive or mechanical drive, fountain, cooling tower in a lake or cooling canal has been applied in coal-fired power plants and plants, where the heat release need to assist cooling system.In coal-fired power stations, some device is used to increase the thermal energy, they are (1) economizer and air preheater, they can reduce the heat loss; (2) water heater, he can increase the temperature of water into boiling water heaters; (3) they can increase and filter the thermal impeller.Coal-fired power plants usually requires a lot of coal and coal reservoirs, however the fuel system in power plant fuel handling equipment is very simple, and almost no fuel oil plants.The gas turbine power plants use gas turbine, where work is burning gas fluid. Although the gas turbine must burn more expensive oil or gas, but their low cost and time is short, and can quickly start, they are very applicable load power plant. The gas turbine burn gas can achieve 538 degrees Celsius in the condensing turbine, however, the temperature is lower, if gas turbine and condenser machine, can produce high thermal efficiency. In gas turbine turbine a combined cycle power plant. The gas through a gas turbine, steam generator heat recovery in there were used to generate vapor heat consumption. Water vapor and then through a heated turbine. Usually a steam turbine, and one to four gas turbine power plant, it must be rated output power.。

(完整版)电力系统外文英语文献资料Electric Power SystemElectrical power system refers to remove power and electric parts of the part,It includes substation, power station and distribution. The role of the power grid is connected power plants and users and with the minimum transmission and distribution network disturbance through transport power, with the highest efficiency and possibility will voltage and frequency of the power transmission to the user fixed .Grid can be divided into several levels based on the operating voltage transmission system, substructure, transmission system and distribution system, the highest level of voltage transmission system is ZhuWangJia or considered the high power grids. From the two aspects of function and operation, power can be roughly divided into two parts, the transmission system and substation. The farthest from the maximum output power and the power of the highest voltage grade usually through line to load. Secondary transmission usually refers to the transmission and distribution system is that part of the middle. If a plant is located in or near the load, it might have no power. It will be direct access to secondary transmission and distribution system. Secondary transmission system voltage grade transmission and distribution system between voltage level. Some systems only single second transmission voltage, but usually more than one. Distribution system is part of the power system and its retail service to users, commercial users and residents of some small industrial users. It is to maintain and in the correct voltage power to users responsible. In most of the system, Distribution system accounts for 35% of the total investment system President to 45%, andtotal loss of system of the half .More than 220kv voltage are usually referred to as Ultra high pressure, over 800kv called high pressure, ultra high voltage and high pressure have important advantages, For example, each route high capacity, reduce the power needed for the number of transmission. In as high voltage to transmission in order to save a conductor material seem desirable, however, must be aware that high voltage transmission can lead to transformer, switch equipment and other instruments of spending increases, so, for the voltage transmission to have certain restriction, allows it to specific circumstances in economic use. Although at present, power transmission most is through the exchange of HVDC transmission, and the growing interest in, mercury arc rectifier and brake flow pipe into the ac power generation and distribution that change for the high voltage dc transmission possible.Compared with the high-voltage dc high-voltage ac transmission has the following some advantages: (1) the communication with high energy; (2) substation of simple maintenance and communication cost is low; (3) ac voltage can easily and effectively raise or lower, it makes the power transmission and high pressure With safety voltage distribution HVDC transmission and high-voltage ac transmission has the following advantages: (1) it only need two phase conductors and ac transmission to three-phase conductors; (2) in the dc transmission impedance, no RongKang, phase shift and impact overvoltage; (3) due to the same load impedance, no dc voltage, and transfer of the transmission line voltage drop less communication lines, and for this reason dc transmission line voltage regulator has better properties; (4) in dc system withoutskin effect. Therefore, the entire section of route conductors are using; (5) for the same work, dc voltage potential stress than insulation. Therefore dc Wire need less insulation; (6) dc transmission line loss, corona to little interference lines of communication; (7) HVDC transmission without loss of dielectric, especially in cable transmission; (8) in dc system without stability and synchronization of trouble.A transmission and the second transmission lines terminated in substation or distribution substations, the substation and distribution substations, the equipment including power and instrument transformer and lightning arrester, with circuit breaker, isolating switch, capacitor set, bus and a substation control equipment, with relays for the control room of the equipment. Some of the equipment may include more transformer substations and some less, depending on their role in the operation. Some of the substation is manual and other is automatic. Power distribution system through the distribution substations. Some of them by many large capacity transformer feeders, large area to other minor power transformer capacity, only a near load control, sometimes only a doubly-fed wire feeders (single single variable substation)Now for economic concerns, three-phase three-wire type communication network is widely used, however, the power distribution, four lines using three-phase ac networks.Coal-fired power means of main power generating drive generators, if coal energy is used to produce is pushing the impeller, then generate steam force is called the fire. Use coal produces steam to promote the rotating impeller machine plant called coal-fired power plants. In the combustion process, the energy stored in the coal to heat released,then the energy can be transformed into the form within vapor. Steam into the impeller machine work transformed into electrical energy.Coal-fired power plants could fuel coal, oil and natural gas is. In coal-fired power plant, coal and coal into small pieces first through the break fast, and then put out. The coal conveyer from coal unloader point to crush, then break from coal, coal room to pile and thence to power. In most installations, according to the needs of coal is, Smash the coal storage place, no coal is through the adjustable coal to supply coal, the broken pieces of coal is according to the load changes to control needs. Through the broken into the chamber, the coal dust was in the second wind need enough air to ensure coal burning.In function, impeller machine is used to high temperature and high pressure steam energy into kinetic energy through the rotation, spin and convert electricity generator. Steam through and through a series of impeller machine parts, each of which consists of a set of stable blade, called the pipe mouth parts, even in the rotor blades of mobile Li called. In the mouth parts (channel by tube nozzle, the steam is accelerating formation) to high speed, and the fight in Li kinetic energy is transformed into the shaft. In fact, most of the steam generator is used for air is, there is spread into depression, steam turbine of low-pressure steam from the coagulation turbine, steam into the condenses into water, and finally the condensate water is to implement and circulation.In order to continuous cycle, these must be uninterrupted supply: (1) fuel; (2) the air (oxygen) to the fuel gas burning in the configuration is a must; (3) and condenser, condensed from the condensed water supply, sea and river to lake. Common coolingtower; (4) since water vapour in some places in circulation, will damage process of plenty Clean the supply.The steam power plant auxiliary system is running. For a thermal power plant, the main auxiliary system including water system, burning gas and exhaust systems, condensation system and fuel system. The main auxiliary system running in the water pump, condensation and booster pump, coal-fired power plants in the mill equipment. Other power plant auxiliary equipment including air compressors, water and cooling water system, lighting and heating systems, coal processing system. Auxiliary equipment operation is driven by motor, use some big output by mechanical drive pump and some of the impeller blades, machine drive out from the main use of water vaporimpeller machine. In coal-fired power plant auxiliary equipment, water supply pump and induced draft fan is the biggest need horsepower.Most of the auxiliary power generating unit volume increased significantly in recent years, the reason is required to reduce environment pollution equipment. Air quality control equipment, such as electrostatic precipitator, dust collection of flue gas desulfurization, often used in dust in the new coal-fired power plants, and in many already built in power plant, the natural drive or mechanical drive, fountain, cooling tower in a lake or cooling canal has been applied in coal-fired power plants and plants, where the heat release need to assist cooling system.In coal-fired power stations, some device is used to increase the thermal energy, they are (1) economizer and air preheater, they can reduce the heat loss; (2) water heater, he can increase the temperature of water into boiling water heaters; (3) they can increase and filter the thermal impeller.Coal-fired power plants usually requires a lot of coal and coal reservoirs, however the fuel system in power plant fuel handling equipment is very simple, and almost no fuel oil plants.The gas turbine power plants use gas turbine, where work is burning gas fluid. Although the gas turbine must burn more expensive oil or gas, but their low cost and time is short, and can quickly start, they are very applicable load power plant. The gas turbine burn gas can achieve 538 degrees Celsius in the condensing turbine, however, the temperature is lower, if gas turbine and condenser machine, can produce high thermal efficiency. In gas turbine turbine a combined cycle power plant. The gas through a gas turbine, steam generator heat recovery in there were used to generate vapor heat consumption. Water vapor and then through a heated turbine. Usually a steam turbine, and one to four gas turbine power plant, it must be rated output power.。

和电力系统相关的专业英语电力系统 power system发电机 generator励磁 excitation励磁器 excitor电压 voltage电流 current升压变压器 step-up transformer母线 bus变压器 transformer空载损耗 no-load loss铁损 iron loss铜损 copper loss空载电流 no-load current有功损耗 reactive loss无功损耗 active loss输电系统 power transmission system高压侧 high side输电线 transmission line高压 high voltage低压 low voltage中压 middle voltage功角稳定 angle stability稳定 stability电压稳定 voltage stability暂态稳定 transient stability电厂 power plant能量输送 power transfer交流 AC直流 DC电网 power system落点 drop point开关站 switch station调节 regulation高抗 high voltage shunt reactor 并列的 apposable裕度 margin故障 fault三相故障 three phase fault分接头 tap切机 generator triping高顶值 high limited value静态 static (state)动态 dynamic (state)机端电压控制 AVR电抗 reactance电阻 resistance功角 power angle有功(功率) active power 电容器 Capacitor电抗器 Reactor断路器 Breaker电动机 motor功率因数 power-factor定子 stator阻抗 impedance功角 power-angle电压等级 voltage grade有功负载: active load PLoad 无功负载 reactive load档位 tap position电阻 resistor电抗 reactance电导 conductance电纳 susceptance上限 upper limit下限 lower limit正序阻抗 positive sequence impedance 负序阻抗 negative sequence impedance 零序阻抗 zero sequence impedance无功(功率) reactive power功率因数 power factor无功电流 reactive current斜率 slope额定 rating变比 ratio参考值 reference value电压互感器 PT分接头 tap仿真分析 simulation analysis下降率 droop rate传递函数 transfer function框图 block diagram受端 receive-side同步 synchronization保护断路器 circuit breaker摇摆 swing阻尼 damping无刷直流电机 Brusless DC motor刀闸(隔离开关) Isolator机端 generator terminal变电站 transformer substation永磁同步电机 Permanent-magnet Synchronism Motor异步电机 Asynchronous Motor三绕组变压器 three-column transformer ThrClnTrans双绕组变压器 double-column transformer DblClmnTrans 固定串联电容补偿 fixed series capacitor compensation 双回同杆并架 double-circuit lines on the same tower 单机无穷大系统 one machine - infinity bus system励磁电流 Magnetizing current补偿度 degree of compensation电磁场:Electromagnetic fields失去同步 loss of synchronization装机容量 installed capacity无功补偿 reactive power compensation故障切除时间 fault clearing time极限切除时间 critical clearing time强行励磁 reinforced excitation并联电容器 shunt capacitor<下降特性 droop characteristics线路补偿器 LDC(line drop compensation)电机学 Electrical Machinery自动控制理论 Automatic Control Theory电磁场 Electromagnetic Field微机原理 Principle of Microcomputer电工学 Electrotechnics电路原理 Principle of circuits电机学 Electrical Machinery电力系统稳态分析 Steady-State Analysis of Power System电力系统暂态分析 Transient-State Analysis of Power System 电力系统继电保护原理 Principle of Electrical System's Relay Protection 电力系统元件保护原理 Protection Principle of Power System 's Element电力系统内部过电压 Past Voltage within Power system模拟电子技术基础 Basis of Analogue Electronic Technique数字电子技术 Digital Electrical Technique电路原理实验 Lab. of principle of circuits电气工程讲座 Lectures on electrical power production电力电子基础 Basic fundamentals of power electronics高电压工程 High voltage engineering电子专题实践 Topics on experimental project of electronics 电气工程概论 Introduction to electrical engineering电子电机集成系统 Electronic machine system电力传动与控制 Electrical Drive and Control电力系统继电保护 Power System Relaying Protection 主变压器 main transformer升压变压器 step-up transformer降压变压器 step-down transformer工作变压器 operating transformer备用变压器 standby transformer公用变压器 common transformer三相变压器 three-phase transformer单相变压器 single-phase transformer带负荷调压变压器 on-load regulating transformer变压器铁芯 transformer core变压器线圈 transformer coil变压器绕组 transformer winding变压器油箱 transformer oil tank变压器外壳 transformer casing变压器风扇 transformer fan变压器油枕transformer oil conservator(∽ drum变压器额定电压 transformer reted voltage变压器额定电流 transformer reted current变压器调压范围 transformer voltage regulation rage配电设备 power distribution equipment SF6断路器 SF6 circuit breaker开关 switch按钮 button隔离开关 isolator,disconnector真空开关 vacuum switch刀闸开关 knife-switch接地刀闸 earthing knife-switch电气设备 electrical equipment变流器 current converter电流互感器 current transformer电压互感器 voltage transformer电源 power source交流电源 AC power source直流电源 DC power source工作电源 operating source备用电源 Standby source强电 strong current弱电 weak current继电器 relay信号继电器 signal relay电流继电器 current relay电压继电器 voltage relay跳闸继电器 tripping relay合闸继电器 closing relay中间继电器 intermediate relay时间继电器 time relay零序电压继电器 zero-sequence voltage relay差动继电器 differential relay闭锁装置 locking device遥控 telecontrol遥信 telesignalisation遥测 telemetering遥调 teleregulation断路器 breaker,circuit breaker少油断路器 mini-oil breaker,oil-mini-mum breaker 高频滤波器 high-frequency filter组合滤波器 combined filter常开触点 normally opened contaact常闭触点 normally closed contaact并联电容 parallel capacitance保护接地 protective earthing熔断器 cutout,fusible cutout电缆 cable跳闸脉冲 tripping pulse合闸脉冲 closing pulse一次电压 primary voltage二次电压 secondary voltage并联电容器 parallel capacitor无功补偿器 reactive power compensation device消弧线圈 arc-suppressing coil母线 Bus,busbar三角接法 delta connection星形接法 Wye connection原理图 schematic diagram一次系统图 primary system diagram二次系统图 secondary system diagram两相短路 two-phase short circuit三相短路 three-phase short circuit单相接地短路 single-phase ground short circuit短路电流计算 calculation of short circuit current 自动重合闸 automatic reclosing高频保护 high-freqency protection距离保护 distance protection横差保护 transverse differential protection纵差保护 longitudinal differential protection线路保护 line protection过电压保护 over-voltage protection母差保护 bus differential protection瓦斯保护 Buchholtz protection变压器保护 transformer protection电动机保护 motor protection远方控制 remote control用电量 power consumption载波 carrier故障 fault选择性 selectivity速动性 speed灵敏性 sensitivity可靠性 reliability电磁型继电器 electromagnetic无时限电流速断保护 instantaneously over-current protection 跳闸线圈 trip coil工作线圈 operating coil制动线圈 retraint coil主保护 main protection后备保护 back-up protection定时限过电流保护 definite time over-current protection三段式电流保护 the current protection with three stages 反时限过电流保护 inverse time over-current protection 方向性电流保护 the directional current protection零序电流保护 zero-sequence current protection阻抗 impedance微机保护 Microprocessor Protection。

电力系统 power system 发电机 generator 励磁 excitation励磁器 excitor 电压 voltage 电流 current升压变压器 step—up transformer 母线 bus 变压器 transformer空载损耗:no-load loss 铁损:iron loss 铜损:copper loss空载电流:no-load current 无功损耗:reactive loss 有功损耗:active loss 输电系统 power transmission system高压侧 high side 输电线 transmission line高压: high voltage 低压:low voltage 中压:middle voltage功角稳定 angle stability 稳定 stability 电压稳定 voltage stability暂态稳定 transient stability 电厂 power plant 能量输送 power transfer交流 AC 直流 DC 电网 power system落点 drop point 开关站 switch station 调节 regulation高抗 high voltage shunt reactor 并列的:apposable 裕度 margin故障 fault 三相故障 three phase fault 分接头:tap切机 generator triping 高顶值 high limited value 静态 static (state)动态 dynamic (state) 机端电压控制 AVR 电抗 reactance电阻 resistance 功角 power angle 有功(功率) active power电容器:Capacitor 电抗器:Reactor 断路器:Breaker电动机:motor 功率因数:power-factor 定子:stator阻抗电压:阻抗:impedance 功角:power-angle 电压等级:voltage grade有功负载: active load/PLoad 无功负载:reactive load 档位:tap position 电阻:resistor 电抗:reactance 电导:conductance电纳:susceptance 上限:upper limit 下限:lower limit正序阻抗:positive sequence impedance 负序阻抗:negative sequence impedance 零序阻抗:zero sequence impedance无功(功率) reactive power 功率因数 power factor 无功电流 reactive current斜率 slope 额定 rating 变比 ratio参考值 reference value 电压互感器 PT 分接头 tap仿真分析 simulation analysis 下降率 droop rate 传递函数 transfer function框图 block diagram 受端 receive—side 同步 synchronization保护断路器 circuit breaker 摇摆 swing 阻尼 damping无刷直流电机:Brusless DC motor 刀闸(隔离开关):Isolator 机端 generator terminal变电站 transformer substation永磁同步电机:Permanent-magnet Synchronism Motor异步电机:Asynchronous Motor三绕组变压器:three-column transformer ThrClnTrans双绕组变压器:double-column transformer DblClmnTrans固定串联电容补偿fixed series capacitor compensation双回同杆并架 double—circuit lines on the same tower单机无穷大系统 one machine - infinity bus system励磁电流:magnetizing current 补偿度 degree of compensation电磁场Electromagnetic fields 失去同步 loss of synchronization装机容量 installed capacity 无功补偿 reactive power compensation故障切除时间 fault clearing time 极限切除时间 critical clearing time强行励磁 reinforced excitation 并联电容器:shunt capacitor下降特性 droop characteristics 线路补偿器 LDC(line drop compensation)电机学 Electrical Machinery 自动控制理论 Automatic Control Theory电磁场 Electromagnetic Field微机原理 Principle of Microcomputer电工学 Electrotechnics电路原理Principle of circuits电机学Electrical Machinery电力系统稳态分析 Steady-State Analysis of Power System电力系统暂态分析 Transient—State Analysis of Power System电力系统继电保护原理 Principle of Electrical System's Relay Protection 电力系统元件保护原理 Protection Principle of Power System ’s Element电力系统内部过电压 Past Voltage within Power system模拟电子技术基础 Basis of Analogue Electronic Technique数字电子技术 Digital Electrical Technique电路原理实验Lab. of principle of circuits电气工程讲座 Lectures on electrical power production电力电子基础Basic fundamentals of power electronics高电压工程High voltage engineering电子专题实践Topics on experimental project of electronics电气工程概论Introduction to electrical engineering电子电机集成系统electronic machine system电力传动与控制Electrical Drive and Control电力系统继电保护 Power System Relaying Protection。

电力系统power system发电机generator励磁excitation励磁器 excitor电压 voltage电流 current升压变压器 step-up transformer母线 bus变压器 transformer空载损耗 no-load loss铁损 iron loss铜损 copper loss空载电流 no-load current有功损耗 active loss无功损耗reactive loss输电系统 power transmission system 高压侧 high side输电线 transmission line高压 high voltage低压 low voltage中压 middle voltage功角稳定 angle stability稳定 stability电压稳定 voltage stability暂态稳定 transient stability电厂 power plant能量输送 power transfer交流 AC直流 DC电网 power system落点 drop point开关站 switch station调节 regulation高抗 high voltage shunt reactor 并列的 apposable裕度 margin故障 fault三相故障 three phase fault分接头 tap切机 generator triping高顶值 high limited value静态 static (state)动态 dynamic (state)机端电压控制 AVR电抗 reactance电阻 resistance功角 power angle有功(功率) active power电容器 Capacitor电抗器 Reactor断路器 Breaker电动机 motor功率因数 power-factor定子 stator阻抗 impedance功角 power-angle电压等级 voltage grade有功负载: active load PLoad 无功负载 reactive load档位 tap position电阻 resistor电抗 reactance电导 conductance电纳 susceptance上限 upper limit下限 lower limit正序阻抗 positive sequence impedance 负序阻抗 negative sequence impedance 零序阻抗 zero sequence impedance无功(功率) reactive power功率因数 power factor无功电流 reactive current斜率 slope额定 rating变比 ratio参考值 reference value电压互感器 PT分接头 tap仿真分析 simulation analysis下降率 droop rate传递函数 transfer function框图 block diagram受端 receive-side同步 synchronization保护断路器 circuit breaker摇摆 swing阻尼 damping无刷直流电机 Brusless DC motor刀闸(隔离开关) Isolator机端 generator terminal变电站 transformer substation永磁同步电机 Permanent-magnet Synchronism Motor异步电机 Asynchronous Motor三绕组变压器 three-column transformer ThrClnTrans双绕组变压器 double-column transformer DblClmnTrans 固定串联电容补偿 fixed series capacitor compensation双回同杆并架 double-circuit lines on the same tower 单机无穷大系统 one machine - infinity bus system励磁电流 Magnetizing current补偿度 degree of compensation电磁场:Electromagnetic fields失去同步 loss of synchronization装机容量 installed capacity无功补偿 reactive power compensation故障切除时间 fault clearing time极限切除时间 critical clearing time强行励磁 reinforced excitation并联电容器 shunt capacitor<下降特性 droop characteristics线路补偿器 LDC(line drop compensation)电机学 Electrical Machinery自动控制理论 Automatic Control Theory电磁场 Electromagnetic Field微机原理 Principle of Microcomputer电工学 Electrotechnics电路原理 Principle of circuits电机学 Electrical Machinery电力系统稳态分析 Steady-State Analysis of Power System电力系统暂态分析Transient-State Analysis of Power System电力系统继电保护原理 Principle of Electrical System's Relay Protection电力系统元件保护原理 Protection Principle of Power System 's Element电力系统内部过电压 Past Voltage within Power system模拟电子技术基础 Basis of Analogue Electronic Technique数字电子技术 Digital Electrical Technique电路原理实验 Lab. of principle of circuits电气工程讲座 Lectures on electrical power production电力电子基础Basic fundamentals of power electronics高电压工程 High voltage engineering电子专题实践 Topics on experimental project of electronics电气工程概论 Introduction to electrical engineering电子电机集成系统 Electronic machine system电力传动与控制 Electrical Drive and Control电力系统继电保护 Power System Relaying Protection主变压器main transformerstep-up transformer降压变压器step-down transformer工作变压器operating transformer备用变压器standby transformer公用变压器common transformer三相变压器three-phase transformer单相变压器single-phase transformer带负荷调压变压器on-load regulating transformer 变压器铁芯transformer core变压器线圈transformer coiltransformer winding变压器油箱transformer oil tank变压器外壳transformer casing变压器风扇transformer fan变压器油枕transformer oil conservator(∽ drum 变压器额定电压transformer reted voltage变压器额定电流transformer reted current变压器调压范围transformer voltage regulation rage 配电设备power distribution equipmentSF6断路器SF6 circuit breaker开关switch按钮button隔离开关isolator,disconnector 真空开关vacuum switch刀闸开关knife-switch接地刀闸earthing knife-switch 电气设备electrical equipment 变流器current converter电流互感器current transformer 电压互感器voltage transformer电源power source交流电源AC power source 直流电源DC power source 工作电源operating source 备用电源Standby source强电strong current弱电weak current继电器relay信号继电器signal relay电流继电器current relay电压继电器voltage relay跳闸继电器tripping relay合闸继电器closing relay中间继电器intermediate relay时间继电器time relay零序电压继电器zero-sequence voltage relay 差动继电器differential relay闭锁装置locking device遥控telecontrol遥信telesignalisationtelemetering遥调teleregulation断路器breaker,circuit breaker少油断路器mini-oil breaker,oil-mini-mum breaker 高频滤波器high-frequency filter组合滤波器combined filter常开触点normally opened contaact常闭触点normally closed contaact并联电容parallel capacitance保护接地protective earthingcutout,fusible cutout电缆cable跳闸脉冲tripping pulse合闸脉冲closing pulse一次电压primary voltage二次电压secondary voltage并联电容器parallel capacitor无功补偿器reactive power compensation device 消弧线圈arc-suppressing coil母线Bus,busbar三角接法delta connection星形接法Wye connection原理图schematic diagram一次系统图primary system diagram二次系统图secondary system diagram两相短路two-phase short circuit三相短路three-phase short circuit单相接地短路single-phase ground short circuit 短路电流计算calculation of short circuit current 自动重合闸automatic reclosing高频保护high-freqency protection距离保护distance protection横差保护transverse differential protection 纵差保护longitudinal differential protection 线路保护line protection过电压保护over-voltage protection母差保护bus differential protection瓦斯保护Buchholtz protection变压器保护transformer protection电动机保护motor protection远方控制remote control用电量power consumption载波carrier故障fault选择性selectivity速动性speed灵敏性sensitivity可靠性reliability电磁型继电器electromagnetic无时限电流速断保护instantaneously over-current protection跳闸线圈trip coil工作线圈operating coil制动线圈retraint coil主保护main protection后备保护back-up protection定时限过电流保护definite time over-current protection 三段式电流保护the current protection with three stages 反时限过电流保护inverse time over-current protection 方向性电流保护the directional current protection 零序电流保护zero-sequence current protection阻抗impedance微机保护Microprocessor Protection(注:文档可能无法思考全面,请浏览后下载,供参考。

电力系统 power system 发电机 generator 励磁 excitation励磁器 excitor 电压 voltage 电流 current升压变压器 step-up transformer 母线 bus 变压器 transformer空载损耗:no—load loss 铁损:iron loss 铜损:copper loss空载电流:no—load current 无功损耗:reactive loss 有功损耗:active loss 输电系统 power transmission system高压侧 high side 输电线 transmission line高压: high voltage 低压:low voltage 中压:middle voltage功角稳定 angle stability 稳定 stability 电压稳定 voltage stability暂态稳定 transient stability 电厂 power plant 能量输送 power transfer交流 AC 直流 DC 电网 power system落点 drop point 开关站 switch station 调节 regulation高抗 high voltage shunt reactor 并列的:apposable 裕度 margin故障 fault 三相故障 three phase fault 分接头:tap切机 generator triping 高顶值 high limited value 静态 static (state)动态 dynamic (state) 机端电压控制 AVR 电抗 reactance电阻 resistance 功角 power angle 有功(功率) active power电容器:Capacitor 电抗器:Reactor 断路器:Breaker电动机:motor 功率因数:power-factor 定子:stator阻抗电压: 阻抗:impedance 功角:power-angle 电压等级:voltage grade有功负载: active load/PLoad 无功负载:reactive load 档位:tap position 电阻:resistor 电抗:reactance 电导:conductance电纳:susceptance 上限:upper limit 下限:lower limit正序阻抗:positive sequence impedance 负序阻抗:negative sequence impedance 零序阻抗:zero sequence impedance无功(功率) reactive power 功率因数 power factor 无功电流 reactive current斜率 slope 额定 rating 变比 ratio参考值 reference value 电压互感器 PT 分接头 tap仿真分析 simulation analysis 下降率 droop rate 传递函数 transfer function框图 block diagram 受端 receive—side 同步 synchronization保护断路器 circuit breaker 摇摆 swing 阻尼 damping无刷直流电机:Brusless DC motor 刀闸(隔离开关):Isolator 机端 generator terminal变电站 transformer substation永磁同步电机:Permanent-magnet Synchronism Motor异步电机:Asynchronous Motor三绕组变压器:three-column transformer ThrClnTrans双绕组变压器:double—column transformer DblClmnTrans固定串联电容补偿fixed series capacitor compensation双回同杆并架 double—circuit lines on the same tower单机无穷大系统 one machine - infinity bus system励磁电流:magnetizing current 补偿度 degree of compensation电磁场Electromagnetic fields 失去同步 loss of synchronization装机容量 installed capacity 无功补偿 reactive power compensation故障切除时间 fault clearing time 极限切除时间 critical clearing time强行励磁 reinforced excitation 并联电容器:shunt capacitor下降特性 droop characteristics 线路补偿器 LDC(line drop compensation)电机学 Electrical Machinery 自动控制理论 Automatic Control Theory电磁场 Electromagnetic Field微机原理 Principle of Microcomputer电工学 Electrotechnics电路原理Principle of circuits电机学Electrical Machinery电力系统稳态分析 Steady—State Analysis of Power System电力系统暂态分析 Transient—State Analysis of Power System电力系统继电保护原理 Principle of Electrical System's Relay Protection 电力系统元件保护原理 Protection Principle of Power System ’s Element电力系统内部过电压 Past Voltage within Power system模拟电子技术基础 Basis of Analogue Electronic Technique数字电子技术 Digital Electrical Technique电路原理实验Lab。
电力专业英语阅读与翻译第一课一、Summary of glossary 术语1.电力系统(electric) power systempower generation 发电transmission system(network) 输电系统(网络)distribution system 配电系统2.发电power generationpower plant 发电厂powerhouse 发电站hydropower plant 水力发电厂nuclear plant 核电厂thermal plant 热电厂fossil-power plant火电厂3.负荷分类load classificationindustrial loads 工业负荷residential loads 居民负荷commercial loads 商业负荷4.拓扑结构system topologyradial system 辐射状系统loop system 环状系统network system 网状系统二、Wording-buildingGeneral Introduction 专业英语词汇和构词方法简介专业词汇的形成主要有三种情况:1.借用日常英语词汇或其他学科的专业词汇,但是词义和词性可能发生了明显的变化。
例如:在日常英语中表示“力量、权力”和在机械专业表示“动力”的power,数学上表示“幂”,在电力专业领域可以仍作为名词,表示“电力、功率、电能”;也可以作为动词,表示“供以电能”。
在日常英语中表示“植物”的plant,在电力专业领域中用来表示“电厂”等。
2.由日常英语词汇或其他学科的专业词汇,直接合成新的词汇。
例如:over和head组合成overhead,表示“架空(输电线)”;super和conductor 合成superconductor,表示“超导体”等。
3.由基本词根和前缀或后缀组成新的词汇。
大部分专业词汇属于这种情况。
外文原文:Electric power system1 Technical Characteristics of Electric PowerThe electric power has unique technical characteristics which give the power industry certain unique characteristics.1Intangibility. The customer cannot directly detect a kilowatt-hour with any of his physical senses.2Quality. The quality of service can be measured by service continuity or reliability, uniformity of voltage at the proper level, proper and uniformfrequency of the alternating voltage.3Product storage. Unlike most businesses, the electric power utility must create its product simultaneously with its use because there is no storage ofelectricity.4Responsibility for power service. Because the utility delivers its product to the customer’s premises it must assume responsibility for the safe andreliable delivery of its product.5Public Safety. The utility must provide reasonably adequate protection for the public and its own skilled workers.2 Power System PlanningIn anticipation of continued growth in the loads served by the electric utilities, power systems must be continually expanded in capability. Long-range planning is essential to assure that necessary additions are technically adequate, reasonable in cost and fit into a growth pattern.The difficulties encountered by the long-range planner include: uncertainty of load growth with respect to both geography and time, the probability of new invention or technological development.Good system planning strives for optimum design on a system-wide basis, not necessarily for minimum cost in one part of the system without regard to the effect on the other parts.In recent years, there has been an emphasis on economy in planning andoperation.Now there is increased emphasis on reliability and environmental factors.Before planning decisions are made, many factors must be carefully considered:(1)Equipment decision have long-term effects requiring a forecast and study period of 15-25 years.(2)There are many alternate means of generating electric power nuclear, base-load fossil, mid-range combustion turbines or hydro, and in large-medium or small-size plants, and different forms of energy storage.(3)There are several alternate means of transmitting electric power, for example, by alternating or direct current, overhead or underground cable, and all over a wide range of voltages.(4)The planning decisions are affected by load management techniques and the load patterns.(5)Uncertainty exists concerning the factors, such as future fuel cost, interest rates on money and capital availability, equipment forced-outage rates, new technologies and environmental restrictions.3 Electrical Distribution3.1 Primary Distribution SystemsThe wiring between the generating station and the final distribution point is called the primary distribution systems. There are several methods used for transmitting the power between these two points. The two most common methods are the radial system and the loop system.(1)The Radial SystemsThe term radial comes from the word radiate, which means to send out or emit from one central point. A radiate system is an electrical transmission system which begins at a central station and supplies power to various substations.In its simplest from, a radial system consists of a generating station which produces the electrical energy. This energy is transmitted from the generator(s) to thecentral station, which is generally part of, or adjacent to, the generating station. At the central station the voltage is stepped up to a higher value for long-distance transmission.From the central station, several lines carry the power to various substations. At the substations the voltage is usually lowered to a value more suitable for distribution in populated areas. From the substations, lines carry the power to distribution transformers. These transformers lower the voltages to the value required by the consumer.(2)The loop systemThe loop system starts from the central station or a substation and makes a complete loop through the area to be served, and back to the starting point. This results in the area being supplied from both ends, allowing sections to be isolated in case of a breakdown. An expanded version of the loop system consists of several central stations joined together to from a very large loop.(3)Consumer Distribution SystemsThe type of distribution system that the consumer uses to transmit power within the premises depends upon the requirements of the particular installation. Residential occupancies generally use the simplest type. Commercial and industrial systems vary widely with load requirements.3.2 Single-phase SystemsMost single-phase systems are supplied from a three-phase primary. The primary of a single-phase transformer is connected to one phase of the three-phase system. The secondary contains two coils connected in series with a midpoint tap to provide a single-phase, three-wire system. This arrangement is generally used to supply power to residential occupancies and some commercial establishments.For residential occupancies, the service conductors are installed either overhead or underground. Single-family and small multifamily dwellings have the kilowatt-hour metes installed on the outside of the building. From the kilowatt-hourmeter, the conductors are connected to the main disconnect.Three separate disconnecting means are used with one common ground.From the main disconnect, the conductors supply power to the branch circuit panels. For dwelling occupancies there are three basic types of branch circuits: general lighting circuits, small appliance and laundry circuits, and individual branch circuits. The individual branch circuits are frequently used to supply central heating and/or air-conditioning system, water heaters, and other special loads.(1)Grounding RequirementsAll AC services are required to be grounded on the supply side of the service disconnecting means. This grounding conductor runs from the combination system and equipment ground to the grounding electrode. For multifamily occupancies it is permitted to use up to six service disconnecting means. A single grounding conductor of adequate size should be used for the system ground.(2)Commercial and Industrial InstallationsCommercial and industrial installations are more complex than small residential installations. Large apartment complexes and condominiums, although classified as residential occupancies, often use commercial-style services .A single-phase, three-wire service or a three-phase, four-wire service may be brought into the building, generally from underground. The service-entrance conductors terminate in a main disconnects. From this point, the conductors are connected to the individual kilowatt-hour meters for each apartment and then to smaller disconnecting means and over-current protective devices. Branch-circuit panels are generally installed in each apartment. Feeder conductors connect the individual disconnecting means to the branch-circuit panels. Commercial and/or industrial buildings may have more than one kilowatt-hour meter, depending upon the number of occupancies. The service is usually a three-phase, four-wire system. The available voltages may be 120/208V or 277/480v. If the system provides 277/480V, a transformer must be installed in order to obtain 120V. If the building covers a largearea, it is recommended that the service be installed near the center of the building. This arrangement minimizes line loss on feeder and branch-circuit conductors. Some utilities supply a three-phase, three-wire or three-phase, four-wire delta system. The common voltages that may be obtained from the three-wire delta system are 240V, 440V, or 550V. With this arrangement, a transformer must be used to obtain 120V. The usual voltages supplied from the four-wire delta system are 240V, three phase and 120V, single phase.Many large consumers purchase the electrical energy at the primary voltage, and transformers are installed on their premises. Three-phase voltages up to 15 KV are often used.The service for this type of installation generally consists of metal cubicles called a substation unit. The transformers are either installed within the cubicle or adjacent to it. Isolation switches of the drawer type are installed within the cubicle. These switches are used to isolate the main switch or circuit breaker from the supply during maintenance or repair.3.3 Consumer Loop SystemsAlthough the radial system of distribution is probably the most commonly used system of transmitting power on the consumer’s property, the loop system is also employed.When installing any system, over-current protection and grounding must be given primary consideration. Electrical personnel who design and install these systems must comply with the NEC and local requirements.3.4 Secondary High-voltage DistributionLarge industrial establishments may find it more economical to distribute power at voltages higher than 600V. Depending upon the type of installation and the load requirements, voltages as high as 2300V may be used. Step-down transformers are installed in strategic locations to reduce the voltage to a practical working value.Sometimes the high-voltage system may be radial, and the low-voltage systemmay be connected into a loop. Another method is to have both the primaries and secondary connected to from a loop.(1)Secondary Ties Loop SystemIt is frequently convenient to connect loads to the secondary conductors at points between transformers. These conductors are called secondary ties. Article 450 of the NEC gives specific requirements regarding the conductor sizes and over-current protection.(2)Grounding of Electrical SystemsIn general, most electrical systems must be grounded. The purpose of grounding is to limit the magnitude of voltage caused by lightning, momentary surges, and accidental contact with higher voltages. System grounds must be arranged to provide a path of minimum impedance in order to ensure the operation of over-current devices when a ground fault occurs. Current should not flow though the grounding conductor during normal operation.Direct-current systems generally have the grounding conductor connected to the system at the supply station, and not at the individual service. Alternation-current system, on the other hand, must be grounded on the supply side of the main disconnect at each individual service. For specific information on the location and method of grounding, refer to NEC Article 250.3.5 Grounding of Electrical EquipmentMetal conduit and cases which enclose electrical conductors must be grounded. If the ungrounded conductor comes in contact with a metal enclosure which is not grounded, a voltage will be present between the enclosure and the ground. This presents a potential hazard. Persons coming in contact with the enclosure and ground will complete a circuit.All non-current-carrying metal parts of electrical installations should be tightly bonded together and connected to a grounding electrode. Good electrical continuity should be ensured though all metal enclosures. The current caused byaccidental grounds will be conducted though the enclosures, the grounding electrode to the earth.If the current is large enough, it will cause the over-current device to open. (1)Ground-Fault ProtectionA ground-fault protector is a device which senses ground faults and opens the circuit when the current to ground reaches a predetermined value. A ground-fault circuit interrupter is a device which opens the circuit when very small currents flow to ground.There is no way to determine in advance the impedance of an accidental ground. Most circuits are protected by 15A or larger over-current devices. If the impedance of a ground fault is low enough, such devices will open the circuit. What about currents of less than 15A? It has been proven that currents as small as 50mA though the heart, lungs, or brain can be fatal.Electrical equipment exposed to moisture or vibration may develop high-impedance grounds. Arcing between a conductor and the frame of equipment may cause a fire, yet the current may be less than 1 ampere. Leakage current caused by dirt and/or moisture may take place between the conductor and the frame. Portable tools are frequently not properly grounded, and the only path to ground is through the body of the operator.The ground-fault circuit interrupter was developed to provide protection against ground-fault currents of less than 15A. The GFCI is designed to operate on two-wire circuits in which one of the two wires is grounded. The standard circuit voltages are 120V and 277V .The time it takes to operate depends upon the value of the ground-fault current. Small currents of 10mA or less may flow for up to 5s before the circuit is opened. A current of 20mA will cause the GFCI to operate in less than 0.04s. This time/current element provides a sufficient margin of safety without nuisance tripping.The GFCI operates on the principle that an equal amount of current is flowingthrough the two wires. When a ground fault occurs, some of the current flowing though the ungrounded wire; it completes the circuit though the accidental ground. The GFCI senses the difference in the value of current between the values of current between the two wires and opens the circuit. GFIC s may be incorporated into circuit breaks, installed in the line, or incorporated into a receptacle outlet or equipment.Ground-fault protectors are generally designed for use with commercial and/or industrial installations. They provide protection against ground-fault currents from 2A up to 2000A.GFPs are generally installed on the main, submain, and/or feeder conductors. GFCIs are installed in the branch circuits.A ground-fault protector installed on supply conductors must enclose all the circuit conductors, including the neutral, if present. When the operating is under normal conditions, all the current to and from the load flows though the circuit conductors. The algebraic sum of the flux produced by these currents is zero. When a phase-to-ground fault occurs, the fault current returns though the grounding conductor. Under this condition an alternating flux is produced within the sensing device. When the fault current reaches a predetermined value, the magnetic flux causes a relay to actuate a circuit breaker.Sometimes the GFP is installed on the grounding conductor of the system. Under this condition, the unit senses the amount of phase-to-ground current flowing in the grounding conductor. When the current exceeds the setting of the GFP, it will cause the circuit breaker to open.The ground-fault protector is actually an especially design current transformer connected to a solid-state relay.(2)Three-phase SystemsThe various three-phase systems in normal use will be described. Under ideal conditions, these systems operate in perfect balance, and if a neutral conductor is present it carries zero current. In actual practice, perfectly balanced systems areseldom encountered. The electrical worker, therefore, must be able to calculate values of current and voltage in unbalanced systems. Single-phase loads are frequently supplied from three-phase systems. The single-phase load requirements vary considerably, making it virtually impossible to maintain a perfect balance.To calculate the line currents in an unbalanced three-phase system, the method in the following example may be used.4 Selection of Power TransformerThe selection of the transformer can have a major impact on the cost of a substation, since the transformer represents the major cost plate rating is only a aide to transformer application, and should only be used as a first step in the selection process.The selection of the transformer should involve a careful evaluation of a number of other factors:(1)Impedances should be selected considering their effects on short-circuitduties and low-side breaker ratings both for initial and future stationdevelopments.In addition, impedance is important to achieve a proper loaddivision in the parallel operation of transformers.(2)No load tap ranges should be selected to provide an adequate low-side busvoltage.(3)If the high-side or low-side voltages vary over a wide range during the load cycle, it may be necessary to provide bus regulation.The actual regulation can be calculated using the system and load characteristics.5 SwitchgearSwitchgear is a general term covering switching and interrupting devices, also associated devices with control, metering, protective and regulatory equipment.Switchgear mainly includes circuit breaker, disconnecting switch, load-break switch and fuse.The disconnect switch is the simplest switch on the basis of function, operating only in the absence of appreciable current.This switch cannotopen normal load current and its function is to disconnect or connect transformers, circuit breakers, other pieces of equipment and short length of high voltage conductors only after current through them has been interrupted by opening a circuit breaker or load-break switch. A load-break switch will switch normal load currents but will not interrupt short circuit currents. However, circuit breakers will perform the switching functions of the above two classes, but will, if applied within rating, interrupt all short circuit currents that may occur on the system. Fuses consist essentially of a fusible element and an arc-extinguishing means.C ircuit breakers and disconnect switches should not be blown open or otherwise damaged by short circuit currents within their short time ratings.The circuit breakers and disconnecting switches should be designed or protected to withstand normal operating voltages across the device in the open position.6 Means of Reactive Power CompensationT he capacitance of a line has two related voltage effects.One is the rise in voltage along the line resulting from the capacitive current of the line flowing through the line inductance.The second effect is the rise in voltage resulting from the capacitive current of the line flowing through the source impedance.These effects are corrected by the generator voltage regulators.If the line delivers too much charging current, the generator field excitation will become very low which reduces the stability limit and is unacceptable.These voltages can be reduced by the application of shunt reactors.The degree of compensation provided by a reactor is usually quantified by the percentage of the line capacitance that is compensated.The percent shunt compensation of EHV lines in service ranges from 0% to 90% with the reactors located in the substations at one or both ends of the line.The basic purpose of a shunt capacitor bank is to increase the local circuit voltage or improve the load power factor carried by the circuit.Many large capacitor banks are switched on and off as the system need for reactive kilovolt amperes changes.System requirements govern whether a certain bank should or should notbe switched.If the voltage at the capacitor would be too high during knight load, some or all of the capacitors are switched off.Very large banks are usually switched in steps.This procedure has the disadvantage of requiring more switches and thus increasing the total equipment cost per kilovar. It, however, provide a means of keeping the voltage change per step within permissible limits.A synchronous condenser is nothing more than a synchronous machine running at synchronous speed witch no mechanical load.The condenser has a control circuit that controls the field excitation to provide voltage control.When the system voltage starts to fall below the desired values, the control circuit will automatically increase the field excitation which causes the synchronous condenser to supply vats to the system. This will increase the system voltage at the point.7 Overvoltage and Insulation CoordinationA n area of critical importance in the design of power system is the consideration of the insulation requirements for lines, cables and stations.W hen lightning strikes a phase conductor of transmission line, the current of the lightning stroke will encounter the surge impedance of the conductor so that overvoltage will be built up and propagate to the substation along the transmission line in wave form.This type of overvoltage is called lightning incoming wave.It will danger electric equipment in substations.Insulation coordination is the process of determining the proper impulse insulation level and switching insulation level required in various electrical equipments together with the proper surge arrester. This process is determined from the known surge characteristics of equipment and the characteristics of surge arresters.8 GroundingGrounding in power system is for the purpose of operation consideration, lightning proof and safety of personnel and equipment. Grounding means connecting to a low resistance earth electrode or an excellent earthing system. Theearthing installations must have a current-carrying capacity sufficient to deal with the maximum fault currents, and a grounding resistance low enough to prevent a dangerous voltage appearing between any points which a man could reach simultaneously. The earthing arrangements should also be such as to ensure that, under fault conditions, the lowest practical voltage appears between earthed points of the equipment and the main body of the earth, so that insulation breakdown or burning does not occur on equipment which is earthed. During a fault, the flow of current to earth will result in voltage gradients on the surface within and around a substation. Unless proper precautions are taken, the voltage differences along the ground may be great enough to endanger a person walking there. In addition, such voltage differences can sometimes exist.Between“grounded” structures or equipment frames and the nearby earth. As a result of these concerns, it is common practice for substations to have an electrical ground system consisting of a gird of horizontal and buried conductor.中文译文:电力系统1 电力的技术特点电力具有独特的技术特点,这使得电力工业具有独特的行业特点。
汽车学院毕业设计科技文献翻译《Power Supply and Distribution System》《供配电系统》姓名xxx专业电气工程及其自动化学号xxxxxxxxxxxxx班级2班指导教师赵洪亮2013年 4月Power Supply and Distribution SystemABSTRACT:The basic function of the electric power system is to transport the electric power towards customers. The l0kV electric distribution net is a key point that connects the power supply with the electricity using on the industry, business and daily-life. For the electric power, allcostumers expect to pay the lowest price for the highest reliability, but don't consider that it's self-contradictory in the co-existence of economy and reliable.To improve the reliability of the power supply network, we must increase the investment cost of the network construction But, if the cost that improve the reliability of the network construction, but the investment on this kind of construction would be worthless if the reducing loss is on the power-off is less than the increasing investment on improving the reliability .Thus we find out a balance point to make the most economic,between the investment and the loss by calculating the investment on power net and the loss brought from power-off.KEYWORDS:power supply and distribution, power distribution reliability,reactive compensation, load distributionThe revolution of electric power system has brought a new big round construction,which is pushing the greater revolution of electric power technique along with the application of new technique and advanced equipment. Especially, the combination of the information technique and electric power technique, to great ex- tent, has improved reliability on electric quality and electric supply. The technical development decreases the cost on electric construction and drives innovation of electric network. On the basis of national and internatio- nal advanced electric knowledge, the dissertation introduces the research hotspot for present electric power sy- etem as following.Firstly, This dissertation introduces the building condition of distribution automation(DA), and brings forward two typical construction modes on DA construction, integrative mode and fission mode .It emphasize the DA structure under the condition of the fission mode and presents the system configuration, the mainstation scheme, the feeder scheme, the optimized communication scheme etc., which is for DA research reference.Secondly, as for the (DA) trouble measurement, position, isolation and resume, This dissertation analyzes the changes of pressure and current for line problem, gets math equation by educing phase short circuit and problem position under the condition of single-phase and works out equation and several parameter s U& , s I& and e I& table on problem . It brings out optimized isolation and resume plan, realizes auto isolation and network reconstruction, reduces the power off range and time and improves the reliability of electric power supply through problem self- diagnoses and self-analysis. It also introduces software flow and use for problem judgement and sets a model on network reconstruction and computer flow.Thirdly, electricity system state is estimated to be one of the key techniques in DA realization. The dissertation recommends the resolvent of bad measurement data and structure mistake on the ground of describing state estimate way. It also advances a practical test and judging way on topology mistake in state estimate about bad data test and abnormity in state estimate as well as the problem and effect on bad data from state measure to state estimate .As for real time monitor and control problem, the dissertation introduces a new way to solve them by electricity break and exceptional analysis, and the way has been tested in Weifang DA.Fourthly, about the difficulty for building the model of load forecasting, big parameter scatter limit and something concerned, the dissertation introduces some parameters, eg. weather factor, date type and social environment effect based on analysis of routine load forecasting and means. It presents the way for electricity load forecasting founded on neural network(ANN),which has been tested it’s validity by example and made to be good practical effect.Fifthly, concerning the lack of concordant wave on preve nting concordant wave and non-power compensation and non-continuity on compensation, there is a topology structure of PWM main circuit and nonpower theory on active filter the waves technique and builds flat proof on the ground of Saber Designer and proves to be practical. Meanwhile, it analyzes and designs the way of non-power need of electric network tre- nds and decreasing line loss combined with DA, which have been tested its objective economic benefit throu- gh counting example.Sixthly, not only do the dissertation design a way founded on the magrginalelectric price fitted to our present national electric power market with regards to future trends of electric power market in China and fair trade under the government surveillance, that is group competitio n in short-term trade under the way of grouped price and quantity harmony, but also puts forward combination arithmetic, math model of trading plan and safty economical restriction. It can solve the original contradiction between medium and long term contract price and short term competitive price with improvement on competitive percentage and cut down the unfair income difference of electric factory, at the same time, it can optimize the electric limit for all electric factories and reduce the total purchase charge of electric power from burthen curve of whole electric market network.The distribution network is an important link among the power system. Its neutral grounding mode and operation connects security and stability of the power system directly. At the same time, the problem about neutral grounding is associated with national conditions, natural environment, device fabrication and operation. For example, the activity situation of the thunder and lightning, insulating structure and the peripheral interference will influence the choice of neutral grounding mode Conversely, neutral grounding mode affects design, operation, debugs and developing. Generally in the system higher in grade in the voltage, the insulating expenses account for more sizable proportion at the total price of the equipment. It is very remarkable to bring the economic benefits by reducing the insulating level. Usually such system adopt the neutral directly grounding and adopt the autoreclosing to guarantee power supply reliability. On the contrary, the system which is lower in the voltage adopts neutral none grounding to raise power supply reliability. So it is an important subject to make use of new- type earth device to apply to the distribution network under considering the situation in such factors of various fields as power supply reliability, safety factor, over-voltage factor, the choice of relay protection, investment cost, etc.The main work of this paper is to research and choice the neutral grounding mode of the l0kV distribution network. The neutral grounding mode of the l0kV network mainly adopts none grounding, grounding by arc suppressing coil, grounding by reactance grounding and directly grounding. The best grounding mode is confirmed through the technology comparison. It can help the network run in safety and limit the earth electric arc by using auto-tracking compensate device and using the line protection with the detection of the sensitive small ground current. The paperintroduces and analyzes the characteristic of all kind of grounding modes about l0kV network at first. With the comparison with technological and economy, the conclusion is drawn that the improved arc suppressing coil grounding mode shows a very big development potential.Then, this paper researches and introduces some operation characteristics of the arc suppressing coil grounding mode of the l0kV distribution network. And then the paper put emphasis on how to extinguish the earth electric arc effectively by utilizing the resonance principle. This paper combines the development of domestic and international technology and innovative achievement, and introduces the computer earth protection and autotracking compensate device. It proves that the improved arc suppressing coil grounding mode have better operation characteristics in power supply reliability, personal security, security of equipment and interference of communication. The application of the arc suppressing coil grounding mode is also researched in this paper.Finally, the paper summarizes this topic research. As a result of the domination of the arc suppressing coil grounding mode, it should be more popularized and applied in the distribution network in the future.The way of thinking, project and conclusions in this thesis have effect on the research to choose the neutral grounding mode not only in I0kV distribution network but also in other power system..The basic function of the electric power system is to transport the electric power towards customers. The l0kV electric distribution net is a key point that connects the power supply with the electricity using on the industry, business and daily-life. For the electric power, all costumers expect to pay the lowest price for the highest reliability, but don't consider that it's self-contradictory in the co-existence of economy and reliable. To improve the reliability of the power supply network, we must increase the investment cost of the network con- struction But, if the cost that improve the reliability of the network construction, but the investment on this kind of construction would be worthless if the reducing loss is on the power-off is less than the increasing investment on improving the reliability .Thus we find out a balance point to make the most economic, between the investment and the loss by calculating the investment on power net and the loss brought from power-off. The thesis analyses on the economic and the reliable of the various line modes, according to the characteristics various line modes existed in the electric distribution net in foshan..First, the thesis introduces as the different line modes in the l0kV electric distribution net and in some foreign countries. Making it clear tow to conduct analyzing on the line mode of the electric distribution net, and telling us how important and necessary that analyses are.Second, it turns to the necessity of calculating the number of optimization subsection, elaborating how it influences on the economy and reliability. Then by building up the calculation mode of the number of optimization subsection it introduces different power supply projects on the different line modes in brief. Third, it carries on the calculation and analyses towards the reliability and economy of the different line modes of electric distribution net, describing drafts according by the calculation. Then it makes analysis and discussion on the number of optimization subsection.At last, the article make conclusion on the economy and reliability of different line modes, as well as, its application situation. Accordion to the actual circumstance, the thesis puts forward the beneficial suggestion on the programming and construction of the l0kV electric distribution net in all areas in foshan. Providing the basic theories and beneficial guideline for the programming design of the lOkV electric distribution net and building up a solid net, reasonable layout, qualified safe and efficiently-worked electric distribution net.References[1] Wencheng Su. Factories power supply [M]. Machinery Industry Publishing House. 1999.9[2] Jiecai Liu. Factories power supply design guidance [M]. Machinery Industry Publishing House.1999.12[3] Power supply and distribution system design specifications[S].China plans Press. 1996[4] Low-voltage distribution design specifications [S].China plans Press. 1996.6英文翻译供配电系统摘要:电力系统的基本功能是向用户输送电能。
Electric Power System and Power System AutomaticElectirc Prower Systems,components that transform other types of energy into electrical energy and transmit this energy to a consumer. The production and transmission of electricity relavtively efficient and inexpensive,although unlike other forms of energy,electricity is not easily stored-up and thus must generally be used as it is being produced.Components of an Electric Power SystemA modern electric power system consists of six main components:(1)the power station, (2)a set of transformers to raise the generated power to the high voltages used on the transmission lines,(3)the transmission lines,(4) the substations at which the power is stepped down to the voltage on the distribution lines,(5)the distrib ution lines,and(6)the transformers that lower the distribution voltage to the level used by the consumer's equipment.Power Station The power station of a power system consist of a prime mover, such as a turbine driven by water,steam,or combustion gases that operate a system of electric motors and generators.Most of the world's electric power is generated in steam plants driven by coal,oil,nuclear energy,or gas.A smaller percentage of the world's electric power is generated by hydroelectric(waterpower ),diesel,and internal-combustion plants.Transformers Modern electric power system use transformer to convert electricity into different voltage.With transformers,each stage of the system can be operated at an appropriate voltage.In a typical system, the generators at the power station deliver a voltage of from 1,000 to 26,000 volts(V ).Transformers step this voltage up to values ranging form 138,000to 765,000 V for the long-distance primary transmission line because higher voltage can be transmitted more efficiently over long distances.At the substation the voltage may be transformed down to levels of 69,000 to 138,000 V for further transfer on the distribution system. Another set of transformers step the voltage down again to a distribution level such as 2,400 or 4,160 V or 15,27,or 33 kilovolts(KV ).Finally the voltage is transformed once again at the distribution transformer near the point of use to 240 or 120 V.Transmission Lines The line of high-voltage transmission systems are usually composed of wires of copper, aluminum, or copper-clad or aluminum-clad steel, while are suspended from tall latticework towers of steel by strings of porcelain insulator. By the use of clad steel wires and high towers, the distance between towers can be increased, and the cost of the transmission line thus reduced.In modern installation with essentially straight paths, high-voltage lines may be built with as few as few as six towers to the kilometre. In some areas high-voltage lines are suspended from tall wooden polestar spaced more closely together.For lower voltage distribution lines, wooden poles are generally used rather than steel towers,In cities and other areas where open lines create a safety hazard or are considered unattractive, insulated underground cables are used for distribution.Some of these cables have a hollow core through which oil circulates under low pressure. The oil provides temporary protection from water damage to the enclosed wiresshould the cable develop a leak. Pipe-type cables in which three cables are enclosed in a pipe filled with oil under high pressure (14 kg per sq cm/200psi )are frequently used. These cables are used for transmission of current at voltages as high as 345,000V(or 345kV ).Supplementary Equipment Any electric-distribution system involves a large amount of supplementary equipment to protect the generators, transformers, and the transmission lines themselves. The system often include devices designed to regulate the voltage or other characteristics of power delivered to consumers.To protect all elements of a power system from short circuit and overloads, and for normal switching operation, circuit breakers are employed.These breakers are large switches that normal activated automatically in the event of a short circuit or other condition that produces a sudden rise of current.Because a current forms across the terminals of the circuit breaker at the moment when the current is interrupted, some large breakers (such as those used to protect a generator or a section of primary transmission line )are immersed in a liquid that is a poor conductor of electricity, such as oil, to quench the current. In large air-type circuit breakers, as well as in oil breakers, magnetic fields are used to break up the current. Small air-circuit breakers are used for protection in shops, factories, and in modern home installations. In residential electric wiring, fuses were once commonly employed for the same purpose.A fuse consists of a piece of alloy with a low melting point, inserted in the circuit, which melts, breaking the circuit if the current rises above a certain value.Most residences now use air-circuit breakers.Power FailuresIn most parts of the world, local or national electric utilities have joined in grid systems. The linking grids allow electricity generated in one area to be shared with others.Each utility that agrees to share gain an increased reserve capacity, use of large, more efficient generators, and the ability to respond to local power failures by obtaining energy from a linking grid.These interconnected grids are large, complex systems that contain elements operated by different groups. These system offer the opportunity for economic savings and improve overall reliability but can create a risk of widespread failure. For example, the worst blackout in in the history of the United Stated and Canada occurred August 14, 2003, when 61,800 megawatts of electrical power was lost in an area covering 50 million people.(one megawatt of electricity is roughly the amount needed to power 750 residential home.)The blackout prompted calls to replace aging equipment and raised questions about the reliability of the national power grid.Despite the potential for rare widespread problems, the interconnected grid system provides necessary backup and alternate paths for power flow, resulting in much higher overall reliability than is possible with isolated system. National or regional grids can also cope with unexpected outages such as those caused by storms, earthquakes, landslides, and forest fires, or due to human error or deliberate acts of sabotage.Power QualityIn recent years electricity has been used to power more sophisticated andtechnically complex manufacturing processes, computers and computer networks, and a variety of other high-technology consumer goods. These products and processes are sensitive not only to the continuity of power supply but also to the constancy of electrical frequency and voltage. Consequently, utilities are taking new measures to provide necessary reliability and quality of electrical power, such as by providing additional electrical equipment to assure that the voltage and other characteristics of electrical power are constant.V oltage Regulation Long transmission lines have considerable inductance and capacitance. When a current flows through the line, inductance and capacitance have the efficient of varying the voltage on the line as the current varies. Thus the supply voltage varies with the load. Several kinds of devices are used to overcame this undesirable variation in an operation called regulation of the voltage. The devices include induction regulators and three-phase synchronous motors (called synchronous condensers), both of which vary the effective amount of inductance and capacitance in transmission circuit.Inductance and capacitance react with a tendency to nullify one another. When a load circuit has more inductive than capacitive reactance, as almost invariably occurs in large power systems, the amount of power delivered for a given voltage and current is less than when the two are equal. The ratio of these two amounts of power is called the power factor. Because transmission-line losses are proportional to current, capacitance is added to the circuit when possible, thus bringing the power factor as nearly as possible to 1. For this reason, large capacitors are frequently inserted as a part of power-transmission systems.World Electric Power Production Over the period from 1950 to 2003, the most recent year for which data are available, annual world electric power production and consumption rose from slightly less than 1trillion kilowatt-hours(KW.H )to 15.9 trillion kW-h. A change also took place in the type of power generator. In 1950 about two-thirds of the world's electricity came from steam-generating source and about one-third from hydroelectric source. In 2003 thermal power produced 65 percent of the power ,but hydroelectric had declined to 17 percent,and nuclear power accounted for 16percent of the total. The growth in nuclear power slowed in some countries, notably the United States, in response to concerns about safety. Nuclear plants generated 20 percent of U.S. Electricity in 2003; in France , the world leader, the figure was 78 percent.ConservationMuch of the world's electricity is produce from the use of nonrenewable resource, such as natural gas, coal, oil, and uranium. Coal, oil, and natural gas contain carbon, and buring these fossil fuels contribution to global emission of carbon dioxide and other pollutants. Scientists believes that carbon dioxide is the principal gas responsible for global warming, a steady rise in earth's surface temperature.Consumer of electricity can save money and help protect the environment by elimination unnecessary use of electricity, such as turning off lights when leavings a room. Other conservation methods include buying and using energy-efficient appliance and light bulbs, and using appliances, such as washing machines and dryers,at off-peak production hours when rates are lower. Consumers may also consider environment measure such as purchasing "green power " when it is offer by a local utility. "green power" is usually more expensive but relies on renewable and environment friendly energy source, such as wind turbines and geothermal power plants.OverviewPower provides constantly deal with demands to increase productivity and reduce costs. This translates into the need for administrators, engineers, operators, planners, field crews and others to collect and act on decision making information. Power system vendors are following a trend to mack device smarter so they can create and communicate this information. The term "power system " describes the collection of device that make up the physical systems that generate, transmit, and distribute power. The term "instrumentation and control system "refers to the collection of devices that monitor, control, and protect the system.Power system automation refers to using refers to using I&C devices to perform automatic decision making and control of the power system.Data Acquisition Data acquisition refers to acquiring ,or collecting, data. This data is collected in the form of measured analog current or voltage values or the open or closed status of contact points. Acquired data can be used locally within the device collecting it, sent to another device in a substation, or sent from the substation to one or several databases for use by operators engineers, planners, and administrators.Power System Supervision Computer processes and personnel supervise, or monitor, the condition and status of the power system using this acquired data. Operators and engineers monitor the information remotely on computer display and graphical wall displays or locally, at the device, on front-panel displays and laptop computers .Power System Control Control refers to sending command message to a device to operate the I&C and power system device. Traditional supervisory control and data acquisition(SCADA )system rely on operators to supervisory the system and initiate command from an operators console on the master computer. Field personnel can also control device using front-panel push buttons or a laptop computer.Power System Automation System automation is the act of automation control the power system via automation processes within computer and and intelligent I&C device. The processes rely on date acquisition, power system supervisory, and power system control all working together in a coordinate automation fashion. The commands are generator automation and then transmit in the same fashion as operator initiated commands.I&C System IEDS I&C devices built using microprocessors are commonly referred to as intelligent electricity device (IEDS ). Microprocessor are single chip computer that allow the devices into which they are built to processes data, accept command, and communicate information like a computer. Automatic processes can be run in the IEDS,and communications are handled through a serial port like the communications ports on a computer. IEDS are found in the substation and on the pole-top.Equipment for Power System AutomaticPower system automatic includes a variety of equipment. The principal items are listed and briefly described below.Instrument Transformer Instrument transformer are used to sense powe r system current and voltage values. They are physical connected to power system apparatus and convert the actual power system signals, which include high voltage and current magnitudes, down to lower signal levels.Transducer Transducer convert the analong output of an instrument transformer from one magnitude to another or from one value type to another, such as from an ac current to dc voltage.Remote Terminal Unit As the name implies, a remote terminal device , RTU, is an IDE that can be installed in a remote location, and acts as a terminal point for field contacts. A dedicated pair of copper conductors are used to sense every contacts and transducer value. These conductors originate at the power system device, are installed in trenches or overhead cable trays and are then terminal on panels within the RTU. The RTU can transfer collected data to other device and receive data and control command from other devices through a serial port. User programmable RTUs are referred to as "smart RTUs ".Communications Port Switch A communications switch is a device that switches between several serial Ports when it is told to do so. The remote user initiates communicate with the port switch via a connection to the substation, typically a leased line or dial-up telephone connection. Once connected, the user can route their communications through the port switch to one of the connected substation IEDS. The port switch merely "passes through "the IED communications.Meter A meter is an IED that is used to create accurate measurements of power system current, voltage, and power values. Metering values such as demand and peak are saved within the meter to create history information about the activity of the power system.Digital Fault Recorder A digital fault recorder ,is an IED that recorders information about power system disturbance. It is capable of storing data in a digital format when triggered by conditions detected on the power system. Harmonics, frequency, and voltage are examples of data captured by DFRS.Load Tap Changer(LTC ) Load tap changers are devices used to Changer the tap position on transformers. These devices work automatically or can be controlled via another local IED or from a remote operator or process.Recloser Controller Recolser controllers remotely control the operation of automatic mated reclosers and switches. These devices monitor and store power system conditions and determine when to perform control actions.They also accept commands from a remote operator or processes.Time Synchronization Source A time synchronization source is an IED that creates a time-of-day values which is then broadcast to the IEDS in order to set all their clocks to the same time.Protocol Gateway IEDS communicate over serial connected by speaking a particular language or protocol. A protocol gateway converts communications fromone protocol to another.This task is often performed by software on a personnel computer.Human Machines Interface The front panel display and push buttons or a personnel computer act as interfaces to system data and controls for personnel in the substation.Programmable Logic Controller (PLC ) As the name implies, a programmable logic controller ,is an IDE that can be programmed to perform logical control. As with the RUT, a dedicated pair of copper conductor and transducer value are terminated on panels within the PLC. Personnel familiar with the PLC development environment can program PLCS to create information from sensor data and perform automation. The PLC can transfer collected data to other device and receive data and control commands from other devices through a serial port.Protective Relay A protective relay is an IED designed to sense power system to protect personnel and equipment. The relay has local termination so that the copper conductors for each connect do not have to be routed to a central termination panel associated with RTUS and PLCS. Transducer are not necessary since the relay accepts signals directly from the instrument transformers. Protective relays create metering information, collect system status information, and store historical records of power system operation.Communications Processor A communication processor is a substation controller that incorporates the function of many other I&C devices into one IDE.It has many communication ports to support multiple simultaneous communication links. The communication the data it acquires for transmission to one or many master inside and outside the substation. The communication processor incorporates features of many of the other IEDS including an RUT, and a limited PLC communication port switch, a protocol gateway, a time synchronization source, and a limited PLC functionality. The communication processor has locally termination I/O and can perform dial-out to alert personal or processes when a status change.Power System AutomationPower System Integration Power system integration is the act of communication data to, from, or among IEDs in the I&C system and remote users. Substation integration refers to combine data from the IED's local to a substation so that there is a single point of contact in the substation controller acting as a single point of connect. Some system bypass the substation controller by using direct connect to the people devices, such as RTUS, protective relays, and controllers.Power Systems Automation Power systems I&C equipment through the automatic control of power system behavior.Substation automation IED refers to the use of data, and automatically adjust the internal substation contro l and control commands from a remote user to control power system equipment.Because the real substation substation automation depends on the integration of the two terms are usually interoperable.Electric power system automation covers all aspects of the production and delivery.Some aspects related to power transmission and distribution of all levels, namely, power distribution automation.Hoisted to the peak for the substation and power transmission system monitoring can reduce the incidence ofpower outages, shorten the off time.IED, communication protocols and communication methods described above to work together as a system, power system automation.Power Delivery Automation Although all the different public sectors, but most of that power distribution automation, power distribution substations and feeder lines should include: monitoring and data acquisition - operator monitoring and control, distribution automation - fault location, automatic isolation, autosegmentation, since the resumption of power supply, substation automation - Circuit Breaker (failure), automatic reclosing, battery monitoring, fault substation substation load transfer and transfer of energy management systems - trends, reactive power and voltage monitoring, power control, transformer andfeed line load balancing, fault analysis and equipment maintenance.No automatic control system still has a remote monitoring and control of power system equipment operator benefits include: automatic switch remote monitoring circuit breakers and remote monitoring of non-automatic switch and fuse combination of remote monitoring remote monitoring capacitance and voltage control of remote power quality monitoring.Power System Automation FeaturesIEDS described in the overview are used to perform power system integration and automation. Most design require that one IED act as the substation controller and perform data acquisition and control of the other IDES.Substation controller also requires support systems automation munications equipment industry, uses the term client / server, master or client to get data from other devices, or servers from the device to send data to other device client/server to dynamically send and receive data.Data concentrator to collect, focus on dynamic data from other devices to create substation database.In this way, important data from each IED subset of a data transfer by sending to the master device.Data Concentrator IED database used indirect connection between the data transfer.Substation file client/server from several devices to collect, store data.Easy for users to archive data retrieval.Substation IED life is now very different.Most of the IED is still useful but the lack of the latest agreement.Through specific communication baud rate and protocol with the IED, IED communication processor to extend the time available for ing the communication processor for substation integration can be easily adapted to future IED.In the substation upgrade project, abandon all existing IED is rare.Power System Automation Benefits to UtilityThe benefits of monitoring, remote control, and automation of power delivery include improve employee and public safety, and deferment of the cost of purchasing new eauipment. Also, reduce operation and maintenance cost are realized through improved use of existing facilities and operation performance of the power system through reduced losses associated with outage and improve voltage profile. Collection of information can result in better planning and system design, and increased customer satisfaction will result from improve responsiveness, service reliability, and power quality.电力系统及电力系统自动化电力系统把其它形式的能源转化为电能并输送给用户。
外文翻译Electric Power SystemElectric Power System, components that transform other types of energy into electrical energy and transmit this energy to a consumer. The production and transmission of electricity is relatively efficient and inexpensive, although unlike other forms of energy, electricity is not easily stored ad thus must generally be used as it is being produced.Components of an Electric Power SystemA modern electric power system consists of six main components: (1) the power station, (2)a set of transformers to raise the generated power to the high voltages used on the transmission lines, (3) the transmission lines, (4) the substations at which the power is stepped down to the voltage on the distribution lines, (5) the distribution lines, and (6) the transformers that lower the distribution voltage to the level used by the consumer’s equipment.Power Station, the power station of a power system consists of a prime mover, such as a tribune driven by water, steam, or combustion gases that operat e a system of electric motors and generators. Most of the world’s electric power is generated in steam plants driven by hydroelectric (water power), diesel, and internal-combustion plants.Transformers, Modern electric power systems use transformers to convert electricity into different voltages. With transformers, each stage of the system can be operated at an appropriate voltage. In a typical system, the generators at the power station deliver a voltage of from 1,000 to 26,000volts (v). Transformers step this voltage up to values ranging from 138,000 to 765,000 V for torture transfer on the distribution system. Another set of transformers step the voltage down again to a distribution level such as 2,400 or 4,160 V or 15, 27, or 33 kilovolts (kV). Finally the voltage is transformed once again the distribution transformed near the point of use to 240 or 120 V.Transmission Lines, The lines of high voltage transmission system areusually composed of wires of copper, aluminum-clad steel, which are suspended form tall latticework towers of steel by strings of porcelain insulators. By the use of clad steel wires and high towers, the distance between towers can be increased, and the cost of the transmission line thus reduced. In modern installations with essentially straight paths, high-voltage lines may be built with as few as six towers to the kilometer. In some areas high-voltage lines are suspended from tall wooden poles spaced more closely together.For lower voltage distribution lines, wooden poles are generally used rather than steel towers. In cites and other areas where open lines create a safety hazard or are considered unattractive, insulated underground cables are used for distribution. Some of these cables have a hollow core through which oil circulates under low pressure. The oil provides temporary protection from water damage to the enclosed wires should the cable develop a leak. Pipe-type cables in which three cables are enclosed in a pipe filled with oil under high pressure (14 kg per sq cm/200psi) are frequently used. These cables are used for transmission of current at voltage as high as 345,000V (or 345 kV).Supplementary Equipment Any electric-distribution system involves a large amount of supplementary equipment to protect the generators, transformers, and the transmission lines themselves. The system often includes devices designed to regulate the voltage or other characteristics of power delivered to consumers.To protect all elements of a power system from short circuits and overloads, and for normal switching operations, circuit breakers are employed. These breakers are large switches that are activated automatically in the event of a short circuit or other condition that produces a sudden rise of current. Because a current forms across the terminals of the circuit breaker at the moment where the current is interrupted, some large breakers (such as those used to protect a generator or a section of primary transmission line) are immersed in a liquid that is a poor conductor of electricity, such as oil, to quench the current. In large air-type circuit breakers, as well as in oil breakers, magnetic fields are used to break up the current. Small air-circuit breakers areused for protection in shops, factories, and in modern home installations. In residential electric wiring, fuses were once commonly employed for the same purpose. A fuse consists of piece of alloy with a low melting point, inserted in the circuit, which melts, breaking the circuit if current rises above a certain value. Most residences now use air-circuit breakers.Power FailuresIn most parts of the world, local or national electric utilities have joined in grid systems. The linking grids allow electricity generated in one area to be shared with others. Each utility that agrees to share gains an increased reserve capacity, use of larger, more efficient generators, and the ability to respond to local power failures by obtaining energy from a linking grid.These interconnected grids are large, complex systems that contain elements operated by different groups. These systems offer the opportunity for economic saving and improve overall reliability but can create a risk of widespread failure. For example, the worst blackout in the history of the United States and Canada occurred august 14, 2003, when 61,800 megawatts of electrical power was lost in an area covering 50 million people. (One megawatts of electricity is roughly the amount needed to power 750 residential homes.) The blackout prompted calls to replace aging equipment and raised questions about the reliability of the national power grid.Despite the potential for rare widespread problems, the interconnected grid system provides necessary backup and alternate paths for power flow, resulting in much higher overall reliability than is possible with isolated systems. National or regional grids can also cope with unexpected outages such as those caused by storms, earthquakes, landslides, and forest fires, or due to human error or deliberate acts of sabotage.Power qualityIn recent years electricity has been used to power more sophisticated and technically complex manufacturing processes, computers and computer network, and a variety of other high-technology consumer goods. These products and processes are sensitive not only to the continuity of power supplybut also to the constancy of electrical frequency and voltage. Consequently, utilities are taking new measure to provide the necessary reliability and quality of electrical power, such as by providing additional electrical equipment assure that the voltage and other characteristics of electrical power are constant.Voltage Regulation long transmission lines have considerable inductance and capacitance. When current flows through the lines, inductance and capacitance have the effect of varying the voltage on the line as the current varies. Thus the supply voltage varies with the load. Several kinds of devices are used to overcome this undesirable variation in an operation called regulation of the voltage. The devices include induction regulation and three-phase synchronous motors (called synchronous condensers), both of which vary the effective amount of inductance and capacitance in the transmission circuit.Inductance and capacitance react with a tendency to nullify one another. When a load circuit has more inductive than capacitive reactance, as almost invariably occurs in large power systems, the amount of power delivered for a given voltage and current is less than when the two are equal. The ratio of these two amounts of power is called the power factor. Because transmission-line losses are proportional to current, capacitance is added to the circuit when possible, thus bringing the power factor as nearly as possible to 1. For this reason, large capacitors are frequently inserted as a part of power-transmission systems.World Electric Power Production Over the period from 1950 to 2003, the most recent year for which data are available, annual world electrical power production and consumption rose from slightly less than 1 trillion kilowatt-hours (kw h ∙) to 15.9 trillion kw h ∙ A change also took place in the type of power generation. In 1950 about two-thirds of the world’s electricity came from steam-generating sources and about one-third from hydro electric sources. In 2003thermal sources produced 65 percent of the power, but hydropower had declined to 17 percent, and nuclear power accounted for 16percent of the total. The grown in nuclear power showed in some countries, notably the United States, in response to concerns about safety. Nuclear plants generated 20 percent of U.S. electricity in 2003; in France, the world leader, the figure was 78 percent.ConservationMuch of the world’s electricity is produced from the use of nonrenewable resources, such as natural gas, coal, oil, and uranium. Coal, oil, and natural gas contain carbon, and burning these fossil fuels contributes to global emissions of carbon dioxide and other pollutants. Scientists believe that carbon dioxide is the principal gas respon sible for global warming, a steady rise in Earth’s surface temperature.Consumers of electricity can save money and help protect the environment by eliminating unnecessary use of electricity, such as turning off lights when leaving a room. Other conservation methods include buying and using energy-efficient appliances and light bulbs, and using appliances such as washing machines and dryers, at off-peak production hours when rates are lower. Consumers may also consider environmental measures such as purchas ing “green power” when it is offered by a local utility, “Green power” is usually more expensive but relies on renewable and environmentally friendly energy sources, such as wind turbines and geothermal power plants.电力系统介绍电力系统把其它形式的能源转化为电能并输送给用户。
汽车学院毕业设计科技文献翻译《Power Supply and Distribution System》《供配电系统》姓名xxx专业电气工程及其自动化学号xxxxxxxxxxxxx班级2班指导教师赵洪亮2013年 4月Power Supply and Distribution SystemABSTRACT:The basic function of the electric power system is to transport the electric power towards customers. The l0kV electric distribution net is a key point that connects the power supply with the electricity using on the industry, business and daily-life. For the electric power, allcostumers expect to pay the lowest price for the highest reliability, but don't consider that it's self-contradictory in the co-existence of economy and reliable.To improve the reliability of the power supply network, we must increase the investment cost of the network construction But, if the cost that improve the reliability of the network construction, but the investment on this kind of construction would be worthless if the reducing loss is on the power-off is less than the increasing investment on improving the reliability .Thus we find out a balance point to make the most economic,between the investment and the loss by calculating the investment on power net and the loss brought from power-off.KEYWORDS:power supply and distribution, power distribution reliability,reactive compensation, load distributionThe revolution of electric power system has brought a new big round construction,which is pushing the greater revolution of electric power technique along with the application of new technique and advanced equipment. Especially, the combination of the information technique and electric power technique, to great ex- tent, has improved reliability on electric quality and electric supply. The technical development decreases the cost on electric construction and drives innovation of electric network. On the basis of national and internatio- nal advanced electric knowledge, the dissertation introduces the research hotspot for present electric power sy- etem as following.Firstly, This dissertation introduces the building condition of distribution automation(DA), and brings forward two typical construction modes on DA construction, integrative mode and fission mode .It emphasize the DA structure under the condition of the fission mode and presents the system configuration, the mainstation scheme, the feeder scheme, the optimized communication scheme etc., which is for DA research reference.Secondly, as for the (DA) trouble measurement, position, isolation and resume, This dissertation analyzes the changes of pressure and current for line problem, gets math equation by educing phase short circuit and problem position under the condition of single-phase and works out equation and several parameter s U& , s I& and e I& table on problem . It brings out optimized isolation and resume plan, realizes auto isolation and network reconstruction, reduces the power off range and time and improves the reliability of electric power supply through problem self- diagnoses and self-analysis. It also introduces software flow and use for problem judgement and sets a model on network reconstruction and computer flow.Thirdly, electricity system state is estimated to be one of the key techniques in DA realization. The dissertation recommends the resolvent of bad measurement data and structure mistake on the ground of describing state estimate way. It also advances a practical test and judging way on topology mistake in state estimate about bad data test and abnormity in state estimate as well as the problem and effect on bad data from state measure to state estimate .As for real time monitor and control problem, the dissertation introduces a new way to solve them by electricity break and exceptional analysis, and the way has been tested in Weifang DA.Fourthly, about the difficulty for building the model of load forecasting, big parameter scatter limit and something concerned, the dissertation introduces some parameters, eg. weather factor, date type and social environment effect based on analysis of routine load forecasting and means. It presents the way for electricity load forecasting founded on neural network(ANN),which has been tested it’s validity by example and made to be good practical effect.Fifthly, concerning the lack of concordant wave on preve nting concordant wave and non-power compensation and non-continuity on compensation, there is a topology structure of PWM main circuit and nonpower theory on active filter the waves technique and builds flat proof on the ground of Saber Designer and proves to be practical. Meanwhile, it analyzes and designs the way of non-power need of electric network tre- nds and decreasing line loss combined with DA, which have been tested its objective economic benefit throu- gh counting example.Sixthly, not only do the dissertation design a way founded on the magrginalelectric price fitted to our present national electric power market with regards to future trends of electric power market in China and fair trade under the government surveillance, that is group competitio n in short-term trade under the way of grouped price and quantity harmony, but also puts forward combination arithmetic, math model of trading plan and safty economical restriction. It can solve the original contradiction between medium and long term contract price and short term competitive price with improvement on competitive percentage and cut down the unfair income difference of electric factory, at the same time, it can optimize the electric limit for all electric factories and reduce the total purchase charge of electric power from burthen curve of whole electric market network.The distribution network is an important link among the power system. Its neutral grounding mode and operation connects security and stability of the power system directly. At the same time, the problem about neutral grounding is associated with national conditions, natural environment, device fabrication and operation. For example, the activity situation of the thunder and lightning, insulating structure and the peripheral interference will influence the choice of neutral grounding mode Conversely, neutral grounding mode affects design, operation, debugs and developing. Generally in the system higher in grade in the voltage, the insulating expenses account for more sizable proportion at the total price of the equipment. It is very remarkable to bring the economic benefits by reducing the insulating level. Usually such system adopt the neutral directly grounding and adopt the autoreclosing to guarantee power supply reliability. On the contrary, the system which is lower in the voltage adopts neutral none grounding to raise power supply reliability. So it is an important subject to make use of new- type earth device to apply to the distribution network under considering the situation in such factors of various fields as power supply reliability, safety factor, over-voltage factor, the choice of relay protection, investment cost, etc.The main work of this paper is to research and choice the neutral grounding mode of the l0kV distribution network. The neutral grounding mode of the l0kV network mainly adopts none grounding, grounding by arc suppressing coil, grounding by reactance grounding and directly grounding. The best grounding mode is confirmed through the technology comparison. It can help the network run in safety and limit the earth electric arc by using auto-tracking compensate device and using the line protection with the detection of the sensitive small ground current. The paperintroduces and analyzes the characteristic of all kind of grounding modes about l0kV network at first. With the comparison with technological and economy, the conclusion is drawn that the improved arc suppressing coil grounding mode shows a very big development potential.Then, this paper researches and introduces some operation characteristics of the arc suppressing coil grounding mode of the l0kV distribution network. And then the paper put emphasis on how to extinguish the earth electric arc effectively by utilizing the resonance principle. This paper combines the development of domestic and international technology and innovative achievement, and introduces the computer earth protection and autotracking compensate device. It proves that the improved arc suppressing coil grounding mode have better operation characteristics in power supply reliability, personal security, security of equipment and interference of communication. The application of the arc suppressing coil grounding mode is also researched in this paper.Finally, the paper summarizes this topic research. As a result of the domination of the arc suppressing coil grounding mode, it should be more popularized and applied in the distribution network in the future.The way of thinking, project and conclusions in this thesis have effect on the research to choose the neutral grounding mode not only in I0kV distribution network but also in other power system..The basic function of the electric power system is to transport the electric power towards customers. The l0kV electric distribution net is a key point that connects the power supply with the electricity using on the industry, business and daily-life. For the electric power, all costumers expect to pay the lowest price for the highest reliability, but don't consider that it's self-contradictory in the co-existence of economy and reliable. To improve the reliability of the power supply network, we must increase the investment cost of the network con- struction But, if the cost that improve the reliability of the network construction, but the investment on this kind of construction would be worthless if the reducing loss is on the power-off is less than the increasing investment on improving the reliability .Thus we find out a balance point to make the most economic, between the investment and the loss by calculating the investment on power net and the loss brought from power-off. The thesis analyses on the economic and the reliable of the various line modes, according to the characteristics various line modes existed in the electric distribution net in foshan..First, the thesis introduces as the different line modes in the l0kV electric distribution net and in some foreign countries. Making it clear tow to conduct analyzing on the line mode of the electric distribution net, and telling us how important and necessary that analyses are.Second, it turns to the necessity of calculating the number of optimization subsection, elaborating how it influences on the economy and reliability. Then by building up the calculation mode of the number of optimization subsection it introduces different power supply projects on the different line modes in brief. Third, it carries on the calculation and analyses towards the reliability and economy of the different line modes of electric distribution net, describing drafts according by the calculation. Then it makes analysis and discussion on the number of optimization subsection.At last, the article make conclusion on the economy and reliability of different line modes, as well as, its application situation. Accordion to the actual circumstance, the thesis puts forward the beneficial suggestion on the programming and construction of the l0kV electric distribution net in all areas in foshan. Providing the basic theories and beneficial guideline for the programming design of the lOkV electric distribution net and building up a solid net, reasonable layout, qualified safe and efficiently-worked electric distribution net.References[1] Wencheng Su. Factories power supply [M]. Machinery Industry Publishing House. 1999.9[2] Jiecai Liu. Factories power supply design guidance [M]. Machinery Industry Publishing House.1999.12[3] Power supply and distribution system design specifications[S].China plans Press. 1996[4] Low-voltage distribution design specifications [S].China plans Press. 1996.6英文翻译供配电系统摘要:电力系统的基本功能是向用户输送电能。
外文资料翻译Electric Power SystemIntroductionElectric Power System,components that transform other types of energy into electrical energy and transmit this energy to a consumer.The production and transmission of electricity is relatively efficient and inexpensive,although unlike other forms of energy,electricity is not easily stored and thus must generally be used as it is being produced.Components of an Electric Power SystemA modern electric power system consists of six main components:(1)the power station,(2)a set of transforms to raise the generated power to the high voltages used on the transmission lines,(3)the transmission,(4)the substations at which the power is stepped down to the voltage on the distribution lines,(5)the distribution lines,and(6)the transformers that lower the distribution voltage to the level used by the consumer's equipment.Power Station The power station of a power system consists of a prime mover,such as a turbine driven by water,steam,or combustion gases that operate a system of electric motors and generators.Most of the world's electric power is generated in steam plants driven by coal,oil,nuclear energyor gas.A smaller percentage of the world's electric power is generated by hydroelectric(waterpower),diesel,and internal-combustion plants.Transformers Modern electric power systems use transformers to convert electricity into different voltages.With transformers,each stage of the system can be operated at an appropriate voltage.In a typical system,the generators at the power station deliver a voltage of from 1,000 to 26,000 volts(V).Transformers step this voltage up to values ranging from 138,000 to 765,000 V for the long-distances.At the substation the voltage may be transformed down to levels of 69,000 to 138,000 V for further transfer on the distribution system.Another set of transformers step the voltage down again to a distribution level such as 2,400or 4,160 V or 15,27,or 33 kilovolts(KV).Finally the voltage is transformed once again at the distribution transformer near the point of use to 240 or 120 V.Transmission Lines The lines of high-voltage transmission systems are usually composed of wires of copper,aluminum,or copper-clad or aluminum-clad steel,which are suspend from tall latticework towers of steel by strings of porcelain insulators.By the use of clad steel wires and high towers,the distance between towers can be increased,and the cost of the transmission line thus reduced.In modern installationswith essentially straight paths,high-voltage lines may be built with as few as six towers to the kilometer.In some areas high-voltage lines are suspended from tall wooden poles spaced more closely together.For lower voltage distribution lines,wooden poles are generally used rather than steel towers.In cities and other areas where open lines create a safety hazard or are considered unattractive,insulated underground cables are used for distribution.Some of these cables have a hollow core through which oil circulates under low pressure.The oil provides temporary protection from water damage to the enclosed wires should the cable develop a leak.Pipe-type cables in which three cables are enclosed in a pipe filled with oil under high pressure(14 kg per sq cm/200psi)are frequently used. These cables are used for transmission of current at voltage as high as 345,000 V(or 345 KV).Supplementary Equipment Any electric-distribution system involves a large amount of supplementary equipment to protect the generators,transforms,and the transmission linesthemselves.The system often includes devices designed to regulate the voltage or other characteristics of power delivered to consumers.To protect all elements of a power system from short circuits and overloads,and for normal switching operations,circuit breakers are employed.These breakers are large switches that are activated automatically in the event of a short circuit or other condition that produces a sudden rise of current. Because a current forms across the terminals of the circuit breaker at the moment when the current is interrupted,some large breakers(such as those used to protect a generator or a section of primary transmission line)are immersed in a liquid that is a poor conductor of electricity, such as oil, to quench the current. In large air-type circuit breakers, as well as in oil breakers, magnetic fields are used to break up the current.Small air-circuit breakers are used for protection in shops, factories,and in modern home installations.In residential electric wiring, fuses were once commonly employed for the same purpose.A fuse consists of a piece of alloy with a low melting point, inserted in the circuit,which melts,breaking the circuit if the current rises above a certain value. Most residences now use air-circuit breakers.Power FailuresIn most parts of the world, local or national electric utilities have joined in grid systems.The linking grids allow electricity generated in one area to be shared with others. Each utility that agrees to share gains an increased reserve capacity, use of larger, more efficient generators, and the ability to respond to local power failures by obtaining energy from a linking grid.These interconnected grids are large, complex systems that contain elements operated by different groups. These systems offer the opportunity for economic savings and improve overall reliability but can create a risk of widespread failure. For example, the worst blackout in the history of the United States and Canada occurred August 14, 2003, when 61,800 megawatts of electrical power was lost in an area covering 50 million people.(One megawatt of electricity is roughly the amount neededto power 750 residential homes.)The blackout prompted calls to replace aging equipment and raised questions about the reliability of the national power grid.Despite the potential for rare widespread problems, the interconnected grid system provides necessary backup and alternate paths for power flow, resulting in much higher overall reliability than is possible with isolated systems .National or regional grids can also cope with unexpected outage such as those caused by storms, earthquakes,landslides,and forest fires, or due to human error or deliberate acts of sabotage.Power QualityIn recent years electricity has been used to power more sophisticated and technically complex manufacturing processes, computers and computer networks, and a variety of other high-technology consumer goods. These products and processes are sensitive not only to the continuity of power supply but also to the constancy of electrical frequency and voltage. Consequently, utilities are taking new measures to provide the necessary reliability and quality of electrical power, such as by providing additional electrical equipment to assure that the voltage and other characteristics of electrical power are constant.Voltage Regulation Long transmission lines have considerable inductance and capacitance.When acurrent flows through the line, inductance and capacitance have the effect of varying the voltage on the line as the current varies. Thus the supply voltage varies with the load. Several kinds of devices are used to overcome this undesirable variation in an operation called regulation of the voltage. The device include induction regulators and three-phase synchronous motors(called synchronous condensers), both of which vary the effective amount of inductance and capacitance in the transmission circuit.Inductance and capacitance react with a tendency to nullify one another. When a load circuit has more inductive than capacitive reactance, as almost invariably occurs in large power systems, the amount of power delivered for a given voltage and current is less than when the two are equal. The ratio of these two amounts of power is called the power factor. Because transmission-line losses are proportional to current, capacitance is added to the circuit when possible, thus bringing the power factor as nearly as possible to 1. For this reason, large capacitors are frequently inserted as a part of power-transmission systems.World Electric Power Production Over the period from 1950 to 2003, the most recent year for which data are available, annual world electric power production and consumption rose from slightly less than 1 trillion kilowatt-hours(kW.h) to 15.9 trillion kW.h. A change also took place in the type of power generation. In 1950 about two-thirds of the world’s electricity came from steam-generating sources and about one-third from hydroelectric sources.In 2003 thermal sources produced 65 percent of the power, but hydropower had declined to 17 percent, and nuclear power accounted for 16 percent of the total. The growth in nuclear power slowed in some countries,notably the United States, in response to concerns about safety. Nuclearplants generated 20 percent of U.S. electricity in 2003; in France, the world leader, the figure was 78 percent.ConservationMuch of the world’s electricity is produced from the use of nonrenewable resources, such as natural gas, coal, oil, and uranium. Coal, oil, and natural gas contain carbon, and burning these fossil fuels contributes to global emissions of carbon dioxide and other pollutants. Scientists believe that carbon dioxide is the principal gas responsible for global warming, a steady rise in Earth’s surface temperature.Consumers of electricity can save money and help protect the environment by eliminating unnecessary use of electricity, such as turning off light when leaving a room. Other conservation methods include buying and using energy-efficient appliances and light bulbs, and using appliances, such as washing machines and dryers, at off-peak production hours when rates are lower. Consumers may also consider environmental measures such as purchasing “green power” when it is offered by a local utility.”Green power”is usually more expensive but relies on renewable and environmentallyfriendly energy sources, such as wind turbines and geothermal power plants.电力系统介绍电力系统把其它形式的能源转化为电能并输送给用户。