ABAQUS常用DOS命令总结
- 格式:pdf
- 大小:86.80 KB
- 文档页数:1


ABAQUS学习技巧总结1.学习软件基本操作:了解软件的界面布局和主要功能,掌握常用的菜单和工具栏命令。
可以通过阅读官方文档或者参考书籍,或者通过在线教程学习基础操作。
2.学习输入文件语法:ABAQUS是通过输入文件来定义模型和分析任务的,学习输入文件的语法和格式对于理解和修改模型是非常重要的。
可以通过查阅ABAQUS官方文档或者参考书籍来学习输入文件的语法规则。
3. 学习命令行操作:ABAQUS可以通过命令行进行一些常用操作,比如运行求解器、查看日志文件等。
掌握常用的命令行操作可以提高工作效率。
可以通过在命令提示符下输入“abaqus help”来查看命令行操作的帮助文档。
4.学习宏命令:宏命令是一种批处理脚本,可以自动化执行一系列操作。
学习宏命令可以提高工作效率,尤其是在进行重复性操作时。
可以通过学习宏命令的语法和编写技巧,自己编写一些常用的宏命令。
5. 学习Python脚本编程:ABAQUS支持Python脚本编程,可以通过编写Python脚本来扩展软件的功能。
学习Python脚本编程可以编写更复杂的宏命令,或者编写自己的特定功能的插件。
可以通过学习Python编程的相关书籍或者在线教程来学习Python编程技巧。
6.学习后处理技巧:ABAQUS提供了丰富的后处理功能,可以对分析结果进行可视化和分析。
学习后处理技巧可以帮助理解模型的行为,并对分析结果进行合理的解释和评估。
可以通过阅读ABAQUS官方文档或者参考书籍来学习后处理的相关知识。
7.学习错误处理技巧:在使用ABAQUS时,经常会遇到各种错误和警告信息。
学习错误处理技巧可以帮助快速定位和解决问题。
可以通过阅读ABAQUS官方文档或者参考书籍,或者在相关论坛上寻求帮助来学习错误处理技巧。
总之,学习ABAQUS需要不断实践和积累经验。
通过掌握基本操作、学习输入文件语法、掌握命令行操作、学习宏命令和Python脚本编程、学习后处理技巧和错误处理技巧等技能,可以提高对ABAQUS的理解和应用能力。

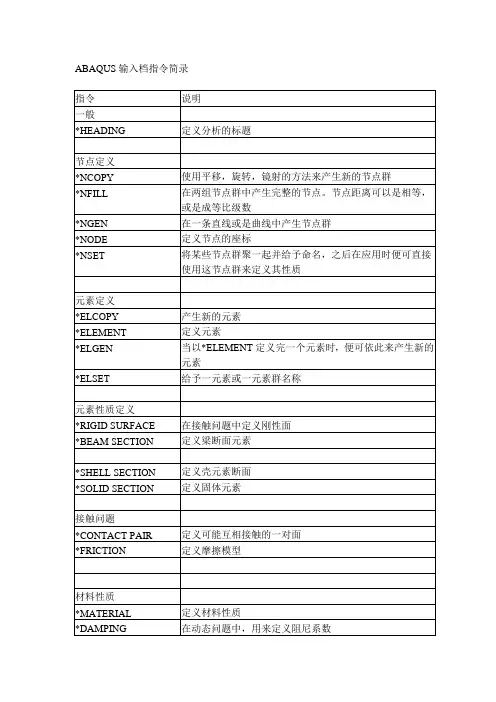
ABAQUS命令汇总及参数的默认设置1.**MESH**:用于生成网格的命令- **MESH Tie**:将两个表面网格进行连接- **MESH Part**:对零件进行网格划分- **MESH Assembly**:对总装进行网格划分默认设置参数:-**TIEBEHAVIOR**:将网格连接到边界时的行为,默认为AUTOMATIC,表示自动选择适当的行为-**ELEMENTTYPE**:网格单元类型,默认为C3D8,表示八节点三维线性六面体单元2.**PART**:用于创建零件的命令-**PART,OPTION**:创建部分模型,并设置部分模型选项默认设置参数:-**EXITCOMMAND**:设置退出PART命令时的行为,默认为QUIT,表示退出命令后继续执行下一个命令-**CREATENODES**:设置是否创建节点,默认为YES,表示创建节点3.**INSTANCE**:用于在程序中实例化零件及其网格- **INSTANCE Creation**:创建零件实例默认设置参数:-**COPYMODELDATA**:设置是否将模型数据复制到实例,默认为YES,表示复制数据4.**STEP**:用于定义步骤的命令-**STEP,NLSTATIC**:定义非线性静态分析步骤-**STEP,NLGEOM**:定义非线性几何分析步骤默认设置参数:-**NLGEOM**:设置是否进行非线性几何分析,默认为NO,表示不进行非线性几何分析5.**BOUNDARY**:用于定义边界条件的命令-**BOUNDARY,PLANAR**:用于定义平面约束-**BOUNDARY,COORD**:用于定义坐标约束默认设置参数:-**TYPE**:设置约束类型,默认为ENCASING,表示将节点限制在一个边界框内6.**LOAD**:用于定义加载的命令-**LOAD,FILE**:从文件中读取加载数据-**LOAD,DISP**:定义位移加载默认设置参数:-**TYPE**:设置加载类型,默认为DISPLACEMENT,表示位移加载-**AMPLITUD**:设置加载量的幅值,默认为1.0这只是ABAQUS中一小部分命令及其默认设置的示例。

abaqus产生几类文件:1. model_database_name.cae模型信息、分析任务等。
2. model_databse_name.jnl日志文件:包括用于复制已存储模型数据库的abaqus/cae命令*.cae与*.jnl构成支持CAE的两个重要文件,要保证CAE下打开一个项目,这两个文件必须同时同在;3. job_name.inp输入文件。
由abaqus Command支持计算起始文件,它也可由CAE打开;4. job_name.dat数据文件:文本输出信息,记录分析、数据检查、参数检查等信息。
ABAQUS/Explicit的分析结果不会写入这个文件5. job_name.sta状态文件:包括分析过程信息6. job_name.msg是计算过程的详细记录,分析计算中的平衡迭代次数,计算时间,警告信息,等等可由此文件获得。
用STEP模块定义7. job_name.res重启动文件,用STEP模块定义8. job_name.odb输出数据库文件,即结果文件,需要由visuliazition打开9. job_name.fil也为结果文件,可被其他应用程序读入的分析结果表示格式。
ABAQUS/Standard记录分析结果。
ABAQUS/Explicit的分析结果要写入此文件中则需要转换,convert=select 或 convert=all10.abaqus.rpy记录一次操作中几乎所有的ABAQUS/CAE命令11.job_name.lck阻止并发写入输出数据库,关闭输出数据库则自行删除12.model_database_name.rec包含用于恢复内存中数据库的ABAQUS/CAE命令13.job_name.ods场输出变量的临时操作运算结果,自动删除14.job_name.ipm内部过程信息文件:启动ABAQUS/CAE分析时开始写入,记录了从ABAQUS/STANDARD或ABAQUS/Explicit到ABAQUS/CAE的过程日志15.job_name.log日志文件:包含了ABAQUS执行过程的起始时间等16.job_name.abqABAQUS/Explicit模块才有的状态文件,记录分析、继续与恢复命令。

cmd提交inp文件小结有时候需要用command提交inp文件(比如少数keywords不为CAE识别),以下是对aba版中提交inp中出现问题的一个小结。
(假设将运行的inp是jobname1.inp jobname2.inp等等,也假设这些inp是可以运行的。
1、提交方式:在WINDOWS中点击 [开始] → [程序] → [ABAQUS 6.x] → [ABAQUS Command],然后在DOS窗口中输入:提交任务:abaqus job=jobname1 int(int就是interactive)任务暂停:abaqus suspend job=jobname1 int (可恢复)恢复运算:abaqus resume job=jobname1 int(从上次分析结束的地方重新开始分析)杀死任务:abaqus terminate job=jobname1 int (一般不可恢复),杀死任务不可恢复,但是如果有restart文件的话,可以restart继续计算:restart重启计算: abaqus job=xnewx oldjob=xoldx int打开CAE界面:abaqus cae %(aba后处理界面即出现)打开viewer后处理界面:abaqus viewer %(aba后处理界面即出现)查看aba帮助文件:abaqus doc %(aba帮助文件即在默认浏览器中出现)查看cmd命令帮助:abaqus help %(这个太有用了,通过这个可以找到以上所有命令。
)2、几点说明:1)Old job files exist. Overwrite?<y/n>问是否可以覆盖。
如果是文件重名,应该键入n;把现有inp改名,重新提交,以免覆盖以前的文件。
如果可以覆盖,键入y。
3)想多cpu运算(比如4cpus):提交任务:abaqus job=jobname1 int改为提交任务:abaqus job=jobname1 cpus=4 int4)有些显式运算,incretment太多的话(比如多余30w),建议用双精度:提交任务:abaqus job=jobname1 int 改为提交任务:abaqus job=jobname1 double int 但是谁都知道双精度比单精度费时,所以没有如果必要的话,就不需要加这个了。

abaqus产生几类文件:1. model_database_name.cae模型信息、分析任务等。
2. model_databse_name.jnl日志文件:包括用于复制已存储模型数据库的abaqus/cae命令*.cae与*.jnl构成支持CAE的两个重要文件,要保证CAE下打开一个项目,这两个文件必须同时同在;3. job_name.inp输入文件。
由abaqus Command支持计算起始文件,它也可由CAE打开;4. job_name.dat数据文件:文本输出信息,记录分析、数据检查、参数检查等信息。
ABAQUS/Explicit的分析结果不会写入这个文件5. job_name.sta状态文件:包括分析过程信息6. job_name.msg是计算过程的详细记录,分析计算中的平衡迭代次数,计算时间,警告信息,等等可由此文件获得。
用STEP模块定义7. job_name.res重启动文件,用STEP模块定义8. job_name.odb输出数据库文件,即结果文件,需要由visuliazition打开9. job_name.fil也为结果文件,可被其他应用程序读入的分析结果表示格式。
ABAQUS/Standard记录分析结果。
ABAQUS/Explicit的分析结果要写入此文件中则需要转换,convert=select 或 convert=all10.abaqus.rpy记录一次操作中几乎所有的ABAQUS/CAE命令11.job_name.lck阻止并发写入输出数据库,关闭输出数据库则自行删除12.model_database_name.rec包含用于恢复内存中数据库的ABAQUS/CAE命令13.job_name.ods场输出变量的临时操作运算结果,自动删除14.job_name.ipm内部过程信息文件:启动ABAQUS/CAE分析时开始写入,记录了从ABAQUS/STANDARD或ABAQUS/Explicit到ABAQUS/CAE的过程日志15.job_name.log日志文件:包含了ABAQUS执行过程的起始时间等16.job_name.abqABAQUS/Explicit模块才有的状态文件,记录分析、继续与恢复命令。

Abaqus批处理命令****************************call abq6131 job=jobname1 cpus=20 intdel jobname1.sst//删除文件,有时生成的一些文件很大,会占用大量硬盘空间。
计算完成后删除多余文件为下一次计算留下空间。
call abq6131 job=jobname2 cpus=20 intdel jobname2.datpause//保留DOS框界面,计算出错也不会退出。
****************************restart 上一个文件call abq6131 job=jobname1 intcall abq6131 job=jobname2 oldjob=jobname1 intcall abq6131 job=jobname3 oldjob=jobname2 int说明:有时为节约计算时间,设置重启动文件,那么批处理文件里面就可以像上面的写法,在计算第二个job的时候调用第一个job。
当然使用这个的前提是已经确保计算时设置了正确的重启动,并且重启动需要的文件都在。
****************************计算完成后,自动关机call abaqus job=jobname1 cpus=20 intcall abaqus job=jobname2 cpus=20 intshutdown –s –f –t 1 “1秒后自动强制关机”****************************其它几个不太常用的命令call abaqus terminate job=jobname1 int“杀死任务,一般不可恢复”call abaqus suspend job=jobname1 int“暂停任务,可恢复”call abaqus resume job=jobname1 int “从上次结束的地方恢复计算”****************************abaqus不是内部命令,不能批处理提交解决方案:假如你的abaqus.bat在D:\SIMULIA\Abaqus\Commands下,那么在dos下输入命令path=%path%;D:\SIMULIA\Abaqus\Commands即可。


ABAQUS命令汇总及参数的默认设置(ABAQUS Command Summary and Command line default parameters)2011-02-13 20:33:50| 分类:ABAQUS | 标签:|字号大中小订阅Command summaryabaqus job=job-name[analysis | datacheck | parametercheck | continue | convert={select | odb |state | all} | recover | syntaxcheck | information={environment | local| memory | release | support | system | all}][input=input-file][user={source-file | object-file}][oldjob=oldjob-name][fil={append | new}][globalmodel={results file-name | output database file-name}][cpus=number-of-cpus][parallel={domain | loop}][domains=number-of-domains][mp_mode={mpi | threads}][standard_parallel={all | solver}][memory=memory-size][interactive | background | queue=[queue-name][after=time]][double={explicit | both}][scratch=scratch-dir][output_precision={single | full}][madymo=MADYMO-input-file][port=co-simulation port-number][host=co-simulation hostname][timeout=co-simulation timeout value in seconds][unconnected_regions={yes | no}]Command line default parametersThe following parameters provide default values for various settings that would otherwise have to be specified on the command line (see “Execution procedure for Abaqus/Standard and Abaqus/Explicit,” Section 3.2.2). Values given on the command line overridevalues specified in the environment files.cpusNumber of processors to use if parallel processing is available. The default is 1.domainsThe number of parallel domains in Abaqus/Explicit. If the value is greater than 1, the domain decomposition will be performed regardless of the values of the parallel and cpus parameters. However, if parallel=domain, the value of cpus must be evenly divisible into the value of domains. If this parameter is not set, the number of domains defaults to the number of processors used during the analysis run if parallel=domain or to 1 if parallel=loop.double_precisionThe default precision version of Abaqus/Explicit to run if you do not specify the precision version on the abaqus command line.Possible values are EXPLICIT (only the Abaqus/Explicit analysis is run in double precision) or BOTH (both the Abaqus/Explicit packager and analysis are run in double precision). The default is EXPLICIT.parallelThe default parallel method in Abaqus/Explicit if you do not specify the parallel method on the abaqus command line. Possible values are DOMAIN or LOOP; the default value is DOMAIN.run_modeDefault run mode (interactive, background, or batch) if you do not specify the run mode on the abaqus command line. The default for abaqus analysis is "background", while the default for abaqus viewer is "interactive".scratchDirectory to be used for scratch files. This directory must exist (i.e., it will not be created by Abaqus) and must have write permission assigned. On UNIX platforms the default value is the value of the $TMPDIR environment variable or /tmp if $TMPDIR is not defined. On Windows platforms the default value is the value of the %TEMP% environment variable or \TEMP if this variable is not defined. During the analysis a subdirectory will be created under this directory to hold the analysis scratch files. The name of the subdirectory is constructed from your user name, the job id, and the job's process identifier. The subdirectory and itscontents are deleted upon completion of the analysis.standard_parallelThe default parallel execution mode in Abaqus/Standard if you do not specify the parallel mode on the abaqus command line. If this parameter is set equal to ALL, both the element operations and the solver will run in parallel. If this parameter is set equal to SOLVER, only the solver will run in parallel. The default parallel execution mode is ALL.unconnected_regionsIf this variable is set to ON, Abaqus/Standard will create element and node sets in the output database for unconnected regions in the model during a datacheck analysis. Element and node sets created with this option are named MESH COMPONENT N, where N is the component number. The default value is OFF.System resource parametersThe following environment file variable can be set after the code has been installed to change the resources used by Abaqus and, therefore, to improve system performance. By default, Abaqus detects the physical memory on a machine (or on each compute node in a cluster) and allocates a percentage of the available memory based on the machine platform (for details, refer to the SIMULIA Online Support System, which is accessible from the My Support page at ). You can override the default percentage by specifying a number followed by the percentage sign. The variable can also be defined as the number of megabytes or the number ofgigabytes. More detailed information about changing the system resources used by Abaqus is given in “Managing memory and diskuse in Abaqus,” Section 3.4.1.memoryMaximum amount of memory or maximum percentage of the physical memory that can be allocated during the input file preprocessing and during the Abaqus/Standard analysis phase. For parallel execution on computer clusters, this memory limit specifies the maximumamount of memory that can be allocated on each process.System customization parametersThe following is a discussion of some additional environment file parameters that are commonly used. A complete listing of parameterscan be found in the Abaqus Installation and Licensing Guide.ask_deleteIf this parameter is set equal to OFF, you will not be asked whether old job files of the same file name should be deleted; the files willbe deleted automatically. The default value is ON.auto_calculateIf this parameter is set equal to ON, the postprocessing calculator will be launched automatically at the end of an analysis if the execution procedure detects that output database file conversion is necessary. If this parameter is set to OFF, the postprocessing calculator will not run at the end of an analysis even if the execution procedure detects that it is necessary. The default value is ON.auto_convertIf this parameter is set equal to ON and an Abaqus/Explicit analysis is run in parallel with parallel=domain, the convert=select, convert=state, and convert=odb options will be run automatically at the end of the analysis. The default valueis ON.average_by_sectionThis parameter is used only for an Abaqus/Standard analysis. If this parameter is set equal to OFF, the averaging regions for output written to the data (.dat) file and results (.fil) file are based on the structure of the elements. If this parameter is set equal to ON, the averaging regions also take into account underlying values of element properties and material constants. In problems with manysection and/or material definitions the default value of OFF will, in general, give much better performance than the nondefault value of ON. See “Output to the data and results files,” Section 4.1.2, for further details on the averaging scheme.mp_host_listList of host machine names to be used for an MPI-based parallel Abaqus analysis, including the number of processors to be used oneach machine; for example,mp_host_list=[['maple',1],['pine',1],['oak',2]]indicates that, if the number of cpus specified for the analysis is 4, the analysis will use one processor on a machine called maple, one processor on a machine called pine, and two processors on a machine called oak. The total number of processors defined in the host list has to be greater than or equal to the number of cpus specified for the analysis. If the host list is not defined, Abaqus willrun on the local system. When using a supported queuing system, this parameter does not need to be defined. If it is defined, it will getoverridden by the queuing environment.mp_modeSet this variable equal to MPI to indicate that the MPI components are available on the system. Set mp_mode=THREADS to use the thread-based parallelization method. The default value is MPI where applicable.odb_output_by_defaultIf this parameter is set equal to ON, output database output will be generated automatically. If this parameter is set equal to OFF, output database request keywords must be placed in an input file to obtain output database output. The default value is ON.onCaeStartupOptional function to be executed before Abaqus/CAE begins. See “Customizing Abaqus/CAE startup,” Section 4.3.3 of the AbaqusInstallation and Licensing Guide, for examples of this function.Co-simulation parametersThe following environment file variables provide default settings for co-simulation between two Abaqus analyses or between Abaqusand AcuSolve.cosimulation_portSet cosimulation_port equal to the port number used for the connection. The default value is 48000.cosimulation_timeoutSet cosimulation_timeout equal to the timeout period in seconds. Abaqus terminates if it does not receive any communication from the coupled analysis program during the time specified. The default value is 3600 seconds.。
Inp文件中单元类型改变时,一定要注意,划分网格的时候是否,选用了一种望各类型,比如4变形和3变形的区别,如果用注意将所有的单元类型都做相应的修改。
这说明单元类型由2个因素决定,1网格形状,2计算任务.inp编码介绍(一).ABAQUS头信息文件段(1-4)1.*PREPRINT 输出求解过程所要求的信息(在dat文件中)ie:*PREPRINT, ECHO=YES, HISTORY=YES, MODEL=YES2.*HEADING 标题输出文件(出现在POST/VIEW窗口中,且出现在结果输出文件中)ie:*HEADINGSTRESS ANAL YSIS FOR A PLATE WITH A HOLE3.*RESTART 要求abaqus/standard输出其POST/view模块所需要的.res文件。
其中的FREQ =?控制结果在每次迭代(或载荷步)输出的次数。
ie:*RESTART, WRITE, FREQ=14.*FILE FORMAT 要求abaqus/standard输出到.fil中的某些信息。
它也用于post。
对于在后处理中得到x-y形式的诸如应力-时间、应力-应变图有用!ie: *FILE FORMA T, ZERO INCREMENT(二).ABAQUS网格生成段定义结点、单元,常用的命令有:结点定义(*NODE,*NGEN),单元定义(*ELEMENT,*ELGEN等)。
1.*NODE 定义结点,其格式为:*NODE结点号,x轴坐标,y轴坐标,(z轴坐标)2.*NGEN 在已有结点的基础上进行多个结点的生成,一般是在两结点间以某种方式(直线、圆)产生一定分布规律的结点。
如:*NGEN, LINE=C, NSET=HOLE,119, 1919, 100, 101 在两结点(结点号为119,1919)间以圆弧形式生成多个结点,100为任意相邻结点的单元号增量,101为圆弧形成时圆心位置的结点(对于直线形式生成没有此结点)。
abaqus常用命令abaqus常用指令小结*HEADING 定义分析的标题,输出地显示示窗口,无参数。
数据行:1、标题标题可以是几行长,但只有第一行的前80个字符会被保存并显示。
*RESTART保存重用数据及分析结果本选项可能导致产生大量数据。
用于控制重启数据的要求读,至少有以下一个参数:READ:本次分析是对前次分析的重启,基本模型定义数据(单元、材料、结点)本次重启不能更改;但是单元集、结点集、振幅表可以增加,本部件并发产生的历史数据可能改变已分析产生的历史数据。
WRITE:本次分析将写入重启数据。
如果使用了READ参数以下能数可选:ENDSTEP:用户希望在该点终止现在的STEP与STED相对使用INC:使本参数等于“STEP”参数定义的步骤数之内的一个增量,在读步后可以重新进行分析STEP:本参数等于重启时的步骤数,省略时分析在最后一步重启如果使用了WRITE参数以下参数可选FREQVENCY:重启信息数据写入的频率,如FREQVENCY=2则在第2、4、6?步时写入数据。
FREQVENCY=0则停止重启数据的写入OVERLAY:覆盖上一步所产生的数据,省略则写入每步的数据*NODE定义结点,用于通过坐标直接定义结点。
可选参数INPVT:等于外部数据文件名 NSET:等于节点集的名称SYSTEM:缺省SYSYEM=R代表坐标直角点(X、Y、Z),SYSTEM=C代表圆柱坐标(R、?、Z),SYSTEM=S代表球坐标(R、?、?)定义节点的数据行:第一行数据:1、节点号2、节点坐标第一分量3、节点坐标第二分量4、节点坐标第三分量5、与标准节点间的第一方向导弦(可选参数)6、与标准节点间的第二方向导弦(可选参数),圆柱坐标或球形坐标数为角度(度数)7、与标准节点间的第三方向导弦(可选参数),圆柱坐标或球形坐标数为角度(度数)重复以上数据行定义多个结点*NGEN依次产生结点可选参数: LINE:LINE=P接抛物线产生结点,用户必须定义额外的点,该中点在两端点之间,LINE=C接圆弧线方式产生结点,用户必须定义额外的点,该点是圆弧的中心,省略的话接直线方式产生。
Abaqus操作技巧总结打开abaqus,然后点击file——set work directory,然后选择指定文件夹,开始建模,建模完成后及时保存,在进行运算以前对已经完成的工作保存,然后点击job,修改inp文件的名称进行运算。
切记切记!!!!!!1、如何显示梁截面(如何显示三维梁模型)显示梁截面:view->assembly display option->render beam profiles,自己调节系数。
2、建立几何模型草绘sketch的时候,发现画布尺寸太小了1)这个在create part的时候就有approximate size,你可以定义合适的(比你的定性尺寸大一倍);2)如果你已经在sketch了,可以在edit菜单--sketch option ——general--grid更改3、如何更改草图精度可以在edit菜单--sketch option ——dimensions--display——decimal更改如果想调整草图网格的疏密,可以在edit菜单--sketch option ——general——grid spacing中可以修改。
4、想输出几何模型part步,file,outport--part5、想导入几何模型?part步,file,import--part6、如何定义局部坐标系Tool-Create Datum-CSYS--建立坐标系方式--选择直角坐标系or柱坐标系or球坐标7、如何在局部坐标系定义载荷laod--Edit load--CSYS-Edit(在BC中同理)选用你定义的局部坐标系8、怎么知道模型单元数目(一共有多少个单元)在mesh步,mesh verify可以查到单元类型,数目以及单元质量一目了然,可以在下面的命令行中查看单元数。
Query---element 也可以查询的。
9、想隐藏一些part以便更清楚的看见其他part,edge等view-Assembly Display Options——instance,打勾10、想打印或者保存图片File——print——file——TIFF——OK11、如何更改CAE界面默认颜色view->Grahphic options->viewport Background->Solid->choose the wite colour!然后在file->save options.12、如何施加静水压力hydrostaticload --> Pressure, 把默认的uniform 改为hydrostatic。
cmd提交inp文件小结有时候需要用command提交inp文件(比如少数keywords不为CAE识别),以下是对aba版中提交inp中出现问题的一个小结。
(假设将运行的inp是jobname1.inp jobname2.inp等等,也假设这些inp是可以运行的。
1、提交方式:在WINDOWS中点击 [开始] → [程序] → [ABAQUS 6.x] → [ABAQUS Command],然后在DOS窗口中输入:提交任务:abaqus job=jobname1 int(int就是interactive)任务暂停:abaqus suspend job=jobname1 int (可恢复)恢复运算:abaqus resume job=jobname1 int(从上次分析结束的地方重新开始分析)杀死任务:abaqus terminate job=jobname1 int (一般不可恢复),杀死任务不可恢复,但是如果有restart文件的话,可以restart继续计算:restart重启计算: abaqus job=xnewx oldjob=xoldx int打开CAE界面:abaqus cae %(aba后处理界面即出现)打开viewer后处理界面:abaqus viewer %(aba后处理界面即出现)查看aba帮助文件:abaqus doc %(aba帮助文件即在默认浏览器中出现)查看cmd命令帮助:abaqus help %(这个太有用了,通过这个可以找到以上所有命令。
)2、几点说明:1)Old job files exist. Overwrite?<y/n>问是否可以覆盖。
如果是文件重名,应该键入n;把现有inp改名,重新提交,以免覆盖以前的文件。
如果可以覆盖,键入y。
3)想多cpu运算(比如4cpus):提交任务:abaqus job=jobname1 int改为提交任务:abaqus job=jobname1 cpus=4 int4)有些显式运算,incretment太多的话(比如多余30w),建议用双精度:提交任务:abaqus job=jobname1 int 改为提交任务:abaqus job=jobname1 double int 但是谁都知道双精度比单精度费时,所以没有如果必要的话,就不需要加这个了。
ABAQUS常用DOS命令总结
1)abaqus help:可以显示所有ABAQUS命令的语法规则
2)abaqus cae:启动ABAQUS/CAE
3)abaqus job=job_name:提交分析作业
注:提交的*.inp必须要在ABAQUS默认的工作目录下
4)abaqus python script_file:运行脚本文件。
script_file是脚本文件名称
注:如果没有给出脚本文件名称,则进入脚本语言界面
5)abaqus findkeyword:在帮助文档中找到包含所需关键词的INP文件。
如包含重启动*RESTART的INP文件
6)abaqus fetch job=job name:提取帮助文档中所提供的INP文件、用户子程序和JNL文件等。
提取后的文件保存在ABAQUS默认工作目录下
注:可以利用5)查找所需INP文件,然后利用6)将其提取出来
7)abaqus doc:打开ABAQUS的帮助文档
8)abaqus viewer:进入ABAQUS/CAE的Vissualization模块
9)abaqus append:将两个结果文件*.fil合并到一起。