
IEEE International Workshop on Intelligent Data Acquisition and Advanced Computing Systems: Technology and Applications 21-23 September 2009, Rende (Cosenza), Italy
FPGA-based Low-cost Automatic Test Equipment for
Digital Integrated Circuits
Luca Mostardini, Luca Bacciarelli, Luca Fanucci 1, Lorenzo Bertini, Marco Tonarelli, Marco De Marinis 2
1
Dept. of Information Engineering - University of Pisa - Via Caruso 16, I-56122, Pisa - Italy -
{name}.{surname}@iet.unipi.it
2
SensorDynamics AG - Via Giuntini 25, I-56023 Navacchio (Pisa) - Italy -
{lbe, mto, agb, mdm}@https://www.doczj.com/doc/d716922988.html,
Abstract - Digital circuits complexity and density are increasing while, at the same time, more quality and reliability are required. These trends, together with high test costs, make the validation of VLSI circuits more and more difficult. Beside high-end ATE machines, strictly necessary in ASIC production phase, low-cost ATE test systems take place into market to implement a valid support in ASIC development phase.
In this paper a case study of low-cost, reconfigurable, versatile and easy-to-use FPGA-based test environment is presented. It allows patterns to be extracted from HDL-simulation and stimuli to be generated to ASIC prototypes, especially when a high-end test machine setup isn’t foreseen or isn’t available yet. This is the ideal solution for engineers to develop test programs and perform device tests and yield analysis on their desktop and then transfer the test program directly to production. The result is low-cost automatic test equipment, able to execute a preliminary digital test, using just a Laptop and an FPGA-equipped board.
I. I NTRODUCTION Many The VLSI test problems are more and more challenging in high-reliability design and will only worsen as circuit size increases and transistor feature size decreases. Circuit complexity, possible anomalies and high test costs make the validation of VLSI circuits more and more critical.
Two main categories of ATE machines are available nowadays on the market: high-end ATE and low-cost ATE. Machines belonging to the arena of high-end ATE, for example Verigy [1], Advantest [2], Teradyne [3] ones, are usually find located in testing companies and their operation is strictly interrelated with production.
ASIC manufacturers generally resort to these companies when chip development phase has been resolved and an accurate digital test program is ready to be executed by these high-end commercial ATEs.
In these cases testing is used to distinguish between lots of good or faulty modules.
High-end ATEs are characterized by high grade of automation (such as handlers for mechanical automation), digital and analog test capability, high-current pin protections and high-speed test execution. On the other hand they are very expensive and require an accurate setup and skilled people, so ASIC manufacturers also needs some other testing solution, which can be executed in house during preliminary chip evaluation phase, when the use of an aforementioned ATE should be unnecessary in terms of time and money.
In last decade, beside this range of performing ATE machines low-cost ATEs took place in market.
Chip testing and project verifying is essential above all during preliminary chip evaluation when customer is involved [4]. Inovys [5], Nextest [6], Teseda [7] and others trademarks participate in a competition in the arena of low-cost ATE offering products able to be used directly from ASIC designers during chip development phase.
For example, Maverick Personal Tester System produced by Nextest [6] allows to check functionality of up to 64 or 128 pin ASIC, and its testing capability is oriented and optimized towards electronic devices such as microcontrollers, specialty logic and flash memory devices.
In this paper we propose a case study of a low-cost,
easy-to-use and reconfigurable automatic test machine referred as FATE (FPGA-based ATE) in the following. The FPGA development occurred in the last years allows us to project and realize a home-made low-cost ATE based on a standard commercial FPGA.
Many vendors propose into market various kinds of quick, flexible and feature-rich development boards featuring various sized FPGA. The boards can support one or more standard interfaces to add further application-specific modules.
This scenario gives engineers the flexibility to acquire a
right-sized board and the module(s) to obtain the required capability in a quite cheap way.
FATE allows executing home-made digital tests, only using a Laptop and a FPGA-based board and can be easily
modified accordingly to the DUT (Device Under Test) saving time and money [8,
9]. After this introduction Section 2 briefly introduces the FATE system. Section 3 presents FATE architectures. The operation flow for testing execution is discussed in Section 4 while testing methodology is presented in Section 5. Experimental results are discussed in Section 6, future development in Section 7, and finally, conclusions are drawn in Section 8.
II.FATE S YSTEM
Presented ATE, which joins in low-cost ATE arena, makes always available an architecture optimized to the DUT [10, 11] thanks to FPGA characteristic of dynamic configurability.
With respect to most of other low-cost ATEs, no microprocessor or microcontroller is fitted on the programmable resource. After FATE setting for target DUT testing, designer disposes of an “ad hoc” instrument, unable to perform other low-cost ATEs generality (i.e. the possibility of implementing mathematical functions), but optimized in terms of simplicity and maximum speed available.
To generate test patterns and traduce them in ASIC stimuli a software tool has been developed for FATE.
The purpose is to use this test system in an ASIC development flow linked to a production tester. FPGA based structural tester provides a lower-cost way to conduct test pattern validation, test program development, and debug-diagnosis or failure analysis that is related to fails on a production tester learning during ramp-to-volume. Moreover it provides high flexibility, portability and a better response time.
The resulting architecture allows any kind of digital test to be executed on the DUT. It is also possible to use the same testbench used during the HDL project development to automatically generate or regenerate relevant test patterns.
Besides the physical platform, a virtual one has been also realized in order to verify by means of a further simulation the automatically generated test-patterns. This tool allows generated test vectors to be cross-checked using them as stimuli for the ASIC netlist.
FATE system, (including both hardware and software components), results in an instrument allowing engineers to validate vectors and develop the test program or to trace the root causes of systemic failures in early time.
III.FATE A RCHITECTURE
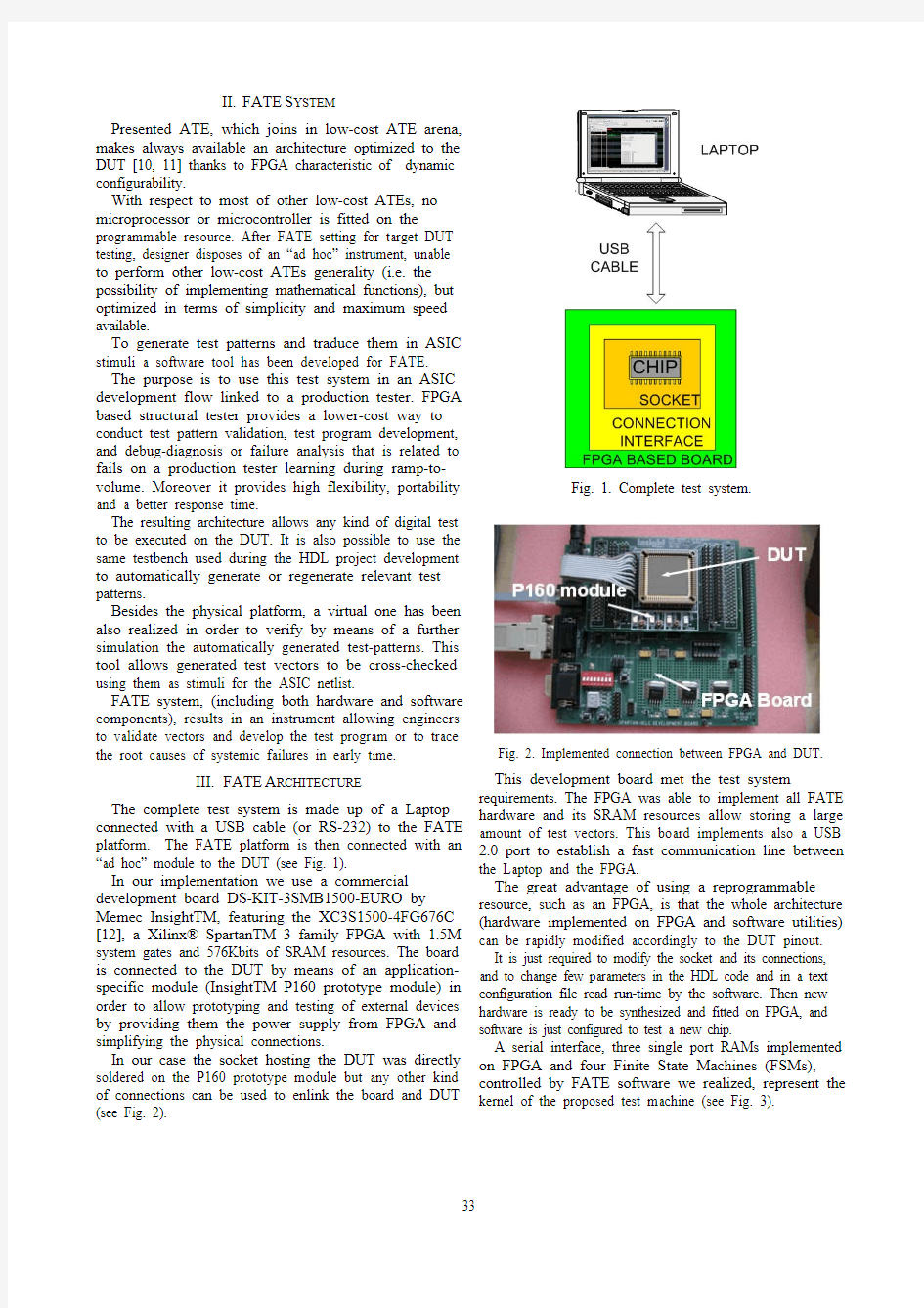
The complete test system is made up of a Laptop connected with a USB cable (or RS-232) to the FATE platform. The FATE platform is then connected with an “ad hoc” module to the DUT (see Fig. 1).
In our implementation we use a commercial development board DS-KIT-3SMB1500-EURO by Memec InsightTM, featuring the XC3S1500-4FG676C [12], a Xilinx? SpartanTM 3 family FPGA with 1.5M system gates and 576Kbits of SRAM resources. The board is connected to the DUT by means of an application-specific module (InsightTM P160 prototype module) in order to allow prototyping and testing of external devices by providing them the power supply from FPGA and simplifying the physical connections.
In our case the socket hosting the DUT was directly soldered on the P160 prototype module but any other kind of connections can be used to enlink the board and DUT (see Fig. 2).
Fig. 1. Complete test system.
Fig. 2. Implemented connection between FPGA and DUT. This development board met the test system
requirements. The FPGA was able to implement all FATE hardware and its SRAM resources allow storing a large amount of test vectors. This board implements also a USB 2.0 port to establish a fast communication line between the Laptop and the FPGA.
The great advantage of using a reprogrammable resource, such as an FPGA, is that the whole architecture (hardware implemented on FPGA and software utilities) can be rapidly modified accordingly to the DUT pinout.
It is just required to modify the socket and its connections, and to change few parameters in the HDL code and in a text configuration file read run-time by the software. Then new hardware is ready to be synthesized and fitted on FPGA, and software is just configured to test a new chip.
A serial interface, three single port RAMs implemented on FPGA and four Finite State Machines (FSMs), controlled by FATE software we realized, represent the kernel of the proposed test machine (see Fig. 3).
Fig. 3. Block scheme of architecture on FPGA.
All hardware structure is synthesized accordingly to generic parameters of the HDL package; only new SRAM memories must be created again every time the DUT pinout changes. These memory elements must be generated accordingly to FPGA available resources; anyhow main FPGA development kit tools provide an automatic SRAM generator.
This test environment foresees to implement 3 optimized SRAM elements: one is organized to contain pin timing data and its size is set accordingly to DUT pinout; the second one to contain patterns to be applied and the third to collect samples. The length of the second and third memories is set accordingly to DUT pinout, but their depth is a free parameter. The depth of the aforementioned second and third memories is the same because every test vector stored in a row of pattern memory when applied on DUT produces a sample line stored in a row of sample memory.
This solution allows targeting our architecture on every board FPGA-based. The flexibility in the setting of the depth parameters allows loading the maximum number of test vectors permitted by the RAM resources of the adopted FPGA.
IV.T EST M ACRO-O PERATIONS
In this section the macro-operations executed during a complete test flow are described.
Setup operations foresee these preliminary steps: user has to compile a text configuration file containing information about pin-timing and generate or compile the patterns file. After that it is possible to execute test in a fully automatic mode. The software is in charge of sending to the FATE the above mentioned two files, automatically converted in machine format. A proper FSM implemented on FPGA (FSM1: LOAD) acquires these data and loads them into two optimized SRAM (TIMING SRAM and PATTERNS SRAM).
The communication between PC and FPGA is realized by an USB cable thanks to an USB to UART Bridge Controller available on the InsigthTM board. Data can be processed by a versatile UART interface implemented on FPGA and able to support any baud-rate in order to interface a USB converter.
If target FPGA board doesn’t support an USB to UART converter, a serial cable communication is also available. In this case, baud rate is selectable in a predefined range of discrete values.
Once the SRAMs have been loaded, the effective testing starts; a further FSM (FSM4: GEN/SAM) on FPGA will generate the stimuli to the DUT accordingly to the patterns and to the pin-timing information and save the sample in another dedicated SRAM (SAMPLES SRAM). Then a sample gathering begins and FPGA sends all logic values sampled on DUT pinout to the Laptop. In practical cases, when testing complex DUTs, the required patterns file usually exceed the depth of the PATTERNS SRAM on FPGA, so an automatic loop of loading patterns, executing test and downloading samples takes place. The patterns are split in more slices and they are applied in consecutive cycles. Finally, when last cycle has been applied, and so the sample file is complete, the software generates a report file. This file, written in a STIL (Standard Test Interface Language) format, is a list of errors containing the possible differences between expected and sampled values. Complete test flowchart execution highlighting the above mentioned macro-operations is showed in Fig. 4.
POSSIBILE LOOP
Fig. 4. Flowchart of complete test execution operations.
V. T ESTING M ETHODOLOGY
The frequency of the clock generated to stimulate the
DUT is different from the frequency of the on-board
oscillator which controls the FSMs. This solution allows
stimulating DUT pinout and acquiring samples in instants
different from the test-clock rising edge.
Test period length is selectable at run-time, by setting an
appropriate prescaler reduction value and configuring
available DCM (Digital Clock Manager) test can be executed
at the required frequency. Maximum test frequency is
however 1/10 of the on-board frequency oscillator.
An external clock source or a more performing FPGA may
be used wherever it needs to execute test at higher speed.
Pin-timing file is used to keep information about timing
edges DUT pinout. For each pin, whose name is assigned
by user, signal type (RZ, NRZ or RO), delay, duration and
sample time in the test period are specified.
Test period, indeed, is divided into 10 intervals and every
signal in the test period must be brought back to one of
these signal types: a Return to Zero (RZ), a Non Return to
Zero (NRZ) or a Return to One (RO). Fig. 5 shows the three
signal types examples and time base: (a) NRZ signal with
delay = 4; (b) RZ signal with delay = 3 and duration = 5 (it
may be, for example, the DUT clock, with a duty cycle of
50%); (c) RO signal with delay = 4 and duration = 3.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
00
1
1
01
0(a)
(b)
(c)
Time
L o g i c l e v e l
NRZ
RZ
RO
Fig. 5. Possible signal type in time base.
Summarizing, during setup phase, user has to set signal
type, delay, duration and sample time for each pin of DUT; signal transitions and sample times have to be reproduced aligning as much as possible to the waveform
of testbench. Stimuli generation and sample logic are
driven accordingly to patterns and pin-timing file.
Software, which constantly interfaces Laptop and user, controls hardware operations. It manages data transferring, compiles others user friendly files, processes patterns and generates the machine format of source user text configuration file. User may configure test execution in debug mode or in fully automatic mode. In both solutions user may check each operation result simply reading messages out coming on screen. Debug mode allows executing one by one a pre-fixed number of test vectors. This feature is very useful in ASIC development phase, because of designer, using a standard oscilloscope, may directly control logic level and edges of
all DUT pinout during test execution.
Fully automatic mode is useful when patterns have just
be verified and designer needs to execute more than one
digital test on a single ASIC. In this case source files have
to be located in predefined path and software drives the
execution of the digital test program.
Possible errors in source text files, CRC (Cyclic
Redundancy Check) failures or others misunderstandings
(such as compiling errors) are signaled. When the FATE
software tool isn’t able to automatically correct generated
error the user is invited to solve manually the problem.
A relevant feature is that software acquires all
parameters from text files, which have to be modified
every time it needs to change settings.
This solution allows the software running without a C
compiler installed on your Laptop.
Software includes also a compression data technique,
able to reduce the size of patterns file when the same test
vector is repeated twice or more times.
As already aforementioned, the great advantage of the
proposed test-platform is that designer can use the same
testbench written during HDL project development to
generate patterns. This solution is possible because the
project includes the HDL code of an entity (text_gen) which can be compiled and directly instantiated by the testbench itself. It needs only to execute this modified testbench to obtain, as further result, the patterns generation properly formatted to be acquired by software. Fig. 6 shows the new testbench object.
Fig. 6. Automatic test patterns generation. Besides this physical platform, a virtual one has been realized too, which allows simulating again the generated patterns to check their validity. FATE environment also includes a HDL description of a machine (text_verify) to be instantiated in a new testbench and connected to the DUT netlist. Launching this new simulation is it possible to obtain a possible list of mistakes made during patterns generation.
Fig. 7 shows the further testbench to be compiled to implement this virtual platform.
Patterns generation and verification loop is now complete, designer can launch the same simulation used in ASIC project phase with the further result of obtaining patterns. After that, designer uses provided HDL-testbench to cross-check if aforementioned patterns are really consistent with DUT netlist.
Fig. 7. Automatic test patterns validation
If new simulation result generates no error, virtual platform gives place to physical one and patterns becomes real stimuli applied to ASIC. Fig. 8 schematizes test loop operations.
Fig. 8. Patterns generation and verification flow.
VI.E XPERIMENTAL R ESULTS
The proposed FATE system has been successfully used
to test tens of prototypes of two Systems on Chip (SoC) developed to realize control systems based on Micro Electro Mechanical (MEM) sensors.
These two ASIC has been produced using different technologies, but they have some common characteristics: each of them contains an analog and a digital part, a CPU, some I/O peripherals, others to control the analog part, several ADCs, DACs and memory elements: ROM, single port and dual port SRAM etc. Either SoC ASIC prototypes we tested have just 20 digital pins, but given example doesn’t loose in generality.
Memec InsightTM [12] also provides board disposing of more than one P160 interfaces and it is possible to reach up more than 128 pin connections, overcoming the limitation
of most of low-cost ATEs. In our experiment it was enough
to implement the test machine on a board supporting the aforementioned SpartanTM 3 Xilinx? FPGA. The nature
of the MEMs under test allows using a maximum test clock frequency of a few MHz, which can be easily reached by the implementation of FATE on used FPGA.
FPGA SRAM resources, as expected, aren’t able to store the whole pattern but they allow execution of a single test run loop of 10000 test vectors. Anyway, the synchronous nature of tested chip allows no precaution to
be used between every loop of test vectors.
Digital part testing of this kind of ASIC is complex, so full test has been split in two complementary tests which have been separately executed: Built In Self Test (BIST) and Automatic Test Pattern Generation (ATPG). BIST is used to check only DUT memory elements and the ATPG
is used to validate all DUT standard cells and connections.
In ASIC first phase design, FATE has been used in debug mode to circumscribe errors due to a wrong patterns generation; in the second phase a digital test program has been provided to execute in a fully automatic mode ATPG and BIST test on a single ASIC.
Time requested by executing aforementioned two digital tests of a single unit is valid for our application. Complete test run of these two tests, which globally consists of an amount of 4.500.000 test vectors, takes about 20 minutes (15 minutes ATPG and 5 minutes BIST).
Actual FATE implementation can work at a maximum frequency of 6 MHz, (1/10 of 60 MHz on-board oscillator) which guarantees to cover the addressed sensor-conditioning applications. For example aforementioned BIST and ATPG tests can be successfully realized at 1 MHz, accordingly to the specifics ordered by designers. We used the proposed architecture on tens of these ASICs for both SoCs and this approach provided to
be very useful.
VII.E XPERIMENTAL R ESULTS
The realized test environment is suitable for present applications, but an interesting reduction in the overall test duration can be achieved by using an external flash
memory to store all test patterns. The used development board supports, in fact, another standard interface to further enlarge the connectivity from the FPGA to other external devices, so the flash memory could be physically integrated in the whole system without big efforts. All test vectors should be loaded in the flash memory just the first time, skipping to reload them each time when testing equivalent parts.
To completely benefit of this development, report generation logic should be modified. In the current version all samples are sent to the Laptop to generate the report file, also when testing good modules. We are taking in account the improvement of performing a hardware logic match directly in the FPGA which could send back to the Laptop only few control data when testing good parts, or to a failure sample list when testing faulty ones.
VIII.C ONCLUSIONS
In this paper we have described a low cost FPGA-based automatic test equipment to validate the digital parts of VLSI chip. Main features of FATE environment are low cost, high flexibility and simplicity of use. It is particularly useful in the VLSI project phase to debug few tens of prototypes when setup for commercial test machine has not been developed yet.
Using FATE, engineers can validate test vectors and develop the test program to quickly trace the root causes of systemic failures, with the consequent reduction of "time-to-market", "time-to-yield" and "time-to volume”. Experimental results obtained using this test machine for the screening of digital part of complex SoCs confirmed its validity, at least for the addressed applications. Produced error report file allows both to identify project errors in the VLSI design and to select good parts of tens of chips.
R EFERENCES
[1]https://www.doczj.com/doc/d716922988.html,/ (Verigy website)
[2]https://www.doczj.com/doc/d716922988.html,/ (Advantest website)
[3]https://www.doczj.com/doc/d716922988.html,/ (Teradyne website)
[4] C.F. Hawkins, H.T. Nagle, R.R. Fritzemeier, J.R. Guth, “The VLSI
circuit test problem-a tutorial Industrial Electronics,” IEEE
Transactions, vol. 36, Issue 2, May 1989, pp. 111 – 116.
[5]https://www.doczj.com/doc/d716922988.html,/ (Inovys website)
[6]https://www.doczj.com/doc/d716922988.html,/ (Nextest website)
[7]https://www.doczj.com/doc/d716922988.html,/ (Teseda website)
[8] E.M. Saad, I.E. Talkhan, I.M. Sayed, “A proposed ATE for digital
systems Radio Science Conference,” 1996. NRSC '96., Thirteenth National, 19-21 March, 1996, pp. 209 – 220.
[9] C. Giaconia, A. Di Stefano, G. Capponi, “Reconfigurable digital
instrumentation based on FPGA System-on-Chip for Real-Time Applications,” 2003. Proceedings. The 3rd IEEE International Workshop, 30 June-2 July 2003, pp. 120 – 122.
[10]S. Hauch, “The roles on FPGA’s in reprogrammable systems,” in
Proceedings of The IEEE, vol. 86, no. 4, April 1998.
[11]S. Trimberger, “A reprogrammable gate array and applications,” in
Proceedings of The IEEE, vol. 81, no. 7, July 1993.
[12]https://www.doczj.com/doc/d716922988.html,/ (Memec website)
雅思历年真题口语题目汇总 version 01old person describe an old man influenced you 1.who was he 2.when did you know him 3.what he did and explain why he influenced you part3 1.老人的经验有什么问题存在? 2.喜欢什么艺术品? 3.给老人拍照片时候注意什么呢? 4.你们国家对老年人是什么态度? 5.你认为这个社会在哪些方面对老年人不太好? 6.老人在你们家有什么影响? 7.你认为老年人在看问题的时候跟年轻人有什么不一样? 8.他们对大家有什么影响? version 02 city 1.where it is located? 2. what special for you? 3. why you want to stay there? part 3 1.please compare 100 hundred years old city and modern city and what predict about the city in the future. 2.上海是个怎样的城市 3.都有那些著名建筑
4.你想为这个城市做些什么? 5.有哪些现象有待提高或者那些提倡 version 03 room part2: 1.what's your favorite room in your home 2.what it likes you live 3.what you do in the room normally and explain why you like it part3: 1.你认识你的邻居吗? 2.城市里的房子和乡村有什么不同? 2003年9月换题后的口语topic Old person Describe a older person you know You should say:Who he or she is How you know him or her How he or she is And explain what infection he or she give you and in what aspect Further question: 1、你们国家对老年人是什么态度? 2、你认为这个社会在哪些方面对老年人不太好? 3、老人在你们家有什么影响? 4、你认为老年人在看问题的时候跟年轻人有什么不一样? 5、他们对大家有什么影响?
Google搜索从入门到精通 v4.0 (一) 1、前言 我是在2000年上半年知道GOOGLE的。在这之前,我搜索英文信息通常用AltaVista,而搜索中文信息则常用 Sina。但自使用了GOOGLE之后,它便成为我的Favorite Searchengine了。这也得感谢新浪网友曹溪,因为当初正是因为他的大力推介,才使我识得了GOOGLE。 记得1996年夏季的时候,当我第一次接触Internet,便被扑面而来的魔力征服了。那种天涯咫尺的感觉,真是妙不可言。在经历了疯狂的WWW冲浪和如痴如醉的BBS沉迷之后,我意识到Internet对我影响至深的还是在于学习方式的变迁。 如何来描述这种变迁呢?以前的学习,一般需要预先在肚子里存储下足够的知识,必要时,就从海量的信息中提取所需的部分。这种学习方式造就了很多“才高八斗,学富五车”的大才子。但是,到了信息领域大大超出“四书五经”的新时期,预先无目的的吞下海量信息的学习方式就有些不合时宜了。比方说,我们到了大型的图书城,往往有一种不知所措的感觉。旧有的学习方式需要变更以适应这个信息爆炸的年代。目的明确的去学习,即先知道要学什么,然后有目的的去寻找答案,这种方式看上去更加有效率。我不妨把这称为“即学式”,相应的,旧有的称为“预学式”。不过,“即学式”的实施是有前提的。首先,要求学习者拥有一个包罗万象的信息库,以供随时抽取各种目的信息;其次,是需要一个强劲的信息检索工具,以便高效率的从信息库中提取信息。很明显,Internet可以充当那个海量的信息库,而搜索引擎,则正是寻找光明之火的绝好工具。 “公欲善其事,必先利其器”。Internet只有一个,而搜索引擎则有N多个。有搜索高手说,所谓搜索,就是“在正确的地方使用正确的工具和正确的方法寻找正确的内容”。但是,对于普通人而言,掌握诸多搜索引擎的可能性似乎不大。用一两个相对强劲的具代表性的工具达到绝大多数搜索目的更为人们所迫切希望。不同的时期,涌现出不同的强者。就目前而言,我们非常幸运的有了: *****GOOGLE***** 2、摘要 本文简要的介绍了GOOGLE的历史和特点,GOOGLE的基本搜索语法和高级搜索语法,GOOGLE的特
学院lqzydm lqzymc录取人数(不含推免生)001010101马克思主义哲学3 001010102中国哲学2 001010103外国哲学2 001010104逻辑学1 001010105伦理学3 001010108科学技术哲学2 0010101Z2管理哲学1 001030200政治学9 0010302Z1地方政府与社会管理2 001120100管理科学与工程1 001120401行政管理19 001120402社会医学与卫生事业管理4 001120405土地资源管理1 001125200公共管理257 002020105世界经济1 002020200应用经济学18 002025100金融15 002025300税务7 002025400国际商务3 002120200工商管理15 002125100工商管理324 002125300会计111 003030101法学理论6 003030102法律史5 003030103宪法学与行政法学8 003030104刑法学6 003030105民商法学10 003030106诉讼法学5 003030107经济法学4 003030108环境与资源保护法学2 003030109国际法学7 003035101法律(非法学)107 003035102法律(法学)90 004040100教育学22 004040200心理学17 004045101教育管理3 004045400应用心理50 004120403教育经济与管理2 005040300体育学21 005045200体育69 006010106美学3 006040102课程与教学论2 006045103学科教学(语文)52 006045300汉语国际教育40 006050100中国语言文学33 007050300新闻传播学6 007055200新闻与传播41 007055300出版11 007130300戏剧与影视学5 008085237工业设计工程1 008130100艺术学理论1 008130400美术学3 008130500设计学7 008135107美术19 008135108艺术设计79
雅思为各位考生推荐复习材料-剑 5 口语 Test4 Part3-Purpose of festivals and celebrations;需要本教程其他单元口语范文的考生请点击:剑 5 口语Test3 Part1-Entertainment;剑5 口语 Test3 Part2-Describe one of your friends;剑5 口语 Test3 Part3范文-Qualities of Friends。 PART 3: Purpose of festivals and celebrations Q: Why do you think festivals are important events in the working year? Answer: Yeah. It’s very important for two reasons. For the country, it’s a time to remember our cultural origin and our historical past. The whole country celebrates our root and it’s very inspiring. We become so proud of our past. I guess that’s why festivals are important. For the individual, festivals give us a chance for relaxation as we often have a few days off. It’s a time of fun, meeting friends, entertainment. So after that we feel like a new man. In a sense, holidays restore our balance between work and leisure. That’s also why we need festivals for China. Q: Would you agree that the original significance of festival is often lost today? 构思: 节日的初衷: 庆祝传统, 承上启下, 结束也是开始 现在的节日: 人们繁忙, 感觉不到开始和结束的意义, 过完节,马上就再次投入到工作中, 有些单位甚至连节假日都加班. 人们也不在那么感动传统,倒是好好的利用节日放松了一下,
《市场营销基础知识》期末考试卷与答案 (2011-06-16 12:59:56) 转载▼ 标签: 杂谈 一、单项选择题(每小题1分,共20分) 1.环境保护意义与市场营销观念相结合所形成的市场观念称为()。 A.大市场营销 B.直接市场营销 C.关系市场营销 D.绿色市场营销 2.下列()因素是企业的微观环境因素? A.人口 B.购买力 C.公众 D.自然环境 3.消费者的购买决策很大程度上受()的影响。 A.社会文化因素 B.心理因素 C. 个人因素 D. 以上三个因素都是 4.麦当劳与肯德基、可口可乐与百事可乐持续不断的竞争,实行的是()。 A. 避强定位 B. 迎头定位 C. 重新定位 D. 产品差异化 5.企业为那些当场付清货物的顾客进行的一种减价行为,称为()折扣。 A.数量折扣 B.季节折扣 C.现金折扣 D.交易折扣 6.生产者通过两个或两个以上的同类中间商来销售自己的产品的渠道是 ()。 A.长渠道 B.短渠道 C.宽渠道 D.窄渠道 7.消费者的购买行为过程的起点和终点是()。 A.一手钱一手货,交换结束,购买行为就结束 B.从顾客向售货员询问到交易完双方道别 C.从走进商店到交易完走出商店 D.从需求产生到对所买商品的最终评价 8.一辆摩托车,有人觉得骑上它神气十足,而有人觉得骑上它危险较多,这说明消费者()。
A.性格特征不同 B.价值观念不同 C.消费习俗不同 D.社会阶层不同 9.下列()的需求弹性最小。 A.手表 B.食盐 C.化妆品 D.时装 10.中国电信规定每日21:00-24:00拨打国内长途电话按半价收费。这种定价策略属于()。 A.成本加成策略 B.差别定价策略 C.心理定价策略 D.组合定价策略 11.市场包括三个基本因素:有某种需要的人、为满足这种需要的购买能力和()。 A.购买渠道 B.供应产品的厂商 C.购买行为 D.购买场所 12.目标市场营销由三个步骤组成:一是市场细分;二是选择目标市场;三是进行()。 A.推销 B.促销 C.竞争 D.市场定位 13.采用统一品牌策略的各种产品必须具有相近的()。 A.性能特点 B.规格型号 C.质量水平 D.价格水平 14.需求层次理论是20世纪50年代由美国心理学家()提出的。 A.波登 B.赫杰特齐 C.马斯洛 D.温得尔.斯密 15.市场营销学最早产生于()。 A.美国 B.英国 C.中国 D.日本 16.自古至今许多经营者奉行"酒好不怕巷子深"的经商之道,这种市场营销管理哲学属于()。 A.推销观念 B.产品观念 C.生产观念 D.市场营销观念 17.许多冰箱生产厂家近年来高举“环保”、“健康”旗帜,纷纷推出无氟冰箱。它们所奉行的市场营销管理哲学是()。 A.推销观念 B.生产观念 C.市场营销观念 D.社会市场营销观念 18.相对于黑白电视机而言,纯平彩色电视机属于()。 A.全新产品 B.换代产品 C. 改进产品 D. 仿制产品 19生产者在某一地区仅通过少数几个精心挑选的中间商来分销产品,这是 ()分销策略。 A.广泛 B.密集 C.强力 D.选择性 20.公共关系是一项()促销方式。 A.一次性 B.长期 C.短期 D.偶然性
电动汽车充电技术国内外研究现况及发展趋势 班级: 姓名: 学号:
摘要:对国内外电动汽车、电动汽车充电技术及规划布局等方面现状进行了研究,并对电动汽车充电需求进行了分析。介绍了国内外电动汽车充电设施的发展状况,对未来我国电动汽车发展前景进行了初步研究,提出积极推动电动汽车充电设施建设应是电网企业义不容辞的责任以及未来发展机遇。 关键词:电动汽车充电技术研究现状发展趋势 1.前言 电动汽车是全部或部分由电能驱动电机作为动力系统的汽车,按照目前技术的发展方向或者车辆驱动原理,可划分为纯电动汽车、混合动力汽车和燃料电池电动汽车三种类型。近年来,我国电动汽车行业取得了快速发展,攻克了一系列关键技术难题,在部分领域已实现了与日美欧等国同步发展。目前我国发展电动汽车已具有消费市场规模大、制造成本低、技术取得局部突破、资源保障能力强的四大优势。在技术突破和政策扶持的双重刺激下,我国电动汽车已处于市场引爆的临界点,预计未来两年电动汽车的市场规模和生产规模将迅速扩大,电动汽车将进入快速成长期。电动汽车充电设施是电动汽车产业链的重要组成部分,在电动汽车产业发展的同时还应该充分考虑充电设施的发展。 1 电动汽车充电的基本方式 目前常用的电动汽车充电方式有慢充、快充和快换三种: (1) 慢充方式。慢充一般以较小交流电流进行充电,充电时间通常为6~10 h,慢充方式一般利用晚间进行充电,充电时可以采用晚间低谷电价,有利于降低充电成本,但是难以满足使用者紧急或者长距离行驶需求。慢充一般采用单相220V/16A 交流电源,通过车载充电器对电动汽车进行充电,车载充电器可采用国标三口插座,基本不存在接口标准的问题。电动汽车慢充一般通过充电桩进行。 (2) 快充方式。快充又称应急充电,以较大直流电流在20 min 至1 h 内,为电动汽车提供短时充电服务,快充方式可以解决续航里程不足时电能补给问题,但是对电池寿命有影响,因电流较大,对技术、安全性要求也较高。快充的特点是高电压、大电流,充电时间短(约1 h)。目前,这种充电方式的充电插口的针脚定义、电压、电流值、控制协议等均没有国家标准,也没有国际标准,已投入使用的充电机和电动车电池充电插口均由各生产厂家自定,世界各国都在积极争夺标准的制订权,各大电动汽车厂家也纷纷抢先投放产品,抢占市场、提高占有率,试图使多数充电站不得不采用其充电设备,从而成为事实标准。快充方式主要在充电站中进行。 (3) 快换方式。快换则是通过直接更换车载电池的方式补充电能,换电时间与燃油汽车加油时间相近,大约需要5~10 min。快换方式最为便捷,但是需要电动汽车和车载电池实现标准化,而且快换过程中需要专业人员进行操作。快换可以在充电站也可在专用电池更换站完成。这种方式的优点是电动车电池不需现场充电,更换电池时间较短,但要求电池的外形、容量等参数完全统一,同时,还要求电动汽车的构造设计能满足更换电池的方便性、快捷性。 2 国外电动汽车充电设施发展状况
雅思历年真题口语题目汇总 version01old person describe an old man influenced you 1.who was he 2.when did you know him 3.what he did and explain why he influeced you part3 1.老人的经验有什么问题存在? 2.喜欢什么艺术品? 3.给老人拍照片时候注意什么呢? 4.你们国家对老年人是什么态度? 5.你认为这个社会在哪些方面对老年人不太好? 6.老人在你们家有什么影响? 7.你认为老年人在看问题的时候跟年轻人有什么不一样? 8.他们对大家有什么影响? version02city 1.where it is located? 2.what special for you? 3.why you want to stay there? part3 1.please compare100hundred years old city and modern city and what predict about the city in the futu re. 2.上海是个怎样的城市 新东方批改网(https://www.doczj.com/doc/d716922988.html,),在线雅思作文批改,雅思口语批改。语法纠错、恶补,制定考试计划,
3.都有那些著名建筑 4.你想为这个城市做些什么? 5.有哪些现象有待提高或者那些提倡 version03room part2: 1.what's your favorite room in your home 2.what it likes you live 3.what you do in the room normally and explain why you like it part3: 1.你认识你的邻居吗? 2.城市里的房子和乡村有什么不同? 2003年9月换题后的口语topic Old person Describe a older person you know You should say:Who he or she is How you know him or her How he or she is And explain what infection he or she give you and in what aspect Further question: 1、你们国家对老年人是什么态度? 2、你认为这个社会在哪些方面对老年人不太好? 3、老人在你们家有什么影响? 新东方批改网(https://www.doczj.com/doc/d716922988.html,),在线雅思作文批改,雅思口语批改。语法纠错、恶补,制定考试计划,
?法磊推荐的书,网站 ●英语写作能力:《高级英语写作手册》(英文版北京外国语大学出版社) ●双语能力:英汉对照读物 ●做个知识渊博的杂家:1)先去国内各大门户网站了解一下新闻,再去 China Daily,新华网英文版了解英文的表达法,可以学到本土特色东西的表 达法。 2)浏览国外新闻网站,就同一个话题,摘取一段换,揣摩表达方法。 3)浏览论坛,如翻译中国,译网情深,https://www.doczj.com/doc/d716922988.html,/ 4)《中国翻译》 5)http://blog.hjenglish/wuzhongdong北外教授博客 6)《Google 从入门到精通》 ?翻译路上的交通证(考证一方面是一种凭证,另一方面也是一种 学习过程) ●上海高级口译证书和CATTI笔译二级证书 ●参加比赛:韩素音青年翻译奖 CCTV希望之星英语风采大赛 ?翻译路上的工具 ●搜索引擎:1)缩略语的搜索:缩略语+所属范畴 专有名词的搜索:如,中国银行业监督管理委员会+bank 2)名言名句的翻译要事先搜索是否有更地道的翻译 3)对于不确定的搭配可利用搜索引擎搜索,如果超过20个网页有这样的 表达,且大多数为外国网站,则可以运用 4)小语种的翻译可以借助先转换为英语再转换为中文(资料少的情况下) 语种互译网站:https://www.doczj.com/doc/d716922988.html,/translate-t ●TRADOS软件 ●专业术语在线词典:https://www.doczj.com/doc/d716922988.html,/ ●word,excel,ppt,pdf,autocad(工科翻译)的熟练使用,包括排版 ?翻译中的思维与方法 ●以段为单位,理解大意后,再翻译每个句子,然后再从整段出发修改 句子。翻译的句子要考虑阅读者的思维习惯。 ●只要保证语义不变,句子形式、语法结构都可以改变。 ●翻译中的修改,1)先修改低级错误,如标点,错别字 2)对照原文逐句看翻译正确与否 3)抛开原文,看译文是否通顺 4)再对照 5)搁置几天后再修改 ●翻译初期,要先做英译中,学学正确的英语表达方法。
一、单项选择题(共15分,每小题1分) 1.市场营销观念的中心是()。 A.推销已经生产出来的产品 B.发现需要并设法满足它们 C.制造质优价廉的产品 D.制造大量产品并推销出去 2.做为市场营销中介的物流公司,通常被称为( )。 A.供应商 B.商人中间商 C.代理中间商 D.辅助商 3.企业购买者做出购买决策最少的购买情况是()。 A.直接重购 B.修订重购 C.新购 D.变更收购 4.下列调查方法中不属于访问法的是()。 A.邮寄调查 B.留置问卷调查 C.电话访问 D.直接观察 5.某油漆公司不仅生产油漆,同时还拥有和控制200家以上的油漆商店,这就叫()。 A.前向一体化B.后向一体化 C 横向一体化D.多角化6.下列不属于市场营销组合要素的是( )。 A.产品 B.促销 C.渠道 D.利润 7.对经济、收入和税收因素的分析属于( )。 A.技术环境分析 B.政治环境分析 C.经济环境分析 D.社会环境分析8.如一种产品的销售增加必然引起另一种产品销售的减少,那么,这两种产品是( )。 A. 互补品 B. 独立品 C. 条件品 D. 替代品 9.人们购买制冷用的空调主要是为了在夏天获得凉爽空气。这属于空调产品整体概念中的()。 A.核心产品 B.有形产品 C.附加产品 D.直接产品 10.细分消费者市场必须注意以下五方面的要求:()。 A.市场要有同质性、应变性,市场范围相对较小 B.市场要有可进人性、可变性、垄断性、同质性
C.市场具有可测量性、需求大量性、效益性、应变性等 D.市场要有足够的购买潜力、可进入性、可衡量性、可盈利性等 11.相对于黑白电视机而言,彩色电视机属于()。 A.全新产品 B.换代产品 C .改进产品 D.仿制产品 12.产品生命周期指的是()。 A.产品使用寿命B.产品物理寿命 C.产品合理寿命D.产品市场寿命 13.企业只推出单一产品,运用单一的市场营销组合,力求在一定程度上适合尽可能多的顾客的需求,这种战略是()。 A.无差异市场营销战略 B.密集市场营销战略 C.差异市场营销战略 D.集中市场营销战略 14.宝洁公司有包括洗衣粉、牙膏、肥皂、纸尿布、纸巾在内的5个产品线,其中“5”代表的是企业的产品组合的()。 A.宽度 B.深度 C.长度 D.关联度 15.消费者对价格敏感,生产与销售成本低,竞争者易进入,商品差异性小的新产品定价,应采用( )。 A.高价策略B.低价策略 C.满意策略D.折扣策略 二、名词解释(共15分,每小题3分)。 1.关系市场营销 2.后向一体化 3.市场预测 4.核心产品 5.需求的交叉弹性 三、简答题(共30分,每小题6分) 1.影响消费者购买行为的主要因素有哪些?
【雅思口语预测】雅思口语话题题库范文 雅思口语精准预测刘薇简介环球雅思北京学校副校长最受欢迎口语教师授课时激情中透着温婉幽默里渗入励志秉承让学生 "轻松复习事半功倍"的教学理念。 从事雅思教学多年北京大学传播学硕士曾学术访问哈佛大学 耶鲁大学等世界顶尖名校。 著作《雅思九天口语高分之路》、《剑桥雅思全真试题原版解析8》。本月预测重点本预测适用于xx年4月雅思考试超高频和重回题库考题、一级重点、都是重点类别需要考生准备细致答案。二级重点考生考生准备思路即可。 Part 1 分类汇总一基本信息类 1. Name 什么名字,中文名含义,未来换吗 2. Study or work 上班还上学上学问专业或最喜欢学科上班工作内容,参加过培训吗,未来换工作吗 3. Hometown 家乡哪里,有什么特别的地方,未来想居住的地方 4. Weather 喜欢什么天气家乡天气,家乡天气今年的变化 5. Family 家庭情况,家庭时间如何度过,全家人喜欢一起做什么二衣食住行类 1. Living 住flat还是house,最喜欢的房间,如果重装修会怎么做 2. Building 喜欢什么建筑,你们国家的人更喜欢传统还是时尚建筑,未来建筑的发展 3.
Countryside 喜欢郊区吗,郊区与城市的区别,什么人喜欢郊区 4. Transport 家乡交通特点,公共交通和私人交通的优缺点,未 来如何改善 5. Boating 划过船吗,坐过船吗,好处,你们国 家水运多吗 6. Clothes and fashion 喜欢什么衣服,喜欢时 尚吗,时尚对生活的影响 7. Bags 平时背包包吗,什么类型的 宝宝,知道哪些包包,丢过包包吗 8. Keeping healthy and fit 如何保持健康,如何保持身材 9. Daily routine and favorite time in a day 典型的一天,一天中最喜欢的时间段 10. Sleeping 几点睡几点起,睡不着怎么办,如何培养好的睡眠习惯 三娱乐休闲 1. Music 喜欢什么类型音乐,喜欢在家听还是concert hall。会乐器吗,什么乐器。 2. dancing 会舞蹈吗,中国人喜欢什么舞蹈,传统舞蹈得到了 传承吗 3. photography 喜欢摄影吗,喜欢给别人拍还是别人 给你拍,喜欢收藏照片吗 4. painting 会画画儿吗,小孩子学 习绘画的好处,有什么绘画技巧吗 5. sport 最喜欢什么运 动,好处 6. museum 喜欢去博物馆吗,好处,博物馆该收费吗7. leisure and relaxation 喜欢什么休闲活动,跟谁,在哪 儿,好处,中国人都喜欢什么休闲 8. weekends 如何度过周 末,周末加班吗,老板应该给发工资吗 9. postcards 喜欢 ___吗,发给别人或者收到过吗,跟email的区别 10. public park 喜欢去公园吗,做什么,应该有更多公园吗四科技生活
苏州大学汉语言文学本科函授 “中国现当代文学” 教学大纲 苏州大学文学院 2009年12月
中国现当代文学是高等教育中文专业的一门基础课程,内容包括从“五四”时期到九十年代末的中国主要文学思潮流派及作家作品。 《中国现当代文学》课程的考试内容、考核目标和考试命题,应当充分体现文学课的性质,正确处理中国历史、文学现象和文艺理论三者的关系,充分体现以教材为中心,以考试大纲为导向的基本原则,帮助学生理解教材,解答疑难问题,注意理论联系实际,遵循取精用弘的原则,对作家作品和文学现象给予恰如其分的评价。 《中国现当代文学》课程设置的目的,是为了使学生系统掌握20世纪中国文学的发展线索、文学思潮和流派、主要作家及其代表作品的思想艺术成就,努力提高对中国现当代文学作品的鉴赏水平和分析能力,提升自身的文学素养和审美能力,以更好地推动社会主义文化建设。
第一章五四文学 第一节五四文学革命的兴起与发展 1、了解五四文学经历的三个阶段; 2、掌握五四文学革命的特征。 第二节鲁迅的小说创作 1、了解《狂人日记》的基本内容及其在文学史上的地位; 2、领会《狂人日记》的创作方法; 3、掌握阿Q的人物形象特点; 4、识记《阿Q正传》的艺术风格; 5、了解《呐喊》和《彷徨》中的几种题材类型; 6、掌握《呐喊》和《彷徨》中的人物形象; 7、了解《故事新编》的文学史地位; 8、识记《故事新编》的写作特点。 第三节三种类型小说:问题小说、乡土小说与浪漫抒情小说 1、掌握叶绍均小说的艺术特色; 2、识记许地山初期小说浪漫主义的主要因素及其代表作品; 3、了解许地山创作现实主义转向的标志性作品; 4、领会冰心小说的个人风格; 5、识记郁达夫抒情小说的鲜明特征。 第四节20年代新诗 1、了解初期白话诗创作的主要诗人及其基本特征; 2、掌握徐志摩诗歌创作的艺术特点; 3、领会闻一多诗歌理论的核心内容; 4、了解《女神》的文学史地位及其在新诗史上的意义; 5、领会《女神》的主题内涵;
剑桥雅思口语真题解析 Part 1: 1.1姓名 1. What’s your full name? 2. Can I have your name, please? 3. Are there any special meanings of your name? 4. Do you like your name? Why? 5. Do Chinese people like changing their names? 6. What kind of people in China like changing their names? 7. Is there any rule for Chinese people giving names to their children? 1.2故乡 My hometown is Guangzhou. It is the capital of Guangdong province in the southwest of China. It is a large industrial city. It is close to Hong Kong so a lot of the industries involve trade and retail. It is also a finance area. The people in Guangzhou are very genial and helpful, also are very easy to get around. If you lose your way and ask someone, he will give you the direction immediately, he can also give you a hand if you are in trouble. By the year 2011, it is believed that my hometown Guangzhou has become the economic center of China. 2. Where is it located? 3. How about the climate in your hometown? Which season do you like? In my hometown Guangzhou, the four seasons are not evident, which only has spring and summer. It is too hot in the summer and it is also humid in the winter. I like summer better, for we will go swimming and start our outdoor activities in the summer, it gives us pretty environment, which full of various kinds of colors. Another reason is that it is suitable for traveling around. 4. How about the people in your hometown? The people in my hometown Guangzhou are very genial and helpful, also are very easy to get around. People will always give you a hand with things. If you lose your way and ask someone, he will give you the direction immediately, he can also give you a hand if you are in trouble. 5. What do most people do in your hometown? 6. Oh yes. Even though Guangzhou is very modern, it has some interesting temples and streets. There is one called the Temple of Six Banyan Trees and it was built about 1500 years ago. There is also a famous cultural and commercial street in Guangzhou called Beijing Road. In this street, you can not only see a historic exhibition about different years roadbed, which has more than thousand histories, but also has many business shops sale almost all kinds of things. Besides, you can taste traditional snacks and refreshments or experience temples with /unusual special architectural style nearby. Anyway, it is an interesting place so worth to visit! 7. How about the style of the building in your hometown? 8. What is one of the greatest changes having taken place over the years? 9. What problems still exist in your hometown? 10. How to improve the situation in your hometown? 11. Where is Chinese population mainly distributed? 12. What changes have occurred in people’s dwelling? 1.3学习 1. Are you an employee or a student? (Are you working or studying?) 2. What is your major?
2014年市场营销考试试题及答案 (考试必备) 一、单项选择题(每题1分,共30分) 1. 夏季,“波司登”羽绒服通过打折等促销措施而出现了淡季热销的局面。可见,该厂家深刻领悟到羽绒服的需求属于( ) A. 潜伏需求 B. 充分需求 C. 不规则 需求 D. 过量需求 2. 许多冰箱生产厂家近年来高举“环保”、“健康”旗帜,纷纷推出无氟冰箱。它们所奉行的市场营销管理哲学是( ) A. 推销观念 B. 生产观念 C. 市场营销观念 D. 社会市场营销观念 3. 在微波炉行业,格兰仕占了一半以上的市场份额,财源滚滚而入。根据波士顿咨询集团分析法,微波炉是格兰仕的( ) A. 问号类战略业务单位 B. 明星类战略业务单位 C. 现金牛类战略业务单位 D. 狗类战略业务单位 4. 山东“三联”的主营业务是家电销售,近年将触角伸向餐饮、房地产.旅游等业务,这种多角化增长方式属于( ) A. 集团多角化 B. 同心多角化 C. 水平多角化 D. 关联多角化 5. 同行业中如果有几家企业都实行无差异市场营销,较大子市场的竞争会日益激烈,而较小子市场的需求将得不到满足。这种追求最大子市场的倾向叫( ) A. 市场营销近视 B. 超细分战略 C. 反细 分战略 D. 多数谬误 6. 在春节、中秋节、情人节等节日即将来临的时候,许多商家都大作广告。以促销自己的产品。他们对市场进行细分的方法是( ) A. 地理细分 B. 人口细分 C. 心理细分 D. 行为细分 7. 市场营销管理者采取一系列行动,使实际市场营销工作与原规化尽可能一致,在控制中通过不断评审和信息反馈,对战略不断修正。这种行为称为( ) A. 年度计划控制 B. 赢利能力控制 C. 效 率控制 D. 战略控制 8.“捷安特”自行车公司是“桑塔纳”轿车生产厂的( ) A. 愿望竞争者 B. 一般竞争者 C. 产品 形式竞争者 D. 品牌竞争者 9. 高机会和高威胁的业务属于( ) A. 理想业务 B. 冒险业务 C. 成熟业务 D. 困难业务 10. 王刚正在购买一套两室两厅的单元房,其购买行为应该属于( ) A. 习惯性购买行为 B. 寻求多样化购买行为 C. 化解不协调购买行为 D. 复杂购买行为 11. 某公司在实验设计时,首先选择若干经销商并检查其每周销售情况;然后举办展销会并测量其可能的销售额;最后,将该销售额与以前的销售额相比较,作出最后决策。这种实验设计是( ) A. 简单时间序列实验 B. 重复时间序列实验 C. 前后控制组分析 D. 阶乘设计 12. 为产品大类.企业部门或销售代表确定的销售目标称为( ) A. 企业潜量 B. 市场需求 C. 销售配额 D. 市场潜量 13. 在预测一种新产品的销售情况和现有产品在新的地区或通过新的分销渠道的销售情况时,最好采用( ) A. 专家意见法 B. 市场试验法 C. 时间序列分析法 D. 直线趋势法 14. 企业选择复用包装决策的目的是( ) A. 节约成本 B. 方便顾客购买和使用 C. 通过给消费者额外利益而扩大产品销售 D. 避免某一商品推销失败而影响其他商品的声誉 15. 我国洗衣机行业正处于成熟期,生产厂家可以采权( ) A. 集中决策 B. 收缩决策 C. 快速掠取决策 D. 产品改良决策 16. 相对于黑白电视机而言,纯平彩色电视机属于( ) A. 全新产品 B. 换代产品 C. 改进产品 D. 仿制产品 17. 在为产品线定价时须考虑各产品项目之间相互影响的程度,如果需求的交叉弹性为正值,则此两项产品为( ) A. 互补品 B. 选购品 C. 条件品 D. 替代品 18. 某汽车制造商给全国各地的地区销售代理商一种额外折扣,以促使它们执行销售.零配件供应.维修和信息提供“四位一体”的功能。这种折扣策略属于( ) A. 现金折扣 B. 数量折扣 C. 贸易折扣 D. 促销折扣 19. 有些公司让消费者通过视频信息系统操作一个小型终端,用对讲式闭路电视订购屏幕上显示的商品,这种分销形式属于( ) A. 直接销售 B. 购货服务 C. 自动售货 D. 直复营销 20. 一般说来,批发商最主要的类型是( ) A. 经纪人 B. 商人批发商 C. 代理商 D. 制造商代表 21. 某企业选择仓库设置地点时,使仓库尽可能接近运量大网点,从而使较大运量的商品走相对较短的路程。这种方法被称为( ) A. 重心法 B. 最大运量法 C. 最小运距法 D. 最小运费法 22. 不同的促销工具对购买者知晓.了解.信任和订货等不同购买准备阶段的作用是不同的,其中在信任阶段,对购买者影响最大的是( ) A. 广告 B. 销售促进 C. 宣传 D. 人员推销 23. 在某一特定时期内,不同的人或家庭至少一次展露在媒体计划下的数目称为( ) A. 展露的频率 B. 展露的送达率 C. 展露的影响 D. 加权展露数 24. 企业销售人员在访问推销过程中可以亲眼观察到顾客的反应,并揣摩其心理,不断改进推销陈述和推销方法,最终促成交易。这说明人员推销具有 ) A. 公关性 B. 针对性 C. 灵活性 D. 复杂性 市场营销学试卷第 1 页共7 页
关于电动汽车国内外现状的研究 化学系 0907401班贺绍飞 [摘要] 文章论述了电动汽车的发展过程和技术现状(主要是能源系统(电池技术)的现状),以及国内外电动汽车的发展现状和电动汽车的优缺点,同时对电动汽车技术的发展趋势进行了分析。 [关键词] 电动汽车;能源系统;优缺点 1引言 世界汽车工业的迅速发展,推动了世界经济交通能源工业等各方面的发展,却也带来了很大弊端;燃油造成的大气污染日益严重。加之目前世界石油资源日益枯竭。因此,百余年来作为人类最主要交通工具之一的汽车的动力系统以燃油为根本的地位开始发生动摇,而电动汽车这一无污染且能源又可多样化配置的动力方案已引起世人的普遍关注。 电动汽车的诞生距今已有120年的历史,但长期以来,一直无法解决电池高功率容量及充电等方面的问题,只好让燃油汽车垄断市场。进入本世纪80年代末,节能与环保问题已成为世界各国所关注的主要社会发展问题,进而电动汽车的研究又成为许多发达国家及各大汽车公司的重要发展项目。由于近年来高新技术的飞跃发展,新型高能电池不断开发利用,以及燃料电池的应用成功,使电动汽车进入了一个新的发展时期,开始步入实用化阶段。可以预计,21世纪将是电动汽车风靡全球的新时代。 2电动汽车的发展过程 电动汽车和内燃机汽车同样历史悠久,早在世界第一辆燃油汽车诞生于1886年之前,1881年在法国巴黎街上就出现了世界上第一台电动汽车,它是法国工程师Gusave Trouve装配的以铅酸蓄电池为动力的三轮车。此后电动汽车曾盛行一时,1904年,纽约、波士顿和芝加哥等大城市,有1/3的车辆是电动的,其中不仅有轿车,也有载货车。1915年,美国电动汽车的产量达5000辆。但由于电动汽车的蓄电池太重,充电时间长,每一次充电后的行车路程太短,同时汽油机技术发展趋于完善,其轻便、快速、舒适,一次加油能持续行驶400-500公里,燃料费低廉且价格便宜,由于这些原因,使电动车辆逐渐没落了。然而在20世纪末,随着排放法规的日趋严格,电动汽车的优点便显现出来,同时科学的进步也使电动车辆的实用化成为可能。现代电动汽车绝不是百年前阵旧技术的重复,它是汽车、电力拖动、电子、智能控制、化学能源、计算机、新能源、新材料工程技术最新成果的集成产物。 3电动汽车的技术现状 电动汽车与燃油汽车在外形上没有什么区别,它们之间的主要区别见下表一,其余部分基本相同。
法律英语学习经验 1、法律专业且英语较好,或英语专业,掌握一定法律知识。个人觉得前者比后者更容易学好法律英语。本人属于前者。 2、学习外语最重要的是工具书,学习法律英语也不例外,拥有一本好的工具书是非常重要的。下面推荐几本很不错的工具书。 (1) Black’s Law Dictionary (7th版) 布莱克法律辞典(第七版),1999年出版,共1738页,英文原版,价格697元,网络上有卖的。大些的法律书店也有卖的。 (2)牛津现代法律用语辞典 法律出版社引进的英文原版,共953页,价格170元。该书主要是对一些法律词语进行了语法、语义上的分析,比如同义词、近义词比较,一些词语的拼写不同等。 (3)元照英美法词典 价格是380元,质量在国内同类工具书中算是最好的,但也存在一些错误和不足。详见本论坛帖子《元照英美法词典》求疵。 以上三本工具书是我用过的,都很不错。下面是我没用过的,但其他专家推荐的: (4) Oxford Law Dictionary 牛津法律词典 (5) Merriam-Webster’s Law Dictionary 1996年版,16美元。 此外陈忠诚所著《英汉汉英法律用语辩证词典》也不错,有真材实料。至于其他的英汉、汉英法律辞典,最好别买,大概都是剪刀加浆糊的产物;人云亦云,有很多错误的,误人子弟。 宋雷也主编过一大部头的、与元照同样规模的法律英语词典,其内容还未仔细研读,在此不作评论。 如果大家没钱,可以用网上词典,在此推荐https://www.doczj.com/doc/d716922988.html,,很不错的词典搜索引擎。
3、多读英文原版教材和文章,理解词的具体运用和英美法律制度,扩大词汇量。 4、多看他人有关文章、著作及有关法律的正式英文译本,去伪存真。前提是你的知识量足够大,能一眼看出其真伪对错。《中国翻译》、《上海翻译》、《中国科技翻译》经常刊载法律翻译方面的文章,可惜多为泛泛之作,少见精品。 关于如何学好法律英语,我的经验大体就这些。但如果要作一个好的法律翻译,这些显然是不够的,这又是另外一个话题了。 关于如何学好法律英语,每个人的基础不一样,学习的习惯也不一样,所以很难有一个"万精油"的方法。 这里仅有几点个人经验,供参考: 1.坚持看原版的法律新闻,最好的地方如下: https://www.doczj.com/doc/d716922988.html,/ ,如果上网方便,最好每天去一次,哪怕是时间只够把新闻标题看完…… 2.坚持用原版的法律词典,最好的当然是black’s law dictionary,不过,这两个地方的法律词典也不 错:https://www.doczj.com/doc/d716922988.html, ,https://www.doczj.com/doc/d716922988.html, .当然,刚开始用原版的法律词典可能有些不习惯,从长远来看,这是非常有好处的。 3.坚持读原版的法律书籍, 4.坚持听原版的法律节目,cnn和abc及bbc每周都有与法律有关的节目,这些节目网上也可以收听,只不过要通过代理服务器,还好,这个网站可以访问:https://www.doczj.com/doc/d716922988.html, , 只是这里的节目没有原文对照,听起来有些难。还有一些:坚持分析原版的案件,坚持用英语写读书笔记和日记,坚持用英语思考,用英语和朋友,和