人教版新目标九年级英语Unit5单元教案
- 格式:docx
- 大小:30.25 KB
- 文档页数:31


人教版英语九年级Unit 5《What are the shirts made of》全单元教学设计一. 教材分析人教版英语九年级Unit 5《What are the shirts made of》主要讨论了关于衣服的材料和颜色等话题。
通过本单元的学习,学生能够掌握有关衣服的材料、颜色和价格等词汇,学会用一般现在时询问和描述衣物的特点,并能用英语进行简单的购物交流。
本单元包括两个阅读文本,分别是关于衣服的材料和颜色的讨论,以及一个购物场景的对话。
二. 学情分析九年级的学生已经具备了一定的英语基础,能够听懂并运用简单的英语进行日常交流。
然而,对于一些关于衣物专业的词汇和表达方式,他们可能还不够熟悉。
此外,学生对于一般现在时的运用可能还不够熟练,需要通过大量的练习来提高。
三. 教学目标1.知识目标:学生能够掌握有关衣服的材料、颜色和价格等词汇;学会用一般现在时询问和描述衣物的特点。
2.技能目标:学生能够用英语进行简单的购物交流;能够听懂并运用本单元所学词汇和句型进行日常对话。
3.情感目标:培养学生对英语学习的兴趣,提高他们的自信心和自主学习能力。
四. 教学重难点1.重点:掌握有关衣服的材料、颜色和价格等词汇;学会用一般现在时询问和描述衣物的特点。
2.难点:对于一些关于衣物专业的词汇和表达方式;一般现在时的运用。
五. 教学方法1.任务型教学法:通过设置各种任务,让学生在实际语境中运用所学知识,提高他们的语言实际运用能力。
2.情境教学法:创设各种真实的购物场景,让学生在情境中学习并运用本单元所学词汇和句型。
3.合作学习法:学生分组进行讨论和练习,培养他们的团队合作意识和沟通能力。
六. 教学准备1.教学材料:教材、多媒体课件、衣物图片、购物场景视频等。
2.教学设备:计算机、投影仪、音响设备等。
七. 教学过程1.导入(5分钟)通过展示各种衣物的图片,引导学生谈论衣服的材料和颜色,激发学生的学习兴趣。
2.呈现(10分钟)教师通过PPT展示本单元的主要词汇和句型,如“What are the shirts made of? They are made of cotton.”等,并用例句进行解释和示范。

人教版新目标九年级英语Unit5单元集体备课教案They were made in a XXX.②The pencil is made of wood and graphite。
It was made in a XXX.③The desk is made of wood。
It was made in a XXX.④The computer is made of metal and plastic。
It was made in an XXX.Step 2新词研究1.Introduce the new words: produce。
widely。
process.2.Have students repeat the words and explain the meanings.e the words in XXX students understand their usage.Step 3词组研究1.Introduce the new phrases: be made of/from。
be made in sw。
the art and science fair。
environmental n。
grass and leaves。
be known for/be famous for。
as far as I know。
on the sides of mountains.2.Have students repeat the phrases and explain the meanings.e the XXX students understand their usage.Step 4句型研究1.Introduce the sentence patterns: What is the model plane made of。
What is the painting made from。
Is this ring made of silver。

第一课时Sect i on A(1a~2d)1.produce(v.)生产;制造2.wide ly(adv.)广泛地;普遍地3.process(v.)加工;处理8.on the s ides o f mount a ins在山边上.What i s the model p lane made of?这个飞机模型是用什么制成的?2.What i s the pa in t ing made f rom?这幅油画是用什么制成的?3.—Is th i s r ing made of s i lver?这枚戒指是由白银制成的吗?—Yes,and i t was made in Tha i land.是的。
并且它是在泰国制造的。
4.Where i s t ea p roduced in China?在中国,哪些地方产茶?Teacher: P lease t ake out your th ings on your desk.We use them every day,do you rea l ly know them?Ques t ions:教学过程Step 2完成教材1a-1c的任务5.小结训练。
要求学生在规定的时间内完成一个小练习。
并请若干学生给出自己的答案。
有错误的话及时纠正。
(2分钟)用括号内所给动词的正确形式填空。
1)The apples a re sen t(send)to the fac tory f or p rocess ing.2)We are a l l r eady bu t Tom hasn’t packed (pack) h i s c lo thes ye t.3)The windows of the room are c leaned(c lean)every day.4)The bes t co t ton i s p r oduced(p roduce)in Xing J iang in China.5)The song isn’t liked (no t l ike) by mos t o f us.环节说明:通过学习1a,使学生对被动结构有所了解;通过1b,锻炼学生的听力及抓取关键信息的能力;通过1c的训练锻炼学生的口头表达能力,同时巩固对一般现在时被动结构的认识。

人教版新目标九年级英语Unit5单元教案Unit 5 What are the shirts made of?Section A (1a-2d)学习目标1.重点单词:chopstick,coin,fork,blouse,silver,glass,cotton,steel,fair,grass,leaf,produce,widely,process,pack2.重点短语:be made of,be made in,be made from,as far as sb. know,be known for3.重点句式:What are the shirts made of?—This ring looks nice.Is it made of silver?—Yes,and it was made in Thailand.What is the painting made from?How is tea produced?As far as I know,tea plants are grown on the sides of mountains. People say that tea is good for both health and business! 学习重点1.重点短语和句型2.一般现在时态和一般过去时态的被动语态学习难点一般现在时态和一般过去时态的被动语态自主学习一、预习课本P33-34新单词并背诵,完成下面的汉译英。
1.筷子________ 2.硬币________3.叉子________ 4.衬衫________5.银器________ 6.玻璃________7.棉花________ 8.钢铁________9.展览会________ 10.草地________11.叶子________ 12.生产________13.普遍地________ 14.加工________15.包装________二、认真预习1a-2d找出下列短语和句型。


Unit5 What are the shirts made of ?单元学习目标:1.知识与技能:熟练记忆和灵活运用本单元的词汇,短语及一般现在时态的被动语态;2.过程与方法:通过独立学习、合作交流、互相帮助的学习方法来获得知识,培养学生的自学能力。
3.情感态度与价值观:培养和传承中华民族勤劳智慧的传统美德。
第1课时I.Contents: Section A 1a~2dII.学习目标:1.英语有两种语态:主动语态和被动语态。
主动语态:表示主语是动作的执行者。
(即:主语与谓语是主谓关系),被动语态:表示主语是动作的承受着。
((即:主语与谓语是动宾关系) 。
被动语态的谓语构成:be+动词的过去分词(p.p)本单元重点学习一般现在时态的被动语态。
eg:Many people speak English in China. →English is spoken (by many people) in China. 主动变被动的方法:宾变主,谓语变为be done 形,主语变成by后宾(可以省略),主被时态要一致,人称与数同主语。
2. be made of “由…制成”, 一般指能够看出原材料This chair is made of bamboo. 这个椅子是用竹子做成的。
3.be made from“由…制成”,一般指看不出原材料Bread is made from corn.面包是小麦做的。
4.be made in 在…制造/生产This printing machine was made in Beijing.这台印刷机是北京生产的。
5. be made into 被制成为…This piece of wood will be made into a small bench.这块木头将要被制成一个小凳。
6.be made by sb. 由某人制成7.be made up from 由….构成8.be famous/known/wellknown for 以... 著称; 因…而著名be famous/known/wellknown as “作为……而著名”,be widely known for因为…众所周知Liu Huan is known as a singer.刘欢作为一个歌手而出名。

9年级英语教案人教版 人教版&Unit 5 What are the shirts made of?Section A 1 (1a-2d)一、教学目标:1. 语言知识目标:1) 能掌握以下单词:chopsticks, coin, fork, blouse, silver, glass, cotton, steel, grass,leaf, produce, widely, be known for, process, pack 能掌握以下句型:①—This ring looks nice. Is it made of silver?—Yes, and it was made in Thailand.②What is it made of/from?③China is famous for tea, right?④Where is tea produced in China?2) 能够用英语描述及询问物品的制作材料,正确理解被动语态的用法及句子结构。
2. 情感态度价值观目标:了解一些日常用品的制成材料,增加生活常识,养成良好的生活习惯;了解一些地方知名产品或传统艺术品的制作过程以及制作材料,培养学生的民族自豪感及爱国主义精神。
二、教学重难点1. 教学重点:1) 掌握本课时中出现的生词2) 能够用英语描述及询问物品的制作材料3)正确理解被动语态的用法及句子结构。
2. 教学难点:理解被动语态的用法及句子结构。
三、教学过程Ⅰ. Lead in1. 播放动画片《造纸过程》的视频,让学生们了解这个中国传统发明的情况。
T: Who invented paper first?S1: Can Lun invented it in Han dynasty.T: What was paper made of then?S2: It was mainly made of bamboo.T: was it easy for people to make paper then?S1: No, it was very difficult then.T: What is paper made of now?S3: It’s mainly made of wood, bamboo, and cotton.…Ⅱ. Presentation1. Present the sentence structure, using the pictures on the big screen:—What’s the golden medal made of?—It’s made of gold.—Is this table made of wood?—No, it isn’t. It’s made of glass.—Is Butter made from meat?—No. It’s made from cream?让学生们学习掌握be made of/from句型的用法,及be made of与be made from的区别。
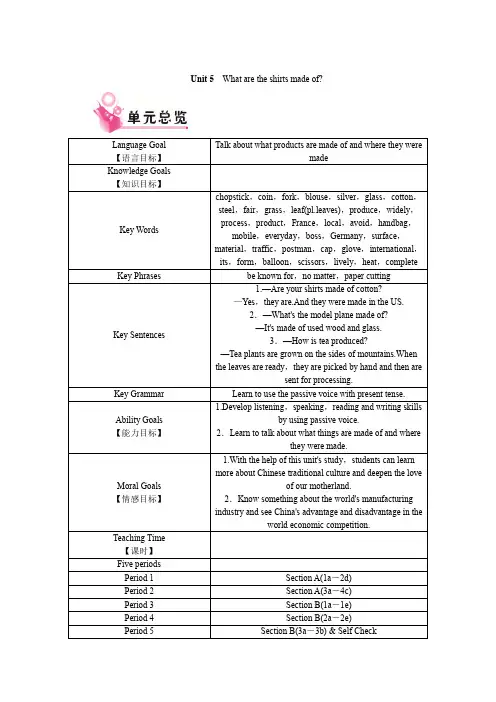
Unit 5What are the shirts made of?Language Goal 【语言目标】Talk about what products are made of and where they weremadeKnowledge Goals 【知识目标】Key Words chopstick,coin,fork,blouse,silver,glass,cotton,steel,fair,grass,leaf(pl.leaves),produce,widely,process,product,France,local,avoid,handbag,mobile,everyday,boss,Germany,surface,material,traffic,postman,cap,glove,international,its,form,balloon,scissors,lively,heat,completeKey Phrases be known for,no matter,paper cuttingKey Sentences1.—Are your shirts made of cotton?—Yes,they are.And they were made in the US.2.—What's the model plane made of?—It's made of used wood and glass.3.—How is tea produced?—Tea plants are grown on the sides of mountains.When the leaves are ready,they are picked by hand and then aresent for processing.Key Grammar Learn to use the passive voice with present tense.Ability Goals 【能力目标】1.Develop listening,speaking,reading and writing skillsby using passive voice.2.Learn to talk about what things are made of and wherethey were made.Moral Goals 【情感目标】1.With the help of this unit's study,students can learn more about Chinese traditional culture and deepen the loveof our motherland.2.Know something about the world's manufacturing industry and see China's advantage and disadvantage in the world economic competition.Teaching Time【课时】Five periodsPeriod 1Section A(1a-2d)Period 2Section A(3a-4c)Period 3Section B(1a-1e)Period 4Section B(2a-2e)Period 5Section B(3a-3b) & Self Check本单元的话题是谈论日常生活用品是用什么材料制造的以及出产地是什么地方,要求学生学习并掌握一些日常生活用品的名称和制造的材料的基本词汇,同时在语言学习训练中接触并学习被动语态。

人教版新目标九年级英语Unit5单元教案Unit 5 What are the shirts made of?Section A (1a-2d)学习目标1.重点单词:chopstick,coin,fork,blouse,silver,glass,cotton,steel,fair,grass,leaf,produce,widely,process,pack2.重点短语:be made of,be made in,be made from,as far as sb. know,be known for3.重点句式:What are the shirts made of?—This ring looks nice.Is it made of silver?—Yes,and it was made in Thailand.What is the painting made from?How is tea produced?As far as I know,tea plants are grown on the sides of mountains. People say that tea is good for both health and business! 学习重点1.重点短语和句型2.一般现在时态和一般过去时态的被动语态学习难点一般现在时态和一般过去时态的被动语态自主学习一、预习课本P33-34新单词并背诵,完成下面的汉译英。
1.筷子________ 2.硬币________3.叉子________ 4.衬衫________5.银器________ 6.玻璃________7.棉花________ 8.钢铁________9.展览会________ 10.草地________11.叶子________ 12.生产________13.普遍地________ 14.加工________15.包装________二、认真预习1a-2d找出下列短语和句型。
Unit 5What are the shirts made of?Section A 3a—3c一、教学目标1. 熟练掌握下列词汇和短语:product, France, local, avoid, handbag, mobile, everyday, no matter, avoid doing sth.2. 熟练掌握下掌握和运用下列句型:No matter what you may buy, you might think those products were made in those countries.He found it interesting that so many products in the local shops were made in China.He realized that Americans can hardly avoid buying products made in China.Kang Jian thinks it’s great that China is so good at making these everyday things.3. 读懂有关中国制造的产品的英文文章,并能够根据文段中的信息完成相应的阅读任务。
4. 能够谈论产品是由什么制造的以及它们在哪儿制造的。
5. 通过阅读有关在美国购物的文章,了解“中国制造”在世界的地位,增强民族自豪感。
二、教学重点及难点重点:1. 掌握本课时重点词汇、短语和句型表达。
2. 能够阅读有关“中国制造”的文章。
难点:能够运用一般现在时的被动语态谈论产品是由什么制造的以及它们在哪儿制造的。
三、教学准备教师:教学课件;多媒体设备学生:课前预习四、教学过程Step 1 Warming-upLook at some pictures and talk about the questions.【设计意图】利用图片来导入课堂,引出本节课中有关产品制造地的话题及学习相关词汇,为下文3a的阅读作好铺垫。
Unit 1 How do you study for a testSection A1. How do you study for a test? 你怎样为考试做准备?2. by 1)通过…..方式(途径)。
(by doing sth 通过做某事)例:I learn English by listening to tapes. 2)在…..旁边。
例:by the window/the door 3)乘坐交通工具例:by bus/car4)在……之前,到……为止。
例:by October在10月前5)被例:English is spoken by many people.6) 由于by mistake 7) 连接one by one 一个接着一个3. ask:1) ask sb (not)to do sth .请某人(不要)做某事2) ask sb about sth .询问某人关于某事He asked me about the meeting.3) ask for…. 请求/要……如:I’ll ask for two days off. 我将请两天假。
4) ask sb for sth 向某人请求/要某物ask the teacher for help 向老师求助4. practice doing 练习做某事She often practice speaking English. 她经常练习说英语。
5. What/ how about +doing sth.? 做某事如何?6. aloud / loudly / loud1)aloud: adv,强调发出的声音能被听见,意为“出声地”或“大声地”,常与read,call连用,无比较级和最高级。
He read the story aloud to his son.他朗读那篇故事给他儿子听。
2)loud: adj/adv “响亮的/地;大声的/地;高声地”,侧重发出的声音大,传得远。
Unit 5 It must belong to Carla.Ⅰ. Analysis of the Teaching MaterialStatus and FunctionThe topic of this unit is a picnic, In this unit, students learn to make inferences.Such topic is helpful to activate students’imagination and improve students’ability to deduce. Either less or more advanced students will be active in the activities in class. So it’s useful to improve students’ spoken English and communicative competence.(1) The first period mainly introduces the key vocabulary and the target language to students. Through listening and oral practice, students have a brief understanding of how to make inferences.(2)In the second period, students learn the exact meanings of the words must, might, could and can’t.Meanwhile, students practice listening and writing the target language.(3) When reading an article, students can’t help meeting with some new words. In the third period, students are asked to practise using the target language by talking about the new words, It’s helpful to arouse students’ learning interest and improve students’ listening and speaking skills. (4) The fourth period gives students further listening and oral practice using the target language by talking about an alien is chasing a man.In this class, students have a better understanding of the words must, might, could and can’t. (5) In the fifth period, students learn more vocabulary words first, and then practice reading and writing the target language. All the activities are designed to improve students’ reading and writing skills.(6)In the last period, students learn a lot of proverbs. Proverbs are full of truth and advice. Students will benefit a lot in this class.2. Teaching Aims and Demands(1) Knowledge ObjectsIn this unit, students learn to make inferences using the words must, might, could and can’t. (2) Ability ObjectsTo train students’ listening, speaking, reading and writing skills.To train students’ ability to deduce.(3) Moral ObjectsWhen you are on a picnic, remember to bring litter back to keep our environment clean and tidy. We’ll benefit a lot by learning proverbs.3. Teaching Key PointsTo learn the key vocabulary words and the target language.To learn to make inferences using the words must, might, could and can’t.4. Teaching Difficult PointsTo train students’ listening, speaking, reading and writing skills.To enable students to grasp the usage of must, might, could and can’t.5. Studying WayTeach students how to make inferences using must, might, could and can’t.Ⅱ. Language FunctionMake inferencesⅢ. Target LanguageWhose volleyball is this?It must be Carla’s. She loves volleyball.It could be Ted’s.Ⅳ. Structuremust, might, could and can’tⅤ. Vocabularypicnic, chase, escape, belong to, toy car, plate’, mystery, appointment, worried, wake, neighbor, garbageⅥ. Recyclingsuit, land, volleyball, magazine, book, CD, bat, earring, T-shirt, UFO, whose, owner, exercise, dream, anxiousⅦ. Learning Strategies1. Sequencing2. DeducingⅧ. Teaching TimeSix periodsThe First PeriodI. Teaching Aims and Demands1. Knowledge Objects(1) Key V ocabularybelong, belong to, plate, author, toy, picnic(2)Target LanguageWhose book is this?It must be Mary’s. Wanda Wilbur is her favourite author.2. Ability Objects(1) Train students’ listening skill.(2) Train students’ communicative competence using the target language.3. Moral ObjectsWhen you are on a picnic, remember to bring litter back to keep our environment clean and tidy. Ⅱ.Teaching Key Points1. Key vocabulary2. Target languageⅢ.Teaching ProceduresStep I RevisionCheck homework. Invite different students to say the answers to the exercises on pages 12~14 of the workbook.Step Ⅱ1aThis activity introduces the key vocabulary.Write the key vocabulary words on the blackboard. Say the words one by one and have students repeat several times until they can read them fluently and accurately.Ask different students to explain in their own words the meanings of the words belong to, author and picnic.Belong means to be owned by somebody.An author is a writer of a book or a play.A picnic is a meal eaten out of doors.Then invite two students to draw a plate next to the word plate and a toy car next to toy.Focus attention on the picture. Have students point to each item and say its name. Call students attention to the chart with the headlines clothing. Funthings and kitchen things at the top. Invite different students to explain the meanings of the column heads.Say, Please look at the picture and write the things you see in the correct columns in the chart. Point out the sample answers. Get students to complete the task on their own. As they work, move around the room checking their progress and answering any questions they may have.Show the correct answers on the screen by a projector.Step ⅢlbThis activity gives students practice in understanding the target langugage in spoken conversation. Call students’ attention to the chart. Set a time limit of two minutes. Students read the persons, the things and the reasons.Say, You will hear a conversation. As you listen, draw lines to connect the person in the first column with the thing in the second column. Then draw another line to connect the thing in the second line with the reason in the third column.Point out the sample answer. Say, The name Carla in the first column connects to volleyball in the second column because that’s the thing they are talking about. And the word volleyball in the second column connects with the sentence she loves volleyball in the third column.Play the recording the first time.Students only listen. Play the recording again. This time students listen and match each person with a thing and a reason.Check the answers.Step Ⅳ1cThis activity provides oral practice using the target language.Point to the picture in Activity lb. Invite pair of students to say the conversation in the speech bubbles.Point out the conversation in the box. Invite another pair of students to say it to the class. S A : Whose book is this?S B: It must be Mary’s. Wanda Wilbur is her favourite author.Write the conversation on the blackboard.Point out the chart in Activity 1b. Say.Now work with a partner. Start by reading the conversations in the picture and in the box: Then make conversations using the information in the chart in Activity 1b. Talk about who each thing might belong to and give a reason. Get students to practice in pairs. As they work, move around the classroom listening in on various pairs and offering help with language and pronunciation as needed.After all the students have had an opportunity to ask and answer questions, stop the activity. Get different pairs of students to say their conversations to the class.Step ⅤSummarySay, In this class, we’ve learned the key vocabulary words belong to, plate, author, toy and picnic and done much listening and oral practice using the target language.Step ⅥHomework(1) Say and remember the spelling of the vocabulary words.(2)Say the conversations in Activity 1c to get a further understanding of the target language.Unit 5 It must belong to Carla.The Second PeriodI. Teaching Aims and Demands1. Knowledge Objects(1) Key V ocabularydrop, symphony, optometrist, appointment, algebra, crucial, count, because of, Chinese-English dictionary, Oxford University(2) Target LanguageWhat do you think "anxious" means?Well, it can’t mean "happy".It might mean "worried".Oh, yes, she is worried because of her test.Here are some earrings. The owner can’t be a boy.Well, it could be a boy. The earrings might be a present for his mother.2. Ability Objects(1) Train students’ reading skill.(2) Train students’ communicative competence using the target language.Moral ObjectWhen you are in trouble, send an e-mail message to your friends to ask for help.Ⅱ. Teaching Key Points1.Reading practice2.Oral practice using the target languageⅢ. Teaching Difficult Points1. Key vocabulary2. Target languageⅣ. Teaching ProceduresStep I RevisionRevise the usage of the words must, might, could and can’t by checking homework.Ask students to exchange their exercises books and help correct any errors with each other, As they are doing this, move around the classroom offering language support as needed. Then invite different students to say their sentences to the class.Step Ⅱ3aThis activity provides reading practice using the target language.Call students’attention to the picture.Ask students to tell what’s happening in the picture.T: What’s the girl doing?S s: She is using the computer to write e-mail.Point to the parts of the e-mail message.Tell students that this is the message the girl in the picture writes. Say, Right now the parts are in the wrong order. When they are in the right order, they will make a clear message. Now please read the parts carefully. Number them in order. When you are doing this, you will meet with some words you don’t know.Don’t worry too much about them. Just circle them. We’ll talk about what they mean later.Get students to complete the task on their own. Point out the sample answer.Say. The first sentence of the e-mail message is I’m really anxious, because I can’t find my backpack.Check the answers.Step Ⅲ3bThis activity provides oral practice using the target language.Read the instructions to the class. Point to the sample conversation. Invite a pair of students to say it to the class.S A: What do you think "anxious" mean? S B: Well, it can’t mean "happy".S A: It might mean "worried". S B: Oh, yes. She is worried because of her test.Write the conversation on the blackboard.Say, You are to talk about the circled words in Activity 3a. Use the words can’t, must, could or might as in the sample.Get students to work with a partner. As they work in pairs, move around the classroom helping students with pronunciation and answering any questions they may have. Some time later, stop the activity. Ask different students to share their conversations with the class. Make a list of the words students are talking about on the blackboard.Practice the pronunciation of these words and explain the meaning of each word. Step ⅣPart 4This activity provides oral practice using the target language.Call students’ attention to the picture. Get students to name each item in it.Write the new words Chinese-English dictionary and Oxford University on the blackboard. Point to the sample conversation. Invite a pair of students to read it to the class.Write the conversation on the black board. Explain the meaning of each sentence. Focus attention on the chart with the headlines Can’t, Could/might and Must at the top. Point out the sample answer.Read the instructions to the class.Get students to complete the task in pairs. As the pairs work together, move around the classroom helping students with pronunciation, sentence formation or anything else they ask for help with.Ask some pairs to say their conversations to the class.Note: Answers to the chart will vary.Step ⅤSummarySay, In this class, we’ve learned some vocabulary words, such as drop, symphony.And we’ve done much oral practice using the target language.Step ⅥHomework1. Read the letter in Activity 3a again for further understanding of the vocabularywords.2. Read the conversations in Activities 3b and 4 again for further understanding of the target language.3. Finish off the exercises on pages 15~16 of the workbook.The Third PeriodI. Teaching Aims and Demands1. Knowledge Objects(1) Key Vocabulary:chase, creature(2) Target LanguageWhy do you think the man is running?He could be running for exercise.No, he’s wearing a suit. He might be running to catch a bus.2. Ability Objects(1)Train students’ listening skill.(2)Train students’ writing skill.3. Moral ObjectThe UFO and alien are both unreal. As students, we must work hard to explore the universe in the future.Ⅱ. Teaching Key Points1. Listening practice2. Writing practiceⅢ. Teaching Difficult Points1. Write a sentence about each picture.2. Write two or three sentences to finish the story.3. Listen and complete the sentences.Ⅳ. Teaching ProceduresStep ⅠRevision1. Invite a student to read the thank you message Linda wrote to Anna to the class.2. Get different pairs of students to read the conversations in Activities 3band 4.3. Check answers to the exercises on pages 15~16 of the workbook.StepⅡPart lThis activity provides writing practice using the target language.Read the instructions to the class. Read the words in the box and have students repeat several times. Invite different students to explain the meaning of each word in their own words.Get students to look at the three pictures carefully. Say, You are to use the words from the box to write a sentence about each picture. Point out where to write the sentences. Ask a student to say the sample answer to the class. Get students to complete the activity individually. As students work, walk around the classroom offering language support as needed.Check the answers on the blackboard.Step Ⅲ2aThis activity gives students practice understanding and writing the target language in spoken conversation.Read the instructions to the class. Point to the three pictures in Activity 1. Say, You will hear a conversation about these pictures. As you listen, write a number in the box in the left corner of each picture to show the order of the events.Point out the sample answer in the box of the third picture. Say, You will hear the man is running first. Play the recording the first time. Students only listen. Play the recording again. This time students listen and number the pictures. Encourage students to write two or three sentences to finish the story.Answers will vary. Write a sample version on the blackboard. Ask students to use it as a model.Step Ⅳ2bThis activity gives students practice listening to and writing the target language.Point to the chart with sentence startersThey see …The man says…and The woman says…Say, You are to listento the same recording again. And complete each sentence.Point out the sample answers. Say, They see a man running. The man says he could be running for exercise. The woman says he might be late for work. Explain the meaning of the word creature to the students.Play the recording once or twice, using the Pause button as necessary.Show the answers on the screen by a projector so thatStep Ⅴ2cThis activity provides oral practice using the target languagePoint out the sample conversation in the box. Invite a pair of students to read it to the class.S A: Why do you think the man is running?S B: He could be running for exercise.S A: No, he’s wearing a suit. He might be running to catch a bus.Write it on the blackboard.Say, Now work with a partner. Start by reading the conversation in the box with your partner. Then role play conversations using information in Activity 2b.Get students to work in pairs. As the pairs work together, walk around the classroom listening in on various pairs and offering help needed. Ask several pairs to say their conversations to the class.Step ⅥSummarySay, In this class, we’ve mainly done much listening and writing practice using the target language.Step ⅦHomeworkAsk students to collect pictures of different kinds and then talk about them using must, could, might and can’t.The Fourth PeriodI. Teaching Aims and Demands1. Knowledge Objects(1) Key Vocabularyextremely, worried, neighbor, garbage, mystery, director, escape, ocean(2) Target LanguageIn my dream, I was swimming in an ocean of paper.Maybe it means you’re afraid of too much homework!2. Ability Objects(1) Train students’ reading skill. (2) Train students’ writing skill.(3) Train students’ integrating skills.3. Moral ObjectEveryone has had a dream. But don’t dream away your time.Ⅱ. Teaching Key Points1. Key vocabulary2. Reading practice3. Writing practiceⅢ. Teaching Difficult Points1. Reading practice2. Writing practiceⅣ. Teaching ProceduresStep ⅠRevisionCheck homework.Collect pictures from students on the teacher’s desk. Hold up one at a time and ask students to describe it using the target language introduced in the preceding classes. For example:T: (Holding up a picture with a boy swimming in an ocean of books) What do you think is happening to the person in the picture?S1: He must be a student. S2: He could be having a dream. S3: He might like reading books. Step Ⅱ3aThis activity provides reading practice using the target language.Show the key vocabulary words on page 38 on the screen by a projector.Say the words one by one and have students repeat several times until they can pronounce them fluently and accurately. Read the title of the newspaper article strange events in Bell Tower neighborhood to the class. And then point to the picture and ask students. How is the person feeling? Help students to answer. He is confused and upset.Call students’ attention to the article. Read it to the class. Say, Now please read the article individually and underline what people think could be causing the strange things that are happening in Bell Tower. Point out the sample answer.Get students to complete the task individually. As they work, walk around the classroom answering any questions they may have and offering help as needed. Check the answers.Answersan animal, teenagers, the wind, a dogStep Ⅲ3bThis activity provides reading and writing practice using the target language.Get students to discuss any words or sentences they don’t know in Activity 3a with one another. Call students’attention to the three sets of notes. Ask different students to read them to the class.Chu family--late night footsteps in the hallway--might be the neighborsLao Zheng--someone trying to get in the window--might be the windXiao Ning--finds garbage in front of her house--might be catsSay, You are to write another paragraph about Bell Town using these notes. You may use the article inActivity 3a as a model. Ask students to write their paragraphs on their own in the exercise books. As they work, move around the classroom offering language support as needed. Get a few students to read their works to the class. Answers will vary. Write the sample version on the blackboard.Step Ⅳ3cThis activity provides writing practice using the target language.Read the title No more mystery in Bell Tower neighborhood to the class and explain the meaning of the word mystery. Invite a student to read the opening sentences to the class. Divide the class in to groups of four to discuss what should be included in the article.Two or three minutes later, stop the activity. Say, Now please finish the article about the strange events in Bell Tower. Use the ideas you discussed along with original ideas of your own to complete the article. Get students to complete the task on their own in the exercise books. As they are writing, move around the classroom offering help as needed. Ask some students to read their articles to the class.Collect students’ works and write a comment on each paper before returning them.Step ⅤPart 4This activity provides reading, writing, listening and speaking practice using the target language. Read the instructions to the class. Point to the picture. Ask students to tell what is happening in it. Invite a pair of students to read the sample conversation in the box to the class.Say, Once I had a dream. In my dream, I was eating a state dinner. What might the dream mean? Students may answer.Maybe it means you are too hungry. Say. Think of a dream you had recently and tell your classmates about it Your classmates guess what the dream might mean. Please work with a partner. Start practice by reading the sample conversation. As the pairs work together, walk around the room offering help with pronunciation and language. Ask different pairs to tell the class about their dream and what they may mean.Step ⅥSummarySay, In this class, we’ve mainly done much reading and writing practice using the target language. We’ve learned some vocabulary words as well.Step ⅦHomework1. Reread the newspaper article in Activity 3a.2. Review the paragraph in Activity 3b,The Fifth PeriodI. Teaching Aims and Demands1. Knowledge Objects(1)Key Vocabularyfinger, stone, ant, poor, dishonest, bark, wake, pretend, use up, attempt(2)Fill in blanks and make sentences using vocabulary words.(3)Learn some proverbs.(4)Circle the word that doesn’t belong.2. Ability Objects(1)Train students’ writing skill.(2)Train students’ ability of reading comprehension.(3)Train students’ ability of clarifying.3. Moral ObjectWe’ll benefit a lot by learning proverbs.Ⅱ. Teaching Key Points1. Make sentences using vocabulary words.2. Say the meanings of different proverbs in your own words.3. Circle the word that doesn’t belong.Ⅲ. Teaching Difficult Points1. Make sentences using vocabulary words.2. Say the meanings of different proverbs in your own words.Ⅳ.Teaching ProceduresStep ⅠRevisionAsk several students to read the newspaper article in Activity 3a to the class.Step ⅡPart 1This activity provides a comprehensive review of vocabulary presented in the unit.of the word, for example adjusting for tense or subject/verb agreement.Ask students to fill in the blanks on their Own.Check the answers. Five students each read a sentence, filling in the blanks. The rest of the students check their answers.Answers1. favourite2. careful3. anxious4. worried5. strangeAsk students to make their own sentences with the words, preferably sentences that are meaningful. Move around the room. Collect a few students’answers with mistakes on the blackboard.Help correct the mistakes.Sample answers1. What’s your favourite song?2. Be careful while crossing a road.3. We are anxious for his safety.4. You don’t have to be worried about me.5. I had a strange dream last night.Step ⅢPart 2This activity provides reading, writing, listening and speaking practice using the target language. Show the vocabulary words on the screen by a projector.Say the words and have students repeat them until they can pronounce them fluently and accurately. Read the instructions to the class. Explain to the students that a proverb is a short well-known saying that states a general truth or gives advice.Read the first proverb to the class. One finger cannot lift a small stone. Elicit the interpretation from the students(It’s better to have help to do even small jobs).Say, Please read the proverbs, Discuss with your classmates what they might mean.Get students to work in groups of four.As the groups work together, walk around the room to make sure that students are discussing the topic in English. Invite different students to say what they think each proverb means.There can be more than one interpretation for each proverb. Check the answers by showing the sample answers on the screen by a projector.Step ⅥPart 3This activity focuses on the new vocabulary introduced in this unit.Ask students to read the five lines of words in the box.Point out the first line. In this line, escape, chase and run are all verbs. However, the word owner is a noun. So we circle it. Now please circle the word that doesn’t belong in each line.Get students to complete the task on their own. As they are doing this, move aroundthe classroom checking their progress and offering help as needed.Check the answers by asking a student to read his or her circled words to the class. Answers :1. owner 2. alien 3. land 4. exercise 5. lostStep ⅤJust for Fun!This activity provides reading and speaking practice with the target language.Ask all the students to read the cartoon story. Ask students why it is funny. Help students to answer. The boys think they are going to land on an island. Instead, they have landed on the back of a whale.Step ⅥSummarySay. In this class, we’ve practiced filling in blanks and making sentences with some vocabulary words introduced in this unit. And we’ve learned several proverbs.StepⅦHomework(1) Read and remember the proverbs learned in Activity 2.(2) Each student collects ten proverbs.(3) Finish off the exercises on pages 16~17,of the workbook.Step Ⅷ。
人教版新目标九年级英语Unit5单元教案Unit 5 hat are the shirts ade f?Setin A (1a-2d)学习目标1.重点单词:hpstik,in,frk,bluse,silver,glass,ttn,steel,fair,grass,leaf,prdue,widely,press,pak2.重点短语:be ade f,be ade in,be ade fr,as far as sb. knw,be knwn fr3.重点句式:hat are the shirts ade f?—This ring lks nie.Is it ade f silver?—yes,and it was ade in Thailand.hat is the painting ade fr?Hw is tea prdued?As far as I knw,tea plants are grwn n the sides f untains.Peple say that tea is gd fr bth health and business!学习重点1.重点短语和句型2.一般现在时态和一般过去时态的被动语态学习难点一般现在时态和一般过去时态的被动语态自主学习一、预习课本P33-34新单词并背诵,完成下面的汉译英。
1.筷子________ 2.硬币________3.叉子________ 4.衬衫________5.银器________ 6.玻璃________7.棉花________ 8.钢铁________9.展览会________ 10.草地________11.叶子________ 12.生产________13.普遍地________ 14.加工________15.包装________二、认真预习1a-2d找出下列短语和句型。
1.由……制造___________________________________________________ _____________________2.在……制造___________________________________________________ _____________________3.据……所知___________________________________________________ _____________________4.以……闻名___________________________________________________ _____________________5.这些衬衫是用什么制成的?___________________________________________________ _____________________6.—这个指环看起很漂亮。
它是银制的吗?—是的,它是泰国生产的。
___________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ _____________________7.这幅油画是由什么制成的?___________________________________________________ _____________________8.据我所知茶树生长在山的侧面。
___________________________________________________ _____________________9.人们说茶对健康和商业都有好处。
___________________________________________________ _____________________课堂导学Step 1 情景导入The teaher pints at a desk in the lassr and asks:Teaher: hats this?Student1:Its a desk.Teaher:hat is it ade f?Student2:Its ade f wd.The teaher writes “hat is it ade f?Its ade f wd.”n the blakbard.Then help students t say se sentenes like these.环节说明:由学生身边的物品为载体学习句型,易于学生理解。
Step 2 完成教材1a-1的任务1.组长领读1a中的单词,学生跟读,然后两人一组互相提问单词。
(3分钟)。
2.你认为方框左栏中的物品是由什么制成的?将物品和原材料匹配(答案不是唯一的),完成后小组内交流核对答案。
(2分钟)3.学生齐读1a中的短语,为听力做好准备。
(2分钟)4.听录音将物品、原材料和产地匹配,完成后集体核对答案。
(3分钟)5.再听一遍录音,并跟读对话。
(2分钟)6.结对练习1中的对话,并请一些学生表演对话。
(3分钟)7.模仿1中的对话,用1b听力材料中的信息与同伴编练新对话,并邀请几组学生表演对话。
(5分钟)参考案例A:This ring lks nie.Is it ade f silver?B:yes, and it was ade in Thailand.8.小结训练。
(3分钟)(A)1.—hat are the rings ________.—Silver.A.ade f B.ade in.ade fr D.ade by(D)2.The bys bedr ______ every day by his ther.A.leans B.leaned.will lean D.is leaned()3.—yur at lks very nie.Is it ________ hina?—f urse.A.ade f B.ade fr.ade in D.ade by环节说明:听说结合,第一时间向学生传达语言目标,通过结对对话练习和小结训练,使语言目标得以强化。
Step 3 完成教材2a-2的任务1.小组内齐读2a中的短语和2b中的句子,为听力做好准备。
(3分钟)2.听Nik和arus的对话录音,勾画出主要的话题,集体核对答案。
(3分钟)3.再认真听一遍录音,根据对话内容回答2b中的四个问题,完成后集体核对答案。
(3分钟)4.听第三遍录音,学生跟读。
(3分钟)5.仿照2的形式,利用2a和2b中的信息,两人一组编练新的对话,完成后邀请几组学生表演对话。
(5分钟) 参考案例A:hat did yu see at the art and siene fair?B:I saw...A:hat is it ade f/fr?B:...6.小结训练。
(3分钟)(D)1.ur teahing building ________ tw years ag.A.has built B.built.were built D.was built()2.D yu knw what paper is ________?A.ade f B.ade in.ade fr D.ade by(B)3.—here is ane?—She ________ t help ut the sik hildren.A.alled B.was asked.tld D.wanted环节说明:通过听、说、读、写学习训练让学生掌握了被动语态的构成;并且使学生的口语表达能力在这一环节得到提升。
Step 4 完成教材2d的任务1.学生自读对话,回答下面的问题。
(5分钟)1)here is tea prdued in hina?2)hih ities are widely knwn fr their tea?3)Hw is tea prdued?2.大声朗读2d中的对话,读熟后与同伴结对练习,分角色表演对话。
(3分钟)3.邀请三组学生表演对话。
(5分钟)4.小结训练。
(3分钟)1.中国因茶叶而出名。
hina_is_faus_fr_tea.2. 据我所知,他们去美国了。
As_far_as_I_knw,they_have_gne_t_Aeria.3.人们说茶对健康和商业都有好处。
Peple_say_that_tea_is_gd_fr_bth_health_and_business.4.据我所知,茶树生长在山的侧面。
As_far_as_I_knw,tea_plants_are_grwn_n_the_sides_f_untains.环节说明:将对话问题化,既能锻炼学生的思维能力又能加深对课的理解。
小结训练又对对话中的重要句型进行了巩固加深。
Step 5 问题探究1.一般现在时态的被动语态教室每天都被我们打扫。
The_lassr_is_leaned_by_us_everyday.被动语态中动作接受者作句子主语,动作执行者置于句末,用by连接,有时可以省去不用。
谓语动词由“be+动词的过去分词”构成。
①一般现在时被动语态的结构为:主语(动作接受者)+is/are+动词的过去分词+(by+动作执行者);②被动语态的否定句:主语+be+nt+过去分词+(by +动作执行者);③一般疑问句:Be+主语+过去分词+(by+动作执行者);④特殊疑问句:特殊疑问词+be+主语+过去分词+(by+动作执行者)。
2.be ade f,be ade fr和be ade in1)这张桌子是木头制成的。
The_desk_is_ade_f_wd.2)纸是木材制造的。
The_paper_is_ade_fr_wd.3)这辆汽车是中国制造的。
The_ar_is_ade_in_hina.be ade f+原材料:表示“由……制成”,从制成的物体上能看出原材料,制作过程发生了物理变化。
be ade fr+原材料:表示“由……制成”,从制成的物体上看不出原材料,制作过程发生了化学变化。
be ade in+地名:表示“某物生产于某地”。
当堂评价请学生们做前面课时训练部分。
Setin A (3a-3)学习目标1.重点单词:prdut,Frane,lal,brand,avid,prdut,handbag,bile,everyday2.重点短语:n atter,everyday things,high­tehnlgy prduts3.重点句式:N atter what yu ay buy,yu ight think thse prduts were ade in thse untries.He fund it interesting that s any prduts in the lal shps were ade in hina.He realized that Aerians an hardly avid buying prduts ade in hina.学习重点1.重点短语和句型2.一般现在时态的被动语态及代词的指代作用学习难点1.重点短语和句型2.一般现在时态的被动语态及代词的指代作用自主学习一、预习课本P35新单词并背诵,完成下面的汉译英。