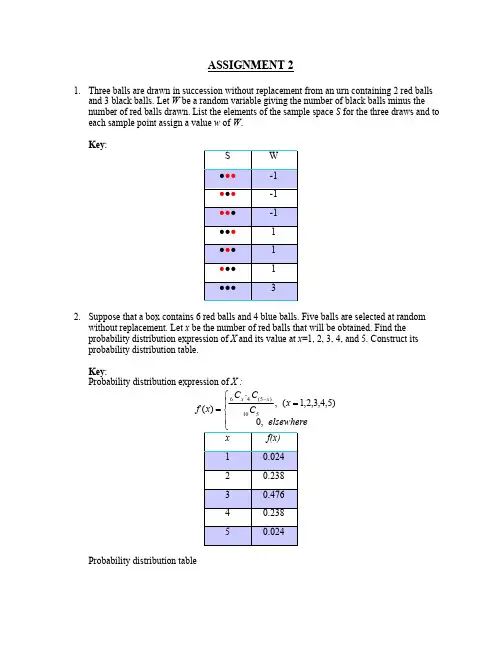
Assignment_2_Solutions
- 格式:doc
- 大小:83.50 KB
- 文档页数:3
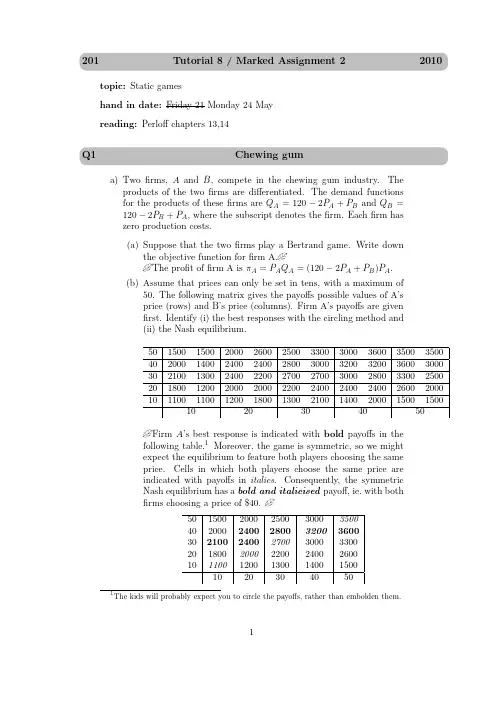
201Tutorial8/Marked Assignment22010 topic:Static gameshand in date:day21Monday24Mayreading:Perloffchapters13,14Q1Chewing guma)Twofirms,A and B,compete in the chewing gum industry.Theproducts of the twofirms are differentiated.The demand functionsfor the products of thesefirms are Q A=120−2P A+P B and Q B=120−2P B+P A,where the subscript denotes thefirm.Eachfirm haszero production costs.(a)Suppose that the twofirms play a Bertrand game.Write downthe objective function forfirm A.The profit offirm A isπA=P A Q A=(120−2P A+P B)P A.(b)Assume that prices can only be set in tens,with a maximum of50.The following matrix gives the payoffs possible values of A’sprice(rows)and B’s price(columns).Firm A’s payoffs are givenfirst.Identify(i)the best responses with the circling method and(ii)the Nash equilibrium.150015002500330035003500 402400240032003200210013002700270033002500 2020002000240024001100110013002100150015002040Firm A’s best response is indicated with bold payoffs in thefollowing table.1Moreover,the game is symmetric,so we mightexpect the equilibrium to feature both players choosing the sameprice.Cells in which both players choose the same price areindicated with payoffs in italics.Consequently,the symmetricNash equilibrium has a bold and italicised payoff,ie.with bothfirms choosing a price of$40.1500250035002000280036002100270033001800220026001100130015002040(c)Now assume that prices can be any nonnegative real number.Take afirst-order condition and use it tofind the best-response function of eachfirm.Firm A’s optimal price satisfies thefirst-order condition∂πA.Similarly,firm B’s reaction4function is P B=120+P Ax 2be the location of Firm 2.Assume that the location decisions are made simultaneously.The payoffs to the two firms are:π1(x 1,x 2)=12−x 21−(x 2−x 1)2π2(x 1,x 2)=12−(1−x 2)2−(x 2−x 1)2a)Derive best response functions for the two firms.Sketch them in(x 1,x 2)space.MB 1=−2x 1+2(x 2−x 1)=0and MB 2=2(1−x 2)−2(x 2−x 1)=0.So the two best response functions are:B 1(x 2)=x 22.b)Identify the Nash equilibrium.State it and also show it in your dia-gram. x 1=1300.20.40.60.81.000.20.40.60.81.0x 2x 1(x 1)3Q3WarrantiesAcura and Volvo offer warranties on their cars,where w A is the number of years of an Acura warranty and w V is the number of years of a Volvo warranty.The revenue forfirm i,i=A for Acura and V for Volvo,is R i= 27,000w i/(w A+w V).The cost of providing the warranty is C i=2,000w i.Acura and Volvo play a warranty-setting game in which they simultaneously set the length of warranties.2Volvo’s indifference curves are drawn in(w V,w A)space below.a)Sketch Volvo’s best response function into the indifference curve dia-gram.The trick is tofind the point of zero slope of each indifference curveand then connect the dots.You should get a backward-bending best-response for Volvo,as illustrated by the blue curve.Note that thetwo diagrams don’t have the same scale-the second one starts from(1,1)rather than(0,0).In fact the best response goes to(0,0)in thelimit,but it is next to impossible to determine that from looking atthe indifference curve diagram.Unfortunately,I did give them the payofffunctions,so although I amnot expecting or requiring it,some people may attempt a mathemat-ical derivation.If they do,Volvo’s FOC is27w A/(w A+w V)2−2=0.Solving for w V gives the best response function w V=B V(w A)=2Technically,payoffs are undefined when wA=w V=0,so let’s ignore warranties of zero length.4The students haven’t been taught about contract curves,as general equilibrium is no longer in the course.So don’t be distraught if they mostly don’t get this right.1234561 2 3 4 5 627*y/(y+x)2-227*x/(y+x)2-25。

Course Meeting Time and Location:Mondays and Wednesdays, 11:15am - 12:40pmClass meets in room 220 of the Stuart Building (220 SB)Textbook:Chi-Tsong Chen, Linear System Theory and Design, 3rd ed., Oxford University Press, 1999. ISBN: 0-19-511777-8Course Objectives:After completing this course, the student should be able to do the following things correctly: ∙formulate state space descriptions of linear dynamical systems, in both time-invariant and time-varying cases, and for both continuous-time and discrete-time systems;∙find the analytic solution of state equations and give a geometric interpretation of the state space in terms of the system dynamics;∙apply the concepts of stability, controllability and observability in interpreting and analyzing system behavior;∙formulate input-output descriptions of linear dynamical systems, in both time-invariant and time-varying cases, and for both continuous-time and discrete-time systems;∙construct realizations of input-output system descriptions via state space system dynamics;∙use state feedback to reshape system dynamics;∙use observers to infer knowledge of the system states given input and output measurements;∙use computer-based analysis and design tools (such as {\sc Matlab} software) in the analysis of linear, time-invariant systems.Course Documents:These documents are available in pdf or html format.∙Course syllabuso Syllabus as an html documento Syllabus as an Excel document∙Suggested additional references∙The Kalman Decomposition: a document describing how to find the coordinate transformation leading to the Kalman decomposition and giving an example of theapproach.Homework Policy and Assignments:Please follow these rules when submitting homework papers. Any exceptions to these basic policies should be confirmed with the instructor before submitted your paper.∙Use 8 1/2 x 11 inch or A4 paper (other sizes are not accepted), with multiple pages stapled together in the upper left corner. Do not use any means other than stapling tohold pages together (in that event, the grader has full authority to discard all but the first page).∙Your homework paper should present answers to the questions in the same order that they appear in the assignment. At the grader's discretion, zero credit may be given forwork the appears out of order.∙No email submissions are accepted unless prior arrangements have been made due to special circumstances, or unless the assignment specifically requests email submission.∙No late homeworks will be accepted without prior approval by the instructor. (Generally, approval of late homework submission requires there to be very extenuatingcircumstances. I drop the lowest homework score in part to accommodate the commonsituations that prevent persons from completing the assignments on time.)Homework assignments, when available, will be posted here in pdf format.∙Assignment #1 [posted 26 Jan 2007] (due 7 February 2007) [Note the new (later) due date!]∙Assignment #2 [posted 7 Feb 2007] (due 14 February 2007)∙Assignment #3 [posted 14 Feb 2007] (due 28 February 2007)∙Assignment #4 [posted 13 Mar 2007] (due 28 March 2007) [Problem #1 typo corrected15 Mar 2007]o Here are a couple of supplementary problems for controllable and Kalman decompositions that are non-degenerative (unlike problems 4 and 5 on HomeworkAssignment \#4). For your convenience the various system matrices are stored inthe file hw4_supp_data.mat. To access the variables, save this file to yourcomputer, and change the working directory of Matlab to the directory where yousaved the file (or alternatively add that directory to Matlab's path). You then loadin the system matrices by typing "load hw4_supp_data" at the Matlab prompt.▪Assignment #4 supplement▪hw4_supp_data.mat∙Assignment #5 [posted 26 Mar 2007] (due 13 April 2007, on-campus students please submit homework by putting it in my mailbox in the ECE Department; off campusstudents may submit homework in the usual way)∙Assignment #6 [posted 12 Apr 2007] (due 25 April 2007)Homework Solutions:Homework solutions will be posted either here or at the Galvin Library's Electronic Reserves.∙Solutions to Assignment #1 [submitted for posting at the Galvin Library's Electronic Reserves on 7 Feb 2007 and posted there on 8 Feb 2007]∙Solutions to Assignment #2 [submitted for posting at the Galvin Library's Electronic Reserves on 14 Feb 2007 and posted there on 15 Feb 2007]∙Solutions to Assignment #3 [submitted for posting at the Galvin Library's Electronic Reserves on 28 Feb 2007 and posted there on 1 Mar 2007]o ECE531_07S_hw3_p3.m: Matlab m-file for problem 3 of Assignment #3 (save to your own computer and run from there)∙Solutions to Assignment #4 [submitted for posting at the Galvin Library's Electronic Reserves on 28 Mar 2007 and posted there on 28 Mar 2007]∙Solutions to Assignment #5 [submitted for posting at the Galvin Library's Electronic Reserves on 16 Apr 2007 and posted there on 17 Apr 2007]∙Solutions to Assignment #6 [submitted for posting at the Galvin Library's Electronic Reserves on 25 Apr 2007 and posted there on 26 Apr 2007]Examinations:There will be two take-home examinations during the course of the term, and one in-class final examination. The take-home examinations, when available, will be posted here in pdf format.∙Take-home Exam #1 (due 7 March 2007 at 11:25am) [Problem 8 corrected on 2 March 2007 to include a missing transpose.]o Solutions to Take-home Exam #1 [submitted for posting at the Galvin Library's Electronic Reserves on 22 Mar 2007 and posted there on 23 Mar 2007] ∙Take-home Exam #2 (due 2 May 2007 at 11:25am)o Solutions to Take-home Exam #2 [submitted for posting at the Galvin Library's Electronic Reserves on 7 May 2007 and posted there on 7 May 2007]. Note: theproblem 2 solutions shown here are for a problem not on the exam. The problem 3solutions solve problem 2 on the exam. The problem 4 solutions solve problem 3.Problem 4's solutions are missing, but are included in the supplement.o Supplement to solutions to Take-home Exam #2 [submitted for posting at the Galvin Library's Electronic Reserves on 7 May 2007 and posted there on 7 May2007]. These are the missing problem 4 solutions.∙In-class final examination: Wednesday, 9 May 2007, 2:00 - 4:00pm∙Sample in-class examinations are available as follows:o Final Exam, Spring 2001o Final Exam, Spring 2002o Final Exam, Spring 2004o Final Exam, Spring 2005o Final Exam, Spring 2006Grading:∙Homework: 20% (best 5 of 6 assignments)∙Take-home Exam #1: 30%∙Take-home Exam #2: 30%In-class Final: 20% (the final is comprehensive)Academic Honesty:It is your responsibility to be familiar with IIT's Code of Academic Honesty. (Consult the IIT Student Handbook for this code.)In particular, the work that you submit for homework and individual project assignments and your work on examination papers must be your own. You may consult with other students about homework and project assignments. In fact, discussion of the assignments is encouraged. However, the written material that is submitted must be your own. Such written material includes computer programs and the results of using computer programs (computed values, plots, etc.). If the above policy or any part of IIT's Code of Academic Honesty is violated in regard to a submitted homework assignment, a grade of zero will be assigned to the work. If the above policy or any part of IIT's Code of Academic Honesty is violated in regard to a submitted project assignment or an examination paper, a punitive failing grade will be given in the course. In both cases, the matter will be reported to the appropriate university officials and offices. In the case of a second offense (with the first offense in this or any other course), expulsion from the university will be advocated.。
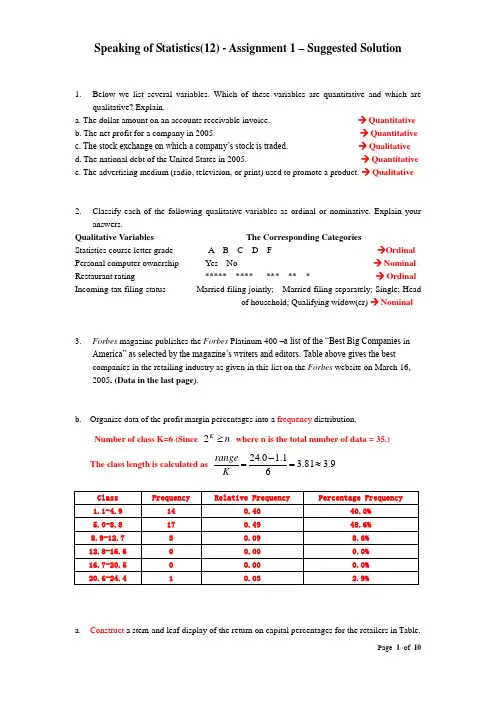
Speaking of Statistics(12) - Assignment 1 – Suggested Solution1. Below we list several variables. Which of these variables are quantitative and which arequalitative? Explain.a. The dollar amount on an accounts receivable invoice. → Quantitativeb. The net profit for a company in 2005. → Quantitativec. The stock exchange on which a company’s stock is traded. → Qualitative d. The national debt of the United States in 2005. → Quantitativee. The advertising medium (radio, television, or print) used to promote a product. → Qualitative2. Classify each of the following qualitative variables as ordinal or nominative. Explain youranswers.Qualitative Variables The Corresponding CategoriesStatistics course letter grade A B C D F →Ordinal Personal computer ownership Yes No → Nominal Restaurant rating ***** **** *** ** * → Ordinal Incoming tax filing status Married filing jointly; Married filing separately; Single; Headof household; Qualifying widow(er) → Nominal3. Forbes magazine publishes the Forbes Platinum 400 –a list of the ―Best Big Companies inAmerica‖ as selected by the magazine’s writers and editors. Table above gives the best companies in the retailing industry as given in this list on the Forbes website on March 16, 2005. (Data in the last page ).b. Organize data of the profit margin percentages into a frequency distribution.Number of class K=6 (Since n K≥2 where n is the total number of data = 35.) The class length is calculated as 9.381.361.10.24≈=-=K rangea. Construct a stem-and leaf display of the return on capital percentages for the retailers in Table.Find the median and then describe the distribution of the return.The median is the 18th measurement, 15.4.The data are widely spread out, with majority falling in the range [8.3, 22.8]. The distribution is somewhat symmetric, with extreme values at both ends.c.Construct a histogram of the profit margin percentages.4. In order to control costs, a company wishes to study the amount of money its sales forcespends entertaining clients. The following is a random sample of six entertaining expenses (dinner costs for four people) from expense reports submitted by members of the sales force $157 $132 $109 $145 $125 $139a. Show the equivalence of the following two formulas:,.Solutions:()⎥⎦⎤⎢⎣⎡--=⎥⎥⎦⎤⎢⎢⎣⎡⎪⎪⎭⎫ ⎝⎛+--=++++++-+++-=+-+++-++--=-++-+--=--=--=∑∑∑∑∑∑∑∑22222221222212222222121222212221 1 1)(2(11)]...()2...22()...[(11)]2(...)2()2[(11])(...)()[(11)(111)(i i i i i i n n n n n i ix n x n n x n x n x x n x x x x x x x x x x x n x x x x x x x x x x x x n x x x x x x n x x n n x x sb. Calculate x , 2s , and s for the expense data, use the two different formulas in (a) to calculate 2s .Solutions 5.1346139125145109132157=+++++=x7.27616)5.134 139()5.134 132()5.134 157(2222=+++= s , 63.167.276==sOr using another formula:925,1091391251451091321572222222=+++++=∑ix()249,651)807()139125145109132157(222==+++++=∑ix()⎥⎦⎤⎢⎣⎡--=∑∑2221 1 1i i x n x n s 7.276)249,651(61–925,1091–61=⎥⎦⎤⎢⎣⎡=5. On February 15, 2005, the Gallup Organization released the results of a Gallup UK poll regarding Internet usage in Great Britain. Each of 1,009 randomly selected UK adults was asked to respond to the following question:How much time, if at all, do you personally spend using the Internet-more than an hour a day, up to one hour a day, a few times a week, a few times a month or less, or never?The poll’s results were as follows: More than an hour a day (22%); Up to an hour a day (14%);A few times a week (15%); A few times a month or less (10%); Never (39%). Use these datato construct a bar chart and a pie chart.Bar Chart:Pie Chart:6. Thirteen internists in the Midwest are randomly selected, and each internist is asked to report last year’s income. The incomes obtained (in thousands of dollars) are127 132 138 141 144 146 152 154 162 171 177 192 241 Find:There are 13 measurements in total (n=13). They are already in ascending order. a. The 90th percentile.Calculate the index of the 90thpercentile: 7.111310090=⨯=i Round 11.7 up to 12, hence the 90th percentile is the 90th measurement 192.b. The median.The median is equivalent to the 50thpercentile: 5.61310050=⨯=i Round 6.5 up to 7, hence the median is the 7th measurement 152.c. The first quartile.We know the index of the first quartile can be found as: 25.31310025=⨯=i Round 3.25 up to 4, hence the first quartile is the 4th measurement 141.d. The third quartileWe know the index of the third quartile can be found as: 75.91310075=⨯=i Round 9.75 up to 10, hence the third quartile is the 10th measurement 171.e. The 10th percentile.Calculate the index of the 10thpercentile: 3.11310010=⨯=i Round 1.3 up to 2, hence the 10th percentile is the 2nd measurement 132.f. The interquartile range.Interquartile range is the difference between first and third quartile3014117113=-=-=Q Q IQRg. Develop a five-number summary and a box-and-whiskers display.7. According to the website, the 2004 total return percentages for several popular funds were as follow:Fund 2004 Total Return% Vanguard 500 Index 10.7Wasatch Core Growth 21.7 Fidelity Stock Selector 9.9 Fidelity Dividend Growth6.0Janus Worldwide 5.2Suppose that an investor had $100,000 invested in the Vanguard 500 Index fund, $500,000 invested in the Wasatch Core Growth fund, $500,000 invested in the Fidelity Stock Selector fund, $200,000 invested in the Fidelity Dividend Growth fund, and $50,000 invested in the Janus Worldwide fund.a. Compute a weighted mean that measures the 2004 average total return for the investor ’s portfolio.Compare your weighted mean with the un-weighted mean of the five total return percentages. Explain why they differ.The weighted mean is%56.13000,350,1000,305,18000,50000,200000,500000,500000,100)5.5(000,50)8.5(000,200)9.9(000,500)7.21(000,500)7.10(000,100==++++++++=μAnd the un-weighted mean is%72.1055.58.59.97.217.10=++++The average total return calculated using weighted mean is higher because more money was invested in funds with larger gains, such as Wasatch Core Growth.8. As given on the Morningstar website, the mean return for Fidelity Leveraged Company Stock is 17.98 percent with a standard deviation of 10.02 percent, while the mean return for Baron Opportunity Retail Stock is 16.43 percent with a standard deviation of 12.23 percent. Which stock do you buy? (Which is riskier than the other one?)The mean return for Fidelity Leveraged Company Stock is higher than of Baron Opportunity Retail Stock.When we compute and compare the coefficient of variation for these two stocks using 100mean deviationstandard ⨯ , we find that the coefficient of variation of Fidelity Leverage(73.5510017.9810.02=⨯) is lower than the one of Baron Opportunity (44.7410016.4312.23=⨯), meaning the variation in returns for the Baron Opportunity is higher, so investing in Baron Opportunity is riskier.Therefore investing in Fidelity Leveraged Company Stock is more advisable.9. The card game of Euchre employs a deck that consists of all four of each of the aces, kings, queens, jacks, tens, and nines (one of each suit —clubs, diamonds, spades, and hearts). Find the probability that a randomly selected card from a Euchre deck isThere are a total of 24 cards (4 aces, 4 kings, 4 queens, 4 jacks, 4 tens and 4 nines.a. A jack (J)The probability of selecting a jack is ()61244==J P b. A spade (S)The probability of selecting a spade card is 41246)(==S P c. A jack or an ace (A)The probability of selecting a jack OR an ace is()()()()3106161=-+=⋂-+=⋃A J P A P J P A J P d. A jack or a spade.The probability of selecting a jack OR a spade card is()()()()832414161=-+=⋂-+=⋃S J P S P J P S J P e. Are the events J and A mutually exclusive? J and S? Why or Why not?The events J and A are mutually exclusive because one cannot draw a Jack AND an Ace at the same time in one single draw.The events J and S are NOT mutually exclusive because one can draw a jack of spade under one single draw, hence J and S could occur simultaneously.10. Fifteen percent of the employees in a company have managerial positions, and 25 percent of the employees in the company have MBA degrees. Also, 60 percent of the managers have MBA degree.a. What proportion of employees are managers and have MBA degrees. 9% of employees are managers AND have MBA degrees09.0)6.0)(15.0()|()()(===⋂Manager MBA P Manager P MBA Manager Pb. What proportion of MBAs are managers. 36% of MBAs are managers36.025.009.0)()()|(==⋂=MBA P MBA Manager P MBA Manager Pc. Are the events being a manager and having an MBA independent? Justify your answer.No. Because 15.0)(36.0)|(=≠=ManagerP MBA Manager P11. In a survey of 100 insurance claims, 40 are fire claims (FIRE ), 16 of which are fraudulent (FRAUD ). Also, there are a total of 40 fraudulent claims. a. Construct a contingency table summarizing the claims data. Use the pairs of events FIRE and FIRE , FRAUD and FRAUD .Contingency Table:FireFIRETotal Fraud 16 24 40 Fraud 24 36 60Total4060100b. What proportion of the fire claims are fraudulent? 40% of the fire claims are fraudulent4.04016)()()|(==⋂=Fire P Fire Fraud P Fire Fraud Pc. Are the events a claim is fraudulent and a claim is a fire claim independent? Use your probability of part b to prove your answer. Yes. Because10040)(4.0)|(===Fraud P Fire Fraud P12. Each month a brokerage house studies various companies and rates each company’s stock as being either ―low risk‖ or ―moderate to high risk.‖ In a recent report, the brokerage house summarized its findings about 15a.The probability that the company’s stock is moderate to high risk giventhat the firm is an aerospace company.P(ModToHigh | Areo) = 9/15=0.6b.T he probability that the company’s stock is moderate to high risk giventhat the firm is a food retailer.P(ModToHigh | Food) = 10/25=0.4c.Determine if the company type is independent of the level of risk of thefirm’s stock.If the company type is independent of the level of risk of the firm’s stock, the we should find equalities such asP(Aero | Low) = P(Aero)However, P(Aero | Low) = 2/7 while P(Aero) = 3/8.The two probabilities are not equal. Hence the two events are dependent.Table for question 3:The Forbes platinum list: Best-performing retailers as listed at on March 16, 2005。

(Partial) Solutions to Assignment 2pp.73-761.16In each of the following systems, let or be the input and or be the output. Determine whether each systems is (1) linear, (2) time invariant, (3) causal, (4) BIBO stable(g).(i).ans: omitted----------------------------------------------------1.17 A linear time invariant system has impulse response Determine the output sequence for each of the followign input signals:(b)(f)(b) ans:h n is given byThe z-transform of []where ROC1:x n is given byz-transform of []where ROC2:h n is given byTherefore, the z-transform of the output []y nPerform inverse z to get [](f) ans: using the same method as in (b) (details omitted )----------------------------------------------------1.18. A linear time invariant system is defined by the difference equationb. Determine the output of the system when the intpu isc. Determine the output of the system when the input isans: omitted----------------------------------------------------1.19 The following expressions define linear time invariant systems. For each one determine the impulse respnose(a)(e)(a) ans: the impulse response is(e) ans: the impulse response is----------------------------------------------------1.20 Each of the following expressions defines a linear time invariant system. For each one determine whether it is BIBO stable or not(g)(k)BIBO: Bounded input and bounded output(g) ans: omitted(k) ans: omitted----------------------------------------------------1.21. Using the geometric series, for each of the following sequence determine the z-transform and its ROC(d)(g)(i)(d) ans:where ROC:(g) ans:The first part is equal towhere ROC1 isThe second part is equal towhere ROC2 isTherefore combining both parts:where ROC={ROC1 and ROC2}:(i) ans:where ROC: whole complex domain----------------------------------------------------1.22. You know what the and are. Using theproperties only (do not reuse the definition of the z-transform.) determine the z-transform of the following signals(c)(g)where ROC1:where ROC2:(c) ans: using z-transform property:We have:where ROC:(g) ans:details omitted. The final answer isTherefore combining both parts:where ROC={ROC1 and ROC2}:----------------------------------------------------1.23 Using partial fraction expansion, determine the inverse z-transform of the following functions:(c) ,(e) ,(c) ans:(e) ans:procedures are the same as above. details omitted.----------------------------------------------------1.24. For each of the followign linear difference equations, determine the impulse response, and indicate whether the system is BIBO stable or not(a)(c)(a) ans:Take z-transform on both sideswhere ROC:Because is finiteTherefore, the system is BIBO stable(c) ans: omitted (the same as (a))----------------------------------------------------1.25. Although most of the time we assume causality, a linear difference equation can be interpreted in a number of ways. Consider the linear difference equation(a) Determine the transfer function and the impulse response. Is the system causal ? BIBO stable ?(a) omitted.----------------------------------------------------1.26. 1.26 Consider the linear difference equation(a) Determine the transfer function . Do you have enough information to determine theregion of convergenceans:Don't have enough information to determine ROC.----------------------------------------------------1.27. Given the system described by the linear difference equationDetermine the output for each of the following input signals(a)(e)(a) ans:Take z-transform on both sides:----------------------------------------------------1.28. Repeat Problem 1.27 when the system is given in terms of the impulse responseBefore you do anything, is the system stable ? Does the frequency responseexist ?ans: omitted.----------------------------------------------------1.29. Repeat Problem 1.27 when the system isgiven by the linear difference equationBefore you do anything, is the system stable ? Does the frequency response exist ?Ans: omitted.----------------------------------------------------。

AK/ADMS 4503 3.0 Derivative SecuritiesFall 2008Assignment #1 SolutionsInstructions:(1) This assignment is to be done individually . You must sign and submit the standard cover page supplied as the last page of this assignment.(2) This assignment is due on October 19, 2008.(3) The work can be typed or handwritten. If it is handwritten and too difficultto read due to messiness and poor handwriting, it will receive zero credit.(4) You must show your work to receive full credit.(5) This assignment contains 5 questions and carries a total of 30 points .Question 1 (6 marks)The NASDAQ-100 futures trade at the CME, and each contract is on $100 times the index. The NASDAQ-100 spot is 1,670 points, and is expected to pay a dividend yield of 1% per annum continuously compounded. The risk-free rate is 2% per annum continuously compounded.(a) What is the theoretical 1-year futures price? (2 marks)(b) The 1-year futures price is 1,701 points. Show that there is an arbitrage and show how to benefit from it? Show all details. (4 marks)Solution(a) The theoretical 1-year futures price given by:()()78.686,11%)1%2(exp 670,1)(exp 0=×−×=×−×=T T F T q r S F(b) Since the market overprices the contract, there is an arbitrage that consists in shorting the 1-year futures contract, borrow the money at the risk-free rate to buy the index today. By doing this, you lock in a net profit of $1,421.62. Here are the details:Today, you must: - Short one 1-year contract to sell the index at 1,701 in 1 year - Borrow exactly exp(-1%) x 1,670 = 1,653.38 , at the risk-free rate 2% for1 year (to buy 0.99005 units of the index)In 1 year:- The dividend yield paid on your holdings will make you having exactly 1unit of index- You deliver the index for 1,701 according to your short contract- You pay back your loan at 1,653.38 x exp(2%) = 1,686.78 - Your profit is then (1,701 – 1,686.78) = 14.2162Your net dollar profit is $100 x 14.2162 = $1,421.62Question 2 (6 marks)Consider a coupon-bearing bond selling at $950 and paying coupons in 5 months and 11 months from today. The risk-free interest is 2% per annum continuously compounded. The face value of the bond is $1,000.(a) If the 1-year forward contract on this bond is selling at a fair price of $949.05, what is the coupon rate? (2 marks)(b) What is the theoretical 6-month forward price? (1 mark)(c) The 6-month forward contract is selling at $955 in the market. Is there any arbitrage opportunity? If yes, show how to benefit from it. Show all details.(3 marks)Solution(a) We know that %)2exp()950($05.949$×−=I where:())12/11%2exp()12/5%2exp(×−+×−×=Coupon ISolving for the coupon, we find that the coupon is $10, which means that the coupon rate 2% APR semi-annually compounded.(b) Given that the coupon is $10, the theoretical price for the 6-month contract must be:()[]53.949$)5.0%2exp(12/5%2exp 10$950$0=×××−−=F(c) Since the contract is overpriced by the market, an arbitrageur can lock in a profit by borrowing/buying the bond and taking a short 6-month forward.Here are the details of the strategy:Today- Borrow a total amount of $950 to buy the bond:o Borrow $9.92 at 2% today to be reimbursed at $10 in 5 months (thisis exactly the coupon that you would receive in 5 months)o Borrow ($950 - $9.92 = $940.08) at 2% today to be reimbursed at$949.53 in 6 months-Short one forward contract today to sell the bond at $955 in 6 monthsIn 5 months-Receive the coupon of $10 and pay back the small part of the loanIn 6 months-Deliver the bond at $955-Pay back the large part of the loan at $949.53-The net profit is $5.47Question 3 (6 marks)Consider a Canadian company that is planning to buy some equipment from aBritish manufacturer in Oct 1, 2009 (that is in one year). The cost of this machinery is GBP 10 million. You have been asked to analyze the consequencesof entering into a futures contract to reduce the company’s exposure to foreign exchange risk. The current quotes are available from the market:Spot CAD/GBP 1.90Canadian TBill Rate 2%UK TBill Rate 3%(a) What is the theoretical 1-year (October 2009 contract) forward CAD/GBP?(2 marks)(b) Based on the following scenarios for the spot exchange rate one year fromnow, CAD/GBP = 1.7 or 2.1, explain why the company should hedge itscurrency risk exposure. Explain which strategy may be appropriate for thecompany and what will be the total cost (for the equipment) in CAD in oneyear. (2 marks)(c) Assume now that you enter into the strategy proposed in (b) and that aftersix months, i.e. April 1, 2009, the management of the company decides tobuy immediately the equipment from the British manufacturer and to closeout the forward position. Assume that on April 1, 2009, the spot CAD/GBP= 1.95, the forward (with six months remaining to the maturity) rateCAD/GBP = 1.93, what is the effective total cost in CAD for theequipment? (2 marks)Solution(a) The 1-year forward contract is given by:()()8811.11%)3%2(exp 90.1)(exp 000=×−×=×−×=F T r r S F f(b) CAD/GBP 1.70 2.10Cost CAD 17 million CAD 21 millionThis shows that the company has a considerable exchange rate risk exposure. If the exchange rate moves from 1.9 to 1.95 over one year, the company makes a loss of CAD 500,000! The company will face a loss if the exchange rate CAD/GBP increases dramatically since it will have to buy GBP 10 million.To hedge against any dramatic increase, the firm must take a long position in the 1-year forward to buy GBP at CAD 1.8811. The total cost will be CAD 18.811 million (= GBP 10 million x 1.8811) whatever the spot exchange rate will be in one year.(c) The company decides to buy the machinery after six months for GBP 10 million at CAD/GBP = 1.95, that is a cost of CAD 19.5 million. On the other hand, the company makes a net profit of CAD 0.4841 million on the forward position, (1.93 – 1.8811) x exp(-2% x 0.5) x 10 = 0.4841. Therefore, the effective total cost is 19.5 – 0.4841 = CAD 19.0159 million, or equivalently a CAD/GBP of 1.9016.Question 4 (6 marks)The Aluminum sells at $1.20 per pound and it has a convenience yield y = 2%, and a storage cost of 1% (per annum continuously compounded). The risk-free interest rate is 4% per annum continuously compounded. An investor takes a short position in a 1-year futures contract on Aluminum today. Assume that each contract is on 44,000 pounds.(a) What is the 1-year futures price per pound? (2 marks)(b) Suppose that the investor closes out her position 9 months from now and makes a total profit of $2,200. What is the spot price of Aluminum 9 months from now if there is no arbitrage? (4 marks)Solution(a) The theoretical 1-year futures price is $1.20 x exp(4% + 1% - 2%) = $1.2365(b) If the investor makes a $2,200 total profit on her short position in 9 months, or a $0.05 (= 2,200 / 44,000) profit per pound, this means that the futures price 9 months from now is $1.1865 and that the contract has 3 months remaining. The spot price in 9 months is then given by:S = 1.1865 x exp(-3% x 0.25) = $1.1777Question 5 (6 marks)A portfolio manager has sold short a portfolio of stocks worth $100 million for three months. The beta of the portfolio is 2. The manager would like to use the CME futures contract on the S&P 500 index to hedge the portfolio over the next three months. The index is currently 1,200 points, and each contract is on $250 times the index. The S&P 500 dividend yield is 1% and the risk-free rate is 2%.(a) How many long or short positions should the manager take? (4 marks)(b) What would be the net gain/loss in three months in the following scenarios? (2 marks)Scenario Portfolio value In 3 months S&P 500 Futures In 3 months 1 $110 million 12602 $90 million 1140Solution(a) First, we need to calculate the theoretical S&P 500 futures price today:1200 x exp[(2%-1%) x .25] = 1203.Since the manager is short selling the portfolio, any rise in the stock market would cause big losses. The manager should then take long S&P 500 futures contracts, exactly 665 contracts:6651203250$000,000,100$2*=××==F P N β(b) The net gain/loss for each scenario is given by the gain/loss on the shortposition on the portfolio added to the gain/loss on the futures position.Scenario 1: (100 – 110) million + 665 x 250 x (1260 – 1203) = –$523,750 Scenario 2: (100 – 90) million + 665 x 250 x (1140 – 1203) = –$473,750Atkinson Faculty of Liberal and Professional StudiesYORK UNIVERSITYToronto, OntarioADMS 4503 3.0Derivative SecuritiesTahaniProfessor NabilSections A and BAssignment #1Due Date: October 19, 2008Personal Work StatementI, the undersigned:•warrant that the work submitted herein is my work and not the work of others •acknowledge that I have read and understood the Senate Policy on Academic Honesty•acknowledge that it is a breach of the University Regulations to give and receive unauthorized assistance on a graded piece of workName (typed or printed) York Student # Signature。



Chapter 5+6+8 AssignmentsP5.Consider the 5-bit generator, G= 10011, and suppose that D has the value 1010101010. What is the value of CRC?Solution:If we divide 10011 into 1010101010 0000, we get 1011011100, with a remainder of R=0100.P21. Suppose nodes A and B are on the same 10Mbps Ethernet bus, and the propagation delaybetween the two nodes is 245 bit times. Suppose A and B send frames at the same time, the frames collide, and then A and B choose different values of K in the CSMA/CD algorithm. Assuming no other nodes are active, can the retransmissions from A and B collide? For our purposes, it suffices to work out the following example. Suppose A and B begin transmission at t =0 bit times. They both detect collisions at t =245 bit times. They finish transmitting a jam signal at t = 245 + 48 = 293 bit times. Suppose K A =0 and K B = 1. At what time does B schedule its retransmission? At what time does A begin transmission? (Note: The nodes must wait for an idle channel after returning to Step 2 -- see protocol.) At what time does A's signal reach B? Does B refrain from transmitting at its scheduled time?Solution:Because A's retransmission reaches B before B's scheduled retransmission time (805+96), B refrains from transmitting while A retransmits. Thus A and B donot collide. Thus the factor 512 appearing in the exponential backoff algorithm is sufficiently large.P23. Suppose four nodes, A, B, C, and D, are all connected to a hub via 10Mbps Ethernet cables.The distances between the hub and these four nodes are 300m, 400m, 500m, and 700m, respectively. Recall that the CSMNCD protocol is used for this Ethernet. Assume that the signal propagation speed is 2*108m/sec.a. What is the minimum required frame length?b. If all frames are 1500 bits long, find the efficiency of this Ethernet.Solution:a). minimum required frame length is given by2*d prop* BW=2*(500+700)/( 2 108) * 10 * 106=120 bits.There is no maximum required packet length.b). Efficiency is given by1/(1+5* d prop/ d trans) =1/(1+5*120/2/1500 )=0.83P37. In this problem, you will put together much of what you have learned about Internetprotocols. Suppose you walk into a room, connect to Ethernet, and want to download a web page. What are all the protocol steps that take place starting from powering on your PC to getting the web page? Assume there is nothing in our DNS or browser caches when you power on your Pc. (Hint: the steps include the use of Ethernet, OHCP, ARP, ONS, TCP, and HTTP protocols.) Explicitly indicate in your steps how you obtain the IP and MAC addresses of a gateway router.Solution:(The following description is short, but contains all major key steps and key protocols involved.)Your computer first uses DHCP to obtain an IP address. You computer first creates a special IP datagram destined to 255.255.255.255 in the DHCP server discovery step, and puts it in a Ethernet frame and broadcast it in the Ethernet. Then following the steps in the DHCP protocol, you computer is able to get an IP address with a given lease time.A DHCP server on the Ethernet also gives your computer a list of IP addresses of first-hop routers, the subnet mask of the subnet where your computer resides, and the addresses of local DNS servers (if they exist).Since your computer’s ARP cache is initially empty, your computer will use ARP protocol to get the MAC addresses of the first-hop router and the local DNS server.Your computer first will get the IP address of the Web page you would like to download. If the local DNS server does not have the IP address, then your computer will use DNS protocol to find the IP address of the Web page.Once your computer has the IP address of the Web page, then it will send out the HTTP request via the first-hop router if the Web page does not reside in a local Web server. The HTTP request message will be segmented and encapsulated into TCP packets, and then further encapsulated into IP packets, and finally encapsulated into Ethernet frames. Your computer sends the Ethernet frames destined to the first-hop router. Once the router receives the frames, it passes them up into IP layer, checks its routing table, and then sends the packets to the right interface out of all of its interfaces.Then your IP packets will be routed through the Internet until they reach the Web server.The server hosting the Web page will send back the Web page to your computer via HTTP response messages. Those messages will be encapsulated into TCP packets and then further into IP packets. Those IP packets follow IP routes and finally reach your first-hop router, and then the router will forward those IP packets to your computer by encapsulating them into Ethernet frames.Additional 1: Please answer the following question after reading Chapter 6 and referring tothe ftp:///chapt6.pdf . What are MAC methods for WiFi, Bluetooth, WiMax and Cellular network respectively? What are RDT approaches for WiFi, Bluetooth, WiMax and Cellular network respectively? error detection + retransmisstion or error correction?Solution:The following table summarizes the wireless MAC and RDT technologies. Each needs to be explained in detail.Additional 2:Why WiFi can’t CSMA/CD?Solution:Because Collisions Detection is difficult for WiFi:∙hidden terminal problem !∙difficult to sense because of fading∙Most radios are half duplexAdditional 3: Please explain how public key cryptography RSA is used in email security protocol: PGP (Pretty Good Privacy). Please refer to Chapter 8Solution:Step 1: Calculate hash (MD5) of message H(m). => you’ve got the digest of the messageStep 2: Encrypt H(m) with Alice’s private key => you’ve got Alice’s signature.Step 3: Append signature to text, then encrypt it with shared key Ks.Step 4: Encrypt shared key Ks with Bob’s public key, then append to the cipher text of step 2 => Bob can get the Ks.Step 5: The result message of step 4 is converted to base64 and be put into an RFC 822 body and be expected to arrive unmodified.D2 (don’t submit) Many of the functions of an adapter can be performed in software that runs onthe node's CPU. What are the advantages and disadvantages of moving this functionality from the adapter to the node?。

Core Marker’s Comment SheetCourse Name: Strategic Financial Management (PA2)Assignment: 2Module: 2General CommentsCore Marker’s Comments are not full solution sets to the case assignments. Rather, they are intended to provide students with guidance in responding to each of the assignment questions by providing direction as how to respond, clarification/direction on complex readings; layout and format suggestions; and from time to time, illustrations of possible response segments.Part A: Multiple-choice questionsFor the multiple-choice questions, these Marker’s Comments will provide you with the correct answer for each question, as well as the rationale for why the answer is the best choice, and the linkage to the main competency being assessed. Compare these comments with your own responses and rationale to identify areas where you may need further review of the Module Notes or other resources provided in the course material.Question 1a) The correct answer is 3. Arbitrary allocations of fixed cost are not to be considered whiledetermining whether a product line should be continued or dropped.Options 1, 2, and 4: These are incorrect as they are important factors to be considered in the decision on whether to drop a product line.Competency:PK:MA:03 — Identifies, assesses, and advises on information required for management decision making (cost-volume-profit relationships, cost classifications and flows, market or industry data, non-financial factors)b) The correct answer is 1. Sufficient appropriate evidence of the physical existence and conditionof inventory is a GAAS requirement.Option 2: This is incorrect because a 100% verification of inventory is not required if sufficient audit procedures are undertaken.Option 3: This is incorrect because supervision of inventory counts is not required if considered to be impracticable and the auditor conducts alternative audit procedures.Option 4: This is incorrect because the auditor can use the services of an employee or specialist hired by the client who has special expertise in the nature of the inventory.Competency:PK:AS:06 — Develops and/or modifies procedures for the engagement or management audit (prepares review or audit procedures, modifies audit procedures in the presence of fraud risk factors or known errors)c) The correct answer is 3. It is a violation of professional ethical standards to divulge confidentialinformation to one’s own personal advantage. (CEPROC R203)Options 1, 2, and 4: These are incorrect since they breach the Professional Code of Ethics.Competency:PR:ET:06 — Ensures confidentiality of stakeholder information (protects proprietary information) d) The correct answer is 2. CAS 710.18 states that the auditor should communicate themisstatement with the appropriate level of management. There is no mention of an audit committee, so the President would be the next appropriate level.Option 1: This is incorrect because you cannot ignore material misstatements found in the prior year’s financial statements.Option 3: This is incorrect because this does not provide any communication to the appropriate level of management or to the predecessor firm.Option 4: This is incorrect because you cannot re-audit/re-issue the previous year’s financial statements.Competency:PK:AS:06 — Develops and/or modifies procedures for the engagement or management audit (prepares review or audit procedures, modifies audit procedures in the presence of fraud risk factors or known errors)e) The correct answer is 1. “Componentization” (PPE IAS 16) requires that each separate physicalcomponent be capitalized and amortized as a separate component of the asset over the period that the benefit is enjoyed.Option 2: This is incorrect because it is not an expense. It is a substantial amount and the benefit is more than one period.Option 3: This is incorrect because it is not an expense.Option 4 is incorrect because the depreciation would be over the period for which the benefit of the amount spent is realized, not over the useful life of the machine.Competency:PK:FA:01 — Formulates, analyzes, and processes transactions in accordance with applicable professional standards (standards for not-for-profit, public and private corporations, and the public sector)f) The correct answer is 4. A change in accounting policy may involve restatement or retrospectivetreatment, and the prospective approach that is used for accounting changes may not be used to report.Options 1, 2, and 3: This is incorrect because the prospective approach may be used in this situation.Competency:PK:FA:02 — Evaluates, interprets, and advises on accounting policies and procedures in accordance with professional standards (standards for not-for-profit, public and private corporations, and the public sector)g) The correct option is 4. This is passive rental income and not in the nature of “business,” and is tobe taxed as Income from Property.Options 1, 2, and 3: This is incorrect because it is an “active” rental income and is to be taxed as Income from Business.Competency:PK:TX:02 — Determines and advises on taxpayer’s tax liability (taxes related to income, consumption, payroll, property)h) The correct option is 1. External auditors are required to be independent of the company beingaudited and also must evaluate the knowledge, competence, and independence of the internal auditor.Option 2: This is incorrect because an external auditor is not an employee of the company;rather, they are hired on a contractual basis.Option 3: This is incorrect because the scope and objectives of internal audit vary widely and may depend on the size and structure of the company and the requirements of its management. The objectives of internal audit may differ from those of the external auditor.Option 4: This is incorrect because a duty of care is required on the part of both the internal and external auditor (as laid out in the code of ethics).Competency:PK:AS:05 — Develops a plan for the engagement or management audit (staffing, use of specialists, time budget, technological tools, timing of the engagement, timing of the management audit)Part B: Case questionQuestion 1: Synamex Effects Limited (SEL)For this question, you are to assume the role of SEL’s new controller and write a memo to the owners of the company. Under the “Required” there is minimal guidance as to what is required. Thus, you need to read the case carefully to determine the issues which need to be addressed in your memo.The main issues and core and core-related competency areas that you should have identified and discussed in your written solution include:1. Financial accounting and reporting: identifying the weaknesses of the current financial reportingsystem, such as the lack of forecasting tools. You could have also included recommendations, such as advising on specific reports that should be prepared on a regular basis.2. Management accounting: explanation on how the new accounting software package could beuseful to the company, in particular with providing costing information.3. Finance: key risks in SEL’s business should have been identified and discussed. These risks mayhave included lack of accounting experience and foreign exchange risk. As well, issues related to the current cash flow management problems should have been identified and explained.4. Ethics and trust: concerns should have been raised about the delay in paying the liabilityinsurance.5. Assurance: the impact on the company’s assurance needs as a result of the proposed IPOshould have been identified and discussed. This may have included discussion points such as: (i) audited financial statements prepared under IFRS required and (ii) audit costs are higher.6. Information technology: an evaluation should have been completed on the three accountingsoftware packages. The features and benefits of each package should have been compared and contrasted with the others. An overall recommendation supported by the evaluation may have been made.Your solution should have also demonstrated the professional qualities and skills competencies which were also being assessed. In order to have adequately demonstrated these competencies, you may have included the following points or demonstrated the following:1. Communication: ensuring the written response was in a memo format and properly addressed tothe owners of SEL. The memo should be well-organized, use appropriate headings, and be understandable (few assumptions are required to be made).2. Professional self-evaluation: explaining that an IT specialist be hired.3. Problem solving: ensuring that relevant information and features of each accounting packagewere brought into the evaluation.4. Integrative approach: focusing solutions, where appropriate, beyond the short-term. For example,explaining the benefits of preparing long-term budgets for SEL.A leadership competency was also being assessed in this case.Comments on the solutionYou may not be expected to provide all the issues and areas mentioned, but this would be a good approach to the case. Also, remember that these comments are not exhaustive – you may have raised other relevant and valid issues for which credit would be given.Be sure to use the correct format (in this case a memo addressed to the owners) and follow through each issue with an analysis and a logical recommendation.。
(Partial) Solutions to Assignment 2pp.73-761.16In each of the following systems, let or be the input and or be the output. Determine whether each systems is (1) linear, (2) time invariant, (3) causal, (4) BIBO stable(g).(i).ans: omitted----------------------------------------------------1.17 A linear time invariant system has impulse response Determine the output sequence for each of the followign input signals:(b)(f)(b) ans:h n is given byThe z-transform of []where ROC1:x n is given byz-transform of []where ROC2:h n is given byTherefore, the z-transform of the output []y nPerform inverse z to get [](f) ans: using the same method as in (b) (details omitted )----------------------------------------------------1.18. A linear time invariant system is defined by the difference equationb. Determine the output of the system when the intpu isc. Determine the output of the system when the input isans: omitted----------------------------------------------------1.19 The following expressions define linear time invariant systems. For each one determine the impulse respnose(a)(e)(a) ans: the impulse response is(e) ans: the impulse response is----------------------------------------------------1.20 Each of the following expressions defines a linear time invariant system. For each one determine whether it is BIBO stable or not(g)(k)BIBO: Bounded input and bounded output(g) ans: omitted(k) ans: omitted----------------------------------------------------1.21. Using the geometric series, for each of the following sequence determine the z-transform and its ROC(d)(g)(i)(d) ans:where ROC:(g) ans:The first part is equal towhere ROC1 isThe second part is equal towhere ROC2 isTherefore combining both parts:where ROC={ROC1 and ROC2}:(i) ans:where ROC: whole complex domain----------------------------------------------------1.22. You know what the and are. Using theproperties only (do not reuse the definition of the z-transform.) determine the z-transform of the following signals(c)(g)where ROC1:where ROC2:(c) ans: using z-transform property:We have:where ROC:(g) ans:details omitted. The final answer isTherefore combining both parts:where ROC={ROC1 and ROC2}:----------------------------------------------------1.23 Using partial fraction expansion, determine the inverse z-transform of the following functions:(c) ,(e) ,(c) ans:(e) ans:procedures are the same as above. details omitted.----------------------------------------------------1.24. For each of the followign linear difference equations, determine the impulse response, and indicate whether the system is BIBO stable or not(a)(c)(a) ans:Take z-transform on both sideswhere ROC:Because is finiteTherefore, the system is BIBO stable(c) ans: omitted (the same as (a))----------------------------------------------------1.25. Although most of the time we assume causality, a linear difference equation can be interpreted in a number of ways. Consider the linear difference equation(a) Determine the transfer function and the impulse response. Is the system causal ? BIBO stable ?(a) omitted.----------------------------------------------------1.26. 1.26 Consider the linear difference equation(a) Determine the transfer function . Do you have enough information to determine theregion of convergenceans:Don't have enough information to determine ROC.----------------------------------------------------1.27. Given the system described by the linear difference equationDetermine the output for each of the following input signals(a)(e)(a) ans:Take z-transform on both sides:----------------------------------------------------1.28. Repeat Problem 1.27 when the system is given in terms of the impulse responseBefore you do anything, is the system stable ? Does the frequency responseexist ?ans: omitted.----------------------------------------------------1.29. Repeat Problem 1.27 when the system isgiven by the linear difference equationBefore you do anything, is the system stable ? Does the frequency response exist ?Ans: omitted.----------------------------------------------------。
VIDEOMANAGER 15.2.3 RELEASE NOTE Software updated in 15.2.3●Motorola Solutions VideoManager for Windows●Motorola Solutions VideoManager for CentOS Linux●VT50 / VT100 firmware●EdgeController firmware●User Import ToolChanges since 15.2.1New feature: VT50 / VT100 microphone fault detectionVT50 / VT100 devices can now self-detect damage to the microphone. If a problem is detected, the fault is reported on the device details page and in the equipment report. Battery faults detected by cameras are reported in the same way. [SW-1739]Software updated in 15.2●Motorola Solutions VideoManager for Windows●Motorola Solutions VideoManager for CentOS Linux●VB400 firmware●EdgeController firmware●DockController firmware●User Import ToolChanges since 15.1.11New feature: TranscriptionsThere is now a transcription editor which makes it easy to manually enter a transcription of the audio on an incident clip. The resulting transcription can be overlaid on the video during export or included in evidence exports as a PDF file. [SW-1093]Terminology change: Videos are now MediaIn recognition of the fact that many customers use Motorola Solutions VideoManager to store media and assets which are not video files, the UI now uses the term "media" where previously it used the term "video" or "videos". [SW-1257]New feature: VB400 WiFi access point modeVB Companion can now be configured in WiFi Access Point mode. The VB400 will act as a WiFi access point which can be connected to by a mobile device running a version of VB Companion that supports this connectivity mode. In access point mode the WiFi status LED will blink when the access point is ready and go solid when a device connects. When the VB companion isconfigured in access point mode in the selected device profile it is not possible to select a WiFi profile, because the VB400 cannot support being both a WiFi access point and a WiFi station.[S34W-1481, SW-1960]New feature: VB companion proximity security modeThe VB Companion Settings in Motorola Solutions VideoManager can now configure a new "Proximity controlled security" mode. When used in conjunction with versions of the VB companion that support this mode, the VB400 will connect with a nearby mobile device that is attempting to connect. To activate the connection on the VB400, a new "Connect device" button action can be configured in the device profile. [SW-1611]New role permissionsPermission Section Notes On upgrade, granted toView transcription (new/existing/duplicate)Incidentpermissions/Incidentclips(3 permissions)System AdministratorEdit transcription (new/existing/duplicate)Incidentpermissions/Incidentclips(3 permissions)System AdministratorImport transcription (new/existing/duplicate)Incidentpermissions/Incidentclips(3 permissions)System AdministratorExport transcription (new/existing/duplicate)Incidentpermissions/Incidentclips(3 permissions)System AdministratorEdit user property (supervised/any)Userpermissions/User(2 permissions)Roles with permission toedit authentication IDMinor enhancements and bug fixes (Motorola Solutions VideoManager) Issue Id SummarySW-1718Added support for two new ways of connecting the VB Companion to a camera: WifiDirect and Wifi AP mode (which requires a new 'connect peripheral' gesture for thedevice when used in conjunction with 'proximity security' mode). Note that not allversions of the VB Companion app support all connection methods.SW-1680Added support for "proximity security" model for the VB Companion app which allows the app to be provisioned without connectivity between the app and MotorolaSolutions VideoManager. Note that not all versions of the VB Companion appsupport this mode.SW-1424The system will automatically create three new "media" roles on new installs.SW-1603An auto-file export can now optionally include a metadata file created from a template.SW-1549Auto-file export now supports advanced template generation of file names and folders for auto export.SW-1623User's now have a new editable and importable field called "user property". This field can be accessed in filename and metadata file templates in export.VM-22411You can now configure which media fields are displayed in the "large" video summary view.VM-22400The list of columns shown in the media list view is now configurable.VM-23076The device profile now allows you to enable APX radio integration (if you enable this feature in the "Experimental Features" page).VM-22294You can now create a "preparation" on a video as well as a still image.VM-22307The media list view now has a "play" button which allows you to play all the videos in the list in turn.VM-22891The user import tool can now clear fields (e.g. touch assign ID) by importing the value 'NO_VALUE'.VM-22293Media support: import of MP4 files which use the Opus 3 audio codec is now supported.SW-1790The user import tool can now be configured to execute SQL statements prior to importing data to support advanced data manipulation.SW-1564In the device profile when radio integration is enabled, you can now configure a "regex" to control which radios the VB400 will attempt to connect to automatically(based on the Bluetooth name of the radio).SW-955The system can now be configured to send an HTTP notification when a live stream is no longer available.SW-898When live streaming via the VB Companion app, the device ID of the device runningthe app is now available via the device status API.SW-199 A new installation now requires that the administrator enter a complex and long password for the initial account.VM-23340When using the config import function to import roles from different source systems, the roles assigned to users were wrongly swapped around in certain circumstances.SW-935Reduced the server-side CPU utilization required for VB400 live view.VM-23241The "include forgotten devices" checkbox in the device list filter was not cleared when the filter was reset.VM-23124Export profile import/export no longer attempts to import or export the "restrict to users/groups" setting.VM-23142The evidence export profile editor did not allow filename templates to be configured if the inclusion of that file was optional in the profile.SW-1659Configuring Video Metadata Overlay settings which were unsupported by old sites/EdgeControllers broke configuration replication to old sites/EdgeControllers.SW-1780Ensure that new settings use their default values when importing device profiles exported from older versions of the product.SW-964Added the API/Swagger documentation for the device status and assignment APIs.SW-1284Security change: the list of users in the system is no longer cacheable by the browser for auto completion purposes.SW-1660The login via email function now shows an error message if the user does not log in via the public web address.SW-654Security update: Updated many libraries used, including fixing some containing CVEs. None of these CVEs are believed to have represented a vulnerability inMotorola Solutions VideoManager.VM-23242The DockController list filter panel is no longer minimized when it is reset.VM-23165The system now better regulates the replication of metadata replication from sites to ensure that central manager systems with a slow database are not overwhelmed. SW-1910Minor improvements have been made to the way that columns are laid out in the video list and incident list.VM-23021The documentation shortcut installed in the Windows Start menu did not point to the correct file.SW-1168The system no longer produces a file in the backup folder containing a list of all files which are in incidents.Minor enhancements and bug fixes (VB400)Issue IdSummary SW-1481SW-1960Support has been added for WiFi access point mode.SW-1611Support has been added for VB companion proximity security mode.SW-1387Support has been added for VB companion WiFi direct mode.SW-1109SW-1563The Motorola radio integration now supports APX radio models & additional MOTOTRBO models.SW-1618The VB400 did not always reconnect to newly paired MOTOTRBO radios after reassignment.SW-1558On some recent revisions of the VB400 the GPS subtitle track was missing from MP4video files.SW-1595The battery state of charge as shown in the VB companion and video metadata overlay is now available if the battery is being charged.SW-1853If the VB400 was docked with the VB companion connected with WiFi, then theVB400 could attempt to reconnect WiFi after reassigning & undocking even if the VBcompanion is no longer connected.SW-1941Live view in the VB companion did not work if the audio codec for VB400 recordingsand streaming was configured as PCM.VM-22200Playback in the VB companion sometimes required a manual scrub to play beyond acertain point.SW-1453SW-2018The LED battery status shown on a button press was not always correctly showingred for critical if the VB400 was docked and undocked without being charged to anon-critical level.Minor enhancements and bug fixes (VT50/VT100)Issue IdSummary SW-1496The device can now self-detect damage to the microphone.SW-1576Devices unable to connect to Motorola Solutions VideoManager for a long time couldbecome "Locked" and inoperable.Minor enhancements and bug fixes (DockController)Issue Id SummarySW-1341Security update: use the latest version of OpenSSL.Minor enhancements and bug fixes (EdgeController)Issue Id SummarySW-1341Security update: use the latest version of OpenSSL.Minor enhancements and bug fixes (User Import Tool)Issue Id SummaryVM-22891The user import tool can now clear fields (e.g. touch assign ID) by importing the value 'NO_VALUE'.SW-1790The user import tool can now be configured to execute SQL statements prior to importing data to support advanced data manipulation.Earlier changesSee the V15.11 release notes for earlier changes.Known issuesVB400 Bluetooth and Wifi are incompatibleWiFi streaming and download over WiFi cannot be used on a VB400 when it is configured to connect to the VB Companion App over Bluetooth.VB400 Live-view for Android companion app does not work with X-100 or X-200The Live-view for Android companion app feature does not currently work if the X-100 or X-200 external cameras are attached.VB400 WiFi offload of footage can make X-100 or X-200 unreliableIf you configure the device to offload footage over WiFi, then in-progress offloads can sometimes cause the operation of an X-100 or X-200 external camera to be unreliable. It is not currently recommended to enable WiFi offload if using an external camera.DockController assignment groups with overriden device settingsIf you set up multiple DockControllers to share a single RFID reader, then you must ensure that all the DockControllers in the group share the same RFID assignment charge criteria (these can now be overridden for each DockController). If the charge criteria for the DockControllers in the group are not the same, then you may unexpectedly be unable to assign a device in some circumstances.Large Numbers of Incident Clip CountsThe system performs poorly when more than 200 incident clips are created in a single incident. You should not create incidents with more than this many clips. Some functions may not work properly if this limit is exceeded, e.g. export may fail.Upgrade notesInternet Explorer support has endedInternet Explorer is no longer a supported browser.Postgres database upgradeIf you are using the bundled Postgres database server rather than Microsoft SQL Server, and you are upgrading a version earlier than 15.1.0, be aware that when this release is installed, the database must be upgraded to Postgres 13.3. Depending on the size of your database, this can be a time consuming process and it temporarily consumes a significant amount of disk space.HTTP Basic Authentication DisabledSome security analysts now consider the ability to authenticate HTTP requests with "Basic" authentication to be a security vulnerability. For this reason, the Motorola Solutions VideoManager web APIs no longer allow clients to use HTTP Basic authentication. If you directly access the API and you use Basic authentication then you should either switch to using HTTP Digest authentication, or you can re-enable Basic authentication by adding the following text to Admin>System>Advanced Settings:api.key.basic.auth=trueYou should only do this if you are satisfied this does not constitute a security risk in your environment.Microsoft SQL Server TLS requirementsFor installations which use Microsoft SQL Server as the Motorola Solutions VideoManager database, be aware that SQL Server must support TLS 1.2 encryption or the Motorola Solutions VideoManager service cannot connect to it. If you are using SQL Server 2012 and 2014 please ensure that you have the latest service packs installed to ensure TLS 1.2 compatibility.Software assurance requirement for upgradeIn order to upgrade to this version from an older version, you must have software assurance coverage up to 10 September 2021. If you are upgrading from a version older than 10.2, then you must upgrade to 10.2 and install software assurance before installing this version.Licensing change: Asset Import Licensing ChangesThe way that asset import is licensed has changed. The feature is now automatically enabled on all installations by default (along with the media properties feature). However, asset import will only work if your system has a sufficient number of "media user" licenses. A media user is any user who has permission to use the asset import feature. Existing customers should be unaffected by these changes as existing asset import licenses will grant an unlimited number of "media user" licenses. Also note that as a consequence, the built-in "System Administrator" role no longer grants permission to perform an asset import. [SW-1423, SW-1086]Central manager site upgradesWhen upgrading a central manager installation, replication of certain configuration settings from the central manager to sites (including EdgeControllers) will not occur until those sites are upgraded.If you use any of the "Shared configuration settings" - on the Auto-fetch settings page - to replicate configuration information to sites, then the site will use out-of-date configuration information until upgraded to the minimum required version for that setting. Configuration changes made on the central system will have no effect until the site is upgraded.The following table shows the minimum required version of Motorola Solutions VideoManager running at the site in order for each shared configuration setting to replicate correctly.Shared configuration setting Minimum compatible site versionKeys 5.1.0Roles & Password Rules 6.4.0Users14.5.0 **User Groups14.0.0Device Profiles 6.4.1Deletion policies 6.4.0User-defined fields14.1.0 if you enable playback reason auditing14.0.0 if you define any tag list fields6.4.0 otherwiseDevice states and locations10.0.0** - users can be replicated to sites running 7.0.1 to 14.4.x, but an incompatibility warning will be shown and bluetooth pairing information will not be replicated.Supported platformsMotorola Solutions VideoManager is supported on the following platforms:●Windows 8.1 Pro & Enterprise 64-bit‡●Windows 10 Pro & Enterprise 64-bit●Windows 11 Pro & Enterprise●Windows Server 2012 Essentials, Standard & Datacenter *●Windows Server 2012 R2 Essentials, Standard & Datacenter *●Windows Server 2016 Essentials, Standard & Datacenter * **●Windows Server 2019 Essentials, Standard & Datacenter * **●Windows Server 2019 Essentials, Standard & Datacenter * **●Windows Server 2022 Essentials, Standard & Datacenter * **‡ This is the last major version of VideoManager that will support Windows ers still running VideoManager on Windows 8.1 should plan to upgrade to Windows 10 or a suitable server edition of Windows before the next major release of VideoManager.* Accessing the Motorola Solutions VideoManager web application from a web browser running on a Windows Server desktop is not supported. However, Windows Server can be used for running the Motorola Solutions VideoManager service.** USB attached devices are not supported on Windows Server 2016 and later.Supported browsersThe Motorola Solutions VideoManager web application is supported on the following browsers:●Microsoft Edge 79+ (Windows 10/11)●Chrome 48+ (Windows 7/8.1/10/11, MAC OS X v10.10)●Firefox 68 ESR+ (Windows 10/11, Ubuntu 18.04+) *The security settings of your browser may prevent some features of the Motorola Solutions VideoManager web application from working correctly. In particular, some browsers maysilently prevent the download of files from the Motorola Solutions VideoManager web application. Adding Motorola Solutions VideoManager web application to the list of trusted websites will normally fix this.Accessing the Motorola Solutions VideoManager web application from a web browser running on a Windows Server desktop is not supported.* When using Firefox on Windows, you may need to run Windows Media Player once to install codecs before video playback will work. Firefox video playback only works if the operating system provides an MP3 codec. When using Firefox on Ubuntu, you must install a package which provides H.264 and AAC codecs for Firefox, e.g. libavcodec-extra.Supported device firmwareWe do not support assignment of devices running firmware older than version 6.0. These devices will still connect but only for the purposes of upgrading them.Included device firmwareThis release of Motorola Solutions VideoManager includes the following firmware:VB400 firmware V15.2.0VB200 / VB300 firmware V14.4.4VT50 / VT100 firmware V15.1.11DockController firmware V15.2.0Supported radiosThe VB400 Motorola radio integration features are supported in conjunction with the following models:●Any TETRA Radio with Bluetooth hardware and MR19 software or higher with BluetoothConnectivity and Bluetooth Radio Control features enabled.。
Homework Assignment 2InstructionsThis assignment is due to be turned in at the start of class on Wednesday February 11. You can work on this assignment by yourself or in a team of two. If you choose to work in a team of two, you should turn in only one assignment per team (with both member’s student IDs on the assignment).The assignment consists of two parts. Part A contains discussion questions. These are NOT to be turned in, they are intended to solidify your understanding of the theoretical concepts that we have discussed. I suggest writing down your answers and comparing them with the solutions that I will upload once the assignments have been turned in. Part B contains assignment problems that must be turned in. Remember that these assignments are graded on a √- ,√, √+ system as detailed in the syllabus. You are free to turn in printouts or a clear, legible, handwritten assignment.Part A: Discussion questions (not to be turned in).1.Explain carefully why liquidity preference theory is consistent with the observation thatthe term structure of interest rates tends to be upward sloping more often than it is downward sloping.If long-term rates were simply a reflection of expected future short-term rates, we would expect the term structure to be downward sloping as often as it is upward sloping. (This is based on the assumption that half of the time investors expect rates to increase and half of the time investors expect rates to decrease). Liquidity preference theory argues that long term rates are high relative to expected future short-term rates. This means that the term structure should be upward sloping more often than it is downward sloping.2.What is meant by (a) an investment asset and (b) a consumption asset? Why is thedistinction between investment and consumption assets important in the determination of forward and futures prices?An investment asset is an asset held for investment by a significant number of people or companies. A consumption asset is an asset that is nearly always held to be consumed(either directly or in some sort of manufacturing process). The forward/futures price can be determined from the spot price for an investment asset. In the case of a consumptionasset all that can be determined is an upper bound for the forward/futures price.3.What is the cost of carry for (a) a non-dividend-paying stock, (b) a stock index, (c) acommodity with storage costs, and (d) a foreign currency?a)the risk-free rate, b) the excess of the risk-free rate over the dividend yield c) therisk-free rate plus the storage cost, d) the excess of the domestic risk-free rate over theforeign risk-freerate.4. Do we expect the futures price of a stock index to be greater than or less than the expected future value of the index? Explain your answer.The futures price of a stock index is always less than the expected future value of the index. This follows from Section 5.14 and the fact that the index has positive systematic risk. For an alternative argument, let μ be the expected return required by investors on the index so that ()0()q T T E S S e -=μ. Because r >μ and ()00r q T F S e -=, it follows that 0()T E S F >.Part B: Homework problems (to be turned in)1. The cash prices of six-month and one-year Treasury bills are 94.0 and 89.0. A 1.5-year bond that will pay coupons of $4 every six months currently sells for $94.84. A two-year bond that will pay coupons of $5 every six months currently sells for $97.12. Calculate the six-month, one-year, 1.5-year, and two-year zero rates.The 6-month Treasury bill provides a return of 6946383%/=. in six months. This is 2638312766%⨯.=. per annum with semiannual compounding or2ln(106383)1238%.=. per annum with continuous compounding. The 12-month rate is 118912360%/=. with annual compounding or ln(11236)1165%.=. with continuous compounding. For the 112year bond we must have 012380501165115441049484R e e e -.⨯.-.⨯-.++=.where R is the 112year zero rate. It follows that 15153763561049484084150115R R e e R -.-..+.+=.=.=.or 11.5%. For the 2-year bond we must have012380501165101151525551059712R e e e e -.⨯.-.⨯-.⨯.-+++=. where R is the 2-year zero rate. It follows that 2079770113R e R -=.=.or 11.3%.2. Problem 4.9. What rate of interest with continuous compounding is equivalent to 15% per annum with monthly compounding?The rate of interest is R where: 12015112R e .⎛⎫=+ ⎪⎝⎭i.e., 01512ln 112R .⎛⎫=+ ⎪⎝⎭01491=.The rate of interest is therefore 14.91% per annum.3. Problem4.12. A three-year bond provides a coupon of 8% semiannually and has a cash price of 104. What is the bond’s yield?Ans: The bond pays $4 in 6, 12, 18, 24, and 30 months, and $104 in 36 months. The bondyield is the value of y that solves05101520253044444104104y y y y y y e e e e e e -.-.-.-.-.-.+++++= Using the Solver or Goal Seek tool in Excel 006407y =. or 6.407%.4. Problem 4.14. Suppose that zero interest rates with continuous compounding are as follows:Calculate forward interest rates for the second, third, fourth, and fifth years.For year4 2,$1*exp(2+f)=exp(2*3)f=6-2 = 4%Year 2: 4.0%Similarly, for year 3, 2*3+f = 3.7*3. Therefore f=5.1%Year 3: 5.1%Year 4: 5.7%Year 5: 5.7%5. A stock is expected to pay a dividend of $1 per share in two months and in five months. The stock price is $50, and the risk-free rate of interest is 8% per annum with continuous compounding for all maturities. An investor has just taken a short position in a six-month forward contract on the stock.a. What are the forward price and the initial value of the forward contract?b. Three months later, the price of the stock is $48 and the risk-free rate of interest is still 8% per annum. What are the forward price and the value of the short position in the forward contract?a) The present value, I , of the income from the security is given by:0082120085121119540I e e -.⨯/-.⨯/=⨯+⨯=. From equation (5.2) the forward price, 0F , is given by:008050(5019540)5001F e .⨯.=-.=.or $50.01. The initial value of the forward contract is (by design) zero. The fact that the forward price is very close to the spot price should come as no surprise. When the compounding frequency is ignored the dividend yield on the stock equals the risk-free rate of interest.b) In three months:00821209868I e -.⨯/==. The delivery price, K , is 50.01. From equation (5.6) the value of the short forward contract, f , is given by008312(48098685001)201f e -.⨯/=--.-.=.and the forward price is008312(4809868)4796e .⨯/-.=.6. The current price of silver is $30 per ounce. The storage costs are $0.48 per ounce per year payable quarterly in advance. Assuming that interest rates are 10% per annum for all maturities, calculate the futures price of silver for delivery in nine months.The present value of the storage costs for nine months are0.12 + 0.12e −0.10×0.25 + 0.12e −0.10×0.5 = 0.351or $0.351. The futures price is from equation (5.11) given by 0F whereF 0 = (30 + 0.351)e 0.1×0.75= 32.72i.e., it is $32.72 per ounce.7. In early 2012, the spot exchange rate between the Swiss Franc and U.S. dollar was 1.0404 ($ per franc). Interest rates in the U.S. and Switzerland were 0.25% and 0% per annumrespectively, with continuous compounding. The three-month forward exchange rate was1.0300 ($ per franc). What arbitrage strategy was possible? How does youranswer change if the exchange rate is 1.0500 ($ per franc).The true forward price should be:F =Se(r-rf)T= 1.0404 * exp((0.25% -0)*3/12)= 1.04105With the three month forward at 1.03 $ per franc , rather than the 1.04105 $ per franc it should be, I want to convert $s to Francs 3 months forward. Therefore, I borrow 1 franc, convert it spot to get 1.0404 dollars and invest them at the risk free rate. I also buy a 3 month swiss francs forward. My US investment yields:1.0404*exp(0.25%*0.25)=1.04105. I convert that using the forward contract, to yield1.04105/1.03 = 1.01073 francs. I thus make a risk free profit of 0.01073 per francinvested..With three month forward rate as 1.05, my strategy is: Borrow 1 dollar, convert it spot to francs, (I get 1/1.0400 francs) in Switzerland, sell francs forward. Use the forward to convert it back to dollars. At the end of three months, I need to pay out exp(0.25%*0.25) = 1.00063 from my US borrowing. I have 1.0500*1/1.0404 =1.00927. I thereby make a profit of 1.00927-1.00063 =0.00864 for every dollar invested.8.The current spot price of oil is $67.25 per barrel, the 6 month futures price is$69.75/barrel, and the risk-free rate is 4.2% (annualized and continuously compounded).What is the implied storage cost of oil expressed as an annualized continuously compounded rate? Whose storage cost do you think this reflects (Hint: Could you store oil at this rate?)F0 = S0e(r+s)T69.75=67.25e(0.042+s)0.5s = 2* (Ln(69.75/67.25)-0.021)= 3.1%This is the storage cost for the firm with the lowest marginal storage cost in the market. If for example this was not true, and there exists someone with lower marginal storage costs than 3.1% per year,they would execute the strategy of buying spot, and storing and be able to make a risk free arbitrage profit. They would do so until either (1) their marginal storage cost rose, or (2) the forward price fell to reflect their cost.。
Illumination:The Assignment_4 is a combination of chapter 4, 5 and 6.Copy this file first; then type your answers in the file immediately below each question; finally email your file to me no later then Monday Oct. 11st, at midnight. Keep a copy for yourself is smart, especially, when you do not get my confirm information. Assigning date: Sept. 30st, 2010Due date:Oct. 11st, 2010 (midnight)Submission: electronic submission ONLY.Individual effort (no group work): You must finish the assignment_4 by yourself. You may discuss these problems with other students in the class (in fact, you are encouraged to do so) and/or look into other documents (books, web sites), with the exception of published solutions, without copy others’ results. If you have discussed any of the problems with other students, indicate their name(s) here: . ★Any intentional transgression of these rules will be considered an honor code violation. You will be omitted the score of the assignment_4, and you won’t get the remedial chance.Total marks: 8% of the final marks.Assignment_4I. Heuristic SearchConsider the following state graph:The state space consists of states S, A, B, C, D, E, G1, and G2. S is the initial state and G1 and G2 are the goal states. The possible actions between states are indicated by arrows. So, the successor function for state S returns {A, B}; for A it returns {C, D}, etc... The number labeling each arc (roughly at the mid-point of the arc) is the actual cost of the action. For example, the cost of going from S to A is 3. The number in bold italic near each state is the value of the heuristic function h at that state. For example, the value of h at state C is 3.Graph- 11.Fill the following table with the nodes successively added to the fringe by the best-first search algorithm using the evaluation function f(N) = g(N) + h(N), where g(N) is the cost of the path found from the initial node to node N. The algorithm does not check if a state is a re-visited one or not (hence, there may be several nodes with the same state in the search tree). It terminates only when it removes a goal node from the fringe. The states produced by the successor function are always ordered in alphabetic order. In the rightmost column (#exp), indicate the order in which nodes are expanded (i.e., are removed from the fringe). If a node is not expanded, leave the corresponding cell empty. The first line of the table is filled for you. It is possible that you do not need all the rows in the table. In this problem, you don’t have to justify your answers.N State g(N) h(N) f(N) #exp1 S 0 10 10 123456789101112132.Is the heuristic function h defined by values provided in the figure admissible? How do you know? How doesthis affect the search?II.CSP(Constrain Satisfaction Problem)We have only four variables: A, B, C and D and each of them have only two legal values, which we will write as: A1, A2 (for variable A), B1, B2 (for variable B), C1, C2 (for variable C) and D1, D2 (for variable D). The only legal assignments for each pair of variables are:A-B: A1-B1, A2-B1A-C: A1-C1, A2-C2B-D: B1-D1C-D: C2-D1B-C: No constraint.A-D: No constraint.No other combination of variable values is legal. Let’s say that that”an assignment is generated” every time a variable in the problem gets a new (tentative) assignment. We assume that the variables are examined in alphabetical order and the values in numerical order. Below, we ask you to solve this problem using pure backtracking and also by using backtracking with forward checking. Stop when a valid solution is found.The search tree for this problem is given below. Each node (except the root) is labeled with the value involved in the assignment; the variable involved is obvious given the value. Your answers will be a space-separated sequence of these values involved in the assignments as they are generated during the appropriate search. For example, A1 B1 etc.:(a) Pure backtracking: How many total assignments are made before finding an answer?(b) Pure backtracking: Show the assignments in order.(c) Backtracking with forward checking: How many assignments are made before finding an answer?(d) Backtracking with forward checking: Show the assignments in order..III.Alpha-Beta AlgorithmConsider the following game tree. The value of the evaluation function at each leaf is shown just below the leaf node, from the point of view of the first player.The first player is the maximizing player MAX. Perform depth-first search (with the ordering of the nodes from left to right) of the game tree with alpha-beta pruning. Answer the following questions without explanation:1.Give the final α or β value at each node of the game tree that has not been pruned and indicate allthe nodes for which no α or β value has been computed (the “pruned” nodes).2.What move will MAX make?。
scipy linear_sum_assignment 算法-概述说明以及解释1.引言1.1 概述在计算机科学领域,线性求和分配(linear sum assignment)问题是一类经典的组合优化问题,其在各种应用场景中都有着重要的作用。
该问题的目标是在二维矩阵中找到最优的一组元素匹配,使得匹配到的元素之和达到最大或最小。
对于具有不同权重或成本的元素,线性求和分配算法可以帮助我们找到最优的匹配方式,从而优化资源利用和成本控制。
在本文中,我们将重点介绍scipy库中的linear_sum_assignment 算法,该算法是一种高效的解决线性求和分配问题的方法。
我们将深入探讨该算法的原理、实现细节以及在实际应用中的具体应用场景。
通过对该算法的深入了解,读者将能够更好地理解和应用它来解决各种实际问题,提高工作效率和解决难题能力。
1.2 文章结构本文主要分为三个部分:引言、正文和结论。
在引言部分中,我们将简要介绍本文的研究背景和意义,解释文章的结构和目的。
在正文部分中,我们将首先介绍scipy库的基本概念和功能,然后详细阐述linear_sum_assignment算法的原理和实现方法,最后探讨该算法在实际应用中的具体场景和效果。
在结论部分中,我们将对全文进行总结概括,分析linear_sum_assignment算法的优缺点,以及展望未来可能的发展方向。
1.3 目的本文旨在探讨scipy库中的linear_sum_assignment算法,该算法是解决最优匹配问题的一种经典算法。
通过深入了解该算法的原理和应用,我们可以更好地理解其在实际问题中的作用和效果。
同时,我们也将分析该算法的优缺点,为读者提供更全面的视角。
最终,我们希望读者能够对linear_sum_assignment算法有一个清晰的认识,为其在实际项目中的应用提供有力的支持。
2.正文2.1 scipy库简介:Scipy是一个基于Python的开源科学计算库,它提供了许多用于科学计算的常用函数和工具。
一、介绍1.1 Python 最优化算法的概念 1.2 指派问题的定义二、Python 优化算法介绍2.1 蚁裙算法2.2 遗传算法2.3 粒子裙算法2.4 其他常用的优化算法三、指派问题的实例分析3.1 问题背景及需求3.2 模型建立3.3 算法选择及实现3.4 结果分析及优化四、案例研究4.1 实际案例介绍4.2 数据收集与整理4.3 模型建立及算法选择4.4 结果分析五、 Python 最优化算法的应用5.1 物流配送问题5.2 人员安排问题5.3 作业调度问题六、总结与展望6.1 研究成果总结6.2 存在问题及改进方向6.3 未来发展趋势七、参考文献Python 最优化算法指派问题实例一、介绍1.1 Python 最优化算法的概念Python 是一种高级编程语言,广泛应用于数据分析、科学计算和人工智能等领域。
优化算法是解决复杂问题的重要工具之一,而 Python 语言具有优秀的易用性和灵活性,因此 Python 最优化算法在实际应用中具有较大优势。
1.2 指派问题的定义指派问题是一类组合优化问题,通常用于确定若干个任务分配给若干个执行者,以使得总成本或总收益达到最优。
指派问题在实际中有着广泛的应用,如物流配送、人员调度、作业安排等领域。
二、Python 优化算法介绍2.1 蚁裙算法蚁裙算法是一种模拟蚁裙寻找食物的行为而提出的一种启发式算法,通过模拟蚁裙在解决问题中的信息交流和协作行为,以寻找最优解。
蚁裙算法在解决指派问题中有着较好的效果,能够有效地找到全局最优解。
2.2 遗传算法遗传算法是受到自然界进化论启发而提出的一种优化算法,通过模拟自然选择和基因遗传的过程,实现解空间的搜索和优化。
在指派问题中,遗传算法能够通过种裙的演化,找到较优的任务分配方案。
2.3 粒子裙算法粒子裙算法是模拟鸟裙觅食的行为而提出的一种优化算法,通过模拟粒子在解空间中的搜索和协作,以找到最优解。
在指派问题中,粒子裙算法能够通过多个粒子的协同搜索,找到适合的任务分配方案。
Chapter 2: Term Structure of Interest Rate
1. Song: page 31, #1
Answer:
(1) If we assume that the coupon is paid annually,
For T-Bills: We have r n P n 12
1100+=, so: 1-month: r 1211100653.99+=
, r = 4.178%; 3-month: r 12
31100866.98+=, r = 4.588% 6-month: r 12
61100766.97+=, r = 4.570%; 1-year: r +=1100666.95, r = 4.530% For T-Bonds and T-Notes :
We have n n n n n n n n n r i r i r i r i P )
1(100)1()1(111221+++++++++=-- , so 1)1(110011-+⨯-+=∑-=n n t t t n n n
n r i p i r ,
We have already known that r 1 = 4.530%, so we can calculate other zero rates by Excel: 2-year: r 2 = 4.522%;
3-year: r 3 = 4.532%;
4-year: r 4 = 4.551%;
5-year: r 5 = 4.562%;
6-year: r 6 = 4.624%;
7-year: r 7 = 4.571%;
8-year: r 8 = 4.632%;
Since there ’s no available information for the values from r 9 to r 19, we should use linear interpolation to determine them. The formula is )(n m n j r r n
m n j r r ---+
=, where n = 8, m = 20, r 8 = 4.632%, so: 9-year: r 9 =202012
1%2463.4%)632.4(82089%632.4r r +=---+; 10-year: r 10 = 2061%8603.3r +;
11-year: r 11 = 2041%4742.3r +
; 12-year:
r 12 = 2031%0882.3r +; 13-year:
r 13 = 20125%7022.2r +; 14-year:
r 14 = 2021%3162.2r +; 15-year:
r 15 = 20127%9301.1r +; 16-year:
r 16 = 2032%5441.1r +; 17-year:
r 17 = 2043%1581.1r +; 18-year:
r 18 = 2065%7721.0r +; 19-year: r 19 = 2012
11%386.0r +;。
Finally, we can get an high order equation about r 20. Solve this equation in Excel by trial-and-error.
Similarly, we can get the value of r 25and r 30 by solving another two equations.
(2) If we assume that the coupon is paid semiannually,
For T-Bills, the results are the same as in (1).
For T-Bonds and T-Notes, We have:
23
0.51 1.5222122221()()220.50.50.5(1/2)(1/2)(1/2)0.50.50.5*(1/2)(1/2)(1/2)n n n n n n n n n n
n n n i par i par i par P r r r i par i par i par par r r r ----⨯⨯⨯⨯⨯⨯=+++++⨯⨯⨯⨯⨯+++++++
term
r term r 1
4.530% 4.5 4.568% 1.5
4.535% 5 4.573% 2
4.539%
5.5 4.611% 2.5
4.545% 6 4.650% 3
4.551% 6.5 4.619% 3.5
4.558% 7 4.588% 4
4.564% 7.5 4.618% 8 4.649%
Use linear interpolation to determine the values of zero rates with a maturity longer than 8 years.
2. Song: page 32, #2 Answer:
n
n n n n n n n n r i r i r i r i P )1(100)1()1(111221+++++++++=-- , Then 1)1(110011-+⨯-+=∑-=n n t t t n n n
n r i p i r
r 1 =3.465%
r 2 =3.762%
r 3 =3.815%
r 4 =3.949%
r 5 =4.143% Finally, 5
5511
1(1)1(1)t t t r i r =-
+=+∑=4.12%
3. The term structure is upward sloping. Put the following in order of magnitude:
a) The five-year zero rate.
b) The yield on a five-year coupon-bearing bond.
c) The forward rate corresponding to the period between 5 and 4
15years in the future. What is the answer to this question when the term structure is downward sloping?
Answer:
When term structure is upward sloping, c>a>b
When term structure is downward sloping, b>a>c
4. A $100 million interest rate swap has a remaining life of 10 months. Under the terms of the
swap, six-month LIBOR is exchanged for 12% per annum (compounded semiannually). The average of the bid-ask rate being exchanged for six-month LIBOR in swaps of all maturities is currently 10% per annum with continuous compounding. The six-month LIBOR rate was
9.6% per annum two months ago. What is the current value of the swap to the party paying floating? What is its value to the party paying fixed?
Answer:
Current value to the party paying floating:
-0.1*1/3-0.1*5/6-0.1*1/3
6e +106e 104.8e 103.328-101.364
=1.964million
-= value to the party paying fixed: -1.964million。