MSC优化Patran实例PPT课件
- 格式:ppt
- 大小:1.14 MB
- 文档页数:42





SimOffice之MSCPatran作者:MSC.software2004年9月28日MSC.Software发布了MSC.SimOffice-V2005产品系列,该产品系列将MSC.Software传统的主线产品MSC.Nastran、MSC.Patran、MSC.ADAMS、MSC.Marc、MSC.Dytran及MSC.EASY5等整合在一起,帮助众多用户从容应对多学科、多层面、集成化、跨平台等诸多新的挑战。
MSC.Patran v2005MSC.Patran是机械CAE分析软件的开放式前后处理平台,它为工程设计、分析和分析结果评估提供完整的三维CAE环境。
MSC.Patran2005具有更加精确多样的CAD几何接口集成系统,更为完善的CAD数据组织和分组功能;高级曲面网格划分功能的进一步加强大大缩短了网格前处理的时间;与各种CAE分析软件MSC.Marc,MSC.Dytran,MSC.Nastran,以及LS-DYNA等交互式接口的进一步提高和完善使得各个领域的分析都变得更加便捷;有限元结果数据分量的合成显示等新功能的加入使Patran2005在结果处理上更易于理解。
具体功能如下:一、前处理部分1.支持HP-UX和AIX新的3GB内存的使用,对于处理超大模型更加方便;2.更好的CAD数据输入接口,根据CAD分层信息自动分组;3.直接Pro/ENGINEER接口/网格划分,Patran2005直接读入Pro/E模型,不需要做任何的几何修补直接生成网格;Patran2005在输入Pro/E文件的时候,相关的材料数据信息随同输入,从Pro/E输入的材料信息包括以下内容:材料名称(标准的PTC part参数)材料特性(标准的PTC part参数)材料参考说明(客户化扩展,使用用户自定义的参数)4.CAD输出数据接口的扩展从MSC.Patran2005开始,支持以下的通用几何输出格式:* Parasolid xmt * IGES * Patran Neutral * STEP 203 * STEP 209 * I-DEAS 10 * ACIS 13.0 * VDA * STEP 214 * CATIA V4.1.9几何实体的输出类型包括:线,面和体如果Parasolid转换文件包含特征,特征同样可以输出。


课程 1. 入门目的:本次练习中,学习内容如下:⏹进入MSC/PATRAN并运行一个过程文件⏹对窗口和框架进行移动、调整尺寸及图标化操作⏹熟悉屏幕拾取⏹熟悉在线帮助的使用模型描述:本练习中,将学习如何进入MSC/PATRAN、生成一个MSC/PATRAN数据库及运行一个已存在的过程文件以生成一个用于这次练习的MSC/PATRAN模型。
还将练习对图形窗口和主框架进行移动、调整尺寸及图标化操作。
此外,还要学习如何使用在线帮助。
由于本次练习的重点是学习MSC/PATRAN的基本知识,因此,在练习的过程中穿插讨论了一些MSC/PATRAN的通用命令格式及操作。
练习过程:1.在X—窗口中键入patran。
此窗口中将会显示有关状态信息。
之后MSC/PATRAN主框架将出现。
Main Form如下图:最初,除File菜单外,主框架中的其它菜单都是灰色的。
通常,为利于操作,MSC/PATRAN将把不可能执行的选项设成灰色。
例如,移动鼠标光标到Main Form的File上,单击鼠标左键。
在下拉式菜单中,只出现与数据库有关的操作。
因为运行MSC/PATRAN之后的第一件事是创建或打开一个数据库。
建立一个新的数据库并命名为exereise_1.db。
File/NewNew Database Name:片刻之后,出现绘图窗口。
当建立一个新数据库时,将出现New Model Preferences对话框。
选择框中容差区的不同选项,可使MSC/PATRAN以两种不同方式区分模型中相邻的两个点。
在Tolerance中选Based on Model时,是以模型中最大尺寸的0.05%做为容差,若选Default,则以缺省值0.005作为模型的容差。
在这个练习中,选择Default选项。
在New Model Preferences对话框中,还可以选择Analysis Code 和Analysis Type,它们将影响建模期间各种对话框的内容。


基于MSC 1P atran/N astran 的桥式起重机主梁优化设计郑州大学机械工程学院 秦东晨 王迎佳 朱晓芳 陈江义 刘竹丽 摘 要:针对现行主梁设计中存在的结构笨重、材料浪费严重的问题,基于MSC.Patran 平台,构造某型桥式起重机箱型主梁模型,应用MSC.Nastran 对其进行结构和受力分析;以主梁各板厚度为优化变量,以强度和刚度指标为约束,应用MSC.Nastran 提供的优化方法,进行以主梁结构轻量化为目标的优化计算,得到合理的优化结果。
对我国桥式起重机的现行设计方法进行了一些改进和探索。
关键词:桥式起重机;箱型主梁;MSC.Patran/Nastran ;优化Abstract :Applying current methods to design overhead traveling crane girder has the problem of cumbers ome structure and serious material waste.This takes box girder of the 5-16t overhead traveling crane as study object and presents an improved de 2sign method.The m odel of the girder is built based on MSC.Patran and structure and force analysis is performed using MSC.Nastran.The optimal method provided by MSC.Nastran is used to conduct optimal calculation to obtain as light girder as possible with girder plate thickness as optimal variables ,and strength and stiffness as constraints.The optimization results are reas onable.K eyw ords :traveling crane ;box girder ;MSC.Patran/Nastran ;optimization 采用有限单元法和优化设计方法,以某型正轨箱型梁桥式起重机为研究对象,通过计算机仿真分析起重机主梁的强度、刚度和稳定性,找出最大应力和最大变形处,然后在此基础上,完成以结构轻量化为主要目标的优化计算。
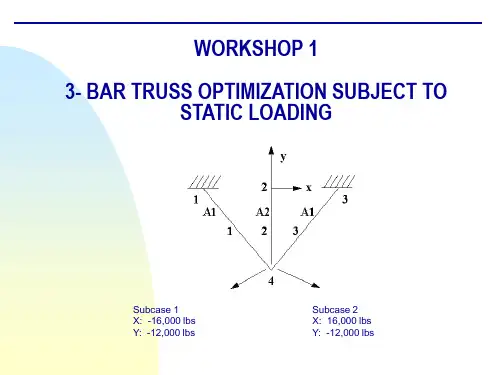
WORKSHOP PROBLEM 2Unrestricted and restrictedTopology Optimization of aPlateObjectivess Generation of the FE-models Unrestricted topology optimizations Restricted topology optimization- exclude elements- frozen elements- initial elements (nucleus for material removal)s Global stiffness / ComplianceMSC/CONSTRUCT Exercise Workbook2-12-2MSC/CONSTRUCT Exercise WorkbookWorkshop 2Topology optimization of a plateMSC/CONSTRUCT Exercise Workbook2-3Model Description:The goal of this exercise is to find the optimized topology for a plate subject to a single force with different options.Figure 2.1 below shows the geometry and boundary conditions of the plate.Figure 2.1 Geometry and boundary conditions of the plateYoung’s Modulus: 2.1 * 105 N/mm 2 Poisson Ration:0.3Length: 480mm Width: 320mm Thickness: 20mm Loading:600N480320xF=600NyIntroductionWithin MSC/CONSTRUCT various restrictions can be specified toinfluence the topology optimization process in order to meet functional orproduction requirements.E. g. you cana)- exclude elements from the optimization group(see workshop example No. 1)b)- freeze elements (frozen elements)c)- mark areas where to start the optimization (initial elements)d)- limit the maximum displacement of the structure (global stiffness)Items a) - d) shall be applied in this example but first of all an unrestrictedtopology optimization shall be carried out.2-4MSC/CONSTRUCT Exercise WorkbookWorkshop 2Topology optimization of a plateMSC/CONSTRUCT Exercise Workbook2-5Exercise Procedure:1. Unrestricted topology optimization1.1Prepare the FE-Model with MSC/PATRANIn comparison to workshop example 1 take into account the modified geometry and use 20 units as the ’’Global Edge Length ’’.Fix the nodes 1, 26, 376, 401 in x- and y- direction and "smear" the single force F = 600N over the nodes 25, 50, 75.Create the Nastran Input Deck topo_var.bdf for the optimization with MSC/PATRAN.1.2Creation of the MSC/NASTRAN Input Deck without MSC/PATRANThe generated MSC/NASTRAN input deck has to be modified for the optimization process like in workshop example No. 1 (see page 1-12)1.3Create the parameter file for the topology optimization in MSC/PATRAN1.3.1 Start the MSC/CONSTRUCT Interface in MSC/PATRAN.MSC/CONSTRUCT Action: Create Object: Parameter File Method:Topology Parameter FilesName: simpleInput Parameter...2-6MSC/CONSTRUCT Exercise Workbook1.3.2 Create the Data Input SectionLoad the FE-Model data (nodes and elements) for the optimization 1.3.3.Create the Object Definition SectionInclude all elements in the optimization group..1.3.4.Create the Optimization SectionSpecify the formula for the stress calculation --> Stress hypothesis: von Mises hypothesis Select Input File Select Input File Input Files:topo_var.bdfOK CreateGroups Group Name:DESIGN_ELEM Type:Element Select Elements:Elm 1:384Add CreateLoad Calculation Load Calc Name:LOAD_CALC_1Type:Hypo Component:MisesCreateWorkshop 2Topology optimization of a plateMSC/CONSTRUCT Exercise Workbook2-7Define the objective function --> Objective function is the relative volume Specify the optimization type and assign the design variables, an objective function and the stress hypothesis. Highlight the names in the boxes.- Specify the maximum number of iteration cycles 1.3.5 Create the Output SectionObjective Function Objective Name:OBJ_FUNC_1Type:Relative Volume Variable:None Value:0.60CreateOptimization Existing Groups:DESIGN_ELM Existing Load Calc:LOAD_CALC_1Existing Objective:OBJ_FUNC_1CreateTermination Criteria Type:Maximum Iteration Number of Iteration:30CreateOutput Request Predefined Macros:uf_topo_pat.macCreate2-8MSC/CONSTRUCT Exercise WorkbookEnd the Construct Interface and save the parameter file.The created parameter file is shown in Figure 2.2Figure 2.2 Parameter file simple.par !! INPUT FILE FOR TOPOLOGY OPTIMIZATION ! MODEL :simple ! AUTHOR :training! DATE :08-Dec-97 10:19:18! LAST CHANGE :! REMARKS :! DESCRIPTION :! - - - - -DATA INPUT SECTION READ, topo_var.bdf! - - - - -OBJECT DEFINITION SECTION SELECT, ELEM, S, ELEM, 1,384,1GROUP_DEF,ELEM, DESIGN_ELEM! - - - - -OPTIMIZATION SECTIONLOAD_CALC, LOC_DEF_1, HYPO, MISESOBJ_FUNC, USER_OBJ_FUNC_1,REL_VOL, 0.60OPTIMIZE, TOPO, DESIGN_ELEM, USER_OBJ_FUNC_1,LOC_DEF_1STOP, ITER_MAX, 30! - - - - -OUTPUT SECTION INCLUDE, uf_topo_pat.mac SA VE EXITEnd you patran session.1.4Carry out the optimizationBecause the name of the parameter file and the MSC/NASTRAN input file are not the same you have to start the optimization with the command:construct -type all -job simple -nas topo_var.bdfOK ApplyWorkshop 2Topology optimization of a plateMSC/CONSTRUCT Exercise Workbook2-91.5Postprocessing1.5.1 Material distributionFigure 2.3 Material distribution after the 14th iteration1.5.2 AnimationWithin MSC/PATRAN with the Insight tool you can create an animation of the material removal from the first to the last iteration.In order to animate the model you have to carry out the following steps:x Insight Action: Create Tool:Isosurface Isosurface Value: x ResultsResult Selection Current Load Case:select all iterationsUpdate resultsAnimation AttributesÌEnable AnimationAnimation Type:x Global VariableGlobal Variable: IterationOKIsosurface Result MP, ValueIsovalue SetupIsovalue:10000OK x Global VariableResult OptionsElement Result Mapping:x Element ConstantOKOKIsosurface AttributesÌClip at Isosurface< Display:Free Edge> Display:ShadedOKApplyFor start the animation go to in the menubar toInsight Control / Animation ControlSetup ...Animation Mode Animate Tools - 3DAnimation Tool Is-Isos_1 IterationFrames:17Animate2-10MSC/CONSTRUCT Exercise WorkbookWorkshop 2Topology optimization of a plate If you want to finish the animation click on Clear.In general: all SELECT and GROUPING operations as well as all otheroperations can be carried out with the MSC/CONSTRUCT preprozessorfor non MSC/PATRAN user. But for more complicated problems thisbecomes very tedious as one explicitly has to extract nodal and/orelement information from the finite element model.2. Restricted Topology Optimization2.1Explizit definition of the design spaceExclude two element rows from the design space which are attached to the left edge of the plate as well as these elements which are involved in the introduction of the load.Define additional the volume reduction in the first iteration and the speed for the volume reduction in the second and subsequent iteration.Modify the Object Definition Section and the Optimization Section in the existing parameter file simple.par and generate a new one, called design.par .2.1.1 Read in the existing parameter file simple.par .2.1.2 Modify the Object Definition SectionDefine the design space without the two element rows on the left edge as well as the elements which are assigned with the load ( see in the following picture, Figure 2.4)MSC/Construct Action: ReadObject:Parameter FileSelect Parameter File Parameter File Name:.../simple Apply Action: Create Object: Parameter File Method:Topology Parameter File Name:.../simple.par Input ParameterWorkshop 2Topology optimization of a plate Figure 2.4 Design Elements.GroupsGroup Name:DESIGN_ELEMType:ElementSelect Elements:Element 3:23 27:47 51:7275:96 99:120 123:144147:168 171:192 195:216219:240 243:264 267:288291:312 315:336 339:360363:384AddCreate2.1.3 Modify the Optimization Section.Define the volume reduction in the first iteration Define the speed for the volume reduction in the second and subsequent iteration.Save the parameter file under the new name design.parSolution Control Type:Start Option:Percent Value:0.1Existing Groups:DESIGN_ELEMCreateSolution Control Type:Speed Option:Moderate Existing Groups:DESIGN_ELEMCreateWorkshop 2Topology optimization of a plateFigure 2.5 Parameter file design.par! INPUT FILE FOR TOPOLOGY OPTIMIZATION! MODEL :design! AUTHOR :training! DATE :08-Dec-97 10:19:18! LAST CHANGE :! REMARKS :! DESCRIPTION :! - - - - -DATA INPUT SECTIONREAD,topo_var.bdf! - - - - OBJECT DEFINITION SECTIONSELECT, ELEM, S, ELEM, 3, 23, 1SELECT, ELEM, A, ELEM, 27, 47, 1SELECT, ELEM, A, ELEM, 51, 72, 1SELECT, ELEM, A, ELEM, 75, 96, 1SELECT, ELEM, A, ELEM, 99, 120, 1SELECT, ELEM, A, ELEM, 123, 144, 1SELECT, ELEM, A, ELEM, 147, 168, 1SELECT, ELEM, A, ELEM, 171, 192, 1SELECT, ELEM, A, ELEM, 195, 216, 1SELECT, ELEM, A, ELEM, 219, 240, 1SELECT, ELEM, A, ELEM, 243, 264, 1SELECT, ELEM, A, ELEM, 267, 288, 1SELECT, ELEM, A, ELEM, 291, 312, 1SELECT, ELEM, A, ELEM, 315, 336, 1SELECT, ELEM, A, ELEM, 339, 360, 1SELECT, ELEM, A, ELEM, 363, 384, 1! - - - -OPTIMIZA TION SECTION!LOAD_CALC, LOC_DEF_1, HYPO, MISESOBJ_FUNC, USER_REF_1,REL_VOLUM, 0.60OPTIMIZE, TOPO, DESIGN_ELEM, USER_REF_1,LOC_DEF_1CONT_TOPO, DESIGN_ELEM, START, PROZ, 0.1CONT_TOPO, DESIGN_ELEM, SPEED_TOPO, MODERA TESTOP, ITER_MAX, 30! - - - - -OUTPUT SECTIONINCLUDE,uf_topo_pat.macSA VEEXITStart the optimization and check the results.Figure 2.6 Material distribution after the 18th optimization cycleWorkshop 2Topology optimization of a plate2.2 Use frozen elementsDefines which elements are excluded from the optimization. The volume of these elements however is included in determining the objective function. (difference to the further example )2.2.1 Read in the existing parameter file simple.par .Look page 2-12 in order to read in an existing parameter file.2.2.2 Modify the Object Definition SectionDefine all elements as Design Elements Define the Frozen ElementsAll elements which were excluded from the design space in workshop example 2.1 now should be assigned to a frozen element group. Select these elements and create a group called Frozen_Elem ( Figure 2.7 )Groups Group Name:DESIGN_ELEM Type:Element Select Elements:Element 1:384Add CreateFigure 2.7 Frozen ElementsAnother possibility to create a construct group is at first to create a MSC/ PATRAN group with the neccassary elements and then to create the MSC/ CONSTRUCT group from the MSC/PATRAN group.Create the MSC/PATRAN group in the Group-Menu in PatranGroup/CreateNew Group Name:Frozen_ElemType:ElementEntity Selection:Elm 1, 2, 24, 25, 26, 48, 49, 50,73, 74, 97, 98, 121, 122, 145,146, 169, 170, 193, 194, 217,218, 241, 242, 265, 266, 289, 290313, 314, 337, 338, 361, 362ApplyWorkshop 2Topology optimization of a plateCreate the MSC/CONSTRUCT group in the Construct-Menu 2.2.3 Modify the Optimization Section.- Define which elements during the optimization may be not modified as a restrictionDefine the speed for the volume reduction in the second and subsequent iteration.Groups Type:Element Patran Groups:Frozen_ElemCreateTopology Restrictions Type:Frozen Existing Element Group:Frozen_ElemCreateSolution Control Type:Speed Option:Moderate Existing Groups:DESIGN_ELEMCreateSave the parameter file under the new name frozen.par Figure 2.8 Parameter file frozen.par! INPUT FILE FOR TOPOLOGY OPTIMIZATION! MODEL :frozen! AUTHOR :training! DATE :09-Dec-97 14:49:18! LAST CHANGE :! REMARKS :! DESCRIPTION :! - - - - -DATA INPUT SECTIONREAD, topo_var.bdf! - - - - OBJECT DEFINITION SECTIONSELECT, ELEM, S, ELEM, 1, 384, 1GROUP_DEF, ELEM, DESIGN_ELEMSELECT, ELEM, S, ELEM, 1SELECT, ELEM, A, ELEM, 2SELECT, ELEM, A, ELEM, 24, 26, 1SELECT, ELEM, A, ELEM, 48, 50, 1SELECT, ELEM, A, ELEM, 73SELECT, ELEM, A, ELEM, 74SELECT, ELEM, A, ELEM, 97SELECT, ELEM, A, ELEM, 98SELECT, ELEM, A, ELEM, 121SELECT, ELEM, A, ELEM, 122SELECT, ELEM, A, ELEM, 145SELECT, ELEM, A, ELEM, 146SELECT, ELEM, A, ELEM, 169SELECT, ELEM, A, ELEM, 170SELECT, ELEM, A, ELEM, 193SELECT, ELEM, A, ELEM, 194SELECT, ELEM, A, ELEM, 217SELECT, ELEM, A, ELEM, 218SELECT, ELEM, A, ELEM, 241SELECT, ELEM, A, ELEM, 242SELECT, ELEM, A, ELEM, 265SELECT, ELEM, A, ELEM, 266SELECT, ELEM, A, ELEM, 289SELECT, ELEM, A, ELEM, 290SELECT, ELEM, A, ELEM, 313SELECT, ELEM, A, ELEM, 314SELECT, ELEM, A, ELEM, 337SELECT, ELEM, A, ELEM, 338SELECT, ELEM, A, ELEM, 361SELECT, ELEM, A, ELEM, 362GROUP_DEF, ELEM, Frozen_Elem! - - - - -OPTIMIZATION SECTIONLOAD_CALC, LOC_DEF_1, HYPO, MISESOBJ_FUNC, USER_REF_1,REL_VOLUM, 0.60OPTIMIZE, TOPO, DESIGN_ELEM, USER_REF_1,LOC_DEF_1 CONT_TOPO, DESIGN_ELEM, SPEED_TOPO, MODERATEREST_TOPO, FROZEN_ELEM, FROZENSTOP, ITER_MAX, 30! - - - - -OUTPUT SECTIONINCLUDE, uf_topo_pat.macSA VEEXITWorkshop 2Topology optimization of a plateStart the optimization and check the resultsFigure 2.9 Material distribution after the 20th optimization cycle usingFrozen ElementsWith the same objective function (60% material removal) more materialwill be removed using frozen elements rather then excluding elementsfrom the design space ( compare Figure 2.6 with Figure 2.9). The reasonis that the volume of the frozen elements is included in the determinationof the objective function.2.3Use frozen and initial elementsBy specifying initial elements the location where material will be removed first, can be determined. This may be necassary for symmetrical loaded and constraint structures.Figure 2.10 shows the initial elements (black shaded) proposed for this example. They have to be selected and grouped first and then defined in the optimization section of the parameter file according to Figure 2.11.In addition these elements should be frozen at which boundary conditions ( forces and supports) are applied.Figure 2.10 Initial Elements2.2.1 Read in the existing parameter file simple.par.Read in the existing parameter file how it is described in page 2-122.2.2 Modify the Object Definition SectionUse the defined MSC/CONSTRUCT group Design_Elem from the readed parameter fileWorkshop 2Topology optimization of a plateDefine the Initial ElementsInclude as Initial Elements these elements which are in the upper edge (see Figure 2.11).Define the Frozen ElementsInclude as Frozen Elements these elements which are applied with the load and the boundary conditions.2.2.3 Modify the Optimization Section.- Define which elements during the optimization may be not modified as a restrictionGroups Group Name:Initial_Elem Type:ElementSelect Elements:Element 264:360:24 380:384Add CreateGroups Group Name:Frozen_Elem Type:Element Select Elements:Elm 1 24 48 361Add CreateTopology Restrictions Type:Frozen Existing Element Group:Frozen_ElemCreate- Define the initial restiction Save the parameter file under the new name initial.par according Figure 2.12, carry out the optimization and compare the material distribution after 17th iteration with Figure 2.13.Figure 2.12 Parameter file with initial elements! INPUT FILE FOR TOPOLOGY OPTIMIZATION ! MODEL :initila ! AUTHOR :training! DATE :15-Dec-97 10:19:18! LAST CHANGE :! REMARKS :! DESCRIPTION :! - - - - -DATA INPUT SECTION READ, topo_var.bdf! - - - - OBJECT DEFINITION SECTION SEL, ELEM, S,1,384,1GROUP_DEF,ELEM, DESIGN_ELEM SELECT, ELEM, S, 380SELECT, ELEM, A, 381SELECT, ELEM, A, 382SELECT, ELEM, A, 383SELECT, ELEM, A, 384SELECT, ELEM, A, 288SELECT, ELEM, A, 312SELECT, ELEM, A, 336SELECT, ELEM, A, 360GROUP_DEF, ELEM, Initial-Elem SELECT, ELEM, S, 1SELECT, ELEM, A, 361SELECT, ELEM, A, 24SELECT, ELEM, A, 48GROUP_DEF, ELEM, Frozen_Elem! -- - - -OPTIMIZATION SECTIONLOAD_CALC, LOC_DEF_1, HYPO, MISESOBJ_FUNC, USER_OBJ_FUNC_FUNC_1, REL_VOLUM, 0.50OPTIMIZE, TOPO, DESIGN_ELEM, USER_REF_1,LOC_DEF_1REST_TOPO, Initial_Elem, INITIAL, LINE REST_TOPO, Froezen_Elem, FROZEN STOP, ITER_MAX, 30! - - - - -OUTPUT SECTION INCLUDE.uf_topo_pat.mac SA VE EXITTopology Restrictions Type:Initial Option:Line Existing Element Group:Initial_ElemCreateWorkshop 2Topology optimization of a plate Figure 2.13 Material distribution after 17th iteration3. Global stiffness / ComplianceThe global stiffness is declared as the objective function when the maximum allowed displacement of the structure is specified.Within MSC/CONSTRUCT a maximum allowable displacement could be defined in the objective function. This displacement value is based on the maximum total displacement calculated in the first FE-analysis. The material distribution will be determined based on this results. In addition other restrictions can be used like frozen or initial elements.Besides the discussed definitions for the parameter file (element selection etc.) variables have to defined and assigned3.1Define the variables in the Object Definition Section.3.1.1 Read in the existing parameter file simple.par.Read in the existing parameter file simple.par how it is described in page2-123.1.2 Modify the Object Definition SectionDefine all elements as Design Elements except the element on which theload and boundary condition are applied.GroupsGroup Name:DESIGN_ELEMType:ElementSelect Elements:Element 2:23 25:4749:360 362:384CreateCreateWorkshop 2Topology optimization of a plateNodes are necassary for the determination of the displacement. Thats why a group has to be created which includes all nodes..q Define the maximum allowed displacement- Assign a variable to the maximum displacement value of the first FE-analysis named TAR_STIFF1- Assign a variable to the maximum allowed displacement value for the optimization named TAR_STIFF2Groups Group Name:DISP_NODES Type:Nodes Select Elements:Node 1:425Create CreateNumerical Variable Variable Name:Tar_Stiff_1Type:BASE Value:DISP_ABS Option:MAX Existing Group:DISP_NODESCreateNumerical Variable Variable Name:Tar_Stiff_2Type:FIX Value: 1.15Create- Multiply both variables and named the result TAR_STIFF33.2Define the Optimization SectionDefine the objective function 2.1.3 Modify the Optimization Section.Define the speed for the volume reduction in the second and subsequent iteration.Numerical Variable Variable Name:Tar_Stiff_3Type:OPER Value:MULT Variable:Tar_Stiff_1Variable:Tar_Stiff_2CreateObjective Function Objective Name:OBJ_FUNC_1Type:Stiffness Variable:FIRST Existing Variables:Tar_Stiff_3Existing Variables:Tar_Stiff_1CreateSolution Control Type:Speed Option:Moderate Existing Groups:DESIGN_ELEMCreateWorkshop 2Topology optimization of a plateSpecify the tolerance file accordingly.Save the parameter file under the new name stiffness.par and check the results with Figure 2.15Figure 2.14 Parameter file stiffness.par! INPUT FILE FOR TOPOLOGY OPTIMIZATION ! MODEL :stiffness ! AUTHOR :training! DATE :16-Dec-97 17:17:09! LAST CHANGE :! REMARKS :! DESCRIPTION :! - - - - -DATA INPUT SECTION READ, topo_var.bdf! - - - - OBJECT DEFINITION SECTION SELECT, ELEM, S, ELEM, 264, 360, 24SELECT, ELEM, A, ELEM, 380, 384, 1GROUP_DEF, ELEM, DESIGN_ELEM SELECT, NODE, S, NODE, 1, 425, 1GROUP_DEF, NODE, DISP_NODES! - - - - -OPTIMIZATION SECTIONLOAD_CALC, LOC_DEF_1, HYPO, MISESVARIABLE,TAR_STIFF1,BASE,DISP_ABS,MAX,DISP_NODES VARIABLE,TAR_STIFF2,FIX,1.15VARIABLE,TAR_STIFF3,OPER,MULT,TAR_STIFF1,TAR_STIFF2OBJ_FUNC, USER_REF_1,STIFFNESS,TAR_STIFF3,FIRST,TAR_STIFF1OPTIMIZE, TOPO, DESIGN_ELEM, USER_REF_1,LOC_DEF_1CONT_TOPO, DESIGN_ELEM, SPEED_TOPO, MODERATE CONT_TOPO, DESIGN_ELEM, EPSILON, PROZ, 0.05 STOP, ITER_MAX, 30! - - - - -OUTPUT SECTION INCLUDE,uf_topo_pat.mac SA VE EXITSolution Control Type:Epsilon Option:Percent Value:0.05Existing Groups:DESIGN_ELEMCreateFigure 2.15 Material distribution after the 14th iteration。