语言学树形图课后问题详解
- 格式:doc
- 大小:308.94 KB
- 文档页数:23

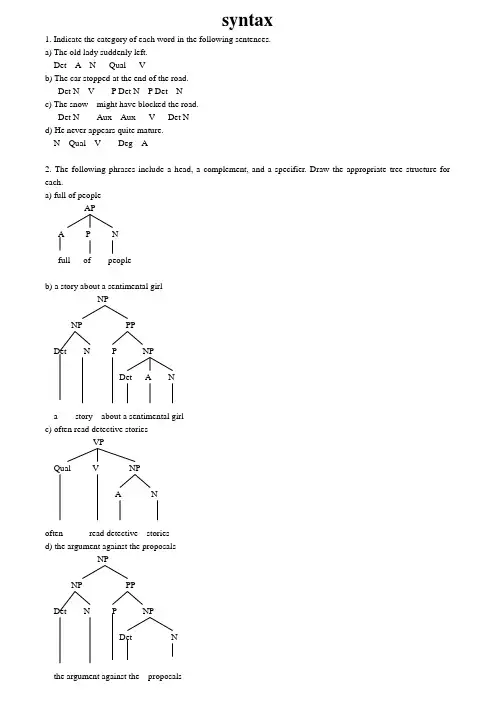
syntax1. Indicate the category of each word in the following sentences.a) The old lady suddenly left.Det A N Qual Vb) The car stopped at the end of the road.Det N V P Det N P Det Nc) The snow might have blocked the road.Det N Aux Aux V Det Nd) He never appears quite mature.N Qual V Deg A2. The following phrases include a head, a complement, and a specifier. Draw the appropriate tree structure for each.a) full of peopleAPA P Nfull of peopleb) a story about a sentimental girlNPNP PPDet N P NPDet A Na story about a sentimental girlc) often read detective storiesVPQual V NPA Noften read detective storiesd) the argument against the proposalsNPNP PPDet N P NPDet Nthe argument against the proposalse) move towards the windowVPV PPP Det Nmove towards the window3. Draw phrase structure trees for each of the following sentences.a) The jet landed.InflP(=S)NP Infl VPDet N Pst VThe jet landedb) Mary became very ill.InflP(=S)NP Infl VPN Pst V APDeg AMary became very illc) What will you talk about?CPNP C SN Infl NP Infl VPVP NPV P NWhat will you e talk about ed) The apple might hit the man.SNP VPDet N Aux V NPDet NThe apple might hit the manORInflP(=S)NP Infl VPDet N V NPDet NThe apple might hit the mane) He often reads detective stories.SNP VPN Qual V NPA NHe often reads etective storiesORInflP(=S)NP Infl VPPresN Qual V NPA NHe often reads etective stories4. The following sentences contain modifiers of various types. For each sentence, first identify the modifier(s), then draw the tree structures.a) A frightened passenger landed the crippled airplane.InflP(=S)NP Infl VPDet A N Pst V NPDet A NA frightened passenger landed the crippled airplaneb) A huge moon hung in the black sky.InflP(=S)NP Infl VPDet A N Pst V PPP NPDet A NA huge moon hung in the black skyc) An unusual event occurred before the meeting.InflP(=S)NP Infl VPDet A N Pst V PPP NPDet NAn unusual event occurred before the meetingd) A quaint old house appeared on the grassy hill.InflP(=S)NP Infl VPDet A NP Pst V PPA N P NPDet A NA quaint old house appeared on the grassyhill5. The following sentences all contain conjoined categories. Draw a tree structure for each of the sentences.a) Jim has washed the dirty shirts and pants.InflP(=S)NP VPN Aux V NPDet A NPN CON NJim has washed thedirty shirts and pantsORInflP(=S)NP VPN Infl V NPDet ANPN CON NJim has washed the dirty shirts and pantsb) Helen put on her clothes and went out.SNP VPN VP CON VPVP NP V AdvV P Det NHelen put on her clothes and went outORInflP(=S)NP Infl VPN Pst VP CON VPVP NP V AdvV P Det NHelen put on her clothes and went outc) Mary is fond of literature but tired of statistics.SNP VPN VP CON VPVP NP VP NPV A P N V A PNMary is fond of literature but (is) tired of statisticsORInflP(=S)NP Infl VPN Pres VP CON VPVP NP VPNPV A P N V A PNMary is fond of literature but (is)tired of statisticsd) The detective went out and the mysterious mancame in.SS CON SNP VP NP VPDet N V Adv Det A N VAdvThe detective went out and the mysteriousman came ine) Crusoe knows that spring will come and the snowwill melt.SNP VPCPN V C SSCON SNP VP NP VPN Aux VDet N Aux VCrusoe knows that spring willcome and the snow will melt6. The following sentences all contain embeddedclauses that function as complements of a verb, anadjective, a preposition or a noun. Draw a treestructure for each sentence.a) You know that I hate war.SNP VPCPN V C SNPVPNPNV NYou know that Ihate warOR CPC InflP(=S)NP Infl VPCPN Pres V C SNPVPNV NPNYou know that I hate warb) He said that Tom asked whether the class was over.SNP VPCPN V CSNPVPCPN V C SNP VPDet N VL AHe said that Tom askedwhether the class was overc) Gerry can’t believe the fact that Anna flunkedthe English exam.SNP VPN VP NPCPAux Neg V NPC SDet NNP VPN V NPDet A NGerry can not believe thefact thatAnna flunked the English examd) Chris was happy that his father bought him aRolls-Royce.SNP VPCPN VL A C SNPVPDet N VNP NPN Det NChris was happy that hisfather bought him a Rolls-Roycee) The children argued over whether bats had wings.SNP VPCPDet N VP C SV P NPVPN VNPNThe children argued over whether batshad wings7. Each of the following sentences contains arelative clause. Draw the deep structure and thesurface structure trees for each of the sentences.a) The essay that he wrote was too long.Deep structureCPC SNPVPDet N CP V APC S Deg PNP Infl VPN V NPNThe essay he wrote thatwas too longSurface StructureCPC SNPVPDet N CP V APC S Deg PNP NP Infl VPN N Pst V NPNThe essay that he wrote ewas too longb) The dog that he keeps bites.Deep structureCPC SNPVPDet N CP VC Infl SPres NP VPN V NPNThe dog he keeps thatbitesSurface StructureCPC SNPVPDet N CP VC SNP NP Infl VPN N Pres V NPNThe dog that he keeps e bitesc) Herbert found the man she loved.Deep structureCPC SNP VPN Infl V NPCPDet N C SNP Infl VPNPN VNHerbert found the man she loved whoSurface StructureCPC SNP VPN Infl V NPCPDet N SCNP Infl VPNP NPN VN NHerbert found the man(whom) she loved ed) The girl whom he often quarrels with majors inlinguistics.Deep structureCPC SNPVPDet N CP V PPP NPC Infl SNNP VPPPN Qual VPNPV PNThe girl he oftenquarrels with whom majors in linguisticsSurface StructureCPC SNPVPDet N CP V PPP NPC SNNP NP Infl VPPPN N Qual VPNPV PN。
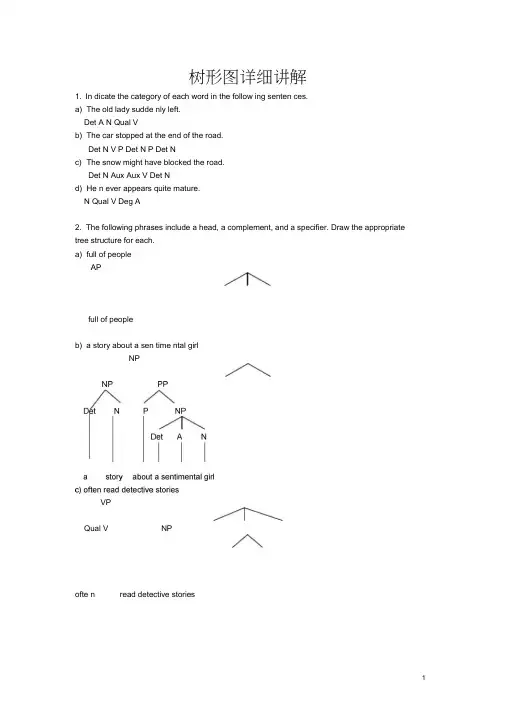
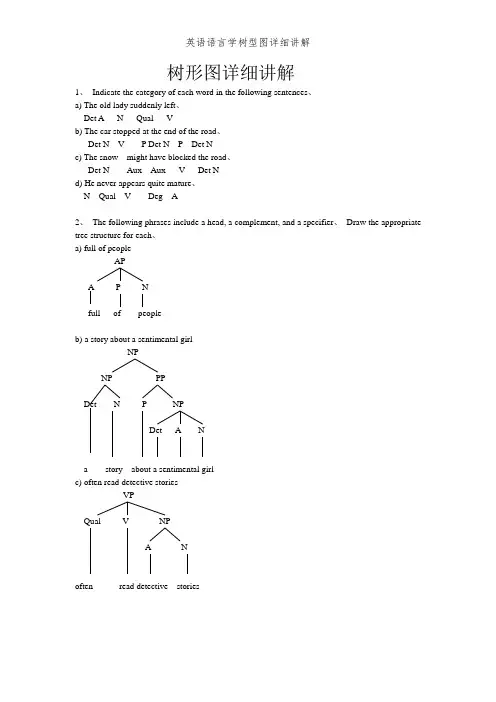
树形图详细讲解1. In dicate the category of each word in the follow ing senten ces.a) The old lady sudde nly left.Det A N Qual Vb) The car stopped at the end of the road.Det N V P Det N P Det Nc) The snow might have blocked the road.Det N Aux Aux V Det Nd) He n ever appears quite mature.N Qual V Deg A2. The following phrases include a head, a complement, and a specifier. Draw the appropriate tree structure for each.a) full of peopleAPfull of peopleb) a story about a sen time ntal girlNPVPQual V NPofte n read detective storiesd) the argume nt aga inst the proposalsthe argume nt aga inst the proposals e) move towards the win dowVPmove towards the win dow3. Draw phrase structure trees for each of the followi ng sentences, a) The jet la nded.The jet Ian dedb) Mary became very ill.DegA Mary became veryillNPPPNPDetNV PP P Det NInflP(=S)NP Infl VP Det N Pst VIn flP(=S)NP Infl VPN Pst VAPc) What will you talk about?NPd) The apple might hit theORThe apple might hit the manInflWhat willNP Infl VPVP NPyou e talk about e TheDet Napple might hit the manInflP(=S)VPVCPC Sman.Se) He ofte n reads detectivestories.He ofte n reads etective storiesORInflP(=S)reads etective storiesHe ofte n4. The following sentences contain modifiers of various types. For each sentence, first identify the modifier(s), the n draw the tree structures.InflP(=S)NP Infl VPa) A frighte ned passe nger Ian ded the crippled airpla ne.Det A N Pst V NPDet A NA frighte ned passe nger Ian ded the crippled airpla neb) A huge moon hung in the black sky.c) An unu sual eve nt occurred before the meet ing.In flP(=S)An unu sual event occurred before the meet ingd) A qua int old house appeared on the grassy hill.5. The follow ing sentences all contain conj oined categories. Draw a tree structure for each ofthe senten ces.A hugeDet A N Pst VDetPDet A NA qua int oldhouse appeared on the grassyhillInflP(=S)NPInfl VPDet AN Pst VPPmoonNP Infl VPDeInflP(=S)NPInfl VPAPPORa) Jim has washed the dirty shirts and pants.In flP(=S)NP VPN AuxJim has washedN CON Nthe dirty shirts and pants N InflN CON NJim has washed the dirty shirts and pantsb) Hele n put on her clothes and wentout.SN CONVHele n put on her clothes and went outMary is fond of literature but (is) tired of statisticsORMary is fond of literature but (is) tired of statisticsORInflP(=S)Infl VPNPN CONVP Det NHele n put on her clothes andc) Mary is fond of literature but tired of statistics.Swent outNP VPCONN VP VPVPV ANPInflP(=S)N CONNP NYoud) The detective went out and the mysterious man came in.e) Crusoe knows that spri ng will come and the snow will melt.6. The followi ng sentences all con tain embedded clauses that fun cti on as compleme nts of a verb, an adjective, a prepositi on or a noun. Draw a tree structure for each sentence. a) You know that I hate war.The detective Crusoeknows that spri ng will SCONSSwent outNP Ncome and the snow will meltSVPb) He said that Tom asked whether the class was over. Ssaid that Tom asked whether the class was overORYouknow that I NP Nhate warHec) Gerry can 'believe the fact that Anna flun ked the En glish exam. Scan not believethe fact thatA nna flun ked the En glishexamGerryd) Chris was happy that his father bought him a Rolls-Royce.e) The childre n argued over whether bats had wings.7. Each of the followi ng sentences contains a relative clause. Draw the deep structure and the surface structure trees for each of the senten ces.NPVLChrisVPCPA CwasThe childre nargued over whether bats had wingsa) The essay that he wrote was too long.Surface StructurePstDeep structureNPDet N CPC SThe essay he wrote that was too long CPSNPNVPVDet CPSInflNP NP VPAPDeg The essay that he wrote e was too longNPb) The dog that he keeps bites.Surface StructureDeep structureCPSThe dog he keeps that bitesCPSSInflNP NP VPPres V NPThe dog that he keeps e bitesc) Herbert found the man she loved.Surface StructureDeep structureCPSNP VPVInflHerbert foundCPSN Infl VHerbert foundNPNed) The girl whom he ofte n quarrels with majors in linguistics.Deep structureCPNP VPDetThe girlCPInflNPheVP/X—Qual VPofte nquarrelsSurface StructurePPNP CPVwith whom majors in linguisticsSSInflNP NP VPQual VPVPPThe girl whom he ofte n quarrels with e majorsNPin linguistics8. The derivati ons of the followi ng sentences in volve the in versio n tran sformatio n. Give the deep structure and the surface structure trees for each of these senten ces.a) Would you come tomorrow?Deep structureAdvPAdvyou would come tomorrowSurface structureAdvPAdvyouwould come tomorrowb) Can you pass me the newspaper?Deep structureyou can pass me the n ewspaper Surface structureCan you e pass me the n ewspaperc) Should the stude nts report the in cide nt? Deep structurethe stude nts shouldreport the in cidentCPC SSurface structuree report the in cidentshould the stude ntsd) What did you eat for lunch?Deep structureSurface structuree) Who should this be reported toDeep structurewhomthis should be reported to whom Surface structureNPNNP should this e be reported to ef) What was Hele n bringing to theparty?Deep structureSurface structure。

【关键字】英语树形图详细讲解1. Indicate the category of each word in the following sentences.a) The old lady suddenly left.Det A N Qual Vb) The car stopped at the end of the road.Det N V P Det N P Det Nc) The snow might have blocked the road.Det N Aux Aux V Det Nd) He never appears quite mature.N Qual V Deg A2. The following phrases include a head, a complement, and a specifier. Draw the appropriate tree structure for each.a) full of peopleAPA P Nfull of peopleb) a story about a sentimental girlNPNP PPDet N P NPDet A Na story about a sentimental girlc) often read detective storiesVPQual V NPA Noften read detective storiesd) the argument against the proposalsNPNP PPDet N P NPDet Nthe argument against the proposalse) move towards the windowVPV PPP Det Nmove towards the window3. Draw phrase structure trees for each of the following sentences.a) The jet landed.InflP(=S)NP Infl VPDet N Pst VThe jet landedb) Mary became very ill.InflP(=S)NP Infl VPN Pst V APDeg A Mary became very illc) What will you talk about?CPNP C SN Infl NP Infl VPVP NPV P N What will you e talk about e d) The apple might hit the man.SNP VPDet N Aux V NPDet NThe apple might hit the manORInflP(=S)NP Infl VPDet N V NPDet NThe apple might hit the mane) He often reads detective stories.SNP VPN Qual V NPA NHe often reads etective storiesORInflP(=S)NP Infl VPPresN Qual V NPA NHe often reads etective stories4. The following sentences contain modifiers of various types. For each sentence, first identify the modifier(s), then draw the tree structures.a) A frightened passenger landed the crippled airplane.InflP(=S)NP Infl VPDet A N Pst V NPDet A NA frightened passenger landed the crippled airplaneb) A huge moon hung in the black sky.InflP(=S)NP Infl VPDet A N Pst V PPP NPDet A NA huge moon hung in the black skyc) An unusual event occurred before the meeting.InflP(=S)NP Infl VPDet A N Pst V PPP NPDet NAn unusual event occurred before the meetingd) A quaint old house appeared on the grassy hill.InflP(=S)NP Infl VPDet A NP Pst V PPA N P NPDet A NA quaint old house appeared on the grassy hill5. The following sentences all contain conjoined categories. Draw a tree structure for each of the sentences.a) Jim has washed the dirty shirts and pants.InflP(=S)NP VPN Aux V NPDet A NPN CON N Jim has washed the dirty shirts and pants ORInflP(=S)NP VPN Infl V NPDet A NPN CON N Jim has washed the dirty shirts and pantsb) Helen put on her clothes and went out.SNP VPN VP CON VPVP NP V AdvV P Det NHelen put on her clothes and went outORInflP(=S)NP Infl VPN Pst VP CON VPVP NP V AdvV P Det NHelen put on her clothes and went outc) Mary is fond of literature but tired of statistics.SNP VPN VP CON VPVP NP VP NPV A P N V A P N Mary is fond of literature but (is) tired of statistics ORInflP(=S)NP Infl VPN Pres VP CON VPVP NP VP NPV A P N V A P N Mary is fond of literature but (is) tired of statisticsd) The detective went out and the mysterious man came in.SS CON SNP VP NP VPDet N V Adv Det A N V AdvThe detective went out and the mysterious man came ine) Crusoe knows that spring will come and the snow will melt.SNP VPCPN V C SS CON SNP VP NP VPN Aux V Det N Aux V Crusoe knows that spring will come and the snow will melt 6. The following sentences all contain embedded clauses that function as complements of a verb, an adjective, a preposition or a noun. Draw a tree structure for each sentence.a) You know that I hate war.SNP VPCPN V C SNP VPN V NPNYou know that I hate warOR CPC InflP(=S)NP Infl VPCPN Pres V C SNP VPN V NPNYou know that I hate warb) He said that Tom asked whether the class was over.SNP VPCPN V C SNP VPCPN V C SNP VPDet N VL A He said that Tom asked whether the class was overc) Gerry can’t believe the fact that Anna flunked the English exam.SNP VPN VP NPCPAux Neg V NP C SDet N NP VPN V NPDet A N Gerry can not believe the fact thatAnna flunked the English examd) Chris was happy that his father bought him a Rolls-Royce.SNP VPCPN VL A C SNP VPDet N V NP NPN Det NChris was happy that his father bought him a Rolls-Roycee) The children argued over whether bats had wings.SNP VPCPDet N VP C SV P NP VPN V NPNThe children argued over whether bats had wings7. Each of the following sentences contains a relative clause. Draw the deep structure and the surface structure trees for each of the sentences.a) The essay that he wrote was too long.Deep structureCPC SNP VP Det N CP V APC S Deg PNP Infl VPN V NPNThe essay he wrote that was too longSurface StructureCPC SNP VP Det N CP V APC S Deg PNP NP Infl VPN N Pst V NPNThe essay that he wrote e was too longb) The dog that he keeps bites.Deep structureCPC SNP VP Det N CP VC Infl SPres NP VPN V NPNThe dog he keeps that bitesSurface StructureCPC SNP VP Det N CP VC SNP NP Infl VPN N Pres V NPNThe dog that he keeps e bitesc) Herbert found the man she loved.Deep structureCPC SNP VPN Infl V NPCPDet N C SNP Infl VPNPN VNHerbert found the man she loved whoSurface StructureCPC SNP VPN Infl V NPCPDet N SCNP Infl VPNP NPN VN N Herbert found the man (whom) she loved ed) The girl whom he often quarrels with majors in linguistics.Deep structureCPC SNP VPDet N CP V PPP NPC Infl SNNP VPPPN Qual VP NPV P NThe girl he often quarrels with whom majors in linguisticsSurface StructureCPC SNP VPDet N CP V PPP NPC SNNP NP Infl VPPPN N Qual VP NPV P NThe girl whom he often quarrels with e majors in linguistics8. The derivations of the following sentences involve the inversion transformation. Give the deep structure and the surface structure trees for each of these sentences.a) Would you come tomorrow?Deep structureCPC SVPNP AdvPN Infl V Advyou would come tomorrowSurface structureCPC SVPNP AdvPInflN Infl V Advwould you e come tomorrowb) Can you pass me the newspaper?Deep structureCPC SVPNP NP NPN Infl V N Det Nyou can pass me the newspaperSurface structureCPC SVPInfl NP NP NPN Infl V N Det NCan you e pass me the newspaperc) Should the students report the incident?Deep structureCPC SVPNP NPDet N Infl V Det Nthe students should report the incidentSurface structureCPC SVPInfl NP NPDet N Infl V Det N should the students e report the incident d) What did you eat for lunch?Deep structureCPC SVPNP PPNP NPN Infl V PN Nyou did eat what for lunch Surface structureCPNP C SVPInfl NP PPNP NP N N Infl V PN N what did you e eat e for lunche) Who should this be reported to ?Deep structureCPC SVPNP PPVP NPN Infl V V PNthis should be reported to whom Surface structureCPNP C SVPN Infl NP PPVP NPN Infl V V PN whom should this e be reported to ef) What was Helen bringing to the party?Deep structureCPC SVPNP PPNP NPN Infl V PN Det NHelen was bringing what to the partySurface structureCPNP C SVPN Infl NP PPNP NPN Infl V PN Det N what was Helen e bringing e to the party此文档是由网络收集并进行重新排版整理.word可编辑版本!。
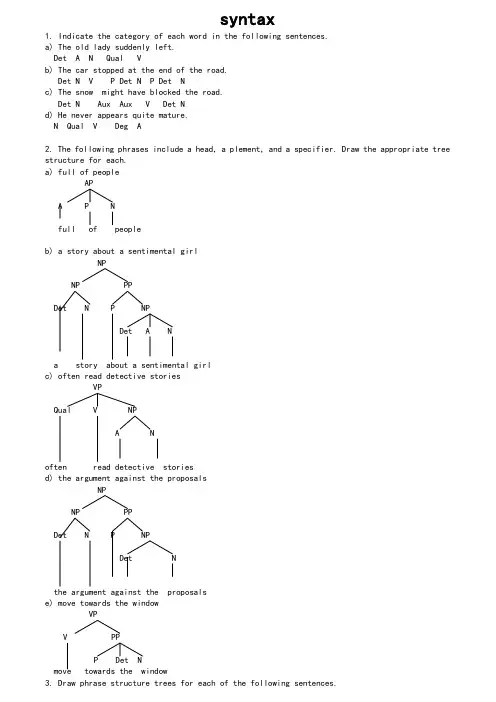
syntax1. Indicate the category of each word in the following sentences.a) The old lady suddenly left.Det A N Qual Vb) The car stopped at the end of the road.Det N V P Det N P Det Nc) The snow might have blocked the road.Det N Aux Aux V Det Nd) He never appears quite mature.N Qual V Deg A2. The following phrases include a head, a plement, and a specifier. Draw the appropriate tree structure for each.a) full of peopleAPA P Nfull of peopleb) a story about a sentimental girlNPNP PPDet N P NPDet A Na story about a sentimental girlc) often read detective storiesVPQual V NPA Noften read detective storiesd) the argument against the proposalsNPNP PPDet N P NPDet Nthe argument against the proposalse) move towards the windowVPV PPP Det Nmove towards the window3. Draw phrase structure trees for each of the following sentences.a) The jet landed.InflP(=S)NP Infl VPDet N Pst VThe jet landedb) Mary became very ill.InflP(=S)NP Infl VPN Pst V APDeg AMary became very illc) What will you talk about?CPNP C SN Infl NP Infl VPVP NPV P NWhat will you e talk about eSNP VPDet N Aux V NPDet NThe apple might hit the manORInflP(=S)NP Infl VPDet N V NPDet NThe apple might hit the mane) He often reads detective stories.SNP VPN Qual V NPA NHe often reads etective storiesORInflP(=S)NP Infl VPPresN Qual V NPA NHe often reads etective stories4. The following sentences contain modifiers of various types. For each sentence, first identify the modifier(s), then draw the tree structures.a) A frightened passenger landed the crippled airplane.InflP(=S)NP Infl VPDet A N Pst V NPDet A NA frightened passenger landed the crippled airplaneb) A huge moon hung in the black sky.InflP(=S)NP Infl VPDet A N Pst V PPP NPDet A NA huge moon hung in the black skyc) An unusual event occurred before the meeting.InflP(=S)NP Infl VPDet A N Pst V PPP NPDet NAn unusual event occurred before the meetingd) A quaint old house appeared on the grassy hill.InflP(=S)NP Infl VPDet A NP Pst V PPA N P NPDet A NA quaint old house appeared on the grassy hill5. The following sentences all contain conjoined categories. Draw a tree structure for each of the sentences.a) Jim has washed the dirty shirts and pants.InflP(=S)NP VPN Aux V NPDet A NPN CON NJim has washed the dirty shirts and pantsORInflP(=S)NP VPN Infl V NPDet A NPN CON NJim has washed the dirty shirts and pantsb) Helen put on her clothes and went out.SNP VPN VP CON VPVP NP V AdvV P Det NHelen put on her clothes and went outORInflP(=S)NP Infl VPN Pst VP CON VPVP NP V AdvV P Det NHelen put on her clothes and went outc) Mary is fond of literature but tired of statistics.SNP VPN VP CON VPVP NP VP NPV A P N V A P NMary is fond of literature but (is) tired of statisticsORInflP(=S)NP Infl VPN Pres VP CON VPVP NP VP NPV A P N V A P NMary is fond of literature but (is) tired of statisticsd) The detective went out and the mysterious man came in.SS CON SNP VP NP VPDet N V Adv Det A N V AdvThe detective went out and the mysterious man came ine) Crusoe knows that spring will e and the snow will melt.SNP VPCPN V C SS CON SNP VP NP VPN Aux V Det N Aux VCrusoe knows that spring will e and the snow will melt6. The following sentences all contain embedded clauses that function as plements of a verb, an adjective, a preposition or a noun. Draw a tree structure for each sentence.a) You know that I hate war.SNP VPCPN V C SNP VPNPN V NYou know that I hate warOR CPC InflP(=S)NP Infl VPCPN Pres V C SNP VPN V NPNYou know that I hate warb) He said that Tom asked whether the class was over.SNP VPCPN V C SNP VPCPN V C SNP VPDet N VL AHe said that Tom asked whether the class was overc) Gerry can’t believe the fact that Anna flunked the English exam.SNP VPN VP NPCPAux Neg V NP C SDet N NP VPN V NPDet A NGerry can not believe the fact thatAnna flunked the English exam d) Chris was happy that his father bought him a Rolls-Royce.SNP VPCPN VL A C SNP VPDet N V NP NPN Det NChris was happy that his father bought him a Rolls-Royce e) The children argued over whether bats had wings.SNP VPCPDet N VP C SV P NP VPN V NPNThe children argued over whether bats had wings7. Each of the following sentences contains a relative clause. Draw the deep structure and the surface structure trees for each of the sentences.a) The essay that he wrote was too long.Deep structureCPC SNP VPDet N CP V APC S Deg PNP Infl VPN V NPNThe essay he wrote that was too longSurface StructureCPC SNP VPDet N CP V APC S Deg PNP NP Infl VPN N Pst V NPNThe essay that he wrote e was too longb) The dog that he keeps bites.Deep structureCPC SNP VPDet N CP VC Infl SPres NP VPN V NPNThe dog he keeps that bitesSurface StructureCPC SNP VPDet N CP VC SNP NP Infl VPN N Pres V NPNThe dog that he keeps e bitesc) Herbert found the man she loved.Deep structureCPC SNP VPN Infl V NPCPDet N C SNP Infl VPNP N VNHerbert found the man she loved whoSurface StructureCPC SNP VPN Infl V NPCPDet N SCNP Infl VPNP NPN VN NHerbert found the man (whom) she loved eDeep structureCPC SNP VPDet N CP V PPP NPC Infl SNNP VPPPN Qual VP NPV P NThe girl he often quarrels with whom majors in linguisticsSurface StructureCPC SNP VPDet N CP V PPP NPC SNNP NP Infl VPPPN N Qual VP NPV P NThe girl whom he often quarrels with e majors in linguistics8. The derivations of the following sentences involve the inversion transformation. Give the deep structure and the surface structure trees for each of these sentences.a) Would you e tomorrow?Deep structureCPC SVPNP AdvPN Infl V Advyou would e tomorrowSurface structureCPC SVPNP AdvPInflN Infl V Advwould you e e tomorrowb) Can you pass me the newspaper?Deep structureCPC SVPNP NP NPN Infl V N Det Nyou can pass me the newspaperSurface structureCPC SVPInfl NP NP NPN Infl V N Det N Can you e pass me the newspaperDeep structureCPC SVPNP NPDet N Infl V Det Nthe students should report the incidentSurface structureCPC SVPInfl NP NPDet N Infl V Det Nd) What did you eat for lunch?Deep structureCPC SVPNP PPNP NPN Infl V PN Nyou did eat what for lunchSurface structureCPNP C SVPInfl NP PPNP NPN N Infl V PN Ne) Who should this be reported to ?Deep structureCPC SVPNP PPVP NPN Infl V V PNthis should be reported to whomSurface structureCPNP C SVPN Infl NP PPVP NPN Infl V V PNwhom should this e be reported to ef) What was Helen bringing to the party?Deep structureCPC SVPNP PPNP NPN Infl V PN Det NHelen was bringing what to the partySurface structureCPNP C SVPN Infl NP PPNP NPN Infl V PN Det Nwhat was Helen e bringing e to the party。

树形图详细讲解1. Indicate the category of each word in the following sentences.a) The old lady suddenly left.Det A N Qual Vb) The car stopped at the end of the road.Det N V P Det N P Det Nc) The snow might have blocked the road.Det N Aux Aux V Det Nd) He never appears quite mature.N Qual V Deg A2. The following phrases include a head, a complement, and a specifier. Draw the appropriate tree structure for each.a) full of peopleAPA P Nfull of peopleb) a story about a sentimental girlNPNP PPDet N P NPDet A Na story about a sentimental girlc) often read detective storiesVPQual V NPA Noften read detective storiesd) the argument against the proposalsNPNP PPDet N P NPDet Nthe argument against the proposalse) move towards the windowVPV PPP Det Nmove towards the window3. Draw phrase structure trees for each of the following sentences.a) The jet landed.InflP(=S)NP Infl VPDet N Pst VThe jet landedb) Mary became very ill.InflP(=S)NP Infl VPN Pst V APDeg AMary became very illc) What will you talk about?CPNP C SN Infl NP Infl VPVP NPV P NWhat will you e talk about ed) The apple might hit the man.SNP VPDet N Aux V NPDet NThe apple might hit the manORInflP(=S)NP Infl VPDet N V NPDet NThe apple might hit the mane) He often reads detective stories.SNP VPN Qual V NPA NHe often reads etective storiesORInflP(=S)NP Infl VPPresN Qual V NPA NHe often reads etective stories4. The following sentences contain modifiers of various types. For each sentence, first identify the modifier(s), then draw the tree structures.a) A frightened passenger landed the crippled airplane.InflP(=S)NP Infl VPDet A N Pst V NPDet A NA frightened passenger landed the crippled airplaneb) A huge moon hung in the black sky.InflP(=S)NP Infl VPDet A N Pst V PPP NPDet A NA huge moon hung in the black skyc) An unusual event occurred before the meeting.InflP(=S)NP Infl VPDet A N Pst V PPP NPDet NAn unusual event occurred before the meetingd) A quaint old house appeared on the grassy hill.InflP(=S)NP Infl VPDet A NP Pst V PPA N P NPDet A NA quaint old house appeared on the grassy hill5. The following sentences all contain conjoined categories. Draw a tree structure for each of the sentences.a) Jim has washed the dirty shirts and pants.InflP(=S)NP VPN Aux V NPDet A NPN CON NJim has washed the dirty shirts and pantsORInflP(=S)NP VPN Infl V NPDet A NPN CON NJim has washed the dirty shirts and pantsb) Helen put on her clothes and went out.SNP VPVP NP V AdvV P Det NHelen put on her clothes and went outORInflP(=S)NP Infl VPN Pst VP CON VPVP NP V AdvV P Det NHelen put on her clothes and went outc) Mary is fond of literature but tired of statistics.SNP VPN VP CON VPVP NP VP NPV A P N V A P NMary is fond of literature but (is) tired of statistics ORInflP(=S)NP Infl VPN Pres VP CON VPVP NP VP NPV A P N V A P NMary is fond of literature but (is) tired of statistics d) The detective went out and the mysterious man came in.SS CON SNP VP NP VPDet N V Adv Det A N V AdvThe detective went out and the mysterious man came in e) Crusoe knows that spring will come and the snow will melt. SNP VPCPS CON SNP VP NP VPN Aux V Det N Aux VCrusoe knows that spring will come and the snow will melt6. The following sentences all contain embedded clauses that function as complements of a verb, an adjective, a preposition or a noun. Draw a tree structure for each sentence.a) You know that I hate war.SNP VPCPN V C SNP VPNPN V NYou know that I hate warOR CPC InflP(=S)NP Infl VPCPN Pres V C SNP VPN V NP NYou know that I hate warb) He said that Tom asked whether the class was over.SNP VPCPN V C SNP VPCPN V C SNP VPDet N VL AHe said that Tom asked whether the class was overc) Gerry can’t believe the fact that Anna flunked the English exam.SNP VPN VP NPCPAux Neg V NP C SDet N NP VPN V NPDet A NGerry can not believe the fact thatAnna flunked the English examd) Chris was happy that his father bought him a Rolls-Royce.SNP VPCPN VL A C SNP VPDet N V NP NPN Det NChris was happy that his father bought him a Rolls-Royce e) The children argued over whether bats had wings.SNP VPCPDet N VP C SV P NP VPN V NPNThe children argued over whether bats had wings7. Each of the following sentences contains a relative clause. Draw the deep structure and the surface structure trees for each of the sentences.a) The essay that he wrote was too long.Deep structureCPC SNP VPDet N CP V APC S Deg PNP Infl VPN V NPNThe essay he wrote that was too long Surface StructureCPC SNP VPDet N CP V APC S Deg PNP NP Infl VPN N Pst V NPNThe essay that he wrote e was too long b) The dog that he keeps bites.Deep structureCPC SNP VPDet N CP VC Infl SPres NP VPN V NPNThe dog he keeps that bites Surface StructureCPC SNP VPDet N CP VC SNP NP Infl VPN N Pres V NPNThe dog that he keeps e bites c) Herbert found the man she loved.Deep structureCPC SNP VPN Infl V NPCPDet N C SNP Infl VP NP N VNHerbert found the man she loved who Surface StructureCPC SNP VPN Infl V NPCPDet N SCNP Infl VPNP NPN VN NHerbert found the man (whom) she loved e d) The girl whom he often quarrels with majors in linguistics.Deep structureCPC SNP VPDet N CP V PPP NPC Infl SNNP VPPPN Qual VP NPV P NThe girl he often quarrels with whom majors in linguisticsSurface StructureCPC SNP VPDet N CP V PPP NPC SNNP NP Infl VPPPN N Qual VP NPV P NThe girl whom he often quarrels with e majors in linguistics 8. The derivations of the following sentences involve the inversion transformation. Give the deep structure and the surface structure trees for each of these sentences.a) Would you come tomorrow?Deep structureCPC SVPNP AdvPN Infl V Advyou would come tomorrowSurface structureCPC SVPNP AdvPInflN Infl V Advwould you e come tomorrowb) Can you pass me the newspaper?Deep structureCPC SVPNP NP NPN Infl V N Det Nyou can pass me the newspaper Surface structureCPC SVPInfl NP NP NPN Infl V N Det NCan you e pass me the newspaperc) Should the students report the incident?Deep structureCPC SVPNP NPDet N Infl V Det Nthe students should report the incidentSurface structureCPC SVPInfl NP NPDet N Infl V Det Nshould the students e report the incidentd) What did you eat for lunch?Deep structureCPC SVPNP PPNP NPN Infl V PN Nyou did eat what for lunchSurface structureCPNP C SVPInfl NP PPNP NPN N Infl V PN Nwhat did you e eat e for lunch e) Who should this be reported to ?Deep structureCPC SVPNP PPVP NPN Infl V V PNthis should be reported to whomSurface structureCPNP C SVPN Infl NP PPVP NPN Infl V V PNwhom should this e be reported to ef) What was Helen bringing to the party?Deep structureCPC SVPNP PPNP NPN Infl V PN Det NHelen was bringing what to the party Surface structureCPNP C SVPN Infl NP PPNP NPN Infl V PN Det Nwhat was Helen e bringing e to the party。
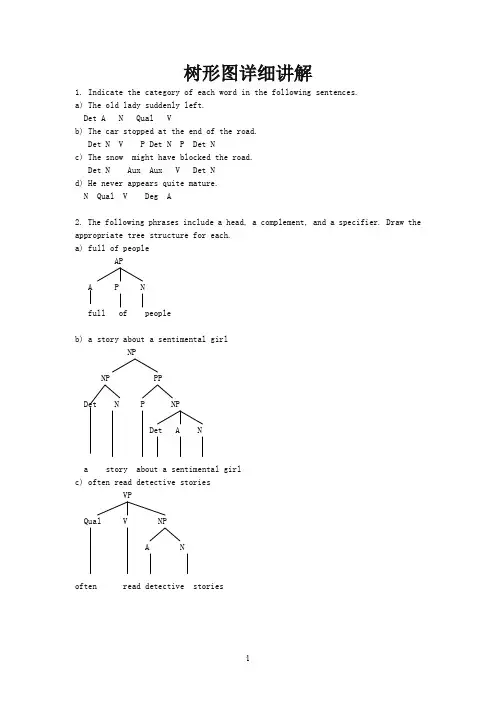
树形图详细讲解1. Indicate the category of each word in the following sentences.a) The old lady suddenly left.Det A N Qual Vb) The car stopped at the end of the road.Det N V P Det N P Det Nc) The snow might have blocked the road.Det N Aux Aux V Det Nd) He never appears quite mature.N Qual V Deg A2. The following phrases include a head, a complement, and a specifier. Draw the appropriate tree structure for each.a) full of peopleAPA P Nfull of peopleb) a story about a sentimental girlNPNP PPDet N P NPDet A Na story about a sentimental girlc) often read detective storiesVPQual V NPA Noften read detective storiesd) the argument against the proposalsNPNP PPDet N P NPDet Nthe argument against the proposalse) move towards the windowVPV PPP Det Nmove towards the window3. Draw phrase structure trees for each of the following sentences.a) The jet landed.InflP(=S)NP Infl VPDet N Pst VThe jet landedb) Mary became very ill.InflP(=S)NP Infl VPN Pst V APDeg AMary became very illc) What will you talk about?CPNP C SN Infl NP Infl VPVP NPV P NSNP VPDet N Aux V NPDet NThe apple might hit the man ORInflP(=S)NP Infl VPDet N V NPDet NThe apple might hit the mane) He often reads detective stories.SNP VPN Qual V NPA NHe often reads etective storiesORInflP(=S)NP Infl VPPresN Qual V NPA NHe often reads etective stories4. The following sentences contain modifiers of various types. For each sentence, first identify the modifier(s), then draw the tree structures.a) A frightened passenger landed the crippled airplane.InflP(=S)NP Infl VPDet A N Pst V NPDet A NA frightened passenger landed the crippled airplaneb) A huge moon hung in the black sky.InflP(=S)NP Infl VPDet A N Pst V PPP NPDet A NA huge moon hung in the black skyc) An unusual event occurred before the meeting.InflP(=S)NP Infl VPDet A N Pst V PPP NPDet NAn unusual event occurred before the meetingd) A quaint old house appeared on the grassy hill.InflP(=S)NP Infl VPDet A NP Pst V PPA N P NPDet A NA quaint old house appeared on the grassy hill5. The following sentences all contain conjoined categories. Draw a tree structure for each of the sentences.a) Jim has washed the dirty shirts and pants.InflP(=S)NP VPN Aux V NPDet A NPN CON NJim has washed the dirty shirts and pantsORInflP(=S)NP VPN Infl V NPDet A NPN CON NJim has washed the dirty shirts and pantsb) Helen put on her clothes and went out.SNP VPN VP CON VPVP NP V AdvV P Det NHelen put on her clothes and went outORInflP(=S)NP Infl VPN Pst VP CON VPVP NP V AdvV P Det NHelen put on her clothes and went outc) Mary is fond of literature but tired of statistics.SNP VPN VP CON VPVP NP VP NPV A P N V A P NMary is fond of literature but (is) tired of statistics ORInflP(=S)NP Infl VPN Pres VP CON VPVP NP VP NPV A P N V A P NMary is fond of literature but (is) tired of statisticsd) The detective went out and the mysterious man came in.SS CON SNP VP NP VPDet N V Adv Det A N V AdvThe detective went out and the mysterious man came ine) Crusoe knows that spring will come and the snow will melt.SNP VPCPN V C SS CON SNP VP NP VPN Aux V Det N Aux VCrusoe knows that spring will come and the snow will melt6. The following sentences all contain embedded clauses that function as complements of a verb, an adjective, a preposition or a noun. Draw a tree structure for each sentence.a) You know that I hate war.SNP VPCPN V C SNP VPN V NPNYou know that I hate warOR CPC InflP(=S)NP Infl VPCPN Pres V C SNP VPN V NP NYou know that I hate warb) He said that Tom asked whether the class was over.SNP VPCPN V C SNP VPCPN V C SNP VPDet N VL AHe said that Tom asked whether the class was overc) Gerry can’t believe the fact that Anna flunked the English exam.SNP VPN VP NPCPAux Neg V NP C SDet N NP VPN V NPDet A NGerry can not believe the fact thatAnna flunked the English examd) Chris was happy that his father bought him a Rolls-Royce.SNP VPCPN VL A C SNP VPDet N V NP NPN Det NChris was happy that his father bought him a Rolls-Roycee) The children argued over whether bats had wings.SNP VPCPDet N VP C SV P NP VPN V NPNThe children argued over whether bats had wings7. Each of the following sentences contains a relative clause. Draw the deep structure and the surface structure trees for each of the sentences.a) The essay that he wrote was too long.Deep structureCPC SNP VPDet N CP V APC S Deg PNP Infl VPN V NPNThe essay he wrote that was too longSurface StructureCPC SNP VPDet N CP V APC S Deg PNP NP Infl VPN N Pst V NPNThe essay that he wrote e was too longb) The dog that he keeps bites.Deep structureCPC SNP VPDet N CP VC Infl SPres NP VPN V NPNThe dog he keeps that bitesSurface StructureCPC SNP VPDet N CP VC SNP NP Infl VPN N Pres V NPNThe dog that he keeps e bitesc) Herbert found the man she loved.Deep structureCPC SNP VPN Infl V NPCPDet N C SNP Infl VPNPN VNHerbert found the man she loved whoSurface StructureCPC SNP VPN Infl V NPCPDet N SCNP Infl VPNP NPN VN Nd) The girl whom he often quarrels with majors in linguistics.Deep structureCPC SNP VPDet N CP V PPP NPC Infl SNNP VPPPN Qual VP NPV P NThe girl he often quarrels with whom majors in linguisticsSurface StructureCPC SNP VPDet N CP V PPP NPC SNNP NP Infl VPPPN N Qual VP NPV P NThe girl whom he often quarrels with e majors in linguistics8. The derivations of the following sentences involve the inversion transformation. Give the deep structure and the surface structure trees for each of these sentences.a) Would you come tomorrow?Deep structureCPC SVPNP AdvPN Infl V Advyou would come tomorrowSurface structureCPC SVPNP AdvPInflN Infl V Advwould you e come tomorrowb) Can you pass me the newspaper?Deep structureCPC SVPNP NP NPN Infl V N Det Nyou can pass me the newspaperSurface structureCPC SVPInfl NP NP NPN Infl V N Det N Can you e pass me the newspaperc) Should the students report the incident?Deep structureCPC SVPNP NPDet N Infl V Det Nthe students should report the incidentSurface structureCPC SVPInfl NP NPDet N Infl V Det Nshould the students e report the incidentd) What did you eat for lunch?Deep structureCPC SVPNP PPNP NPN Infl V PN Nyou did eat what for lunchSurface structureCPNP C SVPInfl NP PPNP NPN N Infl V PN Nwhat did you e eat e for lunche) Who should this be reported to ?Deep structureCPC SVPNP PPVP NPN Infl V V PNthis should be reported to whomSurface structureCPNP C SVPN Infl NP PPVP NPN Infl V V PNwhom should this e be reported to ef) What was Helen bringing to the party?Deep structureCPC SVPNP PPNP NPN Infl V PN Det NHelen was bringing what to the partySurface structureCPNP C SVPN Infl NP PPNP NPN Infl V PN Det Nwhat was Helen e bringing e to the party欢迎您的下载,资料仅供参考!致力为企业和个人提供合同协议,策划案计划书,学习资料等等打造全网一站式需求。
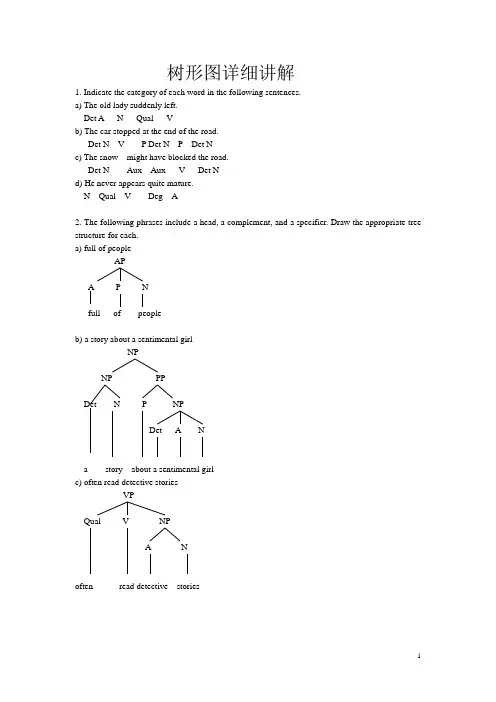
树形图详细讲解1. Indicate the category of each word in the following sentences.a) The old lady suddenly left.Det A N Qual Vb) The car stopped at the end of the road.Det N V P Det N P Det Nc) The snow might have blocked the road.Det N Aux Aux V Det Nd) He never appears quite mature.N Qual V Deg A2. The following phrases include a head, a complement, and a specifier. Draw the appropriate tree structure for each.a) full of peopleAPA P Nfull of peopleb) a story about a sentimental girlNPNP PPDet N P NPDet A Na story about a sentimental girlc) often read detective storiesVPQual V NPA Noften read detective storiesd) the argument against the proposalsNPNP PPDet N P NPDet Nthe argument against the proposalse) move towards the windowVPV PPP Det Nmove towards the window3. Draw phrase structure trees for each of the following sentences.a) The jet landed.InflP(=S)NP Infl VPDet N Pst VThe jet landedb) Mary became very ill.InflP(=S)NP Infl VPN Pst V APDeg AMary became very illc) What will you talk about?CPNP C SN Infl NP Infl VPVP NPV P NSNP VPDet N Aux V NPDet NThe apple might hit the manORInflP(=S)NP Infl VPDet N V NPDet NThe apple might hit the mane) He often reads detective stories.SNP VPN Qual V NPA NHe often reads etective storiesORInflP(=S)NP Infl VPPresN Qual V NPA NHe often reads etective stories4. The following sentences contain modifiers of various types. For each sentence, first identify the modifier(s), then draw the tree structures.a) A frightened passenger landed the crippled airplane.InflP(=S)NP Infl VPDet A N Pst V NPDet A NA frightened passenger landed the crippled airplaneb) A huge moon hung in the black sky.InflP(=S)NP Infl VPDet A N Pst V PPP NPDet A NA huge moon hung in the black skyc) An unusual event occurred before the meeting.InflP(=S)NP Infl VPDet A N Pst V PPP NPDet NAn unusual event occurred before the meetingd) A quaint old house appeared on the grassy hill.InflP(=S)NP Infl VPDet A NP Pst V PPA N P NPDet A NA quaint old house appeared on the grassy hill5. The following sentences all contain conjoined categories. Draw a tree structure for each of the sentences.a) Jim has washed the dirty shirts and pants.InflP(=S)NP VPN Aux V NPDet A NPN CON N Jim has washed the dirty shirts and pantsORInflP(=S)NP VPN Infl V NPDet A NPN CON NJim has washed the dirty shirts and pantsb) Helen put on her clothes and went out.SNP VPN VP CON VPVP NP V AdvV P Det NHelen put on her clothes and went outORInflP(=S)NP Infl VPN Pst VP CON VPVP NP V AdvV P Det NHelen put on her clothes and went outc) Mary is fond of literature but tired of statistics.SNP VPN VP CON VPVP NP VP NPV A P N V A P NMary is fond of literature but (is) tired of statistics ORInflP(=S)NP Infl VPN Pres VP CON VPVP NP VP NPV A P N V A P N Mary is fond of literature but (is) tired of statisticsd) The detective went out and the mysterious man came in.SS CON SNP VP NP VPDet N V Adv Det A N V AdvThe detective went out and the mysterious man came ine) Crusoe knows that spring will come and the snow will melt.SNP VPCPN V C SS CON SNP VP NP VPN Aux V Det N Aux V Crusoe knows that spring will come and the snow will melt6. The following sentences all contain embedded clauses that function as complements of a verb, an adjective, a preposition or a noun. Draw a tree structure for each sentence.a) You know that I hate war.SNP VPCPN V C SNP VPN V NPNYou know that I hate warOR CPC InflP(=S)NP Infl VPCPN Pres V C SNP VPN V NPNYou know that I hate warb) He said that Tom asked whether the class was over.SNP VPCPN V C SNP VPCPN V C SNP VPDet N VL A He said that Tom asked whether the class was overc) Gerry can’t believe the fact that Anna flunked the English exam.SNP VPN VP NPCPAux Neg V NP C SDet N NP VPN V NPDet A N Gerry can not believe the fact thatAnna flunked the English examd) Chris was happy that his father bought him a Rolls-Royce.SNP VPCPN VL A C SNP VPDet N V NP NPN Det NChris was happy that his father bought him a Rolls-Roycee) The children argued over whether bats had wings.SNP VPCPDet N VP C SV P NP VPN V NPNThe children argued over whether bats had wings7. Each of the following sentences contains a relative clause. Draw the deep structure and the surface structure trees for each of the sentences.a) The essay that he wrote was too long.Deep structureCPC SNP VP Det N CP V APC S Deg PNP Infl VPN V NPNThe essay he wrote that was too longSurface StructureCPC SNP VP Det N CP V APC S Deg PNP NP Infl VPN N Pst V NPNThe was too longb) The dog that he keeps bites.Deep structureCPC SNP VP Det N CP VC Infl SPres NP VPN V NPNThe dog he keeps that bitesSurface StructureCPC SNP VP Det N CP VC SNP NP Infl VPN N Pres V NPNThe dog bitesc) Herbert found the man she loved.Deep structureCPC SNP VPN Infl V NPCPDet N C SNP Infl VPNPN VNHerbert found the man she loved whoSurface StructureCPC SNP VPN Infl V NPCPDet N SCNP Infl VPNP NPN VN N Herbert found thed) The girl whom he often quarrels with majors in linguistics.Deep structureCPC SNP VPDet N CP V PPP NPC Infl SNNP VPPPN Qual VP NPV P NThe girl he often quarrels with whom majors in linguisticsSurface StructureCPC SNP VPDet N CP V PPP NPC SNNP NP Infl VPPPN N Qual VP NPV P NThe girl majors in linguistics8. The derivations of the following sentences involve the inversion transformation. Give the deep structure and the surface structure trees for each of these sentences.a) Would you come tomorrow?Deep structureCPC SVPNP AdvPN Infl V Advyou would come tomorrowSurface structureCPC SVPNP AdvPInflN Infl V Advcome tomorrowb) Can you pass me the newspaper?Deep structureCPC SVPNP NP NPN Infl V N Det Nyou can pass me the newspaperSurface structureCPC SVPInfl NP NP NPN Infl V N Det Npass me the newspaperc) Should the students report the incident?Deep structureCPC SVPNP NPDet N Infl V Det Nthe students should report the incidentSurface structureCPC SVPInfl NP NPDet N Infl V Det Nreport the incidentd) What did you eat for lunch?Deep structureCPC SVPNP PPNP NPN Infl V PN Nyou did eat what for lunchSurface structureCPNP C SVPInfl NP PPNP NP N N Infl V PN Nfor lunche) Who should this be reported to ?Deep structureCPC SVPNP PPVP NPN Infl V V PNthis should be reported to whomSurface structureCPNP C SVPN Infl NP PPVP NPN Infl V V PNf) What was Helen bringing to the party?Deep structureCPC SVPNP PPNP NPN Infl V PN Det NHelen was bringing what to the partySurface structureCPNP C SVPN Infl NP PPNP NPN Infl V PN Det Nto the party21。
树形图详细讲解1、Indicate the category of each word in the following sentences、a) The old lady suddenly left、Det A N Qual Vb) The car stopped at the end of the road、Det N V P Det N P Det Nc) The snow might have blocked the road、Det N Aux Aux V Det Nd) He never appears quite mature、N Qual V Deg A2、The following phrases include a head, a complement, and a specifier、Draw the appropriate tree structure for each、a) full of peopleAPA P Nfull of peopleb) a story about a sentimental girlNPNP PPDet N P NPDet A Na story about a sentimental girlc) often read detective storiesVPQual V NPA Noften read detective storiesd) the argument against the proposalsNPNP PPDet N P NPDet Nthe argument against the proposalse) move towards the windowVPV PPP Det Nmove towards the window3、Draw phrase structure trees for each of the following sentences、a) The jet landed、InflP(=S)NP Infl VPDet N Pst VThe jet landedb) Mary became very ill、InflP(=S)NP Infl VPN Pst V APDeg AMary became very illc) What will you talk about?CPNP C SN Infl NP Infl VPVP NPV P NSNP VPDet N Aux V NPDet NThe apple might hit the manORInflP(=S)NP Infl VPDet N V NPDet NThe apple might hit the mane) He often reads detective stories、SNP VPN Qual V NPA NHe often reads etective storiesORInflP(=S)NP Infl VPPresN Qual V NPA NHe often reads etective stories4、The following sentences contain modifiers of various types、For each sentence, first identify the modifier(s), then draw the tree structures、a) A frightened passenger landed the crippled airplane、InflP(=S)NP Infl VPDet A N Pst V NPDet A NA frightened passenger landed the crippled airplaneb) A huge moon hung in the black sky、InflP(=S)NP Infl VPDet A N Pst V PPP NPDet A NA huge moon hung in the black skyc) An unusual event occurred before the meeting、InflP(=S)NP Infl VPDet A N Pst V PPP NPDet NAn unusual event occurred before the meetingd) A quaint old house appeared on the grassy hill、InflP(=S)NP Infl VPDet A NP Pst V PPA N P NPDet A NA quaint old house appeared on the grassy hill5、The following sentences all contain conjoined categories、Draw a tree structure for each of the sentences、a) Jim has washed the dirty shirts and pants、InflP(=S)NP VPN Aux V NPDet A NPN CON N Jim has washed the dirty shirts and pantsORInflP(=S)NP VPN Infl V NPDet A NPN CON NJim has washed the dirty shirts and pantsb) Helen put on her clothes and went out、SNP VPN VP CON VPVP NP V AdvV P Det NHelen put on her clothes and went outORInflP(=S)NP Infl VPN Pst VP CON VPVP NP V AdvV P Det NHelen put on her clothes and went outc) Mary is fond of literature but tired of statistics、SNP VPN VP CON VPVP NP VP NPV A P N V A P NMary is fond of literature but (is) tired of statistics ORInflP(=S)NP Infl VPN Pres VP CON VPVP NP VP NPV A P N V A P N Mary is fond of literature but (is) tired of statisticsd) The detective went out and the mysterious man came in、SS CON SNP VP NP VPDet N V Adv Det A N V AdvThe detective went out and the mysterious man came ine) Crusoe knows that spring will come and the snow will melt、SNP VPCPN V C SS CON SNP VP NP VPN Aux V Det N Aux V Crusoe knows that spring will come and the snow will melt6、The following sentences all contain embedded clauses that function as complements of a verb, an adjective, a preposition or a noun、Draw a tree structure for each sentence、a) You know that I hate war、SNP VPCPN V C SNP VPN V NPNYou know that I hate warOR CPC InflP(=S)NP Infl VPCPN Pres V C SNP VPN V NPNYou know that I hate warb) He said that Tom asked whether the class was over、SNP VPCPN V C SNP VPCPN V C SNP VPDet N VL A He said that Tom asked whether the class was overc) Gerry can’t believe the fact that Anna flunked the English exam、SNP VPN VP NPCPAux Neg V NP C SDet N NP VPN V NPDet A N Gerry can not believe the fact thatAnna flunked the English examd) Chris was happy that his father bought him a Rolls-Royce、SNP VPCPN VL A C SNP VPDet N V NP NPN Det NChris was happy that his father bought him a Rolls-Roycee) The children argued over whether bats had wings、SNP VPCPDet N VP C SV P NP VPN V NPNThe children argued over whether bats had wings7、Each of the following sentences contains a relative clause、Draw the deep structure and the surface structure trees for each of the sentences、a) The essay that he wrote was too long、Deep structureCPC SNP VP Det N CP V APC S Deg PNP Infl VPN V NPNThe essay he wrote that was too longSurface StructureCPC SNP VP Det N CP V APC S Deg PNP NP Infl VPN N Pst V NPNThe was too longb) The dog that he keeps bites、Deep structureCPC SNP VP Det N CP VC Infl SPres NP VPN V NPNThe dog he keeps that bitesSurface StructureCPC SNP VP Det N CP VC SNP NP Infl VPN N Pres V NPNThe dog bitesc) Herbert found the man she loved、Deep structureCPC SNP VPN Infl V NPCPDet N C SNP Infl VPNPN VNHerbert found the man she loved whoSurface StructureCPC SNP VPN Infl V NPCPDet N SCNP Infl VPNP NPN VN N Herbert found thed) The girl whom he often quarrels with majors in linguistics、Deep structureCPC SNP VPDet N CP V PPP NPC Infl SNNP VPPPN Qual VP NPV P NThe girl he often quarrels with whom majors in linguisticsSurface StructureCPC SNP VPDet N CP V PPP NPC SNNP NP Infl VPPPN N Qual VP NPV P NThe girl majors in linguistics8、The derivations of the following sentences involve the inversion transformation、Give the deep structure and the surface structure trees for each of these sentences、a) Would you come tomorrow?Deep structureCPC SVPNP AdvPN Infl V Advyou would come tomorrowSurface structureCPC SVPNP AdvPInflN Infl V Advcome tomorrowb) Can you pass me the newspaper?Deep structureCPC SVPNP NP NPN Infl V N Det Nyou can pass me the newspaperSurface structureCPC SVPInfl NP NP NPN Infl V N Det Npass me the newspaperc) Should the students report the incident?Deep structureCPC SVPNP NPDet N Infl V Det Nthe students should report the incidentSurface structureCPC SVPInfl NP NPDet N Infl V Det Nreport the incidentd) What did you eat for lunch?Deep structureCPC SVPNP PPNP NPN Infl V PN Nyou did eat what for lunchSurface structureCPNP C SVPInfl NP PPNP NP N N Infl V PN Nfor lunche) Who should this be reported to ?Deep structureCPC SVPNP PPVP NPN Infl V V PNthis should be reported to whomSurface structureCPNP C SVPN Infl NP PPVP NPN Infl V V PN英语语言学树型图详细讲解f) What was Helen bringing to the party?Deep structureCPC SVPNP PPNP NPN Infl V PN Det NHelen was bringing what to the partySurface structureCPNP C SVPN Infl NP PPNP NPN Infl V PN Det Nto the party。

英语语⾔学树形图举例新树形图详细讲解1. Indicate the category of each word in the following sentences.a) The old lady suddenly left.Det A N Qual Vb) The car stopped at the end of the road.Det N V P Det N P Det Nc) The snow might have blocked the road.Det N Aux Aux V Det Nd) He never appears quite mature.N Qual V Deg A2. The following phrases include a head, a complement, and a specifier. Draw the appropriate tree structure for each.a) full of peopleAPA P Nfull of peopleb) a story about a sentimental girlNPNP PPDet N P NPDet A Na story about a sentimental girlc) often read detective storiesVPQual V NPA Noften read detective storiesd) the argument against the proposalsNPNP PPDet N P NPNe) move towards the windowP Det Nmove towards the window3. Draw phrase structure trees for each of the following sentences.a) The jet landed.InflP(=S)NP Infl VPDet N Pst VThe jet landedb) Mary became very ill.InflP(=S)NP Infl VPN Pst V APDeg AMary became very illc) What will you talk about?CPNP C SN Infl NP Infl VPVP NPV P NSNP VPDet N Aux V NPDet NThe apple might hit the manORInflP(=S)NP Infl VPDet N V NPDet NThe apple might hit the mane) He often reads detective stories.A NHe often reads etective storiesORInflP(=S)NP Infl VPPresentN Qual V NPA NHe often reads etective stories4. The following sentences contain modifiers of various types. For each sentence, first identify the modifier(s), then draw the tree structures.a) A frightened passenger landed the crippled airplane.InflP(=S)NP Infl VPDet A N Pst V NPDet A NA frightened passenger landed the crippled airplaneb) A huge moon hung in the black sky.InflP(=S)NP Infl VPDet A N Pst V PPP NPDet A NA huge moon hung in the black skyc) An unusual event occurred before the meeting.InflP(=S)NP Infl VPDet A N Pst V PPP NPDet NAn unusual event occurred before the meetingd) A quaint old house appeared on the grassy hill.InflP(=S)Det A NA quaint old house appeared on the grassy hill5. The following sentences all contain conjoined categories. Draw a tree structure for each of the sentences.a) Jim has washed the dirty shirts and pants.InflP(=S)NP VPN Aux V NPDet A NPN CON NJim has washed the dirty shirts and pants ORInflP(=S)NP VPN Infl V NPDet A NPN CON NJim has washed the dirty shirts and pants b) Helen put on her clothes and went out.SNP VPN VP CON VPVP NP V AdvV P Det NHelen put on her clothes and went outORInflP(=S)NP Infl VPN Pst VP CON VPVP NP V AdvV P Det NHelen put on her clothes and went outc) Mary is fond of literature but tired of statistics.SNP VPV A P N V A P NMary is fond of literature but (is) tired of statisticsORInflP(=S)NP Infl VPN Pres VP CON VPVP NP VP NPV A P N V A P NMary is fond of literature but (is) tired of statisticsd) The detective went out and the mysterious man came in.SS CON SNP VP NP VPDet N V Adv Det A N V AdvThe detective went out and the mysterious man came ine) Crusoe knows that spring will come and the snow will melt.SNP VPN V C SS CON SNP VP NP VPN Aux V Det N Aux VCrusoe knows that spring will come and the snow will melt6. The following sentences all contain embedded clauses that function as complements of a verb, an adjective, a preposition or a noun. Draw a tree structure for each sentence.a) You know that I hate war.SNP VPCPN V C SNP VPNPN V NYou know that I hate warCPN Pres V C SNP VPN V NPNYou know that I hate warb) He said that Tom asked whether the class was over.SNP VPCPN V C SNP VPCPN V C SNP VPN V AHe said that Tom asked whether the class was overc) Gerry can’t believe the fact that Anna flunked the English exam. SNP VPN VP NPCPAux Neg V NP C SDet N NP VPN V NPDet A NGerry can not believe the fact thatAnna flunked the English exam d) Chris was happy that his father bought him a Rolls-Royce.SNP VPCPN VL A C SChris was happy that his father bought him a Rolls-Roycee) The children argued over whether bats had wings.SNP VPCPDet N VP C SV P NP VPN V NPNThe children argued over whether bats had wings7. Each of the following sentences contains a relative clause. Draw the deep structure and the surface structure trees for each of the sentences.a) The essay that he wrote was too long.Deep structureCPC SNP VPDet N CP V APC S Deg ANP Infl VPN V NPNThe essay he wrote that was too longSurface StructureCPC SNP VPDet N CP V APC S Deg PNP NP Infl VPN N Pst V NPNb) The dog that he keeps bites.Deep structureCPC SNP VP Det N CP VC Infl SPres NP VPN V NPNThe dog he keeps that bitesSurface StructureCPC SNP VP Det N CP VC SNP NP Infl VPN N Pres V NPNThe dog bitesc) Herbert found the man she loved. Deep structureCPC SNP VPN Infl V NPCPDet N C SNP Infl VPNPN VN Herbert found the man she loved who Surface StructureN Infl V NPCPDet N SCNP Infl VPNP NPN VN NHerbert found theDeep structureCPC SNP VPDet N CP V PPP NPC Infl SNNP VPPPN Qual VP NPV P NThe girl he often quarrels with whom majors in linguistics Surface StructureCPC SNP VPDet N CP V PPP NPC SNNP NP Infl VPThe girl majors in linguistics8. The derivations of the following sentences involve the inversion transformation. Give the deep structure and the surface structure trees for each of these sentences.a) Would you come tomorrow?Deep structureCPC SVPNP AdvPN Infl V Advyou would come tomorrowSurface structureCPC SVPNP AdvPInflN Infl V Advcome tomorrowb) Can you pass me the newspaper?Deep structureCPC SVPNP NPN Infl V N Det Nyou can pass me the newspaperSurface structureCPC SN Infl V N Det Nyou e pass me the newspaperc) Should the students report the incident? Deep structureCPC SVPNP NPDet N Infl V Det Nthe students should report the incident Surface structureCPC SVPInfl NP NPDet N Infl V Det Nreport the incidentd) What did you eat for lunch?Deep structureCPC SVPNP PPNP NPN Infl V PN N you did eat what for lunchSurface structureCPNP C SVPInfl NP PPNP NP N N Infl V Pfor lunche) Who should this be reported to ?Deep structureCPC SVPNP PPVP NPN Infl V V PNthis should be reported to whomSurface structureCPNP C SVPN Infl NP PPVP NPN Infl V V PNf) What was Helen bringing to the party? Deep structureCPC SVPNP PPNP NPN Infl V PN Det N Helen was bringing what to the party Surface structureCPNP C SN Infl NP PP NP NPN Infl V PN Det Nto the party。
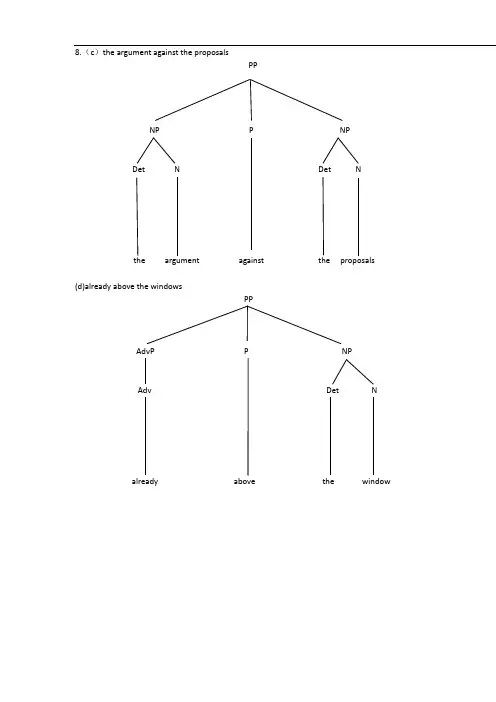
8.(c)the argument against the proposalsPPNP P NPDet N Det Nargument against the proposals(d)already above the windowsPPAdvP P NPAdv Det Nalready above the window9.(b) A huge moon hung in the sky.SNP Infl VPDet AP N V PPA P NPDet AP NA huge moon hung in the black sky (C) The man examined his car carefully yeseterdaySNP Infl VPDet N pst V NP AdvPDet N AdvP AdvAdvA man examined his car carefully yesterday 10.(b)Helen put on her clothes and went outSNP Infl VPV PP Con V PPP NP PDet NHelen put on her clothes and went outc)Mary is fond of literature but tired of statistics.SNP Infl VPN Pre V AP Con APA PP A PPP NP P NPNMary is fond of literature but tired of statistics 11.(b) Gerry belives the fact that Anna fluncked the English exam.SNP Infl VPN Pre V NPDet N CPC SNP Infl VPNP N Pst V NPDet AP NAGerry believes the fact that Anna fluncked the English exam(c) Chiris was happy that his father bought him a Roll-Royce.SNP Infl VPN Pst V APA CPC SNP NP Infl VPDet N V NPN Det N Chris was happy that his father bought him a Roll-Royce(d) The children argued over whether bats had wings.SNP Infl VPDet N Pst V PPP CPC SNP Infl VPN V NPN The children argued over whether bats had wings 12.(a) Herbert bought a house that she loved .SNP Infl VPN Pst NPDet N CPC SNP Infl VPN Pst V NP Herbert bought a house(c) The girl whom he adores majors in linguistics.SNP Infl VPDet N CP Pre V PPC S P NPNP Infl VP NN Pre V NPThe girl adores e majors in linguistics13.(a) Would you come tomorrow?CPC SAux NP Infl VPN Aux V AdvpAdv(b)What did Helen bring to the party?CPSpec C SN Infl NP Infl VPPst N Pst V NPN PPP Det NPNto the party。
syntax1. Indicate the category of each word in the following sentences.a) The old lady suddenly left.Det A N Qual Vb) The car stopped at the end of the road.Det N V P Det N P Det Nc) The snow might have blocked the road.Det N Aux Aux V Det Nd) He never appears quite mature.N Qual V Deg A2. The following phrases include a head, a complement, and a specifier. Draw the appropriate tree structure for each.a) full of peopleAPA P Nfull of peopleb) a story about a sentimental girlNPNP PPDet N P NPDet A Na story about a sentimental girlc) often read detective storiesVPQual V NPA Noften read detective storiesd) the argument against the proposalsNPNP PPDet N P NPe) move towards the windowVPV PPP Det Nmove towards the window3. Draw phrase structure trees for each of the following sentences.a) The jet landed.InflP(=S)NP Infl VPDet N Pst VThe jet landedb) Mary became very ill.InflP(=S)NP Infl VPN Pst V APDeg AMary became very illc) What will you talk aboutCPNP C SN Infl NP Infl VPVP NPV P Nd) The apple might hit the man.SNP VPDet N Aux V NPDet NThe apple might hit the manORInflP(=S)NP Infl VPDet N V NPDet NThe apple might hit the mane) He often reads detective stories.SNP VPN Qual V NPA NHe often reads etective storiesORInflP(=S)NP Infl VPPresN Qual V NPA NHe often reads etective stories4. The following sentences contain modifiers of various types. For each sentence, first identify the modifier(s), then draw the tree structures.a) A frightened passenger landed the crippled airplane.InflP(=S)NP Infl VPDet A N Pst V NPDet A NA frightened passenger landed the crippled airplaneb) A huge moon hung in the black sky.InflP(=S)NP Infl VPDet A N Pst V PPP NPDet A NA huge moon hung in the black skyc) An unusual event occurred before the meeting.InflP(=S)NP Infl VPDet A N Pst V PPP NPDet NAn unusual event occurred before the meetingd) A quaint old house appeared on the grassy hill.InflP(=S)NP Infl VPDet A NP Pst V PPA N P NPDet A NA quaint old house appeared on the grassy hill5. The following sentences all contain conjoined categories. Draw a tree structure for each of the sentences.a) Jim has washed the dirty shirts and pants.InflP(=S)NP VPN Aux V NPDet A NPN CON NN Infl V NPDet A NPN CON NJim has washed the dirty shirts and pants b) Helen put on her clothes and went out.SNP VPN VP CON VPVP NP V AdvV P Det NHelen put on her clothes and went outORInflP(=S)NP Infl VPN Pst VP CON VPVP NP V AdvV P Det NHelen put on her clothes and went outc) Mary is fond of literature but tired of statistics.SNP VPN VP CON VPVP NP VP NPV A P N V A P NN Pres VP CON VPVP NP VP NPV A P N V A P NMary is fond of literature but (is) tired of statisticsd) The detective went out and the mysterious man came in.SS CON SNP VP NP VPDet N V Adv Det A N V AdvThe detective went out and the mysterious man came ine) Crusoe knows that spring will come and the snow will melt.SNP VPCPN V C SS CON SNP VP NP VPN Aux V Det N Aux VCrusoe knows that spring will come and the snow will melt6. The following sentences all contain embedded clauses that function as complements of a verb, an adjective, a preposition or a noun. Draw a tree structure for each sentence.a) You know that I hate war.SNP VPCPN V C SNP VPNPN V NOR CPC InflP(=S)NP Infl VPCPN Pres V C SNP VPN V NPNYou know that I hate warb) He said that Tom asked whether the class was over.SNP VPCPN V C SNP VPCPN V C SNP VPDet N VL AHe said that Tom asked whether the class was overc) Gerry can’t believe the fact that Anna flunked the English exam.SNP VPN VP NPCPAux Neg V NP C SDet N NP VPN V NPDet A Nd) Chris was happy that his father bought him a Rolls-Royce.SNP VPCPN VL A C SNP VPDet N V NP NPN Det NChris was happy that his father bought him a Rolls-Roycee) The children argued over whether bats had wings.SNP VPCPDet N VP C SV P NP VPN V NPNThe children argued over whether bats had wings7. Each of the following sentences contains a relative clause. Draw the deep structure and the surface structure trees for each of the sentences.a) The essay that he wrote was too long.Deep structureCPC SNP VPDet N CP V APC S Deg PNP Infl VPN V NPNThe essay he wrote that was too longSurface StructureCPC SNP VPDet N CP V APC S Deg PNP NP Infl VPN N Pst V NPNThe was too longb) The dog that he keeps bites.Deep structureCPC SNP VPDet N CP VC Infl SPres NP VPN V NPNThe dog he keeps that bitesSurface StructureCPC SNP VPDet N CP VC SNP NP Infl VPN N Pres V NPNThe dog bitesc) Herbert found the man she loved.Deep structureCPC SNP VPN Infl V NPCPDet N C SNP Infl VPNPN VNHerbert found the man she loved whoSurface StructureCPC SNP VPN Infl V NPCPDet N SCNP Infl VPNP NPN VN N Herbert found thed) The girl whom he often quarrels with majors in linguistics.Deep structureCPC SNP VPDet N CP V PPP NPC Infl SNNP VPPPN Qual VP NPV P NThe girl he often quarrels with whom majors in linguisticsSurface StructureCPC SNP VPDet N CP V PPP NPC SNNP NP Infl VPPPN N Qual VP NPV P NThe girl majors in linguistics8. The derivations of the following sentences involve the inversion transformation. Give the deep structure and the surface structure trees for each of these sentences.a) Would you come tomorrowDeep structureCPC SVPNP AdvPN Infl V Advyou would come tomorrowSurface structureCPC SVPNP AdvPInflN Infl V Advcome tomorrowb) Can you pass me the newspaperDeep structureCPC SVPNP NP NPN Infl V N Det Nyou can pass me the newspaperSurface structureCPC SVPInfl NP NP NPN Infl V N Det Npass me the newspaperc) Should the students report the incidentDeep structureCPC SVPNP NPDet N Infl V Det Nthe students should report the incidentSurface structureCPC SVPInfl NP NPDet N Infl V Det Nreport the incidentd) What did you eat for lunchDeep structureCPC SVPNP PPNP NPN Infl V PN Nyou did eat what for lunchSurface structureCPNP C SVPInfl NP PPNP NP N N Infl V PN Nfor lunche) Who should this be reported toDeep structureCPC SVPNP PPVP NPN Infl V V PNthis should be reported to whomSurface structureCPNP C SVPN Infl NP PPVP NPN Infl V V PNf) What was Helen bringing to the partyDeep structureCPC SVPNP PPNP NPN Infl V PN Det NHelen was bringing what to the partySurface structureCPNP C SVPN Infl NP PPNP NPN Infl V PN Det Nto the party。
syntax1.Indicate the category of each word in the following sentences.a) The old lady suddenly left.Det A N Qual Vb) The car stopped at the end of the road.Det N V P Det N P Det Nc) The snow might have blocked the road.Det N Aux Aux V Det Nd) He never appears quite mature.N Qual V Deg A2. The following phrases include a head, a complement, and a specifier. Draw the appropriate tree structure for each.a)full of peopleAPA P Nfull of peopleb)a story about a sentimental girlNPNP PPDet N P NPDet A Na story about a sentimental girlc)often read detective storiesVPQual V NPA Noften read detective storiesd)the argument against the proposalsNPNP PPDet N P NPDet Ne)move towards the windowVPV PPP Det Nmove towards the window3.Draw phrase structure trees for each of the following sentences.a) The jet landed.InflP(=S)NP Infl VPDet N Pst VThe jet landedb)Mary became very ill.InflP(=S)NP Infl VPN Pst V APDeg AMary became very illc)What will you talk about?CPNP C SN Infl NP Infl VPVP NPV P NWhat will you e talk about ed)The apple might hit the man.SNP VPDet N Aux V NPDet NThe apple might hit the manORInflP(=S)NP Infl VPDet N V NPDet NThe apple might hit the mane)He often reads detective stories.SNP VPN Qual V NPA NHe often reads etective storiesORInflP(=S)NP Infl VPPresN Qual V NPA NHe often reads etective stories4. The following sentences contain modifiers of various types. For each sentence, first identify the modifier(s), then draw the tree structures.a)A frightened passenger landed the crippled airplane.InflP(=S)NP Infl VPDet A N Pst V NPDet A NA frightened passenger landed the crippled airplaneb)A huge moon hung in the black sky.InflP(=S)NP Infl VPDet A N Pst V PPP NPDet A NA huge moon hung in the black skyc)An unusual event occurred before the meeting.InflP(=S)NP Infl VPDet A N Pst V PPP NPDet NAn unusual event occurred before the meetingd)A quaint old house appeared on the grassy hill.InflP(=S)NP Infl VPDet A NP Pst V PPA N P NPDet A NA quaint old house appeared on the grassy hill5. The following sentences all contain conjoined categories. Draw a tree structure for each of the sentences.a)Jim has washed the dirty shirts and pants.InflP(=S)NP VPN Aux V NPDet A NPN CON NJim has washed the dirty shirts and pantsN Infl V NPDet A NPN CON NJim has washed the dirty shirts and pants b)Helen put on her clothes and went out.SNP VPN VP CON VPVP NP V AdvV P Det NHelen put on her clothes and went outORInflP(=S)NP Infl VPN Pst VP CON VPVP NP V AdvV P Det NHelen put on her clothes and went outc)Mary is fond of literature but tired of statistics.SNP VPN VP CON VPVP NP VP NPV A P N V A P NMary is fond of literature but(is) tired of statisticsN Pres VP CON VPVP NP VP NPV A P N V A P NMary is fond of literature but (is)tired of statisticsd)The detective went out and the mysterious man came in.SS CON SNP VP NP VPDet N V Adv Det A N V AdvThe detective went out and the mysterious man came ine)Crusoe knows that spring will come and the snow will melt.SNP VPCPN V C SS CON SNP VP NP VPN Aux V Det N Aux VCrusoe knows that spring will come and the snow will melt6. The following sentences all contain embedded clauses that function as complements of a verb, an adjective,a preposition or a noun. Draw a tree structure for each sentence.a) You know that I hate war.SNP VPCPN V C SNP VPNPN V NYou know that I hate warOR CPC InflP(=S)NP Infl VPCPN Pres V C SNP VPN V NPNYou know that I hate warb)He said that Tom asked whether the class was over.SNP VPCPN V C SNP VPCPN V C SNP VPDet N VL AHe said that Tom asked whether the class was overc)Gerry can’tbelieve the fact that Anna flunked the English exam.SNP VPN VP NPCPAux Neg V NP C SDet N NP VPN V NPDet A N Gerry can not believe the fact thatAnna flunked the English examd)Chris was happy that his father bought him a Rolls-Royce.SNP VPCPN VL A C SNP VPDet N V NP NPN Det NChris was happy that his father bought him a Rolls-Roycee)The children argued over whether bats had wings.SNP VPCPDet N VP C SV P NP VPN V NPNThe children argued over whether bats had wings7. Each of the following sentences contains a relative clause. Draw the deep structure and the surface structure trees for each of the sentences.a)The essay that he wrote was too long.Deep structureCPC SNP VPDet N CP V APC S Deg PNP Infl VPN V NPNThe essay he wrote that was too longSurface StructureCPC SNP VPDet N CP V APC S Deg PNP NP Infl VPN N Pst V NPNThe essay that he wrote e was too longb)The dog that he keeps bites.Deep structureCPC SNP VPDet N CP VC Infl SPres NP VPN V NPNThe dog he keeps that bitesSurface StructureCPC SNP VPDet N CP VC SNP NP Infl VPN N Pres V NPNThe dog that he keeps e bitesc)Herbert found the man she loved.Deep structureCPC SNP VPN Infl V NPCPDet N C SNP Infl VPNPN VNHerbert found the man she loved whoSurface StructureCPC SNP VPN Infl V NPCPDet N SCNP Infl VPNP NPN VN NHerbert found the man (whom)she loved ed)The girl whom he often quarrels with majors in linguistics.Deep structureCPC SNP VPDet N CP V PPP NPC Infl SNNP VPPPN Qual VP NPV P NThe girl he often quarrels with whom majors in linguisticsSurface StructureCPC SNP VPDet N CP V PPP NPC SNNP NP Infl VPPPN N Qual VP NPV P NThe girl whom he often quarrels with e majors in linguistics8.The derivations of the following sentences involve the inversion transformation. Give the deep structure and the surface structure trees for each of these sentences.a) Would you come tomorrow?Deep structureCPC SVPNP AdvPN Infl V Advyou would come tomorrowSurface structureCPC SVPNP AdvPInflN Infl V Advwould you e come tomorrowb)Can you pass me the newspaper?Deep structureCPC SVPNP NP NPN Infl V N Det Nyou can pass me the newspaperSurface structureCPC SVPInfl NP NP NPN Infl V N Det N Can you e pass me the newspaperc) Should the students report the incident?Deep structureCPC SVPNP NPDet N Infl V Det Nthe students should report the incidentSurface structureCPC SVPInfl NP NPDet N Infl V Det N should the students e report the incidentd)What did you eat for lunch?Deep structureCPC SVPNP PPNP NPN Infl V PN Nyou did eat what for lunchSurface structureCPNP C SVPInfl NP PPNP NP N N Infl V PN N what did you e eat e for lunche)Who should this be reported to ?Deep structureCPC SVPNP PPVP NPN Infl V V PNthis should be reported to whomSurface structureCPNP C SVPN Infl NP PPVP NPN Infl V V PNwhom should this e be reported to ef)What was Helen bringing to the party?Deep structureCPC SVPNP PPNP NPN Infl V PN Det NHelen was bringing what to the partySurface structureCPNP C SVPN Infl NP PPNP NPN Infl V PN Det N what was Helen e bringing e to the party。
syntax1. Indicate the category of each word in the following sentences.a) The old lady suddenly left.Det A N Qual Vb) The car stopped at the end of the road.Det N V P Det N P Det Nc) The snow might have blocked the road.Det N Aux Aux V Det Nd) He never appears quite mature.N Qual V Deg A2. The following phrases include a head, a complement, and a specifier. Draw the appropriate tree structure for each.a) full of peopleAPA P Nfull of peopleb) a story about a sentimental girlNPNP PPDet N P NPDet A Na story about a sentimental girlc) often read detective storiesVPQual V NPA Noften read detective storiesd) the argument against the proposalsNPNP PPDet N P NPDet Ne) move towards the windowVPV PPP Det Nmove towards the window3. Draw phrase structure trees for each of the following sentences.a) The jet landed.InflP(=S)NP Infl VPDet N Pst VThe jet landedb) Mary became very ill.InflP(=S)NP Infl VPN Pst V APDeg AMary became very illc) What will you talk about?CPNP C SN Infl NP Infl VPVP NPV P NWhat will you e talk about ed) The apple might hit the man.SNP VPDet N Aux V NPDet NThe apple might hit the manORInflP(=S)NP Infl VPDet N V NPDet NThe apple might hit the mane) He often reads detective stories.SNP VPN Qual V NPA NHe often reads etective storiesORInflP(=S)NP Infl VPPresN Qual V NPA NHe often reads etective stories4. The following sentences contain modifiers of various types. For each sentence, first identify the modifier(s), then draw the tree structures.a) A frightened passenger landed the crippled airplane.InflP(=S)NP Infl VPDet A N Pst V NPDet A NA frightened passenger landed the crippled airplaneb) A huge moon hung in the black sky.InflP(=S)NP Infl VPDet A N Pst V PPP NPDet A NA huge moon hung in the black skyc) An unusual event occurred before the meeting.InflP(=S)NP Infl VPDet A N Pst V PPP NPDet NAn unusual event occurred before the meetingd) A quaint old house appeared on the grassy hill.InflP(=S)NP Infl VPDet A NP Pst V PPA N P NPDet A NA quaint old house appeared on the grassy hill5. The following sentences all contain conjoined categories. Draw a tree structure for each of the sentences.a) Jim has washed the dirty shirts and pants.InflP(=S)NP VPN Aux V NPDet A NPN CON NJim has washed the dirty shirts and pantsN Infl V NPDet A NPN CON NJim has washed the dirty shirts and pants b) Helen put on her clothes and went out.SNP VPN VP CON VPVP NP V AdvV P Det NHelen put on her clothes and went outORInflP(=S)NP Infl VPN Pst VP CON VPVP NP V AdvV P Det NHelen put on her clothes and went outc) Mary is fond of literature but tired of statistics.SNP VPN VP CON VPVP NP VP NPV A P N V A P NMary is fond of literature but (is) tired of statisticsN Pres VP CON VPVP NP VP NPV A P N V A P NMary is fond of literature but (is) tired of statisticsd) The detective went out and the mysterious man came in.SS CON SNP VP NP VPDet N V Adv Det A N V AdvThe detective went out and the mysterious man came ine) Crusoe knows that spring will come and the snow will melt.SNP VPCPN V C SS CON SNP VP NP VPN Aux V Det N Aux VCrusoe knows that spring will come and the snow will melt6. The following sentences all contain embedded clauses that function as complements of a verb, an adjective, a preposition or a noun. Draw a tree structure for each sentence.a) You know that I hate war.SNP VPCPN V C SNP VPNPN V NYou know that I hate warOR CPC InflP(=S)NP Infl VPCPN Pres V C SNP VPN V NPNYou know that I hate warb) He said that Tom asked whether the class was over.SNP VPCPN V C SNP VPCPN V C SNP VPDet N VL AHe said that Tom asked whether the class was overc) Gerry can’t believe the fact that Anna flunked the English exam.SNP VPN VP NPCPAux Neg V NP C SDet N NP VPN V NPDet A N Gerry can not believe the fact thatAnna flunked the English examd) Chris was happy that his father bought him a Rolls-Royce.SNP VPCPN VL A C SNP VPDet N V NP NPN Det NChris was happy that his father bought him a Rolls-Roycee) The children argued over whether bats had wings.SNP VPCPDet N VP C SV P NP VPN V NPNThe children argued over whether bats had wings7. Each of the following sentences contains a relative clause. Draw the deep structure and the surface structure trees for each of the sentences.a) The essay that he wrote was too long.Deep structureCPC SNP VPDet N CP V APC S Deg PNP Infl VPN V NPNThe essay he wrote that was too longSurface StructureCPC SNP VPDet N CP V APC S Deg PNP NP Infl VPN N Pst V NPNThe essay that he wrote e was too longb) The dog that he keeps bites.Deep structureCPC SNP VPDet N CP VC Infl SPres NP VPN V NPNThe dog he keeps that bitesSurface StructureCPC SNP VPDet N CP VC SNP NP Infl VPN N Pres V NPNThe dog that he keeps e bitesc) Herbert found the man she loved.Deep structureCPC SNP VPN Infl V NPCPDet N C SNP Infl VPNPN VNHerbert found the man she loved whoSurface StructureCPC SNP VPN Infl V NPCPDet N SCNP Infl VPNP NPN VN N Herbert found the man (whom) she loved ed) The girl whom he often quarrels with majors in linguistics.Deep structureCPC SNP VPDet N CP V PPP NPC Infl SNNP VPPPN Qual VP NPV P NThe girl he often quarrels with whom majors in linguisticsSurface StructureCPC SNP VPDet N CP V PPP NPC SNNP NP Infl VPPPN N Qual VP NPV P NThe girl whom he often quarrels with e majors in linguistics8. The derivations of the following sentences involve the inversion transformation. Give the deep structure and the surface structure trees for each of these sentences.a) Would you come tomorrow?Deep structureCPC SVPNP AdvPN Infl V Advyou would come tomorrowSurface structureCPC SVPNP AdvPInflN Infl V Advwould you e come tomorrowb) Can you pass me the newspaper?Deep structureCPC SVPNP NP NPN Infl V N Det Nyou can pass me the newspaperSurface structureCPC SVPInfl NP NP NPN Infl V N Det N Can you e pass me the newspaperc) Should the students report the incident?Deep structureCPC SVPNP NPDet N Infl V Det Nthe students should report the incidentSurface structureCPC SVPInfl NP NPDet N Infl V Det N should the students e report the incidentd) What did you eat for lunch?Deep structureCPC SVPNP PPNP NPN Infl V PN Nyou did eat what for lunchSurface structureCPNP C SVPInfl NP PPNP NP N N Infl V PN N what did you e eat e for lunche) Who should this be reported to ?Deep structureCPC SVPNP PPVP NPN Infl V V PNthis should be reported to whomSurface structureCPNP C SVPN Infl NP PPVP NPN Infl V V PNwhom should this e be reported to ef) What was Helen bringing to the party?Deep structureCPC SVPNP PPNP NPN Infl V PN Det NHelen was bringing what to the partySurface structureCPNP C SVPN Infl NP PPNP NPN Infl V PN Det N what was Helen e bringing e to the party。
syntax1. Indicate the category of each word in the following sentences.a) The old lady suddenly left.Det A N Qual Vb) The car stopped at the end of the road.Det N V P Det N P Det Nc) The snow might have blocked the road.Det N Aux Aux V Det Nd) He never appears quite mature.N Qual V Deg A2. The following phrases include a head, a complement, anda specifier. Draw the appropriate tree structure for each.a) full of peopleAPA P Nfull of peopleb) a story about a sentimental girlNPNP PPDet N P NPDet A Na story about a sentimental girlc) often read detective storiesVPQual V NPA Noften read detective storiesd) the argument against the proposalsNPNP PPDet N P NPDet Nthe argument against the proposalse) move towards the windowVPV PPP Det Nmove towards the window3. Draw phrase structure trees for each of the following sentences.a) The jet landed.InflP(=S)NP Infl VPDet N Pst VThe jet landedb) Mary became very ill.InflP(=S)NP Infl VPN Pst V APDeg AMary became very illc) What will you talk about?CPNP C SN Infl NP Infl VPVP NPV P NWhat will you e talk about ed) The apple might hit the man.SNP VPDet N Aux V NPDet NThe apple might hit the manORInflP(=S)NP Infl VPDet N V NPDet NThe apple might hit the mane) He often reads detective stories.SNP VPN Qual V NPA NHe often reads etective storiesORInflP(=S)NP Infl VPPresN Qual V NPA NHe often reads etective stories4. The following sentences contain modifiers of various types. For each sentence, first identify the modifier(s), then draw the tree structures.a) A frightened passenger landed the crippled airplane.InflP(=S)NP Infl VPDet A N Pst V NPDet A NA frightened passenger landed the crippled airplaneb) A huge moon hung in the black sky.InflP(=S)NP Infl VPDet A N Pst V PPP NPDet A NA huge moon hung in the black skyc) An unusual event occurred before the meeting.InflP(=S)NP Infl VPDet A N Pst V PPP NPDet NAn unusual event occurred before the meetingd) A quaint old house appeared on the grassy hill.InflP(=S)NP Infl VPDet A NP Pst V PPA N P NPDet A NA quaint old house appeared on the grassy hill5. The following sentences all contain conjoined categories. Draw a tree structure for each of the sentences.a) Jim has washed the dirty shirts and pants.InflP(=S)NP VPN Aux V NPDet A NPN CON NJim has washed the dirty shirts and pantsORInflP(=S)NP VPN Infl V NPDet A NPN CON NJim has washed the dirty shirts and pantsb) Helen put on her clothes and went out.SNP VPN VP CON VPVP NP V AdvV P Det NHelen put on her clothes and went outORInflP(=S)NP Infl VPN Pst VP CON VPVP NP V AdvV P Det NHelen put on her clothes and went outc) Mary is fond of literature but tired of statistics.SNP VPN VP CON VPVP NP VP NPV A P N V A P NMary is fond of literature but (is) tired of statisticsORInflP(=S)NP Infl VPN Pres VP CON VPVP NP VP NPV A P N V A P NMary is fond of literature but (is) tired of statisticsd) The detective went out and the mysterious man came in. SS CON SNP VP NP VPDet N V Adv Det A N V AdvThe detective went out and the mysterious man came ine) Crusoe knows that spring will come and the snow will melt.SNP VPCPN V C SS CON SNP VP NP VPN Aux V Det N Aux VCrusoe knows that spring will come and the snow will melt6. The following sentences all contain embedded clauses that function as complements of a verb, an adjective, a preposition or a noun. Draw a tree structure for each sentence.a) You know that I hate war.SNP VPCPN V C SNP VPN PN VNYou know that I hate warOR CPC InflP(=S)NP Infl VPCPN Pres V C SNP VPN VNPNYou know that I hate warb) He said that Tom asked whether the class was over.SNP VPCPN V C SNP VPCPN V C SNP VPDet N VL AHe said that Tom asked whether theclass was overc) Gerry can’t believe the fact that Anna flunked theEnglish exam.SNP VPN VP NPCPAux Neg V NP C SDet N NP VPN V NPDet A NGerry can not believe the fact thatAnna flunked the English examd) Chris was happy that his father bought him a Rolls-Royce.SNP VPCPN VL A C SNP VPDet N V NP NPN Det NChris was happy that his father bought him a Rolls-Roycee) The children argued over whether bats had wings.SNP VPCPDet N VP C SV P NP VPN V NPNThe children argued over whether bats had wings7. Each of the following sentences contains a relative clause. Draw the deep structure and the surface structure trees for each of the sentences.a) The essay that he wrote was too long.Deep structureCPC SNP VPDet N CP V APC S Deg PNP Infl VPN V NPNThe essay he wrote that was too long Surface StructureCPC SNP VPDet N CP V APC S Deg PNP NP Infl VPN N Pst V NPNThe essay that he wrote e was too longb) The dog that he keeps bites.Deep structureCPC SNP VPDet N CP VC Infl SPres NP VPN V NPNThe dog he keeps that bitesSurface StructureCPC SNP VPDet N CP VC SNP NP Infl VPN N Pres V NPNThe dog that he keeps e bitesc) Herbert found the man she loved.Deep structureCPC SNP VPN Infl V NPCPDet N C SNP Infl VPNPN VNHerbert found the man she loved whoSurface StructureCPC SNP VPN Infl V NPCPDet N SCNP Infl VPNP NPN VN NHerbert found the man (whom) she loved ed) The girl whom he often quarrels with majors in linguistics.Deep structureCPC SNP VPDet N CP V PPP NPC Infl SNNP VPPPN Qual VP NPV P NThe girl he often quarrels with whommajors in linguisticsSurface StructureCPC SNP VP。
语言学学习在于理解掌握了图形就很容易了树形图详细讲解1. Indicate the category of each word in the following sentences.a) The old lady suddenly left.Det A N Qual Vb) The car stopped at the end of the road.Det N V P Det N P Det Nc) The snow might have blocked the road.Det N Aux Aux V Det Nd) He never appears quite mature.N Qual V Deg A2. The following phrases include a head, a complement, and a specifier. Draw the appropriate tree structure for each.a) full of peopleAPA P Nfull of peopleb) a story about a sentimental girlNPNP PPDet N P NPDet A Na story about a sentimental girlc) often read detective storiesVPQual V NPA Noften read detective storiesd) the argument against the proposalsNPNP PPDet N P NPDet Nthe argument against the proposalse) move towards the windowVPV PPP Det Nmove towards the window3. Draw phrase structure trees for each of the following sentences.a) The jet landed.InflP(=S)NP Infl VPDet N Pst VThe jet landedb) Mary became very ill.InflP(=S)NP Infl VPN Pst V APDeg AMary became very illc) What will you talk about?CPNP C SN Infl NP Infl VPVP NPV P NSNP VPDet N Aux V NPDet NThe apple might hit the manORInflP(=S)NP Infl VPDet N V NPDet NThe apple might hit the mane) He often reads detective stories.SNP VPN Qual V NPA NHe often reads etective storiesORInflP(=S)NP Infl VPPresN Qual V NPA NHe often reads etective stories4. The following sentences contain modifiers of various types. For each sentence, first identify the modifier(s), then draw the tree structures.a) A frightened passenger landed the crippled airplane.InflP(=S)NP Infl VPDet A N Pst V NPDet A NA frightened passenger landed the crippled airplaneb) A huge moon hung in the black sky.InflP(=S)NP Infl VPDet A N Pst V PPP NPDet A NA huge moon hung in the black skyc) An unusual event occurred before the meeting.InflP(=S)NP Infl VPDet A N Pst V PPP NPDet NAn unusual event occurred before the meetingd) A quaint old house appeared on the grassy hill.InflP(=S)NP Infl VPDet A NP Pst V PPA N P NPDet A NA quaint old house appeared on the grassy hill5. The following sentences all contain conjoined categories. Draw a tree structure for each of the sentences.a) Jim has washed the dirty shirts and pants.InflP(=S)NP VPN Aux V NPDet A NPN CON N Jim has washed the dirty shirts and pantsORInflP(=S)NP VPN Infl V NPDet A NPN CON NJim has washed the dirty shirts and pantsb) Helen put on her clothes and went out.SNP VPN VP CON VPVP NP V AdvV P Det NHelen put on her clothes and went outORInflP(=S)NP Infl VPN Pst VP CON VPVP NP V AdvV P Det NHelen put on her clothes and went outc) Mary is fond of literature but tired of statistics.SNP VPN VP CON VPVP NP VP NPV A P N V A P NMary is fond of literature but (is) tired of statistics ORInflP(=S)NP Infl VPN Pres VP CON VPVP NP VP NPV A P N V A P N Mary is fond of literature but (is) tired of statisticsd) The detective went out and the mysterious man came in.SS CON SNP VP NP VPDet N V Adv Det A N V AdvThe detective went out and the mysterious man came ine) Crusoe knows that spring will come and the snow will melt.SNP VPCPN V C SS CON SNP VP NP VPN Aux V Det N Aux V Crusoe knows that spring will come and the snow will melt6. The following sentences all contain embedded clauses that function as complements of a verb, an adjective, a preposition or a noun. Draw a tree structure for each sentence.a) You know that I hate war.SNP VPCPN V C SNP VPN V NPNYou know that I hate warOR CPC InflP(=S)NP Infl VPCPN Pres V C SNP VPN V NPNYou know that I hate warb) He said that Tom asked whether the class was over.SNP VPCPN V C SNP VPCPN V C SNP VPDet N VL A He said that Tom asked whether the class was overc) Gerry can’t believe the fact that Anna flunked the English exam.SNP VPN VP NPCPAux Neg V NP C SDet N NP VPN V NPDet A N Gerry can not believe the fact thatAnna flunked the English examd) Chris was happy that his father bought him a Rolls-Royce.SNP VPCPN VL A C SNP VPDet N V NP NPN Det NChris was happy that his father bought him a Rolls-Roycee) The children argued over whether bats had wings.SNP VPCPDet N VP C SV P NP VPN V NPNThe children argued over whether bats had wings7. Each of the following sentences contains a relative clause. Draw the deep structure and the surface structure trees for each of the sentences.a) The essay that he wrote was too long.Deep structureCPC SNP VP Det N CP V APC S Deg PNP Infl VPN V NPNThe essay he wrote that was too longSurface StructureCPC SNP VP Det N CP V APC S Deg PNP NP Infl VPN N Pst V NPNThe was too longb) The dog that he keeps bites.Deep structureCPC SNP VP Det N CP VC Infl SPres NP VPN V NPNThe dog he keeps that bitesSurface StructureCPC SNP VP Det N CP VC SNP NP Infl VPN N Pres V NPNThe dog bitesc) Herbert found the man she loved.Deep structureCPC SNP VPN Infl V NPCPDet N C SNP Infl VPNPN VNHerbert found the man she loved whoSurface StructureCPC SNP VPN Infl V NPCPDet N SCNP Infl VPNP NPN VN N Herbert found thed) The girl whom he often quarrels with majors in linguistics.Deep structureCPC SNP VPDet N CP V PPP NPC Infl SNNP VPPPN Qual VP NPV P NThe girl he often quarrels with whom majors in linguisticsSurface StructureCPC SNP VPDet N CP V PPP NPC SNNP NP Infl VPPPN N Qual VP NPV P NThe girl majors in linguistics8. The derivations of the following sentences involve the inversion transformation. Give the deep structure and the surface structure trees for each of these sentences.a) Would you come tomorrow?Deep structureCPC SVPNP AdvPN Infl V Advyou would come tomorrowSurface structureCPC SVPNP AdvPInflN Infl V Advcome tomorrowb) Can you pass me the newspaper?Deep structureCPC SVPNP NP NPN Infl V N Det Nyou can pass me the newspaperSurface structureCPC SVPInfl NP NP NPN Infl V N Det Npass me the newspaperc) Should the students report the incident?Deep structureCPC SVPNP NPDet N Infl V Det Nthe students should report the incidentSurface structureCPC SVPInfl NP NPDet N Infl V Det Nreport the incidentd) What did you eat for lunch?Deep structureCPC SVPNP PPNP NPN Infl V PN Nyou did eat what for lunchSurface structureCPNP C SVPInfl NP PPNP NP N N Infl V PN Nfor lunche) Who should this be reported to ?Deep structureCPC SVPNP PPVP NPN Infl V V PNthis should be reported to whomSurface structureCPNP C SVPN Infl NP PPVP NPN Infl V V PNf) What was Helen bringing to the party?Deep structureCPC SVPNP PPNP NPN Infl V PN Det NHelen was bringing what to the partySurface structureCPNP C SVPN Infl NP PPNP NPN Infl V PN Det Nto the party21。
树形图详细讲解1. Indicate the category of each word in the following sentences. a) The old lady suddenly left. DetA N Qual Vb) The car stopped at the end of the road.Det N V P Det N P Det N c) The snow might have blocked the road.Det N Aux Aux V Det N d) He never appears quite mature. N Qual V Deg A2. The following phrases include a head, a complement, and a specifier. Draw the appropriate tree structure for each. a) full of peopleAPAfull b) a story P Nof peopleabout a sentimental girlNPNPDetstory PPNPNabout a sentimental girl c) often read detective storiesVPQualoftenV NPA Nread detective storiesPDetNAad) the argument against the proposalsNPNP DetPPP NPDetthe argument against the proposalse) move towards the windowVPVmovePPP Det Ntowards the window3. Draw phrase structure trees for each of the following sentences.a) The jet landed.InflP(=S)NPDetTheNjetInflPstVPVlandedb) Mary became very ill.InflP(=S)NP Infl VPNMaryPst V APDegbecame very illNNAc) What will you talk about?CPNP C SNWhatInflwillNP Inflyou eVPVP NPV P Ntalk about ed) The apple might hit the man.SDetTheORNPNappleVPAux V NPDetmight hit theInflP(=S)DetTheNPNappleInflmightVPV NPDethit themanmanNNe) He often reads detective stories.SNP VPN Qual V NPHeORInflP(=S)NP Infl VPPresN Qual V NPA NHe often reads etective stories4. The following sentences contain modifiers of various types. For each sentence, first identify the modifier(s), then draw the tree structures.a) A frightened passenger landed the crippled airplane.InflP(=S)NP Infl VPDet A N Pst V NPDet A NA frightened passenger landed the crippled airplaneoften reads etective storiesNAb)A huge moon hung in the black sky.InflP(=S)NP Infl VPDetAA N Pst Vhuge moon hungPPPinNPDettheNskyc)An unusual event occurred before the meeting.InflP(=S)NP Infl VPDet A N Pst VAn unusual event occurred before thed) A quaint old house appeared on the grassy hill.InflP(=S)NP Infl VPNP Pst V PPAA quaint old5. The following sentences all contain conjoined categories. Draw a tree structure for each of the sentences.P NPDethouse appeared on theN PmeetingNPAgrassyDet AhillDetPPNNblackAa) Jim has washed the dirty shirts and pants.InflP(=S)NP VPAuxDet AN CONshirts andORInflP(=S)NPNDet AN CONthe dirty b) Helen put on her clothes and went out.SNP VPNVP VP NP DetNCONVPV AdvHelen put on her clothes and went outthe dirty shirts andwashedwashedpantspantshas hasJimJimInflNPNPNPNPVPNNNVVVPORNP NInflP(=S)Infl VP Pst VPVP NPDetHelen put on her clothes and went out c) Mary is fond of literature but tired of statistics.SOR Mary isNP VPVPNPNliteratureInflP(=S)CONbutVPVP NPV A P N(is) tired of statistics NP Infl VPN Pres VPV A Pfond of literatureCON VPV A P N(is) tired of statisticsV AdvCON VPNV PNVNPbutMary isA PNfond ofVP NP VPVPd) The detective went out and the mysterious man came in.SDet TheSNPV Advwent outCONNP VPDet Aand the mysterious man came ine) Crusoe knows that spring will come and the snow will melt.SNPNCONVP NPV Det Ncome and the snow6. The following sentences all contain embedded clauses that function as complements of a verb, an adjective, a preposition or a noun. Draw a tree structure for each sentence.a) You know that I hate war.SNPN YouVPCPV CNPNPNknow thatknows that spring will will meltSdetectiveAux V Crusoehate warAdvAuxNPVPVPVP VPCPNNN NVVVCSS SSIOR CPC InflP(=S)NPNNPNPNwarb) He said that Tom asked whether the class was over.SNPNHeVVPSthatNPNVPCPSNP VPDet N VL Asaid Tom asked whether the class was overCPknow thatV ChateYouPresInflVPVPCPN VSIV CCc) Gerry can ’t believe the fact that Anna flunked the English exam.SNP NGerry VPVPAux Neg Vcan not believeDettheNPCP SN V NPN NP VPfact thatAnna flunked the English examDet A NNPCd) Chris was happy that his father bought him a Rolls-Royce.SNPNChrisVPCPCNPV NP Nwas happy that his father bought him aNRolls-Roycee) The children argued over whether bats had wings.SNPCPDet The Nchildren7. Each of the following sentences contains a relative clause. Drawsurface structure trees for each of the sentences.the deep structure and thewhether batsargued over Det NwingshadDet NP VLNP VPNP VP VP VPNNA VVCPSSa) The essay that he wrote was too long.Deep structureCPCNPDetCtoo longSurface StructureCPCNPDetTheNessay CPC SNP NP Infl VPNthat Nhe Pst V NPNwrote eVwasAPDeg Ptoo longInfl VPwrote essayDegwasthatTheheNP NP VPVPCPAP N N NVVPSS Sb) The dog that he keeps bites.Deep structureCPCNPDetC Infl SPres NPNkeepsSurface StructureCPCNPDetTheNdog CPC SNP NP Infl VPNthatNhePres VkeepsNPNeVPVbitesVPVbitesthatdogTheheNP VP CPNNVSSc) Herbert found the man she loved.Deep structureCPCNP VPN InflHerbertNPCPN CInfl VPNPVNwhoSurface StructureCPCNP VPInflCPDetCInfl VPNPNN Herbert found the man (whom) she loved efound lovedman shetheDetNPNPNPNP NNNNVVVSSSSd) The girl whom he often quarrels with majors in linguistics.Deep structureCPCNPVPPNPP NPP PNPNwith whom majors in linguisticsSurface StructureCPCNPDet N CPNP The girl whomVPQual VPVoften quarrels NPNhePP P NPin linguisticsoften quarrels e majors C Infl SQual VPInfl VPwith girlTheheDet NP NP VPVPCP PPNNNNN VVC PSSS8. The derivations of the following sentences involve the inversion transformation. Give the deep structure and the surface structure trees for each of these sentences. a) Would you come tomorrow?Deep structureCPCVPAdvPAdvtomorrowSurface structure CPCInflwouldSVPAdvPAdvtomorrowwouldcomecomeyouyouInfl Infl NP NP NN V V eSb) Can you pass me the newspaper? Deep structureCPCVPNPInflcanSurface structure CPCInflCanSInflmeNPDet Nthe newspaperNPDet Nthe newspaperVPNP passyoumeNPN NV SyoupassN NP eNVc)Should the students report the incident?Deep structureCPCVPNPDet studentsSurface structureCPCInfl shouldSVPNPDet N Infl Vthe students e reportthe incidentNPDettheNincidentshould reporttheDet InflNPN NVSd) What did you eat for lunch?Deep structureCPC SVPNPNyou Surface structureCP InfldidVeatNPNwhatPPPforNPN lunchNP N C Inflwhat didSVPNPNPInflNlunchPPNPPeat eyou forNNVee) Who should this be reported to ?Deep structureCPCVPNPNPInflNwhom Surface structureCPNP NwhomCInflshouldSVPNPNPInflNreportedreportedshouldthisthisbebetotoVPVPPPPPNNV VV VeePPS21f) What was Helen bringing to the party?Deep structureCPCSNPVPPPN Infl VHelen was bringingSurface structure CPNPNwhatNPPDet Nthe partyNPNwhatCInflwasSVPNPNPInfl VDete bringingPPNP Pto thepartyHelentoNNNe。
创作编号:GB8878185555334563BT9125XW创作者:凤呜大王*树形图详细讲解1. Indicate the category of each word in the following sentences.a) The old lady suddenly left.Det A N Qual Vb) The car stopped at the end of the road.Det N V P Det N P Det Nc) The snow might have blocked the road.Det N Aux Aux V Det Nd) He never appears quite mature.N Qual V Deg A2. The following phrases include a head, a complement, and a specifier. Draw the appropriate tree structure for each.a) full of peopleAPA P Nfull of peopleb) a story about a sentimental girlNPNP PPDet N P NPDet A Na story about a sentimental girlc) often read detective storiesVPQual V NPA N often read detective storiesd) the argument against the proposalsNPNP PPDet N P NPDet Nthe argument against the proposalse) move towards the windowVPV PP创作编号:GB8878185555334563BT9125XW创作者:凤呜大王* P Det Nmove towards the window3. Draw phrase structure trees for each of the following sentences.a) The jet landed.InflP(=S)NP Infl VPDet N Pst VThe jet landedb) Mary became very ill.InflP(=S)NP Infl VPN Pst V APDeg A Mary became very illc) What will you talk about?CPNP C SN Infl NP Infl VPVP NPV P NSNP VPDet N Aux V NPDet NThe apple might hit the manORInflP(=S)NP Infl VPDet N V NPDet NThe apple might hit the mane) He often reads detective stories.SNP VPN Qual V NPA N创作编号:GB8878185555334563BT9125XW创作者:凤呜大王*He often reads etective storiesORInflP(=S)NP Infl VPPresN Qual V NPA NHe often reads etective stories4. The following sentences contain modifiers of various types. For each sentence, first identify the modifier(s), then draw the tree structures.a) A frightened passenger landed the crippled airplane.InflP(=S)NP Infl VPDet A N Pst V NPDet A NA frightened passenger landed the crippled airplaneb) A huge moon hung in the black sky.InflP(=S)NP Infl VPDet A N Pst V PPP NPDet A NA huge moon hung in the black skyc) An unusual event occurred before the meeting.InflP(=S)NP Infl VPDet A N Pst V PPP NPDet NAn unusual event occurred before the meetingd) A quaint old house appeared on the grassy hill.InflP(=S)NP Infl VPDet A NP Pst V PPA N P NPDet A NA quaint old house appeared on the grassy hill5. The following sentences all contain conjoined categories. Draw a tree structure for each of the sentences.a) Jim has washed the dirty shirts and pants.InflP(=S)NP VPN Aux V NPDet A NPN CON N Jim has washed the dirty shirts and pantsORInflP(=S)创作编号:GB8878185555334563BT9125XW创作者:凤呜大王*NP VPN Infl V NPDet A NPN CON NJim has washed the dirty shirts and pantsb) Helen put on her clothes and went out.SNP VPN VP CON VPVP NP V AdvV P Det NHelen put on her clothes and went outORInflP(=S)NP Infl VPN Pst VP CON VPVP NP V AdvV P Det NHelen put on her clothes and went outc) Mary is fond of literature but tired of statistics.SNP VPN VP CON VPVP NP VP NPV A P N V A P NMary is fond of literature but (is) tired of statistics ORInflP(=S)NP Infl VPN Pres VP CON VPVP NP VP NPV A P N V A P N Mary is fond of literature but (is) tired of statisticsd) The detective went out and the mysterious man came in.SS CON SNP VP NP VPDet N V Adv Det A N V AdvThe detective went out and the mysterious man came ine) Crusoe knows that spring will come and the snow will melt.SNP VPCPN V C SS CON SNP VP NP VPN Aux V Det N Aux VCrusoe knows that spring will come and the snow will melt创作编号:GB8878185555334563BT9125XW创作者:凤呜大王*6. The following sentences all contain embedded clauses that function as complements of a verb, an adjective, a preposition or a noun. Draw a tree structure for each sentence.a) You know that I hate war.SNP VPCPN V C SNP VPN V NPN You know that I hate warOR CPC InflP(=S)NP Infl VPCPN Pres V C SNP VPN V NPNYou know that I hate warb) He said that Tom asked whether the class was over.SNP VPCPN V C SNP VPCPN V C SNP VPDet N VL A He said that Tom asked whether the class was overc) Gerry can’t believe the fact that Anna flunked the English exam.SNP VPN VP NPCPAux Neg V NP C SDet N NP VPN V NPDet A NGerry can not believe the fact thatAnna flunked the English examd) Chris was happy that his father bought him a Rolls-Royce.SNP VPCPN VL A C SNP VPDet N V NP NPN Det NChris was happy that his father bought him a Rolls-Roycee) The children argued over whether bats had wings.SNP VPCPDet N VP C SV P NP VPN V NPN创作编号:GB8878185555334563BT9125XW创作者:凤呜大王*The children argued over whether bats had wings7. Each of the following sentences contains a relative clause. Draw the deep structure and the surface structure trees for each of the sentences.a) The essay that he wrote was too long.Deep structureCPC SNP VP Det N CP V APC S Deg PNP Infl VPN V NPNThe essay he wrote that was too longSurface StructureCPC SNP VP Det N CP V APC S Deg PNP NP Infl VPN N Pst V NPNThe was too longb) The dog that he keeps bites.Deep structureCPC SNP VP Det N CP VC Infl SPres NP VPN V NPNThe dog he keeps that bitesSurface StructureCPC SNP VP Det N CP VC SNP NP Infl VPN N Pres V NPNThe dog bitesc) Herbert found the man she loved.Deep structureCPC SNP VPN Infl V NPCPDet N C SNP Infl VPNPN VNHerbert found the man she loved whoSurface StructureCPC S创作编号:GB8878185555334563BT9125XW创作者:凤呜大王*NP VPN Infl V NPCPDet N SCNP Infl VPNPNPN VNNHerbert found the man (whom) she loved ed) The girl whom he often quarrels with majors in linguistics.Deep structureCPC SNP VPDet N CP V PPPNPC Infl SNNP VPPPN Qual VP NPV P NThe girl he often quarrels with whom majors in linguisticsSurface StructureCPC SNP VPDet N CP V PPPNPC SNNP NP Infl VPPPN N Qual VP NPV P NThe girl whom he often quarrels with e majors inlinguistics8. The derivations of the following sentences involve the inversion transformation. Give the deep structure and the surface structure trees for each of these sentences.a) Would you come tomorrow?Deep structureCPC SVPNP AdvPN Infl V Advyou would come tomorrowSurface structureCPC SVPNP AdvPInflN Infl V Advcome tomorrowb) Can you pass me the newspaper?Deep structureCPC SVPNP NP NPN Infl V N Det Nyou can pass me the newspaperSurface structureCPC SVPInfl NP NP NPN Infl V N Det Npass me the newspaperc) Should the students report the incident?Deep structureCPC SVPNP NPDet N Infl V Det N创作编号:GB8878185555334563BT9125XW创作者:凤呜大王*the students should report the incidentSurface structureCPC SVPInfl NP NPDet N Infl V Det Nreport the incidentd) What did you eat for lunch?Deep structureCPC SVPNP PPNP NPN Infl V PN Nyou did eat what for lunchSurface structureCPNP C SVPInfl NP PPNP NP N N Infl V PN Nfor lunche) Who should this be reported to ?Deep structureCPC SVPNP PPVP NPN Infl V V PNthis should be reported to whomSurface structureCPNP C SVPN Infl NP PPVP NPN Infl V V PNf) What was Helen bringing to the party?Deep structureCPC SVPNP PPNP NPN Infl V PN Det NHelen was bringing what to the partySurface structureCPNP C SVPN Infl NP PPNP NPN Infl V PN Det Nwhat was Helen e bringing e to the创作编号:GB8878185555334563BT9125XW创作者:凤呜大王*。
树形图详细讲解网上的相对理想的树形图答案,注意正两点:1. 短语和中心词在一竖线上2. 含有形容词修饰语的名词短语的画法NPDet NA Na little boy1. Indicate the category of each word in the following sentences.a) The old lady suddenly left.Det A N Qual Vb) The car stopped at the end of the road.Det N V P Det N P Det Nc) The snow might have blocked the road.Det N Aux Aux V Det Nd) He never appears quite mature.N Qual V Deg A2. The following phrases include a head, a complement, and a specifier. Draw the appropriate tree structure for each.a) full of peopleAPA P Nfull of peopleb) a story about a sentimental girlNPNP PPDet N P NPDet A Na story about a sentimental girl c) often read detective storiesVPQual V NPA Noften read detective storiesd) the argument against the proposalsNPNP PPDet N P NPDet Nthe argument against the proposalse) move towards the windowVPV PPP Det Nmove towards the window3. Draw phrase structure trees for each of the following sentences.a) The jet landed.InflP(=S)NP Infl VPDet N Pst VThe jet landedb) Mary became very ill.InflP(=S)NP Infl VPN Pst V APDeg AMary became very illc) What will you talk about?CPNP C SN Infl NP Infl VPVP NPV P NSNP VPDet N Aux V NPDet NThe apple might hit the man ORInflP(=S)NP Infl VPDet N V NPDet NThe apple might hit the mane) He often reads detective stories.SNP VPN Qual V NPA NHe often reads detective storiesORInflP(=S)NP Infl VPPresN Qual V NPA NHe often reads detective stories4. The following sentences contain modifiers of various types. For each sentence, first identify the modifier(s), then draw the tree structures.a) A frightened passenger landed the crippled airplane.InflP(=S)NP Infl VPDet A N Pst V NPDet A NA frightened passenger landed the crippled airplaneb) A huge moon hung in the black sky.InflP(=S)NP Infl VPDet A N Pst V PPP NPDet A NA huge moon hung in the black skyc) An unusual event occurred before the meeting.InflP(=S)NP Infl VPDet A N Pst V PPP NPDet NAn unusual event occurred before the meetingd) An old house appeared on the grassy hill.InflP(=S)NP Infl VPDet A NP Pst V PPA N P NPDet A NAn old house appeared on the grassy hill5. The following sentences all contain conjoined categories. Draw a tree structure for each of the sentences.a) Jim has washed the dirty shirts and pants.InflP(=S)NP VPN Aux V NPDet A NPN CON NJim has washed the dirty shirts and pantsORInflP(=S)NP VPN Infl V NPDet A NPN CON NJim has washed the dirty shirts and pantsb) Helen put on her clothes and went out.SNP VPN VP CON VPVP NP V AdvV P Det NHelen put on her clothes and went outORInflP(=S)NP Infl VPN Pst VP CON VPVP NP V AdvV P Det NHelen put on her clothes and went outc) Mary is fond of literature but tired of statistics.SNP VPN VP CON VPVP NP VP NPV A P N V A P NMary is fond of literature but (is) tired of statistics ORInflP(=S)NP Infl VPN Pres VP CON VPVP NP VP NPV A P N V A P NMary is fond of literature but (is) tired of statisticsd) The detective went out and the mysterious man came in.SS CON SNP VP NP VPDet N V Adv Det A N V AdvThe detective went out and the mysterious man came ine) Crusoe knows that spring will come and the snow will melt.SNP VPCPN V C SS CON SNP VP NP VPN Aux V Det N Aux VCrusoe knows that spring will come and the snow will melt6. The following sentences all contain embedded clauses that function as complements of a verb, an adjective, a preposition or a noun. Draw a tree structure for each sentence.a) You know that I hate war.SNP VPCPN V C SNP VPN V NPNYou know that I hate warOR CPC InflP(=S)NP Infl VPCPN Pres V C SNP VPN V NP NYou know that I hate warb) He said that Tom asked whether the class was over.SNP VPCPN V C SNP VPCPN V C SNP VPDet N VL AHe said that Tom asked whether the class was overc) Gerry can’t believe the fact that Anna flunked the English exam.SNP VPN VP NPCPAux Neg V NP C SDet N NP VPN V NPDet A NGerry can not believe the fact thatAnna flunked the English examd) Chris was happy that his father bought him a Rolls-Royce.SNP VPCPN VL A C SNP VPDet N V NP NPN Det NChris was happy that his father bought him a Rolls-Roycee) The children argued over whether bats had wings.SNP VPCPDet N VP C SV P NP VPN V NPNThe children argued over whether bats had wings7. Each of the following sentences contains a relative clause. Draw the deep structure and the surface structure trees for each of the sentences.a) The essay that he wrote was too long.Deep structureCPC SNP VPDet N CP V APC S Deg PNP Infl VPN V NPNThe essay he wrote that was too longSurface StructureCPC SNP VPDet N CP V APC S Deg PNP NP Infl VPN N Pst V NPNThe essay that he wrote e was too longb) The dog that he keeps bites.Deep structureCPC SNP VPDet N CP VC Infl SPres NP VPN V NPNThe dog he keeps that bitesSurface StructureCPC SNP VPDet N CP VC SNP NP Infl VPN N Pres V NPNThe dog that he keeps e bitesc) Herbert found the man she loved.Deep structureCPC SNP VPN Infl V NPCPDet N C SNP Infl VPNPN VNHerbert found the man she loved whoSurface StructureCPC SNP VPN Infl V NPCPDet N SCNP Infl VPNP NPN VN Nd) The girl whom he often quarrels with majors in linguistics.Deep structureCPC SNP VPDet N CP V PPP NPC Infl SNNP VPPPN Qual VP NPV P NThe girl he often quarrels with whom majors in linguisticsSurface StructureCPC SNP VPDet N CP V PPP NPC SNNP NP Infl VPPPN N Qual VP NPV P NThe girl whom he often quarrels with e majors in linguistics8. The derivations of the following sentences involve the inversion transformation. Give the deep structure and the surface structure trees for each of these sentences.a) Would you come tomorrow?Deep structureCPC SVPNP AdvPN Infl V Advyou would come tomorrowSurface structureCPC SVPNP AdvPInflN Infl V Advwould you e come tomorrowb) Can you pass me the newspaper?Deep structureCPC SVPNP NP NPN Infl V N Det Nyou can pass me the newspaperSurface structureCPC SVPInfl NP NP NPN Infl V N Det N Can you e pass me the newspaperc) Should the students report the incident?Deep structureCPC SVPNP NPDet N Infl V Det Nthe students should report the incidentSurface structureCPC SVPInfl NP NPDet N Infl V Det Nshould the students e report the incidentd) What did you eat for lunch?Deep structureCPC SVPNP PPNP NPN Infl V PN Nyou did eat what for lunchSurface structureCPNP C SVPInfl NP PPNP NPN N Infl V PN Nwhat did you e eat e for lunche) Who should this be reported to ?Deep structureCPC SVPNP PPVP NPN Infl V V PNthis should be reported to whomSurface structureCPNP C SVPN Infl NP PPVP NPN Infl V V PNwhom should this e be reported to ef) What was Helen bringing to the party?Deep structureCPC SVPNP PPNP NPN Infl V PN Det NHelen was bringing what to the partySurface structureCPNP C SVPN Infl NP PPNP NPN Infl V PN Det Nwhat was Helen e bringing e to the party。