
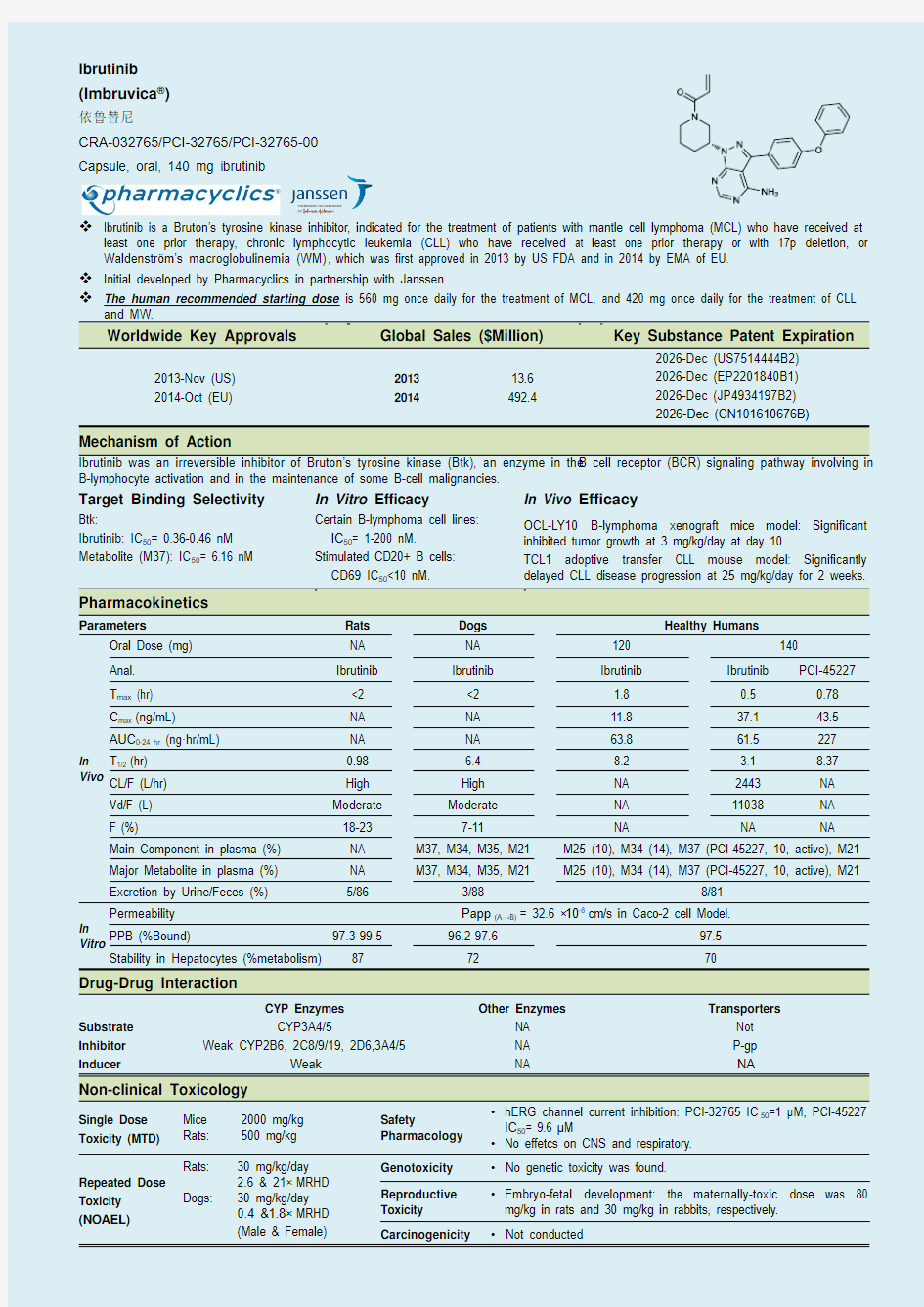
Ibrutinib (Imbruvica ?)
依鲁替尼
CRA-032765/PCI-32765/PCI-32765-00 Capsule, oral, 140 mg ibrutinib
Ibrutinib is a Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitor, indicated for the treatment of patients with mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) who have received at
least one prior therapy, chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) who have received at least one prior therapy or with 17p deletion, or Waldenstr?m’s macroglobulinemia (WM), which was first approved in 2013 by US FDA and in 2014 by EMA of EU.
Initial developed by Pharmacyclics in partnership with Janssen.
The human recommended starting dose is 560 mg once daily for the treatment of MCL, and 420 mg once daily for the treatment of CLL
and MW.
Worldwide Key Approvals Global Sales ($Million) Key Substance Patent Expiration
2013-Nov (US)
2014-Oct (EU)
2013 2014 13.6 492.4
2026-Dec (US7514444B2) 2026-Dec (EP2201840B1) 2026-Dec (JP4934197B2) 2026-Dec (CN101610676B)
Mechanism of Action
Ibrutinib was an irreversible inhibitor of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (Btk), an enzyme in the B cell receptor (BCR) signaling pathway involving in B-lymphocyte activation and in the maintenance of some B-cell malignancies.
Target Binding Selectivity
In Vitro Efficacy
In Vivo Efficacy
Btk:
Ibrutinib: IC 50= 0.36-0.46 nM Metabolite (M37): IC 50= 6.16 nM
Certain B-lymphoma cell lines: IC 50= 1-200 nM.
Stimulated CD20+ B cells: CD69 IC 50<10 nM.
OCL-LY10 B-lymphoma xenograft mice model: Significant inhibited tumor growth at 3 mg/kg/day at day 10.
TCL1 adoptive transfer CLL mouse model: Significantly delayed CLL disease progression at 25 mg/kg/day for 2 weeks.
Pharmacokinetics
Parameters
Rats Dogs Healthy Humans
In Vivo
Oral Dose (mg) NA NA 120 140
Anal. Ibrutinib Ibrutinib Ibrutinib Ibrutinib PCI-45227 T max (hr) <2 <2 1.8 0.5 0.78 C max (ng/mL) NA NA 11.8 37.1 43.5 AUC 0-24 hr (ng ·hr/mL) NA NA 63.8 61.5 227 T 1/2 (hr) 0.98 6.4 8.2 3.1 8.37 CL/F (L/hr)
High High NA 2443 NA Vd/F (L) Moderate Moderate NA 11038 NA F (%)
18-23
7-11
NA
NA
NA
Main Component in plasma (%) NA M37, M34, M35, M21 M25 (10), M34 (14), M37 (PCI-45227, 10, active), M21 Major Metabolite in plasma (%) NA M37, M34, M35, M21 M25 (10), M34 (14), M37 (PCI-45227, 10, active), M21
Excretion by Urine/Feces (%) 5/86
3/88 8/81 In
Vitro
Permeability
Papp (A→B) = 32.6 ×10-6 cm/s in Caco-2 cell Model.
PPB (%Bound) 97.3-99.5 96.2-97.6
97.5 Stability in Hepatocytes (%metabolism) 87
72
70
Drug-Drug Interaction
Substrate Inhibitor Inducer
CYP Enzymes CYP3A4/5
Weak CYP2B6, 2C8/9/19, 2D6,3A4/5
Weak
Other Enzymes
NA NA NA
Transporters
Not P-gp NA
Non-clinical Toxicology
Single Dose Toxicity (MTD)
Mice 2000 mg/kg Rats: 500 mg/kg Safety
Pharmacology ? hERG channel current inhibition: PCI-32765 IC 50=1 μM, PCI-45227 IC 50= 9.6 μM
? No effetcs on CNS and respiratory. Repeated Dose
Toxicity
(NOAEL)
Rats:
30 mg/kg/day 2.6 & 21× MRHD Dogs: 30 mg/kg/day 0.4 &1.8× MRHD (Male & Female)
Genotoxicity ? No genetic toxicity was found.
Reproductive Toxicity ? Embryo-fetal development: the maternally-toxic dose was 80 mg/kg in rats and 30 mg/kg in rabbits, respectively. Carcinogenicity
? Not conducted
Ibrutinib
(Imbruvica?)
依鲁替尼
Research code: CRA-032765/PCI-32765/PCI-32765-00§1 General Information
Ibrutinib is a Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (B tk) inhibitor, which was first approved in the worldwide in 2013 by US FDA of US and in 2014 by EMA of EU.
Initial developed by Pharmacyclics in partnership with Janssen.
Ibrutinib inhibites BTKs and prohibits the BTKs signal pathway through the B-cell surface receptor, which is nec-essary for B-cell trafficking, chemotaxis, adhesion, and proliferation.
Indicated for the treatment of patients with mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) who have received at least one prior therapy, chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) who have received at least one prior therapy or with 17p deletion, or Waldenstr?m’s macroglobulinemia (WM).
Available as an orally capsules, containing 140 mg of ibru-tinib and the recommended starting dose is 560 mg once daily for the treatment of MCL; and 420 mg once daily for the treatment of CLL and WM.
--Key Approvals around the World--
--Worldwide Sales--
*Source: Annual Report of Pharmacyclics was based on the period of natural year. --Active Ingredient--
Molecular formula: C25H24N6O2
Molecular weight: 440.50
CAS No.: 936563-96-1 (Ibrutinib) Parameters of Lipinski’s “Rule of 5”
440.50 2 8 5 99.2 ?2 4.472±
1.376
a: Calculated by ACD/Labs software V11.02
--Drug Product--
Dosage route: Oral.
Strengths: 140 mg
Dosage forms: Capsule
Inactive ingredients:
Croscarmellose sodium, Magnesium stearate, Micro-
crystalline cellulose, Sodium lauryl sulfate.
The capsule shell contains:
Gelatin, Titanium dioxide and Black ink.
Recommended Dose:
Mantle cell lymphoma (MCL): 560 mg taken orally
once daily (four 140 mg capsules once daily).
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and Walden-
str?m's macroglobulinemia (WM): 420 mg taken orally
once daily (three 140 mg capsules once daily).
*Sourced from the FDA drug label information.
150
300
450
600
Y2013Y2014
Ibrutinib Worldwild Sales (US$ million)
NDA NO. 205552 EMEA/H/C/003791
Brand Name Imbruvica?Imbruvica?
Indication
Mantle cell lymphoma
Chronic lymphocytic
Mantle cell lymphoma
Chronic lymphocytic leu-
*: Till May. 2015, it has not been approved by PMDA (Japan) and CFDA (China).
--Key Patents--
Inhibitors of bruton's tyrosine kinase
Product (Substance/
Pharmacyclics Inc WO2008039218A2 PCT/US2006/049626 2006/9/22 2006/12/28 Composition/Uses)
US7514444B2 2006/12/28 2009/4/7 2013/11/13 0 day (TD) 2026/12/28
US8008309B2 2006/12/28 2011/8/30 2013/11/13 83 days (TD) 2026/12/28
US8697711B2 2006/12/28 2013/7/30 2013/11/13 0 day (TD) 2026/12/28
EP2201840B1 2006/12/28 2011/11/2 2014/10/21 / 2026/12/28
JP4934197B2 2006/12/28 2012/2/24 NA NA 2026/12/28
JP5193256B2 2006/12/28 2013/2/8 NA NA2026/12/28
CN101610676B 2006/12/28 2013/3/27 NA/ 2026/12/28
§2 Chemistry
Route 1: Original Discovery Route[1-5]
1
Discovery of selective irreversible inhibitors
for bruton's tyrosine kinase
ChemMedChem, 2007, 2, 58-61 Key Ref.
2 Pyrazolopyrimidines as therapeutic agents WO2001019829A2/US6660744B1
3 Inhibitors of bruton's tyrosine kinase US20080108636A1
4 Pyrazolo-pyrimidine inhibitor of bruton's tyrosine kinase WO2011046964A2/US7718662B1
5 Methods and composition for inhibition of bone resorption
WO2013003629A3
US20130178483A1
6 Inhibitors of bruton's tyrosine kinase US20080076921A1
The Pharmaceutical Index – Worldwide 2013 NCEs 4 Route 2[6]:
1 Preparation method of Ibrutinib CN103626774A Key Ref.
Ibrutinib 5
§3 Pharmacology
?
Mechanism of Action
● Ibrutinib was an irreversible inhibitor of Bruton ’s tyrosine kinase (Btk), an enzyme in the B cell receptor (BCR) signal-ing pathway involving in B-lymphocyte activation and in the maintenance of some B-cell malignancies. ● Ibrutinib covalently bound to a cysteine (Cyt481) in the ac-tive site of Btk with the IC 50 of 0.46 nM [7]. ● Ibrutinib showed anti-cancer activity against cells derived from B-cell malignancies, including MCL and CLL lines both in vitro cell culture and in vivo xenograft models. ● The active metabolite M37 (PCI-45227) of ibrutinib was ap-proximately 15 times less active than ibrutinib in the inhibi-tion of Btk based on IC 50 values (IC 50= 6.16 nM), and some-what more selective for Btk inhibition relative to other ki-nases such as EGFR and LCK [7]. ● Ibrutinib also inhibited Bmx/ETK (another member of tyro-sine kinase family, IC 50= 0.76 nM), BLK (B lymphocyte kinase, IC 50= 0.52 nM), and other kinases with IC 50s up to 4 nM: CSK (IC 50= 2.25 nM), FGR (IC 50= 2.31 nM), Brk (IC 50= 3.34 nM), HCK (IC 50= 3.67 nM)[7].
? In Vitro Efficacy
● Ibrutinib inhibited Btk, Btk-mediated cell signaling, and BCR-stimulated cell activity in B cell lymphoma derived cells [7,
8]:
In human CD20+ B cells: CD69 inhibition of IC 50< 10 nM.
In isolated human PMBC: Btk active site occupancy (IC 50= 100 nM) and CD69 inhibition (IC 50= 200 nM). In DOHH2 cell line: inhibition of Btk autophosphorylation (IC 50= 11 nM), the phosphorylation of Btk substrate PLC γ (IC 50= 29 nM) and the downstream kinase, ERK (IC 50= 13 nM).
● Ibrutinib inhibited the adhesion of MCL (mantle cell lymphoma) and CLL cells as well as the normal B cells to fibronectin
and vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1), suggesting the potential for ibrutinib to affect the trafficking of B-cells [7, 9, 10]. ● Ibrutinib inhibited cell proliferation of certain B cell lymphoma derived cell lines and CLL cells [7]. ? In Vivo
Efficacy ● In ex vivo studies, Btk active site occupancy was found in splenocyte in ibrutinib pre-treated mice [7]. ● Xenograft models in SCID mice [7]:
OCI-Ly-10 cell lines: significant tumor growth inhibition: oral daily 3 mg/kg on day 10. Mino mantle cell lymphoma i.v. injection model: oral 12 mg/kg daily on study day 70:
Substantively lower numbers of hCD19+ mantle cells in bone marrow, PBMC and lymph nodes, no effect on hCD19+ cell counts in the spleen.
● In TCL1 adoptive transfer CLL mouse model, ibrutinib significantly delayed CLL disease progression [11]:
At 25 mg/kg, oral daily for 16 days. ● In Spontaneous Canine B-cell Lymphoma, tumor burden was reduced 77% by ibrutinib [9]:
At 20 mg/kg, oral daily for 4 weeks.
--Mechanism of Action --
Ibrutinib R-enantiomer 0.36-0.46b 1 PCI-32769 S-enantiomer 1.4 3.6 PCI-45227
Metabolite: M37
6.16
15
a: fold change in IC 50 value compared to IC 50 of ibrutinib. b: Values were tested difference in different experiments.
[8]. J. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2010, 107, 13075-13080, S13075/13071-S13075/13073. [9]. Blood 2013, 122, 2412-2424. [10]. Blood 2012, 119, 2590-2594. [11].
Blood 2012, 119, 1182-1189.
6 The Pharmaceutical Index – Worldwide 2013 NCEs
Btk 0.46 1 LCK 33.24 72 Bmx/ETK 0.76 1.6 TEC 77.76 169 BLK 0.52 1.1 Lyn 200.45 436 FGR 2.31 5 ABL 86.12 187 CSK 2.25 4.9 Fyn 95.55 208 Brk 3.34 7 C-src 170.75 371 HCK 3.67 8 FER 8070.00 17543 EGFR 5.55 12 FLT3 72.90 158 YES 6.51 14 JAK2 >10000 >25000 JAK3 16.13 35 SYK
>10000
>25000
ITK
10.70
23
Note: Human kinases of interest were fused to a proprietary tag in the Ambite kinome-scan (an active-site dependent competition-binding assay), PCI-31523 (the racemic mixture containing ibrutinib[R] and PCI-32769[S]) inhibited 17 of 155 kinases with an IC 99<10 μM. Inhibition of ibrutinib was tested in purified kinases which were identified in the Ambite kinase-scan using 33P-ATP and substrates of purified enzyme.
--In Vitro Efficacy --
Human CD20+ B cell Anti-IgM CD69 Inhibition d <10 <10 Human Primary T Cell Anti-CD3/anti-CD28
antibody
CD69 Inhibition >10000 >1000 Isolated Human PBMC
Anti-IgM
CD69 Inhibition 200 NT e Btk Occupancy f 100 NT DOHH2 Anti-IgG
Btk autophosphorylation g
11 NT PLC γ phosphorylation g 29 NT ERK phosphorylation g
13
NT
a: Cells were treated with ibrutinib for 1 hr and then stimulated for 18 hrs. b: Inhibitor-containing cell medium was replaced with fresh medium before stimulation. c: Continuous exposure to ibrutinib for 18 hrs. d: CD69, the early lymphocyte activation marker. Cells were analyzed by flow cytometer after PE-CD69 stain. e: NT, not test. f: Btk active site
occupancy was tested using a Btk active site fluorescent probe, PCI-33880. g: Proteins phosphorylation was tested using phosphor-specific antibody.
JeKo 1 Mantle Cell Lymphoma Anti-IgM >50 >70 HBL 2 Mantle Cell Lymphoma
Anti-IgM >50 >50 CLL Cells
CLL patients
Anti-IgM
75
~100
Note: Relative adhesion was compared to cells without anti-IgM (BCR) stimulated, on 2 cell adhesion molecules, fibronectin and VCAM-1. a: at ibrutinib 100 nM.
[8].
J. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2010, 107, 13075-13080, S13075/13071-S13075/13073.
Ibrutinib
7
TMD8 WT CARD11 DLBCL a 1 DHL-4 DLBCL 530 OCILY10 WT CARD11 DLBCL 2 DHL10 DLBCL 3,700 OCI-LY3 Activating CARD11
DLBCL
12,000 Ramos Burkitt’s 5,500 LY10 DLBCL 100 LY19 DLBCL >10,000 WSU-HNL FL 120 LY3 DLBCL >10,000 DOHH2 FL 120 DB FL >10,000 Mino Mantle Cell 150 Raji Burkitt’s >10,000 DHL-6 DLBCL 180 Granta-519 Mantle Cell >10,000 WSU-DLCL2
FL
500
JeKo-1
Mantle Cell
>10,000
a: Mutations in CARD11, an oncogene, driven the activation of NF-κB and enhance d the survival of ABC DLBCL (activated B cell-like diffuse large B cell lymphoma) cells.
--In Vivo Efficacy --
Balb/C Mice
PCI-33880a
Intravenous/Intraperitoneal
5 2
Complete Oral
50
2
Complete
Intravenous/ Subcutane-ous/Oral
50 1/3/5/7 Complete 24 Partial Note: Ibrutinib was administered, vehicle: 20% HP-β-Cyclodextrin, and the binding affinity and specificity toward Btk actives sites were assessed in isolated splenocytes via moni-toring signaling of a Btk fluorescent probe, PCI-33880. Active-site occupancy was measured indirectly by the degree to which PCI-33880 was inhibited from binding to Btk. a: PCI-
OCL-L Y 10
DLBCL
SCID Female
Solid tumor xenograft subcutaneous
Oral
(QD×5+R×2)
×6
3, 12
3
Significant tumor growth in-hibition: day 10 at 3 mg/kg or
day 8 at 10 mg/kg. Btk occu-pancy 43-46%, no dose re-sponse.
DOHH2
FL
SCID Male
Solid tumor Xenograft subcutaneous
IP QD×14 5, 30, 120 30
Same efficacy which had best
efficacy on Day 5.
IV QD×14 30, 60, 90
Oral
BID×14
10, 25
10×2
25 mg/kg/dose BID had best
efficacy in TGI (43%-54% in
[9]. Blood 2013, 122, 2412-2424. [10]. Blood 2012, 119, 2590-2594.
8
The Pharmaceutical Index – Worldwide 2013 NCEs
DLCL2 FL
SCID Male
Solid tumor Xenograft subcutaneous
Oral
BID×14
90
90b
Maximum inhibition re-sponse: day 8 at 90 mg/kg
dose (~95% TGI).
Mino
MCL
SCID Female
Xenograft 4×107 cells i.v. injection c
Oral
QD×70
12
12
Treatment with ibrutinib: sub-stantively lower numbers of
hCD19+ mantle cells in bone marrow, PBMC and lymph nodes, no effect on hCD19+ cell counts in the spleen d .
TCL 1-192
CLL
SCID
TCL1 adoptive transfer CLL mouse model e
Oral
QD×16
2.5, 25
25
Ibrutinib significantly de-layed CLL disease progres-sion at 25 mg/kg (CLL counts
in peripheral blood, volume and weight of the spleen, pPLCγ in splenocytes).
population. On study day 70, the spleen, liver, bone marrow and lymph nodes were collected to determine levels of hCD19+ Mino-cell lymphocytes using a human-specific CD19 antibody and FACS analysis. d: significantly effect on hCD19+ cell counts in lymph nodes. e: 5×106 TCL1-192 cells were i.v. injected into SCID mice.
Figure A. Inhibition of CLL Cells in Peripheral Blood by Ibrutinib in TCL1 Adoptive Transfer CLL Mouse Model [11]
Study: TCL1 adoptive transfer CLL mouse model. Animal: SCID mice.
Model: 5×106 TCL1-192 cells were i.v. injected into mice. Starting: 3 weeks after injection cells.
Administration: Oral for once daily for 16 days, ibrutinib 2.5 or 25 mg/kg/day, vehicle (1% HP-β-CD). Test: CLL counts in peripheral blood at 1 and 2 weeks post cell transfer. Result: Ibrutinib significantly delayed CLL disease progression at 25 mg/kg. [9]. Blood 2013, 122, 2412-2424. [11]. Blood 2012, 119, 1182-1189.
Ibrutinib 9 §4 ADME & Drug-Drug Interaction
?Absorption
?Oral bioavailability of ibrutinib was low to moderate in fasted rats and dogs, ranging from 18 - 23% in rats and 7-11% in dogs. The bioavailability study was not performed in humans, but it was likely low.
?Ibrutinib was absorbed rapidly with the T max occurring 0.5 to 2 hrs in non-clinical species and humans, and T max of the metabolite PCI-45227 was 0.78 hrs.
?The half-life of ibrutinib in humans (5.9 hrs) with capsule was longer than that with solution formation (3.1 hrs), in rats
(0.98 hr) and in dogs (6.4 hrs).The half-life of PCI-45227 was 8.4 hrs.
?The clearance of ibrutinib in humans (2443 L/hr) and non-clinical species were higher comparable to liver blood flow.
?The apparent volume of distribution was high in humans (11038 L), suggesting ibrutinib had an extensive distribution in tissues in humans, but Vd may be overestimated duo to the low bioavailability. The apparent volume of distribution was moderate in non-clinical species.
?The permeability of ibrutinib was high with the Papp (A-B) (32.6) ×10-6cm/s in Caco-2 cells model.
?Distribution
?The plasma protein binding of ibrutinib ranged from 96 to 99% in mice, rats, dogs and humans, and the Cb:Cp were less than 1, suggesting low penetration into red blood cells.
?The tissue distribution after a single oral administration:
High concentrations of [14C] ibrutinib was detected in the following tissues at 1 hr postdose following administra-tion of 10 mg/kg radiolabeled ibrutinib: small intestine > esophagus> liver > urinary bladder > kidney.
The high concentrations of radioactivity were found in bile, suggesting a biliary excretion of [14C] ibrutinib derived radioactivity
Radioactivity was not detected in tissues of the central nervous system with the exception of olfactory lobe.
Tissue:plasma concentration ratios were less than 1.0 for most tissues, with detectable levels of radioactivity present through 24 hrs postdose.
Elimination was nearly complete for most tissues by 168 hrs postdose.
?Metabolism
?Ibrutinib was extensively metabolized in liver microsomes from all species and the metabolism of ibrutinib was investi-gated in rat, dog, and human liver microsomes, hepatocytes and recombinant CYP450 isozymes.
?The main circulating entities in human plasma were M21, M25, M34 and M37 and ibrutinib, but ibrutinib and M37 combined constituted less than 10% of total circulating radioactivity.
?CYP3A4 and 3A5 was the major isozymes involved in the metabolism of ibrutinib.
?M37 (PCI-45227) was an active metabolite, with inhibitory activity towards Btk approximately 15 times lower than that of ibrutinib.
?Excretion
?Ibrutinib was primarily metabolized and excreted through the feces (80.6%) mostly as oxidative metabolites (0.77% unchanged drug), and the renal route appeared to be a minor elimination pathway (7.8%) in humans.
?Drug-Drug Interaction
?Ibrutinib had no inhibition on CYP1A2 and CYP2E1, and ibrutinib exerted weak inhibition on the rest of the CYP450 isozymes tested (CYP2B6, CYP2C8, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6 and CYP3A4/5).
?PCI-45227 was not an inhibitor of CYP1A2, CYP2C19, CYP2E1 and CYP3A4/5. It was a weak inhibitor of CYP2B6, CYP2C8, CYP2C9 and CYP2D6.
?Both ibrutinib and the PCI-45227 were weak inducers of CYP450 isoenzymes in vitro.
?Ibrutinib was not a substrate of P-gp but PCI-45227 was a substrate of P-gp.
?Ibrutinib was an inhibitor of P-gp with an IC50of 2.15 μg/mL, but PCI-45227 was not.
10 The Pharmaceutical Index – Worldwide 2013 NCEs
--Absorption --
Non-clinical species: After oral administration, ibrutinib exhibited rapid absorption in preclinical species. The mean T max of
ibrutinib generally occurred within 2 hrs postdose. Ibrutinib was a high clearance with a moderate volume of distribution. The mean terminal half-life of ibrutinib following oral administration ranged from 0.98 hr in rats to 6.4 hrs in dogs. Humans: The AUC of a solution formation compared to a capsule formulation appeared comparable, and the fraction ab-sorbed was close 1, suggesting the absorption from GI tract may not be the limiting factor to the bioavailability.
14[12]C max (ng/mL)
11.8±6.7 37.1±22.4 43.5±9.09 123 ± 145 147 ± 143 AUC 0-24 (ng·hr/mL) 63.8±37.3 61.5±39.2 227±56 603 ± 542 802 ± 668 T max (hr) 1.8 (1.0-3.0) 0.5 (0.5-1.5) 0.78 (0.5-1.5) 2 (0.5 - 24) 2 (0.8 - 23) T 1/2 (hr) 8.2±3.2 3.1±0.8 8.37±0.88 5.9 ± 2.4 5.9 ± 2.0 Vd/F(L) NA 11038 NA NA NA CL/F(L/hr)
NA
2443
NA
NA
NA
PK parameters presented as Mean ± SD except T max was presented as Median (min- max). NA= not applicable. a: administration to healthy humans. b: administration to patients.
Figure B: Mean (±SD, n=6) Ibrutinib and PCI-45227 Plasma Concentration Following a Single Oral Administration of 140 mg [14C] Ibrutinib to humans [12]
[12]
Ibrutinib
32.6
High permeability
--Distribution --
[7]
Mice 99.2 98.5 NA NA Rats
(pigmented) In vivo 1 hr 0.6 Rats 99.5 97.3 NA NA p.o. 24 hr 1.20 Dogs 96.2 97.6 NA NA 10 mg/kg 168 hr 9.43 Humans
97.5
97.5
96
24-76a
Humans In vitro
100-500 ng/mL
0.7-0.8
[12]. Drug@FDA, NDA2055520 Clinical Pharmacology Review(s).
Ibrutinib
11
[7]
Blood 0.511 0.696 0.955 1.74 7.12 NA Adrenal Gland 0.813 0.503 0.618 1.89 NA NA Bile 33.2 36.4 NA NA NA NA Kidney 1.81 1.21 1.04 2.06 7.83 NA Large Intestine 0.516 1.66 4.37 NA NA NA Liver 6.87 6.47 5.25 7.36 11.9 NA Lung 0.392 0.469 0.618 1.18 NA NA Small Intestine 26.2 15.6 1.54 NA NA NA Stomach
1.49
0.618
0.551
1.13
NA
NA
NA= not applicable.
--Metabolism --
[13]
Monkeys 629±80.2 2.20 NA NA NA NA Rats 596±60.9 2.33 10 90a 60 87b Humans 549±68.8 2.52 10 66 a 60 70 Dogs 107±5.47 13.0 10 51 a 60 72 Rabbits
NA
NA
10
21a
60
98b
[7]
M17 +(N ring open OH+O) - - - - √ - - - - - M21 +96 (+O+SO3) - - - - - - √ - √ √ M25 +32(Ring open COOH) √ - - √ √ √ √ √ √ √ M26 +307(+2H+GSH) - - - - - - - - √ - M27 +305(+GSH) - - - - - - √ √ √ - M29 +34(N ring open PH+O) - - - - √ - - - - - M34 +18(N ring open OH)
- - - - - - √ √ √ √ M35 +16(+O) - - - - - - √ √ √ √ M37 +34(dihydrodiol)
√ √ √ √ √ √ √ √ √ √ M38 +16(+O) √ √ √ √ - √ √ √ √
√ M39 +16(+O) √ √ √ - √ √ √ √ √ M40 +16(+O) √ √ √ √ - √ √ √ √ √ M41 -2(-2H) √ √ √ √ - √ √ √ √ UD
Unchanged ibrutinib
√
√
√
√
-
√
√
√
√
√
√:observed;-not observed [13]. Drug@EMA, EMEA/H/C/003791 Imbruvica : EPAR - Public assessment report.
12 The Pharmaceutical Index – Worldwide 2013 NCEs
M7 - - NA NA - - <2e <1 NA M11 NA - - NA -
2.6 <1 NA M17 - - NA 8-12 √
3.8 <1 NA M20 - - NA NA - 7.1 <1 NA M21 78.4 √ - NA √ - <1 47 M24 - - NA NA - 2 <1 NA M25 36.9 - NA NA - 6.1 <1 NA M29 NA - NA NA - 2.9 <1 NA M34 33.3 √ NA 16 - 9.1 <1 NA M35 - √ - 14 √ - <1 NA M36 - - NA - 2.9 <1 NA M37 32 √ 0.12e NA - 2.9 <1
NA M39 NA - - NA - - <1 NA M40 NA - - NA - - <1 NA Ibrutinib
26.9
-
-
NA
1.43-3.49
0.77
<1
-
Feces metabolites in dogs: >5%. NA= not applicable. ND=not detected. LOQ= limit of Quantity. a: Mean data from 6 subjects. b: Samples pooled from 6 subjects. c: Co-elution with M20 and M24. d: Co-elution with M31 and M35. Ibrutinib and PCI-45227 combined constituted less than 10% of total circulating radioactivity. e: All the metabolites in rat urine was <2% of dose.
--Excretion --
Table 15: Species Comparison of Excretion Data of [14C] Ibrutinib after a Single Oral or Intravenous Administra-[12, 13]Rats/Male 2.0 i.v. 0-168 - 5.16 83.5 92.2 10 p.o. 0-96 - 1.54 90.6 92.3 Rats/Female 10 p.o. 0-96 - 1.75 89.1 91.2 Rats/BDC Male 10 p.o. 0-48 47 1.31 40.7 97.4 Dogs/Male 30 p.o. 0-72 - 3.26 87.5 90.7 Humans/Male
140
p.o.
0-96
-
7.81
80.6
88.5
Formulation was a 30% hydroxypropyl-cyclodextrin solution with ibrutinib 5 mg base.
[12]. Drug@FDA, NDA2055520 Clinical Pharmacology Review(s).
[13]. Drug@EMA, EMEA/H/C/003791 Imbruvica : EPAR - Public assessment report.
Ibrutinib 13
--Drug-Drug Interaction --
[12]
1A2 Ethoxyresorufin (1) >44a NC NC NC 2B6 Bupropion (100) 2.1 0.08 4.04 0.03 2C8 Paclitaxel (10) 5.3 0.03 7.84 0.02 2C9 Diclofenac (10) 2.6 0.06 13.8 0.009 2C19 Omeprazole (0.5) 2.9 0.06 >47.5* NC 2D6 Dextromethorphan (5) 5.5 0.03 18.1 0.007 2E1 Chlorzoxazone (100) NC NC NC NC 3A4/5 Midazolam (5) 5.3 0.03 NC NC 3A4/5
Testosterone (50)
4.4
0.04
>47.5*
NC
a: IC 50 reported . NC: not calculated. Phenacetin 10 μM
was used as substrate.
[12]Ibrutinib 0.5-10 >2 < 20% - - PCI-45227
10
-
-
3.75
6.7
Table 18: In Vitro Evaluation of Ibrutinib and Metabolite (PCI-45227) as an Inhibitor and a Substrate of Uptake
Ibrutinib 57.9±1.09 7.55±1.01 0.13/ NO Ibrutinib 2.15/Yes NO NO NO NO PCI-45227
NA
NA
2/Yes
PCI-45227 NO
NA
NA
NA
NA
[12]. Drug@FDA, NDA2055520 Clinical Pharmacology Review(s).
14 The Pharmaceutical Index – Worldwide 2013 NCEs
§5 Non-Clinical Toxicology
?Single Dose Toxicology
?Single dose oral administration of ibrutinib in different species:
Mice MTD: 2000 mg/kg.
Rats MTD: 500 mg/kg.
?Repeat Dose Toxicology
?Repeated dose oral administration of ibrutinib in different species from 2 to 13 weeks:
For rats: The NOAEL was 30 mg/kg/day (2.6 and 21×MRHD for males and females, respectively), determined by 13-week toxicity study. Toxicity target organs were bone, GI track, lymphoid tissues/organs, pancreas, and skin.
Drug related T1/2 prolongation was found.
For dogs: The NOAEL was 30 mg/kg/day (0.4 and 1.8×MRHD for males and females, respectively), determined by 13-week toxicity study. Decrease in heart rate (with associated increased RR intervals), intestinal inflammation,
lymphoid depletion of Peyer’s paths, and gastric smooth muscle degeneration were mainly toxicity found.
?Safety Pharmacology
?Ibrutinib inhibited hERG channel currents with an IC50value of approximately 1 μM and may be considered a low-potency blocker.
?In a single-dose safety pharmacology study in Beagle dogs, an oral ibrutinib dose up to 150 mg/kg did not induce QT interval prolongation; increases in the RR interval were observed. The effect occurred at 1 hr postdose.
?One of the major metabolites of ibrutinib, PCI-45227, inhibited hERG channel currents with an IC50 value of 9.6 μM,
i.e. ten fold less potency for blocking the Ikr current compared to the parent drug.
?Genotoxicity
?Ibrutinib was not mutagenic in bacterial Ames test or clastogenic in a chromosome aberration test in Chinese hamster ovary cells (CHO).
?Ibrutinib did not increase micronucleus formation in mice after oral doses up to 2000 mg/kg.
?Reproductive and Developmental Toxicology
?Ibrutinib was administered orally to pregnant rats:
Increased post-implantation loss and increased resorption occurred at the high dose of 80 mg/kg. Fetal toxicities (visceral malformations and variations, and skeletal variations) were observed at the high dose of 80 mg/kg. Re-
duced fetal weight was seen at ibrutinib doses at 40 mg/kg and 80 mg/kg. The dose of 80 mg/kg resulted in maternal toxicities.
The dose of 80 mg/kg/day in animals resulted in exposures (total AUC) approximately 14 times the AUC in patients with MCL (ibrutinib dose of 560 mg/day). The exposure at 40 mg/kg/day was approximately 6 times the AUC in
patients with MCL.
?Ibrutinib was administered orally to pregnant rabbits:
At the ibrutinib dose of 100 mg/kg, which was greater than the maternally-toxic dose (≥30 mg/kg/day), there were embryo-fetal toxicities. Findings included increases in resorption and implantation loss, decreases in viable fetuses
and fetal body weights, as well as spontaneous abortions.
Ibrutinib 15
--Single Dose Toxicity --
[7]Mice
p.o.
0, 500, 1000,
2000
2000
500 and 1000 mg/kg: Mild to moderate rough coat
2000 mg/kg: Mild to moderate inactivity, ptosis and/or decreased body temperature and
laboured respiration.
Rats
p.o.
0, 400, 1000,
2000
400
400 mg/kg: ↓BWG (M)
1000 mg/kg: 1F died on day 1 (no macroscopic findings), ↓BW M/F day 2, ↓BWG M/F day 0-2, ↑BWG F day 2-7.
2000 mg/kg: 1M died on day 6 (distended stomach and intestine), 1M and 1F died on day
7 (M, red matting of the skin and dark red contents of the stomach. F, without findings), ↓ BW and BWG day 0-2, ↑BWG day 7-14, abnormal excreta, various discoloured areas due to discharges/excreta, thin body, cool to the touch, red discharge from left eye (1M); abnormal respiration (rales), dermal atonia, hair loss on anogenital area or ventral trunk and swollen ears (1F). Died at 1000 and 2000 mg/kg. toxicity mainly GI and skin tox-icity.
i.v.
0, 50, 100, 150
50
50 mg/kg: Mild inactivity at 30 min postdosing.
100 and 150 mg/kg bolus: All rats died within 10 mins after dose administration, after
showing ataxia, gasping and inactivity and tonic convulsions.
100 mg/kg 60 min infusion: Mild ataxia and inactivity at end of infusion period, mild rough coat and inactivity at 1 hr after infusion.
100 mg/kg 30 min infusion: Moderate ataxia and inactivity.
Dogs p.o./s.c.
0, 10, 20, 100,
200
ND
10 mg/kg, p.o.: No test-article related observations. 10 mg/kg, s.c.: Flinching, scratching. ↑ leukocyte counts . 20 mg/kg, s.c.: Flinching, scratching. ↑ leukocyte counts .
40 mg/kg, s.c.: Squirming and thrashing. Biting and scratching at dose sites immediately after dosing. Ataxia and hypoactivity up to 4 hrs after dosing. ↑ leukocyte counts. 100 mg/kg, p.o., solution: Mild ataxia at 2 hrs postdosing. 100 mg/kg, p.o., suspension: Mild ataxia at 2 hrs postdosing.
200 mg/kg, p.o., suspension without sodium lauryl sulfate: Mild ataxia and hypoactivity at 2 hrs postdosing; glassy appearance to the eyes at 1 to 8 hrs postdosing. Complete oc-cupancy of Btk for at least 24 hrs postdosing.
200 mg/kg, p.o., suspension with sodium lauryl sulfate: Mild ataxia and hypoactivity at 2 hrs postdosing; glassy appearance to the eyes at 1 to 8 hrs postdosing. Complete occu-pancy of Btk for at least 24 hrs postdosing No animal died. Mild ataxia and/or hypoactiv-ity at 2 hrs post-dosing. Active site of Btk in peripheral blood mononuclear cells showed that a single 100 mg/kg dose of ibrutinib resulted in complete active-site occupancy for at least 24 hrs postdosing.
Vehicles: not available.
--Repeated Dose Toxicity --
[7, 12, 14, 15]SD
Rats
2
0, 12, 35, 120
12 NA NA
≥12 mg/kg: K↓.
≥36 mg/kg : Pancreas acinar atrophy. F: TP↓, M: HT↓. 120 mg/kg: HDW↑, HT↓. M: MCV↓, F: NEU↑. ALT↑,
ALB↓ Ca↓, TP↓ ALP↓.
4
0, 2.5, 40, 300/150a
2.5
140/180
0.1/0.2
1 found dead in male HD at Day 16.
Elevated neutrophil and monocyte counts at HD re-flected skin and GI inflammation.
Drug accumulation observed after repeated drug admin-istration, and prolonged T 1/2 in HD significantly.
[12]. Drug@FDA, NDA2055520 Clinical Pharmacology Review(s). [14]. Drug@FDA, NDA2055520 Medical Review(s).
16 The Pharmaceutical Index – Worldwide 2013 NCEs [15]. Blood2012, 120, 4684-4691.
Ibrutinib 17
(--continued)
SD Rats 13
0, 30, 100,
300/175b
30
2480/19712
2.6/21
Mortalities occurred at 300 mg/kg/day in both genders. Dose level for females of HD reduced to 175 mg/kg/day
on Day 8 due to severe body weight loss.
Toxicity target organs were bone, GI track, lymphoid tis-sues/organs, pancreas, and skin.
Beagle Dogs
2
0, 4, 12, 40
40
NA
NA
≥4 mg/kg : Liver weight ↑(M), hepatocellular glyco-gen↑(M).
≥12 mg/kg : Soft faeces (M).
40 mg/kg: Soft faeces, l iver weight↑, hepatocellular gly-cogen↑.
4
0, 1.5, 24, 150 1.5 17/21 0.02/0.02
GI toxicities included inflammation/atrophy, diarrhea/mu-coid feces, and corneal dystrophy at high dose
13
0, 30, 80/60c , 220/120c
30 377/1683 0.4/1.8
Dose range changed from 80 and 220 to 60 and 120 re-spectively at Day 42 due to mortality found at 80 and 220 mg/kg/day in males on Day 31.
Drug related findings included reduction in red blood cell counts, serum albumin and serum γ-glutamyltransferase, decrease in heart rate (with associated increased RR inter-vals), intestinal inflammation, lymphoid depletion of Peyer’s path s, and gastric smooth muscle degeneration.
Accumulated exposure of ibrutinib and its metabolite PCI-45227 was observed.
a: male 300 mg/kg, female 150 mg/kg. b: The dose level for the females at 300 mg/kg/day was reduced to 175 mg/kg/day on Day 8 due to severe body weight loss. c: The dosage levels for Group 3 and Group 4 were lowered to 60 and 120 mg/kg/day, respectively, beginning on study day 42 ( start of study week 6). d: Male/female. Vehicle for 4 weeks re-peated dose administration: 0.5% methylcellulose, 0.4% cremophor EL (not included in clinical formulation), and 0.1% sodium lauryl sulfate. Vehicle for 13 weeks administration: 0.5% Methylcellulose (400 cps) and 0.1% sodium lauryl sulfate in water. ALB: albumin, ALP, ALT: alanine aminotransferase, HT: hematocrit, MCH: mean haemoglobin concentra-tion, NEU: neutrophile granulocyte count, TP: total protein. The steady-state AUC observed in patients at 560 mg was (mean ± standard deviation) 953 ± 705 ng·hr/mL.
--Safety Pharmacology --
[7]Central Nervous Sys-tem
Ibrutinib SD rats Single p.o.
0, 2.5, 40, 150 mg/kg No observation Respiratory Effects
Ibrutinib
SD rats
Single p.o. 0, 2.5, 40, 150 mg/kg No observation
Cardiovascular Ef-fects
Ibrutinib
Conscious Beagle Dogs
Single p.o.
0, 1.5, 24, 150 mg/kg
Mean RR interval prolongation up to 23% and 35% at 24 and 150 mg/kg, respectively. Mean heart rates were depressed up to 20% and 30%,
respectively, peaking at 5 hrs post dose. Ibrutinib HEK-293-hERG Cells/In vitro hERG
Potassium Channel Inhibition 0, 0.3, 1, 3, 10 μM IC 50= 0.97 μM PCI-45227 (M37)
HEK-293-hERG Cells/In vitro hERG
Potassium Channel Inhibition
0, 3, 10, 30, 100 μM
IC 50= 9.6 μM
Vehicle: 0.5% methylcellulose, 0.4% Cremophor and 0.1% sodium lauryl sulfate suspension in vivo and buffered physiological saline + 0.3% DMSO in vitro
18 The Pharmaceutical Index – Worldwide 2013 NCEs
--Genotoxicity --
[7]Bacterial Reverse Mu-tation Assay TA98, TA100, TA1535, TA1537, WP2 uvr A ±S9 in vitro 50-5000 μg/plate No toxicity was observed Chromosomal Aberra-tion Study CHO-K1 (Chinese ham-ster ovary) cells
±S9 in vitro 5-80 μg/mL Negative
Cell growth inhibition at 40
μg/mL was 58%.
Micronucleus Test
ICR Mice
+ in vivo
Single p.o.
500, 1000, 2000 mg/kg
Negative
Vehicle: 0.5% methylcellulose, 0.4% Cremophor EL, and 0.1% sodium lauryl sulfate for in vivo tests, while DMSO for in vitro tests.
--Reproductive and Developmental Toxicity --
[7]SD Rats
10
1278 1.3 Adverse uterine effects (increased post-implantation loss and increased resorption) were evident at the high dose of 80 mg/kg ibrutinib.
Fetal toxicities (visceral malformations and variations, and skeletal variations) were most evident at high dose of 80 mg/kg.
Reduced fetal weight was seen at mid dose (40 mg/kg) and high dose (80 mg/kg).
Maternal toxicities were observed mainly at 80 mg/kg.
40 5348 5.6 80 13729 14 Rabbits 10
565
0.6
Oral administration of ibrutinib (GD 7-19) in time mated rabbits elicited maternal
toxicities, including mortality and abortions at 100 mg/kg, and clinical signs (reduced defecation, small feces), reduction in body weight and food consumption at ≥ 30 mg/kg.
Embryonic toxicity (increases in resorption and implantation loss, decreases in viable fetuses and fetal body weights) were observed at 100 mg/kg. There were no changes in net body weights, net body weight gains and gravid uterine weights.
No apparent teratogenic effects were observed.
30 1310 1.4
100 21000 22
Fertility or postnatal toxicity studies were not conducted. Vehicle: 0.5% methylcellulose and 0.1% sodium lauryl sulfate in water.
a: the steady-state AUC observed in patients at 560 mg was (mean ± standard deviation) 953 ± 705 ng·hr/mL.