第五章Simulink常用模块介绍和应用技巧
- 格式:ppt
- 大小:1.09 MB
- 文档页数:34


1.阻抗测量模块:阻抗测量模块是用于测量一线性电路中两个节点之间的阻抗的模块,其测量的阻抗是频率的函数。
它由一个连接在阻抗测量模块的第一个和第二个输入端之间的电流源z I 和一个连接于电流源的两端的电压测量z V 组成。
系统阻抗是通过传递函数()s H 计算得出的,即是由输入到状态空间(state-space )模型的电流到输出的电压的传递函数。
()()()s I s V s H z z =通过Powergui 模块的阻抗依频特性测量工具就可以显示出测量阻抗的相频特性和幅频特性。
阻抗测量模块考虑了断路器和理想开关的初始状态,也可以测量含有分布参数线路模块的电路的阻抗。
测量模块在计算阻抗时也考虑了电源的阻抗。
通过定义,将电压源的阻抗置为0(即认为电压源模块是短路的),将电流源的阻抗置为无穷大(即认为电流源模块是开路的)。
但是在某些应用中,需要手动删除电流源或是电压源模块以忽略它们对计算阻抗的影响。
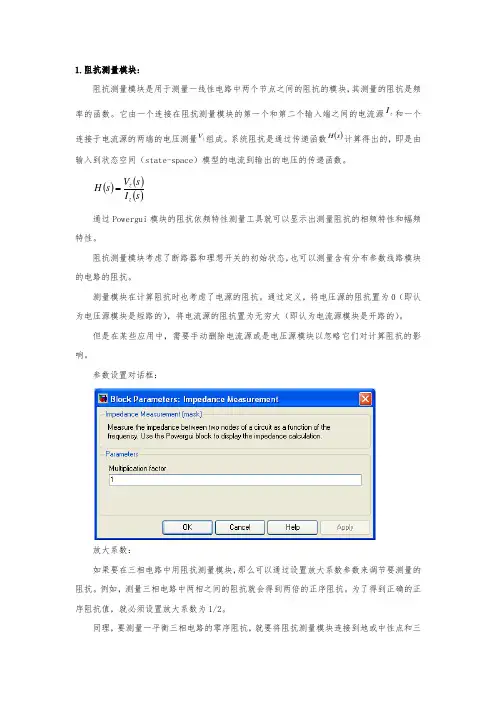
参数设置对话框:放大系数:如果要在三相电路中用阻抗测量模块,那么可以通过设置放大系数参数来调节要测量的阻抗。
例如,测量三相电路中两相之间的阻抗就会得到两倍的正序阻抗。
为了得到正确的正序阻抗值,就必须设置放大系数为1/2。
同理,要测量一平衡三相电路的零序阻抗,就要将阻抗测量模块连接到地或中性点和三相连接的一点之间。
在这种情况下,就会得到零序阻抗的1/3,因此,还必须将放大系数设置为3才能得到正确的零序阻抗值。
限制条件:在计算阻抗时仅仅考虑了断路器、三相断路器、三相故障、理想开关和分布参数线路这些非线性模块。
而如电机和电力电子设备等非线性模块就没有考虑在内,在测量阻抗过程中,它们被认为是断开的。
如果你要将阻抗测量模块与电感、电流源或是任何非线性元件串联,就必须在模块的两端增加一个大电阻,这是由于阻抗测量模块是作为一个电流源进行仿真的。
2.三相变压器(双绕组)实现了可配置绕组连结的三相变压器描述:三相变压器(双绕组)模块通过三个单相变压器实现了一个三相变压器。

simulink 常用模块解释-回复Simulink是一款由MathWorks公司开发的基于模型的设计和仿真环境,广泛应用于系统建模、仿真和设计。
Simulink的强大之处在于它提供了一系列常用模块,这些模块可以构建模型并模拟各种复杂系统的行为。
在本文中,我将为您介绍一些Simulink中常用的模块,并逐步详细解释它们的功能和应用。
1. Gain模块:Gain模块用于指定信号的增益系数。
它可以根据输入信号的幅值对信号进行缩放或放大。
Gain模块在控制系统设计和信号处理中经常使用,例如可以用来放大或缩小控制信号或者调整系统的增益。
2. Sum模块:Sum模块用于对输入信号进行求和操作。
它可以实现多个输入信号的相加,并输出它们的和。
Sum模块在控制系统中的控制逻辑实现、滤波器设计和信号处理中经常使用,例如可以用来实现控制器的误差计算。
3. Product模块:Product模块用于对输入信号进行乘法操作。
它可以实现多个输入信号的相乘,并输出它们的积。
Product模块在控制系统和信号处理中广泛应用,例如可以用来实现控制器的输出计算或者信号的调制。
4. Integrator模块:Integrator模块用于对输入信号进行积分操作。
它可以实现对输入信号积分并输出积分结果。
Integrator模块在控制系统设计和信号处理中常常使用,例如可以用来实现低通滤波器或者计算控制系统的状态变量。
5. Derivative模块:Derivative模块用于对输入信号进行微分操作。
它可以实现对输入信号的微分运算并输出微分结果。
Derivative模块在控制系统设计和信号处理中经常使用,例如可以用来实现对输入信号的速度或加速度测量。
6. Saturation模块:Saturation模块用于对输入信号进行限幅操作。
它可以设置输入信号的上下限,并限制信号在这个范围内。
Saturation模块在控制系统和信号处理中广泛应用,例如可以用来限制控制器的输出或者对信号进行幅值调整。
simulink模块的分类及用途Commsim 2001 Education模块化通信仿真软件产品编号:808-110(单),112 (10), 115 (25)Commsim 2001是一个理想的通信系统的教学软件。
它很适用于如’信号与系统’、’通信’、’网络’ 等课程,难度适合从一般介绍到高级。
使学生学的更快并且掌握的更多。
Commsim200含有200多个通用通信和数学模块,包含工业中的大部分编码器,调制器,滤波器,信号源,信道等,Commsin2001中的模块和通常通信技术中的很一致,这可以确保你的学生学会当今所有最重要的通信技术。
要观察仿真的结果,你可以有多种选择:时域,频域,XY图,对数坐标,比特误码率,眼图和功率谱。
Scalable Fun cti on alityLike all other Electronics Workbench products Commsim 2001 is available in three tiers for the education community:Single: For use by professors/teachers in the creation of lectures, lessons, assignments etcLab: For use by students in on-campus computer labsStudent:A special version for use by students on home PCs onlyHow Commsim is UsedCommsim 2001 is a powerful yet easy to use simulation tool that provides fast, accurate viewing of signals at anypoint in your system, via a natural sequence of steps. This power is presented to the user through an intuitive GUI(graphicalUser Interface) enabling drag and drop simplicity, just like all of the other products in the Electronics Workbench Family.Features at a Glan ce:* Industry's Largest Library«200+ Blocks«Communication & Math Blocks«Build your own Blocks/Models«Drag and Drop Diagram Construction* Analog, Digital & Mixed Systems«Automatic Wiring* Analog and Digital Modulators/Demodulators«Wide variety of Encoders/Decoders«Adaptive Equalizers«Vector and Matrix Operations* All popular Channel Models* Filter Design Wizard and Response Viewer«PLLs* RF Elements and Accurate Distortion* Complex Math* Complex Envelope Representation* Continuous, Discrete and Hybrid Simulation* Autorestart and Single Step Algorithms« Euler, Trapezoidal and Runge Kutta Integration Methods * Look-up Table Wizard* Signal Probes«Large variety of Plot Options«Mathcad, Matlab OLE IntegrationPlac ing and Conn ect ing BlocksPlace desired blocks from the library by dragging and dropping(from either the menusor the toolbar) any of the over 200 functional blocks available. Once placed, connecting blocks is extremely straightforward-just click on one block's output then on other blocks input and Commsim takes care of the rest. Its that simple!You can also make use of hierarchical blocks to break up more complex systems, each of whichcan be assigned its own symbol.Blocks LibrariesThe science of understanding and teaching communication systems lies in being aware of a widevariety of "functional blocks" of technology available to "construct" the optimal transmitter or receiver, given a particular type of signal and channel.Commsim 2001 helps you to ensure your students learn all of today's most important communication technologies by delivering blocks to match all of the commonly used techniques in communications.The commsimlibrary contains the industry's largest selection of coders, modulators, filters, sources, channels etc. You can even create your own blocks using equations or lower level functional blocks.Library BlocksBecause the right library is so essential to a good communications simulator, we have explained each family of blocks in detail. Simply click on the family to view more information.ChannelsEncoding/DecodingModulators/DemodulatorsOther Communication BlocksBasic BlocksChann elsModeling the medium through which a transmitted signal must pass is essential to accurately capture delay and distortion effects. Channels include copper wire, fiber, free space, etc.Cha nnel Blocks Modeled in Commsim 2001* Add.White Gaussian Noise (Complex & Real)* Binary Symmetric Channel* Jakes MobileMultipathPropagation Loss * Rice/Rayleigh Fading« Rummler Multipath« TWTAEn cod in g/Decod ingSingle encoding is performed to increase the reliability of information transfer and can include companding and quantization (analog signals) or forward error correction (using convolutional or trellis cooling on digital signals).Commsim 2001 in cludes the followi ng En coders/Decoders* Block Interleaver* Convolutional Encoder«Convolutional Interleaver* Gray Decoder«Gray Encoder* Trellis Decoder« Viterbi Decoder (Hard & Soft)Modulators/DemodulatorsCommsim provides the following analog and digital modulators/demodulation blocks, a subset of which use coherent methods(require phase synchronization in demodulation):Commsim 2001 in cludes the followi ng Modulators/Demodulators* AM* DQPSK* pi/4-DQPSK* FM* FSK* I/Q* MSK* PM* PAM (4,8)* PPM* PSK (2,4,8,16)* QAM (16,32,64,256)* SQPSK・DQPSK・pi/4-DQPSK Detector« FM Demodulator・PPM Demodulator« PSK Detector (2,4,8,16)«PAM Detector (2,4,8,16)・QAM Detector (16,32,64,256)Other BlocksCommsim 2001 also provides many other communication blocks (filters, PLLs, digital etc.) and general mathematical functions (complex math, estimatio, etc.)Communication & General Mathematical Blocks Modeled in Commsim 2001• Addtion• Conjugate•Conversions (Complex &Real)• Division• Inverse• Multiplication• Power• Square Root*Adaptive Equalizer(Complex & Real)* File FIR* FIR* IIR* MagPhase* Sampled FileFIR* Sampled FIR* Binary Counter* Bits to Symbol* Divide by N* D Flip Flop * JK Flip Flop* Mux/Demux *Paralell toSerial* Queue*Serial toParalell* Symbol to Bits• Charge Pump• PLL Loop Filters (2nd &3rd Order)•Type 2 PhaseDetector•Type3Phase/Frequency Detector•Type4Phase/Frequency DetectorBasic BlocksCommsir2001 offers over 90 blocks for linear, non linear, continous, discrete-time, time varying, and hybrid system design.Basic Blocks Modeled in Commsim 2001* Animation* Annotation* Arithmetic* BooleanDDEIntegrationLinear SystemsMatlab InterfaceMatrix OperationsNonlinearOptimizationRandom GeneratorSignal ConsumerSignal ProducerTime DelayTranscendentalCDM軀信系统的MATLA仿真学习好资料张广森,王虎(中国民航学院通信工程系,天津300300 )摘要:在简要介绍MATLAB^言的基础上,对使用MATLAB^言仿真的CDMA 通信系统进行描述。

simulink各模块中文详解Simulink是一种基于模块化建模方式的仿真软件,它可以用来进行系统级的设计、建模和仿真。
Simulink提供了丰富的模块库,包括信号处理、控制系统、通信系统等各个领域的模块,这些模块可以通过连接线连接起来,构成一个完整的系统模型。
在Simulink中,每个模块都有特定的功能和参数设置,下面我们将对Simulink的一些常用模块进行中文详解。
一、信号源模块信号源模块是Simulink中最基础的模块之一,它用于生成各种不同类型的信号。
常见的信号源模块包括正弦波信号源、方波信号源、脉冲信号源等。
这些信号源模块可以设置信号的幅值、频率、起始时间等参数,用于模拟各种不同的输入信号。
二、数学运算模块数学运算模块用于进行各种数学运算,比如加法、减法、乘法、除法等。
Simulink提供了各种数学运算模块,包括加法器、乘法器、除法器等。
这些模块可以对输入信号进行各种数学运算,生成输出信号。
三、滤波器模块滤波器模块用于对信号进行滤波处理,常见的滤波器模块包括低通滤波器、高通滤波器、带通滤波器等。
这些模块可以通过设置滤波器的截止频率、阶数等参数,对输入信号进行滤波,去除不需要的频率成分,得到所需的输出信号。
四、控制系统模块控制系统模块用于建立和仿真各种控制系统,包括PID控制器、状态空间模型、传递函数模型等。
这些模块可以通过设置控制器的参数,对输入信号进行控制,使系统输出达到期望值。
五、状态空间模块状态空间模块用于建立和仿真线性时不变系统的状态空间模型。
状态空间模型描述了系统的状态变量和输入输出关系,可以通过状态空间模块进行系统的分析和控制。
六、通信系统模块通信系统模块用于建立和仿真各种通信系统,包括调制解调器、信道模型、误码率计算器等。
这些模块可以模拟通信系统的发送、传输和接收过程,对信号进行调制解调、传输信道建模等操作。
七、数据存储模块数据存储模块用于存储和读取仿真过程中的数据,包括存储器、查找表、文件读写模块等。




matlab simulink每一模块的介绍
MATLAB Simulink是一款用于建立和仿真动态系统模型的软
件工具。
它基于MATLAB编程语言,并提供了图形化界面,
用户可以使用各种模块来构建复杂的系统模型。
以下是Simulink中一些常用模块的介绍:
1. Constant(常数):用于设置系统中的常数值,如常数信号
输入、定值代码等。
2. Gain(增益):用于调整或放大输入信号的幅度,可以根据需求进行增益设置。
3. Sum(求和):用于将多个输入信号相加,可以选择不同的
输入端口进行加法运算。
4. Product(乘积):用于将多个输入信号相乘,可以选择不
同的输入端口进行乘法运算。
5. Integrator(积分器):用于对输入信号进行积分运算,可以用于模拟系统的积分环节。
6. Derivative(导数器):用于对输入信号进行求导运算,可
以用于模拟系统的微分环节。
7. Transfer Fcn(传递函数):用于建立系统的传递函数模型,可以根据系统参数设置传递函数的分子和分母。
8. Scope(作用域):用于显示系统模型中的信号变化情况,
可以在仿真过程中实时监测信号。
9. To Workspace(输出到工作区):用于将信号输出到工作区,以便后续分析或处理。
这仅是Simulink中一小部分常用模块的介绍,实际上
Simulink提供了大量的模块供用户选择和使用,可以根据具体
的系统模型需求进行选择和组合。
同时,用户还可以借助自定义模块进行更复杂系统的建模和仿真。

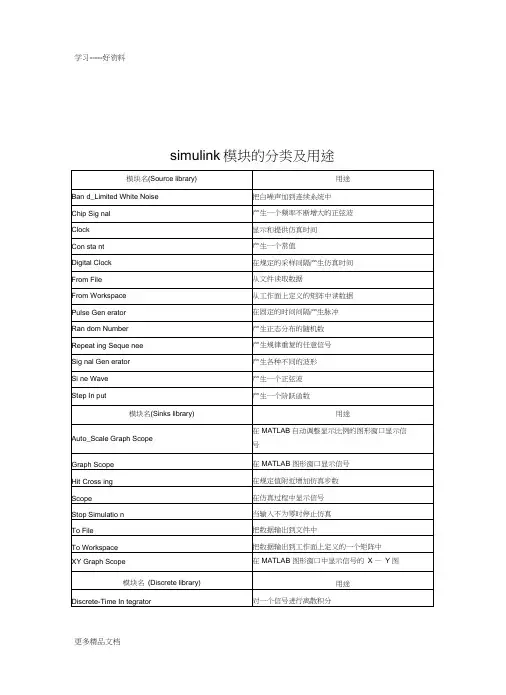
Simulink常用模块名称中英文对照Sources库Band-Limited White Noise 宽带限幅白噪声模块,把一个白噪声引入到连续系统中Chirp Signal 线性调频信号(频率按时间线性变化的正弦波)模块,产生频率增加的正弦信号Clock 时钟信号模块,显示或者提供仿真时间Constant 常量输入模块,产生一个常数值Digital Clock 数字时钟模块,按指定的间隔产生采样时间Digital Pulse Generator 产生具有固定间隔的脉冲From File 从一个文件读取数据From Work space 从在工作空间定义的矩阵读入数据Ground 接地模块,将一个未连接的输入端接地In1 输入端口模块Pulse Generator 脉冲信号发生器模块,产生固定间隔的脉冲Ramp 斜坡信号输入模块,产生一个以常数斜率增加或者减小的信号Random Number 产生正态分布的随机数Repeating Sequence 产生一个可重复的任意信号Signal Generator 产生多种多样的普通信号Signal Builder 自定义信号发生器Sine Wave 产生正弦波信号Step 阶跃信号模块,产生一个单步函数Uniform Random Number 产生均匀分布的随机数Sinks库Display 实时数字显示模块,显示其输入信号的值Floating Scope 浮动示波器模块Out1 输出端口模块Scope 示波器模块,显示在仿真过程产生的信号的波形Stop Simulation 仿真终止模块,当它的输入信号非零时,就结束仿真Terminator 信号终结模块,结束一个未连接的输出端口To File 写数据到文件To Workspace 把数据写进工作空间里定义的矩阵变量XY Graph 用一个MATLAB图形窗口来显示信号的X-Y坐标的图形Continuous库主要用于连续系统的仿真Derivative 微分模块,输出为输入信号的微分。
simulink 常用模块解释Simulink是一种常用的软件工具,用于建模、仿真和分析动态系统。
它通常与MATLAB配合使用,提供了一种图形化的方法,使工程师和科学家能够更容易地设计和测试各种控制系统。
下面是几个常用的Simulink模块的解释:1.信号发生器(Block: Signal Generator)信号发生器模块用于生成各种类型的信号,例如正弦波、方波、锯齿波等。
用户可以通过设置频率、振幅、相位等参数来生成所需的信号。
2.积分器(Block: Integrator)积分器模块用于对输入信号进行积分操作。
它可以将一个输入信号的积分值作为输出,对于需要进行累加操作的系统建模非常有用。
3.微分器(Block: Derivative)微分器模块用于对输入信号进行微分操作。
它可以将输入信号的导数作为输出,对于需要对信号变化率进行建模和分析的系统非常有用。
4.增益(Block: Gain)增益模块用于对输入信号进行比例缩放操作。
用户可以通过设置增益参数来放大或缩小输入信号的幅度。
5.触发器(Block: Trigger)触发器模块用于在满足一定条件时触发或延迟系统的某些操作。
例如,当一个信号超过某个阈值时,触发器可以将相应的操作信号输出。
6.多路选择器(Block: Selector)多路选择器模块用于从多个输入信号中选择一个输出信号。
用户可以通过设置选择参数来指定要选择的输入信号。
以上仅是Simulink中的一些常用模块。
这些模块可以根据特定的系统需求被组合在一起,以建立复杂的控制系统、信号处理系统或其他动态系统的模型。
通过使用Simulink,工程师和科学家可以更方便地进行系统设计和分析,并进行仿真来验证其性能。
SIMULINK常用库模块介绍一、SIMULINK简介1、简介SIMULINK是一个对动态系统(包括连续系统、离散系统和混合系统)进行建模、仿真和综合分析的集成软件包,是MATLAB的一个附加组件,其特点是模块化操作、易学易用,而且能够使用MATLAB提供的丰富的仿真资源。
在 SIMULINK环境中,用户不仅可以观察现实世界中非线性因素和各种随机因素对系统行为的影响,而且也可以在仿真进程中改变感兴趣的参数,实时地观察系统行为的变化,因此已在许多领域,如通信、信号处理、DSP、电力、金融、生物系统等获得重要应用。
对信息类专业的学生来说,无论是学习专业课程或相关课程设计,还是在今后的工作中,SIMULINK都是一个重要的仿真建模工具。
2、预备知识⏹SIMULINK的启动首先启动MATLAB,然后在MATLAB主界面中单击上面的Simulink按钮,如下图所示:或在命令窗口中输入simulink命令打开。
⏹SIMULINK的模块库Simulink的模块库有两部分组成:基本模块和各种应用工具箱,如下图所示。
对通信系统仿真来说,主要用到Simulink基本库,通信系统工具箱和数字信号处理工具箱。
二、SIMULINK的模块库1、SIMULINK基本库(1)连续模块Continuous名称功能说明Derivative 微分Integrator 积分器Integrator Limited 定积分Integrator, Second-Order 二阶积分Integrator, Second-Order Limited 二阶定积分PID Controller PID控制器PID Controller (2DOF) PID控制器State-Space 状态空间Transfer Fcn 传递函数Transport Delay 传输延时Variable Transport Delay 可变传输延时Zero-Pole 零—极点增益模型(2)非连续模块Discontinuous名称功能说明Backlash 间隙非线性Coulomb&Viscous Friction 库仑和黏度摩擦非线性Dead Zone 死区非线性Dead Zone Dynamic 动态死区非线性Hit Crossing 冲击非线性Quantizer 量化非线性Rate Limiter 静态限制信号的变化速率Rate Limiter Dynamic 动态限制信号的变化速率Relay 滞环比较器,限制输出值在某一范围内变化Saturation 饱和输出,让输出超过某一值时能够饱和Saturation Dynamic 动态饱和输出Wrap To Zero 还零非线性(3)离散模块Discrete名称功能说明Delay 延时器Difference 差分环节Discrete Derivative 离散微分环节Discrete FIR Filter 离散FIR滤波器Discrete Filter 离散滤波器Discrete PID Controller 离散PID控制器Discrete PID Controller (2DOF) 离散PID控制器Discrete State-Space 离散状态空间系统模型Discrete Transfer-Fcn 离散传递函数模型Discrete Zero-Pole 以零极点表示的离散传递函数模型Discrete-time Integrator 离散时间积分器First-Order Hold 一阶保持器Memory 输出本模块上一步的输入值Tapped Delay 延迟Transfer Fcn First Order 离散一阶传递函数Transfer Fcn Lead or Lag 传递函数Transfer Fcn Real Zero 离散零点传递函数Unit Delay 一个采样周期的延迟Zero –Order Hold 零阶保持器(4)逻辑和位操作模块Logic and Bit Operations名称功能说明Bit Clear 位清零Bit Set 位置位Bitwise Operator 逐位操作Combinatorial Logic 组合逻辑Compare To Constant 和常量比较Compare To Zero 和零比较Detect Change 检测跳变Detect Decrease 检测递减Detect Fall Negative 检测负下降沿Detect Fall Nonpositive 检测非负下降沿Detect Increase 检测递增Detect Rise Nonnegative 检测非负上升沿Detect Rise Positive 检测正上升沿Extract Bits 提取位Interval Test 检测开区间Interval Test Dynamic 动态检测开区间Logical Operator 逻辑操作符Relational Operator 关系操作符Shift Arithmetic 移位运算(5)查找表模块Lookup Table名称功能说明1-D Lookup Table 一维输入信号的查询表(线性峰值匹配)2-D Lookup Table 两维输入信号的查询表(线性峰值匹配)Cosine 余弦函数查询表Direct Lookup Table (n-D) N个输入信号的查询表(直接匹配)Interpolation using PreLookup 输入信号的预插值Lookup Table Dynamic 动态查询表PreLookup 预查询索引搜索Sine 正弦函数查询表n-D Lookup Table N维输入信号的查询表(线性峰值匹配)(6)数学模块Math Operations名称功能说明Abs 取绝对值Add 加法Algebraic Constraint 代数约束Assignment 赋值Bias 偏移Complex to Magnitude-Angle 由复数输入转为幅值和相角输出Complex to Real-Imag 由复数输入转为实部和虚部输出Divide 除法Dot Product 点乘运算Find Nonzero Elements 查找非零元素Gain 比例运算Magnitude-Angle to Complex 由幅值和相角输入合成复数输出Math Function 包括指数函数、对数函数、求平方、开根号等常用数学函数Matrix Concatenation 矩阵级联MinMax 最值运算MinMax Running Resettable 最大最小值运算Permute Dimensions 按维数重排Polynomial 多项式Product 乘运算Product of Elements 元素乘运算Real-Imag to Complex 由实部和虚部输入合成复数输出Reciprocal Sqrt 开平方后求倒Reshape 取整Rounding Function 舍入函数Sign 符号函数Signed SqrtSine Wave Function 正弦波函数Slider Gain 滑动增益Sqrt 平方根Squeeze 删去大小为1 的"孤维"Subtract 减法Sum 求和运算Sum of Elements 元素和运算Trigonometric Function 三角函数Unary Minus 一元减法Vector ConcatenateWeighted Sample Time Math 权值采样时间运算(7)模型检测模块Model Verification名称功能说明Assertion 确定操作Check Dynamic Gap 检查动态偏差Check Dynamic Range 检查动态范围Check Static Gap 检查静态偏差Check Static Range 检查静态范围Check Discrete Gradient 检查离散梯度Check Dynamic Lower Bound 检查动态下限Check Dynamic Upper Bound 检查动态上限Check Input Resolution 检查输入精度Check Static Lower Bound 检查静态下限Check Static Upper Bound 检查静态上限(8)模型扩充模块Model-Wide Utilities名称功能说明Block Support Table 功能块支持的表DocBlock 文档模块Model Info 模型信息Timed-Based Linearization 时间线性分析Trigger-Based Linearization 触发线性分析(9)端口和子系统模块Ports&Subsystems名称功能说明Atomic Subsystem 单元子系统CodeReuseSubsystem 代码重用子系统Configurable Subsystem 可配置子系统Enable 使能Enabled Subsystem 使能子系统Enabled and Triggered Subsystem 使能和触发子系统For Each Subsystem For Each子系统For Iterator Subsystem For迭代子系统Function-Call Feedback Latch 函数调用反馈锁存Function-Call Generator 函数调用生成器Function-Call Split 函数调用切换Function-Call Subsystem 函数调用子系统If If操作If Action Subsystem If操作子系统In1 输入端口Model 模型Model Variants 模型变种Out1 输出端口Subsystem 子系统Subsystem Examples 子系统例子Switch Case Switch Case语句Switch Case Action Subsystem Switch Case 操作子系统Trigger 触发操作Triggered Subsystem 触发子系统Variant SubsystemWhile Iterator Subsystem While迭代子系统(10)信号属性模块Signal Attributes名称功能说明Bus to Vector 总线到矢量转换Data Type Conversion 数据类型转换Data Type Conversion Inherited 数据类型继承Data Type Duplicate 数据类型复制Data Type Propagation 数据类型传播Data Type Propagation Examples 数据类型传播示例Data Type Scaling Strip 数据类型缩放IC 信号输入属性Probe 探针点Rate Transition 速率转换Signal Conversion 信号转换Signal Specification 信号特征指定Weighted Sample Time 加权的采样时间Width 信号宽度(11)信号线路模块Signal Routing名称功能说明Bus Assignment 总线分配Bus Creator 总线生成Bus Selector 总线选择Data Store Memory 数据存储Data Store Read 数据存储读取Data Store Write 数据存储写入Demux 分路Environment Controller 环境控制器From 信号来源Goto 信号去向Goto Tag Visibility Goto标签可视化Index Vector 索引矢量Manual Switch 手动选择开关Merge 信号合并Multiport Switch 多端口开关Mux 合路Selector 信号选择器Switch 开关选择,当第二个输入端大于临界值时,输出由第一个输入端而来,否则输出由第三个输入端而来Vector Concatenate 矢量拼接(12)接收器模块Sinks名称功能说明Display 数字显示器Floating Scope 浮动示波器Out1 输出端口Scope 示波器Stop Simulation 停止仿真Terminator 终止符号(To File 将输出数据写入数据文件保护To Workspace 将输出数据写入MATLAB的工作空间XY Graph 显示二维图形(13)输入源模块Sources名称功能说明Band-Limited White Noise 带限白噪声Chirp Signal 产生一个频率不断增大的正弦波Clock 显示和提供仿真时间Constant 常数信号Counter Free-Running 无限计数器Counter Limited 有限计数器Digital Clock 数字时钟Enumerated Constant 枚举常量From File 来自文件From Workspace 来自MATLAB的工作空间Ground 接地In1 输入信号Pulse Generator 脉冲发生器Ramp 斜坡输入Random Number 产生正态分布的随机数Repeating Sequence 产生规律重复的任意信号Repeating Sequence Interpolated 重复序列内插值Repeating Sequence Stair 重复阶梯序列Signal Builder 信号创建器Signal Generator 信号发生器,可产生正弦、方波、锯齿波及随意波Sine Wave 正弦波信号Step 阶跃信号Uniform Random Number 均匀分布随机数(14)用户自定义函数模块User-Defined Functions名称功能说明Fcn 用自定义的函数(表达式)进行运算Interpreted MATLAB Function 解释的Matlab函数Level-2 MATLAB S-Function 二级Matlab S函数MATLAB Function 利用MATLAB的现有函数进行运算S-Function 调用自编的S函数的程序进行运算S-Function Builder S函数创建S-Function Examples S函数例子2、通信系统工具箱Communication System Toolbox(1)信道 Channel名称功能说明AWGN Channel 加性高斯白噪声信道Binary Symmetric Channel 二进制对称信道Multipath Rayleigh Fading Channel 多径瑞利衰落信道Multipath Rician Fading Channel 多径莱斯衰落信道(2)通信滤波器 Comm Fliter名称功能说明Gaussian Filter 高斯滤波器Integrate and Dump 积分清零Raised Cosine Transmit Filter 升余弦发送滤波器Ideal Rectangular Pulse Filter 理想矩形脉冲滤波器Raised Cosine Receive Filter 升余弦接收滤波器Windowed Integrator 窗积分器(3)通信信宿Comm Sinks名称功能说明Discrete-Time Eye Diagram Scope 离散时间眼图示波器Discrete-Time Signal Trajectory Scope 离散时间信号轨迹示波器Discrete-Time Scatter Plot Scope 离散时间散点图示波器Error Rate Calculation 误码率计算(4)通信信源Comm Sources1)噪声发生器Noise Generators名称功能说明Gaussian Noise Generator 高斯噪声发生器Rayleigh Noise Generator 瑞利噪声发生器Rician Noise Generator 莱斯噪声发生器Uniform Noise Generator 均匀噪声发生器2)随机数据源Random Data Sources名称功能说明Bernoulli Binary Generator 伯努利二进制发生器Random Integer Generator 随机整数发生器Poisson Integer Generator 泊松整数发生器3)序列发生器Sequence Generators名称功能说明Barker Code Generator 巴克码发生器Hadamard Code Generator Hadamard码发生器OVSF Code Generator OVSF码发生器Walsh Code Generator 沃尔什码发生器Gold Sequence Generator Gold序列发生器Kasami Sequence Generator Kasami序列发生器PN Sequence Generator PN序列发生器(5)检错与纠错Error Detection and Correction3)卷积码Convolutional名称功能说明APP Decoder APP译码器Turbo Decoder Turbo译码器Viterbi Decoder 维特比译码器Convolutional Encoder 卷积码编码器Turbo Encoder Turbo编码器(6)调制Modulation1)模拟调制Analog Passband Modulation名称功能说明DSB AM Demodulator Passband 双边带调幅解调器DSBSC AM Demodulator Passband 抑制载波调幅解调器FM Demodulator Passband FM解调器PM Demodulator Passband PM解调器SSB AM Demodulator Passband 单边带调幅解调器DSB AM Modulator Passband 双边带调幅调制器DSBSC AM Modulator Passband 抑制载波调幅调制器FM Modulator Passband FM调制器PM Modulator Passband PM调制器SSB AM Modulator Passband 单边带调幅调制器2)数字调制Digital Passband Modulation①调幅AM名称功能说明General QAM Demodulator Baseband 通用QAM解调基带M-PAM Demodulator Baseband M-PAM解调基带Rectangular QAM Demodulator Baseband矩形QAM解调基带General QAM Modulator Baseband 通用QAM调制器基带M-PAM Modulator Baseband M-PAM调制器基带Rectangular QAM Modulator Baseband 矩形QAM调制基带② CPM名称功能说明CPFSK Demodulator Baseband CPFSK解调器CPM Demodulator Baseband CPM解调器GMSK Demodulator Baseband GMSK解调器MSK Demodulator Baseband MSK解调器CPFSK Modulator Baseband CPFSK调制器CPM Modulator Baseband CPM调制器GMSK Modulator Baseband GMSK调制器MSK Modulator Baseband MSK调制器③ FM名称功能说明M-FSK Demodulator Baseband M-FSK解调器M-FSK Modulator Baseband M-FSK调制器④ PM名称功能说明BPSK Demodulator Baseband BPSK 解调器DBPSK Demodulator Baseband DBPSK解调器DQPSK Demodulator Baseband DQPSK解调器M-DPSK Demodulator Baseband M-DPSK解调器M-PSK Demodulator Baseband M-PSK解调器OQPSK Demodulator Baseband OQPSK 解调器QPSK Demodulator Baseband QPSK解调器BPSK Modulator Baseband BPSK 调制器DBPSK Modulator Baseband DBPSK调制器DQPSK Modulator Baseband DQPSK调制器M-DPSK Modulator Baseband M-DPSK调制器M-PSK Modulator Baseband M-PSK调制器OQPSK Modulator Baseband OQPSK调制器QPSK Modulator Baseband QPSK调制器⑤ TCM名称功能说明General TCM Decoder 通用TCM解码器M-PSK TCM Decoder M-PSK TCM解码器Rectangular QAM TCM Decoder 矩形QAM TCM解码器General TCM Encoder 通用TCM编码器M-PSK TCM Encoder M-PSK TCM编码器Rectangular QAM TCM Encoder 矩形QAM TCM编码器3、DSP系统工具箱DSP System Toolbox(1)信号管理 Signal Management1)缓存 Buffers名称功能说明Buffer 缓存(串并转换)Delay Line 延迟线Queue 队列寄存器(FIFO)Stack 堆栈Unbuffer 解缓存(并串转换)2)信号属性 Signal Attributes名称功能说明Check Signal Attributes 信号属性校验Convert 1-D to 2-D 1维到2维转换Convert 2-D to 1-D 2维到1维转换Data Type Conversion 数据类型转换Frame Conversion 帧信号和采样信号转换Inherit Complexity 实数、复数类型继承(2)信号操作 Signal Operations名称功能说明Constant Ramp 常数斜升信号Convolution 卷积Delay 延迟Downsample 下采样Interpolation 内插NCO 数控振荡器NCO HDL Optimized HDL优化的NCOOffset 数据偏移Pad 头部或尾部添补数据Peak Finder 峰值搜索器Repeat 重复Sample and Hold 采样保持Triggered Signal From Workspace 触发的工作空间信号Unwrap 相位不连续处理Upsample 上采样Variable Fractional Delay 可变分数延迟Variable Integer Delay 可变整数延迟Window function 窗函数Zero Crossing 零交叉检验(2)输出 Sinks名称功能说明Display 数据显示Matrix Viewer 矩阵观察器Signal to Workspace 输出信号到工作空间Spetrum Analyzer 频谱分析仪Time Scope 时域示波器To Audio Device 输出到音频设备To Multimedia 输出到多媒体Triggered To Workspace 触发输出到工作空间UDP Send UDP发送Vector Scope 矢量示波器Waterfall 多矢量数据示波器。
SIMULINK模块介绍SIMULINK是一款由MathWorks公司开发的仿真软件,它是MATLAB软件的一个附属工具箱。
SIMULINK提供了一个可视化的建模环境,用户可以通过图形化方式搭建模型,并进行仿真和分析。
SIMULINK模块是SIMULINK软件中的一些组件,可以帮助用户进行系统建模、仿真和控制设计。
本文将介绍SIMULINK中的一些常用模块。
1.数学运算与逻辑模块:这些模块包括常见的数学运算符(加减乘除、幂运算、取余等)和逻辑运算符(与、或、非等),可以用于进行数据运算和逻辑判断。
在建模过程中,通过连接这些模块,用户可以实现各种数学运算和逻辑控制,从而实现复杂的系统行为。
2.信号生成器模块:这些模块包括常见的信号发生器(正弦波、方波、脉冲等)和信号生成器(连续或离散的步进信号),可以生成各种基本信号。
用户可以使用这些模块来生成输入信号,用于系统的仿真和测试。
3.数值源与作用器模块:这些模块用于输入和输出数值。
数值源模块可以用于指定模型的初始值,或者作为参数输入到仿真模型中。
作用器模块用于将仿真模型的输出结果传递给其他系统或模型进行实时控制。
4.状态空间模块:这些模块用于描述系统的状态空间方程。
用户可以将系统的状态空间表达式输入到这些模块中,然后连接其他模块进行模型的搭建和仿真。
5.运动控制模块:这些模块用于实现对物体的运动控制。
例如,用户可以使用PID控制器模块对电机进行速度或位置控制,或者使用运动传感器模块来实时监测物体的位置和速度。
6.信号处理模块:这些模块用于对信号进行采样、处理和分析。
用户可以使用滤波器模块对输入信号进行滤波操作,或者使用频谱分析模块对信号的频谱进行分析。
7.光学模块:这些模块用于光学系统的建模和分析。
例如,用户可以使用光学元件模块来描述光学系统中的镜头、透镜等元件,或者使用光传输模块来模拟光束在系统中的传输和传播。
8.通信模块:这些模块用于通信系统的建模和仿真。
Simulink模块库Sources库◼也可称为信号源库,该库包含了可向仿真模型提供信号的模块。
它没有输入口,但至少有一个输出口。
◼双击图标即弹出该库的模块图:➢在该图中的每一个图标都是一个信号模块,这些模块均可拷贝到用户的模型窗里。
用户可以在模型窗里根据自己的需要对模块的参数进行设置(但不可在模块库里进行模块的参数设置).1.Sources库①Sine Wave:产生幅值、频率可设置的正弦波信号。
➢双击图标(认定该模块已拷贝到用户模型窗,以下均如此),弹出正弦波的参数设置框图。
图中参数为Simulink默认值,用户可根据需要对这些参数重新设置。
➢幅值、频率为2,基准为0.5,其波形如下图所示:1.Sources库②Step:产生幅值、阶跃时间可设置的阶跃信号。
➢双击图标,弹出阶跃信号的参数设置框图。
图中参数为Simulink默认值。
➢当设置幅值为0.8,阶跃时间为1秒时,阶跃波形如下图所示:Sinks库◼该库包含了显示和写模块输出的模块。
双击即弹出该库的模块图:①:数字表,显示指定模块的输出数值。
②:X-Y绘图仪用同一图形窗口,显示X-Y坐标的图形(需先在参数对话框中设置每个坐标的变化范围),当X、Y分别为正、余弦信号时,其显示图形如下:2.Sinks 库③:示波器。
显示在仿真过程产生的信号波形。
双击该图标,弹出示波器窗如右图所示:分别管理X-Y 、X 和Y 轴向变焦取当前窗中信号最大、最小值为纵坐标的上下限把当前轴的设置保存为该示波器的缺省设置打开示波器属性对话框设置为浮动示波器2.Sinks库➢示波器属性对话框设置Y轴个数设置显示的时间范围选择轴的标注方法确定显示频度(每隔n-1个数据点显示一次)确定显示点的时间间隔(缺省为0表示连续显示)示波器属性对话框General页2.Sinks 库➢示波器属性对话框示波器属性对话框Data history 页设定缓冲区接受数据的长度,勾选为缺省状态,其值为5000确定示波器数据是否保存到MATLAB 工作空间。