护理常用英文缩写大全讲课稿
- 格式:doc
- 大小:33.50 KB
- 文档页数:9

护士英文缩写引言概述:护士英文缩写是指在医疗领域中常用的一些英文缩写,用于简化医疗术语和常用短语,提高工作效率和沟通准确性。
了解和掌握这些缩写对于护士们来说至关重要,本文将详细介绍护士英文缩写的四个主要部份。
一、临床护理相关缩写1.1 ADL(Activities of Daily Living):日常生活活动,指患者在日常生活中的基本活动能力,如进食、洗澡、穿衣等。
1.2 BID(Twice a Day):每天两次,常用于药物给药频率的表示,指每天需要服用两次药物。
1.3 IV(Intravenous):静脉内,用于表示药物或者液体的给药途径,通过静脉注射赋予患者治疗。
二、医学检查与诊断缩写2.1 CBC(Complete Blood Count):全血细胞计数,用于评估患者的血液状况,包括血红蛋白、白细胞计数等指标。
2.2 ECG(Electrocardiogram):心电图,通过记录心脏电活动来评估患者的心脏功能和心电异常情况。
2.3 MRI(Magnetic Resonance Imaging):磁共振成像,一种无创的医学影像技术,用于观察和诊断患者的内部器官结构。
三、药物治疗相关缩写3.1 NSAIDs(Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs):非甾体类抗炎药,用于缓解疼痛和减轻炎症反应。
3.2 PRN(Pro Re Nata):需要时赋予,常用于药物给药频率的表示,表示根据患者的需要进行给药。
3.3 OTC(Over-the-Counter):非处方药,指可以在药店等地方直接购买的药物,无需医生处方。
四、病情和护理状态相关缩写4.1 NPO(Nil Per Os):禁食,用于表示患者需要禁止口服摄入食物和液体。
4.2 SOB(Shortness of Breath):呼吸难点,用于描述患者的呼吸状况,常见于心脏和肺部疾病。
4.3 LOC(Level of Consciousness):意识水平,用于评估患者的神经系统功能,包括清醒程度和反应能力。


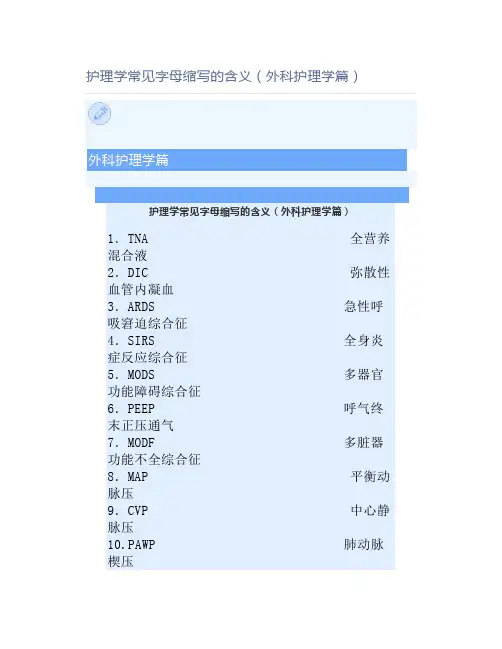
护理学常见字母缩写的含义(外科护理学篇)
外科护理学篇
护理学常见字母缩写的含义(外科护理学篇)
1.TNA 全营养混合液
2.DIC 弥散性血管内凝血
3.ARDS 急性呼吸窘迫综合征
4.SIRS 全身炎症反应综合征
5.MODS 多器官功能障碍综合征
6.PEEP 呼气终末正压通气
7.MODF 多脏器功能不全综合征
8.MAP 平衡动脉压
9.CVP 中心静脉压
10.PAWP 肺动脉
楔压
11.SB 标准碳酸氢盐
12.AB 实际碳酸氢盐
13.BB 缓冲碱
14.BE 剩余碱
15.AG 阴离子间隙
r 内生肌酐清除率
17.TAT 破伤风抗毒素
18.Dixon手术经腹直肠癌切除术
es手术经腹会阴联合直肠癌根治术
20.AFP 甲胎蛋白
21.ALP 碱性磷酸酶
22.PTC 经皮肝穿刺胆道造影
23.ERCP 经内镜逆行胰胆管造影
24.PTCD 经皮肝穿刺置管引流
25.SCA 选择性腹腔动脉造影
26.Perthes试验深静脉回流试验
27.Trendelenburg试验浅静脉及交通支瓣膜功能试验
28.BTA 膀胱肿瘤抗原
29.PSA 前列腺特异性抗原
30.KUB 尿路平片
31.IVP 排泄性尿路造影
32. ESW 体外冲击波碎石术
33.Colles骨折桡骨远端伸直型骨折
34.Smith骨折桡骨远端屈曲型骨折。



临床护理常见英文缩写一、常见药物缩写葡萄糖:GS葡萄糖氯化钠: GNS氯化钠: NaCl氯化钾: KCl生理盐水: 0.9% NaCl 或NS支链氨基酸(肝脑清): AA-BC 、复方氨基酸3AA 复方氨基酸: AA-CO 、复方氨基酸18AA青霉素:PG维生素:Vit地塞米松:DXM胰岛素:RI亚硫酸氢钠甲萘醌:Vit K3复方氯化钠:林格氏液乳酸钠林格液:平衡液盐酸布桂嗪:强痛定盐酸哌替啶:杜冷丁间羟胺:阿拉明酚妥拉明:利其丁呋塞米:速尿盐酸异丙嗪:非那根马来酸氯苯那敏:扑尔敏地西泮:安定盐酸甲氧氯普氨:胃复安二羟丙茶碱:喘定盐酸消旋山莨菪碱:654-2二、常见医嘱英文缩写qd 每日一次bid 每日两次tid 每日三次qid 每日四次qh 每小时一次q2h 每两小时一次q4h 每四小时一次q6h 每六小时一次qn 每晚一次qod 隔日一次biw 每周两次hs 临睡前am 上午pm 下午St 立即DC 停止、取消prn 需要时(长期)sos 需要时(限用一次,12小时内有效)ac 饭前pc 饭后12n 中午12点12mn午夜12点gtt 滴ID 皮内注射H 皮下注射IM 肌肉注射IV 静脉注射处方上左上角的RP代表“请取”的意思,如果某种药后面是qd、bid、tid,分别代表每日一次、每日两次、每日三次。
如果是po、m、h、v、ivgtt分别代表口服、肌肉注射、皮下注射静脉注射、静脉滴注等,还有很多。
aa——各 et——及、和Rp.——取、请取 sig./S.——用法、指示St./Stat.——立即、急速 Cit.——急速s.o.s.——需要时 p.r.n——必要时a.c.——饭前 p.c.——饭后a.m.——上午 p.m.——下午q.n.——每晚 h.s.——睡前q.h.——每小时 q.d.——每日1次B.i.d.——每日2次 T.i.d.——每日3次Q.i.d.——每日4次 q.4h.——每4小时1次p.o.——口服 ad us.int.——内服ad us.ext.——外用 H.——皮下注射im./M.——肌肉注射 iv./V.——静脉注射iv gtt.——静脉滴注 Inhal.——吸入O.D.——右眼 O.L.——左眼O.S.——单眼 O.U.——双No./N.——数目、个 s.s——一半ug.——微克 mg.——毫克g.——克 kg.——千克(公斤)ml.——毫升 L.——升q.s——适量 Ad.——加至Aq.——水 Aq.dest.——蒸馏水Ft.——配成 Dil——稀释M.D.S.——混合后给予 Co./Comp.——复方的Mist——合剂 Pulv.——散剂Amp.——安瓿剂 Emul.——乳剂Syr.——糖浆剂 Tr.——酊剂Neb.——喷雾剂 Garg.——含漱剂rtt./gutt.——滴、滴眼剂 collyr.——洗眼剂Ocul.——眼膏 Liq.——溶液剂Sol.——溶液 Lot.——洗剂Linim.——擦剂 Crem.——乳膏剂(冷霜)Ung.——软膏剂 Past.——糊剂Ol.——油剂 Enem.——灌肠剂Supp.——栓剂 Tab.——片剂Pil.——丸剂 Caps.——胶囊剂Inj.——注射剂如果是处方常用不多一般qd,qid,bid,tid,iv,ivgtt。

护士经常遇到的缩写一药物拉丁缩写:GS(葡萄糖注射液)NS(生理盐水)NG(硝酸甘油)NE(去甲肾上腺素)PG(青霉素G)SMZ(磺胺甲恶唑)SG(磺胺脒)SB(碳酸氢钠)ABOB(吗啉胍)DXM(地塞米松)PAMBA(止血芳酸)TAT(破伤风)FU(氟脲嘧啶) RFP(利福平)EM(红霉素)ISO(异丙肾上腺素)Vit(维生素)二处方缩写:tid(一日三次)bid(一日两次)qid(每天四次)qd/sid(每天一次)qn(每晚)hs(睡前)ac(饭前)Pc(饭后)aj(空腹时)am(上午)pm(下午)tid每天3次qh每小时一次q2h每小时两次q4h每小时三次q6h每小时六次st立即执行 prn需要时(长期) sos需要时(限用一次,12小时内有效)ID皮内注射 H皮下注射IM肌内注射IV 静脉注射1.胃管肛门排气,肠蠕动恢复,每种手术时间不一样,胃部手术大约3-7天.2.尿管术后能下床自行排尿,先要进行膀胱括约肌的训练,扎住尿管后有需要小便的感觉。
有些会阴部、直肠或泌尿系手术根据个人情况。
3.腹腔负压球术后7-10天左右,引流量逐渐减少,24小时少于20毫升,颜色有鲜红转为淡红或无色。
4.T型管:“T”型管放置十天以上可先夹闭引流管,必要时做胆囊造影,如确定胆管下端已通畅(夹闭时无不适症状)时,一般两周后可以拔管。
根据黄志强的手术学是胃管留置到胃肠功能畅通为止尿管留置到可以自己排尿为止肛管留置到可以自己解大便为止引流管留置到没有引流物为止我理解的就是到不需要为止是不是有点废话???拔管时间(六版外科)乳胶片在术后1-2天烟卷引流4-7天T型管14天胃肠减压管在肛门排气后在临床上,引流管拔除的时间根据每位医生的习惯有所不同.橡皮片引流:一般用于浅表伤口引流,目的是防止皮下积血、积液,术中应防止皮片被缝线缝在皮下而致拨除困难,术后应妥善固定,24~48h后可拨除。
胃肠减压管:根据患者病情若为非胃肠道的腹部手术(如:肝胆手术)则患者肠鸣音恢复即可拔管,若为胃肠道手术,特别是有吻合口的胃肠道手术则必须待肛门恢复排气后方能考虑拔管尿管术后能下床自行排尿,先要进行膀胱括约肌的训练,扎住尿管后有需要小便的感觉。

护士英文缩写引言概述:在医疗领域中,护士们经常使用各种英文缩写来简化和快速传递信息。
这些缩写在医疗记录、护理计划和医疗报告中广泛使用。
本文将介绍一些常见的护士英文缩写,以帮助护士们更好地理解和运用这些缩写。
一、病情和症状相关的缩写1.1 ROS(Review of Systems):系统回顾,用于描述病人的身体系统状况。
1.2 SOB(Shortness of Breath):呼吸困难,表示患者感到呼吸不畅或气短。
1.3 N/V(Nausea/Vomiting):恶心/呕吐,指患者出现恶心或呕吐症状。
二、医疗程序和药物相关的缩写2.1 IV(Intravenous):静脉内,用于描述给药途径,表示药物通过静脉注射。
2.2 CPR(Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation):心肺复苏,指急救人员通过按压胸部和进行人工呼吸来恢复心脏和呼吸功能。
2.3 NPO(Nil Per Os):禁食,表示患者不能进食或饮水。
三、检查和测试相关的缩写3.1 ECG(Electrocardiogram):心电图,用于记录心脏电活动的图形。
3.2 CBC(Complete Blood Count):全血细胞计数,用于评估患者的血液状况。
3.3 MRI(Magnetic Resonance Imaging):磁共振成像,一种用于生成身体内部图像的无创检查方法。
四、疾病和疾病管理相关的缩写4.1 COPD(Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease):慢性阻塞性肺疾病,一组慢性呼吸系统疾病的统称。
4.2 UTI(Urinary Tract Infection):尿路感染,指泌尿系统的感染疾病。
4.3 DM(Diabetes Mellitus):糖尿病,一种慢性代谢性疾病。
五、身体部位和医疗设备相关的缩写5.1 CNS(Central Nervous System):中枢神经系统,包括大脑和脊髓。

护理知识点缩写总结在医学和护理领域中,缩写常常用于简洁地描述各种概念、治疗方法、疾病名称等。
对于护士来说,熟悉并掌握这些缩写是非常重要的,因为它们经常出现在护理记录、医嘱等文件中。
本文将对一些常见的护理知识点缩写进行总结,以便护士们更好地了解和使用这些缩写。
1. 基础护理缩写常见的基础护理缩写包括:- ADL:活动日常生活(Activities of Daily Living)- VS:生命体征(Vital Signs)- C&S:培养和敏感性测试(Culture and Sensitivity)- Fx:骨折(Fracture)- I&D:切开和引流(Incision and Drainage)- IV:静脉内(Intravenous)- NGT:鼻胃管(Nasogastric Tube)- NPO:禁食(Nothing by Mouth)- PRN:需要时(As Needed)2. 疾病和症状缩写对于常见的疾病和症状,也有一些常见的缩写,包括:- CAD:冠状动脉疾病(Coronary Artery Disease)- COPD:慢性阻塞性肺疾病(Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease)- DM:糖尿病(Diabetes Mellitus)- HTN:高血压(Hypertension)- MI:心肌梗死(Myocardial Infarction)- URI:上呼吸道感染(Upper Respiratory Infection)- UTI:泌尿道感染(Urinary Tract Infection)3. 药物和治疗缩写常见的药物和治疗缩写包括:- ABX:抗生素(Antibiotics)- ASA:阿司匹林(Aspirin)- BID:每日两次(Twice Daily)- HRT:激素替代治疗(Hormone Replacement Therapy)- PT:理疗(Physical Therapy)- Sx:手术(Surgery)- Tx:治疗(Treatment)4. 诊断和检查缩写对于一些常见的诊断和检查,也有一些常见的缩写,包括:- CXR:胸部X射线(Chest X-ray)- EKG:心电图(Electrocardiogram)- MRI:磁共振成像(Magnetic Resonance Imaging)- RBC:红细胞计数(Red Blood Cell Count)- WBC:白细胞计数(White Blood Cell Count)- Dx:诊断(Diagnosis)- Rx:处方(Prescription)5. 专业术语缩写在医学领域中,有一些专业术语的缩写也经常出现在护理记录中,如:- ICU:重症监护病房(Intensive Care Unit)- ER:急诊室(Emergency Room)- NICU:新生儿特别护理病房(Neonatal Intensive Care Unit)- OR:手术室(Operating Room)- PICC:经皮中心静脉导管(Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter)- PPE:个人防护装备(Personal Protective Equipment)总结以上是一些常见的护理知识点缩写总结,熟悉并掌握这些缩写对于护士们来说非常重要。
了解护理术语常见的医学缩写解析在医疗领域,各种缩写术语被广泛使用,其中护理术语的医学缩写尤为常见。
对于不熟悉这些缩写的人来说,阅读和理解相关文献和文件可能会变得困难。
因此,本文将为您详细解析一些常见的护理术语医学缩写,以帮助您更好地了解和应用于实践。
1. ADLs: 日常生活活动(Activities of Daily Living)ADLs是指人们日常生活中必须进行的基本活动,包括洗漱、进食、穿衣、行走等。
这些活动在疾病或伤残等情况下可能受到限制,因此了解ADLs的概念和相关缩写,在评估病人的日常生活能力时非常有用。
2. BID: 双倍(Twice a day)BID是医学缩写,意味着一个药物需要每天两次使用。
了解这一缩写可帮助护士和医生准确控制药物使用的频率,并确保病人按照规定用药。
3. C/O: 抱怨(Complains Of)C/O是用于记录患者所抱怨的症状或不适的缩写。
这一术语广泛应用于病人的病历和护理评估中,帮助医务人员了解病人的主要问题。
4. DNR: 不进行复苏(Do Not Resuscitate)DNR用于标示病人不希望在心脏骤停等紧急情况下接受复苏措施。
了解这一缩写对于遵循病人的意愿以及进行合适的医疗决策至关重要。
5. EHR: 电子病历(Electronic Health Record)EHR是指电子化的病人健康记录系统。
在当今数字化时代,越来越多的医疗机构采用EHR系统来存储和管理病人的健康信息。
了解EHR的含义和应用可以帮助护士和其他医务人员更好地处理病人数据。
6. IV: 静脉内(Intravenous)在医疗环境中常见的IV缩写表示将药物或液体通过插管注入静脉。
护士和医生需要了解这一缩写,以确保正确地给予药物和液体治疗。
7. NPO: 禁食(Nil Per Os)NPO用于指示病人在一定时间内禁止饮食。
这可能是为了医疗手术、检查或者其他特殊治疗而需要病人空腹的情况。
护理常用英文缩写(原创实用版)目录1.引言:介绍护理常用英文缩写的重要性2.常见护理英文缩写分类2.1 医疗机构和专业术语2.2 疾病和症状2.3 药物和治疗2.4 医疗设备和器械2.5 护理操作和程序3.缩写的使用和规范4.结论:总结护理常用英文缩写的应用价值正文一、引言在现代护理工作中,英文缩写被广泛应用于医疗记录、护理文件以及医护人员之间的沟通,极大地提高了工作效率。
熟练掌握这些常用英文缩写,对于护理人员来说具有重要意义。
本文将介绍护理常用英文缩写的分类和使用规范。
二、常见护理英文缩写分类1.医疗机构和专业术语(1)ICU:Intensive Care Unit,重症监护室(2)CCU:Coronary Care Unit,冠心病监护室(3)NICU:Neonatal Intensive Care Unit,新生儿重症监护室2.疾病和症状(1)COPD:Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease,慢性阻塞性肺疾病(2)MI:Myocardial Infarction,心肌梗死(3)CP:Cerebral Palsy,脑瘫3.药物和治疗(1)NSAID:Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drug,非甾体抗炎药(2)DNA:Deoxyribonucleic Acid,脱氧核糖核酸(3)PCI:Percutaneous Coronary Intervention,经皮冠状动脉介入治疗4.医疗设备和器械(1)ECG:Electrocardiogram,心电图(2)BP:Blood Pressure,血压(3)SPO2:Saturation of Peripheral Oxygen,外周血氧饱和度5.护理操作和程序(1)PIV:Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter,外周插入中心静脉导管(2)Foley Catheter:福莱氏导尿管(3)CPAP:Continuous Positive Airway Pressure,持续正压通气三、缩写的使用和规范在实际应用中,护理英文缩写应遵循以下规范:1.确保准确性:使用正确的缩写,避免歧义。
护理常用英文缩写摘要:1.护理常用英文缩写的概述2.常用护理英文缩写的分类3.护理英文缩写的实际应用4.学习护理英文缩写的重要性正文:1.护理常用英文缩写的概述在护理专业的学习和工作中,英文缩写是非常重要的,它们可以提高沟通效率,减少错误的发生。
护理常用英文缩写涵盖了众多领域,如疾病诊断、药物治疗、护理操作等。
熟练掌握这些缩写,对于护理人员来说,是提高工作效率和准确性的关键。
2.常用护理英文缩写的分类(1)疾病诊断缩写:例如,COPD 代表慢性阻塞性肺病,MI 代表心肌梗死。
(2)药物治疗缩写:例如,NSAID 代表非甾体抗炎药,ATP 代表腺苷三磷酸。
(3)护理操作缩写:例如,BP 代表血压,Pulse 代表脉搏。
(4)其他相关缩写:例如,IQ 代表智商,PIO 代表输入输出。
3.护理英文缩写的实际应用在护理实践中,英文缩写被广泛应用。
例如,在记录患者病情时,护理人员会使用缩写来表示患者的疾病诊断、药物治疗情况和护理操作结果。
这样可以提高记录的效率,减少错误。
此外,护理英文缩写在学术论文和书籍中也有广泛应用。
熟练掌握这些缩写,可以帮助护理人员更快速地理解相关文献,提高自身专业素养。
4.学习护理英文缩写的重要性学习护理英文缩写对于护理人员来说具有重要意义。
首先,熟练掌握英文缩写可以提高护理人员的专业素养,增强其在同行中的竞争力。
其次,英文缩写可以提高护理工作的效率,减少错误的发生。
最后,学习护理英文缩写有助于护理人员更好地与国际接轨,了解国际护理发展的最新动态。
总之,护理常用英文缩写在护理工作中具有重要作用。
熟练掌握这些缩写,可以提高护理人员的工作效率和准确性,提升专业素养。
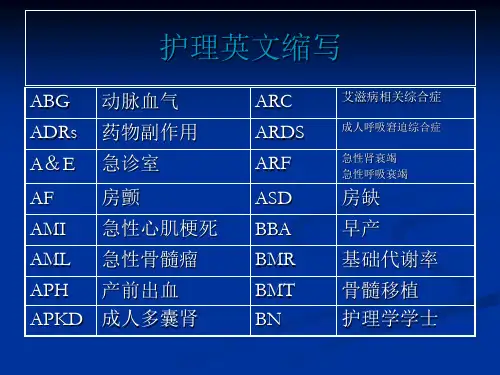
护理常用英文缩写大全IV intravenous injection IM intramuscular injection PO per oral/by mouthNG nasogastricIT intrathecalPR per rectumPV per vaginaSUBCUT subcutaneousGutt eye dropTop MA topical metered aerosalNeb nebulizerNED nebulizerSubling sublingualMDI/metered dose inhaler/inhaler metered dose inhaler mL millilitermgg microgram milligramgramwrite microgram 'in fullac bd tds Qid before food twice daily three times daily four times dailyc gttmane mist nocte with drops morning mixture nightpc PRNqhq2hq4hq6hq8h stat after meals as required every hour every 2 hoursevery 4 hours every 6 hours every 8 hours immediately ung ointmentunit(s) international unit(s)AEAFAIAPASASADLABGAFBASDAMIAVDAVRARFAIDS ARDS APTTAdmAlbA flutter Angios AV Block As tolair entryatrial fibrillationaortic incompetenceangina pectorisaortic stenosisaortic stenosisactivities of daily livingarterial blood gasacid fast bacilliatrial septal defectacute myocardial infarctionaortic valve diseaseaortic valve replacementacute heart failureacquired immune deficiency syndrome acute respiratory distress syndrome activated partial thromboplastinadmissionalbumenatrial fluttercoronary angiogramsatrio ventricular blockAs toleratedBE BiPAP Bronch BCC BUSE BasoBiliBld Cult. BBBBOBNO BIBA BMBSL/BGL BPBUN base excessbilevel positive airway pressure bronchoscopy basal cell carcinomablood urea & serum electrolytes blood level basophilsbilirubinBlood culturebundle branch blockbowels openbowels not openbrought in by ambulancebowel movementblood sugar/glucose levelblood pressureblood urea nitrogenbiopsyCAL COAD CPAPCaCTD CWMSCa++ Card. EnZ. CKCICreatC/S CABG CADCCFCHDCPRCVACVLCVPCSFCCUCATCXRCVPCO COPDchronic airflow limitationchronic obstructive airway disease continuous positive airway pressure cancercarpel tunnel decompression colour, warmth, movement, sensation calcium Cardiac enzymes creatine kinase chloride creatinineculture and sensitivitycoronary artery bypass graftcoronary artery disease congestive cardiac failure congenital heart disease cardio pulmonary resuscitation cerebral vascular accidentcentral venous linecentral venous pressure cerebrospinal fluidcardiac or critical care unit computed axial tomography chest X-Raycentral venous pressure cardiac output chronic obstructive pulmonary diseaseDNA DD D/C DNCBDOBDXTDiffDVT d DD& CD5Wdid not attenddangerous drug discharge domiciliary nursing care benefit date of birthdeep X-Ray therapy differentialdeep vein thrombosisday dosedilatation and curettage 5% dextrose in waterBxEPS EUA ESR Echo ER ECG electrophysiological studies examination under anaesthetic erythrocyte sedimentation rate echocardiographyemergency room electrocardiogramFBCFUO FHx Fx# FNAB FEV FVC FWBfull blood countfever of unknown origin family historyfracturefine needle aspiration biopsy forced expiratory volume forced vital capacity full weight bearingGTTG GIT GCS GA glucose tolerance test gramgastro intestinal tract Glasgow coma scale general anaestheticHACCHNPU HR Hx Hb HCO3 HRT HSV home and community care has not passed urine heart rate historyhaemoglobinbicarbonatehormone replacement therapy herpes simplex virusIDC IVT IV IM ICU IABA IHD IVC ICC IPPV indwelling catheter(urinary) intravenous therapyintravenousintramuscularintensive care unitintra aortic balloon pumpischaemic heart diseaseintravenous catheterintercostals catheterintermittent positive pressure ventilationJVP jugular venous pressure K+ potassiumLVF LGL LFT S LCA LHC LV LFT LUL LLL LFTleft ventricular failurelowne ganong Levine syndrome liver function tests leftcoronary arteryleft heart catheterleft ventriclelung function testleft upper lobeleft lower lobeliver function testMUA MAP MIM/C/S M/S/U MVA MRSA MIMS MVR MVD MSA Mm HGmanipulation under anaestheticmean arterial pressuremyocardial infarctionmicroscopic/culture/sensitivitymid stream urinemotor vehicle accidentmethicillin resistant staphylococcus aureus mitral incompetence mitral stenosismitral valve replacementmitral valve diseasemental state assessmentmillimeters of mercuryNGTNSNONAD NBM/NPO NGT NIDDM NKA NOFN/G tube NWBNa+NaClnasogastric tubenormal salinenil orallynil abnormalities detectednil by mouthnaso gastric tubenon-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus(better to use Type 2 DM) no known allergiesneck of femurnaso-gastric tubenon weight bearingsodiumsodium chlorideO2 Obs OE OR ORIF OT O/A oxygenobservationon examinationoperating roomopen reduction and internal fixation occupational therapy/ operating theatre on admissionPAC Pre-med PD PICC PUPO2 PTE POP PathPTPDA PVDPSPE PCA PEEP PR PTCA PEG PNDpressure area carepre-medicationprovisional diagnosis/patient diagnosis/peritoneal dialysis peripherally inserted cardiac catheterpassed urinepartial pressure of oxygenpulmonary thrombotic embolusplaster of parispathologyprothrombin timepatent ductus arteriosusperioheral vascular diseasepulmonary stenosispulmonary embolus/physical examinationpatient controlled analgesiapositive end-expiratory pressurepulse ratepercutaneous transluminal coronary angioplastypercutaneous endoscopic gastronomy tubeparoxysmal nocturnal dyspnoea/postnatal depressionRO RLL RUL ROM RR RFTRMZ RA RCA RV RTW RIB RBC's removal ofright lower lobe right upper lobe range of movement respiratory rate respiratory function test right mid zone right atrialright coronary artery right ventriclereturn to ward rest in bedred blood cellsRVFRTIROSright ventricular failure respiratory tract infection removal of suturesSA SBE SR SB ST SVT sinoatrialsubacute bacterial endocarditis sinus rhythmsinus brachycardiasinus tachycardiasupra ventricular tachycardiaSOB/SOBE shortness of breath/shortness of breath on exertionSOOB SaO2 SCC SV SNS sit out of bedoxygen saturations squamous cell carcinoma stroke volume sympathetic nervous systemTTB TKR THR TURP Tx TAH TPR TAT TLC TV TIA TPN TGA TOF temperaturetuberculosistotal knee replacementtotal hip replacementtransuretheral resection of the prostate treatmenttotal abdominal hysterectomy temperature, pulse & respiration transaxillary thoracotomytotal lung capacitytidal volumetransient ischaemic attacktotal parental nutritiontransposition of great arteriestetralogy of fallotUA URTI UTI UWSD urinalysisupper respiratory tract infection urinary tract infection under water sealed drainageVF VT VC VSD ventricular fibrillation ventricular tachycardia vital capacity ventricular septal defectWCC white cell count。
护士英文缩写引言概述:在医疗领域中,护士扮演着至关重要的角色。
为了提高工作效率和沟通效果,护士们经常使用英文缩写。
本文将介绍一些常见的护士英文缩写,以便更好地理解和运用。
一、患者相关缩写1.1 PT:患者(Patient)- PT是护士们常用的患者缩写,用于代表病房或诊所中的病人。
在医疗记录中,护士可能会使用PT来标识患者的基本信息,如姓名、年龄和性别。
1.2 Hx:病史(History)- Hx是指患者的病史,包括既往疾病、手术历史、过敏反应等。
护士在与医生或其他护士交流时,常常使用Hx来简洁地描述患者的病史信息。
1.3 CC:主诉(Chief Complaint)- CC是指患者最主要的症状或问题,通常是患者在就诊时所描述的原因。
护士在接待患者时,会记录下患者的主诉,以便医生进行进一步的评估和治疗。
二、医疗设备缩写2.1 BP:血压(Blood Pressure)- 护士经常测量患者的血压,以评估患者的健康状况。
BP缩写常用于护士的护理记录中,用于记录患者的血压数值。
2.2 ECG:心电图(Electrocardiogram)- ECG用于检测患者的心脏功能,并记录下心电图结果。
护士在进行心电图检查时,会使用ECG缩写,以便在医疗记录中标识相关信息。
2.3 IV:静脉注射(Intravenous)- 护士常常需要给患者进行静脉注射,以输送药物或液体。
IV是护士们常用的静脉注射缩写,用于记录患者的静脉注射情况。
三、药物相关缩写3.1 PRN:需要时使用(Pro Re Nata)- PRN是指根据需要使用药物的意思。
护士在给患者开具药物医嘱时,可能会使用PRN缩写,表示患者只在需要时才使用该药物。
3.2 PO:口服(Per Os)- PO是指通过口服给药的方式。
护士在记录患者的用药情况时,可能会使用PO缩写,以标识患者所需的口服药物。
3.3 IM:肌肉注射(Intramuscular)- IM是指通过肌肉注射给药的方式。
护理常用英文缩写大全IV intravenous injectionIM intramuscular injectionPO per oral/by mouthNG nasogastricIT intrathecalPR per rectumPV per vaginaSUBCUT subcutaneousGutt eye dropTop topicalMA metered aerosalNeb nebulizerNED nebulizerSubling sublingualMDI/metered dose inhaler/inhaler metered dose inhaler mL millilitermg milligramg grammicrogram write ‘microgram’ in fullac before foodbd twice dailytds three times dailyQid four times dailyc withgtt dropsmane morningmist mixturenocte nightpc after mealsPRN as requiredqh every hourq2h every 2 hoursq4h every 4 hoursq6h every 6 hoursq8h every 8 hoursstat immediatelyung ointmentunit(s) international unit(s)AE air entryAF atrial fibrillationAI aortic incompetenceAP angina pectorisAS aortic stenosisAS aortic stenosisADL activities of daily livingABG arterial blood gasAFB acid fast bacilliASD atrial septal defectAMI acute myocardial infarctionAVD aortic valve diseaseAVR aortic valve replacementARF acute heart failureAIDS acquired immune deficiency syndrome ARDS acute respiratory distress syndrome APTT activated partial thromboplastinAdm admissionAlb albumenA flutter atrial flutterAngios coronary angiogramsAV Block atrio ventricular blockAs tol As toleratedBE base excessBiPAP bilevel positive airway pressureBronch bronchoscopyBCC basal cell carcinomaBUSE blood urea & serum electrolytes blood level Baso basophilsBili bilirubinBld Cult. Blood cultureBBB bundle branch blockBO bowels openBNO bowels not openBIBA brought in by ambulanceBM bowel movementBSL/BGL blood sugar/glucose levelBP blood pressureBUN blood urea nitrogenBx biopsyCAL chronic airflow limitationCOAD chronic obstructive airway disease CPAP continuous positive airway pressure Ca cancerCTD carpel tunnel decompression CWMS colour, warmth, movement, sensation Ca++ calciumCard. EnZ. Cardiac enzymesCK creatine kinaseCI chlorideCreat creatinineC/S culture and sensitivityCABG coronary artery bypass graftCAD coronary artery diseaseCCF congestive cardiac failureCHD congenital heart diseaseCPR cardio pulmonary resuscitationCVA cerebral vascular accidentCVL central venous lineCVP central venous pressureCSF cerebrospinal fluidCCU cardiac or critical care unitCAT computed axial tomographyCXR chest X-RayCVP central venous pressureCO cardiac outputCOPD chronic obstructive pulmonary disease DNA did not attendDD dangerous drugD/C dischargeDNCB domiciliary nursing care benefit DOB date of birthDXT deep X-Ray therapyDiff differentialDVT deep vein thrombosisd dayD doseD& C dilatation and curettageD5W 5% dextrose in waterEPS electrophysiological studies EUA examination under anaesthetic ESR erythrocyte sedimentation rate Echo echocardiographyER emergency roomECG electrocardiogramFBC full blood countFUO fever of unknown origin FHx family historyFx# fractureFNAB fine needle aspiration biopsy FEV forced expiratory volume FVC forced vital capacityFWB full weight bearingGTT glucose tolerance testG gramGIT gastro intestinal tractGCS Glasgow coma scaleGA general anaestheticHACC home and community care HNPU has not passed urineHR heart rateHx historyHb haemoglobinHCO3 bicarbonateHRT hormone replacement therapy HSV herpes simplex virusIDC indwelling catheter(urinary) IVT intravenous therapyIV intravenousIM intramuscularICU intensive care unitIABA intra aortic balloon pump IHD ischaemic heart diseaseIVC intravenous catheterICC intercostals catheterIPPV intermittent positive pressure ventilationJVP jugular venous pressureK+ potassiumLVF left ventricular failureLGL lowne ganong Levine syndromeLFT’s liver function testsLCA left coronary arteryLHC left heart catheterLV left ventricleLFT lung function testLUL left upper lobeLLL left lower lobeLFT liver function testMUA manipulation under anaestheticMAP mean arterial pressureMI myocardial infarctionM/C/S microscopic/culture/sensitivityM/S/U mid stream urineMVA motor vehicle accidentMRSA methicillin resistant staphylococcus aureusMI mitral incompetenceMS mitral stenosisMVR mitral valve replacementMVD mitral valve diseaseMSA mental state assessmentMm HG millimeters of mercuryNGT nasogastric tubeNS normal salineNO nil orallyNAD nil abnormalities detectedNBM/NPO nil by mouthNGT naso gastric tubeNIDDM non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus(better to use Type 2 DM) NKA no known allergiesNOF neck of femurN/G tube naso-gastric tubeNWB non weight bearingNa+ sodiumNaCl sodium chlorideO2 oxygenObs observationOE on examinationOR operating roomORIF open reduction and internal fixationOT occupational therapy/ operating theatreO/A on admissionPAC pressure area carePre-med pre-medicationPD provisional diagnosis/patient diagnosis/peritoneal dialysis PICC peripherally inserted cardiac catheterPU passed urinePO2 partial pressure of oxygenPTE pulmonary thrombotic embolusPOP plaster of parisPath pathologyPT prothrombin timePDA patent ductus arteriosusPVD perioheral vascular diseasePS pulmonary stenosisPE pulmonary embolus/physical examinationPCA patient controlled analgesiaPEEP positive end-expiratory pressurePR pulse ratePTCA percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplastyPEG percutaneous endoscopic gastronomy tubePND paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnoea/postnatal depression RO removal ofRLL right lower lobeRUL right upper lobeROM range of movementRR respiratory rateRFT respiratory function testRMZ right mid zoneRA right atrialRCA right coronary arteryRV right ventricleRTW return to wardRIB rest in bedRBC’s red blood cellsRVF right ventricular failureRTI respiratory tract infectionROS removal of suturesSA sinoatrialSBE subacute bacterial endocarditisSR sinus rhythmSB sinus brachycardiaST sinus tachycardiaSVT supra ventricular tachycardiaSOB/SOBE shortness of breath/shortness of breath on exertion SOOB sit out of bedSaO2 oxygen saturationsSCC squamous cell carcinomaSV stroke volumeSNS sympathetic nervous systemT temperatureTB tuberculosisTKR total knee replacementTHR total hip replacementTURP transuretheral resection of the prostateTx treatmentTAH total abdominal hysterectomyTPR temperature, pulse & respirationTAT transaxillary thoracotomyTLC total lung capacityTV tidal volumeTIA transient ischaemic attackTPN total parental nutritionTGA transposition of great arteriesTOF tetralogy of fallotUA urinalysisURTI upper respiratory tract infectionUTI urinary tract infectionUWSD under water sealed drainageVF ventricular fibrillationVT ventricular tachycardiaVC vital capacityVSD ventricular septal defect WCC white cell countWBC’s white blood cellsWHO world health organization Wt weightyo years old。