
Effect of high pressure carbon dioxide on the quality of carrot juice
Linyan Zhou 1,Yuanyuan Wang 1,Xiaosong Hu,Jihong Wu,Xiaojun Liao ?
College of Food Science and Nutritional Engineering,China Agricultural University,China Key Lab of Fruit and Vegetable Processing,Ministry of Agriculture,China
Engineering Research Centre for Fruit and Vegetable Processing,Ministry of Education,Beijing 100083,China
a b s t r a c t
a r t i c l e i n f o Article history:
Received 10July 2008Accepted 11January 2009Keywords:
High pressure carbon dioxide Carrot juice Color Cloud
Particle size distribution
The effect of high pressure carbon dioxide (HPCD)on the quality of carrot juice was investigated.The L -value of HPCD-treated juices increased signi ?cantly (P b 0.05)as compared to untreated juices,and the a -value exhibited an increase tendency with increasing the treatment time.However,the b -value of HPCD-treated juices did not change.The browning degree (BD)and pH of HPCD-treated juices decreased,the cloud and titratable acidity (TA)increased signi ?cantly,the UV –visible spectra of juices were lower,but the total soluble solid (TSS)and the carotenoids of juices were stable.The particle size of juices treated by HPCD for 15,30and 45min increased signi ?cantly (P b 0.05),for 60min showed a noticeable decrease and was almost close to untreated juice.HPCD treatment could not alter the Newtonian ?ow behavior of the carrot juice,but caused a signi ?cant increase in juice viscosity (P b 0.05).
Industrial relevance:Carrot juice is one of the most popular vegetable juices,but it requires severe heat treatment for protection from spoilage due to a higher pH,its heat-sensitive quality is inevitably destructed.In this study,HPCD can avoid the drawbacks of the heat treatment as a novel non-thermal pasteurization,available data are provided for the application and evaluation of HPCD in the juice industry.
?2009Elsevier Ltd.All rights reserved.
1.Introduction
Carrot juice is one of the most popular vegetable juices (Marx,Stuparic,Schieber,&Carle,2003),and it is preferably used as a natural source of provitamin A in the carotenoid drinks (Yoon,Cha,Shin,&Kim,2005).In many countries,a steady increase of carrot juice consumption has been reported.From 1995to 1999,German carrot juice production increased by 69%(Schieber,Stintzing,&Carle,2001).The consumption of carrot juice is increasing very fast in China (Wang et al.,2006).Since carrot juice is a low-acid food of approximately pH 6.0,it has a higher risk of bacterial contamination than other acidic foods (Park,Lee,&Park,2002).Hence,it requires severe heat treatment (105to 121°C)for protection from spoilage (Kim &Gerber,1988;Chen,Peng,&Chen,1995).However,thermal energy inevitably leads to destruction of heat-sensitive nutrients,texture,color,and ?avor (Kim &Gerber,1988).
High pressure carbon dioxide (HPCD)is a novel non-thermal technology for pasteurization or sterilization.Many investigations have shown that this technology can effectively inactivate micro-organisms (Corwin &Shellhammer,2002;Liao,Hu,Chen,Wu,&Liao,2007)and enzymes (Truong,Boff,Min,&Shellhammer,2002;Kincal et al.,2006).However,there have been relatively few studies,which monitor the physical,chemical and sensory quality of liquid foods following HPCD treatment (Garcia-Gonzalez et al.,2007).Damar and
Balaban (2006)described that HPCD retained the fresh-like sensory,nutritional,and physical properties of many liquid foods by avoiding thermal effects of traditional pasteurization.Studies with orange juice showed that HPCD treatment could improve some physical and nutritional quality attributes such as cloud formation and stability,color,and ascorbic acid retention (Arreola et al.,1991;Kincal,2000;Kincal et al.,2006).Dagan and Balaban (2006)observed that aroma and ?avor of HPCD-treated beer was not signi ?cantly different from fresh beer,but beer haze was signi ?cantly reduced by HPCD.Yagiz,Lim,and Balaban (2005)reported that HPCD enhanced cloud up to 38.4%,increased lightness and yellowness,and decreased redness of mandarin juice.Damar and Balaban (2005)concluded that overall likeability of HPCD-treated coconut water was not signi ?cantly different from fresh control,whereas heat-pasteurized samples were rated signi ?cantly lower.Park et al.(2002)studied the carrot juice using a combination of 4.9MPa HPCD and 600MPa ultra-high pressure.However,the effect of HPCD alone at higher pressures on the quality of carrot juice was not evaluated until today.
Recently,the industrial application of HPCD was developed by Praxair Inc.(Burr Bidge,IL,US).Based on the technology licensed from the University of Florida (Balaban,Marshall,&Wicker,1995;Balaban,2004),Praxair developed a continuous system which uses HPCD process as a non-thermal alternative to thermal pasteurization (Connery,Shah,Coleman,&Hunek,2005).This system has been commercialized under the Trade Mark “Better Than Fresh (BTF)”.Praxair has constructed four mobile BTF units for processing about 1.5L per minute of juice for demonstration purposes (Connery et al.,2005).
Innovative Food Science and Emerging Technologies 10(2009)321–327
?Corresponding author.Tel.:+861062737434602;fax:+861062737434604.E-mail address:liaoxjun@https://www.doczj.com/doc/151952710.html, (X.Liao).1
Were equally the ?rst
authors.
1466-8564/$–see front matter ?2009Elsevier Ltd.All rights reserved.doi:
10.1016/j.ifset.2009.01.002
Contents lists available at ScienceDirect
Innovative Food Science and Emerging Technologies
j o u r n a l h o me p a g e :w w w.e l sev i e r.c om /l o c a t e /i fs e t
This work aimed to evaluate the effect of HPCD on the quality of carrot juice,the quality indices included color,pH,TA,TSS,carotenoid, cloud,particle size distribution(PSD)and?ow behavior.
2.Materials and methods
2.1.Preparation of carrot juice
The carrot de?ned as No.1Orange-red variety grew in Beijing Vegetable Experimental Station of the Chinese Academy of Agriculture Science in2006autumn season.After harvesting,the fresh carrot was transported to the laboratory by truck at about20°C,and stored in woven polypropylene bags(75g/m2)in batches of approximately15kg each.Storage temperature was0±1°C and the relative humidity was 85–95%.The storage time was less than1month before processing.
The raw material carrot was randomly separated into3batches,and each batch of carrot was separately pressed into juice and was separate into6×3portions,each portion of juice was used as a replication.Fresh carrot was washed with tap water,and blemished carrots were discarded,then carrots of good quality were sliced into about2mm thick.The pressing of juice was?nished with ZHJ-308A1juice extractor (Fushan Ouke Electric Appliance Co.,China),and the ratio of carrot slices and de-ionized water(2000D de-ionized water machine, Changfeng Instrument Co.,Ltd,China)was1:0.5(w/w).4-fold cheesecloth was used for juice?ltration,and then the juice was centrifuged using Model TDL-5-A Centrifuge(Shanghai Yiheng Scienti?c and Technology Co.,Shanghai,China)at3000rpm for 5min at ambient temperature(approx.25°C).The resulting juice was treated by HPCD immediately or stored at4°C.
2.2.HPCD process system
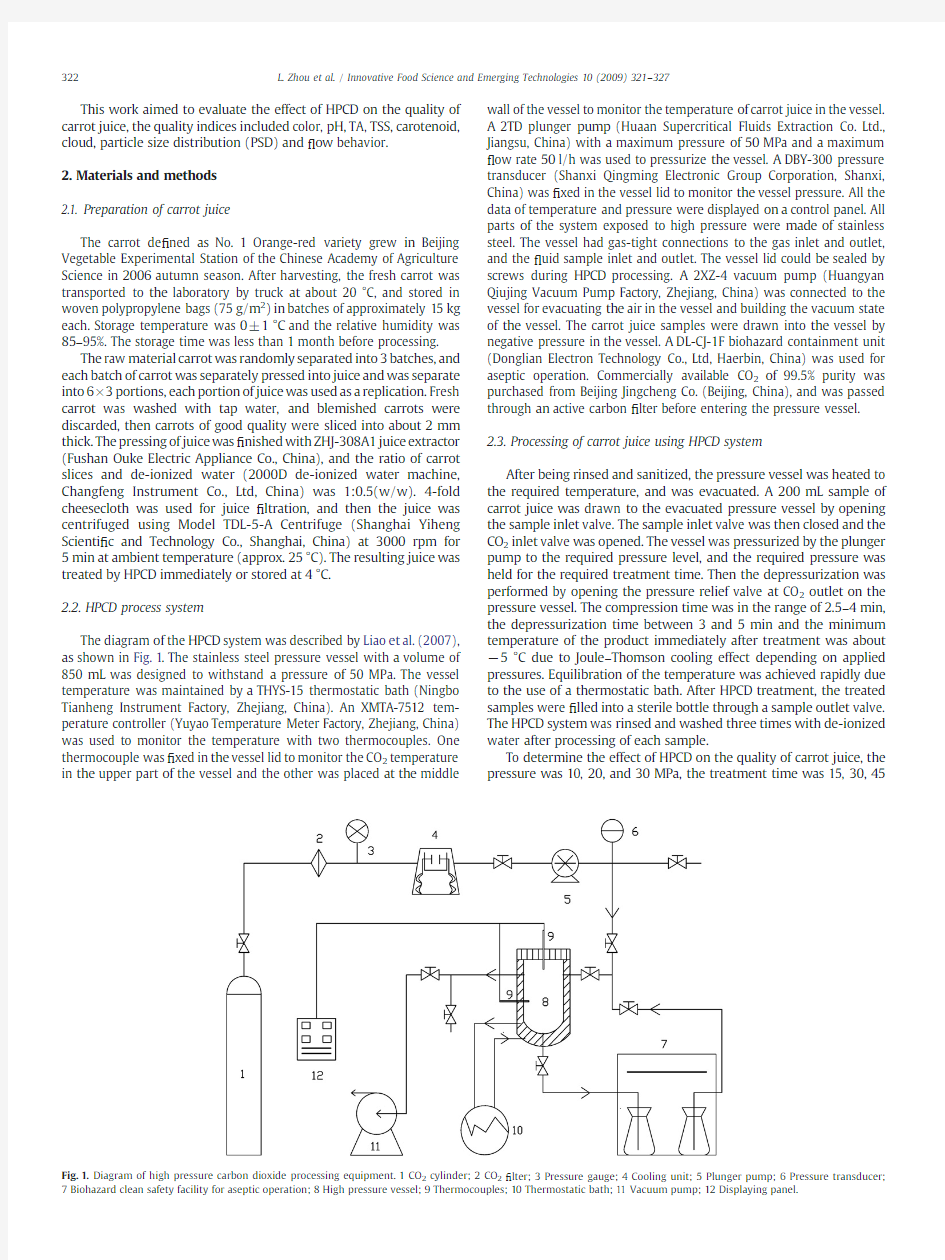
The diagram of the HPCD system was described by Liao et al.(2007), as shown in Fig.1.The stainless steel pressure vessel with a volume of 850mL was designed to withstand a pressure of50MPa.The vessel temperature was maintained by a THYS-15thermostatic bath(Ningbo Tianheng Instrument Factory,Zhejiang,China).An XMTA-7512tem-perature controller(Yuyao Temperature Meter Factory,Zhejiang,China) was used to monitor the temperature with two thermocouples.One thermocouple was?xed in the vessel lid to monitor the CO2temperature in the upper part of the vessel and the other was placed at the middle wall of the vessel to monitor the temperature of carrot juice in the vessel. A2TD plunger pump(Huaan Supercritical Fluids Extraction Co.Ltd., Jiangsu,China)with a maximum pressure of50MPa and a maximum ?ow rate50l/h was used to pressurize the vessel.A DBY-300pressure transducer(Shanxi Qingming Electronic Group Corporation,Shanxi, China)was?xed in the vessel lid to monitor the vessel pressure.All the data of temperature and pressure were displayed on a control panel.All parts of the system exposed to high pressure were made of stainless steel.The vessel had gas-tight connections to the gas inlet and outlet, and the?uid sample inlet and outlet.The vessel lid could be sealed by screws during HPCD processing.A2XZ-4vacuum pump(Huangyan Qiujing Vacuum Pump Factory,Zhejiang,China)was connected to the vessel for evacuating the air in the vessel and building the vacuum state of the vessel.The carrot juice samples were drawn into the vessel by negative pressure in the vessel.A DL-CJ-1F biohazard containment unit (Donglian Electron Technology Co.,Ltd,Haerbin,China)was used for aseptic https://www.doczj.com/doc/151952710.html,mercially available CO2of99.5%purity was purchased from Beijing Jingcheng Co.(Beijing,China),and was passed through an active carbon?lter before entering the pressure vessel.
2.3.Processing of carrot juice using HPCD system
After being rinsed and sanitized,the pressure vessel was heated to the required temperature,and was evacuated.A200mL sample of carrot juice was drawn to the evacuated pressure vessel by opening the sample inlet valve.The sample inlet valve was then closed and the CO2inlet valve was opened.The vessel was pressurized by the plunger pump to the required pressure level,and the required pressure was held for the required treatment time.Then the depressurization was performed by opening the pressure relief valve at CO2outlet on the pressure vessel.The compression time was in the range of2.5–4min, the depressurization time between3and5min and the minimum temperature of the product immediately after treatment was about ?5°C due to Joule–Thomson cooling effect depending on applied pressures.Equilibration of the temperature was achieved rapidly due to the use of a thermostatic bath.After HPCD treatment,the treated samples were?lled into a sterile bottle through a sample outlet valve. The HPCD system was rinsed and washed three times with de-ionized water after processing of each sample.
To determine the effect of HPCD on the quality of carrot juice,the pressure was10,20,and30MPa,the treatment time was15,30,
45 Fig.1.Diagram of high pressure carbon dioxide processing equipment.1CO2cylinder;2CO2?lter;3Pressure gauge;4Cooling unit;5Plunger pump;6Pressure transducer; 7Biohazard clean safety facility for aseptic operation;8High pressure vessel;9Thermocouples;10Thermostatic bath;11Vacuum pump;12Displaying panel.
322L.Zhou et al./Innovative Food Science and Emerging Technologies10(2009)321–327
and60min,and the temperature was25°C.The parameters of pressure and time were selected based on Liao et al.(2007)study,and were effective in inactivating microbes.
2.4.Heat treatment of carrot juice
Carrot juice was placed in a stainless steel cup(80×100mm,wall thickness1.15mm)and heated to90°C at the centre of juice for1min in a water bath.The heated juice was immediately cooled to about15°C in ice water bath,and then stored at4°C for various measurements.
2.5.Measurements of quality indices
2.5.1.Determination of color
Color assessment was conducted at25°C,using a SC-80Color Difference Meter(Kangguang Co.,China)in the re?ectance mode. Hunter L-,a-,and b-value of juices was measured and the total color difference(ΔE)was calculated as:
ΔE=L?L0
eT2+a?a0
eT2+b?b0
eT2
h i1=2
where L—lightness of treated juice,L0—lightness of untreated juice,a—redness of treated juice,b—yellowness of treated juice,a0—redness of untreated juice,and b0—yellowness of untreated juice(Gui et al., 2006b).
2.5.2.Determination of browning degree(BD)
Juice BD was evaluated using a spectrophotometric method described by Roig,Bello,and Rivera(1999).Carrot juice was centrifuged with a TGL-16G-A refrigerated centrifuge(Anting apparatus Co.,Shanghai,China)at 10,000×g at4°C for20min,and then passed through a0.45μm cellulose nitrate membrane(Beijing Bomex Co.,Beijing,China).The BD value was determined by measuring A420(absorbance at420nm)using an UV-762 spectrophotometer(Lingguang,Shanghai,China)at ambient tempera-ture(25±1°C)with a1cm path length cell.
2.5.
3.Measurement of residual activity of polyphenol oxidase
The activity of polyphenol oxidase(PPO)was assayed by a spectro-photometric method(Sánchez-Ferrer,Bru,Cabanes,&Garcia-Carmona, 1988)with some modi?cations.Catechol was chosen as the substrate, and0.1M catechol substrate solution was prepared with0.1M phosphate buffer(pH6.5).The assay was performed for all samples by adding 100μL juice into2.9mL substrate solution.The increase in absorbance at 420nm was monitored at intervals of0.1s?1immediately after incubation with a Cary50spectrophotometer(Varian Co.Ltd.,California, USA),which was equipped with a peltier thermostatted cell holder,a water pump(Varian Co.Ltd.,California,USA)to keep temperature at 20±0.1°C and an inbuilt electromagnetic stirring to mix up the substrate and juice.Prior to measurement,a pre-equilibrium at20°C of the substrate solution as well as the peach juice by the peltier thermostatted cell holder is obtained.The slope of the very?rst linear part of the reaction curve was taken as the PPO speci?c activity(Abs/min).The PPO residual activity was estimated with the following equation.
Residual activity=
specific activity of PPO after treatment specific activity of PPO before treatment
×100k:
2.5.4.Determination of UV–visible spectroscopy
Carrot juice was centrifuged with a TGL-16G-A refrigeration centrifuge(Anting apparatus Co.,Shanghai,China)at10,000×g at 4°C for20min,and then the supernatant passed through a0.45μm cellulose nitrate membrane(Beijing Bomex Co.,Beijing,China).The supernatant was scanned from200to800nm,using a Cary-50UV–visible spectrophotometer(Varian Co.,Palo Alto,USA)at ambient temperature(25±1°C)with a1cm path length cell.2.5.5.Determination of pH
pH was measured at20°C with a Thermo Orion868pH meter (Thermo Fisher Scienti?c,Inc.,MA,U.S.A),which was calibrated with pH4.0and7.0buffer.
2.5.6.Determination of titratable acidity(TA)
10mL juice was titrated using standardized0.02mol/L NaOH to the phenolphthalein end point(pH=8.2±0.1).The volume of NaOH was converted to mg citric acid per L juice(Rodrigo et al.,2003). 2.5.7.Determination of total soluble solid(TSS)
Juice TSS was determined as Brix using a WAY-2S digital Abbe Refractionmeter(Shanghai Precision and Scienti?c Instrument Co., Shanghai,China)at20°C(Wang et al.,2006).
2.5.8.Determination of carotenoids
The measurement of carotenoids was proposed by Liao et al. (2007)with a little modi?cation,which was determined by measur-ing the A450(absorbance at450nm)at ambient temperature by a spectrophotometer(UV-762,Lingguang,Shanghai,China).2mL of carrot juice was mixed with10mL chloroform/methanol of analytical grade(2:1,V/V)in a separator funnel.After shaking,the organic phase separating from the aqueous phase was dehydrated with anhydrous sodium sulfate,?ltered using Bush funnel and then collected.The aqueous phase was repeatedly extracted with5mL chloroform/ methanol(2:1,V/V)until it was colorless.All the extracts collected were mixed and diluted to a?nal50mL with chloroform/methanol (2:1,V/V).
2.5.9.Determination of cloud
The cloud of carrot juice was determined using a portable WGZ-200turbidimeter(Shanke apparatus Co.,Shanghai,China),and was reported as Nephelometric Turbidity Units(NTU)(Reiter,Stuparic, Neidhart,&Carle,2003).Carrot juice was diluted with distilled water (1:25,V/V)and measured in a5cm cuvette.
2.5.10.Determination of particle size distribution(PSD)
PSD of juice was determined by a LS230particle size analyzer (Beckman coulter,Inc.,Florida,U.S.A).The system used a laser light with a wavelength of750nm to measure particles from0.4to 2000μm by light diffraction.Fourier optics collected the diffracted light and the PSD was calculated by Fraunhofer model.
Firstly,distilled water from a tank was pumped into a sample cell at the speed of approximately8L/min until the cell was full.The juice was added into the cell using a pipette and mixed with distilled water. Particles in juice were dispersed and suspended in distilled water. When the obscuration percentage increased from0to10%,the measurement was performed.Data obtained were analyzed using software LS v3.29.Volume mean diameter D[4,3]and surface mean diameter D[3,2]were determined for all samples.
2.5.11.Determination of viscosity
The dynamic viscosity of carrot juice was determined using an AR550 rheometer(TA Instruments,Waters Co.,Ltd.,Surrey,Great Britain)with a Conical End Concentric Cylinder(stator radius=15.00mm,rotor radius=14.00mm,immersed height=42.00mm,gap=5920μm).
19.6mL juice was applied at each measurement with25±0.1°C controlled by circulating water in a thermostatic system.Viscosities were calculated from the average of seven points of the?ow curves obtained in the shear rate range between4and63s?1.
2.6.Statistical analysis
Analysis of variance(ANOVA)was carried out by using the software Microcal Origin7.5(Microcal Software,Inc.,Northampton,U.S.A). ANOVA test was carried out for all experimental runs to determine
323
L.Zhou et al./Innovative Food Science and Emerging Technologies10(2009)321–327
signi ?cance at α=0.05level.All experiments were performed in triplicates.
3.Results and discussion 3.1.Effect on juice color
The effect of HPCD and heat treatment on juice color was shown in Table 1.As compared with untreated and HPCD-treated juices,the value of L ,a ,and b for heated juice decreased signi ?cantly (P b 0.05).The decrease in L of heated juice re ?ected the darkening of juice surface color,and the decrease in a and b indicated less red and less yellow in juice color,which was possibly due to the susceptibility of juice particles to the coagulation and precipitation after exposure to heat.A noticeable difference can be visualized between two colors when they differ by ΔE N 2–3.5(Krapfenbauer,Kinner,Gossinger,Schonlechner,&Berghofer,2006).The ΔE values of all heated juices were greater than 2,indicating that heating resulted in a visible color difference.
The L -value of HPCD-treated juices increased signi ?cantly (P b 0.05)as compared with that of untreated juices,and the a -value exhibited an increase tendency with increasing the treatment time (Table 1).Park et al.(2002)reported that HPCD alone showed a signi ?cant increase of the L -value of carrot juice.Kincal et al.(2006)also reported a signi ?cant increase of the L -value of HPCD-treated orange juice.In contrast,Park et al.(2002)and Kincal et al.(2006)reported that HPCD resulted in a signi ?cant decrease in the a -value of carrot juice and orange juice.For the b -value,it exhibited no signi ?cant change (P N 0.05)after HPCD treatment in this study,which was in agreement with the observation displayed by Kincal et al.(2006).However,Park et al.(2002)reported that HPCD at 4.9MPa raised signi ?cantly the b -value of carrot juice.The ΔE values of the juices treated at 10MPa for 45and 60min,at 20or 30MPa for 60min were greater than 2,suggesting that longer treatment time of HPCD leads to a visible color difference of juice.
3.2.Effect on juice BD,PPO residual activity and UV –visible spectra As shown in Table 1,the BD value of HPCD-or heat-treated juices decreased signi ?cantly (P b 0.05)as compared to untreated juices.This difference possibly resulted from the enzymatic browning in juices.As shown in Fig.2,PPO in untreated juice was active and catalyzed the
browning reaction.However,the residual activity of PPO for HPCD-treated juices was 2–3%independent of pressure and could not be detected for heat-treated juices,indicating that PPO in carrot juices was inactivated after heat or HPCD-treatment.Similar observations were previously reported.Kim,Park,Cho,and Park (2001)investi-gated that thermal treatment of carrot juices caused 98.3%loss of PPO.Kincal et al.(2006)suggested that a reduction of PPO activity was 89%using HPCD.Park et al.(2002)reported that a combined treatment of HPCD and 400MPa high hydrostatic pressure showed a residual PPO activity of 19%.Although the BD values of HPCD-or heat-treated juices showed ?uctuation,there was no signi ?cant difference (P N 0.05).
Furthermore,the UV –visible absorbance spectra of all the juices at different conditions were measured.Fig.3shows the spectral curves of HPCD-treated juices at 10MPa as a function of treatment time.Since the spectral curves of HPCD-treated juices at 20or 30MPa were similar,related data are not shown.Obviously,the spectral curve of untreated juice was higher than those of HPCD-or heat-treated juices,and the curves of HPCD-or heat-treated juices almost superposed.These observations also con ?rmed that HPCD and heat treatment effectively inhibited the enzymatic browning in juices.
Table 1
Characteristics of carrot juices treated by different HPCD treatment conditions.Treatment conditions Color BD
pH TA
(mg/L)TSS (Brix)Carotenoids (mg/100mL)Cloud (NTU)Viscosity (mPa s)D [4,3](μm)D [3,2](μm)L a b ΔE Untreated
A
24.01c
11.39b
22.58a
0.000.644a 6.74a 0.38b 4.30a 5.27a 72.5c 1.23c 3.38d 1.44d 10Mpa,15min 24.51c 11.21b 22.78a 1.070.348b 5.95b 1.09a 4.30a 5.27a 80.0bc 1.20c 22.12b 5.56b 10MPa,30min 24.73b c 11.51b 23.39a 1.420.359b 5.95b 1.06a 4.30a 5.34a 83.5bc 1.20c 17.30c 3.07c 10MPa,45min 25.44b 12.20b 23.28a 2.080.357b 5.94b 1.04a 4.30a 5.57a 91.0b 1.24c 16.42c 3.18d 10MPa,60min 26.70a 14.20a 22.72a 4.000.306b 5.93b 1.12a 4.35a 5.62a 115.5a 1.27b 6.50d 1.87d Heat treatment 22.65d 11.13c 20.25b 2.750.328b 6.69a 0.37b 4.30a 5.13a 67.0d 1.51a 57.43a 21.87a Untreated B
24.65c 11.09c 24.14a 0.000.779a 6.55a 0.50b 4.60a 5.18a 65.0c 1.30c 3.63d 1.48d 20MPa,15min 25.49b 12.12ab 24.82a 1.610.272b 6.02b 0.99a 4.50a 5.22a 76.5b 1.24c 15.75b 3.07b 20MPa,30min 25.39b 11.93b 23.96a 1.200.258b 5.99b 1.04a 4.50a 5.19a 79.5b 1.23c 13.60bc 2.69c 20MPa,45min 25.37b 12.25ab 24.38a 1.580.278b 6.00b 0.97a 4.50a 5.22a 82.0ab 1.24c 12.71c 2.84c 20MPa,60min 26.11a 12.91a 24.64a 2.460.247b 6.09b 0.91a 4.55a 5.15a 94.0a 1.33b 3.79d 1.57d Heat treatment 22.30d 10.68d 19.09b 5.590.242b 6.54a 0.48b 4.60a 5.25a 38.5d 1.37a 73.32a 27.12a Untreated C
25.14c 11.63c 23.96a 0.000.461a 6.63a 0.46b 5.10a 5.99a 71.5c 1.22c 2.85d 1.44d 30MPa,15min 25.83b 11.95bc 23.93a 0.790.208b 6.18b 0.84a 5.05a 6.21a 77.0bc 1.26c 17.49b 3.95b 30MPa,30min 25.86b 12.12ab 23.60a 0.950.207b 6.21b 0.83a 5.05a 5.94a 80.5bc 1.38b 10.71c 2.90c 30MPa,45min 26.27b 12.84ab 23.50a 1.720.205b 6.20b 0.82a 5.05a 5.79a 83.5b 1.46b 10.47c 3.10c 30MPa,60min 26.97a 13.01a 23.68a 2.310.228b 6.15b 0.97a 5.00a 5.69a 90.0a 1.39b 3.16d 1.57d Heat treatment
24.32d
11.43d
21.66b
2.48
0.209b
6.57a
0.48b
4.95a
5.52a
54.5d
1.46a
50.54a
18.22a
Values are means,n =3;TA,titratable acidity;TSS,total soluble solid.A,B,C
represent the ?rst,second and third batch of carrot juice,respectively.a,b,c,d
different letters represent a signi ?cant difference within the same column (P b
0.05).
Fig.2.The residual activity of PPO in untreat juice and HPCD-treated carrot juices at different pressures for 15min at 25°C.
324L.Zhou et al./Innovative Food Science and Emerging Technologies 10(2009)321–327
3.3.Effect on juice TSS,carotenoids,pH and TA
The heat treatment caused no signi ?cant alteration in TSS,carot-enoids,pH and TA of juice (P N 0.05).However,HPCD had a different in ?uence on these indices of juices (Table 1).The pH of the juices decreased and its TA increased signi ?cantly (P b 0.05)after HPCD treatment.Park et al.(2002)observed a similar decrease of pH from 6.5to 4.4in juices after HPCD treatment.Gui,(2006a)also reported a pH reduction from 5.6to 5.3in horseradish peroxide solution.The decrease pH and increase in TA was due to CO 2dissolution into juices or solutions,which further dissociated into bicarbonate,carbonate and hydrogen ions.However,Kincal et al.(2006)found an increase in TA and no alteration in pH of HPCD-treated orange juice.This was attributed to a lower pH (3.7–3.8)in original orange juice,at this pH the carbonic acid formed by CO 2dissolution into juice dif ?cultly dissociated into free hydrogen ions,because the dissociation constants of carbonic acid and bicarbonate were pKa=6.57and pKa=10.62(Damar &Balaban,2006),respectively.The TSS and carotenoids of juices showed ?uctuations,but did not change signi ?cantly after HPCD treatment.
3.4.Effect on juice cloud
Cloud stability is an important quality parameter in fresh un-pasteurized juice (Park et al.,2002).As shown in Table 1,the cloud of heated juices decreased.The larger particles of protein coagulation induced by heat rapidly precipitated and caused the loss of juice cloudiness.Blanching of carrots was a practice to inactivate pectin-esterase (PE)or pectin methyl-esterase (PME)to maintain the cloud stability of carrot juice prior to pressing.However,the cloud of HPCD-treated juices increased signi ?cantly (P b 0.05),it was hypothesized that HPCD led to the homogenization effect causing smaller particles of the juice colloid (Kincal et al.,2006).This observation was in agreement with previous investigations.Arreola et al.(1991)reported that HPCD treatment of orange juice stabilized and enhanced cloud,even in the presence of active PE.Kincal et al.(2006)investigated that the cloud for the HPCD-treated juice increased in spite of active PE.It was well known that the cloud of citrus juice is related to the activity of PE,which could lead to precipitation of pectin in juice with subsequent loss of cloud.Therefore,no link was found between PE inactivation and cloud retention in juice with HPCD (Kincal et al.,2006).
The increase in the cloud of HPCD-treated carrot juice was incon-sistent with the observation obtained by Park et al.(2002),who
reported that HPCD caused a loss of carrot juice cloud in a non-enzymatic way.This contradiction was possibly due to a larger difference in parameters of HPCD.In this study,the pressure (≥10MPa)and
the
Fig.3.The UV –visible spectra of carrot juice exposed to HPCD at 10MPa and 25°C for 15,30,45and 60min and heat
treatment.
Fig.4.The cumulative volume (%)against PSD of carrot juice with HPCD a)at 10MPa and 25°C;b)at 20MPa and 25°C;c)at 30MPa and 25°C.○Untreated;■15min;?
30min;△45min;?60
min;he
time (≥15min)were far greater than that (4.9MPa and 10min)in Park et al.(2002)study,the HPCD-induced homogenization effect was more intensive than the acid-induced coagulation and precipita-tion of HPCD.
It was dif ?cult to evaluate the cloud of HPCD-treated juices at 10,20and 30MPa for the same treatment time due to different batches of carrot juice in this study.However,it was comparable for those juices treated by the same pressure level due to the same batch juices.At the same pressure level,the juice cloud increased signi ?cantly (P b 0.05)with increasing the treatment time,indicating that the longer the treatment time was,the more intensive the HPCD-induced homo-genization effect was.3.5.Effect on juice PSD
Fig.4a –c showed the change in PSD against the cumulative volume of juices at different conditions.Obviously,the particle size of heat-treated juice signi ?cantly increased as compared with that of untreated juice at the same cumulative volume (P b 0.05).D [4,3]and D [3,2]for heated juices was maximized and for untreated juices was minimized (Table 1),this was possibly attributed to heat-induced protein coagulation.Reiter et al.(2003)reported that heat-coagulated proteins were supposed to cause cloud particle precipitation following thermal treatment of juices extracted from unblanched carrots.
The particle size of HPCD-treated juices for 15,30and 45min increased signi ?cantly as compared with untreated juices (P b 0.05)(Fig.4a –c).However,for the 60min treatment,it showed a noticeable decrease and was almost close to untreated juice.The HPCD-induced increase of juice particle size was possibly due to acid-induced protein coagulation.Precipitation caused by pH shift was characteristic of proteins (Reiter et al.,2003).As previously suggested in this study,pH decline of HPCD-treated juices was due to the dissociation of carbonic acid formed by CO 2dissolution into the juices.The decrease in particle size of HPCD-treated juices for 60min was probably attributed to HPCD-induced homogenization effect which caused smaller juice particle (Kincal et al.,2006).The longer the treatment time or the higher the pressure was,the more intensive the homogenization effect was.Therefore,the alteration of the particle size for HPCD-treated juices was an interaction between the acid-induced protein coagulation and the HPCD-induced homogenization effect,the acid-induced protein coagulation seemed to dominate for a short treatment time and the HPCD-induced homogenization effect alter-nated for longer treatment time.
3.6.Effect on juice ?ow behavior and viscosity
Fig.5showed the viscosity of HPCD-treated juices at 10MPa as a function of shear rate.The viscosity of all the juices at different conditions showed no signi ?cant alteration in the shear rate range between 4and 63s ?1(P N 0.05,)suggesting that the juices followed the Newtonian ?ow behavior.This result was similar to what Reiter et al.(2003)proposed,indicating that HPCD or heat treatment didn't change the ?ow behavior of the carrot juice.Since the viscosity of HPCD-treated juices at 20or 30MPa exhibited similar trends,related data were not shown.
However,the viscosity of heat-treated juice was signi ?cantly higher than that of untreated juice (P b 0.05),which could be attributed to an increase in solubilization of pectin in cell walls.With HPCD at 10MPa for 30,45and 60min,or at 20MPa for 60min,or at 30MPa for 15,30,45and 60min,the viscosity of juices also increased signi ?cantly (P b 0.05,Table 1),indicating that pressure or time had a signi ?cant in ?uence on juice viscosity.The HPCD-induced homogenization effect under these conditions possibly contributed to an increase in solu-bilization of pectin in cell walls into juices.4.Conclusions
The browning degree and pH of HPCD-treated carrot juices decreased,the cloud and the titratable acidity increased signi ?cantly (P b 0.05),the UV –visible spectra lowed,polyphenol oxidase was inactivated,and the total soluble solid and carotenoids were stable.As compared with untreated juices,the particle size of HPCD-treated juices for 15,30and 45min increased signi ?cantly (P b 0.05)in a similar way and showed a noticeable decrease for the 60min treatment getting close to that of untreated juice.HPCD could not alter the Newtonian ?ow behavior of the carrot juice,but caused a signi ?cant increase in carrot juice viscosity.Acknowledgments
This research work was supported by Project No.20060019016of Doctoral Foundation of Ministry of Education and Project No.2006BAD05A02of the Science and Technology Support in the Eleventh Five Plan of China.References
Arreola,A.G.,Balaban,M.O.,Marshall,M.R.,Replow,A.J.,Wei,C.I.,&Cornell,J.A.
(1991).Supercritical carbon dioxide effects on some quality attributes of single strength orange juice.Journal of Food Science ,56,1030–1033.
Balaban,M.O.,(2004).Method and apparatus for continuous ?ow reduction of
microbial and/or enzymatic activity in a liquid product using carbon https://www.doczj.com/doc/151952710.html, Patent 6,723,365B2(Apr.20,2004)and US Patent Application 2004/0131739A1(Jul.8,2004).
Balaban,M.O.,Marshall,M.R.,&Wicker,L.(1995).Inactivation of enzymes in foods
with pressureized CO https://www.doczj.com/doc/151952710.html, Patent 5,393,547(Feb.28,1995)and WO Patent 90/02799(Mar.22,1990).
Chen,B.H.,Peng,H.Y.,&Chen,H.E.(1995).Changes of carotenoids,color,and vitamin A
contents during processing of carrot juice.Journal of Agriculture and Food Chemistry ,43,1912–1918.
Corwin,H.,&Shellhammer,T.H.(2002).Combined carbon dioxide and high pressure
inactivation of pectin methylesterase,polyphenol oxidase,Lactobacillus plantarum and Escherichia coli .Journal of Food Science ,67,697–701.
Connery,K.A.,Shah,P.,Coleman,L.,&Hunek,B.(2005).Commercialization of Better Than
Fresh ?dense phase carbon dioxide processing for liquid food.Orlando,USA:ISSF.Dagan,G.F.,&Balaban,M.O.(2006).Pasteurization of beer by a continuous dense-phase CO 2system.Journal of Food Science ,71,164–169.
Damar,S.,&Balaban,M.O.(2005).Cold pasteurization of coconut water with a dense-phase CO 2system.IFT Annual Meeting Book of Abstracts (pp.1).New Orleans,La:Institute of Food Technologists.
Damar,S.,&Balaban,M.O.(2006).Review of dense phase CO 2technology:Microbial
and enzyme inactivation,and effects on food quality.Journal of Food Science ,71,1–11.
Garcia-Gonzalez,L.,Geeraerd,A.H.,Spilimbergo,S.,Elst,K.,Van Ginneken,L.,Debevere,
J.,et al.(2007).High pressure carbon dioxide inactivation of microorganisms in foods:The past,the present and the future.International Journal of Food Microbiology ,117,1–
28.
Fig.5.The viscosity (mPa·S)of carrot juice against shear rate (1/s )with HPCD at 10MPa and 25°C for 15,30,45and 60min and heat treatment.○Untreated;■15min;?
30min;△45min;?60
min;heat treatment.
326L.Zhou et al./Innovative Food Science and Emerging Technologies 10(2009)321–327
Gui,F.Q.,Wang,Z.F.,Wu,J.H.,Chen,F.,Liao,X.J.,&Hu,X.S.(2006a).Inactivation and reactivation of horseradish peroxidase treated with supercritical carbon dioxide.
European Food Research and Technology,222,105–111.
Gui,F.Q.,Wu,J.H.,Chen,F.,Liao,X.J.,Hu,X.S.,Zhang,Z.H.,et al.(2006b).Change of polyphenol oxidase activity,color,and browning degree during storage of cloudy apple juice treated by supercritical carbon dioxide.European Food Research and Technology,223,427–432.
Kim,H.Y.,&Gerber,L.E.(1988).In?uence of processing on quality of carrot juice.
Korean Journal of Food Science and Technology,20,683–690.
Kim,Y.S.,Park,S.J.,Cho,Y.H.,&Park,J.(2001).Effects of combined treatment of high hydrostatic pressure and mild heat on the quality of carrot juice.Journal of Food Science,66,1355–1360.
Kincal, D.(2000).A continuous high pressure carbon dioxide system for cloud retention,microbial reduction and quality change in orange juice[MSci thesis](pp.
110).Gainesville,Fla.:University of Florida.
Kincal,D.,Hill,W.S.,Balaban,M.,Portier,K.M.,Sims,C.A.,Wei,C.I.,et al.(2006).A continuous high-pressure carbon dioxide system for cloud and quality retention in orange juice.Journal of Food Science,71,338–344.
Krapfenbauer,G.,Kinner,M.,Gossinger,M.,Schonlechner,R.,&Berghofer,E.(2006).
Effect of thermal treatment on the quality of cloudy apple juice.Journal of Agriculture and Food Chemistry,54,5453–5460.
Liao,H.M.,Hu,X.S.,Chen,F.,Wu,J.H.,&Liao,X.J.(2007).Inactivation of Escherichia coli inoculated into cloudy apple juice exposed to high pressure carbon dioxide.Inter-national Journal of Food Microbiology,118,126–131.
Liao,H.M.,Sun,Y.,Ni,Y.Y.,Liao,X.J.,Hu,X.S.,Wu,J.H.,et al.(2007).The effect of enzymatic mash treatment,pressing,centrifugation,homogenization,deaeration, sterilization and storage on carrot juice.Journal of Food Process Engineering,30, 421–435.
Marx,M.,Stuparic,M.,Schieber,A.,&Carle,R.(2003).Effects of thermal processing on trans-cis-isomerization ofβ-carotene in carrot juices and carotene-containing preparations.Food Chemistry,83,609–617.Park,S.J.,Lee,J.I.,&Park,J.(2002).Effects of a combined process of high-pressure carbon dioxide and high hydrostatic pressure on the quality of carrot juice.Journal of Food Science,67,1827–1834.
Reiter,M.,Stuparic,M.,Neidhart,S.,&Carle,R.(2003).The role of process technology in carrot juice cloud stability.Swiss Society of Food Science and Technology,36,165–172. Rodrigo,D.,Arranz,J.I.,Koch,S.,Frigola,A.,Rodrigo,M.C.,Esteve,M.J.,et al.(2003).
Physicochemical characteristics and quality of refrigerated Spanish orange-carrot juices and in?uence of storage conditions.Journal of Food Science,68,2111–2116. Roig,M.G.,Bello,J.F.,&Rivera,Z.S.(1999).Studies on the occurrence of non-enzymatic browning during storage of citrus juice.Food Research International,32,609–619. Sánchez-Ferrer,A.,Bru,R.,Cabanes,J.,&Garcia-Carmona,F.(1988).Characterization of catecholase and cresolase activities of monastrell grape polyphenol oxidase.Phy-tochemistry,27,319–321.
Schieber,A.,Stintzing,F.C.,&Carle,R.(2001).By-products of plant food processing as a source of functional compounds—recent development.Trends in Food Science and Technology,12,401–413.
Truong,T.T.,Boff,J.M.,Min,D.B.,&Shellhammer,T.H.(2002).Effects of carbon dioxide in high-pressure processing on pectinmethylesterase in single-strength orange juice.Journal of Food Science,67,3058–3062.
Wang,H.Y.,Hu,X.S.,Chen,F.,Wu,J.H.,Zhang,Z.H.,&Liao,X.J.(2006).Kinetic analysis of non-enzymatic browning in carrot juice concentrate during storage.European Food Research and Technology,223,282–289.
Yagiz,Y.,Lim,S.L.,&Balaban,M.O.(2005).Continuous high pressure CO2processing of mandarin juice.IFT annual meeting book of abstracts(pp.1).New Orleans La: Institute of Food Technologists.
Yoon,K.Y.,Cha,M.,Shin,S.R.,&Kim,K.S.(2005).Enzymatic production of a soluble-?ber hydrolyzate from carrot pomace and its sugar composition.Food Chemistry,92, 151–157.
327
L.Zhou et al./Innovative Food Science and Emerging Technologies10(2009)321–327
胡萝卜橙子汁的功效 很多人都喜欢买个榨汁机,自己在家里榨果汁或者蔬菜汁喝,因为榨出来的果汁和蔬菜汁不仅可以当水喝,而且自身有丰富的营养价值。胡萝卜这种蔬菜具有丰富的维生素,对于预防夜盲症有着很好的效果,橙子也是大家家中常见的一种水果,它里面也含有丰富的维生素,那么使用胡萝卜和橙子一起榨汁的功效是什么呢? 橙子能和胡萝卜一起榨汁吗 当然是可以的呀。不但好喝,两者混着的营养价值非常高的,建议每天喝一杯对身体健康很有帮助。 橙子的功效作用 1、和胃降逆,橙子味酸,性寒凉,入肝、胃经。有和中开胃,降逆止呕之功。善用于饮食停滞而引起的呕吐,胃中浮风恶气,肝胃郁热等疾病。 2、宽胸开结,橙子性寒,有清热降逆之功、善清肺胸之热,由于肺中蕴热,或外感风热,热灼津液为痰,痰热结于胸中,气机痹阻,引起胸部疼痛,咳喘,咯痰黄稠,甚则咳血,或痰腥臭,烦闷发热,苔黄腻,脉象滑数,治宜用橙子,泄热涤痰,宽胸开结,凉血止血,功效显著。 3、消瘿,因外邪所侵,或情志内伤,以及体质虚弱,使气机阻滞,津液积聚为痰。 4、杀鱼蟹之毒,橙子味酸芳香,酸能杀菌,有除醒脾,和胃
降逆,对于因饮酒过量,或做鱼蟹之菜肴,均有较好的调味和解毒醒酒作用。使菜肴更加可口适中,味香鲜美。 5、鉴别应用,橙子与橙子核,一为橙子肉,一是橙核,肉偏于止呕恶,宽胸膈,消瘿,鲜鱼蟹之毒。而橙子核偏于治疝气,诸淋病,腰痛,外用可治面黔粉刺,橙子偏于治肝肺之病,而橙核偏于治肾脏之患。 橙子的营养价值 橙子中含量丰富的维生素C、p,能增加机体抵抗力,增加毛细血管的弹性,降低血中胆固醇。高血脂症、高血压、动脉硬化者常食橙子有益。橙子所含纤维素和果胶物质,可促进肠道蠕动,有利于清肠通便,排除体内有害物质。橙皮性味甘苦而温,止咳化痰功效胜过陈皮,是治疗感冒咳嗽、食欲不振、胸腹胀痛的良药。 胡萝卜的营养价值及功效: 1、益肝明目: 胡萝卜含有大量胡萝卜素,这种胡萝卜素的分子结构相当于2个分子的维生素A,进入机体后,在肝脏及小肠粘膜内经过酶的作用,其中50%变成维生素A,有补肝明目的作用,可治疗夜盲症; 2、利膈宽肠: 胡萝卜含有植物纤维,吸水性强,在肠道中体积容易膨胀,是肠道中的“充盈物质”,可加强肠道的蠕动,从而利膈宽肠,通便防癌; 3、健脾除疳: 维生素A是骨骼正常生长发育的必需物质,有助于细胞增殖
胭脂花根有哪些功效和作用 文章导读 胭脂花根除了叫这个名字,还有很多其他的名称,胭脂花根在平时的药用价值 非常广泛,首先,其中含有大量有机酸和大量淀粉,能保证身体健康的同时有利于吸收,使用方法也非常简单,不过一定要注意进行区分和诊断,并且要明确了解到其中的药理作用,这样在用到此药的时候,也不至于觉得惊慌和担心。 简介紫茉莉根异名有:入地老鼠、花粉头(《岭南采药录》),水粉头(《修订增补天宝 本草》),粉子头、胭脂花头(《四川中药志》),为紫茉莉科植物紫茉莉的块根。 紫茉莉(《草花谱》),又名:胭脂花(《草花谱》),粉团花(《盛京通志》),野茉莉、粉 豆花(《植物名实图考》),丁香、粉孩儿、未时花、胭脂水粉、水粉子花、长春花。 药用价值化学成分紫茉莉根含氨基酸、有机酸及大量淀粉。紫茉莉花含多种甜菜黄素等黄色素。 采集方法秋、冬挖取块根,洗净泥沙,晒干。 性状性状鉴别 很长圆锥形或圆柱形,有的压扁,有的可见支根,长5-10cm,直径1.5-5cm。表面灰 黄色,有纵皱纹及须根痕。顶端有茎基痕。质坚硬,不易折断,断面不整齐,可见环纹。 经蒸煮者断面角质样。无臭,味淡,有刺喉感。 显微鉴别 根横切面:木栓层细胞达数十列,暗棕褐色,或木栓层多已除去。皮层较窄。异常维管 束多轮间断排列成环。维管束外韧型,木质部导管圆多角形。本品薄壁细胞含大量草酸钙 针晶束与糊化淀粉粒。(图3)粉末特征:淡白色。①草酸钙针晶极多,成束或分散,长50-150μm。②导管主为网纹,亦有梯纹,直径15-130μm;网纹导管的纹孔多呈狭长形,壁木化。③淀粉粒颇多,呈不规则类圆形块状。云朵状,大小不等,边缘不整齐。 药理作用根含树脂,对皮肤、粘膜有刺激性。花在晚上吐出浓郁的香气,可麻醉及驱 除蚊虫。
概括人物性格形象品质的常用词语概括人物性格、形象、品质的常用词语 1. 性格类: 善解人意、心细如发、体贴、富有爱心、温柔沉静、心灵手巧、富有情趣、通情达理、纯真质朴、聪明伶俐、天真可爱、顽皮淘气、富有活力、朝气蓬勃、懂事能干、有主见、有骨气、人穷志不短、自尊自爱、倔强、沉稳果断、开朗自信、真诚善良、友好谦恭、宽容忍让、勤劳朴实、节俭、慈爱宽厚、和蔼可亲、平易近人、彬彬有礼、不拘小节、睿智大气、聪慧通达、幽默风趣、善于变通、隐忍内敛、个性张扬、心直口快、耿直偏激、严厉苛刻、严慈相济向往自由、追求平等、热爱生活、热爱自然、珍爱自己、乐于挑战、永不服输、富有智慧、精明强干、大智若愚、足智多谋、沉着冷静、从容镇定、勇敢、目光敏锐、狂放不羁、特立独行、 (反面: 胆小怯懦、逆来顺受、妥协退让、敏感自闭、固步自封、妄自菲薄、固执、吝啬、冷漠自私、粗鲁莽撞、粗俗不雅、饶舌多事、骄横火爆、横行霸道、狂妄自大、目中无人、孤傲自负、刚愎自用、奸诈多疑、老气横秋、消极悲观、自卑、圆滑世故、尖酸刻薄、利欲熏心、唯利是图、争强好胜、孤芳自赏、) 2. 拼搏类: 顽强拼搏、自强不息、不怕困难、坚强不屈、知难而进、积极乐观、身残志坚、自食其力、自立自强、坚持不懈、锲而不舍、矢志不渝、勤勉刻苦、不畏艰辛、吃苦耐劳 (反面:贪图享乐、自暴自弃、拈轻怕重) 3.奉献类:无私奉献、自我牺牲、任劳任怨、默默无闻、不事张扬、默默奉献、毫无所求、兢兢业业、勤勤恳恳、废寝忘食、爱子情深、舐犊情深(反面:斤斤计较、自私自利)
4.职责类:恪尽职守、尽职尽责、爱岗敬业、治学严谨、教学有方、诲人不倦、以校为家、爱厂如家、关心下属、秉公执法、不徇私情、勇于探索、锐意进取、敢于创新、技术精湛、才华横溢、博学善谈、以身殉职、奉公守法、铁面无私、赏罚分明、妙手回春、文武双全、智勇双全、博古通今、见多识广、明察秋毫、严以律己、临危不惧、 (反面:以权谋私、徇私枉法、畏首畏尾、墨守成规、贪生怕死) 5. 品质类:洁身自好、淡泊名利、安贫乐道、仁义守信、乐善好施、虚怀若谷、胸有大志、志存高远、心胸宽广、宽宏大量、豁达大度、坦荡无私、德艺双馨、诚实守信、有责任心、孝顺、清正廉洁、知恩图报、宠辱不惊、有修养、礼贤下士、宠辱不惊、言而有信、表里如一、言行一致、德才兼备、不耻下问、与世无争、不慕权贵、自知之明、知错就改、 (反面:爱慕虚荣、追名逐利、鼠肚鸡肠、投机取巧) 6.大爱类:热爱集体、爱国、没有民族偏见、居安思危、忍辱负重、关注民生、忧国忧民、精忠报国、壮志凌云、民族气节、舍生取义、浩然正气、无私无畏、勇于担当、深明大义、识见高远、顾大体识大局、有领导组织才干、尊重弱者、关爱他人、乐于助人、舍生取义、忠心耿耿、公而忘私、大义灭亲、嫉恶如仇、扶危济困、刚正不阿、远见卓识、 (反面:狭隘的爱国主义、有民族偏见、) 概括景、物特点常用词语:(外形、颜色、 神态、氛围) 素雅、灿烂、柔弱、清丽、俊美、柔婉美丽、美好可爱、乖巧可爱、惹人爱怜、优美、美妙、多彩、清新脱俗、生动活泼、妖娆、葱茏、郁郁葱葱、鲜妍明媚、袅娜多姿、生机勃勃、生命力旺盛、富有活力、辉煌、雄浑、壮美、旷远、恢弘博大、气势非凡、气势磅礴、宏伟壮丽、圣洁、广阔、雄壮、豪迈、强劲、刚
自制土豆胡萝卜苹果汁 土豆胡萝卜苹果汁的疗效很神奇,他的舅舅有肺癌,但天天坚持喝土豆胡萝卜苹果汁,把病根都清除了。但是生土豆一定要精选没发芽的,表皮没发青的。因为发芽发青的土豆都有毒。我半信半疑他说的神奇疗效,但却对这种三合一蔬菜水果汁饶有兴趣。 购买了胡萝卜,生土豆,红苹果,另外还买了两根鲜玉米棒。先全部都洗净了,然后把一根玉米棒一粒一粒的剥下来盛在碗里,再把一根胡萝卜切成薄片,把马铃薯去皮后切成薄片,把苹果去核切成片,满满一大碗倒入豆浆机里,掺入一小杯纯净水把黏糊的“果煳”倒入过滤杯中,用附送的搅拌器搅拌压榨“果煳”,清香的液态果汁透过滤网坠流入杯底,不一会儿一大杯纯液态的果汁浮现在眼前。把榨干的果渣倒掉,把果汁重新倒入豆浆机中,再掺入一杯酸奶,两勺白糖,在启动“果汁/搅拌”功能,立刻一大杯土豆胡萝卜苹果汁新鲜“出炉”了。 色泽呈奶黄,轻摇杯体,一条乳白色的晕圈淡淡浮现,又慢慢消散开来。轻轻品一口,一种酸酸的,微甜又微苦,“胛”舌而耐人回味的复杂味道填满了口中。把吸管插入杯中,斜坐在书房窗台边的摇椅,脚搭在书桌上慢慢的品尝起来。客厅播放着音乐,窗外暖暖的阳光撒在身上,周末的早上难得的悠闲时刻呀。 上网查了一下,原来这生土豆胡萝卜和苹果榨汁是一个日本高僧的偏方,确实有许多的神奇疗效: 胡萝卜苹果汁 原料:4个胡萝卜,2个大的苹果 做法:将胡萝卜擦洗干净,保留其顶部的有机叶子。将苹果洗净。先将胡萝卜榨汁,然后再将苹果榨汁。混合、搅拌,并立即饮用。 功效:这是少数几种能混合的果蔬汁之一。 胡萝卜、苹果汁不但美味,而且是你能找到的最好的排毒剂和身体补充剂之一。这道混合汁还具有美容的作用,非常有益于皮肤。红苹果的味道很甜,因此如果在榨汁时你用的是红苹果,由于胡萝卜也很甜,这会使得榨出来的汁非常甜。所以,你也可以用青苹果来榨汁。β-胡萝卜素、叶酸、维生素C、钙、果胶、镁、钾、磷。维生素B1、维生素B2、维生素B3、维生素B6和维生素E、铜、铁、锌 胡萝卜苹果土豆汁:均衡营养,针对贫血 现代人尽管在饮食上可选择性大,却容易因缺乏必要的养分而导致营养失调。吃,并不等于平息空腹感。最重要的是要让身体获得必要的养分,早餐辟谷法里的胡萝卜苹果土豆汁,就是营养均衡的选择。人体所需的维生素、矿物质,胡萝卜苹果汁里几乎都有。胡萝卜被欧美自然疗法医师认为是可治百病的最佳药方,其中所含的矿物质具有强效净化力,所含胡萝卜素等的植化素可增强抵抗力。而苹果所含有的钙质具有利尿作用,能有效改善水肿。胡萝卜和苹果都是性温平的食物,饮用时最好兑入温水(无论天气冷暖),在温热的温度喝下,就不会有寒凉的感觉。土豆含有丰富的B族维生素和优质纤维素,在人体延缓衰老过程中有重要作用。土豆中含的优质蛋白首屈一指,即使是人体需要的其他营养素如碳水化合物、各种维生素、矿物质等,也都比米面更全面。同时,中医认为土豆能和胃调中、健脾益气,对治疗胃溃疡,习惯性便秘等疾病有裨益,还有解毒、消炎的作用。早上只喝生姜红枣茶就可以了,但肌肤干燥、有贫血现象的人,再搭配胡萝卜苹果土豆汁效果更好。 具体做法 材料:胡萝卜2根,苹果1个,土豆一个,柠檬汁少许。 做法:①挤入柠檬汁,柠檬具有防止氧化的效果。 ②洗净的胡萝卜、土豆和苹果连皮带籽直接切成适当大小放进果汁机榨汁。 ③杯上放滤茶器,将步骤2倒入杯里,搅拌均匀即可。
蜜薯的营养价值 与普通的红薯不同,蜜薯是一种甜味更家的地瓜,而且蜜薯的营养价值也与普通的地瓜不同。蜜薯在补气和血方面的具有较大的作用,所以每天吃一些蜜薯可以让脸色看起来更加的红润,让人更显年轻。另外,蜜薯还有很好的提高免疫力的作用,可以起到预防感冒提高身体健康指数的作用。 蜜薯的功效与作用 1、补气和血:常吃蜜薯,皮肤会逐渐变得润泽,气色会变得红润。其补气血的作用可以跟大枣相提并论,且不容易生湿热。 2、提高免疫力:比一般蔬菜含有更多的抗氧化物,可以预防感冒、提高免疫力。 3、双向调节肠道功能:便秘的人可以常吃煮红薯来促进肠胃蠕动、润肠通便;而脾胃不好经常腹泻的人,可以吃烤红薯来缓解不适并加强肠道功能。 4、净化血液:蜜薯中丰富的叶绿素可以帮助排出毒素从而起到净化血液的功效。 5、预防高血压:蜜薯中含有丰富的钾,有助于控制血压。 6、改善更年期症状:通过蜜薯中含有的植固醇起到类似于荷尔蒙的调节身体机能的作用。 7、外用(消炎去毒):将生蜜薯捣碎敷在热毒疮的周围,不仅可以缓解疼痛,还能促进皮肤生长、加快伤口愈合。 蜜薯的营养价值
1、蜜薯中含有丰富的膳食纤维,有利于女性排毒养颜。蜜薯虽然味道甘甜,但热量很低,同等质量的蜜薯和大米,蜜薯的热量只有大米的1/3,低脂肪低热量使其成为健美人士、减肥人士的理想之选。 2、蜜薯所含的膳食纤维和粘液蛋白等成份也可以润滑关节、润肠通便、防癌的功效,是老少皆宜的食品。 3、蜜薯中富含β-胡萝卜素,β-胡萝卜素在人体内可以转化为维生素A,100g蜜薯含有125个单位的维生素A,可以有效预防维生素A缺乏症,并起到保护视力的作用。 4、蜜薯中含有较多的叶黄素。叶黄素有“植物黄体素”之称,能够预防心血管疾病以及衰老引起的多种退化性疾病。 这样看来,蜜薯中富含的各种营养物质对身体健康起着积极促进的作用,也带来了许多神奇的功效。大家可以适当地多吃一些蜜薯,让自己变得更加美丽又健康。
able 有才干的,能干的 active 主动的,活跃的 adaptable 适应性强的 aggressive 有进取心的 alert 机灵的 ambitious 有雄心壮志的 amiable 和蔼可亲的 analytical 善于分析的 apprehensive 有理解力的 aspiring 有志气的,有抱负的 audacious 大胆的,有冒险精神的capable 有能力的,有才能的 careful 办理仔细的 candid 正直的 charitable 宽厚的 competent能胜任的 confident 有信心的 conscientious 认真的,自觉的considerate 体贴的 constructive 建设性的 contemplative 好沉思的 cooperative 有合作精神的 creative 富创造力的 dashing 有一股子冲动劲的,有拼搏精神的dedicated 有奉献精神的 devoted 有献身精神的 dependable 可靠的 diplomatic 老练的,有策略的 disciplined 守纪律的 discreet (在行动、说话等方面)谨慎的dutiful 尽职的 dynamic 精悍的 earnest 认真的 well-educated 受过良好教育的 efficient 有效率的 energetic 精力充沛的
enthusiastic 充满热情的expressivity 善于表达 faithful 守信的,忠诚的 forceful (性格)坚强的 frank直率的,真诚的 friendly 友好的 frugal 俭朴的 generous 宽宏大量 genteel有教养的 gentle 有礼貌的 hard-working 勤劳的 hearty 精神饱满的 honest 诚实的 hospitable 殷勤的humble 恭顺的humorous 有幽默i mpartial 公正的independent 有主见的industrious 勤奋的 ingenious 有独创性的 initiative 首创精神 have an inquiring mind爱动脑筋intellective 有智力的 intelligent 理解力强的 inventive有发明才能,有创造力的just 正直的 kind-hearted 好心的knowledgeable 有见识的 learned 精通某门学问的 liberal 心胸宽大的 logical 条理分明的 loyal 忠心耿耿的 methodical 有方法的 modest 谦虚的 motivated 目的明确的 objective 客观的 open-minded 虚心的 orderly 守纪律的
胡萝卜汁的加工工艺 胡萝卜中含有丰富的胡萝卜素和大量的维生素及矿物质,因此作为营养价值很高的蔬菜被人们广泛的接受。胡萝卜汁是用新鲜的胡萝卜为原料,通过破碎取汁或打浆等工艺制得的产品,在风味和营养上十分接近于新鲜原料,所以它营养丰富,是良好的保健食品。 一、工艺流程 胡萝卜清洗→去皮→切分→热烫→打浆→酶反应→灭酶→榨汁→过滤→杀菌→冷却→灌装→清汁产品 二、操作要点 1、原料选择:用于制汁的胡萝卜一般选择脆嫩,味甜,含纤维素少,色彩艳丽的,剔除病虫害和腐烂者。 2、去皮:有化学去皮和人工去皮法。生产中一般采用碱液去皮法,碱液浓度为2%—4%,温度为70—95℃,煮制时间为1—3min。然后用清水冲洗干净,修整切片。 3、热烫:这一过程主要作用是钝化酶活性,防止酶褐变,软化原料组织,提高出汁率。预煮液中加人少量的柠檬酸、醋酸或维生素C以维持原料的色泽和稳定性。 4、酶处理:在果蔬汁生产中加入酶制剂,可以显著提高果蔬的出汁率及压榨性能。常用的有果胶酶、纤维素酶、半纤维素酶等。常用温度是在90℃作用,作用时5—10min。 5、调配:调配时主要考虑产品的风味和价格因素。常用的甜味剂有蔗糖、葡萄糖、麦芽糖醇、甜蜜素、甘草等,酸度调节剂有柠檬酸、
乳酸、苹果酸、酒石酸等。此外,还可适量加入食用香料、着色剂、防腐剂、抗氧化剂、增稠剂等。 6、均质,脱气:均质的目的是使胡萝卜中的悬浮颗粒进一步破碎细化,使果胶均匀的分布于汁液中,防止出现分层的现象。脱气可以减少或避免胡萝卜汁的氧化,减少其色泽和风味的破坏以及营养成分和维生素C的氧化。据报道,生产上目前多采用真空脱气机,温度控制在40—50℃,压力在0.008—0.01MPa之间,均质压力在20MPa左右,2—3min。 7、杀菌:杀菌的目的在于杀死致病菌和钝化酶的活性。包括冷杀菌和热力杀菌两种,热力杀菌主要采用高温短时杀菌(一般温度为95℃,时间为l5—20s)和超高温瞬时杀菌(杀菌温度为120—130 ℃,时间为3—6s)。
紫茉莉花语 紫茉莉的俗名是胭脂花,也称野茉莉。其实紫茉莉的外型一点也不像茉莉,但有淡淡的茉莉香,而“野”字却当之无愧——因为随便丢几粒种子到土里,紫茉莉便生机勃勃地长出一大丛,并且年复一年扩大自己的领域。紫茉莉的花语是什么呢,它又有什么美丽的花语传说呢?一起来看看吧。 紫茉莉花语贞洁、质朴、玲珑、臆测、猜忌、成熟美、胆小、怯懦 什么是紫茉莉紫茉莉(学名:Mirabilis jalapa L.):草本,高可达1米。根肥粗,倒圆锥形,黑色或黑褐色。茎直立,圆柱形,多分枝,无毛或疏生细柔毛,节稍膨大。叶片卵形或卵状三角形,全缘,两面均无毛,脉隆起。花常数朵簇生枝端,总苞钟形,长约1厘米,5裂,裂片三角状卵形;花被紫红色、黄色、白色或杂色,高脚碟状,筒部长2-6厘米,檐部直径2.5-3厘米,5浅裂;花午后开放,有香气,次日午前凋萎。瘦果球形,直径5-8毫米,革质,黑色,表面具皱纹;种子胚乳白粉质。花期6-10月,果期8-11月。原产热带美洲。中国南北各地常栽培,为观赏花卉,有时逸为野生。根、叶可供药用,有清热解毒、活血调经和滋补的功效。种子白粉可去面部癍痣粉刺。 紫茉莉名字由来紫茉莉,又叫草茉莉、胭脂花、地雷花、粉豆花,是紫茉莉科、紫茉莉属的多年生草本花卉,因其花朵紫红,香如茉莉
而得名,是常见的观赏花卉。 紫茉莉因紫红色的花朵而得名,但它的花色丰富,常见的有红色、黄色、白色、杂色,夏季开花时,一株上密布着许多不同颜色的紫茉莉花朵,非常可爱美观。紫茉莉花朵娇艳,清香宜人,常被种植在花坛、路边做观赏用,也可制作成盆景放在家中观赏。 紫茉莉生长健壮,极易成活。而且有抗二氧化硫的特性,因此无论居民阳台或工矿污染区均可栽植。家庭养殖时,若能不时以洗肉鱼水、淘米水浇之,则花开更旺,花色愈艳。 胭脂花不仅幽香,其种子和叶尚有美容、清热和解毒的功效。种子成熟时,外观黑色如球形,内呈白色。美容时可采取成熟种子若干,研成粉末,去皮后取粉搽脸,可除面斑等,使面部光洁、白皙,收美容之功效。 另外,手面上生有水泡疮时,亦可取粉加水调匀抹于患处,收除湿解毒之功效。当皮肤创伤或行痈疮时,摘取胭脂花鲜叶数片,捣烂敷于创处患处即可。 紫茉莉形态特征紫茉莉是一年生草本植物,高可达1米。根肥粗,倒圆锥形,黑色或黑褐色。茎直立,圆柱形,多分枝,无毛或疏生细柔毛,节稍膨大。叶片卵形或卵状三角形,长3-15厘米,宽2-9厘米,顶端渐尖,基部截形或心形,全缘,两面均无毛,脉隆起;叶柄长1-4厘米,上部叶几无柄。花常数朵簇生枝端;花梗长1-2毫米;总苞钟形,长约1厘米,5裂,裂片三角状卵形,顶端渐尖,无毛,具脉纹,果时宿存;花被紫红色、黄色、白色或杂色,高脚碟状,筒部
实验六胡萝卜汁饮料制造实验 一、实验目的 1.了解浑浊胡萝卜汁饮料的制造原理; 2.掌握胡萝卜的漂烫和碱法去皮的方法; 3.掌握调配的方法和影响澄清度的因素; 4.掌握均质和杀菌的方法。 二、实验原理 胡萝卜汁饮料的生产是将胡萝卜经过去杂、清洗、去皮、预煮、打浆等物理方法,制取胡萝卜汁,加入白砂糖(等甜味剂)、柠檬酸(等酸味剂)、香精及(或)果汁,混合调整后,经过脱气、均质、杀菌、灌装等加工工艺,脱去氧气,钝化酶,杀死微生物,制成符合产品标准的胡萝卜汁饮料。 三、原料及试剂 水果、柠檬酸、D-异抗坏血酸钠、白砂糖、水果型香精、去离子水、氢氧化钠、碳酸钠、羧甲基纤维素钠、海藻酸钠、山梨酸钾等。 四、仪器、器皿及材料 榨汁机、高温蒸汽灭菌锅、夹层锅、半自动液体灌装机、胶体磨、手持糖量计、pH计、离心过滤机、250mL大容量离心机、捣碎机、均质机、电热水浴锅、真空脱气罐、200~300目不锈钢筛、不锈钢锅、不锈钢刀、电炉、500ml玻璃烧杯、500ml量桶、饮料瓶、纱布等。 五、工艺流程 原料选择→清洗→碱法去皮→切分→预煮→捣碎→过滤→调配→均质→脱气→装瓶→灭菌→冷却→成品。 六、操作方法 1.原料选择个体较大,表面光滑,中间黄心较少的胡萝卜。 2.清洗用自来水洗去表面的杂质。
3.碱法去皮将1%氢氧化钠和1%碳酸钠的混合溶液煮沸后,把胡萝卜放入后至表皮脱去为止,取出后用清水洗净。 4.切分将胡萝卜用刀切至1厘米的薄片,然后放入2倍体积的沸水中煮制15分钟左右,至组织软烂为宜。 表1 胡萝卜汁添加量的单因素实验 建议:饮料最终定容至100毫升。 表2 蔗糖添加量的单因素实验 注:①X由表1的最佳值得到;②饮料最终定容至100毫升。 表3 柠檬酸添加量的单因素实验
胡萝卜牛奶汁的功效与做法是什么胡萝卜中含有丰富的维生素及微量元素,胡萝卜中的木质素很高,能快速消灭癌细胞,同时提高肾上腺素的合成,对降压强身有着很高的作用,胡萝卜可有效增强抵抗力和免疫功能,胡萝卜搭配牛奶汁是常见饮品,不仅香甜可口,在喝的过程中可以补充维生素,还能改变胡萝卜中原有的味道,让胡萝卜更美味。 ★胡萝卜的功效与作用 1.增强抵抗力 胡萝卜中的木质素也能提高,间接消灭癌细胞。 2.降糖降脂
降低血脂,促进肾上腺素的合成,还有降压,强心作用,是高血压、冠心病患者的食疗佳品。 3.明目 胡萝卜含有大量胡萝卜素,进入机体后,在肝脏及小肠粘膜内经过酶的作用,其中50%变成维生素A,有补肝明目的作用,可治疗夜盲症。 4.利膈宽肠 植物纤维增加胃肠蠕动,促进代谢,通便防癌。 ★胡萝卜的营养价值
1.胡萝卜素转变成维生素A,在预防上皮细胞癌变的过程中具有重要作用,胡萝卜中的木质素也能提高。作为一种抗氧化,具有抑制氧化及保护机体正常细胞免受氧化损害的防癌作用。 2.胡萝卜素既有造血功能补充人体所需的血液,从而改善贫血或冷血症,同时含有丰富的钾。 3.胡萝卜含有植物纤维吸水性强在肠道中体积容易膨胀是 肠道中的“充盈物质”。 4.胡萝卜中的维生素A是骨骼正常发育的必需物质,有利于细胞的生殖与增长。
★萝卜牛奶汁 4.3分 6位评价 收藏 食谱号 200968 阅读 41,563次收藏 29次 siah82 材料 红萝卜250g,冰水500ml,淡奶100ml,,砂糖40g 做法
1、萝卜切小块放进搅拌机,加入一半的冰水,用搅拌机搅烂。 2、将萝卜渣汁倒入隔渣布袋,挤出萝卜汁。 3、加入剩下的冰水,淡奶和砂糖搅拌至融化,萝卜牛奶汁就做好了。 ★甘蔗雪梨牛奶汁 材料 红皮甘蔗,梨,牛奶(三者比例:2:1:1),榨汁机 做法 1.为方便榨汁,新鲜甘蔗去皮切成小断,梨去皮切小块。 2.甘蔗和梨先榨出汁。
英文简历的个人品质常用词汇able 有才干的,能干的 adaptable 适应性强的 active 主动的,活跃的 aggressive 有进取心的 ambitious 有雄心壮志的 amiable 和蔼可亲的 amicable 友好的 analytical 善于分析的 apprehensive 有理解力的 aspiring 有志气的,有抱负的 audacious 大胆的,有冒险精神的 capable 有能力的,有才能的 careful 办理仔细的 candid 正直的 competent 能胜任的
constructive 建设性的cooperative 有合作精神的creative 富创造力的 dedicated 有奉献精神的dependable 可靠的 diplomatic 老练的,有策略的disciplined 守纪律的 dutiful 尽职的 well--educated 受过良好教育的efficient 有效率的 energetic 精力充沛的expressivity 善于表达 faithful 守信的,忠诚的 frank 直率的,真诚的generous 宽宏大量的 genteel 有教养的
gentle 有礼貌的humorous 有幽默impartial 公正的independent 有主见的industrious 勤奋的ingenious 有独创性的motivated 目的明确的intelligent 理解力强的learned 精通某门学问的logical 条理分明的methodical 有方法的modest 谦虚的 objective 客观的precise 一丝不苟的punctual 严守时刻的
榨胡萝卜汁的做法 胡萝卜的营养价值是特别高的,但是我们在平时都会很少吃胡萝卜吧,特别是小孩子就更不喜欢吃胡萝卜了,经常吃饭的时候孩子都会把胡萝卜挑出来,大家要知道胡萝卜也叫小人参,对我们的身体很好,要经常吃一些胡萝卜,而且胡萝卜榨成汁的营养就更丰富了,下面看看榨胡萝卜汁的做法。 胡萝卜的食疗价值是很高的,那么大家在平时喝过胡萝卜汁吗,胡萝卜汁对女性朋友是很好的,它的美容养颜的效果很好,也可以用胡萝卜汁直接涂抹在脸上,能够祛斑,下面我们看看榨胡萝卜汁的做法。 做法一 制作材料 主料:胡萝卜150克,鸡蛋50克 调料:蜂蜜5克,香油3克 制作流程 1、将胡萝卜搅碎取汁; 2、将水烧开; 3、将鸡蛋打碎,倒入沸水中; 4、再加入胡萝卜汁、蜂蜜、香油 做法二 1、胡萝卜五百公克,切成适量大小,置于研钵中捣碎成泥状。 2、以纱布包之,榨挤出汁液。
3、加入一大匙蜂蜜于胡萝卜汁中即成。 其实用榨汁机比较方便,榨时可加适量水。可以加热 做法三 原料:2个橙子,3个胡萝卜 做法:将橙子去皮,胡萝卜擦洗干净。榨汁后立即饮用。如果你觉得汁太甜,可以加入一些薄荷叶。 食疗价值 胡萝卜中含有丰富的胡萝卜素,在肠道中经酶的作用后可变成人体所需的维生素A,人体缺乏维生素A,易患干眼并夜盲证,易引起皮肤干燥,以及眼部、呼吸道、泌尿道、肠道粘膜的抗感染能力降低。儿童缺乏维生素A,牙齿和骨骼发育还会受到影响。现代药理研究证明,胡萝卜中含有一种能够降低血糖的成分。即将胡萝卜经石油醚提取后可得到一种不定型的黄色物质,对动物和人都有明显的降低血糖作用。此外,人若每天服三次胡萝卜汁,可降低血压,并有抗肺癌作用。英国癌症研究会主席理多尔认为,吸烟者常吃些胡萝卜,癌症发病率比不吃胡萝卜者会明显下降。 萝卜汁能明目 胡萝卜含有的多种营养物质,都对眼睛健康有保护作用。尤其是丰富的胡萝卜素,被吸收利用后转变成维生素A,维生素A 和蛋白质可结合成视紫红质,此物是眼睛视网膜的杆状细胞感弱光的重要物质。同时,维生素A还可使上皮细胞分泌黏液,防止发生干眼病。 大家应该知道了榨胡萝卜汁的做法,平时是不是要去多喝一些胡萝卜汁呢,胡萝卜汁的效果是很多的,特别是对女性朋友的
2013届毕业生毕业论文苹果胡萝卜复合果蔬汁饮料的研究 学生姓名樊世明 学号7031209226 所属学院生命科学学院 专业食品科学与工程 班级13-2 指导教师叶林 日期2013年5月 塔里木大学教务处制
目录 摘要 (1) 1前言 (1) 1.1苹果概述 (2) 1.1.1苹果的发展状况 (2) 1.1.2国内苹果研究现状分析 (2) 1.1.3苹果的营养价值及功效 (3) 1.2胡萝卜概述 (3) 1.2.1 胡萝卜的开发现状研究 (3) 1.2.2 胡萝卜的营养价值及保健功能 (3) 1.3本课题研究的目的与意义 (4) 2.材料与方法 (4) 2.1材料 (4) 2.1.1试验材料 (4) 2.1.2仪器与试剂 (4) 2.2方法 (5) 2.2.1工艺流程 (5) 2.2.2操作要点 (5) 2.2.3苹果的护色试验 (5) 2.2.4胡萝卜的去味试验 (5) 2.2.5苹果、胡萝卜复合果蔬汁最佳配方研究 (5) 2.2.6产品感官品质评价方法 (6) 2.2.7对产品进行理化检测的方法 (6) 2.2.8对产品进行微生物检测的方法 (6) 3结果与分析 (6) 3.1苹果的护色 (6) 3.2胡萝卜的去味 (7) 3.3苹果汁与胡萝卜汁的比例对复合果蔬汁的影响 (7) 3.4柠檬酸添加量对复合果蔬汁的影响 (7) 3.5蔗糖添加量对复合果蔬汁的影响 (8) 3.6稳定剂添加量对复合果蔬汁的影响 (8) 3.7配方优选试验确定 (9) 3.8验证实验 (10) 3.9部分理化指标及微生物指标 (10)
4结论与讨论 (10) 参考文献 (10) 致谢 (11)
紫茉莉有什么种植方法 紫茉莉如何种植 1、土壤:紫茉莉家庭盆栽土壤可选肥沃的沙质和半沙质土壤为好,在pH值6至6.5的微酸性土壤种植,则根系茂密,生长健旺,如土质黏重,缺少有基质,肥力较低,通气性不良,则根系少,植株矮,茎叶纤细,花少而小。 2、浇水:紫茉莉不耐旱,但又忌积水,多雨季节要及时倾倒盆内积水,否则叶片易发黄。夏季炎热晴天每天要浇水两次,早晚各一次,如发现叶片卷垂应喷水于叶片,促进生长,雨季需常松土,使盆内不积水。春秋季隔几天浇透1次水。冬季应保持盆土湿润即可,浇水过多,根部会发黑腐烂,叶片枯黄、脱落。 3、光照:紫茉莉是喜光植物,生长发育需要有充足的光照,长日照直射光更有利于它的生长发育。光照强,叶色浓绿,枝干粗壮,花蕾多,着色好、香气高。如光照不足或过于荫蔽,则叶色淡绿,叶片大而薄,光合作用产物减少,生理活动受到抑制,植株发育不良,花的产量低,质量差。 4、温度:紫茉莉花对温度较敏感,要求温热湿润的气候,并能适应较高的气温,不耐低温,抗寒能力差。气温在10℃以下,生长极其缓慢,甚至停止生长。19℃左右可以萌芽,25℃以上才孕育花蕾,30~40℃时花蕾形成及发育较好,成熟开放适宜温度是32~38℃。 5、施肥:盛夏高温季节是紫茉莉生长的旺期,多施有机肥和磷钾肥,如花生饼粉、骨粉、过磷酸钙以及多元素花肥,每月施两次。紫茉莉在夏季生长期常出现枝叶繁茂但不开花的现象,主要原因是施了过多的氮肥,造成枝叶徒长,遇到这样情况要控制肥水,增施磷钾肥,促使孕育花蕾,同时要注意把紫茉莉移到阳光充足、通风良好之处。 6、病虫:紫茉莉常有螟蛾幼虫和介壳虫、红蜘蛛为害,以7月至9月最为严重,常蛀食花蕾,可用万能粉或杀灭菊酯加水200倍进行喷洒,每半月喷洒一次,即未发生病虫害也应进行喷洒,做到预防在先,喷洒时间以晴天上午9时和下午4时为宜,中午烈日不宜喷洒,防止药害。 7、修剪:紫茉莉夏天生长很快,要及时修剪,盆栽紫茉莉修剪保留基部10厘米至15厘米,促发多数粗壮新梢,如新梢长势很旺,应在生长10厘米时摘心,促发二次梢,则开花较多,且株形紧凑。花凋谢后应及时把花枝剪去,减少养分消耗,也能促长新梢,使枝密、芽多、开花多。 紫茉莉是否有毒
概括人物性格、形象、品质的常用词语 1. 性格类: 善解人意、心细如发、体贴、富有爱心、温柔沉静、心灵手巧、富有情趣、通情达理、纯真质朴、聪明伶俐、天真可爱、顽皮淘气、富有活力、朝气蓬勃、懂事能干、有主见、有骨气、人穷志不短、自尊自爱、倔强、沉稳果断、开朗自信、真诚善良、友好谦恭、宽容忍让、勤劳朴实、节俭、慈爱宽厚、和蔼可亲、平易近人、彬彬有礼、不拘小节、睿智大气、聪慧通达、幽默风趣、善于 变通、隐忍内敛、个性张扬、心直口快、耿直偏激、严厉苛刻、严慈相济向往自由、追求平等、 热爱生活、热爱自然、珍爱自己、乐于挑战、永不服输、富有智慧、精明强干、大智若愚、足智 多谋、沉着冷静、从容镇定、勇敢、目光敏锐、狂放不羁、特立独行。 (反面:胆小怯懦、逆来顺受、妥协退让、敏感自闭、固步自封、妄自菲薄、固执、吝啬、冷漠 自私、粗鲁莽撞、粗俗不雅、饶舌多事、骄横火爆、横行霸道、狂妄自大、目中无人、孤傲自负、刚愎自用、奸诈多疑、老气横秋、消极悲观、自卑、圆滑世故、尖酸刻薄、利欲熏心、唯利是图、争强好胜、孤芳自赏) 2. 拼搏类: 顽强拼搏、自强不息、不怕困难、坚强不屈、知难而进、积极乐观、身残志坚、自食其力、自立 自强、坚持不懈、锲而不舍、矢志不渝、勤勉刻苦、不畏艰辛、吃苦耐劳。 (反面:贪图享乐、自暴自弃、拈轻怕重) 3.奉献类:无私奉献、自我牺牲、任劳任怨、默默无闻、不事张扬、默默奉献、毫无所求、兢兢 业业、勤勤恳恳、废寝忘食、爱子情深、舐犊情深。 (反面:斤斤计较、自私自利) 4.职责类:恪尽职守、尽职尽责、爱岗敬业、治学严谨、教学有方、诲人不倦、以校为家、爱厂 如家、关心下属、秉公执法、不徇私情、勇于探索、锐意进取、敢于创新、技术精湛、才华横溢、博学善谈、以身殉职、奉公守法、铁面无私、赏罚分明、妙手回春、文武双全、智勇双全、博古 通今、见多识广、明察秋毫、严以律己、临危不惧。(反面:以权谋私、徇私枉法、畏首畏尾、 墨守成规、贪生怕死) 5. 品质类:洁身自好、淡泊名利、安贫乐道、仁义守信、乐善好施、虚怀若谷、胸有大志、志 存高远、心胸宽广、宽宏大量、豁达大度、坦荡无私、德艺双馨、诚实守信、有责任心、孝顺、
胡萝卜汁:每天喝上一定数量的鲜胡萝卜汁,能改善整个机体的状况。胡萝卜汁能提高人的食欲和对感染的抵抗力。哺乳期的母亲每天多喝些胡萝卜汁,分泌出的奶汁质量要比不喝这种汁的母亲高得多。患有溃疡的人,饮用胡萝卜汁可以显著减轻症状,胡萝卜汁还有缓解结膜炎以及保养整个视觉系统的作用。 芹菜汁:芹菜味道清香,可以增强人的食欲。在天气干燥炎热的时候,清晨起床后喝上一杯芹菜汁,自我感觉会好得多。在两餐之间最好也喝些芹菜汁。芹菜汁也可作为利尿和轻泻剂以及降压良药。由于芹菜的根叶含有丰富的维生素A、B1、B2、C和P,故而芹菜汁尤其适合于维生素缺乏者饮用。 白菜汁:白菜,又称圆白菜。白菜对于促进造血机能的恢复、抗血管硬化和阻止糖类转变成脂肪、防止血清胆固醇沉积等具有良好的功效。白菜汁中的维生素A,可以促进幼儿发育成长和预防夜盲症。白菜汁所含的硒,除有助于防治弱视外,还有助于增强人体内白细胞的杀菌力和抵抗重金属对机体的毒害。当牙龈感染引起牙周病时,饮用白菜和胡萝卜混合汁,不仅可以为人体供应大量维生素C,同时还可以清洁口腔。 黄瓜汁:医学家排列的黄瓜汁医用价值表上,利尿功效名列前茅。黄瓜汁在强健心脏和血管方面也占有重要位置,能调节血压,预防心肌过度紧张和动脉粥样硬化。黄瓜汁还可使神经系统镇静和强健,能增强记忆力。黄瓜汁对牙龈损坏及对牙周病的防治也有一定的功效。黄瓜汁所含的许多元素都是头发和指甲所需要的,能预防头发脱落和指甲劈裂。黄瓜汁含脂肪和糖较少,是比较理想的减肥饮料。 番茄汁:医学专家认为,每人每天吃上2-3个番茄,就可以满足一天维生素C的需要。喝上几杯番茄汁,可以得到一昼夜所需要的维生素A的一半。番茄含有大量柠檬酸和苹果酸,对整个机体的新陈代谢过程大有补益,可促进胃液生成,加强对油腻食物的消化。番茄中的维生素P有保护血管、防治高血压的作用,并能改善心脏的工作。此外,常饮番茄汁可使皮肤健美。番茄汁兑上苹果汁、南瓜汁和柠檬汁,还可起到减肥的作用。 豆腐小面膜 做菜时,若有用剩下的豆腐小块,不妨尝试用来做面膜。豆腐具有高度的滋润与美白作用,经常使用,一个月后就能看到肌肤变白嫩了。 材料:豆腐适量 做法:1.将手洗干净,将豆腐块放在手掌心。 2.轻轻地揉搓豆腐,然后将豆腐泥敷在脸部,轻轻按摩。 3.15~20分钟后洗净即可。 蜂蜜面膜 使皮肤光洁亮丽,可改善皮肤暗沉现象,减低黑色素,蜂蜜与蛋清也能够有效滋养皮肤。 材料:蜂蜜2大匙,蛋清2大匙,麦片2大匙 做法:1.将蜂蜜、蛋清与麦片混合均匀。 2.用小刷子沾取面膜均匀地涂在脸上。 3.20分钟后用清水冲洗。
龙源期刊网 https://www.doczj.com/doc/151952710.html, 浅谈紫茉莉应用与管理 作者:何会流 来源:《农家科技》2018年第08期 摘要:紫茉莉是我国南北方比较常见的药用草花花卉,基于实践对紫茉莉应用进行了总结,对其养护管理提供了一些建议。 关键词:紫茉莉;园林应用;养护管理 紫茉莉(Mirabilis jalapa L.)别名胭脂花、夜饭花、状元花、粉豆花、苦丁香、丁香叶等。紫茉莉科(Nyctaginaceae)紫茉莉属(Mirabilis L.),原产热带美洲。中国南北各地常栽培,常用园林观赏花卉,有时逸为野生。 一、形态特征、生活习性 紫茉莉是多年生草本花卉,高可达1m。根肥粗,倒圆锥形,黑色或黑褐色。茎直立,圆柱形,多分枝,无毛或疏生细柔毛,节稍膨大。叶卵形或卵状三角形,顶端渐尖,基部截形或心形,全缘,两面均无毛,脉隆起,叶柄长1-4cm,上部叶几无柄。花常数朵簇生枝端,花梗长1-2 mm;总苞钟形,长约1 cm,5裂,裂片三角状卵形,顶端渐尖,无毛,具脉纹,果时宿存;花被紫红色、黄色、白色或杂色,高脚碟状,筒部长2-6cm,5浅裂;花午后开放,有香气,次日午前凋萎。瘦果球形,直径5-8mm,革质,黑色,表面具皱纹;种子胚乳白粉质。花期6-10月,果期8-11月。 紫茉莉性喜温和而湿润的气候条件,不耐寒,冬季地上部分枯死。在江南地区地下部分可安全越冬而成为宿根草花,来年春季续发长出新的植株。花朵在傍晚至清晨开放,在强光下闭合,夏季在树荫则生长开花良好,烈日酷暑下往往有脱叶的现象。 二、园林应用 园林绿化中,紫茉莉品种并不多,目前具有观赏价值的品种与类型约有9种,暂无通过审定的品种。选育的观赏品种为株型矮、重瓣花型,白天亦具有观赏价值的品种。(张西西,2006)。紫茉莉品系较少,以花型划分,有重瓣和单瓣之分;以花色划分,有粉色、白色、黄色、玫红、彩色、条纹等。 园林景观设计中,紫茉莉的形体尺度适中,花和叶均有较高的观赏价值,是园林常用观赏花卉品种,广泛应用于各类园林景观项目。紫茉莉花期长、花色漂亮,可与其他景观植物组合,应用构建不同形式的花坛。紫茉莉可与不同品种、不同尺度的植物如组合为形式丰富的花境,常做花境的背景材料。此外,散点种植的紫茉莉景观具良好野趣,常应用在草地开阔处、树丛周围及路旁等景观区域成片栽植作观赏花带,适合应用于公园、学校、度假地、风景旅游区等景观项目中。紫茉莉也是居家阳台、屋顶花园绿化美化的优质植物。如果作盆栽观赏花
薯类的营养与健康 中国疾病预防控制中心 杜松明 我们人类的食物是多种多样的,各种食物所含的营养成分不完全相同,除母乳对0到6个月的婴儿外任何一种天然的食物都不能提供人体所需要的全部营养素,因此,我们要提倡平衡膳食,平衡膳食有多种食物组成这样才能够满足人体对各种营养素的需求达到合理营养促进健康的目的。 我们人类的食物通常可分为五大类,第一类为谷类及薯类,谷类包括米、面、杂粮、薯类包括马铃薯、甘薯、木薯等主要提供碳水化合物、蛋白质、膳食纤维及B族维生素。第二类为动物性食物包括肉、禽、鱼、奶、蛋等主要提供蛋白质、脂肪、矿物质、维生素A、B族维生素。第三类为豆类和坚果,包括大豆其他干豆类及花生、核桃、杏仁等坚果类,主要提供蛋白质、脂肪、膳食纤维矿物质、B族维生素和维生素E。第四类为蔬菜、水果和菌藻类主要提供膳食纤维、矿物质、维生素C、胡萝卜素、维生素K及有益健康的植物化学物质。第五类为纯能量食物包括动植物油、淀粉、食用糖和酒类主要提供能量,动植物油还可提供维生素E和必须脂肪酸。 在2007年的时候中国营养学会颁布了《中国居民膳食指南》,它的目的是为了帮助我国居民合理选择食物并进行适量的身体活动以改善人们的营养和健康状况减少或预防慢性疾病发生,从而提高国民的健康素质。《中国居民膳食指南》包括有十条,其中第二条就是多吃蔬菜、水果和薯类。 为了帮助人们在日常生活中实践《中国居民膳食指南》,中国营养学会专家委员会又对1997年的中国居民平衡膳食宝塔进行了修订,以直观的形式告诉居民每天应该摄入的食物种类合理的数量以及适宜的身体活动。膳食宝塔一共分为五层,包含我们每天应该吃的食物种类,膳食宝塔各层的位置和面积不同,这在一定程度上反映出各类食物在膳食间的定位以及应占的比重。其中谷类食物在最低层,每人每天应该吃250克到400克,蔬菜和水果占第二层每天应该吃300克到500克和200克到400克,鱼、禽、肉蛋等动物性食品位于第三层,每天应该吃150克到225克左右。奶类和豆类食品在第四层每天应该吃相当于鲜奶300克的奶类及 奶制品和相当于干豆30到50克的大豆及制品,第五层是烹调油和食盐每天烹调油不应该超过25克或30克,食盐不应该超过6克。新的膳食宝塔中还增加了水和身体活动的形象,强调足量饮水和增加身体活动的重要性。 我们刚才说了在膳食宝塔的第一层指的是薯类,膳食宝塔的第一层指的是谷类、薯类和杂豆类。薯类主要包括有红薯、马铃薯等,可以代替部分粮食,谷类薯类、杂豆是膳食中能量的主要来源。谷类、薯类和杂豆食物的选择应该多样化注重粗细搭配适量选择一些全谷类食物,其他谷类杂豆及薯类。 先了解薯类的营养,薯类又称根茎类食物,常见的薯类有甘薯、马铃薯、木薯、芋薯,其中甘薯又称为红薯、白薯、山芋、地瓜等,马铃薯 又称为土豆、洋芋、木薯又称为树薯、木蕃薯,最后一种是芋薯,包括有芋头、山药。 薯类有哪些营养特点?更多的研究已经表明薯类含有丰富的碳水化合物和维生素C,维生素B1、维生素B2等多种维生素以及钙、磷、镁、钾等矿物质,薯类中丰富的碳水化合物以多糖为主容易被人体消化吸收可以作为人体所需要能量的主要来源。薯类中含有大量的膳食纤维对人体健康也有重要的。 具体的来说薯类对健康的作用主要表现为以下四个方面,第一维护健康,第二保持肠道正常的功能,第三提高机体的免疫能力,第四降低患肥胖、糖尿病、高血压等慢性疾病的风险。 薯类中含有丰富的膳食纤维具有很好的饱腹感,所以在吃薯类的时候就可以相应的减少其他主食的摄取,就有利于减肥,薯类中的膳食纤维进入肠道后能够吸水膨胀使肠内的内容物体积增大从而促进肠道蠕
【雅思口语词汇】个人品质(音标,例句) adaptable [??d?pt?bl]适应性强的 Children are highly adaptable—they just need time to readjust. 儿童的适应能力很强—他们只是需要时间重新适应。 active 主动的,活跃的 Although he's nearly 80, he is still very active. 尽管快80岁了,他还是十分活跃。 aggressive [??gres?v] 有进取心的 He is respected as a very aggressive and competitive executive. 他是一位锐意进取、竞争意识很强的主管,颇受尊敬。 ambitious [?m?b???s] 有雄心壮志的 Nowadays it's acceptable for women to be ambitious. But it wasn't then. 如今,女性胸怀大志也能被接受,但那时候不是这样。 amiable [?e?mi?bl]和蔼可亲的 The next - door neighbours are very amiable people. 隔壁的邻居很和蔼. amicable [??m?k?bl]友好的 Our discussions were amicable and productive. 我们的讨论气氛非常友好并且富有成果。 analytical [??n??l?t?kl] 善于分析的 She has a clear analytical mind. 她头脑清醒,善于分析。