Stock Valuation
- 格式:dps
- 大小:150.00 KB
- 文档页数:11

第一章财务管理总论Overview of Financial Man agement一、主要专业术语或概念中英文对照财务管理financial management财务管理的目标the goal of financial management关于企业财务目标的三种综合表述:利润最大化profit maximization (maximize profit)每股盈余最大化earnings per share maximization股东财富最大化stockholder (shareholder) wealth maximization利益相关者stakeholder股东stockholder/shareholder债权人creditor/bondholder顾客customer职工employee政府government股东价值的影响因素the factors that affect the stockholder value (2008注会财管教材P4图1-1)经营现金流量operating cash flows资本成本cost of capital销售及其增长/成本费用revenues and its growth/cost and expense资本投资/营运资本capital investment/working capital资本结构/破产风险/税率/股利政策capital structure/bankruptcy risk/tax rate/dividend policy经营活动operating activity投资活动investing activity筹资活动financing activity股东、经营者和债权人利益的冲突与协调Conflicts of interest between shareholders,managers and creditors and their reconciliationAn agency relationship(代理关系) exists whenever a principal (委托人) hires an agent(代理人)to act on their behalf。

记帐:Bookkeeping Service对帐:Auditing Service联行:Associated Banks Service 或Affiliated Banks Service(我还是不明白这与5有何区别,但Associated和Affiliated不是动词原形,是形容词)代理业务: Agency Service银行卡接柜:Inter-Bank Bankcard Business Service现金审批:Cash Approval Service开销户: Account Opening/Closing Service开户的标牌还可以用:New Account/New Clientbig macs, big/large-cap stock, mega-issue 大盘股offering, list 上市bourse 证交所Shanghai Exchange 上海证交所pension fund 养老基金share 股票valuation 股价underwriter 保险商government bond 政府债券saving account 储蓄账户equity market 股市shareholder 股东delist 摘牌inventory 存货traded company, trading enterprise 上市公司market fundamentalist 市场经济基本规则damage-control machinery 安全顾问efficient market 有效市场opportunistic practice 投机行为entrepreneur 企业家cook the book 做假账regulatory system 监管体系portfolio 投资组合money-market 短期资本市场capital-market 长期资本市场volatility 波动diversification 多元化real estate 房地产option 期权call option 看涨期权put option 看跌期权merger 并购arbitrage 套利Securities and Exchange Commission 〈美〉证券交易委员会dollar standard 美元本位制budget 预算deficit 赤字bad debt 坏账macroeconomic 宏观经济fiscal stimulus 财政刺激a store of value 保值transaction currency 结算货币forward exchange 期货交易intervention currency 干预货币Treasury bond 财政部公债pickup in price 物价上涨Federal Reserve 美联储inflation 通货膨胀deflation 通货紧缩tighter credit 紧缩信贷monetary policy 货币政策foreign exchange 外汇spot transaction 即期交易forward transaction 远期交易quote 报价常见银行英语词汇account number 帐目编号depositor 存户pay-in slip 存款单a deposit form 存款单a banding machine 自动存取机to deposit 存款deposit receipt 存款收据private deposits 私人存款certificate of deposit 存单deposit book, passbook 存折credit card 信用卡principal 本金overdraft, overdraw 透支to endorse 背书endorser 背书人to cash 兑现to honor a cheque 兑付to dishonor a cheque 拒付to suspend payment 止付cheque,check 支票cheque book 支票本crossed cheque 横线支票blank cheque 空白支票rubber cheque 空头支票cheque stub, counterfoil 票根cash cheque 现金支票traveler's cheque 旅行支票cheque for transfer 转帐支票outstanding cheque 未付支票canceled cheque 已付支票forged cheque 伪支票Bandar's note 庄票,银票banker 银行家president 行长savings bank 储蓄银行Chase Bank 大通银行National City Bank of New York 花旗银行Hongkong Shanghai Banking Corporation 汇丰银行Chartered Bank of India, Australia and China 麦加利银行Banque de I'IndoChine 东方汇理银行central bank, national bank, banker's bank 中央银行bank of issue, bank of circulation 发行币银行commercial bank 商业银行,储蓄信贷银行member bank, credit bank 储蓄信贷银行discount bank 贴现银行exchange bank 汇兑银行requesting bank 委托开证银行issuing bank, opening bank 开证银行advising bank, notifying bank 通知银行negotiation bank 议付银行confirming bank 保兑银行paying bank 付款银行associate banker of collection 代收银行consigned banker of collection 委托银行clearing bank 清算银行local bank 本地银行domestic bank 国内银行overseas bank 国外银行unincorporated bank 钱庄branch bank 银行分行trustee savings bank 信托储蓄银行trust company 信托公司financial trust 金融信托公司unit trust 信托投资公司trust institution 银行的信托部credit department 银行的信用部commercial credit company(discount company) 商业信贷公司(贴现公司)neighborhood savings bank, bank of deposit 街道储蓄所credit union 合作银行credit bureau 商业兴信所self-service bank 无人银行land bank 土地银行construction bank 建设银行industrial and commercial bank 工商银行bank of communications 交通银行mutual savings bank 互助储蓄银行post office savings bank 邮局储蓄银行mortgage bank, building society 抵押银行industrial bank 实业银行home loan bank 家宅贷款银行reserve bank 准备银行chartered bank 特许银行corresponding bank 往来银行merchant bank, accepting bank 承兑银行investment bank 投资银行import and export bank (EXIMBANK) 进出口银行joint venture bank 合资银行money shop, native bank 钱庄credit cooperatives 信用社clearing house 票据交换所public accounting 公共会计business accounting 商业会计cost accounting 成本会计depreciation accounting 折旧会计computerized accounting 电脑化会计general ledger 总帐subsidiary ledger 分户帐cash book 现金出纳帐cash account 现金帐journal, day-book 日记帐,流水帐bad debts 坏帐investment 投资surplus 结余idle capital 游资economic cycle 经济周期economic boom 经济繁荣economic recession 经济衰退economic depression 经济萧条economic crisis 经济危机economic recovery 经济复苏inflation 通货膨胀deflation 通货收缩devaluation 货币贬值revaluation 货币增值international balance of payment 国际收支favourable balance 顺差adverse balance 逆差hard currency 硬通货soft currency 软通货international monetary system 国际货币制度the purchasing power of money 货币购买力money in circulation 货币流通量note issue 纸币发行量national budget 国家预算national gross product 国民生产总值public bond 公债stock, share 股票debenture 债券treasury bill 国库券debt chain 债务链direct exchange 直接(对角)套汇indirect exchange 间接(三角)套汇cross rate, arbitrage rate 套汇汇率foreign currency (exchange) reserve 外汇储备foreign exchange fluctuation 外汇波动foreign exchange crisis 外汇危机discount 贴现discount rate, bank rate 贴现率gold reserve 黄金储备money (financial) market 金融市场stock exchange 股票交易所broker 经纪人commission 佣金bookkeeping 簿记bookkeeper 簿记员an application form 申请单bank statement 对帐单letter of credit 信用证strong room, vault 保险库equitable tax system 等价税则specimen signature 签字式样banking hours, business hours 营业时间(Consumer Price Index) 消费者物价指数business 企业商业业务financial risk 财务风险sole proprietorship 私人业主制企业partnership 合伙制企业limited partner 有限责任合伙人general partner 一般合伙人separation of ownership and control 所有权与经营权分离claim 要求主张要求权management buyout 管理层收购tender offer 要约收购financial standards 财务准则initial public offering 首次公开发行股票private corporation 私募公司未上市公司closely held corporation 控股公司board of directors 董事会executove director 执行董事non- executove director 非执行董事chairperson 主席controller 主计长treasurer 司库revenue 收入profit 利润earnings per share 每股盈余return 回报market share 市场份额social good 社会福利financial distress 财务困境stakeholder theory 利益相关者理论value (wealth) maximization 价值(财富)最大化common stockholder 普通股股东preferred stockholder 优先股股东debt holder 债权人well-being 福利diversity 多样化going concern 持续的agency problem 代理问题free-riding problem 搭便车问题information asymmetry 信息不对称retail investor 散户投资者institutional investor 机构投资者agency relationship 代理关系net present value 净现值creative accounting 创造性会计stock option 股票期权agency cost 代理成本bonding cost 契约成本monitoring costs 监督成本takeover 接管corporate annual reports 公司年报balance sheet 资产负债表income statement 利润表statement of cash flows 现金流量表statement of retained earnings 留存收益表fair market value 公允市场价值marketable securities 油价证券check 支票money order 拨款但、汇款单withdrawal 提款accounts receivable 应收账款credit sale 赊销inventory 存货property,plant,and equipment 土地、厂房与设备depreciation 折旧accumulated depreciation 累计折旧liability 负债current liability 流动负债long-term liability 长期负债accounts payout 应付账款note payout 应付票据accrued espense 应计费用deferred tax 递延税款preferred stock 优先股common stock 普通股book value 账面价值capital surplus 资本盈余accumulated retained earnings 累计留存收益hybrid 混合金融工具treasury stock 库藏股historic cost 历史成本current market value 现行市场价值real estate 房地产outstanding 发行在外的a profit and loss statement 损益表net income 净利润operating income 经营收益earnings per share 每股收益simple capital structure 简单资本结构dilutive 冲减每股收益的basic earnings per share 基本每股收益complex capital structures 复杂的每股收益diluted earnings per share 稀释的每股收益convertible securities 可转换证券warrant 认股权证accrual accounting 应计制会计amortization 摊销accelerated methods 加速折旧法straight-line depreciation 直线折旧法statement of changes in shareholders’equity 股东权益变动表source of cash 现金来源use of cash 现金运用operating cash flows 经营现金流cash flow from operations 经营活动现金流direct method 直接法indirect method 间接法bottom-up approach 倒推法investing cash flows 投资现金流cash flow from investing 投资活动现金流joint venture 合资企业affiliate 分支机构financing cash flows 筹资现金流cash flows from financing 筹资活动现金流time value of money 货币时间价值simple interest 单利debt instrument 债务工具annuity 年金future value 终至present value 现值compound interest 复利compounding 复利计算pricipal 本金mortgage 抵押credit card 信用卡terminal value 终值discounting 折现计算discount rate 折现率opportunity cost 机会成本required rate of return 要求的报酬率cost of capital 资本成本ordinary annuity普通年金annuity due 先付年金financial ratio 财务比率deferred annuity 递延年金restrictive covenants 限制性条款perpetuity 永续年金bond indenture 债券契约face value 面值financial analyst 财务分析师coupon rate 息票利率liquidity ratio 流动性比率nominal interest rate 名义利率current ratio 流动比率effective interest rate 有效利率window dressing 账面粉饰going-concern value 持续经营价值marketable securities 短期证券liquidation value 清算价值quick ratio 速动比率book value 账面价值cash ratio 现金比率marker value 市场价值debt management ratios 债务管理比率intrinsic value 内在价值debt ratio 债务比率mispricing 给……错定价格debt-to-equity ratio 债务与权益比率valuation approach 估价方法equity multiplier 权益乘discounted cash flow valuation 折现现金流量模型long-term ratio 长期比率undervaluation 低估debt-to-total-capital 债务与全部资本比率overvaluation 高估leverage ratios 杠杆比率option-pricing model 期权定价模型interest coverage ratio 利息保障比率contingent claim valuation 或有要求权估价earnings before interest and taxes 息税前利润promissory note 本票cash flow coverage ratio 现金流量保障比率contractual provision 契约条款asset management ratios 资产管理比率par value 票面价值accounts receivable turnover ratio 应收账款周转率maturity value 到期价值inventory turnover ratio 存货周转率coupon 息票利息inventory processing period 存货周转期coupon payment 息票利息支付accounts payable turnover ratio 应付账款周转率coupon interest rate 息票利率cash conversion cycle 现金周转期maturity 到期日asset turnover ratio 资产周转率term to maturity 到期时间profitability ratio 盈利比率call provision赎回条款gross profit margin 毛利润call price 赎回价格operating profit margin 经营利润sinking fund provision 偿债基金条款net profit margin 净利润conversion right 转换权return on asset 资产收益率put provision 卖出条款return on total equity ratio 全部权益报酬率indenture 债务契约return on common equity 普通权益报酬率covenant 条款market-to-book value ratio 市场价值与账面价值比率trustee 托管人market value ratios 市场价值比率protective covenant 保护性条款dividend yield 股利收益率negative covenant 消极条款dividend payout 股利支付率positive covenant 积极条款financial statement财务报表secured deht担保借款profitability 盈利能力unsecured deht信用借款viability 生存能力creditworthiness 信誉solvency 偿付能力collateral 抵押品collateral trust bonds 抵押信托契约debenture 信用债券bond rating 债券评级current yield 现行收益yield to maturity 到期收益率default risk 违约风险interest rate risk 利息率风险authorized shares 授权股outstanding shares 发行股treasury share 库藏股repurchase 回购right to proxy 代理权right to vote 投票权independent auditor 独立审计师straight or majority voting 多数投票制cumulative voting 积累投票制liquidation 清算right to transfer ownership 所有权转移权preemptive right 优先认股权dividend discount model 股利折现模型capital asset pricing model 资本资产定价模型constant growth model 固定增长率模型growth perpetuity 增长年金mortgage bonds 抵押债券。

CFA InstituteA Simplified Common Stock Valuation ModelAuthor(s): Russell J. Fuller and Chi-Cheng HsiaSource: Financial Analysts Journal, Vol. 40, No. 5 (Sep. - Oct., 1984), pp. 49-56Published by: CFA InstituteStable URL: /stable/4478774Accessed: 19/10/2010 21:09Your use of the JSTOR archive indicates your acceptance of JSTOR's Terms and Conditions of Use, available at/page/info/about/policies/terms.jsp. JSTOR's Terms and Conditions of Use provides, in part, that unless you have obtained prior permission, you may not download an entire issue of a journal or multiple copies of articles, and you may use content in the JSTOR archive only for your personal, non-commercial use.Please contact the publisher regarding any further use of this work. Publisher contact information may be obtained at/action/showPublisher?publisherCode=cfa.Each copy of any part of a JSTOR transmission must contain the same copyright notice that appears on the screen or printed page of such transmission.JSTOR is a not-for-profit service that helps scholars, researchers, and students discover, use, and build upon a wide range of content in a trusted digital archive. We use information technology and tools to increase productivity and facilitate new forms of scholarship. For more information about JSTOR, please contact support@.CFA Institute is collaborating with JSTOR to digitize, preserve and extend access to Financial AnalystsJournal.。
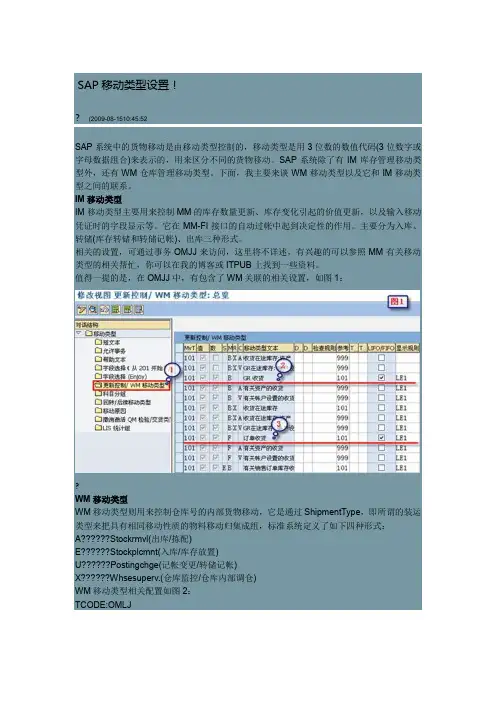
SAP移动类型设置!?(2009-08-1510:45:52SAP系统中的货物移动是由移动类型控制的,移动类型是用3位数的数值代码(3位数字或字母数据组合)来表示的,用来区分不同的货物移动。
SAP系统除了有IM库存管理移动类型外,还有WM仓库管理移动类型。
下面,我主要来谈WM移动类型以及它和IM移动类型之间的联系。
IM移动类型IM移动类型主要用来控制MM的库存数量更新、库存变化引起的价值更新,以及输入移动凭证时的字段显示等。
它在MM-FI接口的自动过帐中起到决定性的作用。
主要分为入库、转储(库存转储和转储记帐)、出库三种形式。
相关的设置,可通过事务OMJJ来访问,这里将不详述,有兴趣的可以参照MM有关移动类型的相关帮忙,你可以在我的博客或ITPUB上找到一些资料。
值得一提的是,在OMJJ中,有包含了WM关联的相关设置,如图1:?WM移动类型WM移动类型则用来控制仓库号的内部货物移动,它是通过ShipmentType,即所谓的装运类型来把具有相同移动性质的物料移动归集成组,标准系统定义了如下四种形式:A??????Stockrmvl(出库/拣配)E??????Stockplcmnt(入库/库存放置)U??????Postingchge(记帐变更/转储记帐)X??????Whsesuperv.(仓库监控/仓库内部调仓)WM移动类型相关配置如图2:TCODE:OMLJ?其中,装运类型可通过事务OMLI来定义,如图3:?WM作货物移动时,会考虑以下问题:1)货物要作做样的移动?(入库、出库、记帐变更、仓位调整?)2)货物从哪里移动?(源存储类型是什么?源仓位是什么?)3)货物移动到哪里?(目的地存储类型是什么?目的地仓位是什么?)WM移动类型为货物移进或移出仓库提供了以下一些所需要的信息:·?????临时存储区·?????临时仓位的类型(预定义,动态,固定)·?????用于处理、确认和打印转储订单的控制标识·?????是否允许手工创建TR及TO·?????TO创建时相关控制参数(如是否允许预分配库存、超量交货等)·?????TO的创建方式(是否自动)及确定方式·?????用于搜索仓库内存储类型的标识(干预存储类型检索的因子)IM移动类型与WM移动类型的关联那么,IM移动类型是如何跟WM移动类型联系到一块呢?这里,我们需要引入一个新概念:“IM-WM参考移动类型”(ReferenceMovementtype),它是架起IM移动类型与WM移动类型之间的桥梁。

⾦融市场与机的构Madura第九版题库ch11Chapter 11Stock Valuation and Risk1. The common price-earnings valuation method applied the ______ price-earnings ratio to ________earnings per share in order to value the firm’s stock.A) firm’s; industryB) firm’s; firm’sC) average industry; industryD) average industry; firm’sANSWER: D2. A firm is expected to generate earnings of $2.22 per share next year. The mean ratio of share price toexpected earnings of competitors in the same industry is 15. Based on this information, the valuation of the firm’s shares based on the price-earnings (PE) method isA) $2.22.B) $6.76.C) $33.30.D) none of the aboveANSWER: C3. The PE method to stock valuation may result in an inaccurate valuation for a firm if errors are madein forecasting the firm’s future earnings or in choosing the industry composite used to derive the PE ratio.A) TrueB) FalseANSWER: A4. Bolwork Inc. is expected to pay a dividend of $5 per share next year. Bolwork’s dividends areexpected to grow by 3 percent annually. The required rate of return for Bolwork stock is 15 percent.Based on the dividend discount model, a fair value for Bolwork stock is $_______ per share.A) 33.33B) 166.67C) 41.67D) 60.00ANSWER: C5. Protsky Inc. just paid a divid end of $2.20 per share. The dividend growth rate for Protsky’s dividendsis 3 percent per year. If the required rate of return on Protsky stock is 12 percent, the stock should be valued at $_______ pershare according to the dividend discount model.A) 24.44B) 25.182 Stock Valuation and RiskC) 18.88D) 75.53ANSWER: B6. The limitations of the dividend discount model are more pronounced when valuing stocksA) that pay most of their earnings as dividends.B) that retain most of their earnings.C) that have a long history of dividends.D) that have constant earnings growth.ANSWER: B7. Hancock Inc. retains most of its earnings. The company currently has earnings per share of $11.Hancock expects its earnings to grow at a constant rate of 2 percent per year. Furthermore, theaverage PE ratio of all other firms in Hancock’s industry is 12. Hancock is expected to pay dividends per share of $3.50 during each of the next three years. If investors require a 10 percent rate of return on Hancock stock, a fair price for Hancock stock today is $________.A) 113.95B) 111.32C) 105.25D) none of the aboveANSWER: A8. When evaluating stock performance, ______ measures variability that is systematically related tomarket returns; ______ measures total variabili ty of a stock’s returns.A) beta; standard deviationB) standard deviation; betaC) intercept; betaD) beta; error termANSWER: A9. The ___________ is commonly used as a proxy for the risk-free rate in the Capital Asset PricingModel.A) Treasury bond rateB) prime rateC) discount rateD) federal funds rateANSWER: A10. Arbitrage pricing theory (APT) suggests that a stock’s price is influenced only by a stock’s beta.A) TrueB) FalseANSWER: BStock Valuation and Risk 3 11. Stock prices of U.S. firms primarily involved in exporting are likely to be ________ affected by aweak dollar and __________ affected by a strong dollar.A) favorably; adverselyB) adversely; adverselyC) favorably; favorablyD) adversely; favorablyANSWER: A12. A weak dollar may enhance the value of a U.S. firm whose sales are dependent on the U.S. economy.A) TrueB) FalseANSWER: A13. The January effect refers to the __________ pressure on ______ stocks in January of every year.A) downward; largeB) upward; largeC) downward; smallD) upward; smallANSWER: D14. The expected acquisition of a firm typically results in ____________ in the target’s stock price.A) an increaseB) a decreaseC) no changeD) none of the aboveANSWER: A15. The _______ index can be used to measure risk-adjusted performance of a stock while controlling forthe stock’s volatility.A) SharpeB) TreynorC) arbitrageD) marginANSWER: A16. The _______ index can be used to measure risk-adjusted performance of a stock while controlling for the stock’s beta.A) SharpeB) TreynorC) arbitrageD) marginANSWER: B4 Stock Valuation and Risk17. Stock price volatility increased during the credit crisis.A) TrueB) FalseANSWER: A18. The Sharpe Index measures theA) average return on a stock.B) variability of stock returns per unit of returnC) stock’s beta adjusted for risk.D) excess return above the risk-free rate per unit of risk.ANSWER: D19. A stock’s average return is 11 percent. The average risk-free rate is 9 percent. The stock’s beta is 1and its standard deviation of returns is 10 percent. What is the Sharpe Index?A) .05B) .5C) .1D) .02E) .2ANSWER: E20. A stock’s average return is 10 percent. The average risk-free rate is 7 percent. The standarddeviation of the stock’s return is 4 percent, and the stock’s beta is 1.5. What is the Treynor Index for the stock?A) .03B) .75C) 1.33D) .02E) 50ANSWER: D21. If security prices fully reflect all market-related information (such as historical price patterns) but do not fully reflect all other public information, security markets areA) weak-form efficient.B) semi-strong form efficient.C) strong form efficient.D) B and CE) none of the aboveANSWER: A22. If security markets are semi-strong form efficient, investors cannot solely use ______ to earn excess returns.A) previous price movementsB) insider informationStock Valuation and Risk 5C) publicly available informationD) A and CANSWER: D23. The ______ is commonly used to determine what a stock’s price should have been.A) Capital Asset Pricing ModelB) Treynor IndexC) Sharpe IndexD) B and CANSWER: A24. A stock’s beta is estimated to be 1.3. The risk-free rate is 5 percent, and the market return is expected to be 9 percent. What is the expected return on the stock based on the CAPM?A) 5.2 percentB) 11.7 percentC) 16.7 percentD) 4 percentE) 10.2 percentANSWER: E25. According to the text, other things being equal, stock prices of U.S. firms primarily involved inexporting could be ______ affected by a weak dollar. Stock prices of U.S. importing firms could be ______ affected by a weak dollar.A) adversely; favorablyB) favorably; adverselyC) favorably; favorablyD) adversely; adverselyANSWER: B26. The demand by foreign investors for the stock of a U.S. firm sold on a U.S. exchange may be higherwhen the dollar is expected to ______, other things being equal. (Assume the firm’s operations are unaffected by the value of the dollar.)A) strengthenB) weakenC) stabilizeD) B and CANSWER: A27. A higher beta of an asset reflectsA) lower risk.B) lower covariance between the asset’s returns and market returns.C) higher covariance between the asset’s returns and the market returns.D) none of the above6 Stock Valuation and RiskANSWER: C28. The “January effect” refers to a largeA) rise in the price of small stocks in January.B) decline in the price of small stocks in January.C) decline in the price of large stocks in January.D) rise in the price of large stocks in January.ANSWER: A29. Technical analysis relies on the use of ______ to make investment decisions.A) interest ratesB) inflationary expectationsC) industry conditionsD) recent stock price trendsANSWER: D30. The arbitrage pricing theory (APT) differs from the capital asset pricing model (CAPM) in that it suggests that stock pricesA) are influenced only by the market itself.B) can be influenced by a set of factors in addition to the market.C) are not influenced at all by the market.D) cannot be influenced at all by the industry factors.ANSWER: B31. According to the capital asset pricing model, the required return by investors on a security isA) inversely related with the risk-free rate.B) inversely related with the firm’s beta.C) inversely related with the market return.D) none of the aboveANSWER: D32. Boris stock has an average return of 15 percent. Its beta is 1.5. Its standard deviation of returns is 25 percent. The average risk-free rate is 6 percent. The Sharpe index for Boris stock isA)0.35.B)0.36.C)0.45.D)0.28.E)none of the aboveANSWER: B33. Morgan stock has an average return of 15 percent, a beta of 2.5, and a standard deviation of returns of20 percent. The Treynor index of Morgan stock isA)0.04.B)0.05.Stock Valuation and Risk 7C)0.35.D)0.03.E)none of the above34. Zilo stock has an average return of 15 percent, a beta of 2.5, and a standard deviation of returns of 20percent. The Sharpe index of Zilo stock isA)0.36.B)0.35.C)0.28.D)0.45.E)none of the aboveANSWER: B35. Sorvino Co. is expected to offer a dividend of $3.2 per share per year forever. The required rate ofreturn on Sorvino stock is 13 percent. Thus, the price of a share of Sorvino stock, according to the dividend discount model, is $_________.A) 4.06B) 4.16C)40.63D)24.62E)none of the aboveANSWER: D36. Kudrow stock just paid a dividend of $4.76 per share and plans to pay a dividend of $5 per share nextyear, which is expected to increase by 3 percent per year subsequently. The required rate of return is15 percent. The value of Kudrow stock, according to the dividend discount model, is $__________.A)39.67B)41.67C)33.33D)31.73E)none of the aboveANSWER: B37. LeBlanc Inc. currently has earnings of $10 per share, and investors expect that the earnings per sharewill grow by 3 percent per year. Furthermore, the mean PE ratio of all other firms in the sameindustry as LeBlanc Inc. is 15. LeBlanc is expected to pay a dividend of $3 per share over the next four years, and an investor in LeBlanc requires a return of 12 percent. What is the forecasted stock price of LeBlanc in four years, using the adjusted dividend discount model?A)$150.00B)$163.91C)$45.00D)$168.83E)none of the above8 Stock Valuation and Risk38. Tarzak Inc. has earnings of $10 per share, and investors expect that the earnings per share will growby 3 percent per year. Furthermore, the mean PE ratio of all other firms in the same industry asTarzac is 15. Tarzac is expected to pay a dividend of $3 per share over the next four years, and an investor in Tarzac requires a return of 12 percent. The estimated stock price of Tarzak today should be __________ using the adjusted dividend discount model.A)$116.41B)$104.91C)$161.15D)none of the aboveANSWER: A39. The standard deviation of a stock’s returns is used to measure a stock’sA)volatility.B)beta.C)Treynor Index.D)risk-free rate.ANSWER: A40. The formula for a stock portfolio’s volatility does not contain theA)weight (proportional investment) assigned to each stock.B)variance (standard deviation squared) of returns of each stock.C) correlation coefficients between returns of each stock.D) risk-free rate.ANSWER: D41. If the returns of two stocks are perfectly correlated, thenA) their betas should each equal 1.0.B) the sum of their betas should equal 1.0.C) their correlation coefficient should equal 1.0.D) their portfolio standard deviation should equal 1.0.ANSWER: C42. A stock’s beta can be measured from the estimate of the using regression analysis.A) interceptB) market returnC) risk-free rateD) slope coefficientANSWER: D43. A beta of 1.1 means that for a given 1 percent change in the value of the market, theis expected to change by 1.1 percent in the same direction.A)risk-free rateB)stock’s valueStock Valuation and Risk 9C)s tock’s standard deviationD)correlation coefficientANSWER: B44. Stock X has a lower beta than Stock Y. The market return for next month is expected to be either–1 percent, +1 percent, or +2 percent with an equal probability of each scenario. The probability distribution of Stock X returns for next month isA)the same as that of Stock Y.B)more dispersed than that of Stock Y.C)less dispersed than that of Stock Y.D)zero.ANSWER: C45. The beta of a stock portfolio is equal to a weighted average of theA)betas of stocks in the portfolio.B)betas of stocks in the portfolio, plus their correlation coefficients.C)standard deviations of stocks in the portfolio.D)correlation coefficients between stocks in the portfolio.ANSWER: A46. Value at risk estimates the a particular investment for a specified confidence level.A)beta ofB)risk-free rate ofC)largest expected loss toD)standard deviation ofANSWER: C47. A stock has a standard deviation of daily returns of 1 percent. It wants to determine the lowerboundary of its probability distribution of returns, based on 1.65 standard deviations from theexpected outcome. The stock’s expected daily return is .2 percent. The lower boundary isA)–1.45 percent.B)–1.85 percent.C)0 percent.D)–1.65 percent.ANSWER: A48. A stock has a standard deviation of daily returns of 3 percent. It wants to determine the lower boundary of its probability distribution of returns, based on 1.65 standard deviations from the expected outcome. The stock’s expected daily return is .1 percent. The lower boundary isA)–1.65 percent.B)–3.00 percent.C)–4.85 percent.D)–5.05 percent.10 Stock Valuation and RiskANSWER: C49. Which of the following is not commonly used as the estimate of a stock’s volatility?A)the estimate of its standard deviation of returns over a recent periodB)the trend of historical standard deviations of returns over recent periodsC)the implied volatility derived from an option pricing modelD)the estimate of its option premium derived from an option pricing modelANSWER: D50. The credit crisis only affected the stock performance of stocks in the U.S.A) TrueB) FalseANSWER: B51. When new information suggests that a firm will experience lower cash flows than previously anticipated or lower risk, investors will revalue the corresponding stock downward.A) TrueB) FalseANSWER: B52. A relatively simple method of valuing a stock is to apply the mean price-earnings (PE) ratio of all publicly traded competitors in the respective industry to the firm’s expected earnings for the year.ANSWER: A53. While the previous year’s earnings are often used as a base for forecast ing future earnings, the recent year’s earnings do not always provide an accurate forecast of the future.A) TrueB) FalseANSWER: A54. If investo rs agree on a firm’s forecasted earnings, they will derive the same value for that firm using the PE method to value the firm’s stock.A) TrueB) FalseANSWER: B55. The dividend discount model states that the price of a stock should reflect the present value of the stock’s future dividends.A) TrueB) FalseStock Valuation and Risk 11 ANSWER: A56. The dividend discount model can be adapted to assess the value of any firm, even those that retain most or all of their earnings.A) TrueB) FalseANSWER: A57. For firms that do not pay dividends, a more suitable valuation may be the free cash flow model.A) TrueB) FalseANSWER: A58. The capital asset pricing model (CAPM) is based on the premise that the only important risk of a firm is unsystematic risk.A) TrueB) FalseANSWER: B59. The prime rate is commonly used as a proxy for the risk-free rate in the capital asset pricing model60. A stock with a beta of 2.3 means that for every 1 percent change in the market overall, the stock tends to change by 2.3 percent in the same direction.A) TrueB) FalseANSWER: A61. Stocks that have relatively little trading are normally subject to less price volatility.A) TrueB) FalseANSWER: B62. A firm’s stock price is affected not only by macroeconomic and market conditions but also by firm specific conditions.A) TrueB) FalseANSWER: A12 Stock Valuation and Risk63. Stock repurchases are commonly viewed as an unfavorable signal about the firm.A) TrueB) FalseANSWER: B64. The main source of uncertainty in computing the return of a stock is the dividend to be received next year.A) TrueB) FalseANSWER: B65. A stock portfolio has more volatility when its individual stock returns are uncorrelated.A) TrueB) FalseANSWER: B66. Beta serves as a measure of risk because it can be used to derive a probability distribution of return67. The value-at-risk method is intended to warn investors about the potential maximum loss that couldoccur.A) TrueB) FalseANSWER: A68. Regarding the value-at-risk method, the same methods used to derive the maximum expected loss ofone stock can be applied to derive the maximum expected loss of a stock portfolio for a givenconfidence level.A) TrueB) FalseANSWER: A69. Portfolio managers who monitor systematic risk rather than total risk are more concerned about stockvolatility than about beta.A) TrueB) FalseANSWER: BStock Valuation and Risk 13 70. Regarding the implied standard deviation, by plugging in the actual option premium paid by investorsfor a specific stock in the option-pricing model, it is possible to derive the anticipated volatility level.A) TrueB) FalseANSWER: A71. One way to forecast a portfolio’s beta is to first forecast the betas of the individual stocks in theportfolio and then sum the individual forecasted betas, weighted by the market value of each stock.A) TrueB) FalseANSWER: B72. If beta is thought to be the appropriate measure of risk, a stock’s risk-adjusted returns should bedetermined by the Sharpe index.ANSWER: B73. The Treynor index is similar to the Sharpe index, except that is uses beta rather than standarddeviation to measure the stock’s risk.A) TrueB) FalseANSWER: A74. Fabrizio, Inc. is expected to generate earnings of $1.50 per share this year. If the mean ratio of shareprice to expected earnings of competitors in the same industry is 20, then the stock price per share is $_________.A)13.33B) 3.00C)20.00D)30.00E)none of the aboveANSWER: D75. Which of the following is not a reason the PE ratio method may result in an inaccurate valuation for afirm?A)potential errors in the forecast of the firm’s betaB)potential errors in the forecast of the firm’s future earningsC)potential errors in the choice of the industry composite used to derive the PE ratioD)All of the above are reasons the PE ratio method may result in an inaccurate valuation for a firm.ANSWER: A14 Stock Valuation and Risk76. Sorvino Co. is expected to offer a dividend of $3.2 per share per year forever. The required rate ofreturn on Sorvino stock is 13 percent. Thus, the price of a share of Sorvino stock, according to the dividend discount model, is $_________.A) 4.06B) 4.16C)24.62D)40.63E)none of the aboveANSWER: Csubsequently. The required rate of return is 15 percent. The value of Kudrow stock, according to the dividend discount model, is $__________.A)39.67B)33.33C)31.73D)41.67E)none of the aboveANSWER: D78. The limitations of the dividend discount model are most pronounced for a firm thatA)has a high beta.B)has high expected future earnings.C)distributes most of its earnings as dividends.D)retains all of its earnings.E)none of the aboveANSWER: D79. Which of the following is incorrect regarding the capital asset pricing model (CAPM)?A)It is sometimes used to estimate the required rate of return for any firm with publicly traded stock.B)It is based on the premise that the only important risk of a firm is systematic risk.C)It is concerned with unsystematic risk.D)All of the above are true.ANSWER: C80. The _______________ is not a factor used in the capital asset pricing model (CAPM) to derive thereturn of an asset.A)prevailing risk-free rateB)dividend growth rateC)market returnD)covariance between the asset’s returns and market returnsE)All of the above are factors used in the CAPM.NSWER: BStock Valuation and Risk 15 81. Schwimmer Corp. has a beta of 1.5. The prevailing risk-free rate is 5 percent and the annual marketreturn in recent years has been 11 percent. Based on this information, the required rate of return on Schwimmer Corp. stockB) 6.5C)16.5D)14.0E)none of the aboveANSWER: D82. Which of the following is not a type of factor that drives stock prices, according to your text?A)economic factorsB)market-related factorsC)firm-specific factorsD)All of the above are factors that affect stock prices.ANSWER: D83. ______________ is (are) not a market-related factor(s) that affect(s) stock prices.A)Interest ratesB)Noise tradingC)TrendsD)January effectE)All of the above are market-related factors that affect stock prices.ANSWER: A84. _____________ is (are) not a firm-specific factor(s) that affect(s) stock prices.A)Exchange ratesB)Dividend policy changesC)Stock offerings and repurchasesD)Earnings surprisesE)All of the above are firm-specific factors that affect stock prices.ANSWER: A85. The ____________ is not a measure of a st ock’s risk.A)stock’s price volatilityB)stock’s returnC)stock’s betaD)value-at-risk methodE)All of the above are measures of a stock’s risk.ANSWER: B86. If the standard deviation of a stock’s returns over the last 12 quarters i s 4 percent, and if there is no16 Stock Valuation and RiskB)68; 8C)95; 8D)95; 6E)none of the above ANSWER: A。

股指期货的四种定价方法[摘要]我国金融市场已经推出沪深300股票指数期货,本文吸收借鉴了国内外的研究成果,说明了股指期货四种定价理论和相关的实证结果,并提出今后理论研究的方向。
[关键词]股指期货定价定价理论实证研究研究方向一、定价理论1、持有成本定价模型Comell&French(1983)最早提出在无摩擦市场以及借贷利率相等且保持不变情况下的股指期货持有成本定价公式,股指期货的理论价格为■。
该模型假设条件较多,且定价偏差大,但是最经典的定价模型。
2、连续时间模型Ramaswamy&Sundaresan(1985)修正了期权定价模型进而推导出随机利率条件下无套利股指期货的理论价格。
该模型有四个假设条件:采用单因子CIR描述无风险利率,无风险贴现债券用局部期望假设来描述,无摩擦市场,股指服从对数正态分布。
Cakici&Chatterjee(1999)引入另一种利率模型,通过对S&P500实证比较发现,利率的平方根过程和对数正态过程对定价没有显著性影响。
3、一般均衡定价模型Cox和Ross等人在1985年推出资产定价的一般均衡模型, 随后Hemler&Longstaff(1991)推导出利率随机波动和市场随机波动情况下的股指期货一般均衡定价模型。
该模型有四个假设:经济个体同质预期,企业产品被消费或被投资,投资回报率是随机过程,经济体状态变量X 和Y均值复归。
股指期货的偏微分方程的PDE解析解和持有成本定价模型异曲同工。
4、区间定价模型Klemkosky&Lee(1991)考虑交易成本、股利和借贷利率不相等因素,“做多指数现货,做空指数期货”得到套利区间的上限,“做多指数期货,做空指数现货”得到套利区间的下限,在此区间内不可套利,在此区间外可套利。
国内对股指期货定价的理论探索较少,其中陈晓杰,黄志刚(2007)在无风险套利原理下,改良B-S方程通解,推导出股指期货的定价模型。

仓库盘点英语仓库盘点英语仓库盘点是一项重要的工作,旨在确保仓库存货的准确性和完整性。
通过进行盘点,我们可以对仓库中的存货进行清点和核对,以便及时发现并纠正任何差异或问题。
以下是一些与仓库盘点相关的常用英语词汇和短语,供参考和学习。
1. Inventory(存货)- 所有存放在仓库中的商品、物料和产品的总称。
2. Stocktaking(盘点)- 对仓库的存货进行清点和核对的过程。
3. Physical count(实物盘点)- 对存货进行实地清点的过程,通常使用人工或计数设备。
4. Cycle count(循环盘点)- 根据计划和排定的时间表,定期对仓库的一部分存货进行盘点。
5. Bin location(储位)- 用于存放特定商品的特定位置或区域。
6. Variance(差异)- 盘点结果与记录数量之间的差异。
7. Overstock(库存过多)- 存货数量超过需求或可保持的水平。
8. Understock(库存不足)- 存货数量低于需求或可保持的水平。
9. Damaged goods(破损货物)- 经检查发现有缺陷或受损的商品或物料。
10. Expiry date(过期日期)- 商品或物料的有效期限。
11. Reconciliation(调节)- 将盘点结果与记录进行核对和调整的过程。
12. FIFO (First-In, First-Out)(先进先出)- 一种存货管理方法,根据存货的进货日期来优先销售最早进入仓库的商品。
13. LIFO (Last-In, First-Out)(后进先出)- 一种存货管理方法,根据存货的进货日期来优先销售最晚进入仓库的商品。
14. Barcode scanner(条码扫描器)- 用于扫描商品或物料上的条码,以便快速而准确地记录数量和信息。
15. Recordkeeping(记录保管)- 对存货相关信息和交易进行准确记录的过程。
在仓库盘点过程中,以下是一些常用的英语对话和表达方式,可供参考:1. Asking for assistance and instructions: - Could you please guide me through the inventory check process? - Can you explain how to use the barcode scanner? - What should I do if I find any damaged goods during the inventory?2. Reporting discrepancies: - I have noticed a variance between the recorded and physical count of this product. - The inventory count suggests an understock of item X. - There seems to be an overstock of item Y according to the physical count.3. Seeking clarification: - Could you clarify the location of this product in the warehouse? - What is the procedure forreconciling the inventory discrepancies? - Is there a specific order in which I should conduct the cycle count?4. Confirming actions: - I will scan each barcode to ensure accurate recording of quantities. - I will report any damaged goods immediately for further action. - I will review the expiry dates of perishable items during the inventory check.5. Concluding the inventory process: - The inventory check has been completed for all items in this section. - All discrepancies have been reconciled, and the inventory count now matches the records. - The final inventory report will be prepared and submitted to the management.以上是关于仓库盘点英语的一些常用词汇、短语和对话,希望能对您的工作有所帮助。

英语课程中的投资与证券交易词汇在如今全球化的商业环境下,掌握英语对于从事金融和投资领域的人来说至关重要。
尤其是在投资与证券交易方面,了解相关词汇和术语是提高沟通能力和拓宽职业发展的关键因素之一。
本文将介绍一些在英语课程中常见的投资与证券交易词汇,以帮助读者更好地理解和运用这些词汇。
一、投资词汇1. Investment(投资)指将资金或其他资源用于期望获取回报的行为或活动。
2. Portfolio(投资组合)指个人或机构持有的所有投资项目的集合。
3. Asset(资产)指拥有的有价值的物品或权益,如股票、债券、不动产等。
4. Equity(股权)指投资者在公司中所持有的股份或股权。
5. Risk(风险)指投资可能面临的损失或不确定性。
6. Return(回报)指投资所产生的利润、收益或回报。
7. Diversification(分散投资)指将资金投资于多个不同的资产类别或领域,以降低风险。
二、证券交易词汇1. Stock(股票)指公司向公众发行的股份,代表持有者在公司中的权益。
2. Shareholder(股东)指持有某公司股份的个人或机构。
3. Dividend(红利)指公司根据盈利情况向股东支付的利润分配。
4. Bond(债券)指借款人以借款为基础发行给债权人的债务证券。
5. Coupon(票息)指债券上规定的每年支付给债券持有者的利息。
6. Principal(本金)指债券上规定的借款人要偿还给债权人的原始金额。
7. Maturity(到期日)指债券或其他金融产品到期的日期。
8. Yield(收益率)指投资产品的盈利能力及其相对于投资成本的比例。
三、其他相关词汇1. Broker(经纪人)指在买卖证券或货币等产品过程中充当中介的个人或公司。
2. Exchange(交易所)指进行证券交易的市场,例如纽约证券交易所(NYSE)。
3. Bull market(牛市)指证券市场价格持续上涨的市场状态。

CEO 首席行政官##CFA注册财务分析师##CFO首席财务官##COGS已售商品成本##COO首席营运官##CPA注册公共会计师##CPI消费物价指数##Calendar Year日历年##Call买入期权##Call Date买回日期##Call Loan短期同业拆借,通知贷款##Call Loan Rate短期同业拆借利率,通知贷款利率##Call Option买入期权######Call Warrant买入认股权证##Callable Bond可买回债券##Callable Preferred Stock可买回优先股##CAMELS Rating SystemCAMELS 评级制度######Capital Account资本帐户##Capital Adequacy Ratio(CAR)资本充足率##Capital Appreciation资本升值##Capital Asset资本资产############Capital Budgeting资本预算##########Capital Expenditure资本开支##Capital Gain资本收益##Capital Goods 资本财货##Capital资本/资本金Capital Asset PricingModel (CAPM)资本资产计价模型Call Premium买回溢价Capital Base资本金基础Capital Employed运用资本####Concession销售报酬##Concession Agreement 特许协议##Conglomerate综合企业##Consumer Confidence Index (CCI)消费者信心指数##Consumer Credit 消费信贷##Consumer Price Index (CPI)消费物价指数######Conversion Premium 转换溢价##Conversion Price 转换价格##Convertible Bond 可转换债券##Convertible Debenture 可转换公司信用债券##Convertible Preferred Stock可转换优先股##Convertible Subordinated Note可转换次级票据##Convertibles 可转换证券##Conveyance 地产让与证书##Contingency 偶然事故##Corporate Bond企业债券##Corporate Cannibalism 企业自我竞争##Corporate Finance 企业融资##Corporate Governance 企业治理##Corporate Tax 公司税##Corporation 公司、企业##Cost Basis成本基础##Cost of Capital 资本成本##########Cost of Funds资金成本##Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)已售商品成本##Cost Synergy 成本协同效益##Counterparty Risk 交易对手风险##Country Risk 国家风险##Coupon息票##Coupon Bond 有息票债券##Covenant契约##Coverage Initiated 纳入研究范围######Credit Default Swap 信贷违约掉期##Credit信贷、信用、贷项Conversion转换Cost of Equity 股本成本##Custodian 保管人##Cyclical Industry 周期性行业##Cyclical Stock 周期性股票##Cyclical Unemployment 周期性失业##DJIA 道琼斯工业平均指数######DJUA 道琼斯公用事业平均指数##Data Mining 数据探索##################Debenture 公司债券##Debit 借项、借方##Debt 债务############Debt Equity Swap 债换股交易##Debt Financing 债务融资##Debt Ratio 负债比率##Debt Restructuring 债务重组##Debt Security 债务证券##Debt Service 还本付息##########Debtor 债务人##Debt Overhang 债务积压##Declaration Date 股息宣告日##########Default Risk 违约风险##Defeasance 宣告(合约)无效、废止契约##Days Payable Outstanding (DPO)应付账款天数Days Sales Outstanding (DSO)应收账款天数DJTA 道琼斯交通平均指数Deep Discount Bond 高折扣债券Default 违约,未能履行合约Debt Equity Ratio 债务股本比Debt Service Coverage Ratio债务偿付比率Underwriting Spread 承销价差##Unearned Income非劳动收入##Unearned Revenue未实现收入##Unit Trust (UT)单位信托##Unrealized Gain未实现收益##Unrealized Loss未实现损失##Unsecured Creditor无抵押债权人##Unsecured Loan无抵押贷款##U.S. Treasury美国财政部##Valuation估值##Value-Added增值##Value-Based Pricing以价值为基础的定价##Value Chain价值链##Value at Risk (VAR)风险价值##Value Investing价值投资##Value Stock价值股票##Vanilla Option单纯期权##Variable Cost可变成本##Variable Life InsurancePolicy可变寿险保单##Vendor Financing供应商融资##Venture创业项目##Venture Capital创业资本##Venture Capital Fund创业基金##Venture Capitalist创业基金投资者##Vertical Integration纵向整合##Vertical Market纵向市场##Vertical Merger纵向合并######Volume Of Trade交易量、成交量##Voting Right投票权##Voting Shares投票股票##Voting Trust投票信托##Voting Trust Agreement投票信托协议######Vulture Fund兀鹫基金########Vulture Capitalist兀鹫投资者WACC 加权平均资本成本Volatility波动性##################WTO 世界贸易组织########War Bond 战争债券##Warrant 认股权证##Warrant Coverage 认股权证比重##Warrant Premium 认股权证溢价##Wealth Added Index (WAI)财富增值指数##Wealth Effect 财富效应##Wealth Management 财富管理##########################Weighted Average Market Capitalization加权平均总市值##White Elephant 白象##White Knight 白武士##White Paper 白皮书##Wholesale Banking 批发银行##Wholly Owned Subsidiary 全资拥有子公司##Withholding 预扣(税)##Withholding Tax 预扣(税)##Working Capital 营运资金##Working Capital Turnover 营运资金周转率##Working Ratio 流动比率##Work in Progress 在建项目##Wall Street 华尔街Weighted Average Cost of Capital (WACC)加权平均资本成本一项由一名代理人同时代表买方与卖方的交易,也称为撍卮砣藬决定一项房地产在税务上价值的地方政府官员个人或一家企业拥有、具有经济价值的任何物品。

股票术语中英文对照以及解释套利(Arbitrage)在不同的市场同时买入和卖出单一证券,以赚取差价。
ffffff资产(Assets)公司的所有权,可以是有形的、无形的、固定或流动的。
ffffff自行处理权(At Discretion)客户给经纪买或卖处理权的指示类型。
限额(At Limit)客户给股票经纪不能买超过或卖低于某一价位的限制。
At The Market以现行价格买或卖证券的订单。
额定资本(Authorized Capital)在公司联合备忘录中协订的实缴资本的最高金额。
平均(Averaging)以不同的价格买或卖同样的股票的过程,以建立平均成本。
基本点(Basic Points)指债券收益率。
债券收益率中每一个百分点等于100个基本点。
如果债券收益率从7.25%变为7.39%,即升高了14个基本点。
熊市(Bear)预测股价将跌落而抛售股票。
熊市是股价下跌的延伸期,通常为下跌20%或更多。
牛市(Bull)预期股价将上扬而买入股票。
牛市表明市场持续上扬走势。
B系数(Beta)衡量股市风险的一种尺度。
0.7意味着股价可能按市场同样方向移动70%。
-1.3意味着股价可能与市场相反方向移动130%。
fffff蓝筹股(Blue Chip)在投资中级别最高的普通股。
债券(Bond)记录借款的凭证,承诺在特定时间支付债券持有人特别利息,并于到期日偿还借款额。
发行红(利)股(Bonus Issue)以无偿发行股票的形式(通常是以资本项目)分配资金给股东。
簿记截止日(Book Closing Date)公司股东记录截止登记日,以决定股息、红利或附加股的授权。
簿记价值(Book value)公司资产簿记帐面价值。
簿记价值不必与购买成本或市场价值一致。
经纪费,佣金(Brokerage)股票经纪人因其买或卖股票服务而收取的费用。
业务循环(Business Cycle)经济活动的周期性变动,带动收入和就业变动。

1. The stock valuation model that determines the current stock price by dividing the next annual dividend amount by the excess of the discount rate less the dividend growth rate is called the _____ model.A. zero growthB. dividend growthC. capital pricingD. earnings capitalizationE. differential growth2. Next year's annual dividend divided by the current stock price is called the:A. yield to maturity.B. total yield.C. dividend yield.D. capital gains yield.E. earnings yield.3. The rate at which a stock's price is expected to appreciate (or depreciate) is called the _____ yield.A. currentB. totalC. dividendD. capital gainsE. Earnings4. A form of equity which receives no preferential treatment in either the payment of dividends or in bankruptcy distributions is called _____ stock.A. dual classB. cumulativeC. deferredD. preferredE. common5. Payments made by a corporation to its shareholders, in the form of either cash, stock or payments in kind, are called:A. retained earnings.B. net income.C. dividends.D. redistributions.E. infused equity. 6. The constant dividend growth model is:A. generally used in practice because most stocks have a constant growth rate.B. generally used in practice because the historical growth rate of most stocks is constant.C. generally not used in practice because most stocks grow at a non constant rate.D. generally not used in practice because the constant growth rate is usually higher than the required rate of return.E. based on the assumption Dow 30 represents a good estimate of the market index.7. The constant dividend growth model:I. assumes that dividends increase at a constant rate forever.II. can be used to compute a stock price at any point of time.III. states that the market price of a stock is only affected by the amount of the dividend.IV. considers capital gains but ignores the dividend yield.A. I onlyB. II onlyC. III and IV onlyD. I and II onlyE. I, II, and III only8. The underlying assumption of the dividend growth model is that a stock is worth:A. the same amount to every investor regardless of their desired rate of return.B. the present value of the future income which the stock generates.C. an amount computed as the next annual dividend divided by the market rate of return.D. the same amount as any other stock that pays the same current dividend and has the same required rate of return.E. an amount computed as the next annual dividend divided by the required rate of return.9. Assume that you are using the dividend growth model to value stocks. If you expect the market rate of return to increase across the board on all equity securities, then you should also expect the:A. market values of all stocks to increase, all else constant.B. market values of all stocks to remain constant as the dividend growth will offset the increase in the market rate.C. market values of all stocks to decrease, all else constant.D. stocks that do not pay dividends to decrease in price while the dividend-paying stocks maintain a constant price.E. dividend growth rates to increase to offset this change.10. Latcher's Inc. is a relatively new firm that is still ina period of rapid development. The company plans on retaining all of its earnings for the next six years. Seven years from now, the company projects paying an annual dividend of $.25 a share and then increasing that amount by 3% annually thereafter. To value this stock as of today, you would most likely determine the value of the stock _____ years from today before determining today's value.A. 4B. 5C. 6D. 7E. 811. The Robert Phillips Co. currently pays no dividend. The company is anticipating dividends of $0, $0, $0, $.10, $.20, and $.30 over the next 6 years, respectively. After that, the company anticipates increasing the dividend by 4% annually. The first step in computing the value of this stock today, is to compute the value of the stock when it reaches constant growth in year:A. 3B. 4C. 5D. 6E. 7 12. Differential growth refers to a firm that increases its dividend by:A. three or more percent per year.B. a rate which is most likely not sustainable over an extended period of time.C. a constant rate of two or more percent per year.D. $.10 or more per year.E. an amount in excess of $.10 a year.13. The total rate of return earned on a stock is comprised of which two of the following?I. current yieldII. yield to maturityIII. dividend yieldIV. capital gains yieldA. I and II onlyB. I and IV onlyC. II and III onlyD. II and IV onlyE. III and IV only14. Fred Flintlock wants to earn a total of 10% on his investments. He recently purchased shares of ABC stock at a price of $20 a share. The stock pays a $1 a year dividend. The price of ABC stock needs to _____ if Fred is to achieve his 10% rate of return.A. remain constantB. decrease by 5%C. increase by 5%D. increase by 10%E. increase by 15%15. The Scott Co. has a general dividend policy whereby it pays a constant annual dividend of $1 per share of common stock. The firm has 1,000 shares of stock outstanding. The company:A. must always show a current liability of $1,000 for dividends payable.B. is obligated to continue paying $1 per share per year.C. will be declared in default and can face bankruptcy if it does not pay $1 per year to each shareholder on a timely basis.D. has a liability which must be paid at a later date should the company miss paying an annual dividend payment.E. must still declare each dividend before it becomes an actual company liability.16. The value of common stock today depends on:A. the expected future holding period and the discount rate.B. the expected future dividends and the capital gains.C. the expected future dividends, capital gains and the discount rate.D. the expected future holding period and capital gains.E. None of the above.17. The closing price of a stock is quoted at 22.87, with a P/E of 26 and a net change of 1.42. Based on this information, which one of the following statements is correct?A. The closing price on the previous day was $1.42 higher than today's closing price.B. A dealer will buy the stock at $22.87 and sell it at $26 a share.C. The stock increased in value between yesterday's close and today's close by $.0142.D. The earnings per share are equal to 1/26th of $22.87.E. The earnings per share have increased by $1.42 this year.18. A stock listing contains the following information: P/E 17.5, closing price 33.10, dividend .80, YTD% chg 3.4, and net chg - .50. Which of the following statements are correct given this information?I. The stock price has increased by 3.4% during the current year.II. The closing price on the previous trading day was $32.60.III. The earnings per share are approximately $1.89. IV. The current yield is 17.5%.A. I and II onlyB. I and III onlyC. II and III onlyD. III and IV onlyE. I, III, and IV only19. The discount rate in equity valuation is composed entirely of:A. the dividends paid and the capital gains yield.B. the dividend yield and the growth rate.C. the dividends paid and the growth rate.D. the capital gains earned and the growth rate.E. the capital gains earned and the dividends paid. 20. The net present value of a growth opportunity, NPVGO, can be defined as:A. the initial investment necessary for a new project.B. the net present value per share of an investment in a new project.C. a continual reinvestment of earnings when r < g.D. a single period investment when r > g.E. None of the above.21. Angelina's made two announcements concerning its common stock today. First, the company announced that its next annual dividend has been set at $2.16 a share. Secondly, the company announced that all future dividends will increase by 4% annually. What is the maximum amount you should pay to purchase a share of Angelina's stock if your goal is to earn a 10% rate of return?A. $21.60B. $22.46C. $27.44D. $34.62E.$36.0022. How much are you willing to pay for one share of stock if the company just paid an $.80 annual dividend, the dividends increase by 4% annually and you require an 8% rate of return?A. $19.23B. $20.00C. $20.40D. $20.80E.$21.6323. Lee Hong Imports paid a $1.00 per share annual dividend last week. Dividends are expected to increase by 5% annually. What is one share of this stock worth to you today if the appropriate discount rate is 14%? A. $7.14 B. $7.50 C. $11.11 D. $11.67 E.$12.2524. Majestic Homes' stock traditionally provides an 8% rate of return. The company just paid a $2 a year dividend which is expected to increase by 5% per year. If you are planning on buying 1,000 shares of this stock next year, how much should you expect to pay per share if the market rate of return for this type of security is 9% at the time of your purchase? A. $48.60 B. $52.50 C. $55.13 D. $57.89 E.$70.0025. Leslie's Unique Clothing Stores offers a common stock that pays an annual dividend of $2.00 a share. The company has promised to maintain a constant dividend. How much are you willing to pay for one share of this stock if you want to earn a 12% return on your equity investments? A. $10.00 B. $13.33 C. $16.67 D. $18.88 E.$20.0026. Martin's Yachts has paid annual dividends of $1.40, $1.75, and $2.00 a share over the past three years, respectively. The company now predicts that it will maintain a constant dividend since its business has leveled off and sales are expected to remain relatively constant. Given the lack of future growth, you will only buy this stock if you can earn at least a 15% rate of return. What is the maximum amount you are willing to pay to buy one share today? A. $10.00 B. $13.33 C. $16.67 D. $18.88 E.$20.0027. The common stock of Eddie's Engines, Inc. sells for $25.71 a share. The stock is expected to pay $1.80 per share next month when the annual dividend is distributed. Eddie's has established a pattern ofincreasing its dividends by 4% annually and expects to continue doing so. What is the market rate of return on this stock? A. 7% B. 9% C. 11% D. 13% E.15%28. The current yield on Alpha's common stock is 4.8%. The company just paid a $2.10 dividend. The rumor is that the dividend will be $2.205 next year. The dividend growth rate is expected to remainconstant at the current level. What is the required rate of return on Alpha's stock? A. 10.04% B. 16.07% C. 21.88% D. 43.75% E. 45.94%29. Martha's Vineyard recently paid a $3.60 annual dividend on its common stock. This dividend increases at an average rate of 3.5% per year. The stock is currently selling for $62.10 a share. What is the market rate of return? A. 2.5% B. 3.5% C. 5.5% D. 6.0% E.9.5%30. Bet'R Bilt Bikes just announced that its annual dividend for this coming year will be $2.42 a share and that all future dividends are expected to increase by 2.5% annually. What is the market rate of return if this stock is currently selling for $22 a share? A. 9.5% B. 11.0% C. 12.5% D. 13.5% E.15.0%31. Shares of common stock of the Samson Co. offer an expected total return of 12%. The dividend is increasing at a constant 8% per year. The dividend yield must be: A. -4%. B. 4%. C. 8%. D. 12%. E.20%.32. The common stock of Grady Co. had an 11.25% rate of return last year. The dividend amount was $.70 a share which equated to a dividend yield of 1.5%. What was the rate of price appreciation on the stock? A. 1.50% B. 8.00% C. 9.75% D. 11.25% E. 12.75%g = .1125 - .015 = .0975 = 9.75%33. Weisbro and Sons' common stock sells for $21 a share and pays an annual dividend that increases by 5% annually. The market rate of return on this stock is 9%. What is the amount of the last dividend paid by Weisbro and Sons? A. $.77 B. $.80 C. $.84 D. $.87 E.$.8834. The common stock of Energizer's pays an annual dividend that is expected to increase by 10% annually. The stock commands a market rate of return of 12% and sells for $60.50 a share. What is the expected amount of the next dividend to be paid on Energizer's common stock? A. $.90 B. $1.00 C. $1.10 D. $1.21 E.$1.3335. The Reading Co. has adopted a policy ofincreasing the annual dividend on its common stock at a constant rate of 3% annually. The last dividend it paid was $0.90 a share. What will the company's dividend be in six years? A. $0.90 B. $0.93 C. $1.04 D. $1.07 E.$1.1136. A stock pays a constant annual dividend and sells for $31.11 a share. If the dividend yield of this stock is 9%, what is the dividend amount? A. $1.40 B. $1.80 C. $2.20 D. $2.40 E.$2.8037. You have decided that you would like to own some shares of GH Corp. but need an expected 12% rate of return to compensate for the perceived risk of such ownership. What is the maximum you are willing to spend per share to buy GH stock if the company pays a constant $3.50 annual dividend per share? A. $26.04 B. $29.17 C. $32.67 D. $34.29 E.$36.5938. Turnips and Parsley common stock sells for$39.86 a share at a market rate of return of 9.5%. The company just paid its annual dividend of $1.20. What is the rate of growth of its dividend? A. 5.2% B. 5.5% C. 5.9% D. 6.0% E.6.3%39. B&K Enterprises will pay an annual dividend of $2.08 a share on its common stock next year. Last week, the company paid a dividend of $2.00 a share. The company adheres to a constant rate of growth dividend policy. What will one share of B&K common stock be worth ten years from now if the applicable discount rate is 8%? A. $71.16 B. $74.01 C. $76.97 D. $80.05 E.$83.2540. Wilbert's Clothing Stores just paid a $1.20 annualdividend. The company has a policy whereby the dividend increases by 2.5% annually. You would like to purchase 100 shares of stock in this firm but realize that you will not have the funds to do so for another three years. If you desire a 10% rate of return, how much should you expect to pay for 100 shares when you can afford to buy this stock? Ignore trading costs. A. $1,640 B. $1,681 C. $1,723 D. $1,766 E. $1,810P 3 = $17.66; Purchase cost =100 $17.66 = $1,76641. The Merriweather Co. just announced that it will pay a dividend next year of $1.60 and is establishing a policy whereby the dividend will increase by 3.5% annually thereafter. How much will one share beworth five years from now if the required rate of return is 12%? A. $21.60 B. $22.36 C. $23.14 D. $23.95 E.$24.79P 5 = $22.3642. The Bell Weather Co. is a new firm in a rapidlygrowing industry. The company is planning onincreasing its annual dividend by 20% a year for the next four years and then decreasing the growth rate to 5% per year. The company just paid its annualdividend in the amount of $1.00 per share. What is the current value of one share if the required rate of return is 9.25%? A. $35.63 B. $38.19 C. $41.05 D. $43.19 E. $45.81Dividends for the first 4 years are: $1.20, $1.44, $1.728, and $2.0736.43. The Extreme Reaches Corp. last paid a $1.50 per share annual dividend. The company is planning on paying $3.00, $5.00, $7.50, and $10.00 a share over the next four years, respectively. After that thedividend will be a constant $2.50 per share per year. What is the market price of this stock if the market rate of return is 15%? A. $17.04 B. $22.39 C. $26.57 D. $29.08 E.$33.7144. Can't Hold Me Back, Inc. is preparing to pay its first dividends. It is going to pay $1.00, $2.50, and $5.00 a share over the next three years, respectively. After that, the company has stated that the annual dividend will be $1.25 per share indefinitely. What is this stock worth to you per share if you demand a 7% rate of return? A. $7.20 B. $14.48 C. $18.88 D. $21.78 E.$25.0645. NU YU announced today that it will begin paying annual dividends. The first dividend will be paid next year in the amount of $.25 a share. The following dividends will be $.40, $.60, and $.75 a share annually for the following three years, respectively. After that, dividends are projected to increase by 3.5% per year. How much are you willing to pay to buy one share of this stock if your desired rate of return is 12%? A. $1.45 B. $5.80 C. $7.25 D. $9.06 E.$10.5846. Now or Later, Inc. recently paid $1.10 as an annual dividend. Future dividends are projected at $1.14, $1.18, $1.22, and $1.25 over the next four years, respectively. After that, the dividend is expected to increase by 2% annually. What is one share of this stock worth to you if you require an 8% rate of return on similar investments? A. $15.62 B. $19.57 C. $21.21 D. $23.33 E.$25.9847. The Red Bud Co. just paid a dividend of $1.20 a share. The company announced today that it will continue to pay this constant dividend for the next 3 years after which time it will discontinue payingdividends permanently. What is one share of this stock worth today if the required rate of return is 7%? A. $2.94 B. $3.15 C. $3.23 D. $3.44 E.$3.6048. Bill Bailey and Sons pays no dividend at the present time. The company plans to start paying an annual dividend in the amount of $.30 a share for two years commencing two years from today. After that time, the company plans on paying a constant $1 a share dividend indefinitely. Given a required return of 14%, what is the value of this stock? A. $4.82 B. $5.25 C. $5.39 D. $5.46 E.$5.5849. The Lighthouse Co. is in a downsizing mode. The company paid a $2.50 annual dividend last year. The company has announced plans to lower the dividend by $.50 a year. Once the dividend amount becomes zero, the company will cease all dividendspermanently. The required rate of return is 16%. What is one share of this stock worth? A. $3.76 B. $4.08 C. $4.87 D. $5.13 E.$5.3950. Mother and Daughter Enterprises is a relatively new firm that appears to be on the road to great success. The company paid its first annual dividend yesterday in the amount of $.28 a share. The company plans to double each annual dividend payment for the next three years. After that time, it is planning on paying a constant $1.50 per share indefinitely. What is one share of this stock worth today if the market rate of return on similar securities is 11.5%? A. $9.41 B. $11.40 C. $11.46 D. $11.93 E. $12.43Dividends for the next three years are $.56, $1.12, and$2.24.51. BC ‘n D just paid its annual dividend of $.60 a share. The projected dividends for the next five years are $.30, $.50, $.75, $1.00, and $1.20, respectively. After that time, the dividends will be held constant at $1.40. What is this stock worth today at a 6% discount rate? A. $20.48 B. $20.60 C. $21.02 D. $21.28 E.$21.4352. Beaksley, Inc. is a very cyclical type of business which is reflected in its dividend policy. The firm pays a $2.00 a share dividend every other year. The last dividend was paid last year. Five years from now, the company is repurchasing all of the outstanding shares at a price of $50 a share. At an 8% rate of return, what is this stock worth today? A. $34.03 B. $37.21 C. $43.78 D. $48.09 E.$53.1853. Last week, Railway Cabooses paid its annual dividend of $1.20 per share. The company has been reducing the dividends by 10% each year. How much are you willing to pay to purchase stock in this company if your required rate of return is 14%? A. $4.50 B. $7.71 C. $10.80D. $15.60E.$27.0054. Nu-Tek, Inc. is expecting a period of intense growth and has decided to retain more of its earnings to help finance that growth. As a result it is going to reduce its annual dividend by 10% a year for the next three years. After that, it will maintain a constant dividend of $.70 a share. Last month, the company paid $1.80 per share. What is the value of this stock if the required rate of return is 13%? A. $6.79 B. $7.22 C. $8.22 D. $8.87 E.$9.0155. The Double Dip Co. is expecting its ice cream sales to decline due to the increased interest in healthy eating. Thus, the company has announced that it will be reducing its annual dividend by 5% a year for the next two years. After that, it will maintain a constant dividend of $1 a share. Two weeks ago, the company paid a dividend of $1.40 per share. What is this stock worth if you require a 9% rate of return? A. $10.86 B. $11.11 C. $11.64 D. $12.98 E.$14.2356. Which of the following amounts is closest to what should be paid for Overland common stock? Overland has just paid a dividend of $2.25. These dividends are expected to grow at a rate of 5% in the foreseeable future. The required rate of return is 11%. A. $20.45 B. $21.48 C. $37.50 D. $39.38 E. $47.70Value of stock = D 0(1 + g)/(r - g) = $2.25(1 + 0.05)/(0.11 - 0.05) = $39.37557. What would be the maximum an investor should pay for the common stock of a firm that has no growth opportunities but pays a dividend of $1.36 per year? The next dividend will be paid in exactly 1 year. The required rate of return is 12.5%. A. $9.52 B. $10.88 C. $12.24 D. $17.00E. None of the above $1.36/.125 = $10.8858. Mortgage Instruments Inc. is expected to paydividends of $1.03 next year. The company just paid a dividend of $1. This growth rate is expected to continue. How much should be paid for Mortgage Instruments stock just after the dividend if the appropriate discount rate is 5%. A. $20.00 B. $21.50 C. $34.75 D. $50.00 E. $51.50g = (D 1 - D 0)/D 0 = ($1.03 - $1.00)/$1.00 = 0.03 (g = 3%)Value of stock = D 1/(r - g) = $1.03/(0.05 - 0.03) = $51.5059. The Felix Corp. projects to pay a dividend of $.75 next year and then have it grow at 12% for thefollowing 3 years before growing at 8% indefinitely thereafter. The equity has a required return of 10% in the market. The price of the stock should be ____. A. $9.38 B. $17.05 C. $41.67 D. $59.80 E. $62.38Value of stock = [($.75/1.1) + ($.84/(1.1)2) +($.94/(1.1)3) + ($1.05/(1.1)4) + (($1.13/.02)/(1.1)4) = $41.67Chapter 09 - Stock Valuation9-1160. If a company paid a dividend of $0.40 last month and it is expected to grow at 7% for the next 6 years and then grow at 4% thereafter, the dividend expected in year 8 is ___. A. $0.63 B. $0.65 C. $0.68 D. $0.69 E. $0.74Div 8 = $.4*(1 + .07)6 (1.04)2 = $.6561. The Lory Company had net earnings of $127,000 this past year. Dividends of $38,100 were paid. The company's equity was $1,587,500. If Lory has 100,000 shares outstanding with a current marketprice of $11.625 per share, and the growth rate is 5.6%, what is the required rate of return? A. 4.2% B. 6% C. 9% D. 14%E. None of the aboveR = Div/P 0 + g = (.381(1.056))/11.625) + .056 = (.40/11.625) + .056 = .0346 + .056 = .0906 = 9% 62. Doctors-On-Call, a newly formed medical group, just paid a dividend of $.50. The company's dividend is expected to grow at a 20% rate for the next 5 years and at a 3% rate thereafter. What is the value of the stock if the appropriate discount rate is 12%? A. $8.08 B. $11.17 C. $14.22 D. $17.32 E. $30.90Years 1-5: ($.50(1.2)t /(1.12)t + (1.28/.09)/(1.12)5 = $11.1763. A stock you are interested in paid a dividend of $1 last week. The anticipated growth rate in dividends and earnings is 20% for the next year and 10% the year after that before settling down to a constant 5% growth rate. The discount rate is 12%. Calculate the expected price of the stock. A. $17.20 B. $17.90 C. $18.20 D. $19.40 E. $19.75Price = $1.00(1.20)/1.12 + $1.20(1.100)/1.2544 + [$1.32(1.05)/(.12 - .05)]/1.2544 = $17.9064. A stock you are interested in paid a dividend of $1 last month. The anticipated growth rate in dividends and earnings is 25% for the next 2 years before settling down to a constant 5% growth rate. The discount rate is 12%. Calculate the expected price of the stock. A. $15.38 B. $20.50 C. $21.04 D. $22.27 E. $26.14Price = $1.00(1.25)/1.12 + $1.25(1.25)/1.2544 + [$1.5625(1.05)/(.12 - .05)]/1.2544 = $21.0465. Which of the following values is closest to the amount that should be paid for a stock that will pay a dividend of $10 in one year and $11 in two years? The stock will be sold in 2 years for an estimated price of $120. The appropriate discount rate is 9%. A. $114.60 B. $119.43 C. $124.20 D. $129.50 E. $138.75Value of stock = D 1/(1 + r) + (D 2 + P 2)/(1 + r)2 = $10/(1 + 0.09) + ($11 + $120)/(1 + 0.09) 2 = $119.43。
高盛财经词典 - 英汉对照English Terms(A)中文翻译详情解释/例子Accelerated Depreciation 加快折旧任何基于会计或税务原因促使一项资产在较早期以较大金额折旧的折旧原那么Accident and Health Benefits 意外与健康福利为员工提供有关疾病、意外受伤或意外死亡的福利。
这些福利包括支付医院及医疗开支以及有关时期的收入。
Accounts Receivable (AR) 应收账款客户应付的金额。
拥有应收账款指公司已经出售产品或效劳但仍未收取款项Accretive Acquisition 具增值作用的收购工程能提高进行收购公司每股盈利的收购工程Acid Test 酸性测试比率一项严谨的测试,用以衡量一家公司是否拥有足够的短期资产,在无需出售库存的情况下解决其短期负债。
计算方法:(现金+ 应收账款+短期投资)流动负债Act of God Bond 天灾债券保险公司发行的债券,旨在将债券的本金及利息与天然灾害造成的公司损失联系起来Active Bond Crowd 活泼债券投资者在纽约股票交易所内买卖活泼的定息证券Active Income 活动收入来自提供效劳所得的收入,包括工资、薪酬、奖金、佣金,以及来自实际参与业务的收入Active Investing 积极投资包含持续买卖行为的投资策略。
主动投资者买入投资,并密切注意其走势,以期把握盈利时机Active Management 积极管理寻求投资回报高于既定基准的投资策略Activity Based Budgeting 以活动为根底的预算案一种制定预算的方法,过程为列举机构内每个部门所有牵涉本钱的活动,并确立各种活动之间的关系,然后根据此资料决定对各项活动投入的资源Activity Based Management 以活动为根底的管理利用以活动为根底的本钱计算制度改善一家公司的运营Activity Ratio 活动比率一项用以衡量一家公司将其资产负债表内账项转为现金或营业额的能力的会计比率Actual Return 实际回报一名投资者的实际收益或损失,可用以下公式表示:预期回报加上公司特殊消息及总体经济消息Actuary 精算保险公司的专业人员,负责评估申请人及其医疗纪录,以预测申请人的寿命Acquisition 收购一家公司收购另一家公司的多数股权Acquisition Premium 收购溢价收购一家公司的实际本钱与该公司收购前估值之间的差额Affiliated Companies 联营公司一家公司拥有另一家公司少数权益〔低于50%〕的情况,或指两家公司之间存在某些关联Affiliated Person 关联人士能影响一家企业活动的人士,包括董事、行政人员及股东等After Hours Trading 收盘后交易主要大型交易所正常交易时间以外进行的买卖交易After Tax Operating Income - ATOI 税后营运收入一家公司除税后的总营运收入。
H股H Stock一篮子备兑证Basket Covered Warrants入限价买盘Buy Limit Order三角形Triangle三底Triple Bottoms三顶Triple Tops下降楔形Falling Wedge下降旗形Falling Flag下降轨Downward Trendline下跌风险Downside Risk上升楔形Rising Wedge上升旗形Rising Flag上升轨Upward Trendline上升风险Upside Risk大手成交Large Transaction大利市机Teletext中央结算系统Central Clearing and Settlement System 互惠基金Mutual Funds分拆Spin-off升水Premium引伸波幅Implied Volatility手Lot Size支持线Support Line止蚀盘Stop Loss Order止赚盘Stop Profit Order牛市Bull Market出限价沽盘Sell Limit Order可换股债券Convertible Bonds市价盘Market Order市盈率Price-to-earnings Ratio (P/E Ratio)平价At the Money未平仓合约Open Interest未平仓合约Open Interest生产物价指数Producer Price Index (PPI)生产物价指数Producer Price Index, PPI交叉盘Cross Trade名义利率Nominal Interest Rate合并Merger回报Return成分股Constituent Stock成交量Volume收市价Closing Price老鼠仓Rat Trading自动对盘Automatching行使价Exercise Price优先股Preferred Stock价外Out of the Money价内In the Money孖展户口Margin Account庄家Market Maker低水Discount利率Interest Rate即日鲜Day Trading批股Share Placement折让Discount投资组合理论Portfolio Theory投资银行Investment Banker杠杆比率Gearing Ratio每日波幅限额Daily Fluctuation Limit 系统性风险Systematic Risk供股Right Issue供股Right Issue供股权Rights固定资产Fixed Asset定息债券Fixed Income Securities所有普通股指数All-Ordinaries Index招股书Prospectus拋空Short Sale拆出利率Offer Rate注资Asset Injection沽空Short Sale波浪理论Wave Theory波幅Volatility股市指数Stock Index股份回购Share Buyback/Repurchase 股息Dividend股票市场Stock Market股票孖展Share Margin股东股本利益Shareholer’s Equity金管局Hong Kong Monetary Authority 阻力区Resistance Level阻力线Resistance Line信贷评级机构Credit Rating Institution 按金户口指数备兑证Index Covered Warrants柱状图Bar Chart流动比率Current Ratio流动负债Current Liabilities流动资产Current Asset相反理论Contrarian Theory美国联邦贴现率Federal Discount Rate背驰Divergence衍生工具Derivatives限价盘Limit Order香港银行同业拆息Hong Kong Interbank Offer Rate (HIBOR)恒生一百指数Hang Seng 100 Index恒生中国企业指数Hand Seng China-affiliated Corp Index(HSCCI) 恒生中资企业指数Hang Seng China Enterprises Index (HSCEI) 恒生五十中型股指数Hang Seng Midcap 50 Index恒生指数Hang Seng Index套戥Arbitrage息率Dividend Yield效率市场假设Efficient Market Hypothesis核数师意见Auditor Opinion消费物价指数Consumems特别成交Special Trade?除息Ex-dividend除净Ex-all除权Ex-right高水Premium第一市场Primary Market第一市场直接批股Direct Placement第二市场Secondary Market通胀Inflation最优惠利率Prime Rate循环理论Cyclical Theory普通股Common Se。
MinicaseStock Valuation at Ragan, Inc.Ragan, Inc., was founded nine years ago by brother and sister Carrington and Genevieve Ragan. The company manufactures and installs commercial heating, ventilation, and cooling (HVAC) units. Ragan, Inc., has experienced rapid growth because of a proprietary technology that increases the energy efficiency in its units. The company is equally owned by Carrington and Genevieve. The original partnership agreement between the siblings gave each 50,000 shares of stock. In the event either wished to sell stock, the shares first had to be offered to the other at a discounted price.Although neither sibling wants to sell, they have decided they should value their holdings in the company. The get started, they have gathered the following information about their main competitors:Expert HVAC Corporation’s negative earnings per share were the result of an accounting write-off last year. Without the write-off, earnings per share for the company would have been $1.06.Last year, Ragan, Inc., had an EPS of $4.54 and paid a dividend to Carrington and Genevieve of $63,000 each. The company also had a return on equity of 25%. The siblings believe that 20% is an appropriate required return for the company.Questions:1. Assuming the company continues its current growth rate, what is the value per share of the company’s stock?The total dividend paid by the company is 126,000.Total earnings are:100,000x4.54=454,000Therefore, payout ratio is 126,000/454,000=0.28Retention ratio=1-0.28=0.72It is easy to calculate g=ROExb=0.25x0.72=0.18D0=63,000/50,000=1.26Therefore, P0= D1/(R-g)=1.26(1.2)/(0.2-0.18)=75.6In conclusion, the value per share of the company’s stock is 75.6 dollars2. To verify their calculations, Carrington and Genevieve have hired Josh Schlessman as a consultant. Josh was previously an equity analyst and covered the HVAC industry. Josh has examined the company’s financial statements, as well as examining its competitors. Although Ragan, Inc., currently has a technological advantage, his research indicates that other companies are investigating methods to improve efficiency. Given this, Josh believes that the company’stechnological advantage will last only for the next five years. After this period, the company’s growth will likely slow to the industry growth average. Additionally, Josh believes that the equired return used by the company is too high. He believes the industry average required return is more appropriate. Under this growth rate assumption, what is your estimate of the stock price?Since the Expert HCAC has a write-off to affect the real answer, we need to recalculate it. Industry EPS=(0.79+1.38+1.06)/3=1.08Industry payout ratio=0.4/1.08=0.37Industry retention ratio=1-0.37=0.63Therefore, g=0.1233x0.63=0.078The company will continue to grow in five yearsSo, D1=1.26(1.18)=1.4868D2=1.4868(1.18)=1.754424D3=1.754424(1.18)=2.07D4=2.07(1.18)=2.44286D5=2.44286(1.18)=2.8825D6=2.8825(1.18)=3.4The stock price in year 5 with the industry required return will be:Stock value in year 5 =3.4/(0.1167-0.078)=87.85It is easy to calculate the total value today is:53 dollars3. What is the industry average price-earnings ratio? What is the price-earnings ratio for Ragan, Inc.? Is this the relationship you would expect between the two ratios? Why?industry average price-earnings ratio=0.51/13.09=0.0389price-earnings ratio for Ragan, Inc.=4.54/53=0.0856the relationship between the two ratios is:Positive correlation which means that with the rise of industry average price-earnings ratio, the price-earnings ratio for Ragan, Inc. will rise. Because industry average measures the average level of the Arctic Cooling, Inc , National Heating & Cooling and Expert HVAC Corp. If industry average rise, means the average level of the Arctic Cooling, Inc , National Heating & Cooling and Expert HVAC Corp has risen, therefore, price-earnings ratio for Ragan, Inc will rise for its business are the same to the three subjects above.4. Carrington and Genevieve are unsure how to interpret the price-earnings ratio. After some head scratching, they’ve come up with the following expression for the price-earnings ratio:Beginning with the constant dividend growth model, verify this result. What does this expression imply about the relationship between the dividend payout ratio, the required return on the stock, and the company’s ROE?As we known b is Retention ratio which equals 1- payout ratioTherefore, P/E= D/(R-g)E=1-b/R-(ROExb)D/E=(R-g)(1-b)/R-(ROExb)R=(DxROE+Dxb-Exg-Exgxb)/(D-E+b)So,the company’s ROE and R has positive correlation.5. Assume the company’s growth rate slows to the industry average in five years. What future return on equity does this imply, assuming a constant payout ratio?It implies that the value of the stock price of Ragan, Inc will get lower because of the lower growth rate. We can get the answer with the formula we have used above.6.After discussing the stock value with Josh, Carrington and Genevieve agree that they wouldlike to increase the value of the company stock. Like many small business owners, they want to retain control of the company, but they do not want to sell stock to outside investors.They also feel that the company’s debt is at a manageable level and do not want to borrow more money. How can they increase the price of the stock? Are there any conditions under which this strategy would not increase the stock price?We can increase the price of the stock by issuing more dividends. As we know, we calculate the stock price by the formula D/(R-g).But, when the growth rate of Ragan, Inc get lower, this strategy would not increase the stock price. We can also get the answer with the formula above ,and if dividends are not paid in cash such as shares, this strategy would also not increase the stock price.唐庆飞11210690142 金融工程管理。
Stock Valuation and Learning about Pro¯tability ·LUBO·S P¶ASTOR and PIETRO VERONESI*July8,2002ABSTRACTWe develop a simple approach to valuing stocks in the presence of learning about average pro¯tability.The market-to-book ratio(M/B)increases with uncertainty about average pro¯tability,especially for¯rms that pay no dividends.M/B is predicted to decline over a¯rm's lifetime due to learning,with steeper decline when the¯rm is young.These pre-dictions are con¯rmed empirically.Data also support the predictions that younger stocks and stocks that pay no dividends have more volatile returns.Firm pro¯tability has become more volatile recently,helping explain the puzzling increase in average idiosyncratic return volatility observed over the past few decades.*Both authors are at the Graduate School of Business,University of Chicago.Both are also a±liated with the CEPR and NBER.Helpful comments were gratefully received from Dan Bens,Tony Bernardo,Michael Brennan,John Campbell,George Constantinides,Gene Fama,Ken French,Chris Geczy,Rick Green,John Heaton,Boyan Jovanovic,Rob Stambaugh,Per StrÄo mberg,Tuomo Vuolteenaho,Larry Wall,Franco Wong, Yihong Xia,an anonymous referee,and seminar participants at the Federal Reserve Bank of Atlanta,the Federal Reserve Bank of Chicago,the University of Chicago,the University of Pennsylvania,and the2002 ESSFM(CEPR)at Gerzensee.The past two decades have witnessed an unprecedented surge in the number of newly listed ¯rms on the major U.S.stock exchanges.According to Fama and French(2001b),over550 new¯rms per year appeared between years1980and2000,on average,compared to less than150¯rms in the previous two decades.Some of these new¯rms command valuations that might seem too high to be justi¯ed by reasonable assumptions about expected future pro¯tability.For example,more than one in ten of all¯rms listed between years1962and 2000are worth more than seven times their book value at the end of their year of listing,and almost one in50¯rms are worth more than20times their book value.Naturally,investors attempting to value the newly listed¯rms are confronted with substantial uncertainty about their future pro¯tability.We argue that this uncertainty contributes to the high valuations of young¯rms,and that the resolution of this uncertainty over time tends to be accompanied by a decline in the valuation ratios.The basic idea is simple.Let B denote a¯rm's book equity today(at time0)and g its constant growth rate,so the value of book equity at time T is B exp(gT).Assuming that competition eliminates the¯rm's expected abnormal earnings by T,the¯rm's market value at T equals its book value,and the market value today is the expected book value at T discounted at some rate r.If g is unknown and assumed to be normally distributed with mean¹g and variance¾2,the market-to-book ratio(M/B)today isM=E f exp[(g¡r)T]g=exp£(¹g+¾2=2¡r)T¤:(1) The M/B ratio is increasing in the uncertainty about book equity growth,¾2,thanks to the convex relation between the growth rate and terminal value.1We argue that uncertainty declines over a¯rm's lifetime due to learning.As a result,younger¯rms have higher¾2and hence also higher M/B ratios,holding other things(such as¹g and r)constant.The valuation model developed in the paper is more realistic than the baby model outlined above,and thus it has a richer set of implications.Firm pro¯tability,measured as the accounting rate of return on book equity,is assumed to revert to an unknown mean whose value investors learn over ing techniques of Bayesian updating,we obtain a closed-form solution for the¯rm's M/B ratio.M/B is shown to increase with expected pro¯tability and decrease with expected stock return,consistent with the existing literature.The previous paragraph shows that M/B increases with uncertainty about the average growth rate of book equity.Since the growth rate of book is pro¯tability minus the dividend yield,M/B also increases with uncertainty about average pro¯tability.This uncertainty is shown to have no e®ect on expected stock returns.Even if¯rm pro¯tability is correlated with the exogenously speci¯ed stochastic discount factor,the updates in the estimates of mean pro¯tability areuncorrelated with it,so any additional return volatility is idiosyncratic.Uncertainty about mean pro¯tability therefore leads to higher valuations because it increases expected future payo®s without a®ecting the discount rate.In the presence of external¯nancing constraints,which are common for young¯rms and assumed in the paper,dividend payouts reduce the growth rate of book equity,thereby weakening the convexity between the growth rate and the future value of book equity.As a result,the model implies that the relation between M/B and the uncertainty about average pro¯tability should be stronger for no-dividend-paying stocks.Calibrating the model to a typical¯rm in our sample,we¯nd that the e®ect of the uncertainty on M/B can be quantitatively large,especially for stocks that pay no dividends.Our empirical analysis con¯rms the model's predictions on a large panel of data covering the years1963through2000.Since uncertainty declines over time due to learning,the model implies that a younger¯rm should have a higher M/B ratio than an otherwise identical older ¯rm.Indeed,we¯nd a signi¯cantly negative cross-sectional relation between¯rm age and M/B,even after controlling for other well-known determinants of M/B.We also¯nd that this relation is stronger for¯rms that pay no dividends,con¯rming another prediction of the model.The results are both statistically and economically signi¯cant.For example,we ¯nd a di®erence of over5%between the valuations of a typical two-year-old¯rm and an otherwise identical one-year-old¯rm.Among¯rms that pay no dividends,this valuation di®erence is over12%,and the di®erence between the valuations of a typical¯ve-year-old dividend non-payer and an otherwise identical one-year-old non-payer is almost27%.In addition,age is shown to predict future changes in M/B.The decline of M/B over time is signi¯cantly steeper for younger¯rms,consistent with the model.One alternative explanation for the observed high valuations of young¯rms is that these ¯rms are expected to be highly pro¯table.However,M/B is related to age even after con-trolling for current and future pro¯tability.Another possibility is that(irrational)investors are on average too optimistic about the future pro¯tability of young¯rms.Average stock re-turns for young¯rms should then be low or even negative,as investors gradually revise their high expectations downward.In contrast,we provide a rational model of learning in which young¯rms can have high valuations without having low returns.The debate on whether the returns on young¯rms are too low is still raging.2Since we¯nd a relation between M/B and age even after controlling for future returns,the learning e®ect seems distinct from any potential over-optimism e®ect.Of course,we do not argue that our model fully explains the observed valuations.We only argue that valuations that appear excessively high at¯rstsight do not necessarily imply that investors are irrational.3Apart from implications for valuation ratios,our model has consequences for return volatility as well.Idiosyncratic return volatility increases with uncertainty about the¯rm's average pro¯tability as well as with idiosyncratic volatility of pro¯tability.In the data, volatility indeed tends to be higher for younger¯rms and for¯rms with more volatile prof-itability.Volatility is also higher for¯rms that pay no dividends,as the model predicts.While the bulk of asset pricing research related to stock valuation focuses on the discount rate,our emphasis is on cash°ow.We model cash°ow using accounting information such as earnings and book equity,similar to several other recent studies.Ang and Liu(2001),build-ing on Feltham and Ohlson(1999),specify a±ne processes for selected accounting variables and derive a nonlinear relation between M/B and stochastic interest rates,pro¯tability,and growth in book value.Bakshi and Chen(2001)develop a stock valuation model in which the expected earnings growth rate follows a mean-reverting process,and obtain a number of implications for the price-earnings ratio.Schwartz and Moon(2000)propose a valuation approach in which the expected sales growth rate follows a mean-reverting process with a time-varying drift.They argue that high¯rm valuations can be justi¯ed if the mean and volatility of the sales growth rate are su±ciently high.In addition,Berk,Green,and Naik (1999)and Gomes,Kogan,and Zhang(2001)derive the value of an optimally-investing¯rm as a sum of assets in place and growth options.In their models,M/B appears in the dy-namics of conditional expected returns,helping explain various properties of stock returns. Although all of these papers address various interesting issues related to dynamic stock val-uation,none of them incorporates uncertainty and learning about company fundamentals into the valuation framework.In this paper,learning is done by investors valuing a¯rm.Related literature explores the implications of learning by¯rms about their own e±ciency and resources(e.g.Jovanovich, 1982,Bernardo and Chowdry,2002).The¯nance literature on learning also includes Tim-merman(1993),David(1997),Veronesi(1999,2001),Brennan and Xia(2001),Lewellen and Shanken(2002),and others.Among other things,these articles show that learning about a hidden state variable such as the dividend growth rate has equilibrium implications that are in line with certain empirical regularities,such as excess volatility and predictability of stock returns.These articles do not investigate the implications of learning for stock valuation ratios such as M/B,which is the subject of the present article.The paper is organized as follows.Section I develops our valuation approach.The ¯rst subsection derives the expressions for M/B and stock returns in the benchmark casewhen average¯rm pro¯tability is assumed to be known.The second subsection extends the analysis to the case of unknown average pro¯tability.Section II empirically tests the main implications of the model,and Section III concludes.I.The Valuation FrameworkThis section develops a continuous-time framework for valuing stocks of¯rms whose pro¯tability is mean-reverting.Pro¯tability is de¯ned as the¯rm's instantaneous accountingreturn on equity:½t=Y t B t;where Y t denotes the¯rm's earnings at time t,and B t denotes the book value of the¯rm's equity at time t.Pro¯tability is assumed to follow a simple mean-reverting process:d½t=Á(½¡½t)dt+¾½dW t;(2)where½is mean pro¯tability,sometimes also referred to as average pro¯tability,Áis the speed of mean reversion,¾½=(¾½;1;¾½;2)is a1£2vector of constants,and dW t is a2£1 vector of independent Brownian motions.To avoid unnecessary complexity,we do not model the¯rm's investment policy.Instead,we simply assume that the resulting pro¯tability is mean-reverting,consistent with the existing empirical literature.4Note that½t is not required to be positive,which is useful in light of our interest in the valuation of young¯rms,whose earnings are sometimes negative.The¯rm is assumed to pay out a constant fraction of its book equity in dividends:D t=c B t;c¸0:(3)This assumption of constant dividend yield with respect to book value re°ects the common corporate policy of smoothing dividends over time.5Since young¯rms often pay no dividends and since the fraction of dividend-paying¯rms has been decreasing steadily(see Fama and French,2001a),the special case of c=0receives particular attention in our analysis.We assume that the¯rm is¯nanced only by equity and that there are no new equity issues. External¯nancing is costly for many reasons,including transaction costs and asymmetric information problems(see Myers,1984,and Myers and Majluf,1984).Both reasons are likely to be relevant for young¯rms and¯rms with uncertain pro¯tability,which are at the focus of this study.The process for book equity is governed by the clean surplus relation.This accounting identity states that,in the absence of external capital contributions or withdrawals,book equity increases by current earnings and decreases by current dividends:6dB t=(Y t¡D t)dt=(½t¡c)B t dt:(4) In words,the growth rate of book equity equals pro¯tability minus the dividend yield.To build a bridge between accounting values and market values,we assume that the market value of equity will equal the book value at some future time T.To motivate this assumption,consider the abnormal earnings model of Ohlson(1990,1995)and Feltham and Ohlson(1995),which is essentially just another accounting identity.This model equates market equity with book equity plus the discounted sum of abnormal earnings,de¯ned as earnings in excess of those earned at the rate equal to the cost of capital.Since¯rms are often created to pursue pro¯table ventures based on novel ideas and technologies,which are sometimes patent-protected,the pro¯tability of a new¯rm can be abnormal for an extended period of time.However,it seems reasonable to assume that abnormal earnings are gradually reduced by competitive market forces.We assume that,at some known future time T,the ¯rm reaches\maturity"in the sense that the present value of expected future abnormal earnings is zero.At that point,M T=B T.Some readers may¯nd it unnatural to relate market value to book value,as many ac-counting features seem irrelevant for valuation.Such readers may¯nd it useful to replace earnings by net cash°ows and to view book value as the cumulative net cash°ow that is reinvested in the¯rm.The assumption that M T=B T then means that average net future cash°ow is zero at maturity,and all of our theoretical results can be interpreted from the cash°ow perspective.Our choice of accounting-based exposition is motivated mainly by practical concerns{the concepts of earnings,book value,and pro¯tability are well-known and commonly reported,making the model easier to test and to use in practice.The market value of the¯rm's equity at any point in time is given by the sum of the discounted value of all future dividends and the terminal value M T=B T:M t=E t·Z Tt¼s¼tD s ds¸+E t·¼T¼tB T¸:(5)The stochastic discount factor¼t is assumed to follow the log-normal processd¼tt=¡rdt¡¾¼dW t;(6)where r denotes a constant risk-free interest rate and ¾¼=(¾¼;1;0)is a 1£2vector.We assume that changes in ¼t are driven only by the ¯rst element of dW t (i.e.¾¼;2=0),so that we can interpret dW 1;t as a systematic shock and dW 2;t as an idiosyncratic shock.The valuation framework presented above can be generalized in numerous ways.Many assumptions can be relaxed or modi¯ed without a®ecting any conclusions,as discussed in Section I.C.Our aim is to present a parsimonious yet reasonably realistic model that high-lights the importance of learning about mean pro¯tability in stock valuation.A.No Uncertainty about Mean Pro¯tabilityThis subsection assumes perfect knowledge of all model parameters,including mean prof-itability ½.The results developed here are useful for comparison with the next subsection,in which ½is treated as unknown.The following function is used repeatedly:Z (½;½t ;s )=exp ½¡(r +c ¡½)s +1Á¡1¡e ¡Ás ¢(½t ¡½)+Q (s )¾;(7)where Q (s )=¾½¾0½2Á3·1¡e ¡2Ás 2+Ás ¡2¡1¡e ¡Ás ¢¸+¾¼¾0½Á2¡1¡e ¡Ás ¡Ás ¢:(8)As shown in the appendix,the function Z has a simple economic interpretation as expected discounted growth in book equity:Z (½;½t ;s )=E t ·¼t +s B t +s t t¸:(9)The following proposition,proved in the appendix,obtains closed-form solutions for the ¯rm's M/B ratio and for the ¯rst two moments of stock returns.Throughout,¿=T ¡t .Proposition 1.Assume ½is known with certainty.Then(a)The ¯rm's ratio of market value of equity to book value of equity is given by M t t =G (½;½t ;¿)´c Z ¿0Z (½;½t ;s )ds +Z (½;½t ;¿):(10)(b)The process for excess stock returns,dR t =(dM t +D t dt )=M t ¡rdt ,is given bydR t =¹R;t dt +¾R;t dW t ;where¹R;t=F (½t ;¿;c )¾½¾0¼Á;(11)¾R;t =F (½t ;¿;c )1Á¾½;(12)and F(½t;¿;c)is given in equation(A7)in the appendix.In the special case when the ¯rm pays no dividends(c=0),we have¹R;t=¡1¡e¡Á¿¢¾½¾0¼Á;(13)¾R;t=¡1¡e¡Á¿¢1¾½:(14)Note that the expressions for M/B and the moments of stock returns are fully explicit for c=0.In the presence of dividends,c>0,the integral in equation(10)as well as its counterpart in the expression for F(½t;¿;c)in the appendix can be computed in a split-second using standard numerical techniques.Moreover,the solution is su±ciently explicit to allow full characterization of the properties of the M/B ratio.These properties are summarized in the following corollaries,obtained immediately from equations(7)and(10)with the help of the fact that sÁ>1¡e¡Ás>0for all s>0.Corollary1.The M/B ratio increases if(i)average pro¯tability½increases;(ii)current pro¯tability½t increases;(iii)¾½¾0¼,the key determinant of expected excess stock return¹R;t,decreases;(iv)the interest rate r decreases;(v)¾½¾0½,the instantaneous variance of the pro¯tability process,increases.Corollary2.The M/B ratio is convex in½.The results in Corollary1are intuitive.Increases in½or½t push M/B up because they raise expectations of future pro¯tability.7Decreases in¹R;t or r lift M/B as they reduce expected stock returns.In other words,M/B increases with expected accounting returns(pro¯tability)and decreases with expected stock returns,as discussed for example in Vuolteenaho(2000).More volatile pro¯tability increases M/B because it increases expected future payo®s due to the convex relation between future payo®s and their growth rate.This relation is discussed later in the paper in more detail.The M/B ratio also depends on the speed of mean reversionÁand the dividend yield c,but the dependence is slightly more complex.The e®ect ofÁon M/B is ambiguous as a result of two e®ects working in the opposite directions.IncreasingÁensures that½t varies less around its mean½.Since future payo®s become more certain,both systematic and nonsystematic components of return volatility decline,together with the required rate ofreturn,and M/B increases.On the other hand,the lower dispersion of½t decreases expected future payo®s,again due to the convex relation between future payo®s and their growth rate, and M/B decreases.The e®ect of c on M/B is ambiguous as well.A higher dividend yield increases M/B since the payo®s are received earlier on average,but it also decreases M/B since it reduces the growth rate of book equity.One would expect that when pro¯tability is su±ciently high,paying dividends reduces M/B,and vice versa.This intuition is con¯rmed in Figure1,which plots M/B against½for three values of c:0,0.04,and0.10.For su±ciently large values of½,increasing c reduces M/B,and vice versa.********************INSERT FIGURE1HERE********************Figure1is constructed using parameter values that correspond to typical values observed in the data(described in the next section).The value of½t is set equal to0.11,which is the grand median,across stocks and years,of all valid annual returns on equity(ROE)in our sample.To estimateÁand¾½,we estimate an AR(1)model for each stock's ROE,using the longest continuous series of the stock's valid annual ROEs.That series is required to be at least10years long(using15or20years leads to almost identical results).The slope coe±cients are adjusted for small-sample bias following the approach of Marriott and Pope (1954)and Kendall(1954).The value ofÁ=0:3968used in the calibration is the median of the estimated coe±cients across all4,571stocks.8In addition,we choose¿=15years,r=0:03,¾¼;1=0:6,¾½1=0:0584,and¾½2=0:0596.The latter three values were chosento imply¹R;t=0:0883,a reasonable value for expected annual excess return in light of the data,as well as p¾½¾0½=0:0834,which is equal to the median of the residual volatility of pro¯tability across all4,571stocks.Finally,the grand median of the ratios of common stock dividends to last year's book equity(c)is0.0105.(Interestingly,the cross-sectional median is zero in each year since1985.Most¯rms do not pay dividends nowadays.)The grand median of c calculated only across¯rms that pay dividends is0.0434.These numbers have guided our choices for c in Figure1as well as in the subsequent¯gures.Figure1shows that the relation between M/B and½is convex.This relation is stated formally in Corollary2,and the proof of the convexity of G(½;½t;¿)in equation(10)is provided in the appendix.The intuition is explained in the introduction.Also note that the convexity is higher at higher growth rates.Since dividends reduce the growth rate of book equity,the convexity of M/B in½should be less pronounced for higher values of c.This observation is also con¯rmed in Figure1.Finally,the stock return process displayed in Proposition1exhibits a mechanical property worth commenting on.As¿!0,F(½t;¿;c)!0and hence also¾R;t!0and¹R;t!0.Inwords,as maturity approaches,stock returns become less risky,and at maturity they become riskless.This property is an artifact of the¯nite horizon assumption,since at time T,the stockholder receives a locally riskless payo®B T.We are not overly concerned about the return behavior close to maturity,as we are interested in valuing young¯rms whose horizons are relatively long.If the horizon¿is long enough,expected returns and return volatility are essentially constant over time.For example,using the parameter values from Figure1, we have¹R;t=7:1%for¿=5years,¹R;t=8:0%for¿=10years,and¹R;t=8:1%for ¿=15years.Moreover,these¯nite horizon e®ects disappear in frameworks with random or in¯nite horizon(see Section I.C.),which have very similar qualitative implications.B.Learning about Mean Pro¯tabilityThis subsection investigates the e®ects of uncertainty and learning about mean pro¯tabil-ity on valuation and stock returns.Throughout,mean pro¯tability½is treated as unknown. At any time t,investors'beliefs about½are summarized by a probability density function p t(½),and investors rationally update their beliefs about½over time.Equations(5),(10),and the law of iterated expectations immediately implyM t=Z R G(½;½t;¿)p t(½)d½:(15)B tLoosely speaking,the¯rm's M/B ratio under uncertainty is the average of the M/B ratios for all possible values of½,weighted by the current probabilities assigned to each½.One of our key results is that higher uncertainty about½increases M/B.Recall from Corollary2that G(½t;½;¿)is a convex function of½.Hence,greater dispersion in p t(½) increases the expected value of G(½t;½;¿).(Greater dispersion is interpreted as a mean-preserving-spread,de¯ned in Rothschild and Stiglitz,1970.)Higher uncertainty about½increases the probability that future growth rate of book equity will be persistently high or persistently low.Due to the convex nature of compounding,a persistently high growth rate has a bigger impact on the future book value than a persistently low growth rate and the expected future book value increases,together with M/B.To obtain closed-form solutions for prices and returns,we assume that the prior distri-bution p0(½)at time t=0is normally distributed,and that investors update their beliefs using the Bayes rule.The resulting posterior distribution p t(½)is also normal,as shown by the following lemma,proved in the appendix.Lemma1.Suppose the prior distribution of½at time t=0is normal,½»N(b½0,b¾20):Then the posterior distribution of½at time t>0conditional on F t=f(¼¿;½¿):0·¿·t g is alsonormal,½j F t»N(b½t,b¾2t),where(a)The conditional mean b½t=E[½jF t]evolves according to the processd b½t=b¾2tÁ¾½;2d f W2;t;(16)where f W2;t is the idiosyncratic component of the Wiener process capturing investors' perceived expectation errors(see equation A9in the appendix).(b)The mean squared error b¾2t=E[(½¡b½t)2jF t]is non-stochastic and given byb¾2t=11b¾20+¾2½;2t:(17)Note that the variance b¾2t of the posterior distribution declines over time due to learning, and the speed of this decline increases with the ratioÁ=¾½;2.A higher value ofÁmeans that½t will be close to the mean½more often,making it easier to learn the value of the latter.A smaller value of¾½;2also leads to quicker learning because it implies a less noisy pro¯tability process.Figure2plots the evolution of b¾t using the same parameter values as in Figure1,except thatÁassumes three di®erent values,0.2,0.4,and0.6.Note that learning is rather slow.With the prior standard deviation of b¾0=0:10,or10%per year,the posterior standard deviation b¾t after10years is still large,over4%.This number corresponds to Á=0:4,obtained for the median¯rm in our sample.Even when mean reversion is faster,Á=0:6,the uncertainty after10years remains substantial,about3%.********************INSERT FIGURE2HERE********************It is useful to de¯ne the following function:Z U¡b½t;b¾2t;½t;s¢=Z(b½t;½t;s)exp ½12Á2b¾2t¡Ás¡1+e¡Ás¢2¾;(18)where Z(b½t;½t;s)is de¯ned in equation(7).Proposition2,proved in the appendix,is a counterpart of Proposition1in the case of unknown mean pro¯tability.As before,¿=T¡t.Proposition2.Assume that investors rationally learn about the unknown value of½,and that the assumptions stated in Lemma1are satis¯ed.Then(a)The¯rm's ratio of market value of equity to book value of equity is given byM tB t=c Z¿0Z U¡b½t;b¾2t;½t;s¢ds+Z U¡b½t;b¾2t;½t;¿¢:(19)。
市盈率与市净率(Price earnings ratio and net profit ratio)Many of the price level of stock valuation methods, some are complicated, some very fancy a little cool, but I love this one simple truth, love is not gorgeous boastful; for the stock is so, the valuation of the value of the investment is one of the central issues, price earnings ratio valuation method is the most primitive and the most simple although there are many limitations, but does not prevent it as a practical method of valuation, it should be said that the line with my motto: simple and practical is good.When it comes to the limitation of earnings that is very much, such as assets and liabilities, cash, accounts receivable, all these trends are not considered, but we don't have repeatedly said in the hope that an indicator of all problems, a certain index can explain one aspect, like a person may not for each field in the same; for this to have a correct understanding of the price earnings ratio is an important indicator, but never hope to correct reaction of stock price, better asset quality not the company is good or bad reaction.Of course, the ideal method of stock price earnings ratio is not valued, but in your own valuation method has not formed before the very useful. The price earnings ratio or earnings, is an important index to reflect the investment returns and risk one, the cumulative number of years reflect the enterprise according to the current level of profitability need considerable profit to the current stock price. For investors earnings multiples as small as possible, the general description of higher investment value; multiple general means of virtual high price, high investment risk; price earningsmultiples usually seen in 10-30 times is a reasonable interval, different industry prospect and trend of development of enterprise depends on; if the calculated in static earnings ratio greatly, beyond the scope of the general can be determined to overestimate or underestimate, but not too complicated calculation method.The price earnings ratio (P/E) between the price and earnings per share of stock proportion, also can be the total market value and net profit ratio. The price earnings ratio is based on historical earnings as the basis, thus resulting in a sense of belonging is prospective; itself implies an assumption that the company historical record of profitability as a reference, this identity can be used to analyze the basis of future profitability.Earnings can be divided into static and dynamic earnings ratio are the same with the current price of molecular or total market capitalization, the static and dynamic difference is that the denominator is different, the dynamic price earnings ratio in recent earnings for the divisor can generally have three different algorithms, one is the stock market software using the "current profit the current quarter / *4"; two is the most recent four quarter data add; three is the last year for performance. The static price earnings ratio to years of profit for the divisor can be three years, five years, eight years, it does not have a unified standard, did not say that a data is most correct, people think that three years is too short perhaps an economic cycle is not finished, the data can reflect the environment in a variety of the performance of eight or more years too long, those data have now not state enterprises,proposed in the last 5 years profit for the calculation of the standard, it is also about a cycle time, profitability is more reasonable, the real reaction of the enterprise; my childhood is very love this 5 words. In the book of 5 representatives in the house, placed at the center of gossip, it is a symbol of moderation and harmony in China culture. Two earnings calculation methods are as follows:Dynamic price earnings ratio = price per share this year, net profit per share = total market value / net profit this yearThe static price earnings ratio = share price / five average annual net profit per share of the total market value of 83019 five = average annual net profitWe usually think of the static price earnings ratio may help explain a company's stock price level, especially for the cyclical industry especially, dynamic earnings can not explain the problem, when the profit of only a few good times, bad times in the profitability can have hundreds of times, as long as the years of the static price earnings ratio average profit after,In order to compare the objective response periodic just real industry profitability. But there are also a problem, the static price earnings ratio was relatively slow, it is not good that moment environment and the changes in the past can not represent the future, there is now a situation that the business situation is deteriorating, the static earnings ratio is none of my business.There is also a need to pay attention to, also cannot see staticearnings trends, such as the two companies, a year profit of 50 million, another nearly five years of earnings are: 10 million, 20 million, 30 million, 40 million, 50 million, the current market value is 500 million, the first in terms of dynamic and static the earnings are also 10 times, for second dynamic price earnings ratio is also 10 times the static price earnings ratio is 16.67 times, only from the static price earnings ratio of two per share price higher than the first expensive, but in fact in the perspective of development, second higher than the first value, because of its the development trend of many than the first strong, now the market value is equivalent, that is to say second to now cheaper than the first.Example: "ZTE" (000063)According to today's closing share price, stock quotes software shows ZTE dynamic price earnings ratio of 123.6 times, it ignored the fact that the company 08 years a quarter net profit accounted for 3.67% of the proportion of 09, net profit in the first quarter accounted for the proportion of 3.2%, 09 in the first quarter net profit of 7865.5 yuan, net profit in the first quarter of this year 10986.4 yuan, belong to the normal level of growth; that is to say, the first quarter of this year, not surprisingly, I'm afraid of total annual net profit ratio will be below 5%, with 5%*4 = 20% to 100% is obviously inappropriate, the middle has appeared more than 80% deviation, also appeared 123.6 times the dynamic price earnings ratio. In essence it has lost its should have the reference significance.Now in 5 years according to the static price earnings ratiocalculation, ZTE 2009 -2005 net profit of 2458121000 yuan, 1660199000 yuan, 1252158000 yuan, 766972000 yuan, 1194343000 yuan, 5 years for a total of 7331793000 yuan, an average of 1466358600 yuan per year, which is approximately equal to 1 billion 466 million yuan; the company's total market capitalization of 44 billion 380 million yuan, 443.8 yuan/14.66 yuan = 30.27 times the static price earnings ratio of 30 times between the dynamic earnings ratio of 123 times and the gap is more than 4 times. It makes the net profit in more and more growing by reason, dynamic earnings should continue to decline, but according to market software algorithm, but this is counterintuitive phenomenon. But also said in front of the static price earnings ratio itself has many defects, at least it is not an ideal method of valuation, but it can't deny the judgment for the stock price has the important reference significance.-------------In an article on the price earnings ratio has been discussed is not repeated, now the city net rate introduce, and then discuss the relationship between earnings and book value, city net rate refers to the ratio of the price per share and net assets per share, with a total market capitalization ratio can also be the net assets of the city; the net rate of stock price can be used as a reference, in general, the net rate of stock investment value is more low.The calculation method of net rate is: city net rate (P/B) = the market price per share, net assets per share; the main difference between earnings and book value measure of stockprice is the profit as a reference, the latter to net assets as a reference. As for the more important, more valuable? Such a comparison is not much practical significance, if you must decide that I think we should pay more attention to the relative earnings; between the front said countless times of each index are complementary rather than competitive relationship, because earnings is inadequate to reference city net rate.Net assets per share book value of equity divided by total equity is obtained, the book value of assets to purchase cost, including fixed assets,We have discussed that the net assets can not provide effective protection for investment security, that is to say PB is a subject of investment relative to the reference price, and can not be understood as the level of protection on investment; for example PB is equal to 2 times, that if the company now bankruptcy liquidation, the 10 yuan the investment can get 5 yuan, this understanding in practice is definitely wrong. Although PB does not represent the profitability, is not representative of the investment security level, but this does not prevent the reference index for investment.The article said that the dynamic price earnings ratio is easy to fluctuate, because profit is very difficult to have the stable performance, especially for small and medium sized enterprises and the cyclical industry is even more so, it will appear as "ZTE" (000063) this phenomenon; net assets in addition to capital operation is generally not significantly changed suddenly, so city net rate was relatively stable; the main factors lead to short-term changes because the stock pricedoes not appear, such as profit for the period increased significantly while PE becomes very low or declining PE become very high phenomenon, so can better reflect the changes of low price.Because the city net rate of only the net assets without considering the profitability of assets, if the long-term net rate is very low and the price earnings ratio is very high, this part of the assets can not reach the normal level of profitability, has basically lost the meaning of operation. The enterprise can barely operating in good times, if macroeconomic or industry once what companies such as wind sways grass, like chaff on the playground, do not know will be blown to the place. If the A shares is not a backdoor listing this, there will be a lot of company PB is less than 1, but now the prices of these companies who are expensive, not because of the outbreak of the growth performance, but because of the reorganization of assets such as expected, this phenomenon is not healthy, adverse long-term development of the market.There is a subtle relationship between earnings and book value, we first consider such a question: in the same ratio under the condition of high net rates or low city net rate? Most people will answer certainly low city net rate, because the lower PB that shares cheaper, safer investment. Is it really true that it would start to analyze it.Suppose that there are two companies, the price earnings ratio (PE) is 20 times, the first city net rate (PB) is 2 times, second city net rate (PB) was 4 times that of other security situation, including asset liability ratio, industry, location, brandadvantage and so on. Now the two companies look at the specific data, assuming that the two companies are the total market value of 200 million yuan, then the 20 times PE last year is 10 million yuan, the first PB is equal to 2 times net assets is 100 million yuan, second PB equals 4 times net assets is 50 million yuan. The general understanding of the people is to buy the net assets of 100 million with 200 million of the total 50 million strong than to buy it, but from the fact that second of the 50 million assets is two times the first 100 million profitability of assets, a clear understanding of the facts seem to be second companies than the first company more attractive.Through the above analysis, it can draw the PB of a company as high as this conclusion, this is contrary to common sense, do not look at the issue of such absolute. Now Chinese most is not only the strength, but the way of thinking Chinese full to non pattern, black and white do not think the bad is good, one of the other party is wrong, drama must have a heinous villain, must not apply leather life and no room for improvement, such thinking is very superficial, strange is the "book of changes" of the "theory of relativity" is this nation forward, anyway, if you want to change to analyze the problem and non black and white in this mode of thinking can not be. If a company is PE 8 times, PB is 8 times, the serious doubt whether the profit level of sustainability, don't believe people can win days, the investment should depend on is common sense, it plays an irreplaceable role,So to see that it is natural to think of the company have a lot of disposable income, and the current stock price has been far overestimated.Of course, simple valuation by PE, the PB is not ideal, but their play is "common sense", many are not actually fooled common sense test, I have their own set of valuation methods in accordance with our investment ideas, but if there is a company that the valuation results with PE and PB I would be the first to be quite different in common sense, do not hesitate to choose and why I believe that knowledge, find the results of the valuation and common sense does not meet. After considering the dynamic and static price earnings ratio, and the city net rate to determine the stock price reaction can objectively is a serious bubble, but no way to obtain the specific valuation; Buffett said: "very few cases can clearly see the price too underestimate or overestimate, but 90% of the time I do not know." To see this situation, PE PB can do. Tall buildings from the ground up, perhaps you should go to the blind pursuit of Buffett such as the valuation of ability now, and start learning from simple and practical, and the use of PE PB, as to realize the level of investment in the future, in addition to the talent and vision, sometimes also by chance, you will not what good results. Above mentioned numerous times the value of the investment character, just as important as the character and vision, why sidesteps the importance of vision, because the character to some extent can be learned, but almost no way to look for learning, no way to change do not blow out the aspiring value investors fellow. It is not that there is no good eye became not only the last value investors, can reach the height of different.Example: "Shahe shares" (000014), "Southern Airlines" (600029)Shares in Shahe stock market software shows the current dynamic price earnings ratio of 7.7 times, only from the look on the words is undervalued shares should be the city net rate is 3.96 times that of the real estate industry also shows that the share price is not low, a closer look at the first quarter earnings last year, and before the year is still a loss last year. Net profit of only 80 million 226 thousand and 800 yuan, while the first quarter of this year net profit of 68 million 462 thousand, mainly due to real estate projects into the settlement period. That is to say, this performance is not sustainable, the dynamic price earnings ratio will mislead some people know the truth".China Southern Airlines stock quotes software shows the current dynamic price earnings ratio of 8.7 times, only from the words on the stock price has also been underestimated, the city net rate of up to 4.18 times more matched with Shahe shares, a quarter year-on-year growth of 424%, mainly due to the sale of Zhuhai free trade zone motianyu aviation engine maintenance company limited 50% equity investment income 1 billion 100 million due to the total profit of 1 billion 419 million yuan, net profit, that is to say, in addition to 1 billion 100 million yuan of investment income is 3.19 yuan, this performance is also not sustainable, city net rate here can remind investors to uncover the secret behind the profit.。
2.3按订单生产(MTO)本文所属图书>SAP后勤模块实施攻略—SAP在生产、采购、销售、物流中的应用本书综合讲解SAP系统的生产、采购、销售、物流,以及跨后勤模块的实施方案与配置方法,用大量实例介绍了优秀的解决方案,以及各个模块之间的交互设置,还包括项目实施中需要注意的方方面面。
本书作者有丰富的实战...按订单生产(MTO)是指接到客户订单后再进行生产,生产订单与销售订单是直接关联的,广义的MTO 包括三种类型:狭义的MTO、ATO和ETO。
本节将通过三小节对MTO、ATO、ETO进行介绍。
MTO(Make To Order/按订单生产)可与销售订单BOM、销售订单工艺结合,与MTS模式相比较,主要差异点(特点)如下。
1)有更多方法实现客户对产品的特殊要求。
在MTS模式下,客户对产品的特定需求可以通过建立新的料号和BOM来体现,MTO模式下,除了新建物料,还可以建立销售订单BOM和工艺,在销售订单BOM和工艺中指定客户的特殊要求,这样MRP运行、采购计划和生产订单发料时,都可以根据客户特定要求去采购、发料、生产。
2)销售订单与生产订单之间的紧密关系。
由于在生产订单中记录销售订单号码,这样可以跟踪产成品的执行情况,从而能够更好向客户进行反馈、确认。
当销售订单发生变更后对生产的影响更为清晰,反过来,生产订单的变更对销售订单的影响也非常清晰。
3)库存的可用性对MRP、生产的影响。
在MTO模式下,生产入库将会形成销售订单库存,销售发货时,只能从销售订单库存发货,销售订单库存与正常的非限制库存互不影响、互相不可用,即MTO属于单独计划(Individual Planning)。
假设当前存在可用的非限制库存100个,在MTO模式,如果客户订单需求为50个,创建销售订单进行可用性检查时,确认数量为0,在此情况下,系统默认应该是安排生产,产生50个销售订单库存,根据需要也可以修改计划策略从MTO修改为MTS或者将非限制库存转为销售订单库存。
Stock Valuation Learning Module
•Firms obtain their long-term sources of equity financing by issuing common and preferred stock.
•The payments of the firm to the holders of these securities are in the form of dividends.
•The common stockholders are the owners of the firm and have the right to vote on important matters to the firm, such as the election of the Board of Directors.•Preferred stock, on the other hand, is a hybrid form of financing, sharing some features with debt and some with common equity.
•The value of these securities, as with other assets, is based upon the discounted value of their expected future cash flows. The value of a share of stock is often calculated as the present value of the stream of dividends the stock is expected to provide in the future.
•We will illustrate the valuation of a constant growth stock, i.e.,a stock whose dividends are growing at a rate.
•Preferred stock is a perpetuity and is a little easier to value than common stock.
•Constant Growth Stock Price:
P0= [D0(1+g)]/(r –g) = D1/(r-g)
•You can also solve for the expected return: r = (D1/P0) + g
•Preferred Stock:
P p= D p/ r
•where:
= the stock price at time 0
–P
= the current dividend
–D
= the next dividend (i.e.,at time 1) –D
1
–g = the growth rate of the dividends
–r = the required return on the stock
–Note that g < r.
–P p= the preferred stock price
–D p= the preferred dividend
Constant Growth Stocks
• A constant growth stock is a stock whose dividends are expected to grow at a constant rate in the forseeable future.
•This condition fits some established firms, which tend to grow over the long run at the same rate as the economy.
•There are numerous, more complicated models which we will not discuss in this learning module.
•Find the stock price given that the current dividend is $2 per share, dividends are expected to grow at a rate of 5% in the forseeable future, and the required return is 10%
•Step 1 –Draw Timeline 0Infinity $5g = 5%
r = 10%
•Step 2 –Write equation
P0= D0(1+g)/(r –g) = D1/(r –g)
•Step 3 –Fill in equation
P0= $2 (1 + 5%)/(10% -5%)
•Step 4 –Solve equation
P0= $2.10/5% = $2.10/0.05 = $42
•This means that the value of the stock at time zero is $42 dollars given a required rate of return of 10%, a growth rate of 5% and a dividend at time zero of $2.
Preferred Stock
•Preferred stock is defined as equity with priority over common stock with respect to the payment of dividends and the
distribution of assets in a liquidation.
•Preferred stock has the following features:
–Par Value-The par value represents the claim of the preferred stockholder against the value of the firm.
–Preferred Dividend / Preferred Dividend Rate-The preferred dividend rate is expressed as a percentage of the par value of the preferred stock. The
annual preferred dividend is determined by multiplying the preferred
dividend rate times the par value of the preferred stock.
•Since preferred dividends are generally fixed, preferred stock can be valued as a constant growth stock with a dividend growth rate equal to zero.
An Example
•Find the price of a share of preferred stock given that the par value is $100 per share, the preferred dividend rate is 10%, and the required return is 12%.
• A timeline is not really needed, because the dividends of preferred stock are fixed. However, you can always draw one if it helps.
•Step 2 –Write equation
P p= D p/r
Note: The formula is the same as a constant growth stock with g = 0, so
P0= D1/(r –g) = P p= D p/r when g = 0.
An Example
•Step 3 –Fill In Equation P p= $10/12%
•Step 4 –Solve Equation P p= $83.33。