Software Testing Verification and Validation:软件测试验证和确认.
- 格式:ppt
- 大小:145.01 KB
- 文档页数:14



Below is given annual work summary, do not need friends can download after editor deleted!!!!!! Welcome to visit againXXXX annual work summaryDear every leader, colleagues:Look back end of XXXX, XXXX years of work, have the joy of success in your work, have a collaboration with colleagues, working hard, also have disappointed when encountered difficulties and setbacks. Imperceptible in tense and orderly to be over a year, a year, under the loving care and guidance of the leadership of the company, under the support and help of colleagues, through their own efforts, various aspects have made certain progress, better to complete the job. For better work, sum up experience and lessons, will now work a brief summary.To continuously strengthen learning, improve their comprehensive quality. With good comprehensive quality is the precondition of completes the labor of duty and conditions. A year always put learning in the important position, trying to improve their comprehensive quality. Continuous learning professional skills, learn from surrounding colleagues with rich work experience, equip themselves with knowledge, the expanded aspect of knowledge, efforts to improve their comprehensive quality.The second Do best, strictly perform their responsibilities. Set up the company, to maximize the customer to the satisfaction of the company's products, do a good job in technical services and product promotion to the company. And collected on the properties of the products of the company, in order to make improvement in time, make the products better meet the using demand of the scene.Three to learn to be good at communication, coordinating assistance. On‐site technical service personnel should not only have strong professional technology, should also have good communication ability, a lot of a product due to improper operation to appear problem, but often not customers reflect the quality of no, so this time we need to find out the crux, and customer communication, standardized operation, to avoid customer's mistrust of the products and even the damage of the company's image. Some experiences in the past work, mentality is very important in the work, work to have passion, keep the smile of sunshine, can close the distance between people, easy to communicate with the customer. Do better in the daily work to communicate with customers and achieve customer satisfaction, excellent technical service every time, on behalf of the customer on our products much a understanding and trust.Fourth, we need to continue to learn professional knowledge, do practical grasp skilled operation. Over the past year, through continuous learning and fumble, studied the gas generation, collection and methods, gradually familiar with and master the company introduced the working principle, operation method of gas machine. With the help of the department leaders and colleagues, familiar with and master the launch of the division principle, debugging method of the control system, and to wuhan Chen Guchong garbage power plant of gas machine control system transformation, learn to debug, accumulated some experience. All in all, over the past year, did some work, have also made some achievements, but the results can only represent the past, there are some problems to work, can't meet the higher requirements. In the future work, I must develop the oneself advantage, lack of correct, foster strengths and circumvent weaknesses, for greater achievements. Looking forward to XXXX years of work, I'll be more efforts, constant progress in their jobs, make greater achievements. Every year I have progress, the growth of believe will get greater returns, I will my biggest contribution to the development of the company, believe in yourself do better next year!I wish you all work study progress in the year to come.。

Verification and validationNovember 9th 2016Copyright © 2016 BSI. All rights reserved.1Trev and Spike present the definitive guide to Verification and validationObjectivesDescriptions and definitionsExamplesISO 13485:2016 requirementsUse of Statistics3Verification (BS EN ISO 9001:2015) 3.8.12confirmation, through the provision of objective evidence that specified requirements have been fulfilled.Any set of criteria can be subjected to verification.VERIFICATION: Did we make what we said we would make?Validation (BS EN ISO 9001:2015) 3.8.13Confirmation, through the provision of objective evidence, that the requirements for a specific intended use or application have been fulfilled.The intended purpose is achieved, validation.Does it do what it says on the tin?Quality (BS EN ISO 9001:2015)3.6.2degree to which a set of inherent characteristics of an object fulfils requirements.What to conduct V&V on…..DesignTransferProcessPackagingProductRelationship, Risk and V&VP r o d u c t v e r i f i c a t i o n (t e s t )P r o d u c t v e r i f i c a t i o n (t e s t ) P r o d u c t v e r i f i c a t i o n (t e s t )P r o d u c t v e r i f i c a t i o n (t e s t )RISKTimeV a l i d i n t e r v a lV a l i d i n t e r v a lV a l i d i n t e r v a lRISKRISKV&V Examples Copyright © 2016 BSI. All rights reserved.SterilisationSoftware verification EN ISO 62304 5.1.6 The MANUFACTURER shall include or reference in the software development plan the following VERIFICATION information:a)DELIVERABLES requiring VERIFICATION;b)the required VERIFICATION TASKS for each life cycle ACTIVITY;c)milestones at which the DELIVERABLES are VERIFIED; andd)the acceptance criteria for VERIFICATION of the DELIVERABLES.Software Validation EN ISO 62304This standard does not cover validation and final release of the MEDICAL DEVICE, even when the MEDICAL DEVICE consists entirely of software.Processes which cannot be verified•Welding•Soldering•Aseptic filling•Packaging•Gluing/bondingV&V and ISO 13485OverviewDesignSoftwareSpecial processesCopyright © 2016 BSI. All rights reserved.ISO 13485 Audits.7.3.2 Design and development planning During design and development planning, the organization shall document: ……c) the verification, validation, and design transfer activities that are appropriate at each design and development stage;7.3.6 Design and development verification Design and development verification shall be performed in accordancewith planned and documented arrangements to ensure that the design and development outputs have met the design and development input requirements.The organization shall document verification plans that include methods, acceptance criteria and, as appropriate, statistical techniques with rationale for sample size.7.3.6 Design and development verification (Continued)If the intended use requires that the medical device be connected to, or have an interface with, other medical device(s), verification shall include confirmation that the design outputs meet design inputs when so connected or interfaced.Records of the results and conclusions of the verification and necessary actions shall be maintained (see 4.2.4 and 4.2.5).Design and development validation shall be performed in accordance with planned and documented arrangements to ensure that the resulting product is capable of meeting the requirements for the specified application or intended use.The organization shall document validation plans that include methods, acceptance criteria and, as appropriate, statistical techniques with rationale for sample size.(Continued)Design validation shall be conducted on representative product. Representative product includes initial production units, batches or their equivalents. The rationale for the choice of product used for validation shall be recorded (see 4.2.5).As part of design and development validation, the organization shall perform clinical evaluations or performance evaluations of the medical device in accordance with applicable regulatory requirements. A medical device used for clinical evaluation or performance evaluation is not considered to be released for use to the customer.(…and finally)If the intended use requires that the medical device be connected to, or have an interface with, other medical device(s), validation shall include confirmation that the requirements for the specified application or intended use have been met when so connected or interfaced.Validation shall be completed prior to release for use of the product to the customer.Records of the results and conclusion of validation and necessary actions shall be maintained (see 4.2.4 and 4.2.5).7.3.8 Design and development transferThe organization shall document procedures for transfer of design and development outputs to manufacturing. These procedures shall ensure that design and development outputs are verified as suitable for manufacturing before becoming final production specifications and that production capability can meet product requirements.7.3.9 Control of design and development changesDesign and development changes shall be identified. Before implementation, the changes shall be:a) reviewed;b) verified;c) validated, as appropriate;d) approved.7.3.10 Design and development filesThe organization shall maintain a design and development file for each medical device type or medical device family. This file shall include or reference records generated todemonstrate conformity to the requirements for design and development and records for design and development changes.4.1.6 General requirementsThe organization shall document procedures for the validation of the application of computer software used in the quality management system. Such software applications shall be validated prior to initial use and, as appropriate, after changes to such software or its application.The specific approach and activities associated with software validation and revalidation shall be proportionate to the risk associated with the use of the software.7.5.6 Validation of processes for production and service provisionThe organization shall validate any processes for production and service provision where the resulting output cannot be or is not verified by subsequent monitoring or measurement ……….The organization shall document procedures for the validation of the application of computer software used in production and service provision.Such software applications shall be validated prior to initial use and, as appropriate, after changes to such software or its application. The specific approach and activities associated with software validation and revalidation shall be proportionate to the risk associated with the use of the software, including the effect on the ability of the product to conform to specifications.7.6 Control of monitoring and measuring equipmentThe organization shall document procedures for the validation of the application of computer software used for the monitoring and measurement of requirements. Such software applications shall be validated prior to initial use and, as appropriate, after changes to such software or its application. The specific approach and activities associated with software validation and revalidation shall be proportionate to the risk associated with the use of the software, including the effect on the ability of the product to conform to specifications.Use of Statistics Copyright © 2016 BSI. All rights reserved.PopulationWhat is statistics?The science of Statistics is:Analysis of Statistics, not of Parameters.Statistics are used to estimate Parameters.Sample Statistics ParametersWhat do we look for?1.Objective (what is the question to be answered?)2.Sample (what sampling method?)3.Analyse the data (what method of analysis?)4.Draw the correct conclusions5.Can the conclusions be traced back to the statistics?Example 1- Collecting good data•Factory move, to statistically prove their manufacturing process is validated after the factory move•Due to large number of products, they chose to justify their answer by using a representative sample of their whole product range •Selected their representative sample based on the highest volume productExample 1- Collecting good data•Factory move, to statistically prove their manufacturing process is validated after the factory move•Due to large number of products, they chose to justify their answer by using a representative sample of their whole product range •Selected their representative sample based on the highest volume product ✓✓XExample 2- Analysing the data•Same manufacturer, same factory move•Stated they made 200•Sample size of 57 for testing (90% Confidence Interval, 90% Reliability), fail on any 1 sample failing•Stated 4 failed, but 196 passed•Concluded because 196 passed > 57, then study proves the process is validatedExample 2- Analysing the data•Same manufacturer, same factory move•Stated they made 200•Sample size of 57 for testing (90% Confidence Interval, 90% Reliability), fail on any 1 sample failing•Stated 4 failed, but 196 passed•Concluded because 196 passed > 57, then study proves the process is validated✓ X✓ ✓Summary•Verification – does is meet the criteria? •Validation – does it meet the intended use? •Quality – the measure of verification and validationQuestions。
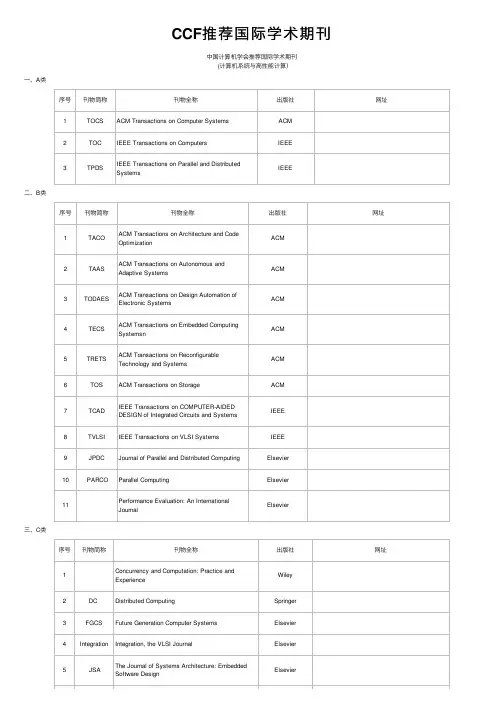
CCF推荐国际学术期刊中国计算机学会推荐国际学术期刊 (计算机系统与⾼性能计算)⼀、A类序号刊物简称刊物全称出版社⽹址1TOCS ACM Transactions on Computer Systems ACM2TOC IEEE Transactions on Computers IEEE3TPDS IEEE Transactions on Parallel and DistributedSystemsIEEE⼆、B类序号刊物简称刊物全称出版社⽹址1TACO ACM Transactions on Architecture and Code OptimizationACM2TAAS ACM Transactions on Autonomous andAdaptive SystemsACM3TODAES ACM Transactions on Design Automation ofElectronic SystemsACM4TECS ACM Transactions on Embedded ComputingSystemsnACM5TRETS ACM Transactions on ReconfigurableTechnology and SystemsACM6TOS ACM Transactions on Storage ACM7TCAD IEEE Transactions on COMPUTER-AIDEDDESIGN of Integrated Circuits and SystemsIEEE8TVLSI IEEE Transactions on VLSI Systems IEEE 9JPDC Journal of Parallel and Distributed Computing Elsevier 10 PARCO Parallel Computing Elsevier11Performance Evaluation: An InternationalJournalElsevier三、C类序号刊物简称刊物全称出版社⽹址1Concurrency and Computation: Practice andExperienceWiley2DC Distributed Computing Springer 3FGCS Future Generation Computer Systems Elsevier 4Integration Integration, the VLSI Journal Elsevier5 JSA The Journal of Systems Architecture: EmbeddedSoftware DesignElsevier6Microprocessors and Microsystems: EmbeddedHardware DesignElsevier7JGC The Journal of Grid computing Springer 8TJSC The Journal of Supercomputing Springer9JETC The ACM Journal on Emerging Technologies inComputing SystemsACM10JET Journal of Electronic Testing-Theory andApplicationsSpringer中国计算机学会推荐国际学术刊物(计算机⽹络)⼀、A类序号刊物简称刊物全称出版社⽹址1TON IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking IEEE, ACM2JSAC IEEE Journal of Selected Areas inCommunicationsIEEE3TMC IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing IEEE⼆、B类序号刊物简称刊物全称出版社⽹址1TOIT ACM Transactions on Internet Technology ACM2TOMCCAP ACM Transactions on Multimedia Computing, Communications and ApplicationsACM3TOSN ACM Transactions on Sensor Networks ACM4CN Computer Networks Elsevier5TOC IEEE Transactions on Communications IEEE6TWC IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications IEEE三、C类序号刊物简称刊物全称出版社⽹址1Ad hoc Networks Elsevier2CC Computer Communications Elsevier3TNSM IEEE Transactions on Network and ServiceManagementIEEE4IET Communications IET 5JNCA Journal of Network and Computer Applications Elsevier 6MONET Mobile Networks & Applications Springer 7Networks Wiley 8PPNA Peer-to-Peer Networking and Applications Springer9WCMC Wireless Communications & Mobile Computing Wiley.10Wireless Networks Springer中国计算机学会推荐国际学术刊物 (⽹络与信息安全)⼀、A类序号刊物简称刊物全称出版社⽹址1TDSC IEEE Transactions on Dependable and SecureComputingIEEE2TIFS IEEE Transactions on Information Forensicsand SecurityIEEE3 Journal of Cryptology Springer⼆、B类序号刊物简称刊物全称出版社⽹址1TISSEC ACM Transactions on Information and SystemSecurityACM2 Computers & Security Elsevier3 Designs, Codes and Cryptography Springer4JCS Journal of Computer Security IOS Press三、C类序号刊物简称刊物全称出版社⽹址1CLSR Computer Law and Security Reports Elsevier2 EURASIP Journal on Information Security Springer3 IET Information Security IET4IMCS Information Management & Computer Security Emerald5ISTR Information Security Technical Report Elsevier6IJISP International Journal of InformationSecurity and PrivacyIdea GroupInc7IJICS International Journal of Information andComputer SecurityInderscience8SCN Security and Communication Networks Wiley中国计算机学会推荐国际学术刊物 (软件⼯程、系统软件与程序设计语⾔)⼀、A类序号刊物简称刊物全称出版社⽹址1TOPLAS ACM Transactions on ProgrammingLanguages & SystemsACM2TOSEM ACM Transactions on Software Engineering MethodologyACM3TSE IEEE Transactions on Software Engineering IEEE⼆、B类序号刊物简称刊物全称出版社⽹址1ASE Automated Software Engineering Springer2Empirical Software Engineering Springer3 TSC IEEE Transactions on Service Computing IEEE4 IETS IET Software IET5 IST Information and Software Technology Elsevier6JFP Journal of Functional Programming Cambridge University Press7Journal of Software: Evolution and Process Wiley8JSS Journal of Systems and Software Elsevier9RE Requirements Engineering Springer10SCP Science of Computer Programming Elsevier11SoSyM Software and System Modeling Springer12SPE Software: Practice and Experience Wiley13STVR Software Testing, Verification and Reliability Wiley三、C类序号刊物简称刊物全称出版社⽹址1Computer Languages, Systems and Structures Elsevier2IJSEKE International Journal on Software Engineering andKnowledge EngineeringWorld Scientific3STTT International Journal on Software Tools forTechnology TransferSpringer4Journal of Logic and Algebraic Programming Elsevier5JWE Journal of Web Engineering Rinton Press6Service Oriented Computing and Applications Springer 7 SQJ Software Quality Journal Springer8TPLP Theory and Practice of Logic Programming Cambridge University Press中国计算机学会推荐国际学术刊物 (数据库、数据挖掘与内容检索)⼀、A类序号刊物简称刊物全称出版社⽹址1TODS ACM Transactions on Database Systems ACM2TOIS ACM Transactions on Information andSystemsACM3TKDE IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and DataEngineeringIEEE ComputerSociety4VLDBJ VLDB Journal Springer-Verlag⼆、B类序号刊物简称刊物全称出版社⽹址1TKDD ACM Transactions on Knowledge Discoveryfrom DataACM2AEI Advanced Engineering Informatics Elsevier3DKE Data and Knowledge Engineering Elsevier4DMKD Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery Springer5EJIS European Journal of Information Systems The OR Society 6GeoInformatica Springer7IPM Information Processing and Management Elsevier8Information Sciences Elsevier9IS Information Systems Elsevier10JASIST Journal of the American Society for InformationScience and Technology American Society for Information Science andTechnology11JWS Journal of Web Semantics Elsevier12KIS Knowledge and Information Systems Springer13 TWEB ACM Transactions on the Web ACM三、C类序号刊物简称刊物全称出版社⽹址1DPD Distributed and Parallel Databases Springer2I&M Information and Management Elsevier3IPL Information Processing Letters Elsevier4Information Retrieval Springer5IJCIS International Journal of Cooperative InformationSystemsWorld Scientific6IJGIS International Journal of GeographicalInformation ScienceTaylor & Francis7IJIS International Journal of Intelligent Systems Wiley 8IJKM International Journal of Knowledge Management IGI9IJSWIS International Journal on Semantic Web andInformation SystemsIGI10JCIS Journal of Computer Information Systems IACIS 11JDM Journal of Database Management IGI-Global12JGITM Journal of Global Information TechnologyManagementIvy LeaguePublishing13JIIS Journal of Intelligent Information Systems Springer14JSIS Journal of Strategic Information Systems Elsevier中国计算机学会推荐国际学术刊物 (计算机科学理论)⼀、A类序号刊物简称刊物全称出版社⽹址1IANDC Information and Computation Elsevier2SICOMP SIAM Journal on Computing SIAM⼆、B类序号刊物简称刊物全称出版社⽹址1TALG ACM Transactions on Algorithms ACM2TOCL ACM Transactions on ComputationalLogicACM3TOMS ACM Transactions on MathematicalSoftwareACM4Algorithmica Springer 5Computational complexity Springer 6FAC Formal Aspects of Computing Springer 7Formal Methods in System Design Springer 8INFORMS Journal on Computing INFORMS9JCSS Journal of Computer and SystemSciencesElsevier10JGO Journal of Global Optimization Springer 11Journal of Symbolic Computation Elsevier12MSCS Mathematical Structures in ComputerScienceCambridgeUniversityPress13TCS Theoretical Computer Science Elsevier三、C类序号刊物简称刊物全称出版社⽹址1Annals of Pure and Applied Logic Elsevier2Acta Informatica Springer3Discrete Applied Mathematics Elsevier4Fundamenta Informaticae IOS Press5Higher-Order and SymbolicComputationSpringer6Information Processing Letters Elsevier 7JCOMPLEXITY Journal of Complexity Elsevier8LOGCOM Journal of Logic and ComputationOxford University Press9Journal of Symbolic Logic Association for Symbolic Logic10LMCS Logical Methods in Computer Science LMCS11SIDMA SIAM Journal on Discrete Mathematics SIAM12Theory of Computing Systems Springer中国计算机学会推荐国际学术期刊(计算机图形学与多媒体)⼀、A类序号刊物简称刊物全称出版社⽹址1TOG ACM Transactions on Graphics ACM2TIP IEEE Transactions on Image Processing IEEE3TVCG IEEE Transactions on Visualization andComputer GraphicsIEEE⼆、B类序号刊物简称刊物全称出版社⽹址1TOMCCAP ACM Transactions on MultimediaComputing, Communications andApplicationACM2CAD Computer-Aided Design Elsevier 3CAGD Computer Aided Geometric Design Elsevier 4CGF Computer Graphics Forum Wiley 5GM Graphical Models Elsevier6 TCSVT IEEE Transactions on Circuits andSystems for Video TechnologyIEEE7TMM IEEE Transactions on Multimedia IEEE8JASA Journal of The Acoustical Society ofAmericaAIP9SIIMS SIAM Journal on Imaging Sciences SIAM10SpeechComSpeech Communication Elsevier三、C类序号刊物简称刊物全称出版社⽹址1CAVW Computer Animation and Virtual Worlds Wiley2C&G Computers & Graphics-UK Elsevier3CGTA Computational Geometry: Theory andApplicationsElsevier4DCG Discrete & Computational Geometry Springer 5IET Image Processing IET 6IEEE Signal Processing Letter IEEE7JVCIR Journal of Visual Communication and Image RepresentationElsevier8MS Multimedia Systems Springer9MTA Multimedia Tools and Applications Springer10Signal Processing Elsevier11Signal procesing:image communication Elsevier12TVC The Visual Computer Springer中国计算机学会推荐国际学术刊物(⼈⼯智能与模式识别)⼀、A类序号刊物简称刊物全称出版社⽹址1AI Artificial Intelligence Elsevier2TPAMI IEEE Trans on Pattern Analysis and Machine IntelligenceIEEE3IJCV International Journal of Computer Vision Springer4JMLR Journal of Machine Learning Research MIT Press⼆、B类序号刊物简称刊物全称出版社⽹址1TAP ACM Transactions on Applied Perception ACM2TSLP ACM Transactions on Speech andLanguage ProcessingACM3Computational Linguistics MIT Press 4CVIU Computer Vision and Image Understanding Elsevier5DKE Data and Knowledge Engineering Elsevier6Evolutionary Computation MIT Press7TAC IEEE Transactions on Affective Computing IEEE8TASLP IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech, andLanguage ProcessingIEEE9IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics IEEE10TEC IEEE Transactions on EvolutionaryComputation IEEE11TFS IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems IEEE12TNNLS IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks andlearning systemsIEEE13IJAR International Journal of ApproximateReasoningElsevier14JAIR Journal of AI Research AAAI 15Journal of Automated Reasoning Springer16JSLHR Journal of Speech, Language, and HearingResearchAmericanSpeech-LanguageHearingAssociation17Machine Learning Springer18Neural Computation MIT Press19Neural Networks Elsevier20Pattern Recognition Elsevier三、C类序号刊物简称刊物全称出版社⽹址1TALIP ACM Transactions on Asian LanguageInformation ProcessingACM3Applied Intelligence Springer 4AIM Artificial Intelligence in Medicine Elsevier 5Artificial Life MIT Press6AAMAS Autonomous Agents and Multi-AgentSystemsSpringer7Computational Intelligence Wiley8Computer Speech and Language Elsevier9Connection Science Taylor & Francis10DSS Decision Support Systems Elsevier 11EAAI Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence Elsevier 12Expert Systems Blackwell/Wiley 13ESWA Expert Systems with Applications Elsevier 14Fuzzy Sets and Systems Elsevier15T-CIAIG IEEE Transactions on ComputationalIntelligence and AI in GamesIEEE16IET Computer Vision IET 17IET Signal Processing IET 18IVC Image and Vision Computing Elsevier 19IDA Intelligent Data Analysis Elsevier20IJCIA International Journal of ComputationalIntelligence and ApplicationsWorld Scientific21IJDAR International Journal on Document Analysisand RecognitionSpringer22IJIS International Journal of Intelligent Systems Wiley23IJNS International Journal of Neural Systems World Scientific24IJPRAI International Journal of Pattern Recognitionand Artificial IntelligenceWorld Scientific25International Journal of Uncertainty,Fuzziness and KBSWorld Scientific26JETAI Journal of Experimental and TheoreticalArtificial IntelligenceTaylor & Francis27KBS Knowledge-Based Systems Elsevier 28Machine Translation Springer 29Machine Vision and Applications Springer 30Natural Computing Springer31NLE Natural Language Engineering Cambridge University32NCA Neural Computing & Applications Springer 33NPL Neural Processing Letters Springer 34Neurocomputing Elsevier 35PAA Pattern Analysis and Applications Springer 36PRL Pattern Recognition Letters Elsevier 37Soft Computing Springer38WIAS Web Intelligence and Agent Systems IOS Press中国计算机学会推荐国际学术期刊(⼈机交互与普适计算)⼀、A类序号刊物简称刊物全称出版社⽹址1TOCHI ACM Transactions on Computer-HumanInteractionACM2IJHCS International Journal of Human Computer Studies Elsevier⼆、B类序号刊物简称刊物全称出版社⽹址1CSCW Computer Supported Cooperative Work Springer2HCI Human Computer Interaction Taylor & Francis3IWC Interacting with ComputersOxford University Press4UMUAI User Modeling and User-Adapted Interaction Springer三、C类序号刊物简称刊物全称出版社⽹址1BIT Behaviour & Information Technology Taylor & Francis2IJHCI International Journal of Human-ComputerInteractionTaylor & Francis3PMC Pervasive and Mobile Computing Elsevier4PUC Personal and Ubiquitous Computing Springer中国计算机学会推荐国际学术期刊(前沿、交叉与综合)⼀、A类序号刊物简称刊物全称出版社⽹址1Proc. IEEE Proceedings of the IEEE IEEE2JACM Journal of the ACM ACM⼆、B类序号刊物简称刊物全称出版社⽹址1Bioinformatics Oxford UniversityPress2Briefings in Bioinformatics Oxford UniversityPress3Cognition Cognition:International Journal ofCognitive ScienceElsevier4PLOS Computational Biology Public Libraryof Science5TMI IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging IEEE6TGARS IEEE Transactions on Geoscienceand Remote SensingIEEE7TITS IEEE Transactions on IntelligentTransportation SystemsIEEE8TR IEEE Transactions on Robotics IEEE9TASAE IEEE Transactions on AutomationScience and EngineeringIEEE10JCST Journal of Computer Science andTechnologySCIENCEPRESS/Springer11JAMIA Journal of the American MedicalInformatics AssociationBMJ Journals12Science China Information Sciences Science in China Press/Springer13The Computer Journal Oxford UniversityPress三、C类序号刊物简称刊物全称出版社⽹址1BMC Bioinformatics BioMed Central2Cybernetics and Systems Taylor & Francis3IEEE Geoscience and RemoteSensing LettersIEEE4TITB IEEE Transactions on InformationTechnology in BiomedicineIEEE5TCBB IEEE-ACM Transactions onComputational Biology andBioinformaticsIEEE/ACM6IET Intelligent Transport Systems IET 7Medical Image Analysis Elsevier8FCS Frontiers of Computer Science Higher EducationPress。

软件测试常用英语词汇静态测试:Non-Execution-Based Testing或Static testing 代码走查:Walkthrough代码审查:Code Inspection技术评审:Review动态测试:Execution-Based Testing白盒测试:White-Box Testing黑盒测试:Black-Box Testing灰盒测试:Gray-Box Testing软件质量保证SQA:Software Quality Assurance软件开发生命周期:Software Development Life Cycle冒烟测试:Smoke Test回归测试:Regression Test功能测试:Function Testing性能测试:Performance Testing压力测试:Stress Testing负载测试:Volume Testing易用性测试:Usability Testing安装测试:Installation Testing界面测试:UI Testing配置测试:Configuration Testing文档测试:Documentation Testing兼容性测试:Compatibility Testing安全性测试:Security Testing恢复测试:Recovery Testing单元测试:Unit Test集成测试:Integration Test系统测试:System Test验收测试:Acceptance Test测试计划应包括:测试对象:The Test Objectives测试范围: The Test Scope测试策略: The Test Strategy测试方法: The Test Approach,测试过程: The test procedures,测试环境: The Test Environment,测试完成标准:The test Completion criteria测试用例:The Test Cases测试进度表:The Test Schedules风险:Risks接口:Interface最终用户:The End User正式的测试环境:Formal Test Environment确认需求:Verifying The Requirements有分歧的需求:Ambiguous Requirements运行和维护:Operation and Maintenance.可复用性:Reusability可靠性: Reliability/Availability电机电子工程师协会IEEE:The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers) 正确性:Correctness实用性:Utility健壮性:Robustness可靠性:Reliability软件需求规格说明书:SRS (software requirement specification )概要设计:HLD (high level design )详细设计:LLD (low level design )统一开发流程:RUP (rational unified process )集成产品开发:IPD (integrated product development )能力成熟模型:CMM (capability maturity model )能力成熟模型集成:CMMI (capability maturity model integration )戴明环:PDCA (plan do check act )软件工程过程组:SEPG (software engineering process group )集成测试:IT (integration testing )系统测试:ST (system testing )关键过程域:KPA (key process area )同行评审:PR (peer review )用户验收测试:UAT (user acceptance testing )验证和确认:V&V (verification & validation )控制变更委员会:CCB (change control board )图形用户界面:GUI (graphic user interface )配置管理员:CMO (configuration management officer )平均失效间隔时间:(MTBF mean time between failures )平均修复时间:MTTR (mean time to restoration )平均失效时间:MTTF (mean time to failure )工作任务书:SOW (statement of work )α测试:alpha testingβ测试:beta testing适应性:Adaptability可用性:Availability功能规格说明书:Functional Specification软件开发中常见英文缩写和各类软件开发文档的英文缩写:英文简写文档名称MRD market requirement document (市场需求文档)PRD product requirement document (产品需求文档)SOW 工作任务说明书PHB Process Handbook (项目过程手册)EST Estimation Sheet (估计记录)PPL Project Plan (项目计划)CMP Software Management Plan( 配置管理计划)QAP Software Quality Assurance Plan (软件质量保证计划)RMP Software Risk Management Plan (软件风险管理计划)TST Test Strategy(测试策略)WBS Work Breakdown Structure (工作分解结构)BRS Business Requirement Specification(业务需求说明书)SRS Software Requirement Specification(软件需求说明书)STP System Testing plan (系统测试计划)STC System Testing Cases (系统测试用例)HLD High Level Design (概要设计说明书)ITP Integration Testing plan (集成测试计划)ITC Integration Testing Cases (集成测试用例)LLD Low Level Design (详细设计说明书)UTP Unit Testing Plan ( 单元测试计划)UTC Unit Testing Cases (单元测试用例)UTR Unit Testing Report (单元测试报告)ITR Integration Testing Report (集成测试报告)STR System Testing Report (系统测试报告)RTM Requirements Traceability Matrix (需求跟踪矩阵)CSA Configuration Status Accounting (配置状态发布)CRF Change Request Form (变更申请表)WSR Weekly Status Report (项目周报)QSR Quality Weekly Status Report (质量工作周报)QAR Quality Audit Report(质量检查报告)QCL Quality Check List(质量检查表)PAR Phase Assessment Report (阶段评估报告)CLR Closure Report (项目总结报告)RFF Review Finding Form (评审发现表)MOM Minutes of Meeting (会议纪要)MTX Metrics Sheet (度量表)CCF ConsistanceCheckForm(一致性检查表)BAF Baseline Audit Form(基线审计表)PTF Program Trace Form(问题跟踪表)领测国际科技(北京)有限公司领测软件测试网 /软件测试中英文对照术语表A• Abstract test case (High level test case) :概要测试用例• Acceptance:验收• Acceptance criteria:验收标准• Acceptance testing:验收测试• Accessibility testing:易用性测试• Accuracy:精确性• Actual outcome (actual result) :实际输出/实际结果• Ad hoc review (informal review) :非正式评审• Ad hoc testing:随机测试• Adaptability:自适应性• Agile testing:敏捷测试• Algorithm test (branch testing) :分支测试• Alpha testing:alpha 测试• Analyzability:易分析性• Analyzer:分析员• Anomaly:异常• Arc testing:分支测试• Attractiveness:吸引力• Audit:审计• Audit trail:审计跟踪• Automated testware:自动测试组件• Availability:可用性B• Back-to-back testing:对比测试• Baseline:基线• Basic block:基本块• Basis test set:基本测试集• Bebugging:错误撒播• Behavior:行为• Benchmark test:基准测试• Bespoke software:定制的软件• Best practice:最佳实践• Beta testing:Beta 测试领测国际科技(北京)有限公司领测软件测试网 /• Big-bang testing:集成测试• Black-box technique:黑盒技术• Black-box testing:黑盒测试• Black-box test design technique:黑盒测试设计技术• Blocked test case:被阻塞的测试用例• Bottom-up testing:自底向上测试• Boundary value:边界值• Boundary value analysis:边界值分析• Boundary value coverage:边界值覆盖率• Boundary value testing:边界值测试• Branch:分支• Branch condition:分支条件• Branch condition combination coverage:分支条件组合覆盖率• Branch condition combination testing:分支条件组合测试• Branch condition coverage:分支条件覆盖率• Branch coverage:分支覆盖率• Branch testing:分支测试• Bug:缺陷• Business process-based testing:基于商业流程的测试C• Capability Maturity Model (CMM) :能力成熟度模型• Capability Maturity Model Integration (CMMI) :集成能力成熟度模型• Capture/playback tool:捕获/回放工具• Capture/replay tool:捕获/重放工具• CASE (Computer Aided Software Engineering) :电脑辅助软件工程• CAST (Computer Aided Software Testing) :电脑辅助软件测试• Cause-effect graph:因果图• Cause-effect graphing:因果图技术• Cause-effect analysis:因果分析• Cause-effect decision table:因果判定表• Certification:认证• Changeability:可变性• Change control:变更控制• Change control board:变更控制委员会• Checker:检查人员• Chow's coverage metrics (N-switch coverage) :N 切换覆盖率• Classification tree method:分类树方法• Code analyzer:代码分析器• Code coverage:代码覆盖率领测国际科技(北京)有限公司领测软件测试网 /• Code-based testing:基于代码的测试• Co-existence:共存性• Commercial off-the-shelf software:商用离岸软件• Comparator:比较器• Compatibility testing:兼容性测试• Compiler:编译器• Complete testing:完全测试/穷尽测试• Completion criteria:完成标准• Complexity:复杂性• Compliance:一致性• Compliance testing:一致性测试• Component:组件• Component integration testing:组件集成测试• Component specification:组件规格说明• Component testing:组件测试• Compound condition:组合条件• Concrete test case (low level test case) :详细测试用例• Concurrency testing:并发测试• Condition:条件表达式• Condition combination coverage:条件组合覆盖率• Condition coverage:条件覆盖率• Condition determination coverage:条件判定覆盖率• Condition determination testing:条件判定测试• Condition testing:条件测试• Condition outcome:条件结果• Confidence test (smoke test) :信心测试(冒烟测试)• Configuration:配置• Configuration auditing:配置审核• Configuration control:配置控制• Configuration control board (CCB) :配置控制委员会• Configuration identification:配置标识• Configuration item:配置项• Configuration management:配置管理• Configuration testing:配置测试• Confirmation testing:确认测试• Conformance testing:一致性测试• Consistency:一致性• Control flow:控制流• Control flow graph:控制流图• Control flow path:控制流路径• Conversion testing:转换测试• COTS (Commercial Off-The-Shelf software) :商业离岸软件• Coverage:覆盖率• Coverage analysis:覆盖率分析领测国际科技(北京)有限公司领测软件测试网 /• Coverage item:覆盖项• Coverage tool:覆盖率工具• Custom software:定制软件• Cyclomatic complexity:圈复杂度• Cyclomatic number:圈数D• Daily build:每日构建• Data definition:数据定义• Data driven testing:数据驱动测试• Data flow:数据流• Data flow analysis:数据流分析• Data flow coverage:数据流覆盖率• Data flow test:数据流测试• Data integrity testing:数据完整性测试• Database integrity testing:数据库完整性测试• Dead code:无效代码• Debugger:调试器• Debugging:调试• Debugging tool:调试工具• Decision:判定• Decision condition coverage:判定条件覆盖率• Decision condition testing:判定条件测试• Decision coverage:判定覆盖率• Decision table:判定表• Decision table testing:判定表测试• Decision testing:判定测试技术• Decision outcome:判定结果• Defect:缺陷• Defect density:缺陷密度• Defect Detection Percentage (DDP) :缺陷发现率• Defect management:缺陷管理• Defect management tool:缺陷管理工具• Defect masking:缺陷屏蔽• Defect report:缺陷报告• Defect tracking tool:缺陷跟踪工具• Definition-use pair:定义-使用对• Deliverable:交付物• Design-based testing:基于设计的测试• Desk checking:桌面检查领测国际科技(北京)有限公司领测软件测试网 /• Development testing:开发测试• Deviation:偏差• Deviation report:偏差报告• Dirty testing:负面测试• Documentation testing:文档测试• Domain:域• Driver:驱动程序• Dynamic analysis:动态分析• Dynamic analysis tool:动态分析工具• Dynamic comparison:动态比较• Dynamic testing:动态测试E• Efficiency:效率• Efficiency testing:效率测试• Elementary comparison testing:基本组合测试• Emulator:仿真器、仿真程序• Entry criteria:入口标准• Entry point:入口点• Equivalence class:等价类• Equivalence partition:等价区间• Equivalence partition coverage:等价区间覆盖率• Equivalence partitioning:等价划分技术• Error:错误• Error guessing:错误猜测技术• Error seeding:错误撒播• Error tolerance:错误容限• Evaluation:评估• Exception handling:异常处理• Executable statement:可执行的语句• Exercised:可执行的• Exhaustive testing:穷尽测试• Exit criteria:出口标准• Exit point:出口点• Expected outcome:预期结果• Expected result:预期结果• Exploratory testing:探测测试领测国际科技(北京)有限公司领测软件测试网 /F• Fail:失败• Failure:失败• Failure mode:失败模式• Failure Mode and Effect Analysis (FMEA) :失败模式和影响分析• Failure rate:失败频率• Fault:缺陷• Fault density:缺陷密度• Fault Detection Percentage (FDP) :缺陷发现率• Fault masking:缺陷屏蔽• Fault tolerance:缺陷容限• Fault tree analysis:缺陷树分析• Feature:特征• Field testing:现场测试• Finite state machine:有限状态机• Finite state testing:有限状态测试• Formal review:正式评审• Frozen test basis:测试基线• Function Point Analysis (FPA) :功能点分析• Functional integration:功能集成• Functional requirement:功能需求• Functional test design technique:功能测试设计技术• Functional testing:功能测试• Functionality:功能性• Functionality testing:功能性测试G• glass box testing:白盒测试H• Heuristic evaluation:启发式评估• High level test case:概要测试用例• Horizontal traceability:水平跟踪领测国际科技(北京)有限公司领测软件测试网 /I• Impact analysis:影响分析• Incremental development model:增量开发模型• Incremental testing:增量测试• Incident:事件• Incident management:事件管理• Incident management tool:事件管理工具• Incident report:事件报告• Independence:独立• Infeasible path:不可行路径• Informal review:非正式评审• Input:输入• Input domain:输入范围• Input value:输入值• Inspection:审查• Inspection leader:审查组织者• Inspector:审查人员• Installability:可安装性• Installability testing:可安装性测试• Installation guide:安装指南• Installation wizard:安装向导• Instrumentation:插装• Instrumenter:插装工具• Intake test:入口测试• Integration:集成• Integration testing:集成测试• Integration testing in the large:大范围集成测试• Integration testing in the small:小范围集成测试• Interface testing:接口测试• Interoperability:互通性• Interoperability testing:互通性测试• Invalid testing:无效性测试• Isolation testing:隔离测试• Item transmittal report:版本发布报告• Iterative development model:迭代开发模型K• Key performance indicator:关键绩效指标领测国际科技(北京)有限公司领测软件测试网 /• Keyword driven testing:关键字驱动测试L• Learnability:易学性• Level test plan:等级测试计划• Link testing:组件集成测试• Load testing:负载测试• Logic-coverage testing:逻辑覆盖测试• Logic-driven testing:逻辑驱动测试• Logical test case:逻辑测试用例• Low level test case:详细测试用例M• Maintenance:维护• Maintenance testing:维护测试• Maintainability:可维护性• Maintainability testing:可维护性测试• Management review:管理评审• Master test plan:综合测试计划• Maturity:成熟度• Measure:度量• Measurement:度量• Measurement scale:度量粒度• Memory leak:内存泄漏• Metric:度量• Migration testing:移植测试• Milestone:里程碑• Mistake:错误• Moderator:仲裁员• Modified condition decision coverage:改进的条件判定覆盖率• Modified condition decision testing:改进的条件判定测试• Modified multiple condition coverage:改进的多重条件判定覆盖率• Modified multiple condition testing:改进的多重条件判定测试• Module:模块• Module testing:模块测试• Monitor:监视器• Multiple condition:多重条件• Multiple condition coverage:多重条件覆盖率领测国际科技(北京)有限公司领测软件测试网 /• Multiple condition testing:多重条件测试• Mutation analysis:变化分析• Mutation testing:变化测试N• N-switch coverage:N 切换覆盖率• N-switch testing:N 切换测试• Negative testing:负面测试• Non-conformity:不一致• Non-functional requirement:非功能需求• Non-functional testing:非功能测试• Non-functional test design techniques:非功能测试设计技术O• Off-the-shelf software:离岸软件• Operability:可操作性• Operational environment:操作环境• Operational profile testing:运行剖面测试• Operational testing:操作测试• Oracle:标准• Outcome:输出/结果• Output:输出• Output domain:输出范围• Output value:输出值P• Pair programming:结队编程• Pair testing:结队测试• Partition testing:分割测试• Pass:通过• Pass/fail criteria:通过/失败标准• Path:路径• Path coverage:路径覆盖• Path sensitizing:路径敏感性• Path testing:路径测试领测国际科技(北京)有限公司领测软件测试网 / • Peer review:同行评审• Performance:性能• Performance indicator:绩效指标• Performance testing:性能测试• Performance testing tool:性能测试工具• Phase test plan:阶段测试计划• Portability:可移植性• Portability testing:移植性测试• Postcondition:结果条件• Post-execution comparison:运行后比较• Precondition:初始条件• Predicted outcome:预期结果• Pretest:预测试• Priority:优先级• Probe effect:检测成本• Problem:问题• Problem management:问题管理• Problem report:问题报告• Process:流程• Process cycle test:处理周期测试• Product risk:产品风险• Project:项目• Project risk:项目风险• Program instrumenter:编程工具• Program testing:程序测试• Project test plan:项目测试计划• Pseudo-random:伪随机Q• Quality:质量• Quality assurance:质量保证• Quality attribute:质量属性• Quality characteristic:质量特征• Quality management:质量管理领测国际科技(北京)有限公司领测软件测试网 /R• Random testing:随机测试• Recorder:记录员• Record/playback tool:记录/回放工具• Recoverability:可复原性• Recoverability testing:可复原性测试• Recovery testing:可复原性测试• Regression testing:回归测试• Regulation testing:一致性测试• Release note:版本说明• Reliability:可靠性• Reliability testing:可靠性测试• Replaceability:可替换性• Requirement:需求• Requirements-based testing:基于需求的测试• Requirements management tool:需求管理工具• Requirements phase:需求阶段• Resource utilization:资源利用• Resource utilization testing:资源利用测试• Result:结果• Resumption criteria:继续测试标准• Re-testing:再测试• Review:评审• Reviewer:评审人员• Review tool:评审工具• Risk:风险• Risk analysis:风险分析• Risk-based testing:基于风险的测试• Risk control:风险控制• Risk identification:风险识别• Risk management:风险管理• Risk mitigation:风险消减• Robustness:健壮性• Robustness testing:健壮性测试• Root cause:根本原因S• Safety:安全领测国际科技(北京)有限公司领测软件测试网 /• Safety testing:安全性测试• Sanity test:健全测试• Scalability:可测量性• Scalability testing:可测量性测试• Scenario testing:情景测试• Scribe:记录员• Scripting language:脚本语言• Security:安全性• Security testing:安全性测试• Serviceability testing:可维护性测试• Severity:严重性• Simulation:仿真• Simulator:仿真程序、仿真器• Site acceptance testing:定点验收测试• Smoke test:冒烟测试• Software:软件• Software feature:软件功能• Software quality:软件质量• Software quality characteristic:软件质量特征• Software test incident:软件测试事件• Software test incident report:软件测试事件报告• Software Usability Measurement Inventory (SUMI) :软件可用性调查问卷• Source statement:源语句• Specification:规格说明• Specification-based testing:基于规格说明的测试• Specification-based test design technique:基于规格说明的测试设计技术• Specified input:特定输入• Stability:稳定性• Standard software:标准软件• Standards testing:标准测试• State diagram:状态图• State table:状态表• State transition:状态迁移• State transition testing:状态迁移测试• Statement:语句• Statement coverage:语句覆盖• Statement testing:语句测试• Static analysis:静态分析• Static analysis tool:静态分析工具• Static analyzer:静态分析工具• Static code analysis:静态代码分析• Static code analyzer:静态代码分析工具• Static testing:静态测试• Statistical testing:统计测试领测国际科技(北京)有限公司领测软件测试网 /• Status accounting:状态统计• Storage:资源利用• Storage testing:资源利用测试• Stress testing:压力测试• Structure-based techniques:基于结构的技术• Structural coverage:结构覆盖• Structural test design technique:结构测试设计技术• Structural testing:基于结构的测试• Structured walkthrough:面向结构的走查• Stub: 桩• Subpath: 子路径• Suitability: 符合性• Suspension criteria: 暂停标准• Syntax testing: 语法测试• System:系统• System integration testing:系统集成测试• System testing:系统测试T• Technical review:技术评审• Test:测试• Test approach:测试方法• Test automation:测试自动化• Test basis:测试基础• Test bed:测试环境• Test case:测试用例• Test case design technique:测试用例设计技术• Test case specification:测试用例规格说明• Test case suite:测试用例套• Test charter:测试宪章• Test closure:测试结束• Test comparator:测试比较工具• Test comparison:测试比较• Test completion criteria:测试比较标准• Test condition:测试条件• Test control:测试控制• Test coverage:测试覆盖率• Test cycle:测试周期• Test data:测试数据• Test data preparation tool:测试数据准备工具领测国际科技(北京)有限公司领测软件测试网 / • Test design:测试设计• Test design specification:测试设计规格说明• Test design technique:测试设计技术• Test design tool: 测试设计工具• Test driver: 测试驱动程序• Test driven development: 测试驱动开发• Test environment: 测试环境• Test evaluation report: 测试评估报告• Test execution: 测试执行• Test execution automation: 测试执行自动化• Test execution phase: 测试执行阶段• Test execution schedule: 测试执行进度表• Test execution technique: 测试执行技术• Test execution tool: 测试执行工具• Test fail: 测试失败• Test generator: 测试生成工具• Test leader:测试负责人• Test harness:测试组件• Test incident:测试事件• Test incident report:测试事件报告• Test infrastructure:测试基础组织• Test input:测试输入• Test item:测试项• Test item transmittal report:测试项移交报告• Test level:测试等级• Test log:测试日志• Test logging:测试记录• Test manager:测试经理• Test management:测试管理• Test management tool:测试管理工具• Test Maturity Model (TMM) :测试成熟度模型• Test monitoring:测试跟踪• Test object:测试对象• Test objective:测试目的• Test oracle:测试标准• Test outcome:测试结果• Test pass:测试通过• Test performance indicator:测试绩效指标• Test phase:测试阶段• Test plan:测试计划• Test planning:测试计划• Test policy:测试方针• Test Point Analysis (TPA) :测试点分析• Test procedure:测试过程领测国际科技(北京)有限公司领测软件测试网 /• Test procedure specification:测试过程规格说明• Test process:测试流程• Test Process Improvement (TPI) :测试流程改进• Test record:测试记录• Test recording:测试记录• Test reproduceability:测试可重现性• Test report:测试报告• Test requirement:测试需求• Test run:测试运行• Test run log:测试运行日志• Test result:测试结果• Test scenario:测试场景• Test script:测试脚本• Test set:测试集• Test situation:测试条件• Test specification:测试规格说明• Test specification technique:测试规格说明技术• Test stage:测试阶段• Test strategy:测试策略• Test suite:测试套• Test summary report:测试总结报告• Test target:测试目标• Test tool:测试工具• Test type:测试类型• Testability:可测试性• Testability review:可测试性评审• Testable requirements:需求可测试性• Tester:测试人员• Testing:测试• Testware:测试组件• Thread testing:组件集成测试• Time behavior:性能• Top-down testing:自顶向下的测试• Traceability:可跟踪性U• Understandability:易懂性• Unit:单元• unit testing:单元测试• Unreachable code:执行不到的代码领测国际科技(北京)有限公司领测软件测试网 /• Usability:易用性• Usability testing:易用性测试• Use case:用户用例• Use case testing:用户用例测试• User acceptance testing:用户验收测试• User scenario testing:用户场景测试• User test:用户测试V• V -model:V 模式• Validation:确认• Variable:变量• Verification:验证• Vertical traceability:垂直可跟踪性• Version control:版本控制• Volume testing:容量测试W• Walkthrough:走查• White-box test design technique:白盒测试设计技术• White-box testing:白盒测试• Wide Band Delphi:Delphi 估计方法。

移动应用安全漏洞扫描和性能安全测试报告一、引言移动应用的广泛应用给人们的生活带来了便利,然而随着移动应用的不断发展,移动应用的安全问题逐渐凸显。
在这篇文章中,我们将对移动应用的安全漏洞扫描和性能安全测试进行详细的报告和分析。
二、移动应用安全漏洞扫描1. 扫描工具介绍移动应用安全漏洞扫描是通过使用专业的扫描工具对移动应用进行全面的安全性检测。
常见的扫描工具包括静态扫描工具和动态扫描工具。
2. 静态扫描测试静态扫描测试主要通过检测源代码及其相关配置文件,查找潜在的安全漏洞。
在本次测试中,我们使用了静态扫描工具A,对目标移动应用进行了分析。
3. 动态扫描测试动态扫描测试是通过模拟用户的交互过程,检测移动应用的特定行为及其可能存在的漏洞。
本次测试中,我们使用了动态扫描工具B,对目标移动应用进行了测试。
4. 测试结果分析经过静态扫描和动态扫描测试,我们发现了以下几个安全漏洞:- 漏洞1:存在不安全的数据传输方式,导致敏感信息泄露的风险;- 漏洞2:应用代码中存在未经验证的用户输入,可能被攻击者用于注入攻击;- 漏洞3:未加密的存储数据可能被攻击者非法获取;- 漏洞4:应用的用户身份认证机制存在破解的可能性。
5. 安全建议针对上述发现的安全漏洞,我们提出以下几点建议:- 建议使用安全的数据传输方式,如HTTPS协议,保护敏感信息的传输安全;- 建议对应用的输入进行严格的验证和过滤,防止注入攻击;- 建议对存储的敏感数据进行加密,以免被非法获取;- 建议增强用户身份认证机制的安全性,例如采用多因素身份认证。
三、性能安全测试1. 测试环境介绍在进行性能安全测试时,我们搭建了一套与实际使用环境相似的测试环境,包括服务器、移动设备等。
2. 测试内容性能安全测试主要包括负载测试和压力测试两个方面。
在负载测试中,我们模拟了多用户同时使用应用的场景,评估了应用在高负载情况下的性能表现。
在压力测试中,我们对应用进行了大数据量的输入,评估了应用在处理大规模数据时的性能状况。


检验过程英语范文Testing ProcessIntroductionTesting is an essential part of the software developmentlife cycle. It involves evaluating and verifying the functionality, performance, and reliability of a software product. Proper testing helps to identify defects and bugs, ensuring that the software meets the requirements and quality standards set by the stakeholders. In this article, we will discuss the testing process, including its goals, types of testing, and the steps involved.Goals of TestingThe primary goal of testing is to find as many defects as possible to ensure the software's quality. However, testing also helps to achieve other important objectives:1. Verification and Validation: Testing helps to verify that the software meets the specified requirements and validate that it works as expected.2. Reliability and Stability: Testing helps to improve the software's reliability and stability, ensuring that it operates without errors or crashes.3. Performance: Testing evaluates the software's performance, ensuring that it performs efficiently under different loads and scenarios.5. Security: Testing evaluates the software's security measures, identifying vulnerabilities and ensuring data protection.Types of Testing3. System Testing: It tests the entire software system as a whole to validate its functionality, performance, andreliability.4. Acceptance Testing: This type of testing is performed by end-users to validate if the software meets their requirements and expectations.5. Performance Testing: It evaluates how the software performs under different workloads and stress conditions.6. Security Testing: This testing ensures that the softwareis secure against threats and vulnerabilities.7. Usability Testing: It focuses on evaluating thesoftware's user interface and user experience.Steps Involved in the Testing ProcessThe testing process generally follows a series of steps:1. Test Planning: In this step, the testing team determines the scope, objectives, and resources required for testing. The test plan is created, including the testing approach, test cases, and schedules.2. Test Design: In this step, the test cases are designed based on the requirements and specifications. The test scenarios and data are also identified.3. Test Environment Setup: The required hardware, software, and test data are set up for testing. The test environmentshould replicate the production environment as closely as possible.5. Defect Tracking: In this step, the identified defects are logged in a defect tracking system. The defects are categorized, prioritized, and assigned to the development team for fixing.6. Test Reporting: Test reports are generated, summarizing the testing activities, including the test coverage, test results, and defect metrics.7. Retesting and Regression Testing: Once the defects are fixed, the retesting is performed to ensure that the defectshave been resolved. Regression testing is also conducted toverify that the changes or fixes have not introduced new defects.ConclusionThe testing process is crucial to ensure the quality and reliability of software products. It helps to identify defects and verify that the software meets the specified requirements. By following the steps involved in the testing process and performing different types of testing, developers can deliver software that is functional, performant, and secure.。

A类期刊和会议:中国科学Journal of ACMACM Transactions on Programming Languages and SystemsACM Transactions on Software Engineering and MethodologyACM Transactions on Embedded Computing SystemsFormal Methods in System DesignIEEE Transactions on Software EngineeringIEEE Transactions on Dependable and Secure ComputingInternational Conference on Computer Aided Verification (CAV)IEEE Symposium on Logic in Computer Science (LICS)International Conference on Model Driven Engineering Languages and Systems (MODELS) ACM SIGPLAN Conference on Programming Language Design and Implementation (PLDI) ACM SIGPLAN - SIGACT Symposium on Principles of Programming Languages (POPL) IEEE Real-Time Systems Symposium (RTSS)International Conference on Embedded Software (EMSOFT)International Conference on Cyber-Physical Systems (ICCPS)International Conference on Formal Methods on Computer Aided Design (FMCAD) International Conference on Hybrid Systems: Computation and Control (HSCC)IEEE International Conference on Program Comprehension (ICPC)ACM SIGSOFT International Symposium on the Foundations of Software Engineering (FSE)B类期刊和会议:ACM Transactions on Autonomous and Adaptive SystemsACM Transactions on Design Automation of Electronic SystemsAutomated Software EngineeringFormal Aspects of ComputingIET SoftwareInformation and Software TechnologyInternational Journal of Software Tools and Technology TransferInnovations in Systems and Software EngineeringJournal of Logic and Algebraic ProgrammingJournal of Software Maintenance and Evolution: Research and PracticeJournal of Systems and SoftwareReal-Time SystemsScience of Computer ProgrammingSoftware: Practice and ExperienceSoftware Testing, Verification and ReliabilitySoftware and Systems ModelingSoftware Quality JournalThe Computer JournalInternational Conference on Aspect-Oriented Software Development (AOSD)International Conference on Automated Software Engineering (ASE)International Conference on Concurrency Theory (CONCUR)European Joint Conferences on Theory and Practice of Software (ETAPS)International Symposium on Formal Methods (FM)International Symposium on Software Testing and Analysis (ISSTA)Design, Automation & Test in Europe Conference (DATE)C类期刊和会议:计算机学报、软件学报、电子学报Annual ACM Symposium on Applied Computing (ACM SAC)Asia-Pacific Software Engineering Conference (APSEC)International Conference on Reliable Software Technologies (Ada-Europe)European Conference on Model Driven Architecture® - Foundations and Applications (ECMDA-FA) International IEEE EDOC Conference (EDOC)International Conference on Formal Modelling and Analysis of Timed Systems (FORMATS) International Conference on Formal Methods for Networked and Distributed Systems (FORTE) Haifa Verification Conference (HVC)International Colloquium on Automata, Languages and Programming (ICALP)International Conference on Formal Engineering Methods (ICFEM)IEEE International Conference on Software Maintenance (ICSM)IEEE International Conference on Software Testing, Verification and Validation (ICST)IEEE International Conference on Web Services (ICWS)International Conference on Integrated Formal Methods (IFM)International Conference on Real-Time and Network Systems (RTNS)IEEE International Working Conference on Source Code Analysis and Manipulation (SCAM) International SDL Forum (SDL)International Conference on Verification, Model Checking, and Abstract Interpretation (VMCAI) International Conference on Runtime Verification (RV)D类期刊和会议导师组认可的国际期刊和国际会议注:Short papers、Tool papers酌情减分。
Software Verification and Validation Plan (SVVP) Template Items that are intended to stay in as part of your document are in bold; explanatory comments are in italic text. Plain text is used where you might insert wording about your project.This document is an annotated outline for a Software Verification and Validation Plan, adapted from the IEEE Standard for Software Verification and Validation Plans (Standard 1012), and the IEEE Guide for Software Verification and Validation Plans (Guide 1059).Tailor as appropriate. Where you decide to omit a section, you might keep the header, but insert a comment saying why you omit the element (e.g., “This section is not applicable to the plan.”)(Agency)(Project)Software Verification and Validation Plan Version: (n)Date: (mm/dd/yyyy)T ABLE OF C ONTENTS1. P URPOSE32. R EFERENCED D OCUMENTS43. D EFINITIONS54. V ERIFICATION AND V ALIDATION O VERVIEW54.1 Organization 54.2 Master Schedule64.3 Resource Summary64.4 Responsibilities74.5 Tools, Techniques, and Methodologies75. L IFECYCLE V ERIFICATION AND V ALIDATION75.1 Management of V&V75.2 Concept Phase85.3 Requirements Phase95.4 Design Phase95.5 Implementation Phase105.6 Test Phase115.7 Installation and Checkout Phase115.8 Operation and Maintenance Phase126. Reporting12T ABLE OF C ONTENTS (CONTINUED)7. Administrative Procedures137.1 Anomaly Reporting and Resolution137.2 Task Iteration Policy137.3 Deviation Policy137.4 Control Procedures147.5 Standards, Practices, and Conventions148.Plan Approvals141. P URPOSE(N OTE 1: T HE S OFTWARE V ERIFICATION AND V ALIDATION P LAN GUIDELINES WEREDERIVED AND DEVELOPED FROM IEEE S TANDARD FOR S OFTWARE V ERIFICATION AND V ALIDATION (S TANDARD 1012) AND THE IEEE G UIDE FOR S OFTWARE V ERIFICATION AND V ALIDATION P LANS (G UIDE 1059)).(Note 2: The ordering of Software Verification and Validation Plan (SVVP) elements is not meant to imply that the sections or subsections must be developed orpresented in that order. The order of presentation is intended for ease of use, not as a guide to preparing the various elements of the Software Verification and Validation Plan. If some or all of the content of a section is in another document, then areference to that material may be listed in place of the corresponding content.)(The Purpose section of the Software Verification and Validation Plan defines the purpose, scope, and goals of the plan. The software project must be identified and the specificsoftware product items, covered by the plan, must be identified. The specific goals of the verification and validation effort must be specified.The SVVP purpose section provides the highest level description of verification andvalidation efforts. The following topics must be addressed:•Project identification,•Plan goals,•Summary of verification and validation efforts,•Responsibilities conveyed with the plan,•Software to be verified and validated,•Identification of waivers and changes to organization standards, andSVVP assumptions.)Software verification and validation (V&V) is a disciplined approach to assessing software products throughout the software development life cycle. Verification and validation strives to ensure that quality is built into the software and that the software satisfies business functional requirements.Software verification and validation employs review, analysis, and testing techniques to determine whether a software product and its intermediate deliverables comply with requirements. These requirements include both business functional capabilities and quality attributes.The objectives of the V&V effort are to find defects and to determine if required functions and attributes are built into the software system. V&V activities are designed to support:1.Verification that the products of each software life cycle phase:-Comply with previous life cycle phase requirements and products forcorrectness, completeness, consistency, and accuracy,-Satisfy the standards, policies, practices, procedures, and conventions of the phase, and-Establish the proper basis for initiating the next life cycle phase.2.Validate that the completed end product complies with established software andsystem requirements.Verification and validation provide management with insights into the state of the project and the software products, allowing for timely change in the products or in the software development life cycle approach.(Verification and validation effort is typically applied in parallel with software development and support activities. Verification and validation planning may be broken down into the following steps:-Identify the V&V scope,-Establish specific objectives from the general project scope,-Analyze the project input prior to selecting V&V tools and techniques,-Select tools and techniques, and-Develop the Software Verification and Validation Plan (SVVP)).2. R EFERENCE D OCUMENTS(This section shall identify the binding compliance documents, documents referenced in the plan, and any supporting documents required to implement, or supplement, the SVVP.Ensure that the reference document list is consistent with other project documentation.Ensure that all documents listed in the plan are referenced. Specify documents completelyincluding the version and date reference.)3. Definitions(The definition section provides a reference to the definition of all terms required to properly interpret the SVVP. This section also notes acronyms and notations used in the plan. Include only terms necessary for understanding the SVVP. Refer to other project documentation for a comprehensive list of project definitions (e.g., Software Project Management Plan, Software Quality Assurance Plan). For SVVP purposes, the following definitions apply:) SVVP – Software Verification and Validation Plan.Validation – The process of evaluating software at the end of the software developmentprocess to ensure compliance to software requirements.Verification – The process of determining whether or not products of a given phase of thesoftware development process fulfill the requirements established during the previous phase.V&V – Verification and validation.4. V ERIFICATION AND V ALIDATION O VERVIEW(Describe the organization, schedule, resources, responsibilities, tools, techniques, andmethodologies to be deployed in order to perform the verification and validation activities.)4.1 Organization(Define the relationship of verification and validation to other efforts such asdevelopment, project management, quality assurance, and configurationmanagement. Define the lines of communication within the verification andvalidation effort, the authority for resolving issues, and the authority forapproving verification and validation deliverables.)(The specific organization structure of the V&V effort will depend on the nature of the system under development, the developing organizations, and anycontractual arrangements.)4.2 Master Schedule(The master schedule summarizes the various verification and validation tasks and their relationship to the overall project.)(Describe the project life cycle and project milestones including completion dates.Summarize the schedule of verification and validation tasks and how verification and validation results provide feedback to the development process to support overall project management functions.)(The objective of this section is to define an orderly flow of material betweenproject activities and verification and validation tasks. Use reference to PERT, CPM, and Gantt Charts to define the relationship of activities.)(If the life cycle used in the SVVP differs from the life cycle model defined in IEEE Standard 1012, this section must show how all requirements of the Standard will be satisfied. The summary of tasks may be in narrative, tabular, or graphic form.)4.3 Resource Summary(This section summarizes the resources needed to perform verification andvalidation tasks, including staffing, facilities, tools, finances, and specialprocedural requirements such as security, access rights, and documentationcontrol. In this section:•Use graphs and tables to present resource utilization,•Include equipment and laboratory resources required,•Summarize the purpose and cost of hardware and software tools to be employed, and•Take all resources into account and allow for additional time and money to cope with contingencies.)4.4 Responsibilities(Identify the organization responsible for performing verification and validationtasks. There are two levels of responsibility – general responsibilities assigned todifferent organizations and specific responsibilities for the V&V tasks to beperformed should be assigned to individuals. General responsibilities should besupplemented with specific responsibility for each task in the verification andvalidation plan.)4.5 Tools, Techniques, and Methodology(Identify the special software tools, techniques, and methodologies to be employedby the verification and validation team. The purpose of each should be definedand plans for the acquisition, training, support, and qualification of each shall bedescribed in this section. This section may be in narrative or graphic format. Aseparate tool plan may be developed for software tool acquisition, development,or modification. In this case, a separate Tool Plan section may be added to theplan.)5. L IFECYCLE V ERIFICATION AND V ALIDATION(This section of the SVVP provides the detailed plan for the verification and validationtasks throughout the project life cycle. Please refer to IEEE Standard 1012 and IEEEGuide 1059 for detailed descriptions of lifecycle verification and validation activities.)5.1 Management of V & VThis section shall address the following general topics:•Verification and validation tasks,•Methods and criteria,•Inputs and outputs,•Schedule,•Resources,•Risks and assumptions, and•Roles and responsibilities.(In addition, all sub-sections of this major heading (5) must specifically address all seven of the topics noted above.)(For all software projects, the Management of Verification and Validation section must include the following minimum tasks:•Software Verification and Validation Plan Generation,•Baseline Change Assessment,•Management Review of V&V, and•Review Support.)(Initiate the Software Verification and Validation Plan during the Concept phase of the project life cycle. However, verification and validation planning may bedependent on things outside of your control. Therefore, V&V planning may bemost effectively performed in conjunction with the overall software developmentplanning effort. The SVVP is often best developed incrementally.)(Evaluate proposed software changes for effects on previously completed V&Vtasks. The request for baseline change assessment should be formally documented in a change proposal.)(Conduct periodic reviews of V&V efforts, technical accomplishments, resourceutilization, future planning, and risk management. Management review comprises all of the general responsibilities of management for monitoring, controlling,reporting, and managing the plan.)(Identify key review support milestones. Correlate V&V task results to supportproject management and technical reviews.)5.2 Concept Phase(This section of the plan shall address the seven topics identified in section 5.1 ofthis document. Evaluate concept documentation to determine if the proposedproject concept satisfies user needs and project objectives. Identify majorconstraints of interfacing systems and limitations of the proposed approach.Assess the criticality of each software item.)(The concept phase establishes the reason for the system. Evaluation in theconcept phase should establish that the objectives of the system define the userneeds to be addressed and the technical and business advantages to be expected.)5.3 Requirements Phase(The requirements phase is when the functional and technical capabilities of thesoftware product are defined and documented. The product from therequirements phase (Software Requirements Specification) should accurately state the software mission and what the software is intended to do. Requirements must be traceable to user needs and the system concept.)(This section of the plan shall address the seven topics identified in section 5.1 ofthis document. For critical software, Requirements Phase Verification andValidation must include the following tasks:•Software requirements traceability analysis, (Trace SRS requirements to system requirements in concept documentation. Analyze identifiedrelationships for correctness, consistency, completeness, and accuracy. Do therequirements completely satisfy the capabilities specified in the conceptdocument?)•Software requirements evaluation, (Evaluate SRS requirements forcorrectness, consistency, completeness, accuracy, readability, and testability.Assess the technical merits of the requirements.)•Software requirements interface analysis, (Evaluate the SRS with hardware, user, operator, and software interface requirements documentation forcorrectness, consistency, completeness, accuracy, and readability Ensure thatall external interfaces to the software and internal interfaces betweensoftware functions are complete and correctly specified.) and•Test plan analysis for-System test, and-Acceptance test.)5.4 Design Phase(The design phase in the software life cycle involves the designs for architecture,software components, interfaces, and data creation, documentation, andverification. Design must trace back to requirements.)(This section of the plan shall address the seven topics identified in section 5.1 ofthis document. For critical software, design phase V&V will include the following tasks:•Software design traceability analysis (Trace design documentation to requirements. Analyze identified relationships for correctness, consistency,completeness, and accuracy.),•Software design evaluation (Evaluate design for correctness, consistency, completeness, accuracy, readability, and testability. Assess the technicalmerits of the requirements and compliance to organization standards.),•Software design interface analysis, (Evaluate design with hardware, operator, and software interface requirements documentation for correctness,consistency, completeness, accuracy, and readability At a minimum, analyzedata elements at each interface.) and•Test design generation-Component test plan, and-Integration test plan.)5.5 Implementation Phase(This section of the plan shall address the seven topics identified in section 5.1 ofthis document. Implementation phase V&V must include the following tasks:•Source code traceability analysis (Trace source code to design specification and assess correctness, consistency, completeness, and accuracy.),•Source code evaluation (evaluate source code for correctness, consistency, completeness, accuracy, and testability. Assess code quality and compliance toorganization standards.),•Source code interface evaluation (Evaluate source code with hardware, operator, and design documentation for correctness, consistency,completeness, and accuracy.),•Source code documentation evaluation (Evaluate draft code-related documents with source code to ensure completeness, correctness, andconsistency.),•Test case generation for:-Component test-Integration test-System test and-Acceptance test,•Test procedure generation for:-Component test-Integration test and-System test,•Component test execution.)5.6 Test Phase(This section of the plan shall address the seven topics identified in section 5.1 ofthis document. The following tasks must be included in this section:•Acceptance test procedure generation, (Develop test procedures for acceptance test) and•Test execution-Integration test,-System test, and-Acceptance test.)5.7 Installation and Checkout Phase(This section of the plan shall address the seven topics identified in section 5.1 ofthis document. The following verification and validation tasks must be included in this section:•Installation configuration audit, (Audit installation package to determine that all software products required to correctly install and operate the system arepresent and correct), and•Final V&V report generation, (Summarize all V&V activities and results including the status and disposition of anomalies in the V&V final report).)5.8 Operation and Maintenance Phase(This section of the plan shall address the seven topics identified in section 5.1 ofthis document. Any modifications, enhancements, or additions to software duringthis phase shall be treated as development activity and shall be verified andvalidated. If the original software was verified and validated under this standard,the standard must continue to be followed in the Operations and Maintenancephase. The minimum V&V tasks to include:-Software verification and validation plan revision,-Anomaly Evaluation,-Proposed change assessment, and-Phase task iteration.)(The operation and maintenance phase is the period of time in the software lifecycle during which the software product is employed in an operationalenvironment, monitored for satisfactory performance, and modified to correctproblems or respond to changing requirements. Operation and maintenance maynot be a “phase” but a sequence of repetitions or subsets of the softwaredevelopment life cycle.)6. Reporting(This section describes how the results of implementing the SVVP will be documented.Verification and validation reporting will occur throughout the software life cycle.Specify the content, format, and timing of all verification and validation reports.The required V&V reports include:-Anomaly reports,-Task reporting,-Phase summary reports, and-Final report.)7. Administrative Procedures(This section should identify any existing administrative procedures that are to beimplemented as part of the SVVP. Verification and validation efforts consist of bothmanagement and technical tasks. At least three audiences should be identified for the V&V information – personnel performing the V&V tasks, personnel performing development tasks, and management.)7.1 Anomaly Reporting and Resolution(Identify the method of reporting and resolving anomalies including the criteriafor reporting an anomaly, anomaly report distribution, and the authority and timeline for resolving anomalies. This section should have the following sub-sections:-Methods and criteria for reporting,-Report distribution,-Methods and criteria for anomaly resolution,-Anomaly criticality scheme,-Resolution timing.)7.2 Task Iteration Policy(Describe the criteria used to determine when V&V tasks must be re-performedbecause input has changed. These criteria include assessments of change,criticality, cost, schedule, and effects on product quality.)7.3 Deviation Policy(Describe the procedures and forms used to request a deviation from the SVVP.The information required for deviation must include task identification, deviationrationale, and effect on software quality. Authority for approving deviations fromthe plan must also be identified.)7.4 Control Procedures(Identify all control procedures applied to the verification and validation effort.At a minimum, control procedures should be identified for:-Configuration management,-Archive and retrieval,-Security, and-Access control.)7.5 Standards, Practices, and Conventions(This section identifies the standards, practices, and conventions that govern theperformance of verification and validation tasks. Include IEEE, IRMC, andorganizational standards, policies, procedures, and guidelines.)8. Plan Approvals(Identify the plan approvers. List the name, signature and date of plan approval.)。
sttt综述投稿要求
STTT是Springer出版的期刊,全称为Software Testing, Verification and Reliability。
STTT期刊接收关于软件测试、验
证和可靠性方面的研究论文。
投稿给STTT期刊需要满足一定的要求,以下是关于投稿要求的综述:
1. 领域范围,STTT期刊主要关注软件测试、验证和可靠性领
域的研究,包括但不限于自动化测试、软件质量保证、验证方法、
可靠性建模等方面的内容。
2. 原创性和重要性,投稿给STTT期刊的论文需要具有较高的
原创性和重要性,能够为该领域的研究和实践提供新的见解和方法。
3. 格式要求,投稿的论文需要符合STTT期刊的格式要求,包
括但不限于文稿长度、引用格式、图表要求等方面。
4. 语言要求,STTT期刊接收英文论文投稿,因此投稿的论文
需要使用规范的英文撰写。
5. 审稿流程,投稿给STTT期刊的论文会经过严格的同行评审
流程,作者需要准备好随时对审稿意见进行修改和回复。
6. 伦理规范,投稿的论文需要遵守学术伦理规范,不得涉及剽窃、造假等行为。
总的来说,投稿给STTT期刊需要作者具备扎实的研究基础和丰富的实践经验,论文内容需要具有创新性和学术价值,同时也需要符合期刊的格式和伦理要求。
希望以上综述能够帮助你更好地了解STTT期刊的投稿要求。
CHEAPER 11.What is testing?Finding defects in a controlled manner发现缺陷控制的方式Detecting the level of quality of the test object检测测试对象的质量水平Find the gap between specifications and the actual product发现产品规格和实际之间的差距2.What is software testing?Software testing is the process of executing software in a controlled manner , in order to answer the question “Does the software behave as specified?”软件测试是软件控制的方式执行的过程,为了回答这个问题“指定的软件像什么?”Why do we test?Provide confidence in the system提供系统的信心Identify areas of weakness找到薄弱环节Establish the degree of quality建立质量的程度Establish the extent that the requirements have been met.建立需求满足的程度。
To provide an understanding of the overall system.提供一个对整个系统的理解。
3.Why testing is Important?All Software has defects (bugs)所有的软件缺陷(bug)All software products are ‘prototypes’.所有的软件产品是“原型”。
Software products are getting larger and more complicated 软件产品是变得更大、更复杂Software is written by human –human make mistakes软件是由人类,人类犯错误Software testing looks to find the most important defects as early as possible –increasing confidence that the software meets specification.软件测试看起来尽可能早地发现最重要的缺陷,增加信心,软件符合规范。
iAbout the T utorialTesting is the process of evaluating a system or its component(s) with the intent to find whether it satisfies the specified requirements or not.Testing is executing a system in order to identify any gaps, errors, or missing requirements in contrary to the actual requirements.This tutorial will give you a basic understanding on software testing, its types, methods, levels, and other related terminologies.AudienceThis tutorial is designed for software testing professionals who would like to understand the Testing Framework in detail along with its types, methods, and levels. This tutorial provides enough ingredients to start with the software testing process from where you can take yourself to higher levels of expertise.PrerequisitesBefore proceeding with this tutorial, you should have a basic understanding of the software development life cycle (SDLC). In addition, you should have a basic understanding of software programming using any programming language.Copyright & DisclaimerCopyright 2018 by Tutorials Point (I) Pvt. Ltd.All the content and graphics published in this e-book are the property of Tutorials Point (I) Pvt. Ltd. The user of this e-book is prohibited to reuse, retain, copy, distribute or republish any contents or a part of contents of this e-book in any manner without written consent of the publisher.We strive to update the contents of our website and tutorials as timely and as precisely as possible, however, the contents may contain inaccuracies or errors. Tutorials Point (I) Pvt. Ltd. provides no guarantee regarding the accuracy, timeliness or completeness of our website or its contents including this tutorial. If you discover any errors on our website or in this tutorial, please notify us at **************************iiT able of ContentsAbout the Tutorial (1)Audience (1)Prerequisites (1)Copyright & Disclaimer (1)Table of Contents (2)1. SOFTWARE TESTING – OVERVIEW (5)What is Testing? (5)Who does Testing? (5)When to Start Testing? (5)When to Stop Testing? (6)Verification & Validation (6)2. SOFTWARE TESTING – MYTHS (7)3. SOFTWARE TESTING – QA, QC, AND TESTING (9)Testing, Quality Assurance, and Quality Control (9)Audit and Inspection (9)Testing and Debugging (10)4. SOFTWARE TESTING – ISO STANDARDS (11)ISO/IEC 9126 (11)ISO/IEC 9241-11 (11)ISO/IEC 25000:2005 (11)ISO/IEC 12119 (12)Miscellaneous (12)5. SOFTWARE TESTING – TYPES OF TESTING (14)Manual Testing (14)iiiAutomation Testing (14)What to Automate? (14)When to Automate? (15)How to Automate? (15)Software Testing Tools (15)6. SOFTWARE TESTING – TESTING METHODS (17)Black-Box Testing (17)White-Box Testing (17)Grey-Box Testing (18)A Comparison of Testing Methods (19)7. SOFTWARE TESTING – TESTING LEVELS (20)Functional Testing (20)Unit Testing (20)Integration Testing (21)System Testing (21)Regression Testing (22)Acceptance Testing (22)Non-Functional Testing (23)Usability Testing (24)Security Testing (25)Portability Testing (26)8. SOFTWARE TESTING – DOCUMENTATION (27)Test Plan (27)Test Scenario (27)Test Case (28)Traceability Matrix (29)iv9. SOFTWARE TESTING – ESTIMATION TECHNIQUES (30)Functional Point Analysis (30)Test Point Analysis (30)Mark-II Method (30)Miscellaneous (30)vSoftware Testing 1What is T esting?Testing is the process of evaluating a system or its component(s) with the intent to find whether it satisfies the specified requirements or not. In simple words, testing is executing a system in order to identify any gaps, errors, or missing requirements in contrary to the actual requirements. According to ANSI/IEEE 1059 standard, Testing can be defined as - A process of analyzing a software item to detect the differences between existing and required conditions (that is defects/errors/bugs) and to evaluate the features of the software item .Who does T esting?It depends on the process and the associated stakeholders of the project(s). In the IT industry, large companies have a team with responsibilities to evaluate the developed software in context of the given requirements. Moreover, developers also conduct testing which is called Unit Testing . In most cases, the following professionals are involved in testing a system within their respective capacities: ∙ Software Tester∙ Software Developer∙ Project Lead/Manager∙ End UserDifferent companies have different designations for people who test the software on the basis of their experience and knowledge such as Software Tester, Software Quality Assurance Engineer, QA Analyst, etc.It is not possible to test the software at any time during its cycle. The next two sections state when testing should be started and when to end it during the SDLC.When to Start T esting?An early start to testing reduces the cost and time to rework and produce error-free software that is delivered to the client. However in Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC), testing can be started from the Requirements Gathering phase and continued till the deployment of the software. It also depends on the development model that is being used. For example, in the Waterfall model, formal testing is conducted in the testing phase; but in the incremental model, testing is performed at the end of every increment/iteration and the whole application is tested at the end. Testing is done in different forms at every phase of SDLC:1. Software Testing – OverviewSoftware Testing 2∙ During the requirement gathering phase, the analysis and verification of requirements arealso considered as testing.∙ Reviewing the design in the design phase with the intent to improve the design is alsoconsidered as testing.∙ Testing performed by a developer on completion of the code is also categorized as testing. When to Stop T esting?It is difficult to determine when to stop testing, as testing is a never-ending process and no one can claim that a software is 100% tested. The following aspects are to be considered for stopping the testing process:∙ Testing Deadlines∙ Completion of test case execution∙ Completion of functional and code coverage to a certain point∙ Bug rate falls below a certain level and no high-priority bugs are identified∙ Management decisionV erification & V alidationThese two terms are very confusing for most people, who use them interchangeably. The following table highlights the differences between verification and validation.S.N.Verification Validation 1 Verification addresses the concern: "Areyou building it right?"Validation addresses the concern: "Are you building the right thing?" 2 Ensures that the software system meetsall the functionality.Ensures that the functionalities meet the intended behavior. 3 Verification takes place first and includesthe checking for documentation, code,etc.Validation occurs after verification and mainly involves the checking of the overall product. 4Done by developers. Done by testers.Software Testing 35 It has static activities, as it includescollecting reviews, walkthroughs, andinspections to verify a software.It has dynamic activities, as it includes executing the software against the requirements. 6 It is an objective process and nosubjective decision should be needed toverify a software.It is a subjective process and involves subjective decisions on how well a software works.Software Testing 4Given below are some of the most common myths about software testing. Myth 1: Testing is Too ExpensiveReality : There is a saying, pay less for testing during software development or pay more for maintenance or correction later. Early testing saves both time and cost in many aspects, however reducing the cost without testing may result in improper design of a software application rendering the product useless.Myth 2: Testing is Time-ConsumingReality : During the SDLC phases, testing is never a time-consuming process. However diagnosing and fixing the errors identified during proper testing is a time-consuming but productive activity. Myth 3: Only Fully Developed Products are TestedReality : No doubt, testing depends on the source code but reviewing requirements and developing test cases is independent from the developed code. However iterative or incremental approach as a development life cycle model may reduce the dependency of testing on the fully developed software.Myth 4: Complete Testing is PossibleReality : It becomes an issue when a client or tester thinks that complete testing is possible. It is possible that all paths have been tested by the team but occurrence of complete testing is never possible. There might be some scenarios that are never executed by the test team or the client during the software development life cycle and may be executed once the project has been deployed.Myth 5: A Tested Software is Bug-FreeReality : This is a very common myth that the clients, project managers, and the management team believes in. No one can claim with absolute certainty that a software application is 100% bug-free even if a tester with superb testing skills has tested the application.Myth 6: Missed Defects are due to TestersReality : It is not a correct approach to blame testers for bugs that remain in the application even after testing has been performed. This myth relates to Time, Cost, and Requirements changing Constraints. However the test strategy may also result in bugs being missed by the testing team.2. Software Testing – MythsSoftware TestingMyth 7: Testers are Responsible for Quality of ProductReality: It is a very common misinterpretation that only testers or the testing team should be responsible for product quality. Tester s’ responsibilities include the identification of bugs to the stakeholders and then it is their decision whether they will fix the bug or release the software. Releasing the software at the time puts more pressure on the testers, as they will be blamed for any error.Myth 8: Test Automation should be used Wherever Possible to Reduce Time Reality: Yes, it is true that Test Automation reduces the testing time, but it is not possible to start test automation at any time during software development. Test automaton should be started when the software has been manually tested and is stable to some extent. Moreover, test automation can never be used if requirements keep changing.Myth 9: Anyone can Test a Software ApplicationReality: People outside the IT industry think and even believe that anyone can test a software and testing is not a creative job. However testers know very well that this is a myth. Thinking alternative scenarios, try to crash a software with the intent to explore potential bugs is not possible for the person who developed it.Myth 10: A Tester’s Only Task is to Fi nd BugsReality: Finding bugs in a software is the task of the testers, but at the same time, they are domain experts of the particular software. Developers are only responsible for the specific component or area that is assigned to them but testers understand the overall workings of the software, what the dependencies are, and the impacts of one module on another module.5Software TestingEnd of ebook previewIf you liked what you saw…Buy it from our store @ https://6。
软件测试部分中英文对照Acceptance testing : 验收测试Acceptance Testing:可接受性测试Accessibility test : 软体适用性测试actual outcome:实际结果Ad hoc testing : 随机测试Algorithm analysis : 算法分析algorithm:算法Alpha testing : α测试analysis:分析anomaly:异常application software:应用软件Application under test (AUT : 所测试的应用程序Architecture : 构架Artifact : 工件ASQ:自动化软件质量(Automated Software Quality Assertion checking : 断言检查Association : 关联Audit : 审计audit trail:审计跟踪Automated Testing:自动化测试Backus-Naur Form:BNF范式baseline:基线Basic Block:基本块basis test set:基本测试集Behaviour : 行为Bench test : 基准测试benchmark:标杆/指标/基准Best practise : 最佳实践Beta testing : β测试Black Box Testing:黑盒测试Blocking bug : 阻碍性错误Bottom-up testing : 自底向上测试boundary value coverage:边界值覆盖boundary value testing:边界值测试Boundary values : 边界值Boundry Value Analysis:边界值分析branch condition combination coverage:分支条件组合覆盖branch condition combination testing:分支条件组合测试branch condition coverage:分支条件覆盖branch condition testing:分支条件测试branch condition:分支条件Branch coverage : 分支覆盖branch outcome:分支结果branch point:分支点branch testing:分支测试branch:分支Breadth Testing:广度测试Brute force testing: 强力测试Buddy test : 合伙测试Buffer : 缓冲Bug : 错误Bug bash : 错误大扫除bug fix : 错误修正Bug report : 错误报告Bug tracking system: 错误跟踪系统bug:缺陷Build : 工作版本(内部小版本Build Verfication tests(BVTs: 版本验证测试Build-in : 内置Capability Maturity Model (CMM: 能力成熟度模型Capability Maturity Model Integration (CMMI: 能力成熟度模型整合capture/playback tool:捕获/回放工具Capture/Replay Tool:捕获/回放工具CASE:计算机辅助软件工程(computer aided software engineering CAST:计算机辅助测试cause-effect graph:因果图certification :证明change control:变更控制Change Management :变更管理Change Request :变更请求Character Set : 字符集Check In :检入Check Out :检出Closeout : 收尾code audit :代码审计Code coverage : 代码覆盖Code Inspection:代码检视Code page : 代码页Code rule : 编码规范Code sytle : 编码风格Code Walkthrough:代码走读code-based testing:基于代码的测试coding standards:编程规范Common sense : 常识Compatibility Testing:兼容性测试complete path testing :完全路径测试completeness:完整性complexity :复杂性Component testing : 组件测试Component:组件computation data use:计算数据使用computer system security:计算机系统安全性Concurrency user : 并发用户Condition coverage : 条件覆盖condition coverage:条件覆盖condition outcome:条件结果condition:条件configuration control:配置控制Configuration item : 配置项configuration management:配置管理Configuration testing : 配置测试conformance criterion:一致性标准Conformance Testing:一致性测试consistency :一致性consistency checker:一致性检查器Control flow graph : 控制流程图control flow graph:控制流图control flow:控制流conversion testing:转换测试Core team : 核心小组corrective maintenance:故障检修correctness :正确性coverage :覆盖率coverage item:覆盖项crash:崩溃criticality analysis:关键性分析criticality:关键性CRM(change request management: 变更需求管理Customer-focused mindset : 客户为中心的理念体系Cyclomatic complexity : 圈复杂度data corruption:数据污染data definition C-use pair:数据定义C-use使用对data definition P-use coverage:数据定义P-use覆盖data definition P-use pair:数据定义P-use使用对data definition:数据定义data definition-use coverage:数据定义使用覆盖data definition-use pair :数据定义使用对data definition-use testing:数据定义使用测试data dictionary:数据字典Data Flow Analysis : 数据流分析data flow analysis:数据流分析data flow coverage:数据流覆盖data flow diagram:数据流图data flow testing:数据流测试data integrity:数据完整性data use:数据使用data validation:数据确认dead code:死代码Debug : 调试Debugging:调试Decision condition:判定条件Decision coverage : 判定覆盖decision coverage:判定覆盖decision outcome:判定结果decision table:判定表decision:判定Defect : 缺陷defect density : 缺陷密度Defect Tracking :缺陷跟踪Deployment : 部署Depth Testing:深度测试design for sustainability :可延续性的设计design of experiments:实验设计design-based testing:基于设计的测试Desk checking : 桌前检查desk checking:桌面检查Determine Usage Model : 确定应用模型Determine Potential Risks : 确定潜在风险diagnostic:诊断DIF(decimation in frequency : 按频率抽取dirty testing:肮脏测试disaster recovery:灾难恢复DIT (decimation in time: 按时间抽取documentation testing :文档测试domain testing:域测试domain:域DTP DETAIL TEST PLAN详细确认测试计划Dynamic analysis : 动态分析dynamic analysis:动态分析Dynamic Testing:动态测试embedded software:嵌入式软件emulator:仿真End-to-End testing:端到端测试Enhanced Request :增强请求entity relationship diagram:实体关系图Encryption Source Code Base:加密算法源代码库Entry criteria : 准入条件entry point :入口点Envisioning Phase : 构想阶段Equivalence class : 等价类Equivalence Class:等价类equivalence partition coverage:等价划分覆盖Equivalence partition testing : 等价划分测试equivalence partition testing:参考等价划分测试equivalence partition testing:等价划分测试Equivalence Partitioning:等价划分Error : 错误Error guessing : 错误猜测error seeding:错误播种/错误插值error:错误Event-driven : 事件驱动Exception handlers : 异常处理器exception:异常/例外executable statement:可执行语句Exhaustive Testing:穷尽测试exit point:出口点expected outcome:期望结果Exploratory testing : 探索性测试Failure : 失效Fault : 故障fault:故障feasible path:可达路径feature testing:特性测试Field testing : 现场测试FMEA:失效模型效果分析(Failure Modes and Effects AnalysisFMECA:失效模型效果关键性分析(Failure Modes and Effects Criticality Analysis Framework : 框架FTA:故障树分析(Fault Tree Analysisfunctional decomposition:功能分解Functional Specification :功能规格说明书Functional testing : 功能测试Functional Testing:功能测试G11N(Globalization : 全球化Gap analysis : 差距分析Garbage characters : 乱码字符glass box testing:玻璃盒测试Glass-box testing : 白箱测试或白盒测试Glossary : 术语表GUI(Graphical User Interface: 图形用户界面Hard-coding : 硬编码Hotfix : 热补丁I18N(Internationalization: 国际化Identify Exploratory Tests –识别探索性测试IEEE:美国电子与电器工程师学会(Institute of Electrical and Electronic Engineers Incident 事故Incremental testing : 渐增测试incremental testing:渐增测试infeasible path:不可达路径input domain:输入域Inspection : 审查inspection:检视installability testing:可安装性测试Installing testing : 安装测试instrumentation:插装instrumenter:插装器Integration :集成Integration testing : 集成测试interface : 接口interface analysis:接口分析interface testing:接口测试interface:接口invalid inputs:无效输入isolation testing:孤立测试Issue : 问题Iteration : 迭代Iterative development: 迭代开发job control language:工作控制语言Job:工作Key concepts : 关键概念Key Process Area : 关键过程区域Keyword driven testing : 关键字驱动测试Kick-off meeting : 动会议L10N(Localization : 本地化Lag time : 延迟时间LCSAJ:线性代码顺序和跳转(Linear Code Sequence And Jump LCSAJ coverage:LCSAJ覆盖LCSAJ testing:LCSAJ测试Lead time : 前置时间Load testing : 负载测试Load Testing:负载测试Localizability testing: 本地化能力测试Localization testing : 本地化测试logic analysis:逻辑分析logic-coverage testing:逻辑覆盖测试Maintainability : 可维护性maintainability testing:可维护性测试Maintenance : 维护Master project schedule :总体项目方案Measurement : 度量Memory leak : 内存泄漏Migration testing : 迁移测试Milestone : 里程碑Mock up : 模型,原型modified condition/decision coverage:修改条件/判定覆盖modifiedcondition/decision testing :修改条件/判定测试modular decomposition:参考模块分解Module testing : 模块测试Monkey testing : 跳跃式测试Monkey Testing:跳跃式测试mouse over:鼠标在对象之上mouse leave:鼠标离开对象MTBF:平均失效间隔实际(mean time between failures MTP MAIN TEST PLAN 主确认计划MTTF:平均失效时间(mean time to failure MTTR:平均修复时间(mean time to repair multiple condition coverage:多条件覆盖mutation analysis:变体分析N/A(Not applicable : 不适用的Negative Testing : 逆向测试, 反向测试, 负面测试negative testing:参考负面测试Negative Testing:逆向测试/反向测试/负面测试off by one:缓冲溢出错误non-functional requirements testing:非功能需求测试nominal load:额定负载N-switch coverage:N切换覆盖N-switch testing:N切换测试N-transitions:N转换Off-the-shelf software : 套装软件operational testing:可操作性测试output domain:输出域paper audit:书面审计Pair Programming : 成对编程partition testing:分类测试Path coverage : 路径覆盖path coverage:路径覆盖path sensitizing:路径敏感性path testing:路径测试path:路径Peer review : 同行评审Performance : 性能Performance indicator: 性能(绩效指标Performance testing : 性能测试Pilot : 试验Pilot testing : 引导测试Portability : 可移植性portability testing:可移植性测试Positive testing : 正向测试Postcondition : 后置条件Precondition : 前提条件precondition:预置条件predicate data use:谓词数据使用predicate:谓词Priority : 优先权program instrumenter:程序插装progressive testing:递进测试Prototype : 原型Pseudo code : 伪代码pseudo-localization testing:伪本地化测试pseudo-random:伪随机QC:质量控制(quality controlQuality assurance(QA: 质量保证Quality Control(QC : 质量控制Race Condition:竞争状态Rational Unified Process(以下简称RUP:瑞理统一工艺Recovery testing : 恢复测试recovery testing:恢复性测试Refactoring : 重构regression analysis and testing:回归分析和测试Regression testing : 回归测试Release : 发布Release note : 版本说明release:发布Reliability : 可靠性reliability assessment:可靠性评价reliability:可靠性Requirements management tool: 需求管理工具Requirements-based testing : 基于需求的测试Return of Investment(ROI: 投资回报率review:评审Risk assessment : 风险评估risk:风险Robustness : 强健性Root Cause Analysis(RCA: 根本原因分析safety critical:严格的安全性safety:(生命安全性Sanity testing : 健全测试Sanity Testing:理智测试Schema Repository : 模式库Screen shot : 抓屏、截图SDP:软件开发计划(software development plan Security testing : 安全性测试security testing:安全性测试security.:(信息安全性serviceability testing:可服务性测试Severity : 严重性Shipment : 发布simple subpath:简单子路径Simulation : 模拟Simulator : 模拟器SLA(Service level agreement: 服务级别协议SLA:服务级别协议(service level agreementSmoke testing : 冒烟测试Software development plan(SDP: 软件开发计划Software development process: 软件开发过程software development process:软件开发过程software diversity:软件多样性software element:软件元素software engineering environment:软件工程环境software engineering:软件工程Software life cycle : 软件生命周期source code:源代码source statement:源语句Specification : 规格说明书specified input:指定的输入spiral model :螺旋模型SQAP SOFTWARE QUALITY ASSURENCE PLAN 软件质量保证计划SQL:结构化查询语句(structured query languageStaged Delivery:分布交付方法state diagram:状态图state transition testing :状态转换测试state transition:状态转换state:状态Statement coverage : 语句覆盖statement testing:语句测试statement:语句Static Analysis:静态分析Static Analyzer:静态分析器Static Testing:静态测试statistical testing:统计测试Stepwise refinement : 逐步优化storage testing:存储测试Stress Testing : 压力测试structural coverage:结构化覆盖structural test case design:结构化测试用例设计structural testing:结构化测试structured basis testing:结构化的基础测试structured design:结构化设计structured programming:结构化编程structured walkthrough:结构化走读stub:桩sub-area:子域Summary:总结SVVP SOFTWARE Vevification&Validation PLAN:软件验证和确认计划symbolic evaluation:符号评价symbolic execution:参考符号执行symbolic execution:符号执行symbolic trace:符号轨迹Synchronization : 同步Syntax testing : 语法分析system analysis:系统分析System design : 系统设计system integration:系统集成System Testing : 系统测试TC TEST CASE 测试用例TCS TEST CASE SPECIFICATION 测试用例规格说明TDS TEST DESIGN SPECIFICATION 测试设计规格说明书technical requirements testing:技术需求测试Test : 测试test automation:测试自动化Test case : 测试用例test case design technique:测试用例设计技术test case suite:测试用例套test comparator:测试比较器test completion criterion:测试完成标准test coverage:测试覆盖Test design : 测试设计Test driver : 测试驱动test environment:测试环境 test execution technique:测试执行技术 test execution:测试执行 test generator:测试生成器 test harness:测试用具 Test infrastructure : 测试基础建设 test log:测试日志 test measurement technique:测试度量技术 Test Metrics :测试度量 test procedure:测试规程 test records:测试记录 test report:测试报告 Test scenario Test Script:测试脚本 Test Specification:测试规格 Test strategy test suite:测试套 Test target Test ware Testability testability:可测试性 Testing bed : 测试平台 : 测试目标 : 测试工具 : 测试策略 : 测试场景 : 可测试性Testing coverage : 测试覆盖 Testing environment : 测试环境 Testing item Testing plan Testing procedure Thread testing time sharing:时间共享 time-boxed TIR : 固定时间测试事故报告 : 测试项 : 测试计划 : 测试过程 : 线程测试 test incident report ToolTip:控件提示或说明 top-down testing:自顶向下测试 TPS TEST PEOCESS SPECIFICATION 测试步骤规格说明 Traceability : 可跟踪性 traceability analysis:跟踪性分析 traceability matrix:跟踪矩阵 Trade-off transaction:事务/处理 transaction volume:交易量 transform analysis:事务分析 trojan horse:特洛伊木马 truth table:真值表 TST TEST SUMMARY REPORT 测试总结报告 : 平衡Tune System : 调试系统 TW TEST WARE :测试件 Unit Testing :单元测试Usability Testing:可用性测试 Usage scenario : 使用场景 User acceptance Test : 用户验收测试 User database User interface(UI User profile User scenario :用户数据库 : 用户界面 : 用户信息 : 用户场景 V&V (Verification & Validation : 验证&确认 validation verification version Virtual user :确认 :验证 :版本 : 虚拟用户 volume testing:容量测试VSS(visual source safe): VTP Verification TEST PLAN 验证测试计划 VTR Verification TEST REPORT 验证测试报告 Walkthrough Waterfall model Web testing : 走读 : 瀑布模型 : 网站测试White box testing : 白盒测试 Work breakdown structure (WBS : 任务分解结构Zero bug bounce (ZBB : 零错误反弹。