《新编英语语法教程》语法术语精编
- 格式:docx
- 大小:782.05 KB
- 文档页数:12


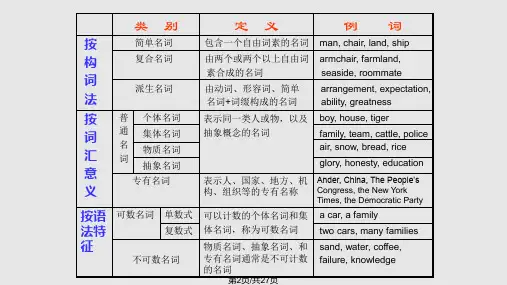

英语语法专业术语1. Noun phrase: A group of words that functions as a noun in a sentence, such as "the old house" or "a beautiful sunset."2. Verb phrase: A group of words that functions as a verb in a sentence, such as "is running" or "has been studying."3. Adjective phrase: A group of words that functions as an adjective in a sentence, such as "very tall" or "extremely funny."4. Adverb phrase: A group of words that functions as an adverb ina sentence, such as "quite quickly" or "very quietly."5. Prepositional phrase: A group of words that begins with a preposition and functions as a modifier, such as "in the park" or "on the table."6. Relative clause: A clause that begins with a relative pronoun (such as "who," "whom," "whose," "which," or "that") and provides additional information about a noun or pronoun in a sentence, such as "The girl who lives next door is my best friend."7. Independent clause: A clause that can stand alone as a complete sentence, such as "She went to the store." It contains a subject anda verb and expresses a complete thought.8. Dependent clause: A clause that cannot stand alone as a complete sentence and functions as a noun, adjective, or adverb within a sentence. It relies on an independent clause for its meaning, such as "Although she was tired."9. Direct object: The noun or noun phrase that receives the action of a transitive verb, such as "He ate an apple."10. Indirect object: The noun or noun phrase that is the recipient of the direct object, typically introduced with a preposition like "to" or "for," such as "She gave a gift to her friend."11. Subject-verb agreement: The rule that states that a singular subject must agree with a singular verb, and a plural subject mustagree with a plural verb, such as "He runs" or "They run."12. Passive voice: A sentence construction in which the subject of the sentence receives the action of the verb, rather than performing the action. It is formed using a form of the verb "to be" followed by the past participle of the main verb, such as "The book was read by her."13. Clause: A group of words that contains a subject and a verb and expresses a complete thought. It can be either independent or dependent.14. Phrase: A group of related words that do not contain a subject and a verb and do not express a complete thought. Phrases can either function as nouns, verbs, adjectives, or adverbs within a sentence.。


1.1 Linguistics is generally defined as the scientific study of language.It is a scientific study because it (a) is based on the systematic investigation of linguistic data. It (b) discovers the nature and rules of the underlying language system. It (c) collects language facts that display some similarities, and generalizations are made about them.The study of language as a whole if often called general linguistics.phonetics(语音学): the study of soundsphonology(音位学): how sounds are put together and used to convey meaningmorphology(形态学): how morphemes(词素) are arranged and combined to form wordssyntax(句法学): the study of rules that govern the combination of words to form grammaticallypermissible sentencessemantics(语义学): the study of meaningpragmatics(语用学): the study of meaning in the context of language useinterdisciplinary branches: sociolinguistics(社会语言学), psycholinguistics(心理语言学), applied linguistics(应用语言学)Important distinctions in linguisticsprescriptive(规定性old linguistics) vs. descriptive(描述性modern linguistics)synchronic(共时性) vs. diachronic(历时性): most linguistic studies are of synchronic descriptions,which is prior in modern linguisticsspeech and writing: speech is prior to writing in modern linguisticslangue(语言系统abstract linguistic system) and parole(话语/言语realization of langue in actualuse): Swiss linguist F. de Saussure----forefather of modern linguisticscompetence(语言能力ideal user’s knowledge of rules of his language) and performance(语言运用actual realization of this knowledge): American linguist N. Chomskytraditional grammar and modern linguistics: Saussure’s book “Course in General Linguistics”marked the beginning of modern linguistics1.2 Language is a system of arbitrary vocal symbols used for human communication.LAD: Language Acquisition Device -----ChomskyArbitrariness (任意性): Different sounds are used to refer to the same object in different languages.Productivity/creativity (能产性): Construction and interpretation of new signals are possible, so that large number of sentences can be produced.Duality (双层性): Two levels enable people to talk about anything within their knowledge. lower level(sounds)---higher level(words)Displacement(移位性): enable people to talk about a wide range of things, free from barriers caused by separation in time or place.Cultural transmission(文化传承): We are born with the ability to acquire language, the details of language system have to be taught and learned.2.1 Speech and writing are the two media for communication, of which speech ismore basic/primary.The sounds which are produced by humans through their speech organs and meaningful in communication constitute the phonic medium of language. The individual sounds within this range are the speech sounds.2.2 Phonetics is the study of the phonic medium of language, which concerned with all the sounds thatoccur in the world’s languages.articulatory phonetics, auditory phonetics, acoustic phoneticsSpeech organs:pharyngeal; cavity---throat; oral cavity---mouth; nasal cavity---noseIPA: 国际音标diacritics: 变音符broad transcription: 宽式标音(used in dictionaries and teaching textbooks)narrow transcription: 严式标音(used by phoneticians in their study)vowels(the air stream meets with no obstruction) and consonants(obstructed)stops(塞音), fricatives(擦音), affricates(塞擦音), liquids(流音), nasals, glides, bilabial(双唇音), laviodental(唇齿音), dental(齿音), alveolar(齿龈音), palatal(腭音), velar(软腭音), glottal(喉音)close vowels, semi-close vowels, semi-open vowels, open vowels(openness)unrounded vowels, rounded vowels(shape of the lips)long/tense vowels----short/lax vowelsmonophthongs(单元音), diphthongs(双元音) (single or combined)2.3 Phonology and phonetics differ in their approach and focus.phonology: how speech sounds form patterns and are used to convey meaningconcerned with sound system of a particular languagephonetics: of a general nature, interested in all the speech soundsA phone(音素) is a phonetic unit or segment.(speech sounds are all phones)a phone does not necessarily distinguish meaningA phoneme(音位) is a phonological unit.(an abstract unit of distinctive value)not particular sound, but is realized by a certain phone in a certain phonetic context The different phones which can represent a phoneme in different phonetic environments are called the allophones(音位变体) of that phoneme.Rules in phonology:Sequential rules(序列规则)---rules that govern the combination of sounds in a particular language.Assimilation rule(同化规则)---assimilates one sound to another by “copying”a feature of a sequential phoneme, thus making the two phones similar. for ease of articulation(清晰发音)e.g. green, screamDeletion rule(省略规则)---e.g. desi g nationSuprasegmental features(超切分特征): the phonemic features that occur above the level of the segments.stress(重音)---word stress and sentence stressThe location of stress in English distinguishes meaning.E.g. ‘import (n.) im’port (v.) // blackbird vs. black birdtone(语调)---pitch variation(音高变体) distinguish meaning E.g. 汉语四声Intonation(音调)---English tones: falling tone, rising tone, fall-rise tone, rise-fall toneE.g. That’s not the book he wants.3.1 Morphology: study of the internal structure of words, and rules by which words are formed3.2 open class words(开放类): new words can be added—nouns, verbs, adjective and adverbsclosed class words(封闭类): “grammatical” or “functional” words3.3 Word is the smallest free form found in language.Morphemes are the minimal units of meaning.Free and bound morphemes(自由词素can be a word by itself粘着词素must be attached to another one---affix)3.4 V----teachN Af----er3.5 Derivational and inflectional morphemes(派生词素和屈折词素)Free morphemes Bound morphemesRoot Root Affixdog, cat -ceive Prefix Suffixgrammar -vert Derivational Derivational Inflectional …-mit un-, dis- -ment -s, -ing, -‘s, -er3.6 Morphological rules determine how morphemes combine to form words. E.g. un-accept-able3.8 Another way to form words is compounding. E.g. bittersweetWord Formations: compounding, blending, backformation, shortening4.1 Syntax studies the rules that govern the formation of sentences.4.2 Category is a group of linguistic items which fulfill the same or similar functions in a particular languagesuch as a sentence, a noun phrase or a verb.Syntactic categories—word-level categories:major lexical categories (often assumed as the heads around which phrases are built)---Noun (N) Verb (V) Adjective (A) Preposition (P)minor lexical categories---Determiner (Det) Degree words (Deg) Qualifier (Qual) Auxiliary (Aux) Conjunction (Con)Three criteria(条件) determining a word’s category: meaning, inflection (变形) and distribution (分布)A word’s category can be determined only by all three criteria.Phrase category is determined by the word category around which the phrase is built.noun phrase (NP), verb phrase (VP), adjective phrase (AP), prepositional phrase (PP)phrases that are formed of more than one word usually contain : head, specifier, complement4.3 Phrase structure rule---special type of grammatical mechanism regulating the arrangement of elementsthat make up a phraseNP→(Det) N (PP) an NP consists of a determiner, an N head, and a PP complementVP→(Qual) V (NP) a VP consists of a qualifier, a V head, and an NP complementAP→(Deg) A (PP) ……PP→(Deg) P (NP) ……XP rule: XP→(specifier) X (complement)Coordination rule: coordinate structures (consist a conjunction “and”/”or”)X→X *Con XEither an X or an XP can be coordinated; one or more categories can occur to the left of the Con.4.4 Phrase elements: specifiers, complements, modifiersspecifiers determiner qualifier degree wordheads N V A / Pcomplementizers (Cs)—words introducing the sentence complementcomplement clause—sentence introduced by the complementizer complement phrase(CP)matrix clause—construction in which the CP embeded嵌入As, Ns, Ps can all take CP. Adjectives: (heads) afraid, certain, awareNouns: (heads) fact, claim, belief Prepositions: (heads)over, aboutmodifiers: all lexical categories can have modifiers.AP(+Ns): precedes the head e.g. a very careful girl PP(+Vs): follows the head e.g. open with care AdvP(+Vs): precedes or follows the head e.g. read carefully/carefully readThe Expanded XP rule: XP→(Spec) (Mod) X (Complement*) (Mod)4.5 The S rule: S→NP VP ------ Inflp (=S)→NP Infl VP ------Infl can be taken by an abstract category encodedin a verb indicating tense or an auxiliary(助动词)4.6 Transformation a special rule that can move an element from one position to anotherauxiliary movement(助动词移位) inversion: move Infl to the left of the subject NP.within larger CPs (embedded or not): inversion: move Infl to C. P53 Figure 4-8 do insertion(插入): insert interrogative do into an empty Infl position, than move Infl to C.deep and surface structure: e.g. Will the train arrive?Deep: S Surface:NP VPDet Infl Vthe train will arriveThe XP rule→D structure→transformations→S structurewh movement: move the wh phrase to the beginning of the sentence/the specifier position under CPP57 Figure 4-16 P58 Figure 4-18move αand constraints on transformationsmove α: general rule for all the movement rules α: any element that can be movedlimits: inversion can move an auxiliary from the Infl to the nearest C positionno element may be removed from a coordinate structure5.1 Semantics is the study of meaning (from a linguistic point of view.)5.2 The naming theory: The words used in a language are simply labels of the objects they stand for.The limitations of this theory are obvious. There’s verbs, adjectives, etc. and also abstract nouns.The conceptualist view: Words and things are related through the mediation of concepts in the mind.Contextualism: The meaning of a word is its use in the language.Behaviorism: The meaning of a language form is the situation in which the speaker utters it and the response it calls forth in the hearer.5.3 Sense and reference are two terms often encountered in the study of word meaning, which are relatedbut different aspects of meaning.Sense: e.g. “dog”---a domesticated mammal... refer to any animal that meets the features described Reference: “dog”---A said to B:” The dog’s barking.”refer to a certain dog known to both A&BMajor sense relations:synonymy---words that are close in meaningdialectal syn.(autumn in BE & fall in AE), stylistic syn.(daddy & father),syn. that differ in emotive or evaluative meaning(same meaning, different emotions)collocational syn.(different usage), semantically different syn.(differ slightly in meaning) polysemy(one word may have more than one meaning)homonymy (homophones--- two words same in sound, homographs---same in spelling, complete homonyms---same in both sound and spelling)hyponymy(relation between a general word—superordinate, and a specific word--hyponyms)antonymy(words that are opposite in meaning)gradable ant.---e.g. hot vs. cold complementary ant.---e.g. male vs. femalerelational ant.---e.g. husband vs. wife5.4 Sense relations between sentences:X is synonymous with Y. E.g. He was a bachelor all his life. / He never married….X, True—Y, True; X, False---Y FalseX is inconsistent with Y. E.g. John’s married. / John’s a bachelor. X, T—Y, F; X, F—Y, TX entails Y. E.g. He’s been to France. / He’s been to Europe. X, T—Y, T; X, F—Y, may be T or FX presupposes Y. E.g. John’s bike needs repairing. / John has a bike. X, T—Y, T; X, F—Y, TX is a contradiction. E.g. My unmarried sister married a bachelor. X is always false.X is semantically anomalous. (absurd in the sense)5.5 componential analysis----lexical meaning E.g. man---+HUMAN, +ADULT, +ANIMATE, +MALEpredication(谓项) analysis---sentence meaning E.g. The kids like apples. ---KID, APPLE (LIKE) Tom smokes. ---TOM (SMOKE) It is hot. --- (BE HOT)6.1 Pragmatics studies how speakers of a language use sentences to effect successful communication(meaning in a certain context).Sentence meaning vs. utterance meaningUtterance is the realization of the abstract meaning of a sentence in a real situation of communication or context, it is context-dependent.6.2 Speech act theory: aim to answer “What do we do when using language?”----John Austin in late 1950slocutionary act(言内行为—字面意思), illocutionary act(言外行为—目的), perlocutionary act(言后行为—结果) John Searle: classification of illocutionary acts---five general types of things we do with languageSpecific acts that fall into each type share the same illocutionary point1. representatives/assertive: stating or describing, saying what the speaker believes to be trueE.g. The earth is a globe.2. directives: trying to get the hearer to do something E.g. Close the door. / Will you close the door?3. commissives: committing the speaker himself to some future course of actionE.g. I promise to come. / I will bring you the book tomorrow without fail.4. expressive: expressing feelings or attitude towards an existing stateE.g. It’s kind of you to ... / I’m sorry for the mess I’ve made.5. declarations: bringing about immediate changes by saying somethingE.g. I now declare the meeting open. / I appoint you chairman of the committee.Indirect speech act--primary speech act (goal of communication) + secondary speech act (means by which he achieves the goal) ----Searle6.3 Conventional implicature(暗示) & nonconventional implicature-----GriceCon. imp. E.g. He is rich but he is not greedy. imp. Rich people are usually greedy.The participants must first of all be willing to cooperate to converse with each other. The general principle is called the Cooperative Principle. (CP)Four maxims(准则) under CP: The maxim of quantity (informative but no more than required), quality (don’t say what you believe to be false or what you lack adequate evidence), relation (be relevant), manner (avoid obscurity or ambiguity & be brief and orderly)These maxims can be violated. (when misleading, lying, etc.)Chap. 7 Language change (diachronic 历时的) Historical linguisticsphonological changes: vowels---the most dramatic changemorphological and syntactic change:morphological: Addition of affixes (Fusion 融合word word---base +suffix /prefix +base)Loss of affixes---some are via sound changessyntactic: change of word order Old English: subject-object-verbchange in negation rule Old English: I love thee not.lexical and semantic change:lexical: Addition of new words---takes place obviously and quicklyCoinage (coin for new things and objects), Clipped words (缩略构词),Blending (combine parts of other words, e.g. brunch),Acronyms (首字构词e.g. WTO),Back-formation (subtract affixes from old words, e.g. donate---from “donation”)Functional shift /Conversion (shift without adding affixes, e.g. to knee/cool; a reject)Borrowing (borrow from other languages, e.g. bonus from Latin, cycle from Greek…)Loss of words---takes place gradually over several generationsSome words are short-lived because of the discontinuation of the object they name.semantic: three processes of semantic change---semantic broadening: e.g. holiday = holy day in the past, but any rest day todaysemantic narrowing: e.g. girl = young person of either sex in the pastsemantic shift: e.g. nice = ignorant a thousand years agorecent trends: moving towards greater informality, influence of American English,influence of science and technology (space travel, computer and internet lang. etc.) causes of language change: development of science &tech., social & political changes and needs,the way children acquire language, grammar simplification, elaboration &complication, etc. No single causeChap. 8 Language and societySociolinguistics is the sub-field of linguistics that studies the relation between language and society, between the uses of language and the social structures in which the users of languagelive. (社会语言学) Halliday & HudsonLanguage is used to communicate meaning, and to establish and maintain social relationships.Social background determines the kind of language one uses, and language reflects one’s info.speech community---the social group that is singled out for any special studyVarious social groups exist within a speech community. A social group may distinguish itself fromthe rest of the community by the educational background, the occupation, the gender, the age ,of the ethnic affiliation of its members.speech variety(变体)---any distinguishable form of speech used by a speaker or a group of speakersthree types of speech variety of special interest: regional dialects, sociolects, registersTwo approaches to sociolinguistic studies: macro-sociolinguistics & micro-sociolinguisticsThe varieties of language are related to the users and the use to which the language is put.Dialectal varieties: regional dialect (linguistic variety used by people living in the same geographical region---geographical barrier), sociolect (characteristic of a particular socialclass---different social conditions), language and gender (female speech is less assertive andthus sounds more polite), language and age (old people are more conservative and like usingold words more), idiolect (personal dialect), ethnic dialect (social dialect of a languagecutting across regional differences e.g. Black English)Register: the type of language which is selected as appropriate to the type of situation linguistic repertoire---the totality of linguistic varieties possessed by an individualthree social variables that determine the register(the features appropriate to the situation): field of discourse (语场purpose and subject-matter of communication non-technical or technical, determines the vocabulary used and the phono. & gramm. features), tenor of discourse (语旨who the participants are and the relationship between them determines the formality and the level of technicality),mode of discourse(语式the means of communication)E.g. a lecture on biology in a technical collegeField: scientific (biological) Tenor: teacher—student (formal, polite) Mode: oral (lecturing) Degree of formality: intimate—casual—consultative—formal—frozenStandard dialects (employed by government, used by mass media, taught in edu. institutions, based on a selected variety of lang., usually local speech of political or commercial centers,for official purposes or any formal occasions)Pidgin (a variety that mixes or blends languages) and Creole (a pidgin becoming the primary lang.of a speech community of which the children acquire the pidgin as native lang.)Chap. 9 Language and culture are interdependent on each other and have evolved together.Culture is integrated pattern of human knowledge, belief, & behavior. (material & spiritual cult.) Relationship between lang. &cult. : Language symbolizes cultural reality, plays a major role in perpetuating of a culture, is related to what the culture is and affects a culture’s way ofthinking. Language is to culture what part is to whole.discourse communities--- members of the social group use similar lang. to meet their needsdiscourse accents---unique uses of each group’s language, the ways and the style of their talking Sapir-Whorf Hypothesis (SWH): Language filters people’s perception and the way they categorize their experiences.Language reflects cultural preoccupations and constrains the way people think.Context is important in complementing the meanings encoded in the language.Any linguistic sign has a denotative (指示意义—内含), connotative (暗涵意义—外延), or iconic(图像意义) kind of meaning. All these types of meanings are bound with cultural encodings orassociations.some cultural differences in language use: greeting and terms of address, gratitude and compliments, color words, privacy and taboos(禁忌), rounding off numbers, words andcultural specific connotations, cultural-related idioms, proverbs and metaphors Culture contact--- acculturation(文化移入political conquests and expansions), assimilation (吸收immigration), amalgamation (合并ethnical mix / synthesis rather than the elimination orabsorption)Cultural overlap (文化重叠owe to similarities in natural environ. and human psychology)Cultural diffusion (文化扩展e.g. loan words gradually and unceasingly)cultural imperialism (文化帝国主义)---owe to linguistic imperialismspecial language policy protecting the purity of their languages---linguistic nationalism Chap. 10 Language acquisition---child’s acquisition of his mother tongueThree theories: the behaviorist (行为主义语言习得观), the innatist(语法天生…),the interactionist (互动主义…)Behaviorist: language is a kind of behavior, language learning is simply a matter of imitation and habit formation. Children imitate words selectively and according to their ownunderstanding of the sounds or patterns, which is based on what the children have alreadyknown instead of what is “available” in the environment. This theory fails to explain howthey acquire more complex grammatical structures of the languageInnatist: LAD was described as an imaginary “black box” existing somewhere in the human brain.It is said to contain principles that are universal to all human languages.Universal Grammar: innate knowledge of basic grammatical systemChildren ‘s acquisition of grammatical rules is guided by principles of an innate UG.Interactionist: language is a result of the complex interplay between the human characteristics of the child and the environment in which he grows.child directed speech (CDS)(slow rate, high pitch音高, rich intonation抑扬, shorter andsimpler sentence structure)The cognitive development relates to language acquisition mainly in two ways:First, as children’s conceptual development leads to their language development, theirlanguage development also helps in the formation and enhancement of the concept.Second, the cognitive factors determine how the child makes sense of the linguistic systemhimself instead of what meanings the child perceives (理解) and expresses.Two factors remarkably relevant to children’s language developmentLanguage environment is essential in providing input for language acquisition:Behaviorist: language environment plays a major roleInnatist: environment is a stimulus that triggers the pre-equipped LADInteractionist: call for the quality of the language samples available in the ling. environmentAge they start to learn the language:Critical Period Hypothesis (CPH): LAD works successfully only when it’s stimulated at the righttime—a specific and limited time period for language acquisition (Eric Lenneberg)Two versions of CPH: strong one—children must acquire their first language by pubertyweak one—language learning will be more difficult and incomplete after puberty ----consensus: there’s a critical period for first language acquisitionStages in child language development:Phonological development—children must pass one stage before proceeding to the nextVocabulary development—under-extension, over-extensionVocabulary development goes together with the child’s knowledge of the environment.Children may under-extend or overextend it when learning a new word.under-extension: e.g. child gets confused hearing the color of white used for paper when he first thought it as the word for snowover-extension: a child takes a property of an object and generalizes it. likely to occur later Grammatical developmentPragmatic developmentAtypical development (非典型发展)hearing impairment (听力损伤), mental retardation (智力缺陷), autism (孤独症), stuttering(口吃), aphasia (失语症), dyslexia (诵读困难), dysgraphia (书写困难)Chap. 11 Second language acquisition (SLA) is the systematic study of how one person acquires a second language subsequent to his native language (NL/L1).Whether the target language (TL) to be learnt is called a second language (SL/L2) or a foreignlanguage (FL) depends on its status as a second language or foreign language in the country.Contrastive Analysis (CA)--1960s :positive/negative transfer: the former facilitate target language learning, the latter interfereCA compares the forms and meanings across two languages to locate the mismatches or differences so as to predict the possible learning difficulty.It was soon found problematic: uninformative, inaccurateError Analysis (EA): independently describe the learners’ interlanguage (their version of the target language and the target language itself), and compare the two forms to locate mismatches.It gives less consideration to learner s’ native language than CA. reach heyday in 1970sTwo main sorts of errors: interlingual errors (语际错误result from cross-linguistic interferenceat different levels—phonological, lexical…), intralingual errors (语内错误result from faultyor partial learning of the TL, independent of the NL e.g. learning strategies-based error)Overgeneralization—the use of previously available strategies in new situationsCross-association—interference of two words similar in meaning, spelling and pronunciationEA was criticized for its neglect of learners’ role as active participants in learning. (mid-1970s)Interlanguage: Three important characteristics—systematicity (系统性), permeability (渗透性), fossilization (石化a process occurring from time to time in which incorrect linguistic features become apermanent part of the way a person speaks or writes a language. fossilized pronunciation leads to accent) Input Hypothesis---Krashen: two independent means or routes of second language learning: acquisition: subconscious process learning: conscious effortsLearners advance their language learning gradually by receiving “comprehensible input”. ”i+1”It received criticism later, for he mistook “input” as “intake”.Individual differences: language aptitude (天资), age of acquisition, personalitymotivation----instrumental motivation (for external goal), integrative motivation (for the wish toidentify with the target culture), resultative motivation (for external purposes), intrinsicmotivation (for pleasure),learning strategies (motivation plays an important role in use of learning strategies)----cognitive strategies (认知策略involved in analyzing, synthesizing(合成) and internalizing(内在化) what has been learned), metacognitive strategies (元认知策略the techniques inplanning, monitoring and evaluating one’s learning), affect/social strategies (deal with theways learners interact or communicate with other speakers, native or non-native)Chap. 12 Language and the brainneurolinguistics (神经语言学): study of language disorders and the relationship between the brain and language. lateralization (侧化)—cognitive functions controlled by either side of the brainThe brain is divided into two sections:the lower section—brain stem(脑干shared by all animals to keep the body alive by maintaining the essential functions)the higher section—cerebrum(大脑differs in different species, not essential for life)cerebellum—at the rear of the brain , beneath the cerebrum, behind the brainstemneuron神经元Neurons form the cortex(脑皮层the surface of the brain)The cortex has many wrinkles: a ridge (hills) called sulcus, a deep and prominent sulcus called fissure The cortex is the decision-making organ of the body and “storehouse” of “memory”, it makes human distinctive in the animal world—animals have no cortex.The cortex is separated by the longitudinal fissure into the left and right cerebral hemispheres, the。
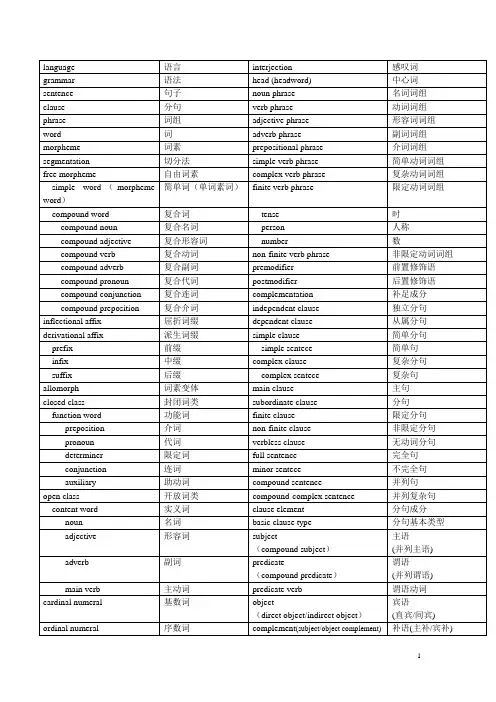
language 语言interjection 感叹词grammar 语法head (headword) 中心词sentence 句子noun phrase 名词词组clause 分句verb phrase 动词词组phrase 词组adjective phrase 形容词词组word 词adverb phrase 副词词组morpheme 词素prepositional phrase 介词词组segmentation 切分法simple verb phrase 简单动词词组free morpheme 自由词素complex verb phrase 复杂动词词组simple word(morphemeword)简单词(单词素词)finite verb phrase 限定动词词组compound word 复合词tense 时compound noun 复合名词person 人称compound adjective 复合形容词number 数compound verb 复合动词non-finite verb phrase 非限定动词词组compound adverb 复合副词premodifier 前置修饰语compound pronoun 复合代词postmodifier 后置修饰语compound conjunction 复合连词complementation 补足成分compound preposition 复合介词independent clause 独立分句inflectional affix 屈折词缀dependent clause 从属分句derivational affix 派生词缀simple clause 简单分句prefix 前缀simple sentece 简单句infix 中缀complex clause 复杂分句suffix 后缀complex sentece 复杂句allomorph 词素变体main clause 主句closed class 封闭词类subordinate clause 分句function word 功能词finite clause 限定分句preposition 介词non-finite clause 非限定分句pronoun 代词verbless clause 无动词分句determiner 限定词full sentence 完全句conjunction 连词minor sentece 不完全句auxiliary 助动词compound sentence 并列句open class 开放词类compound-complex sentence 并列复杂句content word 实义词clause element 分句成分noun 名词basic clause type 分句基本类型adjective 形容词subject(compound subject)主语(并列主语)adverb 副词predicate(compound predicate)谓语(并列谓语)main verb 主动词predicate verb 谓语动词cardinal numeral 基数词object(direct object/indirect object)宾语(直宾/间宾)ordinal numeral 序数词complement(subject/object complement)补语(主补/宾补)adverbial 状语indefinite article 不定冠词SVC, SV, SVO, SV oO, SVOC,SV A, SVOA zero article 零冠词concord/agreement 一致possessive determiner 物主限定词subject-verb agreement 主动一致/主谓一致genitive noun 名词属格grammatical concord 语法一致原则demonstrative determiner 指示限定词notional concord 意义一致原则relative determiner 关系限定词principle of proximity 就近原则interrogative determiner 疑问限定词coordinate subject 并列结构作主语indefinite determiner 不定限定词noun phrase of amount or quality 表示数量概念的名词词组multiplicative numeral 倍数词relative clause 关系分句fractional numeral 分数词relative pronoun 关系代词quantifier 量词antecedent 先行项specific reference 特指cleft sentence 分裂句generic reference 类指focus element 中心成分definite specific reference 确定特指existential sentence 存在句anaphoric specific reference 前照应特指notional subject 实义主语cataphoric specific reference 后照应特指coordinate construction 并列结构situational reference 语境照应(特指)coordinate element 并列成分definite quantity 确定数量simple noun 简单名词indefinite quantity 非确定数量compound noun 复合名词referential meaning 所指意义derivative noun 派生名词predeterminer 前位限定词common noun 普通名词central determiner 中位限定词individual noun 个体名词postdeterminer 后位限定词collective noun 集体名词person pronoun 人称代词material noun 物质名词subjective case 主格abstract noun 抽象名词objective case 宾格proper noun 专有名词genitive case 属格countable/count noun 可数名词possessive pronoun (genitive pronoun)物主代词(属格代词) uncountable/non-count noun 不可数名词nominal genitive pronoun 名词性属格代词number 数possessive genitive pronoun 限定词属格代词singular number 单数reflexive pronoun 反身代词plural number 复数reciprocal pronoun 相互代词regular plural 规则复数demonstrative pronoun 指示代词irregular plural 不规则复数indefinite pronoun 不定代词partitive/unit noun 单位词/单位名词interrogative pronoun 疑问代词case 格relative pronoun 关系代词common case 通格gender 性possessive case/genitive case 所有格/(名词)属格masculine gender 阳性independent genitive 独立属格feminine gender 阴性double genitive 双重属格neuter gender 中性determiner 限定词common gender 通性definite airicle 定冠词noun of common gender 通性名词person 人称complementation 补足成分first person 第一人称transitive verb 及物动词second person 第二人称intransitive verb 不及物动词third person 第三人称linking verb 连系动词Reflexive form 反身形式dynamic verb 动态动词emphatic use 强调用法stative verb 静态动词unemphatic use 非强调用法single-word verb 单词动词reference 照应,所指phrasal verb 词组动词pronoun reference 代词照应finite verb (finite form)限定动词(限定形式)anaphoric reference 前照应non-finite verb(non-finite form)非限定动词(非限定形式)cataphoric reference 后照应base form 原形situational reference 语境照应grammatical form 语法形式person reference 人称照应simple tense 一般现在时demonstrative reference 指示照应simple past 一般过去时tense 时present progressive 现在进行时present tense 现在时past progressive 过去进行时past tense 过去时present perfective 现在完成时aspect 体past perfective 过去完成时progressive aspect 进行体present perfective progressive 现在完成进行时perfective aspect 完成体past perfective progressive 过去完成进行时voice 态future tense 将来时active voice 主动态operator 操作词passive voice(be-passive/get-passive/passi ve infinitive)被动态(be型/get型被动态/不定式被动态)predication 述谓成分mood 式Old English 古英语indicative mood 陈述式prediction 预见statement(declarative sentence)陈述句willingness 意愿question(interrogative sentence)疑问句intention 意图imperative mood 祈使式infinitive(to-infinitive/bare-infinitive)不定式(带to/不带to不定式) subjunctive mood 虚拟式-ing participle ing分词hypothetical meaning 假设意义-ed participle ed分词non-factual meanig 非事实意义conditional 条件句Be-subjunctive Be型虚拟式implied conditional 含蓄条件句Were-subjunctive Were型虚拟式ability 能力auxiliary 助动词possibility 可能primary auxiliary 基本助动词permission 许可modal auxiliary 情态助动词obligation 义务(必须,应该)semi-auxiliary 半助动词necessity 必然simple verb phrase 简单动词词组determination 决心complex verb phrase 复杂动词词组epistemic 推测性notional verb 实义动词non-epistemic 非推测性deep structure 深层结构emphasizer 强调词surface structure 表层结构reinforcement tag 强调附加结构dynamic adjective 动态形容词double negative 双重否定stative adjective 静态形容词rhetorical question 修辞疑问句present participle 现在分词partial negation 局部否定past participle 过去分词question(interrogative sentence)疑问句gerund 动名词general question(yes-no question)一般疑问句(是非疑问句)dangling participle (unattached participle) 悬垂分词(无依着分词)special question (wh-question)特殊疑问句(wh-问句)attachment rule 依着规则alternative question 选择疑问句logical suject 逻辑主语tag question 附加疑问句one-word adjective 单词形容词non-assertive word 非肯定词compound adjective 复合形容词command (imperative sentence) 祈使句central adjective 中心形容词existential sentence 存在句peripheral adjective 外围形容词notional subject 实义主语gradable ajective 等级形容词real subject 真主语non-gradable ajective 非等级形容词locative adverbial 地点状语causative construction 使役结构temporal adverbial 时间状语simple adverb 简单副词nonreferring it 非指代性it derivative adverb 派生副词empty it 虚义it adverb of manner 方式副词anticipatory it 先行it adverb of degree 程度副词pseudo-clef sentence 拟似分裂句adverb of time 时间副词coordinator 并列(连)词adverb of frequency 频率副词correlative coordinator 关联并列连词adverb of place 地点副词coordinate construction 并列结构conjunctive adverb 连接副词subordination 从属explanatory adverb 解说副词subordinator 从属连词adjunct 修饰/结合性状语simple subordinator 简单从属连词dsjunct 评注/分离性状语complex subordinator 复杂从属连词conjunct 连接性状语correlative subordinator 关联从属连词positive/absolute degree 原级marginal subordinator 边际从属连词comparative degree 比较级one-word subordinator 单词从属连词superlative degree 最高级adverbial clause of time 时间状语分句synthetic form 综合形式adverbial clause of place 地点状语分句analytic form 分析形式adverbial clause of manner 方式状语分句comparative constructure 比较结构adverbial clause of cause 原因状语分句analytic language 分析性语言adverbial clause of result 结果状语分句simple preposition 简单介词adverbial clause of purpose 目的状语分句complex preposition 复杂介词adverbial clause of condition 条件状语分句two-word preposition 双词介词adverbial clause of concession 让步状语分句three-word preposition 三词介词Infinitive clause 不定式分句four-word preposition 四词介词-ing participle clause -ing分词分句exclamation(exclamatory sentence)感叹句-ed participle clause -ed分词分句quasi-coordinator 近似并列连词end weight 句尾重心absolute construction 独立结构information focus 信息焦点relative word 关系词information unit 信息单位relative pronoun 关系代词old information (given information) 旧信息(已知信息)relative adverb 关系副词new information 新信息relative determiner 关系限定词full inversion 全部倒装attributive clause (relative clause) 定语从句(关系分句)partial inversion 部分倒装restrictive relative clause 限定性关系分句cohesion 粘着性non-restrictive relative clause 非限定性关系分句coherence 连贯性double relative clause 双重关系分句unity 统一性embedded relative clause 嵌入式关系分句redundancy 累赘conditional 条件句correctness 正确性real conditional 真实条件句communicative pfunction 交际功能unreal conditional 非真实条件句transitional words/phrases 过渡词语basic form 基本形式logical connectors 逻辑纽带variant form 变体形式grammatical connectors 语法纽带alternative form 替换形式coreference pro-form 指代词direct speech 直接引语comparative reference 对比照应indirect speech 间接引语parallel construction 平行结构reporting verb 引述动词key word 关键词modification 修饰语synonym (near-synonym) 同义词(近义词)restrictive modifier 限制性修饰语sentence group 句群(语段)non-restrictive modifier 非限制性修饰语text 语篇discontinuous modification 分隔修饰single-sentence group text 单语段语篇appositive 同位语multi-sentence group text 多语段语篇restrictive appositive 限制性同位语top sentence 主题句non-restrictive appositive 非限制同位语topic sentence group 主题语段substitute 替代词supporting sentence 辅助句nominal substitute 名词性替代词supporting sentence group 辅助语段verbal substitute 动词性替代词clausal substitute 分句性替代词substitution 替代nominal substitution 名词性替代verbal substitution 动词性替代clausal substitution 分句性替代ellipsis 省略word order 词序normal order 正常词序natural order 自然词序postponement 后置fronting 前置end focus 句尾焦点。

英语语法转业术语语法 grammar 句法 syntax 词法 morphology 结构 structure 层次 rank句子 sentence 从句 clause 词组 phrase 词类 part of speech 单词 word实词 notional word 虚词 structrural word名词 noun 专有名词 proper noun普通名词 common noun 可数名词 countable noun 不可数名词 uncountable no 抽象名词 abstract noun 具体名词 concret moun 物质名词 material noun集体名词 collective noun 个体名词 individual noun介词 preposition连词 conjunction动词 verb 主动词 main verb 及物动词 transitive verb不及物动词 intransitive verb 系动词 link verb 助动词 auxiliary verb情态动词 modal verb 规则动词 regular verb 不规则动词 irregular verb短语动词 phrasal verb 限定动词 finite verb 非限定动词 infinite verb使役动词 causative verb 感官动词 verb of senses 动态动词 event verb静态动词 state verb 感叹词 exclamation形容词 adjective副词 adverb方式副词 adverb of manner 程度副词 adverb of degree 时间副词 adverb of time 地点副词 adverb of place 修饰性副词 adjunct 连接性副词 conjunct疑问副词 interogative adverb 关系副词 relative adverb代词 pronoun 人称代词 personal pronoun 物主代词 possesive pronoun 反身代词reflexive pronoun相互代词 reciprocal pronoun 指示代词 demonstrative pronoun疑问代词 interrogative pronoun 关系代词 relative pronoun 不定代词 indefinite 物主代词 possecive pronoun 名词性物主代词 nominal possesive 形容词性物主代词adjectival possesive pronoun冠词 article 定冠词 definite article 不定冠词 indefinite article数词 numeral 基数词 cardinal numeral 序数词 ordinal numeral分数词 fractional numeral形式 form 单数形式 singular form 复数形式 plural form限定动词 finite verb form 非限定动词 non-finite verb form原形 base form从句 clause 从属句 subordinate clause 并列句 coordinate clause名词从句 nominal clause 定语从句 attributive clause 状语从句 adverbial clause宾语从句 object clause 主语从句 subject clause 同位语从句 appositive clause时间状语从句 adverbial clause of time 地点状语从句 adverbial clause of place方式状语从句 adverbial clause of manner 让步状语从句 adverbial clause of concession 原因状语从句 adverbial clause of cause 结果状语从句 adverbial clause of result 目的状语从句 adverbial clause of purpose 条件状语从句 adverbial clause of condition 真实条件状语从句 adverbial clause of real condition 非真实条件状语从句 adverbial clause of unreal condition 含蓄条件句 adverbial clause of implied condition 错综条件句 adverbial clause of mixed condition句子 sentence 简单句 simple sentence 并列句 compound sentence复合句 complex sentence 并列复合句 compound complex sentence陈述句 declarative sentence 疑问句 interrogative sentence一般疑问句 general question 特殊疑问句 special question 选择疑问句 alternative question 附加疑问句 tag question 反义疑问句 disjunctive question 修辞疑问句rhetorical question 感叹疑问句 exclamatory question 存在句 existential sentence 肯定句 positive sentwence 否定句 negative sentence祈使句 imperative sentence 省略句 elliptical sentence 感叹句 exclamatory sentence 基本句型 basic sentence patern句子成分 members of sentences 主语 subject 谓语 predicate 宾语 object 双宾语dual object直接宾语 direct object 间接宾语 indirect object 复合宾语 complex object 同源宾语cognate object补语 complement 主补 subject complement 宾补 object complement 表语predicative定语 attribute 同位语 appositive 状语 adverbial句法关系 syntatic relationship 并列 coordinate 从属 subordination 修饰modification前置修饰 pre-modification 后置修饰 post-modification 限制 restriction 双重限制double-restriction非限制 non-restriction数 number 单数形式 singular form 复数形式 plural form 规则形式 regular form 不规则形式 irregular form格 case 普通格 common case 所有格 possessive case 主格 nominative case 宾格objective case性 gender 阳性 masculine 阴性 feminine 通性 common 中性 neuter人称 person 第一人称 first person 第二人称 second person 第三人称 third person时态 tense 过去将来时 past future tense 过去将来进行时 past future continuous tense过去将来完成时 past future perfect tense 一般现在时 present simple tense 一般过去时past simple tense 一般将来时 future simple tense 现在完成时 past perfect tense 过去完成时 present perfect tense 将来完成时 future perfect tense 现在进行时present continuous tense过去进行时 past continuous tense 将来进行时 future continuous tense 过去将来进行时past future continuous tense 现在完成进行时 present perfect continuous tense过去完成进行时 past perfect continuous tense语态 voice 主动语态 active voice 被动语态 passive voice语气 mood 陈述语气 indicative mood 祈使语气 imperative mood 虚拟语气subjunctive mood否定 negation 否定范围 scope of negation 全部否定 full negation 局部否定 partial negation转移否定 shift of negation语序 order 自然语序 natural order 倒装语序 inversion 全部倒装 full inversion 部分倒装 partial inversion直接引语 direct speech 间接引语 indirect speech 自由直接引语 free direct speech自由间接引语 free indirect speech一致 agreemen 主谓一致 subject-predicate agreement 语法一致 grammatical agreement概念一致 notional agreement 就近原则 principle of proximity强调 emphasis 重复 repetition 语音 pronunciation 语调 tone 升调 rising tone 降调falling tone降升调 falling-rising tone文体 style 正式文体 formal 非正式文体 informal 口语 spoken/oral English 套语formulistic expression英国英语 British English 美国英语 American English 用法 usage 感情色彩emotional coloring褒义 commendatory 贬义 derogatory 幽默 humorous 讽刺 sarcastic 挖苦 ironicGerund 动名词 H Hyphen 连字号 I Imperative Mood 祈使语气 Imperative Sentences 祈使句 Indefinite Case 独立成分 Indicative Mood 主句 Material Nouns 物质名词 Members of the Sentence 句子的成分 Modal Verbs 情态动词 Mood 语气 Morphology 词法 N Natural Word-order 否定疑问句 Non-finite Forms of the Verb 动词的非限定形式 Non-restrictive Attributive Clauses 非限制性定语从句B Brackets 括号 Classification of Nouns 名词的分类 Clauses 从句(分句)Cognate Object 同源宾语 Collective Nouns 集体名词 Colon 冒号 Comma 逗号Common Case 普通格 Common Nouns 普通名词 Comparative Degree 比较级Complex Object 复合宾语 Complex Sentences 复合句 Compound Complex Sentences 并列复合句 Compound Nominal Predicate 表性状的复合谓语Compound Predicate 复合谓语 Compound Sentences 并列句 Compound Verbal Predicate 表行为的复合谓语 Compound Words 合成词 Compounding( Composition ) 合成 Conditional Sentences of Mixed Time 错综时间条件句Conjunction 连词 Conjunctive Adverbs 连接副词 Conjunctive Pronouns 连接代词Conversion 转化 Co-ordinating Conjunctions 并列连词 Countable Nouns 可数名词 D Dash 破折号 Declarative Sentences 陈述句 Definite Article 定冠词 Degrees of Comparison 比较的级别 Demonstrative Pronouns 指示代词 Derivation( Affixation ) 派生(词缀法) Descriptive Attributes 描绘性定语 Direct Address 呼语 Direct Object 直接宾语 Direct Speech 直接引语 Disjunctive Questions 反意问句 E Ellipsis 省略 Elliptical Sentences 省略句 Exclamation Mark 感叹号Exclamatory Sentences 感叹句 F Finite Forms of the Verb 动词的限定形式 Form Words 虚词 Fractional Numerals 分数词 Full Inversion 完全倒装 Future Continuous 将来进行时 Future Indefinite 一般将来时 Future Perfect 将来完成时Future Perfect Continuous 将来完成进行时Absolute Constructions 独立结构 Absolute Forms of Possessive Pronouns 物主代词的绝对形式 Abstract Nouns 抽象名词 Active Voice 主动语态 Adverbial Clauses of Manner 方式状语从句 Adverbial Clauses of Place 地点状语从句 Adverbial Clauses of Purpose 目的状语从句 Adverbial Clauses of Time 时间状语从句Adverbs of Degree 程度副词 Adverbs of Frequency 频度副词 Adverbs of Manner 方式副词 Adverbs of Place 地点副词 Adverbs of Time 时间副词 Alternative Questions 选择问句 Analysis of Sentences 句子分析 Apostrophe 省略号Appositive 同谓语 Appositive Clauses 同位语从句 Auxiliary Verbs 助动词Parenthesis 插入语 Partial Inversion 部分倒装 Participial Phrases 分词短语Participle 分词 Particle 小品词 Parts of Speech 词类 Past Forms 过去式 Past Participle 过去分词 Period ( Full Stop ) 句号 Person 人称 Personal Pronouns 人称代词 Phrasal Verbs 成语动词 Predicate 谓语 Predicative 表语 Predicative Clauses 表语从句 Prefix ( es ) 前缀 Prepositional Phrases 介词短语 Present Forms 现在式 Present Participle 现在分词 Principal Forms of verbs 动词的主要形式Proper Nouns 专有名词 Punctuation 标点符号 Question Mark 问号 QuestionMarks 引号 Reciprocal Pronouns 相互代词 Relative Adverbs 关系副词 Relative Pronouns 关系代词 Restrictive Attributive Clauses 限制性定语从句 Self Pronouns 自身代词 Semicolon 分号 Sentences of Real Condition 真实条件句 Sentences of Unreal Condition 虚拟条件句 Sequence of Tenses 时态的呼应 Special Questions 特殊问句 Subjunctive Mood 虚拟语气 Suffix ( es ) 后缀 Superlative Degree 最高级Syntax 句法 Transformation of Sentences 句型的转换 Two-member Sentences 双部句 Uncountable Nouns 不可数名词 Verb Phrases 动词短语 Verbal Noun 名词化的动词 Word Building 构词法。

英语语法术语语法grammar句法syntax词法morphology结构structure层次rank句子sentence从句clause词组phrase词类part of speech单词word实词notional word虚词structural word单纯词simple word派生词derivative复合词compound词性part of speech名词noun专有名词proper noun普通名词common noun可数名词countable noun不可数名词uncountable noun 抽象名词abstract noun具体名词concret noun物质名词material noun集体名词collective noun个体名词individual noun介词preposition连词conjunction动词verb主动词main verb及物动词transitive verb不及物动词intransitive verb 系动词link verb助动词auxiliary verb情态动词modal verb规则动词regular verb不规则动词irregular verb 短语动词phrasal verb限定动词finite verb非限定动词infinite verb使役动词causative verb感官动词verb of senses动态动词event verb静态动词state verb感叹词exclamation形容词adjective副词adverb方式副词adverb of manner程度副词adverb of degree时间副词adverb of time地点副词adverb of place修饰性副词adjunct连接性副词conjunct疑问副词interrogative adverb关系副词relative adverb代词pronoun人称代词personal pronoun物主代词possessive pronoun反身代词reflexive pronoun相互代词reciprocal pronoun指示代词demonstrative pronoun 疑问代词interrogative pronoun 关系代词relative pronoun不定代词indefinite pronoun物主代词possessive pronoun名词性物主代词nominal possessive pronoun形容词性物主代词adjectival possessive pronoun冠词article定冠词definite article不定冠词indefinite article数词numeral基数词cardinal numeral序数词ordinal numeral分数词fractional numeral形式form单数形式singular form复数形式plural form限定动词finite verb form非限定动词non-finite verb form 原形base form从句clause从属句subordinate clause并列句coordinate clause名词从句nominal clause定语从句attributive clause状语从句adverbial clause宾语从句object clause主语从句subject clause同位语从句appositive clause时间状语从句adverbial clause of time地点状语从句adverbial clause of place方式状语从句adverbial clause of manner让步状语从句adverbial clause of concession原因状语从句adverbial clause of cause结果状语从句adverbial clause of result目的状语从句adverbial clause of purpose条件状语从句adverbial clause of condition真实条件状语从句adverbial clause of real condition 非真实条件状语从句adverbial clause of unreal condition含蓄条件句adverbial clause of implied condition错综条件句adverbial clause of mixed condition句子sentence简单句simple sentence并列句compound sentence复合句complex sentence并列复合句compound complex sentence陈述句declarative sentence疑问句interrogative sentence 一般疑问句general question特殊疑问句special question选择疑问句alternative question 附加疑问句tag question反义疑问句disjunctive question 修辞疑问句rhetorical question感叹疑问句exclamatory question存在句existential sentence肯定句positive sentence基本句型basic sentence pattern 否定句negative sentence祈使句imperative sentence省略句elliptical sentence感叹句exclamatory sentence句子成分members of sentences 主语subject谓语predicate宾语object双宾语dual object直接宾语direct object间接宾语indirect object复合宾语complex object同源宾语cognate object补语complement主补subject complement宾补object complement 表语predicative定语attribute同位语appositive状语adverbial句法关系syntactic relationship 并列coordinate从属subordination修饰modification前置修饰pre-modification后置修饰post-modification限制restriction双重限制double-restriction非限制non-restriction数number单数形式singular form复数形式plural form规则形式regular form不规则形式irregular form格case普通格common case所有格possessive case主格nominative case宾格objective case性gender阳性masculine阴性feminine通性common中性neuter人称person第一人称first person第二人称second person第三人称third person时态tense过去将来时past future tense过去将来进行时past future continuous tense过去将来完成时past future perfect tense一般现在时present simple tense 一般过去时past simple tense一般将来时future simple tense 现在完成时past perfect tense 过去完成时present perfect tense 将来完成时future perfect tense 现在进行时present continuous tense过去进行时past continuous tense将来进行时future continuous tense过去将来进行时past future continuous tense现在完成进行时present perfect continuous tense过去完成进行时past perfect continuous tense语态voice主动语态active voice被动语态passive voice语气mood陈述语气indicative mood祈使语气imperative mood虚拟语气subjunctive mood否定negation否定范围scope of negation全部否定full negation局部否定partial negation转移否定shift of negation语序order自然语序natural order倒装语序inversion全部倒装full inversion部分倒装partial inversion直接引语direct speech间接引语indirect speech自由直接引语free direct speech 自由间接引语free indirect speech一致agreement主谓一致subject-predicate agreement语法一致grammatical agreement 概念一致notional agreement 就近原则principle of proximity 强调emphasis重复repetition语音pronunciation语调tone升调rising tone降调falling tone降升调falling-rising tone文体style正式文体formal非正式文体informal口语spoken/oral English套语formulistic expression英国英语British English美国英语American English用法usageTerms of English Language Teaching Methodology感情色彩emotional coloring褒义commendatory贬义derogatory幽默humorous讽刺sarcastic挖苦ironic英语教学法术语Aachievement test 成绩测试acquisition 习得,语言习得acquisition 语言习得顺序active mastery 积极掌握active vocabulary 积极词汇,主动词汇affective filtering 情感筛选aim,objective 目的,目标analysis of errors 错误分析analytic approach 分析教学法,分析法analytical reading 分析性阅读application to practice 运用于实践applied linguistics 应用语言学approach 教学路子aptitude test 能力倾向测验Army method 陆军法associative learning 联想性学习auditory discrimination 辨音能力auditory feedback 听觉反馈auditory memory 听觉记忆auditory perception 听觉audio-lingual method 听说法audio-visual method 视听法aural-oral approach 听说教学法,听说法aural-oral method 听说法Bbasic knowledge 基本知识basic principle 基本原则basic theory 基本理论basic training 基本训练basic vocabulary 基本词汇behaviourism 行为主义bilingual 双语的bilingual education 双语教育blank filling 填空Cchain drill 链式操练,连锁操练choral repetition 齐声照读,齐声仿读class management 课常管理classroom interaction 课常应对cloze 完形填空coach 辅导cognitive approach 认知法common core 语言的共同核心,语言共核communicative drill 交际性操练communicative exercise 交际练习communicative langunge teaching 交际派语言教学法,交际教学法community language learning 集体语言学习法comparative method 比较法communicative approach 交际法comprehensible input 不难理解的输入comprehensive method 综合法computer-managed instruction 计算机管理教学concord and coordination 默契与配合console 控制台consonant cluster 辅音连缀context 上下文controlled composition 控制性作文course density 课堂密度course design 课程设计cramming method 灌输式cue word 提示词curriculum 课程,教学大纲curriculum development 课程编制,课程设计cultrual objective,aim 教养目的cclical approach 循环教学法,循环法Ddeductive learning 演绎性学习deductive method 演绎法delayed auditory feedback 延缓听觉反馈demonstration 演示demonstration lesson 示范教学describe a picture in writing 看图说话describe a picture orally 描写语言学diagram 图解diagnostic test 诊断性测验dicto-comp 听写作文direct application 直接应用direct comprehension 直接理解direct learning 直接学习direct method 直接教学法Eeducational objective, aim 教育目的EFL 英语作为外语EGP 通用英语ELT 英语教学English as a Foreign Language 英语作为外语English as an InternationalLanguage 英语作为国际语言English environment 英语环境English for Academic Purposes 学术英语English for general prupose 普通英语English for General Purposes 通用英语English for specific purposes 专用英语ESOL English for Speakers of OtherLanguages 供非英语民族使用的英语English medium school 英语授课学校English teaching;teaching English 英语教学WSD(English as a Second Dialect)英语作为第二方言WSL(English as a Second Language)英语作为第二语言ESL Programme(English as a Second Language Programme)英语(第二语言)教程ESP(English for Special Purposes)专用英语EST(English for Science andTechnology)科技英语evaluation 评语,评价examination 考试examination question 考题experimental method 实验法extensive reading 泛读external speech 外语言语extra-curiculum activity 课外活动extra-curriculum club,group 课外小组Ffacial expression 面部表情feedbace 反馈film projector 电影放映机filmstrip 电影胶片final stage 高级阶段first language 第一语言,母语formative evaluation 自由作文free practice 自由练习frequency of word 词的频率al approach 功能法al syllabus 功能派教学大纲word 功能词Ggeneral linguistics 普通语言学gestalt style 格式塔式(学习),整体式(学习)gesture 手势getting students ready for class 组织教学global learning 整体式学习,囫囵吞枣式学习global question 综合性问题gradation 级进法,分级递升法graded direct method 循序直接法grading 级进法,分级递升法;评分grammar lesson 语法课grammar method 语法法grammar translation method 语法翻译法grammatical analysis 语法分析group reading 集体朗读group training 集体练习guided composition 引导性作文Hheuristic method of teaching 启发式教学法heurstics 启发法;探索法humanistic approach 人本主义教学法Iidealism 唯心主义imitatiom 模仿immersion programme 沉浸式教学imparting knowledge 传授知识incomplete plosive 不完全爆破independent composition 独立作文individualized instruction 个别教学individual training 个别练习inductive learning 归纳性学习inductive method 归纳法inflection,inflexion 词形变化information,processing 信息处理initial beginning stage 初级阶段inner speech 内语言语in-service training 在职培训instructional objective 语言教学目标integrative teaching 综合教学integrated approach 综合教学法,综合法intelligent memory 理解性记忆language training 强化教学intensive training 精读intermediate stage 中级阶段interpretation 头口翻译International Phonetic Alphabet 国际音标Jjuncture 连读,音渡junior high school 初级中学junior school 初级学校junior sceondary school 初级中等学校junior-senior high school 初高中junior technical college(orschool) 初级职业学院(或学校)junior year 大学三年级Kkey words 基本词,关键字kinesics 身势语,身势学kinesthetic memory 动觉记忆knowledge 知识knowledge structure 知识结构Llanguage acquisition 语言习得language acquisition device 语言习得机制language arts 语言技能language competence,or knowledge 语言知识language learning capability 语言学习能力language laboratory;lab 语言实验室language leaning capacity 语言学习能力language pedagogy 语言教育language performance 语言行为language program design 语言课程设计language test 语言测试learning by deduction 演绎性学习learning by induction 归纳性学习learning process 学习过程learning style 学习方式lesson conducting 教课lesson plan 课时计划,教案lesson preparation 备课lesson type 课型linguistics 语言学linguistic competence 语言能力linguistic method 口语领先教学法living language 活的语言long-term memory 长期记忆look-and-say method 看图说话法Mmeaningful drill 有意义的操练neabubgful exercise 有意义的练习meaningful learning 理解性学习means of teaching 教学手段mechanical drill 机械操练mechanical exercise 机械练习mechanical memory 机械记忆mechanical translation 机器翻译medium of instruction 教学媒介语,教学语言memory 记忆,记忆力memory span 记忆幅度memorizing 用记记住method 方法methodology of teaching 教学法methodology of teaching English 英语教学法microteaching 微型教学mim-mem method 模仿—记忆法minimal pair 最小对立体(一种辨音练习)model 模型modeling 示范教学modern equipment 现代化设备modern language 现代语言monitor hypothesis 语言监控说mother tongue 母语motivation 引起动机Nnative language 本族语natural appoach 自然教学法,自然法natural method 自然法needs analysis 需要分析new lesson 新课nine-pile grading 九堆法notional approach 意念法notional-al syllabus 意念-功能派教学大纲notional syllabus 意念大纲、意念派教学大纲Oobservation lesson 观摩教学objective 教学目标optimum age hypothesis 学习最佳年龄说operating principle 操作原则oral approach 口语教学法,口语法oral exercise 口语练习oral method 口授法oral reading 朗读order of acquisition 语言习得顺序organization of teaching materials 教材组织organs of speech 发音器官outside reading 课外阅读overlearing 过量学习Ppaired-associate learning 配对联想学习法pair work 双人作业,双人练习passive vocabulary 消极词汇pattern drill 句型操练pattern practice 句型练习pdeagogical grammar 教学语法pedagogy 教育法peer teaching 同学互教penmanship handwriting 书法perception 知觉performance objective 语言实践目标personality 个性philosophy 哲学phoneme 音素phonetics 语音法phonetic method 按字母音值拼读法phonology 音位学picture 图画phasement test 分班测验plateau of learning 学习高原practical objective 实用目的practice effect 练习效应practice of teaching 教学实践presentation of new materials 提出新材料pre-teaching 预教primary of speech 口语领先principle of communication 交际性原则principle of teaching 教学原则problem solving 习题解答production stage 活用阶段,产出阶段productive exercise 活用练习productive mastery 活用掌握productive vocabulary 活用词汇proficiency 熟练program desing 课程设计psycho-linguistics 心理语言学psychological method 心理法Qqualified teacher 合格教师question band 试题库questionnaire 调查问卷questions 提问Rrapid reading 快速阅读,快读rate of reading 阅读速度readability 易读性read by turns 轮读reading 阅读reading lesson 阅读课reading method 阅读法reading speed 阅读速度reading vocabulary 阅读词汇,阅读词汇量receptive language knowledge 接受性语言知识receptive vocabulary 领会词汇reformed method 改良法regression 回看,重读reinforcement 巩固reinforcement lesson 巩固课repetition drill 复述操练repetition-stage 仿照阶段response 反应retelling 复述retention 记忆teview;tevision 复习review(revise)and check up 复习检查review(revision)lesson 复习课rewriting 改写rhythm 节奏role-play 扮演角色rote learning 强记学习法,死记硬背Sscanning 查阅,扫瞄school practice 教学实习scientific way of thinking 科学的思想方法second language 第二语言segment 音段,切分成分semantics 语义学seminar 课堂讨论sentence completion 完成句子short-term memory 短期记忆sight vocabulary 一见即懂的词汇silent reading 默读silent way 沉默法,静授法simplification 简写simplified reader 简写读本simulation 模拟,模拟性课堂活动simultaneous interpretation 同声翻译situational method 情景法situational language teaching 情景派语言教学法,情景教学法situational method 情景教学法situational syllabus 情景派教学大纲situation reinforcement 情景强化法skimming 略读,济览slide 幻灯片slide projector 幻灯片socialized speech 社会化言语socio-linguistics 社会语言学soft ware 软件speech disorder 言语缺陷speech pathology 言语病理学speech perception 言语知觉speech reading 唇读法speed reading 快速阅读,快读speelling 正字法spiral approach 螺旋式教学法,螺旋法spoken lauguang 口语stage of teaching 教学阶段stick drawing;mathch drawing 简笔画stimulus and response 刺激与反应stress accent 重音,重读structuralism 结构主义(语言学)structural method 结构法student-centered 学生中心student-centered learning 学生为主学习法student teacher 实习教师student teaching 教育实习submersion programme 沉浸式教程substitution 替换substitution table 替换表subvocal reading 默读suggestopaedia 暗示教学法syllabus 教学大纲syllabus design 教学大纲设计syllabus for middle school English 中学英语教学大纲synthetic approach 综合性教学法,综合法synthetical reading 综合性阅读Ttarget language 目的语,译文语言teacher’s book 教师用书teacher’s manual 教师手册teaching experience 教学经验teaching objective,aim 教学目的teaching procedure 教学过程teaching tools;property 教具teaching words in isolation 孤立教单词theory of teaching 教学理论TEFL 英语(外语)教学TESL 英语(第二语言)教学TESOL 对非英语民族教英语time allotment 时间分配total physical response method 整体动作反应法transformation drill 转换操练translation method 翻译法transformational generativegrammar 转化生成语法Uunconscious 潜意识underclassman 低年级学生undergraduate 大学本科生undergraduate course 大学本科课程undergraduate school 大学本科学院undergraduate special 大学特殊课程unified studied 统一课程university high school 大学附属中学university of the air 广播电视大学updating courses/training 现代化课程/训练upgrading courses/training 进修课程/训练upperclassman 高年级学生use and usage 使用和用法utterance 语段Vverbal association 词语联想verbal learning 语言学习,单词学习video 电视,影象videotape 录象磁带visual perception 视觉visual aid 直观手段visit a class 听课visual memory 视觉记忆vocabulary control 词汇控制Wword association 词际联想word list 词表word study 词的研究word frequency 词汇重复率written language 书面语感情色彩emotional coloring褒义commendatory贬义derogatory幽默humorous讽刺sarcastic挖苦ironic英语教学术语Approach教学路子Communicative approach交际法Communicative language teaching 交际语言教学Method教学方法Syllabus design教学大纲设计Frist language母语Second language第二语言Foreign language外语Target language目的语言Techniques技巧Brainstorm指就某一问题随便发表观点或建议的过程Group-work小组活动Pair-work两人一组的活动View of work语言理论或对语言的认识Structural view结构主义语言理论Functional view功能主义语言理论Interactional view交互语言理论Behaviourist theory行为主义学习理论Cognitive theory认知学习理论Process-oriented theory强调过程的语言学习理论Condition-oriented theory强调条件的语言学习理论Audiolingual theory外语教学听说法TPR:total physical respone 全身反应法Silent way沉默法Natural approach自然法Reflective teaching反思教学Communicative approach交际法或交际路子Communicative competence交际能力Linguistic competence语言能力Teaching procedures教学步骤Teaching aids教学辅助材料和设备Variety多样性Flexibility灵活性Learnability可学性Linkage连接Micro planning微观备课Macro planning宏观备课RP:received p ronunciation英国伦敦附近的一种方言。

英语语法基础术语概述(中英对照)英语语法基础术语概述(中英对照)
在研究英语语法方面,理解常用的基础术语是很重要的。
本文将对一些基本术语进行简要概述,旨在帮助读者更好地掌握英语语法。
名词/Noun
名词是指人、事物、地方或抽象概念,如“人”、“桌子”、“加油站”、“爱情”等等。
动词/Verb
动词描述动作或状态。
动作动词包括“跑”、“跳”、“走”等,状态动词包括“是”、“有”、“喜欢”等。
形容词/Adjective
形容词用于描述名词或代词,如“美丽的”、“晴朗的”、“重要的”。
副词/Adverb
副词用于描述动词、形容词、其他副词和整个句子的意义,如“快速地”、“非常”、“可能”等。
代词/Pronoun
代词用于替代名词,以避免重复,如“他”、“她”、“它”等。
冠词/Article
冠词用于限定名词,并指明其在句子中的身份,包括“a/an”和“the”。
介词/Preposition
介词用于表达位置、方向、时间、方式和目的,如“在”、“到”、“在...之前”、“以...的方式”等。
连词/Conjunction
连词用于连接句子或句子的不同部分,包括“and”,“but”,“or”等。
感叹词/Interjection
感叹词用于表达情感、愤怒或惊讶,并不与其他部分相关,如“哦”、“嗨”等。
以上就是英语语法基础术语的简要概述。
希望本文能对您的英
语语法学习有所帮助。

* (2) Classification in terms of grammatical functionNoun phrase Verb phraseAdjective phrase Adverb phrase Preposition phraseConjunction(1) I ndependent clause & Subordinate clause独立分句和从属分句(2) S imple clause & Complex clause (*complex sentence)简单分句和复杂分句(*复杂句)(3) M ain clause & Subordinate clause主句和从句(4) F inite clause, non-finite clause and Verbless clause限定分句、非限定分句、无动词分句(1) Full sentence &Minor sentence 完全句和不完全句(2)Simple sentence, Compound sentence, Complex sentence & Compound complex sentence 简单句、并列句、复杂句、并列复杂句(3)Declarative sentence, imperative sentence, interrogative sentence, exclamatory sentence《新编英语语法教程》主要章节语法术语Introduction: Grammatical Hierarchy (导论一语法层次)1. Morpheme词素Free morpheme 自 由词素 Bound morpheme 粘附词素 j Allomorph 词素变体 2. Parts of speech (word class) Simple words 简单词 Derivatives 派生词Compounds 复合词 *(1) Classification in terms of word formationOpen-class words (content words)开放词类(实义词)NounVerb Adjective AdverbClosed-class words (function words封闭词类(功能词)Preposition PronounDeterminer Conjunction AuxiliaryIntermediate class(中间词类)NumeralsInterjection3. Phrases词组4. Clause分句5. Sentence句子Lecture 1 Sentence Structure ( L1 )Sentence elements: S (subject)V (predicate verb)O (object)主语 谓语动词 宾语1. Two ways of sentence analysis 1) SVOSentence ClauseSentence = Subject + Predicate (Predicate Verb + Object, Complement, Adverbial, etc.)句子由主语和谓语构成,进一步把谓语剖析为谓语动词、宾语、补语、状语等。
导论———语法层次0.1 词素1)自由词素2)粘附词素0.2 词1)简单词、派生词、符合词2)封闭词类和开放词类0.3 词组1)名词词组2)动词词组3)形容词词组4)副词词组5)介词词组0.4分句1)独立分句和从属分句2)简单分句和复杂分句3)主句和从句4)限定分句、非限定性分句、无动词分句0.5 句子1)完全句和不完全句2)简单句、并列句、复杂句、并列复杂句第1讲句子结构1.1 主谓结构和句子分析1)主语和谓语2)句子分析1.2 基本句型及其转换与扩大1)基本句型2)基本句型的转换与扩大第2讲主谓一致(一)2.1指导原则1)语法一致2)意义一致和就近原则2.2 以-s 结尾的名词作主语的主谓一致问题1)以-s结尾的疾病名称和游戏名称2)以-s结尾的学科名称3)以-s结尾的地理名称4)其他以-s结尾的名词2.3 以集体名词作主语的主谓一致问题1) 通常作复数的集体名词2)通常作不可数名词的集体名词3)既可作单数也可作复数的集体名词4)a committee of 等+复数名词第3讲主谓一致(二)3.1 以并列结构作主语的主谓一致问题1)由and/both... And 连接的并列主语2)由or/nor/either...or 等连接的并列主语3)主语+as much as 等4)主语+as well as 等3.2 以表示数量概念的名词词组作主语的主谓一直问题1)以表示确定数量的名词词组作主语2) 以表示非确定数量的名词词组作主语3.3 其他方面的主谓一致问题1)以名词性分句作主语的主谓一致问题2)以非限定分句作主语的主谓一致问题3)关系分句中的主谓一致问题4)分裂句中的主谓一致问题5)存在句中的主谓一致问题第4讲4.1 名词分类和名词词组的句法功能1)名词分类2)名词词组的句法功能4.2 名词的数1)规则复数和不规则复数2)集体名词、物质名词、抽象名词、专有名词的数4.3 单位词1)一般表示个数的单位词2)表示形状的单位词3)表示容积的单位词4)表示动作状态的单位词5)表示成双、成对、成群的单位词第5讲5.1 名词属格的构成、意义和用法1)名词属格的构成2)名词属格的意义3)名词属格的用法5.2 独立属格和双重属格1)独立属格2)双重属格第6讲限定词(一)6.1限定词与三类名词的搭配关系1)能与三类名词搭配的限定词2)只能与单数名词搭配的限定词3)只能与复数名词搭配的限定词4)只能与不可数名词搭配的限定词5)能与单、复数名词搭配的限定词6)能与单数名词和不可数名词搭配的限定词7)能与复数名词和不可数名词搭配的限定词6.2 限定词与限定词的搭配关系1)中位、前位、后位限定词2)三类限定词的搭配关系6.3 若干限定词用法比较1)many, much, a lot of, lots of, plenty of 等2)(a) few ,(a) little3) some, any.4) all,both ,every,each ,either,neither,any第7讲限定词(二)7.1 冠词的类指和特指1)冠词的类指用法2)冠词的特指用法3)后照应特指、前照应特指、语境特指7.2 各类名词前的冠词用法1)冠词与专有名词2)冠词与普通名词3)冠词的其他用法第8讲代词(一)8.1 代词及其先行项的“数的一致”1)先行项为every-, some-等符合词时代词的选择2)先行项为某些并列结构时代词的选择3)先行项为某些集体名词时代词的选择4)先行项为“复数名词或代词+each”时代词的选择8.2 代词及其先行项的“性”的一致1)先行项为阳性或阴性名词时代词的选择2)先行项为通性名词时代词的选择3)先行项为中性名词时代词的选择8.3 代词及其先行项的“人称”一致1)代词及其先行项在句中的人称一致2)语篇中的人称一致第9讲代词(二)9.1 代词的格1)用主格还是用宾格2)用宾格还是用属格9.2 物主代词、反身代词、人称代词的类指用法1)物主代词2)反身代词3)人称代词的类指用法9.3 代词照应1)后照应、前照应、语境照应2)人称照应3)指示照应第10讲10.1 动词分类(一)1)主动词和助动词2)及物动词、不及物动词、连系动词3)动态动词和静态动词10.2 动词分类(二)4)单词动词和词组动词5)限定动词和不限定动词6)规则动词和不规则动词10.3 动词的时、体、态、式该说1)动词的时、体形式2)主动态和被动态3)陈述式、祈使式、虚拟式4)限定动词词组和非限定动词词组第11讲动词的时和体(一)11.1 一般现在式的用法1)表示不受时限的客观存在2)表示现在习惯动作3)表示现时状态和现在瞬间动作4)表示将来时间5)表示过去时间11.2 一般过去时的用法1)表示过去的时间2)表示现在时间和将来时间11.3 现在进行体的用法1)表示说话时正在进行的动作2)表示现阶段正在进行的动作3)表示按计划近期内即将发生的动作4)现在进行体的其他用法11.4 过去进行体的用法1)表示过去某时正在进行的动作2)表示过去某种习惯性动作3)表示过去将来时间里的动作4)表示现在时间和将来时间里的动作5)过去进行体与一般过去时用法比较第12讲动词的时和体(二)12.1 现在完成体和现在完成进行体的用法1)现在完成体的用法2)现在完成进行体的用法3)现在完成(进行)体与过去时用法比较12.2 过去完成体和过去完成进行体的用法1)过去完成体的用法2)过去完成进行体的用法3)在由when/before/after/until等连词引导的分句中过去完成体的用法4)过去完成体的想象性用法12.3关于完成体用法的几点补充说明1)完成体与since-分句2)完成体与have got /have got to3)完成体在“It is the first time + that-分句”中的使用第13 讲将来时间表示法13.1 表示将来时间的多种结构1)will/shall +不定式2)will/shall +不定式进行体/完成体3)be going to +不定式4)be + ing (现在进行体)5)be to + 不定式6)一般现在时13.2 过去将来时间表示法1)would +不定式2)was/ were going to +不定式3)was/ were to + 不定式4)过去进行体和一般过去式5)was/ were about to + 不定式第14 讲被动态(一)14.1 主动句和被动句1)主动句变被动句的转换规则2)主动句与被动句相互转换的限制性14.2 词组动词的被动态1)一般词组动词的被动态2)“动词+ 名词+介词”的被动态14.3 非限定动词的被动态1)不定式的被动态2)-ing 分词的被动态3)不定式被动态和-ing 分词被动态的用法比较15.1 被动句的用法1)被动句的使用场合2)两种被动句型的转换15.2 被动结构和被动意义1)英汉被动意义表示法比较2)主动结构表示被动意义的问题3)被动结构还是系补结构第16 讲虚拟式16.1 be- 型虚拟式1)用于表示命令、决定、建议等词语之后的that 分句中2)用于由if,though等引导的分局中3)由于某些公式化语句中16.2 were-型虚拟式1)用于某些状语分句中2)用于某些名词性分句中16.3 假设意义表示法综述1)用动词的过去时形态表示假设意义2)用情态助动词过去时形式表示假设意义第17 讲助动词(一)17.1 情态意义表示法1)表示“能力”和“可能”2)表示“许可”和“不许”3)表示“义务”和“必然”4)表示“预见”和“推测”5)表示“意愿”、“意图”和“决心”6)其他情态意义17.2 情态助动词的推测性用法和非推测性用法1)能作推测性用法的情态助动词2)能作推测性用法的情态助动词的句法特征3)能作推测性用法的情态助动词与所指时间第18 讲助动词(二)18.1 半助动词1)半助动词的类型2)半助动词与“it...that”结构18.2 助动词的缩略形式1)否定缩略形式2)肯定缩略形式3)非缩略形式的使用场合19.1 不定式的结构形式1)不定式的一般形式、进行体和完成体形式2)带to不定式与不带to不定式19.2 关于不定式符号的几个问题1)不定式符号的单独使用问题2)不定式符号的省略问题3)不定式符号to 与介词to的辨别问题第20 讲不定式(二)20.1 不定式与形容词的搭配关系1)主句主语是不定式结构的逻辑主语2)主句主语是不定式结构的逻辑宾语3)主句主语是不定式结构的逻辑主语或宾语20.2 不定式与名词的搭配关系1)主——动关系,动——宾关系、同位关系2)用主动态还是用被动态3)“名词+不定式”与“名词+介词+ing分词”20.3 不定式与动词的搭配关系1)动词+不定式2)动词+宾语+不定式3)动词+(宾语)+不定式第21 讲—ING分词21.1 —ing分词与动词的搭配冠词1)能带—ing分词而不能带不定式动词的动词2)动词+宾语+介词+ing分词21.2 既能直接带不定式又能直接带—ing分词的动词1)既能带不定式和--ing分词而意义无甚区别的动词2)既能带不定式和--ing分词而意义不同的动词第22 讲---ED分词22.1 --ed分词作前置修饰语1)来自及物动词的-ed分词作前置修饰语2)来自不及物动词的-ed分词作前置修饰语22.2 -ed分词作补语1)古英语遗留下来的几个—ed 分词的用法问题2)能带—ed分词作宾语补语的动词分类22.3 关于“悬念分词”1)“依着法则”和“悬念分词”2)关于“悬念分词”的可接受性问题第23 讲形容词和形容词词组23.1 形容词分类1)单词形容词和复合形容词2)中心形容词和外围形容词3)动态形容词和静态形容词4)等级形容词和非等级形容词23.2 形容词与分词1)由—ing分词转化来的形容词2)有—ed分词转化来的形容词3)主动意义和被动意义23.3 形容词(词组)作名词修饰语1)形容词(词组)的前置和后置2)补语形容词3)形容词词组与关系分句23.4 形容词词组作补语1)形容词+介词词组2)形容词+不定式3)形容词+that-分句第24 讲副词和副词词组24.1 副词和副词词组的主要用法1)副词在词组中作修饰语2)副词词组在句中作状语24.2 兼有两种形式的副词1)关于clean / cleanly 2)关于clear / clearly 3)关于close / closer 4)关于dead / deadly 5)关于direct / directly 6)关于easy / easily 7)关于fair / fairly 8)关于firm / firmly 9)关于high / highly 10)关于loud / loudly 11)关于pretty / prettily 12)关于right / rightly 13)关于sharp / sharply 14)关于slow / slowly 15)关于sure / surely第25 讲比较等级和比较结构25.1 形容词和副词的比较等级1)形容词比较等级和最高级的规则形式2)副词比较级和最高级的规则形式3)形容词、副词比较级和最高级的不规则形式25.2 比较结构1)as....as.....结构2)more ....than 结构3)“the + 形容词/副词最高级+比较范围”结构25.3 关于比较结构用法的补充说明1)more....than结构的其他用法2)not so...as 与not so much....as3)not more / -er than 与no more / -er than 4)the more... the more与more and more第26 讲介词和介词词组26.1 介词与形容词、动词、名词的搭配关系1)介词与形容词的搭配2)介词与动词的搭配3)介词与名词的搭配26.2 复杂介词1)双词介词2)三词介词3)四词介词26.3 介词词组与某些限定分句的转换关系1)介词词组在意义上相当于that-分词2)介词词组在意义上相当于状语分词3)介词词组在意义上相当于关系分句第27 讲陈述句、疑问句、祈使句、感叹句27.1 陈述句1)肯定陈述句2)否定陈述句27.2 疑问句1)一般疑问句2)特殊疑问句3)选择疑问句4)附加疑问句27.3 祈使句和感叹句1)祈使句2)感叹句第28 讲存在句28.1 存在句的结构特征1)存在句的引导词2)存在句的实义主语3)存在句的谓语动词28.2 存在句的非限定形式1)作介词补足成分2)作宾语3)作主语和宾语第29 讲IT- 句型29.1 “虚义”it 和“先行”it1)“虚义”it2)“先行”it29.2 “分裂句引导词”it1)什么是分裂句2)“分裂句引导词”it与“先行”it3)“拟似”分裂句第30 讲30.1 并列结构的各种形式1)并列结构的构成2)并列连词和标点符号3)并列结构中的插入语4)并列结构中的对称组合30.2 并列连词的意义和用法1)以and为代表的表示语义引申的并列连词2)以or为代表的表示选择的并列连词3)以but为代表的表示语义转折和对比的并列连词第31讲从属结构(一)31.1 并列与从属1)从属是语义上分清主次的手段2)从属连词31.2 限定从属分句1)名词性分句2)形容词性分句(关系分句)3)副词性分句(状语分句)31.3 关于状语分句的几点补充说明1)when,while,as,before,after,until的用法2)because,for,since,as, now that结构3)关于so that 和so ... that 结构4)关于unless 和if...not5)关于though 和although第32讲从属结构(二)32.1 不定式分句1)不定式分句的结构模式2)不定式分句的句法功能32.2 -ing分词分句1)-ing分词分句的结构模式2)-ing分词分句的句法功能32.3 -ed分词分句1)-ed分词分句的结构模式2)-ed分词分句的句法功能32.4 无动词分句1)无动词分句的结构模式2)无动词分句的句法功能32.5 关于“独立结构”1)“独立结构”的实质和类型2)“独立结构”的用法和意义第33 讲关系分句33.1 限制性关系分句和非限制性关系分句1)限制性关系分句2)非限制性关系分句33.2 关系词的选择1)在限制性关系分句中关系代词的选择2)在限制性关系分句中关系代词的其他用法3)在非限制性关系分句中关系代词的选择4)关系词的省略问题33.3 由“介词+关系代词”引导的分句结构1)由“介词+关系代词”引导的限定分句2)由“介词+关系代词”引导的非限定分句33.4 双重关系分句和嵌入式关系分句1)双重关系分句2)嵌入式关系分句第34 讲条件句34.1 第一种类型条件句(Type 1 )1)表示普遍真理和客观事实2)表示现在习惯动作3)表示过去习惯动作34.2 第二种类型条件句(Type 2 )1)第二种类型条件句的基本形式2)第二种类型条件句的变体形式3)第二种类型条件句的替换形式34.3 第三种类型条件句(Type 3 )1)第三种类型条件句的基本形式2)第三种类型条件句的变体形式34.4 第四种类型条件句(Type 4 )1)第四种类型条件句的基本形式2)第四种类型条件句的变体形式第35 讲直接引语和间接引语35.1 陈述句的间接引语1)现在时间推移到过去时间2)过去时间推移到过去的过去3)将来时间推移到过去将来时间4)人称代词、限定词、时间状语、地点状语的变化35.2 疑问句的间接引语1)疑问句间接引语的引导词问题2)疑问句间接引语的交际功能问题35.3 祈使句和感叹句的间接引语1)祈使句的间接引语2)感叹句的间接引语35.4 各类句子混杂使用时的间接引语1)根据表意需要增添词语2)根据表意需要调整句子结构或改变说法第36 讲修饰36.1 名词修饰语1)前置修饰语和后置修饰语2)限定性修饰语和非限定性修饰语3)分隔修饰36.2 同位语1)名词词组同位语的结构形式2)名词词组同位语的引导词3)名词词组同位语的附加修饰成分4)限定性同位语和非限定性同位语36.3 状语1)修饰性状语2)评注性状语3)连接性状语第37 讲替代37.1 名词性替代1)什么是名词性替代2)替代词one / ones 的用法3)替代词one ,类指代词one和数词one4)替代词one / ones 和实义词one /ones37.2 动词性替代1)什么是动词性替代2)动词替代词的用法37.3 分句性替代1)什么是分句性替代2)分句替代词的用法第38 讲省略38.1 并列结构中的省略现象1)并列句中的省略现象2)名词词组中的省略现象3)介词词组中的省略现象38.2 主从结构中的省略现象1)主句中的省略现象2)状语分句中的省略现象3)名词性that-分句中的省略现象4)名词性wh-分句中的省略现象第39 讲后置、前置、倒装39.1 后置1)句尾焦点和句尾重心2)关键词语的后置39.2 前置与倒装1)不引起倒装的前置2)引起倒装的前置第40 讲从句到篇40.1 句子和语篇1)句子的意义和交际功能2)句子结构的正确性和适合性40.2 语篇纽带1)连句成篇的逻辑纽带2)连句成篇的语法纽带3)连句成篇的语汇纽带40.3 语篇结构——句子、语段、语篇1)什么是语段2)从语段到语篇40.4 主题语段和辅助语段1)单语段语篇和多语段语篇2)主题语段(或主题句)和辅助语段(或辅助句)。
Words and phrases:(1) legacy: n. money or property that someone receives from someone else after his or her deathe.g. The two brothers split on inheriting the legacy of their parents.The poor man received a small legacy from his aunt whom he had never met before.(2) amount to: figures, sums, etc. equal a total when added togethere.g. His debts amount to five thousand dollars.The total sales of the company amounted to 3 million dollars last year.(3) literary: a. relating to literaturee.g. He is considered to be one of the twentieth century’s literary giants.Literary theory in a strict sense is the systematic study of the nature of literature and ofthe methods for analyzing literature.(4) awe: n. a feeling of great respect and liking for someone or somethinge.g. He felt wonder mingled with awe at the Great Wall.Today most people still tend to hold scientists in awe.(5) amazing: a. very good, especially in an unexpected way; surprisingly greate.g. He’s an amazing player to watch.It was amazing that the boy was able to solve the problem so quickly.(6) supposition: n. something that one thinks is true, even though it is not certain and cannot beprovede.g. His version of events is pure supposition.We mustn’t condemn him on mere suppositions.(7) vague: a. unclear because someone does not give enough detailed information or does not sayexactly what they meane.g. He was told not to be vague on matters of principle.The governor gave only a vague outline of his tax plan.(8) thriving: a. very successful, very lively and profitablee.g. A thriving community is highly connected, collaborative, caring and compassionate, andresponsive to the needs of its members.The investigation paints a picture of a depraved yet thriving enterprise.(9) reputation: n. the opinion that people have about someone or something because of what hashappened in the paste.g. It is impossible to calculate Shakespeare’s reputation in his own lifetime and shortlyafter.Your reputation may very well be your organization’s most important asset.(10) gaze: v.look at someone or something for a long time, giving it all your attention, oftenwithout realizing you are doing soe.g. You gaze into my eyes, and I know the feelings are true.With all the ambient light and the pollution of modern cities, delightful moments whenyou can lie and gaze at stars are rare.(11) plot: v. make a schematic or technical drawing of that shows how things work or how they areconstructede.g. A computer is used to plot the movements of everyone in the building.He proposed to plot a graph to show the increase in sales figures of the company.(12) clue: n. evidence that helps to solve a problem, something that helps to find the answer to aproblem or mysterye.g. The research reveals that the hair on your head may give a clue to your health.His new declaration aired on TV gave little clue to his intentions.(13) confirm: v. show that something is definitely true, especially by providing more proof; saythat something is definitely truee.g. The doctor needs to do more tests to confirm his diagnosis.I’m just calling to confirm your appointment tomorrow at 3:00 p.m.(14) conviction: n. [uncountable] the feeling of being sure about something and having no doubtse.g. It was a reasonable explanation, but his voice lacked conviction.He is in the full conviction that he will be promoted.(15) in a flash: without any delaye.g. A smile happens in a flash, but its memory can last a lifetime.In a flash he remembered everything and a plan began to form in his mind.(16) trace: v. find someone or something that has disappeared by searching for them carefullye.g. The mother had never given up her hope of tracing her missing daughter before shefinally found her.Police are trying to trace a young woman who was seen near the accident.(17) sufficiently: ad. to a degree which is as much as needed for a particular purposee.g. The function of the stomach is to digest food sufficiently to enable it to pass into theintestine.His income is not sufficiently great to support his whole family.(18) influential: a.having a lot of influence and therefore changing the way people think andbehavee.g. All these facts are influential in reaching a decision by the government.Most of us are much more influential than we know.(19) make a name for oneself: achieve distinction, become prominent or well knowne.g. He has become the first African footballer to make a name for himself in Europe.Perhaps the best way to make a name for ourselves in the music industry is to get a music degree.(20) marvellous: a. extremely good, enjoyable, impressive, etc.e.g. Let’s all give them a big hand for their marvellous creations.It would be really marvellous to see her again.(21) verse: n. [uncountable] words arranged in the form of poetry; [countable] a set of lines thatforms one part of a song, poem, or a booke.g. Latin verse remained completely incomprehensible to me.These Bible verses about love are for V alentine’s Day, a wedding ceremony, a romantic occasion, or just for sharing with a beloved friend.(22) a mass of: a large amount or quantity of somethinge.g. We can evolve the truth from a mass of confused evidence.Setting to work, I buried myself under a mass of papers.(23) ever since: (duration) continuously since a specified time or event, from then till nowe.g. He started smoking last year and has been coughing ever since.Apparently they have not stopped crying ever since the earthquake happened(24) detailed: a. containing or including a lot of information or detailse.g. He told us that a detailed list of their publications was available on request.The teacher provided her students with a detailed analysis of the learning situation.(25) apparently: ad. from appearances alonee.g. The gentleman was apparently much surprised at the news.My mom had asked me to take out the trash, but apparently someone had already done it for me when I got there.(26) inspire: v. encourage someone by making them feel confident and eager to do somethinge.g. A good play serves to educate and inspire the people.We should associate with the people who can inspire us.(27) attempt: n. an act of trying to do something, especially something difficulte.g. She passed her driving test at the first attempt.The attempt was made without result.(28) astonishing: a. so surprising that it is difficult to believee.g. It was astonishing to everyone that the court had made such a decision.She told me a lot of astonishing stories on our way home.(29) a buddle of: a group of things such as papers, clothes, or sticks that are fastened or tiedtogethere.g. He sold a bundle of old magazines to the second-hand bookstore.Dad found a bundle of spelling mistakes in my composition.。
新编英语教程(大一第一学期)unit7语法点Unit 7 When Lightning Struck1.I was in the tiny bathroom in the back of the plane when I felt the slamming jolt, andthen the horrible swerve that threw me against the door. Oh, Lord, I thought, this is it!Somehow I managed to unbolt the door and scramble out. The flight attendants, already strapped in, waved wildly for me to sit down. As I lunged toward my seat, passengers looked up at me with the stricken expressions of creatures who know they are about to die.2.“I think we got hit by lightning,” the girl in the seat next to mine said. She was from asmall town in east Texas, and this was only her second time on an airplane. She had won a trip to England by competing in a high school geography bee and was supposed to make a connecting flight when we landed in Newark.3.In the next seat, at the window, sat a young businessman who had been confidentlyworking. Now he looked worried. And that really worries me —when confident-looking businessmen look worried. The laptop was put away. “Something’s not right,” he said.4.The pilot’s voice came over the speaker. I heard vaguely through my fear, “Enginenumber two ... emergency landing ... New Orleans.” When he was done, the voice of a flight attendant came on, reminding us of the emergency procedures she had reviewed before takeoff. Of course I never paid attention to this drill, always figuring that if we ever got to the point where we needed to use life jackets, Iwould have already died of terror.5.Now we began a roller-coaster ride through the thunderclouds. I was ready to faint, butwhen I saw the face of the girl next to me, I pulled myself together. I reached for her hand and reassured her that we were going to make it. ”What a story you’re going to tell when you get home!” I said. “After this, London’s going to seem like small potatoes.”6.I wondered where I was getting my strength. Then I saw that my other hand was tightlyheld by a ringed hand. Someone was comforting me —a glamorous young woman across the aisle, the female equivalent of the confident businessman. She must have seen how scared I was and reached over.7.“I tell you,” she confided, “the problems I brought up on this plane with me sure don’ts eem real big right now.” I loved her Southern drawl, her indiscriminate use of per fume, and her soulful squeezes. I was sure that even if I survived the plane crash, I’d have a couple of broken fingers from all the TLC.“Are you okay?” she kept asking me.8.Among the many feelings going through my head during those excruciating 20 minuteswas pride —pride in how well everybody on board was behaving. No one panicked. No one screamed. As we jolted and screeched our way downward, I could hear small pockets of soothing conversation everywhere.9.I thought of something I had heard a friend say about the wonderful gift his dying fatherhad given the family: he had died peacefully, as if not toalarm any of them about an experience they would all have to go through someday.10.And then —yes! —we landed safely.Outside on the ground, attendants and officialswere waiting to transfer us to alternative flights. But we passengers clung together. We chatted about the lives we now felt blessed to be living, as difficult or rocky as they might be.The young businessman lamented that he had not a chance to buy his two little girls a present.An older woman offered him her box of expensive Lindt chocolates, still untouched, tied with a lovely bow. “I shouldn’t be eating the m anyhow,” she said. My glamorous aisle mate took out her cell phone and passed it around to anyone who wanted to make a call to hear the reassuring voice of a loved one.11.There was someone I wanted to call. Back in Vermont, my husband, Bill, wasanticipating my arrival late that night. He had been complaining that he wasn’t ge tting to see very much of me because of my book tour. I had planned to surprise him by getting in a few hours early. Now I just wanted him to know I was okay and on my way.12.When my name was finally called to board my new flight,I felt almost tearful to beparting from the people whose lives had so intensely, if briefly, touched mine.13.Even now, back on terra firma, walking down a Vermont road, I sometimes hear anairplane and look up at that small, glinting piece of metal. I remember the passengers on that fateful, lucky flight and wish I could thank them for the many acts of kindness I witnessed andreceived. I am indebted to my fellow passengers and wish I could pay them back.14.But then, remembering my aisle mate’s hand clutching mine while I clutched the handof the high school student, I feel struck by lightning all over again: the point is not to pay back kindness but to pass it on.Paragraphs 1-4Words and Expressions1. lightning: n. a powerful flash of light in the sky caused by electricity passing from one cloud to another or to the earth, usu. followed by thundere.g. He runs as fast as lightning.Collocation:be struck by lightning: be hit by lightninge.g. The tower has been struck by lightning.Derivation:lightning: adj.2. jolt: n. a sudden rough shaking movemente.g. Residents felt the first jolt of the earthquake at about 8 a.m.Derivation:jolt: v.Comparison: jolt, jerkjerk: a sudden quick movementPractice:1) The train moved off with a ________ (jerk)2) I felt every _________ of the bus. (jolt)3. swerve: n. the act of turning asidee.g. The car made a sudden swerve to avoid the dog.Comparison:swirl: the act of turning around quickly in a circular movementDerivation:swerve: v.4. unbolt:v. unlock; release the bolts of (a door, for example)e.g. The shopkeeper unbolted the door and let the customers in.Comparison: unbolt, untieuntie: undo the knots in something or undo something that has been tiedAntonym:bolt5. scramble:v. climb up or over something with difficulty, using your hands to help youe.g. The boys scrambled over the wall.Collocations:scramble up/down/back, etc.e.g. We scrambled up a rocky slope.Synonym:climbDerivation:scramble: n.6. lunge:v. make sudden forceful forward movements of the body, often to make an attacke.g. He lunged at me with a knife.Comparison: lunge, lunglung: one of the two organs in your body that you breathe withe.g. Smoking can cause lung cancer.Derivation:lunge: n.Translation:They both lunged forwards to catch a ball.他们俩都冲上去抢球。
1.主谓一致主谓一致Subject-Verb Concord即谓语动词在人称和数上要和主语保持一致,主谓一致包括语法一致、意义一致和就近一致。
1.1指导原则(1)语法一致语法一致即谓语动词在单复数形式上要和主语保持一致eg.A grammar book helps you learn something about the rules of a language. (主语是单数形式,谓语也采取单数形式)语法书帮助你学习语言的某些规则.Grammar books help you learn something about the rules of a language. (主语是复数形式,谓语也采取复数形式)语法书帮助你学习语言的某些规则.(2)意义一致和就近原则意义一致就是谓语动词要和主语意义上的单复数保持一致。
补充解释和例句见书P22就近一致就是谓语动词要和靠近它的主语部分保持一致。
常出现在这类句子中的连词有:or, either…or…,neither…nor …,not only…but also …等.例句见书P23英语中,有时几个名词或代词有某些此连接起来一起作句子的主语,此时,谓语动词的形式就须有与之最接近的名词或代词的人称和数决定。
如:(1)There is a desk and five chairs in his room.他房间里有一张办公桌和五把椅子。
There are five chairs and a desk in his room.他房间里有五把椅子和一张办公桌。
(2)Either you or Li Lei is going to be sent there.要么是你要么是李蕾将被派到那里去。
Are either you or Li Lei going to be sent there?是你将被派到那里去还是李蕾将被派到那里去?1.2-s结尾的名词作主语(1)以-s结尾的疾病名称和游戏名称(2)以-ics结尾的学科名称(3)以-s结尾的地理名称(4)其他以-s结尾的名词1.3以集合名词作主语(1)通常作复数的集体名词见书P27【注】goods(货物),clothes(衣服)只有复数形式,且只表示复数意义:Such clothes are very cheap.那样的衣服很便宜。
常用英语语法术语表达语法grammar句法syntax词法morphology结构structure层次rank句子sentence从句clause词组phrase词类part of speech单词word实词notional word虚词structural word单纯词simple word派生词derivative复合词compound词性part of speech名词noun专有名词proper noun普通名词common noun可数名词countable noun不可数名词uncountable noun 抽象名词abstract noun具体名词concrete noun物质名词material noun集体名词collective noun个体名词individual noun介词preposition连词conjunction动词verb主动词main verb及物动词transitive verb不及物动词intransitive verb 系动词link verb助动词auxiliary verb情态动词modal verb规则动词regular verb不规则动词irregular verb短语动词phrasal verb限定动词finite verb非限定动词infinite verb使役动词causative verb感官动词verb of senses动态动词dynamic verb静态动词state verb感叹词exclamation形容词adjective副词adverb方式副词adverb of manner程度副词adverb of degree时间副词adverb of time地点副词adverb of place修饰性副词adverb of adjunct连接性副词adverb of conjunct 疑问副词interrogative adverb关系副词relative adverb代词pronoun人称代词personal pronoun物主代词possessive pronoun反身代词reflexive pronoun相互代词reciprocal pronoun指示代词demonstrative pronoun 疑问代词interrogative pronoun关系代词relative pronoun不定代词indefinite pronoun名词性物主代词nominal possessive pronoun形容词性物主代词adjectival possessive pronoun 冠词article定冠词definite article不定冠词indefinite article数词numeral基数词cardinal numeral序数词ordinal numeral分数词fractional numeral形式form单数形式singular form复数形式plural form限定动词finite verb form非限定动词non-finite verb form原形base form从句clause从属句subordinate clause并列句coordinate clause名词从句nominal clause定语从句attributive clause状语从句adverbial clause宾语从句object clause主语从句subject clause同位语从句appositive clause时间状语从句adverbial clause of time地点状语从句adverbial clause of place方式状语从句adverbial clause of manner让步状语从句adverbial clause of concession原因状语从句adverbial clause of cause结果状语从句adverbial clause of result目的状语从句adverbial clause of purpose条件状语从句adverbial clause of condition真实条件状语从句adverbial clause of real condition非真实条件状语从句adverbial clause of unreal condition 含蓄条件句adverbial clause of implied condition错综条件句adverbial clause of mixed condition句子sentence简单句simple sentence并列句compound sentence复合句complex sentence并列复合句compound complex sentence 陈述句declarative sentence疑问句interrogative sentence一般疑问句general question特殊疑问句special question选择疑问句alternative question附加疑问句tag question反义疑问句disjunctive question修辞疑问句rhetorical question感叹疑问句exclamatory question存在句existential sentence肯定句positive sentence基本句型basic sentence patern否定句negative sentence祈使句imperative sentence省略句elliptical sentence感叹句exclamatory sentence句子成分members of sentences主语subject谓语predicate宾语object双宾语dual object直接宾语direct object间接宾语indirect object复合宾语complex object同源宾语cognate object补语complement主补subject complement宾补object complement表语predicative定语attribute同位语appositive状语adverbial句法关系syntactic relationship 并列coordinate从属subordination修饰modification前置修饰pre-modification后置修饰post-modification限制restriction双重限制double-restriction非限制non-restriction数number单数形式singular form复数形式plural form规则形式regular form不规则形式irregular form格case普通格common case所有格possessive case主格nominative case宾格objective case性gender阳性masculine阴性feminine通性common中性neuter人称person第一人称first person第二人称second person第三人称third person时态tense过去将来时past future tense过去将来进行时past future continuous tense过去将来完成时past future perfect tense一般现在时simple present tense一般过去时simple past tense一般将来时simple future tense现在完成时past perfect tense过去完成时present perfect tense将来完成时future perfect tense现在进行时present continuous tense过去进行时past continuous tense将来进行时future continuous tense过去将来进行时past future continuous tense现在完成进行时present perfect continuous tense 过去完成进行时past perfect continuous tense语态voice主动语态active voice被动语态passive voice语气mood陈述语气indicative mood祈使语气imperative mood虚拟语气subjunctive mood否定negation否定范围scope of negation 全部否定full negation局部否定partial negation 转移否定shift of negation。
《新编英语语法教程》主要章节语法术语Introduction: Grammatical Hierarchy (导论—语法层次)2. Parts of speech (word class)3. Phrases词组4. Clause分句5. Sentence句子1. Morpheme词素Free morpheme 自由词素Bound morpheme 粘附词素Allomorph 词素变体Noun phraseVerb phraseAdjective phraseAdverb phrasePreposition phraseLecture 1Sentence Structure(L1)Sentence elements:S (subject)主语V (predicate verb)谓语动词O (object)宾语C (complement)补足语A (Adverbial)状语1. Two ways of sentence analysis1) SVOSentenceClauseNP VP NPSubject Predicate verb ObjectAll the man have done their best.Sentence = Subject + Predicate (Predicate Verb + Object, Complement, Adverbial, etc.)●句子由主语和谓语构成,进一步把谓语剖析为谓语动词、宾语、补语、状语等。
2) Subject + Predicate (= operator + predication)SentenceClauseSubject PredicateOperator PredicationAll the man have done their best.●句子由主语和谓语构成,进一步把谓语剖析为操作词(operator)和述谓成分(predication)。
2. Basic clause typesSVC, SV, SV A, SVO, SVOA, SVOC, SV oOLecture 2Subject-Verb Concord (L2-3)Guiding principles:Grammatical Concord Notional Concord Principle of Proximity语法一致原则意义一致原则就近原则Nominal clause Non-finite clause Relative clause Cleft sentence Existential clause 名词性分句非限定分句关系分句分裂句存在句Lecture 3Noun and Noun Phrase(L4-5)1. Classification of nounsPartitive (Unit Noun) 单位词2. Cases of NounsNominative case / Subjective case(主格)Accusative case / Objective case(宾格)Genitive case(属格)/ Possessive case(所有格)Dative case (受事格/与格)Genitive caseGenitive cases specifying the reference of the noun phrase.Specific reference (特指)Generic reference(类指)Indefinite genitive phrase(非确定特指)Lecture 4Determiner(L6-7)1.DefinitionDeterminers are function words which are used to determine or fix the reference of a noun.2.Classification3.ArticlesArticle is a major group of determiners used to delimit the scope of reference of nouns (主要用来限定名词的指称范围).*p.74, 7.1.3, 冠词的确定特指(definite specific reference)分为前照应特指(cataphoric specific reference)、后照应特指(anaphoric specific reference)和语境特指(situational reference),这与后面的代词照应(pronoun reference p.104, 9.3)在术语上略有不同。
Lecture 5Pronoun(L8-9)1. ClassificationAntecedent 先行词2. The use of reflexive pronoun (-self)3.Pronoun reference (代词照应)前照应(Cataphoric reference)、后照应(Anaphoric reference)、语境照应(Situational reference)、人称照应(Personal reference)、指示照应(Demonstrative reference)Lecture 6Verb and Verb Phrase(L10-22)1. Classification of verbs动词分类的标准有很多种,如上图所示,记住基本的术语和其用法就是。
比如及物动词、不及物动词、联系动词、助动词、动态动词、静态动词、词组动词、限定动词、非限定动词、不定式,不带to不定式(bare infinitive)等等,还有副词/介词小品词(adverb particle & proposition particle)。
➢Transitive Verbs:followed by objects.➢Intransitive verbs:do not require an object.➢Linking verbs:followed by subject compliments.•SVO主—动—宾(Transitive verb)•SV oO主—动—宾—宾(Ditransitive verb)【双宾语动词】•SVOC主—动—宾—补(Monotransitive verb)【单宾语动词】•SV主—动(Intransitive verb)•SVC主—动—补(Linking verb)•This aspect is of essential importance because the verb type here determines the basic sentence structure of your sentence and how you can expand your sentence.2. Five forms of Verbs(动词的五种基本形式)原形(base form)、第三人称单数(third person singular)、过去式(past tense)、过去分词(past tense)、现在分词(present participle)3. Tense and aspects4.Mood陈述式(Indicative mood)、祈使式(Imperative mood)、虚拟式(Subjunctive mood)5.Non-finite verbspp. 230-1动态形容词(Dynamic Adjective)、静态形容词(Stative Adjective)p.251 前置修饰语(Premodifier)、p.256 悬垂分词(Dangling Participle)/无依着分词(Unattached participle)、依着法则(Attachment rule)Lecture 7Adjective and Adverb(L23-24)1.1Adjective & Adjective Phrase1.2Adjective form1.3Adjective meaning动态形容词、静态形容词、等级形容词、非等级形容词2.1Adverb & Adverb Phrase (Adv P)2.2Adv form2.3Adv Meaningp.274 修饰性状语(Adjunct)、评注性状语(Disjunct)、连接性状语(Conjunct)Lecture 8Degree & Comparative Construction(L25)(比较等级和比较结构)1.Degree formsNotes:(1) -ing and -ed participial Adj takes more ~ & most ~(2) Some irregular forms, e.g., far, good(3) Gradable indefinite Det & Prons: many/much, few, little 2. Comparative construction3. General structure of Comparative constructionNotes:(1)More (less, fewer) can be Det. or Pron.:Model 2 accounted for more variance … than did Model 1. (Det.) It appeared in more than 50% of the request e -mails. (Pron.) (2) As & than are Conj or rarely Prep:John is taller than she (is). / John is taller than her.E.g. Apple is as tasty as tomato.Lecture 9 Statement, Question, Command & Exclamation (L27) (陈述句、疑问句、祈使句、感叹句)Sentence types句子1. Statements2. Questions (Interrogative sentences): General (yes -no) questions, Special (Wh -) questions, Alternative questions, Tag questions (附加疑问句), Rhetorical questions (修辞疑问句)3. Commands and Exclamations4. Tag questions (pp.316-9) Transferred negation (否定转移)Lecture 10 Existential Sentence & It -Patterns (L28-29) (存在句和It -句型)1. Existential sentence存在句、实义主语(Notional Subject )、真主语(Real subject )、地点状语(Locative adverbial )、时间状语(Temporal adverbial )*p.326, 提及的非确定特指,冠词、数词等限定词,见限定词(Determiner )一讲。