最新初中英语语法知识—动词的分类汇编含解析(1)
- 格式:doc
- 大小:45.00 KB
- 文档页数:8

动词的种类初中英语语法动词的种类初中英语语法动词的种类动词是表示动作或状态的词,按其词义和在句子中的作用可分为行为动词,连系动词,助动词和情态动词。
1.行为动词行为动词可分为及物动词(vt)和不及物动词(vi),及物动词表示动作或状态,有完整的词义,能单独作谓语,后跟宾语;不及物动词表示动作或状态,有完整的词义,能单独作谓语,但后面不能直接跟宾语,如要带宾语则与介词或副词构成短语。
如:More and more people study English.(vt)The students are listening to the teacher carefully.(vi)2.连系动词连系动词本身有一定的词义,但不能独立作谓语,必须与表语一起构成谓语。
常用的连系动词有be, get, turn, become, look, feel, grow, seem, sound, taste, smell等。
如:Our country is becoming stronger and stronger.It feels damp.3.助动词助动词本身无词义,不能单独作谓语,只能和主要动词一起构成谓语动词,表示否定,疑问及动词的.时态、语态、人称和数等语法特征,助动词有 be,do,have,shall,will等。
如:How do you usually come to school?The children are playing yo-yo now.4.情态动词情态动词本身有一定的意义,但不能独立作谓语,只能和主要动词原形一起构成谓语,表示说话人的语气和情态。
情态动词没有人称和数的变化。
情态动词有can (could),may(might),must, need, ought to, dare等。
如:Can I help you?- Must we go now? -No, you needn't .a. can与be able to的用法有所区别。

中考英语知识点梳理:动词讲解考点一: 动词的分类动词按照含义及它们在句中的作用分为四类,即行为动词,也称实义动词,(连)系动词、助动词和情态动词。
一、动词的分类1.实义动词的用法(及物动词与不及物动词)实义动词是能独立作谓语的动词。
按其是否跟宾语分为及物动词(vt.)和不及物动词(vi.)。
(1)及物动词及物动词本身意义不完整,需要接宾语才能使其意思表达完整,如reach,ask,return,love,need。
具体用法为:①动词+宾语。
如:He reached Canada yesterday.他昨天到达加拿大。
②动词+宾语+宾语补足语。
如:They asked me to go fishing with them.他们让我一起去钓鱼。
I saw the children play in the park yesterday.昨天我看见孩子们在公园里玩。
注意:带省略 to 的不定式或现在分词作宾补的常考动词有:make,let,have,see,watch,notice,hear 等。
③动词+间接宾语+直接宾语。
如:I will return the storybook to him.我准备把故事书还给他。
注意:带双宾语的常考动词有:give,bring,buy,get,leave,lend,make,offer,pass,teach,tell,r each,return 等。
(2)不及物动词不及物动词本身意思完整,无须接宾语,构成“主语+谓语”的句型,如swim,come,go,run,travel 等;若后面接宾语,必须与介词连用。
如:Lucy is swimming. 露西正在游泳。
I am waiting for you at the school gate.我正在校门口等你。
(3)有些动词既可作及物动词,又可作不及物动词。
如:We study English.我们学习英语。
(及物)We study hard.我们学习努力。

动词分类归纳总结动词是语言中最为重要和常用的词类之一,能够表达动作、状态和变化等含义。
根据动词的不同特点和语法功能,可以将其分为多个不同的分类。
本文将对动词的分类进行归纳总结,并对每种分类进行简要的介绍和举例说明。
一、按照动作性质分类1. 及物动词及物动词是指需要搭配宾语来表达完整意义的动词。
它们可以表示动作的直接对象或间接对象。
例如:- 打电话(直接宾语)- 给她一个礼物(间接宾语)2. 不及物动词不及物动词是指能够独立使用而无需搭配宾语的动词。
它们主要表示主语的动作或状态。
例如:- 跑步- 睡觉二、按照词义分类1. 行为动词行为动词指的是表达个体的行动或具体动作的动词。
例如:- 打字2. 感觉动词感觉动词用来描述人的五官器官感知客观世界的动作。
例如:- 看到- 听见3. 状态动词状态动词用来表示事物获取的状态或特征。
例如:- 是- 变成4. 变化动词变化动词指的是当主语发生变化时,动词的形式也会相应变化的动词。
例如:- 变化- 发展三、按照时态和语态分类1. 时态动词时态动词用来表示动作或状态所处的时间。
例如:- 完成2. 语态动词语态动词用来表示句子中动作的执行者与动作的承受者之间的关系。
例如:- 主动语态- 被动语态四、按照语法功能分类1. 实义动词实义动词是指能够表达真实意义的动词,它们能够独立作为句子的谓语。
例如:- 爱- 做2. 系动词系动词用来连接主语与主语的补足语,表达主语的状态或特征。
例如:- 是- 变得3. 助动词助动词在句子中充当辅助的角色,用来构成各种时态和语态等。
例如:- 可以- 能够五、其他分类1. 情态动词情态动词用来表示说话人对某种行为或状态的看法、态度、愿望、推测、命令等情态。
例如:- 可能- 应该2. 不规则动词不规则动词是指在时态、语态、人称和数等方面变化规律与一般规则动词不同的动词。
例如:- go(过去式:went,过去分词:gone)- have(过去式:had,过去分词:had)综上所述,动词在语言中起到了重要的作用,通过对动词的分类归纳总结,我们可以更好地理解和运用动词,丰富语言表达的方式和技巧。

一、选择题1.Look! Dave __________ on the phone.A.talks B.are talking C.talk D.is talking 2.Boys and girls, there ________an English speech competition in two weeks.A.will have B.has C.is going to be D.are going to be 3.Dick __________ in America, but he has been ___________ Chinese food since he moved to China.A.used to live; used to eatingB.is used to live; used to eatC.is used to live; used to eatingD.used to living; used to eat4.Wang Wei often ________ TV on Sunday evenings, but now he is _______ stories. A.watches; reading B.watching; reads C.looks; reading D.watches; looking 5.It’s 4:00 p.m. The students _____ in the pool.A.swim B.swam C.swims D.are swimming6.I like this dress very much. It soft and smooth.A.feels B.touches C.is felt D.is touched 7.— Morning, Mike! Did you sleep well last night?— Yes. I went to bed at 9:30 because there ______ a math test this afternoon.A.was B.will be C.is going to have 8.Which of the following sentences is correct?A.He came in and sat down.B.We all like <Harry Potter>.C.When we met. He didn't say hello.D.We went out, headed for the bus stop.9.—I called you at three yesterday afternoon, but you weren’t in.—I ________ a meeting at that time.A.had B.was having C.have had D.would have 10.—I'm sorry. There was too much traffic on the road.—Never mind. The meeting________for only 5 minutes.A.has begun B.has stopped C.has been on 11.—Have you written a litter to your brother?—Yes, I have. I________one last Sunday.A.was writing B.wrote C.have written 12.—How long can I _____ the English workbook? —For two weeks.A.borrow B.to borrow C.keep D.to keep 13.Miss Smith in our school since five years ago.A.teaches B.taught C.has taught D.is teaching14.When I was young, my mother ___________ by my side all the time.A.stays B.is staying C.stayed D.will stay 15.—Remember the first time we met, Jim?—Of course I do. You ________ in the library.A.were reading B.have read C.will read D.read 16.Look at Amy. She ________ for the school bus.A.wait B.is waiting C.waits D.waiting 17.The water ______ cool when I jumped into the pool for morning exercise.A.was felt B.is felt C.felt D.feels 18.While I_______ a detective story, someone_______ at the door.A.read, was knockingB.read, knockedC.was reading, knockedD.was reading, was knocking19.---Where have you been recently?---I _______ in Hangzhou on business for a week last month.A.have been B.had gone C.had been D.was 20.It’s 8 o’clock. The students _________ an English class.A.have B.having C.is having D.are having 21.With a book in his hand, the boy ________ in bed.A.lie B.lied C.lay D.lying 22.Don’t talk! The baby ________.A.sleeps B.is sleep C.sleeping D.is sleeping 23.— What do you use MP3 for?— I ________ it ________ to music.A.use; listen B.are listening; listeningC.use; to listen D.is listening; to listening24.My father is a teacher and he ___________ in this school for about twenty years. A.works B.is working C.was working D.has worked 25.—How much is the ticket (票) to Central Park?—One ticket $40, and you can $80 for two persons.A.costs; pay B.cost; spend C.pay; spend D.spends; pay 【参考答案】***试卷处理标记,请不要删除一、选择题1.D【解析】【分析】【详解】句意:看!Dave正在打电话。

一、选择题1.The Great Wall (长城) ________ long and it ________ a long history (历史).A.has; is B.is; is C.is; has D.have; has2.In the past he often made his sister____, but now he is often made ___by his sister.A.to cry; to cry B.cry; cryC.to cry; cry D.cry; to cry3.Coffee is ready. How nice it ______! Would you like some?A.looks B.smells C.sounds D.feels4.—_______everyone get tired today?—Yes, we_______very tired the whole afternoon.A.Does; are all B.Do; are allC.Does; all are D.Is; all are5.The library ______ from 8 a.m. to 3 p.m. on weekdays. But it______ at 5 p.m. on Saturdays and Sundays.A.is open; closes B.opens; closed C.is opened; closes D.is opening; is closed 6.I tried to make the baby ________by singing, and that worked well at last.A.stop crying B.to stop crying C.stop to cry D.to stop to cry 7.Which of the following sentences is right?A.My books on the desk B.Nice meet you, tooC.These are my dictionaries D.Thanks you for your help.8.—He’s never been late for school.—________________.A.So have I B.So am I C.Neither have I D.Nor am I 9.—Hey, Jack. Do you want to go to the library? —That ________ great. I love reading. A.hears B.looks C.sounds D.listens 10.—Would you like to try some pizza?—Yes, please. It lovely and nice.A.sounds, sees B.looks, smells C.hears, turns D.sounds, watches 11.—Do you know whom they will have ________the parts of car together?—Sorry,I have no idea.A.fix B.fixed C.to fix D.fixing12.Hard work can bring you , but if you a re lazy, you won’t become . A.success; success B.successful; successC.success; successful D.successful; succeed13.Alice, it's time for school. Let me _______, or I will be late for class.A.go B.come C.to go D.to come 14.—Do you have an art festival at school?—Yes, ________.A.we have B.we can C.we do15.In fact (事实上), she ________ ________ many ________.A.doesn’t has; toies B.don’t has; toies C.doesn’t have; toys D.don’t have; toys 16.—Where__________ your friend __________from?—He comes from England.A.is; come B.do; come C.does; come D.are; be 17.Their eyes __________blue, but ours_________black.A.are; are B.is; are C.are; is . D.are; is 18.When did your father your mother?A.marry B.marry to C.marry with D.get married 19.—What __________ he do? —He __________ an actor.A.is, is B.does, does C.does, is D.is, does20.Our teachers always make us ________ a lot of homework.A.to do B.do C.does D.doing21.— How ________ your trip to Australia?—Great. I’ll go there again next yea r.A.was B.is C.are D.were22.I often play volleyball after class. But my cousin Lily _________.A.does B.doesn’t C.do D.don’t23.A lot of good teachers __________ their students.A.are strict with B.is strict with C.are strict in24.Tom and I ________ good friends. He is twelve(12岁).A.are B.am C.is D.be25.I have bought a Chinese – English dictionary. When and where_____ you _____ it? A.have, bought B.did buy C.will, buy D.do , buy【参考答案】***试卷处理标记,请不要删除一、选择题1.C解析:C【解析】【分析】【详解】句意:长城很长,而且它有很长的历史。

动词的类型知识点总结1. 行为动词行为动词表示一个人或物的动作或行为,比如“跑、打、吃、写”等。
行为动词可以进一步分为及物动词和不及物动词。
及物动词表示需要接宾语才能构成完整的意义,比如“吃饭、打球、写信”;不及物动词则表示不需要接宾语就能构成完整的意义,比如“坐、走、跳”。
2. 连系动词连系动词是用来连接主语和表语的动词,表明主语的性质、状态、特征、身份等,比如“是、变得、感到、似乎”等。
在句子中,连系动词往往形成主系表结构,起到连接主语和表语的作用。
3. 助动词助动词是用来辅助主要动词构成时态、语态、语气等的动词,比如“be、do、have”等。
助动词在句子中的位置是位于主要动词之前,起到辅助的作用。
4. 情态动词情态动词在句子中表示说话者对某种行为或状态的态度或情感色彩,比如“can、could、may、might、should、must、shall、will、would、ought to”等。
情态动词与主要动词构成的短语具有时态和人称数的一致性,而且情态动词后面可以接动词原形。
5. 及物动词及物动词是需要接受动作的对象才能构成完整的意义的动词,比如“看、吃、打、写”等。
及物动词通常在句子中构成及物动词短语,其宾语可以是名词、代词、动名词、不定式等。
6. 不及物动词不及物动词是不需要接受动作的对象就能构成完整的意义的动词,比如“走、跑、坐、睡”等。
不及物动词在句子中通常构成不及物动词短语,具有自足性和内在的动作方向。
了解和掌握动词的类型及其用法,可以帮助我们更准确地表达自己的意思,提高语言表达和沟通能力。
同时,在学习中要多加练习,通过大量的阅读和写作来巩固和运用动词的不同类型,以便更熟练地掌握其用法。

初中英语知识点总结:动词知识点总结在初中英语的学习中,动词是一个至关重要的部分。
掌握好动词的相关知识,对于我们正确理解和运用英语句子有着不可或缺的作用。
接下来,就让我们一起深入地了解一下初中英语中动词的知识点。
一、动词的分类1、实义动词实义动词是表示具体动作或状态的动词,又可以分为及物动词和不及物动词。
及物动词后面需要接宾语才能表达完整的意思,例如“eat an apple (吃一个苹果)”中的“eat”就是及物动词,“apple”是宾语。
不及物动词后面不需要接宾语就能表达完整的意思,比如“run fast (跑得快)”中的“run”就是不及物动词。
2、系动词系动词用于连接主语和表语,说明主语的状态、性质、特征等。
常见的系动词有 be(am/is/are/was/were)、seem、look、sound、taste、feel、smell 等。
例如:“She is beautiful(她很漂亮。
)”“The soup tastes delicious(这汤尝起来很美味。
)”3、助动词助动词本身没有实际意义,主要用于帮助构成各种时态、语态、语气等。
常见的助动词有 do/does/did、have/has/had、will/would、shall/should 等。
比如:“He doesn't like sports(他不喜欢运动。
)”“They have finished their homework(他们已经完成了作业。
)”4、情态动词情态动词表示说话人的态度、情感或推测等。
常见的情态动词有can/could、may/might、must、need、shall/should、will/would 等。
例如:“You must study hard(你必须努力学习。
)”“Can you swim?(你会游泳吗?)”二、动词的时态1、一般现在时表示经常发生的动作或存在的状态。
当主语是第三人称单数时,动词要发生相应的变化,一般在动词词尾加 s 或 es。


初中英语动词分类讲解动词的分类1. 实义动词实义动词时能独立作谓语的动词。
根据动词在句子中是否可以接宾语,可以把实义动词分为及物动词和不及物动词两种类型。
按其持续性可分为延续性动词和非延续性动词。
(1)及物动词及物动词本身意义不完整,需要接宾语才能使其意思完整。
①动词+宾语My brother is flying the kite on the playground.②动词+宾语+宾补The teacher made his students happy by doing some games.We call the bird Polly.注意:省略to的不定式或现在分词作宾补的动词有:make, let,have, see, watch, notice, hear等。
③动词+双宾语My mother gives me a new bike.注意:有些双宾语动词间接宾语(人)放在直接宾语(事物)后时,间接宾语前要加to。
常用的此类词有bring、give、hand、 pass、pay、post、return、sell、show、teach、tell、throw、lend等。
Hand me that book, please. = Hand that book to me, please.有些双宾语动词间接宾语(人)放在直接宾语(事物)后时,间接宾语前要加for。
常用的此类词有buy、choose、cook、draw、book、find、get、make、order等。
My mom bought me a nice backpack. = My mom bought a nice backpack for me.(2)不及物动词不及物动词一般不可以接宾语,但是有些不及物动词与一些介词、副词等词搭配在一起构成短语动词,它的作用等于一个及物动词。
We arrived at the station at five.He turned off the light when he left.He takes pride in doing a job well.注意:有些动词既可作及物动词也可作不及物动词。

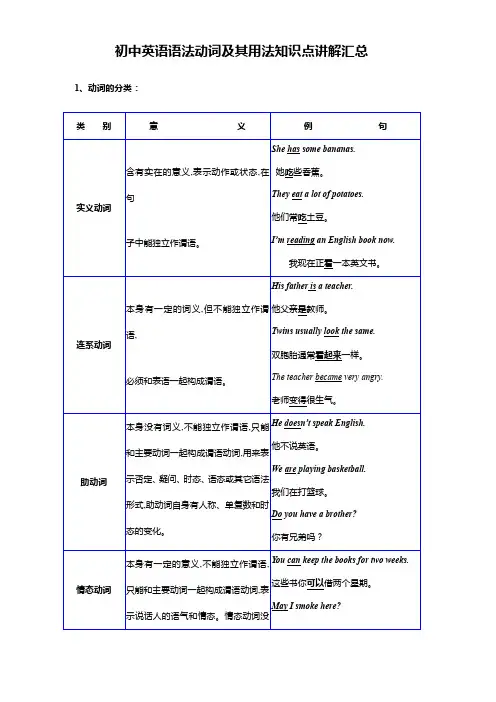
语法动词知识点一、动词的分类。
1. 实义动词(行为动词)- 及物动词(vt.):后面必须跟宾语意义才完整的实义动词。
例如:I love apples.(“love”是及物动词,“apples”是它的宾语)- 不及物动词(vi.):本身意义完整后面不须跟宾语的实义动词。
例如:He runs fast.(“runs”是不及物动词,不需要宾语就能表达完整的意思)2. 系动词(link - v.)- 状态系动词:be(is, am, are, was, were等),用来表示主语的状态。
例如:She is happy.- 持续系动词:keep, remain等,表示主语继续或保持一种状况或态度。
例如:The weather keeps cold.- 表像系动词:seem, appear等,看起来像……。
例如:He seems tired.- 感官系动词:look(看起来)、sound(听起来)、smell(闻起来)、taste (尝起来)、feel(感觉起来)。
例如:The flower smells sweet.- 变化系动词:become, get, turn等,表示主语变成什么样。
例如:The leaves turn yellow in autumn.3. 助动词(aux. v.)- be(am/is/are/was/were):用于进行时态和被动语态。
例如:She is reading a book.(进行时态);The book was written by him.(被动语态)- do/does/did:用于构成疑问句和否定句,以及强调句等。
例如:Do you like music?(疑问句);He doesn't go to school on Sunday.(否定句);I do love you.(强调句)- have/has/had:用于完成时态。
例如:I have finished my homework.4. 情态动词(modal v.)- can/could:表示能力(过去式为could)、许可(在口语中常用)等。
初中英语语法动词及其用法知识点讲解汇总1、动词的分类:★重要注解:(1) 关于实义动词:①英语的实义动词又可分为及物动词和不及物动词两大类:后面必须跟宾语意义才完整的叫及物动词;本身意义完整,后面不需跟宾语的叫不及物动词。
②有些动词通常只作不及物动词。
如:go,come,happen,lie,listen,rise,arrive,hall等。
有些动词通常用作及物动词。
如:say, raise, lay, find, buy等。
③大多数动词可以兼作及物动词和不及物动词。
如:study, sing等。
④有些动词作及物动词与作不及物动词时的意义有所不同。
如:know, wash等。
⑤有些动词常和介词、副词或其它词类一起构成固定词组,形成短语动词。
如:listen,reply,wait,look.(2) 关于连系动词:①连系动词用来连接主语和表语,连系动词后面常为形容词。
②常见的连系动词有:be、become、look、feel、sound、smell、taste、seem、turn、grow、get、go、fall、sit、stand、lie 等。
③有些连系动词来源于实义动词,意思也跟着变化:look(看→看起来)、feel(感觉、摸→感到)、smell(闻、嗅→闻起来)、taste(尝→尝起来)、turn(翻转、转动→变得)、grow(生长→变得)、get(得到、到达→变得)、go(去→变得),所不同的是,作为实义动词时,后面不能跟形容词。
[注释]become、get、go、be、grow、turn的用法区别:become表示“变成”,比较正式,通常不用将来时表示动作已经完成。
get也表示动作已经完成,但是更加口语化,通常表示温度、时间、岁数等变化。
go表示“变得”,常见于某些短语中,后面常有形容词bad、blind、hungry等。
be表示“是、成为、当”,多用于将来时、祈使句或不定式中。
grow表示“变得”,常指逐渐的变化,表示身高、岁数的增长。
一、选择题1.I don't have a Ping-Pong ball, _______ my brother _______.A.but; do B.and; does C.and;do D.but; does 2.Jim a basketball?A.Does; have B.Does; has C.Is; have3.I don’t have a baseball, but AlanA.do B.does C.have D.has 4.—Listen! I can hear someone __________ for help.—Is there __________?A.calling; anything wrong B.call; anything wrongC.calling; wrong anything D.call; wrong anything5.—David, you got any tea?—Yes. Would you like some?A.have B.do C.has6.What kind of music ________ he ________?A.does; listen B.does; listen to C.is; listen D.is; listen to7.A number of visitors ________visiting our school. The number of them________ about 180. A.is;are B.are; is C.is; is D.are; are8.I tried to make the baby ________by singing, and that worked well at last.A.stop crying B.to stop crying C.stop to cry D.to stop to cry 9.—What will the weather _______tomorrow?— It is going to_______ .A.be like; rainy B.be like; rain C.like; rain D.like; rainy 10.Amy and her best friend often________books together.A.read B.reads C.look D.looks 11.—The books on the table_________ Mike’s, right?—Yes, they are.A.am B.is C.are12.Kay looked _________ at the guests who said that the food she cooked tasted _________. A.happily; wonderfully B.happily; wonderfulC.happy; wonderful D.happy; wonderfully13.—I am feeling ill. What should I do?— eating junk food and breakfast every day.A.Stop; having B.Stop; have C.To stop; have. D.To stop; to have 14.—How much ________ this pair of socks?—Two dollars for one pair.A.am B.is C.are15.—Let him __________us to learn English, OK? —Great!A.Helps B.to help C.help D.helping 16.— When and where shall we meet?— Let's ________it half past nine.A.meet B.make C.do17.—What __________ he do? —He __________ an actor.A.is, is B.does, does C.does, is D.is, does 18.Our teachers always make us ________ a lot of homework.A.to do B.do C.does D.doing 19.— How ________ your trip to Australia?—Great. I’ll go there again next year.A.was B.is C.are D.were20.—I saw Betty go to Grandpa Zhang’s home just now.—Yes, she is often seen ________ the old man with his housework.A.help B.to help C.helps D.helped 21.As we all know, the Anti-Japanese War ________ in 1937, and ________ for eight years. A.was broken out; lasted B.broke into;lastedC.broke out; was lasted D.broke out;lasted22.Let’s_________ and play football.A.go B.to go C.going23.— Look at my new watch.—Well, it’s so cool! When and where________you buy it?A.Do B.will C.did D.Are 24.—Do you have an art festival at school?—Yes, ________.A.we have B.we can C.we do25.This pair of pants______gray. What color________your pants?A.are; are B.is;is C.is;are【参考答案】***试卷处理标记,请不要删除一、选择题1.D解析:D【解析】【分析】【详解】句意:我没有乒乓球,但是我兄弟有。
初中英语语法专题—动词讲解动词是英语语法中的重要部分,它用于表示动作、状态或存在。
掌握动词的用法对于正确使用英语至关重要。
以下是初中英语中常见动词的讲解。
一. 动词的分类动词可以分为以下几类:1. 行为动词:表示人或物体的动作,如"run"(跑)、"eat"(吃)等。
行为动词:表示人或物体的动作,如"run"(跑)、"eat"(吃)等。
例句:He runs every morning.(他每天早上跑步)2. 状态动词:表示人或物体的状态,如"be"(是)、"seem"(似乎)等。
状态动词:表示人或物体的状态,如"be"(是)、"seem"(似乎)等。
例句:She is happy today.(她今天很开心)3. 助动词:用于构成各种时态、语态和情态动词,如"be"、"do"、"have"等。
助动词:用于构成各种时态、语态和情态动词,如"be"、"do"、"have"等。
例句:I have been to London.(我去过伦敦)4. 情态动词:用于表示说话者的意图、愿望、能力、许可等,如"can"(能)、"may"(可能)等。
情态动词:用于表示说话者的意图、愿望、能力、许可等,如"can"(能)、"may"(可能)等。
例句:You can go home now.(你现在可以回家了)二. 动词的时态动词的时态用于表示动作或状态发生的时间。
常见的时态有以下几种:1. 一般现在时:表示经常性或惯性的动作或状态。
一般现在时:表示经常性或习惯性的动作或状态。
动词分类及基本用法动词是英语中最重要的词类之一,对于学习英语语法和表达有着至关重要的作用。
动词的种类繁多,用法也各有不同。
接下来,让我们一起深入了解动词的分类及基本用法。
一、动词的分类1、实义动词实义动词是表示具体动作或状态的动词,又可以分为及物动词和不及物动词。
及物动词后面必须跟宾语,意思才能完整。
例如,“I love you”中的“love”就是及物动词,“you”是宾语。
不及物动词本身意义完整,后面不需要跟宾语。
例如,“He runs fast”中的“runs”就是不及物动词。
2、系动词系动词用于连接主语和表语,表示主语的身份、性质、状态等。
常见的系动词有 be(am/is/are/was/were)、seem、look、feel、sound、taste、smell 等。
例如,“She looks beautiful”中“looks”就是系动词。
3、助动词助动词主要用于协助主要动词构成各种时态、语态、语气等。
常见的助动词有 do/does/did、have/has/had、will/would、shall/should 等。
例如,“He doesn't like coffee”中的“doesn't”就是助动词。
4、情态动词情态动词表示说话人的态度、情感或推测等。
常见的情态动词有can/could、may/might、must、shall/should、will/would、ought to 等。
情态动词后面接动词原形。
例如,“You must study hard”中的“must”就是情态动词。
二、动词的基本用法1、实义动词的用法(1)及物动词及物动词在句中必须接宾语,宾语通常是名词、代词、动名词或从句。
例如:“She reads a book every day”(宾语是“a book”);“I enjoy playing football”(宾语是“playing football”);“He knows what I mean”(宾语是“what I mean”)。
初中英语语法知识点整理总结-动词动词是句子的中心词,用来表示人或物的动作、状态、变化等。
掌握动词的正确使用对于研究英语语法至关重要。
以下是初中英语动词知识点的整理总结:1. 动词的分类- 及物动词:表示动作的动词,需要带宾语才能构成完整的意义。
例如:read(读),eat(吃)。
- 不及物动词:表示动作的动词,不需要带宾语。
例如:run (跑),sleep(睡觉)。
- 连系动词:表示状态的动词,连接主语和表语,没有实际意义。
例如:be(是),seem(似乎)。
2. 动词的时态- 现在时:表示目前正在进行的动作或状态。
例如:I read a book.(我正在读一本书。
)- 过去时:表示过去发生的动作或状态。
例如:She ate an apple yesterday.(她昨天吃了一个苹果。
)- 将来时:表示将来要发生的动作或状态。
例如:They will go to the zoo tomorrow.(他们明天会去动物园。
)3. 动词的语态- 主动语态:表示主语是动作的执行者。
例如:Jim cleans the room.(吉姆打扫房间。
)- 被动语态:表示主语是动作的承受者。
例如:The room is cleaned by Jim.(房间被吉姆打扫了。
)4. 动词的情态- can:表示能力或许可。
例如:She can swim.(她会游泳。
)- must:表示必须。
例如:You must finish your homework.(你必须完成你的作业。
)- should:表示建议或义务。
例如:You should help others.(你应该帮助别人。
)以上是初中英语动词的一些基本知识点,希望对你的研究有所帮助。
一、选择题1.—Where_______you come from?—I______from JapanA.are; am B.are; come C.do; come2.—Do you like watching cooking programs on TV?—No, I don’t , but my twin brother . He's very fond of cooking.A.does B.do C.is D.are3.Kay looked _________ at the guests who said that the food she cooked tasted _________. A.happily; wonderfully B.happily; wonderfulC.happy; wonderful D.happy; wonderfully4.Parents always hope their children a happy and healthy life.A.to live B.can live C.living D.should live 5.The woman made her husband_______ outside the gate yesterday afternoon.A.wait B.waiting C.to wait D.waited6.My parents don’t_______me eat_______junk food.A.like; too many B.want; too muchC.ask; too many D.let; too much7.The library ______ from 8 a.m. to 3 p.m. on weekdays. But it______ at 5 p.m. on Saturdays and Sundays.A.is open; closes B.opens; closed C.is opened; closes D.is opening; is closed 8.—Why ______ you so busy these days?—Because they arrived ______ London ______ the morning of July1.A.are; in , in B.are; in , on C.do; on , in D.do; at , on 9.—William, your hat _______ nice.—Thanks.A.buys B.looks C.finds10.This is a photo of my grandpa. He youngA.looks B.feels C.sounds D.hears 11.—He’s never been late for school.—________________.A.So have I B.So am I C.Neither have I D.Nor am I12.In the past he often made his sister____, but now he is often made ___by his sister.A.to cry; to cry B.cry; cryC.to cry; cry D.cry; to cry13.This pair of pants______gray. What color________your pants?A.are; are B.is;is C.is;are14.—How much ________ this pair of socks?—Two dollars for one pair.A.am B.is C.are15.________he_______big________?A.Does; has; foot B.Does; have; feet C.Do; have; foots 16.—Would you like to try some pizza?—Yes, please. It lovely and nice.A.sounds, sees B.looks, smells C.hears, turns D.sounds, watches 17.—I am feeling ill. What should I do?— eating junk food and breakfast every day.A.Stop; having B.Stop; have C.To stop; have. D.To stop; to have 18.—________ you Mary? —Yes, I ________.A.Are; is B.Is; am C.Are; am D.Am; is19.I have bought a Chinese – English dictionary. When and where_____ you _____ it? A.have, bought B.did buy C.will, buy D.do , buy 20.Karen and Helen _______ my brother's friends. I know _______.A.is; her B.are; them C.are; her D.is; them 21.When did your father your mother?A.marry B.marry to C.marry with D.get married 22.A lot of good teachers __________ their students.A.are strict with B.is strict with C.are strict in23.The air _______ fresh after the rain. And the sky is blue.A.feels B.tastes C.smells D.sounds24.________your brother________ a baseball?A.Do; have B.Does; has C.Does; have D.Do; has 25.There________some water in the bottle.A.is B.am C.are D.be【参考答案】***试卷处理标记,请不要删除一、选择题1.C解析:C【解析】【分析】【详解】句意:——你来自哪里?——我来自日本。
考查特殊疑问句。
are是,一般主语是复数;am是,一般与I连用;come来;do助动词或实义动词。
该句是在问:来自哪里,属于一般现在时态。
根据问句中的come from是动词短语,可知该问句要借助助动词does或者是do而不借助于be动词,因为句中问的是you,不是第三人称单数,所以要借助于助动词do。
只有选项C符合题意。
故选C。
2.A解析:A【解析】【详解】句意:——你喜欢看电视上的烹饪节目吗?——不,我不喜欢,但是我的双胞胎哥哥/弟弟喜欢。
他非常喜欢烹饪。
此处用助动词代替动词,用来表示刚提到的动作,以避免重复,排除C和D;主语是my twin brother,第三人称单数,助动词用第三人称单数形式does。
故选A。
3.B解析:B【解析】【详解】句意:Kay高兴地看着客人,他们说她做的菜味道好极了。
考查实义动词与系动词用法。
本题中“looked _______ at”中的look表示“看”这个动作,在此句中属于实义动词,应用副词happily来修饰;“she cooked tasted ______”中的taste“尝起来”属于感官动词,其后应接形容词wonderful来表示“尝起来味道很好”。
故选B。
4.B解析:B【解析】【详解】句意:父母总是希望他们的孩子能过得健康快乐。
考查宾语从句。
hope后要么直接接动词不定式作宾语,要么接宾语从句。
此处是省略引导词that的宾语从句,此处缺从句的谓语,所以用情态动词+动词原形作谓语,又此处不构成虚拟语气,所以排除D,故选B。
5.A解析:A【解析】【详解】句意:昨天下午那个女人让她的丈夫在门外等待。
考查非谓语动词。
wait动词原形;waiting动名词或现在分词形式;to wait动词不定式;waited过去分词。
make是使役动词,后接不带to的不定式作宾语补足语,make sb. do sth.让某人做某事,故选A。
6.D解析:D【解析】【详解】句意:我的父母不让我吃太多垃圾食品。
考查动词辨析及形容词短语。
like 喜欢;want想要,常用于句型want sb. to do sth.;ask 问,要求,常用于句型ask sb. to do sth.;let让,常用于句型let sb. do sth.;too many太多,修饰可数名词;too much太多,修饰不可数名词。
根据句子结构可知,句子使用了动词原形eat在句中作宾补,只有let的句型符合;第二个空后的junk food是不可数名词,用too much修饰。
故选D。
7.A解析:A【解析】【详解】句意:图书馆平日里从早上8点开到下午3点是开着的。
但是它在星期六和星期天下午5点关门。
考查形容词和动词辨析。
is open开着的;closes关闭;opens打开;closed关闭;is opened 被打开;is opening即将开业;is closed关着的。
根据第一句中“from 8 a.m. to 3 p.m. on weekdays”可知,此处是“在平日里早上8点到下午3点这个时间段内,图书馆是开着的”,所以此处用系表结构表示图书馆是开着的这个状态,所以第一空使用is open;第二句句中“at 5 p.m. on Saturdays and Sundays”是“时间点”,表示“在五点关门”,句中主语是it,所以第二空使用动词close的第三人称单数形式closes。
故选A。
8.B解析:B【解析】【详解】句意:——你(们)这些天为什么这么忙?——因为他们在7月1日的早上到达了伦敦。
考查be动词和介词辨析。
根据问句中busy是形容词,主语是they,所以此处应使用be动词are,构成系表结构are busy;第二句中London表示“大地点”,所以此处使用arrive in London;第二句中the morning of July1表示“7月1日的早上”,属于具体某一天的早上,所以前面使用介词on。