英语十六时态表格总结
- 格式:doc
- 大小:88.50 KB
- 文档页数:10


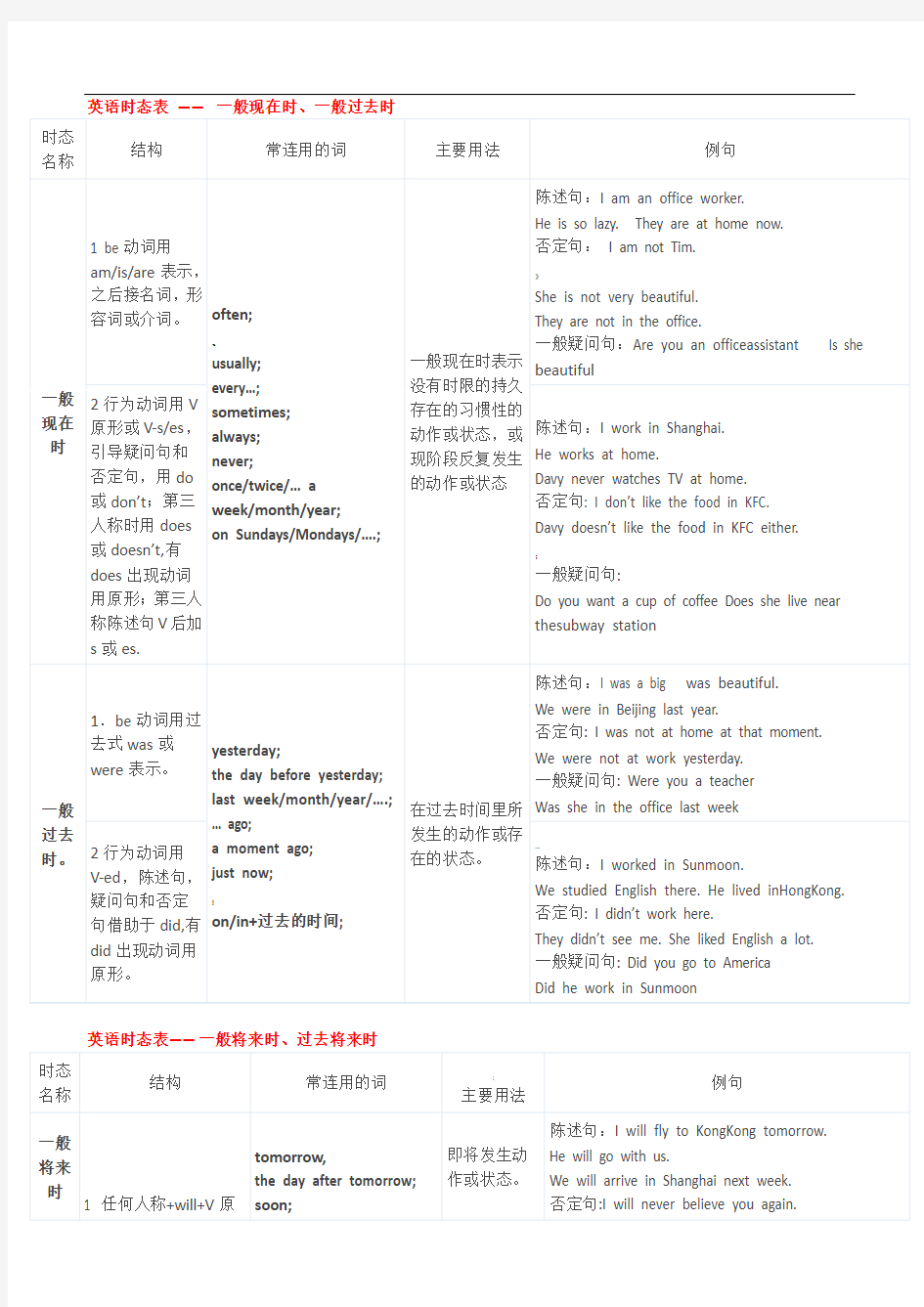
英语时态表——一般现在时、一般过去时
英语时态表——一般将来时、过去将来时
英语时态表——现在进行时、过去进行时
英语时态表——英语时态举例!
英语时态表——详细讲解-一般现在时
通常以动词原形表示。主语为第三人称单数时,用现单三形式。
动词be和have(表示“拥有”)各人称的单数形式为:
第一人称单数第二人称单数第三人称单数
Have Have Have Has
Be Am Are is
一般现在时的否定式、疑问式和简单回答形式如下:
动词be 与have(表示“拥有”):否定式直接把not放在动词之后,疑问式直接把动词放在主语之前,见下表:
否定式疑问式
Be Have Be Have
I am not (I’m not)… I have not (haven’t)… Am i… Have i…
You are not (aren’t)… You have not (haven’t)… Are you… Have you…
He is not (isn’t)… He has not (hasn’t)… Is he … Has he …
动词be 的否定疑问式和简单回答:
否定疑问式肯定回答否定回答
Am I not (aren’t i)… Yes, you are. No, you aren’t
Are you not (aren’t you)… Yes, I am. No, I’m not.
Is he not (isn’t he)… Yes, he is. No, he isn’t
动词be 与have(表示“拥有”):否定式直接把not放在动词之后,疑问式直接把动词放在主语之前,见下表:否定式疑问式
Be Have Be Have
I am not (I’m not)… I have not (haven’t)… Am i… Have I …
You are not (aren’t)… You have not (haven’t)… Are you … Have you…
He is not (isn’t)… He has not (hasn’t)… Is he … Has he …
动词have(表示“拥有”) 的否定疑问式和简单回答:
否定疑问式肯定回答否定回答
Have I not (haven’t i)… Yes, you have. No, you haven’t.
Have you not (haven’t you)… Yes, I have. No, I haven’t.
Has he not (hasn’t he)… Yes, he has. No, he hasn’t.
注意:have 作为行为动词则只能按照行为动词的规则变化。
行为动词(以study为例)一般现在时的否定式、疑问式和简单回答(注意要加助动词do/does)
否定式疑问式
I do not (don’t) study Do I study
You do not (don’t) study Do you study
He does not (doesn’t) study Does he study
否定疑问句式简单回答(肯定/否定)
Do I not (Don’t I) study… Yes, I do. No, I don’t.
Do you not (Don’t you) study… Yes, you do. No, you don’t.
Does he not (Doesn’t he) study… Yes, he does. No, he doesn’t.
英语时态表——详细讲解-现在进行时、一般过去时
由助动词be +现在分词构成。其中be有人称和数的变化,有三种形式:第一人称单数用am, 第三人称单数用is, 其他用are。
现在进行时的否定式是:直接在助动词be后面加上not;疑问式是:把助动词be提到主语之前。以study 为例:
否定式疑问式
I am not studying Am I studying
You are not studying, Are you studying
He is not studying. Is he studying
一般过去时
一般过去时通常由动词过去式表示。一般过去时的否定式、疑问式和简单回答形式要用助动词do 的过去式did, 同时注意实义动词要用原形。以study 为例,其否定式、疑问式和简单回答形式如下:
否定式疑问式
I did not (didn’t) study….Did I study…
You did not (didn’t) study….Did you study…
He did not (didn’t) study….Did he study…
否定疑问式简单回答(肯定/否定)
Did I not (Didn’t I) study…Yes, you did. No, you didn’t.
Di you not (Didn’t you) study…Yes, I did. No, I didn’t.
Did he not (Didn’t he) study…Yes, he did. No, he didn’t.
英语时态表——详细讲解-过去进行时、过去完成时
过去进行时
由助动词be 的过去式+现在分词构成。其中be有人称和数的变化,第一、第三人称单数用was,其他用were.
1)过去进行时动词主要表示在过去某一时刻或某一段时间内正在进行或持续进行的动作。过去进行时经常与过去时配合使用。例如:
This time yesterday, we were having an English lesson. 昨天这个时候,我们正在上英语课。
The teacher was giving us a lesson when Tom walked into the room. 老师在给我们上课时,汤姆走进教室。While we were having supper, all the lights went out. 我们吃饭的时候,灯灭了。
He was reading while she was setting the table. 她摆桌子时,他在读书。
It was getting dark. The wind was rising. 天渐渐黑下来了。风势增强了。
2)过去进行时动词常用always, continually, frequently 等词连用,表示过去经常发生的行为。这种用法表明带有的感情色彩。例如:
The two brothers were frequently quarreling when they were young. 两兄弟小时候常吵架。
In Qing Dynasty, China was always making concessions to western powers. 清朝时,中国总是对西方列强妥协。
过去完成时
一律用had + 过去分词构成。
用法:
1)表示发生在过去某一时间或动作之前的事情,即“过去的过去”。用过去完成时,必须有一个过去的时间或动作来作参照,说明在此之前某事已发生。如果两个动作都是在过去发生的,先发生的用过去完成时,后发生的用一般过去时。例如:
She told me she had been there three times before. 她告诉我她以前到过那里三次。(“去过”发生在“告诉”之前)How long had he taught here by the end of last term 到上学期末为止,他在这里教学多长时间啦(“教学”发生在上学期末结束之前)
When we arrived, the football match had already begun. 我们到的时候,足球赛已经开始了。
She had visited China twice before she came this year. 她今年来中国之前已访问过中国两次了。
2)过去完成时动词可以表示过去某一时刻之前发生的动作或呈现的状态,这一动作一直持续到过去这一时刻或将继续下去。例如:
By the middle of last month, I had lived in Beijing for five years. 到上月中旬,我已在北京住了五年了。
By six o’clock they had worked for eight hours. 到六点为止,他们已工作八小时了。
When I came to Shanghai, he had been there for a long time. 我到上海时,他在那里很长时间了。
3)过去完成时动词常用于间接引语和虚拟语气,我们以后会详细讲述。
4)此外,过去完成时常用于no sooner…than… 和hardly(scarcely) …when… 这两个句型,前面部分用过去完成时,后面部分用一般过去时。例如:
No sooner had he stolen the purse than he was caught red-handed. = He had no sooner stolen the purse than he