
Design and Implementation of a Joint Data Compression and Digital Watermarking System in an MPEG-2Video Encoder
Tsung-Han Tsai &Chih-Yen Wu &Chih-Lun Fang
Received:30March 2012/Revised:7May 2013/Accepted:7May 2013/Published online:18June 2013#Springer Science+Business Media New York 2013
Abstract With the rapid distribution of digital video cap-ture devices,significant videos can be captured effortlessly.The captured videos are often saved in moving pictures expert group-2(MPEG-2)format.To prove copyright own-ership,applying watermarking in MPEG-2videos is neces-sary.However,little research has been devoted to the watermarking design not only for the spatial domain but also for the frequency domain and the realization of watermarking hardware.Thus,a joint data compression and watermarking system with configurable spatial and frequency domain embedding,and its very large scale inte-grated circuit (VLSI)architecture is presented in this paper.First,after analyzing the characteristics of videos,a novel watermarking system with two number-based keys and a shuffled image is built.It is based on the spread spectrum techniques and adaptive human visual system (AHVS).With a consideration of the cost and easiness of use,the proposed system is realized as blind detection which can dispense without the storage of the original-multimedia data.Second,the efficient VLSI architecture of our ap-proach is designed.Various subjective and objective evalu-ations are performed for watermarking analysis.From the evaluation,it is realized that the system can achieve robust watermarking with high flexibility for joint data compres-sion and low hardware complexity.Various attacks and
comparisons also show the efficiency of the proposed watermarking scheme.Furthermore,the VLSI synthesis re-sults demonstrate the high performance of the proposed architecture.Thus,the proposed system is adequate for a specific function intellectual property (IP)combined with a real-time video capture and a surveillance system.Keywords Blind detection technique .Intellectual property .Watermarking system .Watermarking very large scale integrated circuits
1Introduction
In the recent years,digital video capture devices have been more and more popular.These devices help users capture and record significant videos.Since moving pictures expert group-2(MPEG-2)video compression standard has been widely used for the high-quality purpose,the captured videos are often saved in MPEG-2format.Furthermore,to prove copyright ownership,the ownership declaration is em-bedded into the MPEG-2videos when capturing and encoding.In conventional embedding,a visible logo is put on a video frame.Since video content can be modified,distributed,and exchanged,the logo is easily destroyed.To enforce owners ’copyright,the recent proposed digital watermarking technique could be a viable solution to the authentication of multimedia data.However,most water-marking research focuses on still image watermarking.Very little research attention has been devoted to the design of a watermarking algorithm and its hardware in an MPEG-2video encoder.Therefore,a request of designing a joint data-compression and digital-watermarking system in an MPEG-2video encoder has become.
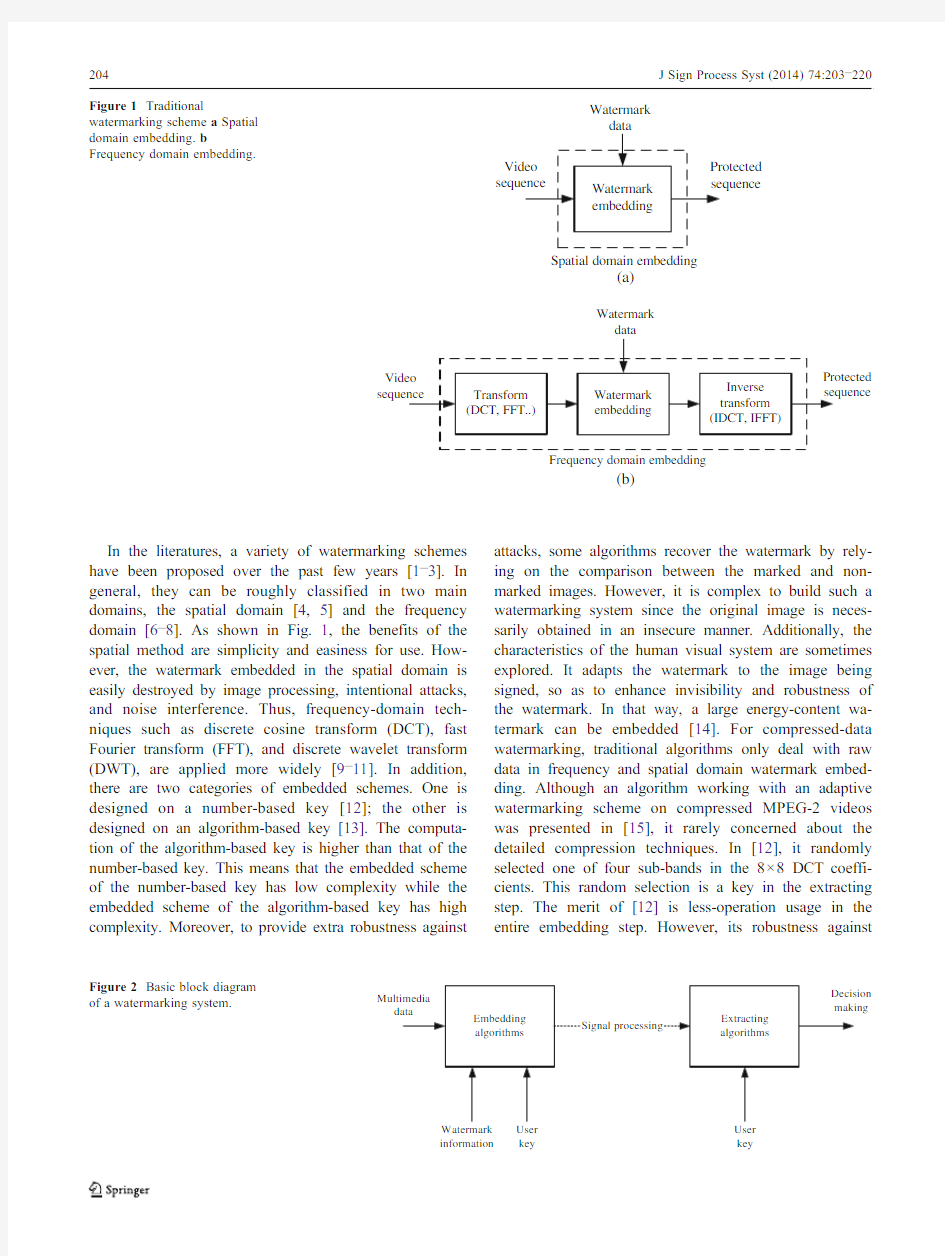
T. Department of Electrical Engineering,National Central University,Taiwan,Republic of China e-mail:han@https://www.doczj.com/doc/b810294369.html,.tw C. e-mail:ch_lai@https://www.doczj.com/doc/b810294369.html,.tw C. e-mail:allen@https://www.doczj.com/doc/b810294369.html,.tw J Sign Process Syst (2014)74:203–220DOI 10.1007/s11265-013-0772-0 In the literatures,a variety of watermarking schemes have been proposed over the past few years [1–3].In general,they can be roughly classified in two main domains,the spatial domain [4,5]and the frequency domain [6–8].As shown in Fig.1,the benefits of the spatial method are simplicity and easiness for use.How-ever,the watermark embedded in the spatial domain is easily destroyed by image processing,intentional attacks,and noise interference.Thus,frequency-domain tech-niques such as discrete cosine transform (DCT),fast Fourier transform (FFT),and discrete wavelet transform (DWT),are applied more widely [9–11].In addition,there are two categories of embedded schemes.One is designed on a number-based key [12];the other is designed on an algorithm-based key [13].The computa-tion of the algorithm-based key is higher than that of the number-based key.This means that the embedded scheme of the number-based key has low complexity while the embedded scheme of the algorithm-based key has high complexity.Moreover,to provide extra robustness against attacks,some algorithms recover the watermark by rely-ing on the comparison between the marked and non-marked images.However,it is complex to build such a watermarking system since the original image is neces-sarily obtained in an insecure manner.Additionally,the characteristics of the human visual system are sometimes explored.It adapts the watermark to the image being signed,so as to enhance invisibility and robustness of the watermark.In that way,a large energy-content wa-termark can be embedded [14].For compressed-data watermarking,traditional algorithms only deal with raw data in frequency and spatial domain watermark embed-ding.Although an algorithm working with an adaptive watermarking scheme on compressed MPEG-2videos was presented in [15],it rarely concerned about the detailed compression techniques.In [12],it randomly selected one of four sub-bands in the 8×8DCT coeffi-cients.This random selection is a key in the extracting step.The merit of [12]is less-operation usage in the entire embedding step.However,its robustness against Spatial domain embedding Watermark (a) Watermark Frequency domain embedding (b) Figure 1Traditional watermarking scheme a Spatial domain embedding.b Frequency domain embedding. information key key Figure 2Basic block diagram of a watermarking system. compression attacks should be considered.The applica-tion of watermarking to control the access of videos was realized in[16].In[13],it modifies the AC coefficients of a set of8×8DCT blocks for image and video embedding. When embedding a watermark in a captured video, the watermark should be hard to remove.This means that the designed watermarking algorithm in an MPEG-2video encoder has to be robust under various attacks. With respect to the spatial or frequency domain embed-ding,if users want to encode the videos with fast processing and lower security,the captured videos are watermarked in the spatial domain.Otherwise,the cap-tured videos are watermarked in the frequency domain. Thus,video watermarking in an MPEG-2video encoder needs an efficient algorithm and hardware architecture not only for the spatial domain but also for the frequen-cy domain.The merit for both spatial and frequency domain is that the embedding system has multiple ap-plications by employing a single algorithm and hard-ware without other cost.In addition,since the designed hardware should be combined with the existing com-pression module,the architecture has to be designed in a low-complexity manner. Obviously,hardware design on a watermarking system is an important issue.Mathai[17]provided the hardware im-plementation perspectives on a video watermarking algo-rithm,but essential hardware information such as the architecture or gate count is not explored.In[18],a combi-nation of a digital still camera(DSC)and a watermarking algorithm is presented.It provided a comprehensive descrip-tion on system-level design;however,it only dealt with the image domain instead of the video domain.In addition, although memory cost is one of the most important issues in many multimedia and consumer applications,there is no description about memory cost in the existing related research. With the drawbacks in existing research,it motivates us to design a robust and configurable watermarking system joined with MPEG-2video compression standard. The proposed watermarking scheme in this system is based on the characteristics of videos,the spread spec-trum techniques,and adaptive human visual system (AHVS).To identify the watermark clearly,an image-based watermark is applied in our system.With the novel watermarking scheme,an efficient watermarking architec-ture based on several advanced techniques is designed. The main contribution of this system is its robustness, low complexity,and configuration in watermark embed-ding.This system is designed not only for frequency embedded watermarking(FEW)but also for spatial em-bedded watermarking(SEW).The entire design was implemented by HDL synthesis with TSMC1P6M 0.18μm standard cell to show the physical performance. This system can be extended adequately and combined with present video coding standards,such as MPEG-1/2/4,H.26x,and Motion JPEG to realize an intellectual Table1The analysis of watermarking functions in traditional and proposed methods. Function[4][5][7][8][19]Ours Comment on advantages Spatial embedded watermarking Yes Yes No No No Yes Fast processing and easy for implementation Frequency embedded watermarking No No Yes Yes Yes Yes High robustness against attack Joint data compression No No Yes No Yes Yes Share the same hardware Visual watermark No Yes No No Yes Yes Easiness and reliability of judgement Number-based key No Yes No No Yes Yes Low computational complexity Blind detection Yes Yes No No Yes Yes Low memory storage Figure3Proposed watermark embedding algorithm. protection (IP)in real-time video capture and surveillance system applications. This paper includes six sections.Section 2describes the background of the watermarking techniques.Section 3pre-sents the proposed watermarking scheme.In Section 4,the design of the architecture is shown.In Section 5,the simu-lation results of the algorithm is provided and discussed.Finally,conclusions are drawn in Section 6. 2Background of Watermarking Techniques Watermarking research has been widely explored with various aspects.For clear illustration,the basic block diagram of the watermarking system is shown in Fig.2.Multimedia data means the plaintext of data such as audios,images,and videos.These data can be the pixels or the coefficients of a sequence.Watermark information indicates the ownership of multimedia data.It can be divided into two kinds of patterns.One is the single bit number or binary sequences [7];the other is rectangles of visual patterns [4].For the single bit number sequence,some techniques are used with the spread spectrum tech-niques to generate the pseudo noise (PN)code as a watermark.For visual patterns,this target is to embed a small image into multimedia data.With the visibility,it is easy and reliable to judge if the watermark exists or not.Visual patterns are also shuffled based on the consider-ation of security.Therefore,some chaotic functions and interleaving mechanisms are applied to those visual pat-terns.The watermark embedding algorithms are classified in two main categories:embedding in the spatial domain and embedding in the frequency domain.In spatial do-main embedding algorithms,a pseudo random set of pixels is selected.The least significant bits of their inten-sity levels are modified to form a statistical property which describes the set of watermark pixels.The benefit of this method is its fast processing and easiness for implementation [4,5].In frequency domain embedding algorithms,a small subset of the frequency spectrum in particular blocks is modified.This subset which belongs to the medium range of the spectrum is processed with perceptual invisibility.The advantage is its robustness in compressed-data embedding [6–8].In addition,a private user key is applied to encrypt and decrypt the watermark information.The key is needed in the embedding and extracting steps.This means a user can not extract the watermark without this key [19].When transferring multi-media data,watermarked multimedia data will be distorted with two kinds of processing.One is typical distortion such as analog/digital and digital/analog conversion,or data com-pression.The other is an intentional attack by a hacker.After the distortion processing,the watermarked data is different from the original data.The quality of the watermarked data is also unavoidably decayed. Extracting algorithms can be classified into blind and non-blind detection.In the extracting step on non-blind detection,the system recovers the watermark by the defined threshold.In this detection,the possibility to access the original multimedia data must be granted.The access of the original multimedia data complicates the setup of the watermarking system and forces the owner of the multimedia data to share it in an insecure manner.Blind detection means that the original multime-dia data is not needed in the extracting step.In this situation,the watermark is extracted by a specified key.In general,the information generated from the specified key has a high correlation with the watermarked data,eg: Table 2The reiteration (T )of Toral operation for retrieving the original image.K 1 2 3 45 6 7 89 1011121314151617181920212223242526272829303132333435 T 4024286203021824703012124240404212123070248 4215206 282440703 4 6 35 (a) (b) Length of PN code vs. BER Frame number B E R Length of PN code vs. PSNR Frame number P S N R Figure 4a The relationship between the lengths of PN code and BER.b The relationship between the lengths of PN code and PSNR. communication-based watermarking [20].Thus,the wa-termark can be distinguished by the correlation between the watermarked data and the information generated from the specified key.After performing extracting algorithms,a decision is made whether a watermark exists or not by computing the correlation between the extracted and the original watermark.In summary,the functions of various watermark embed-ding methods are analyzed in Table 1in detail.The analysis indicates that the method based on spatial/frequency embed-ded watermarking,joint data compression,visual water-marks,number-based keys,and blind detection has more advantages.Therefore,to enhance the robustness and effi-ciency,a novel watermark embedding system was designed Mapping area Mapping area (a)Mapping area for FEW (b) Mapping area for SEW Figure 5The embedded mapping area in the k-th 8×8block for FEW and SEW.a Mapping area for FEW,b Mapping area for SEW. 44 1320 1(a) (b) 500 40030020010001002003004005006007008009001301601901 1201 -----(c) Block number A m p l i t u d e Figure 6The analysis of edge blocks.a 8×8non-overlap blocks in a frame.b Edge blocks in a frame.c Amplitude analysis of blocks. based on these functional considerations and proposed in the following section. 3Proposed Watermark System A novel watermarking system based on the combination of the AHVS and the spread spectrum with the encryp-tion technology is proposed in this section.To achieve the configurable embedding,the proposed watermark em-bedding system is designed for the joint data compres-sion.The consideration of joint data compression is that by using the shared transform kernel,it can apply the frequency domain embedding without the overhead of the transform hardware.Additionally,joint data compression can not only reach the low hardware cost like spatial domain embedding,but also acquire the high robustness against compression of frequency domain embedding.In the proposed watermark embedding,each video frame is divided into non-overlap 8×8blocks initially.Then,an adaptive modulated signal is embedded into the spatial or frequency domain of each frame according to the AHVS model.The detailed embedding process is presented in Section 3.1,and the adaptive embedding is described in 0.0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 2 4 6 8 10 12142 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 F r a m e N u m b e r (a) 0.000.020.040.060.080.100.120.140.160.18 2 46810 12142 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 F r a m e N u m b e r (b) B E R T h e p e r c e n t a g e o f P S N R d e g r a d a t i o n α α Figure 7The objective quality relationship between a αversus BER.b αversus PSNR. Section 3.2.For extracting a watermark,a blind detection based on the correlation of the watermarked data and the information generated from the key is proposed in Section 3.3.3.1Proposed Watermark Embedding Algorithm The aim of watermark embedding is to hide some copyright information in videos against attacks.Thus,the proposed embedding process is based on the consideration of robustness.There are three steps in our embedding flow.Details are described below and illustrated in Fig.3.Step1:A visual watermark image is read and performed by binary transform.The reason of applying a visual watermark image is that the ownership of one video can be reliably recognized by the watermark image even under various attacks.After performing binary transform,Toral ’s auto-morphism [21]is used as a chaotic function to shuffle the binary map and pixel positions of the watermark image.The new position of a pixel by the chaotic function is defined below: x s y s ?1k 1k t1 x y mod N e1T where x s and y s are the horizontal and vertical positions of a pixel in the shuffled watermark image,x and y are the horizontal and vertical Figure 8Proposed watermark extracting algorithm. Figure 9Joint MPEG-2encoder with the proposed embedding algorithm where part A means the SEW flow and part B means the FEW flow. Figure 10Top view of the watermarking IP. positions of a pixel in the original image respec-tively,k is the parameter in Toral ’s automor-phism,and N denotes the number of pixels in the watermark image.The manual parameter specification of k defined in (1)cannot be avoided.However,various numbers of reitera-tions are required to obtain the original image with different k values.Thus,reasonable k values from 1to 35are analyzed as shown in Table 2.It indicates that k determines the number of re-iterations (T )of obtaining the original image.For example,when k value is 11,it needs 30re-iterations to obtain the original image.Therefore,the number of reiterations can be defined as a key and denoted as KeyT.In addition,an error correction code technique,Bose-Chaudhuri-Hocquenghen (BCH)code,is also applied to improve the robustness.In BCH,the length of a message sequence is seven bits and the length of a code word is 15bits after encoding.The manipulation of BCH is represented as BCH<15,7>.Thus,the total number of watermark in-formation bits is 35×35×15/7=2625for a water-mark image with the size of 35×35pixels.After BCH coding,the shuffled image is sent to AHVS based embedding. Step2:To enhance the robustness,a pseudo noise (PN) sequence is applied,denoted as KeyP,and performed as a user key.The KeyP is manipulated to generate a PN code.Since the length of the PN code is an important factor in the watermark em-bedding system,the relationship between lengths of PN codes,bit error ratio (BER),and objective frame quality by PSNR is analyzed as shown in Fig.4.Obviously,the longer the length of the PN code,the higher the BER.In addition,the quality also suffers from the increasing length of the PN code.Thus,the PN sequence (KeyP)is defined as a 12-bit binary data in our system.For spatial and frequency domain embedding,the length of the PN code is 63and 31bits after performing the pseudo noise generator respec-tively.The reason for the different length in the spatial and frequency domain is that low robust-ness occurs in spatial domain embedding.Thus a longer key length than frequency domain embed-ding is required.This PN code is also sent to AHVS based embedding. Embedded Figure 11Watermark embedded system architecture. Step3:After generating the shuffled watermark and the PN code,it is necessary to embed this information into videos for FEW and SEW.Based on the exploita-tion of human visual characteristics,an AHVS inserting function for watermark information is proposed.This function is defined below: w i ?1?P j ;if B k ?0 ?1?P j ;if B k ?1 e2T v i 0?v i tα?w i e3T where w i is the i -th bit value of the modulated watermark,P j is the j -th bit value in the PN code,B k is k -th bit value in the shuffled watermark after BCH coding,v i ′is the i -th pixel value or coefficient value in the k -th block after inserting the watermark,v i is the i -th pixel value or coefficient value in the k -th block before inserting the watermark,and αis the evaluated weighting value.Obviously,the k -th bit value in the shuffled watermark dominates the k -th block embed-ding.From (2),it indicates P j is modulated by B k .If B k is zero,P j is unchanged.However,if B k is one,P j is multiplied by minus one.The relationship between i,j ,and k is illus-trated in Fig.5.The numbers in the k -th 8×8blocks are the index of pixels,which indicates i .j is the index of pixels in the mapping area of the k -th 8×8blocks.For example,in FEW,the third modulated bit in the PN code is embedded into the fourth pixel in the block.Based on the consideration of AHVS in videos,we take the evaluated weighting value into account.The details about the definition of the weighting value are discussed in the next section.3.2Adaptive Embedding with Different Blocks Human visual sensitivity is different for each image.According to this property,the adaptive weighting modulat-ed signal is embedded into each block.In general,the Watson ’s DCT-based visual model [14,22]is manipulated but it is too complex to be implemented.Based on a con-sideration of low complexity,an edge detection model is proposed as follows: If C k 0;0? >T 1and C k 0;1? tC k 1;0? tC k 1;1? eT>T 2Then T B k ?edge block Else T B k ?non ?edge block e4T where C k [0,0]denotes the DC coefficient in the k -th block.C k [0,1],C k [1,0],and C k [1,1]are the three AC coefficients neighboring the DC coefficient in the k -th block.TB k rep-resents the k -th block in a frame.T1and T2are the DC and AC thresholds respectively.The edge block means a block has edge characteristics.In order to obtain the T1and T2in (4),various test sequences with the frame size of 352×240are divided into 8×8non-overlap blocks and transformed into the frequency domain.The three highest AC values of each block in a video frame are summarized and analyzed as the threshold.Figure 6shows one example of these test sequences.Obviously,the sum of three highest AC values in edge blocks is larger than 80.Therefore,from the analy-sis,the threshold of T1and T2are defined as 700and 80respectively. After the blocks are classified,the evaluated weighting value αin (3)is analyzed according to the objective quality relationship between the PSNR and the BER.All of the analysis is conducted under an MPEG-25Mb/s encoding platform.In Fig.7(a),αis simulated from 1to 16.This shows that the optimized weighting value of αis approximated from 4to 12depending on the expected BER.In Fig.7(b),the quality decay is evaluated further.Based on these data,we select an imperceptible weighting value,α=4,for non-edge blocks with a quality decay of 2~4%.In addition,the value of αis defined as 16for edge blocks.Although there is some flicker degradation in (a) d 1i w1Figure 12a DPIC module design.b Processing Element (PE)unit. (a) PN PN (b) (c) Memory2 Memory1 Figure13a PNBSM module. b PRBS sub-module design. Mode indicates SEW or FEW c Modulator sub-module design. SIG (Shuffled image) Figure14Shuffled Image Generator(SIG)module. video,the blocks can still be classified by the single frame processing. 3.3Proposed Watermark Extracting Algorithm After embedding the shuffled watermark into videos,the watermark is in need of being extracted by KeyT and KeyP.With the proposed embedding algorithm in Section 3.2,the corresponding extracting algorithm is depicted in Fig.8.First,the embedded Y-component frame is divided into non-overlap 8×8blocks,and the PN-code generator pro-duces the PN code from KeyP.Second,blind detection is performed to obtain the BCH sequence with the PN code.Due to the high dependency upon the magnitude of the extracted vectors,a cross-correlation is manipulated,where the correlation coefficient is obtained by subtracting the means of the two vectors before computing the normalized correlation between them.The proposed correlation is de-fined as follows:e v i ?v i ?v e5T e w i ?w i ?w e6T cc v ;w eT?nc e v ;e w ?X i e v i ?e w i ????????????????????????????????????????????X i e v i ?e v i X i e w i e w i s e7T where v i and w i are the pixel values or coefficient values of the non-overlap 8×8block and the PN code.v is the mean of the pixel values or coefficient values in the non-overlap 8×8block.w is the mean of the PN code.i denotes the index of the pixels or coefficients in the non-overlap 8×8block and the PN code https://www.doczj.com/doc/b810294369.html, is the cross correlation and nc is the normalized https://www.doczj.com/doc/b810294369.html, (v ,w )in (7)can be simplified as the cosine of the angle between the vectors.Thus,the correlation coefficient can be interpreted as the inner prod-uct of e v i and e w i after each has been normalized to a unit magnitude.Since the interpreted coefficient is bounded be-tween ±1,the blind detection is processed as follows: B k ? 1;if cc k v ;w eT>threshold 0;if cc k v ;w eT e8T where B k is the k -th bit value in the shuffled watermark,cc k (v ,w )is the normalized correlation of the k -th block,and the threshold denotes the median of the range of the coeffi-cient,which is defined as zero.When B k is one,it means the pixel value of the shuffled image is one.Otherwise,it means the pixel value of the shuffled image is zero.Third,after extracting the shuffled image,the BCH decoding is performed and Toral ’s automorphism is executed by KeyT with a natural number.Finally,the visual watermark pattern is generated. 4VLSI Architecture Design 4.1System Architecture The target of the proposed watermarking design is to build up a functional intellectual property (IP)which can be combined in the MPEG-2encoder.Since the MPEG-2encoder is mature in hardware design,we can only ad-dress on the new watermarking algorithm and its VLSI design.The overall system block is shown in Fig.9.SEW and FEW perform the same watermark embedding algo-rithm proposed in Section 3.1.It schematizes that by using the common transform kernel DCT in compressed and watermark embedded domains,it can embed an image logo into the video sequence without extra computation overhead when compressing.Figure 10illustrates the top view of the watermarking system.The number of bits of the input and output in the watermarking system is pro-vided.As illustrated in Fig.11,the system architecture contains three main modules.The first module is the data path and inserting component (DPIC),where P j means the generated PN code and B k means the shuffled image.The second module is the pseudo noise binary sequence mod-ulator (PNBSM)for two lengths of the PN code,63and 31bits.The third module is the shuffled image generator (SIG)with a chaotic and error correction function. Table 3The execution cycle comparison of different RAM types. RAM type Execution cycle Dual-Port RAM KeyT×N 2 Synchronous RAM (KeyT+1)×N 2+1 Frame number B E R Figure 15Robustness for two embedding modes against compression attack. 4.2Module Design The architecture of DPIC is shown in Fig.12.The process-ing order is block by block,and each block is a total of 64pixels or coefficients.Edge blocks and non-edge blocks which are multiplied by the different weighting value are determined by the first ten loaded coefficients of each block.In order to speed up the performance,eight processing elements (PE)are used as parallel processing.In Fig.12(a),w n means the bit of the watermark to the n -th PE,d n means the pixel to the n -th PE,and ED n indicates the clock to the n -th PE.In a PE,a shifter register and a barrel shifter manip-ulate the pixel and the bit of the watermark,respectively.The result is generated after 16clock cycles of latency. The architecture of PNBSM is illustrated in Fig.13.The m-sequence technique is used as the PN code gener-ator.This module produces two different binary sequences with 2m -1bit length by 12-bit length KeyP.SIG[0]means the bit of the shuffled watermark is zero and SIG[1]means the bit of the shuffled watermark is one.These two watermark bits modulate the PN code sequence.Two sub-modules of pseudo random binary sequence (PRBS)are used and shown in Fig.13(b).It is designed as a feedback shift register and configured with different length of the PN code,where 25-1and 26-1bits are used for frequency and spatial domain embedding respectively.Modulator is also the sub-module in PNBSM and depicted in Fig.13(c).Finally,the modulated sequence is sent to DPIC module. The architecture of SIG is shown in Fig.14.The Toral ’s automorphism and BCH <15,7>binary code are implemented in this module.Two 1344×2bits dual-port memory are used to store and swap shuffled bits.The reason of using dual-port memory is provided in Table 3.From the random access memory (RAM)comparison in Table 3,it can reduce the latency of the shuffled image generation by applying the dual-port memory.It shows the execution cycle is reduced with N 2cycles in the dual-port RAM,where N 2is the number of bits in a watermark image.In addition,we apply some low pow-er and area reduction design techniques.By using the look-up table method,it can replace the vector multipli-cation and modulo computations in (1)to save the hardware area.We also apply the gated clock technique to save power dissipation in the memory writing cycle.Although it needs KeyT ×N 2cycles for preparing the shuffled image with an N 2bits watermark image,this overhead could be ignored because the shuffled image generation shares the same time with the video se-quence loaded into the frame memory. Robustness improvement 5Mb/s MPEG-2 encode/decode Frame number B E R Figure 16Robustness improvement with adaptive embedding and error correction code (ECC). Frame number Algorithm comparison 0.050.10.150.20.250.30.35B E R Figure 17Comparisons of several watermarking systems. 5Experiment Results and Discussion In our simulation,an image logo,National Central Univer-sity,is embedded on each video frame to achieve continu-ous copyright protection.With reference to compression corruption,the results are measured under the MPEG-2 with5Mb/s encoding platform.The number of frames in a group of pictures is15and the distance between the I and P frame is three.The embedded watermarking system can be configured as two modes,SEW and FEW.Several video sequences which are often used in other video research are simulated in our system.Except some subjective evalua-tion,the system performance is widely and objectively evaluated from various aspects.They are security,robust-ness,and imperceptibility.Additionally,the proposed watermarking architecture is implemented by HDL to real-ize the gate count,chip area,and power of consumption. 5.1Security Consideration In order to enhance the security,there are two keys used in the proposed watermarking system.One is KeyP with a12bits binary number generating a spec-ified PN code,and the other is KeyT with a natural number to shuffle the watermark image.The PN code depends on an image logo bit and spread on an embed-ded signal.The ownership logo can be extracted if and only if both keys are acquired.There are212*T kinds of various permutations and combinations,where T tends to infinity.With this extremely large set of key value, this means that our proposed method has high security against intentional attacks. 5.2Robustness Analysis To analyze the robustness,several attacks are performed in our embedding system.They are compression attacks and noise attacks.The robustness against these attacks is evaluated by bit error ratio(BER),which relies on the difference of each pixel.For compression attacks,the BER under MPEG-2with5Mb/s encoding/decoding attacks is shown in Fig.15.The BER is below0.18in both SEW and FEW modes under compression attacks. In addition,our approach applies two techniques to Table4The comparison of the security and computational complexity.Method Security Embedding watermark Computational complexity Ours2Number-based keys35×35bytes shuffled image Low [12]1Number-based key64bits shuffled information Low [13]Algorithm-based key33bits shuffled information High (a)(b)(c) (d) Robustness against Gaussian noise attack Frame number B E R Figure18Gaussian noise attack test.a Original uncorrupted I-frame.b Subjective view with variance=0.1and mean=0.c Subjective view with variance= 0.5and mean=0.d Gaussian relationship between BER and each frame. increase the robustness against compression attacks.The first is the proposed adaptive embedding technique in AHVS to enhance the robustness.Two cases of AHVS are selected for simulation.One is a pair in which the edge block is α=11and the non-edge block is α=5.The other is a pair in which the edge block is α=16and the non-edge block is α=4.The second technique is apply-ing the BCH <15,7>of error correction code in the watermark information.From Fig.16,it is evident that the robustness is improved with these techniques. The compression-attack comparisons were made be-tween the proposed and the traditional works in [12]and [13].The energy summation is compared between two sub-sets of M /28×8DCT blocks,where M is the number of 8×8DCT blocks.The compressed data is with the same label bit of 65bits in a single frame.An example about Football sequence is shown in Fig.17.It is realized that the BER can be greatly reduced with 0.01to 0.03 (a) (b) Robustness against pepper & salt noise 00.050.10.150.20.250.31 3 5 791113 15 Frame number B E R Density=0.05Density=0.06Density=0.07Density=0.08Density=0.09Density=0.1 Figure 19Pepper &salt noise attack test.a Subjective view with density =0.1.b Pepper &salt noise relationship between BER and each frame. (a) (b) (c) Robustness against speckle noise 0.02 0.040.060.08 0.10.120.140.160.18Frame number B E R Figure 20Speckle noise attack test.a Subjective view with variance =0.01.b Subjective view with variance =0.05.c Relationship between BER and each frame. Frame number Robustness against Stirmark attack A v e r a g e P S N R Figure 21Average PSNR of several sequences in Stirmark attack. compared with[13].By transforming BER to the number of error pixels,it can reduce12to36error pixels of an image with the size of35by35in comparison with[13]. In addition,our approach can be applied for both spatial and frequency domains,whereas[13]is only applied for the frequency domain.Thus,it can be seen that our approach has the lower BER,higher robustness,and su-perior flexibility.Furthermore,the comparison of the se-curity and computational complexity is shown in Table4. Since our approach is designed based on2number-based keys and a shuffled image with the size of35by35,our method has higher security and lower complexity. For a noisy environment,we choose four different kinds of noise attacks,additive noise,pepper&salt, speckle noise,and Stirmark attacks.First,the additive noise is independent from the multimedia data.This kind of noise is directly added into luminance of images,such as Gaussian white noise.The test sequence is attacked under compression/decompression with various Gaussian white noises.The mean is0,and the variance is from0.1 to0.5.From the results in Fig.18,a logo is detected and propagated from I to P and B frame.When the variance is below0.5,all of the BER are below0.35.This means that the robustness against the additive noise attacks is accept-able.Second,pepper&salt noise is also independent from the multimedia data.This noise changes partial pixels value to saturation in the image frame.The noise density was adjusted from0.05to0.1.The results are provided in Fig.19.Since the BER is below0.27in all the test noises,this indicates that the robustness against pepper&salt noise attacks is acceptable.Third,speckle noise is dependent upon multimedia data and changed on luminance value of images.The variance of the speckle noise was adjusted from0.01to0.05.The robustness against speckle noise attacks is shown in Fig.20.The BER is below0.16in all test noises.Fourth,since Stirmark is the benchmark for testing the robustness of watermarking,the proposed algorithm is unavoidable un-der this attack.The Stirmark contains a noise attack,JPEG attack,rescale attack,and rotation attack.The results of examples against these attacks are shown in Fig.21.Most of average PSNRs are larger than19.8dB for all of the attacks in Stirmark.It means that the proposed method can resist the Stirmark attatcks. 5.3Imperceptibility Evaluation Subjective and objective measurements are performed in this evaluation.The objective test is not only compared with the PSNR of each frame,but also checked with the file size to reveal the overhead of watermark embed-ding.Table5presents the quality comparisons for non-embedding and two proposed embedding modes.Qual-ity degradation in the SEW is more severe than it in the FEW.This result conforms to the methodology of the proposed watermarking method,that SEW is designed for relatively high speed and low quality while FEW is designed for relatively low speed and high quality. Table5PSNR comparisons for non-embedding and two embedding modes. PSNR comparison Test sequence(352×288)Without embedding SEW FEW I(db)P(db)B(db)I(db)%P(db)%B(db)%I(db)%P(db)%B(db)% Football41.537.136.438.8 6.50635.5 4.31334.2 6.04440.9 1.44635.7 3.77435.0 3.846 Garden37.835.534.736.1 4.49733.7 5.07032.9 5.18737.3 1.32333.6 5.35232.7 5.764 Tennis38.139.038.437.1 2.62538.3 1.79537.7 1.69537.80.78738.1 2.30837.2 2.999 Aykio48.850.649.545.7 6.35246.58.10346.6 5.85946.6 4.50848.7 3.75547.7 3.636 Fish48.243.141.444.87.05439.87.65738.17.97145.7 5.18740.3 6.49738.08.213 Child47.744.142.243.58.80541.6 5.66940.0 5.21345.3 5.03140.58.16338.39.242 Table6Number of bit with watermark images for different sequences. Number of bits after embedding Test sequence (352×288)Without embedding (byte) SEW (byte) Percentage (%) FEW (byte) Percentage (%) Football209,074208,816?0.123%208,988?0.041% Garden207,963207,917?0.022%207,878?0.041% Tennis208,567208,407?0.077%208,499?0.033% Aykio208,625208,6560.015%209,0600.209% Fish209,094209,2150.058%209,2680.083% Child208,444208,5020.028%208,5700.060% From Table 6,based on the m-sequence balance prop-erty for spreading the embedded bits,the total number of increased or decreased bits is not more than 0.209%of the original non-embedded file size.We also make the subjective test for each frame type I,P,and B frame in Fig.22.It seems that no obvious subjective difference occurs after watermark embedding.5.4HDL Simulation The overall design is implemented with the cell-based de-sign flow and synthesized by the Design Compiler and SoC Encounter with TSMC 0.18um 1P6M standard cell library.The percentage for individual hardware module area is shown in Fig.23.All of the results are verified with the result of a high level C program.The chip specification is provided in Table 7.The proposed watermarking architec-ture requires 4729.8gate count and 3.21mW power under 100Mhz.The core size is only 1.199×1.190mm 2.In addi-tion,the watermarking throughput of the proposed system reaches 190.73megabytes per second.Furthermore,the chip physical layout is illustrated in Fig.24.It clearly in-dicates that DPIC,PNBSM,and SIG modules are well designed and implemented. (a.1) o riginal I-frame (b.1) marked I-frame (c.1) extract logo with NC=0.9539 (a.2) o riginal I-frame (b.2) marked I-frame (c.2) extract logo with NC=0.9637 (a.3) o riginal I-frame (b.3) marked I-frame (c.3) extract logo with NC=0.8872 Figure 22Subjective evaluation of watermarking system against compression attack.NC means the normalization correlation between the extracted logo and the original embedded logo. Hardware Modules Area Percentage 9% SIG PNBSM DPIC RAM Control Unit Figure 23Hardware estimation percentage. Table 7Chip specification. Specification Technology TSMC 1P6M 0.18um Gate count 4729.8 Die size 1.693×1.683mm 2Core size 1.199×1.190mm 2Clock rate 100MHz Power 3.21mW@100MHz 6Conclusions Since few literatures explored the watermarking system de-sign including an algorithm and architecture level perspec-tives,a novel video watermarking system and its VLSI implementation are presented in this paper.Two different kinds of embedded modes,spatial and frequency domain modes,are supplied in our proposed configured architecture. The spread spectrum technology,AHVS embedding,error correction codes,and PN-codes are applied to build the watermarking system.The corresponding hardware architec-tures are designed.Simulation results show that our approach has high security and robustness against various attacks.In particular,all of the BER under attacks is below0.35.The comparison also demonstrates that the performance of our approach is higher than that of other traditional methods. The proposed architecture was synthesized with TSMC 1P6M0.18μm standard cell.The simulation speed can reach 100MHz,and the chip size is1.199×1.190mm2for4729.8 gate counts.These indicate that the proposed joint data com-pression and watermark embedding mechanism achieves high robustness with low hardware complexity.With this function-ality,our design is adequate for a specific function IP com-bined with the MPEG-2encoder to enforce owners’copyright in the system-on-chip(SOC)design trend. References 1.Hartung,F.,&Kutter,M.(1999).Multimedia watermarking tech- niques.Proceedings of the IEEE,87(7),1079–1107. 2.Swanson,M.D.,Kobayashi,M.,&Tewfik,A.H.(1998). Multimedia data-embedding and watermarking technologies. Proceedings of the IEEE,86(6),1064–1087. https://www.doczj.com/doc/b810294369.html,ngelaar,G.C.,Setyawan,I.,&Lagebdijk,R.L.(2000). Watermarking digital image and video data.IEEE Signal Processing Magazine,17(5),20–46. 4.Van Schyndel,R.G.,Tirkel,A.Z.,&Osborne,C.F.(1994).A digital watermark.Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Image Processing.,2,86–90. 5.Yen,J.C.(2001).Watermarks embedded in the permuted image. Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Symposium on Circuits and Systems,2,53–56. 6.Cox,I.,et al.(1996).A secure,robust watermark for multimedia. In Proc.Workshop on Information Hiding.U.K.:Univ.of Cambridge,pp.175–190. 7.Cox,I.J.,et al.(1997).Secure spread spectrum watermarking for multimedia.IEEE Transactions on Image Processing,6(12), 1079–1107. 8.Tao,B.,&Dickinson,B.(1997).Adaptive watermarking in the DCT domain.In Proc.IEEE Int.Conf.on Acoustics,Speech,and Signal Process vol.4,pp.2985–2988.. 9.Kutter,M.,Jordan,F.,&Bossen,F.(1998).Digital watermarking of clolor images using amplitude modulation.Electronics Letters, 34(8),748–750. 10.Lichtenauer,J.,et al.(2003).Exhaustive geometrical search and the false positive watermark detection probability.In Proc.SPIE-Security and Watermarking of Multimedia Contents V,vol.5020, pp.203–214. 11.Dong,P.,et al.(2002).Geometric robust watermarking through mesh model based correction.In Proc.IEEE Int.Conf.Image Process vol.3,pp.493–496. 12.Christoph,B.,Wolfgang,F.,&Stephen,W.(1999).Digital watermarking from concept to real-time video applications.In Proc.IEEE https://www.doczj.com/doc/b810294369.html,puter Graphics and Applications, vol.19,issue1,pp.25–35. https://www.doczj.com/doc/b810294369.html,ngelaar,G.C.,&Lagendijk,R.L.(2001).Optimal differential energy watermarking of DCT encoded image and video.IEEE Transactions on Image Processing,10(1),148–158. 14.Huang,J.,&Shi,Y.Q.(1998).Adaptive image watermarking scheme based on visual masking.Electronics Letters,34(8),748–750. 15.Biswas,S.,Das,S.R.,&Petriu,E.M.(2005).An adaptive compressed MPEG-2video watermarking scheme.IEEE Trans. on Instrumentation and Measurement,54,1853–1861. 16.Chang,F.C.,Hang,H.M.,&Huang,H.C.(2007).Layered access control schemes on watermarked scalable media.The Journal of VLSI Signal Processing Systems,49(3),443–455. 17.Mathai,N.J.,Kundur, D.,&Sheikholeslami, A.(2003). Hardware implementation perspectives of digital video watermarking algorithms.IEEE Trans.on Signal Process, 51(4),925–938. 18.Tsai,T.H.,&Lu,C.Y.(2004).VLSI design for embedded digital watermarking JPEG encoder based on digital camera system.IEICE Transactions on Fundamentals of Electronics,Communications and Computer Sciences,E87-A(7),1772–1780. 19.Weng,S.J.,Lu,T.T.,&Chang,P.C.(2003).Key-based video watermarking system on MPEG-2.In Proc.SPIE Conf.Electronic Imaging,Santa Clara,CA,pp.516–525. 20.Smith,J.R.,&Comiskey,B.O.(1996).Modulation and informa- tion hiding in image.In Proc.the First Information Hiding Workshop.Canbridge:Isaac Newton Institute,Computer Science, vol.1174,pp.207–226. 21.Tseng,C.C.,Lin,R.D.,&Lee,S.L.(1999).Image watermarking based on Toral automophism,block DC value quantization and error correcting code.In Proc.12th IPPP Conf.on Computer Vision,Graphics and Image Process,vol.I,pp.158–165. 22.Watson,A.B.(1992).DCT quantization matrices visually opti- mized for individual image.In Proc.SPIE Conf.Human Vision, Visual Process.and Digital Display,pp.202– 216. Figure24Chip physical layout. Tsung-Han Tsai received the B.S.,M.S.,and Ph.D.degrees in electrical engineering from the National Taiwan University,Tai- pei,Taiwan,in1990,1994,and 1998respectively.From1999to 2000,he was an Associate Profes- sor of electronic engineering at Fu Jen University.He joined Nation- al Central University in2000. Currently,he is a Professor in the department of electrical engineer- ing at National Central Universi- ty.He has been an IEEE member for over10years,and is also a member of the Audio Engineering Society(AES)and the Institute of Electronics,Information and Communication Engineers(IEICE).Dr.Tsai has been awarded more than15patents and150refereed papers published in international journals and conferences.His research interests include VLSI signal processing,video/audio coding algorithms,DSP architecture design,wireless communication and System-On-Chip design.Dr.Tsai received the Industrial Cooperation Award in2003from the Ministry of Education,Taiwan.He is a member of the Technical Committee of IEEE Circuits and Systems Society,and serves as Technical Program Commit-tee member or Session Chair of several international conferences.Chih-Yen Wu received the M.S.degree in electrical engineering from National Central University,Taoyuan,Taiwan,in2006.Her current research interests include video signal processing and very large-scale integrated signal processing.(No photo). Chih-Lun Fang received the M.S.degree in information tech- nology from the National Taipei University of Education,Taipei, Taiwan,in2003,and the Ph.D. degree in electrical engineering from National Central University, Taoyuan,Taiwan,in2011.His current research interests include video/image processing,very large-scale integrated signal pro- cessing,and computer vision.Dr. Fang is the DAC/ISSCC Student Design Contest Winner in2011. 从实践的角度探讨在日语教学中多媒体课件的应用 在今天中国的许多大学,为适应现代化,信息化的要求,建立了设备完善的适应多媒体教学的教室。许多学科的研究者及现场教员也积极致力于多媒体软件的开发和利用。在大学日语专业的教学工作中,教科书、磁带、粉笔为主流的传统教学方式差不多悄然向先进的教学手段而进展。 一、多媒体课件和精品课程的进展现状 然而,目前在专业日语教学中能够利用的教学软件并不多见。比如在中国大学日语的专业、第二外語用教科书常见的有《新编日语》(上海外语教育出版社)、《中日交流标准日本語》(初级、中级)(人民教育出版社)、《新编基础日语(初級、高級)》(上海译文出版社)、《大学日本语》(四川大学出版社)、《初级日语》《中级日语》(北京大学出版社)、《新世纪大学日语》(外语教学与研究出版社)、《综合日语》(北京大学出版社)、《新编日语教程》(华东理工大学出版社)《新编初级(中级)日本语》(吉林教育出版社)、《新大学日本语》(大连理工大学出版社)、《新大学日语》(高等教育出版社)、《现代日本语》(上海外语教育出版社)、《基础日语》(复旦大学出版社)等等。配套教材以录音磁带、教学参考、习题集为主。只有《中日交流標準日本語(初級上)》、《初級日语》、《新编日语教程》等少数教科书配备了多媒体DVD视听教材。 然而这些试听教材,有的内容为日语普及读物,并不适合专业外语课堂教学。比如《新版中日交流标准日本语(初级上)》,有的尽管DVD视听教材中有丰富的动画画面和语音练习。然而,课堂操作则花费时刻长,不利于教师重点指导,更加适合学生的课余练习。比如北京大学的《初级日语》等。在这种情形下,许多大学的日语专业致力于教材的自主开发。 其中,有些大学的还推出精品课程,取得了专门大成绩。比如天津外国语学院的《新编日语》多媒体精品课程为2007年被评为“国家级精品课”。目前已被南开大学外国语学院、成都理工大学日语系等全国40余所大学推广使用。 Unit1 Americans believe no one stands still. If you are not moving ahead, you are falling behind. This attitude results in a nation of people committed to researching, experimenting and exploring. Time is one of the two elements that Americans save carefully, the other being labor. "We are slaves to nothing but the clock,” it has been said. Time is treated as if it were something almost real. We budget it, save it, waste it, steal it, kill it, cut it, account for it; we also charge for it. It is a precious resource. Many people have a rather acute sense of the shortness of each lifetime. Once the sands have run out of a person’s hourglass, they cannot be replaced. We want every minute to count. A foreigner’s first impression of the U.S. is li kely to be that everyone is in a rush -- often under pressure. City people always appear to be hurrying to get where they are going, restlessly seeking attention in a store, or elbowing others as they try to complete their shopping. Racing through daytime meals is part of the pace 新视野三版读写B2U4Text A College sweethearts 1I smile at my two lovely daughters and they seem so much more mature than we,their parents,when we were college sweethearts.Linda,who's21,had a boyfriend in her freshman year she thought she would marry,but they're not together anymore.Melissa,who's19,hasn't had a steady boyfriend yet.My daughters wonder when they will meet"The One",their great love.They think their father and I had a classic fairy-tale romance heading for marriage from the outset.Perhaps,they're right but it didn't seem so at the time.In a way, love just happens when you least expect it.Who would have thought that Butch and I would end up getting married to each other?He became my boyfriend because of my shallow agenda:I wanted a cute boyfriend! 2We met through my college roommate at the university cafeteria.That fateful night,I was merely curious,but for him I think it was love at first sight."You have beautiful eyes",he said as he gazed at my face.He kept staring at me all night long.I really wasn't that interested for two reasons.First,he looked like he was a really wild boy,maybe even dangerous.Second,although he was very cute,he seemed a little weird. 3Riding on his bicycle,he'd ride past my dorm as if"by accident"and pretend to be surprised to see me.I liked the attention but was cautious about his wild,dynamic personality.He had a charming way with words which would charm any girl.Fear came over me when I started to fall in love.His exciting"bad boy image"was just too tempting to resist.What was it that attracted me?I always had an excellent reputation.My concentration was solely on my studies to get superior grades.But for what?College is supposed to be a time of great learning and also some fun.I had nearly achieved a great education,and graduation was just one semester away.But I hadn't had any fun;my life was stale with no component of fun!I needed a boyfriend.Not just any boyfriend.He had to be cute.My goal that semester became: Be ambitious and grab the cutest boyfriend I can find. 4I worried what he'd think of me.True,we lived in a time when a dramatic shift in sexual attitudes was taking place,but I was a traditional girl who wasn't ready for the new ways that seemed common on campus.Butch looked superb!I was not immune to his personality,but I was scared.The night when he announced to the world that I was his girlfriend,I went along D 实验三关于第三方支付平台(2学时) 1、现在第三方支付平台的格局如何以及各自所占有的市场情况是多少? 2、请同学上网查询目前主要的第三方支付平台有哪些?大的网上商城采用的有哪些?(列表说 明) 网上商 快钱易宝支付宝Paypal 财付通首信易城 淘宝√ 易趣√ 当当网√√√√ 卓越网银行卡 支付 拍拍网√你认为哪几家第三方支付平台最有生命力,会长期生存下去? 我觉得易宝的生命力比较强,会长期生存下去。 (1)如果消费者可以享受到:安全的在线支付,方便的电话支付,免费的会员服务,为您的手机充植,精彩活动积分奖励。 (2)可以为商户提供:网上、电话、汇款,多种收款方式,支持外卡,让你您的生意做到全球,7*24小时客服,技术支持快速反应,接入更简单,交易更安全,结算更及时! (3)功能有:会员登录安全设置:通过验证图片、提示问题、常用机校验等手段实现的双向安全验证机制,确保用户在任意场所登录易宝网站时的安全。 快捷查单服务:消费者通过此项服务可以方便快捷的查到自己选择YeePay易宝支付的网上购物订单!商户通过接入“快捷查单”功能,为客户提供贴心增值服务,提升服务品质和形象! 自主接入服务:商户可通过自助方式网上注册并使用易宝在线支付服务,不仅可以在线收款,而且还能登录商户系统进行定单管理和交易结算。依托易宝强大平台,确保安全交易,并享受7*24小时客户服务及快捷查单等增值服务。 3、第三方支付牌照的颁发会对现行的网络支付以及银联会产生什么样的影响? 易观国际分析认为,牌照发放后,获得牌照的企业将可接入超级网银,第三方支付企业以提高企业资金周转效率的定制化解决方案,将会逐步向传统企业进行渗透,也将出现从单一产业链的支付服务向跨产业链的融合转移的趋势。支付企业通过整合各种支付产品,为企业进行深度定制化服务,加快资金周转效率,而保险、基金等行业将是一个新的蓝海市场。 一旦涉及到钱,那么这个庞大的支付产业必定摆脱不了银行的介入。在《支付机构客户备付金存管暂行办法(06.02会议征求意见稿)》出台前,仅有支付宝等少数国内第三方支付公司委托银行每月对客户的交易保证金做托管审计,其他公司则会依托三四家银行提供备付金托管与清算服务。而随着今年5月26日首批支付牌照正式发放,一场第三方支付公司挑 一、高考小说阅读鉴赏答题技巧(公式化答题) (一)人物形象 1.常见题型 ①结合全文,简要分析人物形象。 ②对文中人物进行客观公正的评析(包括作者自身对人物的态度和读者对人物的评价)——××是一个怎样的人物? ③概括人物的性格特征——××有哪些优秀的品质? ④分析小说对人物进行描写的具体方法及其作用。 ⑤分析某一次要人物的作用。 2.解题思路 通过人物的描写(语言、行动、心理、肖像、细节)分析人物的性格特征。 人物(自身的性格特点,与另一个人物烘托、映衬、反衬)→情节(人物性格决定情节发展)→主题(突显某种主题) 首先总体把握小说人物形象特点,确定作者的感情倾向是褒还是贬,是颂扬还是讽刺。分析主要人物的性格特征可从三个方面入手:分析人物外貌、动作、细节、语言、心理活动的描写,从多方面准确地把握人物形象的特征;着重分析人物与人物、人物与环境的矛盾冲突;思考和发掘人物形象的思想意义。 然后找出小说中关于这个人物生活的环境及言行的语句,以及作者的议论或者作者借作品中其他人物对他的评价的语句。 接着看用了什么描写方法,在此基础上进行归类概括。最后选择恰当的词句表述出来。 3.答题格式 ××是一个……的人物形象。作为什么人,他怎么样,表现了他 怎样的性格(思想品质)。 某一次要人物的作用: ①这一人物的……性格烘托或者反衬主要人物……的性格,使人物性格更加鲜明。 ②通过两个形象的……对比,表达小说的主题……(主题内容概述)。 ③本文描写了……的情节,这一形象安排有推动故事情节发展的作用。 附:人物形象描写的方法 (1)正面描写——直接描写 如概括介绍、肖像描写、语言描写(对话/独白)、行动描写、细节描写、心理描写等。 (2)侧面描写——间接描写、侧面描写,通过其他人物的言行,间接写主人公。 如用有关人物的对话,心理活动,事件叙述等烘托所要描写的主要人物的性格特征;在情节发展中展现人物性格特征;环境描写衬托或烘托。 形象刻画基本技巧——各种描写手法的运用与作用 (1)肖像、神态、动作描写:更好展现人物……的内心世界及……性格特征。 (2)语言描写:①刻画人物……性格,反映人物……心理活动,促进故事情节的发展。 ②描摹人物的语态,使形象刻画栩栩如生、跃然纸上。 (3)心理描写:直接表现人物思想和内在情感(矛盾/焦虑/担心/喜悦/兴奋等),表现人物……思想品质,刻画人物……性格,推动情节发 Unit 1 1学习外语是我一生中最艰苦也是最有意义的经历之一。虽然时常遭遇挫折,但却非常有价值。 2我学外语的经历始于初中的第一堂英语课。老师很慈祥耐心,时常表扬学生。由于这种积极的教学方法,我踊跃回答各种问题,从不怕答错。两年中,我的成绩一直名列前茅。 3到了高中后,我渴望继续学习英语。然而,高中时的经历与以前大不相同。以前,老师对所有的学生都很耐心,而新老师则总是惩罚答错的学生。每当有谁回答错了,她就会用长教鞭指着我们,上下挥舞大喊:“错!错!错!”没有多久,我便不再渴望回答问题了。我不仅失去了回答问题的乐趣,而且根本就不想再用英语说半个字。 4好在这种情况没持续多久。到了大学,我了解到所有学生必须上英语课。与高中老师不。大学英语老师非常耐心和蔼,而且从来不带教鞭!不过情况却远不尽如人意。由于班大,每堂课能轮到我回答的问题寥寥无几。上了几周课后,我还发现许多同学的英语说得比我要好得多。我开始产生一种畏惧感。虽然原因与高中时不同,但我却又一次不敢开口了。看来我的英语水平要永远停步不前了。 5直到几年后我有机会参加远程英语课程,情况才有所改善。这种课程的媒介是一台电脑、一条电话线和一个调制解调器。我很快配齐了必要的设备并跟一个朋友学会了电脑操作技术,于是我每周用5到7天在网上的虚拟课堂里学习英语。 6网上学习并不比普通的课堂学习容易。它需要花许多的时间,需要学习者专心自律,以跟上课程进度。我尽力达到课程的最低要求,并按时完成作业。 7我随时随地都在学习。不管去哪里,我都随身携带一本袖珍字典和笔记本,笔记本上记着我遇到的生词。我学习中出过许多错,有时是令人尴尬的错误。有时我会因挫折而哭泣,有时甚至想放弃。但我从未因别的同学英语说得比我快而感到畏惧,因为在电脑屏幕上作出回答之前,我可以根据自己的需要花时间去琢磨自己的想法。突然有一天我发现自己什么都懂了,更重要的是,我说起英语来灵活自如。尽管我还是常常出错,还有很多东西要学,但我已尝到了刻苦学习的甜头。 8学习外语对我来说是非常艰辛的经历,但它又无比珍贵。它不仅使我懂得了艰苦努力的意义,而且让我了解了不同的文化,让我以一种全新的思维去看待事物。学习一门外语最令人兴奋的收获是我能与更多的人交流。与人交谈是我最喜欢的一项活动,新的语言使我能与陌生人交往,参与他们的谈话,并建立新的难以忘怀的友谊。由于我已能说英语,别人讲英语时我不再茫然不解了。我能够参与其中,并结交朋友。我能与人交流,并能够弥合我所说的语言和所处的文化与他们的语言和文化之间的鸿沟。 III. 1. rewarding 2. communicate 3. access 4. embarrassing 5. positive 6. commitment 7. virtual 8. benefits 9. minimum 10. opportunities IV. 1. up 2. into 3. from 4. with 5. to 6. up 7. of 8. in 9. for 10.with V. 1.G 2.B 3.E 4.I 5.H 6.K 7.M 8.O 9.F 10.C Sentence Structure VI. 1. Universities in the east are better equipped, while those in the west are relatively poor. 2. Allan Clark kept talking the price up, while Wilkinson kept knocking it down. 3. The husband spent all his money drinking, while his wife saved all hers for the family. 4. Some guests spoke pleasantly and behaved politely, while others wee insulting and impolite. 5. Outwardly Sara was friendly towards all those concerned, while inwardly she was angry. VII. 1. Not only did Mr. Smith learn the Chinese language, but he also bridged the gap between his culture and ours. 2. Not only did we learn the technology through the online course, but we also learned to communicate with friends in English. 3. Not only did we lose all our money, but we also came close to losing our lives. 新大学日语简明教程课文翻译 第21课 一、我的留学生活 我从去年12月开始学习日语。已经3个月了。每天大约学30个新单词。每天学15个左右的新汉字,但总记不住。假名已经基本记住了。 简单的会话还可以,但较难的还说不了。还不能用日语发表自己的意见。既不能很好地回答老师的提问,也看不懂日语的文章。短小、简单的信写得了,但长的信写不了。 来日本不久就迎来了新年。新年时,日本的少女们穿着美丽的和服,看上去就像新娘。非常冷的时候,还是有女孩子穿着裙子和袜子走在大街上。 我在日本的第一个新年过得很愉快,因此很开心。 现在学习忙,没什么时间玩,但周末常常运动,或骑车去公园玩。有时也邀朋友一起去。虽然我有国际驾照,但没钱,买不起车。没办法,需要的时候就向朋友借车。有几个朋友愿意借车给我。 二、一个房间变成三个 从前一直认为睡在褥子上的是日本人,美国人都睡床铺,可是听说近来纽约等大都市的年轻人不睡床铺,而是睡在褥子上,是不是突然讨厌起床铺了? 日本人自古以来就睡在褥子上,那自有它的原因。人们都说日本人的房子小,从前,很少有人在自己的房间,一家人住在一个小房间里是常有的是,今天仍然有人过着这样的生活。 在仅有的一个房间哩,如果要摆下全家人的床铺,就不能在那里吃饭了。这一点,褥子很方便。早晨,不需要褥子的时候,可以收起来。在没有了褥子的房间放上桌子,当作饭厅吃早饭。来客人的话,就在那里喝茶;孩子放学回到家里,那房间就成了书房。而后,傍晚又成为饭厅。然后收起桌子,铺上褥子,又成为了全家人睡觉的地方。 如果是床铺的话,除了睡觉的房间,还需要吃饭的房间和书房等,但如果使用褥子,一个房间就可以有各种用途。 据说从前,在纽约等大都市的大学学习的学生也租得起很大的房间。但现在房租太贵,租不起了。只能住更便宜、更小的房间。因此,似乎开始使用睡觉时作床,白天折小能成为椅子的、方便的褥子。 新视野大学英语第一册Unit 1课文翻译 学习外语是我一生中最艰苦也是最有意义的经历之一。 虽然时常遭遇挫折,但却非常有价值。 我学外语的经历始于初中的第一堂英语课。 老师很慈祥耐心,时常表扬学生。 由于这种积极的教学方法,我踊跃回答各种问题,从不怕答错。 两年中,我的成绩一直名列前茅。 到了高中后,我渴望继续学习英语。然而,高中时的经历与以前大不相同。 以前,老师对所有的学生都很耐心,而新老师则总是惩罚答错的学生。 每当有谁回答错了,她就会用长教鞭指着我们,上下挥舞大喊:“错!错!错!” 没有多久,我便不再渴望回答问题了。 我不仅失去了回答问题的乐趣,而且根本就不想再用英语说半个字。 好在这种情况没持续多久。 到了大学,我了解到所有学生必须上英语课。 与高中老师不同,大学英语老师非常耐心和蔼,而且从来不带教鞭! 不过情况却远不尽如人意。 由于班大,每堂课能轮到我回答的问题寥寥无几。 上了几周课后,我还发现许多同学的英语说得比我要好得多。 我开始产生一种畏惧感。 虽然原因与高中时不同,但我却又一次不敢开口了。 看来我的英语水平要永远停步不前了。 直到几年后我有机会参加远程英语课程,情况才有所改善。 这种课程的媒介是一台电脑、一条电话线和一个调制解调器。 我很快配齐了必要的设备并跟一个朋友学会了电脑操作技术,于是我每周用5到7天在网上的虚拟课堂里学习英语。 网上学习并不比普通的课堂学习容易。 它需要花许多的时间,需要学习者专心自律,以跟上课程进度。 我尽力达到课程的最低要求,并按时完成作业。 我随时随地都在学习。 不管去哪里,我都随身携带一本袖珍字典和笔记本,笔记本上记着我遇到的生词。 我学习中出过许多错,有时是令人尴尬的错误。 有时我会因挫折而哭泣,有时甚至想放弃。 但我从未因别的同学英语说得比我快而感到畏惧,因为在电脑屏幕上作出回答之前,我可以根据自己的需要花时间去琢磨自己的想法。 突然有一天我发现自己什么都懂了,更重要的是,我说起英语来灵活自如。 尽管我还是常常出错,还有很多东西要学,但我已尝到了刻苦学习的甜头。 学习外语对我来说是非常艰辛的经历,但它又无比珍贵。 它不仅使我懂得了艰苦努力的意义,而且让我了解了不同的文化,让我以一种全新的思维去看待事物。 学习一门外语最令人兴奋的收获是我能与更多的人交流。 与人交谈是我最喜欢的一项活动,新的语言使我能与陌生人交往,参与他们的谈话,并建立新的难以忘怀的友谊。 由于我已能说英语,别人讲英语时我不再茫然不解了。 我能够参与其中,并结交朋友。 第三方支付平台教学设计 授课人:宋文鑫授课时间:2016年12月30日?学习目标: ?1、认识第三方支付平台的概念组成; ?2、理解两种第三方支付平台的运行机制以及优缺点; ?3、使学生认识到第三方支付平台的发展可以改变我们的生活。 教学过程 一:案例导入 1.共同阅读案例,学生思考案例问题,得出问题答案。 2.进而引出对之前学习的知识的复习,回顾电子商务支付方式。 3.导入本课内容“第三方支付平台”,说明本课的学习目标,开始新课教学。二:新课教学 1.第三方支付平台概念 (1)学生阅读课本,找出第三方平台概念,通过课本知识填写学案。 (2)展示PPT,讲解第三方平台概念。但此概念过长不易记忆,教授学生记忆方法,将概念拆解进行记忆,引出课堂思考。 (3)学生思考学案问题,通过PPT引导学生理解概念以组块的方式进行记忆。 2.第三方支付平台分类 (1)学生阅读课本找出第三方支付平台的种类,可分为网关型第三方支付平台与信用担保型第三方支付平台。 (2)通过PPT学习网关型平台的运行模式以及优缺点,利用画图的方式使学生理解此类平台的运行模式,并回顾之前学过的知识点“支付网关”。 (3)理解信用担保型第三方支付平台运行模式,点出其典型代表支付宝,引出探究讨论。学生分小组讨论“支付宝的工作流程是什么?”并将讨论结果并落实纸面。提问小组代表,而后利用PPT分步展示其工作流程。 (4)简单介绍支付宝的产生、发展以及作用,讲解信用担保型第三方支付平台的优点。结合日常生活中支付宝付款、收款等功能,使学生认识到第三方支付平台的便利,相信第三方支付平台可以改变我们的生活。 三:总结 总结本课所学内容,与本课开始时提出的学习目标相呼应。 四:作业 1.以支付宝为例介绍第三方支付的交易流程并画出其流程图。 2.利用课后时间搜集其他的第三方支付平台,并比较其相同点和不同点。 习惯与礼仪 我是个漫画家,对旁人细微的动作、不起眼的举止等抱有好奇。所以,我在国外只要做错一点什么,立刻会比旁人更为敏锐地感觉到那个国家的人们对此作出的反应。 譬如我多次看到过,欧美人和中国人见到我们日本人吸溜吸溜地出声喝汤而面露厌恶之色。过去,日本人坐在塌塌米上,在一张低矮的食案上用餐,餐具离嘴较远。所以,养成了把碗端至嘴边吸食的习惯。喝羹匙里的东西也象吸似的,声声作响。这并非哪一方文化高或低,只是各国的习惯、礼仪不同而已。 日本人坐在椅子上围桌用餐是1960年之后的事情。当时,还没有礼仪规矩,甚至有人盘着腿吃饭。外国人看见此景大概会一脸厌恶吧。 韩国女性就座时,单腿翘起。我认为这种姿势很美,但习惯于双膝跪坐的日本女性大概不以为然,而韩国女性恐怕也不认为跪坐为好。 日本等多数亚洲国家,常有人习惯在路上蹲着。欧美人会联想起狗排便的姿势而一脸厌恶。 日本人常常把手放在小孩的头上说“好可爱啊!”,而大部分外国人会不愿意。 如果向回教国家的人们劝食猪肉和酒,或用左手握手、递东西,会不受欢迎的。当然,饭菜也用右手抓着吃。只有从公用大盘往自己的小盘里分食用的公勺是用左手拿。一旦搞错,用黏糊糊的右手去拿, 会遭人厌恶。 在欧美,对不受欢迎的客人不说“请脱下外套”,所以电视剧中的侦探哥隆波总是穿着外套。访问日本家庭时,要在门厅外脱掉外套后进屋。穿到屋里会不受欢迎的。 这些习惯只要了解就不会出问题,如果因为不知道而遭厌恶、憎恨,实在心里难受。 过去,我曾用色彩图画和简短的文字画了一本《关键时刻的礼仪》(新潮文库)。如今越发希望用各国语言翻译这本书。以便能对在日本的外国人有所帮助。同时希望有朝一日以漫画的形式画一本“世界各国的习惯与礼仪”。 练习答案 5、 (1)止める並んでいる見ているなる着色した (2)拾った入っていた行ったしまった始まっていた 新视野大学英语第三版第二册读写课文翻译 Unit 1 Text A 一堂难忘的英语课 1 如果我是唯一一个还在纠正小孩英语的家长,那么我儿子也许是对的。对他而言,我是一个乏味的怪物:一个他不得不听其教诲的父亲,一个还沉湎于语法规则的人,对此我儿子似乎颇为反感。 2 我觉得我是在最近偶遇我以前的一位学生时,才开始对这个问题认真起来的。这个学生刚从欧洲旅游回来。我满怀着诚挚期待问她:“欧洲之行如何?” 3 她点了三四下头,绞尽脑汁,苦苦寻找恰当的词语,然后惊呼:“真是,哇!” 4 没了。所有希腊文明和罗马建筑的辉煌居然囊括于一个浓缩的、不完整的语句之中!我的学生以“哇!”来表示她的惊叹,我只能以摇头表达比之更强烈的忧虑。 5 关于正确使用英语能力下降的问题,有许多不同的故事。学生的确本应该能够区分诸如their/there/they're之间的不同,或区别complimentary 跟complementary之间显而易见的差异。由于这些知识缺陷,他们承受着大部分不该承受的批评和指责,因为舆论认为他们应该学得更好。 6 学生并不笨,他们只是被周围所看到和听到的语言误导了。举例来说,杂货店的指示牌会把他们引向stationary(静止处),虽然便笺本、相册、和笔记本等真正的stationery(文具用品)并没有被钉在那儿。朋友和亲人常宣称They've just ate。实际上,他们应该说They've just eaten。因此,批评学生不合乎情理。 7 对这种缺乏语言功底而引起的负面指责应归咎于我们的学校。学校应对英语熟练程度制定出更高的标准。可相反,学校只教零星的语法,高级词汇更是少之又少。还有就是,学校的年轻教师显然缺乏这些重要的语言结构方面的知识,因为他们过去也没接触过。学校有责任教会年轻人进行有效的语言沟通,可他们并没把语言的基本框架——准确的语法和恰当的词汇——充分地传授给学生。 新视野大学英语1课文翻译 1下午好!作为校长,我非常自豪地欢迎你们来到这所大学。你们所取得的成就是你们自己多年努力的结果,也是你们的父母和老师们多年努力的结果。在这所大学里,我们承诺将使你们学有所成。 2在欢迎你们到来的这一刻,我想起自己高中毕业时的情景,还有妈妈为我和爸爸拍的合影。妈妈吩咐我们:“姿势自然点。”“等一等,”爸爸说,“把我递给他闹钟的情景拍下来。”在大学期间,那个闹钟每天早晨叫醒我。至今它还放在我办公室的桌子上。 3让我来告诉你们一些你们未必预料得到的事情。你们将会怀念以前的生活习惯,怀念父母曾经提醒你们要刻苦学习、取得佳绩。你们可能因为高中生活终于结束而喜极而泣,你们的父母也可能因为终于不用再给你们洗衣服而喜极而泣!但是要记住:未来是建立在过去扎实的基础上的。 4对你们而言,接下来的四年将会是无与伦比的一段时光。在这里,你们拥有丰富的资源:有来自全国各地的有趣的学生,有学识渊博又充满爱心的老师,有综合性图书馆,有完备的运动设施,还有针对不同兴趣的学生社团——从文科社团到理科社团、到社区服务等等。你们将自由地探索、学习新科目。你们要学着习惯点灯熬油,学着结交充满魅力的人,学着去追求新的爱好。我想鼓励你们充分利用这一特殊的经历,并用你们的干劲和热情去收获这一机会所带来的丰硕成果。 5有这么多课程可供选择,你可能会不知所措。你不可能选修所有的课程,但是要尽可能体验更多的课程!大学里有很多事情可做可学,每件事情都会为你提供不同视角来审视世界。如果我只能给你们一条选课建议的话,那就是:挑战自己!不要认为你早就了解自己对什么样的领域最感兴趣。选择一些你从未接触过的领域的课程。这样,你不仅会变得更加博学,而且更有可能发现一个你未曾想到的、能成就你未来的爱好。一个绝佳的例子就是时装设计师王薇薇,她最初学的是艺术史。随着时间的推移,王薇薇把艺术史研究和对时装的热爱结合起来,并将其转化为对设计的热情,从而使她成为全球闻名的设计师。 6在大学里,一下子拥有这么多新鲜体验可能不会总是令人愉快的。在你的宿舍楼里,住在你隔壁寝室的同学可能会反复播放同一首歌,令你头痛欲裂!你可能喜欢早起,而你的室友却是个夜猫子!尽管如此,你和你的室友仍然可能成 新视野大学英语2课文翻译(Unit1-Unit7) Unit 1 Section A 时间观念强的美国人 Para. 1 美国人认为没有人能停止不前。如果你不求进取,你就会落伍。这种态度造就了一个投身于研究、实验和探索的民族。时间是美国人注意节约的两个要素之一,另一个是劳力。 Para. 2 人们一直说:“只有时间才能支配我们。”人们似乎是把时间当作一个差不多是实实在在的东西来对待的。我们安排时间、节约时间、浪费时间、挤抢时间、消磨时间、缩减时间、对时间的利用作出解释;我们还要因付出时间而收取费用。时间是一种宝贵的资源,许多人都深感人生的短暂。时光一去不复返。我们应当让每一分钟都过得有意义。 Para. 3 外国人对美国的第一印象很可能是:每个人都匆匆忙忙——常常处于压力之下。城里人看上去总是在匆匆地赶往他们要去的地方,在商店里他们焦躁不安地指望店员能马上来为他们服务,或者为了赶快买完东西,用肘来推搡他人。白天吃饭时人们也都匆匆忙忙,这部分地反映出这个国家的生活节奏。工作时间被认为是宝贵的。Para. 3b 在公共用餐场所,人们都等着别人吃完后用餐,以便按时赶回去工作。你还会发现司机开车很鲁莽,人们推搡着在你身边过去。你会怀念微笑、简短的交谈以及与陌生人的随意闲聊。不要觉得这是针对你个人的,这是因为人们非常珍惜时间,而且也不喜欢他人“浪费”时间到不恰当的地步。 Para. 4 许多刚到美国的人会怀念诸如商务拜访等场合开始时的寒暄。他们也会怀念那种一边喝茶或咖啡一边进行的礼节性交流,这也许是他们自己国家的一种习俗。他们也许还会怀念在饭店或咖啡馆里谈生意时的那种轻松悠闲的交谈。一般说来,美国人是不会在如此轻松的环境里通过长时间的闲聊来评价他们的客人的,更不用说会在增进相互间信任的过程中带他们出去吃饭,或带他们去打高尔夫球。既然我们通常是通过工作而不是社交来评估和了解他人,我们就开门见山地谈正事。因此,时间老是在我们心中的耳朵里滴滴答答地响着。 Para. 5 因此,我们千方百计地节约时间。我们发明了一系列节省劳力的装置;我们通过发传真、打电话或发电子邮件与他人迅速地进行交流,而不是通过直接接触。虽然面对面接触令人愉快,但却要花更多的时间, 尤其是在马路上交通拥挤的时候。因此,我们把大多数个人拜访安排在下班以后的时间里或周末的社交聚会上。 Para. 6 就我们而言,电子交流的缺乏人情味与我们手头上事情的重要性之间很少有或完全没有关系。在有些国家, 如果没有目光接触,就做不成大生意,这需要面对面的交谈。在美国,最后协议通常也需要本人签字。然而现在人们越来越多地在电视屏幕上见面,开远程会议不仅能解决本国的问题,而且还能通过卫星解决国际问题。 文学作品之赏析句子答题技巧 1.修辞: 比喻、排比铺陈、拟人、对偶、反复(突出某种意思,强调某种情感,具有强烈的抒情性和感染力)反问、设问等 2.描写手法: 对比、衬托、人(正面描写之外貌、语言、动作、神态、心理、细节、侧面描写)景(白描、虚实、动静、渲染、视嗅听触结合,侧面烘托等),场景描写 3句式: 长短句,整句结合(整句:对偶、排比、四字格短语等,散句:句子参次不齐、长短不一)。设问、反问、疑问、感叹句、肯定句、否定句等 4.词语: 炼字(动词、形容词、叠词,拟声词,副词、数词、助词、等),引诗词、化典故(富有文采,典雅优美);语体色彩(书面语、口语、方言、文言),语气(呢、呀、啊等),语调(轻快、沉重等),感情色彩(褒贬,是否鲜明) 5语言特色(风格): 平实质朴,含蓄委婉,清新明丽,形象生动、绚丽飘逸,幽默讽刺,达豪放,沉郁悲慨、音律和谐等 6.语句语段作用 典例1:舅舅生性内向,平日不喜欢流露情感。只有拉琴的时候,眯上眼睛,嘴角上扬,跟着节奏摇头晃脑,手腕舞动,很是陶醉。过去每年春节,他都要在外公家给我们表演,用激昂的音乐代替了漂亮的吉祥话。在静养的日子,他不喜欢在家拉琴,常常晚上去公园的小山丘上坐着,孤零零的。舅妈有时去寻他,在背后听完曲子,回来说:声音不一样了。“两个人生活久了,只闻其声,便心领神会。(《再也听不得二胡如泣如诉之声》散文) 1.从描写入手赏析文中画波浪线的句子 (1)神态、动作描写,写舅舅在拉琴时的神态与动作,生动地突出了舅舅的陶醉。(2)对比,描写舅舅先前拉琴时的“激昂漂亮”与病后公园拉琴的“孤零零”,两者形成对比,突出了病后舅舅的心理状态。 (3)侧面描写(衬托),借舅妈借舅妈的感受及语言描写衬托病后舅舅的变化,变得失落、伤感。 典例2:这时,阊门外传来若断若续的琴声,张翰不由得驻足静听。这琴声,如流水淙淙,似雁落平沙,仿佛月下独酌,又像是静夜徘徊。当此夜色,一弦一柱,扣人心扉。他信步而行,不觉来到城河边上。近处的一只船中,漏出隐隐约约的烛光,那清幽的琴声,与烛光一起摇曳,如涟漪般荡漾开来。(小说《抚琴》) 2. 从描写入手赏析文中画波浪线的句子 (1)运用比喻。把琴声比作淙淙流水、雁落平沙、月下独酌、静夜徘徊,化无形为有形,生动形象地写出琴声的清幽孤寂,安闲恬静中夹杂着孤独、茫然、忧伤; 新视野大学英语3第三版课文翻译 Unit 1 The Way to Success 课文A Never, ever give up! 永不言弃! As a young boy, Britain's great Prime Minister, Sir Winston Churchill, attended a public school called Harrow. He was not a good student, and had he not been from a famous family, he probably would have been removed from the school for deviating from the rules. Thankfully, he did finish at Harrow and his errors there did not preclude him from going on to the university. He eventually had a premier army career whereby he was later elected prime minister. He achieved fame for his wit, wisdom, civic duty, and abundant courage in his refusal to surrender during the miserable dark days of World War II. His amazing determination helped motivate his entire nation and was an inspiration worldwide. Toward the end of his period as prime minister, he was invited to address the patriotic young boys at his old school, Harrow. The headmaster said, "Young gentlemen, the greatest speaker of our time, will be here in a few days to address you, and you should obey whatever sound advice he may give you." The great day arrived. Sir Winston stood up, all five feet, five inches and 107 kilos of him, and gave this short, clear-cut speech: "Young men, never give up. Never give up! Never give up! Never, never, never, never!" 英国的伟大首相温斯顿·丘吉尔爵士,小时候在哈罗公学上学。当时他可不是个好学生,要不是出身名门,他可能早就因为违反纪律被开除了。谢天谢地,他总算从哈罗毕业了,在那里犯下的错误并没影响到他上大学。后来,他凭着军旅生涯中的杰出表现当选为英国首相。他的才思、智慧、公民责任感以及在二战痛苦而黑暗的时期拒绝投降的无畏勇气,为他赢得了美名。他非凡的决心,不仅激励了整个民族,还鼓舞了全世界。 在他首相任期即将结束时,他应邀前往母校哈罗公学,为满怀报国之志的同学们作演讲。校长说:“年轻的先生们,当代最伟大的演说家过几天就会来为你们演讲,他提出的任何中肯的建议,你们都要听从。”那个激动人心的日子终于到了。温斯顿爵士站了起来——他只有5 英尺5 英寸高,体重却有107 公斤。他作了言简意赅的讲话:“年轻人,要永不放弃。永不放弃!永不放弃!永不,永不,永不,永不!” Personal history, educational opportunity, individual dilemmas - none of these can inhibit a strong spirit committed to success. No task is too hard. No amount of preparation is too long or too difficult. Take the example of two of the most scholarly scientists of our age, Albert Einstein and Thomas Edison. Both faced immense obstacles and extreme criticism. Both were called "slow to learn" and written off as idiots by their teachers. Thomas Edison ran away from school because his teacher whipped him repeatedly for asking too many questions. Einstein didn't speak fluently until he was almost nine years old and was such a poor student that some thought he was unable to learn. Yet both boys' parents believed in them. They worked intensely each day with their sons, and the boys learned to never bypass the long hours of hard work that they needed to succeed. In the end, both Einstein and Edison overcame their childhood persecution and went on to achieve magnificent discoveries that benefit the entire world today. Consider also the heroic example of Abraham Lincoln, who faced substantial hardships, failures and repeated misfortunes in his lifetime. His background was certainly not glamorous. He was raised in a very poor family with only one year of formal education. He failed in business twice, suffered a nervous breakdown when his first love died suddenly and lost eight political从实践的角度探讨在日语教学中多媒体课件的应用
新视野大学英语全部课文原文
新视野大学英语第三版第二册课文语法讲解 Unit4
第三方支付平台
2016高考之小说阅读鉴赏答题技巧
新视野大学英语读写教程第一册课文翻译及课后答案
新大学日语简明教程课文翻译
新视野大学英语第一册Unit 1课文翻译
第三方支付平台教案
新大学日语阅读与写作1 第3课译文
新视野大学英语(第三版)读写教程第二册课文翻译(全册)
新视野大学英语1课文翻译
新视野大学英语2课文翻译
文学作品之赏析句子答题技巧
新视野大学英语第三版课文翻译