英语动词的分类及其语态和时态讲解共28页文档
- 格式:ppt
- 大小:2.40 MB
- 文档页数:28



动词的时态和语态全析全解动词时态(tense)是一种动词形式,不同的时态用以表示不同时间里所产生的动作或存在的状态。
从种类上看英语有16种时态,而其中常用的有11种,表中斜体字表示的时态不常用。
动词各时态名称如下:1-4 现在:一般现在时现在进行时现在完成时现在完成进行时2-4 过去:一般过去时过去进行时过去完成时过去完成进行时3-4 将来:一般将来时将来进行时将来完成时将来完成进行时4-4 过去将来:一般过去将来时过去将来进行时过去将来完成时过去将来完成进行时各时态的英语表达结构(以write为例):一般/进行/完成/完成进行1、现在write, writesam/is/are writinghave/has writtenhave/has been writing2、过去wrotewas/were writinghad writtenhad been writing3、将来shall/will writeshall/will be writingshall/will have writtenshall/will have been writing4、过去将来should/would writeshould/would be writingshould/would have writtenshould/would have been writing各时态用法说明一. 一般现在时一般现在时主要由动词原形表示,但第三人称单数作主语时谓语动词后要加-s或-es,另外,be和have有特殊的人称形式。
如:1.一般动词:I know it.You know it.He/She knows it.We/You/They know it.2. 动词be:以am, is, are三种形式出现。
I am a teacher.You are a student.He / She is a student.We/You/They are students.3. 动词have:以have, has形式出现。

动词时态专讲一、各种时态的构成二、各种时态的用法◆◆一般现在时: 1.表示经常性或习惯性的动作;2.用在客观真理, 客观存在, 科学事实或格言警句中。
常与表示频度的时间状语连用;3.由when, as soon as, until, before, after引导的时间状语从句或由if, unless, as long as, once引导的条件状语从句中, 一般现在时代替一般将来时。
时间状语: every day, everyother day, sometimes, often, usually, on Sunday …1.I (leave) home for school at 7 _________________ (每天早晨).2、The earth ___________ (go) the sun.3、Shanghai lies in the east of China.上海__________中国的东方。
4.My teacher told us that light _________ (travel) faster than sound.5.Didn’t you father tell you that the sun ________ (be) much larger than the moon?6.I’ll help you as soon as I ___________(到达) Beijing tomorrow.7、I won’t leave unless you __________ (tell) me everything.跟踪练习: 1.Smith does not go fishing on weekdays, ____? _____ , he does.A.does he…NoB.does he…YesC.doesn't he…NoD.doesn't he…Yes2.Mr.Black often _____ fishing on Sundays, _____ he ?A.goes…doesn'tB.goes…isn'tC.doesn't go…doesD.doesn't go…is3.____he ___himself there? No, I don't think so. A.Do…enjoy B.Does…enjoies C..Does…enjoy4.___ your teacher __ from them very often? Certainly.A.Do…hear B.Does…hear C.Do…receive D.receive5._____ your mother _____ some cleaning on Sundays A.Does…does B.Do…does C.Does…do D.Do…do一般过去时: 1.表示在确定的过去时间里所发生的动作或存在的状态。

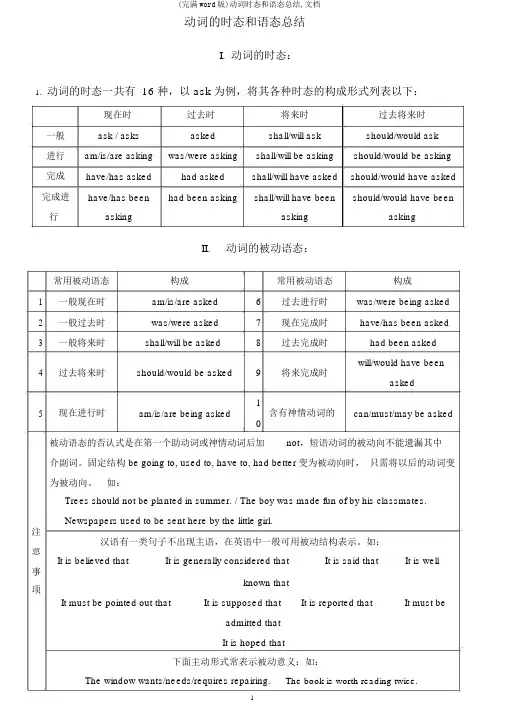
动词的时态和语态总结I.动词的时态:1.动词的时态一共有 16 种,以 ask 为例,将其各种时态的构成形式列表以下:现在时过去时将来时过去将来时一般ask / asks asked shall/will ask should/would ask 进行am/is/are asking was/were asking shall/will be asking should/would be asking 完成have/has asked had asked shall/will have asked should/would have asked 完成进have/has been had been asking shall/will have been should/would have been 行asking asking askingII.动词的被动语态:常用被动语态构成常用被动语态构成1一般现在时am/is/are asked6过去进行时was/were being asked 2一般过去时was/were asked7现在完成时have/has been asked 3一般将来时shall/will be asked8过去完成时had been asked4过去将来时should/would be asked9将来完成时will/would have beenasked5现在进行时am/is/are being asked 1含有神情动词的can/must/may be asked 0被动语态的否认式是在第一个助动词或神情动词后加not,短语动词的被动向不能遗漏其中介副词。
固定结构 be going to, used to, have to, had better变为被动向时,只需将以后的动词变为被动向。
如:Trees should not be planted in summer. / The boy was made fun of by his classmates.Newspapers used to be sent here by the little girl.注汉语有一类句子不出现主语,在英语中一般可用被动结构表示。

动词一、动词概述:动词是表示动作和状态的词。
动词在句中充当谓语,称为谓语动词,不充当谓语则称为非谓语动词。
eg. I like playing football.该句中动词like是谓语动词,由动词play变形而来的playing则是非谓语动词。
根据不同变化形式,动词具有以下相关知识点:1. 动词分类2. 动词时态3. 动词语态(被动语态)4. 非谓语动词二、动词的分类动词的种类特点和例句行为动词或实义动词(可单独使用) 1. 及物动词:后必须跟宾语(宾语由名词、代词或相当于名词的词充当)Eg. They study English.She eats an apple every day.We raise the flag every Monday.我们每周一升旗。
2. 不及物动词:后需加介词才能跟宾语The flag rises. 旗升起来了。
Please stand up. /Please come here.They listen to English every morning. 他们每天早上都听英语。
连系动词(可单独使用) 连系动词后跟表语。
常见的连系动词有:be , become/turn(变得)、look(看起来),smell(闻起来),sound(听起来),feel(摸起来),taste(尝起来)等。
Eg. She is beautiful./She is a student.His face turned red. 他的脸变红了。
Your coat looks nice. 你的外套看起来很漂亮。
The music sounds beautiful. 这音乐听起来很美。
感官动词look,smell, sound, feel,taste后跟形容词,不能用副词。
Eg. sound beautifully. (×)助动词(必须与行为动词或系动词连用构成谓语) 助动词无特殊意义,帮助构成否定句、疑问句、正在进行时态、完成时态或被动语态等,常见助动词有be, do, haveWe don‘t like the film. 我们不喜欢这部电影。

初中英语动词时态和语态讲解动词的时态和语态(一)动词是谓语动所表示的动作或情况发生时间的各种形式。
英语动词有16种时态,但是常用的只有9种:一般现在时、一般过去时、一般将来时、现在进行时、过去进行时、现在完成时、过去完成时、过去将来时、现在完成进行时。
下面分别介绍。
1、一般现在时的用法1)表示经常性、习惯性的动作;表示现在的状态、特征和真理.句中常用 often, usually, every day 等时间状语。
例如:a. He goes to school every day。
b. He is very happy。
c。
The earth moves around the sun。
2)在时间状语从句和条件状语从句中,用一般现在时表示将来。
例如:a。
If you come this afternoon,we’ll have a meeting.b. When I graduate, I'll go to countryside.3) 有时这个时态表示按计划、规定要发生的动作(句中都带有时间状语),但限于少数动词,如:begin, come, leave, go ,arrive, start , stop, return, open, close等。
例如:a. The meeting begins at seven。
b. The rain starts at nine in the morning。
4) 表示状态和感觉的动词(be, like, hate, think, remember, find, sound 等)常用一般现在进行时。
a. I like English very much。
b。
The story sound very interesting.5) 书报的标题、小说等情节介绍常用一般现在时。
2.一般现在时的用法1)表示过去某时间发生的事、存在的状态或过反复发生的动作。
动词的种类、时态、语态第一部分动词的种类一:及物动词、不及物动词1、判断方法:字典......(但不可能随身携带字典吧)我他。
(主动)他被我。
(被动)在上面句子,放入任意一个动词,若翻译成中文后,意思若无毛病,则为及物动词;否则就是不及物动词。
表格(一)及物动词(宾语为名词、代词、不定式、动名词、从句等,构成“主+谓+宾”)不及物动词构成“主+谓+宾”或“主+谓”Kill StarveDo RainPractice LaughProduce LiveNotice ArriveEnjoy DanceLove RunHate HappenBuy Rise表格二:作及物动词作不及物动词Sing 意思:意思:Run 意思:意思:Study 意思:意思:Return 意思:意思:Speak 意思:意思:二:系动词表格三:三:使役动词、知觉动词、认定动词、授予动词表格四:第二部分:动词的时态三:一般体(1)一般现在时:表示现在经常性、习惯性的动作或状态---We have meals three times a day。
我们一日三餐。
(现在的习惯)---He is always help others。
他总是乐于助人。
(现在的状态)一般现在时还可以表示客观真理、科学事实----The sun rises in the east。
太阳从东方升起。
一般现在时还可用在if引导的条件状语从句及as soon as引导的时间状语从句中,“主将从现”,即主句用一般将来时,从句用一般现在时,如---I'll go with you as soon as I finish my work。
我一完成工作就跟你走。
练习:If it tomorrow,I to climb the mountain。
A. does rain;goesB. doesn’t rain;will goC. rains;will goD. raining;will go(2)一般过去时:表示过去发生的动作---He bought an apple yesterday.---I didn’t watch the play before.表示过去连续发生的动作,往往没有表示过去的时间状语,而通过上下文来判断。
动词的时态和语态用法详解在英语中,不同时间里发生的动作或存在的状态需要用动词的不同形式表示出来,动词的这种不同形式就构成了动词的时态。
英语中的时态按动作发生时间分为现在时态、过去时态、将来时态一、时态的分类和基本构成形式二、常见时态的基本用法现在体1. 一般现在时:一般现在时是描述现在或经常性的动作性质或状态的时态。
常和表示频率、时间的副词(短语)always, every time, now and then, occasionally, often, seldom, sometimes, usually等连用。
1)表示经常性或习惯性的动作。
We have three meals a day.2)表示客观事实、真理和自然现象。
Knowledge is power.3)表示现在的情况或状态。
I live in Beijing.4)表示已经“列入日程”的将来的事件,尤其指计划中的和安排好的将来的动作,这些动词往往表示“出发,到达”等含义的词,如,arrive, begin, go, leave, start, stay等。
The train arrives at 10:30. There's plenty of time. 。
考点一:表示永恒的真理,即使出现在过去的语境中,仍用一般现在时。
如:I learned that the earth goes around the sun when I was in primary school.考点二:在时间和条件状语从句中,代替一般将来时;常用的引导词有:时间:when, until, after, before, as soon as, once, the moment/the minute, the day; 条件:if, unless, provided.If he accepts the job, he will get more money soon.考点三:在make sure (certain), see to it, mind, care, matter +宾语从句,从句用一般现在时代替一般将来时。
动词时态与语态、动词时态与语态的构成、注意事项或重点掌握知识点O表达将来时的形式1)在时间、条件、让步状语从句中,使用一般现在时替代将来时。
如:I ' tell him when you ring again.2) 在make sure, make certain, see (to it) 后的that 从句中,谓语动词用一般现在时替代将来时。
如:See to it that you include in the paper whatever questions they didn 'know the answer to last time.O完成时是时态测试的重中之重,注意与完成时连用的句型和时间状语。
1)当by/between/up to/till + 过去时间、since/by the time/when +表示过去发生情况的从句,这时,主句用过去完成时。
屈:1. We had just had our breakfast when an old mancame to the door.2. Between 1897 and 1919 at least 29 motion picturesin which artificial beings were portrayed had been p roduced.2)当by +将来时间、by the time/when +谓语动词是一般现在时的从句,这时,主句用将来完成时。
如:3)1. By the time you arrive in London, we will havestayed in Europe for two weeks.2.1 hope her health will have imp roved greatly by thetime we come back next year.当by now、since+过去时间或in/during/for/over/the p ast/last + 表示多少的词+years/days/weeks, etc,,这时,主句用现在完成时;但在it is +具体时间+since/before这一句型中,表示“有多少时间”时,主句更多的时候不用完成时。