英语的五种基本句型训练
- 格式:docx
- 大小:37.13 KB
- 文档页数:8
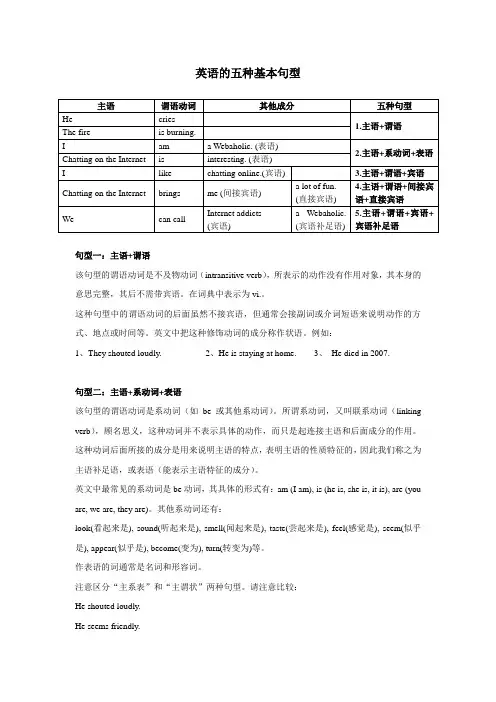
英语的五种基本句型句型一:主语+谓语该句型的谓语动词是不及物动词(intransitive verb),所表示的动作没有作用对象,其本身的意思完整,其后不需带宾语。
在词典中表示为vi.。
这种句型中的谓语动词的后面虽然不接宾语,但通常会接副词或介词短语来说明动作的方式、地点或时间等。
英文中把这种修饰动词的成分称作状语。
例如:1、They shouted loudly.2、He is staying at home.3、He died in 2007.句型二:主语+系动词+表语该句型的谓语动词是系动词(如be或其他系动词)。
所谓系动词,又叫联系动词(linking verb),顾名思义,这种动词并不表示具体的动作,而只是起连接主语和后面成分的作用。
这种动词后面所接的成分是用来说明主语的特点,表明主语的性质特征的,因此我们称之为主语补足语,或表语(能表示主语特征的成分)。
英文中最常见的系动词是be动词,其具体的形式有:am (I am), is (he is, she is, it is), are (you are, we are, they are)。
其他系动词还有:look(看起来是), sound(听起来是), smell(闻起来是), taste(尝起来是), feel(感觉是), seem(似乎是), appear(似乎是), become(变为), turn(转变为)等。
作表语的词通常是名词和形容词。
注意区分“主系表”和“主谓状”两种句型。
请注意比较:He shouted loudly.He seems friendly.句型三:主语+谓语+宾语该句型的谓语动词是及物动词(transitive verb),这种动词告诉我们由主语的动作所作用的对象是什么,这里所作用的对象就是我们通常称之为宾语的,即宾语是主语动作的承受对象,因此这类动词是带有宾语的。
英语中的绝大多数动词都是及物动词,在词典中标为vt.。


2021届高三英语五种简单句〔一〕从英语的句子结构上说,除了修饰名词的定语和修饰动词的状语外,在千变万化的句子中可归纳为五个根本句式,一般地说,某些动词在某一句式中,下面我们把这些句型和常用的动词进行归类,供大家参考。
一、S(主) + Vi (不及物动词) 〔谓〕Time (s) + flies (Vi)两天过去了。
冬天快要来了。
受伤的猫死了。
发生了一宗交通事故。
1)S + Vi + adverbial ( 副词作状语)Birds sing beautifully.他快乐地离开了。
女孩安静地走了进来。
战争和平地结束了。
雨渐渐地停了。
2〕S + Vi + Prep phase (介词短语作状语)He went on holiday.他们会在三点钟到。
那群孩子步行去上学。
3〕S + Vi +Infinitive (不定式作状语)We stopped to have a rest.他起得早是为了读英语。
他希望做医生。
4〕S + Vi +Participle (现在分词作状语)I will go swimming.我们明天一起去钓鱼。
我明天去划船。
昨天他们去逛街。
S〔主〕+ Vt( 及物动词) 〔谓〕+ Object (宾)------- We like English.1)S + Vt + N/ Pron (名词或代词作宾语)I like music. / I like her.他去年教数学。
我们已收到了他们的来信。
2〕S + Vt + Infinitive (不定式作宾语)I want to help him.他爸爸期待拥有一家工厂。
他们假装在看书。
我尝试去解决那个问题。
常用于这个句型的动词有:attempt ,dare ,decide, desire, expect, hope, wish, intend, learn, need, offer, pretend, promise, propose, refuse, want, manage, plan, fail, try, agree等。

精品文档英语简单句的五种基本句型(do sth for sb )do sb sth(get sth for sb ) get sb sth 只包含一个主语(或并列主语)和一个谓语(或简单句:并列谓语)的句子,称作简单句。
(make sth for sb) make sb. sth (pay sth for sb) pay sb. sth 5种基本句型。
简单句的基本句型:简单句有以下(sing sth for sb ) sing sb sth 1不及物动词.主语+ My tooth aches. 例:It is raining heavily. 补足语+ 及物动词5.主语+ + 宾语翻译:I saw her dancing. 例:He told me to clean my room.他昨天锻炼了。
1. 翻译:这只鸭子正在游泳。
2. 我们老师要求我们每天读英语。
1. 3. 这个女孩儿跳舞好。
他总是使我笑。
2. 风筝在天上飞。
4.我发现这部电影有趣。
3. + .主语+ 及物动词宾语2非谓语动词I met John in the street They enjoy the play. 例:yesterday. 【非谓语动词】翻译:构成:(to)+动词原形他喜欢篮球比赛。
1. 动词不定式 2. 他每天打电脑游戏。
3. 她正在弹吉他。
非在句中的作用(除谓语动词外的任何成分)他们经常放风筝。
4. 构成:V.-ing 谓动名词语+ 3.主语+ 系动词表语like 例:It looks Jenny is fine. He is out. 用法(主、宾、表、定)动rain soon. 词翻译:V. -ing / V.-ed(规则变化)构成:他是美国人。
1.分词 2. 苹果尝起来味道很好。
2.用法(表、补、定、状) 3.树变绿了。
4.你的主意听起来不错。
(一)动名词双宾语+ 主语4. 及物动词+ ”构+ing一、动名词的构成:动名词一般由“动词原形The sun gives us light. 例:He bought her a watch.翻译:成1. 他给我讲了个故事。

句子结构句子的五种基本型式英语的句子必须含有动词,但是,由于动词有五个不同种类,因而构成了五种不同的基本句型。
英语中千变万化的句子归根结底都是由以下这五种基本句型组合、扩展、变化而来的:基本句型一:SV(主+谓)基本句型二:SVP(主+系+表)基本句型三:SVO(主+谓+宾)基本句型四:SVoO(主+谓+间宾+直宾)基本句型五:SVOC(主+谓+宾+宾补)A. 主语+不及物动词(主谓)如:The sun rises. 太阳升起来。
The car stopped. 小汽车停下来了。
rise和stop都是不及物动词,因此后边不必加宾语。
B. 主语+系动词+表语(主系表)如:Her brother is a driver.We feel happy.(feel为系动词,表示感到……)It gets dark.天黑了。
(get为系动词,表示变得)Tom looks ill. Tom看上去病了。
(look为系动词,表示看上去,看起来)C. 主语+及物动词+宾语(主谓宾)如:I love my country.He helps me.I like action movies.I buy a book.D. 主语+及物动词+双宾语(直接宾语、间接宾语)(主谓+直宾+间宾)如:He gives Tom a present.(双宾语)他给汤姆一件礼物。
Mother make a new dress for me.(双宾语)妈妈为我做了一件衣服。
E. 主语+及物动词+宾语+宾语补足语(主+谓+宾+宾补)如:They call her Mary.(宾补)他们叫她Mary。
We make our classroom clean and tidy.(宾补)我们使我们的教室干净而整齐。
He always makes us laugh.(宾补)他总使我们笑。
巩固练习:Ⅰ. 请判断下列句子的结构类型。
1. The loud voice from the upstairs made him angry.2. The little boy is asking the teacher all kinds of questions.3. My father bought me a beautiful present.4. Why do you keep your eyes closed?5. I heard the baby crying in the sitting room.6. He will be flying to Beijing.7. The population of Australia is about 19,500,000.8. The old man can hardly dress himself.9. He has handled the job well and deserves a good deal of praise.10. The old man living alone in the little cottage at the foot of the hill at the back of my housewalks by himself every evening along the bank of the river in front of my house.Ⅰ。

英语五大基本句型及练习英语五大基本句型及练习基本概念:与汉语相似,英语句子是由主语(subject), 谓语动词(verb),宾语(object), 表语(predicative),状语(adverbial),宾语补足语(object complement)等成分组成,按照这些成分的组合方式英语句子可分为五种基本句型。
句型一:主语+不及物动词不及物动词本身就可以表达完整的意念,不需要宾语及补语,但有时可有副词,介词短语等状语修饰语.e。
g. The rain stopped .The old man walks in the park 。
句型一的扩展:1.主语+不及物动词+状语e。
g。
The machine works smoothly。
(机器运转正常。
)2。
There +不及物动词+主语e.g。
There is some milk in the bottle .There comes the bus 。
3。
主语+不及物动词+ 动词不定式e.g。
They stopped to take a short rest 。
(他们停下来稍作休息)特别提醒动词stop 可用作不及物动词,也可用作及物动词。
作不及物动词时,通常后接动词不定式,表示停下来的目的是做另一件事。
作及物动词时,通常后接动名词,表示停止做这件事。
e。
g。
They stopped taking a rest .句型二:主语+系动词+表语系动词本身不能表达完整的意念没,需要形容词,名词,介词短语等来补充说明主语,也叫主语补语.e.g. My sister is a nurse .I feel quite hungry .The ball is under the desk .句型三:主语+及物动词+宾语及物动词本身需要一个动作的接受者(宾语),才可以表达一个完整的意念.e.g。
We are learning English 。

语法体系分不清?没关系,只要是英语的句子,都必须符合五种句型。
所以当我们再遇到长难句,不管多长,多复杂,咱都不怕,找出主干就能识别句子大意啦。
我们接下来好好学习一下五种基本句型吧~(一)英语五种基本句型基本句型一:主+系+表此句型的句子有一个共同的特点:句子谓语动词都不能表达一个完整的意思,必须加上一个名词或者形容词,才能表达完整的意思。
系动词分两类:be, look, keep, seem等属一类;get, grow, become, turn等属另一类,表示变化。
be 本身没有什么意义,只起连系主语和表语的作用。
其它系动词仍保持其部分词义。
1. This is an English-Chinese dictionary。
这是本英汉辞典。
2. The dinner smells good。
午餐的味道很好.3. His face turned red. 他的脸红了4. Everything looks different。
一切看来都不同了。
基本句型二:主+谓(不及物动词)此句型的句子有一个共同特点,即句子的谓语动词都能表达完整的意思.这类动词叫做不及物动词,后面可以跟副词,介词短语,状语从句等。
1。
The pen writes smoothly。
这支笔书写流利。
2. The sun rises in the east.太阳从东方升起。
3。
They talked for half an hour. 他们谈了半个小时。
基本句型三:主+谓(及物)+宾此句型句子的共同特点是:谓语动词都具有实义,都是主语产生的动作,但不能表达完整的意思,必须跟有一个宾语,即动作的承受者,才能使意思完整。
这类动词叫做及物动词。
1。
Who knows the answer?谁知道答案?2. He enjoys reading。
他喜欢看书.3。
My sister is writing a letter at this moment。


英语五大基本句型及练习Basic Concept: Similar to Chinese。
English sentences are composed of subject。
verb。
object。
predicative。
adverbial。
and object complement。
According to the n of these elements。
XXX basic XXX.Sentence Pattern 1: Subject + Intransitive VerbIntransitive verbs can XXX object or complement。
but sometimes they can be modified by adverbs。
nal phrases。
etc.XXX.The old man walks in the park.Sentence Pattern 1 n:1.Subject + XXXe.g。
The machine works XXX.2.There + Intransitive Verb + Subjecte.g。
There is some milk in the bottle.There comes the bus.3.Subject + Intransitive Verb + Infinitivee.g。
They ped to take a short rest.Note:The verb "" can be used as an XXX intransitive verb。
it is usually followed by an infinitive to indicate the purpose of ping to do something else。
When used as a transitive verb。
it is usually followed by a gerund to XXX.XXX.Sentence Pattern 2: Subject + Linking Verb + PredicativeLinking verbs cannot XXX adjectives。

Five basic sentence patterns五大基本句型一.五大基本句型:1. I do.S+V主语+谓语动词2. You are beautiful/handsome.S + V + C主语+ 动词+ 主语补足语即“主系表”3. I love you.S+V+O主语+ 谓语+ 宾语4. You make me happy.S+V+O+C主语+谓语+宾语+宾语补足语5. I will give you a kiss.S+V+O+O主语+ 谓语+ 宾语+宾语二.具体讲解1. 基本句型一:S十V主谓结构这种句型中的动词大多是不及物动词:appear, apologize, arrive, come, die, disappear, fall, happen, rise等如:学生们学习很努力;_____________________________________2. 基本句型二: S十V十C主系表结构常见的系动词有:①be动词是;②感官动词: look看起来, feel感到, smell闻起来, ;taste尝起来, sound听起来;③表示状态的: seem似乎, appear似乎,好像, keep保持, remain仍是, stay继续处于...状态等等;④表示转变或结果的: get变得, become成为, turn变得,go变成, grow渐渐变得, fall变得, prove证明1)我们在任何时候都应该保持安静; We should __________ __________ any time.2)这种食物尝起来很糟糕;_________________________________________________.3 春天到了,天气变得越来越暖和;Spring comes. It is ______________________________.4 不要吃那种食物,它已经变质了; Don't have the food. _______________________________.3. 基本句型三: S十V十O主谓宾结构1)我昨天看了一部电影;________________________________________________.2)这些孩子他们照看得很好;They have ________ ________ _________ of the children.4. 基本句型四: S十V十间接宾语“人”十直接宾语“物”结构1)昨天她父亲给她买了一辆自行车作为生日礼物;Yesterday her father _______________ ________ _____ ____________ as a birthday present.2 The old man ___ ______ ____ ________ ________ in the Long March.正在给孩子们讲故事注意:这种句型还可转换为:S + V +直接宾语“物”+for/ to sb. + 间接宾语“人”1)请把你的画给我看一下;Please show me your picture. ==Please _________ ________ __________ _____ _____. 2我买了本书给他; I _______ _______ a book. = I _______a book _____ _____.间接宾语前需要加to 的常用动词有:bring, give, hand, lend, offer, pass, pay, read, sell, send, show, teach, tell wish, write等;间接宾语前需要加for 的常用动词有:buy, choose, make, order, paint, play演奏, sing,等; 5.基本句型五: S十V十O十C 主谓宾宾补结构此句型句子的共同特点是:动词虽然是及物动词,但是只跟一个宾语还不能表达完整的意思,必须加上一个补充成分来补足宾语;如call叫, choose选, find发现, make, name命名等词; 1)请让孩子们安静下来; Keep ______ _________ _________, please.2)他们把门漆成绿色; They painted ______ ______ ________.3)我们必须保持我们的学校洁;We must ______ ______ ________ ______.4 我们发现他是一个懒惰的人;We found _____ _____ ______ _______..5 他要我早点回来;He asked me _______ ________ ________ soon.注意:动词make, let, see, hear,等后面接动词不定式作宾补时,省略to;如:1 The boss ________ _______ _________ all day. 迫使他劳动2 We saw _____ ____ _____. 他出去这些词有:一感feel二听hear, listen to三让使:let, make, have四看:see, look at, watch, notice三.练习:I:判断下面各句分别属于简单句的哪种基本句型:work hard.flower is dead.need water.gives me some seeds.should keep the plants in the shade.6. My name is Li Kang.7. I live in Shijiazhuang.8. I’m writing down my thoughts about it.9. Ms Shen gave us instructions.10. We made him monitor.11. Your sister dances beautifully.12. Doing that would be playing with fire.13. I will tell my friends to protect the environment.14. They kept their marriage a secret.15. She gave me her telephone number.16. Good food keeps you healthy.17. I advise waiting till the right time.18. Did you sleep well19. Horse-riding and shooting are some of the more unusual events.20. Pop music makes people feel easy and forget about the real world.II:翻译下列句子:1. 花闻起来香;2. 昨夜发生火灾;3. 我们希望通过大学入学考试.4. 妈妈给我买了一双鞋;5. 我们要使我们的祖国变得更加美丽;6. 你应当努力学习;7. 她昨天回家很晚;8. 我的兄弟都是大学生;9. 冬季白天短,夜晚长;10. 我不信任那个人;11. 圣诞节我们将去看望外籍教师;先生去年教我们德语;13. 奶奶昨晚给我们讲了一个有趣的故事;14. 我们叫她Alice.15. 他的父母给他取名为John.III: A letter to a friend英国女孩Jenny想在中国找一位笔友;请你根据表格中的内容, 以李洋的名义给Jenny写一封80词左右的信;信的开头与结尾已给出, 不计入要求词数, 内容可适当发挥;Name:Li Yang Age: 13Family: father, mother and IFavourite hobbies: swimming and skatingOther favourite things: Green and yellow, rice and dumplings, dogs and birds其他内容: 1. your age, height, appearance 年龄,身高,外貌 2. your hobbies 爱好3. your family and your home 家庭 4. your dream 梦想Dear Jenny,How are you I am glad to make friends with you. Let me introduce myself at first. _______________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________ Yours, Li Yang。
英语的五种基本句型训练以下五种基本句式是任何英语句子的基本组成部分,其他如定语、状语等均是句子的次要或附加部分。
只要掌握了这五种基本句式,当遇到较复杂的句子时,运用这些基本句式进行分析,对句子的理解也就变得容易多了。
在写作中,必须写好这些最基本的句型。
1.主语+系动词+表语这种句型中的系动词一般可分为下列两类:(1)表示状态的连系动词。
这些词有:be, look, seem, appear, smell, taste, sound, sit, stand, lie, keep, remain, stay,等等。
(2)表示转变或结果的系动词。
这些词有:become, get, grow, turn, go, come, prove,等等.(3)形容词,名词,现在分词,过去分词,不定式,介词都可以放在某些连系动词后做表语。
(1)他是一个运动员。
(2)长大后他成为一位老师。
(turn)(3)这种食物吃起来很糟糕。
(4)天气变得暖和了。
(5)那种食物已经变质了。
(6)事实证明是正确的。
(7)只要你努力,你的梦想一定会实现。
(8)她听到这个好消息后,变得非常开心。
(9)Tom看起来比他的实际年龄更大。
(10)别把他弄得像个傻子一样。
(appear)(11) 那信摊开在他的书桌上。
(lie) (12) 他站在那里一动也不动。
(stand)(13)眼见为实。
(百闻不如一见)(14)这消息听起来挺鼓舞人心的。
(15)三月份她一直呆在中国。
(be) (16)这个玻璃杯碎了。
(be)(17)当他看到那只大狗时,他感到很恐惧。
(18 ) 我们对那个结果很满意。
(19)我的愿望是成为一位作家。
(be) (20)我最喜欢的消遣是踢足球。
(be)(21) 我只得离去。
(不定式做表语)2.主语+谓语(1)这种句型中的动词大多是不及物动词,这些动词常见的有:take place, happen, break out, appear, disappear, apologize, arrive, come, die, exist, fall, rise, hang(可作及物动词或不及物动词)等等。
五种英语基本句型例句1、主语+谓语,如:we agree.2、主语+谓语+宾语,如:I hate him、I love you.3、主语+谓语+间接宾语+直接宾语,如:I give him a book.4、主语+谓语+宾语+宾语补足语,如:I want you to go with me.5、主语+系动词+表语,如:It smells good.扩展资料句型1: Subject (主语) + Verb (谓语):这种句型中的动词大多是不及物动词,所谓不及物动词,就是这种动词后不可以直接接宾语。
1) Li Ming works very hard.李明学习很努力。
2) The accident happened yesterday afternoon.事故是昨天下午发生的。
句型2:Subject (主语) + Link. V(系动词) + Predicate(表语)这种句型主要用来表示主语的特点、身份等。
其系动词一般可分为下列两类:(1)表示状态。
这样的词有:be, look, seem, smell, taste, sound, keep等。
如:This kind of food tastes delicious.这种食物吃起来很可口。
(2)表示变化。
这类系动词有:become, turn, get, grow, go等。
如:Spring comes. It is getting warmer and warmer.春天到了,天气变得越来越暖和。
句型3:Subject(主语) + Verb (谓语) + Object (宾语)这种句型中的动词一般为及物动词, 所谓及物动词,就是这种动词后可以直接接宾语,其宾语通常由名词、代词、动词不定式、动名词或从句等来充当。
例:1) He took his bag and left.(名词)他拿着书包离开了。
2) Li Lei always helps me when I have difficulties. (代词)当我遇到困难时,李雷总能给我帮助。
简单句的五种基本句型讲解及练习题⼀、句⼦成份英语句⼦成分有主语,谓语,宾语,宾语补⾜语,表语,定语,状语等。
顺序⼀般是主语,谓语,宾语,宾语补⾜语,⽽表语,定语,状语的位置要根据情况⽽定。
1、主语:表⽰句⼦主要说明的⼈或事物,⼀般位于句⾸。
但在there be结构、疑问句(当主语不疑问词时)和倒装句中,主语位于谓语、助动词或情态动词后⾯。
主语可由名词、代词、数词、不定式、动名词、名词化的形容词和主语从句等表⽰。
例如:Country music has become more and more popular.(名词)We often speak English in class.(代词)One-third of the students in this class are girls.(数词)To swim in the river is a great pleasure.(不定式)Smoking does harm to the health.(动名词)The rich should help the poor.(名词化的形容词)When we are going to have an English test has not been decided.(主语从句)It is necessary to master a foreign language.(it作形式主语,真正的主语为后⾯的不定式)2、谓语:谓语说明主语的动作,状态或特征。
可以有不同的时态,语态和语⽓。
1)简单谓语:We study for the people.2)复合谓语:I can speak a little English.We are reading books.He has gone to Beijing..3、表语: 它位于系动词(⽐如be)之后,说明主语⾝份,特征,属性或状态。
My sister is a nurse.Is it yours?(代词)The weather has turned cold.(形容词)The speech is exciting.(分词)Three times seven is twenty one?(数词)His job is to teach English.(不定式)His hobby(爱好)is playing football.(动名词)The ruler must be in your box.(介词短语)Time is up. The class is over.(副词)The truth is that he has never been abroad.(表语从句)4、宾语: 宾语表⽰动作⾏为的对象,跟在及物动词之后,We like English. How many dictionaries do you have? I have five.(数词)They helped the old with their housework yesterday.(名词化形容词)It began to rain.(不定式短语)I enjoy listening to popular music.(动名词短语)I think(that)he is fit for his office.(宾语从句)有些及物动词可以带两个宾语,往往⼀个指⼈,⼀个指物,指⼈的叫间接宾语,指物的叫直接宾语。
五种基本句型英语例句英语五种基本句型列式如下:一:SV(主+谓)二:SVP(主+系+表)三:SVO(主+谓+宾)四:SV O O(主+谓+间宾+直宾)五:SVOC(主+谓+宾+宾补)基本句型一:S V(主+谓)S│V(不及物动词)1. The sun │was shining.太阳在照耀着。
2. The moon │rose. 月亮升起了。
3. The universe │remains. 宇宙长存。
4. We all │breathe, eat, and drink. 我们大家都呼吸、吃和喝。
5. Who │cares? 管它呢?6. What he said │does not matter. 他所讲的没有什么关系。
7. They │talked for half an hour. 他们谈了半个小时。
8. The pen │writes smoothly 这支笔书写流利。
基本句型二:SVP(主+系+表)此句型的句子有一个共同的特点:句子谓语动词都不能表达一个完整的意思,必须加上一个表明主语身份或状态的表语构成复合谓语,才能表达完整的意思。
这类动词叫做连系动词。
系动词分两类:be, look, keep, seem等属一类,表示情况;get, grow, become, turn等属另一类,表示变化。
be 本身没有什么意义,只起连系主语和表语的作用。
其它系动词仍保持其部分词义。
感官动词多可用作联系动词:look well/面色好,sound nice/听起来不错,feel good/感觉好,smell bad/难闻S│V(是系动词)│P1. This │is │an English-Chinese dictionary.这是本英汉辞典。
2. The dinner │smells │good. 午餐的气味很好。
3. He │fell │in love. 他堕入了情网。
4. Everything │looks │different. 一切看来都不同了。
五种基本句型句子是由主语、谓语动词、表语、宾语、宾语补足语等组成的。
英语句子有长有短,有简有繁,似乎千变万化,难以捉摸,但其实只有五种基本句型。
所有英语句子都可以看成是这五种基本句型的扩大、组合、省略或倒装。
因此掌握这五大句型,是掌握其他各种英语句子结构的基础。
英语句子依其组合方式可分为以下五种基本句型,句子成分的表示法为:S:Subject(主语), V:Verb (动词),O:Object(宾语), IO : Indirect Object (间接宾语), DO: Direct Object (直接宾语) , P:Predicative(表语), OC:Object Complement(宾语补足语)。
五种基本句型见下表(S=主,V=谓,O=宾,P=表,IO=间宾,DO=直宾,OC=宾补):种类句型例句第1种S+V We work. (不及物)第2种S+V+O He plays (及物) the piano.第3种S+V+P We are(系动词) students.第4种S+V+IO+DO She gave(及物) me a pen.第5种S+V+O+OC He made(及物) the boy laugh.一、第1种句型:S+V(主语+不及物动词)1、Birds fly. 鸟飞。
主语+谓语(不及物动词)2、He runs in the park. 他在公园里跑。
主语+谓语+地点状语(不及物动词)此句型是“主语+不及物动词”构成句子的主体部分。
因为是不及物动词,后面当然不能带宾语了,但是可以有状语来修饰。
例如上面例句中的in the park就是地点状语。
3、Class begins.(begin在句中是不及物动词)上课了。
比较:We begin our class at eight. 我们八点钟开始上课。
该句则属于第2种句型,begin在句中是及物动词,由此可见有些动词既可作及物动词也可以作不及物动词。
英语的五种基本句型训练以下五种基本句式是任何英语句子的基本组成部分,其他如定语、状语等均是句子的次要或附加部分。
只要掌握了这五种基本句式,当遇到较复杂的句子时,运用这些基本句式进行分析,对句子的理解也就变得容易多了。
在写作中,必须写好这些最基本的句型。
1.主语+系动词+表语这种句型中的系动词一般可分为下列两类:(1)表示状态的连系动词。
这些词有:be, look, seem, appear, smell, taste, sound, sit, stand, lie, keep, remain, stay,等等。
(2)表示转变或结果的系动词。
这些词有:become, get, grow, turn, go, come, prove,等等.(3)形容词,名词,现在分词,过去分词,不定式,介词都可以放在某些连系动词后做表语。
(1)他是一个运动员。
(2)长大后他成为一位老师。
(turn)(3)这种食物吃起来很糟糕。
(4)天气变得暖和了。
(5)那种食物已经变质了。
(6)事实证明是正确的。
(7)只要你努力,你的梦想一定会实现。
(8)她听到这个好消息后,变得非常开心。
(9)Tom看起来比他的实际年龄更大。
(10)别把他弄得像个傻子一样。
(appear)(11)那信摊开在他的书桌上。
(lie)(12) 他站在那里一动也不动。
(stand)(13)眼见为实。
(百闻不如一见)(14)这消息听起来挺鼓舞人心的。
(15)三月份她一直呆在中国。
(be)(16)这个玻璃杯碎了。
(be)(17)当他看到那只大狗时,他感到很恐惧。
(18 ) 我们对那个结果很满意。
(19)我的愿望是成为一位作家。
(be)(20)我最喜欢的消遣是踢足球。
(be)(21) 我只得离去。
(不定式做表语)2.主语+谓语(1)这种句型中的动词大多是不及物动词,这些动词常见的有:take place, happen, break out, appear, disappear, apologize, arrive, come, die, exist, fall, rise, hang(可作及物动词或不及物动词)等等。
(2)有些动词如wash, sell, burn,write, clean, draw, cook, read等等可以在后面加副词表示主语的性质。
(1)学生们很努力学习。
(2)太阳每天从东方升起。
(3)他突然停了下来(4)现在我爷爷住在城里。
(5)事故是昨天晚上发生的。
(accident)(6)蓝色的球在移动。
(7) 那个老人在去年冬天死了。
(8)火星上没有生命存在。
(9)当他到达车站时,火车已经开走了。
(10)Jack为他所犯的错误向John道歉。
(11)他在学习上远远落后于他的同学。
(12)墙上挂着一幅画(13)这衣服很容易洗。
(14)这部小说很畅销。
(15)这笔写起来很流畅。
3主语+谓语+宾语这种句型中的动词应为及物动词或者可以后接宾语的动词短语。
同时,句子中有时含有与宾语有关的状语。
作宾语的成分常是:名词、代词、动词不定式、动名词或从句。
如:(1)我要一杯茶。
(2)你可以把书放在书包里。
(3)我昨天看了一部名叫Gone With The Wind的电影。
(4)这些孩子他们照看得很好。
(5)我想她今天不会来参加我们的舞会。
只能跟不定式做宾语的动词有:afford,agree,choose,decide,demand,desire,determine, fail,hope,manage,offer,plan,prepare,pretend,promise,refuse,seek,threaten,wish,arrange,learn,etc.(1)所有男生都喜欢足球。
(2)我想一个人做这项工作。
动词之后只能跟动名词做宾语:acknowledge(承认),admit,appreciate(感激),avoid,consider,delay,deny,dislike,prevent,enjoy,escape,finish,imagine,keep,mind,practice,quit(放弃),risk,(can’t)stand,suggest,advise等;动词短语有:go on,give up,put off,feel like等。
(1) 你真的无法想象再这样的环境下生活。
(imagine)(2)你做完作业了吗?(finish)(3)我们必须避免再犯这样的错误。
avoid(4)你介不介意我在这吸烟?mind(5)我们每天应该在课外练习讲英语。
practice4.主语+谓语+间接宾语+直接宾语这种句型中作间接宾语的常常指“人”,直接宾语常常指“物”。
这类词常有award,give, offer , bring, buy ,show等这种句型还可转换为其他两种句型:1)动词+宾语+for sb.( buy,);2)动词+宾语+to sb.(give,offer,show)如:(1)昨天她父亲给她买了一辆自行车做为生日礼物。
(用两种结构各翻译一句)(2)请把你的画给我看一下。
(用两种结构各翻译一句)(3)她把座位让给我。
(用两种结构各翻译一句)(4)他问了我一个奇怪的问题。
(5)他给我一个苹果。
(用两种结构各翻译一句)5.主语+谓语+宾语+宾语补足语所谓宾语补足语是用来补充说明宾语内容的。
通常放在宾语的后面。
如:The news made me excited. 这里excited 就是me 的宾语补足语。
1)、不定式作宾补A .不定式前带to常用的动词有:advise,cause, allow,drive,encourage,expect, force,intend,invite,permit,tell,trust,urge,persuade,remind,teach,want,warn,get,ask,forbid,beg,require,tempt,enable,lead, instruct等,以及表示"情感状态"的动词love,like,prefer,hate等后面跟带to的不定式作补语.1. 他叫我跟他一起去逛街。
2. 村民们不允许他们做这。
(allow)3. 老师告诉他今晚六点钟过来这里。
4. 他说服了弟弟上床睡觉。
5. 史密斯夫妇邀请我去他们家里吃饭。
6. 玛丽提醒我要准时参加会议7. 爸爸警告我不要吸烟。
8. 他想我跟他一起工作。
9. 我期待他能在考试中成功。
10. 我更喜欢你呆在这里。
11. 我讨厌他今晚过来吃饭。
12. 老师要求我们在9点钟之前交作业。
(require)13. 约翰建议玛丽干什么?14. 石油的短缺(shortage)导致了价格的急剧上升。
15. 我的好朋友鼓励我不要放弃。
16. 最后一辆公共汽车开走了,我被迫要打的。
17. 参观者请勿拍照。
(permit)18. 你可以相信我不会跟任何人讲。
(trust)19. 她力劝他留下。
(urge)20. 你能教我干那活儿吗?21. 他让姐姐帮助他做作业。
(get)22. 在考试过程中禁止离开课室。
(forbid)23. 我希望你今晚可以过来。
(like)24. 饥饿驱使她去偷窃。
25. 她求他别离开。
(beg)26. 这种软件使你能在几秒钟之内便可访问互联网。
(enable)27. 他的话使我去找出真相。
(lead)28. 他指示我开灯。
29. 他打算让他的孩子成为医生。
(intend)30. 我很愿意让他来和我们住在一起。
(love)B .不定式前不带to表示"感觉"的动词see,hear, watch, notice, observe, feel等和三个表示"致使"的动词make,have,let后面跟不带to的不定式作补语.1. 我看到所有的杯子都掉到地上了。
2. 我最终使她改变了主意。
3. 我听到了他在房间里唱歌。
4. 我让他打扫了教室。
5. 我注意到他走进了那家工厂。
6. 我觉得有东西在我的手臂上爬着(crawl up)。
C .不定式为to be在一些动词后面的宾语补足语常是to be,如:believe, consider, declare, find, imagine, know, prove, suppose, feel, think, understand等等。
1. 这个答案证明是错的。
2. 我认为他是一个好学生。
(think)3. 我相信他是诚实的。
(believe)4. 你能想象他成为一名歌星吗?5. 我发觉他很吝啬。
(find)6. 我认为他很蠢。
(consider)7. 总统宣布他成为市长。
declare8. 我们知道她很勤奋。
9. 我猜想他是一个好的领导。
suppose10. 她认为她有责任告诉警察。
consider2)、分词作宾补分词作宾语补足语时,如果分词与宾语构成"主谓关系",用现在分词;如果构成"动宾关系",则用过去分词。
常用分词作宾语补足语的动词有:find, feel , get , have , hear , keep , notice , see , watch,make, leave等。
1. 我发现蛇正在吃鸡蛋。
2. 我发现鸡蛋被蛇吃了。
3. 我发现她的房子重新粉刷过了。
4. 我看到他被人打。
5. 这里太吵了。
别人很难听到我的话。
(make)6. 因为我的英语很差,我不能用英语表达我的意思。
(make)7. 我让别人修理我的车。
(have,make,get)8. 你没隔多久理一次发?(have, get)9. 我把工作留下来给别人做。
leave10. 我让机器整个晚上在运转。
have11. 我听到有人在叫我。
hear12. 我听到我的名字被人叫。
hear13. 我注意到杯子碎了。
notice14. 老师让学生一直在阅读课文。
(keep)15. 我让门锁着。
(keep)3)、形容词作宾补常用形容词作宾补的动词有: keep, leave, find, make, feel, think, consider等1. 学生要保持课室清洁。
2. 不要留着门开着。
3. 我发觉这本书很有趣。
4. 我觉得跟他聊天很有趣。
5. 他把囚犯们都释放了。
(set)6. 我认为不可能在如此短的时间内完成作业。
7. 4)、名词作宾补常用名词作宾补的动词有:find, name, call, elect, make, choose 等1. 我觉得他是一个很聪明的学生。
2. 我们选他作班长。
3. 小孩子们叫他大拇指叔叔。
4. 群众让他当上了总统。
5. 那对夫妇把孩子命名为约翰。
5)、由as构成的短语作宾补常用as构成的短语作宾补的动词有:consider…as, treat…as, regard…as, look on…as, have…as, take…as, think of…as等1. 你决不能认为他是一个自私的人。