done以及状语从句
- 格式:pptx
- 大小:99.69 KB
- 文档页数:43

高中英语状语从句12状语从句分类结果状语从句地点状语从句目的状语从句条件状语从句时间状语从句原因状语从句让步状语从句比较状语从句方式状语从句3u when 意为“当……时候”,从句的动作与主句的动作同时发生或是先于主句动作。
既可指一段时间也可指时间点,可接延续性动词或者短暂性动词。
u while 表示一个时间段,只能与延续性动词连用,也可以表示对比。
u as “一边……一边……”,强调两个动作同时发生,也可以表示“随着”。
While (as) he was studying, his brother was sleeping.When (as) he arrives, I will inform him of it.The girls sang happily as they walked around the lake.As time goes on, he is getting fatter and fatter.before意为“在……之前”,表示从句的动作发生在主句动作之后。
after意为“在……之后”,表示从句的动作发生在主句动作之前。
He had done good preparations before he went to college.After he had tried many times and failed in the end, he gave up.45表示“直到……、到……为止”,表示一个动作持续到某一时刻为止。
二者用法相近,但在句首时只能用until 。
在肯定句中主句要用延续性动词,表示“直到……”;在否定句中,可和非延续性动词连用,not...until...表示“直到……才”。
He waited at home until/till it stopped raining.Until all the lights in the street had been off, the boy went home.He appeared until I waited for a long time.(错)He didn't appear until/before I waited for a long time.(正)not……until可用于强调句或者倒装结构中。

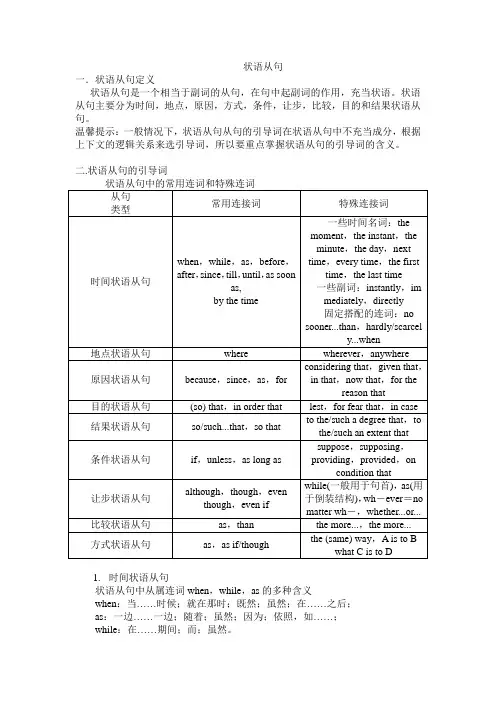
状语从句一.状语从句定义状语从句是一个相当于副词的从句,在句中起副词的作用,充当状语。
状语从句主要分为时间,地点,原因,方式,条件,让步,比较,目的和结果状语从句。
温馨提示:一般情况下,状语从句从句的引导词在状语从句中不充当成分,根据上下文的逻辑关系来选引导词,所以要重点掌握状语从句的引导词的含义。
二.状语从句的引导词一些时间名词:themoment,the instant,theminute,the day,nexttime,every time,the firsttime,the last time一些副词:instantly,immediately,directly固定搭配的连词:nosooner...than,hardly/scarcely...when1.时间状语从句状语从句中从属连词when,while,as的多种含义when:当……时候;就在那时;既然;虽然;在……之后;as:一边……一边;随着;虽然;因为;依照,如……;while:在……期间;而;虽然。
用when,while和as填空:①He will take my place ________ I am away.②I was having my lunch ________ the fire alarm went off.③________ you have finished your work,you may have a rest.④________ he swam,he cried for help.⑤________ the Internet is of great help,I don't think it good to spend too much time on it.【答案】①while②when③When④As⑤Whilebefore的用法注意判断before在状语从句中的含义:才;就;趁……没有;还没来得及;宁可……也不;不知不觉。

状语从句一、状语从句的定义、功能、分类定义:在复合句中作状语的从句。
功能:状语从句在主从复合句中修饰主句中的动词,形容词或副词,或整个主句。
若去掉状语,句子从语义和语法上都是一个完整的句子,状语从句是一个句子作状语,同理,去掉状语从句的主句从语义和语法上都是一个完整的句子。
分类:按意义可分为时间、地点、原因、目的、结果、条件、方式、比较、让步等状语从句。
位置:从句的位置放在句首,也可放在句末。
放在句首时,从句后面常用一个逗号,放在句末时,从句前一般不用逗号。
二、九种常见状语从句用法(一)时间状语从句引导时间状语从句的从属连词1)基本类:before、after、when、while、as、since、till、until、once、as soon as, etc.2)名词类:the moment ,the minute, the second, the instant, etc. (一…就…); every time, each time, next time, the last time, the first time, by the time, the day, the year, the morning, etc.3)副词类:immediately, directly, instantly, etc. (一...就...)4)句型类:no sooner…than…, hardly/scarcely…when…, etc. (一…就…)例句:Tell him I need to see him the minute he arrives. 他一到就告诉他我要见他。
The children ran away from the orchard(果园) the moment they saw the guard.The moment he saw me, he ran away. 他一看见我,就跑了。

状语从句状语从句一什么是状语从句二状语从句位置三状语从句分类四特殊句式五状语从句常见考点六练一练一什么是状语从句状语从句是行使状语功能的从句,因为其作用相当于副词,它可以用来修饰谓语、定语、状语或整个句子。
状语从句通常由一个连接词或起连接词作用的词组引导。
二状语从句位置比较灵活,有时可以放于句首,有时可以置于句末。
状语从句位于句首时,其后常用逗号与后面的句子隔开。
三状语从句分类状语分类常用连接词例句时间状语after,before,when,while,whenever,as soonas,the moment,as,since,until,the minute,the second,immediately,directly,instantly The ball goes up very high after it hits the ground.Wait until you’re called.地点状语where,wherever You can take a walk wherever you liketo.原因状语Because,as,since,now that,seeing(that)considering(that),Since you do not understand,I will explain again.结果状语so that,such that He is so young that he can’t go to work.目的状语so that,in order that Speak clearly so that they mayunderstand you.条件状语if,unless,as(so)long as,once,unless,on condition that,in case He will do anything as long as it is interesting.让步状语though,although,even though,whilewhether,whoever/no matterwho,whatever/no matter what,whenever/ no matter Even though you say so,I do not believe it.比较状语than as…as,the more…the more The more I see him,the less I like him.方式状语as,as if,as though He told me everything as if I were hisbest friend.四特殊句式1时间状语中A:It+be+时间点+when……当某事发生时是什么时候It was11:00PM when he came back last night.B:It is/has been+时间段+since……自从某事发生后已过了多久时间It is/has been two years since I entered the the senior school.C:It+be+时间段+before……在某事发生之前需要多久时间It was8years before we finally drove away the Japanese invaders.It might be a long time before Chinese land on the moon.2让步状语从句A:as引导的让步状语从句,从句的表语、状语必须前置到句首。

非谓语havingdone的用法非谓语动词是指在句中作状语、定语或补足语时不带有时态和人称的动词形式,常用的非谓语动词有不定式、动名词和分词。
其中,非谓语动词“having done”是一个现在分词的完成式,表示动作在谓语动词所表示的动作之前发生或完成。
以下是“having done”用法的详细解释。
一、作状语“having done”作为状语时,常表示时间顺序、原因、条件、目的、结果等,用来修饰整个句子或主句的内容,充当原因、时间等状语。
常见的句式有:1.时间状语从句Having done his homework, Tom went to bed.(做完作业后,汤姆去睡觉了。
)2.假设状语从句(受伤后,约翰无法参加比赛。
)3.结果状语从句Having failed the exam, he felt very disappointed.(考试不及格,他感到非常失望。
)4.目的状语从句Having finished his work, he left the office.(完成工作后,他离开了办公室。
)二、作定语“having done”作为定语时,常用于名词或代词之后,修饰主语,表示主语在句意中的其中一动作已经完成。
1.名词的定语The boy, having finished his homework, went out to play.(那个男孩完成了作业后,出去玩了。
)2.代词的定语She went upstairs, having found the keys.(她找到钥匙后去楼上了。
)三、作补足语“having done”作为补足语时,常跟在宾语之后,用来修饰或补充说明宾语的内容,意义上相当于一个定语从句或独立副词。
1.补充宾语内容I'm happy with my life, having achieved my goals.(实现了我的目标,我对我的生活感到满足。
)2.与宾语同时发生的动作She sat down, having put the heavy bag on the floor.(她放下沉重的包后坐下来。

done的用法总结(整理16篇)篇1:done的用法总结This is the way we've always done it.我们一直是这样干的.。
I haven't been able to get much work done today.我今天未能干多少工作。
The problem is getting it all done in the time available.问题是要在现有的时间内把它全部完成。
I told you we should have done it my way!我跟你说过我们原本应该用我的方法来做这事。
This job could be done equally well by a computer.这个工作用计算机同样可以做得很好。
篇2:done的用法总结例句:What have I done to deserve this?我做了什么事应该得到这种待遇呢?She got done for speeding.她因超速行驶而受到处罚。
Sit there and wait till I've done.坐在那儿等到我做完。
篇3:had done的用法总结may / might have done表示对已经发生过的情况的.肯定推测,语气稍弱。
might have done还可表示“本可能做某事而实际上没有做”。
如:She didn''t come on time. She may / might have missed the bus. He might have given you more help, but he was very busy then. should / ought to have done表示“本该做某事而实际上没有做”,其否定形式表示“本不该做某事而实际上做了”,通常含有责备的意思。
如: The flowers have died. I should / ought to have watered themoften.You shouldn''t / ought not to have told them the truth.篇4:be to be done的用法例句done和tobedone的区别done、to be done还有,being done这三种形式,除了都是表达被动概念以外,在时间上有分别,done表示“已经发生”,to be done表示“即将或将要发生”,而being done则表示“正在发生”。

状语从句(Adverbial Clause)状语从句指句子用作状语时,起副词作用的句子。
它可以修饰谓语、非谓语动词、定语、状语或整个句子。
根据其作用可分为时间、地点、原因、条件、目的、结果、让步、方式和比较等从句。
状语从句一般由连词(从属连词)引导,也可以由词组引起。
从句位于句首或句中时通常用逗号与主句隔开,位于句尾时可以不用逗号隔开。
状语从句的种类状语从句可分为:1.时间状语从句;(adverbial clause of time)2.地点状语从句;(adverbial clause of place)3.原因状语从句;(adverbial clause of cause)4.条件状语从句;(adverbial clause of condition)5.目的状语从句;(adverbial clause of purpose)6.让步状语从句;(adverbial clause of concession)7.比较状语从句;(adverbial clause of comparison)8.方式状语从句;(adverbial clause of manner)9.结果状语从句。
(adverbial clause of result)[编辑本段]状语从句的时态特点一般情况下,时间和条件状语从句的谓语动词一般用“一般现在时”表示“一般将来时”,用“现在完成时”表示“将来完成时”。
例如:I will call you as soon as I arrive in Beijing. 我一到北京就给你打电话。
(这是由as soon as引导的时间状语从句,从句中的谓语动词arrive是一般现在时,表示一般将来时,决不可用will arrive)As soon as I have finished this work, I will go home. 我一完成此工作,就回家。
(从句中的谓语动词用现在完成时have finished,表示将来完成时,决不可用will have finished)If he comes back, please let me know.如果他回来了,请通知我。

非谓语动词作状语高考对非谓语动词作状语的考查多与对动词其他形式的考查同时进行主要包括以下几个方面的内容:1.不定式作状语;2.-ing分词作状语;3.-ed分词作状语。
一、不定式结构作状语不定式结构作状语通常有以下几种情况:1、目的状语(分词一般不能作目的状语)He bought a bicycle to go to town more quickly .To catch the train ,she hurried through her work注:表目的的不定式还常与so as或in order连用,构成so as (not) to do和in order (not) to do 结构,其中so as (not) to do 不能用于句首。
To get there in time, we got up very early.= In order to get there in time, we got up very early.= We got up very early (in order/so as) to get there in time.2、原因状语不定式结构作原因状语常用在作表语用的形容词后。
I’m sorry to hear that .We’re proud to b e young people of China .We are glad to hear the news.3、结果状语不定式结构作结果状语,有时表示未曾预料到的、或令人不快的结果。
(常和only连用)。
He ran all the way to the station ,only to find the train had left .★而现在分词作结果状语常常是可以预料的结果,是伴随谓语动词而产生的自然结果The police opened fire ,killing the robber .He died ,leaving his wife with five children .4. 有时,不定式还可修饰一个句子,表明说话人的态度。

非谓语——作定语和状语一.考点概述:本考点是近几年高考全国卷中考查的重点也是难点,主要是考查非谓语的三种形式即doing; done; to do在句中的用法;考查形式:语法填空和短文改错;其次就是阅读理解和完型填空中长难句以及书面表达等二.考点聚焦1.作定语功能:相当于形容词,修饰名词,在句中作定语位置:一般位于名词之后,没有逗号隔开例如: She is the girl living in China.(作定语)2. 作状语功能:在句中作为插入语,表示伴随;位置:一般也是位于名词或某个句子后,有逗号隔开;例如:She is the girl , living in China.(作状语)三.考点精讲1.doing: 表示主动,进行,性质;2.done:表示被动,完成,状态;3.to do: 表示目的,将来;1)作定语例如:(1)There is the man standing under the tree.(这里the man与stand之间构成的是主动关系,所以用doing形式即standing)(2) That is the bike repaired by Tom.(这里the bike与repair之间构成是被动关系,所以用done的形式即repaired)(3) There is a party to be held next week.( 这里有next week表示将来,所以用to do 形式)2) 作状语(1)在句中或句尾用逗号隔开的例如:Tom, living in China, invented the bike.(作插入语)There is the man, standing under the tree.That is the bike, repaired by Tom.注意:用done或是doing还是依据句中的某个名词或是整个句子与动词间的关系(2) 在句子的开头,用逗号隔开例如:Knowing that he is a student, we try our best to help him.(这里we与know之间是主动关系,所以是doing形式)Absorbed in painting, John didn’t notice evening approaching.(这里John与absorb之间构成被动关系,所以是done形式)To complete the job in time, the staffs were working on weekends.(这里表示目的关系,用to do形式)(3)with +sth+doing/done/to do的结构,表示伴随(看sth与动词间关系)例如:With the society developing rapidly, +句子。
高中英语秋季班(教师版)11 / 6初三英语同步课程秋季班-高中英语-复习课-写作技巧22 / 6初三英语同步课程秋季班-高中英语-复习课-写作技巧v1.0 可编辑可修改33 / 6初三英语同步课程 秋季班-高中英语-复习课-写作技巧一、用动词的适当形式填空:非谓语动词作状语大多相当于一个状语从句A.作时间状语:eg.)①_______ (hear) the bad news, they couldn’t help crying.= _______________, they couldn’t help crying.②When/ While( _____ _____ ) ____ (take) around the city, we were deeply impressed by the city’s new look.While/When (I was) _____ (wander) through the square, I caught sight of a snake-charmer. ③_______ (finish) his work, he went home.=_____________, he went home.B.作原因状语:Eg.) ①_____ (be poor), he could not afford to travel abroad.=____________, he could not afford to travel abroad.________ (encourage) by his heroic deeds, they worked harder._______ (lose) in thought, he almost ran into a post.________ (frighten) by the big forest fire, the animals all ran away._____ (not know) her address, we couldn't get in touch with her.②______ (never be) to the city, he soon got lost._________ (not receive) his letter, I decided to call him up.知识点讲解=_____________.C.方式/伴随状语;Eg.)①She watched the film, _____ (weep ) and ___ (sigh).②The teacher stood there, ______ (surround) by a lot of students.D.作条件状语:Eg.)①______ (give) another chance, I would have done the job far better.=______________ , I would have done the job far better.②(If) _____ (play) all day, you will waste your valuable time.E.作结果状语:(意料中的结果)Eg.)① The hunters fired, _____(shoot) one of the wolves.②The bus was held up by the snowstorm, thus _____ (cause) the delay.区别: 不定式表示意外的结果eg.) He hurried to the station, only ____ (find) the train had left.F.作让步状语:Eg.)①Though ____ (rain) heavily, it cleared up very soon.= _____________, it cleared up very soon.②Though _____ (tell) of the danger, he still risked his life to save the boy.分词作状语时, 需注意事项:A.分词短语作状语时,它的逻辑主语通常应是________ :____ (see) from the hill, the city is beautiful.___ (see) from the hill, you can see the whole city二、使用doing和done简化以下状语从句:44 / 6初三英语同步课程秋季班-高中英语-复习课-写作技巧1.When arriving, send me a telegram. (When you arrive, send me a telegram.) 到达之后,来个电报。
考研英语的六种状语从句考研英语的六种状语从句考研英语中的六种状语从句你了解和复习多少啦,今天就让我们一起走进状语从句的世界吧。
状语从句的主要功能是做主语的状语,由完整的主谓句构成。
以下我们来看看状语从句的种类以及每种不同种类的状语从句的`连接关键词:条件转语从句:1)though:可以倒装2)although:不可倒装,必须放在句首3)even if = even though4)as → 必须倒装1.如果动词,现在分词提前放在句首,谓语要补加助动词do does will2.作表语用的单数可数名词放在句首时,该名词前不加冠词。
eg:Fool as Jane is,she could not have done such thing.3.Much 提前时必须用as ,Much as “尽管非常”(副词作状语)5)while1.从句放在主句之前2.“尽管、虽然”3.表达并列的转折(即主语与从句的动作是同时发生的) whether——or 无论——还是6)no matter how = however (however更广泛)(也可把however换成what、how、where、when)7)译成“尽管”as...as (as) much as for all (that) despite / in spite of the fact that8)译成“即使”assuming that / granting (granted) that /比较状语从句:1)adj. adv.比较级、最高级的用法2)比较级前的修饰语:many much far / a little / a bit / slightly / a great deal / a lot / somewhat / rather3)数词+名词+比较级+than4)本身有“比......年长”、“比......优越”等含义→ infinite superior senior 和to 连用高中语法总结5)本身有“最、极”等含义→ absolute / unique / infinite / round / right /correct / wrong / perfect6)Of a +noun =adj 用more修饰 Eg. He is more of a doctor 他更像个医生7)最高级前的限定词:the 物主代词(作表语不加限定词Her theory is most convincing.)8) the more1....the more “越---越”2.(not) so/as——as “如同......一样,不如“3.the same(...) as “和......一样”4.A not any more than B = A no more than B“正如A不能......B也不能......”5.not...more A than B “与其说是--- 不如说是---”6.not so much...as...“与其......不如......“7.A is to B what C is to D8.as...as possible / one can(could) / can be“尽可能地......”9.no more than= not as...as(不)像…一样10.no less than= as...as时间状语从句:1)when表示“当…的时候”,指一个时间点(段)或持续的动作2)while表示“在…的同时”,只能表示持续性的动作或状态,不表示瞬间的动作。
状语从句一、状语从句概述状语从句是在句中起副词作用的主谓结构。
用来修饰主句中的动词、形容词、副词等。
引导状语从句的关联词是从属连词。
状语从句用陈述语序,一般位于复合句的句首或句末。
当从句在句首时,常用逗号和主句隔开。
状语从句根据其在句中的不同作用分别表示时间、地点、原因、目的、结果、条件、让步、行为方式等,共九种。
(一)when, whenever, while和as引导的时间状语从句when表示的动作与主句的动作同时发生,或先于主句的动作。
When可指一段时间,也可指一点时间,既可以表示一时性的动作,又可表示持续的动作。
Whenever指的是任何一个不具体的时间。
while常用来引导两个同时进行的持续时间较长的动作或状态,不能表示一时性或短暂的动作。
as表示的动作与主句同时发生,具有延续的含义,一般同延续性动词连用。
while和as可译为“一边……一边”。
Whenever my mother or I need a permanent or trim we visited her dear Amalia Toland.As the day progressed, I considered ways to get out of whatever was going down at the Cullen House tonight.Whenever we met with difficulties, they came to help us.When I meet the right man, I will get married.As spring warms the good earth, all flowers begin to bloom.He entered the room when/ while/ as the meeting was going on.When/As he finished the speech, the audience burst into applause.Tom watched TV as he had supper.注意:When和while可用作并列连词,when含义为“突然、这时”;while含义为“而,但是”。
doing done作状语当"doing" 或"done" 充当状语时,它们可以用来表示某个动作或状态的方式或时间。
以下是这两个词作为状语的一些例子:1. "Doing" 作为状语:•"Doing the dishes" (在洗碗时)•"Doing the laundry" (在洗衣服时)•"Doinghomework" (在做作业时)•"Doing research" (在研究时)2. "Done" 作为状语:•"When the job is done" (当工作完成后)•"Once the meal is done" (一旦饭菜做好后)•"If the task is done properly" (如果任务完成得当的话)•"When the project is done" (当项目完成时)需要注意的是,"doing" 和"done" 在充当状语时,通常会与相应的动词或形容词搭配使用,以表达完整的意思。
例如,"Doing the dishes" 指的是正在进行的洗碗动作,"When the job is done" 指的是工作完成的状态。
同时,"done" 还经常用在被动语态的句子中,表示某个动作已经被完成,例如"The homework is done" (作业已经完成了)。
因此,"done" 可以表示过去某个时间发生的动作,而"doing" 则表示正在进行的动作。
状语从句在复合句中作状语的从句叫状语从句。
状语从句有时间、地点、原因、目的、结果、条件、方式、比较、让步等种类。
一、时间状语从句引导时间状语从句的连接词有: when, as, while, after, before, since, ever since, as soon as, once, till, until, whenever, no sooner…than, hardly/scarcely...when, themoment/minute/instant/second, every time, each time, any time, the first time, next time, last time, all the time, by the time, directly, immediately, instantly等。
1.表示“一···就···”的句型1) as soon as/onceAs soon as he arrives, I'll call you.他一到,我就给你打电话。
(as soon as 侧重时间或动作先后衔接紧,而once侧重条件,表示“一旦...”)2) on doing sth/on one's + n.作时间状语On arriving at the station, the thief was arrested.一到达车站,这个小偷就被逮捕了。
On his arrival in Paris, he was recognized as a noble and thrown into prison. 他一到达巴黎,就被认出是一个贵族,并被投入监狱。
3) no sooner ...than , hardly/scarcely...when它们表“一…就”。
结构中的否定词放在句首时,主句要倒装。
having been done 和done作状语摘要:I.引言- 介绍“having been done”和“done”作状语的概念II.“having been done”作状语- 定义及作用- 举例说明III.“done”作状语- 定义及作用- 举例说明IV.总结- 回顾“having been done”和“done”作状语的特点和用途- 强调在英语写作中使用状语的重要性正文:【引言】在英语语法中,状语是用来修饰动词、形容词、副词或整个句子的成分,表示时间、地点、原因、结果等关系。
其中,“having been done”和“done”作为状语,在英语写作中有着广泛的应用。
本文将详细介绍这两种状语的定义、作用及举例说明。
【I.“having been done”作状语】“having been done”作为状语,通常表示动作在谓语动词之前发生,强调动作的完成。
例如:1.The room was cleaned before I entered.(我进入房间之前,房间已经被打扫干净了。
)在这个例子中,“was cleaned”是谓语动词,而“before I entered”是一个时间状语从句,用“having been done”来表示“房间被打扫干净”的动作在“我进入房间”的动作之前发生。
【II.“done”作状语】“done”作为状语,通常表示动作已经完成。
例如:1.The cake has been baked.(蛋糕已经被烤好了。
)在这个例子中,“has been baked”是谓语动词,而“The cake”是主语。
这里的“done”作为状语,强调蛋糕已经被烤好。
【III.总结】综上所述,“having been done”和“done”作状语在英语语法中起着重要的作用。
在英语写作中,正确使用状语能够使句子更加准确、生动。