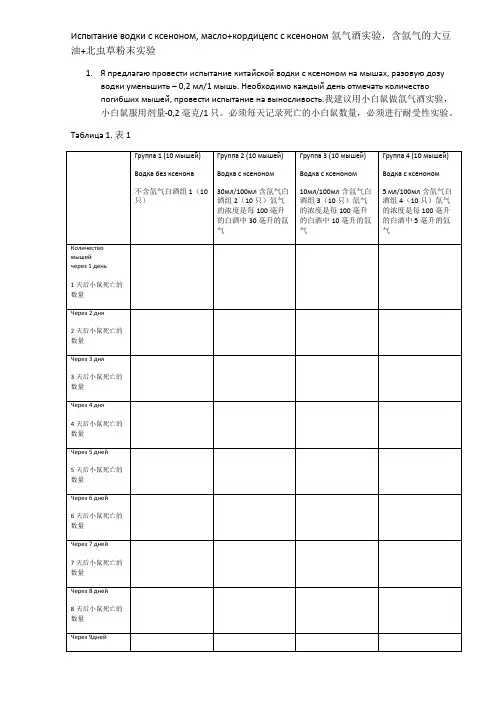
实验经过流程图举例
- 格式:doc
- 大小:233.36 KB
- 文档页数:11

有机化学实验工业乙醇的蒸馏流程图英文回答:Industrial Ethanol Distillation Process Flowchart.Industrial ethanol is a versatile solvent that is used in a wide range of applications, including as a fuel, a feedstock for the chemical industry, and a beverage. Ethanol is typically produced by the fermentation of sugars derived from corn, sugarcane, or other biomass sources. The resulting fermented broth contains ethanol, water, and other impurities. To obtain pure ethanol, the fermented broth must be distilled.The industrial ethanol distillation process consists of the following steps:1. Pre-treatment: The fermented broth is first pre-treated to remove solids and other impurities. This can be done by filtration, centrifugation, or other methods.2. Distillation: The pre-treated broth is thendistilled in a distillation column. The distillation column is a vertical vessel that is divided into a number of plates or trays. As the broth flows down the column, it comes into contact with a stream of warm ethanol vapor rising from the bottom of the column. The ethanol vapor condenses on the plates and flows back down the column. The water and other impurities in the broth remain in a liquid phase and are collected at the bottom of the column.3. Rectification: The ethanol vapor that condenses on the plates is not pure ethanol. It contains some water and other impurities. To obtain pure ethanol, the condensed vapor is rectified in a second distillation column. The rectification column is similar to the distillation column, but it has more plates and a higher reflux ratio. Thereflux ratio is the ratio of condensed vapor that is returned to the column to the amount of product that is taken off. The higher the reflux ratio, the purer the product will be.4. Dehydration: The rectified ethanol still contains a small amount of water. To remove the water, the rectified ethanol is dehydrated using a molecular sieve. A molecular sieve is a material that selectively adsorbs water molecules. The dehydrated ethanol is then cooled and stored.The industrial ethanol distillation process is a complex and energy-intensive process. However, it is an essential process for the production of pure ethanol.中文回答:工业乙醇蒸馏流程图。


有机实验蒸馏及沸点的测定流程图英文回答:Distillation is a commonly used technique in organic chemistry to separate and purify different components of a mixture based on their boiling points. The process involves heating the mixture to vaporize the more volatile component, and then condensing the vapor back into a liquid to collect the purified compound.The first step in the distillation process is settingup the apparatus. This typically includes a round-bottom flask to hold the mixture, a distillation column or fractionating column to separate the vapor, a condenser to cool and condense the vapor, and a collection flask to collect the purified liquid.Once the apparatus is set up, the next step is to heat the mixture. This is usually done using a heating mantle or a Bunsen burner. As the mixture is heated, the compoundwith the lower boiling point will vaporize first. The vapor rises up through the distillation column, where it undergoes repeated condensation and vaporization. Thishelps to separate the different components of the mixture.The vapor then enters the condenser, where it is cooled and condensed back into a liquid. The condenser is usuallya coiled tube that is surrounded by cold water or a cooling bath. The purified liquid drips down into the collection flask, while any remaining impurities or higher boilingpoint compounds are left behind in the round-bottom flask.To determine the boiling point of the purified compound, a thermometer is usually placed in the distillation columnor in the vapor path. As the temperature rises, the boiling point of the compound is reached, and the vapor starts to condense. The boiling point is typically recorded when the temperature remains constant for a period of time.For example, let's say we have a mixture of ethanol and water. Ethanol has a lower boiling point (78.4°C) compared to water (100°C). By heating the mixture, the ethanol willvaporize first and rise up through the distillation column. The vapor is then condensed back into a liquid, and the purified ethanol is collected in the flask. The boiling point of ethanol can be determined by monitoring the temperature during the distillation process.中文回答:蒸馏是有机化学中常用的一种技术,用于根据物质的沸点将混合物中的不同成分进行分离和纯化。

实验方案流程图模板下载温馨提示:该文档是我店铺精心编制而成,希望大家下载以后,能够帮助大家解决实际的问题。
文档下载后可定制随意修改,请根据实际需要进行相应的调整和使用,谢谢!并且,本店铺为大家提供各种各样类型的实用资料,如教育随笔、日记赏析、句子摘抄、古诗大全、经典美文、话题作文、工作总结、词语解析、文案摘录、其他资料等等,如想了解不同资料格式和写法,敬请关注!Download tips: This document is carefully compiled by theeditor. I hope that after you download them,they can help yousolve practical problems. The document can be customized andmodified after downloading,please adjust and use it according toactual needs, thank you!In addition, our shop provides you with various types ofpractical materials,such as educational essays, diaryappreciation,sentence excerpts,ancient poems,classic articles,topic composition,work summary,word parsing,copy excerpts,other materials and so on,want to know different data formats andwriting methods,please pay attention!实验方案流程图一、实验目的[具体说明实验的目的和预期结果。
]二、实验材料和设备1. 实验材料:[列出所需的材料名称、规格和数量。

试验检测步骤图试验检测流程图烘干箱操作规程一、作业前准备1、接上电源后,即可开启工作加热开关。
二、作业中要求2、再将控制器旋钮由0℃位置按顺时针方向旋至达成设置温度,此时箱内开始升温,指示灯亮作指示。
3、当温度升到所需工作温度时此时可再把旋钮作微调至指示灯熄灭处为其恒温(很可能在恒温时,温度仍继续上升,此乃余热影响,此现象约半小时左右即会处于稳定)。
当箱内温度稳定时(即所谓“恒温状态”,如温度计上读数超出或低于所需温度,则可控温器再稍微调整,以达成正确程序为止)。
4、恒温时,可关闭一组加热器工作,以免功率过大,影响恒温灵敏度。
5、温度恒温时,可依据试验需要,令其作一定时间恒温,在此过程,可借箱内控制恒温器自动控温,而不需另加人工管理。
6、欲观察工作室试品情况,可开启箱外门、借箱内一玻璃门观察之。
但箱门以不常开启为宜,以免影响恒温,而且当温度升至300℃时,开启箱门可能使玻璃门急骤冷却而破裂。
三、作业后要求7、停止工作后,关闭电源,待冷却至室温时,清洁箱内卫生。
仪器设备管理制度一、仪器设备管理,包含设备购置、审批、验收、使用、维修、养护、保养、检定/校准、标识、降低、封存、报废等。
二、检验仪器设备购置应由试验单位提出书面购置申请汇报,包企业测试中心审批,经企业主管领导同意后,固定资产部分有企业测试中心购置,低值易耗品由使用单位购置。
三、一起设备到位后,由设备管理员组织开箱验收调试;且检定/校准。
四、验收合格检测设备应立即建立设备档案,并编号登入分帐。
五、珍贵、精密、大型检测设备应由专业技术人员依据仪器使用说明书制订操作规程,经主任审批后上墙。
六、检测仪器设备应严格按操作规程操作,每次使用前后应检验设备情况,并填写使用统计。
七、试验仪器设备使用过程中若发生故障,维修后进行检定,合格后方准使用并填写仪器设备维修统计、存档。
八、大型试验设备不得随意搬动,若需搬动,应经室主任同意,并指定具体搬运方案,安装后重新进行判定/校准。
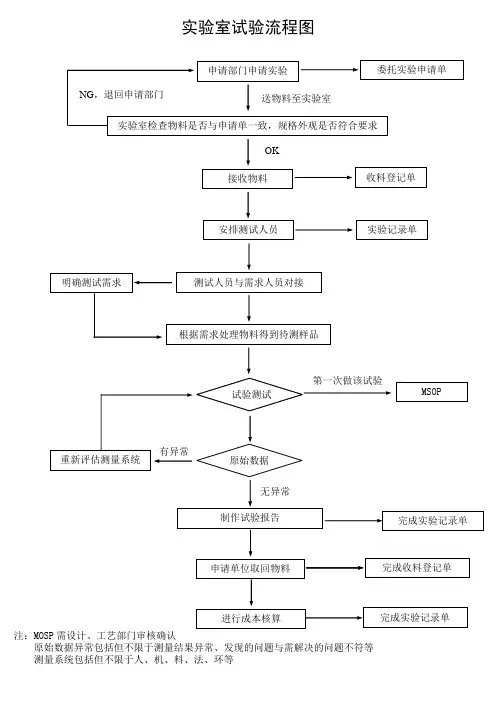
实验室试验流程图
第一次做该试验
试验测试 实验室检查物料是否与申请单一致,规格外观是否符合要求
无异常
有异常
或与 收料登记单
明确测试需求 注:MOSP 需设计、工艺部门审核确认
原始数据异常包括但不限于测量结果异常、发现的问题与需解决的问题不符等 测量系统包括但不限于人、机、料、法、环等 接收物料 安排测试人员 实验记录单
测试人员与需求人员对接
MSOP
试验测试 原始数据
重新评估测量系统 制作试验报告 完成收料登记单
申请单位取回物料 完成实验记录单
根据需求处理物料得到待测样品
申请部门申请实验
委托实验申请单
送物料至实验室 OK
NG ,退回申请部门 进行成本核算
完成实验记录单。

初中生物实验操作图解教案
实验目的:通过观察水中浮游生物,了解水中生物的多样性及其生态意义。
实验材料:显微镜、玻璃片、草溪水样本、滤纸、显微镜载玻片、显微镜盖玻片、移液管、草溪水样本。
实验步骤:
1. 取一滤纸,在滤纸上滴一滴草溪水样本。
2. 将玻璃片轻轻压在草溪水样本上,使水样本在玻璃片上均匀分布。
3. 将玻璃片放在显微镜载玻片上。
4. 在载玻片的水样本下方加一滴水,使水样本在载玻片下顺利移动。
5. 轻轻放置显微镜载玻片在显微镜上,调节显微镜使图像清晰。
6. 用移液管在玻璃片上滴水,使浮游生物随着水流动。
7. 观察显微镜中的浮游生物,观察它们的形态、大小等特征。
实验注意事项:
1. 操作显微镜时要小心轻放,以免损坏显微镜。
2. 使用滤纸时要注意滤纸的干净,以免污染实验样本。
3. 操作过程中注意个人卫生,避免实验污染。
4. 实验结束后要及时清理实验工具,并保持实验室整洁。
实验概述:通过观察水中浮游生物,学生可以了解水中生物的多样性及其在生态系统中的
作用,培养学生对生物多样性的认识和保护意识。

初中化学教材实验图解1、测定空中里氧气的含量现象:红磷燃烧,产生大量的白烟,烧杯中的水倒流进入集气瓶,集气瓶水面上升约1/5结论:氧气约占空气总体积的1/5红磷量要足的原因:为了耗尽集气瓶内的氧气注意:不能用木炭代替红磷,因为木炭燃烧生成了二氧化碳气体,瓶内压强不变;不能用铁丝代替红磷,因为铁丝在空气中不能燃烧2、硫在氧气中燃烧预先放少量水或氢氧化钠溶液的目的:吸收二氧化硫气体,防止空气污染3、铁丝在氧气中燃烧①预先放少量水的目的:防止高温熔融物溅落到瓶底,使集气瓶炸裂②下端系一根火柴的目的:引燃铁丝③盘成螺旋状的目的:增大铁丝受热面积4、过氧化氢的分解二氧化锰的作用:加快过氧化氢的分解速率,但质量和化学性质不会改变4、探究分子的性质实验现象:烧杯A溶液变红,烧杯溶液不变色解释:浓氨水能使酚酞变红(呈碱性)且具有挥发性结论:分子总是在不断运动着5、电解水口诀:正氧负氢现象:①两个电极上均有气泡产生,②正负两极产生的气体体积比=1∶2,③正极产生的气体能使带火星的木条复燃负极产生的气体能燃烧,火焰呈淡蓝色结论:水是由氢元素和氧元素组成的6、质量守恒定律小气球的作用:使装置封闭,平衡压强,收集气体现象:气球先鼓起后变瘪解释:红磷燃烧放热,小气球鼓起,冷却后,小气球变瘪。
原因:红磷燃烧消耗了锥形瓶内的氧气,气体减少,压强减小。
现象:天平不平衡解释:盐酸和碳酸钠粉末反应生成的二氧化碳气体逸出结论:遵守质量守恒定律现象:天平不平衡解释:镁条燃烧时,空气中的氧气参加了反应 结论:遵守质量守恒定律 7、木炭还原氧化铜现象:黑色粉末逐渐变成红色,澄清的石灰水变浑浊 分析:木炭具有还原性金属网罩的作用:使火焰集中,提高温度 8、二氧化碳的性质实验现象:下层的蜡烛先熄灭,上层的蜡烛后熄灭 结论:二氧化碳的密度比空气大, 二氧化碳不能燃烧也不支持燃烧现象:塑料瓶变瘪结论:二氧化碳溶于水,使瓶内压强减小 9、二氧化碳与水的反应10、燃烧条件的探究现象:①铜片上的白磷燃烧而红磷不燃烧 ②水中的白磷也不燃烧解释:①热水的温度达到了白磷的着火点,而没有达到红磷的着火点,所以红磷不燃烧②热水的温度虽然达到了白磷的着火点但烧杯中的白磷没有与氧气接触,所以烧杯中的白磷不燃烧现象:通入氧气后,热水中的白磷燃烧 结论:燃烧需要三个条件: ①可燃物②氧气(或空气)③温度达到燃烧所需的最低温度(着火点) 11、实验室制取氧气装置图①试管口放一团棉花:防止加热时高锰酸钾粉末进入导管和水槽 ②试管口向下倾斜:防止冷凝水倒流进入试管底部,炸裂试管 ③导管口有连续气泡时,才可以收集气体④实验结束时:先移导管,再熄灭酒精灯,防止水槽中的水倒流,使试管破裂 12、实验室制取二氧化碳①长颈漏斗的下端管口要插入液面以下,防止生成的气体逸出②长颈漏斗的优点:便于添加液体药品分液漏斗的优点:便于控制反应速率13、一氧化碳还原氧化铁现象:红棕色粉末逐渐变成黑色,澄清的石灰水变浑浊注意事项:实验开始时①先通CO再“开始加热”,防止加热时CO与空气混合发生爆炸;②实验结束时,先“停止加热”再“停止通CO”,防止还原出来的铁粉被氧化。

初中化学教材实验图解1、测定空中里氧气的含量现象:红磷燃烧,产生大量的白烟,烧杯中的水倒流进入集气瓶,集气瓶水面上升约1/5结论:氧气约占空气总体积的1/5红磷量要足的原因:为了耗尽集气瓶内的氧气注意:不能用木炭代替红磷,因为木炭燃烧生成了二氧化碳气体,瓶内压强不变;不能用铁丝代替红磷,因为铁丝在空气中不能燃烧2、硫在氧气中燃烧预先放少量水或氢氧化钠溶液的目的:吸收二氧化硫气体,防止空气污染3、铁丝在氧气中燃烧①预先放少量水的目的:防止高温熔融物溅落到瓶底,使集气瓶炸裂②下端系一根火柴的目的:引燃铁丝③盘成螺旋状的目的:增大铁丝受热面积4、过氧化氢的分解二氧化锰的作用:加快过氧化氢的分解速率,但质量和化学性质不会改变4、探究分子的性质实验现象:烧杯A溶液变红,烧杯溶液不变色解释:浓氨水能使酚酞变红(呈碱性)且具有挥发性结论:分子总是在不断运动着5、电解水口诀:正氧负氢现象:①两个电极上均有气泡产生,②正负两极产生的气体体积比=1∶2,③正极产生的气体能使带火星的木条复燃负极产生的气体能燃烧,火焰呈淡蓝色结论:水是由氢元素和氧元素组成的6、质量守恒定律小气球的作用:使装置封闭,平衡压强,收集气体现象:气球先鼓起后变瘪解释:红磷燃烧放热,小气球鼓起,冷却后,小气球变瘪。
原因:红磷燃烧消耗了锥形瓶内的氧气,气体减少,压强减小。
现象:天平不平衡解释:盐酸和碳酸钠粉末反应生成的二氧化碳气体逸出结论:遵守质量守恒定律现象:天平不平衡解释:镁条燃烧时,空气中的氧气参加了反应结论:遵守质量守恒定律7、木炭还原氧化铜现象:黑色粉末逐渐变成红色,澄清的石灰水变浑浊分析:木炭具有还原性金属网罩的作用:使火焰集中,提高温度8、二氧化碳的性质实验现象:下层的蜡烛先熄灭,上层的蜡烛后熄灭结论:二氧化碳的密度比空气大,二氧化碳不能燃烧也不支持燃烧现象:塑料瓶变瘪结论:二氧化碳溶于水,使瓶内压强减小9、二氧化碳与水的反应10、燃烧条件的探究现象:①铜片上的白磷燃烧而红磷不燃烧 ②水中的白磷也不燃烧解释:①热水的温度达到了白磷的着火点,而没有达到红磷的着火点,所以红磷不燃烧②热水的温度虽然达到了白磷的着火点但烧杯中的白磷没有与氧气接触,所以烧杯中的白磷不燃烧现象:通入氧气后,热水中的白磷燃烧 结论:燃烧需要三个条件: ①可燃物②氧气(或空气)③温度达到燃烧所需的最低温度(着火点)11、实验室制取氧气装置图①试管口放一团棉花:防止加热时高锰酸钾粉末进入导管和水槽 ②试管口向下倾斜:防止冷凝水倒流进入试管底部,炸裂试管 ③导管口有连续气泡时,才可以收集气体 ④实验结束时:先移导管,再熄灭酒精灯,防止水槽中的水倒流,使试管破裂12、实验室制取二氧化碳①长颈漏斗的下端管口要插入液面以下,防止生成的气体逸出②长颈漏斗的优点:便于添加液体药品 分液漏斗的优点:便于控制反应速率(Ⅰ)(Ⅱ) (Ⅲ) (Ⅳ) 烘干 现象 变红 不变色 不变色 变红 红色→紫色 分析 酸能使紫色石蕊变红 水不能使紫色石蕊变红二氧化碳不能使紫色石蕊变红二氧化碳能与水反应生成碳酸,碳酸能使紫色石蕊变红碳酸不稳定,受热易分解成二氧化碳和水13、一氧化碳还原氧化铁现象:红棕色粉末逐渐变成黑色,澄清的石灰水变浑浊注意事项:实验开始时①先通CO再“开始加热”,防止加热时CO与空气混合发生爆炸;②实验结束时,先“停止加热”再“停止通CO”,防止还原出来的铁粉被氧化。