2013年国际头痛新分类和诊断标准
- 格式:ppt
- 大小:1.38 MB
- 文档页数:23

The international Classification of Headache disorders, 3rd Editon2.1.2 Infrequent episodic tension-type headache not associated with pericranial tenderness2.2.1 Frequent episodic tension-type headache associated with pericranial tenderness2.2.2 Frequent episodic tension-type headache not associated with pericranial tenderness2.3.2 Chronic tension-type headache not associated with pericranial tenderness3.3.1 Short-lasting unilateral neuralgiform headache attacks with conjunctival injection and tearing (SUNCT) 3.3.1.1 Episodic SUNCT3.3.1.2 Chronic SUNCT3.3.2 Short-lasting unilateral neuralgiform headache attacks with cranial autonomic symptoms (SUNA)3.3.2.1 Episodic SUNA3.3.2.2 Chronic SUNA3.4 Hemicrania continua3.5 Probable trigeminal autonomic cephalalgia3.5.1 Probable cluster headache3.5.2 Probable paroxysmal hemicrania3.5.3 Probable short-lasting unilateral neuralgiform headache attacks3.5.4 Probable hemicrania continua4.其它的原发性头痛Other primary headache disorders )4.1 Primary cough headache原发性咳嗽头痛4.1.1 Probable primary cough headache4.2 Primary exercise headache原发性运动性头痛4.2.1 Probable primary exercise headache4.3 Primary headache associated with sexual activity原发性性活动伴随的头痛4.3.1 Probable primary headache associated with sexual activity4.4 Primary thunderclap headache原发性霹雳头痛4.5 Cold-stimulus headache冷刺激性头痛4.5.1 Headache attributed to external application of a cold stimulus4.5.2 Headache attributed to ingestion or inhalation of a cold stimulus4.5.3 Probable cold-stimulus headache4.5.3.1 Headache probably attributed to external application of a cold stimulus4.5.3.2 Headache probably attributed to ingestion or inhalation of a cold stimulus则可两者均可作为诊断4.10 New daily persistent headache (NDPH) 新症每日持续性头痛4.10.1 Probable new daily persistent headach二、继发性头痛(the secondary headaches)5.缘于头、颈部外伤的头痛(Headache attributed to trauma or injury to the head and/or neck)5.1 Acute headache attributed to traumatic injury to the head5.1.1 Acute headache attributed to moderate or severe traumatic injury to the head5.1.2 Acute headache attributed to mild traumatic injury to the head5.2 Persistent headache attributed to traumatic injury to the head5.2.1 Persistent headache attributed to moderate or severe traumatic injury to the head5.2.2 Persistent headache attributed to mild traumatic injury to the head5.3 Acute headache attributed to whiplash5.4 Persistent headache attributed to whiplash5.5 Acute headache attributed to craniotomy5.6 Persistent headache attributed to craniotomy6.缘于头颈部血管疾病的头痛(Headache attributed to cranial or cervical vascular disorder )6.1 Headache attributed to ischaemic stroke or transient ischaemic attack6.1.1 Headache attributed to ischaemic stroke (cerebral infarction)6.1.2 Headache attributed to transient ischaemic attack (TIA)6.2 Headache attributed to non-traumatic intracranial haemorrhage6.2.1 Headache attributed to non-traumatic intracerebral haemorrhage非外伤性脑出血6.2.2 Headache attributed to non-traumatic subarachnoid haemorrhage (SAH)6.2.3 Headache attributed to non-traumatic acute subdural haemorrhage (ASDH)急性硬膜下血肿6.3 Headache attributed to unruptured vascular malformation未破裂的血管畸形6.3.1 Headache attributed to unruptured saccular aneurysm囊性动脉瘤6.3.2 Headache attributed to arteriovenous malformation (AVM) 动静脉畸形6.3.3 Headache attributed to dural arteriovenous fistula (DAVF) 硬膜动静脉瘘6.3.4 Headache attributed to cavernous angioma 海绵窦血管瘤6.3.5 Headache attributed to encephalotrigeminal or leptomeningeal angiomatosis (Sturge Weber syndrome)脑三叉神经或软脑膜血管瘤病6.4 Headache attributed to arteritis6.4.1 Headache attributed to giant cell arteritis (GCA) 颞动脉炎6.4.2 Headache attributed to primary angiitis of the central nervous system (PACNS)6.4.3 Headache attributed to secondary angiitis of the central nervous system (SACNS)6.7.1 Headache attributed to an intracranial endovascular procedure6.7.2 Angiography headache6.7.3 Headache attributed to reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome (RCVS)6.7.3.1 Headache probably attributed to reversible cerebral vasoconstrictionsyndrome (RCVS)6.7.4 Headache attributed to intracranial arterial dissection颅内动脉夹层6.8 Headache attributed to genetic vasculopathy6.8.1 Cerebral Autosomal Dominant Arteriopathy with Subcortical Infarcts and Leukoencephalopathy (CADASIL)6.8.2 Mitochondrial Encephalopathy, Lactic Acidosis and Stroke-like episodes (MELAS)6.8.3 Headache attributed to another genetic vasculopathy6.9 Headache attributed to pituitary apoplexy垂体卒中7.缘于非血管性颅内疾病的头痛(Headache attributed to non-vascular intracranial disorder )7.1 Headache attributed to increased cerebrospinal fluid pressure颅内压增高7.1.1 Headache attributed to idiopathic intracranial hypertension (IIH)7.1.2 Headache attributed to intracranial hypertension secondary to metabolic, toxic or hormonal causes7.1.3 Headache attributed to intracranial hypertension secondary to hydrocephalus7.2 Headache attributed to low cerebrospinal fluid pressure颅内压低下7.2.1 Post-dural puncture headache腰穿后7.2.2 CSF fistula headache脑脊液漏7.2.3 Headache attributed to spontaneous intracranial hypotension自发性低颅压7.3 Headache attributed to non-infectious inflammatory disease非感染性炎性疾病7.3.1 Headache attributed to neurosarcoidosis7.3.2 Headache attributed to aseptic (non-infectious) meningitis7.3.3 Headache attributed to other non-infectious inflammatory disease7.3.4 Headache attributed to lymphocytic hypophysitis7.3.5 Syndrome of transient Headache and Neurological Deficits with cerebrospinal fluid Lymphocytosis (HaNDL)7.4 Headache attributed to intracranial neoplasia颅内新生物7.4.1 Headache attributed to intracranial neoplasm7.4.1.1 Headache attributed to colloid cyst of the third ventricle7.4.2 Headache attributed to carcinomatous meningitis癌性脑膜炎7.4.3 Headache attributed to hypothalamic or pituitary hyper- or hyposecretion7.5 Headache attributed to intrathecal injection鞘内注射7.6 Headache attributed to epileptic seizure7.6.1 Hemicrania epileptica癫痫半颅痛7.6.2 Post-ictal headache癫痫发作后头痛7.7 Headache attributed to Chiari malformation type I (CM1)7.8 Headache attributed to other non-vascular intracranial disorder8.缘于物质或物质戒断的头痛(Headache attributed to a substance or its withdrawal)8.1 Headache attributed to use of or exposure to a substance or its withdrawal缘于某种物质的应用或戒断8.1.1.2 Delayed NO donor-induced headache8.1.2 Phosphodiesterase (PDE) inhibitor-induced headache磷酸二酯酶抑制剂8.1.3 Carbon monoxide (CO)-induced headache一氧化碳诱发8.1.4 Alcohol-induced headache酒精诱发8.1.4.1 Immediate alcohol-induced headache8.1.4.2 Delayed alcohol-induced headache8.1.5 Headache induced by food and/or additive由于食物成分/添加剂诱发8.1.5.1 Monosodium glutamate (MSG)-induced headache谷氨酸单钠盐(味精)8.1.6 Cocaine-induced headache可卡因诱发8.1.7 Histamine-induced headache组织胺诱发8.1.7.1 Immediate histamine-induced headache8.1.7.2 Delayed histamine-induced headache8.1.8 Calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP)-induced headache降钙素基因相关多肽诱发8.1.8.1 Immediate CGRP-induced headache8.1.8.2 Delayed CGRP-induced headache8.1.9 Headache attributed to exogenous acute pressor agent8.1.10 Headache attributed to occasional use of non-headache medication8.1.11 Headache attributed to long-term use of non-headache medication8.1.12 Headache attributed to exogenous hormone8.1.13 Headache attributed to use of or exposure to other substance8.2.4 Opioid-overuse headache鸦片类8.2.5 Combination-analgesic-overuse headache复合制剂过度应用8.2.6 Medication-overuse headache attributed to multiple drug classes not individually over used联合用药所致8.2.7 Medication-overuse headache attributed to unverified overuse of multiple drug classes8.2.8 Medication-overuse headache attributed to other medication8.3 Headache attributed to substance withdrawal物质戒断8.3.1 Caffeine-withdrawal headache咖啡因8.3.2 Opioid-withdrawal headache鸦片类8.3.3 Oestrogen-withdrawal headache雌激素8.3.4 Headache attributed to withdrawal from chronic use of other substance9.缘于感染的头痛(Headache attributed to infection)9.1 Headache attributed to intracranial infection颅内感染9.1.1 Headache attributed to bacterial meningitis or meningoencephalitis细菌性脑膜炎/脑膜脑炎9.1.1.1 Acute headache attributed to bacterial meningitis or meningoencephalitis9.1.1.2 Chronic headache attributed to bacterial meningitis or meningoencephalitis9.1.1.3 Persistent headache attributed to past bacterial meningitis or meningoencephalitis9.1.2 Headache attributed to viral meningitis or encephalitis病毒性脑膜炎或脑炎9.1.2.1 Headache attributed to viral meningitis9.1.2.2 Headache attributed to viral encephalitis9.1.3 Headache attributed to intracranial fungal or other parasitic infection真菌或寄生虫感染9.1.3.1 Acute headache attributed to intracranial fungal or other parasitic infection9.1.3.2 Chronic headache attributed to intracranial fungal or other parasitic infection9.1.4 Headache attributed to brain abscess脑脓肿9.1.5 Headache attributed to subdural empyema硬膜下积脓9.2 Headache attributed to systemic infection系统感染9.2.1 Headache attributed to systemic bacterial infection系统细菌感染9.2.1.1 Acute headache attributed to systemic bacterial infection9.2.1.2 Chronic headache attributed to systemic bacterial infection9.2.2 Headache attributed to systemic viral infection系统病毒感染9.2.2.1 Acute headache attributed to systemic viral infection9.2.2.2 Chronic headache attributed to systemic viral infection9.2.3 Headache attributed to other systemic infection其他系统感染9.2.3.1 Acute headache attributed to other systemic infection9.2.3.2 Chronic headache attributed to other systemic infection10.缘于内环境紊乱的头痛(Headache attributed to disorder of homoeostasis)10.1 Headache attributed to hypoxia and/or hypercapnia缺氧和/或高碳酸血症10.1.1 High-altitude headache高海拔头痛10.1.2 Headache attributed to aeroplane travel飞行头痛10.1.3 Diving headache潜水头痛10.1.4 Sleep apnoea headache睡眠呼吸暂停性头痛10.2 Dialysis headache10.3 Headache attributed to arterial hypertension高血压性头痛10.3.1 Headache attributed to phaeochromocytoma嗜络细胞瘤10.3.2 Headache attributed to hypertensive crisis without hypertensive encephalopathy无高血压脑病的高血压危象10.3.3 Headache attributed to hypertensive encephalopathy高血压脑病10.3.4 Headache attributed to pre-eclampsia or eclampsia先兆子痫10.3.5 Headache attributed to autonomic dysreflexia自主反射障碍10.4 Headache attributed to hypothyroidism甲状腺低下10.5 Headache attributed to fasting禁食10.6 Cardiac cephalalgia心源性头痛10.7 Headache attributed to other disorder of homoeostasis其他内环境稳定失调疾患11.缘于头、颈、眼、耳、鼻、鼻窦、牙、口或其他头面部结构病变的头面痛(Headache or facial pain attributed to disorder of the cranium, neck,eyes, ears, nose, sinuses, teeth, mouth or other facial or cervical structure )11.1 Headache attributed to disorder of cranial bone颅骨11.2 Headache attributed to disorder of the neck 颈部11.2.1 Cervicogenic headache11.2.2 Headache attributed to retropharyngeal tendonitis11.2.3 Headache attributed to craniocervical dystonia11.3 Headache attributed to disorder of the eyes眼睛11.3.1 Headache attributed to acute glaucoma急性青光眼11.3.2 Headache attributed to refractive error屈光不正11.3.3 Headache attributed to heterophoria or heterotropia (latent or persistent squint)斜视11.3.4 Headache attributed to ocular inflammatory disorder11.3.5 Headache attributed to trochleitis11.4 Headache attributed to disorder of the ears耳朵11.5 Headache attributed to disorder of the nose or paranasal sinuses鼻子或鼻窦11.5.1 Headache attributed to acute rhinosinusitis急性鼻窦炎11.5.2 Headache attributed to chronic or recurring rhinosinusitis11.6 Headache attributed to disorder of the teeth or jaw11.7 Headache attributed to temporomandibular disorder (TMD)11.8 Head or facial pain attributed to inflammation of the stylohyoid ligament11.9 Headache or facial pain attributed to other disorder of cranium, neck, eyes, ears, nose,sinuses, teeth, mouth or other facial or cervical structure12.缘于精神疾病的头痛(Headache attributed to psychiatric disorder)12.1 Headache attributed to somatization disorder躯体化障碍12.2 Headache attributed to psychotic disorder精神疾病三、脑神经痛、中枢和原发性颜面痛及其他头痛(painful cranial neuropathies, other facial pains and other headaches)13.脑神经痛和中枢性颜面痛(Painful cranial neuropathies and other facial pains)13.1 Trigeminal neuralgia三叉神经痛13.1.1 Classical trigeminal neuralgia13.1.1.1 Classical trigeminal neuralgia, purely paroxysmal13.1.1.2 Classical trigeminal neuralgia with concomitant persistent facial pain13.1.2 Painful trigeminal neuropathy13.1.2.1 Painful trigeminal neuropathy attributed to acute Herpes zoster13.1.2.2 Post-herpetic trigeminal neuropathy13.1.2.3 Painful post-traumatic trigeminal neuropathy13.1.2.4 Painful trigeminal neuropathy attributed to multiple sclerosis (MS) plaque13.1.2.5 Painful trigeminal neuropathy attributed to space-occupying lesion13.1.2.6 Painful trigeminal neuropathy attributed to other disorder13.2 Glossopharyngeal neuralgia舌咽神经痛13.3 Nervus intermedius (facial nerve) neuralgia中间神经痛(面神经痛)13.3.1 Classical nervus intermedius neuralgia13.6 Headache attributed to ischaemic ocular motor nerve palsy缺血性眼神经麻痹13.7 Tolosa-Hunt syndrome13.8 Paratrigeminal oculosympathetic (Raeder’s) syndrome13.9 Recurrent painful ophthalmoplegic neuropathy复发性痛性眼肌麻痹13.10 Burning mouth syndrome (BMS)13.11 Persistent idiopathic facial pain (PIFP)13.12 Central neuropathic pain中枢神经痛13.12.1 Central neuropathic pain attributed to multiple sclerosis (MS)13.12.2 Central post-stroke pain (CPSP)14. 其他头痛(Other headache disorders)。

The international Classification of Headache disorders, 3rd Editon头痛分类的国际标准(ICHD-III)概述:头痛分为三大组:原发性头痛;继发性头痛;脑神经痛、中枢和原发性颜面痛及其他头痛。
每一种原发性头痛均视为一种独立的疾病;继发性头痛一般只是某种疾病的一种症状,该头痛称为“缘于”此种疾病的头痛。
三大组头痛共分为14类: 一、原发性头痛(the primary headaches ) 1.偏头痛(Migraine ) 1.1 Migraine without aura 无先兆偏头痛 1.2 Migraine with aura 有先兆偏头痛 1.2.1 Migraine with typical aura 1.2.1.1 Typical aura with headache 1.2.1.2 Typical aura without headache 1.2.2 Migraine with brainstem aura 1.2.3 Hemiplegic migraine 偏瘫型偏头痛1.2.3.1 Familial hemiplegic migraine (FHM)—家族性 1.2.3.1.1 Familial hemiplegic migraine type 1 (FHM1) 1.2.3.1.2 Familial hemiplegic migraine type 2 (FHM2) 1.2.3.1.3 Familial hemiplegic migraine type 3 (FHM3) 1.2.3.1.4 Familial hemiplegic migraine, other loci 1.2.3.2 Sporadic hemiplegic migraine —散发性 1.2.4 Retinal migraine 1.3 Chronic migraine 慢性偏头痛1.4 Complications of migraine 偏头痛并发症1.4.1 Status migrainosus 偏头痛持续状态 1.4.2 Persistent aura without infarction 1.4.3 Migrainous infarction 偏头痛脑梗死 1.4.4 Migraine aura-triggered seizure 1.5 Probable migraine 很可能的偏头痛 1.5.1 Probable migraine without aura1.5.2 Probable migraine with aura 1.6 Episodic syndromes that may be associated with migraine 可能与偏头痛有关的发作性综合征1.6.1 Recurrent gastrointestinal disturbance1.6.1.1Cyclical vomiting syndrome 周期性呕吐 1.6.1.2 Abdominal migraine 腹型偏头痛1.6.2 Benign paroxysmal vertigo 良性发作性眩晕1.6.3 Benign paroxysmal torticollis 良性发作性斜颈2.紧张型头痛(Tension-type headache )每次发作持续30min-7d ,慢性者可持续不缓解2.1 Infrequent episodic tension-type headache 偶发性 <1d/月,至少10次以上(<12d/年)2.1.1 Infrequent episodic tension-type headache associated with pericranial tenderness无先兆偏头痛的诊断标准:A :符合B-D 特征,至少发作5次发作B :头痛(未经治疗)发作持续4-72小时C :至少有以下特征中的2项单侧性、搏动性、中重度痛、日常活动会加重D :至少以下一项伴随症状:恶心和/或呕吐、畏光和畏声E :不能归因于其他 先兆性偏头痛的诊断标准:A :符合B-C 特征,至少发作2次发作B :完全可逆以下症状的1项或多项✓ 视觉、感觉、语言障碍(典型先兆)✓ 肢体无力症状(偏瘫型偏头痛)✓ 脑干症状(基底型偏头痛)视网膜症状(视网膜型偏头痛)C :至少有以下特征中的2项 ✓ 至少1个先兆逐渐发展的过程>5min ,和/或 不同先兆接连发生过程>5min ✓ 每个先兆症状持续时间5-60min✓ 至少一个先兆症状为单侧性✓ 先兆发生同时或之后内60min 出现符合偏头痛 D :不能归因于其他 肢体无力症状可以持续至72h ,部分患者肢体无力感可持续数周; 若患者先兆持续1周以上,称为无梗死的持续先兆一般先兆症状多为双侧,可持续数月或数年 若先兆持续60min 至1周以内,则称为propablemigraine with aura若出现影像学梗死灶,则称为偏头痛性脑梗死 (年轻女性,后循环比较常见) 慢性偏头痛:偏头痛发作每月>15天,连续3个月以上 偏头痛持续状态:单次发作持续72小时以上4.5 Cold-stimulus headache 冷刺激性头痛 4.5.1 Headache attributed to external application of a cold stimulus4.5.2 Headache attributed to ingestion or inhalation of a cold stimulus 4.5.3 Probable cold-stimulus headache4.5.3.1 Headache probably attributed to external application of a cold stimulus4.5.3.2 Headache probably attributed to ingestion or inhalation of a cold stimulus 4.6 External-pressure headache 4.6.1 External-compression headache 4.6.2 External-traction headache 4.6.3 Probable external-pressure headache4.6.3.1 Probable external-compression headache 4.6.3.2 Probable external-traction headache 4.7 Primary stabbing headache4.7.1 Probable primary stabbing headache4.8 Nummular headache4.8.1 Probable nummular headache4.9 Hypnic headache4.9.1 Probable hypnic headache4.10 New daily persistent headache (NDPH) 新症每日持续性头痛4.10.1 Probable new daily persistent headach 二、继发性头痛(the secondary headaches )5.缘于头、颈部外伤的头痛(Headache attributed to trauma or injury to the head and/or neck )5.1 Acute headache attributed to traumatic injury to the head5.1.1 Acute headache attributed to moderate or severe traumatic injury to the head5.1.2 Acute headache attributed to mild traumatic injury to the head5.2 Persistent headache attributed to traumatic injury to the head5.2.1 Persistent headache attributed to moderate or severe traumatic injury to the head5.2.2 Persistent headache attributed to mild traumatic injury to the head5.3 Acute headache attributed to whiplash5.4 Persistent headache attributed to whiplash5.5 Acute headache attributed to craniotomy5.6 Persistent headache attributed to craniotomy6.缘于头颈部血管疾病的头痛(Headache attributed to cranial or cervical vascular disorder )6.1 Headache attributed to ischaemic stroke or transient ischaemic attack6.1.1 Headache attributed to ischaemic stroke (cerebral infarction)6.1.2 Headache attributed to transient ischaemic attack (TIA)6.2 Headache attributed to non-traumatic intracranial haemorrhage6.2.1 Headache attributed to non-traumatic intracerebral haemorrhage 非外伤性脑出血6.2.2 Headache attributed to non-traumatic subarachnoid haemorrhage (SAH)6.2.3 Headache attributed to non-traumatic acute subdural haemorrhage (ASDH)急性硬膜下血肿NDPH 诊断标准: A :持续性头痛,符合B-C 的标准B :Distinct and clearly remembered onset, with pain becomingcontinuous and unremitting within 24 hours C :Present for>3 monthsD :除外其他疾患 慢性头痛,起病急,可清晰回忆发病时间为哪一天 疼痛缺乏特点,可以为偏头痛,可以为紧张性,亦可两者混合 若患者符合慢性偏头痛或慢性紧张型头痛的标准,则不诊断NDPH 若患者为药物过度使用性头痛,且符合NDPH 的标准, 则可两者均可作为诊断6.3 Headache attributed to unruptured vascular malformation 未破裂的血管畸形6.3.1 Headache attributed to unruptured saccular aneurysm囊性动脉瘤6.3.2 Headache attributed to arteriovenous malformation (AVM) 动静脉畸形6.3.3 Headache attributed to dural arteriovenous fistula (DAVF) 硬膜动静脉瘘6.3.4 Headache attributed to cavernous angioma 海绵窦血管瘤6.3.5 Headache attributed to encephalotrigeminal or leptomeningeal angiomatosis (Sturge Weber syndrome) 脑三叉神经或软脑膜血管瘤病6.4 Headache attributed to arteritis6.4.1 Headache attributed to giant cell arteritis (GCA) 颞动脉炎6.4.2 Headache attributed to primary angiitis of the central nervous system (PACNS)6.4.3 Headache attributed to secondary angiitis of the central nervous system (SACNS)颞动脉炎诊断标准:美国风湿学会1990年1. 50岁以上发病:50岁以上发现症状2.新发的头痛:出现新发的局限性头痛3.颞动脉异常:颞动脉压痛或者与颈动脉的动脉硬化无关的搏动减弱4.血沉值升高:50mm/h以上5.动脉活检异常:单核细胞为主的细胞浸润或者伴多核巨细胞的肉芽肿出现为特征的血管炎证据5项中如满足3项以上,敏感度93.5%。

The international Classification of Headache disorders, 3rd Editon 头痛分类的国际标准(ICHD-III)概述:头痛分为三大组:原发性头痛;继发性头痛;脑神经痛、中枢和原发性颜面痛及其他头痛。
每一种原发性头痛均视为一种独立的疾病;继发性头痛一般只是某种疾病的一种症状,该头痛称为“缘于”此种疾病的头痛。
三大组头痛共分为14类: 一、原发性头痛(the primary headaches ) 1.偏头痛(Migraine ) 1.1 Migraine without aura 无先兆偏头痛 1.2 Migraine with aura 有先兆偏头痛 1.2.1 Migraine with typical aura1.2.1.1 Typical aura with headache 1.2.1.2 Typical aura without headache 1.2.2 Migraine with brainstem aura 1.2.3 Hemiplegic migraine 偏瘫型偏头痛1.2.3.1 Familial hemiplegic migraine (FHM)—家族性 1.2.3.1.1 Familial hemiplegic migraine type 1 (FHM1)1.2.3.1.2 Familial hemiplegic migraine type 2 (FHM2)1.2.3.1.3 Familial hemiplegic migraine type 3 (FHM3) 1.2.3.1.4 Familial hemiplegic migraine, other loci 1.2.3.2 Sporadic hemiplegic migraine —散发性 1.2.4 Retinal migraine 1.3 Chronic migraine 慢性偏头痛1.4 Complications of migraine 偏头痛并发症1.4.1 Status migrainosus 偏头痛持续状态 1.4.2 Persistent aura without infarction 1.4.3 Migrainous infarction 偏头痛脑梗死 1.4.4 Migraine aura-triggered seizure 1.5 Probable migraine 很可能的偏头痛 1.5.1 Probable migraine without aura1.5.2 Probable migraine with aura 1.6 Episodic syndromes that may be associated with migraine 可能与偏头痛有关的发作性综合征1.6.1 Recurrent gastrointestinal disturbance1.6.1.1Cyclical vomiting syndrome 周期性呕吐 1.6.1.2 Abdominal migraine 腹型偏头痛1.6.2 Benign paroxysmal vertigo 良性发作性眩晕1.6.3 Benign paroxysmal torticollis 良性发作性斜颈2.紧张型头痛(Tension-type headache )每次发作持续30min-7d ,慢性者可持续不缓解2.1 Infrequent episodic tension-type headache 偶发性 <1d/月,至少10次以上(<12d/年)2.1.1 Infrequent episodic tension-type headache associated with pericranial tenderness无先兆偏头痛的诊断标准:A :符合B-D 特征,至少发作5次发作B :头痛(未经治疗)发作持续4-72小时C :至少有以下特征中的2项单侧性、搏动性、中重度痛、日常活动会加重D :至少以下一项伴随症状:恶心和/或呕吐、畏光和畏声E :不能归因于其他 先兆性偏头痛的诊断标准:A :符合B-C 特征,至少发作2次发作B :完全可逆以下症状的1项或多项✓ 视觉、感觉、语言障碍(典型先兆)✓ 肢体无力症状(偏瘫型偏头痛)✓ 脑干症状(基底型偏头痛) 视网膜症状(视网膜型偏头痛) C :至少有以下特征中的2项 ✓ 至少1个先兆逐渐发展的过程>5min ,和/或 不同先兆接连发生过程>5min ✓ 每个先兆症状持续时间5-60min✓ 至少一个先兆症状为单侧性✓ 先兆发生同时或之后内60min 出现符合偏头痛 D :不能归因于其他 肢体无力症状可以持续至72h ,部分患者肢体无力感可持续数周; 若患者先兆持续1周以上,称为无梗死的持续先兆一般先兆症状多为双侧,可持续数月或数年若先兆持续60min 至1周以内,则称为propablemigraine with aura若出现影像学梗死灶,则称为偏头痛性脑梗死 (年轻女性,后循环比较常见) 慢性偏头痛:偏头痛发作每月>15天,连续3个月以上偏头痛持续状态:单次发作持续72小时以上4.3.1 Probable primary headache associated with sexual activity 4.4 Primary thunderclap headache 原发性霹雳头痛 4.5 Cold-stimulus headache 冷刺激性头痛 4.5.1 Headache attributed to external application of a cold stimulus4.5.2 Headache attributed to ingestion or inhalation of a cold stimulus4.5.3 Probable cold-stimulus headache 4.5.3.1 Headache probably attributed to external application of a cold stimulus4.5.3.2 Headache probably attributed to ingestion or inhalation of a cold stimulus4.6 External-pressure headache 4.6.1 External-compression headache 4.6.2 External-traction headache 4.6.3 Probable external-pressure headache4.6.3.1 Probable external-compression headache4.6.3.2 Probable external-traction headache 4.7 Primary stabbing headache 4.7.1 Probable primary stabbing headache 4.8 Nummular headache 4.8.1 Probable nummular headache4.9 Hypnic headache4.9.1 Probable hypnic headache4.10 New daily persistent headache (NDPH) 新症每日持续性头痛4.10.1 Probable new daily persistent headach 二、继发性头痛(the secondary headaches )5.缘于头、颈部外伤的头痛(Headache attributed to trauma or injury to the head and/or neck )5.1 Acute headache attributed to traumatic injury to the head5.1.1 Acute headache attributed to moderate or severe traumatic injury to the head5.1.2 Acute headache attributed to mild traumatic injury to the head5.2 Persistent headache attributed to traumatic injury to the head5.2.1 Persistent headache attributed to moderate or severe traumatic injury to the head5.2.2 Persistent headache attributed to mild traumatic injury to the head5.3 Acute headache attributed to whiplash5.4 Persistent headache attributed to whiplash5.5 Acute headache attributed to craniotomy5.6 Persistent headache attributed to craniotomy6.缘于头颈部血管疾病的头痛(Headache attributed to cranial or cervical vascular disorder )6.1 Headache attributed to ischaemic stroke or transient ischaemic attack6.1.1 Headache attributed to ischaemic stroke (cerebral infarction)6.1.2 Headache attributed to transient ischaemic attack (TIA)6.2 Headache attributed to non-traumatic intracranial haemorrhage6.2.1 Headache attributed to non-traumatic intracerebral haemorrhage 非外伤性脑出血6.2.2 Headache attributed to non-traumatic subarachnoid haemorrhage (SAH)NDPH 诊断标准:A :持续性头痛,符合B-C 的标准B :Distinct and clearly remembered onset, with pain becomingcontinuous and unremitting within 24 hours C :Present for>3 months D :除外其他疾患慢性头痛,起病急,可清晰回忆发病时间为哪一天 疼痛缺乏特点,可以为偏头痛,可以为紧张性,亦可两者混合若患者符合慢性偏头痛或慢性紧张型头痛的标准,则不诊断NDPH 若患者为药物过度使用性头痛,且符合NDPH 的标准, 则可两者均可作为诊断6.2.3 Headache attributed to non-traumatic acute subdural haemorrhage (ASDH)急性硬膜下血肿6.3 Headache attributed to unruptured vascular malformation未破裂的血管畸形6.3.1 Headache attributed to unruptured saccular aneurysm囊性动脉瘤6.3.2 Headache attributed to arteriovenous malformation (AVM) 动静脉畸形6.3.3 Headache attributed to dural arteriovenous fistula (DAVF) 硬膜动静脉瘘6.3.4 Headache attributed to cavernous angioma 海绵窦血管瘤6.3.5 Headache attributed to encephalotrigeminal or leptomeningeal angiomatosis (Sturge Weber syndrome)脑三叉神经或软脑膜血管瘤病6.4 Headache attributed to arteritis6.4.1 Headache attributed to giant cell arteritis (GCA) 颞动脉炎6.4.2 Headache attributed to primary angiitis of the central nervous system (PACNS)6.4.3 Headache attributed to secondary angiitis of the central nervous system (SACNS)颞动脉炎诊断标准:美国风湿学会1990年1. 50岁以上发病:50岁以上发现症状2.新发的头痛:出现新发的局限性头痛3.颞动脉异常:颞动脉压痛或者与颈动脉的动脉硬化无关的搏动减弱4.血沉值升高:50mm/h以上5.动脉活检异常:单核细胞为主的细胞浸润或者伴多核巨细胞的肉芽肿出现为特征的血管炎证据5项中如满足3项以上,敏感度93.5%。

头痛分类的国际标准按照头痛分类的国际标准( ICHD-III)的分类标准,临床上头痛一共有14种类型,每种类型又包含若干种头痛。
偏头痛▎概述临床最常见的原发性头痛,人群中患病率高达5%-10%,也就是说在中国有至少有6500万的患者。
头痛发作位置大多如图所示,疼痛为中重度搏动样头痛,可持续4-72小时,非常影响患者生活。
▎诱因偏头痛的诱因非常复杂,据美国流行病调查统计,大约70%-80%的患者有家族史,同时外界因素(声、光刺激等)和生活规律(食物、睡眠、压力等)也可能引发偏头痛。
▎治疗因此对偏头痛的治疗方案也较多,如果考虑针对病因的治疗,可以让患者记录下每次发作的时间、地点和状况,以便分析其诱因。
针对中轻度头痛,一般治疗可单用非特异性止痛药,如非甾体类消炎药(对乙酰氨基酚、萘普生、布洛芬等)。
对中重度头痛,可选用偏头痛特异性治疗药物如麦角类制剂和曲谱坦类药物。
由于这两类药物有强烈的血管收缩作用,并且长期大量使用可引起严重不良后果,因此,对于以往服用非甾体类消炎药(NSAIDs)效果较好的中重度头痛患者,可以继续给予NSAIDs类药物。
由于偏头痛诱因复杂,部分患者可建议进行心理疏导,对于慢性长期性偏头痛,美国有研究者认为认知行为治疗也是可行的替代方案。
丛集性头痛▎概述此病之所以得这么个名字,是因为它的疼痛成群结队而来,表现为一连串的密集的非搏动性剧痛。
丛集性期长达2周至3个月,每次发作持续15-180分钟。
位置如图,在一侧眼眶或额颞部。
发作时患者坐立不安,部分患者甚至会用拳击打头部以减轻疼痛。
此病发病率比偏头痛较少,近6.8/10万。
▎诱因丛集性头痛一般无家族史,可由饮酒、吸烟、缺氧、热度或高海拔等因素诱发。
其病因尚不明确,一般认为是颅内、外血管扩张导致。
Horton认为与组胺释放有关。
▎治疗对于安定类药物效果不佳的丛集性头痛可给予吸氧(100%氧气8-10L/min,10-15分钟)。
曲普坦类药物可以迅速缓解头痛。

The international Classification of Headache disorders, 3rd Editon4.6.3.2 Probable external-traction headache 4.7.1 Probable primary stabbing headache6.2 Headache attributed to non-traumatic intracranial haemorrhage6.2.1 Headache attributed to non-traumatic intracerebral haemorrhage非外伤性脑出血6.2.2 Headache attributed to non-traumatic subarachnoid haemorrhage (SAH)6.2.3 Headache attributed to non-traumatic acute subdural haemorrhage (ASDH)急性硬膜下血肿6.3 Headache attributed to unruptured vascular malformation未破裂的血管畸形6.3.1 Headache attributed to unruptured saccular aneurysm囊性动脉瘤6.3.2 Headache attributed to arteriovenous malformation (AVM) 动静脉畸形6.3.3 Headache attributed to dural arteriovenous fistula (DAVF) 硬膜动静脉瘘6.3.4 Headache attributed to cavernous angioma 海绵窦血管瘤6.3.5 Headache attributed to encephalotrigeminal or leptomeningeal angiomatosis (Sturge Weber syndrome)脑三叉神经或软脑膜血管瘤病6.4 Headache attributed to arteritis6.4.1 Headache attributed to giant cell arteritis (GCA) 颞动脉炎6.4.2 Headache attributed to primary angiitis of the central nervous system (PACNS)6.4.3 Headache attributed to secondary angiitis of the central nervous system (SACNS)6.8.2 Mitochondrial Encephalopathy, Lactic Acidosis and Stroke-like episodes (MELAS)6.8.3 Headache attributed to another genetic vasculopathy6.9 Headache attributed to pituitary apoplexy垂体卒中7.缘于非血管性颅内疾病的头痛(Headache attributed to non-vascular intracranial disorder )7.1 Headache attributed to increased cerebrospinal fluid pressure颅内压增高7.1.1 Headache attributed to idiopathic intracranial hypertension (IIH)7.1.2 Headache attributed to intracranial hypertension secondary to metabolic, toxic or hormonal causes7.1.3 Headache attributed to intracranial hypertension secondary to hydrocephalus7.2 Headache attributed to low cerebrospinal fluid pressure颅内压低下7.2.1 Post-dural puncture headache腰穿后7.2.2 CSF fistula headache脑脊液漏7.2.3 Headache attributed to spontaneous intracranial hypotension自发性低颅压7.3 Headache attributed to non-infectious inflammatory disease非感染性炎性疾病7.3.1 Headache attributed to neurosarcoidosis7.3.2 Headache attributed to aseptic (non-infectious) meningitis7.3.3 Headache attributed to other non-infectious inflammatory disease7.3.4 Headache attributed to lymphocytic hypophysitis7.3.5 Syndrome of transient Headache and Neurological Deficits with cerebrospinal fluid Lymphocytosis (HaNDL)7.4 Headache attributed to intracranial neoplasia颅内新生物7.4.1 Headache attributed to intracranial neoplasm7.4.1.1 Headache attributed to colloid cyst of the third ventricle7.4.2 Headache attributed to carcinomatous meningitis癌性脑膜炎7.4.3 Headache attributed to hypothalamic or pituitary hyper- or hyposecretion7.5 Headache attributed to intrathecal injection鞘内注射7.6 Headache attributed to epileptic seizure7.6.1 Hemicrania epileptica癫痫半颅痛7.6.2 Post-ictal headache癫痫发作后头痛7.7 Headache attributed to Chiari malformation type I (CM1)7.8 Headache attributed to other non-vascular intracranial disorder8.缘于物质或物质戒断的头痛(Headache attributed to a substance or its withdrawal)8.1 Headache attributed to use of or exposure to a substance or its withdrawal缘于某种物质的应用或戒断8.1.1 Nitric oxide (NO) donor-induced headache一氧化氮诱发8.1.1.1 Immediate NO donor-induced headache8.1.1.2 Delayed NO donor-induced headache8.1.2 Phosphodiesterase (PDE) inhibitor-induced headache磷酸二酯酶抑制剂8.1.3 Carbon monoxide (CO)-induced headache一氧化碳诱发8.1.4 Alcohol-induced headache酒精诱发8.3.4 Headache attributed to withdrawal from chronic use of other substance9.缘于感染的头痛(Headache attributed to infection)9.1 Headache attributed to intracranial infection颅内感染9.1.1 Headache attributed to bacterial meningitis or meningoencephalitis细菌性脑膜炎/脑膜脑炎9.1.1.1 Acute headache attributed to bacterial meningitis or meningoencephalitis9.1.1.2 Chronic headache attributed to bacterial meningitis or meningoencephalitis9.1.1.3 Persistent headache attributed to past bacterial meningitis or meningoencephalitis9.1.2 Headache attributed to viral meningitis or encephalitis病毒性脑膜炎或脑炎9.1.2.1 Headache attributed to viral meningitis9.1.2.2 Headache attributed to viral encephalitis9.1.3 Headache attributed to intracranial fungal or other parasitic infection真菌或寄生虫感染9.1.3.1 Acute headache attributed to intracranial fungal or other parasitic infection9.1.3.2 Chronic headache attributed to intracranial fungal or other parasitic infection9.1.4 Headache attributed to brain abscess脑脓肿9.1.5 Headache attributed to subdural empyema硬膜下积脓9.2 Headache attributed to systemic infection系统感染9.2.1 Headache attributed to systemic bacterial infection系统细菌感染9.2.1.1 Acute headache attributed to systemic bacterial infection9.2.1.2 Chronic headache attributed to systemic bacterial infection9.2.2 Headache attributed to systemic viral infection系统病毒感染9.2.2.1 Acute headache attributed to systemic viral infection9.2.2.2 Chronic headache attributed to systemic viral infection9.2.3 Headache attributed to other systemic infection其他系统感染9.2.3.1 Acute headache attributed to other systemic infection9.2.3.2 Chronic headache attributed to other systemic infection10.缘于内环境紊乱的头痛(Headache attributed to disorder of homoeostasis)10.1 Headache attributed to hypoxia and/or hypercapnia缺氧和/或高碳酸血症10.1.1 High-altitude headache高海拔头痛10.1.2 Headache attributed to aeroplane travel飞行头痛10.1.3 Diving headache潜水头痛10.1.4 Sleep apnoea headache睡眠呼吸暂停性头痛10.2 Dialysis headache10.3 Headache attributed to arterial hypertension高血压性头痛10.3.1 Headache attributed to phaeochromocytoma嗜络细胞瘤10.3.2 Headache attributed to hypertensive crisis without hypertensive encephalopathy无高血压脑病的高血压危象10.3.3 Headache attributed to hypertensive encephalopathy高血压脑病10.3.4 Headache attributed to pre-eclampsia or eclampsia先兆子痫10.3.5 Headache attributed to autonomic dysreflexia自主反射障碍10.4 Headache attributed to hypothyroidism甲状腺低下10.5 Headache attributed to fasting禁食10.6 Cardiac cephalalgia心源性头痛10.7 Headache attributed to other disorder of homoeostasis其他内环境稳定失调疾患11.缘于头、颈、眼、耳、鼻、鼻窦、牙、口或其他头面部结构病变的头面痛(Headache or facial pain attributed to disorder of the cranium, neck,eyes, ears, nose, sinuses, teeth, mouth or other facial or cervical structure )11.1 Headache attributed to disorder of cranial bone颅骨11.2 Headache attributed to disorder of the neck 颈部11.2.1 Cervicogenic headache11.2.2 Headache attributed to retropharyngeal tendonitis11.2.3 Headache attributed to craniocervical dystonia11.3 Headache attributed to disorder of the eyes眼睛11.3.1 Headache attributed to acute glaucoma急性青光眼11.3.2 Headache attributed to refractive error屈光不正11.3.3 Headache attributed to heterophoria or heterotropia (latent or persistent squint)斜视11.3.4 Headache attributed to ocular inflammatory disorder11.3.5 Headache attributed to trochleitis11.4 Headache attributed to disorder of the ears耳朵11.5 Headache attributed to disorder of the nose or paranasal sinuses鼻子或鼻窦11.5.1 Headache attributed to acute rhinosinusitis急性鼻窦炎11.5.2 Headache attributed to chronic or recurring rhinosinusitis11.6 Headache attributed to disorder of the teeth or jaw11.7 Headache attributed to temporomandibular disorder (TMD)11.8 Head or facial pain attributed to inflammation of the stylohyoid ligament11.9 Headache or facial pain attributed to other disorder of cranium, neck, eyes, ears, nose,sinuses, teeth, mouth or other facial or cervical structure12.缘于精神疾病的头痛(Headache attributed to psychiatric disorder)12.1 Headache attributed to somatization disorder躯体化障碍12.2 Headache attributed to psychotic disorder精神疾病三、脑神经痛、中枢和原发性颜面痛及其他头痛(painful cranial neuropathies, other facial pains and other headaches)13.脑神经痛和中枢性颜面痛(Painful cranial neuropathies and other facial pains)13.1 Trigeminal neuralgia三叉神经痛13.1.1 Classical trigeminal neuralgia13.1.1.1 Classical trigeminal neuralgia, purely paroxysmal13.1.1.2 Classical trigeminal neuralgia with concomitant persistent facial pain。


IHC 2013国际头痛疾病分类标准第三版试行版发布医脉通2013-07-15来自2013年国际头痛会议IHC报道,现在已经完成,并准备进行实地测试;工作组负责人丹麦哥本哈根格洛斯卓普医院大学神经学教授Jes Olesen博士称,“ICHD-III已经获得通过,并已经出版,临床医生应该立即开始使用,因为它明显优于第二版”;Olesen博士鼓励参会代表们开始使用这一新的分类方法,并参加现场测试;他说该版本将在未来几年中发挥重要作用,一直到最终版本的出版;Olesen博士说,如果医生发现任何错误,或者有任何意见,他们可以联系相关章节的负责人;他预测,进行轻微的修改是必要的;ICHD-III beta版可在网站上获得;慢性偏头痛在ICHD-III版本中的一个最大的变化是对慢性偏头痛内容的定义,新版本定义慢性偏头痛每月至少发生15天并持续发生3个月以上;Olesen博士说道,在过去,所有这些头痛患者都被诊断为患有偏头痛,不过这些患者是1年发作1次,还是1个月,1周,或1天发作一次;但人们已经有越来越有兴趣在考虑将偏头痛频谱中最严重的部分作为一个单独的存在;在对慢性偏头痛做出诊断之前,除了频繁的头痛发作,还有一些其他条件必须得到满足;其他偏头痛的分类包括:有先兆偏头痛,无先兆偏头痛,伴并发症的偏头痛,很可能偏头痛,伴偏头痛的发作性综合征;有先兆偏头痛划分为典型先兆偏头痛;典型先兆伴头痛;不典型先兆伴头痛;脑干先兆偏头痛;偏瘫型偏头痛;家族性偏瘫型偏头痛若干类型;散发性偏瘫性偏头痛,视网膜性偏头痛;先兆偏头痛的诊断,必须满足以下条件:一个或多个视觉;感觉;声音;运动;脑干;或视网膜症状;4项标准中至少达到2项标准:1至少有1个先兆症状逐渐蔓延,超过5分钟或以上和/或2个或更多相继出现的症状;2每个先兆症状持续5到60分钟;3至少1个先兆症状是单侧的;4先兆症状同时或之后不久出现头痛;Olesen博士说,尽管新分类明确指出一个病人诊断先兆偏头痛需要4个标准中的2个;在附录中,需要有6个标准中的3个;然而将要进行的实地测试将显示哪种诊断标准会更好;同之前的版本,新的分类方法能够区分原发性头痛和由其他原因引起的继发性头痛;其他原发性头痛对于除偏头痛以外的原发性头痛,一些疾病的诊断进行了重新排列和命名;这些头痛主要分为四个亚组:1体力活动诱发的头痛原发性咳嗽相关性头痛;原发性锻炼相关性头痛;原发性性活动相关性头痛;原发性闪电样头痛;2直接物理刺激相关性头痛冷刺激头痛;外部压力性头痛;3头盖部头痛原发性针刺样头痛;硬币形头痛; 线性放射性头痛见附录;4其他睡眠性头痛,每日新发持续性头痛;原发性头痛部分修改内容如下:在性行为相关性头痛的分类下,高潮前头痛和高潮头痛的亚型已被去掉;对闪电样头痛,头痛必须持续至少5分钟;但删除“随后几个星期或几个月不经常反复出现”的标准;睡眠性头痛不再要求在50岁以后发病;删除每日新发持续性头痛部分中一些疼痛的特点;继发性头痛继发性头痛分类标准焕然一新;这部分的变化之一是不再要求疾病诊断之前诱发因素消失,也不再有“很可能继发性头痛”的诊断;继发性头痛分类如下:创伤后头痛;血管疾病相关性头痛;非血管性疾病如肿瘤相关头痛,药物,毒素相关头痛;药物滥用相关头痛;感染相关性头痛;代谢紊乱相关头痛;头,颈,眼耳鼻喉科,牙科疾病相关性头痛,精神疾病相关性头痛;附录列出了伴有各种精神疾病的头痛,包括抑郁症,分离焦虑症,恐慌症,社交焦虑症;此外,在附录中列举了由于太空旅行引起的新颖的头痛,以及由于在飞机旅行着陆过程中的头疼;在附录中另外一个补充是前庭性偏头痛;在此诊断的标准是具有中度或重度,强度持续5分钟到72小时,畏光,视觉先兆症状的前庭症状;新的分类标准新的分类方法的一个重要的规则仍然是“对每一个头痛患者都进行单独一次的诊断”;Olesen博士说道,所以有些患者需要2个,甚至是3个的头痛的诊断;例如,患者可以同时有和的诊断;慢性偏头痛和药物滥用性头痛的患者也将同时存在两个诊断;IHC与会代表提出为什么月经相关偏头痛仍然只是在附录中而不是在书的正文中;Olesen博士解释说这种类型的偏头痛”很重要但不适合”作为主要分类方法,部分原因是因为它不适用于男性,部分是因为对偏头痛会制造“混乱”;Olesen博士说,“有人建议将偏头痛分为是否难治性或无反应的;有人建议将它分为是否与过敏和与过敏不相关的;有人建议用其他各种方式细分偏头痛,但这样使它变得太混乱;”国际头痛疾病分类第一版出版于1988年,并在2004年进行第二次出版;在国际头痛协会网站或世界卫生组织WHO网站上可获得实地测试的信息;实地测试预计将持续3年,更新最终版本将于2016年出版;编译自:New Headache Classification System 03, 2013点击下载:本网站所有内容,凡注明来源为“医脉通”,版权均归医脉通所有,欢迎转载,但请务必注明出处,否则将追究法律责任;本网注明来源为其他媒体的内容为转载,转载仅作观点分享,版权归原作者所有,如有侵犯版权,请及时联系我们;罕见性原发性头痛临床综述2014-08-07 11:09 来源:作者:幸福的味道字体大小- | +目前对于归类为罕见性原发性头痛综合征的疾病知之甚少;本文总结了罕见性原发性头痛综合征的临床表现、病理生理学、流行病学和治疗方法;提高公众对不同类型的罕见性原发性头痛综合征的认识,可以更好地进行研究以及临床诊治;近期国际头痛协会也更新了头痛的分类标准,增加了一些疾病实体,把其他一些疾病归到别的疾病分类中;本文结论认为应该对所有怀疑患有罕见性原发性头痛的患者进行神经影像学检查,以排除继发性头痛的病因;吲哚美辛治疗可能对某些疾病有效,但需要更大型的随机对照研究;简介:当头痛疾病在普通人群中患病率低于1%的时候被认为是罕见性头痛;在欧洲,罕见性头痛定义为患者人数不超过1万人;对于大多数罕见性头痛疾病,真正的患病率仍然是未知的,或者只能依靠来自三级头痛中心的文献病例报告或者小规模队列研究;国际头痛疾病分类ICHD;其他主要头痛,表1第四章第一部分对部分头痛进行了总结;表1. 罕见性原发性头痛的分类ICHD-3 beta版;第四章,第637页2013年发表了新的ICHD-3 beta版本引进临床进行测试;计划未来将会纳入国际疾病分类ICD-11中;其中一些疾病分类为原发性头痛或者是重新进行了分类;例如,钱币形头痛,从原来ICHD-2中附录部分上升到原发性头痛的分类,因为随着越来越多的证据表明它应当被当做原发性头痛;冷刺激性头痛和外部压力性头痛从第13章分出,连续性半侧颅痛最终被分类为三叉神经自发性头痛TAC ;大多数的头痛也可能为继发性头痛,在日常门诊和急诊时都需要考虑到;大多数情况下必须要进行神经影像学检查,必须排除继发性/症状性头痛症状后才能得出确切的原发性头痛的诊断和分类;原发性咳嗽性头痛原发性咳嗽性头痛的特点是由于咳嗽、紧张和/或Valsalva动作导致的或与之相关的头痛发作;头痛通常突然发作,持续1 - 2小时;新的分类将可能的持续时间从30分钟扩展到2 小时;主要是40岁以上人群受累多见;多达40%的咳嗽性头痛的患者是症状性的;因此,应该对所有患者都进行神经影像学以排除颅内病变或异常,如Arnold-Chiari畸形I型、颅中窝或颅后窝肿瘤;有一项研究试图采用修改过的Valsava测试对着有连接管的标准无液血压计进行呼气来区分原发性和继发性咳嗽性头痛;作者研究了16例不伴有其他神经系统症状和体征的咳嗽性头痛患者;其中11例患者出现了Valsava测试的病理性结果,除一例患者外,其他患者均证实有颅后窝疾病,通过手术治疗后缓解;这些结果表明,修改过的Valsava测试可能有助于区分原发性和继发性咳嗽性头痛;尽管这样,对于咳嗽性头痛患者神经影像学检查是必须的;吲哚美辛治疗可能是一种有效的治疗方法,症状有可能缓解,治疗也需要间断性暂停;原发性运动性头痛原发性运动性头痛PEH是指在高强度体育运动之后发生或者同时发生的头痛,通常持续时间可达48小时;文献报道的患病率高达30%;偏头痛患者似乎更容易发生PEH;吲哚美辛可能是有效的预防性治疗药物,此外,需要避免运动过度导致头痛发作;与性活动相关的原发性头痛就像字面意思那样,与性活动相关的原发性头痛是指性活动过程中发生的头痛;头痛程度可能会随着性兴奋性增加而增加;也可能出现在性高潮前或同时发生的强度爆发式头痛;严重程度头痛的时间可以持续1分钟到24小时,轻微的头痛或可持续更长时间;ICHD-2对两种亚型也进行了区分,分别为高潮前头痛和高潮时头痛;但临床研究无法对两个亚型进行区分,因此ICHD-3 beta版又将其合并到一起;这种类型头痛的潜在病理生理学机制仍然是未知的;一项研究表明,与性活动相关的原发性头痛患者更易于出现脑静脉循环的异常;19例患者中12例存在静脉狭窄,而对照者中均为正常;在原发性咳嗽性头痛和原发性劳累性头痛患者中也观察到了类似的结果,这提示这些疾病可能存在一个共同的通路导致剧烈活动后的头痛发生;普萘洛尔和吲哚美辛是有效的预防性治疗药物,可在性活动之前服用曲坦类药物;原发性雷击样头痛原发性雷击样头痛PTH是以非常剧烈的,数秒内达到高峰的头痛为主要特征,可类似于脑动脉瘤破裂的表现;因此,必须排除继发性原因包括脑血管成像在内的影像学和脑脊液检查;头痛达到高峰时间在1分钟内,头痛持续时间必须超过5分中;新的标准扩展了ICHD-2标准,因为旧的标准规定头痛持续为1小时至10天内;但现在认为更长或更短时间的头痛也可能是PTH;ICHD-2还排除了反复发作性雷击样头痛的患者;新的分类标准将此限制放到了一边;然而,它是否是PTH的一种,或者是PTH排除诊断的条件仍是有争议的;因此,ICHD-3 beta版建议不应该作为很可能PTH的诊断;在大部分患者中,雷击样头痛是自限性的,因此不需要额外的治疗;冷刺激性头痛ICHD-3 beta版对冷刺激性头痛的两种亚型进行了区分; 第一个亚型是指由于外部寒冷刺激所致的头痛HEACS;头痛只是在外部寒冷刺激头部后或同时发生;在寒冷刺激去除后30分钟内疼痛可缓解;第二个亚型是指摄入或吸入寒冷刺激导致的头痛HICS,以前也叫冰淇淋头痛;当食入寒冷的食物或吸入冷空气时,寒冷刺激上腭或咽后壁后或同时发生头痛发作;在去除寒冷刺激后10分内疼痛缓解;一项观察性研究调查了414例志愿者对实验性寒冷刺激的反应,使用 ICHD-2对HICS以及冰淇淋头痛的诊断标准;在寒冷刺激刺激上腭时,37%的受试者报告了头痛,其中只有一半的受试者符合ICHD-2的诊断标准;大多数受试者主诉为额部或颞部搏动性头痛;与没有头痛病史的人相比,偏头痛患者更容易出现冰淇淋头痛;原发性刺痛性头痛原发性刺痛性头痛PSH的特点是自发性单一的刺痛或持续几秒的连续性刺痛发作;发作频率不规则,每天从一次发作到数次发作;疼痛主要位于三叉神经第一支的分布区,即眶部,颞叶或顶叶;PSH是一种罕见的头痛综合征,其患病率尚不清楚;Ramon等学者分析了一家三级头痛中心严格单侧发作的100例头痛患者,100例患者中只有一例为PSH;该种类型头痛的潜在病理生理学机制也是未知的;一项研究调查了脑静脉回流障碍与PSH之间可能的相关性;在诊断为其他类型的头痛患者中,比如偏头痛、紧张型头痛、不伴视乳头水肿的颅高血压 ss-IHWOP、劳累型、咳嗽和性活动相关的头痛等患者,其硬脑膜静脉窦狭窄的发病率更高;对8例症状性PSH患者进行回顾性分析表明,在所有患者中,MRV检查显示静脉窦狭窄,作者假设PSH与静脉窦狭窄之间可能存在相关性,并且可能存在未诊断的ss-IHWOP参与PSH的发生;另一项研究证实了上一项研究的结果,7例患者中有5例存在静脉狭窄,但对照者没有狭窄表现;然而,这些结果需要在更大样本量的研究中加以证实;此外,还需进一步证实两者之间的因果相关性;临床采用吲哚美辛治疗效果较好;硬币形头痛硬币形头痛是以单个头皮区域内连续或间断出现的头痛为主要特征;受累的区域有清晰的轮廓,大小和形状固定,为圆形或椭圆形,直径为1-6cm;一个新的综述报道了250多例此种类型的头痛;疼痛主要位于顶叶,轻度到中等强度;通常会观察到疼痛的加重恶化;受累的区域也会额外的感觉症状,比如说感觉异常或触摸痛等;综述中描述了单灶性,双灶性或者多灶性硬币形头痛;因其是一种相对罕见的疾病,目前为止尚没有对照性的研究;加巴喷丁、三环类抗抑郁药和肉毒杆菌毒素治疗可能有效;也可见神经妥乐平治疗单例患者疼痛改善的报道;对所有表现为硬币形头痛的患者均需进行神经影像学检查,以是排除继发性原因尤其是垂体病变;一项病例报道描述了一例头皮钙化的血肿表现为继发性硬币形头痛;手术干预后其疼痛常可缓解;但相反,术后也可能出现硬币形头痛;在一例垂体泌乳素瘤患者进行蝶窦切除术后出现间断的硬币形头痛,采用加巴喷丁治疗后好转;睡眠头痛睡眠头痛的特点是严格与睡眠相关的头痛发作;由于其患病率较低,在小型病例研究或病例报道基础上的诊断标准仍存在争议,但最近的报道也日益增多;因此新的诊断标准也试图反映这些新的数据;仅在睡眠时出现的头痛,发作持续3个月,每个月发作超过10天,每次发作时间至少持续15分钟至4小时的患者可诊断为睡眠头痛;头痛不能伴有自主神经症状或者坐立不安的情况;此外,在新的诊断标准中对患者的年龄不再有要求;然而,大部分患者发病年龄超过50岁;头痛的频率从原来的每月至少15次减少至10次;更重要的是,根据新的分类标准,睡眠头痛允许存在伴随偏头痛的部分特征,例如恶心、畏光和恐声等;最近一项回顾了所有睡眠头痛病例报道的文献综述表明,可能存在一些临床特征不符合新的诊断标准;有些患者报告头痛发作的时间可以更长,达10 h;几乎所有患者在头痛发作时同时伴有某种运动症状;推荐的诊断性检查包括头颅MRI以及24小时血压监测以排除症状性睡眠头痛;在疗效和副作用方面,咖啡因可能是最好的治疗和预防方法;每日新发持续性头痛每日新发持续性头痛NDPH的诊断标准在ICHD-3 beta版中大大的扩宽了;如果患者能记得头痛发生持续超过24小时,则可以诊断为NDPH;头痛至少持续发生3个月以上;ICHD-2标准定义的更加受限,类似偏头痛的特征,例如恶心和呕吐,日常活动加重等表现是不允许出现的;通常,NDPH发生在之前没有任何头痛病史的患者中,但也可见于偏头痛或紧张型头痛患者中;NDPH潜在的病理生理学机制仍不明确;标准建议称NDPH事实上可能并不是一个单独的或者一致性的头痛,可以分为几个亚型;Rozen等学者报道了一例NDPH患者在13个月前发生或雷击样头痛;头痛与持续性计算力缺失相关,神经影像学排除了继发性头痛的原因;有趣的是,采用尼莫地平治疗后,头痛和神经系统症状消失;作者指出,这可能是NDPH亚型的一种,是由于脑脊液内肿瘤坏死因子-αTNF-a水平快速增加导致的脑动脉痉挛;目前为止尚没有有关NDPH的对照研究;应该避免使用过量的导致头痛的药物;颅表逆向线性放射性头痛2008年文献中首次描述了颅表逆向线性放射性头痛,其特点是短暂的阵发性刺痛发作,为中度到重度疼痛,通常从后部头皮起始,迅速辐射至前额部,眼睛和鼻子,遵循线性或Z形发展轨迹;部分患者症状是从前额起始的;起始和结束的区域是属于不同神经支配区;疼痛大多数是单侧的,也可能出现侧别的转换;发作的频率各异,从每年几次到每天数次;发作的持续时间通常为1-15秒;发作有可能是由于触摸某个受累部位而触发,而在发作间期受累区域正常;其他触发因素包括颈部或眼球运动,咳嗽、紧张、Valsalva动作以及情绪方面的压力;迄今文献中共描述了66例这样的患者;女性似乎更多见2:1,发病年龄在23-84岁之间;尝试使用加巴喷丁900 -1200 mg/d,普瑞巴林50 - 150 mg/d,拉莫三嗪100 mg/d,左乙拉西坦500 mg/d和吲哚美辛75 mg/d等治疗似乎有效;有创性治疗方法包括枕大神经GON封闭2 cm3 5%丁哌卡因单用,或与曲安奈德同时使用及GON和眶上神经SON封闭;小结罕见性原发性头痛是一组异质性很强的头痛疾病综合征;所有类型头痛的潜在病理生理学都不太清楚;推荐的治疗都是基于病例报道或者小规模的系列报道,由于患者病较低,缺乏对照性研究;所有的头痛患者均应进行恰当的神经影像学检查以排除继发性病因,某些情况下需要进行腰穿检查;学习要点所有临床表现为罕见性原发性头痛的患者都需要进行神经影像学检查以排除症状性头痛的病因;目前所有罕见性原发性头痛都缺乏对照性研究,治疗推荐主要基因单个的病例报告以及小规模的系列报道;应使用新的ICHD-3 beta版诊断标准对罕见性原发性头痛进行诊断,以进一步验证或修改新的标准;。


偏头痛诊断标准
偏头痛是一种神经性疾病,常表现为周期性的头痛、恶心、呕吐和光、声敏感等症状。
以下是用于偏头痛的国际诊断标准,也被广泛接受和使用:
1. 偏头痛发作特征:
- 至少发作5次,持续4-72小时(未经治疗或未能控制的情况下);
- 有两个或两个以上的以下特征:
- 半侧头痛(头痛仅局限于一侧);
- 中度至重度头痛强度;
- 恶化运动活动(例如行动、上下楼梯);
- 伴随恶心和/或呕吐;
- 光线、声音或气味过敏。
2. 至少两次发作期间符合以下特点:
- 部分或全部头痛符合上述特征;
- 无其他器质性疾病导致的头痛。
3. 排除其他原因引起的头痛:
- 经详尽神经系统检查,无其他神经系统病变;
- 排除药物或物质滥用(例如咖啡因、镇痛药)造成的头痛; - 排除其它头痛疾患的可能性。
请注意,这只是一个基本的诊断标准,并非所有头痛症状都能满足所有条件。
因此,对于头痛问题,始终建议咨询医生进行详细咨询和确诊。

总之,免疫疫苗为A D的预防和治疗开辟了一条新的思路,它的出现具有非常重要的意义。
如果通过不断地探索,证实这种新的方法对人类AD有效,它必将成为一种直接针对AD病因的治疗方法,还能在A D发病之前给予干预,阻止疾病的发生。
并且,目前已知多种神经系统变性疾病均与异常蛋白的沉积有关,如帕金森患者脑中L ewy小体中A-突触素蛋白,亨廷顿患者脑中的H unting ton蛋白等[19],这种新的治疗措施对其他神经系统变性疾病的治疗,指明了一条可探索之路。
参考文献:[1]Schenck D,Barbour R,Dunn W,et al.Immunizatio n w ithamy lo id-B attenuates Alzheimer disease like patholo gy in P DA PP mo use[J].N ature,1999,400(173):173[2]Shibata M,Y amada S,Kumar SR,et al.Clear ance o fA lzheimer c s amyloid ss(1-40)peptide f rom brain by L DLrecept or-related pr otein-1at the bloo d-br ain barr ier[J].JClin Invest,2000,106(12):1489[3]M clean CA,Chermy R A,Fr aser FW,et al.So luble po olo f A B as a det erminant o f sever ity o f neuro deg ener ation inA lzheimer c s disease[J].Ann Neuro l,1999,46:860[4]O ddo S,Billings L,Kesslak JP,et al.A beta immuno ther-apy leads to clearance o f early,but not late,hy per phos-pho ry lated tau ag gr egates v ia the pro teasome[J].N eu-ro n,2004,43(3):321[5]M o rg an D,D iamond DM,G ottschall PE,et al.A betapept ide v accination pr ev ents memor y lo ss in an animal mo del of Alzheimer c s disease[J].N atur e,2000,408 (6815):982[6]Jensen M T,M o ttin M D,Cracchiio lo JR,et al.Lifelongimmunizatio n w ith human beta-amy loid(1-42)pr otects Alzheimer c s transgenic mice against cog nitiv e impairment thr ougho ut ag ing[J].Neuro science,2005,130(3):667 [7]L i SB,w ang H Q,L in X,et al.Specific humo ral immuner esponses in rhesus mo nkey s vaccinated with the A lzhe-imer c s disease-associated B-amy lo id1-15peptide vaccine [J].Chin M ed J(Eng l),2005,118(8):660[8]L emere CA,Beierschmitt A,Iglesias M,et a l.Alzheimer cs disease abeta vaccine reduces central ner vous system abeta lev els in a non-human pr imate,the Car ibbean v er-vet[J].Am J Pat ho l,2004,165(1):283[9]Check E.N erve inflammat ion halts t rial fo r A lzheimer c sdrug[J].Nat ur e,2002,415:462[10]M aslian E,Hansen L,Adame A,et al.A1bet a2v accina-tio n effects o n plaque patholo gy in t he absence o f enceph-alitis in A lzheimer disease[J].Neuro lo gy,2005,64(1): 129[11]Ro ber to F,Elena B,F rancesca S,et al.V accination w ithamy lo id-B peptide induces auto immune encephalomy ekitis in C57/BL6mice[J].Brain,2003,126(2):285[12]G andy S,Demattos RB,L emere CA,et a l.Alzheimer Abeta vaccination o f rhesus monkeys(M acaca mulatta) [J].A lzheimer Dis A ssoc Diso rd,2004,18(1):44 [13]Ho ck C,K onietzko U,Papasso tir opoulos A,et al.G en-er ation of ant-i bodies specific for B-amy loid by vaccinat ion of patients w ith Alzheimer disease[J].N ature M edicine, 2002,8:1270[14]M claurin,Cecal R,K ierstead M E,et al.T herapeutica llyeffect ive antibodies agianse amy lo id B peptide ta rg et amy-loid B r esidues4-10and inhibit cy totox icity and fibr illo-g enesis[J].Nature M edicine,2002,8:1263[15]李国营,胡金家,林贤,等.A B不同片段肽疫苗免疫鼠后血清对A B42诱导细胞毒性作用的影响[J].中山大学学报(医学科学版),2004,25(2):102[16]胡金家,汪华侨,曲怀刚,等.A B及亚单位疫苗诱导小鼠抗体产生及其中和A B42的细胞毒性[J].细胞与分子免疫学杂志,2004,20(2):178[17]林贤,汪华侨,徐杰,等.A B42及其C端亚单位疫苗接种正常大鼠后产生高滴度的抗A B42抗体[J].解剖学报, 2003,34(3):231[18]F renkel D,Dewacher I,V an L euv en F,et al.R educt iono f beta-amy lo id plaques in br ain o f tr ansg enic mo use mo del of A lzheimer c s disease by EF RH-phag e immuniza-tio n[J].Vaccine,2003,21(11-12):1060[19]史树贵,李露斯.细胞凋亡与神经系统变性疾病[J].重庆医学,2003,32(7):928#综述#头痛的最新国际分类、诊断标准和治疗新进展彭瑞强综述,黄祖春审校(重庆医科大学附属第一医院神经内科,重庆市神经病学重点实验室400016)关键词:头痛;分类;诊断;治疗;进展中图分类号:R741.041文献标识码:A文章编号:1671-8348(2006)12-1130-04头痛是临床常见的症状之一,严重影响着患者的生活质量,其原因涉及临床各科,许多颅内疾病、全身性疾病、功能性或精神疾病等均可引起头痛。
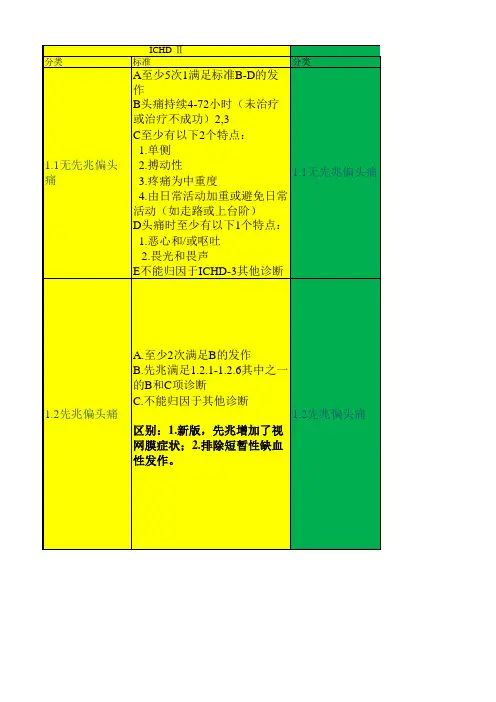
2013年国际头痛新分类和诊断标准简介历史1. 1988第一版2. 2004第二版3. 2013第三版诊断分类原则1.分级,最多5级,一般诊断1-2级2.主要根据最近一年内的病情进行诊断3.明确诊断优于“很可能”诊断4.可以同时两个诊断基本结构一,原发性头痛1.偏头痛2.紧张型头痛3.三叉自主神经性头痛4.其他原发性头痛二,继发性头痛三,痛性脑神经病、其他面部疼痛和其他类头痛偏头痛分类1.1无先兆偏头痛1.2有先兆偏头痛1.3慢性偏头痛1.4偏头痛并发症1.5很可能的偏头痛1.6可能与偏头痛有关的发作性综合症无先兆偏头痛诊断标准A.有符合B-D项特征的至少5次发作B.头痛发作持续4-72小时(2-72)C.有下列中的至少两项头痛特征1.单侧性2.搏动性3.中或重度疼痛4.日常体力活动会加重头痛D.头痛过程中至少伴随下列一项1.恶心或呕吐2.畏光和畏声E.其他ICHD-3诊断不能更好解释典型先兆偏头痛诊断标准A.有符合B-C项的至少2次发作B.先兆由视觉、感觉或言语症状组成,每种先兆完全可逆,没有运动、脑干及视网膜症状C.至少符合下列4项中的2项1.至少一种先兆症状逐渐发展的过程≥5分钟,或两种或多种先兆症状接连发生2.每种先兆症状持续5-60分钟3.至少一种先兆症状是单侧的4.先兆时伴有头痛或在先兆发生后60分钟内出现头痛D.其他ICHD-3诊断不能更好解释,且已排除短暂性脑缺血发作脑干先兆偏头痛诊断标准A.有符合B-D项的至少2次发作B.先兆由视觉、感觉或言语症状组成,每种先兆完全可逆,没有运动及视网膜症状C.至少符合下列脑干症状中的2项1.构音障碍2.眩晕3.耳鸣4.听觉迟钝5.复视6.共济失调7.意识水平下降D.至少符合下列4项中的2项1.至少一种先兆症状逐渐发展的过程≥5分钟,或两种或多种先兆症状接连发生2.每种先兆症状持续5-60分钟3.至少一种先兆症状是单侧的4.先兆时伴有头痛或在先兆发生后60分钟内出现头痛E.其他ICHD-3诊断不能更好解释,且已排除短暂性脑缺血发作偏瘫性偏头痛诊断标准A.有符合B-C项的至少2次发作B.先兆包括下列全部两种症状1.完全可逆的运动无力2.完全可逆的视觉、感觉或言语症状C.至少符合下列4项中的2项1.至少一种先兆症状逐渐发展的过程≥5分钟,或两种或多种先兆症状接连发生2.每种非运动先兆症状持续5-60分钟,运动症状持续<72小时3.至少一种先兆症状是单侧的4.先兆时伴有头痛或在先兆发生后60分钟内出现头痛D.其他ICHD-3诊断不能更好解释,且已排除短暂性脑缺血发作和卒中可能慢性偏头痛诊断标准A.至少有3个月头痛发作每月≥15天,并且符合B,C标准B.至少有5次发作符合1.1无先兆偏头痛标准的B-D项或1.2有先兆偏头痛标准的B-C项C.至少有3个月每月≥8天头痛符合下列的任何一项1. 1.1无先兆偏头痛标准的C和D项2. 1.2有先兆偏头痛标准的B和C项3. 头痛开始时患者本人认为是偏头痛,且头痛在使用曲普坦类或麦角胺类药物后缓解D.其他ICHD-3诊断不能更好解释很可能的偏头痛紧张型头痛分类2.1偶发性紧张型头痛2.2频发性紧张型头痛2.3慢性紧张型头痛2.4很可能的紧张型头痛偶发性紧张型头痛诊断标准A.有符合标准B-D的至少10次发作,平均每月头痛发作不到1天(每年头痛<12天)B.持续30分钟-7天C.至少符合下列四项中的两项1.双侧性2.压迫或紧缩性3.轻中度4.不会因为日常体力活动加重D.符合下列两项1.无恶心和呕吐2.无畏光和畏声,或仅有其中之一E.其他ICHD-3诊断不能更好解释频发性紧张型头痛诊断标准A.有符合标准B-D的至少10次发作,至少3个月每月头痛发作1-14天(每年头痛≥12天,<180天)B.持续30分钟-7天C.至少符合下列四项中的两项1.双侧性2.压迫或紧缩性3.轻中度4.不会因为日常体力活动加重D.符合下列两项1.无恶心和呕吐2.无畏光和畏声,或仅有其中之一E.其他ICHD-3诊断不能更好解释慢性紧张型头痛诊断标准A.有符合标准B-D的至少10次发作,至少3个月每月头痛发作≥15天(每年头痛≥180天)B.持续数小时或数天或持续不断C.至少符合下列四项中的两项1.双侧性2.压迫或紧缩性3.轻中度4.不会因为日常体力活动加重D.符合下列两项1.无畏光、畏声及轻度恶心症状,或仅有其中之一2.无中重度恶心和呕吐E.其他ICHD-3诊断不能更好解释三叉自主神经性头痛分类3.1丛集性头痛3.2阵发性偏侧头痛3.3短时单侧神经痛样头痛发作3.4持续性偏侧头痛3.5很可能的三叉自主神经性头痛丛集性头痛诊断标准A.符合B-D项特征的至少5次发作B.重度或极重度偏侧眶部、眶上或颞部疼痛,疼痛持续15-180分钟C.符合下列一项或两项1.在头痛侧至少有下列一项a.结膜充血或流泪b.鼻塞或流涕c.眼睑水肿d.前额和面部出汗e.前额和面部发红f.感觉耳部胀满g.瞳孔缩小或眼睑下垂2.感觉不安或躁动D.疾病活动期过半数时间头痛发作频率在隔日一次到每日8次之间E.其他ICHD-3诊断不能更好解释。
偏头痛的诊断标准
根据国际头痛学会(International Headache Society)制定的《头痛分类和诊断标准》(ICHD-3)中,偏头痛的诊断标准如下:
1.特发性偏头痛(Migraine without aura)的诊断标准:
- 至少发作五次以上符合下列特征的头痛发作:
a. 持续4-72小时(未经治疗或治疗效果不佳);
b. 头痛为脉冲样、搏动性的;
c. 头痛严重程度适中或重度,影响日常活动;
d. 伴随恶心、呕吐、光过敏或声过敏;
e. 头痛加重或活动加重头痛;
- 排除其他疾病的头痛。
2.特发性偏头痛(Migraine with aura)的诊断标准:
- 至少发作两次以上符合下列特征的头痛发作:
a. 具有可逆性的视觉、感觉性、语言或运动性神经系统症状,通常持续不超过一小时;
b. 头痛在神经系统症状发生后60分钟内开始,或在神经系统症状已解除的48小时内开始;
- 上述神经系统症状不是脑血管疾病的结果;
- 排除其他疾病的头痛。
值得注意的是,以上诊断标准仅适用于成年人。
对于儿童和青少年,诊断标准略有不同。
如果遇到偏头痛症状,最好咨询医生进行详细的病史询问和身体检查,并根据相关诊断标准进行判断。
国际头痛诊断标准国际头痛诊断标准是指世界范围内普遍适用的诊断头痛疾病的标准。
这个标准是由国际头痛协会制定并持续更新的,旨在帮助医生更好地诊断、治疗和管理头痛疾病。
根据国际头痛诊断标准,头痛可以分为两大类:原发性头痛和继发性头痛。
原发性头痛是指没有已知病因的头痛,如偏头痛、紧张性头痛、群集性头痛等。
继发性头痛是指由其他原因引起的头痛,如颅脑损伤、感染、血管疾病等。
根据头痛的临床特点和频率等不同的表现,国际头痛诊断标准进一步将原发性头痛细分为不同的类型。
其中,偏头痛是最常见的类型之一,其诊断标准是:符合以下两个条件中的第一条和第二条,以及所有的三至六条:1. 发作时头痛为中至重度的搏动性、跳动性疼痛,常伴有恶心、呕吐、光过敏、声过敏等症状。
2. 头痛持续时间为4至72小时。
3. 头痛每个月发作至少2次。
4. 头痛符合以下条件之一:a. 位于头的一侧;b. 只在头的一侧或基本只在头的一侧;c. 在头的一侧或基本只在头的一侧,并且头痛的强度或质地在另一侧轻微或部分缺失。
5. 头痛符合以下条件之一:a. 伴有神经系统症状,如视觉障碍、感觉异常、肢体无力等;b. 引起注意力降低或狭窄;c. 发作前出现典型的神经系统症状,如视觉幻觉、口齿不清等。
6. 头痛不符合紧张性头痛、硬膜外血肿、颅内占位性病变、颅内炎症、颅内血管畸形等其他头痛疾病的诊断标准。
此外,国际头痛诊断标准还规定了其他原发性头痛的诊断标准,如紧张性头痛、群集性头痛、原发性咳嗽性头痛等。
继发性头痛的诊断要根据病因进行诊断,如头外伤引起的头痛、脑垂体瘤引起的头痛等。
在诊断头痛疾病时,医生需要仔细询问病史、观察头痛的临床表现、进行必要的检查和鉴别诊断,采用遵循国际头痛诊断标准的方法进行诊断,并针对性地进行治疗和管理。