内蒙古科技大学图书馆检索中文数据库
- 格式:doc
- 大小:44.00 KB
- 文档页数:4

利用英文综合参考数据库——《美国工程索引(Ei)》1、检索课题名称:资源循环与冶金二次资源利用2、课题分析:中文关键词:资源循环冶金二次资源英文主题词:Recycling of resources Metallurgy Two resources3、选择检索工具:《美国工程索引》(Ei village2)4、构建检索策略:Recycling of resources*Metallurgy*Two resources5、简述检索过程:选择快速检索,输入检索词:第一、Recycling of resources;第二、Metallurgy;第三、Two resources 检索结果 73篇6、根据检索结果选择 3 条记录根据检索结果,浏览题录可以确定该文献的收藏单位,从而可以进一步确定是否索取或借阅、复制原文。
Search Results:73 articles found in Compendex for 1969-2014: ((((Recycling of resources) WN All fields) AND ((Metallurgy) WN All fields)) AND ((Two resources) WN All fields))1. Impact of recycling measures on resource- and energy efficiency and greenhouse gas emissions in the iron, steel and zinc industryBartusch, Hauke (Karlsruhe Institute of Technology, Institute for Industrial Production (IIP), Hertzstrae 16, 76187 Karlsruhe, Germany); Schwaderer, Frank; Alcalde, Ana Maria Fernández; Fröhling, Magnus; Schultmann, Frank Source: Proceedings - European Metallurgical Conference, EMC 2011, v 5, p 1539-1552, 2011, Proceedings - European Metallurgical Conference, EMC 2011Database: Compendex2. Recycling potentials of the two refractory metals tantalum and niobiumAngerer, Thomas (Montanuniversität Leoben, Department of Nonferrous Metallurgy, Franz-Josef-Strae 18, 8700 Leoben, Austria); Luidold, Stefan; Antrekowitsch, Helmut Source: European Metallurgical Conference, EMC 2013, p 1069-1084, 2013, European Metallurgical Conference, EMC 2013Database: Compendex3. Equipment and technology for recycling nonferrous metalsLuzgin, V.I. (Ural State Technical University, Ural Polytechnic Institute, Russ. Elec. Eng. Co. RÉLTEK); Petrov, A.Yu.; Timofeev, A.I. Source: Metallurgist, v 48, n 9-10, p 536-538, September 2004Database: Compendex阅读文摘:1. Impact of recycling measures on resource- and energy efficiency and greenhouse gas emissions in the iron, steel and zinc industryBartusch, Hauke1; Schwaderer, Frank1; Alcalde, Ana Maria Fernández1; Fröhling, Magnus1; Schultmann, Frank1Source: Proceedings - European Metallurgical Conference, EMC 2011, v 5, p 1539-1552, 2011, Proceedings - European Metallurgical Conference, EMC 2011; ISBN-13: 9783940276407; Conference: European Metallurgical Conference, EMC 2011, June 26, 2011 - June 29, 2011; Publisher:GDMB-InformationsgesellschaftAuthor affiliation:1 Karlsruhe Institute of Technology, Institute for Industrial Production (IIP), Hertzstrae 16, 76187 Karlsruhe, GermanyAbstract:Rising resource and energy prices as well as climate change have a significant impact on Germany's metal industry. Internal recycling of residues or external recycling in specialised processes are measures to meet these challenges by enhancing resource efficiency and decreasing the dependency on primary resources. As individual measures to increase efficiency become more and more complex, potentials to enhance the resource efficiency may exist if the focus is widened from a single plant to a network wide view. Residue flows can be the central element in such considerations. Steel production with Electric Arc Furnaces (EAFs) and Basic Oxygen Furnaces (BOFs) leads to zinc-bearing dusts. For these residues external recycling processes exist, which produce secondary zinc concentrates for the zinc industry. These material flows connect the processes of the steelmaking, recycling and zinc industry to a network. One possible approach to enhance resource efficiency network wide is a systematic search for external recycling options for materials which are currently disposed. Another possibility is to analyse different internal recycling rates under consideration of the effects on the connected internal and external processes. To evaluate theimpacts of internal and external recycling measures resource efficiency must be seen in context with the results on energy demand and CO2 emissions. Focussing on the residues from an EAF and a BOF this paper presents two example scenarios where actors of the iron and steel industry and the zinc industry are considered in an integrated way. Basing on simulation models of an example EAF, an integrated steelwork, a Waelz kiln, the DK Process and a hydrometallurgical zinc plant mathematical descriptions of the processes are obtained. Afterwards, a scenario analysis is carried out for a systematic examination of possibilities to increase resource efficiency under consideration of economic effects, energy consumption and CO2 emissions.(10 refs)Main heading: Iron and steel industryControlled terms: Basic oxygen converters - Carbon dioxide - Climate change - Complex networks - Computer simulation - Dust - Electric furnaces - Energy efficiency - Energy utilization - Gas emissions - Greenhouse gases - Metallurgy - Recycling - Steelmaking - ZincUncontrolled terms: BOF-dust - EAF-dust - Electric arc furnace - Mathematical descriptions - Recycling options - Resource efficiencies - Systematic searches - Zinc industryClassification Code: 804.2 Inorganic Compounds - 723.5 Computer Applications - 722 Computer Systems and Equipment - 546.3 Zinc and Alloys - 545.3 Steel - 545 Iron and Steel - 532.3 Electric Metallurgical Furnaces - 531.1 Metallurgy - 525.3 Energy Utilization - 525.2 Energy Conservation - 452.3 Industrial Wastes - 451.1 Air Pollution Sources - 451 Air PollutionDatabase: Compendex2. Recycling potentials of the two refractory metals tantalum and niobiumAngerer, Thomas1; Luidold, Stefan1; Antrekowitsch, Helmut1Source: European Metallurgical Conference, EMC 2013, p1069-1084, 2013, European Metallurgical Conference, EMC 2013; Conference: 7th European Metallurgical Conference, EMC 2013, June 23, 2013 - June 26, 2013; Sponsor: Recylex; Aurubis; Befesa; Berzelius Metall; Oschatz; Publisher:GDMB-InformationsgesellschaftAuthor affiliation:1 Montanuniversität Leoben, Department of Nonferrous Metallurgy, Franz-Josef-Strae 18, 8700 Leoben, AustriaAbstract:Tantalum and niobium are two outstanding elements of technological metals. Their applications are widespread and the substitution is only possible in few cases. Europe has no primary mining of the two chemical related elements, so the domestic industry is forced to process secondary raw materials in order to diminish dependencies on foreign raw material suppliers. The comprehensive analysis of material flow startsat the mining, followed by the processing of the ore and the reduction, goes beyond the further processing of diverse intermediate products up to the applications (end product). To find potential secondary resources for these two metals it's very important to know their main as well as the minor application areas and accordingly the whole production cycles of the different products. The scrap, generated during the production (pre consumer scrap) represents an important secondary source of raw materials. Post consumer scrap is also an attractive source but in many cases the lack of a recycling infrastructure hampers the use of it. Another complicacy is the dissipation of tantalum and niobium in the end products and so in the waste materials. In an economical view an extraction is not possible. If one or both metals are enriched in residuals of other recycling processes - e.g. indirect recycling of hard metal scrap - the recovering of niobium and/or tantalum could be an opportunity. Recycling in direction of the two refractory metals is a balancing act between technological and economical feasibilities and sustainable use. The study identifies potentials of secondary sources of Nb and Ta referring to their end products and discusses furthermore some established and newtechnologies for the processing of secondary raw materials.(63 refs)Main heading: Scrap metal reprocessingControlled terms: Metallurgy - Metals - Niobium - Ore analysis - Ore reduction - Ores - Raw materials - Recycling - Reduction - Refractory materials - Refractory metals - Scrap metal - TantalumUncontrolled terms: Comprehensive analysis - Economical feasibility - Intermediate product - Material Flow - Post consumer scraps - Raw material suppliers - Scrap - Secondary Raw MaterialsClassification Code: 951 Materials Science - 812.2 Refractories - 802.2 Chemical Reactions - 801 Chemistry - 549.3 Nonferrous Metals and Alloys excluding Alkali and Alkaline Earth Metals - 543.4 Tantalum and Alloys - 531.1 Metallurgy - 531 Metallurgy and Metallography - 505 Mines and Mining, Nonmetallic - 504 Mines and Mining, Metal - 502 Mines and Quarry Equipment and Operations - 452.4 Industrial Wastes Treatment and Disposal - 452.3 Industrial WastesDatabase: Compendex3. Equipment and technology for recycling nonferrous metalsLuzgin, V.I.1; Petrov, A.Yu.1; Timofeev, A.I.1Source: Metallurgist, v 48, n 9-10, p 536-538, September 2004; ISSN: 00260894; DOI: 10.1007/s11015-005-0021-2; Article number: 21; Publisher: Kluwer Academic/Plenum PublishersAuthor affiliation:1 Ural State Technical University, Ural Polytechnic Institute, Russ. Elec. Eng. Co. RÉLTEKAbstract:The capabilities of medium- and high-frequency induction furnaces developed by RE´ company for convertingnonferrous-metal wastes into a standard product were discussed. The use of two-frequency electromagnetic fields in refining and casting helps to recycle a wide range of metallic wastes in various states of aggregation. It also improves the chemical composition and homogeneity of the melt. The results show that the equipping the induction refining furnaces with casting modules gives maximum flexibility to obtained shaped castings and also makes them highly cost-effective means of recycling nonferrous-metal wastes and scrap.Main heading: Nonferrous metalsControlled terms: Aluminum alloys - Composition - Cost effectiveness - Electromagnetic field effects - Energy resources - Furnaces - Hydraulics - Impurities - Metal casting - Metal refining - Metallurgy - Rare earth elements - Raw materials - RecyclingUncontrolled terms: Ferrous metallurgy - Metallurgical processing - RE´LTEK company (CO) - Recycled products Classification Code: 801 Chemistry - 701.1 Electricity: Basic Concepts and Phenomena - 632.1 Hydraulics - 547.2 Rare EarthMetals - 541.2 Aluminum Alloys - 911.2 Industrial Economics - 534.2 Foundry Practice - 532 Metallurgical Furnaces - 531.1 Metallurgy - 525.1 Energy Resources and Renewable Energy Issues - 452.3 Industrial Wastes - 533.2 Metal RefiningTreatment: Theoretical (THR) - Experimental (EXP) Database: Compendex7、标示原文线索:用中文标示各检索结果的著录事项第一篇文献:一、篇名: Impact of recycling measures on resource- and energy efficiency and greenhouse gas emissions in the iron, steel and zinc industry二、第一责任者:Bartusch, Hauke三、第一责任者单位:Karlsruhe Institute of Technology, Institute for Industrial Production (IIP), Hertzstrae 16, 76187 Karlsruhe, Germany四、文献来源:Proceedings - European Metallurgical Conference, EMC 2011, v 5, p 1539-1552, 2011, Proceedings - European Metallurgical Conference, EMC 2011第二篇文献:一、篇名:Recycling potentials of the two refractory metals tantalum and niobium二、第一责任者:Angerer, Thomas三、第一责任者单位:Montanuniversität Leoben, Department of Nonferrous Metallurgy, Franz-Josef-Strae 18, 8700 Leoben, Austria四、资料来源:European Metallurgical Conference, EMC 2013, p 1069-1084, 2013, European Metallurgical Conference, EMC 2013 第三篇文献:一、篇名:Equipment and technology for recycling nonferrous metals二、第一责任者:Luzgin, V.I.三、第一责任者单位:Ural State Technical University, Ural Polytechnic Institute, Russ. Elec. Eng. Co. RÉLTEK四、资料来源:Metallurgist, v 48, n 9-10, p 536-538, September 2004。



一、内蒙古科技大学图书馆概况1、概述内蒙古科技大学前身为包头钢铁学院,座落于全国首批文明城市之一的包头市。
学校创建于1956年,2003年组建为内蒙古科技大学。
内蒙古科技大学图书馆是学校“教学科研基础大平台”。
经过50多年的建设与发展,本馆已成为一所包头地区馆藏文献最多、现代化程度最高、服务最全面的综合性图书馆。
近年来,本馆秉承“开发利用第一,数字化技术优先,管理服务效益并重”的办馆指导思想,围绕“推广普及阅读,营建书香校园”的办馆宗旨和“馆藏资源数字化、网络资源馆藏化、资源管理一体化、服务形式多样化”的办馆目标,坚持“知识改变命运,学习成就未来”的宣传理念,致力于不断加强传统文献资源建设,大力开展数字化文献资源建设和现代化管理与人文化服务工作,已经形成了实体与虚拟共进的馆藏格局和传统与现代并举的服务模式。
2003年至2011年,本馆连续多次被华北地区高等学校图书馆协会、内蒙古图书馆学会和包头市图书馆学会评为先进图书馆。
2009年和2010年,中国图书馆学会连续两年将本馆评为“全民阅读先进单位”。
2011年,国家文化部和中国图书馆学会联合授予本馆“全民阅读示范基地”,成为内蒙古地区获此殊荣的唯一高校,在全国高校获得广泛好评。
2、馆舍面积扩大,队伍渐趋优良2012年老馆改造全部竣工投入使用,现本馆建筑面积达到4万平方米;各类阅览室近40个;普通阅览座位2376席,电子阅览座位541席,总计达到4000多席。
现设办公室、资源建设部、学科服务部、文献检索教研室、技术部、借阅部、期刊阅览部等七个部门。
不久将根据现代图书馆的管理模式,实行大部制。
现有正式员工59人中,其中研究生24人,占40%,本科生24人,占40%;高级职称17人占总人数29%,中级职称26人占总人数44%,队伍素质结构逐年明显提高。
3、文献逐年增加,资源类型丰富本馆以收集工科文献为主要特色,兼收管理、文学、理学、法学等各科文献。
其中,纸本文献102万余册;中外文数据库检索系统50多个,包括:Elsevier Science Direct数据库、Engineering Village2数据库、EBSCOhost(BSP/ASP)数据库、国道数据库;CNKI 知识总库、维普资讯网、博看期刊数据库;超星数字图书馆、方正Apabi数字图书馆、爱迪科森《网上报告厅》、新东方在线、北大法意网、方正中华数字书苑等;累计引进购入中外文电子图书376万种(册);各类中外文电子期刊3万多种;学位论文近170万篇;会议论文170万余篇。

基于馆藏数据的高校图书馆中文图书采访模式探析--以内蒙古
科技大学图书馆为例
王玮
【期刊名称】《科技情报开发与经济》
【年(卷),期】2015(000)016
【摘要】从图书分类、学科特点、复本数和采购经费等方面,对内蒙古科技大学图书馆2012—2014年入藏的中文纸质图书进行了统计分析,总结了中文纸质资源建设中存在的问题,并提出了更加科学的中文图书采访策略。
【总页数】3页(P48-50)
【作者】王玮
【作者单位】内蒙古科技大学图书馆,内蒙古包头,014010
【正文语种】中文
【中图分类】G258.6
【相关文献】
1.基于馆藏结构分析的高校图书馆中文图书采访策略优化研究——以西安电子科技大学图书馆为例 [J], 贠琳红;林强;黄小强;金洁
2.中文图书预约数据分析和馆藏优化策略——以内蒙古大学图书馆为例 [J], 彭美玲
3.高校图书馆建设硕士学位论文数据库的实践探索——以内蒙古科技大学图书馆为例 [J], 袁红霞;李永霞
4.数据时代高校图书馆纸质馆藏利用分析与服务对策研究——以内蒙古工业大学图
书馆为例 [J], 郭俊平; 顾洁; 宋飞
5.高校图书馆中文图书回溯建库之探析
——以内蒙古工业大学图书馆为例 [J], 李勇
因版权原因,仅展示原文概要,查看原文内容请购买。
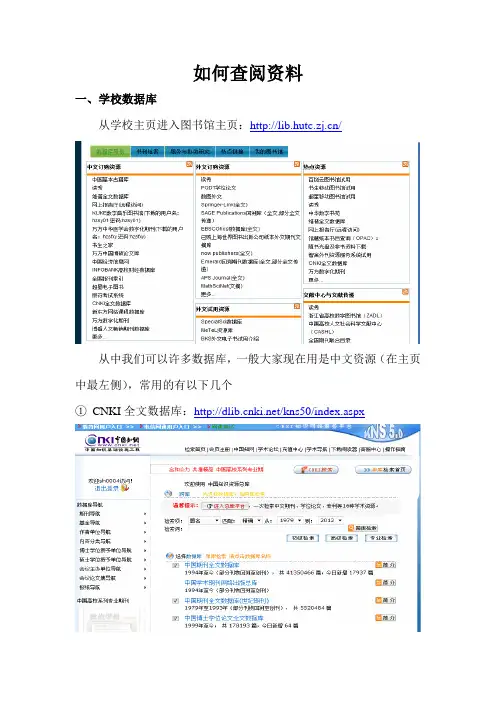
如何查阅资料一、学校数据库从学校主页进入图书馆主页:/从中我们可以许多数据库,一般大家现在用是中文资源(在主页中最左侧),常用的有以下几个①CNKI全文数据库:/kns50/index.aspx②万方数字化期刊/其他数据库大家可以根据自己需要去下载需要的资料,有空多关注图书馆的培训信息,每学期都有图书馆“1小时专题培训”安排,希望大家去听一下。
这是今年上学期的安排,下学期不要忘记了,关注下。
专题名称主讲人讲座简介时间与地点第一讲如何利用CNKI全文数据库查找资料丁兰兰主要介绍CNKI的期刊全文数据库与优秀硕博论文全文数据库3月22日15:30-16:30(星期四)图书馆三楼302室第二讲如何利用万方数据全文数据库查找资料吕元康主要介绍万方数据数字化期刊全文数据库与硕博论文全文数据库3月29日(星期四)15:30-16:30图书馆三楼302室第三讲如何利用手机、PAD等移动设备利用图书馆阮建成1.用户注册2.各种网络的使用技巧及上网4月9日(星期一)二、网上其他文库1.Google学术搜索/schhp?hl=zh-CN&as_sdt=0,5如你需要搜索关于“菲涅尔衍射”的相关论文,那么输入菲涅尔衍射filetype:pdf这些pdf格式基本都可以直接下载,英文文献也可是如此,不过并不是需要的文献都有Pdf供你下载,有些是不提供的。
2.新浪共享资料/(部分下载需注册)3.豆丁网/list.html(部分下载需注册)4.Baidu文库/(部分下载需注册)。

科技信息检索检索报告级专业班学号姓名说明利用所学的文献信息检索知识和检索方法,结合自己的专业,自定检索课题,从多方面广泛收集有关资料,并完成该课题的综合检索报告。
一、数据库选择要求1. 中文数据库:cnki中国知网、万方信息资源系统、维普科技期刊数据库、超星数据图书馆或读秀学术搜索。
3. 搜索引擎:google、百度等。
4. 专利数据库:国家知识产权局(中、美、欧、日)。
二、条目解释1. "检索年限":范围限定在最近十年以内,各种数据库(检索工具)尽量选用同等年限,以便之后根据检索结果进行比较,从而加深对各类数据库(检索工具)的认识。
2. "检索词":列出与课题内容相关的关键词或主题词。
3. "检索式":运用布尔逻辑运算符来表达检索词与检索词之间逻辑关系,以及检索项(如:题名、主题、关键词、摘要、作者、作者单位、来源、全文、参考文献、基金等)。
如:题名=汽车 and 尾气 and 排放and 控制。
请注意各数据库检索式不一定相同。
4. 每种检索系统检索完毕后,记录检索结果(检出文献篇数),按规定条数列出与课题密切相关的文献(只需列出5条最相关的,不足5条请注明原因),注:中外文数据库列出题名、作者、出处、摘要;专利列出专利名称、申请号、申请人和摘要;搜索引擎列出标题、网址、摘要。
三、其它要求按时、按质、按量完成示例1、检索课题名称(中英文)计算机在中学物理中的应用2、分析研究课题随着计算机技术的不断发展,计算机在教育中的作用愈发突出。
在中学物理教育中,同样可以引入计算的先进技术,改进教育方法,提高教学效率。
如今,计算机在中学物理中的应用主要体现在以下几个方面:1) 计算机技术在课件制作中的应用。
2) 计算机在实验仿真中的应用。
3) 计算机在教学数据处理中的应用。
根据以上分析,本课题主要是根据计算机在中学物理教学中的几个应用进行相关材料的查找。

一、根据课程所学内容完成以下填空(每空2分,共60分):1、写出内科大图书馆订购的两种电子期刊数据库(CNKI 维普资讯)2 在我馆的馆藏纸质图书文献中,题名包含“金属冶炼”的全部图书有( 25 )种;我馆收藏的黑色金属冶炼设备是(西安重型机械研究所,鞍山钢铁大学)编写的。
3、逻辑运算与在调整检索策略时的作用是提高(检索结果查全)率。
4、世界著名的三大科技文献检索系统是(SCI(科学引文索引)、EI(工程索引)、ISTP(科技会议录索引)) ,5、在中国知网CNKI期刊数据库中,题名包含“冶金”的期刊有(89)种。
6、《CNKI---中国期刊全文数据库》中精确检索主题包含“中间包”的期刊论文全部数据有(2806)条;其中2011年第3期《钢铁》中的期刊论文有(2 )条。
7、我馆订购的可以实战操作英语四级考试环境的数据库是(银符时代考试试题库)。
8、我馆订购的学位论文的数据库有(3)个。
9指引用户到另一信息源以获得原文或其他细节的一类数据库叫(参考数据库)我校订购的是(EI)10、利用EI 检索在摘要中检索含文献类型为期刊来源为中国的含有metall的记录有(16258)条其中A primary study of 8~14 μm band emittance 是于()年发表的。
11、分别利用CNKI《中国期刊全文数据库》的主题名和摘要途径,检索2011-2012年关键词包含“读书日”的期刊论文分别有相关记录(723)条、(575)条。
12、请在CNKI期刊数据库中检索出2012年内蒙古科技大学发表的论文有(162)篇。
13、当检索结果输出篇数过少时,缩小检索范围的方法有(增加and的限制概念、用not限制将不相关的文献的输出)14:参考数据库主要由( 文档、记录和字段)层次构成。
15、在EI中的专家检索时,atuostemming off 默认方式是(取消)16、《美国工程索引Ei中国镜像站》是(科学文献)数据库。

1、检索课题名称:美国次贷危机对全球经济的影响2、课题分析:本课题研究的是美国次贷危机对全球经济的影响,其中“次贷危机”本就是在美国发生的,并且“次贷危机”对“全球经济”产生的只能是影响而不是其他,因此“影响”可不作为检索词,由此得出如下检索词:中文关键词:(1)次贷危机(2)全球经济英文关键词:(1)Sub-prime Crisis (2)Global economy3、选择检索工具:(1)CNKI数字图书馆:中国期刊全文数据库(2)万方数据库(会议论文)(3)超星数字图书馆(图书检索)。
4、构建检索策略:因“次贷危机”为课题的主体,应优先检索,“全球经济”应在检索结果中同时存在。
故制定如下检索策略。
“()”表示优先、“*”表示并且。
检索算法:(次贷危机)*全球经济时间范围:2006-2013文献范围:期刊论文、会议论文、专著为了保证查全率可考虑使用全文检索途径和高级检索方式。
5、简述检索策略调整的过程:1)在CNKI中国期刊全文数据库中:a、为保证查全率,使用“(次贷危机)*全球经济”检索运算式,检索范围选择:所有专辑、全文中检索,检索出记录22,774条。
b、上述检索策略得到的检索结果240条过多,考虑缩小检索范围。
改全文检索项为篇名检索。
使用“(次贷危机)*全球经济”检索运算式,检索范围选择:所有专辑,篇名中检索,检索出记录14条。
C、上述检索策略得到的检索结果14条太少,考虑扩大检索范围。
改篇名检索项为关键词检索。
使用“(次贷危机)*全球经济”检索运算式,检索范围选择:所有专辑,关键词中检索,检索出记录24条,数量适中。
2)万方数据库(会议论文):a、由于“万方数据库(会议论文)”收录的文献比较单一,为保证查全率,使用“(次贷危机)*全球经济”检索运算式,检索范围选择:全字段中检索,不限定年代,检索出记录32条。
b、上述检索策略得到的检索结果32条,数量适中。
3)超星数字图书馆:A、图书类文献属于成熟类知识,出版的数量少且与课题的相关度低,检索时应尽量扩大检索范围。

作者: 王昕
作者机构: 不详
出版物刊名: 图书馆建设
页码: F0002-F0002页
年卷期: 2013年 第6期
主题词: 科技大学图书馆 内蒙古 综合性图书馆 包头地区 现代化程度 院图书馆 馆藏文献建筑面积
摘要:内蒙古科技大学图书馆前身为包头钢铁学院图书馆,经过50多年的建设与发展,已成为包头地区馆藏文献最多、现代化程度最高、服务最全面的综合性图书馆。
2012年,全馆建筑面积达到4万平方米,中央大厅设蒙古包造型穹顶,通透明亮,新馆与老馆相围合,俯瞰其似翻开的书页,展放于学校中央草坪之中。
《中文科技期刊数据库》检索技巧探讨(兰州交通大学图书馆,甘肃兰州 730070)1007—6921(2021)05—0110—021 引言近几年,维普资讯有限公司对《中文科技期刊数据库》进行了较多的改良和完善,其检索系统也有了相应的改变,然而使用者对这些改变不是很了解。
因此有必要对《中文科技期刊数据库》及其改变内容进行介绍,以关心使用者更好地使用这个数据库。
《中文科技期刊数据库》具有兼容性好、检索途径多、操作简便、界面友好、检索速度快、功能强、输出方式敏捷方便等特点是我国最大的数字期刊数据库,受到国内图书情报界的广泛关注和普遍赞誉,目前已拥有包括港澳台地区在内 2000余家大型机构用户,是我国数字图书馆建设的核心资源之一,高校图书馆文献保障系统的重要组成部分,也是科研工进行科技查证和科技查新的必备数据库。
2 数据库检索技巧2.1 同义词和同名检索同义词检索和同名检索是《中文科技期刊数据库》独有的两个检索功能,对检索者的关心很大。
同义词检索以《汉语主题词表》为基础,参考各个学科的主题词表,通过多年的标引实践,编制了规范的关键词用代词表(同义词库),实现高质量的同义词检索,提高查全率。
同义词库功能只有在选择了关键词检索入口时才生效,默认为关闭,选中既打开。
同义词库的使用方法是:①进入《中文科技期刊数据库》的检索界面,在其左上角,有“同义词〞选择框,在框内打勾;②在“检索入口〞选项内,选“关键词〞;③在检索框内输入您的关键词;④假如同义词表中,有该关键词的同义词,系统就会显示出来,让用户确定是否也用这些同义词检索。
例:输入关键词“土豆〞检索时,会提示“马铃薯、洋芋〞等是否同时选中作为检索条件,从而可提高检索的查全率。
同名检索功能可以关心检索者以“〞或“第一〞人口检索时剔除掉那些检索者并不期望检索的同名同姓,以提高检索结果的精确率。
2.2 复合检索《中文科技期刊数据库》的复合检索可以通过两种方式来实现:一是多次的二次检索,二是直接输入规律表达式检索。
利用英文全文数据库——Elsevier进行文献信息检索1、检索课题名称:促进我国自主创新的知识产权管理研究2、课题分析:中文关键词为:知识产权管理自主创新英文关键词为:Intellectual property management Independent innovation3、选择检索工具:Elsevier数据库4、构建检索策略:Intellectual property managementANDIndependent innovation5、简述检索过程:选定在Elsevier中期刊、图书、文摘数据库等全部文献资源中检索2000年以后的相关文献。
利用确定的检索策略(Intellectual property managementANDIndependent innovation),文献全文(含文献题目、摘要、关键词)中检索,检到6605篇相关文献;检索2005年以后的相关文献,文献全文(含文献题目、摘要、关键词)中检索,检到5390篇相关文献;6、整理检索结果:从以上文献中选择出3条切题文献1.Drivers of innovation capital disclosure in intellectual capitalstatements:Evidence from EuropeqLucia Bellora*,Thomas W.GuentherTechnische Universit?t Dresden(TU Dresden),Faculty of Business Management and Economics, Chair of Business Management,esp.Management Accounting and Control,D-01062Dresden,GermanyAbstractInnovation is one of the major determinants of competitive success.As a result,there is demand for information on the innovation activities of firms among investors,other stakeholders and the ing content analysis,this paper examines the innovationcapital disclosure(INCD)characteristics(i.e.disclosure quantity and quality)in the intellectual capital statements(ICS)of51European for-profit firms.Additionally,the relationships between INCD characteristics and industry,firm size,region of registered officeand the disclosure guidelines adopted are analysed.Our content analysis detects anaverage of29.16items on innovation capital(INC)per ICS.These are mainly qualitative,non-financial and historically orientated.Furthermore,as expected,industry,firm size,region and disclosure guidelines drive the quantity of disclosure.Prior empirical studies of voluntary disclosure in documents other than ICS have also suggested a relationship between firm size and disclosure quality.Interestingly,our results for INCD in ICS do notsupport this relationship.This provides tentative evidence for a similar qualitative level of innovation capital disclosure across firm size.Furthermore,our findings show mostly homogeneous disclosure patterns across the regions in Europe,suggesting that multinational efforts towards fostering INCD has made the ICS phenomenon more a European thana local phenomenon.Keywords:Content analysisDisclosureInnovation capitalIntellectual capital statements2.International low carbon technology transfer:Do intellectual propertyregimes matter?Varun Rai a,b,*,Kaye Schultz a,Erik Funkhouser aa LBJ School of Public Affairs,The University of Texas at Austin,United Statesb Mechanical Engineering Department,The University of Texas at Austin,United States AbstractTransfer of low carbon technologies to developing countries has been recognized as important in global efforts to limit climate change.Yet the mechanics of international technology transfer, especially around intellectual property rights,have remained a controversial issue in international ing a new dataset on international partnerships in China and India in three key low carbon technologies—solar photovoltaics,electric vehicles,and coal gasification/integrated gasification combined cycle—and complementary expert interviews we study the dynamics of the transfer of intellectual property and the underlying drivers that guide the development of business strategies and partnerships in the context of transitioning intellectual property regimes in emerging markets.We find that weak intellectual property regimes are indeed a hindrance to the diffusion of certain classes of low carbon technologies:(i)for cutting-edge technologies,(ii)for fully-embodied(explicitly codified)technologies,and(iii)for small firms.However,we also find that intellectual property issues do not represent a barrier to the diffusion of the relatively mature and low to medium cost low carbon technologies that are materially(at scale)most important for carbon dioxide emissions reduction in the short to medium petitive technology supply, shifting market dynamics,and increasingly vigorous domestic innovation coupled with mechanisms and opportunities to structure credible intellectual property deals allow for the diffusion of key low carbon technologies to occur within the context of existing business,political, and institutional structures.Article history:Received10May2013Received in revised form2October2013Accepted8 October2013Keywords:Technology transferIntellectual propertyJoint venturesDiffusion of innovationsAbsorptive capacityNational innovation system3.Key factors for the successful evaluation and screening of managers of theintellectual property rights specialityMing-Kuen Wang?,Kevin P.HwangDepartment of Transportation and Communication Management Science,National Cheng Kung University,Tainan,Taiwan,ROCAbstract:This research uses the analytical hierarchy process(AHP)to analyze the key factors in evaluating andscreening managers of the intellectual property rights speciality in Taiwan,related to industry. Industrycan utilize the key factors of human resource management to provide self-growth and obtain competitiveadvantage opportunities for expanding the global market share.This research summarizes the evaluationand screening criteria of managers of the intellectual property rights speciality via a questionnaire of29managerial or technical staff from the IP rights-related industries,technology or management expertsfrom the governmental departments related to IP rights industries,and scholars with backgrounds inIP rights related industries who had actually participated in IP rights managers speciality decisions orrelated tasks and who had employed AHP screening criteria.The findings include three key factors inevaluating and screening the managers’speciality:evaluating IP rights competency,locating the core patentgroup competency,and calculating the chance of patents to be granted competency.This research canprovide a reference for Taiwan’s related industry,when evaluating and screening managers of the IPrights speciality.Keywords:Analytical hierarchy processEvaluation and screeningKey factorManagers of intellectual property rightsspeciality6、全文摘录选择一篇:1.Drivers of innovation capital disclosure in intellectual capitalstatements: Evidence from Europeq一、篇名Drivers of innovation capital disclosure in intellectual capitalstatements:Evidence from Europeq二、著者Lucia Bellora*,Thomas W.Guenther三、著者机构Technische Universit?t Dresden(TU Dresden),Faculty of Business Management and Economics,Chair of Business Management,esp.Management Accounting and Control,D-01062Dresden,GermanyBarcelona,Spain Received18December2003?accepted26July2004四、文摘Innovation is one of the major determinants of competitive success.As a result,there is demand for information on the innovation activities of firms among investors,other stakeholders and the ing content analysis,this paper examines the innovationcapital disclosure(INCD)characteristics(i.e.disclosure quantity and quality)in the intellectual capital statements(ICS)of51European for-profit firms.Additionally,the relationships between INCD characteristics and industry,firm size,region of registered officeand the disclosure guidelines adopted are analysed.Our content analysis detects anaverage of29.16items on innovation capital(INC)per ICS.These are mainly qualitative,non-financial and historically orientated.Furthermore,as expected,industry,firm size,region and disclosure guidelines drive the quantity of disclosure.Prior empirical studies of voluntary disclosure in documents other than ICS have also suggested a relationship between firm size and disclosure quality.Interestingly,our results for INCD in ICS do notsupport this relationship.This provides tentative evidence for a similar qualitative level of innovation capital disclosure across firm size.Furthermore,our findings show mostly homogeneous disclosure patterns across the regions in Europe,suggesting that multinational efforts towards fostering INCD has made the ICS phenomenon more a European thana local phenomenon.五、关键词Keywords:Content analysisDisclosureInnovation capitalIntellectual capital statements六、正文1.Introduction and objectives(首段)Innovation capital(INC)is that part of the intellectual capital of a firm that describes the ability of a firm to generate anduse innovative solutions,and related results in terms of intellectual property rights and other tangible,intangible andfinancial assets(Edvinsson&Malone,1997).The transformation of western economies from an industrial to a knowledgebasedstructure increases the relevance of INC.On a macro-economic level,innovation has become a major driver of economicgrowth,while traditional growth enhancers such as investment in physical assets are declining in importance(OECD,2010).On a micro-economic level,innovations are recognised as means of gaining competitive advantage and higher returns(Bowen,Rostami,&Steel,2010).(末段)Our findings also have implications for policy and practice.First,small firms especially may identify ICS as instrumentsadequate for meeting the demand for INCD,as can be seen from the overall use of INCD items in the sample ICS.Second,policymakers may achieve insights into current disclosure practices on INC and find ways to further improve policymaking.For example,policymakers in Nordic countries could recognise in their data the necessity to increase thedisclosure of INC in order to increase the perception of their economies’innovativeness.Finally, guideline-setters mayrecognise that further efforts are needed in order to satisfy the call for homogenisation in disclosure guidelines and thusin disclosure behaviour.七、参考文献ReferencesAbdolmohammadi,M.(2005).Corporate social reporting practices in Western Europe:legitimating corporate behaviour?TheBritishAccounting Review,30(1),1–21.AICPA.(1994).Improving business reporting–A customer focus:Meeting information needs of investors and creditors.Jersey City:AICPA.April,K.A.,Bosma,P.,&Deglon,D.(2003).Intellectual capital measurement and reporting: establishing a practice in South African mining.Journal ofIntellectual Capital,4(2),165–180.Austrian Ministry of Science and Research.(2002).University act.Available on the internet at http://www.bmwf.gv.at/fileadmin/user_upload/wissenschaft/recht/englisch/E_UG.pdf Accessed04.07.10.Austrian Research Centers.(2000).Intellectual capital report1999,research report of the Austrian Research Centers.Seibersdorf:Austrian Research Centers.Backhuijs,J.B.,Holterman,W.G.M.,Oudman,R.S.,Overgoor,R.P.M.,&Zijlstra,S.M. (1999).Reporting on intangible assets,final report for the benefit of theDutch Ministry of Economic Affairs and the intangible assets pilot project sounding board group. Amsterdam:Dutch Ministry of Economic Affairs.Beattie,V.,&Thomson,S.J.(2007).Lifting the lid on the use of content analysis to investigate intellectual capital disclosure.Accounting Forum,31(2),129–163.Beretta,S.,&Bozzolan,S.(2008).利用英文全文数据库——EBSCO(BSP/ASP)进行文献信息检索1、检索课题名称:促进我国自主创新的知识产权管理研究2、课题分析:中文关键词为:知识产权管理自主创新英文关键词为:Intellectual property management Independent innovation3、选择检索工具:EBSCO(BSP/ASP)数据库4、构建检索策略:Intellectual property management AND Independent innovation5、简述检索过程:选定在EBSCO(BSP/ASP)中xt all text等全部文献资源中检索,利用确定的检索策略(Intellectual property management AND Independent innovation),检到34篇相关文献;6、整理检索结果:从以上文献中选择出3条切题文献1、IP Modularity:PROFITING FROM INNOVATION BY ALIGNING PRODUCT ARCHITECTURE WITH INTELLECTUAL PROPERTYJoachim Henkel Carliss Y.Baldwin Willy ShihAbstractFirms seeking to take advantage of distributed innovation and outsourcing can bridge the tension between value creation and value capture by modifying the modular structure of their technical systems.Specifically,this article introduces the concept of“IP modularity,”which seeks to protect and capture value from intellectual property.The article defines what it means for a system to be “IP-modular,”illustrates the application of this concept in a number of practical situations,and presents a comprehensive framework that can be used to design and evaluate value capture strategies for modular systems.(Keywords:Modularity,Value Appropriation,Distributed Innovation,Open Innovation,Intellectual Property)2、INNOVATION MANAGEMENT CHALLENGES OF ASYSTEM INTEGRATOR IN INNOVATION NETWORKSJAAKKO PAASI,KATRI VALKOKARI and TUIJA RANTALAVTT Technical Research Centre of FinlandP.O.Box1300,FI-33101Tampere,FinlandHENRI HYTÖNENVTT Technical Research Centre of FinlandP.O.Box1000,FI-02044VTT,FinlandSOILI NYSTÉN-HAARALA y and LAURA HUHTILAINENUniversity of Eastern FinlandP.O.Box111,FI-80101Joensuu,FinlandAbstractThe paper describes findings from a multiple case study about the innovation management challenges of a system integrator(SI)whose operation is characterized by a high demandof innovation and whose focus of integration capabilities is,accordingly,changing from component assembly to knowledge integration.The study involved six diverse case firms,and it applied the methodology of qualitative research.Innovation networks orchestratedby the SI were categorized,according to the way in which knowledge and intellectualproperty(IP)were explored and exploited in the network,to sourcing(transaction)andco-creation types of networks.The research question of the study was,what aspects of sourcing networks and of co-creation networks support or hinder networked innovationfrom the viewpoint of a SI and innovation management?After iteratively addressing the lessons learned from literature and empirical case findings,sets of supporting and hindering aspects were presented as implications of the study.Keywords:Open innovation;innovation network;system integrator;innovation management; intellectual property.3、ADOPTING INNOVATION MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE IN UNIVERSITY INNOVATION COMMERCIALIZATIOnNINDRIT TROSHANIUniversity of AdelaideAdelaide,SA5005,AustraliaGISEllE RAMPERSADFlinders UniversityAdelaide,SA5001,AustraliaCAROlIN PlEWAUniversity of AdelaideAdelaide,SA5005,AustraliaAbstractDespite the growing prominence of innovation,limited studies have examined the adoption of information systems that support innovation processes.This study investigates the organizational adoption of an innovation management software.It is based on a case study which incorporates a focus group and sixteen in-depth interviews across R&D,marketing,and administration functions. It contributes to current literature by isolating specific intrinsic characteristics of innovation management software,including communication/information flow,accessibility,and accountability,and how these can jointly shape organizational motivations and capabilities asinnovation organizations respond to environmental pressures,including innovation partners’influence,competition,and regulation.Managerial implications for enhancing the adoption of innovation management software are also offered.keywords:innovation,adoption,case study.6、全文摘录选择一篇:2.INNOVATION MANAGEMENT CHALLENGES OF A SYSTEM INTEGRATOR IN INNOVATION NETWORKS一、篇名INNOVATION MANAGEMENT CHALLENGES OF ASYSTEM INTEGRATOR IN INNOVATION NETWORKS二、著者JAAKKO PAASI,KATRI VALKOKARI and TUIJA RANTALAHENRI HYTÖNENSOILI NYSTÉN-HAARALA and LAURA HUHTILAINEN三、著者机构International Journal of Innovation Management.Dec2010,Vol.14Issue6, p1047-1064.18p.四、文摘The paper describes findings from a multiple case study about the innovation management challenges of a system integrator(SI)whose operation is characterized by a high demandof innovation and whose focus of integration capabilities is,accordingly,changing from component assembly to knowledge integration.The study involved six diverse case firms,and it applied the methodology of qualitative research.Innovation networks orchestrated by the SI were categorized,according to the way in which knowledge and intellectualproperty(IP)were explored and exploited in the network,to sourcing(transaction)andco-creation types of networks.The research question of the study was,what aspects of sourcing networks and of co-creation networks support or hinder networked innovationfrom the viewpoint of a SI and innovation management?After iteratively addressing the lessons learned from literature and empirical case findings,sets of supporting and hindering aspects were presented as implications of the study.五、关键词Keywords:Open innovation;innovation network;system integrator;innovation management;intellectual property六、正文1.Introduction and objectives(首段)Since the1990s,there has been a strong trend towards outsourcing in Western companies. Outsourcing is nowadays used for a variety of activities,including core processes such as new product development.Global corporations are typically seeking a few suppliers from whom to buy more complete and complex systems or subsystems.Accordingly,the locus of competition through innovation has been shifting from discrete product innovations to innovations in increasingly complex products,and also then to the design and development process of these complex products itself(Pavitt,2002).Such complex products often consist of pieces from various suppliers put together by an actor called system integrator(SI)(Hobday et al.,2005)(末段)Further studies of the innovation management challenges of SIs in innovation networks should therefore focus on sectoral analyses(and consider similarities between product system integration and high-volume system integration in the automotive and consumer electronics industries),as well as to broaden the perspective beyond innovation management to a wider viewpoint of business management.七、参考文献ReferencesArgyres,N and K Mayer(2007).Contract design as afirm capability:An integration of learning and transaction cost perspectives.Academy of Management Review,32,1060–1077.Arora,A,A Fosfuri and A Gambardella(2001).Markets for Technology:The Economicsof Innovation and Corporate Strategy.MIT Press,Cambridge.Axelrod,RM(1984).The Evolution of Cooperation.Basic Books,New York.Becker M,PH Johnson and N Ruijsenaars(2003).Collaborative Product Development—Case Study within the Swedish Automotive Industry.Lund Institute of Technology,Lund.Brusoni,SA,A Prencipe and K Pavitt(2001).Sharing intellectual property rights—an exploratory study of joint patenting amongst companies.Industrial and Corporate Change,12,1035–1050.Hanel,P(2006).Intellectual property rights business management practices:A survey of the literature.Technovation,26,895–931.Hobday,M,A Davies and A Prencipe(2005).Systems integration:A core capability ofthe modern corporation,Industrial and Corporate Change,14,1109–1143.Jarimo,T(2008).Innovation Incentives and the Design of Value Networks.D.Sc.Thesis.Helsinki University of Technology,Espoo.Järvensivu,T and K Möller(2009).Metatheory of network management:A contingency perspective,Industrial Marketing Management,38,654–mbert,M(1983).Long-term Contracts and Moral Hazard.Bell Journal of Economics,14,441–452.Lee,N(2009).Exclusion and coordination in collaborative innovation and patent law, International Journal of Intellectual Property Management,3,79–93.Leiponen,A(2008).。
(四)利用英文全文数据库——Elsevier进行文献信息检索示例1、检索课题名称:生物医用复合材料的研究进展及趋势2、课题分析:中文关键词为:生物医用复合材料英文关键词为:biomedical Composite materials3、选择检索工具:Elsevier数据库4、构建检索策略:biomedical AND Composite materials5、简述检索过程:选定在Elsevier中期刊、图书、文摘数据库等全部文献资源中检索1996年以后的关于废水处理的相关文献。
利用确定的检索策略(biomedical AND Composite materials),文献全文(含文献题目、摘要、关键词)中检索,检到20919篇相关文献;在文献题目、摘要和关键词中检索,检索到182篇相关文献;在文献关键词中检索到2篇相关文献;在文献题目中检索到33篇相关文献。
6、整理检索结果:从以上文献中选择出3条切题文献Biomedical applications of polymer-composite materials: a review Original Research Article Composites Science and Technology, Volume 61, Issue 9, July 2001, Pages 1189-1224S. Ramakrishna, J. Mayer, E. Wintermantel, Kam W. LeongAbstract:An overview of various biomedical applications of polymer-composite materials reported in the literature over the last 30 years is presented in this paper. For the benefit of the readers, general information regarding structure and function of tissues, types and purpose of implants/medical devices, and various other materials used, are also briefly presented. Different types of polymer composite that are already in use or are investigated for various biomedical applications are presented. Specific advantages of using polymer-composite biomaterials in selected applications are also highlighted. The paper also examines the critical issues and scientific challenges that require further research and development of polymer composite materials for their increased acceptance in the biomedical industry.6、全文摘录选择一篇:1. Biomedical applications of polymer-composite materials: a review Original Research ArticleComposites Science and Technology, Volume 61, Issue 9, July 2001, Pages 1189-1224S. Ramakrishna, J. Mayer, E. Wintermantel, Kam W. Leong一、篇名. Biomedical applications of polymer-composite materials: a review二、著者S. Ramakrishna, J. Mayer, E. Wintermantel, Kam W. Leong三、著者机构Composites Science and Technology, Volume 61, Issue 9, July 2001, Pages 1189-1224四、文摘 AbstractAn overview of various biomedical applications of polymer-composite materials reported in the literature over the last 30 years is presented in this paper. For the benefit of the readers, general information regarding structure and function of tissues, types and purpose of implants/medical devices, and various other materials used, are also briefly presented. Different types of polymer composite that are already in use or are investigated for various biomedical applications are presented. Specific advantages of using polymer-composite biomaterials in selected applications are also highlighted. The paper also examines the critical issues and scientific challenges that require further research and development of polymer composite materials for their increased acceptance in the biomedical industry.五、关键词 Keywords: Durability; Biomaterials; Biocomposites; Polymer composites; Implants; Prosthesis; Medical devices; Biomedical engineering; Bioengineering六、正文1. Introduction (首段)Biomaterials are materials of natural or man-made origin that are used to direct, supplement, or replace the functions of living tissues of the human body [21]. Use of biomaterials dates far back into ancient civilizations. Artificial eyes, ears, teeth, and noses were found on Egyptian mummies [256]. Chinese and Indians used waxes, glues, and tissues in reconstructing missing or defective parts of the body.(末段)However, for successful application, surgeons must be convinced with the long term durability and reliability of polymer composite biomaterials. Monolithic materials have long been used and there is considerable experimental and clinical data supporting their continued usage. Such data with respect to polymer composite biomaterials is relatively small. This requires further research efforts to elucidate the long-term durability of composite biomaterials in the human body conditions.七、参考文献References1. D. Adams, D.F. Williams and J. Hill, Carbon fiber-reinforced carbon as a potential implant material. J. Biomedical Materials Research12 (1978), pp. 35–42. Full Text via CrossRef | View Record in Scopus | Cited By in Scopus (32)3. P. Aebischer and M.B. Goddard, Tissue reaction to fabrics coated with turbostratic carbon: subcutaneous versus vascular implants. Biomaterials9 1 (1988), pp. 80–85. Abstract | PDF (2212 K) | View Record in Scopus | Cited By in Scopus (27)4. M. Akay and N. Aslan, Numerical and experimental stress analysis of a polymeric composite hip joint prostheses. J. Biomedical Materials Research31 (1996), pp. 167–182. Full Text via CrossRef | View Record in Scopus | Cited By in Scopus (40)5. M.S. Ali, G.W. Hastings, T. Rae, N. Rushton, E.R.S. Ross and C.H. Wynn-Jones, Carbon fiber composite bone plates. J. Bone and Joint Surgery72-B 4 (1990), pp. 586–591. View Record in Scopus | Cited By in Scopus (30)6. L. Ambrosio, Carotenuto and L. Nicolais, Composite materials. In: J Black and G Hastings, Editors, Handbook of Biomaterial Properties, Editors, Chapman and Hall, London, UK (1998), pp. 214–269.7. L. Ambrosio, R. De Santis, S. Iannace, P.A. Netti and L. Nicolais, Viscoelastic behavior of composite ligament prostheses. J. Biomedical Materials Research42 1 (1998), pp. 6–12. Full Text via CrossRef | View Record in Scopus | Cited By in Scopus (10)8. L. Ambrosio, P.A. Netti, S. Iannace, S.J. Huang and L. Nicolais, Composite hydrogels for intervertebral disc prostheses. J. Materials Science: Materials in Medicine7 (1996), pp. 251–254. Full Text via CrossRef | View Record in Scopus | Cited By in Scopus (15)9. H.C. Amstutz et al., Mechanism and clinical significance of wear debris-induced osteolysis. Clinical Orthopedics and Related Research276 (1992), pp. 7–18. View Record in Scopus | Cited By in Scopus (374)10. G.B.J. Andersson, Intervertebral disk. In: V Wright and E.L. Radin, Editors, Mechanics of human joints: physiology, pathophysiology, and treatment, Marcel Dekker Inc, New York (1993), pp. 293–311.11. A.G. Andreopoulos, M. Evangelatou and P.A. Tarantili, Properties of maxillofacial silicone elastomers reinforced with silica powder. J. Biomaterials Applications13 (1998), pp. 66–73. View Record in Scopus | Cited By in Scopus (4)13. S.P. Arnoczky, P.A. Torzilli et al., Biologic fixation of ligament prostheses and augmentations. An evaluation of bone in growth in the dog. Am J Sports Med.16 2 (1988), pp. 106–112. Full Text via CrossRef | View Record in Scopus | Cited By in Scopus (28)14. Baidya KP, Ramakrishna, S, Rahman M, Ritchie A. Quantitative radiographic analysis of fiber reinforced polymer composites. J Biomaterials Applications 2001;15(3):279–89.15. Baidya KP, Ramakrishna S, Rahman M, Ritchie A. Advanced textile composite ring for ilizarov external fixator system. J Engineering in Medicine, IME UK 2001;215(H1):11–23.。
1、检索课题名称:促进我国自主创新的知识产权管理研究
2、课题分析:“知识产权管理”是本课题中的主体,“自主创新”是限定“知识产权管理”的内容,而“研究”“促进”是修饰内容,“知识产权管理”能提高我国的“自主创新”,因此“研究”“促进”“我国”都不可作为检索词,由此得出如下检索词:
中文关键词:1、知识产权管理2、自主创新
英文关键词:1、Intellectual property management 2、Independent innovation
3、选择检索工具:(1)CNKI硕士论文库(2)维普期刊数据库
4、构建检索策略:因“知识产权管理”为课题的主体,应优先检索,“自主创新”应在检索结果中同时存在。
所以制定如下检索策略。
“()”表示优先、“*”表示并且。
检索算法:(知识产权管理)*自主创新
时间范围:2005-2014
文献范围:期刊论文、硕士论文
5、简述检索策略调整的过程:
1)在CNKI硕士论文库中:
a、为保证查全率,使用“(知识产权管理)*自主创新”检索运算式,检索范围选择:所有专辑、全文中检索,检索出记录2,644条。
b、上述检索策略得到的检索结果2,644条过多,考虑缩小检索范围。
改全文检索项为关键字检索。
使用“(知识产权管理)*自主创新”检索运算式,检索范围选择:所有专辑,关键字中检索,检索出记录3条。
c、上述检索策略得到的检索结果3条太少,考虑扩大检索范围。
改关键字检索改为摘要检索。
使用“(知识产权管理)*自主创新”检索运算式,检索范围选择:所有专辑,摘要中检索,检索出记录40 条,数量稍多。
d、在摘要检索的基础上增加年份限制,检索2010-2014年的论文,检索出记录22条,数量适中。
2)维普期刊数据库:
a、用“维普期刊数据库”检索文献,使用“(知识产权管理)*自主创新”检索运算式,题名或关键词检索,不限定年代,检索出记录52条。
b、上述检索策略得到的检索结果52条数量偏多。
使用“(知识产权管理)*自主创新”检索运算式,题名或关键词检索,考虑检索加入年限,2005-2014年,适当的减少检索出的数量,检索出记录49条。
数量偏多。
c、采用题名检索,年限2005-2014年,“(知识产权管理)*自主创新”检索运算式,检索出记录9篇。
数量适中。
6、整理检索结果:
(1)CNKI硕士论文库(选1 条):
我国知识产权政府管理问题对策研究
【作者】邹芸潞;
【导师】伍玉林;
【作者基本信息】哈尔滨理工大学,科学技术哲学,2013,硕士
【摘要】随着科学技术的发展和市场竞争的加剧,知识产权在经济生活中的地位日益突显。
国家对于知识产权为科学技术的创新以及经济社会的发展所带来的巨大推动作用越来越重视。
这就要求我国在不断促进自主创新的同时,加强知识
产权管理。
加强知识产权管理是现时代的必然要求,也是中国实施“科教兴国”战略、建设“以人为本”的和谐社会所必须面对和解决的一个重大课题。
而加强知识产权的政府管理,对于落实科学发展观、建设社会主义和谐社会更有着重要的现实作用。
本文在比较和分析相关文献资料的基础上,系统论述了我国知识产权政府管理的相关问题以及解决对策。
通过对研究背景、目的、意义等阐述,进一步明确了研究方向;通过对知识产权政府管理的国内外研究现状分析,掌握了开展研究的理论基础。
从知识产权、知识产权管理的含义入手,引入知识产权政府管理的概念,结合我国知识产权政府管理的现状,分析其存在的问题,在借鉴发达国家政府知识产权管理中的先进经验的基础上,进一步提出完善我国知识产权政府管理的对策和建议。
本文认为要有效地实施国家知识产权战略,完善我国的知识产权制度,必须正确发挥政府的作用,把政府的宏观调控同市场的价值规律有机的结合起来,进而充分发挥...
【关键词】知识产权;知识产权管理;政府管理;
(2)维普期刊数据库(选1 条):
加强知识产权管理提升企业自主创新能力
【作者】焦书浩李东王飞刘春平
【机构地区】中国石油天然气集团公司通信公司
【出处】《石油科技论坛》2011年第30卷第6期9-10页,共2页
【摘要】文章介绍了中国石油天然气集团公司通信公司在知识产权管理及知识产权获取、保护和运用等方面的情况和经验,如必须明确知识产权工作思路,不断完善知识产权管理体系,有效提升全员知识产权保护意识,把知识产权保护融入企业创新全过程,以及在知识产权获取与保护方面要讲究策略等。
公司在知识产
权保护方面做出了卓有成效的工作,5年来公司已申报国际发明专利2项、中国专利99项,取得软件著作权6项,并被评为河北省知识产权优势培育单位,获国家知识产权局企业知识产权战略成果三等奖。
【关键词】创新能力核心竞争力知识产权
7、标示原文线索:
(1)题目:我国知识产权政府管理问题对策研究
【作者】邹芸潞;
【机构】哈尔滨理工大学
【作者基本信息】哈尔滨理工大学,科学技术哲学,2013,硕士
(2)题目:加强知识产权管理提升企业自主创新能力
【作者】焦书浩李东王飞刘春平
【机构地区】中国石油天然气集团公司通信公司
【刊名】石油科技论坛2011年6期。