自动化专业毕业英文及翻译
- 格式:doc
- 大小:152.00 KB
- 文档页数:11

目录Part 1 PID type fuzzy controller and parameters adaptive method (1)Part 2 Application of self adaptation fuzzy-PID control for main steam temperature control system in power station (7)Part 3 Neuro-fuzzy generalized predictive control of boiler steam temperature ..................................................................... (13)Part 4 为Part3译文:锅炉蒸汽温度模糊神经网络的广义预测控制21Part 1 PID type fuzzy controller and Parametersadaptive methodWu zhi QIAO, Masaharu MizumotoAbstract: The authors of this paper try to analyze the dynamic behavior of the product-sum crisp type fuzzy controller, revealing that this type of fuzzy controller behaves approximately like a PD controller that may yield steady-state error for the control system. By relating to the conventional PID control theory, we propose a new fuzzy controller structure, namely PID type fuzzy controller which retains the characteristics similar to the conventional PID controller. In order to improve further the performance of the fuzzy controller, we work out a method to tune the parameters of the PID type fuzzy controller on line, producing a parameter adaptive fuzzy controller. Simulation experiments are made to demonstrate the fine performance of these novel fuzzy controller structures.Keywords: Fuzzy controller; PID control; Adaptive control1. IntroductionAmong various inference methods used in the fuzzy controller found in literatures , the most widely used ones in practice are the Mamdani method proposed by Mamdani and his associates who adopted the Min-max compositional rule of inference based on an interpretation of a control rule as a conjunction of the antecedent and consequent, and the product-sum method proposed by Mizumoto who suggested to introduce the product and arithmetic mean aggregation operators to replace the logical AND (minimum) and OR (maximum) calculations in the Min-max compositional rule of inference.In the algorithm of a fuzzy controller, the fuzzy function calculation is also a complicated and time consuming task. Tagagi and Sugeno proposed a crisp type model in which the consequent parts of the fuzzy control rules are crisp functional representation or crisp real numbers in the simplified case instead of fuzzy sets . With this model of crisp real number output, the fuzzy set of the inference consequence willbe a discrete fuzzy set with a finite number of points, this can greatly simplify the fuzzy function algorithm.Both the Min-max method and the product-sum method are often applied with the crisp output model in a mixed manner. Especially the mixed product-sum crisp model has a fine performance and the simplest algorithm that is very easy to be implemented in hardware system and converted into a fuzzy neural network model. In this paper, we will take account of the product-sum crisp type fuzzy controller.2. PID type fuzzy controller structureAs illustrated in previous sections, the PD function approximately behaves like a parameter time-varying PD controller. Since the mathematical models of most industrial process systems are of type, obviously there would exist an steady-state error if they are controlled by this kind of fuzzy controller. This characteristic has been stated in the brief review of the PID controller in the previous section.If we want to eliminate the steady-state error of the control system, we can imagine to substitute the input (the change rate of error or the derivative of error) of the fuzzy controller with the integration of error. This will result the fuzzy controller behaving like a parameter time-varying PI controller, thus the steady-state error is expelled by the integration action. However, a PI type fuzzy controller will have a slow rise time if the P parameters are chosen small, and have a large overshoot if the P or I parameters are chosen large. So there may be the time when one wants to introduce not only the integration control but the derivative control to the fuzzy control system, because the derivative control can reduce the overshoot of the system's response so as to improve the control performance. Of course this can be realized by designing a fuzzy controller with three inputs, error, the change rate of error and the integration of error. However, these methods will be hard to implement in practice because of the difficulty in constructing fuzzy control rules. Usually fuzzy control rules are constructed by summarizing the manual control experience of an operator who has been controlling the industrial process skillfully and successfully. The operator intuitively regulates the executor to control the process by watching theerror and the change rate of the error between the system's output and the set-point value. It is not the practice for the operator to observe the integration of error. Moreover, adding one input variable will greatly increase the number of control rules, the constructing of fuzzy control rules are even more difficult task and it needs more computation efforts. Hence we may want to design a fuzzy controller that possesses the fine characteristics of the PID controller by using only the error and the change rate of error as its inputs.One way is to have an integrator serially connected to the output of the fuzzy controller as shown in Fig. 1. In Fig. 1,1K and 2K are scaling factors for e and ~ respectively, and fl is the integral constant. In the proceeding text, for convenience, we did not consider the scaling factors. Here in Fig. 2, when we look at the neighborhood of NODE point in the e - ~ plane, it follows from (1) that the control input to the plant can be approximated by(1)Hence the fuzzy controller becomes a parameter time-varying PI controller, itsequivalent proportional control and integral control components are BK2D and ilK1 P respectively. We call this fuzzy controller as the PI type fuzzy controller (PI fc). We can hope that in a PI type fuzzy control system, the steady-state error becomes zero.To verify the property of the PI type fuzzy controller, we carry out some simulation experiments. Before presenting the simulation, we give a description of the simulation model. In the fuzzy control system shown in Fig. 3, the plant model is a second-order and type system with the following transfer function:)1)(1()(21++=s T s T K s G (2) Where K = 16, 1T = 1, and 2T = 0.5. In our simulation experiments, we use thediscrete simulation method, the results would be slightly different from that of a continuous system, the sampling time of the system is set to be 0.1 s. For the fuzzy controller, the fuzzy subsets of e and d are defined as shown in Fig. 4. Their coresThe fuzzy control rules are represented as Table 1. Fig. 5 demonstrates the simulation result of step response of the fuzzy control system with a Pl fc. We can see that the steady-state error of the control system becomes zero, but when the integration factor fl is small, the system's response is slow, and when it is too large, there is a high overshoot and serious oscillation. Therefore, we may want to introduce the derivative control law into the fuzzy controller to overcome the overshoot and instability. We propose a controller structure that simply connects the PD type and the PI type fuzzy controller together in parallel. We have the equivalent structure of that by connecting a PI device with the basic fuzzy controller serially as shown in Fig.6. Where ~ is the weight on PD type fuzzy controller and fi is that on PI type fuzzy controller, the larger a/fi means more emphasis on the derivative control and less emphasis on the integration control, and vice versa. It follows from (7) that the output of the fuzzy controller is(3)3. The parameter adaptive methodThus the fuzzy controller behaves like a time-varying PID controller, its equivalent proportional control, integral control and derivative control components are respectively. We call this new controller structure a PID type fuzzy controller (PID fc). Figs. 7 and 8 are the simulation results of the system's step response of such control system. The influence of ~ and fl to the system performance is illustrated. When ~ > 0 and/3 = 0, meaning that the fuzzy controller behaves like PD fc, there exist a steady-state error. When ~ = 0 and fl > 0, meaning that the fuzzy controller behaves like a PI fc, the steady-state error of the system is eliminated but there is a large overshoot and serious oscillation.When ~ > 0 and 13 > 0 the fuzzy controller becomes a PID fc, the overshoot is substantially reduced. It is possible to get a comparatively good performance by carefully choosing the value of αandβ.4. ConclusionsWe have studied the input-output behavior of the product-sum crisp type fuzzy controller, revealing that this type of fuzzy controller behaves approximately like a parameter time-varying PD controller. Therefore, the analysis and designing of a fuzzy control system can take advantage of the conventional PID control theory. According to the coventional PID control theory, we have been able to propose some improvement methods for the crisp type fuzzy controller.It has been illustrated that the PD type fuzzy controller yields a steady-state error for the type system, the PI type fuzzy controller can eliminate the steady-state error. We proposed a controller structure, that combines the features of both PD type and PI type fuzzy controller, obtaining a PID type fuzzy controller which allows the control system to have a fast rise and a small overshoot as well as a short settling time.To improve further the performance of the proposed PID type fuzzy controller, the authors designed a parameter adaptive fuzzy controller. The PID type fuzzy controller can be decomposed into the equivalent proportional control, integral control and the derivative control components. The proposed parameter adaptive fuzzy controller decreases the equivalent integral control component of the fuzzy controller gradually with the system response process time, so as to increase the damping of the system when the system is about to settle down, meanwhile keeps the proportional control component unchanged so as to guarantee quick reaction against the system's error. With the parameter adaptive fuzzy controller, the oscillation of the system is strongly restrained and the settling time is shortened considerably.We have presented the simulation results to demonstrate the fine performance of the proposed PID type fuzzy controller and the parameter adaptive fuzzy controller structure.Part 2 Application of self adaptation fuzzy-PID control for main steam temperature control system inpower stationZHI-BIN LIAbstract: In light of the large delay, strong inertia, and uncertainty characteristics of main steam temperature process, a self adaptation fuzzy-PID serial control system is presented, which not only contains the anti-disturbance performance of serial control, but also combines the good dynamic performance of fuzzy control. The simulation results show that this control system has more quickly response, better precision and stronger anti-disturbance ability.Keywords:Main steam temperature;Self adaptation;Fuzzy control;Serial control1. IntroductionThe boiler superheaters of modem thermal power station run under the condition of high temperature and high pressure, and the superheater’s temperature is highest in the steam channels.so it has important effect to the running of the whole thermal power station.If the temperature is too high, it will be probably burnt out. If the temperature is too low ,the efficiency will be reduced So the main steam temperature mast be strictly controlled near the given value.Fig l shows the boiler main steam temperature system structure.Fig.1 boiler main steam temperature systemIt can be concluded from Fig l that a good main steam temperature controlsystem not only has adequately quickly response to flue disturbance and load fluctuation, but also has strong control ability to desuperheating water disturbance. The general control scheme is serial PID control or double loop control system with derivative. But when the work condition and external disturbance change large, the performance will become instable. This paper presents a self adaptation fuzzy-PID serial control system. which not only contains the anti-disturbance performance of serial control, but also combines the good dynamic character and quickly response of fuzzy control .1. Design of Control SystemThe general regulation adopts serial PID control system with load feed forward .which assures that the main steam temperature is near the given value 540℃in most condition .If parameter of PID control changeless and the work condition and external disturbance change large, the performance will become in stable .The fuzzy control is fit for controlling non-linear and uncertain process. The general fuzzy controller takes error E and error change ratio EC as input variables .actually it is a non-linear PD controller, so it has the good dynamic performance .But the steady error is still in existence. In linear system theory, integral can eliminate the steady error. So if fuzzy control is combined with PI control, not only contains the anti-disturbance performance of serial control, but also has the good dynamic performance and quickly response.In order to improve fuzzy control self adaptation ability, Prof .Long Sheng-Zhao and Wang Pei-zhuang take the located in bringing forward a new idea which can modify the control regulation online .This regulation is:]1,0[,)1(∈-+=αααEC E UThis control regulation depends on only one parameter α.Once αis fixed .the weight of E and EC will be fixed and the self adaptation ability will be very small .It was improved by Prof. Li Dong-hui and the new regulation is as follow;]1,0[,,,3,)1(2,)1(1,)1(0,)1({321033221100∈±=-+±=-+±=-+=-+=ααααααααααααE EC E E EC E E EC E E EC E UBecause it is very difficult to find a self of optimum parameter, a new method is presented by Prof .Zhou Xian-Lan, the regulation is as follow:)0(),ex p(12>--=k ke αBut this algorithm still can not eliminate the steady error .This paper combines this algorithm with PI control ,the performance is improved .2. Simulation of Control System3.1 Dynamic character of controlled objectPapers should be limited to 6 pages Papers longer than 6 pages will be subject to extra fees based on their length .Fig .2 main steam temperature control system structureFig 2 shows the main steam temperature control system structure ,)(),(21s W s W δδare main controller and auxiliary controller,)(),(21s W s W o o are characters of the leading and inertia sections,)(),(21s W s W H H are measure unit.3.2 Simulation of the general serial PID control systemThe simulation of the general serial PID control system is operated by MATLAB, the simulation modal is as Fig.3.Setp1 and Setp2 are the given value disturbance and superheating water disturb & rice .PID Controller1 and PID Controller2 are main controller and auxiliary controller .The parameter value which comes from references is as follow :667.37,074.0,33.31)(25)(111111122===++===D I p D I p p k k k s k sk k s W k s W δδFig.3. the general PID control system simulation modal3.3 Simulation of self adaptation fuzzy-PID control system SpacingThe simulation modal is as Fig 4.Auxiliary controller is:25)(22==p k s W δ.Main controller is Fuzzy-PI structure, and the PI controller is:074.0,33.31)(11111==+=I p I p k k s k k s W δFuzzy controller is realized by S-function, and the code is as fig.5.Fig.4. the fuzzy PID control system simulation modalFig 5 the S-function code of fuzzy control3.4 Comparison of the simulationGiven the same given value disturbance and the superheating water disturbance,we compare the response of fuzzy-PID control system with PID serial control system. The simulation results are as fig.6-7.From Fig6-7,we can conclude that the self adaptation fuzzy-PID control system has the more quickly response, smaller excess and stronger anti-disturbance.4. Conclusion(1)Because it combines the advantage of PID controller and fuzzy controller, theself adaptation fuzzy-PID control system has better performance than the general PID serial control system.(2)The parameter can self adjust according to the error E value. so this kind of controller can harmonize quickly response with system stability.Part 3 Neuro-fuzzy generalized predictive controlof boiler steam temperatureXiangjie LIU, Jizhen LIU, Ping GUANAbstract: Power plants are nonlinear and uncertain complex systems. Reliable control of superheated steam temperature is necessary to ensure high efficiency and high load-following capability in the operation of modern power plant. A nonlinear generalized predictive controller based on neuro-fuzzy network (NFGPC) is proposed in this paper. The proposed nonlinear controller is applied to control the superheated steam temperature of a 200MW power plant. From the experiments on the plant and the simulation of the plant, much better performance than the traditional controller is obtained.Keywords: Neuro-fuzzy networks; Generalized predictive control; Superheated steam temperature1. IntroductionContinuous process in power plant and power station are complex systems characterized by nonlinearity, uncertainty and load disturbance. The superheater is an important part of the steam generation process in the boiler-turbine system, where steam is superheated before entering the turbine that drives the generator. Controlling superheated steam temperature is not only technically challenging, but also economically important.From Fig.1,the steam generated from the boiler drum passes through the low-temperature superheater before it enters the radiant-type platen superheater. Water is sprayed onto the steam to control the superheated steam temperature in both the low and high temperature superheaters. Proper control of the superheated steam temperature is extremely important to ensure the overall efficiency and safety of the power plant. It is undesirable that the steam temperature is too high, as it can damage the superheater and the high pressure turbine, or too low, as it will lower the efficiency of the power plant. It is also important to reduce the temperaturefluctuations inside the superheater, as it helps to minimize mechanical stress that causes micro-cracks in the unit, in order to prolong the life of the unit and to reduce maintenance costs. As the GPC is derived by minimizing these fluctuations, it is amongst the controllers that are most suitable for achieving this goal.The multivariable multi-step adaptive regulator has been applied to control the superheated steam temperature in a 150 t/h boiler, and generalized predictive control was proposed to control the steam temperature. A nonlinear long-range predictive controller based on neural networks is developed into control the main steam temperature and pressure, and the reheated steam temperature at several operating levels. The control of the main steam pressure and temperature based on a nonlinear model that consists of nonlinear static constants and linear dynamics is presented in that.Fig.1 The boiler and superheater steam generation process Fuzzy logic is capable of incorporating human experiences via the fuzzy rules. Nevertheless, the design of fuzzy logic controllers is somehow time consuming, as the fuzzy rules are often obtained by trials and errors. In contrast, neural networks not only have the ability to approximate non-linear functions with arbitrary accuracy, they can also be trained from experimental data. The neuro-fuzzy networks developed recently have the advantages of model transparency of fuzzy logic and learning capability of neural networks. The NFN is have been used to develop self-tuning control, and is therefore a useful tool for developing nonlinear predictive control. Since NFN is can be considered as a network that consists of several local re-gions, each of which contains a local linear model, nonlinear predictive control based onNFN can be devised with the network incorporating all the local generalized predictive controllers (GPC) designed using the respective local linear models. Following this approach, the nonlinear generalized predictive controllers based on the NFN, or simply, the neuro-fuzzy generalized predictive controllers (NFG-PCs)are derived here. The proposed controller is then applied to control the superheated steam temperature of the 200MW power unit. Experimental data obtained from the plant are used to train the NFN model, and from which local GPC that form part of the NFGPC is then designed. The proposed controller is tested first on the simulation of the process, before applying it to control the power plant.2. Neuro-fuzzy network modellingConsider the following general single-input single-output nonlinear dynamic system:),1(),...,(),(),...,1([)(''+-----=uy n d t u d t u n t y t y f t y ∆+--/)()](),...,1('t e n t e t e e (1)where f[.]is a smooth nonlinear function such that a Taylor series expansion exists, e(t)is a zero mean white noise and Δis the differencing operator,''',,e u y n n n and d are respectively the known orders and time delay of the system. Let the local linear model of the nonlinear system (1) at the operating point )(t o be given by the following Controlled Auto-Regressive Integrated Moving Average (CARIMA) model:)()()()()()(111t e z C t u z B z t y z A d ----+∆= (2) Where )()(),()(1111----∆=z andC z B z A z A are polynomials in 1-z , the backward shift operator. Note that the coefficients of these polynomials are a function of the operating point )(t o .The nonlinear system (1) is partitioned into several operating regions, such that each region can be approximated by a local linear model. Since NFN is a class of associative memory networks with knowledge stored locally, they can be applied to model this class of nonlinear systems. A schematic diagram of the NFN is shown in Fig.2.B-spline functions are used as the membership functions in theNFN for the following reasons. First, B-spline functions can be readily specified by the order of the basis function and the number of inner knots. Second, they are defined on a bounded support, and the output of the basis function is always positive, i.e.,],[,0)(j k j j k x x λλμ-∉=and ],[,0)(j k j j k x x λλμ-∈>.Third, the basis functions form a partition of unity, i.e.,.][,1)(min,∑∈≡j mam j k x x x x μ(3)And fourth, the output of the basis functions can be obtained by a recurrence equation.Fig. 2 neuro-fuzzy network The membership functions of the fuzzy variables derived from the fuzzy rules can be obtained by the tensor product of the univariate basis functions. As an example, consider the NFN shown in Fig.2, which consists of the following fuzzy rules: IF operating condition i (1x is positive small, ... , and n x is negative large),THEN the output is given by the local CARIMA model i:...)()(ˆ...)1(ˆ)(ˆ01+-∆+-++-=d t u b n t y a t y a t yi i a i in i i i a )(...)()(c i in i b i in n t e c t e n d t u b c b -+++--∆+ (4)or )()()()()(ˆ)(111t e z C t u z B z t yz A i i i i d i i ----+∆= (5) Where )()(),(111---z andC z B z A i i i are polynomials in the backward shift operator 1-z , and d is the dead time of the plant,)(t u i is the control, and )(t e i is a zero mean independent random variable with a variance of 2δ. The multivariate basis function )(k i x a is obtained by the tensor products of the univariate basis functions,p i x A a nk k i k i ,...,2,1,)(1==∏=μ (6)where n is the dimension of the input vector x , and p , the total number of weights in the NFN, is given by,∏=+=nk i i k R p 1)( (7)Where i k and i R are the order of the basis function and the number of inner knots respectively. The properties of the univariate B-spline basis functions described previously also apply to the multivariate basis function, which is defined on the hyper-rectangles. The output of the NFN is,∑∑∑=====p i i i p i ip i i i a y aa yy 111ˆˆˆ (8) 3. Neuro-fuzzy modelling and predictive control of superheatedsteam temperatureLet θbe the superheated steam temperature, and θμ, the flow of spray water to the high temperature superheater. The response of θcan be approximated by a second order model:The linear models, however, only a local model for the selected operating point. Since load is the unique antecedent variable, it is used to select the division between the local regions in the NFN. Based on this approach, the load is divided into five regions as shown in Fig.3,using also the experience of the operators, who regard a load of 200MW as high,180MW as medium high,160MW as medium,140MW as medium low and 120MW as low. For a sampling interval of 30s , the estimated linear local models )(1-z A used in the NFN are shown in Table 1.Fig. 3 Membership function for local modelsTable 1 Local CARIMA models in neuro-fuzzy modelCascade control scheme is widely used to control the superheated steam temperature. Feed forward control, with the steam flow and the gas temperature as inputs, can be applied to provide a faster response to large variations in these two variables. In practice, the feed forward paths are activated only when there are significant changes in these variables. The control scheme also prevents the faster dynamics of the plant, i.e., the spray water valve and the water/steam mixing, from affecting the slower dynamics of the plant, i.e., the high temperature superheater. With the global nonlinear NFN model in Table 1, the proposed NFGPC scheme is shown in Fig.4.Fig. 4 NFGPC control of superheated steam temperature with feed-for-ward control.As a further illustration, the power plant is simulated using the NFN model given in Table 1,and is controlled respectively by the NFGPC, the conventional linear GPC controller, and the cascaded PI controller while the load changes from 160MW to 200MW.The conventional linear GPC controller is the local controller designed for the“medium”operating region. The results are shown in Fig.5,showing that, as expected, the best performance is obtained from the NFGPC as it is designed based on a more accurate process model. This is followed by the conventional linear GPC controller. The performance of the conventional cascade PI controller is the worst, indicating that it is unable to control satisfactory the superheated steam temperature under large load changes. This may be the reason for controlling the power plant manually when there are large load changes.Fig.5 comparison of the NFGPC, conventional linear GPC, and cascade PI controller.4. ConclusionsThe modeling and control of a 200 MW power plant using the neuro-fuzzy approach is presented in this paper. The NFN consists of five local CARIMA models.The out-put of the network is the interpolation of the local models using memberships given by the B-spline basis functions. The proposed NFGPC is similarly constructed, which is designed from the CARIMA models in the NFN. The NFGPC is most suitable for processes with smooth nonlinearity, such that its full operating range can be partitioned into several local linear operating regions. The proposed NFGPC therefore provides a useful alternative for controlling this class of nonlinear power plants, which are formerly difficult to be controlled using traditional methods.Part 4 为Part3译文:锅炉蒸汽温度模糊神经网络的广义预测控制Xiangjie LIU, Jizhen LIU, Ping GUAN摘要:发电厂是非线性和不确定性的复杂系统。

1.1In recent years the performance requirements for process plant have become increasingly difficult to satisfy. Stronger competition, tougher (更加严苛的) environmental and safety regulations (法规), and rapidly changing economic conditions have been key factors in the tightening of plant product quality specifications (产品质量规范).A further complication (复杂) is that modern processes have become more difficult to operate because of the trend toward larger, more highly integrated plants with smaller surge capacities (谐振能力) between the various processing units. Such plants give the operators little opportunity to prevent upsets (扰乱) from propagating from one unit to other interconnected units. In view of (考虑到,由于) the increased emphasis placed on safe, efficient plant operation, it is only natural that the subject of process control has become increasingly important in recent years. In fact, without process control it would not be possible to operate most modern processes safely and profitably (有利的), while satisfying plant quality standards.近年来,对过程系统的性能改善需求变得越来越困难.更为激烈的竞争,更加严格的环境和安全规范,以及快速变化的经济条件都是加强工厂产品质量规范的关键因素更为复杂的情况是,由于现代制造业朝着规模更大,集成度更高的方向发展,而使不同的加工环节之间的应变能力更低, 所以加工过程更难控制近年来,考虑到工业制造逐渐加强的安全、高效需求,过程控制这个课题变得越来越受重视. 实际上,对于大多数现代工业,要满足安全、高效,产品质量的要求,没有控制系统是不可能的.It is assumed that the inlet and outlet flow rates are identical (相同的) and that the liquid density ρ (rho) remains consant,that is, the temperature variations are small enough that the temperature dependence of ρ can be neglected. Under these conditions the volu me V of liquid in the tank remains constant.假设输入和输出流量是相等的,并且液体密度保持恒定,也就是说温度变化足够小,密度对温度的影响可以忽略不计. 在这些条件下,槽内液体的体积保持恒定Use a larger tank. If a larger tank is used, fluctuations (波动) in Ti will tend to be damped out (阻尼,衰减) due to the larger thermal capacitance of the tank contents. However, increased volume of tankage would be an expensive solution for an industrial plant due to the increased capital costs of the larger tank.Note that this approach is analogous to the use of water baths in chemistry laboratories where the large thermal capacitance of the bath serves as a heat sink (散热装置) and thus provides an isothermal (恒温的) environment for a small-scale research apparatus (仪器).使用一个更大的槽. 如果使用更大的槽,因为更大的热容,Ti的波动会趋向于衰减. 然而,体积增加使得开支增加,会使工厂系统的解决方案变得更加昂贵.要指出的是这个方法类似于化学实验室中水缸的使用,水缸的大热容量可以看作散热装置,因此可以为小型研究仪器提供一个恒温环境.Note that in feedforward control, the controlled variable T is not measured.在前馈控制中,被控变量T是没有被测量的.1.2The motivation of using feedback, illustrated (说明) by the examples in Section (1), is somewhat oversimplified.In these examples, the use of feedback is shown to be for the purpose of reducing the error between the reference input and the system output.However, the significance of theeffects of feedback in control systems is more complex than is demonstrated by these simple examples.The reduction of system error is merely (仅仅) one of the many important effects that feedback may have upon a system. We show in the following sections that feedback also has effects on such system performance characteristics as stability (稳定性), bandwidth (带宽), overall gain (总增益), disturbance (扰动), and sensitivity (灵敏度).第一节事例中,应用反馈的动机有些过于简单。

机械设计制造及其自动化军训及军事理论Military Training and Military Theory计算机实用基础2 Introduction to Computer Application大学英语College English体育Physical Education工科数学分析2 Advanced Mathematics代数与几何 2 Linear Algebra Advanced Algebra and Geometry思想道德修养与法律基础Ideological and Moral Cultivation and Law Basics大学英语College English体育大学物理2 College Physics工科数学分析2C语言程序设计 C Language中国近现代史纲要Modern History of China法语二外(上)The Second Foreign Language French工业造型设计Modeling Design of Industrial Products大学英语College English大学物理2 College Physics大学物理实验1 Experiment in College Physics概率论与数理统计Probability Theory & Mathematical Statistics电工技术1 Electrical Engineering电工与电子技术综合实验1 Experiment for Electrical and Electronic Engineering工程图学(CAD)1 Mechanical Graphing理论力学1 Theoretical Mechanics工程力学实验1 Experiment for Engineering Mechanics毛泽东思想、邓小平理论和“三个代表”重要思想概论Introduction to Mao Zedong Thoughts, Deng Xiaoping Theory and the Important Thought of "Three Represents"文化素质教育系列讲座Cultural quality education lectures体育西方文明简史History of western civilization Introduction to Functional Materials机械原理课程设计Course Exercise of Mechanical Principle工程训练(金工实习)engineering training Metal Working Practice大学物理实验1电子技术1 Electronic Engineering电工与电子技术综合实验1机械原理Principle of Mechanics Mechanical Principles工程图学(CAD)1工程力学实验(材力)1材料力学1 Mechanics of Materials马克思主义基本原理Principles of Marxism文化素质教育系列讲座文化素质教育系列讲座体育项目管理Project Management法语二外(下)法语入门1机械设计课程设计Course Exercise in Mechanical Design工程训练(电子工艺实习)electronic process practice Practice on Electronic Working Techniques互换性与测量技术基础Basic Technology of Exchangeability Measurement工程流体力学Engineering Fluid Mechanics自动控制原理3 Automatic Control Theory电工学新技术实践The new technology of electronics practice机械设计Mechanical Design工程材料成型技术基础Engineering material molding technology机械工程材料Engineering Materials文化素质教育系列讲座文化素质教育系列讲座创新设计与制作Innovation design and production复变函数与积分变换Complex Function Functions of Complex V ariables & Integral Transformation社会热点问题评价evaluation of social issues知识产权"Intellectual Property Law"认识实习Cognition Practice制造系统自动化技术Automation of Mechanical Manufacture System传热学Heat Transfer文化素质教育系列讲座机电控制系统分析与设计Mechanical-Electrical Control system数控技术Numerical Control Technology机械制造装备设计Machinery manufacturing equipment design液压传动Hydraulic Transmission测试技术与仪器Measurement Fundamentals & Meter Design Measurement Fundamentals & Meter Design机械制造技术基础foundation of machine manufacturing technology综合课程设计1 Comprehensive Course Exercise生产实习Production Practice Field Practice现代机械设计方法The modern machinery design method机械动态设计Mechanical Dynamic Design机械结构有限元分析Finite Element of Mechanical Structures Finite Element Analysis and Programming Finite Element Analysis for Mechanical Structures机电系统智能化控制技术(双语Mechanical and electrical system intelligent control technology 综合课程设计2机械优化设计Optimum Design of MachineryMechanical Optimum Design毕业设计Graduation Thesis工程测试技术Engineering Testing Technique。

《自动化专业英语教程》-王宏文主编-全文翻译PART 1Electrical and Electronic Engineering BasicsUNIT 1A Electrical Networks ————————————3B Three-phase CircuitsUNIT 2A The Operational Amplifier ———————————5B TransistorsUNIT 3A Logical Variables and Flip-flop ——————————8B Binary Number SystemUNIT 4A Power Semiconductor Devices ——————————11B Power Electronic ConvertersUNIT 5A Types of DC Motors —————————————15B Closed-loop Control of DC DriversUNIT 6A AC Machines ———————————————19B Induction Motor DriveUNIT 7A Electric Power System ————————————22B Power System AutomationPART 2Control TheoryUNIT 1A The World of Control ————————————27B The Transfer Function and the Laplace Transformation —————29 UNIT 2A Stability and the Time Response —————————30B Steady State—————————————————31 UNIT 3A The Root Locus —————————————32B The Frequency Response Methods: Nyquist Diagrams —————33 UNIT 4A The Frequency Response Methods: Bode Piots —————34B Nonlinear Control System 37UNIT 5 A Introduction to Modern Control Theory 38B State Equations 40UNIT 6 A Controllability, Observability, and StabilityB Optimum Control SystemsUNIT 7 A Conventional and Intelligent ControlB Artificial Neural NetworkPART 3 Computer Control TechnologyUNIT 1 A Computer Structure and Function 42B Fundamentals of Computer and Networks 43UNIT 2 A Interfaces to External Signals and Devices 44B The Applications of Computers 46UNIT 3 A PLC OverviewB PACs for Industrial Control, the Future of ControlUNIT 4 A Fundamentals of Single-chip Microcomputer 49B Understanding DSP and Its UsesUNIT 5 A A First Look at Embedded SystemsB Embedded Systems DesignPART 4 Process ControlUNIT 1 A A Process Control System 50B Fundamentals of Process Control 52UNIT 2 A Sensors and Transmitters 53B Final Control Elements and ControllersUNIT 3 A P Controllers and PI ControllersB PID Controllers and Other ControllersUNIT 4 A Indicating InstrumentsB Control PanelsPART 5 Control Based on Network and InformationUNIT 1 A Automation Networking Application AreasB Evolution of Control System ArchitectureUNIT 2 A Fundamental Issues in Networked Control SystemsB Stability of NCSs with Network-induced DelayUNIT 3 A Fundamentals of the Database SystemB Virtual Manufacturing—A Growing Trend in AutomationUNIT 4 A Concepts of Computer Integrated ManufacturingB Enterprise Resources Planning and BeyondPART 6 Synthetic Applications of Automatic TechnologyUNIT 1 A Recent Advances and Future Trends in Electrical Machine DriversB System Evolution in Intelligent BuildingsUNIT 2 A Industrial RobotB A General Introduction to Pattern RecognitionUNIT 3 A Renewable EnergyB Electric VehiclesUNIT 1A 电路电路或电网络由以某种方式连接的电阻器、电感器和电容器等元件组成。

unit1 taxe A 电力变压器的结构和原理在许多能量转换系统中,变压器是一个不了缺少的原件。
它使得在经济的发电机所产生电能并以最经历的传输电压传输电能,同时对于特定的使用者合适的电压使用电能成为可能。
变压器同样广泛的应用于低功率低电流的电子电路和控制电路中,来执行像匹配电源组抗和负载以求得最大的传输效率。
隔离一个电路与另一个电路在两个电路之间隔离直流电而保证交流电继续通道的功能。
在本质上,变压器是一个由两个或多个绕组通过相互的磁通耦合而组成的,如果这其中的一个绕组,原边连接到交流电压源将产生交流磁通它的幅值决定于原边的电压所提供的电压频率及匝数。
感应磁通将与其他绕组交链,在副边中将感应出一个电压其幅值将取决于副边的匝数及感应磁通量和频率。
通过使原副边匝数比例适应,任何所期望的电压比例或转换比例都可以得到。
变压器工作的本质仅要求存在与两个绕组相交链的时变的感应磁通。
这样的作用也可以发生在通过空气耦合的两组绕组中,但用铁心或其他铁磁材料可以使绕组之间的耦合作用增强,因为一大部分磁通被限制在与两个绕组交链的高磁导率的路径中。
这种变压器通常被称作为心式变压器。
大部分变压器都是这种类型。
以下的讨论几乎全部围绕心事变压器。
为减少铁心中的涡流所产生的损耗,磁路通常由一叠薄的叠片所组成。
如图1.1所示两种常见的结构形式用示意图表示出来。
芯式变压器的绕组绕在两个矩形铁心柱上,壳式变压器的绕组绕在三个铁心柱中间的那个铁心柱上,。
0.14毫米厚的硅钢片通常被用于在低频率低于几百Hz下运行的变压器中,硅钢片具有价格低铁心损耗小,在高磁通密度下,磁导率高的理想性能,能用做高频率低能耗的标准的通讯电路中的小型变压器的铁心是由被称为铁氧体的粉末压缩制成的铁磁合金所构成的。
在这些结构中,大部分的磁通被限制在固定的铁心中与两个绕组相交链。
绕组也产生多余的磁通,像漏磁通,只经过一个绕组和另外的绕组不相交链。
虽然漏磁通只是所有磁通的一小部分,但它在决定变压器的运行情况中起着重要的作用。

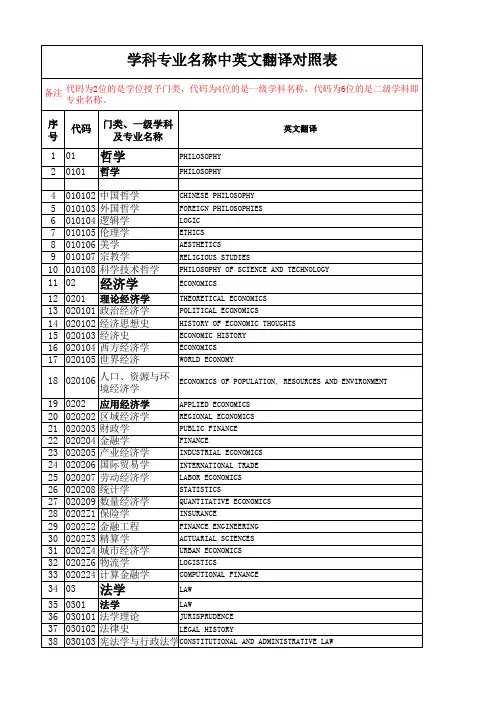
大学各专业名称英文翻译电气工程及其自动化Electronical Engineering and Automation哲学 Philosophy马克思主义哲学 Philosophy of Marxism中国哲学 Chinese Philosophy外国哲学 Foreign Philosophies逻辑学 Logic伦理学 Ethics美学 Aesthetics宗教学 Science of Religion科学技术哲学 Philosophy of Science and Technology经济学 Economics理论经济学 Theoretical Economics政治经济学 Political Economy经济思想史 History of Economic Thought经济史 History of Economic西方经济学 Western Economics世界经济 World Economics人口、资源与环境经济学 Population, Resources and Environmental Economics应用经济学 Applied Economics国民经济学 National Economics区域经济学 Regional Economics财政学(含税收学) Public Finance (including Taxation)金融学(含保险学) Finance (including Insurance)产业经济学 Industrial Economics国际贸易学 International Trade劳动经济学 Labor Economics统计学 Statistics数量经济学 Quantitative Economics中文学科、专业名称英文学科、专业名称国防经济学 National Defense Economics法学 Law法学 Science of Law法学理论 Jurisprudence法律史 Legal History宪法学与行政法学 Constitutional Law and Administrative Law刑法学 Criminal Jurisprudence民商法学(含劳动法学、社会保障法学) Civil Law and Commercial Law (including Science of Labour Law and Science of Social Security Law )诉讼法学 Science of Procedure Laws经济法学 Science of Economic Law环境与资源保护法学 Science of Environment and Natural Resources Protection Law国际法学(含国际公法学、国际私法学、国际经济法学、) International law (including International Public law, International Private Law and International Economic Law)军事法学 Science of Military Law政治学 Political Science政治学理论 Political Theory中外政治制度 Chinese and Foreign Political Institution科学社会主义与国际共产主义运动Scientific Socialism and InternationalCommunist Movement中共党史(含党的学说与党的建设) History of the Communist Party of China(including the Doctrine of China Party and Party Building)马克思主义理论与思想政治教育 Education of Marxist Theory and Education in Ideology and Politics国际政治学 International Politics国际关系学 International Relations外交学 Diplomacy社会学 Sociology社会学 Sociology人口学 Demography人类学 Anthropology民俗学(含中国民间文学) Folklore (including Chinese Folk Literature)民族学 Ethnology民族学 Ethnology马克思主义民族理论与政策 Marxist Ethnic Theory and Policy中国少数民族经济 Chinese Ethnic Economics中国少数民族史 Chinese Ethnic History中国少数民族艺术 Chinese Ethnic Art教育学 Education教育学 Education Science教育学原理 Educational Principle课程与教学论 Curriculum and Teaching Methodology教育史 History of Education比较教育学 Comparative Education学前教育学 Pre-school Education高等教育学 Higher Education成人教育学 Adult Education职业技术教育学 Vocational and Technical Education特殊教育学 Special Education教育技术学 Education Technology心理学 Psychology基础心理学 Basic Psychology发展与心理学 Developmental and Educational Psychology应用心理学 Applied Psychology体育学 Science of Physical Culture and Sports体育人文社会学 Humane and Sociological Science of Sports 运动人体科学 Human Movement Science体育教育训练学 Theory of Sports Pedagogy and Training民族传统体育学 Science of Ethnic Traditional Sports文学 Literature中国语言文学 Chinese Literature文艺学 Theory of Literature and Art语言学及应用语言学 Linguistics and Applied Linguistics汉语言文字学 Chinese Philology中国古典文献学 Study of Chinese Classical Text中国古代文学 Ancient Chinese Literature中国现当代文学 Modern and Contemporary Chinese Literature中国少数民族语言文学 Chinese Ethnic Language andLiterature比较文学与世界文学 Comparative Literature and World Literature 外国语言文学 Foreign Languages and Literatures英语语言文学 English Language and Literature俄语语言文学 Russian Language and Literature法语语言文学 French Language and Literature德语语言文学 German Language and Literature日语语言文学 Japanese Language and Literature印度语言文学 Indian Language and Literature西班牙语语言文学 Spanish Language and Literature阿拉伯语语言文学 Arabic Language and Literature欧洲语言文学 European Language and Literature亚非语言文学 Asian-African Language and Literature外国语言学及应用语言学 Linguistics and Applied Linguistics in Foreign Languages新闻传播学 Journalism and Communication新闻学 Journalism传播学 Communication艺术学 Art艺术学 Art Theory音乐学 Music美术学 Fine Arts设计艺术学 Artistic Design戏剧戏曲学 Theater and Chinese Traditional Opera电影学 Film广播电视艺术学 Radio and television Art舞蹈学 Dance历史学 History历史学 History史学理论及史学史 Historical Theories and History of Historical Science考古学及博物馆学 Archaeology and Museology历史地理学 Historical Geography历史文献学(含敦煌学、古文字学) Studies of Historical Literature (includingPaleography and Studies of Dunhuang)专门史 History of Particular Subjects中国古代史 Ancient Chinese History中国近现代史 Modern and Contemporary Chinese History世界史 World History理学 Natural Science数学 Mathematics基础数学 Fundamental Mathematics计算数学 Computational Mathematics概率论与数理统计 Probability and Mathematical Statistics应用数学 Applied mathematics运筹学与控制论 Operational Research and Cybernetics物理学 Physics理论物理 Theoretical Physics粒子物理与原子核物理 Particle Physics and Nuclear Physics原子与分子物理 Atomic and Molecular Physics等离子体物理 Plasma Physics凝聚态物理 Condensed Matter Physics声学 Acoustics光学 Optics无线电物理 Radio Physics化学 Chemistry无机化学 Inorganic Chemistry分析化学 Analytical Chemistry有机化学 Organic Chemistry物理化学(含化学物理) Physical Chemistry (including Chemical Physics)高分子化学与物理 Chemistry and Physics of Polymers天文学 Astronomy天体物理 Astrophysics天体测量与天体力学 Astrometry and Celestial Mechanics地理学 Geography自然地理学 Physical Geography人文地理学 Human Geography地图学与地理信息系统 Cartography and Geography Information System大气科学 Atmospheric Sciences气象学 Meteorology大气物理学与大气环境Atmospheric Physics and Atmospheric Environment海洋科学 Marine Sciences物理海洋学 Physical Oceanography海洋化学 Marine Chemistry海洋生理学 Marine Biology海洋地质学 Marine Geology地球物理学 Geophysics固体地球物理学 Solid Earth Physics空间物理学 Space Physics地质学 Geology矿物学、岩石学、矿床学 Mineralogy, Petrology, Mineral Deposit Geology地球化学 Geochemistry古生物学与地层学(含古人类学) Paleontology and Stratigraphy (includingPaleoanthropology)构造地质学 Structural Geology第四纪地质学 Quaternary Geology生物学 Biology植物学 Botany动物学 Zoology生理学 Physiology水生生物学 Hydrobiology微生物学 Microbiology神经生物学 Neurobiology遗传学 Genetics发育生物学 Developmental Biology细胞生物学 Cell Biology生物化学与分子生物学 Biochemistry and Molecular Biology 生物物理学 Biophysics生态学 Ecology系统科学 Systems Science系统理论 Systems Theory系统分析与集成 Systems Analysis and Integration科学技术史 History of Science and Technology工学 Engineering力学 Mechanics一般力学与力学基础 General and Fundamental Mechanics固体力学 Solid Mechanics流体力学 Fluid Mechanics工程力学 Engineering Mechanics机械工程 Mechanical Engineering机械制造及其自动化 Mechanical Manufacture and Automation机械电子工程 Mechatronic Engineering机械设计与理论 Mechanical Design and Theory车辆工程 Vehicle Engineering光学工程 Optical Engineering仪器科学与技术 Instrument Science and Technology精密仪器及机械 Precision Instrument and Machinery测试计量技术及仪器Measuring and Testing Technologies and Instruments材料科学与工程 Materials Science and Engineering材料物理与化学 Materials Physics and Chemistry材料学 Materialogy材料加工工程 Materials Processing Engineering冶金工程 Metallurgical Engineering冶金物理化学 Physical Chemistry of Metallurgy钢铁冶金 Ferrous Metallurgy有色金属冶金 Non-ferrous Metallurgy动力工程及工程热物理Power Engineering and Engineering Thermophysics工程热物理 Engineering Thermophysics热能工程 Thermal Power Engineering动力机械及工程 Power Machinery and Engineering流体机械及工程 Fluid Machinery and Engineering制冷及低温工程 Refrigeration and Cryogenic Engineering化工过程机械 Chemical Process Equipment电气工程 Electrical Engineering电机与电器 Electric Machines and Electric Apparatus电力系统及其自动化 Power System and its Automation高电压与绝缘技术 High Voltage and Insulation Technology电力电子与电力传动 Power Electronics and Power Drives电工理论与新技术 Theory and New Technology of Electrical Engineering 电子科学与技术 Electronics Science and Technology物理电子学 Physical Electronics电路与系统 Circuits and Systems微电子学与固体电子学 Microelectronics and Solid State Electronics 电磁场与微波技术 Electromagnetic Field and Microwave Technology 信息与通信工程 Information and Communication Engineering通信与信息系统 Communication and Information Systems信号与信息处理 Signal and Information Processing控制科学与工程 Control Science and Engineering控制理论与控制工程 Control Theory and Control Engineering检测技术与自动化装置 Detection Technology and Automatic Equipment 系统工程 Systems Engineering模式识别与智能系统 Pattern Recognition and Intelligent Systems导航、制导与控制 Navigation, Guidance and Control计算机科学与技术 Computer Science and Technology计算机软件与理论 Computer Software and Theory计算机系统结构 Computer Systems Organization计算机应用技术 Computer Applied Technology建筑学 Architecture建筑历史与理论 Architectural History and Theory建筑设计及其理论 Architectural Design and Theory城市规划与设计(含风景园林规划与设计) Urban Planning and Design (including Landscape Planning and Design)建筑技术科学 Building Technology Science土木工程 Civil Engineering岩土工程 Geotechnical Engineering结构工程 Structural Engineering市政工程 Municipal Engineering供热、供燃气、通风及空调工程 Heating, Gas Supply, Ventilating and Air Conditioning Engineering防灾减灾工程及防护工程Disaster Prevention and Reduction Engineering and Protective Engineering桥梁与隧道工程 Bridge and Tunnel Engineering水利工程 Hydraulic Engineering水文学及水资源 Hydrology and Water Resources水力学及河流动力学 Hydraulics and River Dynamics水工结构工程 Hydraulic Structure Engineering水利水电工程 Hydraulic and Hydro-Power Engineering港口、海岸及近海工程 Harbor, Coastal and Offshore Engineering测绘科学与技术 Surveying and Mapping大地测量学与测量工程 Geodesy and Survey Engineering摄影测量与遥感 Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing地图制图学与地理信息工程 Cartography and Geographic Information Engineering化学工程与技术 Chemical Engineering and Technology化学工程 Chemical Engineering化学工艺 Chemical Technology生物化工 Biochemical Engineering应用化学 Applied Chemistry工业催化 Industrial Catalysis地质资源与地质工程 Geological Resources and Geological Engineering矿产普查与勘探 Mineral Resource Prospecting and Exploration地球探测与信息技术 Geodetection and Information Technology地质工程 Geological Engineering矿业工程 Mineral Engineering采矿工程 Mining Engineering矿物加工工程 Mineral Processing Engineering安全技术及工程 Safety Technology and Engineering石油与天然气工程 Oil and Natural Gas Engineering油气井工程 Oil-Gas Well Engineering油气田开发工程 Oil-Gas Field Development Engineering油气储运工程 Oil-Gas Storage and Transportation Engineering纺织科学与工程 Textile Science and Engineering纺织工程 Textile Engineering纺织材料与纺织品设计 Textile Material and Textiles Design纺织化学与染整工程Textile Chemistry and Dyeing and Finishing Engineering服装设计与工程 Clothing Design and Engineering轻工技术与工程 The Light Industry Technology and Engineering制浆造纸工程 Pulp and Paper Engineering制糖工程 Sugar Engineering发酵工程 Fermentation Engineering皮革化学与工程 Leather Chemistry and Engineering交通运输工程 Communication and Transportation Engineering道路与铁道工程 Highway and Railway Engineering交通信息工程及控制 Traffic Information Engineering & Control交通运输规划与管理 Transportation Planning and Management载运工具运用工程 Vehicle Operation Engineering船舶与海洋工程 Naval Architecture and Ocean Engineering船舶与海洋结构物设计制造Design and Construction of Naval Architecture and Ocean Structure轮机工程 Marine Engine Engineering水声工程 Underwater Acoustics Engineering航空宇航科学与技术Aeronautical and Astronautical Science and Technology飞行器设计 Flight Vehicle Design航空宇航推进理论与工程 Aerospace Propulsion Theory and Engineering航空宇航器制造工程 Manufacturing Engineering of Aerospace Vehicle人机与环境工程 Man-Machine and Environmental Engineering兵器科学与技术 Armament Science and Technology武器系统与运用工程 Weapon Systems and Utilization Engineering兵器发射理论与技术 Armament Launch Theory and Technology火炮、自动武器与弹药工程 Artillery, Automatic Gun and Ammunition Engineering军事化学与烟火技术 Military Chemistry and Pyrotechnics核科学与技术 Nuclear Science and Technology核能科学与工程 Nuclear Energy Science and Engineering核燃料循环与材料 Nuclear Fuel Cycle and Materials核技术及应用 Nuclear Technology and Applications辐射防护及环境保护 Radiation and Environmental Protection农业工程 Agricultural Engineering农业机械化工程 Agricultural Mechanization Engineering农业水土工程 Agricultural Water-Soil Engineering农业生物环境与能源工程 Agricultural Biological Environmental and Energy Engineering农业电气化与自动化 Agricultural Electrification and Automation林业工程 Forestry Engineering森林工程 Forest Engineering木材科学与技术 Wood Science and Technology林产化学加工工程 Chemical Processing Engineering of Forest Products环境科学与工程 Environmental Science and Engineering环境科学 Environmental Science环境工程 Environmental Engineering生物医学工程 Biomedical Engineering食品科学与工程 Food Science and Engineering食品科学 Food Science粮食、油脂及植物蛋白工程Cereals, Oils and Vegetable Protein Engineering农产品加工及贮藏工程 Processing and Storage of Agriculture Products水产品加工及贮藏工程 Processing and Storage of Aquatic Products农学 Agriculture作物学 Crop Science作物栽培学与耕作学 Crop Cultivation and Farming System作物遗传育种学 Crop Genetics and Breeding园艺学 Horticulture果树学 Pomology蔬菜学 Olericulture茶学 Tea Science农业资源利用学 Utilization Science of Agricultural Resources土壤学 Soil Science植物营养学 Plant Nutrition植物保护学 Plant Protection植物病理学 Plant Pathology农业昆虫与害虫防治 Agricultural Entomology and Pest Control农药学 Pesticide Science畜牧学 Animal Science动物遗传育种与繁殖 Animal Genetics, Breeding and ReproductionScience动物营养与饲料科学 Animal Nutrition and Feed Science草业科学 Practaculture Science特种经济动物饲养学(含蚕、蜂等) The Rearing of Special-type EconomicAnimals (including Silkworm, Honeybees, etc.)兽医学 Veterinary Medicine基础兽医学 Basic Veterinary Medicine预防兽医学 Preventive Veterinary Medicine临床兽医学 Clinical Veterinary Medicine林学 Forestry林木遗传育种学 Forest Tree Genetics and Breeding森林培育学 Silviculture森林保护学 Forest Protection森林经理学 Forest Management野生动植物保护与利用 Wildlife Conservation and Utilization园林植物与观赏园艺 Ornamental Plants and Horticulture水土保持与荒漠化防治Soil and Water Conservation and Desertification Combating水产学 Fisheries Science水产养殖学 Aquaculture Science捕捞学 Fishing Science渔业资源学 Science of Fisheries Resources医学 Medicine基础医学 Basic Medicine人体解剖与组织胚胎学 Human Anatomy, Histology and Embryology免疫学 Immunology病原生物学 Pathogenic Organisms病理学与病理生理学 Pathology and Pathophysiology法医学 Forensic Medicine放射医学 Radiation Medicine航空航天与航海医学 Aerospace and Nautical medicine临床医学 Clinical Medicine内科学(含心血管病学、血液病学、呼吸系病学、消化系病学、内分泌与代谢病学、肾脏病学、风湿病学、传染病学) Internal medicine (including Cardiology, Hematology, Respiratory, Gastroenterology, Endocrinology and Metabolism, Nephrology, Rheuma-tology, Infectious Diseases)儿科学 Pediatrics老年医学 Geriatrics神经病学 Neurology精神病与精神卫生学 Psychiatry and Mental Health皮肤病与性病学 Dermatology and Venereology影像医学与核医学 Imaging and Nuclear Medicine临床检验诊断学 Clinical Laboratory Diagnostics护理学 Nursing外科学(含普通外科学、骨外科学、泌尿外科学、胸心血管外科学、神经外科学、整形外科学、烧伤外科学、野战外科学) Surgery (General Surgery, Orthopedics, Urology, Cardiothoracic Surgery, Neurosurgery, Plastic Surgery, Burn Surgery, Field Surgery)妇产科学 Obstetrics and Gynecology眼科学 Ophthalmic Specialty耳鼻咽喉科学 Otolaryngology肿瘤学 Oncology康复医学与理疗学 Rehabilitation Medicine & Physical Therapy 运动医学 Sports Medicine麻醉学 Anesthesiology急诊医学 Emergency Medicine口腔医学 Stomatology口腔基础医学 Basic Science of Stomatology口腔临床医学 Clinical Science of Stomatology公共卫生与预防医学 Public Health and Preventive Medicine流行病与卫生统计学 Epidemiology and Health Statistics劳动卫生与环境卫生学 Occupational and Environmental Health 营养与食品卫生学 Nutrition and Food Hygiene儿少卫生与妇幼保健学 Maternal, Child and Adolescent Health 卫生毒理学 Hygiene Toxicology军事预防医学 Military Preventive Medicine中医学 Chinese Medicine中医基础理论 Basic Theories of Chinese Medicine中医临床基础 Clinical Foundation of Chinese Medicine中医医史文献 History and Literature of Chinese Medicine方剂学 Formulas of Chinese Medicine中医诊断学 Diagnostics of Chinese Medicine中医内科学 Chinese Internal Medicine中医外科学 Surgery of Chinese Medicine中医骨伤科学 Orthopedics of Chinese Medicine中医妇科学 Gynecology of Chinese Medicine中医儿科学 Pediatrics of Chinese Medicine中医五官科学 Ophthalmology and Otolaryngoloy of Chinese Medicine针灸推拿学 Acupuncture and Moxibustion and Tuina of Chinese medicine民族医学 Ethnomedicine中西医结合医学 Chinese and Western Integrative Medicine中西医结合基础医学Basic Discipline of Chinese and Western Integrative中西医结合临床医学Clinical Discipline of Chinese and Western Integrative Medicine药学 Pharmaceutical Science药物化学 Medicinal Chemistry药剂学 Pharmaceutics生药学 Pharmacognosy药物分析学 Pharmaceutical Analysis微生物与生化药学 Microbial and Biochemical Pharmacy药理学 Pharmacology中药学 Science of Chinese Pharmacology军事学 Military Science军事思想学及军事历史学 Military Thought and Military History军事思想学 Military Thought军事历史学 Military History战略学 Science of Strategy军事战略学 Military Strategy战争动员学 War Mobilization战役学 Science of Operations联合战役学 Joint Operation军种战役学(含第二炮兵战役学) Armed Service Operation (including Operation of Strategic Missile Force)战术学 Science of Tactics合同战术学 Combined-Arms Tactics兵种战术学 Branch Tactics军队指挥学 Science of Command作战指挥学 Combat Command军事运筹学 Military Operation Research军事通信学 Military Communication军事情报学 Military Intelligence密码学 Cryptography军事教育训练学(含军事体育学) Military Education and Training (including Military Physical Training)军制学 Science of Military System军事组织编制学 Military Organizational System军队管理学 Military Management军队政治工作学 Science of Military Political Work军事后勤学与军事装备学 Science of Military Logistics and Military Equipment军事后勤学 Military Logistics后方专业勤务 Rear Special Service军事装备学 Military Equipment管理学 Management Science管理科学与工程 Management Science and Engineering工商管理学 Science of Business Administration会计学 Accounting企业管理学(含财务管理、市场营销学、人力资源管理学) Corporate Management (including Financial Management, Marketing, and Human Resources Management)旅游管理学 Tourist Management技术经济及管理学 Technology Economy and Management农林经济管理学 Agricultural and Forestry Economics & Management农业经济管理学 Agricultural Economics & Management林业经济管理学 Forestry Economics & Management公共管理学 Science of Public Management行政管理学 Administration Management社会医学与卫生事业管理学 Social Medicine and Health Management教育经济与管理学 Educational Economy and Management社会保障学 Social Security土地资源管理学 Land Resource Management图书馆、情报与档案学 Science of Library, Information and Archival 图书馆学 Library Science情报学 Information Science档案学Archival Science。

able [`eibl] adj.能够abnormal [Qb`n?:m"l] adj.异常abort ["`b?:t]中断,停止absent [`Qbs"nt] adj. 不在的,缺少的acceleration [Qk.sel"`reiS"n] n. 加速,加速度access [`Qkses] vt. 存取,进入,接近action [`QkS"n]. 动作actuator [`Qktjueit"]n.操作(执行)机构,执行器address ["`dres] 地址adjust ["`d??st] 调整,校正adjustable wrench 活扳手adjustable ["`d??st"bl] 可调整的adjusting screw 调整螺钉adjustment ["`d??stment] 调节、调节装置air compressor空压机 [k"m`pres"] 压缩机air exhaust fan排气扇[ig`z?:st] 排气,抽完air [e"]风,空气alarm ["`lam] 报警align ["`lain] 定位,对准,调整alternating current AC 交流电 [?:l`t?:n"t] 轮流,交替ambient temp 环境温度ambient [`Qmbi"t] 周围的,环境的ammeter [`Qmit"] n. 电流表,安培计amp [Qmp] n. 安培ampere [`QmpE"] n. 安培amplifier [`Qmplifai"] n. 放大器,扩音器analog input [`Qn"l?g] 模拟量输入analog output 模拟量输出analog signal 模拟信号[`Qn"l?g] [`signl]analog [`Qn"l?g] 模拟analog-to-digital A/D 模数转换 [`did?it"l]angle valve 角伐angle [`QNgl] 角度application program 应用程序 [.Qpli`keiS"n] 请求,应用arc [a:k] 电弧,弧光area [`e"ri"] 面积,区域arrester [e`rest"] 避雷器assemble line装配线,生产线["`sembl]assemble ["`sembl] 安装,组装asynchronous motor 异步马达 [ei`siNkr"n"s]atomizing [`Qtm"s.fi"] 雾化attention ["`tenS"n] 注意auto reclose 自动重合闸autoformer 自耦变压器automatic [.?:t"``mQtik] AUTO 自动automatic voltage regulator 自动调压器 [`regjuleit"] auxiliary [?:g`zilj"ri] AUX 辅助的avoid ["`v?id] 避免,回避avometer ["`v?mit"]万用表,安伏欧表计axis [`Qksis] 轴,轴线back pressure 背压back up 支持,备用back wash 反冲洗baffle [`bQfl] 隔板bag filter 除尘布袋balance [`bQl"ns] 平衡,称,天平ball [bc:l] 球bar [ba:] 巴,条杆base [beis] 基础、根据battery [`bQt"ri] n. 电池bearing [`bE"riN] BRG 轴承bell [bel] 铃,钟 (ring 铃声,环)belt tension 皮带张力 [`tenS"n]belt [belt]带,皮带bi rate [bai reit] n.比特率binary [`bain"ri] 二进制,双bit [bit] 比特(二进制)black [blQk] 黑色blade [bleid] 叶片bleed [bli:d] 放气,放水blow [bl"u] 吹blown [`bl"un] 熔断的blue [blu:] 蓝色boiler BLR [`b?il"] 锅炉bolt [b"ult] 螺栓、拧螺丝boolean [`bu:li"n] n. 逻辑boost [bu:st] BST增压,提高boost pump BP 升压泵bore [b?:] 孔,腔both [b"UT] 双方,两者都bottom [`b?t"m] 底部bracket [`brQkit]支架,托架,括号brake [breik] 刹车,制动器,闸break [breik] 断开,断路、破裂、折断breaker coil 跳闸线路breaker [`breik"]断路器,隔离开关brown [braun] 棕色brush [br?S] 电刷,刷子bucket [`b?kit] 斗,吊斗buffer n. [`b?f"] 缓冲器bump [b?mp] 碰,撞击burner [`b":n"] 燃烧器button [`b?tn] 按钮bypass/by pass BYP 旁路byte [bait] 字节(八位)cabinet [`kQbinit] 厨柜,机箱、柜cable [`keibl] 电缆calculator [`kQlkjuleit"] 计算器caliber [`kQlib"] 管径、尺寸、大小cam [kQm] 凸轮cancel [`kQns"l] 取消、省略capacitance [k"`pQsit"ns] n. 容量,电容capacitor [k"`pQsit"] n. 电容器=capacitator card [ka:d](电子)板、卡carton [`ka:t"n] 纸板箱casualty [`kQ?ju"lti] 人身事故、伤亡、故障center [`sent"] 中心central control room 中控室central processing unit CPU 中央处理器centrifugal fan 离心风机centrifugal [sen`trifjug"] 离心的change [tSeind?] 改变character [`kQrikt"] 字符charge indicator 验电器、带电指示器charge [tSA:d?] n. 充电,电荷chassis earth 机壳接地chassis [`SQsi] 底座、机壳check [tSek] 检查chimney [`tSmni] 烟囱、烟道circuit [`s":kit] n. 电路circuit breaker 电路断路器circuit diagram 电路图 [`dai"grQm]circuitry [`s":kitri] n.电路,线路circulating water pump 循环水泵circulating 循环 [`s":kjuleitiN]clamp [klQmp] 夹具、钳class of insulation 绝缘等级 [.insju`leiS"n] class [kla:s] 类、等级、程度clean [kli:n] 清洁的、纯净的cleanse [klenz] 净化、洗净、消毒CLEARING OF FAULT 故障清除clockwise [`kl?kwaiz] 顺时针、右旋的clog [kl?g] 障碍,塞满,粘注close [kl"uz] 关闭closed-loop 闭环 [lu:p]coarse [k?:s] 粗的、不精确的code [k"ud] 代号、密码coder [`k"ud"] 编码器coil [k?il] n.线圈cold [k"uld] 冷,冷的,感冒collect [k"`lekt] 收集colour [`k?l"] 颜色command [k"`ma:nd] 命令、指挥communication [k".mju:ni`keiSn] 通信、通讯compensation [k?mpen`seiS"n]补偿,矫正component [k"m`p"un"nt] 元件compress air 压缩空气 [E"]compress [k"m`pres] 压缩compressor [k"m`pres"] 压缩机computer [k"m`pju:t"] 计算机condensate [k?n`denseit] 冷凝、使凝结condition [k"n`diS"n] 条件、状况、环境conduct [`k?nd?kt] 传导conductivity [.k?nd?k`tiviti] 导电率conductor [k"n`d?kt"] n.导体,导线configure [k"n`fig"] 组态congealer [k"n`d?i:l"] 冷却器、冷冻器connect [k"`nekt] 连接connection [k"`nekS"n] 联接connector [k"`n"kt"] 联接器、接线盒console [k"n`s"ul] 控制台constant [`k?nst"nt] 恒定的contact [`k?ntQkt] n.接触,触点,vt.接触,联系contact to earth 接地、触地、碰地 [":P] contact [`k?ntQkt] 触点contactor [`k?ntQkt"] (电流)接触器、触头continuous [k"n`tinju"s] 连续的control [k"n`tr?l] CNTR/CNTPL 控制control panel 控制盘 [`pQnl] 面板,仪表板,屏幕control valve 调节阀 [vQlv]controller [k"n`tr"ul"] 控制器convert [k"n`v":t]n.转换 vt.使转变,转换.... conveyor [k"n`vei"] 传送带,输送机cooktop [`kukt?p] n.炉灶cool [ku:l] 冷的cooler [`ku:l"] 冷却器cooling fan 冷却风机 [fQn]cooling tower 冷却塔 [`tau"] 塔,城堡cooling water pump 冷却水泵cooling [`ku:liN] 冷却copy [`k?pi] 拷贝core [k?:] 铁心、核心、磁心correct [k"`rekt] 正确的,改正correction [k"`rekS"n] 修正、改正corrosion [k"`r"u?"n] 腐蚀counter [`kaunti"] n.计数器couple [`k?pl] CPL 联轴器curdle [`k":dl] 凝固currency [`k?r"nsi] 流动、流通current [`k?r"nt] n. 电流,水流、当前、气流current transformer CT 电流互感器 [trQns`f?:m"]cursor [`k":s"] 光标curve [k":v] 曲线cutter [`k?t"] 切削工具,刀具ccycle 循环、周期、周波cylinder [`silind"] CYL 汽缸,圆柱体cymometer [sai`m?mit"] 频率表,频率计damage [`dQmid?] 损坏、破坏danger zone 危险区 [z"un]danger [`deind?"] 危险、危险物dangerous [`deind?r"s] 危险的dank [dQNk] 潮湿data base 数据库[beis] 底部,基层,灯座data pool 数据库 [pu:l]data [`deit"] 数据deactivate [di:`Qktiveit] 使无效dead band 死区 [ded] [bQnd] 区,队debugging [di:`b?giN] n.调试deceleration [di:.sel"`reiS"n] n. 减速,减速度decrease [di:`kri:s] DEC 减少deep [di:p] 深度、深的、深default [di`f?:lt] n. 默认(值),缺省(值)degree [di`gri:] 度、等级delay time 延时 [di`lei] 延迟,滞后 relay [`ri:lei] 继电器delay [di`lei] 延迟,滞后delete [di`li:t] 删除,作废defective [di`fektiv] 有缺陷的,损坏,次品,不完全description [dis`kripS"n] 说明、描述detect [di`tekt] 发现、检定detector [di`tekt"] 检测器,探测器deviate [`di:vieit] 背离、偏差device [di`vais] 设备、仪器,装置diagnosis [.dai"g`n"usis] 诊断diagram [`dai"grQm] 图形、图表diameter [dai`Qmit"] 直径dielectric [.daii`lektrik] 介质、绝缘的diesel generator 柴油发电机[`di:z"l] [`d?en"reit"]发电机,振荡器differential [.dif"`renS"] 差别的,差动的,微分differential pressure DP/DSP 差压 [`preS"]digital input/output 数字量输入/输出 [`did?itl] 数字的,数字digital signal 数字信号[`did?itl][`signl]digital [`did?itl] 数字的digital-to-analog D/A 数/模转换 [`Qn"l?g]direct current DC 直流(电) [di`rekt] 直接的disassembly [.dis"`sembli] 拆卸disaster shutdown 事故停机 [`S?tdaUn] 停工(机),关机disaster [di`za:st"] 事故、故障discharge 排除、放电、卸载disconnect switch 隔离开关disconnect 断开,分离disconnector 隔离器、隔离开关discrete [dis`kri:t] adj.不连续的,离散的discrete input 开关量输入discrete output 开关量输出disk [disk] 磁盘diskette [dis`ket] 磁盘,磁碟display [di`splei] 显示、列屏dissipation [.disi`peiS"n] n. 分配,分发distance [`dist"ns] 距离,间隔distilled water DISTL WTR 蒸馏水 [dis`tild] 由蒸馏得来的distributed control system DCS 集散控制系统distributed [dis`tribju:tid] 分布的distributing board 配电盘 [dis`tribju:tiN] [b?:d]double [`d?bl] 两倍的,双重的dowel pin 定位销 [`dau"l] 销子 [pin]down [daun] 向下的,向下download 下载downtime 停机时间drain DRN 疏水、排放drawing [`dr?:iN] 画图.制图 ,图样、牵引drill [dril] 钻孔、钻头、钻床drive nail 钉钉子drive [draiv] 驱动、强迫drop [dr?p] 滴,点滴,落下dry [drai] 干、干燥duct [d?kt] 风道、管道dust catcher 除尘器、吸尘器 [`kQtS"] 捕捉器dust [d?st] 灰尘duty [`dju:ti] 责任,义务dynamic [dai`nQmik] 动态的dynamometer [.dain"`m?mit"] 功率表earth connector 接地线、接地 [":T] [k"`n"kt"]earth fault 接地故障 [f?:lt]earth lead 接地线、接地 [li:d] 引线,领导earth 大地 [":T]eccentricity [eksen`trisiti] 偏心、扰度edit [`edit] 编辑efficiency [i`fiS"ns] 效率ejected [i`d?ekt] 喷射,驱逐,被放出的ejection [i`d?ekS"n] 弹出,排出,喷出,喷射electric failure 触电 [i`lektrik] 电的 [`feilj"] 故障,失败electric spark 电火化 [spa:k]electric [i`lektrik] 电的、电动的、导电的electrical machine 电机 [m"`Si:n] 机器,机械electrical service 供电 [`s":vis] 维修,服务,管理electrical [i`lektrikl] 电的、电气的electric-hydraulic control 电/液控制 [hai`dr?:lik] [k"n`trol] electrician [ilek`triSn] 电工electrode [i`lektreUd] 电极electronic [ilek`tr?nik] 电子的、电子学的electrostatic [i`lektr"u`stQtik] 静电的electrotechnics [i`lektr"u`tekniks] 电工学、电工技术element [`elim"nt]元件、零件、单元] n.电梯,升级机?elevator [`eliveitemergency [i`m":d?nsi] EMERG 紧急事故empty [`empti]排空enable [i`neibl] 使能够,允许enclosure [in`kl"u?"] n.密封,外壳,包围encoder [in`k"ud"] 编码器end cover 端盖end 末端、终结energy meter 电度表energy [`en"d?i] 能、能量engineer [.end?i`ni"] 工程师enter [`ent"] 开始、使进入entry [`entri] 输入equipment [i`kwipm"] 设备error [`er"] 错误escape valve 安全阀 [is`keip]event [i`vent] 事件exceed [ik`si:d] 超过excess [ik`ses] 超过、过度exciter [ik`sait"] 励磁机exit [`eksit] 出口expansion [iks`pQnS"n] EXP 膨胀explosion [iks`pl"u?"n] 爆炸external [eks`t":nl] 外部的、表面的extra-high voltage 超高压 [`ekstr"] 额外的,特大的factor [`fQkt"] 因素、因数factory [`fQkt"ri] 工厂、制造厂failure [`feilj"] FAIL 失败,故障false [f?:ls] 假的、错误的fan [fQn] 风扇、风机fault [f?:lt] 故障faultless [`f?:ltlis]没有缺陷、完美的faulty operation 误操作 [`f?:lti] [.?p"`reiS"n]运算,工作features [`fi:tS"] 特点feed [fi:d] 馈、供给feedback [`fi:dbQk] 反馈fiber optic 光纤 [`faib"] 光纤,纤维 [`?ptik] 光学上的,视觉的field [fi:ld] n.现场,原野file [fail] 文件、锉刀fill [fil] 装填filter [`filt"] n. 过滤器,滤波器,滤网,filter differential pressure FILTR DP 滤网压差final [`fain"l] 最后的fire pump 消防水泵fire [`fai"] 燃烧、火焰fireproof [`fai"pru:f] 防火的、阻燃的fixed [fikst] 固定的、固定、确定、保护屏flank [flQNk] 侧翼、侧面flash lamp 闪光灯flash light 闪光flash [flQS] 闪光、闪烁、闪蒸float-charge浮充电[fl"ut] 浮动 [tSa:d?] 充电,电荷flow [fl"u] 流量、流动flowmeter [`fl"umi:t"] 流量计flue gas 烟气 [gQs] 气体,煤气,毒气,汽油flue [flu:] 烟道fluid [`fluid] 液体flux [fl?ks] n. 流量,通量forbid [f"`bid] 禁止force draft fan 送风机 [drA:ft] 通风force [f?:s] 强制form [f?:m] 形式、形状、形成、构成format [`f?:mQt] 形式、格式frequency [`fri:kw"nsi] 频率friction [`frikS"n] n. 摩擦,摩擦力from [fr?m] 从、来自、今后full speed 额定频率fully [`fuli] 充分的、完全的fume [fju:m] 烟,冒烟function [`f?NkS"n] 功能fuse holder 保险盒 [`h"uld"]fuse [fju:z] 保险丝、熔断器fusible cutout 熔断开关[`fju:z"bl]溶解的,可融的[`k?taut]断流,保险装置gauge [ged?] 仪表、标准gear pump 齿轮泵 [gi"] [p?mp]gear shift housing 变速箱 [Sift]换挡,变化 [`h"uziN]外壳,套gear [gi"] 齿轮gearbox 齿轮箱general control panel总控制屏[`d?en"r"l]普通的,全面的,综合的generator [`d?en"reit"] n. 发电机gland seal 轴封 [glQnd]填料函盖,密封压盖 [si:l] 封,密封,填料glass-paper 砂纸go on 继续goal [g"ul] 目的、目标graphics [`grQfiks] 调节阀grease [gri:s] 图形green [gri:n] 绿色ground [graUnd]地面,场所、接地 earth[":T]地球,接地、大地,泥土guide [gaid] 领路人、向导half [hA:f] 一半、一半的halt instruction 停机指令[h?:lt]停机,中断,暂停[in`str?kS"n]halve [ha:v] vt. 二等分,平分hammer [`hQm"] 锤子hand [hQnd] 手,指针handle[`hQndl]vt.触摸,运用,买卖,处理,操作vi.搬运,易于操纵handwheel [`hQndwi:l] 手轮,驾驶盘hardware [`hA:dwE"] 硬件havoc [`hQv"k] n.严重破坏 vt.损害heat [hi:t] 热、加热heater [`hi:t"] 加热器heating [`hi:tiN] 加热,供暖hertz [`h":ts] HZ 赫兹high pressure HP 高压history [`hist"ri] 历史hold [h"uld] 保持hopper [`h?p"] 漏斗、料斗hose [h"uz] 软管、水龙带hot circuit 通电线路 [`s":kit]hot start 热态启动 [stA:t]hot [h?t] 热的,热情的,辣的hydraulic [hai`dr?:lik] 水力的,液压的,油压的,水压的I/O point 输入/输出点inboard [`inb?:d] 内侧idle [`aidl] 空闲的,空载的、无效的ignitor [ig`nait"] 点火,点燃,点火器impedance [im`pi:d"ns] 阻抗import [im`p?:t] 进口、输入、引入impulse [`imp?ls] 脉冲、冲击、冲量inch [intS] IN 英寸inching [`intSiN] 缓动、点动increase [in`kri:s] INC 增加increment [`inkrim"nt] 增量,加1,递增index [`indeks] 索引、指标,指针,指数indicate [`indikeit] 指示,显示,表明indicator [`indikeit"] 指示器inductance [in`d?kt"ns] 电感,自感应induction motor 异步电动机 [in`d?kS"n] 感应 [`m"ut"]inductive reactance 感抗[in`d?ktiv]电感的,感应的[ri`Qkt"ns]电抗inductor [in`d?kt"] n.电感器,感应器inhibit [in`hibit] 禁止,抑制,约束init 初使化initial [i`niS"l] 初始的,最初的inlet [`inlet] 入口input/output I/O 输入/输出insert [in`s":t] 插入inside [`in`said] 内侧、内部inspection [in`spekS"n] 观察、检查inspector [in`spekt"] n.检测install [in`st?:l] 安装instruction [in`str?kS"n] n. 指令,指导,指示,说明书,instrument panel 仪表盘 [`pQnl]instrument [`instrum"nt] 仪器insufficient [.ins"`fiS"nt] 不足的,不够的insulate [`insjuleit] 绝缘、隔离insulation [.insju`leiS"n] 绝缘insulator [`insjuleit"] n.绝缘体integer [`intid?"] 整数integral [`intigr"l] 积分,积分的interface [`int".feis] n.分界面,界面,接口interface [`int".feis] 接口interference [.int"`fi"r"ns] 干扰、干涉intermediate relay 中间继电器 [.int"`mi:dj"t]中间的,中级,中频internal [in`t":nl] 内部的,内部interrupt [.int"`r?pt] 中断into [`intu] 向内、进入,到...里,进入到...之内inverter [in`v":t"] 逆变器、反相器、非门isolator [`ais"leit"] 隔离器、刀闸,分离器,绝缘体job [d??b] 工作jumper [`d??mp"] 跳线、跨接junction box 接线盒 [`d??NkS"n]key [ki:] 键销、钥匙、键槽keyboard [`ki:b?:d] 键盘kilovolt-ampere KVA 千伏安 [`kil"Uv"Ult`Qmpe"]kink [kiNk] 弯曲、缠绕knack [nQk] 技巧、窍门、诀窍knife-switch 闸刀开关label [`leibl] 标号、标签,商标,标志laboratory [l"`b?r"t"ri] 实验室ladder diagram 梯形图 [`lQd"] [`dai"grQm]ladder logic Diagram 逻辑梯形图[`l?d?ik][`dai"grQm]ladder [`lQd"] 梯子、阶梯lamp [lQmp] n.灯、光源last [la:st] 最后的,末尾的leak [li:k] 泄漏,漏,漏洞(动词)leakage [li:kid?] n. 漏,泄漏,渗漏least [li:st] 最少的、最小的left [left] 左length [leNT] 长度level [`levl] 液位、水平lever [`li:v"] 杆,杠杆,控制杆lifebelt [laifbelt] 安全带、保险带lift [lift] 提、升light run 空转 [lait] [r?n]light [lait] 光,灯,轻,淡,日光,光亮,点,点燃,照亮lightning [`laitniN] 雷电limit [`limit] LMT 极限、限制limit switch [`limit] 限位开关limiter [`limit"] 限制器、限位开关line [lain] 线、直线list [list] 列表、目录liter [`li:t"] 公升little [`litl] 小的,少许,少的load [l"ud] n. 负荷,负载load thrown on 带负荷 [Tr"un]local attendant 现场值班员 ["`tend"nt]维护人员,值班人员,服务员local repair 现场检修 [ri`pE"] 修理,修补local [`l"uk"l] 当地的,局部,本地location [l"u`keiS"n] 位置,定位,单元,场所lock [l?k] 闭锁、密封舱、固定logger [`1?g"] 记录器、拖车logic [`l?d?ik] 逻辑long [l?N] 长loop [lu:p] 环、回路loose [lu:s] 松的、不牢固的loosen [`lu:sn] 松开、松动loss [l?s] 损失、减少low [l"u] 低lower [`l"u"] 较低的、降低low-half 下半 [hA:f]lub oil pump 润滑油泵lub oil 润滑油lubricate [`lu:brikeit] LUB 润滑machine [m"`Si:n] 机器,机械magnet [`mQgnit] 磁main wire 电源线 [`wai"]main [mein] 主要的,主群组maintain [men`tein] 维修、维持、保养maintenance manual 检修手册 [`mQnju"l]maintenance [`meintin"ns] 维护、维护,检修、小修make [meik] 制造 ,是成为make sure 确定 [Su"] 的确,对...有把握make up 补充(补给)malfunction [mQl`f?NkS"n] 故障,出错、误动、失灵management [`mQnid?m"nt] 管理、控制、处理man-machine interaction 人机对话[mQn][m":`Si:n][.int"`QkS"n] man-machine interface MMI 人机接口 [`int".feis] 界面,接口manometer [m"`n?mit"] 压力表manual reject MRE 手动切换 [ri`d?ekt]拒绝,排斥manual [`mQnju"l] 手动、手册manual/Auto station M/A STATION 手动/自动切换站mark [mA:k] 型号、刻度、标志、特征master control room 主控室、中央控制室 [k"n`trol]master [`mA:st"]主人,主要,控制,师傅,正版material [m"`ti"ri"l] n. 材料,原料maximum [`mQksim"m] 最大,最大值,最高,mean [mi:n] 平均,平均值、中间的measure [`me?"] 度量、测量,量,尺寸mechanical trip vlv 机械跳闸阀 [mi`kQnikl] [trip] 脱扣,解扣mechanical [mi`kQnikl] 机械的、力学的mechanism [`mek"niz"m] 机械、力学、方法、装置、机构medial [`mi:dj"l] 中间的、平均的medium [`mi:dj"m] 中间的、中等的、装置、介质、工质melt [melt] 溶解,熔化memory [`mem"ri]存储,存储器,记忆menu [`menju:] n. 菜单metal [`metl] 金属meter [`mi:t"] n.仪表,米,表meter switch 仪表开关method of operation 运行方式 [.?p"`reiS"n]操作,运转method [`meT"d] 方法、规律、程序microphone [`maikr"f"Un] 麦克风、话筒,传声器,扩音器microprocessor [maikr"u`pr"uses"] n.微处理器middle [`midl] MID 中间的,中间,当中,中型mill [mil] 磨、磨粉机、压榨机,铣刀mind [maind] 头脑、精神、介意minimum [`minim"m] 最小的minor overhaul 小修 [main"]次要,副修科目[.auv"`h?:l]检修,大修minute [mai`nju:t] 分钟misfill 误装mishandle [`mis`hQndl] 胡乱操作、误操纵misread [mis`ri:d] 错读miss [mis] 过错,避免,小姐,姑娘,故障,失败miss operation 误动作、误操作 [.?p"`reiS"n]mistake [mis`teik] 错误、事故mixer [`miks"] n. 搅拌器,混合器,混频器modem [`m"ud"m] 调制解调器modify [`m?difai] 修改、更改modulating valve 调节阀 [`m?djuleit] [vQlv]module [`m?dju:l] n.模块,组件,模数moisture [`m?istS"] 湿度、湿汽mold [m"uld]模具monitor [`m?nit"] n.******,监视器,监控器 vt.&vi.监控month [m?nT] 月more than 超过[m?:] 更多的[D"n] 与...相比较,比motor MTR 马达 [`m"ut"]motor winding 电动机组绕组 [`waindiN] 绕组,线圈,绕,缠mount [maunt] 安装、固定mouse [maus] 鼠标move [mu:v] 移动multimeter [`m?ltimit"] 万用表nail [neil] 钉子、钉钉子naught line 零线 [`n?:t] 零,无neck [nek] 颈,管颈needlepoint vlv 针阀 [`ni:dlp?int]negative pressure NEG PRESS 负压negative [`neg"tiv] 负的network [`netw":k] 网络neutral line 中性线 [`nju:tr"l]中性的newly [`nju:li] 最近,重新、新地nipper [`nip"] 钳子、镊子noise remove 消音器 [n?iz][ri`mu:v]noise [n?iz] 噪音no-loading 空载nominal power 额定功率[`n?minl]标称的,额定的[`pau"] nominal [`n?minl] 标称的、额定的normal closed contact 常闭触点 [`k?ntQkt]触头,触点,接点normal [`n?:m"l] 正常的、常规的normally [`n?:m"li] 正常地not available 无效、不能用 ["`veil"bl] 可用的,有用的nozzle [`n?zl] 喷嘴number [`n?mb"] 数字、号码、数目nut [n?t] 螺母、螺帽occur ["`k":] 发生ohm ["um] n.欧姆oil breaker 油开关 [`breik"]oil gun 油枪 [g?n]oil level 机油平面[`levl]oil [?il] 油oiler [`?il"] 注油器,油商oilless [?illes] 缺油的on/off 开/关online [?nlain] 联机的,在线的open circuit 开路 [`"up"n][`s":kit]open-loop 开环 [lu:p]operating panel 操作盘 [`?p"reitiN][`pQnl]operation [.?p"`reiS"n] 操作、运行operational log 运行记录[?.?p"`reiS"n][l?g]operator keyboard 操作员键盘 [`ki:b?:d]operator station 操作员站 [`steiS"n]operator [`?p"reit"] 操作员option switch 选择开关optional [`?pS"n"l] 可选的,选择orbit [`?:bit] n. 轨道,轨迹orientation [.?rien`teiS"n] 方位,定向,定位original ["`rid?"n"l] 初始的、原始的out 出、出口outboard [`autb?:t] 外侧的outage [`autid?] 断电,停机,出故障outlet [`autlet] 出口output [`autput] 产量、产品、输出oven [`?vn] n.烤箱over current 过流 [`k?r"nt]over loading 过载 [`l"udiN]over voltage 过压 [`v"Ultid?]over [`"uv"] 结束,上面的,过分的overcool [`"uv"ku:l] 过冷却overflow [`"uv"`fl"u] 溢流overhaul [."uv"`h?:l] 大修,检修overhead [`"uv"hed] 顶部,高空,架空overheat [."uv"`hi:t] 使过热overload [`"uv"`l"ud]n.过载overload protection 过载保护[`"uv"`l"ud][pr"`tekS"n] package [`pQkid?] 组件、包,插件packaging [`pQkid?iN] n.包装panel [`pQnl] 屏、盘parameter [p"`rQmit"] 参数part [pA:t] 部分、部件password [`pA:sw":d] 口令,密码peak [pi:k] 峰值percent [p"`sent] PCT 百分数percentage [p"`sentid?] 百分比perfect [`p":fikt] 完全的、理想的performance [p"`f?:m"ns] 完成、执行、性能periodic inspection 定期检查 [in`spekS"n]periodic [pi"ri`?dik] 周期的、循环的peripheral equipment 外围设备 [i`kwipm"nt] peripheral [p"`rif"r"l] 周围的,外围设备,周边的permanent [`p":m"n"nt] 永久的、持久的permit [p"`mit] 允许PG 编程器phase not together 缺相、失相[feiz]相[t"`geD"]共同phase [feiz] PH 阶段、状态、方面、相phase sequence 相序 [`si:kw"ns] 次序,顺序,时序phase voltage 相电压phase-failure protection 断相保护 [`feilj"]phase-in 同步photoelectricity [.f"ut"uilek`trisiti] 光电piezometer [.pai"`z?mit"] 压力计pilot [`pail"t] 导向、辅助的、控制的pipe [paip] 管、管道plan [plQn] 计划plant [plA:nt] 工场、车间plastic [`plQstik] 塑料PLC(programmable Logic Controller) 可编程序逻辑控制器pliers [`plai"z] 钳子、老虎钳plug socket 插座 [`s?kit]plug [pl?g] 塞子、栓、插头plus [pl?s] 加pneumatic [nju`mQtik] 气动的point [p?int] 点pointer [`p?int"] 指针,指示器pole [p"ul] 极、柱,极点,电极,电杆pollution [p"`lu:S"n] 污染portion [`p?:S"n] 一部分position [p"`ziS"n] POS 位置potential [p"`tenS l] 电势,电位potential transformer PT 电压互感器[p"`tenS l][trQns`f?:m"] power failure 停电 [`pau"] [`feilj"]故障,失败power [`pau"] PWR 功率、电源,能力,动力PPI(point-to-point Interface)点对点接口preblow 预吹preferential [.pref"`renS"l] n. 优先的,优先权perform [p"`f?:m] 预先形成,预制,预成型坯,粗加工的成品preheat [`pri:hi:t] 预热preheater [`pri:hi:t"] 预热器preliminary [pri`limin"ri] 准备工作present [pri`zent] 出现preset [`pri:`set] 预设、预置press [pres] 压,按,压力pressure [`preS"] PRES 压力primary [`praim"ri] 初级的、一次的principle [`prins"pl] 原理、原则printer [`print"] 打印机probe [pr"ub] 探头process [pr"`ses] 过程、方法production [pr"`d?kS"n] 生产、产品、作品program [`pr"ugrQm] 程序programmable [`pr"ugrQm"bl] adj.可设计的,可编程的prohibit [pr"`hibit] 禁止proportional / integral / derivative PID 比例/积分/微分protection [pr"`tekS"n] PROT 保护、预防protocol [`pr"ut"k?l] n.协议pull [pul] 拖 ,拉pulse [p?ls] 脉冲、脉动pump body 泵体pump [p?mp] 泵purge [p":d?]净化、吹扫push and pull switch 推拉开关push button 按钮push [puS] 推pushbutton [puS`b?tn] n. 按钮pyod [`pai"d] 热电偶quality [`kw?liti] 质量quit [kwit] 停止、离开、推出rack earth 机壳接地 [rQk] 机架,机柜,导轨 [":T] radiation fin 散热片[.reidi`eiS"n] 辐射,发散 fin] 散热片radiator [`reidieit"] n. 散热器,冰箱raise [reiz] 升高range [reind?] 范围、量程rate [reit] 速度,速率rated power [`reitid] 额定功率rated [`reitid] 额定的、比率的ray [rei] 光线、射线read out 读出、结果传达reading 读数real time 实时的 [`ri:"l]receive tank 回收箱、接收箱 [ri`si:v] [tQNk]receive [ri`si:v] 收到,接到,接收,接待recipe [`resipi] 处方、配方reclosing 重合闸recovery time 恢复时间 [ri`k?v"ri]recovery [ri`k?v"ri] 恢复、再生rectification [.rektifi`keiS"n] 整流、检波、调整rectifier [`rektifai"] n.整流器,矫正器red 红色reduction [ri`d?kS"n] 还原、缩小、降低redundancy [ri`d?nd"nsi] 冗余、多余reference [`refr"ns] REF 参考、参照、证明书reflux [`ri:fl?ks] 倒流、回流register [`red?ist"] 寄存器regulate [`regjuleit] 调节、控制relay [`ri:lei] n. 继电器release [ri`li:s] 释放reliability [i"`biliti] 可靠性、安全的relief [ri`li:f] 去载、卸载、释放、解除relieve valve 安全阀、减压阀[ri`li:v] [vQlv] remove 除去、拆卸renewal [ri`nju"l] 更新、更换repair [ri`pE"] 修理repairer 修理工、检修工repeat [ri`pi:t] 重复、反复replace [ri`pleis] 重新、启动、更换、替换replacement parts 备件、替换零件[ri`pleism"nt][pA:t] request [ri`kwest] REO 请求require [ri`kwai"] 要求reserve parts 备件 [ri`z":v]reserved [ri`z":vd] 备用的reset [`ri:set] 复位resist [ri`zist] n.阻抗resistance [ri`zist"ns] n.电阻、阻抗resolution [.rez"`lju:S"n] n. 分辨率response [ris`p?ns] 响应restart [ri:`stA:t] 重新启动retighten [ri`tait"n] 重新紧固retract [ri`trQkt] 可伸缩的、缩回return oil 回油 [ri`t":n]return [ri`t":n] 返回reverse rotation 反转 [ri`v":s]rig [rig] 安装、装配、调整right [rait] 右right-of-way 公用线路ring [riN] 环roller [`r"ul"] 滚筒、辊子rotary switch 转换开关 [`r"ut"ri]rotate [r"u`teit] 旋转rotation [r"u`teiS"n] 旋转,转动,回转rotor [`r"ut"] 转子routine [ru:`ti:n] 例行的、日常的routing inspection 日常检查、日常检测 [in`spekS"n] routing maintenance 日常维护 [`ru:tiN] [`meintin"ns] rubber [`r?b"] 橡胶run back 返回run 运行safe [seif]安全的、可靠的、稳定的safety cap 安全帽safety [`seifti] 安全sample [`sQmpl] 取样、举例sampling [`sA:mpliN] 采样、抽样、取样saw [s?:]锯scale [skeil] 刻度、衡量、比例尺、测量、铁锈水垢scan [skQn] 扫描schedule [`Sekju:l] 时间表、计划表screen [skri:n]] 屏幕screw driver 螺丝刀screw socket 螺口插座screw [skru:] 螺杆、螺丝、旋转seal [si:l] 密封search [s":tS] 寻找、查找second [`sek"nd] 秒、第二seep [si:p] 渗出、渗漏seepage [`si:pid?] 渗漏现象select [si`lekt] 选择selector [si`lekt"] 选择器self-hold [self] [h"uld]自保持self-running 自启动send [send] 发送,寄,发射sensor [`sens"] 传感器sequence [`si:kw"ns] 顺序、序列service manual 维修说明书series [`si"ri:z] n.连续,串联service [`s":vis] 维修.保养.服务、伺服servo [`s":v"u] 伺服servomotor [`s":v"u.m"ut"] 伺服电机set up 安装、调整、建立set [set] 设定shaft [SA:ft] 轴、手柄、矿井shake [Seik] 摇动、振动shield [S i:ld] 屏蔽shift [S ift] 值、替换shock [S?k] 震动,使受电击short circuit 短路short [S ?:t] 短的、短路、使短路should [S ud]应该,将要show [S "u] 展览,显示,指示shut off 关闭 [S ?t] 关闭,关上shut [S?t] 关上,更加shutdown [`S?tdaUn] 停止、停机siccative [`sik"tiv] 干燥剂,使干燥的,side [said] 侧边siemens [`si:m"z] 西门子sifter [`sift"] 筛子、滤波器sign [sain] 标记、注册signal lamp 信号灯signal [`signl] 信号,发信号silencer [`sail"ns"] 消音器simulation [.simju`leiS"n]n.仿真,模拟simulator [`simjuleit"] 仿真机single blade switch 单刀开关 [bleid] 刀刃,刀片single [`siNgl] 单个的、个体的site [sait] 现场size [saiz] 尺寸、大小skip [skip] 空指令、跳跃smoke [sm"uk] 烟、冒烟smokes-stack 烟囱 [stQk] 烟囱,堆,堆栈smooth [smu:D] 平滑的、光滑的socket wrench 套筒扳手socket [`s?kit] 插座software [`s?ftwE"] 软件solenoid [`s"ulin?id] 电磁线圈solid wrench 呆扳手solid [`s?lid] 固体、坚固的、固体的source [s?:s] 源、电源spanner [`spQn"] 扳手spare [sp?"] 备用的、空余的spare parts 备件、备品spark [spA:k] 火花special tool 专用工具special [`speS"l] 特别的、专门的specification [.spesifi`keiS"n] 技术要求,说明书speed [spi:d] 速度spray nozzle 喷嘴 [sprei] 喷雾,喷射spring clutch 弹簧离合器 [kl?tS] 离合器spring [spriN] 弹簧、春天stack [stQk] 烟囱,堆栈stall [st?:l] 停车、阻止standard [`stQnd"d] 标准standby [`stQndbai] 备用、待机star [stA:] 星、星形连接start up 启动start [stA:t] 启动、开始starter [`stA:t"]n.启动器,启动钮starting conditions 启动条件 [`sta:tiN] 启动,开始,出发start-up sequence 启动程序 [`si:kw"ns] 程序,次序,顺序,序列state [steit] 状态statement [`steitm"nt] 声明、语句station [`steiS"n] 站、台,岗位,身份,地点,发电厂,位置stator coil 定子线圈stator core 定子铁芯 [k?:]stator [`steit"] 定子status display 状态显示status [`steit"s] 状态stability [st"`biliti] 稳定性steam [sti:m] STM 蒸汽step [step] 步,步幅step-by-step 步进式,逐步,按部就班的step-by-step motor 步进电动机step-down transformer 降压变压器step-up transformer 升压变压器still [stil] 仍然,还,更stop [st?p] 停止storage battery 蓄电池storage [`st?rid?] 储存strainer [`strein"] 滤网,过滤器streamline [`stri:mlain] 流水线stretching [`stretS iN]拉伸,伸长suction pump 真空泵 [`s?kS "n] 吸入,抽气,superheater [`sju:p"hi:t"] 过热器supply [s"`plai] 供给support [s"`p?:t] 支持、支撑sure [S u"] 确信的、可靠的switch [switS] n. 开关,电闸switch blade 开关闸刀 [bleid] 刀刃,刀片switch [switS] 开关、切换switching off 断开 [`switS iN]switching on 接通switching push button 开关按钮symbol [`simb"l] 符号synchro [`siNkr"u]同步,同步机synchronization [.siNkr"nai`zeiS "n] 同步synchronizer [`siNkr"naiz"] 同步器syren [`sai"r"n] 汽笛、报警器syringe [`sirind?] 注油器system unit 主机system [`sist"m] 系统tab [tQb] 表格,制表tachogenerator [`tQk"`d?en"reit"] 测速发电机tandem [`t Qnd"m] 串联tank [tQNk] 箱temperature compensation 温度补偿 [k?mpen`seiS "n] temperature [`tempritS"] 温度。

翻译翻译Electric Power Systems.The modern society depends on the electricity supply more heavily than ever before. It can not be imagined what the world should be if the electricity supply were interrupted all over the world. Electric power systems (or electric energy systems), providing electricity to the modern society, have become indispensable components of the industrial world. The first complete electric power system (comprising a generator, cable, fuse, meter, and loads) was built by Thomas Edison – the historic Pearl Street Station in New York City which began operation in September 1882. This was a DC system consisting of a steam-engine-driven DC generator supplying power to 59 customers within an area roughly 1.5 km in radius. The load, which consisted entirely of incandescent lamps, was supplied at 110 V through an underground cable system.. Within a few years similar systems were in operation in most large cities throughout the world. With the development of motors by Frank Sprague in 1884, motor loads were added to such systems. This was the beginning of what would develop into one of the largest industries in the world. In spite of the initial widespread use of DC systems, they were almost completely superseded by AC systems. By 1886, the limitations of DC systems were becoming increasingly apparent. They could deliver power only a short distance from generators. To keep transmission power losses ( I 2 R ) and voltage drops to acceptable levels, voltage levels had to be high for long-distance power transmission. Such high voltages were not acceptable for generation and consumption of power; therefore, a convenient means for voltage transformation became a necessity.The development of the transformer and AC transmission by L. Gaulard and JD Gibbs of Paris, France, led to AC electric power systems. In 1889, the first AC transmission line in North America was put into operation in Oregon between Willamette Falls and Portland. It was a single-phase line transmitting power at 4,000 V over a distance of 21 km. With the development of polyphase systems by Nikola Tesla, the AC system became even more attractive. By 1888, Tesla held several patents on AC motors, generators, transformers, and transmission systems. Westinghouse bought the patents to these early inventions, and they formed the basis of the present-day AC systems. In the 1890s, there was considerable controversy over whether the electric utility industry should be standardized on DC or AC. By the turn of the century, the AC system had won out over the DC system for the following reasons: (1)Voltage levels can be easily transformed in AC systems, thus providing the flexibility for use of different voltages for generation, transmission, and consumption.(2)AC generators are much simpler than DC generators.(3)AC motors are much simpler and cheaper than DC motors.The first three-phase line in North America went into operation in 1893——a 2,300 V, 12 km line in southern California. In the early period of AC power transmission, frequency was not standardized. This poses a problem for interconnection. Eventually 60 Hz was adopted as standard in North America, although 50 Hz was used in many other countries. The increasing need for transmitting large amounts of power over longer distance created an incentive to use progressively high voltage levels. To avoid the proliferation of an unlimited number of voltages, the industry has standardized voltage levels. In USA, the standards are 115, 138, 161, and 230 kV for the high voltage (HV) class, and 345, 500 and 765 kV for the extra-high voltage (EHV) class. In China, the voltage levels in use are 10, 35, 110 for HV class, and 220, 330 (only in Northwest China) and 500 kV for EHV class . The first 750 kVtransmission line will be built in the near future in Northwest China. With the development of the AC/DC converting equipment, high voltage DC (HVDC) transmission systems have become more attractive and economical in special situations. The HVDC transmission can be used for transmission of large blocks of power over long distance, and providing an asynchronous link between systems where AC interconnection would be impractical because of system stability consideration or because nominal frequencies of the systems are different. The basic requirement to a power system is to provide an uninterrupted energy supply to customers with acceptable voltages and frequency. Because electricity can not be massively stored under a simple and economic way, the production and consumption of electricity must be done simultaneously. A fault or misoperation in any stages of a power system may possibly result in interruption of electricity supply to the customers. Therefore, a normal continuous operation of the power system to provide a reliable power supply to the customers is of paramount importance. Power system stability may be broadly defined as the property of a power system that enables it to remain in a state of operating equilibrium under normal operating conditions and to regain an acceptable state of equilibrium after being subjected to a disturbance.. Instability in a power system may be manifested in many different ways depending on the system configuration and operating mode. Traditionally, the stability problem has been one of maintaining synchronous operation. Since power systems rely on synchronous machines for generation of electrical power, a necessary condition for satisfactory system operation is that all synchronous machines remain in synchronism or, colloquially "in step". This aspect of stability is influenced by the dynamics of generator rotor angles and power-angle relationships, and then referred to " rotor angle stability "译文:电力系统现代社会比以往任何时候更多地依赖于电力供应。

机械设计制造及自动化专业英语翻译Translation of Mechanical Design, Manufacturing, and Automation MajorIntroductionKey Concepts2. Manufacturing: This refers to the transformation of raw materials into finished products through various production processes. It includes techniques such as casting, machining, welding, and assembly. The goal is to optimize efficiency, quality, and cost-effectiveness.Courses1. Engineering Mechanics: This course covers the fundamental principles of mechanics, including statics, dynamics, and strength of materials. Students learn how to analyze and predict the behavior of mechanical systems and structures underdifferent conditions.3. Manufacturing Processes: This course introduces students to various manufacturing techniques, such as machining, casting, and welding. They learn how to select the appropriate processfor different types of products and understand the factors that affect production efficiency and quality.4. Industrial Robotics: This course provides an in-depth understanding of robotic systems and their applications in industrial settings. Students learn about robot programming, control, and integration to automate manufacturing processes and improve productivity.5. Control Systems: This course covers the principles of control theory and their application in automation. Students learn about sensor technology, feedback control loops, and programming techniques to design and implement control systems for mechanical processes.Conclusion。

自动化专业英语PART 1Electrical and Electronic Engineering BasicsUNIT 1A Electrical Networks —————- ————- —3B Three-phase CircuitsUNIT 2A The Operational Amplifier ———————————5B TransistorsUNIT 3A Logical Variables and Flip-flop —- ——- ——- ——8B Binary Number SystemUNIT 4A Power Semiconductor Devices ——- ——- ————11B Power Electronic ConvertersUNIT 5A Types of DC Motors - ————- - - ——- ——15B Closed—loop Control of DC DriversUNIT 6A AC Machines ———————- - ————- -19B Induction Motor DriveUNIT 7A Electric Power System - ————————- - —22B Power System AutomationPART 2Control TheoryUNIT 1A The World of Control ————————————27B The Transfer Function and the Laplace Transformation —————29 UNIT 2A Stability and the Time Response —————————30B Steady State——- ——- —- - —- ——- -—- 31UNIT 3A The Root Locus - ———- ——- ————- 32B The Frequency Response Methods:Nyquist Diagrams —————33 UNIT 4A The Frequency Response Methods:Bode Piots —- —- —34B Nonlinear Control System 37UNIT 5 A Introduction to Modern Control Theory 38B State Equations 40UNIT 6 A Controllability,Observability,and StabilityB Optimum Control SystemsUNIT 7 A Conventional and Intelligent ControlB Artificial Neural NetworkPART 3 Computer Control TechnologyUNIT 1 A Computer Structure and Function 42B Fundamentals of Computer and Networks 43UNIT 2 A Interfaces to External Signals and Devices 44B The Applications of Computers 46UNIT 3 A PLC OverviewB PACs for Industrial Control, the Future of ControlUNIT 4 A Fundamentals of Single-chip Microcomputer 49B Understanding DSP and Its UsesUNIT 5 A A First Look at Embedded SystemsB Embedded Systems DesignPART 4 Process ControlUNIT 1 A A Process Control System 50B Fundamentals of Process Control 52UNIT 2 A Sensors and Transmitters 53B Final Control Elements and ControllersUNIT 3 A P Controllers and PI ControllersB PID Controllers and Other ControllersUNIT 4 A Indicating InstrumentsB Control PanelsPART 5 Control Based on Network and InformationUNIT 1 A Automation Networking Application AreasB Evolution of Control System ArchitectureUNIT 2 A Fundamental Issues in Networked Control SystemsB Stability of NCSs with Network—induced DelayUNIT 3 A Fundamentals of the Database SystemB Virtual Manufacturing—A Growing Trend in AutomationUNIT 4 A Concepts of Computer Integrated ManufacturingB Enterprise Resources Planning and BeyondPART 6 Synthetic Applications of Automatic TechnologyUNIT 1 A Recent Advances and Future Trends in Electrical Machine DriversB System Evolution in Intelligent BuildingsUNIT 2 A Industrial RobotB A General Introduction to Pattern RecognitionUNIT 3 A Renewable EnergyB Electric VehiclesUNIT 1A 电路电路或电网络由以某种方式连接的电阻器、电感器和电容器等元件组成.如果网络不包含能源,如电池或发电机,那么就被称作无源网络.换句话说,如果存在一个或多个能源,那么组合的结果为有源网络.在研究电网络的特性时,我们感兴趣的是确定电路中的电压和电流。
自动化专业英语原文和翻译Automation in the Field of EngineeringIntroduction:Automation plays a crucial role in various industries, including engineering. As a result, proficiency in both English and technical knowledge is essential for professionals in the field of automation. This article will provide an original text and its translation in English, focusing on the importance of automation in engineering.Original Text:自动化是一种通过使用计算机技术和控制系统来实现自动操作和控制的技术。
在工程领域,自动化被广泛应用于诸如创造、能源、交通、通信等各个方面。
自动化技术的发展使得工程师能够更高效地完成任务,提高生产效率,并减少了人为错误的发生。
自动化系统可以用于监控和控制各种设备和过程,从而实现自动化生产线、智能交通系统和智能家居等应用。
自动化在工程领域的应用非常广泛。
例如,在创造业中,自动化系统可以用于自动装配和生产线控制,从而提高产品质量和生产效率。
在能源领域,自动化系统可以用于监控和控制发电厂的运行,实现能源的高效利用。
在交通领域,自动化技术可以应用于智能交通信号灯控制和车辆导航系统,提高交通效率和安全性。
在通信领域,自动化系统可以用于网络管理和故障诊断,确保通信网络的稳定运行。
自动化专业英语翻译:Automation is a technology that enables automatic operations and control through the use of computer technology and control systems. In the field of engineering, automation finds extensive applications in various sectors such as manufacturing, energy, transportation, and communication. The development of automation technology allows engineers to efficiently complete tasks, enhance productivity, and reduce human errors. Automation systems can be used for monitoring and controlling various devices andprocesses, enabling applications such as automated production lines, intelligent transportation systems, and smart homes.Automation finds wide-ranging applications in the field of engineering. For instance, in the manufacturing industry, automation systems can be employed for automated assembly and production line control, thereby improving product quality and productivity. In the energy sector, automation systems can be utilized for monitoring and controlling the operation of power plants, facilitating efficient utilization of energy resources. In the transportation domain, automation technology can be applied to intelligent traffic signal control and vehicle navigation systems, enhancing traffic efficiency and safety. In the communication field, automation systems can be used for network management and fault diagnosis, ensuring stable operation of communication networks.Conclusion:The integration of automation in the field of engineering has revolutionized various industries, enabling efficient and reliable operations. Proficiency in both technical knowledge and English language skills is essential for professionals in the automation field to effectively communicate and implement automation solutions. By harnessing the potential of automation, engineers can optimize processes, improve productivity, and contribute to the advancement of the engineering industry.。
中英文对照外文翻译Automation of professional developmentAutomation in the history of professional development, "industrial automation" professional and "control" professional development of the two main line, "industrial automation" professional from the first "industrial enterprises electrified" professional.In the 1950s, the New China was just founded, the 100-waste question, study the Soviet Union established system of higher education, Subdivision professional. Corresponding to the country in the construction of industrial automation and defense, military construction in automatic control, successively set up the "electrification of industrial enterprises" professional and "control" professional (at that time in many schools, "Control" professional secrecy is professional) . After several former professional name of evolution (see below), and gradually develop into a "biased towards applications, biased towards strong," Automation, and the latter to maintain professional name of "control" basically unchanged (in the early days also known as the "automatic learning And remote learning, "" Automatic Control System "professional), and gradually develop into a" biased towards theory, biased towards weak, "the automation professional, and come together in 1995, merged into aunified" automatic "professional . In 1998, according to the Ministry of Education announced the latest professional undergraduate colleges and universities directory, adjusted, the merger of the new "automated" professional include not only the original "automatic" professional (including "industrial automation" professional and "control" professional ), Also increased the "hydraulic transmission and control of" professional (part), "electrical technology" professional (part) and "aircraft guidance and control of" professional (part).Clearly, one of China's automation professional history of the development of China's higher education actually is a new development of the cause of a microcosm of the history, but also the history of New China industrial development of a miniature. Below "industrial automation" professional development of the main line of this example, a detailed review of its development process in the many professional name change (in real terms in the professional content changes) and its industrial building at the time of the close relationship.First a brief look at the world and China's professional division history. We know that now use the professional division is largely from the 19th century to the beginning of the second half of the first half of the 20th century stereotypes of the engineering, is basically industry (products) for the objects to the division, they have been the image of people Known as the "industry professionals" or "trade associations." At present the international education system in two categories, with Britain and the United States as the representative of the education system not yet out of "industry professionals" system, but has taken the "generalist" the road of education and the former Soviet Union for Europe (close to the Soviet Union) as the representative The education system, at the beginning of theimplementation of "professionals" education, professional-very small, although reforms repeatedly, but to the current "industry professionals" are still very obvious characteristics.In the 1950s, just after the founding of New China, a comprehensive study and the Soviet Union and sub-professional very small; Since reform and opening up, only to Britain and the United States to gradually as the representative of the education system to move closer, and gradually reduce the professional, the implementation of "generalist" education through a number of professional Restructuring and merger (the total number of professionals from the maximum of 1,343 kinds of gradually reducing the current 249 kinds), although not out of "industry professionals" and "Mei Ming," but many of the colleges and universities, mostly only one of a Professional, rather than the past more than a professional.Before that, China's first professional automation from the National University in 1952 when the first major readjustment of the establishment of professional - electrified professional industrial enterprises. At that time, the Soviet Union assistance to the construction of China's 156 large industrial enterprises, automation of much-needed electrical engineering and technical personnel, and such professional and technical personnel training, and then was very consistent with China's industrial construction. By the 1960s, professional name changed to "industrial electric and automation," the late 1970s when to resume enrollment "Electric Industrial Automation" professional. This is not only professional name changes, but has its profound meaning, it reflects China's industries from "electrified" step by step to the "automatic" into the real history and that part of the development trend of China's automation professional reflects how urgent countries Urgent for the country'seconomic construction services that period of history and development of real direction.1993, after four years of the third revision of the undergraduate professional directories, the State Education Commission issued a call "system integrity, more scientific and reasonable, the harmonization of norms," the "ordinary professional directory of undergraduate colleges and universities." "Electric Industrial Automation" and "production process automation" merger of the two professional electrician to set up a kind of "industrial automation" professional, by the then Ministry of Industry Machinery centralized management colleges and universities to set up industrial automation teaching guide at the Commission, responsible for the "Industrial Automation "professional teaching and guiding work at the same time," Control "was attributable to the professional category of electronic information, the then Ministry of Industry of electronic centralized management control to set up colleges and universities teaching guide at the Commission, responsible for the" control " Professional teaching guide our work. After the professional adjustment, further defined the "industrial automation" professional and "control" professional "- both strong and weak, hardware and software into consideration and control theory and practical system integration, and the movement control, process control and other targets of control "The common characteristics with the training objectives, but also the basic set of" industrial automation "biased towards strong, professional, biased towards applications," Control "professional biased towards weak, biased towards the theory of professional characteristics and pattern of division of labor. 1995, the State Education Commission promulgated the "(University) undergraduate engineering leading professional directory", the electrical category "industrialautomation" professional and the original electronic information such as "control" of professional electronic information into a new category of "automatic" professional . As this is the leading professional directory, are not enforced, coupled with general "industrial automation" strong or weak, both professional "into" a weak professional category of electronic information is not conducive to professional development and thus many Schools remain "industrial automation" professional and "control" the situation of professional co-exist. Since 1996 more, again commissioned by the Ministry of National Education Ministry of Industry and electronic machinery industries of other parts of the establishment of the new session (second session) centralized management guidance at the University Teaching Commission, making the leading professionals have not been effective Implemented.1998, to meet the country's economic construction of Kuan Koujing personnel training needs, further consolidation of professional and international "generalist" education track by the Ministry of Education announced a fourth revision of the latest "Universities Undergraduate Catalog." So far in the use of the directory, the total number of professionals from the third amendments to the 504 kinds of substantially reduced to 249 species, the original directory is strong, professional electrician and a weak professional category such as electronics and information into categories Electric power, the unity of Information, a former electrician at the same time kind of "industrial automation" professional and the type of electronic information "control" professional formal merger, together with the "hydraulic transmission and control of" professional (part) , "Electric technology" professional (part) and "aircraft guidance and controlof" professional (part), the composition of the new (enforcement) are electrical information such as "automatic" professional. According to statistics, so far the country has more than 200 colleges and universities set up this kind of "automatic" professional. If the name of automation as part of their professional expertise (such as "electrical engineering and automation," "mechanical design and manufacturing automation," "agricultural mechanization and automation" and other professionals) included Automation has undoubtedly is the largest in China A professional.Of the characteristics of China's automation professional:Recalling China's professional history of the development of automation, combined with the corresponding period of the construction of China's national economy to the demand for automation and automated the development of the cause, it is not difficult to sum up following professional characteristics:(1) China's automation professional is not only a relatively long history (since 1952 have been more than 50 years), and from the first day of the establishment of professional automation, has been a professional one of the countries in urgent need, therefore the number of students has also been The largest and most employers welcome the allocation of the professional one.(2) China's automation is accompanied by a professional from the electrification of China's industrial automation step by step to the development of stable development, professional direction and the main content from the first prominent electrified "the electrification of industrial enterprises" step by step for the development of both the electric and automation " Industrial electric and automation ", highlighting the electrical automation" Electric Industrial Automation "and prominent automation" industrial automation ", then the merger of professional education reform in1995 and" control "of professional content into a broader" automated " Professional. From which we can see that China's automation professional Although the initial study in the Soviet education system established under the general environment, but in their development and the Soviet Union or the United States and Britain did not copy the mode, but with China's national conditions (to meet national needs for The main goal) from the innovation and development of "cross-industry professionals," features the professional.自动化专业的发展自动化专业的发展历史中,有“工业自动化”专业与“自动控制”专业两条发展主线,其中“工业自动化”专业最早源于“工业企业电气化”专业。
机械设计创造及其自动化毕业论文外文文献翻译INTEGRATION OF MACHINERY译文题目专业机械设计创造及其自动化外文资料翻译INTEGRATION OF MACHINERY(From ELECTRICAL AND MACHINERY INDUSTRY)ABSTRACTMachinery was the modern science and technology development inevitable result, this article has summarized the integration of machinery technology basic outline and the development background .Summarized the domestic and foreign integration of machinery technology present situation, has analyzed the integration of machinery technology trend of development.Key word: integration of machinery ,technology, present situation ,product t,echnique of manufacture ,trend of development0. Introduction modern science and technology unceasing development, impelled different discipline intersecting enormously with the seepage, has caused the project domain technological revolution and the transformation .In mechanical engineering domain, because the microelectronic technology and the computer technology rapid development and forms to the mechanical industry seepage the integration of machinery, caused the mechanical industry the technical structure, the product organization, the function and the constitution, the production method and the management systemof by machinery for the characteristic integration ofdevelopment phase.1. Integration of machinery outline integration of machinery is refers in the organization new owner function, the power function, in the information processing function and the control function introduces the electronic technology, unifies the system the mechanism and the computerization design and the software which constitutes always to call. The integration of machinery development also has become one to have until now own system new discipline, not only develops along with the science and technology, but also entrusts with the new content .But its basic characteristic may summarize is: The integration of machinery is embarks from the system viewpoint, synthesis community technologies and so on utilization mechanical technology, microelectronic technology, automatic control technology, computer technology, information technology, sensing observation and control technology, electric power electronic technology, connection technology, information conversion technology as well as software programming technology, according to the system function goal and the optimized organization goal, reasonable disposition and the layout various functions unit, in multi-purpose, high grade, redundant reliable, in the low energy consumption significance realize the specific function value, and causes the overall system optimization the systems engineering technology .From this produces functional system, then becomes an integration of machinery systematic or the integration of machinery product. Therefore, of coveringtechnology is based on the above community technology organic fusion one kind of comprehensive technology, but is not mechanical technical, the microelectronic technology as well as other new technical simple combination, pieces together .This is the integration of machinery and the machinery adds the machinery electrification which the electricity forms in the concept basic difference .The mechanical engineering technology has the merely technical to develop the machinery electrification, still was the traditional machinery, its main function still was replaces with the enlargement physical strength .But after develops the integration of machinery, micro electron installment besides may substitute for certain mechanical parts the original function, but also can entrust with many new functions,like the automatic detection, the automatic reduction information, demonstrate the record, the automatic control and the control automatic diagnosis and the protection automatically and so on .Not only namely the integration of machinery product is human's hand and body extending, human's sense organ and the brains look, has the intellectualized characteristic is the integration of machinery and the machinery electrification distinguishes in the function essence.2. Integration of machinery development condition integration of machinery development may divide into 3 stages roughly.20th century 60's before for the first stage, this stage is called the initial stage .In this time, the people determination not on own initiative uses the electronic technology the preliminary achievement to consummate the mechanical product the performance .Specially in Second World War period, the war has stimulated the mechanical product and the electronic technology union, these mechanical and electrical union military technology, postwar transfers civilly, to postwar economical restoration positive function .Developed and the development at that time generally speaking also is at the spontaneouscondition .Because at that time the electronic technology development not yet achieved certain level, mechanical technical and electronic technology union also not impossible widespread and thorough development, already developed the product was also unable to promote massively. The 20th century 70~80 ages for the second stage, may be called the vigorous development stage .This time, the computer technology, the control technology, the communication development, has laid the technology base for the integration of machinery development . Large-scale, ultra large scale integrated circuit and microcomputer swift and violent development, has provided the full material base for the integration of machinery development .This time characteristic is :①A mechatronics word first generally is accepted in Japan, probably obtains the quite widespread acknowledgment to 1980s last stages in the worldwide scale ;②The integration of machinery technology and the product obtained the enormous development ;③The various countries start to the integration of machinery technology and the product give the very big attention and the support. 1990s later periods, started the integration of machinery technology the new stagewhich makes great strides forward to the intellectualized direction, the integration of machinery enters the thorough development time .At the same time, optics, the communication and so on entered the integration of machinery, processes the technology also zhan to appear tiny in the integration of machinery the foot, appeared the light integration of machinery and the micro integration of machinery and so on the new branch; On the other hand to the integration of machinery system modeling design, the analysis and the integrated method, the integration of machinery discipline system and the trend of development has all conducted the thorough research .At the same time, because the hugeprogress which domains and so on artificial intelligence technology, neural network technology and optical fiber technology obtain, opened the development vast world for the integration of machinery technology .These research, will urge the integration of machinery further to establish the integrity the foundation and forms the integrity gradually the scientific system. Our country is only then starts from the beginning of 1980s in this aspect to study with the application .The State Councilsummary had considered fully on international the influence which and possibly brought from this about the integration of machinery technology developmenttrend .Many universities, colleges and institutes, the development facility and some large and middle scale enterprises have done the massive work to this technical development and the application, does not yield certain result, but and so on the advanced countries compared with Japan still has the suitable disparity.3. Integration of machinery trend of development integrations of machinery are the collection machinery, the electron, optics, the control, the computer, the information and so on the multi-disciplinary overlapping syntheses, its development and the progress rely on and promote the correlation technology development and the progress .Therefore, the integration of machinery main development direction is as follows:3.1 Intellectualized intellectualizations are 21st century integration of machinery technological development important development directions .Theartificial intelligence obtains day by day in the integration of machinery constructor's research takes, the robot and the numerical control engine bedis to the machine behavior description, is in the control theory foundation, the absorption artificial intelligence, the operations research, the computer science, the fuzzy mathematics, the psychology, the physiology and the chaos dynamics and so on the new thought, the new method, simulate the human intelligence, enable it to have abilities and so on judgment inference, logical thinking, independent decision-making, obtains the higher control goal in order to .Indeed, enable the integration of machinery product to have with the human identical intelligence, is not impossible, also is nonessential .But, the high performance, the high speed microprocessor enable the integration of machinery product to have preliminary intelligent or human's partial intelligences, then is completely possible and essential.In the modern manufacture process, the information has become the control manufacture industry the determining factor, moreover is the most active actuation factor .Enhances the manufacture system information-handling capacity to become the modern manufacture science development a key point .As a result of the manufacture system information organization and structure multi-level, makes the information the gain, the integration and the fusion presents draws up the character, information measure multi-dimensional, as well as information organization's multi-level .In the manufacture information structural model, manufacture information uniform restraint, dissemination processing and magnanimous data aspects and so on manufacture knowledge library management, all also wait for further break through.Each kind of artificial intelligence tool and the computation intelligence method promoted the manufacture intelligence development in the manufacture widespread application .A kind based on the biological evolution algorithm computation intelligent agent, in includes thescheduling problem in the combination optimization solution area of technology, receives the more and more universal attention, hopefully completes the combination optimization question when the manufacture the solution speed and the solution precision aspect breaks through the question scale in pairs the restriction .The manufacture intelligence also displays in: The intelligent dispatch, the intelligent design, the intelligent processing, the robot study, the intelligent control, the intelligent craft plan, the intelligent diagnosis and so on are various These question key breakthrough, may form the product innovation the basic research system. Between 2 modern mechanical engineering front science different science overlapping fusion will have the new science accumulation, the economical development and society's progress has had the new request and the expectation to the science and technology, thus will form the front science .The front science also has solved and between the solution scientific question border area .The front science has the obvious time domain, the domain and the dynamic characteristic .The project front science distinguished in the general basic science important characteristic is it has covered the key science and technology question which the project actual appeared.Manufacture system is a complex large-scale system, for satisfies the manufacture system agility, the fast response and fast reorganization ability, must profit from the information science, the life sciences and the social sciences and so on the multi-disciplinary research results, the exploration manufacture system new architecture, the manufacture pattern and the manufacture system effective operational mechanism .Makes the system optimization the organizational structure and the good movement condition is makes the system modeling , the simulation and the optimized essential target .Not only the manufacture system new architecture to makes the enterprise the agility and may reorganize ability to the demand response ability to have the vital significance, moreover to made the enterprise first floor production equipment the flexibility and may dynamic reorganization ability set a higher request .The biological manufacture view more and more many is introduced the manufacture system, satisfies the manufacture system new request.The study organizes and circulates method and technique of complicated system from the biological phenomenon, is a valid exit which will solve many hard nut to cracks that manufacturing industry face from now on currently .Imitating to living what manufacturing point is mimicry living creature organ of from the organization, from match more, from growth with from evolution etc. function structure and circulate mode of a kind of manufacturing system and manufacturing process.The manufacturing drives in the mechanism under, continuously by one's own perfect raise on organizing structure and circulating mode and thus to adapt the process of[with] ability for the environment .For from descend but the last product proceed together a design and make a craft rules the auto of the distance born, produce system of dynamic state reorganization and product and manufacturing the system tend automatically excellent provided theories foundation and carry out acondition .Imitate to living a manufacturing to belong to manufacturing science and life science of"the far good luck is miscellaneous to hand over", it will produce to the manufacturing industry for 21 centuries huge of influence .机电一体化摘要机电一体化是现代科学技术发展的必然结果,本文简述了机电一体化技术的基本概要和发展背景。
P3U1architecture n. 体系结构instruction set 指令集binary-coded adj. 二进制编码的central processing unit (CPU) 中央处理器processor n. 处理器location n. (存储)单元word length 字长access v. 存取,接近fetch v., n. 取来field n. 域,字段opcode n. 操作码operand n. 操作数address n. 寻址single-precision adj. 单精度的floating-point adj. 浮点的terminal n. 终端complement v. 补充,求补decode v. 解码,译码request n. 请求inactive n. 不活动,停止I/O-mapped adj. 输入/输出映射的(单独编址)memory-mapped adj. 存储器映射的(统一编址)难句翻译[1] …how the instruction execution cycle is broken down into its various components.……指令执行周期怎样分解成不同的部分。
[2] One way to achieve meaningful patterns is to divide up the bits into fields…一种得到(指令)有效形式的方法是将(这些)位分成段……[3] The majority of computer tasks involve the ALU, but a great amount of data movement is required in order to make use of the ALU instructions.计算机的大多数工作涉及到ALU(逻辑运算单元),但为了使用ALU指令,需要传送大量的数据。
Control Engineering and TechnologySome Advances in TechnologyControl engineering is driven by available technology and the pace of the relevant technology advances is now rapid . In this section we mention a few of the advances in technology that currently have ,or will have ,an impact on control engineering . More specific details can be found in the Notes and References at the end of this chapter.1.3 控制工程和技术1.3.1 一些技术上的进步控制工程是由可用的技术和相关技术快速进步的步伐所推动的。
在本节中,我们提到的一些目前拥有或将要拥有的技术进步以及它在控制工程上的影响。
更具体的细节可以在本章末尾的注释和参考中被找到。
note n. 注释,说明;[金融] 票据reference n. [图情] 参考文献;参照;推荐信Integrated and Intelligent SensorsOver the past decade the technology of integrated sensors has been developed . Integrated sensors are built using the techniques of microfabrication originally developed for integrated circuits ; they often include the signal conditioning and interface circuitry on the same chip, in which case they are called intelligent sensors. This signal conditioning might include, for example, temperature compensation. Integrated sensors promise greater reliability and linearity than many conventional sensors, and because they are typically cheaper and smaller than conventional sensors, it will be possible to incorporate many more sensors in the design of control systems than is currently done.集成智能传感器在过去的十年中集成传感器的技术已经得到了发展。
英文原文LED Display Screen Design and Proteus SimulationBased on Single-Chip Microcomputer Abstract—This paper designs a LED display system controlled by AT89C52 MCU (Microcomputer Controller Unit). The AT89C52 controls the external circuit formed by 74HC154 and used to control the real time display. Language C is applied to compile program in KeiluVision3 programming environment. The display system is simulated through Proteus software. In Proteus environment, the schematic diagram is drawn. Through stimulation, it achieves real-time display, static display and dynamic display of Chinese characters. It has switch keys to change display state of details. Through the actual simulation, the biggest controllable screen size of the AT89C52 MCU is 64×32. The AT89C52 controls the entire screen display of Chinese characters of 16×16 dot matrix, a total of eight characters. And the key function can be extended.Keywords-LED display; AT89C52; Proteus; dynamic scanningI. INTRODUCTIONEnergy-saving issue attracts every one’s attention. Thus the products that focus on energy conservation get more recognition. LED (Light Emitting Diode-LED) display produced in the 1970s when it was simply used to display number and text. With the diversification of Led colors and enhancement of brightness, full color outdoors LED display became a reality at the end of the 20th century. The LED of our country appeared in the 1970s and its industrial production inthe 1980s. The development of information and advertising industry brings about the emergence of LED display screen. LED display screens are mainly used in advertising window, train stations, banks and other places. It gets more and more widely used. Its own characteristics could make it occupy a market in the display screen industry in the future.In the design of LED display, the hardest part is hardware debug. In order to solve the signal interference, insufficient solder in hardware connection, component damage and a series of debugging problems, the EDA (Electronic Design Automation-EDA) utility software Proteus that the UK Labcenter electronics company researched can be used to realize the entire hardware system schematic drawing and simulation[1].Proteus simulation environment includes ISIS and ARES. In the ISIS environment, electronic circuit can be directly stimulated in the stage of schematic. It also provides virtual machines, simulation of the input signal which makes a convenient simulation. ARES is mainly used for PCB (Printed Circuit Board-PCB) design. The device library provides schematic device and its package. It can design printed circuit board in this environment.Proteus simulation system currently supports MCU (Micro ControllerUnit-MCU) with ARM7, 8051/52 series, AVRseries, PIC 10/12/16/18 series, HC11 series and the MSP430[2]. It can observe the direct result of hardware debug with proteus simulation. It has the characters such as intuitive, convenient, cost savings, high efficiency and so on.II. THE DESIGN OF LED DISPLAYLED display system is formed by MCU, LED screen display circuit, external circuit and the program for control the system. LED screen display circuit includes LED panel and the driving circuit of row and column. The external function circuit includes key controlling circuit and real-time clock circuit. Display function can be achieved as follows: numbers, characters, Chinese characters, static display of monochrome pictures, and dynamic display. Dynamic display includes the whole display content moving up and left. The shift method is controlled by keys, and also by automatic cycle. The system of real-time clock display provides seconds, minutes, hours, day, date, month, and year information. The overall block diagramof LED display screen is shown in Fig. 1.III. HARDWARE DESIGN OF LED DISPLAYA. Design of Row Driving CircuitThe core of LED display system is the control circuit. The control circuit includes driving circuit, clock circuit and the smallest MCU system which consists of AT89C52 MCU, Crystal oscillator circuit and reset circuit. Row driving chip is 74HC154, 4-to-16 line decoder/ demultiplexer, active LOW outputs. P2.0~P2.3 port of AT89C52 connect to A0~A3 of 74HC154 decoder. According to the operating principle of the decoder, when the MCU system controls its P2 port output 0x00~0x0F, the 74HC154 respectively output LOW level from Y0 to Y15. And then the first line to the sixteenth line of display screen is selected. The P2.4 port of MCU connects to the first 74HC154 decoder’s (1~16 line controller) enable pins, meanwhile connects to the second one enable pins (17~32 line controller) throughinverters. That realizes line scanning method. When scanning from the first line to the sixteenth line, the P2.4 port’s output is jump from 0 to 1. And enable the second 74HC154: the seventeenth line is output. This method achieves scan of low-half LED display. The row driving circuit diagram is shown in Fig. 2.B. Design of Column Driving CircuitP1.0~P1.2 ports of MCU are used to control the column driving chip MC74HC595. 74HC595 is shift register with an 8- bit serial in, serial or parallel out with output latches 3 states. Its control clock and shift clock are separate that brings convenience for controlling. Each character is composed by dot matrix of 16 rows and 16 columns: each character of national standard Chinese character library is represent by 256 dots matrix [3]. The font software generates code of dot matrix which is hexadecimal number of 8 bit a group. In this design row scan is used, so the horizontal font code is taken. Using 74HC595 to control the column data send out. When using 74HC595 to control each characters code display, P1.0 port of MCU will send 8 bit serial data from the first column to the eighth column, which is high after the previous low in this transmission. P1.2 port of MCU outputs shift clock. When P1.0 port outputs a bit data, the electrical level of P1.2 port changes from low to high once, then the content of shift register 74HC595 will move one bit from the high to the low once. When the ninth bit data is sent to SDI port of 74HC595, the 74HC595’s SDO port will serially output the first bit in the shift register to the eighth bit of the next 74HC595 chip, and the new incoming data is sent to the eighth in the first chip. After the end of the data preparation from the 1st column to the 64th column, P1.1 port generates a rising edge pulse which sends to the LCHCLK port of 74HC595. Firstly putting 74HC595 chip in cascade connection, then connecting the parallel output clock pins in series and these clock pins are controlled by P1.1 port. Therefore, when the output clock is valid, every 74HC595’s column data output at the same time. Then to achieve displays this whole row by selecting the homologous row.Continuing to do the steps, it can realize a row scan. As long as the entire screen of the scan rate is highe than 50 times per seconds, people could see static images. The 74HC595 column driving circuit is shown in Fig. 3C. Design of Functional CircuitBesides the above function, the design also has real time display and the key function to switch the display modes. P3.0~P3.3 ports individually connect to four buttons which control static display, moving up display, moving left display and automatic cycle display. The automatic cycle display is from the static, moving up to moving left circle shows. The function is realized by programming of key scan. DS1302 chip is used to control real time clock. The timeinformation such as second, minute, hour, day, date, month, and year is displayed in LED display screen. A 3.6V button battery is connected to the eighth pin of DS1302, which ensures DS1302 continuous operation while LED display system does not work [4]. Three data wires are used to control DS1302 in order to achieve synchronous serial communication. The P3.6 port of MCU controls serial clock SCLK pin, P3.7 port controls the DS1302’s REST/ RST pin, and P3.5 connects to data line I/O. According to the operating principle of DS1302, MCU reads and writes the data, then sends to display in LED panel. The function circuit and the MCU system diagram are shown in Fig4.IV. SOFTWARE DESIGNUsing C language to write the program, the program is compiled in Keil uVision3 development environment. The program uses modular design, which is as follows: time delay function, 74HC595 performance function, DS1302 control function, data display function and the main function. The modular design of LED display program is convenient for writing and changing.Fig.5 is the main function block diagram. It mainly realizes the overall initialization, DS1302 initialization and key scan. When the main function is programmed, sub function should be placed before the main function, or declared in advance. Key scan includes four function keys, which respectively accomplish themoving up, left, cyclic and static display.Fig.6 is DS1302 initialization function block diagram. The function realizes DS1302 internal variable initialization, prohibiting write protection, sending the address of write and read data, and reading date/ time for display in LED screen. When reading or writing data, it needs to close the write protect. And after reading or writing data, it can open the write protect.V. PROTEUS SIMULATIONSimulation in Proteus can control the display size of 8×8, 16×16, and 64×16 and so on. Through the actual simulation, the smallest size of LED panel is 8×8. In order to keep the screen without flickering, the biggest size is 64×32. If the display size increases, the screen will produce flickering phenomenon. The reason is that the frame updating frequency is lower than the frequency of human vision persistence. The control circuits, driving circuit and functional circuit in Proteus are consistent with the Protel schematic. In the Proteus development environment, the LED panel is 64×32 jointed by LED 8×8 modules. Part of the electrical connections is used by Label.Through the actual simulation, it can realize Chinese characters, numbers and characters display, and also can switch display mode by buttons. In the static display, the eight characters are displayed in the screen at the same time, every characters is in the form of 16×16 code. The dynamic display is include four state displays, which include moving up, left, static, and three states cycle display. It also realizes real-time clock display. The Proteus simulation diagram is shown in Fig. 7This design introduces the circuit and control principle of the LED display screen in detail. Adopting AT89C52 as controller, 74HC154 as row driving circuit and 74HC595 as column driving circuit, modular programming through language C, Proteus software as simulation environment, It can display eight Chinese characters or characters and real time, and control display models by buttons. It can achieve the display contents moving up, left, static, and automatic cycle display. The designmainly reflects modular programming ideas. So when the system adds or deletes hardware or software without the need, it is changed little. Using Proteus simulation, it brings convenience to design. Through simulation, the maximum controllable LED panel is 64×32 by AT89C52.英文译文基于单片机的LED显示屏的设计与Proteus仿真摘要:这篇论文设计了一个有A T89C52单片机控制的led显示系统。