宏观经济学期末考卷子
- 格式:doc
- 大小:49.50 KB
- 文档页数:8

宏观经济学A期末考试试题及答案一、单项选择题(每题2分,共20分)1. 宏观经济学主要研究的是()。
A. 个别经济单位的经济行为B. 总体经济现象C. 政府的经济行为D. 企业的生产行为答案:B2. 总需求曲线向下倾斜的主要原因是()。
A. 价格水平上升B. 价格水平下降C. 收入效应D. 替代效应答案:C3. 货币政策的实施机构是()。
A. 财政部B. 国家统计局C. 中央银行D. 证监会答案:C4. 经济衰退时,政府应该采取的财政政策是()。
A. 增加税收B. 减少支出C. 减少税收D. 增加支出5. 货币供应量增加,利率下降,这表明()。
A. 货币需求减少B. 货币需求增加C. 货币供给增加D. 货币供给减少答案:C6. 通货膨胀率上升,货币的实际购买力会()。
A. 增加B. 减少C. 不变D. 不确定答案:B7. 经济中存在失业,政府应该采取的措施是()。
A. 减少公共支出B. 增加公共支出C. 增加税收D. 减少税收答案:B8. 经济增长通常与以下哪个因素有关()。
A. 资本积累B. 人口增长C. 技术进步D. 所有以上答案:D9. 长期总供给曲线是()。
B. 向上倾斜的C. 向下倾斜的D. 向右倾斜的答案:A10. 经济周期中,经济从衰退到复苏的阶段被称为()。
A. 复苏期B. 繁荣期C. 衰退期D. 萧条期答案:A二、简答题(每题10分,共40分)1. 简述凯恩斯主义经济学的主要观点。
答案:凯恩斯主义经济学认为,在短期内,总需求的变化是影响经济波动的主要因素。
政府可以通过财政政策和货币政策来调节总需求,从而实现充分就业和稳定物价。
2. 解释什么是菲利普斯曲线,并说明其在现代宏观经济学中的意义。
答案:菲利普斯曲线描述了失业率与通货膨胀率之间的负相关关系。
在短期内,较低的失业率往往伴随着较高的通货膨胀率。
然而,在长期内,这种关系可能并不稳定,因为通货膨胀预期会改变人们的行为。
3. 描述货币政策的三大工具,并简要说明它们是如何影响经济的。

宏观期末试题及答案宏观经济学期末试题及答案一、选择题1. 宏观经济学主要研究的是()。
A. 个体经济行为B. 产业内部关系C. 市场行为D. 全球经济关系答案:D2. 下列哪种货币供应渠道不属于央行的操作渠道?A. 存款准备金政策B. 开放市场操作C. 货币市场操作D. 贴现贷款操作答案:C3. 当一个国家的货币供应量增加时,该国家的物价水平通常会()。
A. 上升B. 下降C. 保持不变D. 波动答案:A4. 经济增长率的计算公式是()。
A. (GDPt - GDPt-1)/GDPt-1 × 100%B. (GDPt-1 - GDPt)/GDPt-1 × 100%C. (GDPt - GDPt-1)/GDPt × 100%D. (GDPt-1 - GDPt)/GDPt × 100%答案:A5. 下列哪种货币政策工具可以用于调控通货膨胀?A. 货币供应量B. 货币利率C. 外汇储备D. 货币市场利率答案:B二、简答题1. 请解释货币的三个职能。
货币的三个职能分别是价值尺度、流通手段和储藏手段。
首先,货币作为价值尺度,可以衡量和比较各种商品和服务的价值。
其次,货币作为流通手段,可以在市场上作为交换媒介,方便商品和服务的买卖交易。
最后,货币作为储藏手段,人们可以将其储存起来,以备将来使用。
2. 请解释通货膨胀对经济的影响。
通货膨胀对经济的影响有以下几方面:首先,通货膨胀会降低货币的购买力,导致物价上涨,减少人们的消费能力和生活水平。
其次,通货膨胀会扭曲资源配置,由于价格上涨,生产成本增加,导致企业投资意愿下降,影响经济的正常运行。
此外,通货膨胀还会引发收入分配的不平等,对固定收入者和储蓄者造成损失,而对资产持有者带来收益。
最后,通货膨胀会削弱国家货币的国际竞争力,影响国际贸易和债务偿还。
三、论述题中国经济的供给侧结构性改革供给侧结构性改革是指通过改善生产力和供给效率,推动经济结构转型升级的一种改革方式。

《宏观经济学》试卷一、单项选择题:(以下各题的备选答案中,只有一项是正确的。
将正确的序号填在括号内。
)1、在一般情况下,国民收入核算体系中数值最小的是:A、国内生产净值B、个人收入C、个人可支配收入D、国民收入E、国内生产总值2、下列哪一项应计入GDP中:A、面包厂购买的面粉B、购买40股股票C、家庭主妇购买的面粉D、购买政府债券E、以上各项都不应计入。
3、计入GDP的有:A、家庭主妇的家务劳动折算合成的收入B、拍卖毕加索作品的收入C、出神股票的收入D、晚上为邻居照看儿童的收入E、从政府那里获得的困难补助收入4、在下列各项中,属于经济中的注入因素是A、投资;B、储蓄;C、净税收;D、进口。
5、政府支出乘数A、等于投资乘数B、比投资乘数小1C、等于投资乘数的相反数D、等于转移支付乘数E、以是说法都不正确6、在以下情况中,投资乘数最大的是A、边际消费倾向为0.7;B、边际储蓄倾向为0.2;C、边际储蓄倾向为0.4;D、边际储蓄倾向为0.3。
7、国民消费函数为C=80+0.8Y,如果消费增加100亿元,国民收入A、增加100亿元;B、减少100亿元;C、增加500亿元;D、减少500亿元。
8、如果政府支出增加A、对IS曲线无响应B、IS曲线向右移动C、IS曲线向左移动D、以上说法都不正确9、政府税收的增加将A、对IS曲线无响应B、IS曲线向右移动C、IS曲线向左移动D、以上说法都不正确10、位于IS曲线左下方的收入与利率的组合,都是A、投资大于储蓄;B、投资小于储蓄;C、投资等于储蓄;D、无法确定。
11、当经济中未达到充分就业时,如果LM曲线不变,政府支出增加会导致A、收入增加、利率上升;B、收入增加、利率下降;C、收入减少、利率上升;D、收入减少、利率下降。
12、一般地,在IS曲线不变时,货币供给减少会导致A、收入增加、利率上升;B、收入增加、利率下降;C、收入减少、利率上升;D、收入减少、利率下降。

大二宏观经济学期末考试试题及答案A卷一、单项选择题(每题2分,共20分)1. 宏观经济学研究的主要对象是()。
A. 个体经济行为B. 企业经济行为C. 国民经济总体D. 政府经济行为答案:C2. 以下哪项不是宏观经济政策的目标?()。
A. 充分就业B. 价格稳定C. 经济增长D. 企业盈利答案:D3. GDP的计算公式是()。
A. 消费+投资+政府支出+净出口B. 消费+投资+政府支出-净出口C. 消费+投资+净出口-政府支出D. 投资+政府支出+净出口-消费答案:A4. 通货膨胀率是指()。
A. 货币供应量增长率B. 国内生产总值增长率C. 价格水平的增长率D. 失业率答案:C5. 根据菲利普斯曲线,失业率与通货膨胀率之间的关系是()。
A. 正相关B. 负相关C. 不相关D. 正负相关交替出现答案:B二、简答题(每题10分,共20分)1. 简述凯恩斯主义理论的主要观点。
答案:凯恩斯主义理论认为,在经济衰退时期,政府应通过增加支出和减税来刺激总需求,以减少失业和提高产出水平。
2. 解释什么是货币乘数效应,并说明其对经济的影响。
答案:货币乘数效应是指银行系统通过存款创造货币的能力。
当银行收到存款时,它们可以贷款出去一部分,而贷款又会变成新的存款,从而产生更多的贷款和存款。
这个过程可以不断重复,使得初始存款的总效应放大,影响经济中的货币供应量。
三、计算题(每题15分,共30分)1. 假设一个封闭经济体的总支出方程为Y = C + I + G,其中Y是GDP,C是消费,I是投资,G是政府支出。
已知C = 100 + 0.8(Y - T),I = 50,G = 200,T = 50。
请计算均衡GDP。
答案:首先计算消费函数C = 100 + 0.8(Y - 50) = 100 + 0.8Y - 40 = 60 + 0.8Y。
将C、I、G代入总支出方程得到Y = 60 + 0.8Y + 50 + 200。

宏观经济学期末考试试题及答案试卷A一、单项选择题(每题2分,共20分)1. 宏观经济学研究的主要对象是()。
A. 个体经济行为B. 企业经济行为C. 国民经济总体D. 政府经济行为答案:C2. 国内生产总值(GDP)是指()。
A. 一个国家所有居民生产的最终产品和服务的市场价值B. 一个国家所有居民消费的最终产品和服务的市场价值C. 一个国家所有居民收入的总和D. 一个国家所有居民储蓄的总和答案:A3. 通货膨胀是指()。
A. 货币供应量增加B. 货币供应量减少C. 货币购买力下降D. 货币购买力上升答案:C4. 货币政策的主要工具不包括()。
A. 利率B. 货币供应量C. 税收D. 公开市场操作答案:C5. 财政政策的自动稳定器包括()。
A. 税收B. 政府支出C. 政府债务D. 所有以上答案:D6. 经济周期的四个阶段是()。
A. 繁荣、衰退、萧条、复苏B. 繁荣、萧条、衰退、复苏C. 复苏、衰退、萧条、繁荣D. 萧条、复苏、繁荣、衰退答案:A7. 总需求曲线向下倾斜表明()。
A. 价格水平上升,总需求增加B. 价格水平上升,总需求减少C. 价格水平下降,总需求增加D. 价格水平下降,总需求减少答案:B8. 长期总供给曲线是()。
A. 垂直的B. 向右上方倾斜的C. 向右下方倾斜的D. 水平的答案:A9. 货币乘数的大小取决于()。
A. 法定准备金率B. 货币流通速度C. 银行贷款利率D. 以上都不是答案:A10. 菲利普斯曲线描述的是()。
A. 通货膨胀与失业率之间的关系B. 通货膨胀与经济增长之间的关系C. 经济增长与失业率之间的关系D. 货币供应量与失业率之间的关系答案:A二、多项选择题(每题3分,共15分)1. 以下哪些因素会影响总需求()。
A. 消费者信心B. 利率水平C. 政府支出D. 货币供应量答案:ABCD2. 以下哪些是财政政策的工具()。
A. 税收B. 政府支出C. 货币供应量D. 利率答案:AB3. 以下哪些是宏观经济学的主要目标()。

1)奥肯定律[答案]:奥肯定律的含义是失业率与实际国民生产总值之间存在一种高度负相关关系。
奥肯定律的主要内容是:失业率如果超过充分就业界限(通常以4%的失业率为标准)时,每使失业率降低1%,实际国民生产总值则增加3%。
反之,失业率每增加1%,实际国民生产总值则减少3%。
2)一个农民种植了 1 蒲式耳小麦,并以1 美元的价格卖给磨坊主。
磨坊主把小麦磨成面粉,然后以3 美元的价格卖给面包师。
面包师用面粉制造面包,并以6 美元的价格卖给一个工程师,工程师吃了面包。
每个人的增加值是多少?GDP 是多少?[答案] 每个人的增值等于成品的价值减去每个人支付的原材料的成本。
因此农民的增值S1(1刀);面粉厂的增值为S2(3-1=2刀);面包店的增值为S3(6-3=3刀)。
GPD 是总的价值增量,即1+2+3=6刀。
注意:GDP与最终产品(面包)价值相等。
3)把下列交易归入四个支出部分之一:消费、投资、政府购买以及净出口。
A、波音公司向空军出售一架飞机(政府购买)B、波音公司向美国航空公司出售一架飞机(投资)C、波音公司向法国航空公司出售一架飞机(净出口)D、波音飞机向阿密拉•埃尔哈特出售了一架飞机(消费)E、波音公司制造了一架下半年出售的飞机(投资)4)考虑有三种投入的柯布-道格拉斯生产函数。
K 是资本(机器数量)、L 是劳动(工人人数)、H 是人力资本(工人中大学毕业生人数)。
生产函数为:A、推导出劳动的边际产量。
人力资本量的增加如何影响劳动的边际产量?B、推导出人力资本的边际产量的表达式。
人力资本量的增加怎样影响人力资本的边际产量?C、支付给劳动的收入份额是多少?支付给人力资本的收入份额是多少?在这个经济的国民收入核算中。
你认为工人会得到多大的总收入份额?D、一个不熟练工人赚到劳动的边际产量,而一个熟练工人赚到劳动的边际产量加人力资本的边际产量。
用你对(A)和(B)的[答案],找出熟练工人与不熟练工人的比率。

一、单选题(共15题,每题2分,共30分)1. (鼓励独立完成作业,严惩抄袭。
慎交作业,责任自负。
)哪一项计入GDP?()(第 二章,视频教学课件第7-9讲)A. 购买一辆用过的IH 自行车;B. 政府向低保户发放一笔救济金;C. 汽车制造厂买进10吨钢材;D. 银行向某企业收取一笔贷款利息试题编号是否评分:未评分 评价描述:***2. 一国的国内生产总值小于国民生产总值,则该国公民从国外収得的收入()外国国民 从该国取得的收入。
(第二章,视频教学课件第7-9讲) A. 大于 B. 小于 C. 等于D. 不能确定试题编号: 试题类型:单选题 标准答案:和* 试题难度:一般 试题解析:*** 考生答案:B 考生得分:*** 是否评分:未评分 评价描述:***3. 在一个有家庭、企业、政府和国外的部门构成的四部门经济中,GDP 是()的总和。
(第二章,视频教学课件第7-9讲)政府购买和净出口: 政府购买和净出口; 政府购买和总出口; 政府转移支付和净出口 试题编号:试题类型 标准答案 试题难度 试题解析 考生答案考生得分 单选题 *** 一般D*** A. 消费、 B. 消费、 C. 消费、 D. 消费、 总投资、 净投资、 总投资、 总投资、试题类型 标准答案 试题难度 试题解析 考生答案 考生得分 是否评分 评价描述4. 在两部门收入•支出模型中,如果边际消费倾向为0.8,那么自主支出乘数为()o (第 三章,视频教学课件第10-18讲)A. 1.6B. 2.5C. 5D. 4试题编号单选题***一般A*** 未评分试题类型 单选题 标准答案 试题难度 试题解析 考生答案 一般 ***C考生得分:***是否评分 未评分评价描述***5.固定税制度下的自发支出乘数()变动税制下的自发支出乘数。
(第三章,视频教学课 件第10・18讲) A. 大于 B. 小于 C. 等于 D. 不能确定试题编号 试题类型 标准答案 试题难度 试题解析 考生答案 考生得分 单选题 *** 一般 ***C是否评分:未评分 评价描述:***6.当经济出现膨胀缺口时,以下可以使经济达到充分就业均衡水平的措施有()o (第三章,视频教学课件第10-18讲)A.增加白发消费B.增加计划投资C.提高边际消费倾向D.增加进口试题编号:试题类型:单选题标准答案:***试题难度:一般试题解析:***考生答案:D考生得分:***是否评分:未评分评价描述:***7.下列哪项不是人们持有货币的动机()0(第四章,视频教学课件第19・25讲)A.交易动机B.预防动机C.投机动机D.均衡财富试题编号:试题类型:单选题标准答案:***试题难度:一般试题解析:***考生答案:D考生得分:***是否评分:未评分评价描述:***& 利率和收入的组合点出现在IS曲线左下方,LM曲线右下方区域中,则表示()。
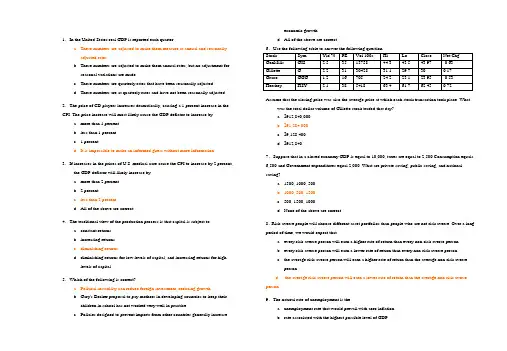
1.In the United States real GDP is reported each quarter.a. These numbers are adjusted to make them measure at annual and seasonallyadjusted rates.b. These numbers are adjusted to make them annual rates, but no adjustment forseasonal variations are made.c. These numbers are quarterly rates that have been seasonally adjusted.d. These numbers are at quarterly rates and have not been seasonally adjusted.2.The price of CD players increases dramatically, causing a 1 percent increase in the CPI. The price increase will most likely cause the GDP deflator to increase bya. more than 1 percent.b. less than 1 percent.c. 1 percent.d. It is impossible to make an informed guess without more information.3.If increases in the prices of U.S. medical care cause the CPI to increase by 2 percent, the GDP deflator will likely increase bya. more than 2 percent.b. 2 percent.c. less than 2 percent.d. All of the above are correct.4.The traditional view of the production process is that capital is subject toa. constant returns.b. increasing returns.c. diminishing returns.d. diminishing returns for low levels of capital, and increasing returns for highlevels of capital.5.Which of the following is correct?a. Political instability can reduce foreign investment, reducing growth.b. Gary's Becker proposal to pay mothers in developing countries to keep theirchildren in school has not worked very well in practice.c. Policies designed to prevent imports from other countries generally increaseeconomic growth.d. All of the above are correct.6.Use the following table to answer the following question.Assume that the closing price was also the average price at which each stock transaction took place. What was the total dollar volume of Gillette stock traded that day?a. $912,840,000b. $91,284,000c. $9,128,400d. $912,8407.Suppose that in a closed economy GDP is equal to 10,000, taxes are equal to 2,500 Consumption equals 6,500 and Government expenditures equal 2,000. What are private saving, public saving, and national saving?a. 1500, 1000, 500b. 1000, 500, 1500c. 500, 1500, 1000d. None of the above are correct.8.Risk-averse people will choose different asset portfolios than people who are not risk averse. Over a long period of time, we would expect thata. every risk-averse person will earn a higher rate of return than every non-risk averse person.b. every risk-averse person will earn a lower rate of return than every non-risk averse person.c. the average risk-averse person will earn a higher rate of return than the average non-risk averseperson.d. the average risk-averse person will earn a lower rate of return than the average non-risk averse person.9.The natural rate of unemployment is thea. unemployment rate that would prevail with zero inflation.b. rate associated with the highest possible level of GDP.c. difference between the long-run and short-run unemployment rates.d. amount of unemployment that the economy normally experiences.10.Suppose that the reserve ratio is 5 percent and that a bank has $1,000 in deposits. Its required reserves area. $5.b. $50.c. $95.d. $950.11.Suppose a bank has $200,000 in deposits and $190,000 in loans. It has a reserve ratio ofa. 5 percentb. 9.5 percentc. 10 percentd. None of the above is correct.12.The inflation taxa. transfers wealth from the government to households.b. is the increase in income taxes due to lack of indexation.c. is a tax on everyone who holds money.d. All of the above are correct.13.In 1898, prospectors on the Klondike River discovered gold. This discovery caused an unexpected price levela. decrease that helped creditors at the expense of debtors.b. decrease that helped debtors at the expense of creditors.c. increase that helped creditors at the expense of debtors.d. increase that helped debtors at the expense of creditors.14.Ivan, a Russian citizen, sells several hundred cases of caviar to a restaurant chain in the United States. By itself, this salea. increases U.S. net exports and has no effect on Russian net exports.b. increases U.S. net exports and decreases Russian net exports.c. decreases U.S. net exports and has no effect on Russian net exports.d. decreases U.S. net exports and increases Russian net exports. 15.Suppose that the real exchange rate between the United States and Kenya is defined in terms of baskets of goods. Which of the following will increase the real exchange rate (that is increase the number of baskets of Kenyan goods a basket of U.S. goods buys)?a. an increase in the number of Kenyan shillings that can be purchased with a dollarb. an increase in the price of U.S. baskets of goodsc. a decrease in the price in Kenyan shillings of Kenyan goodsd. All of the above are correct.16.Use the (hypothetical) information in the following table to answer the next question.In real terms, U.S. goods are more expensive than goods in which country(ies)?a. Brazil and Mexicob. Japan, Sweden, and Thailandc. Japan and Swedend. Thailand.17.Which of the following would tend to shift the supply of dollars in foreign-currency exchange market of the open-economy macroeconomic model to the left?a. The exchange rate rises.b. The exchange rate falls.c. The expected rate of return on U.S. assets rises.d. The expected rate of return on U.S. assets falls.18.The real exchange rate equals the relativea. price of domestic and foreign currency.b. price of domestic and foreign goods.c. rate of domestic and foreign interest.d. None of the above is correct.19.In the open-economy macroeconomic model, if the supply of loanable funds increases, the interest ratea. and the real exchange rate increase.b. and the real exchange rate decrease.c. increases and the real exchange rate decreases.d. decreases and the real exchange rate increases.20.For the followingquestion, use the graph below.The initial effect of an increase in the budget deficit in the loanable funds market isillustrated as a move from a. a to b. b. a to c. c. c to b.d. c to d.21.When the government spends more, the initial effect is that a. aggregate demand shifts right. b. aggregate demand shifts left. c. aggregate supply shifts right.d. aggregate supply shifts left.22.Suppose the economy is in long-run equilibrium. In a short span of time, there is a sharp increase in the minimum wage, a major new discovery of oil, a large influx of immigrants, and new environmental regulations that reduce electricity production. In the short run, we would expect a. the price level to rise and real GDP to fall. b. the price level to fall and real GDP to rise.c. the price level and real GDP both to stay the same.d. All of the above are possible.23.Suppose the economy is in long-run equilibrium. In a short span of time, there is a large influx of skilled immigrants, a major new discovery of oil, and a major new technological advance in electricity production. In the short run, we would expect a. the price level to rise and real GDP to fall. b. the price level to fall and real GDP to rise. c. the price level and real GDP both to stay the same.d. All of the above are possible.24.According to liquidity preference theory, the money supply curve is a. upward sloping.b. downward sloping.c. vertical.d. horizontal.25.When the Fed buys government bonds, the reserves of the banking system a. increase, so the money supply increases. b. increase, so the money supply decreases. c. decrease, so the money supply increases.d. decrease, so the money supply decreases. 26.According to the theory of liquidity preference, an increase in the price level causes the a. interest rate and investment to rise. b. interest rate and investment to fall. c. interest rate to rise and investment to fall.d. interest rate to fall and investment to rise.27.If the stock market crashes, a. aggregate demand increases, which the Fed could offset by increasing the money supply. b. aggregate demand increases, which the Fed could offset by decreasing the money supply. c. aggregate demand decreases, which the Fed could offset by increasing the money supply.d. aggregate demand decreases, which the Fed could offset by decreasing the money supply.28.If the MPC = 3/5, then the government purchases multiplier isa.5/3. b.5/2.c. 5.d. 15.29.If the government raises government expenditures, in the short run, pricesa. rise and unemployment falls.b. fall and unemployment rises.c. and unemployment rise.d. and unemployment fall.30.If the long-run Phillips curve shifts to the left, for any given rate of money growth and inflation the economy will havea. higher unemployment and lower output.b. higher unemployment and higher output.c. lower unemployment and lower output.d. lower unemployment and higher output.31.When an American doctor opens a practice in Bermuda, his production there is part of U.S. GDP.F32.In countries where women are discriminated against, policies that increase their career and educational opportunities are likely to increase the birth rate.F 33.Michael Kramer found that world growth rates have increased as population has.T34.Suppose a small closed economy has GDP of $5 billion, Consumption of $3 billion, and Government expenditures of $1 billion. Then domestic investment and national saving are both $1 billion.T35.According to the efficient markets hypothesis, at any moment in time, the market price is the best guess of the company's value based on available information.T36.According to the efficient markets hypothesis, stocks follow a random walk so that stocks that increase in price one year are more likely to increase than decrease in the next year.F37.In the United States, blacks and whites have similar labor force participation rates, but blacks have a higher unemployment rate.T 38.According to the theory of efficiency wages, firms operate more efficiently if they can pay wages that are below the equilibrium level.F39.In the months of November and December, people in the United States hold a larger part of their money in the form of currency because they intend to shop for the holidays. As a result, the money supply increases, ceteris paribus.F40.In the 1990s, U.S. prices rose at about the same rate as in the 1970s.F41.According to the theory of purchasing-power parity, the real exchange rate defined as foreign goods per unit of U.S. goods will equal the domestic price level divided by the foreign price level.F42.Net capital outflow represents the quantity of dollars supplied in the foreign-currency exchange market.T43.If policymakers impose import restrictions on automobiles, the U.S. trade deficit would shrink.F44.Most economists believe that classical theory explains the world in the short run, but not the long run.F45.Because not all prices adjust instantly to changing conditions, an unexpected fall in the price level leaves some firms with higher-than-desired prices, and these higher-than-desired prices depress sales and induce firms to reduce the quantity of goods and services they produce.T46.All explanations for the upward slope of the short-run aggregate supply curve suppose that output supplied increases when the price level increases more than expected.T47.Both the multiplier and the investment accelerator tend to make the aggregate demand curve shift farther than the increase in government expenditures.T48.During recessions, the government tends to run a budget deficit.T49.If macroeconomic policy expands aggregate demand, unemployment will fall and inflation will rise in the short run.T50.The analysis of Friedman and Phelps argues that any change in inflation that is expected has no impact on the unemployment rate.T三、名词解释(每小题 2 分,共 10 分)51.diminishing returns: the property whereby the benefit from an extra unit of an input declines as the quantity of the input increases.52.nominal exchange rate: the rate at which a person can trade the currency of one country for the currency of another.53.crowding-out effect: the offset in aggregate demand that results when expansionary fiscal policy raises the interest rate and thereby reduces investment spending.54.stagflation: a period of falling output and rising prices.55.automatic stabilizers: changes in fiscal policy that stimulate aggregate demand when the economy goes into a recession without policymakers having to take any deliberate action.四、简答题( 8题中任选6题;每小题 5分,共30 分)56.Why are property rights important for the growth of a nation's standard of living?Property rights are an important prerequisite for the price system to work in a market economy. If an individual or company is not confident that claims over property or over the income from property can be protected, or that contracts can be enforced, there will be little incentive for individuals to save, invest, or start new businesses. Likewise, there will be little incentive for foreigners to invest in the real or financial assets of the country. The distortion of incentives will reduce efficiency in resource allocation and will reduce saving and investment which in turn will reduce the standard of living.57.Suppose that you are a broker and people tell you the following about themselves. What sort of bond would you recommend to each? Defend your choices.a. "I am in a high federal income tax bracket and I don't want to take very much risk."A municipal bond, because generally they have low credit risk and are not subject to federal income tax.b. "I want a high return and I am willing to take a lot of risk to get it."A junk bond. Because of their high risk, they have a high return.c. "I want a decent return and I have enough deductions that I don't value tax breaks highly."A corporate bond that isn't a junk bond. Because they have more risk than government bonds and have nospecial tax treatment, they pay moderate rates of return.58.Draw a simple T-account for First National Bank of Me, which has $5,000 of deposits, a reserve ratio of 10 percent, and excess reserves of $300.First National Bank of MeAssets LiabilitiesReserves $800 Deposits $5,000Loans $4,20059.What are the costs of inflation?The costs of inflation include "shoeleather costs," the cost of reducing your money holdings to reduce your inflation tax; "menu costs," the costs of price adjustments; the costs of resource misallocation that result from the relative-price variability induced by inflation; the costs of inflation-induced tax distortions; the costs of confusion and inconvenience; and the costs associated with the arbitrary redistribution of wealth that accompany unexpected inflation.60.Make a list of things that would shift the long-run aggregate supply curve to the right.Examples in the text (or variations) include increased immigration, a decrease in the minimum wage, more generous unemployment insurance, an increase in the capital stock, an increase in the average level of education, a discovery of new mineral deposits, technology, and removal of barriers to international trade.61.Illustrate the classical analysis of growth and inflation with aggregate demand and long-run aggregate supply curves.Over time technological advances cause the long-run aggregate supply curve to shift right. Increases in the money supply cause the aggregate demand curve to shift right. Output growth puts downward pressure on the price level, but money supply growth contributes to rising prices.62.Why do economists think that the wealth effect and exchange-rate effect are not very important factors in explaining why aggregate demand slopes downward, at least in the United States?The wealth effect is not very important because it operates through changes in the real value of money, and money is only a small fraction of household wealth. So it is unlikely that changes in the price level will lead to large changes in consumption spending through this channel. The exchange-rate effect is not very important in the United States because trade with other countries represents a relatively small fraction of U.S. GDP.63.Describe the process in the money market by which the interest rate reaches its equilibrium value if it starts above equilibrium.If the interest rate is above equilibrium, there is an excess supply of money. People with more money than they want to hold given the current interest rate deposit the money in banks and buy bonds. The increase in funds to lend out causes the interest rate to fall. As the interest rate falls, the quantity of money demanded increases, which tends to diminish the excess supply of money. 64. Assume the economy is in a recession. Explain how each of the following policies would affect consumption and investment. In each case, indicate any direct effects, any effects resulting from changes in total output, any effects resulting from changes in interest rate, and the overall effect. If there are conflicting effects making the answer ambiguous, say so. a). a reduction in taxes; b) an expansion of the money supply.a) 税收减少增加了储蓄的收益、减少了投资的成本,但税收减少对储蓄和投资的影响要视情况而定。

大二宏观经济学期末考试试题及答案A卷一、单项选择题(每题2分,共20分)1. 宏观经济学的主要研究对象是()。
A. 个体经济行为B. 企业经济行为C. 国民经济总体D. 政府经济行为答案:C2. 国内生产总值(GDP)是指()。
A. 一个国家在一定时期内生产的所有最终商品和服务的市场价值B. 一个国家在一定时期内生产的所有商品和服务的市场价值C. 一个国家在一定时期内消费的所有最终商品和服务的市场价值D. 一个国家在一定时期内消费的所有商品和服务的市场价值答案:A3. 通货膨胀是指()。
A. 货币供应量增加B. 货币购买力下降C. 物价总水平持续上升D. 货币流通速度加快答案:C4. 失业率是指()。
A. 失业人数占劳动力总数的比率B. 失业人数占就业人数的比率C. 失业人数占总人口的比率D. 就业人数占劳动力总数的比率答案:A5. 财政政策的主要工具包括()。
A. 税收和货币供应量B. 税收和政府支出C. 利率和货币供应量D. 利率和政府支出答案:B6. 货币政策的主要工具包括()。
A. 税收和政府支出B. 利率和货币供应量C. 利率和税收D. 货币供应量和政府支出答案:B7. 总需求曲线向下倾斜表明()。
A. 价格水平上升,总需求增加B. 价格水平上升,总需求减少C. 价格水平下降,总需求增加D. 价格水平下降,总需求减少答案:B8. 总供给曲线向上倾斜表明()。
A. 价格水平上升,总供给增加B. 价格水平上升,总供给减少C. 价格水平下降,总供给增加D. 价格水平下降,总供给减少答案:A9. 经济周期是指()。
A. 经济总量的长期增长趋势B. 经济总量的短期波动C. 经济结构的长期变化D. 经济结构的短期变化答案:B10. 经济增长是指()。
A. 经济总量的长期增长趋势B. 经济总量的短期波动C. 经济结构的长期变化D. 经济结构的短期变化答案:A二、多项选择题(每题3分,共15分)11. 宏观经济学的主要研究内容有()。

宏观经济学期末试题一、简答题(共60 分,每题15分)1.GDP 统计中的三种方法的区别和联系。
答:GDP统计中的三种方法——生产法、支出法和收入法(1)主要区别在于它们的计算角度和关注点不同:①生产法:从生产角度出发,关注生产过程中创造的增加值,即总产出减去中间投入的部分。
它反映了国民经济各部门在一定时期内的新增价值。
②支出法:从最终使用角度出发,关注最终产品的去向,包括消费、投资、政府购买和净出口(出口额减去进口额)。
它体现了经济社会对最终产品的总需求。
③收入法:从生产要素收入角度出发,关注生产活动中各要素所有者的收入分配情况,包括工资、利润、利息、租金以及折旧等。
它揭示了生产活动的收入分配结构。
(2)三种方法之间的联系是:①本质相同:三种方法都是对同一经济现象——GDP 的度量,反映的是同一时期一个国家或地区的经济总量。
②相互验证:理论上,三种方法计算出的GDP应该相等。
在实践中,它们之间可以相互验证,提高GDP数据的准确性和可靠性。
③互为补充:三种方法各有侧重,互为补充。
生产法反映生产活动的总量和产业结构;支出法展示GDP的构成和各项支出的贡献;收入法则揭示收入分配的结构和变化。
在宏观经济分析和政策制定中,需要综合运用这三种方法,以全面、准确地把握经济运行状况。
2.影响居民消费的因素有哪些,它们对于促进消费有什么政策启示?答:1.影响居民消费的因素主要包括以下几点:①收入因素:居民的可支配收入是影响消费的最直接和最重要的因素。
随着可支配收入的增加,居民的消费能力通常会相应提高。
②价格因素:物价上涨可能导致实际购买力下降,进而抑制消费;而物价下跌则可能刺激消费增加。
③利率因素:利率的变动会对居民的消费和储蓄决策产生影响。
利率提高可能使消费者减少当前消费、增加未来消费(替代效应),但也可能因预期未来收入增加而增加当前消费(收入效应)。
④政府政策:政府的税收政策、社会保障政策等都会对居民消费产生影响。

宏观经济学A期末考试试题及答案一、单项选择题(每题2分,共20分)1. 宏观经济学研究的主要对象是()。
A. 个体经济行为B. 企业经济行为C. 国民经济总体D. 政府经济行为答案:C2. 国内生产总值(GDP)是指()。
A. 一个国家在一定时期内生产的所有最终商品和服务的市场价值B. 一个国家在一定时期内生产的所有商品和服务的市场价值C. 一个国家在一定时期内消费的所有最终商品和服务的市场价值D. 一个国家在一定时期内消费的所有商品和服务的市场价值答案:A3. 通货膨胀是指()。
A. 货币供应量增加B. 货币购买力下降C. 物价水平持续上升D. 货币实际价值下降答案:C4. 凯恩斯主义认为,经济衰退时政府应该采取的政策是()。
A. 增加税收B. 减少政府支出C. 增加政府支出D. 减少货币供应量答案:C5. 菲利普斯曲线描述的是()之间的关系。
A. 通货膨胀与失业率B. 通货膨胀与经济增长C. 经济增长与失业率D. 货币供应量与失业率答案:A6. 货币政策的主要工具是()。
A. 利率B. 货币供应量C. 政府支出D. 税收答案:B7. 总需求曲线向左移动表明()。
A. 总需求增加B. 总需求减少C. 总供给增加D. 总供给减少答案:B8. 经济周期的四个阶段是()。
A. 繁荣、衰退、萧条、复苏B. 衰退、萧条、复苏、繁荣C. 复苏、繁荣、衰退、萧条D. 萧条、复苏、衰退、繁荣答案:A9. 货币乘数是指()。
A. 货币供应量与基础货币的比率B. 基础货币与货币供应量的比率C. 货币供应量与总需求的比率D. 总需求与货币供应量的比率答案:A10. 根据IS-LM模型,当利率下降时,IS曲线会()。
A. 向左移动B. 向右移动C. 保持不变D. 向下移动答案:B二、多项选择题(每题3分,共15分)11. 以下哪些因素可以导致总需求增加?()A. 利率下降B. 消费者信心增强C. 政府支出增加D. 税收增加答案:A、B、C12. 以下哪些因素可以导致总供给增加?()A. 技术进步B. 劳动生产率提高C. 资本存量增加D. 原材料价格上升答案:A、B、C13. 以下哪些政策可以降低失业率?()A. 增加政府支出B. 降低利率C. 提高最低工资D. 增加货币供应量答案:A、B、D14. 以下哪些因素可以导致通货膨胀?()A. 货币供应量增加B. 总需求增加C. 总供给减少D. 工资水平下降答案:A、B、C15. 以下哪些因素可以导致经济衰退?()A. 总需求减少B. 总供给减少C. 利率上升D. 消费者信心下降答案:A、C、D三、判断题(每题2分,共20分)16. 宏观经济学与微观经济学的主要区别在于研究对象的不同。
《宏观经济学》期末综合测试一、名词解释题(本题型共5题。
每题3分,共15分)1.国内生产总值:2.平衡预算乘数:3.流动性偏好:4.菲利普斯曲线:5.自动稳定器:二、单项选择题(本题型共30题。
每题正确答案只有一个。
每题1分,共30分)1.下列哪一项将不计入...当年的GDP()。
A.当年整修过的古董汽车所增加的价值;B.一辆新汽车的价值;C.一辆二手汽车按其销售价格计算的价值;D.一台磨损的高尔夫球清洁机器的替换品。
2.在以支出法计算国内生产总值时,不属于...投资的是()。
A.某企业增加一笔存货;B.某企业建造一座厂房;C.某企业购买一台计算机;D.某企业购买政府债券。
3.中央银行在公开市场上卖出政府债券是企图().A.收集一笔资金帮助政府弥补财政赤字;B.减少商业银行在中央银行的存款;C.减少流通中基础货币以紧缩货币供给;D.通过买卖债券获取差价利益。
4.当实际GDP为1500亿美元,GDP平减指数为120时,名义国民收入为()。
A.1100亿美元;B.1500亿美元;C.1700亿美元;D.1800亿美元。
5.一个家庭当其收入为零时,消费支出为2000元;而当其收入为6000元时,其消费为6000元,在图形上,消费和收入之间成一条直线,则其边际消费倾向为()。
A.2/3;B.3/4;C.4/5;D.1。
6.宏观经济学的核心理论是()。
A.经济决定理论;B.价格决定理论;C.宏观决定理论;D.国民收入决定理论。
7.由于价格水平上升,使人们持有的货币及其他资产的实际价值降低,导致人们消费水平减少,这种效应被称为()。
A.利率效应;B.实际余额效应;C.进出口效应;D.挤出效应。
8.如果边际储蓄倾向为0.3,投资支出增加60亿元时,将导致均衡GDP增加()。
A.20亿元; B.60亿元; C.180亿元; D.200亿元。
9.在IS曲线上存在储蓄和投资均衡的收入和利率的组合点有( )。
A.一个;B.无数个;C.一个或无数个;D.无法确定。
宏观经济学期末考试试卷及答案宏观经济学期末考试试卷及答案 A 卷一、名词解释题本题型共5题。
每题2分共10分将答案写在答题纸上1国民生产总值 2. 消费函数 3. 充分就业 4 经济周期 5. 菲利普斯曲线二、单项选择题本题型共30题。
每题正确答案只有一个从每题的备选答案中选出正确的答案将其英文字母编号填入答题纸上相应的空格内。
每题1分共30分1、今年的名义国内生产总值大于去年的名义国内生产总值说明 A.、今年物价水平一定比去年高了B、今年生产的物品和劳务的总量一定比去年增加了C、今年的物价水平和实物产量水平一定都比去年提高了D、以上三种说法都不一定正确。
2、一国的国内生产总值小于国民生产总值说明该国公民从外国取得的收入外国公民从该国取得的收入 A.、大于B、小于C、等于D、可能大于也可能小于。
3、两部门的均衡是A: IS B: IGST C: IGXSTM D: ADAS。
4、一般地说通货膨胀会使。
A债权人受损债务人受益B债权人受益债务人受损C债权人和债务人都受益D债权人和债务人都受损。
5、在货币总量不变条件下当物价上升货币投机需求减少利率上升从而抑制投资需求和居民信贷消费需求导致产出的下降这种效应被称为 A. 净出口效应 B. 利率效应 C.实际余额效应 D.财富效应。
6、总需求曲线向下倾斜的原因之一是 A. 随着价格水平下降家庭的实际财富下降他们将增加消费 2 B. 随着价格水平上升家庭的实际财富下降他们将减少消费 C.随着价格水平下降家庭的实际财富上升他们将减少消费 D. 随着价格水平上升家庭的实际财富上升他们将增加消费。
7、在LM曲线即定时扩张性的财政政策使IS曲线向。
A: 上移B: 下移C: 不变D: 无联系。
8、假设银行利率为6在下列几项投资中投资者应该选择 A.类投资的平均资本收益率最高的是 2 B.类投资的平均资本收益率最高的是 5 C.类投资的平均资本收益率最高的是8 D.无法确定。
1 Macroeconomics Final Test 2009 I. Multiple choice (1 points per each. In total 40 points) 紅色是答案 1) A car that is produced in 2004 is not sold until 2005. According to the definition of GDP, in which year's GDP should it be counted? A) 2004 B) 2005 C) both years D) 2004 real GDP; 2005 nominal GDP
2) Which of the following transactions would be included in the official calculation of GDP? A) A student buys a used text book at the bookstore. B) Firestone sells $2 million worth of tires to General Motors. C) You wash and wax your father's car as a favor to him. D) You buy a new iPod. E) You illegally download music off the Internet to put on your new iPod.
3) Which of the following accurately describes an effect of the hurricane Katrina on U.S. GDP? A) GDP would decrease reflecting the costs of cleanup. B) GDP would increase reflecting the costs of cleanup. C) GDP would increase reflecting the decrease in production that occurred during the storm and the productive capacity lost in the storm. D) GDP would increase well being.
4) A full time student who is not working is categorized as A) unemployed. B) employed. C) not in the labor force. D) a discouraged worker. E) frictionally unemployed.
5) The labor force participation rate is defined as A) the percentage of the working-age population that is employed. B) the percentage of the working-age population that is unemployed. C) the percentage of the labor force that is employed. D) the percentage of the labor force that is unemployed. E) the percentage of the working-age population in the labor force.
6) ________ are financial securities that represent promises to repay a fixed amount of funds. A) Stocks B) Bonds C) Savings accounts D) Certificates of deposit 2
7) Endogenous growth theory A) states that the rate of technological change is determined outside the working of the market system. B) does not adequately explain the factors that determine productivity. C) states that the rate of technological change is caused by economic incentives. D) states that the rate of technological change is unaffected by economic incentives.
8) An explanation for the productivity slowdown in the U.S.A. from 1973 through 1995, is A) measurement problems. B) creative destruction. C) a decline in oil prices. D) an increase in labor quality.
9) There is an unplanned increase in inventories when A) actual inventory investment equals planned inventory investment. B) actual inventory investment is less than planned inventory investment. C) actual inventory investment is greater than planned inventory investment. D) a firm experiences much higher sales than expected.
10) Which of the following will raise consumer expenditures? A) an increase in interest rates B) a general decline in housing prices C) an increase in expected future income D) an increase in the price level
11) The marginal propensity to consume is defined as A) consumption divided by disposable income. B) disposable income divided by consumption. C) the change in consumption divided by the change in disposable income. D) the change in disposable income divided by the change in consumption.
12) The wealth effect is defined as A) when the price level falls, the real value of household wealth falls. B) when the price level falls, the nominal value of household wealth falls. C) when the price level falls, the nominal value of household wealth rises. D) when the price level falls, the real value of household wealth rises.
13) The interest rate effect is described as A) an increase in the price level raises the interest rate and chokes off government spending. B) an increase in the price level lowers the interest rate and chokes off government spending. C) an increase in the price level raises the interest rate and chokes off investment and consumption spending. D) an increase in the price level lowers the interest rate and chokes off investment and 3
consumption spending. 14) The international trade effect states that A) an increase in the price level will raise net exports. B) an increase in the price level will lower net exports. C) an increase in the price level will raise exports. D) an increase in the price level will lower imports.
15) Suppose the U.S. GDP growth rate is slower relative to other countries' GDP growth rates. This will A) move the economy up along a stationary aggregate demand curve. B) move the economy down along a stationary aggregate demand curve. C) shift the aggregate demand curve to the left. D) shift the aggregate demand curve to the right.