
Chapter 1
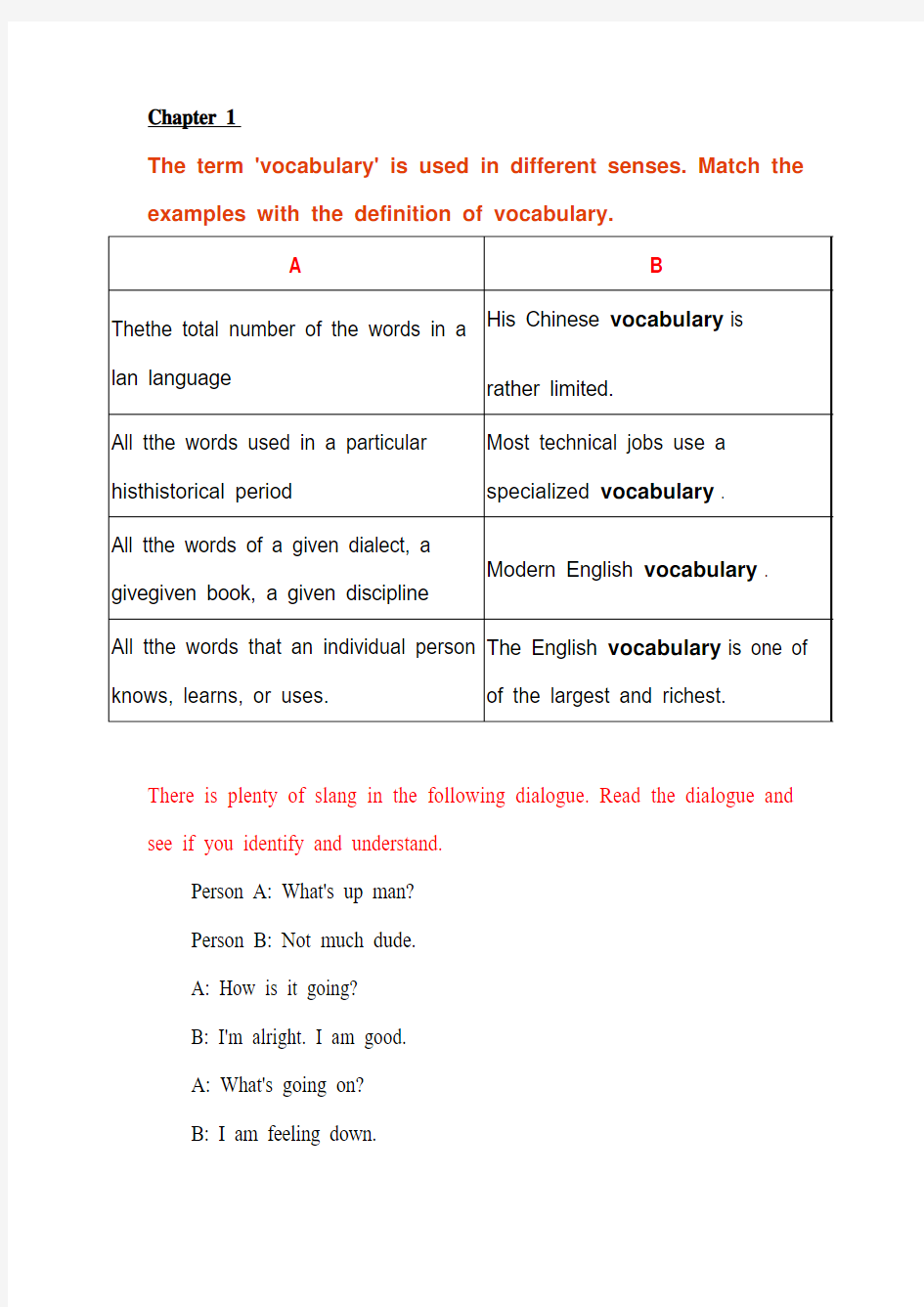
The term 'vocabulary' is used in different senses. Match the examples with the definition of vocabulary.
There is plenty of slang in the following dialogue. Read the dialogue and see if you identify and understand.
Person A: What's up man?
Person B: Not much dude.
A: How is it going?
B: I'm alright. I am good.
A: What's going on?
B: I am feeling down.
A: Why?
B: My girlfriend dumped me. She said that we don't mesh well together.
A: I am so sorry. I feel for you man.
B: It sucks. It's so horrible. I don't want to live without her.
A: There are plenty of other fish in the sea. You can't lose hope over a single chick.
B: I guess you got a point. It's tough though, and it's hard to move on.
A: You'll be good. No worries. Live life and have fun.
B: I can do that. Thank you so much for being there. You're the man.
A: I do what I can, lol.
Here are some of the slang expressions with their explanations man: a term of familiar address to a man or a woman: Hey, man, take it easy.
dude: a man, a fellow
down: depressed
dump: to end one‘s relationship with someone
mesh: to match, coordinate, or interlock
suck:to be disgustingly disagreeable or offensive
feel for: to feel sympathy for or compassion toward; empathize
with: I know you're disappointed and upset, and I feel for you.
fish: person
chick: Often Offensive. a girl or young woman.
lol: laughing out loud
Which of the following words are content words and which are function words? Put them in the correct category.
Read the following excerpt from George W. Bush‘s Farewell Address in 2009 and underline the functional words used in it.
Like all who have held this office before me, I have experienced setbacks. There are things I would do differently if given the chance. Yet I have always acted with the best interests of our country in mind. I have followed the conscience and done what I thought was right. You may not agree with some tough decisions I have made. But I hope you can agree that I was willing to make the tough decisions.
Guess whether the following statements are true or false.
1. Native words are words brought to Britain in the fifth century by the Germanic tribes: the Angles, the Saxons, and the Jutes.
2. Native words are known as Anglo-Saxon words.
3. Words of Anglo-Saxon origin are small in number.
4. Words of Anglo-Saxon origin form the mainstream of the basic word stock and stand at the core of the language.
5. What is true of the basic word stock is also true of native words.
6. The number of functional words is overgrowing.
7.Every morpheme has its variants.
Put the following borrowed words into the correct category.
Denizens: pork port change cup
Aliens: Kowtow Kimono Intermezzo Ketchup Decor
Translation-loans: Masterpiece Black humour
Semantic-loans: Dream Fresh Pioneer Dumb
Explain the relationship between sound and meaning with examples. True or false judgement:
1. individualistic: in, divide, -al, -ist, -ic T ( F (
2. individualistic: in, di, vi, du, -al, -ist, -ic T ( F (
3. undesirables: un, de, sir, -able, -s T ( F (
4. undesirables: un, desire, -able, -s T ( F (
Divide the following words into their constituent morphemes: inaccessibility, unevenly, friendliness, overseas, minimalist, occurrences, assumption, retell, ex-wife, misleading, multimedia, automobile, microcomputer, vice-chairman, semiconductor, underdeveloped, telescope, maltreat, anti-government, forehead, illegal, disobey, unfair, prepaid, de-emphasis, readiness, discouraging, kind-hearted, undoubtedly, stockrooms, prepackaged
Judge how many morphemes the following words have: unrespectable, recollection, irresponsibility, internationalists, impossibility, unpredictable
Write the following words with hyphens between their morphemes.
quickly downstairs fourth poisonous weaken
worldwide internationally inject protrude
Try to find out how many allomorphs does "–ed" has? Illustrate your answer with examples.
What would be considered as allomorphs of the morpheme ?plural‘ from the following set of English words?
data oxen children deer films factories matches
Analyze the words in terms of root and stem.
impracticableness unbelievably
Underline each bound morpheme in the following words.
island surname disclose duckling cranberry reading poets flavourfulness famous subvert
What are the inflectional morphemes in the following phrases or sentences?
1)the boy‘s books
2)the greatest achievements
3)It‘s snowing.
4)John climbed the mountain.
Give all the possible inflections for the following words.
book, forget, short, snap, take, goose, heavy
Chapter 2
Decide whether the following statements are true or false.
1.English is the language of the early inhabitants of the British Isles.
2.The first peoples known to inhabit England were Celts who mainly spoke Latin.
3.The Romans invaded the British Isles and occupied it until about 410. Consequently the Latin of the Roman Legions was a major language used by the early inhabitants of the British Isles.
4.As the German tribes invaded Britain, the Celtic languages
gradually retreated.
5.Celtic made only a small contribution to the English vocabulary.
6.Indo-European refers to the family languages spoken originally in Europe.
https://www.doczj.com/doc/e015222855.html,tin and French belong to the different language groups.
8.English belongs to the West-Germanic language group of Indo-European language family.
9.The first people in England about whose language we have definite knowledge are the Celts.
10.Certain Germanic tribes, Angles, Saxons, and Jutes were the founders of the English nation.
11. About 95 percent of old English are no longer in use.
12.Old English is characterized by the frequent use of compounds which in turn is an important linguistic feature of Germanic language.
13.Old English has much less loan words compared with modern English.
14.Modern English is a language of leveled endings.
Compare Old English with Middle English. What are their respective characteristics?
Chapter 3
On semantic basis, prefixes are divided into nine groups:
1. Negative Prefixes
3. Pejorative prefixes
5. Prefixes of orientation and attitude 7. Prefixes of time and order
9. Miscellaneous prefixes 2. Reversative prefixes
4. Prefixes of degree or size 6. Locative prefixes
8. Number prefixes
Now, compare the meanings of the words with their roots or stems and judge what changes have taken place on meanings. Then please decide which group the prefixes above belong to. Just fill in the numbers that represent the different groups. An example has been done for you.
In the following table, there are 12 words of different part of speech. Match the words with the corresponding suffixes to form a new word. Write out the new word and its part of speech. An example has been done for you.
Analyze the new nouns in the above table. Are they abstract nouns or concrete nouns? Which suffixes will lead to an abstract noun and which to concrete ones? Write A for
Form negatives of each of the following words by using one of these prefixes dis-, il-, im-, in-, ir-, non-, un-
smoker capable practical obey
security relevant mature ability
officially willingness legal agreement
logical loyal convenient athletic
Keys:
nonsmoker,incapable,impractical,disobey,insecurity,irrelevant,immature,inability/disability,unofficially,unwillingness,illegal,disagreement,illogical,disloyal,inconvenient,nonathletic
用否定前缀in-(及其变体)、non-、un-构成下列单词的反义词correct, friendly, wrap, free, rational, consistent, remarked, business, green, expected, smoker, balanced, empty, polite, complete, resistant, trivial, candidate, attention, science, logical, informative , literate, assuming, remitting, mortal, perishable, sane, forgettable
In English, there are quite a few prefixes that connote negation. They include ―a-, un-, in-, dis-, mis-, non-, de-‖, and the like. Can you give one or two examples for each.
How would you distinguish between ―un-‖ and ―non-‖ in terms of their
meaning and use? Can we prefix ―un-‖to adjectives like ―tall, ill‖and ―black‖? Why or why not?
Turn the following nouns and adjectives into verbs with suffixes –en, -ify, -ize and then choose appropriate verbs you have formed to fill in the blanks in the sentences that follow.
hard horror modern memory
false apology deep glory
sterile length intense beauty
fat sympathy
a.He _________ for interrupting her.
b.She tried to _________ her room with posters and plants.
c.A study has been ordered into the feasibility of _________ the airport‘s main runway by two hundred meters.
d.However much they _________ with her, they all felt it was her fault.
e.Soya is excellent food to _________ cattle.
f.She laughed and that seemed to ________ her voice.
g.Forty thousand pound had been spent on _________ the station. h._________ the bottles by immersing them in boiling water for fifteen minutes.
Each of the following sentences contains a word printed in bold type. Complete the sentences by using this word to form a noun to refer to a
person.
a.If you are employed by a company, you are one of its _________. b.A _________ is someone whose job is politics.
c.The ________s in a discussion are the people who participate in it. d.A woman who works as a _________ does the same job as a waiter.
e.The person who conducts an orchestra or choir is called the _________.
f.Your _________ is the person who teaches you.
g.A _________ is someone who earns their living by playing the piano.
h.If someone examines you, you are the _________ and he or she is the _________.
What is the meaning of the prefixes in the following words?
indirect, endanger, dissimilar, unwind, interconnect, misconduct, oversleep, rewrite, untie, redraw, postgraduate, disallow
Fill in the blanks with appropriate suffixes.
a)–able, -ible
consum , comprehens , exchange ,permiss
b)–ant, -ent
absorb , assist , differ , particip
c)–ar, -er, -or
construct , li , begg , edit , develop
d)–ary, -ery
element , station , brew , mock
Change the following words into nouns:
admit, accept, allow, enter, expect, warm, strong, persuade, jealous Provide more examples suffixed with ―-ling‖ (e.g. weakling) and ―-ish‖(e.g. womanish) that are negative in attitude.
Identify the derivational affixes in the following words. Give a meaning or function for each one.
childish, declassify, freedom, illimitable, immovable, insufferable, misapprehension, prejudgment, reconnection, underdeveloped, withdrawal
Decide whether the statements below are true or false.
1.Non- differs un- in frequently expressing a binary contrast (without gradability) rather than the opposite end of a scale.
2.A number of suffixes yield items that can be used both as nouns and as adjectives, such as –ese, -an , -ist, -ite.
3.Some affixes may be polysemic.
4.Some affixes are synonymous.
5.Most of the prefixes may change the part of speech of the root they are attached to. Yet this is seldom the case with suffixes.
6.Suffixes usually do not affect the stress of the word they are attached to. Yet some prefixes may do.
7. Suffixes not only change the meaning of the roots or bases to which they are attached, but also change their word classes.
Read the following compounds, and then guess their meanings.
1. American cloth
2. British warm
3. French leave
4.Spanish athlete
5. Chinese copy
6. Turkish delight
7. Indian meal
8. Dutch treat
美产布料
厚呢短大衣
不辞而别
西班牙运动员
与原物一模一样的复制品
土耳其软糖
印度大餐
各付己帐
彩色漆布
英国式的暖日
法式告别
吹牛者
中国版本
土耳其式狂欢
玉米粉
荷兰招待方式
Decide whether the statements below are true or false.
a. Compounding are words formed by combining affixes and roots.
b. Open compounds look like free phrases as the elements forming each word are written separately.
c. As a rule, the stress of compounds usually falls on the first element.
d. The meaning of a compound is usually the combination of the roots.
e. A compound functions as a single grammatical unit, so the internal structure cannot be changed.
Form compounds using the following either as the first or the second
element of the compound as indicated.
well--woman-wide-minded self-
-related-proof -in-law home-half-
-conscious-based
well-: well-behaved, well-qualified
-woman: sportswoman, chairwoman
-wide: nationwide, college-wide
-minded: strong-minded, narrow-minded
self-: self-taught, serf-image
-related: work-related, age-related
-proof: water-proof, fire-proof
-in-law: mother-in-law, sister-in-law
home-: home-made, home-baked
half-: half-empty, half-forgotten
-conscious: profit-conscious, status-conscious
-based: campus-based, process-based
Tell how the parts in each of the following groups are related to the meanings of the compound.
a.hotline, mainline, redneck, darkroom
b.bookshelf, breadbasket, mailbox, wineglass
c.letterhead, roadside, keyhole, hilltop
d.dropout, go-between, turnout, standby
e.bad-tempered, clear-headed, long-sighted, heavy-hearted
f.grass-green, sky-blue, snow-white, milk-white
Read the following sentences; try to mark the part of speech of the word ―up‖.
Can you lift that box up onto the shelf for me?
We climbed slowly up the hill.
Is something up with Julie? She looks really miserable.
Without saying another word, he upped and left.
Charlie seems to be on an up at the moment. I hope it lasts.
Decide whether the following statements are true or false.
a. Conversion refers to the use of words of one class as that of a different class.( )
b. Words mainly involved in conversion are nouns, verbs and adverbs. ( )
c. Partial conversion and full conversion are concerned with adjectives when converted to nouns. ( )
d. Such words as the poorer, the departed, a Republican are all examples of partial conversion. ( )
e. The conversion between nouns and verbs may involve a change of stress. ( )
f. An alternative for conversion is functional shift. ( )
What is the difference between partial and full conversion? Explain them
with examples.
What are the words in the following examples that stem from conversion? Are they instances of partial conversion or complete conversion?
1.Please hold on. Sudden stops are sometimes necessary.
2.No butts – stub it, bin it!
Pick out the words which you think are converted in the following sentences and explain how they are converted.
a. We can‘t stomach such an insult.
b. Robert Acheson roomed right next to me.
c. He wolfed down his lunch.
d. There is no come and go with her.
e. I‘m one of his familiars.
f. Poor innocents!
g. She flatted her last note.
h. The engineers ahed and ouched at the new machines.
i. Come to the fire and have a warm.
j. Is Bill Jackson a has-been or a might-have-been?
k. He Hamleted at the chance and then he regretted for it.
l. These shoes were an excellent buy.
m. He turned his head and smoothed back the hair over one temple.
n. Women have an equal say in affairs at home.
o. They lifted their rifle butts and hit him in the small of the back.
p. The song quickly became the hit of the country.
q. We must train ourselves to distinguish right from wrong.
r. They braved a 40-below-zero snowstorm to rescue the farm cattle. Keys: a. stomach (n →v) b. roomed (n →v)
c. wolfed (n →v)
d. come, go (v →n)
e. familiars (a →n)
f. innocents (a →n)
g. flatted (a →v) h. ahed, ouched (iht →v)
i. warm (a →n) j. has-been, might-have-been (v →n)
k. Hamlet (n →v) 1. buy (v →n)
m. smoothed (a →n) n. say (v →n)
o. small (a →n) p. hit (v →n)
q. right, wrong (a →n) r. braved (a →v)
Pick out the words which you think are converted in the following sentences and explain how they are converted.
1.At once the villagers formed a circle and stated moving around me,
singing to the accompaniment of a kora.
2.I name this ship Titanic.
3.Agamemnon with the rest of the Greek army sailed away in their ships
at night.
4.A few years ago the landlady locked the front door and installed a bell
and buzzer system, which made burglary more difficult though not impossible.
5.An upstairs tenant, who happened to be looking out of his window,
came running down, questioned the men and demanded their identification.
6.The children headed toward school, carrying slates and followed by
their dogs.
7.Like the trunk of a tree, it rose in the air, branching out as it climbed.
8.They boarded boats and got away, living to tell the tale of the city‘s
destruction.
9.The day-t-day effect of dirty air is hard to measure, and most people
take it for granted.
10.When these gases mix with fog, smog results.
11.T here are a few success stories in battling air pollution.
12.P ollution can be trapped before they pour out of chimneys and a
pollution-free car can be built.
13.If nation traded item for item, such as one automobile for 10,000
bags of coffee, foreign trade would be extremely cumbersome and restrictive.
14.His place on the seat was taken almost immediately by a young man,
fairly well dressed but scarcely more cheerful than the other.
15.The young man quickly removed any doubt by pocketing the money.
16.Calming down, I convinced myself this was something that had to
happen once in a lifetime.
倒装句 一、定义:英语最基本的语序是主语在前,谓语动词在后。但有时由于句子结构的需要或表示强调,就要采用倒装形式。 Eg:The bus comes here. Here comes the bus. 车来了。 二、分类:全倒装:将谓语动词完全移到主语之前称为完全倒装, 半倒装:只将助动词或情态动词放到主语之前称为部分倒装。 Eg:Many years ago there lived an old man in the wooden house. 很多年前有一位老人住在那间木屋里。 Never have I been late for school this term. 这学期,我从来没上学迟到过。 三、全倒装:“五全”=有时表地方 经常与be/come/exist/fall/follow/go/remain/seem/stand(表示移动或动态的不及物动词连用) 或用表示类似“存在”观念的其他不及物动词如:live, stand, come, lie, flow, enter, rise 和appear等?㈠、“有”:在“there be”结构里 Eg:There is a box on the table. 桌子上面有一个盒子。 ?㈡、“时”:表示时间副词,如:now,then, Eg:Now comes your turn. 现在轮到你了。 ?㈢、“表”:表语放句子前,“表语+系动词+主语”的结构 Eg:Present at the party were Mr. Green and many other guests. 格林先生和其他的客人在这个聚会上。 Seated on the ground are a group of young men. 一群年轻人坐在了地上。 ?㈣、“地”:地点状语放在句首 Eg:In south of the river lies a small factory. 小工厂位于河的南方。 From the valley came a cry. 山谷传来一阵哭声。 ?㈤、“方”:表方位的副词here, there 或out, in, up, down, away, off等标志词放在句首
动词变现在分词练习题一、写出下列动词的现在分词: go____________ stand___________ sleep____________ eat____________ sing____________ drink___________ read____________ look____________ walk____________ watch___________ draw____________ fly____________ open____________ jump____________ do____________ paint____________ pick____________ play____________ kick____________ talk____________ cook____________ learn____________ look____________ climb___________ count___________ clean___________ fish____________ come___________ dance___________ close____________ make___________ ride____________ write____________ take____________ phone___________ move___________ have____________ sit____________ hope____________ swim___________ run____________ cut____________ put____________ forget___________ get____________ begin___________ .hit____________ chat____________ stop____________ play________ run__________ swim _________ make__________ go_________ like________ write________ ski___________ read________ have_________ sing ________ dance_________ put_________ see________ buy _________ love____________ live_______ take_________ come ________ get_________ stop________ sit ________ begin________ shop__________ 二、用所给的动词的正确形式填空: 1.The boy ______ ____________ ( draw) a picture now. 2. Listen .Some girls ______ _________ ( sing) in the classroom .
Chapter 1 Introduction I. There are four choices following each statement. Mark the choice that can best complete the statement. 1. If a study describes and analyzes the language people actually use, it is said to be ______________. A. prescriptive B. analytic C. descriptive D. linguistic 2. Which of the following is not a design feature of human language? A. Arbitrariness B. Displacement C. Duality D. Meaningfulness 3. Modern linguistics regards the written language as ____________. A. primary B. correct C. secondary D. stable 4. In modern linguistics, speech is regarded as more basic than writing, because ___________. A. in linguistic evolution, speech is prior to writing B. speech plays a greater role than writing in terms of the amount of information conveyed. C. speech is always the way in which every native speaker acquires his mother tongue. D. All of the above 5. A historical study of language is a ____ study of language. A. synchronic B. diachronic C. prescriptive D. comparative 6. Saussure took a(n) __________ view of language, while Chomsky looks at language from a ________ point of view. A. sociological, psychological B. Psychological, sociological C. applied, pragmatic D. semantic, linguistic 7. According to F. de Saussure, ____ refers to the abstract linguistic system shared by all the members of a speech community. A. parole B. performance C. Langue D. language 8. Language is said to be arbitrary because there is no logical connection between _________ and meanings. A. sense B. Sounds C. objects D. ideas 9. Language can be used to refer to contexts removed from the immediate situations of the speaker. This feature is called_________. A. displacement B. duality C. flexibility D. cultural transmission
初中英语倒装句 英语句子通常有两种语序:一种主语在前,谓语在后,称为自然语序,另一种谓语在前,主语在后,称为倒装语序,按“主语+ 谓语” 这种顺序排列的句子是陈述语序。如果排列顺序变为“谓语(或谓语一部分)+主语”,就是倒装。之所以出现倒装,一方面是因为语法结构的需要,另一方面为了强调,有时两种原因兼有之。倒装句分为部分倒装和全部倒装。以下就分别讲述这两种倒装的用法。如果遇到一句,不知道使用全部倒装还是部分倒装的话,我们主要主要看其标志性的词语。 一、部分倒装 就是把谓语中的be动词、助动词或情态动词置于主语前面。常见于下列几种情况: (一). only所修饰的副词,介词短语或状语从句放在句首时,要用: only+ 状语+ be /助动词/情态动词+主语及其他 Only when he told me the news did I know what had happened. Only in this way can you make progress in your English. Only through education can we rise in the world. 注意:only修饰主语时,不需要倒装。 1. Only in this way ________to make improvement in the operating system. A. you can hope B. you did hope C. can you hope D. did you hope 2.Among all the people, only you know the truth. (二).含有否定意义的副词或连词放在句首时。如:never, little, seldom, not, not only, not until, no sooner (…than), hardly (…when), rarely, scarcely, in no way等。 We seldom get up at four in the morning. = Seldom do we get up at four in the morning. Not a single word from him could express his feelings. Rarely have I heard of such a silly thing. (1) hardly…when; scarcely…when…; no sooner…than… 可以用正常语序had hardly done when… did 或用倒装句式Hardly had + 主语+ done when… did 句式。hardly所在的句子用过去完成时。 The bell hardly had rung when the class began. = Hardly had the bell rung when the class began. No sooner had he arrived in Beijing than he began to work. (2) not only… but also 如连接两个成分时,不用倒装;连接句子时,前面的句子要用倒装。
Warm-up exercises Warm-up exercises One 1.我们无意催促你们作出决定,为你方利益着想,建议你们尽快利用此次报盘We have no intention of urging you to make the decision, thinking about for the interests of you, advise you to utilize this offer as soon as possible 2.将我们的报价与其他公司比较后,相信你们会赞同我们所提供的商品价廉物美。 After comparing our quotation with other companies, it is believed that it is good and cheap that you will agree to the goods that we offer. 3.我方欣然接受你们A103号订单订购1,000件“英雄”牌男式衬衣,请按合同规定的条款开立以我方受益人的即期信用证。 We accept your order No. A103 and order 1,000 " hero " brand shirts in men's style joyfully, the clause that please stipulate according to the contract is opened with our beneficiary's sight letter of credit. 4.依照随函附上的详细情况,我们向贵公司订购中国面料。请注意,货物必须与样品完全相符。如果第一份试购单令人满意,我们将继续大量订购。According with the details enclosed, we purchase the Chinese surface fabric from your company. Please note, the goods must be in full conformity with the samples. If the first trial order is satisfactory, we will continue ordering in a large amount. 5.抱歉,不能接受你们的还盘,因我衬衣的报价与当前市场价格相符。 I am sorry, can't accept your counter offer, because the quotation of my shirt is in conformity with market price at present. Warm-up exercises TWO 1.要求定购我们产品的人越来越多。The demand for our products has kept rising. 2.这些报价比其他任何地方都要低得多。 They are still lower than the quotations you can get elsewhere. 3.我想了解一下贵国的投资环境。 I"d like to know some information about the current investment environment in your country. 4.我们相信双方都有一个光明的前景。We are sure both of us have a brighter future. 5.我们的对外贸易政策一向是以平等互利、互通有无为基础的。 Our foreign trade policy has always been based on equality and mutual benefit and exchange of needed goods. Warm-up exercises 3 我认为你推销时不会有任何困难。I don"t think you"ll have any difficulty in pushing sales. 一般你们报盘的有效期是多长?How long will your offer hold good?
Chapter 4 Revision Exercises 1. What is syntax? Syntax is a branch of linguistics that studies how words are combined to form sentences and the rules that govern the formation of sentences. 2. What is phrase structure rule? The grammatical mechanism that regulates the arrangement of elements (i.e. specifiers, heads, and complements) that make up a phrase is called a phrase structure rule. The phrase structural rule for NP, VP, AP, and PP can be written as follows: NP→(Det) N (PP) ... VP→(Qual) V (NP) ... AP→(Deg) A (PP) ... PP→(Deg) P (NP) ... We can formulate a single general phrasal structural rule in which X stands for the head N, V, A or P. The XP rule: XP→(specifier) X (complement) 3. What is category? How to determine a word’s category? Category refers to a group of linguistic items which fulfill the same or similar functions in a particular language such as a sentence, a noun phrase or a verb. To determine a word's category, three criteria are usually employed, namely meaning, inflection and distribution. The most reliable of determining a word’s category is its distribution. 4. What is coordinate structure and what properties does it have? The structure formed by joining two or more elements of the same type with the help of a conjunction is called coordinate structure. It has four important properties: 1)there is no limit on the number of coordinated categories that can appear prior to the conjunction. 2) a category at any level (a head or an entire XP) can be coordinated. 3)coordinated categories must be of the same type. 4)the category type of the coordinate phrase is identical to the category type of the elements being conjoined. 5. What elements does a phrase contain and what role does each element play? A phrase usually contains the following elements: head, specifier and complement. Sometimes it also contains another kind of element termed modifier. The role each element can play:
英语动词《现在分词》的变化规则 现在分词的变化规则 1.普通动词:格式+ing; think---thinking sleep---sleeping study---studying speak---speaking say---saying cry---crying 2.以不发音的e结尾的动词:去掉e再加ing,格式:去e+ing wake---waking make---making come---coming take---taking leave---leaving have---having dance----dancing ride----riding write---writing 3. 以重读闭音节结尾,呈现“辅,元,辅”结构的动词,先双写末尾的辅音字母,再加ing stop---stopping sit---sitting run---running forget---forgetting begin---beginning cut---cutting get---getting hit---hitting set---setting swim----swimming fit---fitting dig---digging shop---shopping put---putting 英语动词《现在分词》的变化规则 travel---travelling(可双写也可不双写) refer---referring prefer---preferring 4. 以ie结尾的动词,把ie改为y ,再加inglie---lying
die---dyingtie---tying 现在进行时专项练习: 一、写出下列动词的现在分词: play_____________ run______________ swim _____________make______________ go______________ like____________ write_____________ _ski_____________ read_____________ have____________ sing _____________ dance___________ put______________ see____________ buy _____________ love____________ live_________ __ take______________ come _____________ get_____________ stop____________ sit _____________ begin____________ shop___________ 二、用所给的动词的正确形式填空: 1. The boy __________________ ( draw)a picture now. 英语动词《现在分词》的变化规则 2. Listen .Some girls _______________ ( sing)in the classroom . 3. My mother _________________ ( cook )some nice food now.
E111 1125110312 张翩翩 Exercise 5 I. State whether each of the following statements is True or False. (30 points) F 1. A grammatical sentence is also meaningful. F 2. Some words are always superordinates while some others are always hyponyms. F 3. Synonyms are those words that can be used interchangeably in all contexts. F 4. Antonyms have opposite meanings. F 5. All English words have their referents. T 6. The principle of compositionality refers to the idea that the meaning of a sentence depends on the meanings of the constituent words and the way they are combined. T 7. One advantage of componential analysis is that by specifying the semantic features of words, it will be possible to show how these words are related in meaning. F 8. In the classic semantic triangle, the symbol is directly related to the referent. T 9. The superordinate term is more inclusive in meaning than its hyponyms. T 10. To understand a sentence, we need knowledge about its syntactic structure and the meanings of the words used in it. II. Give the respective antonym for each of the following words and then tell to which category they belong. (32 points) 1. boy – ( girl ) ( complementary antonymy ) 2. wide – (narrow) (gradable antonymy) 3. lengthy –(brief ) (gradable antonymy) 4. thin – ( thick) (gradable antonymy ) 5. dead – (alive ) (complementary antonymy) 6. interviewer – (interviewee ) (converse antonymy) 7. sell – (buy) (converse antonymy) 8. teacher – (student ) (converse antonymy) III. Study the following pairs of words. What is the sense relation between these pairs of words? (18 points) (1) shallow / deep ( antonymy ) (2) mature / ripe ( synonymy)
高考倒装句专项练习 Part One 单项选择 1._______ and caught the mouse. A. Up the cat jumped B. The cat up jumped C. Up jumped the cat D. Jumped up the cat 2.______ and the lesson began. A. In came Mr Brown B. Mr Brown in came C. In came he D. came in Mr Brown 3. Over _______ , dead. A. rolling the goat B. rolled the goat C. did the goat roll D. the goat rolled 4.— Where is my shirt, mum? —_________. A. There is it B. There it is C. There is D. Here is it 5. — Where is your father? —Oh, ________. A. here he comes B. he here comes C. here does he come D. here comes he 6.The door opened and there ________ . A. enters an old man B. entered an old man C. did an old man enter D. an old man entered 7. Now ______ your turn to recite the text. A. will come B. comes C. has come D. there is 8. Often _____ them not to smoke here. A. we advised B. advised me C. did we advise D. had we advised 9. ________ playing soldiers. A. Inside the room were two boys B. Inside the room two boys C. Were two boys inside the room D. Inside the room was two boys 10. On the wall _______ two large portraits. A. are hanging B .Hanged C. hang D. hangs 11. _______ who was wounded in the stomach. A. Among them were a soldier B. Among them was a soldier C. Among them a soldier was D. Among they was a soldier 12. Next door to ours ________ , who is no less than eighty. A. that lives an old man B. does an old man live C. lives an old man D. where lives an old man 13.She plays the piano very well, ______. A. so every one of us does B. every one of us does C. so does every one of us D. so do every one of us 14.You say he works hard, ______, and _____. A. so he does; so you do B. so he does; so do you C. so does he; so do you D. so does he; so you do 15. —I thought you women were present at the meeting. —__________. A. So we were B. So we did C. So were we D. So did we 16.I don’t think Jack will come today, _____. A. nor will Mary B. and Mary doesn’t C. Mary will either D. or Mary does 17. She is fond of cooking, _____I . A. so am B. nor am C. neither do D. nor do 18.Marx was born in Germany and German was his native language. A. So it was with Engles B. So was it with Engles C. So was Engles D. So did Engles 19.A fish needs water and without water it will die._______. A. So does a man B. So will a man C. So it is with a man D. So is it with a man 20. So absorbed _______ the work that she often forgot to _____ her meals. A. had she been in; do B. she was in; make C. was she in; take D. she had been in ; have 21.So loudly ______ that every one of the class could hear him. A. did he speak B. did he spoke C. spoke he D. he spoke
动词现在分词的变化规则汇总
动词现在分词的变化规则: Ⅰ. 一般在动词末尾直接加ing Ⅱ. 以不发音字母e结尾的动词,先去掉e, 再加ing 如: skate --- skating have --- having ride --- riding come --- coming make --- making dance --- dancing write --- writing Ⅲ. 以重读闭音节结尾的动词,中间只有一个元音字母,词尾只有一个辅音字母, 应双写末尾的辅音字母,再加ing
如:goes,teaches,washes等。 3、以辅音字母加y结尾的动词,把y变为i,再加es, 如: study--studies,try--tries,carry--carries 等。 4、动词have遇在主语是第三人称单数时,have 改为has, 如:He has an interesting book . 5、动词be遇有主语是第一人称单数时,be改为am,遇有主语是第二人称时,be改为are,遇有主语是第三人称单数时,be改为is。 一、动词第三人称单数的变化规则及发音规律 动词原形变第三人称单数的规则与发音规律同名词单数变复数大致相同,请认真观察。
1、大多数动词在词尾加“S”在清辅音后发音为[s],在浊辅音及元音后发音为 [z]。在t后读[ts],在d后读[dz],如: ①stop-stops [s] ; make-makes [s] ②read-reads [z] ; play-plays [z] 2、以辅音字母加“y”结尾的,要先将“y”变为“i”,然后在加“es”读[iz] 如: fly-flies [z]; carry-carries [z] study-studies [z]; worry-worries 3、以“s, x, ch, sh”结尾的,在词尾加“es”,发音为[iz] 如: teach-teaches [iz]; watch-watches [iz] 4、以“o”结尾的动词,加“es”,读[z] 如: go-goes [z] do-does [z] 下面几个动词变为单数时,原词的元音部分的发音发生了较大的变化,请注意记忆。如:
Unit 4 Exercises 1. Complete the following sentences by translating the part in Chinese into English. (1) establishing business relations with your company (与贵公司建立业务关系) (2) On the recommendation of Dalian Trading Company (承蒙大连贸易公司介绍) (3) have the pleasure to introduce ourselves to you (有幸自荐) (4) As requested (根据你方要求) (5) We are looking forward to (我方期盼) 2. Read the following sentences and try to find out the mistakes and make corrections. There is one mistake in each sentence. (1) to →from (2) on →for (3) trading with →handling (4) enter →enter into / enter →establish (5) by separate cover →under separate cover Or by separate cover →by separate mail 3. Translate the following sentences. Part I T ranslate the following sentences into English. (1) We are one of the leading importers dealing in electronic products in the area, and take this opportunity to approach you in the hope of establishing business relations. (2) We have been engaged in handling importing and exporting of machinery and equipment for many years, and our products have enjoyed great popularity in many countries. (3) We owe your name and address to the Commercial Counselor’s Office of our Embassy in Beijing. (4) We are given to understand that you are a manufacturer of daily chemicals. One of our clients intends to buy cosmetics from your country. We will appreciate it highly if you airmail the catalogue and price list of the goods available at present. (5)For our credit standing, please refer to the Bank of China, Shanghai Branch.
I. Decide whether each of the following statements is True or False: 1. Linguistics is generally defined as the scientific study of language. 2. Linguistics studies particular language, not languages in general. 3. A scientific study of language is based on what the linguist thinks. 4. In the study of linguistics, hypotheses formed should be based on language facts and checked against the observed facts. 5. General linguistics is generally the study of language as a whole. 6. General linguistics, which relates itself to the research of other areas, studies the basic concepts, theories, descriptions, models and methods applicable in any linguistic study. 7. Phonetics is different from phonology in that the latter studies the combinations of the sounds to convey meaning in communication. 8. Morphology studies how words can be formed to produce meaningful sentences. 9. The study of the ways in which morphemes can be combined to form words is called morphology. 10. Syntax is different from morphology in that the former not only studies the morphemes, but also the combination of morphemes into words and words into sentences. 11. The study of meaning in language is known as semantics. 12. Both semantics and pragmatics study meanings. 13. Pragmatics is different from semantics in that pragmatics studies meaning not in isolation, but in context. 14. Social changes can often bring about language changes. 15. Sociolinguistics is the study of language in relation to society. 16. Modern linguistics is mostly prescriptive, but sometimes descriptive. 17. Modern linguistics is different from traditional grammar. 18. A diachronic study of language is the description of language at some point in time. 19. Modern linguistics regards the written language as primary, not the spoken language.