Carbon-enhanced Lead Acid Battery
- 格式:pdf
- 大小:2.94 MB
- 文档页数:33

[单体]电池cell原电池primary cell蓄电池secondary cell电池battery燃料电池fuel cell锂电池lithium cell熔融盐电池molten salt cell碱性电池alkaline cell固体电解质电池solid electrolyte cell非水电解质电池non aqueous cell指示电池pilot cellOEM电池OEM battery替换电池replacement battery储备电池reserve cell应急电池emergency battery缓冲电池buffer battery; back-up battery 电压标准电池standard voltage cell韦斯顿电压标准电池 Weston standard voltage cell激活activation未激活的inactivated全密封电池hermetically /sealed cell极板plate涂膏式极板pasted plate极群plate group负极板negative plate正极板positive plate管式极板tubular plate极群组plate pack极板对plate pair隔离物spacer隔板(plate)separator阀valve电池外壳cell can电池槽cell case电池盖cell lid电池封口剂lid sealing compound整体电池monobloc battery整体槽monobloc container边界绝缘体edge insulator外套jacket[单体电池]电极(cell)electrode端子terminal端子保护套terminal protector;terminal cover负极端子negative terminal正极端子positive terminal电极的活性表面active surface of an electrode阳极anode阴极cathode电解质electrolyte电解质爬渗electrolyte creep电解质保持能力electrolyte containment泄漏leakage活性物质active material活性物质混合物active material mix电池组合箱battery tray输出电缆output cable连接件connector矩形(的)prismatic圆柱形电池cylindrical cell扣式电池button cell; coin cell 电化学反应electrochemical reaction 电极极化electrode polarization 反极polarity reversal cell reversal 结晶极化crystallization polarization活化极化activation polarization阳极极化anodic polarization阴极极化cathodic polarization浓差极化concentration polarization; mass transfer polarization 欧姆极化ohmic polarization反应极化reaction polarization阳极反应anodic reaction阴极反应cathodic reaction副反应side reaction; secondary reaction;容量(电池的)capacity(for cells or batteries)额定容量rated capacity剩余容量residual capacity体积(比)容量volumetric capacity温度系数temperature coefficient(of the capacity)质量(比)容量gravimetric capacity面积(比)容量areic capacity电池能量battery energy(电池)体积(比)能量volumic energy(related to battery)(电池)放电discharge(of a battery)放电电流discharge current放电率discharge rate短路电流(电池的)short-circuit current(related to cells or batteries) 自放电self discharge放电电压(电池的)discharge voltage(related to cells or batteries)闭路电压closed circuit voltage负载电压(拒用)on load voltage (deprecated)初始放电电压initial discharge voltage初始闭路电压initial closed circuit voltage初始负载电压(拒用)initial on load voltage(deprecated)终止电压end-of-discharge voltage; final voltage; cut-off voltage; end-point voltage标称电压nominal voltage开路电压(电池的)open-circuit voltage(related to cells or batteries)开路电压温度系数temperature coefficient of the open-circuit voltage 比特性specific characteristic荷电保持能力charge retention容量保持能力capacity retention表观内阻internal apparent resistance剩余活性物质residual active mass使用质量service mass并联parallel connection并串联parallel series connection串联series connection串并联series parallel connection标称值nominal value电池耐久性battery endurance贮存试验storage test使用寿命service life贮存寿命storage life; shelf life连续工作试验continuous service test金属-空气电池air metal battery碱性锌-空气电池alkaline zinc air battery碱性锌-二氧化锰电池alkaline zinc manganese dioxide battery锌-氧化银电池zinc silver oxide battery中性锌-空气电池neutral electrolyte zinc air battery氯化锌电池zinc chloride battery锌-碳电池zinc carbon battery诸如勒克朗谢电池或氯化锌电池之类的原电池。

Alkaline batteries :碱性电池Capacitor batteries:电容电池Carbon zinc batteries :碳锌电池Lead acid batteries:铅酸电池Lead calcium batteries:铅钙电池Lithium batteries :锂电池Lithium ion batteries :锂离子电池Lithium polymer batteries:锂聚合物电池Nickel cadmium batteries :镍镉电池Nickel iron batteries :镍铁电池Nickel metal hydride batteries :金属氧化物镍氢电池/镍氢电池Nickel zinc batteries:镍锌电池Primary batteries :原电池Rechargeable batteries :充电电池Sealed lead acid batteries:密封铅酸电池Silver cadmium batteries :银钙电池Silver oxide batteries :银氧化物电池Silver zinc batteries:银锌电池Zinc chloride batteries:银氯化物电池Zinc air batteries:锌空电池Environmental Protection batteries:环保电池Lithium batteries :锂电池Lithium ion batteries :锂离子电池Lithium polymer batteries:锂聚合物电池铅酸蓄电池 Lead-acid battery起动铅酸电池 Lead-acid starter batteries摩托车用铅酸电池 Lead-acid batteries for motorcycles内燃机车用铅酸电池 Lead-acid batteries for disel locomotive电动道路车辆用铅酸电池 Lead-acid batteries for electric road vehicles小型阀控密封式铅酸电池 small-sized valve-regulated lead-acid batteries航空用铅酸电池 Aircraft lead-acid batteries固定型阀控密封式铅酸蓄电池 Lead-acid batteries for stationary valve-regulated铅酸电池用极板 plate for lead-acid battery铅锭 lead ingots牵引用铅酸电池 Lead-acid traction batteies电解液激活蓄电池electrolyte activated battery更多电池资讯:/电池产品认证指导网站:/ekeyword.php?ekeyid=6vent valve 排气阀filling device for pleral cells 电池组填充装置negative electrode 负电极negative plate 负极板addition reagent for negative plate 负极板添加剂indicator 指示器top cover 上盖vent plug 液孔塞expanded grid 扩展式板栅specific gravity indicator 比重指示器electrolyte level control pipe 电解液液面控制管electrolyte level indicator 电解液液面指示器electrolyte level sensor 电解液液面传感器hard rubber container 硬橡胶槽envelope separator 包状隔板woven cloth tube 纺布管spongy lead 海绵状铅partition 隔壁over the partition type 越过隔壁型through the partition type 贯通隔壁贯通型separator 隔板(1)battery rack(2)battery stand(3)battery stillage 蓄电池架/蓄电池底垫active material 活性物质glass fiber separator 玻璃纤维隔板glass mat 玻璃纤维绵glass mat tube 玻璃纤维绵管spacing washer 间隔垫圈reinforced fiber separator 强化纤维隔板polarity mark plate 极性标记板pole 极柱pole insulator 极柱绝缘子pole nut 极柱螺母plate 极板plate foot 极板足plate supporter 极板支撑件element 极板群/极群组pole bolt 极柱螺栓plate lug 极板耳dilute sulfuric acid 稀硫酸steel can 金属罐steel container 金属蓄电池槽(1)madribs(2)element rest 鞍子/极群组座tubular plate 管状极板gelled electrolyte 胶体电解液更多电池资讯:/电池产品认证指导网站:/ekeyword.php?ekeyid=6grid板栅caution label 警告标签synthetic resin separator 合成树脂隔板plastics container 塑料蓄电池槽synthetic fiber separator 合成纤维隔板connector sunken type 沉没型连接器connetor exposed type 露出型连接器safety valve test 安全阀测试ampere-hour efficency 安时效率one charge distance range 一次充电行程gas recombination on negative electrode typecut-off discharge 终止放电/截止放电阴极气体再化合型/阴极气体复合型(1)specific characteristic (2)energy density (1)比特性(2)能量密度recovering charge 恢复充电(1)open circuit voltage(2)off-load voltage 开路电压/空载电压overcharge 过充电gassing 析气overcharge life test 过充电寿命试验accelerated life test 加速寿命试验active material utilization 活性物质利用率theoretical capacity of active material 活性物质的理论容量over discharge 过放电intermittent discharge 间歇放电full charge 完全充电full discharge 完全放电reverse charge 反充电/反向充电quick charge 快速放电allowable minimum voltage 允许最小电压equalizing charge 均衡充电creeping 蠕变group voltage 组电压shallow cycle endurance 轻负荷寿命/轻负荷循环寿命characteristic of electrolyte decrease 电解液减少特性nominal voltage 标称电压high rate discharge 高率放电high rate discharge characteristic 高率放电特性5 second voltage at discharge 放电 5 秒电压(1)cold cranking ampere(2)cold cranking performance(1)冷启动电流(2)冷启动性能cycle life test 循环寿命测试maximum voltage at discharge 最大放电电压30 second voltage at discharge 放电 30 秒电压residual capacity 残存容量(1)hour rate(2) discharge rate (1)小时率(2)放电率更多电池资讯:/电池产品认证指导网站:/ekeyword.php?ekeyid=6(1) self discharge (2) local action (1)自放电(2)局部自放电(1) self discharge rate(2) local action rate (1)自放电率(2)局部自放电率actual capacity 实际容量(1)starting capability(2)cranking ability 启动能力cranking current 启动电流battery clamp test 电池夹钳测试power density 功率密度momentary discharge 瞬间放电modified constant voltage charge 修正恒定电压充电initial capacity 初始容量gas recombination by catalyser type 触媒气体复合式initialcharge 初始充电viberation test 振动试验predetermined voltage 预定电压total voltage 总电压activation test for dry charged battery 干式荷电蓄电池活化试验salting 盐析earthquake-proof characteristics 防震性能dielectric voltage withstand test 电介质耐压试验short time discharge 短时间放电escaped acid mist test 酸雾逸出测试terminal voltage 端子电压cell voltage 单电池电压step charge阶段充电short-circuit current 短路电流storage test 保存测试high rate discharge at low temperature 低温高率放电rated voltage 额定电压rated capacity 额定容量fixed resistance discharge 定阻抗放电constant voltage charge 恒压充电constant voltage life test 恒压寿命测试constant current charge 恒流充电constant voltage constant current charge 恒流恒压充电constant current discharge 恒流放电constant watt discharge 恒功率放电low rate discharge characteristics 低率放电特征trickle charge 涓流充电trickle charge current 涓流充电电流trickle charge life test 涓流充电寿命测试thermal runaway 热失控driving pattern test 运行测试capacity in driving pattern test 运行测试更多电池资讯:/电池产品认证指导网站:/ekeyword.php?ekeyid=6boost charge急充电floating charge浮充电floating charge voltage 浮充电电压floating charge current 浮充电电流(1)mean voltage (2)average voltage 平均电压on-load voltage 负载电压discharge duration time 放电持续时间(1)final voltage(2)cut-off voltage(3)end voltagedepth of discharge 放电深度discharge voltage 放电电压discharge current 放电电流discharge current density 放电电流密度discharge watt-hour 放电瓦时discharge characteristics 放电特性discharged ampere-hour 放电安时explosion proof test 防爆测试auxiliary charge 补充电maintenance factor 维护率storage characteristics 保存特性终止电压/截止电压gas recombinating efficiencycharge 充电气体复合效率/气体再化合效率charge acceptance test 充电可接受性试验start-of-charge current 充电开始电流charge efficiency 充电效率end-of-charge voltage 充电结束电压specific gravity of electrolyte at the end of charge充电结束时电解液比重charge voltage 充电电压charge current 充电电流charged watt-hour 充电瓦时charge characteristic 充电特性charge ampere-hour 充电安时deep cycle endurance 重负荷循环寿命/重复合寿命weight engergy density 重量能量密度rubber pad 橡胶垫lower level line 下液面线side terminal 侧端子collective exhaust unit 公共的排放单元sintered plaque 烧结极板sintered separator 烧结隔板sintered plate 烧结极板catalyst plug 催化塞spine 芯骨strap 带更多电池资讯:/电池产品认证指导网站:/ekeyword.php?ekeyid=6spacer 隔离物insulating tube绝缘管intercell connector连接线/连接条connector cover连接管盖float mounted plug 浮动安装的栓(1)pasted plate (2)grid type plate 涂膏式极板braidd tube 编织管(1)flame-arrester vent plug (2)flam-retardant vent plug 安全塞explosion and splash proof construction 防爆防溅结构baffle 保护板pocket type plate 袋式极板bottom hole-down 底孔向下(固定)bolt fastening terminal 螺栓连接端子male blade 阳片monoblock container 整体槽positive electrode 正极positive plate 正极板leading wire terminal 引线端子retainer mat 止动垫片ribbed separator 肋隔板(1)jumping wire (2)inter low wire 跳线end plate 端板filling plug 注液塞plante plate 形成式极板/普朗特极板tubular plate 管式极板low electric resistance separator 低电阻隔板tapered terminal post 锥形接线柱electrolyte 电解液container 蓄电池槽/蓄电池壳set of container 成套蓄电池槽level-scope mounted plug 透视塞/透视栓handle 手柄jug 取液管(1)connector;(2)plug concent (1)连接器;(2)插座式连接器connector wire 连接线connecting bar 连杆connecting bar cover 连杆帽lead 引线/连接线edge insulator 绝缘卡side frame 侧框架battery cubicle 蓄电池箱perforated separator 多孔隔板burning rod (铅)焊条terminal 端子更多电池资讯:/电池产品认证指导网站:/ekeyword.php?ekeyid=6terminal connector 端子连接条terminal cover 端子盖terminal base 端子座tab 接线片lead bushing 铅套corrugated separator 波形隔板(1)lead dioxide;(2)lead peroxide (1)二氧化铅;(2)过氧化铅(1)woven separator;(2)nonwoven separator (1)织物隔板;(2)非织物隔板vent hole 通气孔exhaust tube 排气管antipolar mass 反极性物质output cable 输出电缆microporous rubber separator 微孔像胶隔板specific gravity indicator 比重计leaf separator 叶片式隔板lid sealing compound 密封剂/封口剂sealing gasket 密封衬垫/垫圈lid 蓄电池盖set of lid 系列的盖方通盖板cover board底板solepiece钢珠steel ball压钢珠press steel ball防爆阀valve preventing explosion大电流(倍率)放电discharge in high rate current标称电压Normal voltage标称容量normal capacity放电容量discharge capacity充电上限电压limited voltage in charge放电下限电压更多电池资讯:/电池产品认证指导网站:/ekeyword.php?ekeyid=6terminating voltage in discharge 恒流充电constant current charge恒压充电constant voltage charge恒流放电constant current discharge放电曲线discharge curve充电曲线charge curve放电平台discharge voltage plateau容量衰减capacity attenuation起始容量initial discharge capacity流水线pipelining传送带carrying tape焊极耳welding the current collector卷绕wind叠片layer贴胶带stick tape点焊spot welding超声焊ultrasonic weldingThe terminating voltage in discharge of the battery is 3.0 volt. The limited voltage in charge of the battery is 4.2 volt.三元素Nickle-Cobalt-Manganese Lithium Oxidethree elements materials钴酸锂Cobalt Lithium Oxide锰酸锂Manganese Lithium Oxide石墨graphite更多电池资讯:/电池产品认证指导网站:/ekeyword.php?ekeyid=6烘箱oven真空烘箱vacuum oven搅拌机mixing devicevacuum mixing device涂布机coating equipment裁纸刀paper knife ,,,,,,cutting knife分条机equipment for cutting big piece to much pieces辊压机roll press equipment电阻点焊机spot welding machine超声点焊机ultrasonic spot welding machine卷绕机winder自动叠片机auto laminating machine激光焊机laser welding machine注液机infusing machine真空注液机vacuum infusion machine预充柜pre-charge equipment化成柜formation systems分容柜grading systems测试柜testing systems内阻仪battery inner resistance tester万用表multimeter转盘式真空封口机turntable type vacuum sealing machine更多电池资讯:/电池产品认证指导网站:/ekeyword.php?ekeyid=6自动冲膜机automatic aluminum membrane shaper序号首字母英文中文1 A aging 老化2 B battery charger3 black-fleck 黑斑4 C cap 盖板充电器5 capacity density 能量密度6 capacity grading 分容7 cathode tab welding 极耳超焊8 cell 电芯9 charge(capacity) retention 荷电(容量)保持10 checking code 检码11 concave spot 凹点12 constant current charge 恒流充电13 constant current discharge 恒流放电14 constant voltage charge 恒压充电15 corrective measures 纠正措施16 crack 裂纹17 cut-off voltage 终止电压18 cycle life 循环寿命19 D dark trace 暗痕20 degrade 降级21 dent 凹痕22 discharge depth 放电深度23 distortion 变形24 drape 打折25 E Electrical and MechanicalServices Department 机电部26 electrolyte 电解,电解液27 empaistic 压纹28 end-off voltage 放电截止电压29 environmentally friendly 对环境友好30 equipment first inspection 设备首检31 erode 腐蚀32 explosion-proof line 防爆线33 F first inspection 首检34 formation 化成35 fracture 断裂36 I inspection 检验37 insulate 绝缘38 internal resistance 内阻更多电池资讯:/电池产品认证指导网站:/ekeyword.php?ekeyid=639 J jellyroll 卷芯40 joint 接缝,结合点41 L laser deflecting 偏光42 laser reticle 激光刻线43 laser welding-flatwise weld 激光焊接-平焊laser welding-standing weld 激光焊接-立焊44 leakage 漏液45 leak-checking 测漏46 leaving out of welding 漏焊47 limited charge voltage 充电限制电压48 local action 自放电49 M margin turnly 翘边50 measuring the dimension of cells 电芯卡尺寸51 meet requirement 达到要求52 memory effects 记忆效应53 N nick 划痕54 nominal voltage 标称电压55 notice-board confirmation 看板确认56 nugget 硬块57 O obverse 正面58 open circuit voltage 开路电压59 over charge 过充60 over discharge 过放61 over the thickness 超厚62 P particle 颗粒63 PE membrane PE 膜64 pit 坑点65 placing cells into the box 电芯装盒66 point inspection 点检67 preventive measures 预防措施68 pricking the tapes 扎孔69 process inspection 制程检验70 put the battery piled up 将电芯叠放在一起71 Q qualified products 合格品72 quality assurance 质量保证73 quality control 质量控制74 quality improvement 质量改进75 quality match 品质配对76 quality planning 质量策划77 R rated capacity 额定容量78 recharge 再充电79 refitting the can of cell 电芯壳口整形80 requirment 要求81 reverse 背面,反面更多电池资讯:/电池产品认证指导网站:/ekeyword.php?ekeyid=682 rework 返工83 ringing cells into pyrocondensation films84 S safety vent 安全阀85 sand aperture 砂眼86 scar 疤痕87 secondary battery 二次电池88 select appearance 选外观sharp-set 批锋89 short circuit checking 测短路90 smudginess 污物91 spot welding by laser 激光点焊92 spot welding place 点焊位置93 spraying the code 喷码94 spur 毛刺95 sticking the PVC cover boards 贴面垫96 storing 陈化97 storing with high voltage 高压储存98 T tabs deflection 极耳歪斜99 tabs excursion 极耳错位100 technics requiment 工艺要求101 U ultrasonic welding 超声波焊接102 ultrasonic welding strength 超焊强度103 unqualified products 不合格品104 W wave 波浪105 working procedure 工序套热缩膜Voltage:Units of measuring electrical current, all batteries are rated in volts DC. (DirectCurrent). This determines how much energy is needed to power your equipment. Voltage plateau:(电压平台)A slow decrease in voltage over a long period of time. As a rule, the plateau extendsfrom the first voltage drop at the start of the discharge to the bend of the curveafter which the voltage drops rapidly at the end.Nominal Voltage(标称电压)The voltage of a battery, as specified by the manufacturer, discharging at aspecified rate and temperature.Working voltage(工作电压)The working voltage of a cell or battery begins at its electrical connections as soon as an electrical consumer is connected to it.Discharging voltage, average voltage (放电电压)更多电池资讯:/电池产品认证指导网站:/ekeyword.php?ekeyid=6The average discharging voltage is the average value of the dischargingvoltageduring the entire discharging process with a related discharging current.Open circuit voltage (OCV 开路电压)The voltage of a battery when there is no current flowing.Closed-Circuit Voltage (CCV 闭路电压)The potential or voltage of a battery when it is discharging or charging.State of charge:The rate of charge capacity vs. whole capacity.Initial voltage(起始电压)A battery's initial voltage is the working voltage when discharging begins. End-point voltage (End voltage, Cutoff voltage, Final voltage)截止电压Specified closed circuit voltage at which a service output test is terminated. End-of-discharge voltageThe battery voltage when discharge is terminated.End-of-charge voltageThe battery voltage when charge is terminated.Cutoff voltage (V)The battery voltage at which charge or discharge is terminated.Definition: Capacity(容量)The capacity of a cell is defined as how manymilli-amp-hours (mAh) of current the cell canstore and subsequently deliver.One milli-amp (mA) is 1/1000th of an Amp. Somelarger cell capacities are expressed in Amp-hours(Ah).“Rated capacity” is varies with discharge rate,temperature, and cutoff voltage.Rated capacity is different from power or energyExample:If a cell is rated at 1000 mAh, then it can deliverthe following:1000 mA of current for 1 hour500 mA of current for 2 hours200 mA of current for 5 hours2000 mA of current for 1/2 hourDefinition: Energy Density(能量密度,包括体积比能量和质量比能量)The energy density of a cell is a measure of howmuch energy can be stored in the cell per unitvolume or per unit weight.E (watt-hours) = cell voltage x capacity rating更多电池资讯:/电池产品认证指导网站:/ekeyword.php?ekeyid=6? Energy density per unit volume is called the“volumetric energy density” and is expressed interms of watt-hours/liter (wh/l).Energy density per unit weight is called the“gravimetric energy density” and is expressedin terms of watt-hours/kilogram (wh/kg).These measurements are useful when you aretrying to determine which cell has the mostcapacity per unit volume or weight.1.Self Discharge自放电2.Uniformity of the Li-ion Batteries3.steel strap 钢带4.Burst vent 防爆阀5.Filling port 注液孔锂离子电池的一致性6.spirally wound type cylindrical wound type7.foil 箔圆柱形8.parallel-plate prismatic design 方形叠片式设计Ageing (老化)-Permanent loss of capacity with frequent use orthe passage of time due to unwanted irreversible chemical reactions in the cell.Anode(阳极) - The electrode in an electrochemical cell where oxidation takes place,releasing electrons.During discharge the negative electrode of the cell is the anode.During charge the situation reverses and the positive electrode of the cell is the anode.Cathode(阴极) - The electrode in an electrochemical cell where reduction takesplace, gaining electrons.During discharge the positive electrode of the cell is the cathode. During chargethe situation reverses andthe negative electrode of the cell is the cathode.Cycle (循环)- A single charge and discharge of a battery.Depth of discharge DOD (放电深度)- The ratio of the quantity of electricity orcharge removed from a cell on discharge to its rated capacity.Internal impedance(交流内阻) - Resistance to the flow of AC current within a cell.It takes into account the capacitive effect of the plates forming the electrodes.Internal resistance(直流内阻)- Resistance to the flow of DC electric current withina cell,causing a voltage drop across the cell in closed circuit proportional to the currentdrain from the cell.A low internal impedance is usually required for a high rate cell.更多电池资讯:/电池产品认证指导网站:/ekeyword.php?ekeyid=6锂离子电池的内阻英语概念到底用哪个概念,是Internal resistance还是Internalimpedance,一些电池说明书内阻用 Internal resistance,也有的用 Internal impedance,我认为 Internal impedance 较好些,因为国内测的电池内阻基本都是交流内阻,而外文也有这样定义的(我在别的帖子也粘贴过):Internal impedance(交流内阻) - Resistance to the flow of AC current within a cell.It takes into account the capacitive effect of the plates forming theelectrodes.Internal resistance(直流内阻)- Resistance to the flow of DC electric current withina cell,causing a voltage drop across the cell in closed circuit proportional to the currentdrain from the cell.A low internal impedance is usually required for a high rate cell.在 IEC6196002 中,只定义为 Internal resistance,而用交流的方法测得的内阻,叫Internala.c. resistance(交流内阻)用直流的方法测得的内阻,叫 Internal d.c. resistance(直流内阻),其实 Internal a.c.resistance 测得就是阻抗,这样看来不如用 Internal impedance(交流内阻)和 Internal resistance (直流内阻)这两个概念把它们进行分清,以免混淆。

英语词汇大全—电池1.Alkaline batteries :碱性电池2.Capacitor batteries:电容电池3. secondary battery 二次电池4. Rechargeable batteries :充电电池5. Primary batteries :原电池6. Lithium batteries :锂电池7. Lithium ion batteries :锂离子电池8. Lithium polymer batteries:锂聚合物电池9. Environmental Protection batteries:环保电池10. Nickel iron batteries :镍铁电池11. Nickel cadmium batteries :镍镉电池12. Carbon zinc batteries :碳锌电池13. Nickel zinc batteries:镍锌电池14. Zinc air batteries:锌空电池15. Silver zinc batteries:银锌电池16. Zinc chloride batteries:银氯化物电池17.Silver oxide batteries :银氧化物电池18. Silver cadmium batteries :银钙电池19. Lead calcium batteries:铅钙电池20. Lead acid batteries:铅酸电池21. Lead-acid starter batteries:起动铅酸电池22. Lead-acid traction batteies:牵引用铅酸电池23. Aircraft lead-acid batteries:航空用铅酸电池24. Sealed lead acid batteries:密封铅酸电池25. Lead-acid batteries for stationary valve-regulated:固定型阀控密封式铅酸蓄电池26. small-sized valve-regulated lead-acid batteries:小型阀控密封式铅酸电池27. Lead-acid batteries for motorcycles:摩托车用铅酸电池28. Lead-acid batteries for disel locomotive:内燃机车用铅酸电池29. Lead-acid batteries for electric road vehicles:电动道路车辆用铅酸电池。

[单体]电池cell原电池primary cell蓄电池secondary cell电池battery燃料电池fuel cell锂电池lithium cell熔融盐电池molten salt cell碱性电池alkaline cell固体电解质电池solid electrolyte cell非水电解质电池non aqueous cell指示电池pilot cellOEM电池OEM battery替换电池replacement battery储备电池reserve cell应急电池emergency battery缓冲电池buffer battery; back-up battery电压标准电池standard voltage cell韦斯顿电压标准电池Weston standard voltage cell 激活activation未激活的inactivated全密封电池hermetically /sealed cell极板plate涂膏式极板pasted plate极群plate group负极板negative plate正极板positive plate管式极板tubular plate极群组plate pack极板对plate pair隔离物spacer隔板(plate)separator阀valve电池外壳cell can电池槽cell case电池盖cell lid电池封口剂lid sealing compound整体电池monobloc battery整体槽monobloc container边界绝缘体edge insulator外套jacket[单体电池]电极(cell)electrode端子terminal端子保护套terminal protector;terminal cover 负极端子negative terminal正极端子positive terminal电极的活性表面active surface of an electrode阳极anode阴极cathode电解质electrolyte电解质爬渗electrolyte creep电解质保持能力electrolyte containment泄漏leakage活性物质active material活性物质混合物active material mix电池组合箱battery tray输出电缆output cable连接件connector矩形(的)prismatic圆柱形电池cylindrical cell扣式电池button cell;coin cell电化学反应electrochemical reaction电极极化electrode polarization反极polarity reversal cell reversal结晶极化crystallization polarization活化极化activation polarization阳极极化anodic polarization阴极极化cathodic polarization浓差极化concentration polarization; mass transfer polarization欧姆极化ohmic polarization反应极化reaction polarization阳极反应anodic reaction阴极反应cathodic reaction副反应side reaction; secondary reaction;容量(电池的)capacity(for cells or batteries)额定容量rated capacity剩余容量residual capacity体积(比)容量volumetric capacity温度系数temperature coefficient(of the capacity)质量(比)容量gravimetric capacity面积(比)容量areic capacity电池能量battery energy(电池)体积(比)能量volumic energy(related to battery)(电池)放电discharge(of a battery)放电电流discharge current放电率discharge rate短路电流(电池的)short-circuit current(related to cells or batteries)自放电self discharge放电电压(电池的)discharge voltage(related to cells or batteries)闭路电压closed circuit voltage负载电压(拒用)on load voltage (deprecated)初始放电电压initial discharge voltage初始闭路电压initial closed circuit voltage初始负载电压(拒用)initial on load voltage(deprecated)终止电压end-of-discharge voltage; final voltage; cut-off voltage; end-point voltage 标称电压nominal voltage开路电压(电池的)open-circuit voltage(related to cells or batteries)开路电压温度系数temperature coefficient of the open-circuit voltage比特性specific characteristic荷电保持能力charge retention容量保持能力capacity retention表观内阻internal apparent resistance剩余活性物质residual active mass使用质量service mass并联parallel connection并串联parallel series connection串联series connection串并联series parallel connection标称值nominal value电池耐久性battery endurance贮存试验storage test使用寿命service life贮存寿命storage life; shelf life连续工作试验continuous service test金属-空气电池air metal battery碱性锌-空气电池alkaline zinc air battery碱性锌-二氧化锰电池alkaline zinc manganese dioxide battery锌-氧化银电池zinc silver oxide battery中性锌-空气电池neutral electrolyte zinc air battery氯化锌电池zinc chloride battery锌-碳电池zinc carbon battery诸如勒克朗谢电池或氯化锌电池之类的原电池。

Alkaline batteries :碱性电池Capacitor batteries:电容电池Carbon zinc batteries :碳锌电池Lead acid batteries:铅酸电池Lead calcium batteries:铅钙电池Lithium batteries :锂电池Lithium ion batteries :锂离子电池Lithium polymer batteries:锂聚合物电池Nickel cadmium batteries :镍镉电池Nickel iron batteries :镍铁电池Nickel metal hydride batteries :金属氧化物镍氢电池/镍氢电池Nickel zinc batteries:镍锌电池Primary batteries :原电池Rechargeable batteries :充电电池Sealed lead acid batteries:密封铅酸电池Silver cadmium batteries :银钙电池Silver oxide batteries :银氧化物电池Silver zinc batteries:银锌电池Zinc chloride batteries:银氯化物电池Zinc air batteries:锌空电池Environmental Protection batteries:环保电池Lithium batteries :锂电池Lithium ion batteries :锂离子电池Lithium polymer batteries:锂聚合物电池铅酸蓄电池Lead-acid battery起动铅酸电池Lead-acid starter batteries摩托车用铅酸电池Lead-acid batteries for motorcycles内燃机车用铅酸电池Lead-acid batteries for disel locomotive电动道路车辆用铅酸电池Lead-acid batteries for electric road vehicles小型阀控密封式铅酸电池small-sized valve-regulated lead-acid batteries航空用铅酸电池Aircraft lead-acid batteries固定型阀控密封式铅酸蓄电池Lead-acid batteries for stationary valve-regulated 铅酸电池用极板plate for lead-acid battery铅锭lead ingots牵引用铅酸电池Lead-acid traction batteies电解液激活蓄电池electrolyte activated batteryvent valve 排气阀filling device for pleral cells 电池组填充装置negative electrode 负电极negative plate 负极板addition reagent for negative plate 负极板添加剂indicator 指示器top cover 上盖vent plug 液孔塞expanded grid 扩展式板栅specific gravity indicator 比重指示器electrolyte level control pipe 电解液液面控制管electrolyte level indicator 电解液液面指示器electrolyte level sensor 电解液液面传感器hard rubber container 硬橡胶槽envelope separator 包状隔板woven cloth tube 纺布管spongy lead 海绵状铅partition 隔壁over the partition type 越过隔壁型through the partition type 贯通隔壁贯通型separator 隔板(1)battery rack(2)battery stand(3)battery stillage 蓄电池架/蓄电池底垫active material 活性物质glass fiber separator 玻璃纤维隔板glass mat 玻璃纤维绵glass mat tube 玻璃纤维绵管spacing washer 间隔垫圈reinforced fiber separator 强化纤维隔板polarity mark plate 极性标记板pole 极柱pole insulator 极柱绝缘子pole nut 极柱螺母plate 极板plate foot 极板足plate supporter 极板支撑件element 极板群/极群组pole bolt 极柱螺栓plate lug 极板耳dilute sulfuric acid 稀硫酸steel can 金属罐steel container 金属蓄电池槽(1)madribs(2)element rest 鞍子/极群组座tubular plate 管状极板gelled electrolyte 胶体电解液grid 板栅caution label 警告标签synthetic resin separator 合成树脂隔板plastics container 塑料蓄电池槽synthetic fiber separator 合成纤维隔板connector sunken type 沉没型连接器connetor exposed type 露出型连接器safety valve test 安全阀测试ampere-hour efficency 安时效率one charge distance range 一次充电行程gas recombination on negative electrode type 阴极气体再化合型/阴极气体复合型cut-off discharge 终止放电/截止放电(1)specific characteristic (2)energy density (1)比特性(2)能量密度recovering charge 恢复充电(1)open circuit voltage(2)off-load voltage 开路电压/空载电压overcharge 过充电gassing 析气overcharge life test 过充电寿命试验accelerated life test 加速寿命试验active material utilization 活性物质利用率theoretical capacity of active material 活性物质的理论容量over discharge 过放电intermittent discharge 间歇放电full charge 完全充电full discharge 完全放电reverse charge 反充电/反向充电quick charge 快速放电allowable minimum voltage 允许最小电压equalizing charge 均衡充电creeping 蠕变group voltage 组电压shallow cycle endurance 轻负荷寿命/轻负荷循环寿命characteristic of electrolyte decrease 电解液减少特性nominal voltage 标称电压high rate discharge 高率放电high rate discharge characteristic 高率放电特性5 second voltage at discharge 放电5 秒电压(1)cold cranking ampere(2)cold cranking performance(1)冷启动电流(2)冷启动性能cycle life test 循环寿命测试maximum voltage at discharge 最大放电电压30 second voltage at discharge 放电30 秒电压residual capacity 残存容量(1)hour rate(2) discharge rate (1)小时率(2)放电率(1) self discharge (2) local action (1)自放电(2)局部自放电(1) self discharge rate(2) local action rate (1)自放电率(2)局部自放电率actual capacity 实际容量(1)starting capability(2)cranking ability 启动能力cranking current 启动电流battery clamp test 电池夹钳测试power density 功率密度momentary discharge 瞬间放电modified constant voltage charge 修正恒定电压充电initial capacity 初始容量gas recombination by catalyser type 触媒气体复合式initialcharge 初始充电viberation test 振动试验predetermined voltage 预定电压total voltage 总电压activation test for dry charged battery 干式荷电蓄电池活化试验salting 盐析earthquake-proof characteristics 防震性能dielectric voltage withstand test 电介质耐压试验short time discharge 短时间放电escaped acid mist test 酸雾逸出测试terminal voltage 端子电压cell voltage 单电池电压step charge 阶段充电short-circuit current 短路电流storage test 保存测试high rate discharge at low temperature 低温高率放电rated voltage 额定电压rated capacity 额定容量fixed resistance discharge 定阻抗放电constant voltage charge 恒压充电constant voltage life test 恒压寿命测试constant current charge 恒流充电constant voltage constant current charge 恒流恒压充电constant current discharge 恒流放电constant watt discharge 恒功率放电low rate discharge characteristics 低率放电特征trickle charge 涓流充电trickle charge current 涓流充电电流trickle charge life test 涓流充电寿命测试thermal runaway 热失控driving pattern test 运行测试capacity in driving pattern test 运行测试boost charge 急充电floating charge 浮充电floating charge voltage 浮充电电压floating charge current 浮充电电流(1)mean voltage (2)average voltage 平均电压on-load voltage 负载电压discharge duration time 放电持续时间(1)final voltage(2)cut-off voltage(3)end voltage 终止电压/截止电压depth of discharge 放电深度discharge voltage 放电电压discharge current 放电电流discharge current density 放电电流密度discharge watt-hour 放电瓦时discharge characteristics 放电特性discharged ampere-hour 放电安时explosion proof test 防爆测试auxiliary charge 补充电maintenance factor 维护率storage characteristics 保存特性gas recombinating efficiency 气体复合效率/气体再化合效率charge 充电charge acceptance test 充电可接受性试验start-of-charge current 充电开始电流charge efficiency 充电效率end-of-charge voltage 充电结束电压specific gravity of electrolyte at the end of charge 充电结束时电解液比重charge voltage 充电电压charge current 充电电流charged watt-hour 充电瓦时charge characteristic 充电特性charge ampere-hour 充电安时deep cycle endurance 重负荷循环寿命/重复合寿命weight engergy density 重量能量密度rubber pad 橡胶垫lower level line 下液面线side terminal 侧端子collective exhaust unit 公共的排放单元sintered plaque 烧结极板sintered separator 烧结隔板sintered plate 烧结极板catalyst plug 催化塞spine 芯骨strap 带spacer 隔离物insulating tube 绝缘管intercell connector 连接线/连接条connector cover 连接管盖float mounted plug 浮动安装的栓(1)pasted plate (2)grid type plate 涂膏式极板braidd tube 编织管(1)flame-arrester vent plug (2)flam-retardant vent plug 安全塞explosion and splash proof construction 防爆防溅结构baffle 保护板pocket type plate 袋式极板bottom hole-down 底孔向下(固定)bolt fastening terminal 螺栓连接端子male blade 阳片monoblock container 整体槽positive electrode 正极positive plate 正极板leading wire terminal 引线端子retainer mat 止动垫片ribbed separator 肋隔板(1)jumping wire (2)inter low wire 跳线end plate 端板filling plug 注液塞plante plate 形成式极板/普朗特极板tubular plate 管式极板low electric resistance separator 低电阻隔板tapered terminal post 锥形接线柱electrolyte 电解液container 蓄电池槽/蓄电池壳set of container 成套蓄电池槽level-scope mounted plug 透视塞/透视栓handle 手柄jug 取液管(1)connector;(2)plug concent (1)连接器;(2)插座式连接器connector wire 连接线connecting bar 连杆connecting bar cover 连杆帽lead 引线/连接线edge insulator 绝缘卡side frame 侧框架battery cubicle 蓄电池箱perforated separator 多孔隔板burning rod (铅)焊条terminal 端子terminal connector 端子连接条terminal cover 端子盖terminal base 端子座tab 接线片lead bushing 铅套corrugated separator 波形隔板(1)lead dioxide;(2)lead peroxide (1)二氧化铅;(2)过氧化铅(1)woven separator;(2)nonwoven separator (1)织物隔板;(2)非织物隔板vent hole 通气孔exhaust tube 排气管antipolar mass 反极性物质output cable 输出电缆microporous rubber separator 微孔像胶隔板specific gravity indicator 比重计leaf separator 叶片式隔板lid sealing compound 密封剂/封口剂sealing gasket 密封衬垫/垫圈lid 蓄电池盖set of lid 系列的盖方通盖板cover board底板solepiece钢珠steel ball压钢珠press steel ball防爆阀valve preventing explosion大电流(倍率)放电discharge in high rate current标称电压Normal voltage标称容量normal capacity放电容量discharge capacity充电上限电压limited voltage in charge放电下限电压terminating voltage in discharge恒流充电constant current charge恒压充电constant voltage charge恒流放电constant current discharge放电曲线discharge curve充电曲线charge curve放电平台discharge voltage plateau容量衰减capacity attenuation起始容量initial discharge capacity流水线pipelining传送带carrying tape焊极耳welding the current collector卷绕wind叠片layer贴胶带stick tape点焊spot welding超声焊ultrasonic weldingThe terminating voltage in discharge of the battery is 3.0 volt. The limited voltage in charge of the battery is 4.2 volt.三元素Nickle-Cobalt-Manganese Lithium Oxidethree elements materials钴酸锂Cobalt Lithium Oxide锰酸锂Manganese Lithium Oxide石墨graphite烘箱oven真空烘箱vacuum oven搅拌机mixing devicevacuum mixing device涂布机coating equipment裁纸刀paper knife ,,,,,,cutting knife分条机equipment for cutting big piece to much pieces 辊压机roll press equipment电阻点焊机spot welding machine超声点焊机ultrasonic spot welding machine卷绕机winder自动叠片机auto laminating machine激光焊机laser welding machine注液机infusing machine真空注液机vacuum infusion machine预充柜pre-charge equipment化成柜formation systems分容柜grading systems测试柜testing systems内阻仪battery inner resistance tester万用表multimeter转盘式真空封口机turntable type vacuum sealing machine自动冲膜机automatic aluminum membrane shaper序号首字母英文中文1 A aging 老化2 B battery charger 充电器3 black-fleck 黑斑4 C cap 盖板5 capacity density 能量密度6 capacity grading 分容7 cathode tab welding 极耳超焊8 cell 电芯9 charge(capacity) retention 荷电(容量)保持10 checking code 检码11 concave spot 凹点12 constant current charge 恒流充电13 constant current discharge 恒流放电14 constant voltage charge 恒压充电15 corrective measures 纠正措施16 crack 裂纹17 cut-off voltage 终止电压18 cycle life 循环寿命19 D dark trace 暗痕20 degrade 降级21 dent 凹痕22 discharge depth 放电深度23 distortion 变形24 drape 打折25 E Electrical and MechanicalServices Department 机电部26 electrolyte 电解,电解液27 empaistic 压纹28 end-off voltage 放电截止电压29 environmentally friendly 对环境友好30 equipment first inspection 设备首检31 erode 腐蚀32 explosion-proof line 防爆线33 F first inspection 首检34 formation 化成35 fracture 断裂36 I inspection 检验37 insulate 绝缘38 internal resistance 内阻39 J jellyroll 卷芯40 joint 接缝,结合点41 L laser deflecting 偏光42 laser reticle 激光刻线43 laser welding-flatwise weld 激光焊接-平焊laser welding-standing weld 激光焊接-立焊44 leakage 漏液45 leak-checking 测漏46 leaving out of welding 漏焊47 limited charge voltage 充电限制电压48 local action 自放电49 M margin turnly 翘边50 measuring the dimension of cells 电芯卡尺寸51 meet requirement 达到要求52 memory effects 记忆效应53 N nick 划痕54 nominal voltage 标称电压55 notice-board confirmation 看板确认56 nugget 硬块57 O obverse 正面58 open circuit voltage 开路电压59 over charge 过充60 over discharge 过放61 over the thickness 超厚62 P particle 颗粒63 PE membrane PE 膜64 pit 坑点65 placing cells into the box 电芯装盒66 point inspection 点检67 preventive measures 预防措施68 pricking the tapes 扎孔69 process inspection 制程检验70 put the battery piled up 将电芯叠放在一起71 Q qualified products 合格品72 quality assurance 质量保证73 quality control 质量控制74 quality improvement 质量改进75 quality match 品质配对76 quality planning 质量策划77 R rated capacity 额定容量78 recharge 再充电79 refitting the can of cell 电芯壳口整形80 requirment 要求81 reverse 背面,反面82 rework 返工83 ringing cells into pyrocondensation films 套热缩膜84 S safety vent 安全阀85 sand aperture 砂眼86 scar 疤痕87 secondary battery 二次电池88 select appearance 选外观sharp-set 批锋89 short circuit checking 测短路90 smudginess 污物91 spot welding by laser 激光点焊92 spot welding place 点焊位置93 spraying the code 喷码94 spur 毛刺95 sticking the PVC cover boards 贴面垫96 storing 陈化97 storing with high voltage 高压储存98 T tabs deflection 极耳歪斜99 tabs excursion 极耳错位100 technics requiment 工艺要求101 U ultrasonic welding 超声波焊接102 ultrasonic welding strength 超焊强度103 unqualified products 不合格品104 W wave 波浪105 working procedure 工序Voltage:Units of measuring electrical current, all batteries are rated in volts DC. (Direct Current). This determines how much energy is needed to power your equipment. Voltage plateau:(电压平台)A slow decrease in voltage over a long period of time. As a rule, the plateau extends from the first voltage drop at the start of the discharge to the bend of the curve after which the voltage drops rapidly at the end.Nominal Voltage(标称电压)The voltage of a battery, as specified by the manufacturer, discharging at a specified rate and temperature.Working voltage(工作电压)The working voltage of a cell or battery begins at its electrical connections assoon as an electrical consumer is connected to it.Discharging voltage, average voltage (放电电压)The average discharging voltage is the average value of the discharging voltage during the entire discharging process with a related discharging current.Open circuit voltage (OCV 开路电压)The voltage of a battery when there is no current flowing.Closed-Circuit Voltage (CCV 闭路电压)The potential or voltage of a battery when it is discharging or charging.State of charge:The rate of charge capacity vs. whole capacity.Initial voltage(起始电压)A battery's initial voltage is the working voltage when discharging begins. End-point voltage (End voltage, Cutoff voltage, Final voltage)截止电压Specified closed circuit voltage at which a service output test is terminated. End-of-discharge voltageThe battery voltage when discharge is terminated.End-of-charge voltageThe battery voltage when charge is terminated.Cutoff voltage (V)The battery voltage at which charge or discharge is terminated.Definition: Capacity(容量)? The capacity of a cell is defined as how manymilli-amp-hours (mAh) of current the cell canstore and subsequently deliver.? One milli-amp (mA) is 1/1000th of an Amp. Somelarger cell capacities are expressed in Amp-hours(Ah).? “Rated capacity” is varies with discharge rate,temperature, and cutoff voltage.? Rated capacity is different from power or energy? Example:? If a cell is rated at 1000 mAh, then it can deliverthe following:? 1000 mA of current for 1 hour? 500 mA of current for 2 hours? 200 mA of current for 5 hours? 2000 mA of current for 1/2 hourDefinition: Energy Density(能量密度,包括体积比能量和质量比能量)? The energy density of a cell is a measure of howmuch energy can be stored in the cell per unitvolume or per unit weight.? E (watt-hours) = cell voltage x capacity rating? Energy density per unit volume is called the“volumetric energy density” and is expressed interms of watt-hours/liter (wh/l).? Energy density per unit weight is called the“gravimetric energy density” and is expressedin terms of watt-hours/kilogram (wh/kg).? These measurements are useful when you aretrying to determine which cell has the mostcapacity per unit volume or weight.1.Self Discharge 自放电2.Uniformity of the Li-ion Batteries 锂离子电池的一致性3.steel strap 钢带4.Burst vent 防爆阀5.Filling port 注液孔6.spirally wound type cylindrical wound type 圆柱形7.foil 箔8.parallel-plate prismatic design 方形叠片式设计Ageing (老化)- Permanent loss of capacity with frequent use orthe passage of time due to unwanted irreversible chemical reactions in the cell.Anode(阳极)- The electrode in an electrochemical cell where oxidation takes place, releasing electrons.During discharge the negative electrode of the cell is the anode.During charge the situation reverses and the positive electrode of the cell is the anode.Cathode(阴极)- The electrode in an electrochemical cell where reduction takes place, gaining electrons.During discharge the positive electrode of the cell is the cathode. During chargethe situation reverses andthe negative electrode of the cell is the cathode.Cycle (循环)- A single charge and discharge of a battery.Depth of discharge DOD (放电深度)- The ratio of the quantity of electricity or charge removed from a cell on discharge to its rated capacity.Internal impedance(交流内阻)- Resistance to the flow of AC current within a cell. It takes into account the capacitive effect of the plates forming the electrodes.Internal resistance(直流内阻)- Resistance to the flow of DC electric current within a cell,causing a voltage drop across the cell in closed circuit proportional to the currentdrain from the cell.A low internal impedance is usually required for a high rate cell.锂离子电池的内阻英语概念到底用哪个概念,是Internal resistance 还是Internal impedance,一些电池说明书内阻用Internal resistance,也有的用Internal impedance,我认为Internal impedance 较好些,因为国内测的电池内阻基本都是交流内阻,而外文也有这样定义的(我在别的帖子也粘贴过):Internal impedance(交流内阻)- Resistance to the flow of AC current within a cell.It takes into account the capacitive effect of the plates forming the electrodes.Internal resistance(直流内阻)- Resistance to the flow of DC electric current withina cell,causing a voltage drop across the cell in closed circuit proportional to the currentdrain from the cell.A low internal impedance is usually required for a high rate cell.在IEC6196002 中,只定义为Internal resistance,而用交流的方法测得的内阻,叫Internal a.c. resistance(交流内阻)用直流的方法测得的内阻,叫Internal d.c. resistance(直流内阻),其实Internal a.c. resistance 测得就是阻抗,这样看来不如用Internal impedance(交流内阻)和Internal resistance (直流内阻)这两个概念把它们进行分清,以免混淆。

Alkaline batteries :碱性电池Capacitor batteries:电容电池Carbon zinc batteries :碳锌电池Lead acid batteries:铅酸电池Lead calcium batteries:铅钙电池Lithium batteries :锂电池Lithium ion batteries :锂离子电池Lithium polymer batteries:锂聚合物电池铅酸蓄电池Lead-acid battery起动铅酸电池Lead-acid starter batteries摩托车用铅酸电池Lead-acid batteries for motorcycles内燃机车用铅酸电池Lead-acid batteries for disel locomotive电动道路车辆用铅酸电池Lead-acid batteries for electric road vehicles小型阀控密封式铅酸电池small-sized valve-regulated lead-acid batteries航空用铅酸电池Aircraft lead-acid batteries固定型阀控密封式铅酸蓄电池Lead-acid batteries for stationary valve-regulated 铅酸电池用极板plate for lead-acid battery铅锭lead ingots牵引用铅酸电池Lead-acid traction batteies电解液激活蓄电池electrolyte activated batteryvent valve 排气阀filling device for pleral cells 电池组填充装置negative electrode 负电极negative plate 负极板addition reagent for negative plate 负极板添加剂indicator 指示器top cover 上盖vent plug 液孔塞expanded grid 扩展式板栅specific gravity indicator 比重指示器electrolyte level control pipe 电解液液面控制管electrolyte level indicator 电解液液面指示器electrolyte level sensor 电解液液面传感器hard rubber container 硬橡胶槽envelope separator 包状隔板woven cloth tube 纺布管spongy lead 海绵状铅partition 隔壁over the partition type 越过隔壁型through the partition type 贯通隔壁贯通型separator 隔板(1)battery rack(2)battery stand(3)battery stillage 蓄电池架/蓄电池底垫active material 活性物质glass fiber separator 玻璃纤维隔板glass mat 玻璃纤维绵glass mat tube 玻璃纤维绵管spacing washer 间隔垫圈reinforced fiber separator 强化纤维隔板polarity mark plate 极性标记板pole 极柱pole insulator 极柱绝缘子pole nut 极柱螺母plate 极板plate foot 极板足plate supporter 极板支撑件element 极板群/极群组pole bolt 极柱螺栓plate lug 极板耳dilute sulfuric acid 稀硫酸steel can 金属罐steel container 金属蓄电池槽(1)madribs(2)element rest 鞍子/极群组座tubular plate 管状极板gelled electrolyte 胶体电解液grid 板栅caution label 警告标签synthetic resin separator 合成树脂隔板plastics container 塑料蓄电池槽synthetic fiber separator 合成纤维隔板connector sunken type 沉没型连接器connetor exposed type 露出型连接器safety valve test 安全阀测试ampere-hour efficency 安时效率one charge distance range 一次充电行程gas recombination on negative electrode type 阴极气体再化合型/阴极气体复合型cut-off discharge 终止放电/截止放电(1)specific characteristic (2)energy density (1)比特性(2)能量密度recovering charge 恢复充电(1)open circuit voltage(2)off-load voltage 开路电压/空载电压overcharge 过充电gassing 析气overcharge life test 过充电寿命试验accelerated life test 加速寿命试验active material utilization 活性物质利用率theoretical capacity of active material 活性物质的理论容量over discharge 过放电intermittent discharge 间歇放电full charge 完全充电full discharge 完全放电reverse charge 反充电/反向充电quick charge 快速放电allowable minimum voltage 允许最小电压equalizing charge 均衡充电creeping 蠕变group voltage 组电压shallow cycle endurance 轻负荷寿命/轻负荷循环寿命characteristic of electrolyte decrease 电解液减少特性nominal voltage 标称电压high rate discharge 高率放电high rate discharge characteristic 高率放电特性5 second voltage at discharge 放电5秒电压(1)cold cranking ampere(2)cold cranking performance (1)冷启动电流(2)冷启动性能cycle life test 循环寿命测试maximum voltage at discharge 最大放电电压30 second voltage at discharge 放电30秒电压residual capacity 残存容量(1)hour rate(2) discharge rate (1)小时率(2)放电率(1) self discharge (2) local action (1)自放电(2)局部自放电(1) self discharge rate(2) local action rate (1)自放电率(2)局部自放电率actual capacity 实际容量(1)starting capability(2)cranking ability 启动能力cranking current 启动电流battery clamp test 电池夹钳测试power density 功率密度momentary discharge 瞬间放电modified constant voltage charge 修正恒定电压充电initial capacity 初始容量gas recombination by catalyser type 触媒气体复合式initialcharge 初始充电viberation test 振动试验predetermined voltage 预定电压total voltage 总电压activation test for dry charged battery 干式荷电蓄电池活化试验salting 盐析earthquake-proof characteristics 防震性能dielectric voltage withstand test 电介质耐压试验short time discharge 短时间放电escaped acid mist test 酸雾逸出测试terminal voltage 端子电压cell voltage 单电池电压step charge 阶段充电short-circuit current 短路电流storage test 保存测试high rate discharge at low temperature 低温高率放电rated voltage 额定电压rated capacity 额定容量fixed resistance discharge 定阻抗放电constant voltage charge 恒压充电constant voltage life test 恒压寿命测试constant current charge 恒流充电constant voltage constant current charge 恒流恒压充电constant current discharge 恒流放电constant watt discharge 恒功率放电low rate discharge characteristics 低率放电特征trickle charge 涓流充电trickle charge current 涓流充电电流trickle charge life test 涓流充电寿命测试thermal runaway 热失控driving pattern test 运行测试capacity in driving pattern test 运行测试boost charge 急充电floating charge 浮充电floating charge voltage 浮充电电压floating charge current 浮充电电流(1)mean voltage (2)average voltage 平均电压on-load voltage 负载电压discharge duration time 放电持续时间(1)final voltage(2)cut-off voltage(3)end voltage 终止电压/截止电压depth of discharge 放电深度discharge voltage 放电电压discharge current 放电电流discharge current density 放电电流密度discharge watt-hour 放电瓦时discharge characteristics 放电特性discharged ampere-hour 放电安时explosion proof test 防爆测试auxiliary charge 补充电maintenance factor 维护率storage characteristics 保存特性gas recombinating efficiency 气体复合效率/气体再化合效率charge 充电charge acceptance test 充电可接受性试验start-of-charge current 充电开始电流charge efficiency 充电效率end-of-charge voltage 充电结束电压specific gravity of electrolyte at the end of charge 充电结束时电解液比重charge voltage 充电电压charge current 充电电流charged watt-hour 充电瓦时charge characteristic 充电特性charge ampere-hour 充电安时deep cycle endurance 重负荷循环寿命/重复合寿命weight engergy density 重量能量密度rubber pad 橡胶垫lower level line 下液面线side terminal 侧端子collective exhaust unit 公共的排放单元sintered plaque 烧结极板sintered separator 烧结隔板sintered plate 烧结极板catalyst plug 催化塞spine 芯骨strap 带spacer 隔离物insulating tube 绝缘管intercell connector 连接线/连接条connector cover 连接管盖float mounted plug 浮动安装的栓(1)pasted plate (2)grid type plate 涂膏式极板braidd tube 编织管(1)flame-arrester vent plug (2)flam-retardant vent plug 安全塞explosion and splash proof construction 防爆防溅结构baffle 保护板pocket type plate 袋式极板bottom hole-down 底孔向下(固定)bolt fastening terminal 螺栓连接端子male blade 阳片monoblock container 整体槽positive electrode 正极positive plate 正极板leading wire terminal 引线端子retainer mat 止动垫片ribbed separator 肋隔板(1)jumping wire (2)inter low wire 跳线end plate 端板filling plug 注液塞plante plate 形成式极板/普朗特极板tubular plate 管式极板low electric resistance separator 低电阻隔板tapered terminal post 锥形接线柱electrolyte 电解液container 蓄电池槽/蓄电池壳set of container 成套蓄电池槽level-scope mounted plug 透视塞/透视栓handle 手柄jug 取液管(1)connector;(2)plug concent (1)连接器;(2)插座式连接器connector wire 连接线connecting bar 连杆connecting bar cover 连杆帽lead 引线/连接线edge insulator 绝缘卡side frame 侧框架battery cubicle 蓄电池箱perforated separator 多孔隔板burning rod (铅)焊条terminal 端子terminal connector 端子连接条terminal cover 端子盖terminal base 端子座tab 接线片lead bushing 铅套corrugated separator 波形隔板(1)lead dioxide;(2)lead peroxide (1)二氧化铅;(2)过氧化铅(1)woven separator;(2)nonwoven separator (1)织物隔板;(2)非织物隔板vent hole 通气孔exhaust tube 排气管antipolar mass 反极性物质output cable 输出电缆microporous rubber separator 微孔像胶隔板specific gravity indicator 比重计leaf separator 叶片式隔板lid sealing compound 密封剂/封口剂sealing gasket 密封衬垫/垫圈lid 蓄电池盖set of lid 系列的盖1.精滤器secondary filter high efficiency filter2、反渗透装置主机reverse osmosis unit3、反渗透膜reverse osmosis membrane4、数显示电导仪digital conductivity apparatus5、面板式流量计panel type flow meter6、混合离子交换器mixed-ion exchanger7、配套树脂supporting resin8、732阴树脂732 negative resin9、酸碱再生装置acid and alkali regenerative unit10、直线型铅碇输送机linear type lead ingot conveyer11、自动恒温熔铅炉melting furnace with automatic constant temperature12、铅棒冷却槽lead stick cooling tank13、铅粉视密度lead powder apparent density14、卸料阀discharge valve15、布风屏cloth besel锂离子电池专业英语和大家分享一下,有不足的欢迎大家补充!方通盖板cover board底板solepiece钢珠steel ball压钢珠press steel ball防爆阀valve preventing explosion大电流(倍率)放电discharge in high rate current标称电压Normal voltage标称容量normal capacity放电容量discharge capacity充电上限电压limited voltage in charge放电下限电压terminating voltage in discharge恒流充电constant current charge恒压充电constant voltage charge恒流放电constant current discharge放电曲线discharge curve充电曲线charge curve放电平台discharge voltage plateau容量衰减capacity attenuation起始容量initial discharge capacity流水线pipelining传送带carrying tape焊极耳welding the current collector卷绕wind叠片layer贴胶带stick tape点焊spot welding超声焊ultrasonic weldingThe terminating voltage in discharge of the battery is 3.0 volt. The limited voltage in charge of the battery is 4.2 volt.三元素Nickle-Cobalt-Manganese Lithium Oxidethree elements materials钴酸锂Cobalt Lithium Oxide锰酸锂Manganese Lithium Oxide石墨graphite烘箱oven真空烘箱vacuum oven搅拌机mixing devicevacuum mixing device涂布机coating equipment裁纸刀paper knife ,,,,,,cutting knife分条机equipment for cutting big piece to much pieces 辊压机roll press equipment电阻点焊机spot welding machine超声点焊机ultrasonic spot welding machine卷绕机winder自动叠片机auto laminating machine激光焊机laser welding machine注液机infusing machine真空注液机vacuum infusion machine预充柜pre-charge equipment化成柜formation systems分容柜grading systems测试柜testing systems内阻仪battery inner resistance tester万用表multimeter转盘式真空封口机turntable type vacuum sealing machine自动冲膜机automatic aluminum membrane shaper序号首字母英文中文1 A aging 老化2 B battery charger 充电器3 black-fleck 黑斑4 C cap 盖板5 capacity density 能量密度6 capacity grading 分容7 cathode tab welding 极耳超焊8 cell 电芯9 charge(capacity) retention 荷电(容量)保持10 checking code 检码11 concave spot 凹点12 constant current charge 恒流充电13 constant current discharge 恒流放电14 constant voltage charge 恒压充电15 corrective measures 纠正措施16 crack 裂纹17 cut-off voltage 终止电压18 cycle life 循环寿命19 D dark trace 暗痕20 degrade 降级21 dent 凹痕22 discharge depth 放电深度23 distortion 变形24 drape 打折25 E Electrical and MechanicalServices Department 机电部26 electrolyte 电解,电解液27 empaistic 压纹28 end-off voltage 放电截止电压29 environmentally friendly 对环境友好30 equipment first inspection 设备首检31 erode 腐蚀32 explosion-proof line 防爆线33 F first inspection 首检34 formation 化成35 fracture 断裂36 I inspection 检验37 insulate 绝缘38 internal resistance 内阻39 J jellyroll 卷芯40 joint 接缝,结合点41 L laser deflecting 偏光42 laser reticle 激光刻线43 laser welding-flatwise weld 激光焊接-平焊laser welding-standing weld 激光焊接-立焊44 leakage 漏液45 leak-checking 测漏46 leaving out of welding 漏焊47 limited charge voltage 充电限制电压48 local action 自放电49 M margin turnly 翘边50 measuring the dimension of cells 电芯卡尺寸51 meet requirement 达到要求52 memory effects 记忆效应53 N nick 划痕54 nominal voltage 标称电压55 notice-board confirmation 看板确认56 nugget 硬块57 O obverse 正面58 open circuit voltage 开路电压59 over charge 过充60 over discharge 过放61 over the thickness 超厚62 P particle 颗粒63 PE membrane PE膜64 pit 坑点65 placing cells into the box 电芯装盒66 point inspection 点检67 preventive measures 预防措施68 pricking the tapes 扎孔69 process inspection 制程检验70 put the battery piled up 将电芯叠放在一起71 Q qualified products 合格品72 quality assurance 质量保证73 quality control 质量控制74 quality improvement 质量改进75 quality match 品质配对76 quality planning 质量策划77 R rated capacity 额定容量78 recharge 再充电79 refitting the can of cell 电芯壳口整形80 requirment 要求81 reverse 背面,反面82 rework 返工83 ringing cells into pyrocondensation films 套热缩膜84 S safety vent 安全阀85 sand aperture 砂眼86 scar 疤痕87 secondary battery 二次电池88 select appearance 选外观sharp-set 批锋89 short circuit checking 测短路90 smudginess 污物91 spot welding by laser 激光点焊92 spot welding place 点焊位置93 spraying the code 喷码94 spur 毛刺95 sticking the PVC cover boards 贴面垫96 storing 陈化97 storing with high voltage 高压储存98 T tabs deflection 极耳歪斜99 tabs excursion 极耳错位100 technics requiment 工艺要求101 U ultrasonic welding 超声波焊接102 ultrasonic welding strength 超焊强度103 unqualified products 不合格品104 W wave 波浪105 working procedure 工序Voltage:Units of measuring electrical current, all batteries are rated in volts DC. (Direct Current). This determines how much energy is needed to power your equipment.Voltage plateau:(电压平台)A slow decrease in voltage over a long period of time. As a rule, the plateau extends from the first voltage drop at the start of the discharge to the bend of the curve after which the voltage drops rapidly at the end.Nominal Voltage(标称电压)The voltage of a battery, as specified by the manufacturer, discharging at a specified rate and temperature.Working voltage(工作电压)The working voltage of a cell or battery begins at its electrical connections as soon as an electrical consumer is connected to it.Discharging voltage, average voltage (放电电压)The average discharging voltage is the average value of the discharging voltage during the entire discharging process with a related discharging current.Open circuit voltage (OCV开路电压)The voltage of a battery when there is no current flowing.Closed-Circuit Voltage (CCV闭路电压)The potential or voltage of a battery when it is discharging or charging.State of charge:The rate of charge capacity vs. whole capacity.Initial voltage(起始电压)A battery's initial voltage is the working voltage when discharging begins. End-point voltage (End voltage, Cutoff voltage, Final voltage)截止电压Specified closed circuit voltage at which a service output test is terminated. End-of-discharge voltageThe battery voltage when discharge is terminated.End-of-charge voltageThe battery voltage when charge is terminated.Cutoff voltage (V)The battery voltage at which charge or discharge is terminated.Definition: Capacity(容量)? The capacity of a cell is defined as how manymilli-amp-hours (mAh) of current the cell canstore and subsequently deliver.? One milli-amp (mA) is 1/1000th of an Amp. Somelarger cell capacities are expressed in Amp-hours(Ah).? “Rated capacity” is varies with discharge rate,temperature, and cutoff voltage.? Rated capacity is different from power or energy? Example:? If a cell is rated at 1000 mAh, then it can deliverthe following:? 1000 mA of current for 1 hour? 500 mA of current for 2 hours? 200 mA of current for 5 hours? 2000 mA of current for 1/2 hourDefinition: Energy Density(能量密度,包括体积比能量和质量比能量)? The energy density of a cell is a measure of howmuch energy can be stored in the cell per unitvolume or per unit weight.? E (watt-hours) = cell voltage x capacity rating? Energy density per unit volume is called the“volumetric energy density” and is expressed interms of watt-hours/liter (wh/l).? Energy density per unit weight is called the“gravimetric energy density” and is expressedin terms of watt-hours/kilogram (wh/kg).? These measurements are useful when you aretrying to determine which cell has the mostcapacity per unit volume or weight.1.Self Discharge 自放电2.Uniformity of the Li-ion Batteries 锂离子电池的一致性3.steel strap 钢带4.Burst vent 防爆阀5.Filling port 注液孔6.spirally wound type cylindrical wound type 圆柱形7.foil 箔8.parallel-plate prismatic design 方形叠片式设计Ageing (老化)- Permanent loss of capacity with frequent use orthe passage of time due to unwanted irreversible chemical reactions in the cell.Anode(阳极)- The electrode in an electrochemical cell where oxidation takes place, releasing electrons.During discharge the negative electrode of the cell is the anode.During charge the situation reverses and the positive electrode of the cell is the anode.Cathode(阴极)- The electrode in an electrochemical cell where reduction takes place, gaining electrons.During discharge the positive electrode of the cell is the cathode. During charge the situation reverses andthe negative electrode of the cell is the cathode.Cycle (循环)- A single charge and discharge of a battery.Depth of discharge DOD (放电深度)- The ratio of the quantity of electricity or charge removed from a cell on discharge to its rated capacity.Internal impedance(交流内阻)- Resistance to the flow of AC current within a cell. It takes into account the capacitive effect of the plates forming the electrodes.Internal resistance (直流内阻)- Resistance to the flow of DC electric current within a cell, causing a voltage drop across the cell in closed circuit proportional to the current drain from the cell.A low internal impedance is usually required for a high rate cell.锂离子电池的内阻英语概念到底用哪个概念,是Internal resistance还是Internal impedance,一些电池说明书内阻用Internal resistance,也有的用Internal impedance,我认为Internal impedance较好些,因为国内测的电池内阻基本都是交流内阻,而外文也有这样定义的(我在别的帖子也粘贴过):Internal impedance(交流内阻)- Resistance to the flow of AC current within a cell. It takes into account the capacitive effect of the plates forming the electrodes.Internal resistance (直流内阻)- Resistance to the flow of DC electric current within a cell, causing a voltage drop across the cell in closed circuit proportional to the current drain from the cell.A low internal impedance is usually required for a high rate cell.在IEC6196002中,只定义为Internal resistance,而用交流的方法测得的内阻,叫Internal a.c. resistance(交流内阻)用直流的方法测得的内阻,叫Internal d.c. resistance(直流内阻),其实Internal a.c. resistance测得就是阻抗,这样看来不如用Internal impedance(交流内阻)和Internal resistance (直流内阻)这两个概念把它们进行分清,以免混淆。

EFB与AGM蓄电池的应用、性能和成本的对比研究易琨【摘要】EFB与AGM蓄电池是目前市场上大规模应用的两种汽车用具有怠速启停功能的铅酸蓄电池,由于EFB与AGM蓄电池结构形式不同,导致他们的应用环境和性能特性均有所不同,本文以12V 70Ah汽车用汽车怠速启停功能蓄电池为背景,对AGM蓄电池和EFB蓄电池的应用环境、性能和成本的进行了对比分析.【期刊名称】《电池工业》【年(卷),期】2017(021)001【总页数】5页(P26-30)【关键词】EFB;AGM;怠速启停功能;应用【作者】易琨【作者单位】神龙汽车有限公司技术中心,武汉430056【正文语种】中文【中图分类】TM912.1;U463.6331 引言随着汽车怠速启停功能[1, 2]的广泛应用,对车载起动型蓄电池的性能提出了更高的要求:蓄电池需要经常大电流状态下放电,可以频繁启动发动机,而且发动机熄火后中,蓄电池供给所有用电器的电力,与传统的起动用铅酸蓄电池相比,各个阶段的充放电量均有增加;同时,要求蓄电池应具有较高的耐久性能以及更长的循环寿命。
为提高燃油效率,必须在减速和刹车制动时利用产生的再生制动能量充电,要求在0~10s的短时间内提高蓄电池的充电接受能力。
富液加强型蓄电池(EFB)和贫液阀控吸附式玻璃纤维棉隔板铅酸蓄电池[1](AGM)作为具有怠速启停功能的起动型蓄电池,在实际中都得到了广泛应用。
本文对目前投入实际应用的具有怠速启停功能的这两种起动型蓄电池进行初步的对比分析。
2 EFB与AGM蓄电池概述2.1 贫液阀控吸附式玻璃纤维棉隔板铅酸蓄电池(AGM)AGM蓄电池,全称为贫液阀控吸附式玻璃纤维棉隔板铅酸蓄电池是一种贫液电池,也是一种阀控蓄电池(Valve Regulated Lead-Acid Battery)。
采用吸附式玻璃纤维棉(Absorbed Glass Mat)作隔板[3~6],电解液吸附在极板和隔板中,采取贫电液设计,电池内无流动的电解液,电池可以立放工作,也可以卧放工作。
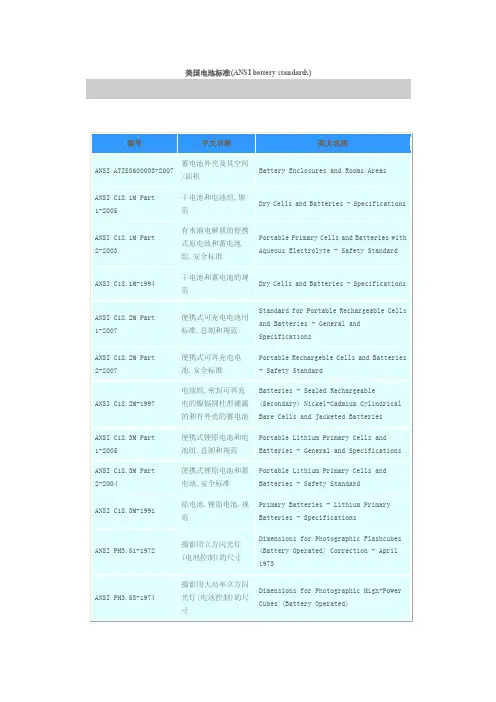
美国电池标准(ANSI battery standards)编号中文名称英文名称ANSI ATIS0600003-2007 蓄电池外壳及其空间/面积Battery Enclosures and Rooms/AreasANSI C18.1M Part 1-2005 干电池和电池组.规范Dry Cells and Batteries - SpecificationsANSI C18.1M Part 2-2003 有水溶电解质的便携式原电池和蓄电池组.安全标准Portable Primary Cells and Batteries withAqueous Electrolyte - Safety StandardANSI C18.1M-1994 干电池和蓄电池的规范Dry Cells and Batteries - SpecificationsANSI C18.2M Part 1-2007 便携式可充电电池用标准.总则和规范Standard for Portable Rechargeable Cellsand Batteries - General andSpecificationsANSI C18.2M Part 2-2007 便携式可再充电电池.安全标准Portable Rechargeble Cells and Batteries- Safety StandardANSI C18.2M-1997 电池组.密封可再充电的镍镉圆柱形裸露的和有外壳的蓄电池Batteries - Sealed Rechargeable(Secondary) Nickel-Cadmium CylindricalBare Cells and Jacketed BatteriesANSI C18.3M Part 1-2005 便携式锂原电池和电池组.总则和规范Portable Lithium Primary Cells andBatteries - General and SpecificationsANSI C18.3M Part 2-2004 便携式锂原电池和蓄电池.安全标准Portable Lithium Primary Cells andBatteries - Safety StandardANSI C18.3M-1991 原电池.锂原电池.规范Primary Batteries - Lithium PrimaryBatteries - SpecificationsANSI PH3.51-1972 摄影用立方闪光灯(电池控制)的尺寸Dimensions for Photographic Flashcubes(Battery Operated) Correction - April1973ANSI PH3.58-1974 摄影用大功率立方闪光灯(电池控制)的尺寸Dimensions for Photographic High-PowerCubes (Battery Operated)ANSI T1.330-1997 电信.电信环境用的阀调的铅酸电池Telecommunications - Valve-regulatedlead-acid batteries used in thetelecommunications environmentANSI T1.405-2002 电信.网络与用户装置接口.利用环路反向电池信令的直接向内拨号模拟音频转换访问线路Telecommunications -InstallationInterfaces - Direct-Inward-DialingAnalog Voicegrade Switched Access UsingLoop Reverse-Battery SignalingANSI T1.411-2001 电信.网络与用户装置接口.使用网络提供的反向电池信令的模拟音频增强型911转换访问线路Telecommunications - Network-to-CustomerInstallation Interfaces - AnalogVoicegrade Enhanced 911 Switched AccessUsing Network-Provided Reverse-BatterySignalingANSI T1.411a Supplement-1996 电信.载体和用户装置之间的接口.用网络提供的蓄电池信令发送进行模拟声音级增强的911转换存取.补充件Telecommunications - Interface betweencarriers and customer installations -Analog voicegrade enhanced 911 switchedaccess using network-providedreserve-battery signaling; SupplementANSI T1.414-1998 电信.网络与用户装置接口.使用环路反向电池信令的增强型模拟音频PSAP访问线路Telecommunications - Network to CustomerInstallation Interfaces - Enhanced 911Analog Voicegrade PSAP Access Using LoopReverse-Battery SignalingANSI/ASME PTC50-2002 燃料电池动力系统性能Fuel Cell Power Systems PerformanceANSI/ASTM D7148-2006 用电解槽测量系统中用碳极测定碱性蓄电池隔板的离子(电阻率)用试验方法Test Method for Determining the Ionic(resistivity) (er) of Alkaline BatterySeparator Using a Carbon Electrode in anElectrolyte Bath Measuring SystemANSI/ASTM E1021-1995 光伏电池光谱响应的测量方法Test Methods for Measuring the SpectralResponse of Photovoltaic CellsANSI/ASTM E1036/E 1036M-1996 利用比对电池测定非浓缩地面光伏电池模拟器电特性的方法(米制)Test Methods for Electrical Performanceof Non-Concentrator TerrestrialPhotovoltaic Modules and Arrays UsingReference Cells (Metric)ANSI/ASTM E1039-1999 球面发光条件下校准和表征非浓缩地面光Test Method for Calibration andCharacterization of Non-Concentrator伏比对电池特性试验方法Terrestrial Photovoltaic Reference Cells Under Global IrradiationANSI/ASTM E1125-1999 利用平行光谱校准初级非浓缩地面光伏比对电池的试验方法Test Method for Calibration of PrimaryNon-Concentrator TerrestrialPhotovolatic Reference Cells Using aTabular SpectrumANSI/ASTM E1362-1999 非浓缩光伏副基准比对电池校准试验方法Test Method for Calibration ofNon-Concentrator Photovoltaic SecondaryReference CellsANSI/ASTM E1596-1999 光伏电池模拟器太阳能辐射风化试验方法Test Method for Solar RadiationWeathering of Photovoltaic ModulesANSI/ASTM E1597-1999 海洋环境用光伏电池模拟器盐水浸没压力和温度测试方法Test Method for Saltwater PressureImmersion and Temperature Testing ofPhotovoltaic Modules for MarineEnvironmentsANSI/ASTM E2047-1999 光伏电池阵列绝缘完整性试验方法Test Method for Wet Insulation IntegrityTesting of Photovoltaic ArraysANSI/ASTM E948-1995 利用比对电池进行非浓缩地面光伏电池的电特性的方法Test Methods for Electrical Performanceof Non-Concentrator TerrestrialPhotovoltaic Cells Using Reference CellsANSI/ASTM E973M-1996 光伏器件和光伏比对电池光谱失配参数测定方法Test Method for Determination of theSpectral Mismatch Parameter between aPhotovoltaic Device and a PhotovoltaicReference Cell (Metric)ANSI/CSA AmericaFC1-2004燃料电池动力装置Fuel Cell Power Plants (same as CGA 12.10)ANSI/CSA FC3-2004 便携式燃料电池动力系统Portable Fuel Cell Power SystemsANSI/EIA 540J000-2000 电子设备用电池支架的分规范Sectional Specification for BatteryHolders for Use in Electronic EquipmentANSI/EIA 540J0AA-2000 电子设备用的圆柱形电池支架标准外形的详细规范Detail Specification for CylindricalBattery Holders, Standard Profile, foruse in Electronic EquipmentANSI/EIA 540J0AB-2001 用于电子设备的币式电池座的详细规范Detail Specification for Coin CellBattery Holders for Use in ElectronicEquipmentANSI/EIA-540J000-2000 电子设备用蓄电池座分规范Sectional Specification for BatteryHolders for Use in Electronic EquipmentANSI/EIA-540J0AA-2000 电子设备用圆柱形电池安装座,标准形状详细规范Detail Specification for CylindricalBattery Holders, Standard Profile, foruse in Electronic EquipmentANSI/EIA-540J0AB-2001 电子设备用硬币式蓄电池座详细规范Detail Specification for Coin CellBattery Holders for Use in ElectronicEquipmentANSI/IEEE 1013-2007 单机光电(PV)系统用酸性铅蓄电池尺寸选定的推荐实施规程Recommended Practice for Sizing Lead-AcidBatteries for Stand-Alone Photovoltaic(PV) SystemsANSI/IEEE 1106-2005 固定设施用带泄漏口的镍镉蓄电池组的安装、维护、测试及更换的推荐实施规程Recommended Practice for Installation,Maintenance, Testing, and Replacement ofVented Nickel-Cadmium Batteries forStationary ApplicationsANSI/IEEE 1115-2000 固定电池组用镍镉蓄电池组规格选择Recommended Practice for SizingNickel-Cadmium Batteries for StationaryApplicationsANSI/IEEE 1184-2006 不可间断电源系统用电池的指南Guide for Batteries for UninterruptiblePower Supply SystemsANSI/IEEE 1187-2002 固定用途的阀调节铅酸蓄电池的安装设计和安装的推荐实施规程Recommended Practice for InstallationDesign and Installation of ValveRegulated Lead-Acid Storage Batteries forStationary ApplicationsANSI/IEEE 1188-2005 固定设备用的阀调节铅酸蓄电池的维修、试验和更换的推荐实施规程Recommended Practice for Maintenance,Testing and Replacement of ValveRegulated Lead-Acid Batteries forStationary ApplicationsANSI/IEEE 1189-1996 固定设备用的阀调节铅酸(VRLA)蓄电池的选择指南Guide for the Selection ofValve-Regulated Lead-Acid (VRLA)Batteries for Stationary ApplicationANSI/IEEE 1361-2003 独立的光电系统中使用的铅酸蓄电池的选择、充电、试验和评定指南Guide for Selection, Charging, Test andEvaluation of Lead-Acid Batteries Used inStand-Alone Photovoltaic (PV) SystemsANSI/IEEE 1375-1998 固定蓄电池组系统的保护指南Guide for Protection of StationaryBattery SystemsANSI/IEEE 1491-2005 固定装置中选择和使用蓄电池监控设备的指南Guide for Selection and Use of BatteryMonitoring Equipment in StationaryApplicationsANSI/IEEE 1536-2002 铁路运输车辆蓄电池物理接口标准Standard for Rail Transit Vehicle BatteryPhysical InterfaceANSI/IEEE 1568-2003 铁路客运工具用镍镉蓄电池电量大小的推荐规程Recommended Practice for ElectricalSizing of Nickel-Cadmium Batteries forRail Passenger VehiclesANSI/IEEE 1578-2007 固定蓄电池电解质溢出处理和管理的推荐实施规程Recommended Practice for StationaryBattery Electrolyte Spill Containment andManagementANSI/IEEE 1625-2004 便携式计算机用可再充电电池Rechargeable Batteries for PortableComputingANSI/IEEE 1725-2006 移动电话用可再充电电池标准Standard for Rechargeable Batteries forCellular TelephonesANSI/IEEE 450-2002 发电站和变电站的大型铅蓄电池组的维护、试验和更换实施规程Maintenance, Testing, and Replacement ofLarge Lead Storage Batteries forGenerating Stations and Substations,Practice forANSI/IEEE 463-2006 电解电池线性工作区的电气安全规程标准Standard for Electrical Safety Practicesin Electrolytic Cell Line Working ZonesANSI/IEEE 484-2002 固定设备用大型铅酸蓄电池组安装设计和安装的实施规程Recommended Practice for InstallationDesign and Installation of VentedLead-Acid Batteries for StationaryApplicationsANSI/IEEE 485-1997 固定装置用的铅酸电池规格选择的推荐实施规程Recommended Practice for Sizing Lead-AcidBatteries for Stationary ApplicationsANSI/IEEE 535-2006 核电站用1E类铅蓄电池的合格证明标准Standard for Qualification of Class 1ELead Storage Batteries for Nuclear PowerGenerating StationsANSI/IEEE 937-2007 光电(PV)系统用铅酸蓄电池组安装和维护实施规程Recommended Practice for Installation andMaintenance of Lead-Acid Batteries forPhotovoltaic (PV) SystemsANSI/SAE J1494-1997 蓄电池升压器电缆Battery Booster CablesANSI/SAE J1495-1998 蓄电池阻燃通风系统Test Procedure for Battery Flame的试验程序Retardant Venting SystemsANSI/SAE J1766-1998 电动和混合电动车蓄电池系统的推荐实施规程.碰撞完整性试验Recommended Practice for Electric andHybrid Electric Vehicle Battery Systems -Crash Integrity TestingANSI/SAE J2380-1998 电动车蓄电池组的振动试验Vibration Testing of Electric VehicleBatteriesANSI/SAE J240-1993 汽车蓄电池的寿命试验Automotive Storage Batteries, Life TestforANSI/SAE J537-1994 蓄电池组Storage BatteriesANSI/SCTE 48-3-2004 用GTEM电池测量编织同轴引入电缆的屏蔽效果的试验规程Test Procedure for Measuring ShieldingEffectiveness of Braided Coaxial DropCable Using the GTEM CellANSI/UL 1236-2006 装载发电机启动器蓄电池用蓄电池充电器的安全标准Standard for Safety for Battery Chargersfor Charging Engine-Starter BatteriesANSI/UL 1564-2006 工业蓄电池充电装置安全标准Standard for Safety for IndustrialBattery ChargersANSI/UL 1839-2007 汽车蓄电池电瓶线的安全标准Standard for Safety for AutomotiveBattery Booster CablesANSI/UL 218A-2004 柴油发动机驱动的离心消防泵用蓄电池接触器Battery Contactors for Use in DieselEngines Driving Centrifugal Fire PumpsANSI/UL 2267-2006 工业电瓶货车设备用燃料电池电源系统安全标准Standard for Safety for Fuel Cell PowerSystems for Installation in IndustrialElectric TrucksANSI/UL 583-2007 工业用蓄电池电力货车标准Standard for Electric-Battery-PoweredIndustrial TrucksANSI/UL 745-4-36-2006 电池组手动工具的特殊要求安全标准Standard for Safety for ParticularRequirements for Battery Operated HandMotor ToolsASME PTC 50-2002 燃料电池电源系统性能(Fuel cell power systems performance)ASTM C 876-1991 混凝土中未涂覆的预应力钢筋的半电池电势的试验方法Test Method for Half-Cell Potentials ofUncoated Reinforcing Steel in ConcreteASTM D 7129-2005 接合蓄电池隔板中氨的测定的标准试验方法Standard Test Method for Determination ofAmmonia Trapping in a Grafted BatterySeparatorASTM D 7131-2005 接合蓄电池隔板中离子交换能力测定的标准试验方法Standard Test Method for Determination ofIon Exchange Capacity (IEC) in GraftedBattery SeparatorASTM D 7148-2007 电解槽测量系统中使用碳极测定碱性蓄电池隔板的离子电阻系数(ER)用标准试验方法Standard Test Method for Determining theIonic Resistivity (ER) of AlkalineBattery Separator Using a CarbonElectrode in an Electrolyte BathMeasuring SystemASTM E 1036-2002 使用标准电池的非聚能地面光电模件和阵列电气性能的标准试验方法Standard Test Methods for ElectricalPerformance of NonconcentratorTerrestrial Photovoltaic Modules andArrays Using Reference CellsASTM E 1040-2005 非集中大地光电参比电池物理特性的标准规范Standard Specification for PhysicalCharacteristics of NonconcentratorTerrestrial Photovoltaic Reference CellsASTM E 1125-2005 用表列光谱校准初级非集中大地光电参比电池的标准试验方法Standard Test Method for Calibration ofPrimary Non-Concentrator TerrestrialPhotovoltaic Reference Cells Using aTabular SpectrumASTM E 1362-2005 非集中光电二次参比电池校准的标准试验方法Standard Test Method for Calibration ofNon-Concentrator Photovoltaic SecondaryReference CellsASTM E 2236a-2005 无聚集器多结光电池和组件的电性能和光谱灵敏度测量的标准试验方法Standard Test Methods for Measurement ofElectrical Performance and SpectralResponse of NonconcentratorMultijunction Photovoltaic Cells andModulesASTM E 948a-2005 在模拟日光下使用参比电池的光电电池电性能的标准试验方法Standard Test Method for ElectricalPerformance of Photovoltaic Cells UsingReference Cells Under Simulated SunlightASTM E 973a-2005 测定光电装置与光电参比电池之间光谱不Standard Test Method for Determination ofthe Spectral Mismatch Parameter Between a协调参数的标准试验方法Photovoltaic Device and a Photovoltaic Reference CellASTM G 95-2007 管道涂层的阴极剥离试验用标准试验方法(附着电池法)Standard Test Method for CathodicDisbondment Test of Pipeline Coatings(Attached Cell Method)IEEE 1013-2000 光电系统用铅酸蓄电池尺寸测量的推荐实施规程(Recommended practice for sizinglead-acid batteries for photovoltaic (PV)systems)IEEE 1106-1995 发电站及变电所用镍-镉蓄电池组的维护,试验及更换用推荐规程(Recommended practice for installation,maintenance, testing, and replacement ofvented nickel-cadmium batteries forstationary applications)IEEE 1115-2000 静态用镍-镉电池组规格的推荐操作规程(Recommended practice for sizingnickel-cadmium batteries for stationaryapplications)IEEE 1144-1996 光电系统用校准镍-镉蓄电池组的推荐规程(Recommended practice for sizingnickel-cadmium batteries forphotovolatic (PV) systems)IEEE 1184-1994 不间断电源系统电池尺寸的规定和选择(Selection and sizing of batteries foruninterruptible power systems)IEEE 1187-2002 固定设备用的阀调节铅酸蓄电池的安装设计和安装的推荐性实施规程(Recommended practice for installationdesign and installation ofvalve-regulated lead-acid storagebatteries for stationary applications)IEEE 1188-1996 发电站用阀调节铅酸(VRLA)蓄电池组的保养、试验和更新的推荐规程(Recommended practice for maintenance,testing, and replacement ofvalve-regulated lead-acid (VRLA)batteries for stationary applications)IEEE 1189-1996 固定设备用调节阀铅酸(VRLA)蓄电池的选择指南(Guide for selection of valve-regulatedlead-acid (VRLA) batteries for stationaryapplications)IEEE 1375-1998 固定蓄电池组的保护指南(Guide for the protection of stationarybattery systems)IEEE 1536-2002 铁路运输车辆蓄电池物理接口(Rail transit vehicle battery physicalinterface)IEEE 450-2002 通气固定铅蓄电池组的维护、试验及更换(Maintenance, testing, and replacement ofvented lead-acid batteries for stationaryapplications)IEEE 484-2002 发电站用透气式铅酸蓄电池组设计、安装推荐规程(Recommended practice for installationdesign and installation of ventedlead-acid batteries for stationaryapplications)IEEE 485-1997 固定设施用酸性铅蓄电池尺寸测定推荐规程(Recommended practice for sizinglead-acid batteries for stationaryapplications)IEEE 535-1986 核电站用1E级铅蓄电池组的鉴定(Qualification of class 1E lead storagebatteries for nuclear power generatingstations)IEEE 650-1990 核电站1E级固定式电池充电器和逆变器的合格鉴定(Qualification of class 1E static batterychargers and inverters for nuclear powergenerating stations)IEEE 937-2000 光电系统用铅酸蓄电池组的安装及维护推荐规程(Recommended practice for installationand maintenance of lead-acid batteriesfor photovoltaic (PV) systems)UL 1236-2002 充电的发动机起动电池组用蓄电池充电器(Battery chargers for chargingengine-starter batteries )UL 1564-1993 工业蓄电池充电器(Industrial battery chargers )UL 1642-1995 锂蓄电池组(Lithium batteries )UL 1989-1996 备用蓄电池组(Standby batteries )UL 2054-1997 家用和商用蓄电池组(Household and commercial batteries ) UL 2089-2003 车辆用蓄电池适配器(Vehicle battery adapters )UL 218A-2004 柴油机中驱动离心点火泵用电池接头标准(Standard for battery contactors for usein diesel engines driving centrifugalfire pumps )UL 745-3-1995 由蓄电池供电的便携工具(Portable battery operated tools )UL 745-4-1-1995 由蓄电池供电的电钻的特殊要求(Particular requirementsbattery-operated drills )UL 745-4-11-1995 由蓄电池供电的往复式锯的特殊要求(Particular requirements forbattery-operated reciprocating saws )UL 745-4-14-1995 由蓄电池供电的刨刀(Particular requirements for的特殊要求battery-operated planers )UL 745-4-17-1995 由蓄电池供电的刻纹机和修剪机特殊要求(Particular requirements forbattery-operated routers and trimmers )UL 745-4-2-1995 由蓄电池供电的旋具和套筒扳手特殊要求(Particular requirements forbattery-operated screwdrivers and impactwrenches )UL 745-4-3-1995 由蓄电池供电的研磨机、磨光器和盘形砂轮机特殊要求(Particular requirements forbattery-operated grinders, polishers,and disk-type sanders )UL 745-4-35-1995 由蓄电池供电的污水清洁器特殊要求(Particular requirements forbattery-operated drain cleaners )UL 745-4-36-1995 由蓄电池供电的手持式电动工具特殊要求(Particular requirements forbattery-operated hand motor tools )UL 745-4-4-1995 由蓄电池供电的砂轮机特殊要求(Particular requirements forbattery-operated sanders )UL 745-4-5-1995 由蓄电池供电的圆盘锯和圆盘刀具特殊要求(Particular requirements forbattery-operated circular saws andcircular knives )UL 745-4-6-1995 由蓄电池供电的锤子的特殊要求(Particular requirements forbattery-operated hammers )UL 745-4-8-1995 由蓄电池供电的剪刀和步冲轮廓机特殊要求(Particular requirements forbattery-operated shears and nibblers )编号中文名称英文名称。

第4卷第6期2015年11月 储 能 科 学 与 技 术 Energy Storage Science and Technology V ol.4 No.6Nov. 2015特约评述铅碳电池储能技术陶占良,陈 军(先进能源材料化学教育部重点实验室,天津化学化工协同创新中心,南开大学化学学院,天津 300071)摘 要:储能技术在太阳能、风能等可再生能源发电、智能电网/微网建设等方面有着广阔的应用前景。
铅酸电池具有价格低、较高电压、性能稳定、宽工作温度范围等优势,占据着固定储能市场的主导地位。
但在智能电网、混合动力车的实际应用中,电池必须在不同的充电状态下操作,特别是在高倍率部分荷电模式。
在这种操作模式下,硫酸盐沉积物积聚在电极表面,限制了铅酸电池的容量和循环寿命。
铅碳电池是由铅酸电池和超级电容器组合形成的新型储能装置,它抑制了放电过程中负极板表面硫酸盐的不均匀分布和充电时较早的析氢现象,具有铅酸电池高能量和超级电容器高功率的优点,在部分荷电态大功率充放电状态具有较高的循环寿命,适合高倍率循环和瞬间脉冲放电等工作状态。
本文介绍了铅碳电池的基本概念及原理,并对铅碳电池储能技术的发展历程和现状进行了总结。
关键词:储能;铅酸电池;铅碳电池;负极材料doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4239.2015.06.002中图分类号:TK 02;TM 912.2 文献标志码:A 文章编号:2095-4239(2015)06-546-10Lead carbon ultrabatteries for energy storageTAO Zhanliang , CHEN Jun(Key Laboratory of Advanced Energy Materials Chemistry, Ministry of Education, Collaborative Innovation Center of ChemicalScience and Engineering, College of Chemistry, Nankai University, Tianjin 300071, China)Abstract: Energy storage technologies show broad application prospects in renewable energy systems such as wind and solar energy, and in the construction of smart grid/micro grids. Lead-acid batteries have dominated the market in stationary energy storage due to their advantages of low price, high-unit voltage, stable performance, and a wide operating temperature range. However, lead-acid batteries under hybrid electric veheciles (HEV) and renewable-energy applications must be operated at different state-of-charge windows. In particular, under high-rate partial-state-of-charge (HRPSoC) duty, lead-acid batteries fail prematurely due to the sulfation of the negative plates. Lead carbon ultrabatteies are a new hybrid energy storage device, which combines a lead acid battery and an asymmetric supercapacitor in single unit, with the advantage of both high energy of lead acid battery and high power of supercapacitor. The uneven distribution of lead sulfate across the cross-section of negative plate during discharge and the early evolution of hydrogen during charge should be suppressed. There fore, lead carbon ultrabatteies have longer cycling life in a wider state-of-charge window, which is suitable for high rate cycling and pulse applications. The concept and the basic principles of lead carbon ultrabatteries and its recent developments are summarized.Key words: energy storage; lead-acid battery; lead carbon ultrabattery; negative active material储能技术在以太阳能、风能发电为主力能源的收稿日期:2015-07-09;修改稿日期:2015-08-31。

Alkaline batteries :碱性电池Capacitor batteries:电容电池Carbon zinc batteries :碳锌电池Lead acid batteries:铅酸电池Lead calcium batteries:铅钙电池Lithium batteries :锂电池Lithium polymer batteries:锂聚合物电池Nickel cadmium batteries:镍镉电池Nickel iron batteries :镍铁电池Nickel metal hydride batteries :金属氧化物镍氢电池/镍氢电池Nickel zinc batteries:镍锌电池Primary batteries :原电池Sealed lead acid batteries:密封铅酸电池Silver cadmium batteries:银钙电池Silver oxide batteries :银氧化物电池Silver zinc batteries:银锌电池Zinc chloride batteries:银氯化物电池Zinc air batteries:锌空电池Environmental Protection batteries:环保电池起动铅酸电池Lead-acid starter batteries摩托车用铅酸电池Lead-acid batteries for motorcycles 航空用铅酸电池Aircraft lead-acid batteries 内燃机车用铅酸电池Lead-acid batteries for disel locomotive电动道路车辆用铅酸电池Lead-acid batteries for electric road vehicles小型阀控密封式铅酸电池small-sized valve-regulated lead-acid batteries固定型阀控密封式铅酸蓄电池Lead-acid batteries for stationary valve-regulated铅酸电池用极板plate for lead-acid battery 铅锭lead ingots牵引用铅酸电池Lead-acid traction batteries 电解液激活蓄电池electrolyte activated batteryvent valve 排气阀filling device for pleral cells 电池组填充装置negative plate 负极板addition reagent for negative plate 负极板添加剂indicator 指示器top cover 上盖vent plug 液孔塞expanded grid 扩展式板栅specific gravity indicator 比重指示器electrolyte level control pipe 电解液液面控制管electrolyte level indicator 电解液液面指示器electrolyte level sensor电解液液面传感器hard rubber container 硬橡胶槽envelope separator 包状隔板woven cloth tube纺布管spongy lead 海绵状铅partition 隔壁over the partition type 越过隔壁型through the partition type 贯通隔壁贯通型separator 隔板(1)battery rack(2)battery stand(3)battery stillage 蓄电池架/蓄电池底垫glass fiber separator 玻璃纤维隔板glass mat 玻璃纤维绵glass mat tube 玻璃纤维绵管spacing washer 间隔垫圈reinforced fiber separator 强化纤维隔板polarity mark plate 极性标记板pole极柱pole insulator 极柱绝缘子pole nut极柱螺母plate 极板plate foot 极板足plate supporter 极板支撑件element 极板群/极群组pole bolt 极柱螺栓plate lug 极板耳dilute sulfuric acid稀硫酸steel can 金属罐steel container 金属蓄电池槽(1)madribs(2)element rest 鞍子/极群组座tubular plate 管状极板gelled electrolyte 胶体电解液grid板栅caution label 警告标签synthetic resin separator 合成树脂隔板plastics container 塑料蓄电池槽synthetic fiber separator 合成纤维隔板connector sunken type 沉没型连接器connetor exposed type 露出型连接器safety valve test 安全阀测试ampere-hour efficency 安时效率positive plate 正极板one charge distance range 一次充电行程gas recombination on negative electrode type阴极气体再化合型/阴极气体复合型specific characteristic比特性energy density能量密度recovering charge 恢复充电off-load voltage空载电压gassing 析气active material utilization 活性物质利用率overcharge life test过充电寿命试验accelerated life test 加速寿命试验theoretical capacity of active material 活性物质的理论容量intermittent discharge 间歇放电reverse charge 反充电/反向充电quick charge快速放电allowable minimum voltage 允许最小电压equalizing charge 均衡充电creeping蠕变group voltage 组电压shallow cycle endurance 轻负荷寿命/轻负荷循环寿命characteristic of electrolyte decrease 电解液减少特性nominal voltage 标称电压high rate discharge 高率放电high rate discharge characteristic 高率放电特性5 second voltage at discharge 放电5秒电压cold cranking ampere冷启动电流cold cranking performance冷启动性能cycle life test 循环寿命测试maximum voltage at discharge最大放电电压30 second voltage at discharge 放电30秒电压residual capacity 残存容量hour rate小时率discharge rate放电率(1) self discharge(rate)自放电(率)(2) local action(rate)局部自放电(率)actual capacity 实际容量starting capability(2)cranking ability 启动能力cranking current启动电流battery clamp test 电池夹钳测试power density 功率密度momentary discharge 瞬间放电modified constant voltage charge修正恒定电压充电initial capacity初始容量gas recombination by catalyser type 触媒气体复合式initial charge 初始充电viberation test 振动试验predetermined voltage 预定电压total voltage 总电压activation test for dry charged battery 干式荷电蓄电池活化试验salting 盐析earthquake-proof characteristics 防震性能dielectric voltage withstand test 电介质耐压试验short time discharge短时间放电escaped acid mist test 酸雾逸出测试terminal voltage端子电压cell voltage单电池电压step charge阶段充电short-circuit current 短路电流storage test保存测试high rate discharge at low temperature 低温高率放电rated voltage 额定电压rated capacity 额定容量fixed resistance discharge 定阻抗放电constant voltage life test 恒压寿命测试floating charge current 浮充电电流constant current (dis)charge 恒流(放)充电constant voltage constant current charge恒流恒压充电constant watt discharge 恒功率放电low rate discharge characteristics 低率放电特征trickle charge 涓流充电trickle charge current 涓流充电电流trickle charge life test涓流充电寿命测试thermal runaway 热失控driving pattern test运行测试capacity in driving pattern test运行测试boost charge急充电floating charge 浮充电floating charge voltage 浮充电电压mean(average)voltage 平均电压on-load voltage负载电压discharge duration time 放电持续时间final(end)voltage 终止电压discharge watt-hour放电瓦时discharge characteristics放电特性discharged ampere-hour放电安时explosion proof test防爆测试auxiliary charge补充电maintenance factor 维护率storage characteristics 保存特性gas recombinating efficiency气体复合效率/气体再化合效率charge acceptance test 充电可接受性试验start-of-charge current 充电开始电流end-of-charge voltage 充电结束电压specific gravity of electrolyte at the end of charge充电结束时电解液比重charged watt-hour充电瓦时chargecharacteristic 充电特性charge ampere-hour充电安时deep cycle endurance重负荷循环寿命/重复合寿命weight engergy density 重量能量密度rubber pad 橡胶垫lower level line下液面线side terminal 侧端子collective exhaust unit 公共的排放单元sintered plaque 烧结极板sintered separator 烧结隔板sintered plate 烧结极板catalyst plug 催化塞spine 芯骨strap 带spacer 隔离物insulating tube 绝缘管intercell connector 连接线/连接条connector cover 连接管盖float mounted plug 浮动安装的栓(1)pasted plate (2)grid type plate 涂膏式极板braidd tube 编织管(1)flame-arrester vent plug (2)flam-retardant vent plug 安全塞explosion and splash proof construction 防爆防溅结构baffle 保护板pocket type plate 袋式极板bottom hole-down底孔向下(固定)bolt fastening terminal 螺栓连接端子male blade 阳片monoblock container 整体槽leading wire terminal 引线端子retainer mat止动垫片ribbed separator肋隔板jumping wire (2)inter low wire 跳线end plate 端板filling plug注液塞plante plate形成式极板/普朗特极板tubular plate 管式极板low electric resistance separator 低电阻隔板tapered terminal post 锥形接线柱electrolyte 电解液container 蓄电池槽/蓄电池壳set of container成套蓄电池槽level-scope mounted plug 透视塞/透视栓handle 手柄jug 取液管(1)connector;(2)plug concent (1)连接器;(2)插座式连接器connector wire 连接线connecting bar 连杆connecting bar cover连杆帽lead引线/连接线edge insulator 绝缘卡side frame 侧框架battery cubicle 蓄电池箱perforated separator多孔隔板burning rod (铅)焊条terminal端子terminal connector 端子连接条terminal cover 端子盖terminal base 端子座tab 接线片lead bushing铅套corrugated separator 波形隔板lead dioxide二氧化铅lead peroxide过氧化铅(1)woven separator;(2)nonwoven separator (1)织物隔板;(2)非织物隔板vent hole 通气孔exhaust tube排气管antipolar mass 反极性物质output cable输出电缆microporous rubber separator微孔像胶隔板specific gravity indicator比重计leaf separator 叶片式隔板lid sealing compound密封剂/封口剂sealing gasket 密封衬垫/垫圈lid 蓄电池盖set of lid 系列的盖方通盖板cover board底板solepiece钢珠steel ball压钢珠press steel ball防爆阀valve preventing explosion大电流(倍率)放电discharge in high rate current标称电压Normal voltage标称容量normal capacity充电上限电压limited voltage in charge Voltage plateau:电压平台Closed-Circuit Voltage (CCV闭路电压)Initial voltage(起始电压)放电下限电压terminating voltage in discharge恒流(压)充电constant current (voltage)charge 放电平台discharge voltage plateau容量衰减capacity attenuation起始容量initial discharge capacity Anode阳极Cathode阴极positive electrode 正极Internal impedance交流内阻Internal resistance直流内阻钴酸锂Cobalt Lithium Oxide锰酸锂Manganese Lithium Oxide流水线pipelining传送带carrying tape焊极耳welding the current collector卷绕wind叠片layer贴胶带stick tape点焊spot welding自动冲膜机automatic aluminum membrane shaper超声焊ultrasonic welding 真空烘箱vacuum oven搅拌机mixing device vacuum mixing device涂布机coating equipment裁纸刀paper knife ,cutting knife分条机equipment for cutting big piece tomuch pieces辊压机roll press equipment电阻点焊机spot welding machine超声点焊机ultrasonic spot welding machine卷绕机winder自动叠片机auto laminating machine激光焊机laser welding machine注液机infusing machine真空注液机vacuum infusion machine预充柜pre-charge equipment化成柜formation systems分容柜grading systems测试柜testing systems内阻仪battery inner resistance tester万用表multimeter 转盘式真空封口机turntable type vacuum sealing machine aging 老化storing 陈化battery charger 充电器black-fleck 黑斑cap 盖板capacity density 能量密度capacity grading 分容cathode tab welding 极耳超焊cell电芯charge(capacity) retention荷电(容量)保持checking code检码concave spot 凹点corrective measures 纠正措施crack裂纹dark trace 暗痕degrade 降级dent 凹痕distortion 变形drape打折Electrical and MechanicalServices Department 机电部empaistic压纹environmentally friendly 对环境友好equipment first inspection 设备首检erode腐蚀explosion-proof line 防爆线first inspection 首检formation化成fracture 断裂inspection 检验insulate 绝缘internal resistance 内阻jellyroll 卷芯joint接缝,结合点laser deflecting 偏光laser reticle激光刻线laser welding-flatwise weld 激光焊接-平焊laser welding-standing weld 激光焊接-立焊leakage 漏液leak-checking测漏leaving out of welding 漏焊limited charge voltage 充电限制电压local action 自放电margin turnly 翘边measuring the dimension of cells 电芯卡尺寸meet requirement 达到要求memory effects 记忆效应nick 划痕nominal voltage 标称电压notice-board confirmation 看板确认nugget 硬块obverse正面reverse 背面,反面over the thickness 超厚PE membrane PE膜pit 坑点placing cells into the box 电芯装盒point inspection 点检preventive measures 预防措施pricking the tapes 扎孔process inspection 制程检验put the battery piled up 将电芯叠放在一起qualified products 合格品quality assurance质量保证quality control 质量控制quality improvement 质量改进quality match品质配对quality planning 质量策划rated capacity 额定容量refitting the can of cell电芯壳口整形rework 返工ringing cells into pyrocondensation films 套热缩膜safety vent安全阀sand aperture砂眼scar 疤痕select appearance选外观sharp-set 批锋short circuit checking 测短路smudginess 污物spot welding by laser激光点焊spot welding place 点焊位置spraying the code喷码spur 毛刺sticking the PVC cover boards贴面垫storing with high voltage高压储存tabs deflection极耳歪斜tabs excursion 极耳错位technics requiment 工艺要求ultrasonic welding超声波焊接ultrasonic welding strength 超焊强度unqualified products不合格品wave 波浪working procedure 工序Uniformity of the Li-ion Batteries 锂离子电池的一致性steel strap 钢带Burst vent防爆阀.Filling port 注液孔spirally wound type cylindrical wound type 圆柱形.parallel-plate prismatic design 方形叠片式设计。

[单体]电池 cell原电池 primary cell蓄电池 secondary cell电池 battery燃料电池 fuel cell锂电池 lithium cell熔融盐电池 molten salt cell碱性电池 alkaline cell固体电解质电池 solid electrolyte cell非水电解质电池 non aqueous cell指示电池 pilot cellOEM电池 OEM battery替换电池 replacement battery储藏电池 reserve cell应急电池 emergency battery缓冲电池 buffer battery; back-up battery电压标准电池 standard voltage cell韦斯顿电压标准电池Weston standard voltage cell 激活 activation未激活的 inactivated全密封电池 hermetically /sealed cell极板 plate涂膏式极板 pasted plate极群 plate group负极板 negative plate正极板 positive plate管式极板 tubular plate极群组 plate pack极板对plate pair隔离物 spacer隔板 (plate)separator阀 valve电池外壳 cell can电池槽 cell case电池盖 cell lid电池封口剂 lid sealing pound整体电池 monobloc battery整体槽 monobloc container边界绝缘体 edge insulator外套 jacket[单体电池]电极 (cell)electrode端子 terminal端子保护套 terminal protector;terminal cover 负极端子 negative terminal正极端子 positive terminal电极的活性外表 active surface of an electrode 阳极 anode阴极 cathode电解质 electrolyte电解质爬渗 electrolyte creep电解质保持能力 electrolyte containment泄漏 leakage活性物质 active material活性物质混合物 active material mix电池组合箱 battery tray输出电缆 output cable连接件 connector矩形〔的〕 prismatic圆柱形电池 cylindrical cell扣式电池 button cell;coin cell电化学反响 electrochemical reaction电极极化 electrode polarization反极 polarity reversal cell reversal结晶极化 crystallization polarization活化极化 activation polarization阳极极化 anodic polarization阴极极化 cathodic polarization浓差极化 concentration polarization; mass transfer polarization 欧姆极化 ohmic polarization反响极化 reaction polarization阳极反响 anodic reaction阴极反响 cathodic reaction副反响 side reaction; secondary reaction;容量〔电池的〕 capacity(for cells or batteries)额定容量 rated capacity剩余容量 residual capacity体积〔比〕容量 volumetric capacity温度系数 temperature coefficient(of the capacity)质量〔比〕容量 gravimetric capacity面积〔比〕容量 areic capacity电池能量 battery energy〔电池〕体积〔比〕能量volumic energy(related to battery)〔电池〕放电 discharge(of a battery)放电电流 discharge current放电率 discharge rate短路电流〔电池的〕short-circuit current(related to cells or batteries)自放电 self discharge放电电压〔电池的〕 discharge voltage〔related to cells or batteries〕闭路电压 closed circuit voltage负载电压〔拒用〕 on load voltage (deprecated)初始放电电压 initial discharge voltage初始闭路电压 initial closed circuit voltage初始负载电压〔拒用〕initial on load voltage(deprecated)终止电压 end-of-discharge voltage; final voltage; cut-off voltage; end-point voltage 标称电压 nominal voltage开路电压〔电池的〕 open-circuit voltage〔related to cells or batteries〕开路电压温度系数temperature coefficient of the open-circuit voltage比特性 specific characteristic荷电保持能力 charge retention容量保持能力 capacity retention表观内阻 internal apparent resistance剩余活性物质 residual active mass使用质量 service mass并联 parallel connection并串联 parallel series connection串联 series connection串并联 series parallel connection标称值 nominal value电池耐久性 battery endurance贮存试验 storage test使用寿命 service life贮存寿命 storage life; shelf life连续工作试验 continuous service test金属-空气电池air metal battery碱性锌-空气电池alkaline zinc air battery碱性锌-二氧化锰电池alkaline zinc manganese dioxide battery锌-氧化银电池zinc silver oxide battery中性锌-空气电池neutral electrolyte zinc air battery氯化锌电池 zinc chloride battery锌-碳电池 zinc carbon battery诸如勒克朗谢电池或氯化锌电池之类的原电池。
Useful Vocabulary about Lithium-ion Battery锂离子电池常用词汇一.Classification of Batteries 电池的分类1.Physical battery 物理电池A.Solar battery 太阳能电池 B.Thermal cell 热电池2.Chemical battery 化学电池A. Non-rechargeable battery(Primary battery)原电池;一次电池Zinc-Air battery 锌空气电池Carbon-Zinc battery 碳锌电池Alkaline battery 碱性电池 Silver Oxide battery 氧化银电池Lithium battery 锂电池B、Rechargeable battery (secondary battery)蓄电池;可充电电池;二次电池Lithium Ion battery 锂离子电池Lithium Polymer battery 锂聚合物电池Nickel Cadmium battery 镍镉电池Nickel Metal hydride battery 镍氢电池Lead-acid battery 铅酸电池C.Fuel cell 燃料电池二.Components 组成篇Positive electrode正极 Negative electrode负极Cathode (Oxidation takes place) 阴极 Anode (Reduction takes place) 阳极 Positive terminal 正极端 Positive tab 正极极耳Negative terminal 负极端 Negative tab 负极极耳Current collector 集流体(collector electrode)Copper foil铜箔 Aluminum foil 铝箔Cathode Active Material 正极(阴极)活性物质Lithium cobalt oxide 锂钴氧 lithium manganese oxide 锂锰氧 Lithium nickel oxide 锂镍氧 Lithium iron phosphate 磷酸亚铁锂 Anode active material 负极(阳极)活性物质Conductive assistant 导电剂conducting polymer导电聚合物Graphite 石墨Natural graphite天然石墨 Artificial graphite人造石墨Modified graphite 改性石墨Mesophase-pitch-based carbon fiber(MCF)中间相沥青碳纤维Soft carbon软碳coke 焦炭 Binder黏结剂Mesophase carbon micro beads(MCMB)中间相碳微球Hard carbon硬碳 Acetylene black乙炔黑Poly-vinylidene fluoride(PVDF)聚偏二氟乙烯Poly-tetrafluoroethylene(PTFE)聚四氟乙烯Separator 隔膜;隔板Poly Propylene(PP)聚丙烯 Poly Ethylene(PE)聚乙烯Steel jacket (Steel-Can)钢壳 Aluminum jacket(Al-Can)铝壳Gasket 垫圈 Top cap 盖板 Electrolyte injection hole注液孔Non-aqueous Electrolyte非水电解液Solute 溶质Solvent 溶剂Additive 添加剂Lithium hexafluorophosphate (LiPF6)六氟磷酸锂N-methyl pyrrolidone(NMP) N-甲基吡咯烷酮/ 1-甲基-2-吡咯烷酮Ethylene carbonate(EC)乙烯碳酸酯/碳酸乙烯酯Propylene carbonate(PC)丙烯碳酸酯/碳酸丙烯酯γ-Butyrolactone(γ-BL)γ-丁内酯Dimethyl carbonate(DMC)二甲基碳酸酯/碳酸二甲酯Diethyl carbonate(DEC)二乙基碳酸酯/碳酸二乙酯Ethyl methyl carbonate(EMC)乙基甲基碳酸酯/碳酸甲乙酯Manufacture Process 制备过程篇The second workshop(二车间)slurry Mixing 混料Positive slurry mixing 正极配料Negative slurry mixing 负极配料Positive slurry coating 正极拉浆Negative slurry coating 负极拉浆Positive electrode preparing 正极制片Cutting into big pieces 裁大片Cutting into small pieces 裁小片(滚切)Weighing & grading 称重分档Pressing 压片 Al tape Jointing 焊接铝带Positive drying正极烤片 positive tape Affixing 正极贴胶带Negative electrode preparing负极制片Automatically cutting 自动分切Negative drying负极烤片Automatically cutting and pressing自动裁压片Weighing & grading 称重分档 Riveting 铆接Negative spot welding 负极点焊Rubberized fabric affixing 贴胶布The third workshop(三车间Winding 卷绕 Rubberized fabric enveloping 包胶布 Gasket installing (gasket setting) 放隔圈 Batch number marking打批号Encasing 套壳 Sinking 沉底Negative spot welding 负极点焊 Positive spot welding正极点焊Tab folding 折极耳 cover board Jointing 点盖板Cover pressing 压盖板 Cover beat 敲电池The fourth workshop(四车间) Laser welding激光焊The fifth workshop(五车间)Silica gel drip 点硅胶 Sealant smearing 涂密封剂Weighing 称重 Washing 清洗Ring 套胶圈 Drying 烘烤Electrolyte injection 注液The sixth workshop(六车间)First aging/Aging before sealing 一次陈化CC charging(constant current charging)恒流化成 Sealing 封口Ocv check( open circuit voltage check) 测电压Steel ball inserting 敲钢珠 Steel ball pressing 压钢珠Rubberized fabric tearing 撕胶纸 Washing 清洗vacuum Extracting 抽真空 Appearance check 外观检查Washer pasting 贴面垫 Capacity check 分容CV charging 恒压化成 Second aging/Aging after sealing 二次陈化四.Test 测试篇Basic Characteristics基本特性Charge 充电 Discharge 放电Current 电流 Voltage 电压Potential 电势;电位 Open circuit voltage(OCV)开路电压Constant current(CC)恒流 Constant voltage(CV)恒压Trickle charge涓流充电 Series and parallel 串并联Depth of discharge(DOD)放电深度 State of charge(SOC)荷电状态Memory effect 记忆效应 C-rate 表示电池充放电时电流大小的比率单位 Charge method 充电方式Nominal capacity 额定容量Nominal voltage 额定电压 Charge voltage 充电电压 General charge current 常规充电电流Max charge current 最大充电电流 Discharge cut-off voltage 放电截至电压Operating temperature 工作温度 Energy density 能量密度Storage temperature 储存温度 Relative humidity 相对湿度Specific energy 比能 Specific power 比功率Specific capacity 比容量 Self discharge 自放电Shape and Physical Dimensions 外形及物理参数Model 型号Prismatic 棱柱形的;方形的Cylindrical 圆柱形的Thickness 厚度 Width 宽度 Height 高度 Weight 重量Diameter 直径Electrical Characteristics 电气特性Electrical tests 电性能测试Complete charged 满充电 Voltage of shipment 出货电压Initial capacity 初始容量 Internal impedance 内阻Cycle life 循环寿命 Capacity recovery rate 容量回复率General temperature storage 常温储存High temperature storage 高温储存Safety Characteristics 安全特性 Mechanical tests 机械试验Environmental tests 环境试验Crush test 挤压测试 Impact test 冲击测试Drop test 跌落测试 Vibration test 振动测试Humidity test 潮湿试验 External short circuit test 外部短路测试 Overcharge test 过充测试Over discharge test 过放测试 Reverse Charge 反充电;Forced discharge 强制性放电Nail penetration test 针刺测试Hot oven 炉温测试(heating test热测试)Temperature cycling test 热循环测试(高低温冲击测试)Low pressure (altitude simulation) test 低压(高空模拟)试验Rupture 破裂leak 漏液Smoke 冒烟 Heat 发热 Catch fire 着火Burn 燃烧 Explode 爆炸Safety valve 安全阀 Fuse 保险丝Positive Temperature Coefficient(PTC)正温度系数Negative Temperature Coefficient(NTC)负温度系数current Interrupt Device(CID)电流切断装置 Thermal resistor热敏电阻。
Alkaline batteries :碱性电池Capacitor batteries :电容电池Carbon zinc batteries :碳锌电池Lead acid batteries :铅酸电池Lead calcium batteries :铅钙电池Lithium batteries :锂电池Lithium ion batteries :锂离子电池Lithium polymer batteries :锂聚合物电池Nickel cadmium batteries :镍镉电池Nickel iron batteries :镍铁电池Nickel metal hydride batteries:金属氧化物镍氢电池/ 镍氢电池Nickel zinc batteries :镍锌电池Primary batteries :原电池Rechargeable batteries :充电电池Sealed lead acid batteries :密封铅酸电池Silver cadmium batteries :银钙电池Silver oxide batteries :银氧化物电池Silver zinc batteries :银锌电池Zinc chloride batteries :银氯化物电池Zinc air batteries :锌空电池Environmental Protection batteries: 环保电池Lithium batteries :锂电池Lithium ion batteries :锂离子电池Lithium polymer batteries :锂聚合物电池铅酸蓄电池 Lead-acid battery起动铅酸电池 Lead-acid starter batteries摩托车用铅酸电池 Lead-acid batteries for motorcycles内燃机车用铅酸电池 Lead-acid batteries for disel locomotive电动道路车辆用铅酸电池Lead-acid batteries for electric road vehicles 小型阀控密封式铅酸电池small-sized valve-regulated lead-acid batteries 航空用铅酸电池 Aircraft lead-acid batteries固定型阀控密封式铅酸蓄电池Lead-acid batteries for stationary valve- regulated 铅酸电池用极板plate for lead-acid battery铅锭 lead ingots牵引用铅酸电池Lead-acid traction batteies电解液激活蓄电池electrolyte activated batteryvent valve排气阀filling device for pleral cells电池组填充装置negative electrode负电极negative plate负极板addition reagent for negative plate负极板添加剂indicator指示器top cover上盖vent plug液孔塞expanded grid扩展式板栅specific gravity indicator比重指示器electrolyte level control pipe电解液液面控制管electrolyte level indicator电解液液面指示器electrolyte level sensor电解液液面传感器hard rubber container硬橡胶槽envelope separator包状隔板woven cloth tube纺布管spongy lead海绵状铅partition隔壁over the partition type 越过隔壁型through the partition type 贯通隔壁贯通型separator 隔板(1)battery rack(2)battery stand(3)battery stillage 蓄电池架 / 蓄电池底垫active material 活性物质glass fiber separator 玻璃纤维隔板glass mat 玻璃纤维绵glass mat tube 玻璃纤维绵管spacing washer 间隔垫圈reinforced fiber separator 强化纤维隔板polarity mark plate 极性标记板pole 极柱pole insulator 极柱绝缘子pole nut 极柱螺母plate 极板plate foot 极板足plate supporter 极板支撑件element 极板群 / 极群组pole bolt 极柱螺栓plate lug 极板耳dilute sulfuric acid 稀硫酸steel can 金属罐steel container 金属蓄电池槽(1)madribs(2)element rest 鞍子 / 极群组座tubular plate 管状极板gelled electrolyte 胶体电解液grid 板栅caution label 警告标签synthetic resin separator 合成树脂隔板plastics container 塑料蓄电池槽synthetic fiber separator 合成纤维隔板connector sunken type 沉没型连接器connetor exposed type 露出型连接器safety valve test 安全阀测试ampere-hour efficency 安时效率one charge distance range 一次充电行程gas recombination on negative electrode type 阴极气体再化合型 /阴极气体复合型 cut-off discharge 终止放电 /截止放电(1 ) specific characteristic (2)energy density (1) 比特性( 2)能量密度recovering charge 恢复充电(1)open circuit voltage(2)off-load voltage开路电压/空载电压overcharge过充电gassing 析气overcharge life test 过充电寿命试验accelerated life test 加速寿命试验active material utilization 活性物质利用率theoretical capacity of active material 活性物质的理论容量over discharge 过放电intermittent discharge 间歇放电full charge 完全充电full discharge 完全放电reverse charge 反充电 /反向充电quick charge 快速放电allowable minimum voltage 允许最小电压equalizing charge 均衡充电creeping 蠕变group voltage 组电压shallow cycle endurance 轻负荷寿命 /轻负荷循环寿命characteristic of electrolyte decrease 电解液减少特性nominal voltage 标称电压high rate discharge 高率放电high rate discharge characteristic 高率放电特性5 second voltage at discharge放电5秒电压(1) cold cranking ampere ( 2) cold cranking performance(1)冷启动电流( 2 )冷启动性能cycle life test 循环寿命测试maximum voltage at discharge 最大放电电压30 second voltage at discharge 放电 30 秒电压residual capacity 残存容量(1)hour rate(2) discharge rate ( 1 )小时率( 2)放电率(1) self discharge (2) local action ( 1 )自放电(2)局部自放电(1) self discharge rate(2) local action rate ( 1)自放电率(2)局部自放电率 actual capacity 实际容量(1)starting capability(2)cranking ability 启动能力cranking current 启动电流battery clamp test 电池夹钳测试power density 功率密度momentary discharge 瞬间放电modified constant voltage charge 修正恒定电压充电initial capacity 初始容量gas recombination by catalyser type 触媒气体复合式initialcharge 初始充电viberation test 振动试验predetermined voltage 预定电压total voltage 总电压activation test for dry charged battery 干式荷电蓄电池活化试验salting 盐析earthquake-proof characteristics 防震性能dielectric voltage withstand test电介质耐压试验short time discharge 短时间放电escaped acid mist test 酸雾逸出测试terminal voltage 端子电压cell voltage 单电池电压step charge 阶段充电short-circuit current短路电流storage test 保存测试high rate discharge at low temperature 低温高率放电rated voltage 额定电压rated capacity 额定容量fixed resistance discharge 定阻抗放电constant voltage charge 恒压充电constant voltage life test 恒压寿命测试constant current charge 恒流充电constant voltage constant current charge 恒流恒压充电constant current discharge 恒流放电constant watt discharge 恒功率放电low rate discharge characteristics 低率放电特征trickle charge 涓流充电trickle charge current 涓流充电电流trickle charge life test 涓流充电寿命测试thermal runaway 热失控driving pattern test 运行测试capacity in driving pattern test 运行测试boost charge 急充电floating charge 浮充电floating charge voltage 浮充电电压floating charge current 浮充电电流(1)mean voltage (2)average voltage平均电压on-load voltage 负载电压discharge duration time 放电持续时间(1)final voltage(2)cut-off voltage(3)end voltage 终止电压 / 截止电压 depth of discharge 放电深度discharge voltage 放电电压discharge current 放电电流discharge current density 放电电流密度discharge watt-hour 放电瓦时discharge characteristics 放电特性discharged ampere-hour 放电安时explosion proof test 防爆测试auxiliary charge 补充电maintenance factor 维护率storage characteristics 保存特性gas recombinating efficiency 气体复合效率 / 气体再化合效率charge 充电charge acceptance test 充电可接受性试验start-of-charge current 充电开始电流charge efficiency 充电效率end-of-charge voltage 充电结束电压specific gravity of electrolyte at the end of charge 充电结束时电解液比重 charge voltage 充电电压charge current 充电电流charged watt-hour 充电瓦时charge characteristic 充电特性charge ampere-hour 充电安时deep cycle endurance 重负荷循环寿命/重复合寿命weight engergy density 重量能量密度rubber pad 橡胶垫lower level line 下液面线side terminal 侧端子collective exhaust unit 公共的排放单元sintered plaque 烧结极板sintered separator 烧结隔板sintered plate 烧结极板catalyst plug 催化塞spine 芯骨strap 带spacer 隔离物insulating tube 绝缘管intercell connector 连接线 /连接条connector cover 连接管盖float mounted plug 浮动安装的栓(1)pasted plate (2)grid type plate涂膏式极板braidd tube 编织管(1)flame-arrester vent plug (2)flam-retardant vent plug 安全塞 explosion and splash proof construction 防爆防溅结构baffle 保护板pocket type plate 袋式极板bottom hole-down 底孔向下(固定)bolt fastening terminal 螺栓连接端子male blade 阳片monoblock container 整体槽positive electrode 正极positive plate 正极板leading wire terminal 引线端子retainer mat 止动垫片ribbed separator 肋隔板(1)jumping wire (2)inter low wire 跳线end plate 端板filling plug 注液塞plante plate 形成式极板 /普朗特极板tubular plate 管式极板low electric resistance separator 低电阻隔板tapered terminal post 锥形接线柱electrolyte 电解液container 蓄电池槽 /蓄电池壳set of container 成套蓄电池槽level-scope mounted plug透视塞/透视栓handle 手柄jug 取液管(1)connector;(2)plug concent (1) 连接器; (2) 插座式连接器connector wire 连接线connecting bar 连杆connecting bar cover 连杆帽lead 引线 /连接线edge insulator 绝缘卡side frame 侧框架battery cubicle 蓄电池箱perforated separator 多孔隔板burning rod ( 铅)焊条terminal 端子terminal connector 端子连接条terminal cover 端子盖terminal base 端子座tab 接线片lead bushing 铅套corrugated separator 波形隔板(1)lead dioxide;(2)lead peroxide (1) 二氧化铅;(2) 过氧化铅(1)woven separator;(2)nonwoven separator (1) 织物隔板;(2) 非织物隔板vent hole通气孔exhaust tube排气管antipolar mass反极性物质output cable输出电缆microporous rubber separator微孔像胶隔板specific gravity indicator比重计leaf separator叶片式隔板lid sealing compound密封剂/封口剂sealing gasket密封衬垫/垫圈lid 蓄电池盖set of lid系列的盖方通盖板cover board底板solepiece钢珠steel ball压钢珠press steel ball防爆阀valve preventing explosion大电流 (倍率 )放电discharge in highrate current标称电压Normal voltage标称容量normal capacity放电容量discharge capacity充电上限电压limited voltage in charge放电下限电压terminating voltage in discharge 恒流充电constant current charge恒压充电constant voltage charge恒流放电constant current discharge放电曲线discharge curve充电曲线charge curve放电平台discharge voltage plateau容量衰减capacity attenuation起始容量initial discharge capacity流水线pipelining传送带carrying tape焊极耳welding the current collector卷绕wind叠片layer贴胶带stick tape点焊spot welding超声焊ultrasonic weldingThe terminating voltage in discharge of the battery is 3.0 volt.The limitedvoltage in charge of the battery is 4.2 volt.三元素Nickle-Cobalt-Manganese Lithium Oxidethree elements materials钴酸锂Cobalt Lithium Oxide锰酸锂Manganese Lithium Oxide石墨graphite烘箱oven真空烘箱vacuum oven搅拌机mixing devicevacuum mixing device涂布机coating equipment裁纸刀分条机equipment for cutting big piece to much pieces辊压机roll press equipment电阻点焊机spot welding machine超声点焊机ultrasonic spot welding machine卷绕机winder自动叠片机auto laminating machine激光焊机laser welding machine注液机infusing machine真空注液机vacuum infusion machine预充柜pre-charge equipment化成柜formation systems分容柜grading systems测试柜testing systems内阻仪Battery inner resistance tester万用表Multimeter转盘式真空封口机Turntable type vacuum sealing machine自动冲膜机Automatic aluminum membrane shaper序号首字母英文中文1 A aging 老化2 B battery charger 充电器3 black-fleck 黑斑4 C cap 盖板5 capacity density 能量密度6 capacity grading 分容7 cathode tab welding极耳超焊8cell电芯9 charge(capacity) retention荷电(容量)保持10 checking code检码11 concave spot 凹点12 constant current charge 恒流充电13 constant current discharge 恒流放电14 constant voltage charge 恒压充电15 corrective measures 纠正措施16 crack 裂纹17 cut-off voltage 终止电压18 cycle life 循环寿命19 D dark trace 暗痕20 degrade 降级21 dent 凹痕22 discharge depth 放电深度23 distortion 变形24 drape 打折25 E Electrical and Mechanical Services Department 机电部 26 electrolyte 电解,电解液27 empaistic 压纹28 end-off voltage 放电截止电压29 environmentally friendly 对环境友好30 equipment first inspection 设备首检31 erode 腐蚀32 explosion-proof line 防爆线33 F first inspection 首检34 formation 化成35 fracture 断裂36 I inspection 检验37 insulate 绝缘38 internal resistance 内阻39 J jellyroll 卷芯40 joint 接缝,结合点41 L laser deflecting 偏光42laser reticle 激光刻线43 laser welding-flatwise weld 激光焊接 -平焊laser welding-standing weld 激光焊接 -立焊44 leakage 漏液45 leak-checking 测漏46 leaving out of welding 漏焊47 limited charge voltage 充电限制电压48 local action 自放电49 M margin turnly 翘边50 measuring the dimension of cells电芯卡尺寸51 meet requirement 达到要求52 memory effects 记忆效应53 N nick 划痕54 nominal voltage 标称电压55 notice-board confirmation 看板确认56 nugget 硬块57 O obverse 正面58 open circuit voltage 开路电压59 over charge 过充60 over discharge 过放61 over the thickness 超厚62 P particle 颗粒63 PE membrane PE 膜64 pit 坑点65 placing cells into the box 电芯装盒66 point inspection 点检67 preventive measures 预防措施68 pricking the tapes 扎孔69 process inspection 制程检验70 put the battery piled up 将电芯叠放在一起71 Q qualified products 合格品72 quality assurance 质量保证73 quality control 质量控制74 quality improvement 质量改进75 quality match 品质配对76 quality planning 质量策划77 R rated capacity 额定容量78 recharge 再充电79 refitting the can of cell 电芯壳口整形80 requirement 要求81 reverse 背面,反面82 rework 返工83ringing cells into pyrocondensation films 套热缩膜84 S safety vent 安全阀85 sand aperture 砂眼86 scar 疤痕87 secondary battery 二次电池88 select appearance 选外观sharp-set 批锋89 short circuit checking 测短路90 smudginess 污物91 spot welding by laser 激光点焊92 spot welding place 点焊位置93 spraying the code 喷码94 spur 毛刺95 sticking the PVC cover boards 贴面垫96 storing 陈化97 storing with high voltage 高压储存98 T tabs deflection 极耳歪斜99 tabs excursion 极耳错位100 technics requirement 工艺要求101 U ultrasonic welding 超声波焊接102 ultrasonic welding strength 超焊强度103 unqualified products 不合格品104 W wave 波浪105 working procedure 工序Voltage :Units of measuring electrical current, all batteries are rated in volts DC.(Direct Current). This determines how much energy is needed to power your equipment. Voltage plateau:(电压平台)A slow decrease in voltage over a long period of time. As a rule, the plateau extends from the first voltage drop at the start of the discharge to thebend of the curve after which the voltage drops rapidly at the end.Nominal Voltage(标称电压)The voltage of a battery, as specified by the manufacturer,discharging at a specified rate and temperature.The working voltage of a cell or battery begins at its electrical connections as soon as an electrical consumer is connected to it.Discharging voltage, average voltage (放电电压)The average discharging voltage is the average value of the dischargingvoltage during the entire discharging process with a related discharging current. Open circuit voltage (OCV开路电压)The voltage of a battery when there is no current flowing.Closed-Circuit Voltage (CCV闭路电压)The potential or voltage of a battery when it is discharging or charging.State of charge:The rate of charge capacity vs. whole capacity.(起始电压)A battery ' s initial voltage is the working voltage when discharging begins. End-point voltage (End voltage, Cutoff voltage, Final voltage)截止电压Specified closed circuit voltage at which a serviceoutput test is terminated. End-of-discharge voltageThe battery voltage when discharge is terminated.End-of-charge voltageThe battery voltage when charge is terminated.Cutoff voltage (V)The battery voltage at which charge or discharge is terminated.Definition: Capacity(容量)The capacity of a cell is defined as how many mill-amp-hours (mAh) ofcurrent the cell can store and subsequently deliver.One mill-amp (mA) is 1/1000th of an Amp. Some larger cellcapacities are expressed in Amp-hours(Ah).“ Rated capacity is” varies with discharge rate, temperature, and cutoff voltage.Rated capacity is different from power or energyExample:If a cell is rated at 1000 mAh, then it can deliver the following:1000 mA of current for 1 hour500 mA of current for 2 hours200 mA of current for 5 hours2000mA of current for 1/2 hourDefinition: Energy Density( 能量密度,包括体积比能量和质量比能量)The energy density of a cell is a measure of how much energy can bestored in the cell per unit volume or per unit weight.E (watt-hours) = cell voltage x capacity ratingEnergy density per unit volume is called the “ volumetric energy density ”and is expressed in terms of watt-hours/liter (wh/l).Energy density per unit weight is called the “ gravimetric energy density ”and is expressed in terms of watt-hours/kilogram (wh/kg).These measurements are useful when you are trying to determine whichcell has the most capacity per unit volume or weight.1.Self Discharge 自放电2.Uniformity of the Li-ion Batteries 锂离子电池的一致性3.steel strap 钢带4.Burst vent 防爆阀5.Filling port 注液孔6.spirally wound type cylindrical wound type 圆柱形7.foil 箔8.parallel-plate prismatic design 方形叠片式设计Ageing (老化) -Permanent loss of capacity with frequent use orThe passage of time due to unwanted irreversible chemical reactions inthe cell. Anode (阳极) -The electrode in an electrochemical cell where oxidation takes place, releasing electrons.During discharge the negative electrode of the cell is the anode.During charge the situation reverses and the positive electrode of the cell is the anode.Cathode(阴极)-The electrode in an electrochemical cell where reductiontakes place, gaining electrons.During discharge the positive electrode of the cell is the cathode. Duringcharge the situation reverses andThe negative electrode of the cell is the cathode.Cycle(循环)-A single charge and discharge of a battery.Depth of discharge DOD (放电深度) -The ratio of the quantity of electricity overcharge removed from a cell on discharge to its rated capacity.Internal impedance (交流内阻) -Resistance to the flow of AC current within a cell. It takes into account the capacitive effect of the plates formingthe electrodes. Internal resistance (直流内阻) -Resistance to the flow of DCelectric current within a cell,the current drain from the cell.A low internal impedance is usually required for a high rate cell.锂离子电池的内阻英语概念到底用哪个概念,是Internal resistance还是Internal impedance,一些电池说明书内阻用Internal resistance,也有的用Internal impedance,我认为Internal impedance较好些,因为国内测的电池内阻基本都是交流内阻,而外文也有这样定义的(我在别的帖子也粘贴过):Internal impedance(交流内阻)-Resistance to the flow of AC current within a cell. It takes into account the capacitive effect of the plates formingthe electrodes.Internal resistance(直流内阻)-Resistance to the flow of DCelectric current within a cell, causing a voltage drop across the cell in closedcircuit proportional to the current drain from the cell.A low internal impedance is usually required for a high rate cell.在 IEC6196002 中,只定义为 Internal resistance ,而用交流的方法测得的内阻,叫 Internal a.c. resistance (交流内阻)用直流的方法测得的内阻,叫Internal d.c. resistance (直流内阻),其实Internal a.c. resistance 测得就是阻抗,这样看来不如用 Internal impedance (交流内阻)和Internal resistance (直流内阻)这两个概念把它们进行分清,以免混淆。
各种电池放电曲线电池放电曲线是指电池在放电过程中电压随时间或电流的变化关系。
不同类型的电池,其放电曲线特性也有所不同。
以下是一些常见电池类型的放电曲线特点:1. 碱性锌碳电池(Alkaline Zinc-Carbon Battery):碱性锌碳电池的放电曲线相对平稳,电压在大部分放电周期内保持在1.4伏左右,直至快速下降至截止电压。
这种电池适用于需要稳定电压输出的设备,如遥控器、闹钟等。
2. 锂离子电池(Lithium-Ion Battery):锂离子电池的放电曲线在初始阶段电压下降较快,然后进入一个较长的平台期,电压基本保持不变,最后在接近截止电压时再次迅速下降。
锂离子电池具有高能量密度和较长的循环寿命,广泛应用于便携式电子设备和电动汽车。
3. 镍氢电池(Nickel-Metal Hydride Battery):镍氢电池的放电曲线与锂离子电池类似,但平台期较短,电压下降速度较快。
镍氢电池具有较高的功率密度和较好的低温性能,常用于需要频繁充放电的设备,如无线电话、电动工具等。
4. 铅酸电池(Lead-Acid Battery):铅酸电池的放电曲线在开始时电压迅速下降,然后在大部分时间内保持相对稳定,直到接近截止电压时再次迅速下降。
铅酸电池成本低廉,但循环寿命较短,通常用于汽车启动、备用电源等领域。
5. 锂聚合物电池(Lithium-Polymer Battery):锂聚合物电池的放电曲线与锂离子电池相似,但因为使用了聚合物电解质,可以提供更好的安全性能和更高的能量密度。
锂聚合物电池在手机、平板电脑等设备中得到了广泛应用。
6. 银氧化物电池(Silver Oxide Battery):银氧化物电池的放电曲线在初始阶段电压较高,可以达到1.5伏以上,随后电压逐渐下降。
这种电池具有高能量密度和较长的储存寿命,但成本较高,通常用于高端电子设备,如笔记本电脑、航空航天设备等。
7. 锂电池(Lithium Battery):锂电池的放电曲线在初始阶段电压较高,可以达到1.5伏以上,随后电压逐渐下降。
Alkaline batteries:碱性电池Capacitor batteries:电容电池Carbon zinc batteries:碳锌电池Lead acid batteries:铅酸电池Lead calcium batteries:铅钙电池Lithium batteries:锂电池Lithium ion batteries:锂离子电池Lithium polymer batteries:锂聚合物电池Nickel cadmium batteries:镍镉电池Nickel iron batteries:镍铁电池Nickel metal hydride batteries:金属氧化物镍氢电池/镍氢电池Nickel zinc batteries:镍锌电池Primary batteries:原电池Rechargeable batteries:充电电池Sealed lead acid batteries:密封铅酸电池Silver cadmium batteries:银钙电池Silver oxide batteries:银氧化物电池Silver zinc batteries:银锌电池Zinc chloride batteries:银氯化物电池Zinc air batteries:锌空电池Environmental Protection batteries:环保电池Lithium batteries:锂电池Lithium ion batteries:锂离子电池Lithium polymer batteries:锂聚合物电池铅酸蓄电池Lead-acid battery起动铅酸电池Lead-acid starter batteries摩托车用铅酸电池Lead-acid batteries for motorcycles内燃机车用铅酸电池Lead-acid batteries for disel locomotive电动道路车辆用铅酸电池Lead-acid batteries for electric road vehicles小型阀控密封式铅酸电池small-sized valve-regulated lead-acid batteries航空用铅酸电池Aircraft lead-acid batteries固定型阀控密封式铅酸蓄电池Lead-acid batteries for stationary valve-regulated 铅酸电池用极板plate for lead-acid battery铅锭lead ingots牵引用铅酸电池Lead-acid traction batteies电解液激活蓄电池electrolyte activated batteryvent valve排气阀filling device for pleral cells电池组填充装置negative electrode负电极negative plate负极板addition reagent for negative plate负极板添加剂indicator指示器top cover上盖vent plug液孔塞expanded grid扩展式板栅specific gravity indicator比重指示器electrolyte level control pipe电解液液面控制管electrolyte level indicator电解液液面指示器electrolyte level sensor电解液液面传感器hard rubber container硬橡胶槽envelope separator包状隔板woven cloth tube纺布管spongy lead海绵状铅partition隔壁over the partition type越过隔壁型through the partition type贯通隔壁贯通型separator隔板(1)battery rack(2)battery stand(3)battery stillage蓄电池架/蓄电池底垫active material活性物质glass fiber separator玻璃纤维隔板glass mat玻璃纤维绵glass mat tube玻璃纤维绵管spacing washer间隔垫圈reinforced fiber separator强化纤维隔板polarity mark plate极性标记板pole极柱pole insulator极柱绝缘子pole nut极柱螺母plate极板plate foot极板足plate supporter极板支撑件element极板群/极群组pole bolt极柱螺栓plate lug极板耳dilute sulfuric acid稀硫酸steel can金属罐steel container金属蓄电池槽(1)madribs(2)element rest鞍子/极群组座tubular plate管状极板gelled electrolyte胶体电解液grid板栅caution label警告标签synthetic resin separator合成树脂隔板plastics container塑料蓄电池槽synthetic fiber separator合成纤维隔板connector sunken type沉没型连接器connetor exposed type露出型连接器safety valve test安全阀测试ampere-hour efficency安时效率one charge distance range一次充电行程gas recombination on negative electrode type阴极气体再化合型/阴极气体复合型cut-off discharge终止放电/截止放电(1)specific characteristic (2)energy density(1)比特性(2)能量密度recovering charge恢复充电(1)open circuit voltage(2)off-load voltage开路电压/空载电压overcharge过充电gassing析气overcharge life test过充电寿命试验accelerated life test加速寿命试验active material utilization活性物质利用率theoretical capacity of active material活性物质的理论容量over discharge过放电intermittent discharge间歇放电full charge完全充电full discharge完全放电reverse charge反充电/反向充电quick charge快速放电allowable minimum voltage允许最小电压equalizing charge均衡充电creeping蠕变group voltage组电压shallow cycle endurance轻负荷寿命/轻负荷循环寿命characteristic of electrolyte decrease电解液减少特性nominal voltage标称电压high rate discharge高率放电high rate discharge characteristic高率放电特性5 second voltage at discharge放电5秒电压(1)cold cranking ampere(2)cold cranking performance(1)冷启动电流(2)冷启动性能cycle life test循环寿命测试maximum voltage at discharge最大放电电压30 second voltage at discharge放电30秒电压residual capacity残存容量(1)hour rate(2) discharge rate(1)小时率(2)放电率(1) self discharge (2) local action(1)自放电(2)局部自放电(1) self discharge rate(2) local action rate(1)自放电率(2)局部自放电率actual capacity实际容量(1)starting capability(2)cranking ability启动能力cranking current启动电流battery clamp test电池夹钳测试power density功率密度momentary discharge瞬间放电modified constant voltage charge修正恒定电压充电initial capacity初始容量gas recombination by catalyser type触媒气体复合式initialcharge初始充电viberation test振动试验predetermined voltage预定电压total voltage总电压activation test for dry charged battery干式荷电蓄电池活化试验salting盐析earthquake-proof characteristics防震性能dielectric voltage withstand test电介质耐压试验short time discharge短时间放电escaped acid mist test酸雾逸出测试terminal voltage端子电压cell voltage单电池电压step charge阶段充电short-circuit current短路电流storage test保存测试high rate discharge at low temperature低温高率放电rated voltage额定电压rated capacity额定容量fixed resistance discharge定阻抗放电constant voltage charge恒压充电constant voltage life test恒压寿命测试constant current charge恒流充电constant voltage constant current charge恒流恒压充电constant current discharge恒流放电constant watt discharge恒功率放电low rate discharge characteristics低率放电特征trickle charge涓流充电trickle charge current涓流充电电流trickle charge life test涓流充电寿命测试thermal runaway热失控driving pattern test运行测试capacity in driving pattern test运行测试boost charge急充电floating charge浮充电floating charge voltage浮充电电压floating charge current浮充电电流(1)mean voltage (2)average voltage平均电压on-load voltage负载电压discharge duration time放电持续时间(1)final voltage(2)cut-off voltage(3)end voltage终止电压/截止电压depth of discharge放电深度discharge voltage放电电压discharge current放电电流discharge current density放电电流密度discharge watt-hour放电瓦时discharge characteristics放电特性discharged ampere-hour放电安时explosion proof test防爆测试auxiliary charge补充电maintenance factor维护率storage characteristics保存特性gas recombinating efficiency气体复合效率/气体再化合效率charge充电charge acceptance test充电可接受性试验start-of-charge current充电开始电流charge efficiency充电效率end-of-charge voltage充电结束电压specific gravity of electrolyte at the end of charge充电结束时电解液比重charge voltage充电电压charge current充电电流charged watt-hour充电瓦时charge characteristic充电特性charge ampere-hour充电安时deep cycle endurance重负荷循环寿命/重复合寿命weight engergy density重量能量密度rubber pad橡胶垫lower level line下液面线side terminal侧端子collective exhaust unit公共的排放单元sintered plaque烧结极板sintered separator烧结隔板sintered plate烧结极板catalyst plug催化塞spine芯骨strap带spacer隔离物insulating tube绝缘管intercell connector连接线/连接条connector cover连接管盖float mounted plug浮动安装的栓(1)pasted plate (2)grid type plate涂膏式极板braidd tube编织管(1)flame-arrester vent plug (2)flam-retardant vent plug安全塞explosion and splash proof construction防爆防溅结构baffle保护板pocket type plate袋式极板bottom hole-down底孔向下(固定)bolt fastening terminal螺栓连接端子male blade阳片monoblock container整体槽positive electrode正极positive plate正极板leading wire terminal引线端子retainer mat止动垫片ribbed separator肋隔板(1)jumping wire (2)inter low wire跳线end plate端板filling plug注液塞plante plate形成式极板/普朗特极板tubular plate管式极板low electric resistance separator低电阻隔板tapered terminal post锥形接线柱electrolyte电解液container蓄电池槽/蓄电池壳set of container成套蓄电池槽level-scope mounted plug透视塞/透视栓handle手柄jug取液管(1)connector;(2)plug concent (1)连接器;(2)插座式连接器connector wire连接线connecting bar连杆connecting bar cover连杆帽lead引线/连接线edge insulator绝缘卡side frame侧框架battery cubicle蓄电池箱perforated separator多孔隔板burning rod (铅)焊条terminal端子terminal connector端子连接条terminal cover端子盖terminal base端子座tab接线片lead bushing铅套corrugated separator波形隔板(1)lead dioxide;(2)lead peroxide (1)二氧化铅;(2)过氧化铅(1)woven separator;(2)nonwoven separator (1)织物隔板;(2)非织物隔板vent hole通气孔exhaust tube排气管antipolar mass反极性物质output cable输出电缆microporous rubber separator微孔像胶隔板specific gravity indicator比重计leaf separator叶片式隔板lid sealing compound密封剂/封口剂sealing gasket密封衬垫/垫圈lid蓄电池盖set of lid系列的盖方通盖板cover board底板solepiece钢珠steel ball压钢珠press steel ball防爆阀valve preventing explosion大电流(倍率)放电discharge in high rate current标称电压Normal voltage标称容量normal capacity放电容量discharge capacity充电上限电压limited voltage in charge放电下限电压terminating voltage in discharge恒流充电constant current charge恒压充电constant voltage charge恒流放电constant current discharge放电曲线discharge curve充电曲线charge curve放电平台discharge voltage plateau容量衰减capacity attenuation起始容量initial discharge capacity流水线pipelining传送带carrying tape焊极耳welding the current collector卷绕wind叠片layer贴胶带stick tape点焊spot welding超声焊ultrasonic weldingThe terminating voltage in discharge of the battery is 3.0 volt. The limited voltage in charge of the battery is 4.2 volt.三元素Nickle-Cobalt-Manganese Lithium Oxidethree elements materials钴酸锂Cobalt Lithium Oxide锰酸锂Manganese Lithium Oxide石墨graphite烘箱oven真空烘箱vacuum oven搅拌机mixing devicevacuum mixing device涂布机coating equipment裁纸刀paper knife ,,,,,,cutting knife分条机equipment for cutting big piece to much pieces 辊压机roll press equipment电阻点焊机spot welding machine超声点焊机ultrasonic spot welding machine卷绕机winder自动叠片机auto laminating machine激光焊机laser welding machine注液机infusing machine真空注液机vacuum infusion machine预充柜pre-charge equipment化成柜formation systems分容柜grading systems测试柜testing systems内阻仪battery inner resistance tester万用表multimeter转盘式真空封口机turntable type vacuum sealing machine自动冲膜机automatic aluminum membrane shaper序号首字母英文中文1 A aging老化2 B battery charger充电器3 black-fleck黑斑4 C cap盖板5 capacity density能量密度6 capacity grading分容7 cathode tab welding极耳超焊8cell电芯9 charge(capacity) retention荷电(容量)保持10 checking code检码11 concave spot凹点12 constant current charge恒流充电13 constant current discharge恒流放电14 constant voltage charge恒压充电15 corrective measures纠正措施16 crack裂纹17 cut-off voltage终止电压18 cycle life循环寿命19 D dark trace暗痕20 degrade降级21 dent凹痕22 discharge depth放电深度23 distortion变形24 drape打折25 E Electrical and MechanicalServices Department机电部26 electrolyte电解,电解液27 empaistic压纹28 end-off voltage放电截止电压29 environmentally friendly对环境友好30 equipment first inspection设备首检31 erode腐蚀32 explosion-proof line防爆线33 F first inspection首检34 formation化成35 fracture断裂36 I inspection检验37 insulate绝缘38 internal resistance内阻39 J jellyroll卷芯40 joint接缝,结合点41 L laser deflecting偏光42 laser reticle激光刻线43 laser welding-flatwise weld激光焊接-平焊laser welding-standing weld激光焊接-立焊44 leakage漏液45 leak-checking测漏46 leaving out of welding漏焊47 limited charge voltage充电限制电压48 local action自放电49 M margin turnly翘边50 measuring the dimension of cells电芯卡尺寸51 meet requirement达到要求52 memory effects记忆效应53 N nick划痕54 nominal voltage标称电压55 notice-board confirmation看板确认56 nugget硬块57 O obverse正面58 open circuit voltage开路电压59 over charge过充60 over discharge过放61 over the thickness超厚62 P particle颗粒63 PE membrane PE膜64 pit坑点65 placing cells into the box电芯装盒66 point inspection点检67 preventive measures预防措施68 pricking the tapes扎孔69 process inspection制程检验70 put the battery piled up将电芯叠放在一起71 Q qualified products合格品72 quality assurance质量保证73 quality control质量控制74 quality improvement质量改进75 quality match品质配对76 quality planning质量策划77 R rated capacity额定容量78 recharge再充电79 refitting the can of cell电芯壳口整形80 requirment要求81 reverse背面,反面82 rework返工83 ringing cells into pyrocondensation films套热缩膜84 S safety vent安全阀85 sand aperture砂眼86 scar疤痕87 secondary battery二次电池88 select appearance选外观sharp-set批锋89 short circuit checking测短路90 smudginess污物91 spot welding by laser激光点焊92 spot welding place点焊位置93 spraying the code喷码94 spur毛刺95 sticking the PVC cover boards贴面垫96 storing陈化97 storing with high voltage高压储存98 T tabs deflection极耳歪斜99 tabs excursion极耳错位100 technics requiment工艺要求101 U ultrasonic welding超声波焊接102 ultrasonic welding strength超焊强度103 unqualified products不合格品104 W wave波浪105 working procedure工序Voltage:Units of measuring electrical current, all batteries are rated in volts DC. (Direct Current). This determines how much energy is needed to power your equipment. Voltage plateau:(电压平台)A slow decrease in voltage over a long period of time. As a rule, the plateau extends from the first voltage drop at the start of the discharge to the bend of the curve after which the voltage drops rapidly at the end.Nominal Voltage(标称电压)The voltage of a battery, as specified by the manufacturer, discharging at a specified rate and temperature.Working voltage(工作电压)The working voltage of a cell or battery begins at its electrical connections as soon as an electrical consumer is connected to it.Discharging voltage, average voltage (放电电压)The average discharging voltage is the average value of the discharging voltage during the entire discharging process with a related discharging current.Open circuit voltage (OCV开路电压)The voltage of a battery when there is no current flowing.Closed-Circuit Voltage (CCV闭路电压)The potential or voltage of a battery when it is discharging or charging.State of charge:The rate of charge capacity vs. whole capacity.Initial voltage(起始电压)A battery's initial voltage is the working voltage when discharging begins. End-point voltage (End voltage, Cutoff voltage, Final voltage)截止电压Specified closed circuit voltage at which a service output test is terminated. End-of-discharge voltageThe battery voltage when discharge is terminated.End-of-charge voltageThe battery voltage when charge is terminated.Cutoff voltage (V)The battery voltage at which charge or discharge is terminated.Definition: Capacity(容量)? The capacity of a cell is defined as how manymilli-amp-hours (mAh) of current the cell canstore and subsequently deliver.? One milli-amp (mA) is 1/1000th of an Amp. Somelarger cell capacities are expressed in Amp-hours(Ah).? “Rated capacity” is varies with discharge rate,temperature, and cutoff voltage.? Rated capacity is different from power or energy? Example:? If a cell is rated at 1000 mAh, then it can deliverthe following:? 1000 mA of current for 1 hour? 500 mA of current for 2 hours? 200 mA of current for 5 hours? 2000 mA of current for 1/2 hourDefinition: Energy Density(能量密度,包括体积比能量和质量比能量)? The energy density of a cell is a measure of howmuch energy can be stored in the cell per unitvolume or per unit weight.? E (watt-hours) = cell voltage x capacity rating? Energy density per unit volume is called the“volumetric energy density” and is expressed interms of watt-hours/liter (wh/l).? Energy density per unit weight is called the“gravimetric energy density” and is expressedin terms of watt-hours/kilogram (wh/kg).? These measurements are useful when you aretrying to determine which cell has the mostcapacity per unit volume or weight.1.Self Discharge自放电2.Uniformity of the Li-ion Batteries锂离子电池的一致性3.steel strap钢带4.Burst vent防爆阀5.Filling port注液孔6.spirally wound type cylindrical wound type圆柱形7.foil箔8.parallel-plate prismatic design方形叠片式设计Ageing(老化)-Permanent loss of capacity with frequent use orthe passage of time due to unwanted irreversible chemical reactions in the cell. Anode(阳极)-The electrode in an electrochemical cell where oxidation takes place, releasing electrons.During discharge the negative electrode of the cell is the anode.During charge the situation reverses and the positive electrode of the cell is the anode.Cathode(阴极)-The electrode in an electrochemical cell where reduction takes place, gaining electrons.During discharge the positive electrode of the cell is the cathode. During charge the situation reverses andthe negative electrode of the cell is the cathode.Cycle(循环)- A single charge and discharge of a battery.Depth of discharge DOD(放电深度)-The ratio of the quantity of electricity or charge removed from a cell on discharge to its rated capacity.Internal impedance(交流内阻)-Resistance to the flow of AC current within a cell. It takes into account the capacitive effect of the plates forming the electrodes. Internal resistance(直流内阻)-Resistance to the flow of DC electric current within a cell,causing a voltage drop across the cell in closed circuit proportional to the current drain from the cell.A low internal impedance is usually required for a high rate cell.锂离子电池的内阻英语概念到底用哪个概念,是Internal resistance还是Internal impedance,一些电池说明书内阻用Internal resistance,也有的用Internal impedance,我认为Internal impedance较好些,因为国内测的电池内阻基本都是交流内阻,而外文也有这样定义的(我在别的帖子也粘贴过):Internal impedance(交流内阻)-Resistance to the flow of AC current within a cell. It takes into account the capacitive effect of the plates forming the electrodes. Internal resistance(直流内阻)-Resistance to the flow of DC electric current within a cell,causing a voltage drop across the cell in closed circuit proportional to the current drain from the cell.A low internal impedance is usually required for a high rate cell.在IEC6196002中,只定义为Internal resistance,而用交流的方法测得的内阻,叫Internal a.c. resistance(交流内阻)用直流的方法测得的内阻,叫Internal d.c. resistance(直流内阻),其实Internal a.c. resistance测得就是阻抗,这样看来不如用Internal impedance(交流内阻)和Internal resistance(直流内阻)这两个概念把它们进行分清,以免混淆。
上海节能节能战略与政策 ENERGY CONSERVATION STRATEGY AND POLICY节能战略与政策国内外电池储能技术的应用及发展现状摘要:随着可再生能源的迅猛发展以及对供电可靠性要求的不断提高,电池储能技术在电力系统中的应用日益增多。
讨论了铅酸电池、铅炭电池、钠硫电池、全钒液流电池、锂离子电池的性能特点,并介绍了不同电池储能技术在电力系统中的应用。
关键词:储能;电池;电力系统基金项目:上海市科委项目(14DZ1201500,14DZ2261000);上海市联盟计划(LM201458);上海市教委科研创新项目(13YZ107);上海市浦东新区科技发展基金创新资金(PKC20I4-M12)。
DOI: 10.13770/ki.issn2095-705x.2015.10.001张利中 赵书奇 廖强强 周国定 上海电力学院刘 宇 中国科学院上海硅酸盐研究所支玉清 国家电网上海市电力公司[作者简介]廖强强:(1971-),男,博士,上海电力学院教授,研究方向为电力储能和电力腐蚀控制。
Zhang Lizhong, Zhao Shuqi, Liao Qiangqiang, Zhou Guoding Shanghai Electrical Power UniversityLiu Yu Shanghai Silicate Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Science Zhi Yuqing Shanghai Electrical Power Company, State GridAbstract: With the rapid development of renewable energy and the continuous improvement of the power supply reliability, battery energy storage technology has been wildly used in electrical power system. The article discusses about features and characteristics of lead acid battery, lead carbon battery, sodium sulfur battery, all vanadium redox flow battery, lithium ion battery. It also introduces electrical power system applications of different batter energy storage technologies.Keywords: Energy Storage, Battery, Electrical Power SystemFund Item: Shanghai Municipal Science and Technology Commission Project(14DZ1201500,14DZ2261000), Shanghai Alliance Program (LM201458), Shanghai Municipal Education Commission Science and Technology Innovation Project (13YZ107), Shanghai Pudong New Area Science and Technology Development Fund Innovation Capital (PKC20I4-M12)节能战略与政策 ENERGY CONSERVATION STRATEGY AND POLICY节能战略与政策 ENERGY CONSERVATION STRATEGY AND POLICY。
SANDIA REPORTSAND2011-8263Unlimited ReleasePrinted October 2011Understanding the Function and Performance of Carbon-enhancedLead-acid BatteriesMilestone Report for the DOE Energy Storage Systems Program (FY11 Quarter 4: July through September 2011)D.G. Enos, S.R. Ferreira, R. ShanePrepared bySandia National LaboratoriesAlbuquerque, New Mexico 87185 and Livermore, California 94550Sandia National Laboratories is a multi-program laboratory managed and operated by Sandia Corporation, a wholly owned subsidiary of Lockheed Martin Corporation, for the U.S. Department of Energy's National Nuclear Security Administration under contract DE-AC04-94AL85000.Approved for public release; further dissemination unlimited.Issued by Sandia National Laboratories, operated for the United States Department of Energy by Sandia Corporation.NOTICE: This report was prepared as an account of work sponsored by an agency of the United States Government. Neither the United States Government, nor any agency thereof, nor any of their employees, nor any of their contractors, subcontractors, or their employees, make any warranty, express or implied, or assume any legal liability or responsibility for the accuracy, completeness, or usefulness of any information, apparatus, product, or process disclosed, or represent that its use would not infringe privately owned rights. Reference herein to any specific commercial product, process, or service by trade name, trademark, manufacturer, or otherwise, does not necessarily constitute or imply its endorsement, recommendation, or favoring by the United States Government, any agency thereof, or any of their contractors or subcontractors. The views and opinions expressed herein do not necessarily state or reflect those of the United States Government, any agency thereof, or any of their contractors.Printed in the United States of America. This report has been reproduced directly from the best available copy.Available to DOE and DOE contractors fromU.S. Department of EnergyOffice of Scientific and Technical InformationP.O. Box 62Oak Ridge, TN 37831Telephone: (865) 576-8401Facsimile: (865) 576-5728E-Mail: reports@Online ordering: /bridgeAvailable to the public fromU.S. Department of CommerceNational Technical Information Service5285 Port Royal Rd.Springfield, VA 22161Telephone: (800) 553-6847Facsimile: (703) 605-6900E-Mail: orders@Online order: /help/ordermethods.asp?loc=7-4-0#online2SAND2011-8263Unlimited ReleasePrinted October 2011Understanding the Function and Performance of Carbon-enhanced Lead-acid Batteries Milestone Report for the DOE Energy Storage Systems Program (FY11 Quarter 4: July through September 2011)D. G. EnosMaterials Reliability DepartmentSandia National LaboratoriesAlbuquerque, NM 87185Summer R. FerreiraAdvanced Power Sources R&D DepartmentSandia National LaboratoriesAlbuquerque, NM 87185R. ShaneEast Penn ManufacturingLyon Station, PA 19536AbstractThis report describes the status of research being performed under CRADA No. SC10/01771.00 (Lead/Carbon Functionality in VRLA Batteries) between Sandia National Laboratories and East Penn Manufacturing, conducted for the U.S. Department of Energy’s Energy Storage Systems Program. The Quarter 4 Milestone was completed on time. The milestone entails the initiation of high rate, partial state of charge (HRPSoC) cycling of the carbon enhanced batteries.The morphology, porosity, and porosity distribution within the plates after 1k and 10k cycles were documented, illustrating the changes which take place in the early life of the carbon containing batteries, and as the battery approaches failure due to hard sulfation for the control battery. Longer term cycling on a subset of the received East Penn cells containing different carbons (and a control) continues, and will progress into FY12.34Project DescriptionCarbon has been explored as an addition to lead-acid battery electrodes in a number of ways. Perhaps the most notable to date has been the hybrid ―Ultrabattery‖ developed by CSIRO where anasymmetric carbon-based electrochemical capacitor is combined with a lead-acid battery into a single cell, dramatically improving high-rate partial-state-of-charge (HRPSoC) operation.1 As illustrated below, the ―Ultrabattery‖ is a hybrid device constructed using a traditional lead -acid battery positive plate (i.e., PbO 2) and a negative electrode consisting of a carbon electrode in parallel with a lead-acid negative plate:Schematic representation of a single cell from the Ultrabattery (after Lam et al. 2007)This device exhibits a dramatically improved cycle life over traditional VRLA batteries, as well as increased charge power and charge acceptance. The ―Ultrabattery‖ has been produced successfully by both The Furukawa Battery Co. and East Penn Manufacturing. An example illustrating the dramatic improvement in cycle life of the Ultrabattery over a conventional VRLA battery is shown in the graph below: 1 L.T. Lam, R. Louey, N.P. Haigh, O.V. Lim, D.G. Vella, C.G. Phyland, L.H. Vu, J. Furukawa, T. Takada, D. Monma, T. Kano, ―Production and test of hybrid VRLA Ultrabattery designed specifically for high -rate partial-state-of-charge operation‖, ALABC Project DP 1.1, Final report, April 2007.Lead-AcidCell Asymmetric Supercapacitor5Discharge voltage as a function of number of cycles under the EUCAR cycle life test.Lam, et al., 2007.In addition to the aforementioned hybrid device, carbon has also been added directly to traditional VRLA batteries as an admixture in both the positive and negative plates, the latter of which has been found to result in similar improvements to battery performance under high-rate partial-state-of-charge (HRPSoC) operation. It is this latter construction, where carbon is added directly to the negativeactive material (NAM) that is the specific incarnation being evaluated through this program. Thus, the carbon-modified (or Pb-C) battery (termed the ―Advanced‖ VRLA battery by East PennManufacturing) is a traditional VRLA battery where an additional component has been added to the negative electrode during production of the negative plate.Schematic representation of a single cell from a carbon-modified or“Advanced” VRLA battery .The addition of select carbon materials to the NAM of VRLA batteries has been demonstrated to increase cycle life by an order of magnitude or more under (HRPSoC) operation. Additionally,battery capacity increases on cycling and, in fact, exceeds the performance of the batteries when new.2+ C6Capacity as a function of cycle life for a commercially available, conventional VRLA, and a carbon-modified VRLA battery where carbon has been added to the NAM. (the increase in capacity observed at 400 cycles for the standard battery was the result of a recovery chargingprocedure) Physically, the mechanism by which carbon extends battery life is generally accepted to be through reduction/elimination of sulfation of the negative electrode. Sulfation is a process that results in theformation of lead sulfate (PbSO 4) crystals that are electrically isolated from the lead in the electrode, and thus are unable to be electrochemically reduced through the recharging process. These PbSO 4crystals eventually block the surface, dramatically reducing the capacity of the negative plate. It is not clear why some carbons accomplish this effect and others do not.Elimination of hard sulfation by carbon additions, allowing more complete usage of thebattery (both images are from cells at end of life). Fernandez et al., 2010.The underlying mechanism responsible for improving capacity on cycling is not known. Developing an understanding of the fundamental physical, chemical, and electrochemical mechanisms underlying both aspects of enhanced performance offers the possibility of significantly improving VRLAbatteries by intentionally designing and fabricating electrode structures with superior performance.Standard Carbon AdditionFurthermore, once understood at a fundamental level, it may be possible to extend this approach to other battery chemistries. In this collaborative effort with East Penn Manufacturing, we will investigate the fundamental physicochemical basis and structure-activity relationships underlying carbon-enhanced VRLA batteries.This program focuses on 1) developing a fundamental physical, chemical, and electrochemical understanding of the mechanism of enhanced performance of carbon-enhanced VRLA batteries;2) demonstrating this understanding by fabricating batteries exhibiting optimum performance; and3) determining to what extent this approach can be applied to other battery chemistries. Engineering the enhanced performance of PbC batteries will ultimately lead to reduced life-cycle cost, which is an enabling factor for many stationary applications including utility ancillary regulation services, wind farm energy smoothing, and solar photovoltaic energy smoothing.FY11 Quarterly MilestonesFirst Quarter—Review relevant literature to establish the current level of understanding of the mechanisms through which carbon additions to the NAM improve VRLA battery performance. This review will identify proposed mechanistic explanations that can be evaluated, built upon, or disproved through the course of the experimental portion of the program. This milestone has been completed. Second Quarter—Characterize the carbon materials that will be used by East Penn Manufacturing to construct carbon-enhanced VRLA batteries that will be evaluated both physically and electrochemically by Sandia National Laboratories. Key physical and electrochemical features of each material will be documented and later combined with the results of complete battery testing in an effort to identify the critical characteristics of the carbon additions required to enhance VRLA battery performance. This milestone has been completed.Third Quarter—Characterize the raw and formed negative plates containing the four carbon materials characterized in the second quarter. The physical and electrochemical activities of the carbon-enhanced negative plates will be documented and then combined first with the knowledge gained in the second quarter on the properties of the carbon raw material, and then with the results of complete battery testing in order to determine if there are any critical features or properties of the raw or formed negative plates that can be correlated with the performance characteristics of a VRLA battery that contains them. This milestone has been completed.Fourth Quarter—Conduct initial cycle testing (i.e., low cycle count), combined with dissection and analysis of tested positive and negative plates for both carbon-enhanced and conventional VRLA batteries to establish their relative performance and physical characteristics. In addition to quantifying the raw performance of the various batteries (and hence, carbon additions), an effort will be made to establish what, if any, chemical or structural changes occur early in the life of the carbon-enhanced VRLA batteries. These observations may provide valuable insight into the mechanism through which carbon additions to the NAM enhance the battery capacity and reduce the development of hard sulfation that ultimately leads to battery failure, as well as the degradation mechanisms that dictate the longevity of the carbon additions in the NAM.7FY11 Quarter 1 Project Status SummaryLiterature reviewMuch of the research presented in the literature that discusses the effect of carbon additions to the NAM focuses primarily on the phenomenological observations (i.e., cycle life increases, resistance to hard sulfation increases) rather than postulating/exploring potential mechanisms through which the effect is achieved. A summary of recent work from groups attempting to establish the mechanisms through which carbon enhances the performance of VRLA batteries is presented below.Looking first to the work of Shiomi, et al.2 where the beneficial effect of carbon added to the NAM was first reported, it was proposed that carbon forms a conductive network between PbSO4 crystals, leading to an enhancement in the rechargability of the negative plate. Ohmae, et al. expressed a similar view, in that a highly conductive carbon was a necessary addition to the NAM in order to retard the sulfation process.3 In other words, the carbon served as a conductor, hindering the formation of PbSO4 crystals that were electrically isolated from the lead within the plate, and thus not able to be reduced during the recharging process. While Shiomi and Ohmae believe that the electrical conductivity of the carbon addition is the critical aspect, other researchers, such as Spence, et al.4, have found that neither electrical conductivity nor surface reactivity were important in determining the effect of a carbon addition to the NAM.Spence, et al.5, argued instead that the beneficial impact of the carbon was due to the alteration of the pore structure of the NAM, enabling electrolyte to be banked within the pore structure, and thus available within the NAM, rather than having to diffuse from the surface. They concluded that any addition, not just carbon, which modified the pore structure in such a manner would result in an improvement in performance. This theory is supported by Calebeck and Micka, et al.6,7,8 where both titania (TiO2) and alumina (Al2O3) were found to provide improvements similar to those obtained by carbon, though their argument was that, in addition to obstructing large pores in the NAM, the additions hindered growth of PbSO4 crystals, preventing the formation of the large crystallites associated with sulfation. Valenciano, et al.9 also observed a beneficial effect of an inert addition, in their case glass fibers, though the resulting improvement appeared to depend on the manner in which the battery itself was assembled.As with Shiomi, Boden, et al.10 observed that the cycle life was increased by eliminating surface buildup of PbSO4 on the negative electrode (i.e., hard sulfation), and also hypothesized that the2 M. Shiomi, T. Funato, K. Nakamura, K. Takahashi, M. Tsubota ―Effects of Carbon in Negative Plates on Cycle-life Performance of Calve-regulated Lead/Acid Batteries.‖ Journal of Power Sources, 64 (1997). pp. 147-152.3T. Ohmae, T. Hayashi, N. Inoue ―Development of 36-V Valve Regulated Lead-acid Battery.‖Journal of Power Sources, 116 (2003), pp.105-109.4M. A. Spence, D. P. Boden, T. D. Wojcinski, ―Identification of the Optimum Specification for Carbon to be Included in the Negative Active Material of a Valve-Regulated Battery in Order to Avoid Accumulation of Lead Sulfate During High-Rate Partial-State-of-Charge Operation.‖ ALABC Research Project D esignation C1.1/2.1A, Progress Report 2, May 2008.5 M. A. Spence, D. P. Boden, T. D. Wojcinski, ―Identification of the Optimum Specification for Carbon to be Included in the Negative Active Material of a Valve-Regulated Battery in Order to Avoid Accumulation of Lead Sulfate During High-Rate Partial-State-of-Charge Operation.‖ ALABC Research Project D esignation C1.1/2.1A, Progress Report 4, October 2009.6M. Calábek, K. Micka, P. Křivák, P. Bača, R. Bilko, R. Lábus ―Significance Of Carbon Additive In Negative lead-Acid Battery Electrodes.‖ ALABC Project No. C 2.2, Final Repor t, April 2008.7K. Micka, M. Calábek, P. Bača, P. Křivák, R. Lábus, R. Bilko ―Studies of Doped Negative Valve-regulated Lead-acid Battery Electrodes.‖Journal of Power Sources, 191 (2009). pp.154-158.8M. Calebek, K. Micka, P. Krivak, P. Baca ―Significan ce of Carbon Additive in Negative Lead-acid Battery Electrodes.‖ Journal of Power Sources, 158 (2006). pp. 864-867.9J. Valenciano, A. Sanchez, F. Trinidad, A.F. Hollenkamp ―Graphite and Fiberglass Additives for Improving High-rate Partial-state-of-charge Cycle Life of Valve-regulated Lead-acid Batteries.‖ Journal of Power Sources, 158 (2006). 851-863. 10D.P. Boden, D.V. Loosemore, M.A. Spence, T.D. Wojcinski ―Optimization Studies of Carbon Additives to Negative Active Materials for the Purpose of Extending the Life of VRLA Batteries in High-rate Partial-state-of-charge Operation.‖ Journal of Power Sources, 195 (2010). pp. 4470-4493.8increased capacity of the carbon-modified battery was due to the increased electrochemical efficiency of the NAM brought about by the more thorough use of the electrode. Boden also reported that metallic lead clusters were observed on the surface of carbon particle, indicating that the soluble lead ions were electrochemically reduced on the carbon surface in the same way as they are on lead surfaces. A number of other researchers have presented results that support the theory that carbon acts as a nucleation site for the recharging process, improving utilization of the NAM. Kozawa, et al.11 explored the addition of colloidal carbon to the electrolyte of a sulfated battery, where they observed that the battery could be electrochemically recovered, with the carbon adsorbing onto the NAM and acting as a nucleation side for Pb deposition during charge. Pavlov, et al.12 also expressed that carbon was electrochemically active in the NAM, providing additional surface area upon whichcharge/discharge reactions could take place. Finally, Boden reported that Brunauer-Emmett-Teller (BET) surface area measurements indicated that the surface area decreased with cycle life, suggesting that the carbon is becoming progressively buried under lead and PbSO4 reaction products and, consequently, losing its beneficial effects. The theory that the carbon serves as an additional electroactive material in the NAM is in contrast to the results reported above by Spence et al., where surface reactivity did not appear to be important.In a recent review of the effects of carbon on the electrochemical behavior of the negative active mass in a lead-acid battery, Moseley offered a number of potential mechanisms through which the performance could be increased.13,14 First, he suggested that the carbon may increase the electrical conductivity of the NAM, facilitating the recharging process (i.e., easing reduction of PbSO4 in the NAM). Another potential mechanism would be the restriction of PbSO4 crystal growth, which constrains the size of PbSO4 crystals and enhances their dissolution rate during recharge, again facilitating the reduction of PbSO4 during recharge. The latter effect has been demonstrated for a series of inert materials, such as titanium oxide (TiO2) as discussed above. A potential mechanism for the increase in capacity that Moseley put forward was that the carbon could be acting as a capacitive component, much like in electrochemical capacitors, adding a capacitive energy storage component to the battery. The addition of a capacitive component was also presented by Fernandez, et al.15 who attributed the dramatic improvement they observed in charge acceptance to the capacitive effect. Moseley also indicated a potential detrimental effect of carbon additions—if their impurity level is high, the impurities may facilitate detrimental side reactions (e.g., such as water reduction) resulting in a loss of capacity.Pavlov’s group has also conducted significant research in this area.16 Their overall theory is similar to that put forth by Boden, where during recharge two parallel processes take place with lead being reduced both on lead surfaces within the NAM as well as on carbon surfaces within the NAM. Thus, the effect of the carbon is to increase the overall electrochemically active surface area within the negative plate, thereby increasing its capacity and facilitating more complete recharge. Pavlov also found that carbon acted to reduce the pore size within the NAM, and that once the pores were reduced to below approximately 1.5 µm the diffusion of sulfuric acid (H2SO4) into the pores was impeded, and lead oxide (PbO), not PbSO4,formed during operation.11A.Kozawa, H. Oho, M. Sano, D. Brodd, R. Brodd ―Beneficial Effect of Carbon-PVA Colloid Additives for Lead-acid Batteries.‖ Journal of Power Sources, 80 (1999). pp.12-16.12D. Pavlov, P. Nikolov, T. Rogachev ―Influence of Expander Components on the Processes at the Negative Plates of Lead-acid Cells on High-rate Partial-state-of-charge Cycling. Part II. Effect of Carbon Additives on the Processes of Charge and Discharge of Negative Plates.‖ Journal of Power Sources, 195 (2010). pp.4444-4457.13P.T. Moseley, R.F. Nelson, A.F. Hollenkamp ―The Role of Carbon in Valve-regulated Lead-acid Battery Technology.‖ Journal of Power Sources, 157 (2006). pp.3-10.14P.T. Moseley ―Consequences of Including Carbon in the Negative Plates of Valve-regulated Lead-acid Batteries Exposed to High-rate Partial-state-of-charge Operation.‖ Journal of Power Sources, 191 (2009). pp. 134-138.15 M. Fernandez, J. Valencia no, F. Trinidad, N. Munoz ―The U se of Activated Carbon and Graphite for the Development of Lead-acid Batteries for Hybrid Vehicle Applications.‖ Journal of Power Sources, 195 (2010). pp. 4458-4469.16 D. Pavlov, T. R ogachev, P. Nikolov, G. Petkova ―Mechanism of Action of Electrochemically Active Carbons on Processes that Take Place at The Negative Plates of Lead Acid Batteries.‖ Journal of Power Sources, 191 (2009). pp. 58-75.9In addition to the number of theories concerning how carbon affects the electrochemical behavior of a VRLA battery, there are a similar number of views as to what the appropriate form of the carbon is. Researchers have found that various forms of graphitic carbon, carbon black, and activated carbon have worked, although the results between researchers appear to vary. For example, Spence, et al. found that the best performance was observed for flake graphite, while Valenciano, et al. determined that flake graphite was detrimental to performance. Seemingly in support of the results of Spence, Sawai, et al.17 explored the use of carbon particulate and fiber, finding that the larger fibrous material was not able to provide an increase in performance. Further, there have been comprehensive studies where numerous forms of carbon were evaluated, such as that reported by Walmet,18 where none of the materials (a series of flake graphites, expanded graphites, carbon blacks, or activated carbons) were able to provide an appreciable increase in performance, and in many cases, reduced performance relative to an unmodified control.Clearly, there is considerable variation from researcher to researcher in terms of both which carbons appear to work and the mechanism by which any beneficial effect that is observed has been achieved. This variability suggests that there may be other factors, such as how the battery was produced(e.g., negative electrode paste formulation, plate production, battery activation, etc.), that play a major role in determining not only which carbons are beneficial, but also the role that they play in the battery’s electrochemistry.Material EvaluationIn this program, four different battery designs are to be evaluated—a control and three different carbon-modified batteries. The carbon containing batteries consist of an acetylene black carbon, an activated carbon, and a combination of carbon black and a graphitic carbon. Batteries demonstrating the desired enhanced performance have been built in the past by East Penn Manufacturing for both the activated carbon and the carbon black/graphite combination. The acetylene black carbon is an electrically conductive material that, based upon theories within the literature, should have a similar beneficial effect. Analysis of the chemical and structural properties of the carbons is in progress. Batteries of each composition have been manufactured; their testing/analysis is in progress.17 K. Sawai, T. Funato, M. Watanabe, H. Wa da, K. Nakamura, M. Shiomi, S. Osumi ―Development of Additives in Negative Active-material to Suppress Sulfation during High-rate, Partial-state-of-charge Operation of Lead-acid Batteries.‖ Journal of Power Sources, 158 (2006). pp.1084-1090.18 P.S. Walmet. Evaluation of Lead/Carbon Devices for Utility Applications. SAND2009-5537 (June 2009).10FY11 Quarter 2 Project Status SummaryIn this program, four different battery designs are to be evaluated – these include a control along with three different carbon modified batteries. The carbon containing batteries consist of an acetylene black carbon, an activated carbon, and a combination of carbon black and a graphitic carbon. Batteries demonstrating the desired enhanced performance have been built in the past by East Penn Manufacturing for both the activated carbon and combination of carbon black and graphite. The acetylene black carbon is an electrically conductive material that, based upon theories within the literature, should have a similar beneficial effect. As it is unclear which characteristics of the carbon might be beneficial, a complete characterization of each material was performed.Structural Analysis of CarbonsPhysically, the acetylene black and carbon black pearls are very similar. Both consist of agglomerations of extremely small particulate (approximately 20-30 nm in size), as illustrated below. The graphitic carbon is very different than the carbon black and acetylene black materials, consisting of numerous platelets of graphite with a particle size on the order of tens of microns. The activated carbon consisted of larger, blocky particles and has a glassy appearance to it (in terms of the fracture surfaces/edges of the particles).SEM image of the acetylene black material. The material consists of agglomerations of small (20-30nm) particlesSEM image of the carbon black material. The material consists of agglomerations of small (20-30nm) particles, similar in appearance to the acetylene black.SEM image of the natural graphitic material. The material consists of numerous plates of graphitic carbon, as expected for such materials.SEM image of the activated carbon material. This material consists of a variety of large and small particles, and has an amorphous appearance to it (based upon the fracture surfaces particularly visible on the larger particles).X-ray diffraction was used to probe the crystalline structure of each of the materials. X-ray diffraction analyses were performed by Mark Rodriguez of Sandia National Labs. The graphitic carbon had well-ordered hexagonal graphite (type 2H) diffraction data, as anticipated for this highly crystalline material. The activated carbon exhibited a diffraction pattern consistent with amorphous material, further supporting the physical observation of a glassy-appearing material. The acetylene black and carbon black had diffraction patterns that were similar to graphite, with the main diffraction peak shifted to larger d-spacings. The shift in spacings and considerable peak broadening suggest that they have a very fine crystallite size. Both of these materials exhibit evidence of a mixture of nano-crystalline as well as amorphous type peaks. This was more easily observed in the carbon black sample which had two distinctly different peak profiles (one sharper, one broader). The acetylene black peak profile fitting resolved two discrete peaks, but the broadness of the peaks made clear distinction of peak location and degree of peak broadening determination difficult.Activated carbonCarbon blackAcetylene blackGraphitic carbonComparison of the x-ray diffraction data from the four carbon materials, illustrating the crystalline structure (or lack thereof) for each material.Based upon the x-ray diffraction data, the degree of crystalline order of the four materials is ranked as follows (from most crystalline to least crystalline (amorphous))1.Graphitic carbon2.Acetylene black carbon3.Carbon black4.Activated carbonIn addition to the basic geometry and phase structure of the carbons, the Brunauer, Emmet, and Teller (BET) surface area (i.e., the specific surface area of the materials per unit mass of material determined via gas adsorption) was analyzed. With one exception, the results are as one might predict from the shape/size of the individual particulate in each material.。