30外国税制 程黎 范信葵 (3)
- 格式:ppt
- 大小:388.00 KB
- 文档页数:30

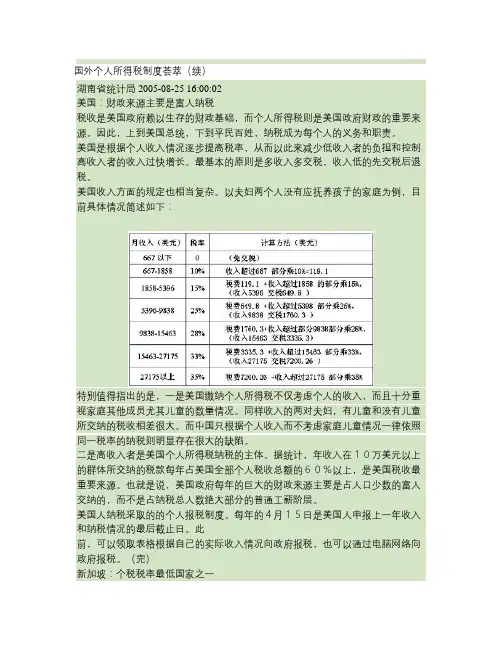
国外个人所得税制度荟萃(续)湖南省统计局 2005-08-25 16:00:02美国:财政来源主要是富人纳税税收是美国政府赖以生存的财政基础,而个人所得税则是美国政府财政的重要来源。
因此,上到美国总统,下到平民百姓,纳税成为每个人的义务和职责。
美国是根据个人收入情况逐步提高税率,从而以此来减少低收入者的负担和控制高收入者的收入过快增长。
最基本的原则是多收入多交税,收入低的先交税后退税。
美国收入方面的规定也相当复杂。
以夫妇两个人没有应抚养孩子的家庭为例,目前具体情况简述如下:特别值得指出的是,一是美国缴纳个人所得税不仅考虑个人的收入,而且十分重视家庭其他成员尤其儿童的数量情况。
同样收入的两对夫妇,有儿童和没有儿童所交纳的税收相差很大。
而中国只根据个人收入而不考虑家庭儿童情况一律依照同一税率的纳税则明显存在很大的缺陷。
二是高收入者是美国个人所得税纳税的主体。
据统计,年收入在10万美元以上的群体所交纳的税款每年占美国全部个人税收总额的60%以上,是美国税收最重要来源。
也就是说,美国政府每年的巨大的财政来源主要是占人口少数的富人交纳的,而不是占纳税总人数绝大部分的普通工薪阶层。
美国人纳税采取的的个人报税制度。
每年的4月15日是美国人申报上一年收入和纳税情况的最后截止日。
此前,可以领取表格根据自己的实际收入情况向政府报税,也可以通过电脑网络向政府报税。
(完)新加坡:个税税率最低国家之一新加坡拥有较为完善的个人所得税征收体系,其中新加坡国内税务局是该国最大的税收机构,负责评估、收取和实施在税收法令下的各种课税。
新加坡是个人所得税税率最低的国家之一,其实行的是13级超额累进税率,也就是以前一年的收入扣除适当项目后,以累计式征税。
每年的4月15日之前,所有应纳税者必须将前一年的各项收入如实填入税务申报登记表中,并及时上报国内税务局。
新加坡的税制是按收入来源地征税的。
新加坡目前的税率为0%至22%。
须纳税的项目包括:在新加坡赚取的收入;以及在新加坡收到的海外收入;属非居民的个人在新加坡所收到的海外收入不需要在新加坡缴税。

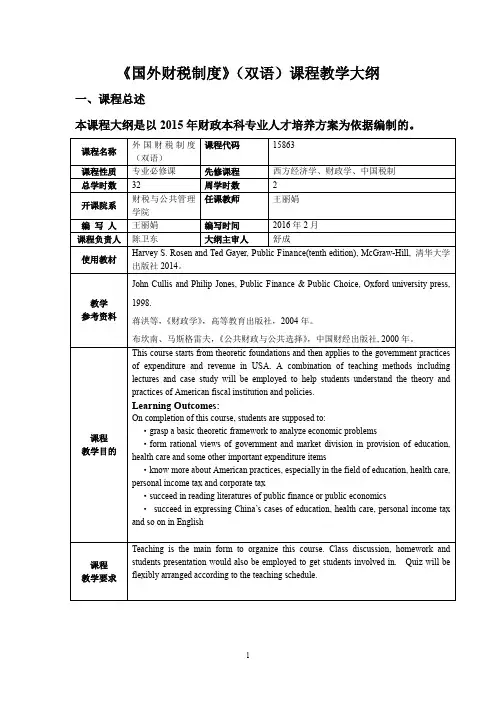
《国外财税制度》(双语)课程教学大纲一、课程总述本课程大纲是以2015年财政本科专业人才培养方案为依据编制的。
二、教学时数分配三、单元教学目的、教学重难点和内容设置Chapter 1 Government At A Glance【Objectives】By learning this chapter, students are going to know more of American government expenditure and revenue. What’s more, they’er supposed to explore and find the datas about the government public finance via internet resources if necessary.【Key points】Federal Government, State and Local Governments, the Size of Government, Budget, Government Expenditures, Government Revenues【Contents】1. Legal Framework2.Unified Budgeternment Expenditureernment RevenueChapter 3 Welfare Economics【Objectives】By learning this chapter, students are supposed to grasp the basic framework of normative analysis, including the two fundamental theorems of welfare economics and the cases when there are market failures.【Key points】Welfare economics, Pareto efficient, Pareto improvement, the first fundamental theorem of welfare economics, fairness, the first fundamental theorem of welfare economics, market failure, government intervention【Contents】1.Welfare economics2.The first fundamental theorem of welfare economics3.Fairness and the second fundamental theorem of welfare economics4.Market failure5.Buying into welfare economicsChapter 7 Education【Objectives】The chapter provides students with a chance to look into the US educational institutions and its fiscal problems concerning education. By comparing the educational practices between China and the US, students will be able to better understand why governments intervene into the field of education.【Key points】public education, government intervention, public good, externality, commodity egalitarianism, charter schools, school voucher, school accountability 【Contents】1.Justifying government intervention in education2.What can government intervention in education accomplish?3.New directions for public educationChapter 9 The Health Care Market【Objectives】The chapter would introduce the unique aspects of the health care market and justify government intervention in the health care provision.【Key points】Health care market, private insurance, social insurance, insurance premium, expected value, actuarially fair insurance premium, expected utility, risk smoothing, risk premium, loading fee, risk pooling, adverse selection, asymmetric information, death spiral, moral hazard, paternalism【Contents】1.The role of insurance2.The role of risk pooling3.Adverse selection in the health insurance market4.Insurance and moral hazard5.Other information problems in the health care market6.Do we want efficient provision of health care?Chapter 10 Government and the Health Care Market 【Objectives】The chapter would discuss the practices of US health care, including private health insurance and the main forms of government provision of health insurance, i.e. Medicare and Medicaid. By analyzing the challenges facing the health care system, proposals as to reform the system are brought about.【Key points】Private health insurance, Employer-provided health insurance, job lock, cost-based reimbursement, fee-for-service, managed care, capitation-based reimbursement, Medicare, hospital insurance, supplementary medical insurance, prospective payment systems, retrospective payment system, Medicaid, health care reform【Contents】1.Private health insuranceernment provision of health insurance: Medicare and Medicaid3.Health care reformChapter 17 The Personal Income Tax【Objectives】This chapter introduces the US personal income tax system. By learning it, students are supposed to learn how to calculate the personal income tax according to the five steps. Detailed explanation will be given as to prove the complexity of tax system.【Key points】adjusted gross income, taxable income, exemption, deductions, rate schedule, capital gain(loss), realized capital gain, unrealized capital gain, imputed rent, lock-in effect, individual retirement account, Roth IRA, 401(k) plan, Keogh Plan, education savings account, itemized deduction, standard deduction, tax credit, tax expenditure, tax reform act of 1986 【Contents】1.Basic structure2.Defining income3.Excludable reforms of money income4.Exemptions and deductions5.Rate structure6.Taxes and inflation7.The alternative minimum tax8.Choice of unit and the marriage tax9.State income taxes10.Politics and tax reform。

346旧中国海关总税务司署通令选编
海关总税务司署通令
第5136号(第二辑)
1935年9月7日于上海
令各关税务司
事由:为1930年中法越南及中国边省关系专约文本事
兹附发关务署第17694号指令抄本及所附1930年5月16日签订之中法越南及中国边省关系专约汉文及法文抄本与各种附件以及两国政府代表间互换之信函抄本,仰即遵行。
另附发关务署第1991号电文抄件,该电通知财政部就专约有关海关部分之施行办法所作之分项规定如下:
(1)专约乙种附表所载之豆蔻,砂仁,肉桂,未硝皮货,木制家具及空破璃瓶等五项商品,其进口税之征收仍应适用现行国定进口税则所规定之税率。
(2)对于直接由越南进口之越南产米及燃率在五或以上之无烟白煤,或凭直接提货单运入云南、广东、广西三省者,其进口税之征收按专约规定,白煤适用每公吨0. 89金单位之约定税率,越米适用每百公斤1. 50金单位之约定税率。
又越米及白煤之救灾附加税及关税附加税,应按上述约定税率各案原定附加税税率百分之五征收。
(3)在全国海关划一征税之现行制度未变更以前,对白煤与越米适用约定税率之办法应暂由全国海关一律施行。
(4)白煤与越米适用约定税率之施行日期,应自中法专约1935年7月22日发 生效力之日起算。
对于在此日及以后进口之白煤与越米未照上述约定税率办理者,其溢征之税款及附加税经海关核明后,予以发还。
上述规定已于1935年9月3日电报通知各口岸,仰各税务司遵照办理为要。
此令。
总税务司
梅乐和。




1930 年关税法》第337 节的简称, 它主要规范的是美国国际贸易委员会(ITC)对进口贸易中的不公平竞争方法和不公平行为进行调查的行为,337条款并不要求实际损害为前提。
若ITC 裁决原告胜诉,ITC 可向美国公司提供有限排除令、普遍排除令和停止令等救济措施,但实践中,337条款更多起到的是一种敲山震虎的作用,往往程序一经启动,未等裁决,出口国方面即会规范自身行为以达到相应标准。
此外还有以SA8000为代表的社会责任壁垒,它是一种以保护劳动环境和劳工权利为主要内容的管理标准体系,以劳动者劳动环境和生存权利为借口采取的贸易保护措施,是全球首个道德规范国际标准,其宗旨是确保供应商的产品符合社会责任标准。
目前,全球的一些大采购集团都非常青睐有SA8000认证企业的产品,这促使很多企业去申请与维护这一认证体系,从而削弱发展中国家在劳动力成本方面的比较优势,我国目前也正在从事这方面的研究,并积极争取参与如ISO26000等相关规则的制定,以保护本国权利。
总之,新贸易保护主义措施日趋表面合法化,可其实质并没有改变。
二、新贸易保护主义对我国经济发展的影响随着经济全球化和区域经济化主义的发展,全球竞争必然不断升级,对于中国而言,其工业自1949年后经过了几十年的保护发展, 自改革开放后开始逐步面对国内外竞争,在这些竞争下中国的多数行业已经具备了一定的竞争力。
从历史的角度看,今日中国面对的挑战跟19世纪初英国面对的类似,一方面要继续开发海外市场以扩大出口,另一方面需要不断从国外进口各种资源。
此外,由于拥有世界上最大的廉价劳动力市场,中国必须保证极大的海外市场以解决就业问题,同时也必须通过外资继续引入外来竞争,避免由于发展初期对国内经济的过度保护而导致的现阶段国有企业的垄断对经济带来的伤害。
当今,中国主要依靠出口和投资拉动经济增长,新贸易保护主义盛行加大了我国企业拓展国际市场的难度,对我国的经济产生了巨大的负面影响。


外国税制(Foreign Tax System)课程代码:20410112学分:2学时:32 (其中:课堂教学学时:32 实验学时:0 上机学时:0 课程实践学时:0 )先修课程:财政学A、中国税制A适用专业:财政学教材:《外国税制教程》,付伯颖主编,北京大学出版社,2017年版一、课程性质与课程目标(一)课程性质《外国税制》是财政学专业的财政专业的一门核心专业课。
该课程目的在于通过对当代外国税制基本原理及具体税收制度的介绍,并与我国的税收制度进行比较,为完善我国的税收制度提供借鉴。
该课程介绍和研究外国税收理论和外国税收制度,让学生通过学习外国税收制度与理论,“洋为中用”,了解和把握各国的税制理论和现状,通过比较分析,更能理解我国税制,更能客观地看待我国税制。
(二)课程目标课程目标1:掌握外国税收制度的基本理论;课程目标2:了解世界其他税制的国情背景、历史演变、主要税制制度及其改革趋势;课程目标3:掌握国外典型国家税收制度的运行情况及对我国的借鉴意义;课程目标4:初步具备分析鉴别一种税制搞下优劣及为我国的税制改革建言献策的能力。
二、课程内容与教学要求第一章外国税制概述(一)课程内容1. 外国税制结构2. 外国税收负担3.世界各国税制改革(二)教学要求1.理解外国税制结构2.掌握外国税收负担水平3.了解世界各国的税制改革情况。
(三)重点与难点1. 重点外国税制结构2.难点外国税收负担水平第二章外国个人所得税制(一)课程内容1.个人所得税制概述2.发达国家的个人所得税制度3.发展中国家的个人所得税制度4.中东欧国家的个人所得税制度(二)教学要求1.了解世界上其他一些典型国家个人所得税制的设置情况2.掌握各国个人所得税制的特点及改革经验(三)重点与难点1. 重点典型国家个人所得税制设置的基本情况2.难点各个人所得税制的比较与借鉴第三章外国公司所得税制(一)课程内容1.公司所得税制概述2.发达国家的公司所得税制度3.发展中国家的公司所得税制度4.中东欧国家的公司所得税制度(二)教学要求1.了解世界上其他一些典型国家公司所得税制的设置情况2.掌握各国公司所得税制的特点及改革经验(三)重点与难点1. 重点典型国家公司所得税制设置的基本情况2.难点各国公司所得税制的比较与借鉴第四章外国资本利得课税(一)课程内容1.资本利得课税概述2.发达国家的资本利得课税制度3.发展中国家的资本利得课税制度4.中东欧国家的资本利得课税制度(二)教学要求1.了解世界上其他一些典型国家资本利得税制的设置情况2.掌握各国资本利得税制的特点及改革经验(三)重点与难点1. 重点典型国家资本利得税制设置的基本情况2.难点各国资本利得税制的比较与借鉴第五章外国社会保障税制(一)课程内容1.社会保障税制概述2.发达国家的社会保障税制度3.发展中国家的社会保障税制度4.中东欧国家的社会保障税制度(二)教学要求1.了解世界上其他一些典型国家社会保障税制度的设置情况2.掌握各国社会保障税制度的特点及改革经验(三)重点与难点1. 重点典型国家社会保障税制度设置的基本情况2.难点各国社会保障税制度的比较与借鉴第六章外国增值税制(一)课程内容1.增值税制概述2.发达国家的增值税制度3.发展中国家的增值税制度4.中东欧国家的增值税制度(二)教学要求1.了解世界上其他一些典型国家社会保障税制度的设置情况2.掌握各国社会保障税制度的特点及改革经验(三)重点与难点1. 重点典型国家社会保障税制度设置的基本情况2.难点各国社会保障税制度的比较与借鉴第七章外国消费税制(一)课程内容1.消费税制概述2.发达国家的消费税制度3.发展中国家的消费税制度4.中东欧国家的消费税制度(二)教学要求1.了解世界上其他一些典型国家消费税制度的设置情况2.掌握各国消费税制度的特点及改革经验(三)重点与难点1. 重点典型国家消费税制度设置的基本情况2.难点各国消费税制度的比较与借鉴第八章外国财产税制(一)课程内容1.财产税制概述2.发达国家的财产税制度3.发展中国家的财产税制度4.中东欧国家的财产税制度(二)教学要求1.了解世界上其他一些典型国家财产税制度的设置情况2.掌握各国财产税制度的特点及改革经验(三)重点与难点1. 重点典型国家财产税制度设置的基本情况2.难点各国财产税制度的比较与借鉴第九章外国遗产税和赠与税制(一)课程内容1.遗产税和赠与税概述2.发达国家的遗产税和赠与税制度3.发展中国家的遗产税和赠与税制度4.中东欧国家的遗产税和赠与税制度(二)教学要求1.了解世界上其他一些典型国家遗产税和赠与税制度的设置情况2.掌握各国遗产税和赠与税制度的特点及改革经验(三)重点与难点1. 重点典型国家遗产税和赠与税制度设置的基本情况2.难点各国遗产税和赠与税制度的比较与借鉴三、学时分配及教学方法四、课程考核五、参考书目及学习资料1.《外国税制》,程黎、范信葵主编高等教育出版社2014年版;2.《外国税制概览》,国家税务总局税收科学研究所,中国税务出版社2012年版;3.《外国税收制度丛书》(共16分册),财政部税收制度国际比较课题组主编,中国财经出版社2008年版。
从美国修订《1930年关税法》看我国外贸战略转型
孟祥铭;李德军;邱爱莲
【期刊名称】《沈阳工业大学学报(社会科学版)》
【年(卷),期】2012(005)004
【摘要】2012年3月,美国参议院通过修订《1930年关税法》的法案,以便对中国、越南等"非市场经济国家"征收反补贴税。
近几年,中美之间的贸易争端处于高发期,金融危机加剧了我国外贸出口中遭受的贸易摩擦。
应尽快转变原有增长方式,提高产品附加值、降低对少数国家的路径依赖,开拓多元化市场、促进内外贸一体化,以实现我国外贸战略的转型升级。
【总页数】5页(P306-310)
【作者】孟祥铭;李德军;邱爱莲
【作者单位】沈阳工业大学经济学院,沈阳110870;沈阳工业大学经济学院,沈阳110870;沈阳工业大学经济学院,沈阳110870
【正文语种】中文
【中图分类】F752
【相关文献】
1.美国修改1930年关税法之我见 [J], 涂文影
2.美国修改1930年关税法之我见 [J], 涂文影
3.美国《1930年关税法》修订案的法律研究 [J], 袁悦
4.投诉美国《1930年关税法》修订案需谨防陷阱 [J], 李仲周
5.从美国《1930年关税法》修订案看中美贸易关系发展 [J], 倪鑫煜
因版权原因,仅展示原文概要,查看原文内容请购买。
借鉴国外先进经验完善我国消费税制
乐康
【期刊名称】《税收经济研究》
【年(卷),期】1999(0)1
【摘要】消费税是世界范围内广泛课征的税种。
我国在实际运作中,消费税作为调节性税种,作用微弱,对消费导向调节不利。
【总页数】3页(P38-40)
【关键词】消费税;调节性税种;征税范围;税收负担
【作者】乐康
【作者单位】武汉大学管理学院
【正文语种】中文
【中图分类】F812.42
【相关文献】
1.借鉴国外先进经验完善我国农业保险体系 [J], 傅颂
2.借鉴国外先进经验完善中国环保税制 [J], 范信葵
3.借鉴国外先进经验完善我国住房保障制度 [J], 吴兰花
4.借鉴国外先进经验完善我国住房保障制度 [J], 吴兰花;
5.借鉴国外先进经验完善我国消费税制 [J], 乐康
因版权原因,仅展示原文概要,查看原文内容请购买。