北方典型盆地同位素水文地质学方法应用(陈宗宇,齐继祥,张兆吉等著)思维导图
- 格式:xmin
- 大小:5.66 KB
- 文档页数:1


同位素水文学与水资源、水环境汪集(中国科学院地质与地球物理研究所,北京100029)收稿日期:2002-06-09作者简介:汪集(1935-),男,中国科学院院士,研究员,长期从事理论和应用地热研究.同位素水文学(isotope hydrolog y)是20世纪50年代发展起来的一门新兴学科,它主要利用同位素技术解决水文学中一些关键问题.众所周知,同位素是指原子核内质子数相同中子数不同的那些原子,可分为稳定同位素和放射性同位素2种.前者指目前尚未发现存在放射性衰变的同位素,而后者则指具有放射性衰变的同位素.存在于自然界的上述2种同位素称为天然同位素或环境同位素,目前在水文学中常用的环境同位素有2H 、3H 、3H e 、4He 、13C 、14C 、18O 、34S 、36Cl 等.不同类型的水(海水、湖水、河水、地下水, ),其化学成分会有很大变化,但同位素组成却相对稳定.因此,水的同位素成分可视作水的指纹 (finger print)或 DNA .也正是基于这一点,水同位素或同位素水文学技术被广泛用来解决或帮助解决各类水资源、水环境问题,诸如水的成因、各类水(雨水、地表水、地下水)的相互作用及转化、地下水系统的封闭程度及水交替强度、各类水体的污染程度及污染源问题等.正是由于同位素水文学的重要性,目前在国际原子能机构(IAEA)内建有同位素水文学部,并设有一个设备齐全、技术先进的同位素水文学实验室.20世纪50年代后期,国际原子能机构(IAEA)与国际气象组织(WM O)共同建立了全球大气降水同位素监测网 (GNIP),自1961年起即向世界各国公布有关数据.最近,IAEA 正拟与联合国教科文组织(UNESCO)联手,在全球42条大江大河(包括我国长江在内)建立类似的水同位素监测网,这对推动同位素水文学的发展将起到不可限量的作用.我国同位素水文学的工作始于20世纪60年代,当时在珠峰地区曾取冰、雪样品做2H 、18O 同位素分析.之后,不同学者在北京、上海及我国东部地区对大气降水的2H 、18O 及3H 进行了测定,得出一些很有意义的结果.1988年,在水利部的大力支持下,我国首批建立的10个大气降水同位素监测站开始运转,并纳入IAEA/WMO 的GNIP 之中.目前,在GNIP 中的中国网站已增至30个.当前,水资源短缺及水环境恶化已成为全球性的大问题.据世界银行(World Bank)预测,若按现有的耗水模式及耗水速率继续下去,则至2025年全球2/3的人将生活在水资源短缺的窘迫状态之中.目前世界银行为解决水资源、水环境问题而投放到发展中国家的资金为每年700~800亿美元.全球对水资源的需求量在未来15年内将增加2倍.为此,包括IAEA 在内的联合国下属24个机构正在制定世界水资源评价计划,以根本解决水资源短缺问题.水多(洪水)、水少(短缺)、水脏(污染)亦是我国水资源、水环境面临的三大问题.黑河流域水资源短缺,太湖地区水环境退化、水污染问题严重已引起国务院的重视并要求切实加以解决.同位素水文学技术对解决上述问题将起到独特甚至是不可替代的作用.总之,机遇与挑战并存,风险与希望同在.目前正是我国在加速同位素水文学发展及水同位素技术中大显身手的大好时机.第27卷第5期地球科学 中国地质大学学报Vol.27 No.52002年9月Ear th Science Journal of China University of Geosciences Sep. 2002Isotope Hydrology and Water Resources plus Hydro -EnvironmentWANG J-i y ang(I nstitute of Geology and Geop hysics,Chinese A cademy o f Sciences,Beij ing 100029,China)Abstract:Isotope hy drology is a new discipline in earth sciences developed since 1950s.Its main targ et is to use isotope technique to solve various problems in hydrology.It is w ell know n that isotope refers to those atoms whose numbers of proton are the same but w hose numbers of neutron are different.Isotopes can be d-i vided into two ty pes:stable and radioactive.For stable isotopes,no radioactive decay has been found so far.But for radioactive isotope,there ex ists radioactive ually,the term natural and/or environmen -tal isotopes w ere used for the tw o types of isotope mentioned above.The environmental isotopes commonlyused in hydrology are:2H ,3H,3He,4He,13C,14C,18O,34S,36Cl,etc.It must be noted that for different types of w a -ter,such as sea w ater,lake water,river water and ground w ater,the isotope com position seems to be quite different but relatively stable,althoug h the w ater chemistry varies greatly.T herefore,the isotope composition can be,to certain degree,regarded as the finger print and/or DNA of the w ater.Also for this reason,the isotope com position in the w ater and the isotope hydrology technique are w idely used to solve various prob -lems in w ater resources assessment and hydro -environment evaluations such as the origin of w ater,the interac -tion of surface and g roundw ater,the rain -off w ater,the degree of openness of a groundw ater system ,the in -tensity of w ater cycling,the pollution deg ree and the pollution source of a w ater body.In recognition of the importance of isotope hydrolog y,an isotope hydrology section has been established in the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA)and an isotope hydrolog y laboratory is set up simultaneously w ith advanced technique and equipment.Since late 1950s,a Global Netw ork for Isotopes in Precipitation (GNIP)has been initiated jointly by IAEA and WM O (World Meteorological Organization)and all the data have been published since 1961.Recently,sponsored by IAEA/UNESCO,a similar global netw ork for isotopes in the large rivers in the w orld is under the w ay to set up.It is of significant importance in promoting isotope hydrology development w orldw ide.In China,isotope hydrolog y studies can be traced back to the late 1960s.In the scientific investigation of w ater resources in Jolmo Lungma reg ion,2H and 18O w ere determ ined in snow and ice sam ples.Since then,2H and 18O have been analyzed for precipitations in Beijing,Shanghai and East China by different researchers with g reat achievement.In 1988,Supported by the M inistry of Water Resources,the first 10stations ,for mon-i toring the isotopes in precipitation in China w ere established and now they have been included in the IAEA/WM O GNIP.At present,the total number of stations has increa sed to 30.Now adays,water resources shortage and hydro -environments degradation become more and more serious w orldw ide.According to the prediction by the World Bank,2/3world population w ill live in a serious water -shortage environment if we follow the present w ater -consuming model.At present,70-80billions of U S do-l lars has been offered to the developing countries to alleviate the annual w ater resources shortag e.The global demand for w ater resources w ill be doubled in the coming 15years.For this reason,altogether 24internation -al organizations including IAEA are w orking on a World Project for Water Resources Assessment to reduce the g lobal w ater shortag e. flood , w ater shortage and water pollution have become three main problems in China now adays.Both the w ater shortages in the Heihe river reg ion and the deg radation of hydro -environment in T aihu lake area have attracted g reat attention from the State Council.The isotope hydrology technique m ay play a particular role in solving these problems.All in all,opportunities and challenges co -exist and it is a right time to ex pedite the development of isotope hydrology in China.533第5期 汪集:同位素水文学与水资源、水环境。



水文地球化学,同位素,温泉,地球化学特征水文地球化学揭示了关于物质运转、物理结构和化学组成的复杂信息。
它将地球化学中的传统成分,如元素和化合物,与水的复杂性结合在一起,并使用有关水的特性来表征地表和潜在过程的研究。
一、水文地球化学的组成水文地球化学的研究包括:1. 同位素:它可以提供对水的示踪组分的活动、形成、运移和改变的信息。
这些组分的活动过程的时间尺度可通过同位素来识别,因为它们具有不同的衰减率和示踪率,有助于了解水的可达性、来源和频率,以及历史流域范围内水的过渡。
2. 温泉:温泉研究理解了水的生成深度,原位置,成分特征和其他可能的流体矿物特征,这些用于建立温泉的地质结构,从而确定温泉的常见特征。
3. 元素组成:水文地球化学可以改变水的元素组成,揭示有关水不同来源和活动状态的元素组成特征。
比如,氯、钠和钾等在水与岩石作用过程中的改变可确定其水文学特征。
4. 化学组成:水文地球化学也可以表征水中的氧化、还原和酸碱度,这些是地球化学特征的重要参数。
例如,酸碱度和氧化还原反应可以表征和验证水的有机和无机化学特征,而水的痕量元素快速筛选可以为后续研究提供重要的知识基础。
二、水文地球化学的重要性水文地球化学可以帮助改善和开发水资源,促进水资源管理系统的改善。
它也可以计算和模拟水的运行行为,帮助能源利用者和其他参与者建立水管理合同,并使社会经济资源的重新利用成为可能。
此外,水文地球化学有助于减少水系统中的污染行为,为水质保护和治理提供必要的数据,它还可以用于评估水文学特征,如水面的相对可利用蒸发量。
总之,水文地球化学是一种新兴的重要学科,它可以为水资源开发和管理提供重要信息,帮助社会经济发展和水環境保護。
它涵盖了水文学和地球化学等多种研究领域,其结果可以为决策者提供实用的参考信息。

同位素水文地质学同位素水文地质学是研究地下水的同位素特征和其在地质和水文过程中的应用的学科。
同位素水文地质学的研究对于理解地下水系统的起源、补给和流动方式以及水资源管理具有重要意义。
背景和定义同位素水文地质学是地理学、地球化学和水文学交叉的学科,利用同位素的比例和分布特征来研究地下水的起源、水文动态以及水文地质过程。
同位素可以是地球自然界中存在的稳定同位素(如氢同位素、氧同位素、碳同位素等)或放射性同位素(如放射性碳-14、放射性锶-90等)。
地质学和水文学的重要性同位素水文地质学在地质学和水文学领域中发挥着重要的作用。
在地质学中,通过分析同位素特征,可以推断地下水体的来源、年龄及其受到的影响。
同位素水文地质学也可以用于研究水文过程,如水循环、水体补给、地下水的流动路径以及地下水与地表水之间的相互作用。
总之,同位素水文地质学在地质学和水文学的研究中具有重要的地位,为我们深入理解地下水体的形成和运动提供了有力的工具和方法。
同位素示踪技术是一种常用于水文地质研究的方法,它能够通过测量水中不同同位素的比例来揭示水文地质过程和水体来源。
同位素示踪技术主要包括同位素稳定性示踪和同位素放射性示踪。
同位素稳定性示踪同位素稳定性示踪是通过测量水体中不同同位素的稳定性同位素比例变化来推断水文地质过程。
稳定性同位素是指在天然环境中相对稳定的同位素,如氢(D/H)、氧(18O/16O)和碳(13C/12C)等。
这些同位素在水文地质中的应用广泛,能够揭示水的源地、水体的混合和水体的循环过程。
例如,氢同位素(D/H)可以用于确定水体的来源和补给方式。
氧同位素(18O/16O)常用于研究地下水与地表水之间的相互作用和补给关系。
碳同位素(13C/12C)则可以用于探究有机污染物的来源和迁移途径。
同位素放射性示踪同位素放射性示踪是利用放射性同位素分析方法来研究水文地质问题。
放射性同位素主要包括碳-14和氚等。
放射性同位素的测量可以揭示水体的循环速率、补给方式以及水体演化的时间尺度。



本文由国家自然科学基金项目(编号:40472126)和国土资源部重点基础研究项目(编号:200010301)联合资助。
改回日期:2004_07_09;责任编辑:周健。
第一作者简介:张光辉,男,1959年生,博士,研究员。
博士生导师,长期从事区域水循环演化规律和地下水可持续利用问题研究;E_mail:Huanjing@ 。
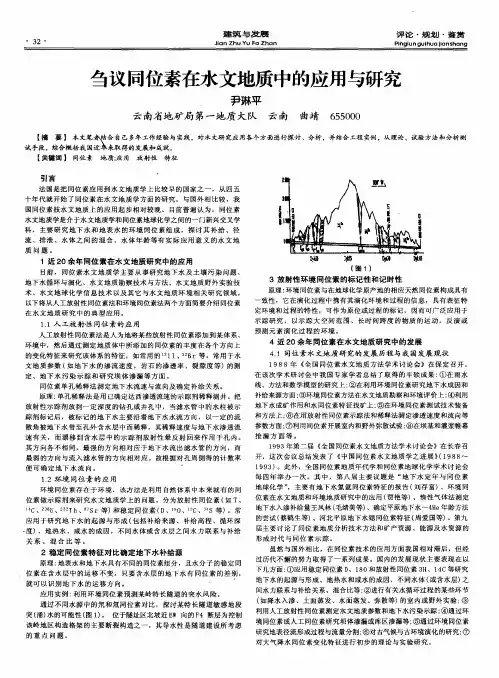
黑河流域地下水同位素特征及其对古气候变化的响应张光辉1) 陈宗宇1) 聂振龙1) 刘少玉1) 张翠云1) 申建梅1)王金哲1) 程旭学2) 张荷生2)1)中国地质科学院水文地质环境地质研究所,石家庄,0500612)甘肃省地勘局水文地质工程地质勘察院,甘肃张掖,734000摘 要 通过环境同位素及其T amers 、IAEA 模型应用研究表明,黑河流域平原区地下水补给及更新与古气候变化密切相关,8000~5000a BP 、3500~2500a BP 和近1000年以来的多雨期是主要补给期;潜水较年轻又更新快,承压水较老又更新慢;东部地下水更新较快,西部更新较慢;祁连山前戈壁带地下水更新较快,细土平原更新较慢;近河道带地下水更新速率大,远离河道则小。
东部以山区降水通过出山地表径流补给为主,西部冰川雪融水和山区基岩裂隙水是主要补给源。
因此,遵循地下水补给与更新的自然规律,与地表水联合优化调控,有利于该区地下水可持续利用及下游区生态环境保护。
关键词 黑河流域 地下水 同位素特征 古气候 更新性Isotopic Characteristics of Groundwater and Its Response to PaleoclimaticVariation in Heihe River BasinZHANG Guanghui 1)CHEN Zong yu 1)NIE Zhenlong 1)LIU Shaoyu 1)ZH ANG Cuiy un 1)SHEN Jianmei 1) WANG Jinzhe 1) CHENG X xue 2) ZH NAG H esheng2)1)I nstitute of Hydrogeology and E nv ironmental Geology,Chinese Academy of Geological S c iences,Shij iaz huang ,0500612)Prospecting and Designing I nstitute of Hydrogeology and Engineering G e ology o f Gansu ,Zha ngye ,Gansu ,734000Abstract Based o n field investigations by such means as envir onmental isotopic features,T amr es model and IAEA model,it is held t hat the gr oundwater recharge and renewable rate is related to paleoclimatic v ar iation and that the r ainy stag es of 8000~5000a BP,3500~2500a BP and last 1000year s ar e the main groundw ater recharg e stages in Heihe R iver basin in N orthwest China.T he shal low groundw ater is relatively young and its renewable rate is g reater than t hat of the confined g roundwater.T he renew able r ate in the eastern ar ea of the middle reaches is g reater than that in t he western ar ea.T he rate i s less in the fine soil zone than in the gobi zone under t he Qilian M ountain,and the rate i s greater near the river bed than far from the riverbed.T he main recharg e source of g round w ater in the eastern area of the middle reaches is the rain from the Qilian M ountain area,w hereas in the western area the source is the snow melt and the crevice groundw ater fro m t he mountain ar ea.I t is therefo re concluded that by adhering to the natural recharge and r enewable regular ity of groundwater and reg ulating and co ntrolling g roundwater and sur face water in a optimal w ay,the sustainable u tilization of groundw ater can be achiev ed,and the eco logical envir onment can be better protected.Key words Heihe River basin g roundw ater isotopic characteristics paleoclimate r enew able rate区域气候变化是西北内陆黑河流域地下水补给与更新演变的驱动力之一。

鄂尔多斯盆地北部地下水环境同位素时空分布特征及其指示意义连英立【摘要】On the basis of field sampling and actual hydrogeological conditions ,Analysis the relationship between recharge ,runoff and discharge via testing different lots at different depths in the aquifer environmental isotopes (δ18O‐δD ) features .The results showed that :in the study area ,groundwater recharge mainly by atmospheric precipitation ,each aquifers vertical hydraulic connection is weak;δ18 O‐δD has obvious characteristics of stratification in the vertical ,δ18 O ,δD value of groundwater gradually negative by the groundwater burial depth increased;it showed that all the aquifers are now affected by atmospheric precipitation by deuterium excess analysis .%在野外采样的基础上,通过测试分析不同地段、不同深度含水层中的环境同位素(δ18 O‐δD )特征,结合实际水文地质条件,分析了研究区地下水的补径排关系。
结果表明:研究区内地下水主要接受大气降水补给,各含水层的垂向水力联系较弱;在垂向上氘氧同位素具有明显的分层性特点,总体上表现为随着地下水埋藏深度的加大,地下水的δ18 O、δD值逐渐偏负;通过氘过量分析表明各含水层均受到了现今大气降水影响。
中国北方第四系地下水同位素分层及其指示意义陈宗宇;张光辉;聂振龙;南云驹【期刊名称】《地球科学:中国地质大学学报》【年(卷),期】2002(27)1【摘要】中国北方第四系地下水中的D ,18O ,3 H和14 C含量存在明显的分层现象 ,这种现象与末次冰期以来的古气候变化有着较好的对应性 ,反映了全新世和末次冰期气候条件的差别以及地下水不同的形成机制 .深层地下水为晚更新世末次冰期时期形成 ,其δ(D)和δ(18O)值与全新世补给形成的浅层地下水相比 ,分别贫4× 10 -3 ~16× 10 -3 和1× 10 -3 ~2× 10 -3 ,说明末次冰期时期年均气温较低 .古地下水中D和18O的大陆梯度与全新世以来地下水中的梯度基本相同 ,说明在过去 30 0 0 0a来尽管气温发生变化 ,但中国北方大陆的大气循环模式没有发生实质性的改变 .地下水同位素分层现象反映了 3种不同的补给机制及参与现代水循环程度 .【总页数】8页(P97-104)【关键词】地下水;同位素;古气候;古水文;补给机制;可持续利用;中国【作者】陈宗宇;张光辉;聂振龙;南云驹【作者单位】吉林大学地球科学学院;中国地质科学院水文地质环境地质研究所【正文语种】中文【中图分类】P641.3;P532【相关文献】1.地下水微量元素与同位素特征对海水入侵和地下水起源的指示意义——以深圳市宝安区为例 [J], 蒋方媛;韩绘芳;陈加红;王谊2.高放废物处置库新疆雅满苏和天湖预选地段地下水同位素特征及其指示意义 [J], 郭永海;李娜娜;周志超;董建楠;张明;刘淑芬3.飞凤山处置场地下水水化学、氢氧稳定同位素特征及其指示意义 [J], 冯瑞; 郑百录; 岳建国; 朱丹; 董云; 李晓4.江汉平原高砷地下水稳定碳同位素特征及其指示意义 [J], 袁晓芳;邓娅敏;杜尧;甘义群5.深州地区浅层地下水同位素组成及其指示意义 [J], 冯欣;高业新;张冰;崔浩浩;张亚哲因版权原因,仅展示原文概要,查看原文内容请购买。
同位素技术在水文学中的应用同位素技术在水文学中的应用一. 基本概念1 .同位素同位素:具有相同原子序数(即质子数相同,因而在元素周期表中的位置相同),但质量数不同,亦即中子数不同的一组核素。
特点:相同元素同位素的化学性质相同。
同位素的分类:按照同位素是否衰变,可将同位素分为:放射性同位素和稳定同位素。
按照同位素是否是由人工产生的,可将同位素分为:天然同位素和人工同位素。
2.同位素技术同位素技术就是利用水中天然存在的环境同位素(如2H、3H、18O、14C 等)来标记和确定水的年龄、特征、来源及其组成,或者在水中加入放射性含量极低的人工同位素作为示踪剂来确定水的运移和变化过程。
前者称为环境同位素技术,后者称为人工同位素示踪技术。
2.1同位素技术方法的一般程序:第一,要按照一定要求,采集待测试的样品,并按规定进行包装;第二,把样品送到实验室进行测试;第三,根据测试结果进行仔细分析。
2.2同位素技术方法:第一,同位素丰度:反映同位素成分组成的指标是同位素绝对丰度和相对丰度。
第二,同位素分馏:由于同位素质量不同,因此在物理、化学及生物化学作用过程中,一种元素的不同同位素在两种或两种以上物质(物相)之间的分配具有不同的同位素比值的现象。
自然界中的化学反应、不可逆反应、蒸发作用、扩散作用、吸附作用、生物化学反应等过程都能引起同位素分馏。
同位素分馏系数(α)表示两种物质之间的同位素分馏程度,等于两种物质的同位素比值(R)之商,即а=R A/R B(式中:R A为分子在A或是A相态中重同位素与轻同位素的比值,R B为分子在B或是B相态中的重同位素与轻同位素的比值)二.同位素在水文学中的应用20 世纪50 年代开始,同位素技术应用于解决各种水文学和水文地质学问题,随着同位素分析技术的发展,通过研究水体及某些溶解盐类的同位素组成,同位素技术和方法已经成为水科学研究的现代手段之一,同位素技术和方法可以有效地示踪水循环,如指示水的来源,水体的运移途径和数量,确定水的年龄,记录水岩相互作用的地球化学过程,环境同位素和人工同位素在水汽来源、地表水与地下水的相互作用、地下水起源及测年、水体污染物的来源以及气候变化和人类活动对水循环的影响等研究领域的应用十分广泛.为确定各类水体的成因和演化机制提供重要的依据,也为合理利用水资源奠定了基础。
第九章同位素水文地球化学方法同位素是指核内质子数相同(即核电荷相同、原子序数相同),而中子数不同(即原子量不同)的同一种元素。
它们在元素周期表中居于同一位置。
同位素水文地球化学可以用来解决水文学、水文地质学、资源和环境学中的许多问题。
在水文学中可用同位素来研究冰川的形成和年龄、河水流量、地表水的弥散作用、湖泊动力学、湖泊和水库的渗漏、悬浮泥沙、底砂搬运和沉积物;在土壤学中解决土壤含水量、土壤密度、非饱和带水的运移;水文地质学中的含水层特征、地下水起源、地下水年龄(滞留时间)、地表水与地下水的联系、含水层间越流、地下水的盐化、地热水的成因、地温;在资源开发中可用同位素来研究矿产的成因;在环境学中用同位素来研究污染源和污染途径;在工程中常用同位素来示踪等。
在同位素水文地球化学中区分有稳定同位素和放射性同位素;环境(天然)同位素和人工示踪同位素等。
以下将对放射性同位素、环境稳定同位素和人工示踪同位素分别进行介绍。
第一节同位素测定地下水年龄法一、测定地下水年龄的同位素数学物理模型1.基本概念根据放射性衰变定律,同位素测定年龄的基本方程为:t = (T1/2/ln2) ln(A0/A t) (9.1.1)式中,半衰期为T1/2 的放射性原子的衰变使它的放射性活度在时间段t内从A0减少为A t。
如果已知t=0时刻的初始放射性活度A0 和t时刻样品的放射性活度A t ,则我们就可以测定年龄。
但事情并非如此简单,一是五十年代热核试验以来,大气降水中的放射性同位素浓度(A0)已不是常量;二是地下水在渗流过程中会发生不同程度的弥散混合。
因此,计算地下水年龄时,首先要建立水混合的物理模型,然后根据同位素物质平衡原理建立数学计算模型。
用这种方法建立的地下水测年模型称之为测定地下水年龄的同位素数学物理模型。
为了建立数学模型,人们引入了地下水年龄分配函数g(t)的概念(Zuber, 1986, 1994)。
g(t)又称系统的反应函数或权重函数,其表达式为:g(t) = C I(t)Q / M (9.1.2)式中,C I(t)为因系统入口处t=0时刻的瞬时注入所导致的在实测点所观测到的示踪剂的浓度;Q为系统的流量;M为注入示踪剂的活度或质量。