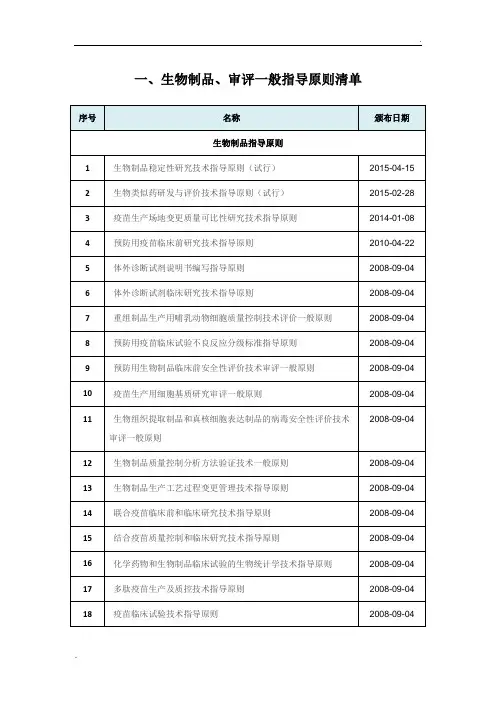
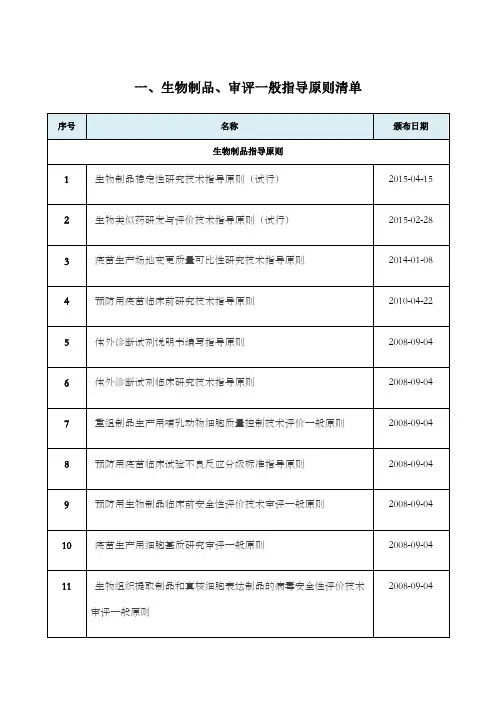
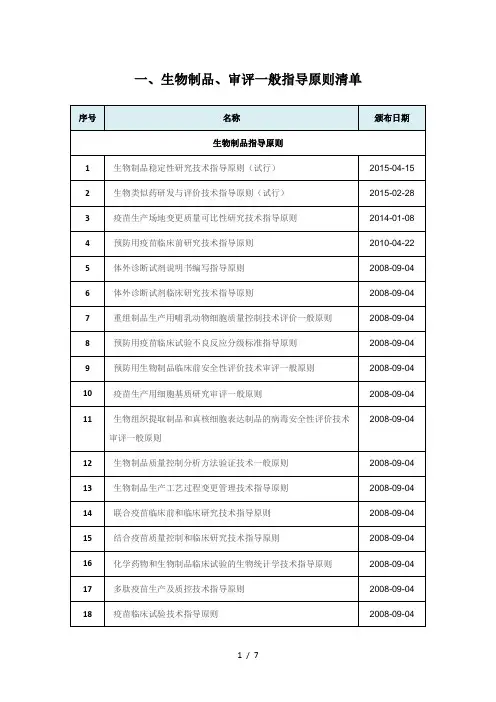
国内外生物制品、审评指导原则及法律法规清单-2017-01-25
- 格式:doc
- 大小:209.50 KB
- 文档页数:7

生物制品生物活性/效价测定方法验证指导原则一、前言对药品质量控制分析方法进行验证的目的是证明采用的方法适合于相应检测要求。
生物制品质量控制中生物活性/效价为反映生物制品有效性的关键质量属性,对相应的测定方法进行规范的验证是保障其适用性的前提。
本指导原则从验证方案的制定、各验证指标的具体验证策略、验证结果的记录和方法的监控及再验证的角度阐述了生物活性/效价测定方法验证相关的要求,旨在对新建的或拟修订的生物制品生物活性/效价测定方法所开展的验证工作进行规范与指导。
本指导原则中的生物活性/效价测定主要是指相对效价测定,该法系将供试品的生物反应与已知标准品产生的反应相比较,从而定量测定供试品相对于标准品的效价。
二、方法验证的基本要素1.验证方案方法验证需根据验证方案来完成。
验证方案不仅应包括验证设计、验证指标、合理的可接受标准和数据分析计划,还应涵盖不符合可接受标准时可采取的措施等。
1.1验证设计验证设计主要涉及样品的选择、实验变异来源的考量及试验重复策略等。
应采用具有代表性的样品进行验证试验,并在验证方案中注明所需样品的类型及数量。
实验变异的来源主要包括样品的制备、试验内和试验间的影响因素。
试验内变异可能受方法开发阶段所确定的实验条件(温度、pH、孵育时间等)、实验设计(动物数量、稀释度组数、每个稀释组的重复数、稀释度间隔等)、试验过程、系统适用性和样品适用性要求、统计分析等因素的影响。
而试验间变异主要受不同分析人员、不同试验时间、不同仪器设备和试剂批次等因素的影响。
因此,一个设计良好的验证方案应综合考量试验内和试验间变异的来源。
此外,每轮验证试验中标准品和供试品均应独立制备。
验证中使用的重复策略应尽量反映影响效价测定结果的实验因素。
1.2验证指标与可接受标准由于相对效价测定方法各具特点,并随分析对象而变化,因此需视具体方法拟订具体的验证指标,关于常见验证指标的具体讨论见本节“2.各验证指标的验证策略”项下。

指导原则编号:【S】G P T2-1预防用生物制品临床前安全性评价技术审评一般原则二零零五年十二月目录一、概述 (2)二、适用范围 (3)三、试验设计中的重点问题 (3)(一)相关动物 (3)(二)免疫毒性 (4)(三)具体问题具体分析 (4)四、研究内容 (5)(一)急性毒性试验 (5)(二)长期毒性试验 (5)(三)局部刺激性试验 (7)(四)过敏试验 (7)(五)生殖毒性试验 (8)(六)其它特殊考虑 (8)1.免疫原性试验和保护力试验 (8)2. 佐剂 (9)3.其它 (10)五、结语 (10)六、参考文献 (10)七、起草说明 (11)八、著者 (117)一、概述预防用生物制品(以下简称疫苗)系指含有抗原、能够诱导人体产生特异性主动免疫的制剂,它可以保护机体免受感染原、毒素,以及感染原引起的抗原性物质的损伤。
疫苗的安全性评价贯穿非临床试验、临床试验和上市后评价。
它包括对原辅材料、生产工艺和过程的控制、理化性质和生物学性质的检定、动物安全性评价、临床安全性评价以及上市后不良反应监测等一系列过程。
本文适用于疫苗的临床前动物安全性评价。
临床前动物安全性评价的主要目的系通过相关动物来考察疫苗的安全性,包括对免疫器官和其它毒性靶器官的影响、毒性的可逆性,以及与临床相关的参数,预测其在大规模人群中使用时可能出现的不良反应,降低临床试验受试者和临床使用者承担的风险,并为临床试验方案的制订提供依据。
疫苗可能导致的毒性反应主要包括:制品成分本身作为毒性物质对机体的直接损伤、诱导免疫系统引起的与免疫相关的毒性,以及污染物和残余杂质引起的毒性。
由于疫苗系通过诱导免疫系统产生抗体及/或效应T细胞发挥作用,因此其最主要的潜在毒性来自与免疫系统相关的毒性,常规药物安全性评价的方法并不完全适用于疫苗。
本文仅代表目前对疫苗安全性评价的基本认识,其中的内容并不完全是注册申请人进行开发时必须完成的内容,仅作为技术审评的一般原则。

国内外生物类似药研究指导原则有很大的不同,但是旨在保护患者的
安全并获得充分的药物疗效。
下面让我们快速看一看国内外生物类似
药研究指导原则的比较。
首先,注册要求为不同的国内外生物类似药研究指导原则提供了不同
的审查要求。
在国外,申请生物类似药的地方有很多,但是国外新药
申请通常要求比国内要求更严格一些。
国外新药申请除了要提供提名
药的药效学,药代动力学和安全性研究证据之外,还要求申请人必须
提供申请提名药的秋季羹准的药物 - 相关的临床研究的结果,以便证实其疗效和安全性。
此外,对制剂要求也有所不同。
在海外,通常会对新药的制造和装配
流程要求更加严格,这样可以确保药品质量,确保患者可以安全实施。
在国内,生产制造商常常只要求按照规定的质量标准生产制造,这样
做更加简单,更容易获得批准。
另外,国内优先用原百威原料生产药品,而国外对各种原料生产都适用。
另外,监督体系也有所不同。
海外的监管机构会更加严格,他们会定
期对新药的效果和安全性进行审核。
而国内的新药申请审查则相对较松,在申请通过后,药品的疗效和安全性的监管也会相对较轻。
总的来说,不管是在国内还是在国外,申请生物类似药的原则和要求
都是一致的,旨在保护患者的安全和实施有效的药物治疗,而有些方
面和要求往往会有所不同,在研究和实施新药前,必须充分了解当地
的新药注册要求。
以上就是国内外生物类似药研究指导原则的比较。
指导原则不仅仅针
对注册要求,对制剂要求和监督体系也有所不同,但所有这些都旨在保护患者的安全,以获得更好的治疗效果。

生物成品GMP查抄指南GMP INSPECTION GUIDELINE FOR BIO-PRODUCT由国家食品药品监督办理局颁布ISSUED BY SFDA OF CHINA1. 机构与人员COMPANY ORGANIZATION AND PERSONNEL→0402:生物成品出产企业出产和质量办理负责人是否具有相应的专业常识〔细菌学、病毒学、生物学、分子生物学、生物化学、免疫学、医学、药学等〕,并具有丰富的实践经验以确保在其出产、质量办理中履行其职责。
Whether the personnel who are in charge of the bio-products production and quality management that have the corresponding knowledge background on Bacteriology, Virology, Biology, Molecular Biology, Biochemistry, Immunology, Medicine,Pharmaceutics etc. and to possess abundant experience to insure fulfilling theresponsibilities in the production and quality management.→0702:从事生物成品制造的全体人员〔包罗清洁人员、维修人员〕是否按照其出产的成品和所从事的出产操作进行专业〔卫生学、微生物学等〕和平安防护培训。
Whether all the personnel (including the cleaning stuff and maintenance stuff) that related with the bio-products production who have received the professional training on production and corresponding knowledge (Hygiene, Microbiology etc.) and security training.2. 厂房与设施PREMISE AND FACILITY→*2201:出产用菌毒种与非出产用菌毒种、出产用细胞与非出产用细胞、强毒与弱毒、死毒与活毒、脱毒前与脱毒后的成品和活疫苗与灭活疫苗、人血液成品、预防成品等加工或灌装是否同时在同一出产厂房内进行。

生物制品相关法规指南汇编English Answer:Guidelines for Regulatory Compliance of Biological Products.Introduction.Biological products are a complex and rapidly evolving field, with new products and technologies emerging all the time. This has led to a growing need for clear and comprehensive regulatory guidance to ensure the safety, efficacy, and quality of these products.Regulatory Framework.The regulatory framework for biological products varies from country to country, but there are some general principles that apply to most jurisdictions. These principles include:Pre-market approval: Biological products must be approved by a regulatory authority before they can be marketed. This approval process typically involves a review of the product's safety, efficacy, and quality.Manufacturing standards: Biological products must be manufactured in accordance with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMPs). GMPs are designed to ensure that products are produced in a consistent and controlled manner.Post-market surveillance: Regulatory authorities typically monitor the safety and efficacy of biological products after they have been marketed. This monitoring can include collecting data on adverse events, conducting clinical trials, and reviewing scientific literature.Specific Regulations.In addition to the general principles outlined above, there are a number of specific regulations that apply to biological products. These regulations vary from country tocountry, but some of the most common include:The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulations for biological products: The FDA has a long history of regulating biological products, and its regulations are considered to be among the most stringent in the world. The FDA's regulations cover a wide range of topics, including pre-market approval, manufacturing standards, post-market surveillance, and product labeling.The European Medicines Agency (EMA) regulations for biological products: The EMA is the European Union's regulatory authority for medicinal products, including biological products. The EMA's regulations are based on the EU's pharmaceutical legislation, and they are similar to the FDA's regulations in many respects.The World Health Organization (WHO) guidelines for the regulation of biological products: The WHO provides guidance on the regulation of biological products to help countries develop their own regulatory frameworks. The WHO's guidelines are based on the latest scientificevidence and best practices.Conclusion.The regulatory landscape for biological products is complex and ever-changing. However, by understanding the general principles and specific regulations that apply to these products, manufacturers and regulators can ensure that they are safe, effective, and of high quality.Chinese Answer:生物制品的相关法规指南汇编。

生物制品验证指导原则英文回答:The principles for validating biological products are essential to ensure their safety, efficacy, and quality. As a regulatory professional in the biopharmaceutical industry, I have extensive experience in following these guidelines. Let me share with you some of the key principles for validating biological products.Firstly, it is crucial to establish a comprehensive validation plan that outlines the specific requirements and objectives of the validation process. This plan should include the scope of the validation, the acceptancecriteria, and the testing methods to be employed. For example, when validating a new vaccine, the plan would outline the necessary tests to assess its efficacy, such as immunogenicity studies in animal models and clinical trials in humans.Secondly, a risk-based approach should be adopted when designing the validation studies. This means that the level of validation required should be proportional to the potential risks associated with the product. For instance, if a biological product is intended for use in critically ill patients, more extensive validation studies may be necessary to ensure its safety and efficacy. On the other hand, if a product is classified as low-risk, a simplified validation approach may be appropriate.Thirdly, validation studies should be conducted using appropriate and validated methods. This ensures that the results obtained are accurate and reliable. For example, when validating the manufacturing process of a monoclonal antibody, analytical methods such as high-performanceliquid chromatography (HPLC) should be used to assess the product's purity and potency.Furthermore, it is important to establish a robust system for documenting and reporting the validation activities. This includes maintaining detailed records of all validation experiments, including the protocols, rawdata, and analysis reports. These records serve as evidence of compliance with regulatory requirements and can be reviewed by regulatory authorities during inspections.Lastly, validation is an ongoing process that should be periodically reviewed and updated as necessary. This is particularly important for biological products due to their inherent complexity and variability. For example, if a manufacturing process undergoes any changes, the validation studies should be repeated to ensure that the product remains safe and effective.中文回答:生物制品验证的原则对于确保其安全性、疗效和质量至关重要。

生物制品统一名称规程生物制品生产、检定用菌种、毒种管理规程生物制品国家标准品的制备和标定规程生物制品分批规程生物制品分装规程吸附百日咳菌苗、白喉、破伤风类毒素混合制剂制造及检定规程吸附百日咳菌苗、白喉类毒素混合制剂制造及检定规程钩端螺旋体菌苗制造及检定规程冻干皮内注射用卡介苗制造及检定规程A群脑膜炎球菌多糖菌苗制造及检定规程冻干皮上划痕用鼠疫活菌苗制造及检定规程皮上划痕人用炭疽活菌苗制造及检定规程冻干皮上划痕人用布氏菌病活菌苗制造及检定规程治疗用布氏菌病菌苗制造及检定规程短棒状杆菌菌苗制造及检定规程流行性乙型脑炎灭活疫苗制造及检定规程冻干流行性乙型脑炎活疫苗制造及检定规程森林脑炎疫苗制造及检定规程人用浓缩狂犬病疫苗制造及检定规程冻干麻疹活疫苗制造及检定规格冻干流行性腮腺炎活疫苗制造及检定规程口服脊髓灰质炎活疫苗制造及检定规程血源乙型肝炎疫苗制造及检定规程冻干黄热活疫苗制造及检定规程吸附精制白喉类毒素制造及检定规程吸附精制破伤风类毒素制造及检定规程成人用吸附精制白喉类毒素制造及检定规程吸附精制白喉、破伤风二联类毒素制造及检定规程精制抗毒素制造及检定规程精制抗蛇毒血清制造及检定规程精制抗炭疽血清制造及检定规程精制抗狂犬病血清制造及检定规程原料血浆采集(单采知浆术)规程人胎盘血白蛋白制造及检定规程人血白蛋白(低温乙醇法)制造及检定规程人血丙种球蛋白制造及检定规程乙型肝炎免疫球蛋白制造及检定规程狂犬病免疫球蛋白制造及检定规程破伤风免疫球蛋白制造及检定规程冻干组织胺丙种球蛋白制造及检定规程冻干人凝血因子Ⅷ浓制剂制造及检定规程冻干人凝血酶原复合物制造及检定规程冻干人纤维蛋白原制造及检定规程冻干基因工程α1b干扰素制造及检定规程冻干基因工程α2a干扰素制造及检定规程冻干精制人白细胞干扰素制造及检定规程旧结核菌素制造及检定规程结核菌素纯蛋白衍化物(TB-PPD)制造及检定规程卡介菌纯蛋白衍化物(BCG-PPD)制造及检定规程布氏菌素制造及检定规程锡克试验毒素制造及检定规程生物制品无菌试验规程生物制品化学规定规程伤寒菌苗制造及检定规程伤寒、副伤寒甲二联菌苗制造及检定规程伤寒、副伤寒甲、乙三联菌苗制造及检定规程生物制品包装规程生物制品储存、运输规程生物制品生产用马匹检疫及管理规程实验动物和动物试验管理规程人二倍体细胞建株、检定及制备疫苗规程生物制品统一名称规程生物制品系指以微生物、寄生虫、动物毒素、生物组织作为起始材料,采用生物学工艺或分离纯化技术制备,并以生物学技术和分析技术控制中间产物和成品质量制成的生物活性制剂,包括菌苗,疫苗,毒素,类毒素,免疫血清,血液制品,免疫球蛋白,抗原,变态反应原,细胞因子,激素,酶,发酵产品,单克隆抗体,DNA重组产品,体外免疫诊断制品等。

附件动物源性医疗器械注册技术审查指导原则(2017年修订版)本指导原则旨在指导注册申请人对动物源性医疗器械的注册申报资料进行准备。
某些医疗器械可能含有动物来源的材料,这些材料是多种多样的,可以构成该器械的主要部件(例如牛/猪源心脏瓣膜、羊肠缝合线、止血材料等)、涂层或者浸渗剂(例如肝素、明胶、胶原等),也可成为生产过程中所用的辅助材料(例如牛脂等)。
动物组织及其衍生物的使用可能会比非生物来源的材料(例如金属、塑料以及织物等)使医疗器械具有更好的性能,但是在另一方面,它们应用到人体则又会增加病毒传播和免疫原性等方面的安全风险,且存在材料表征上的困难,因此对于动物源性医疗器械安全性的评价,需要考虑比常规医疗器械更多方面的内容。
如果注册申请人在准备医疗器械注册申报资料时有上述考虑,将有助于更加充分、科学地评价医疗器械产品的风险受益比。
本指导原则是在注册申报资料中有关的技术性文件(研究资料、风险分析资料、产品技术要求及产品说明书)满足一般性要求的基础上,针对动物源性医疗器械产品的特点提出的需特别关注和增加论述的内容要求。
此外,注册申请人还应按照《医疗器械注册管理办法》(国家食品药品监督管理总局令第4号)、《医疗器械说明书和标签管理规定》(国家食品药品监督管理总局令第6号)、《关于公布医疗器械注册申报资料要求和批准证明文件格式的公告》(国家食品药品监督管理总局公告2014年第43号)以及总局发布的其他相关文件要求并参考YY/T 0771/ISO 22442系列标准等技术性文件提交注册申报资料。
注册申请人应当依据具体产品的特性确定其中的具体内容是否适用。
若不适用,应详细阐述其理由及相应的科学依据。
注册申请人还应依据具体产品的特性对注册申报资料的内容进行充实和细化。
本指导原则是对注册申请人和医疗器械相关管理部门技术审评人员的指导性文件,不限制相关管理部门对该类产品的技术审评以及注册申请人对注册申报资料的准备工作。
治疗用生物制品非临床安全性评价指导原则【S】GPT1-1治疗用生物制品非临床安全性技术审评一般原则药品审评中心二OO七年一月目录一、概述 (1)二、治疗用生物制品的主要特点 (2)三、非临床安全性评价的一般原则 (6)四、非临床安全性评价的主要考虑 (7)五、非临床安全性评价的主要内容和具体要求 (12)六、结语 (18)七、参考文献 (19)2一、概述治疗用生物制品非临床安全性评价的主要目的与化学药物一致,主要为:1)确定潜在的毒性靶器官和毒性反应的性质、程度及其可逆性; 2)推测人体使用的安全起始剂量以及随后的剂量递增方案; 3)确定临床监测的安全性参数。
但是,生物制品非临床安全性研究的方法和内容与常规化学药物存在许多不同之处,常规化学药物的安全性评价方法和模式并不都适用于治疗用生物制品。
生物制品的非临床安全性研究更多强调根据生物制品特点采取具体问题具体分析的原则来评价其安全性,以支持该类生物制品的临床开发和上市批准。
本技术审评一般原则中的治疗用生物制品(以下简称生物制品)是指采用不同表达系统的工程细胞( 如细菌、酵母、昆虫、植物和哺乳动物细胞)所制备的蛋白质、多肽及其衍生物,它包括细胞因子、纤维蛋白溶解酶原激活因子、重组血浆因子、生长因子、融合蛋白、酶、受体、激素和单克隆抗体等。
本技术审评一般原则也可适用于化学合成多肽、从(人)组织提取的单组分的内源性蛋白,但不包括基因治疗产品、体细胞治疗产品、变态反应原制品、由人或动物的组织或者体液提取或者通过发酵制备的具有生物活性的多组份制品、微生态制品、治疗用疫苗、寡核苷酸产品和血细胞组分。
本技术审评一般原则综合考虑了生物制品的特点、药物非临床安全性和有效性评价的一般规律和我国药物研究技术的工作实际,试图科学合理1地阐明治疗用生物制品非临床安全性研究和评价的总体原则,为该类产品的非临床安全性技术审评提供指导,也可为申报单位进行治疗用生物制品非临床安全性研究提供参考。
生物制品生产工艺过程变更管理技术指导原则前言本指导原则适用于已经取得生产文号的生物制品生产过程等发生变更的管理技术指导原则,所指生物制品生产过程变更是指生产者对已获国家药品管理当局批准的生产全过程中的任何过程所进行的任何变动。
包括从开始生产至终产品的全过程,及与生产相配套的辅助设施。
其中包括原液制备,半成品配制及成品分装等;变更后需重新申报按新药管理的或重新申请生产文号的不包括在此范围之内。
本指导原则首先以国家颁布的相关法规及技术指导原则为基础,并应符合国家的相关要求,如国家现行GMP规范要求。
一、原则(一)任何生产过程的改动都是以提高产品的安全性和有效性为基本出发点,在提高或至少不改变最初国家批准产品安全性和有效性的基础上进行相关改进。
(二)拟进行生产过程变更的生产企业应向SFDA提出申请,并递交相关方案和资料,提供证明资料,说明该变更不引起产品质量的内在变化,由SFDA组织专家进行审查并确定变更的类型及应递交的相关材料。
二、概述(一)生产过程变更:根据其对终产品质量的影响,一般分为以下3种情况。
1、变更引起产品内在质量发生改变的,需要按新药申报程序进行申报为I类,请参考《药品注册管理办法》附件4药品补充申请注册事项及申报资料要求;2、变更可能对产品的安全和有效性有影响的为II类,需报SFDA审批;3、一般不影响产品安全性和有效性的为III类,需报SFDA备案。
详见下表。
生产变更分类表(二)生产过程变更均应进行相关的技术评价,并应进行验证。
1.原材料或起始原材料*变更理由说明;*变更后产品有效成分生物学改变情况的研究数据;*变更前、后的有效成分情况的改变、质量标准异同及质量检定报告;*至少连续3批中间产品、原液、成品的质量分析报告及质量标准的修订;*生产过程中有效成分检测及稳定性的数据。
2.培养基主要成份*变更前、后的培养基成份改变情况、检测方法及质量标准和检定报告;*培养基成份改变对产品有效成分生物学影响的技术数据和验证资料;*非BSE牛源地的证明材料。
生物制品近年法规梳理
近年来,生物制品的法规不断发展和完善,重点关注产品质量、安全性以及环保问题。
以下是一些与生物制品相关的近年法规的梳理:
1. 生物制品管理条例(2016年修订):该条例主要针对生物
制品的生产、经营和使用进行管理,明确了生物制品的分类,规定了质量控制、安全监管和责任追究等方面的要求。
2. 生物制品质量管理规范(2018年):该规范是生物制品质
量管理的基本标准,明确了生物制品的质量要求、生产工艺和检验方法等内容,以保证生物制品的质量与安全性。
3. 生物制品GMP认证实施细则(2017年修订):该细则是对
生物制品GMP认证的具体要求和程序进行详细规定,包括认
证申请、评审、验收等流程,以及认证标准和管理要点。
4. 生物制品进出口管理办法(2019年修订):该办法主要针
对生物制品的进出口进行管理,规定了进出口要求、标签和说明书的要求,以及进口生物制品的登记和备案等程序。
5. 生物医药研究与开发支持政策(2019年修订):该政策旨
在促进生物医药领域的研究与开发,包括提供专项资金支持、简化审批程序和鼓励科技创新等方面的政策措施。
6. 生物制品安全事故应急预案(2017年修订):该预案是应
对生物制品安全事故的应急管理措施,规定了事故报告、处置、
调查和责任追究等方面的要求,确保安全事故得到及时有效的处理。
7. 生物制品废弃物管理办法(2018年):该办法主要针对生物制品废弃物的产生、收集、运输和处理进行管理,明确了废弃物分类、运输要求和处理程序,以保护环境和公共安全。
以上是近年来与生物制品相关的一些法规梳理,这些法规的推出和修订旨在提高生物制品的质量与安全性,促进生物制品产业的健康发展。