中考英语语法专题教案---形容词
- 格式:docx
- 大小:107.31 KB
- 文档页数:19


中考英语语法---形容词和副词一、形容词和副词用法形容词修饰名词,副词修饰动词或形容词。
需要注意的是感官动词的后面用形容词,例如:look, taste, sound, smell, feel等。
1、形容词变副词,大部分的形容词加ly变副词。
如:形容词副词quick+ly quicklyslow+ly slowlyquiet+ly quietlyhappy+ly happilycareful+ly carefully注意:1)并不是以ly结尾的单词都是副词,名词+ly可变成形容词。
如:名词形容词friend + ly friendly 朋友般的love + ly lovely 可爱的sister + ly sisterly 姐妹般的2)有些名词+y可以变成形容词。
如:名词形容词rain + y rainy 下雨的snow + y snowy 下雪的cloud + y cloudy 阴天的salt + y salty 咸的sand + y sandy 有沙的fog + y foggy 雾的wind + y windy 有风的( ) 1.–What’s up, Simon? You didn’t look very____ .-- The customers always prefer Debbie ____ me. I can’t understand it.A. happily, withB. pleased, forC. happy, toD. happy, at( ) 2. "A ______ accident happened at 7:30 a.m." said the policeman _______.A. serious, seriousB. seriously, seriouslyC. seriously, seriousD. serious, seriously( ) 3. We love to go to the country in spring as the flowers smell so .A. wellB. niceC. wonderfullyD. nicely( ) 4.—Oh. I’m hungry. Mum, can I have the hamburger on the plate?—No. It tastes .A. terriblyB. terribleC. goodD. well( ) 5.—What do you think of your English teacher?—I love her. She is really . She always has a smile on her face.A. outgoingB. funnyC. friendlyD. serious( )6.---Why don’t you like pigs, Molly?---Because they are ______ .A. cuteB. uglyC. smartD. friendly2、副词区分a. late 与lately late意思是"晚";lately 意思是"最近" 例如:You have come too late. What have you been doing lately?b. hard与hardly hard 表示努力地/的hardly表示―几乎不‖例如:he works hard. I can hardly finish it in a week.c. close与closely close意思是"近";closely 意思是"仔细地" 例如:He is sitting close to me. Watch him closely.d. deep与deeply deep意思是"深"表示空间深度;deeply时常表示感情上的深度,"深深地" 例如:He pushed the stick deep into the mud. Even father was deeply moved by the movie.e. high与highly high表示空间高度;highly表示程度,相当于much 例如The plane was flying high. I think highly of your opinion.f. wide与widely wide表示空间宽度;widely意思是"广泛地","在许多地方" 例如:He opened the door wide. English is widely used in the world.( ) 1 Mingming got up very _______,so he came to school half an hour ______.te; latelyB. lately; lateC. lately; latelyD. late; late二、形容词与副词的原级、比较级和最高级1、形容词和副词有比较级和最高级的变化大多数形容词(性质形容词)和副词有比较级和最高级的变化,即原级、比较级和最高级,用来表示事物的等级差别。


中考语法专题之形容词一 . 形容词概括形容词用来修饰名词或代词,说明事物或人的性质或特色。
例: She is a beautiful girl.He is clever.The box is heavy.二.形容词在句中所做成分(1)做定语例: The strong man is Howard.I have something important to tell you.( 2)做表语例: Howard is strong.【注意】有些形容词只好作表语例:alone, alive,afraid,asleep,ill ,interested,excited, surprised等。
如: That old man feels alone because his children are out.I'm afraid he can't come.而以 ly 结尾的形容词有friendly ,lively ,lovely ,likely 等。
( 3)做宾语补足语做宾补,放在宾语后,常与 make、leave、 keep等词连用 , 即 make/keep/leave + sb./sth + adj例: Howard keeps himself strong.三、形容词与其余词类的地点关系(1) 形容词修饰 something, anything, nothing, everything等不定代词时,形容词放在名词后。
[根源 :例: I have something important to tell you.Is there anything interesting in the film.Can you find anywhere quiet?He has been sent to somewhere particular.Did you see anybody else? 你还看到他人了吗 ?四、某些形容词能够和定冠词连用,表示一类人或事物,其作用相当于一个名词,如: the young(年青人),the poor (穷人),the rich (富人)。
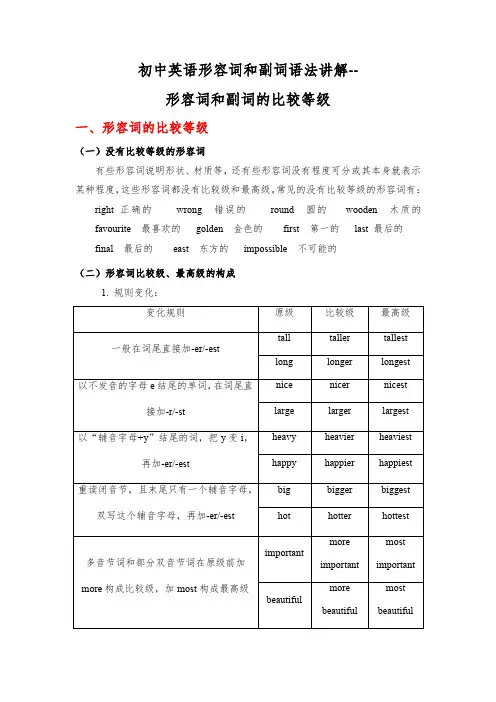
初中英语形容词和副词语法讲解--形容词和副词的比较等级一、形容词的比较等级(一)没有比较等级的形容词有些形容词说明形状、材质等,还有些形容词没有程度可分或其本身就表示某种程度,这些形容词都没有比较级和最高级。
常见的没有比较等级的形容词有:right 正确的wrong 错误的round 圆的wooden 木质的favourite 最喜欢的golden 金色的first 第一的last 最后的final 最后的east 东方的impossible 不可能的(二)形容词比较级、最高级的构成1. 规则变化:变化规则原级比较级最高级一般在词尾直接加-er/-esttall taller tallestlong longer longest以不发音的字母e结尾的单词,在词尾直接加-r/-st nice nicer nicest large larger largest以“辅音字母+y”结尾的词,把y变i,再加-er/-est heavy heavier heaviest happy happier happiest重读闭音节,且末尾只有一个辅音字母,双写这个辅音字母,再加-er/-est big bigger biggest hot hotter hottest多音节词和部分双音节词在原级前加more构成比较级,加most构成最高级importantmoreimportantmostimportant beautifulmorebeautifulmostbeautiful2.不规则变化:原级比较级最高级good/well better bestbad/ill worse worstmany/much more mostlittle less leastold older/elder oldest/eldestfar farther/further farthest/furthest(三)形容词比较等级的用法1.原级的用法(1)肯定句中用“as+原级形容词+as”表示双方在程度、特征等方面相同。


形容词一.定义:用来修饰名词,表示人或事物的性质、状态和特征的词,叫形容词。
二. 形容词的作用,见下表:有些形容词只能作表语,如:alone, afraid, asleep 等。
例如:Don't wake the sleeping baby up. He is asleep.The old man is alone.形容词用来修饰something, anything, nothing, everything等不定代词,要放在这些词的后面。
例如:You'd better tell us something interesting.The police found nothing strange in the room.多个形容词做定语时排列的先后顺序是:1)冠词或人称代词2)数词3)性质4)大小5)形状6)表示老少,新旧7)颜色8)事务、质地、人的国籍、用途。
例如:His grandpa still lives in this small short house.他爷爷还住在这个矮小的房子里。
The woman bought two beautiful Chinese plates.那个妇女买了两个漂亮的中国盘子。
形容词名词化:有些形容词前加定冠词后变成名词,表示一类人,谓语常用复数。
这类词有:rich / poor; good / bad ; young / old ; healthy / ill ; living / dead ; black / white (表示人种等)。
例如:The young should take good care of the old.年轻人应该好好照顾老人。
The rich never help the poor in this country.在这个国家,富人从来不帮助穷人。
形容词短语做定语时要后置。
如:They are the students easy to teach.他们是很容易较的学生。

教学内容形容词和副词知识结构形容词一、形容词的定义形容词是描述人或事物的特征、性质、属性及状态的一种词类,主要用来修饰名词或代词。
二、形容词的句法功能成分说明例句作定语一般放在所修饰词的前面It’s a cold and windy day today. 今天是个寒冷、有风的天气。
1)表示发生时间的副词:►It’s beginning to rain now! 现在开始下雨了!2)表示频繁程度的副词,也称频度副词always, often, usually, sometimes, never, ever, hardly等一般位于系动词、情态动词和助动词之后,实义动词之前。
►She often changes her mind. 她常改变主意。
3)还有一些其他表示时间的副词:►He has just had an operation. 他刚动过手术。
2. 地点副词:here, there, out, somewhere, abroad, home1)有不少表示地点的副词:►She is studying abroad. 她在国外留学。
2)还有一些部分与介词同形的副词。
它们与介词同形,后跟宾语的是介词,否则是副词:①用作介词:Stand up!起立!①用作副词:A cat climbed up the tree. 猫爬上了树。
3)以where构成的副词也是地点副词:It’s the same everywhere. 到处都一样。
3. 方式副词:well, fast, slowly, carefully, quickly1)英语中有大量方式副词,说明行为方式(回答how的问题):►How beautifully your wife dances. 你夫人舞跳得真美。
2)还有相当多的副词,表示某些情绪:►She smiled gratefully. 她感激的笑了笑。
3)还有一些以-ly结尾的副词,表示动作发生的状况:►He left the town secretly. 他悄然离开了这座城市。

形容词、副词考点聚焦和精讲【中考形容词、副词考点聚焦】一形容词的功能和位置1.说明人或事物的性质或特征的词叫形容词。
形容词在句中只要用作定语、表语、宾语补足语和状语。
2. 多个形容词作定语时的排序There is a small old black wooden desk in my room. 在我的房间里有一个又小又旧的黑色木桌。
His living room is decorated with a large green Chinese carpet. 他的起居室里装饰着绿色的中国大地毯。
3. the加上某些形容词相当于名词,表示一类人或事物The poor are very happy, but the rich are sad. 穷人高兴,但是富人悲伤。
4. 以-ly结尾的形容词5. 只能作表语的形容词:6. 只能作定语的形容词:7. 既可做形容词又可做副词的词8. 形容词与名词的转换:(1)名词加后缀变为形容词。
(2)形容词加后缀变为名词。
9. -ing形容词和-ed形容词的比较:-ing形容词表示主动意义,多修饰事或物,多指事物影响到人,意为“使人(感到)……的”;而-ed 形容词往往带有被动含义,修饰人,多指人受到事物的影响,意为“感到……的”,常用于“sb.+ -ed形容词”结构,有时也做定语用。
10. 形容词常用句型:二常用易混形容词用法辨析:(1)whole与all的用法辨析:记住两个词序:① the whole +名词;①all (of) the +名词。
如:He was busy the whole morning.He can remember all the words he learns.(2)tall与high, short与low用法辨析:指人的个子时用tall与short;指其他事物时一般用high 与low。
He’s very tall/short. // A few people live on high mountains.Tall trees are standing on both sides of that avenue.(3)real与true的用法辨析:real一般指东西的真假,意为“真的”;而true则指事情或消息的可靠性,意为“真实的”。
中考英语语法形容词、副词【趋势解读】在历年的中考试题中,形容词、副词是重要的考点之一。
根据对近年中考试题的分析,预计今后几年考查形容词、副词时,主要会考查形容词副词的比较等级、形容词的位置、同义近义形容词副词的辨析、含有形容词的一些特殊句型和固定短语等。
预计形容词副词的考查主要会分布在单项选择题中,完形填空、词汇填空、短文填空题中也会出现一些。
【思维引导】精彩笔记1 形容词和副词的分类及其作用(1)形容词用来修饰名词或不定代词,表示人或事物的性质、特征、状态或属性。
副词是修饰动词、形容词、数词、其他副词或全句的词,表示时间、地点、程度等。
它们在句子中作定语、表语、补语和状语。
如:Tom is a good ( adj.作定语)boy. Tom是个好男孩。
Life here ( adv.作定语)is full of joy.这儿的生活充满欢乐。
We are busy(adj.作表语).我们很忙。
Is he up ( adv.作表语),他起来了吗?We keep our room clean(adj.作room的补足语).我们保持房间干净。
Let me show you out ( adv.作宾语you的补足语).我来带你出去。
Tired and hot ( adj.作状语=Because we were tired and hot ) , we stopped to have a rest.又累又热,我们停下来休息一会儿。
She works carefully(adv.作状语).她认真地工作。
数词+名词(+形容词) a 15-year-old boy,the girls' 800-meter race等形容词(或数词)+名词-ed a middle-aged man,an 18-storeyed building等(2)复合形容词形容词+动词-ing a good-looking man,an ordinary-looking woman等名词+动词-ed a man-made river,a snow-covered house等副词十动词-ed a well-known singer,a well-trained guide等注意:复合形容词是指由几个词共同组成,并起形容词作用的词。
中考英语语法专题讲座:形容词
一、形容词的一般用法
1.作定语,一般放在所修饰词的前面。
It s a cold and windy day.
2.作表语,放在系动词的后面。
(look,feel,smell,sound .)
He looks happy today.
3.形容词修饰something,anything,nothing,everything等复合不定代词时,须放在其后。
Would you like something hot to drink?
4.表示长、宽、高、深及年龄的形容词,应放在相应的名词之后。
How long is the river? It s about two hundred metres long.
5.只能作表语的形容词:afraid;alone;asleep;awake;alive;well健康的;
ill;frightened
The man is ill.(正)
The ill man is my uncle.(误)
6.只能作定语的形容词:little小的;only唯一的;wooden木质的;woolen羊毛质的;elder年长的
My elder brother is in Beijing.(正)
My brother is elder. (误)
7.貌似副词的形容词:lonely;friendly;lively;lovely
二、形容词常用句型
1. It s +adj.+of+sb.+不定式表示某人(做某事)怎幺样。
=Sb +be +adj+to do sth。
2017中考英语语法精讲:形容词和副词【教学目标】掌握形容词和副词的位置,基本用法和比较等级【教学内容】I. 形容词:表示人和事物的特征,对名词起修饰和描绘作用(1)形容词的位置:1.形容词在句中作定语、表语、宾语补足语等,作定语时一般放在名词前。
eg. She has short hair.(作定语)Paul is tall.(作表语)We must keep our room clean.(作宾补)2.形容词修饰不定代词时放在其后。
eg.She has something important to tell us.There’s nothing wrong in the sentence.(2)形容词作定语通常前置,但在有些情况下后置,如下表:修饰some, any, every, no和body, thing, one等构成的复合不定代词时nobody absent, everythingpossible以-able, -ible结尾的形容词可置于有最高级或only修饰的名词之后the best book available, the only solution possiblealive, alike, awake, aware, asleep等可以后置the only person awake 和空间、时间、单位连用时 a bridge 50 meters long成对的形容词可以后置 a huge room simple and beautiful 形容词短语一般后置 a man difficult to get on with(3)多个形容词修饰同一个名词的顺序:代词数词性状形容词冠词前的形容词冠词指示代词不定代词序数词基数词性质状态大小长短形状新旧温度颜色国籍产地材料质地名词(4)有关形容词的重要考点:(一)形容词修饰something, anything, nothing, 或由some, any, no构成的不定代词时,把形容词后置。
第一部分词类语法形容词/副词(Adjective/Adverb)Lookerson see more than players. 当局者迷,旁观者清必知考点1:形容词/副词的构成◇G构成常见的形容词的构成①以[y]结尾:health + [y] →healthy 健康的greed + [y] →greedy 贪婪的②以[al], [ial]结尾:natur(e) + [al] →natural 自然的influent + [ial] →influential 有影响力的③以[ful], [less]结尾:success + [ful] →successful 成功的aim + [less] →aimless 无目标的④以[able]结尾:afford + [able] →affordable 可支持的reason + [able] →reasonable 有原因的⑤以[ive]结尾:product + [ive] →productive 有生产力的attract + [ive] →attractive 有吸引力的⑥以[ly]结尾:friend + [ly] →friendly 友好的live + [ly] →lively 生机勃勃的⑦以[ous], [ious]结尾:fam(e) + [ous] →famous 著名的spac(e) + [ious] →spacious 广大的⑧复合形容词:kind + hearted →kindhearted 心地善良的dark + blue →darkblue 暗蓝色的巧思:对[形容词后缀]的一些建议①不要特意去记,[后缀]只能辅助记忆,不能作为[背单词的手段]a. [形容词]中文翻译带有“的”字;b. 许多[形容词]都是由[差不多意思的其他词性]变换而来,因此背单词时只需要在原有单词含义基础上添加“的”字即可。
②[ful]结尾的形容词含义是:“充满……的”如:success n. 成功+ [ful] =充满成功的:successful③[able]结尾的形容词含义是:“能够……的”如:afford v. 支持+ [able] =可以支持的:affordable④[ive]结尾的形容词含义是:“有……性质的”如:act n. 行为+ [ive] =活力的:active⑤[less]是[否定形容词后缀]如:home n. 家+ [less] =无家可归的:homeless副词的构成①[形容词] + [ly]构成副词:happy →改y为i + [ly] →happily 高兴地careful + [ly] →carefully 认真地②天生就是[副词]:hard adv. 努力地alone adv. 孤独地巧思:不要被[ly]迷惑不是所有的以[ly]结尾的单词都是[副词]a. [adj.] + [ly] →[adv.]successful + [ly] →successfully adv. 成功地b. [v.], [n.] + [ly] →[adj.]like + [ly] →likely adj. 有可能的必知考点2:形容词变副词的细则形容词变副词细则①一般在[形容词]末尾加[ly]quick + [ly] →quickly slow + [ly] →slowly②以[辅音字母加y结尾]的[形容词],把[y]变成[i]再加[ly]happy →变[y]为[i] + [ly] →happily angry →变[y]为[i] + [ly] →angrily③少数以[e]结尾的[形容词],需要去掉[e]再加[y]或[ly]true →去掉[e] + [ly] →truly fortable →去掉[e] + [y] →fortably④有些以[ble], [ple]或[tle]结尾的[形容词],要去掉[e]再加[y]simple →去掉[e] + [y] →simply gentle →去掉[e] + [y] →gentlyterrible →去掉[e] + [y] →terribly⑤以[l]结尾的[形容词]在词尾加[ly],以[ll]结尾的[形容词]在词尾加[y]usual + [ly] →usually full + [y] →fully必考考点1:形容词与副词的用法及位置◇W位置形容词的位置①多数情况下,[形容词]作[前置定语]·Nice and warm days are ing.好且温暖的日子来临了。
专题七形容词一、形容词的用法及位置说明人或事物的特征、性质或状态,常用来修饰名词或不定代词。
1.作定语,放在名词之前,不定代词之后。
如:The princess lived in a beautiful castle.公主住在一座美丽的城堡里。
The headmaster has something important to announce.校长有重要的事情要宣布。
2.作表语,放在系动词之后。
如:The chocolate tastes smooth like silk.这种巧克力尝起来如丝般柔滑。
有少数形容词只能作表语,不能作定语,如alone,afraid,ill,asleep,awake,alive,well等。
3.放于动词make,keep,leave等动词的宾语后作宾语补足语。
如:Computers make it easier for people to do some work.电脑使得人们工作起来容易多了。
The mother made the bed comfortable for the baby.母亲将婴儿的小床铺得舒舒服服的。
注意:①else用作形容词,通常用于疑问代词或不定代词之后,意为“另外的,其他的”。
如:What else do you want?别的您还想来点什么?②系表结构后接动词不定式结构。
如:I am sorry to hear that.听到那件事我很抱歉。
I am glad to meet you here.在这儿遇见你我很高兴。
二、某些形容词说明事物间的关系方位、时间、用途等,不能用程度副词来修饰,也没有比较级的变化,如the same,different,southern,northern,Chinese,Japanese等。
如:The lifestyle in northern China is different from ours.中国北方人民的生活方式与我们的不同。
三、形容词的名词化某些形容词放在定冠词之后,变成名词,表示一类人,常见词有good/bad,rich/poor,young /old,deaf/blind,black/white,living/dead等。
如:The good defeated the bad finally.善最终战胜了恶。
四、形容词的排列顺序当名词由两个以上的形容词修饰时,这些形容词的词序通常遵循一定的规则,一般不得随意调换,也不能依照汉语的意思去排列。
通常可按下面的次序排列:1.限定词,包括:冠词、指示代词、形容词性物主代词、名词所有格、数词等。
2.表示观点的描绘性形容词,如beautiful,fine,interesting等。
3.表示大小、长短、高低及形状的形容词,如tall,high,small,little,round等。
4.表示年龄、新旧的形容词,如young,old,new等。
5.表示颜色的形容词,如black,white,blue等。
6.表示国籍、地区、出处的形容词(名词),如Japanese,American,English,mountain等。
7.形成中心名词的材料的形容词,如stone,plastic,silk,wooden等。
如:my beautiful big round new Chinese wooden bed我漂亮的崭新的中国式木制大圆床五、形容词比较等级的构成1.规则变化1.说明人或事物自身的特征、性质或状态时用形容词原级。
如:The winter in Jinan is cold.济南的冬天很冷。
2.有表示绝对概念的副词very,so,too,enough,quite等修饰时用形容词原级。
如:The hall is big enough to hold a banquet.这个厅大到可以举行一场宴会。
3.表示A与B在某一方面程度相同或不同时用形容词原级。
(1)肯定句中的结构:“A...+as+形容词原级+as+B”。
如:Water is①②③food for plants.对于植物来说,水同养料一样重要。
(2)否定句中的结构:“A...+as/so+形容词原级+as+B”。
如:He seems④⑤⑥before.他看上去健康状况大不如前。
否定句的结构相当于less+形容词原级+than。
如:Guilin is⑦⑧⑨Nanjing in summer.桂林的夏天没有南京热。
(3)表示“A是B的……倍”时用“A...+倍数+as+形容词原级+as+B”结构(一倍:once,两倍:twice,三倍及以上:数字+times)。
如:The lake has been enlarged⑩before.这片湖被拓挖成了原来的三倍大。
(4)“A...+half as+形容词原级+as+B”表示“A是B的一半”。
如:The branch river is the main river.这条支流有主流的一半宽。
八、形容词比较级的用法1.表示两者进行比较时用形容词比较级,其结构为“A...+比较级+than+B”。
如:China’s area is bigger than America’s.中国的疆域比美国的大。
注意:为了避免重复,在从句中常用the one,that,those等词来替代前面出现过的名词。
其中the one 替代可数名词单数形式,the ones或those替代可数名词复数形式,that替代不可数名词。
如:The number of plants in Hainan Heilongiang.海南的植物品种比黑龙江丰富。
2.有表示程度的副词a little,a bit,a few,a lot,much,even,still,far,rather,any等修饰时,用形容词比较级。
如:She is in her thirties than in her twenties.她三十几岁时甚至比二十几岁时还要漂亮。
3.表示两者之间进行选择“哪一个更……”时,用句型“Which/Who is+形容词比较级,A or B?”表示。
如:is,squirrel or sparrow?哪一个较大,喜鹊还是麻雀?4.表示“几倍于……”时,用“倍数+比较级+than”表示。
如:The room is that one.这间房比那间大三倍。
5.表示“两者之间最……的一个(of the two)”时,常用“the+比较级”结构。
如:Jack is of the two brothers.杰克是两兄弟中较高的那个。
6.表示“越来越……”时,用比较级重叠结构,即“比较级+and+比较级”,多音节词和部分双音节词时用“more and more+形容词原级”。
如:The day is getting.白天越来越长了。
7.表示“越……越……”时,用“the+比较级,the+比较级”结构。
如:The,the.越大越好。
九、形容词最高级的用法1.表示三者或三者以上的人或物进行比较时,用形容词最高级。
形容词最高级前必须加定冠词the,句末常跟一个in/of短语来表示范围。
如:It’s day of the latest three days.今天是近三天来最凉爽的一天。
2.表示在三者或三者以上的人或物中进行选择时,用“Which/Who is+the+最高级,A,B or C?”句型。
如:Who is person to be my assistant,Jack,John or Lisa?谁是做我助手最合适的人选,杰克,约翰还是丽莎?3.表示“最……的……之一”时,用“one of the+形容词最高级”结构,该形容词后面的名词要用复数形式。
如:The Y ellow River is rivers in the world.黄河是世界最著名河流之一。
4.形容词最高级前面可以加序数词。
表示“第几最……”。
如:Changjiang River is river in China.长江是中国第一大长河。
5.形容词最高级前面可以有物主代词、指示代词、名词所有格等修饰,此时不能再用定冠词the。
如:This is friend.这是我最好的朋友。
6.形容词比较级结构可以表示最高级含义。
如:Lisa is the most beautiful girl in class.丽莎是班上最漂亮的女生。
=Lisa is more beautiful than any other girl in her class.丽莎比班上其他任何一个女生都漂亮。
=Lisa is more beautiful than the other girls in her class.丽莎比班上其他所有女生都漂亮。
=Lisa is more beautiful than any girl else in her class.丽莎比班上其他任何女生都漂亮。
=O girl is more beautiful than Lisa in her class.在班上没有女生比丽莎还漂亮的。
=Lisa is more beautiful than any of the other girls in her class.丽莎比班上其他任何女生都漂亮。
=Lisa is more beautiful than the rest of the girls in her class.“ 丽莎比班上其余的女生都漂亮。
【常考易错点】1.good , well , nice , fine(1) good 是涵义最广的常用词,属一般用语。
主要指“ 人的品质好” 或“ 东西的质量好” 等 意思。
如:Milk is good for children . 牛奶对儿童有益。
John is a good worker . 约翰是一名好工人。
(2) nice 带有一定的感情色彩。
着重强调人们的感觉,含有“ 漂亮的” 、“ 美妙的” 、“ 美味 的” 等意思;也可表示对人“ 友好和蔼” 。
如:The chips are nice . 这些炸土豆条很好吃。
Nice to meet you . 很高兴见到您。
(3) fine 侧重于表示“ 质量精细” 、“ 身体健康” ,还可以表示“ 天气晴” 等意,语气比 good 重。
如:—How are you ? 你身体好吗?—Fine ,thank you . 很好,谢谢你。
It is a fine day today . 今天天气晴朗。
(4) well 常用作副词, 修饰动词; 也可用作形容词(仅作表语) ,表示“ 身体好” 、 健康的” 、 “ 顺利的” 等意;还可译为“ 满意的;恰当的” 等。